Hearing. 1 Introduction. 1.1 Auditory system. 1.2 Psychoacoustics
|
|
|
- Amice Horn
- 9 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Hearing Sources: Rossing. (1990). The science of sound. Chapters 5 7. Karjalainen. (1999). Kommunikaatioakustiikka. Moore. (1997). An introduction to the psychology of hearing. Contents: 1. Introduction 2. Ear physiology 3. Masking 4. Sound pressure level 5. Loudness 6. Pitch 7. Spatial hearing Hearing 1 1 Introduction! Auditory system can be divided in two parts Peripheral auditory system (outer, middle, and inner ear) Auditory nervous system (in the brain) Hearing 2! Ear physiology studies the peripheral system! Psychoacoustics studies the entire sensation: relationships between sound stimuli and the subjective sensation 1.1 Auditory system Hearing Psychoacoustics Hearing 4! Dynamic range of hearing is wide ratio of a very loud to a barely audible sound pressure level is 1:10 5 (powers 1:10 10, 100 db)! Frequency range of hearing varies a lot between individuals only few can hear from 20 Hz to 20 khz sensitivity to low sounds (< 100Hz) is not very good sensitivity to high sounds (> 12 khz) decreases along with age! Selectivity of hearing listener can pick an instrument from among an orchestra listener can follow a speaker at a cocktail party One can sleep in background noise but still wake up to an abnormal sound! Perception involves information processing in the brain Information about the brain is limited! Psychoacoustics studies the relationships between sound stimuli and the resulting sensations Attempt to model the process of perception For example trying to predict the perceived loudness / pitch / timbre from the acoustic properties of the sound signal! In a psychoacoustic listening test Test subject listens to sounds Questions are made or the subject is asked to describe her sensasions
2 2 Ear physiology Hearing Outer ear Hearing 6! The human ear consists of three main parts: (1) outer ear, (2) middle ear, (3) inner ear! Outer ear consists of: pinna gathers sound; direction-dependent response auditory canal (ear canal) - conveys sound to middle ear Nerve signal to brain [Chittka05] 2.2 Middle ear Hearing Inner ear, cochlea Hearing 8! Middle ear contains Eardrum that transforms sound waves into mechanic vibration Tiny audtory bones: hammer (resting against the eardrum, see figure), anvil and stirrup! The bones transmit eardrum vibrations to the oval window of the inner ear! Acoustic reflex: when sound pressure level exceeds ~80 db, eardrum tension increases and stirrup is removed from oval window Protects the inner ear from damage! The inner ear contains the cochlea: a fluid-filled organ where vibrations are converted into nerve impulses to the brain.! Cochlea = Greek: snail shell.! Spiral tube: When stretched out, approximately 30 millimeters long.! Vibrations on the cochlea s oval window cause hydraulic pressure waves inside the cochlea! Inside the cochlea there is the basilar membrane,! On the basilar membrane there is the organ of Corti with nerve cells that are sensitive to vibration! Nerve cells transform movement information into neural impulses in the auditory nerve
3 2.4 Basilar membrane Hearing 9 Basilar membrane Hearing 10! Figure: cochlea stretched out for illustration purposes Basilar membrane divides the fluid of the cochlea into separate tunnels When hydraulic pressure waves travel along the cochlea, they move the basilar membrane! Different frequencies produce highest amplitude at different sites! Preliminary frequency analysis happens on the basilar membrane Travelling waves: Best freq (Hz) 2.5 Sensory hair cells Hearing 11 3 Masking Hearing 12! Distributed along the basilar membrane are sensory hair cells that transform membrane movement into neural impulses! When a hair cell bends, it generates neural impulses Impulse rate depends on vibrate amplitude and frequency! Each nerve cell has a characteristic frequency to which it is most responsive to (Figure: tuning curves of 6 different cells)! Masking describes the situation where a weaker but clearly audible signal (maskee, test tone) becomes inaudible in the presence of a louder signal (masker)! Masking depends on both the spectral structure of the sounds and their variation over time
4 3.1 Masking in frequency domain Hearing 13 Masking in frequency domain Hearing 14! Model of the frequency analysis in the auditory system subdivision of the frequency axis into critical bands frequency components within a same critical band mask each other easily Bark scale: frequency scale that is derived by mapping frequencies to critical band numbers! Narrowband noise masks a tone (sinusoidal) easier than a tone masks noise! Masked threshold refers to the raised threshold of audibility caused by the masker sounds with a level below the masked threshold are inaudible masked threshold in quiet = threshold of hearing in quiet! Figure: masked thresholds [Herre95] masker: narrowband noise around 250 Hz, 1 khz, 4 khz spreading function: the effect of masking extends to the spectral vicinity of the masker (spreads more towards high freqencies)! Additivity of masking: joint masked thresh is approximately (but slightly more than) sum of the components 3.2 Masking in time domain Hearing 15 Masking: Examples Hearing 16! Forward masking masking effect extends to times after the masker is switched off! Backwards masking masking extends to times before the masker is been switched on! Forward/backward masking does not extend far in time " simultaneous masking is more important phenomenon backward masking forward masking! A single tone is played, followed by the same tone and a higher frequency tone. HF tone is reduced in intensity first by 12 db, then by steps of 5 db. Sequence repeats twice: second time the frequency separation between the tones is increased.! Attempt to mask higher frequencies! Attempt to mask lower frequencies (not masked as easily)
5 Application to audio steganography Hearing 17 4 Sound pressure level Hearing 18! Idea: hide a message in the audio data, keeping the message inaudible yet decodable! Example Here robustness to environmental noise was important! Sound signal s 1 (t) at time t represents pressure deviation from normal atmospheric pressure 2! Sound pressure p is the (linear) RMS-level RMS = E{()} s t of the signal E{ } denotes expectation (RMS = root-mean-square level)! Due to the wide dynamic range, decibel scale is convenient p db = 20 log10 (p RMS / p 0 ) = L p where p 0 is a reference pressure 4.1 Threshold of hearing and db scale Hearing Multiple sources Hearing 20! Threshold of hearing Weakest audible sound pressure at 1 khz frequency is 20 µpa, which has been chosen to be the reference level p 0 of the dbscale L p = 20 log 10 (p/p 0 ) = 10 log 10 (p 2 /p 02 )! Threshold of pain Loudest sound that the auditory system can meaningfully deal with khz! Two sound sources: s(t) = s 1 (t) + s 2 (t)! RMS pressure level of the summary signal: p = E{()} s t = E{ s () t + 2 s () t s () t + s ()} t RMS ! If the signals are uncorrelated Es { 1( ts ) 2( t )} = 0 and the above formula simplifies to p = p + p RMS If p 1 = p 2, the sound pressure level of the summary signal is 3 db higher than that of p 1 (why?)
6 Multiple sources Hearing 21 5 Loudness Hearing 22! Two sources with 80 db sound pressure level Source signals uncorrelated: together produce 83 db level Sources correlate perfectly (same sound): results in 86 db level! Doubling the sound amplitude increases the sound pressure level by 6 db Because: L p = 20 log 10 (2 p/p 0 ) = 20 log 10 (p/p 0 ) + 6 [db] Equivalent to adding another identical source next to the first one! Intuitively: if the two sources do not correlate, the components of the two audio signals may amplify or cancel out each other, depending on their relative phases, and hence the level will be only 83 db! Loudness describes the subjective level of sound Perception of loudness is relatively complex, but consistent phenomenon and one of the central parts of psychoacoustics! The loudness of a sound can be compared to a standardized reference tone, for example 1000 Hz sinusoidal tone Loudness level (phon) is defined to be the sound pressure level (db) of a 1000 Hz sinusoidal, that has the the same subjective loudness as the target sound For example if the heard sound is perceived as equally loud as 40 db 1kHz sinusoidal, is the loudness level 40 phons 5.1 Equal-loudness curves Hearing Critical bands Hearing 24 Sound pressure level (db) Loudness level (phons)! Listening to two sinusoids with nearby frequencies and increasing their frequency difference, the perceived loudness increases when the frequency difference exceeds critical bandwidth Figure: 1 60 db, Critical bandwidth is 160 Hz at 1 khz! Ear analyzes sound at critical band resolution. Each critical band contributes to the overall loudness level Frequency (Hz)
7 5.4 Loudness of a complex sound Hearing 25 6 Pitch Hearing 26! Loudness of a complex sound is calculated by using so-called loudness density as intermediate unit! Loudness density at each critical band is (roughly) proportional to the log-power of the signal at the band (weighted according to sensitivity of hearing and spread slightly by convolving over frequency)! Overall loudness is obtained by summing up loudness density values from each critical band! Figure: integration of loudness for a sinusoidal tone and for wideband noise Loudness density (sones / Bark) Frequency / Bark! Pitch Subjective attribute of sounds that enables us to arrange them on a frequency-related scale ranging from low to high Sound has a certain pitch if human listaners can consistently match the frequency of a sinusoidal tone to the pitch of the sound! Fundamental frequency vs. pitch Fundamental frequency is a physical attribute Pitch is a perceptual attribute Both are measured in Hertz (Hz) In practise, perceived pitch fundamental frequency! "Perfect pitch" or "absolute pitch" - ability to recognize the pitch of a musical note without any reference Minority of the population can do that 6.1 Harmonic sound Hearing Pitch perception Hearing 28! For a sinusoidal tone Fundamental frequency = sinusoidal frequency Pitch sinusoidal frequency! Harmonic sound Trumpet sound: * Fundamental frequency F = 262 Hz * Wavelength 1/F = 3.8 ms! Pitch perception has been tried to explain using two competing theories Place theory: Peak activity along the basilar membrane determines pitch (fails to explain missing fundamental) Periodicity theory: Pitch depends on rate, not place, of response. Neurons fire in sync with signals! The real mechanism is a combination of the above Sound is subdivided into subbands (critical bands) Periodicity of the amplitude envelope (see lowest panel) is analyzed within bands Results are combined across bands
8 6.3 Perceptually-motivated frequency scales Hearing 29 Subjective attributes of sound Hearing 30 mm. on basilar membrane frequency / khz frequency / mel! Sounds are typically described using four main attributes loudness, pitch, timbre, and duration! Table: dependence of the subjective attributes on physical parameters = strongly dependent, = to some extent = weak dependency Subjective attribute Loudness Pitch Timbre Duration frequency / Bark Physical parameter Pressure Frequency Spectrum Duration Envelope 7 Spatial hearing Hearing Monaural source localization Hearing 32! The most important auditory cues for localizing a sound sources in space are 1. Interaural time difference 2. Interaural intensity difference 3. Direction-dependent filtering of the sound spectrum by head and pinnae! Terms Monaural : with one ear Binaural : with two ears Interaural : between the ears (interaural time difference etc) Lateralization : localizing a source in horizontal plane! Diretional hearing works to some extent even with one ear! Head and pinna form a direction-dependent filter Direction-dependent changes in the spectrum of the sound arriving in the ear can be described with HRTFs HRTF = head-related transfer function! HRTFs are crucial for localizing sources in the median plane (vertical localization)
9 Monaural source localization Hearing Localizing a sinusoidal Hearing 34! HRTFs can be measured by recording Sound emitted by a source Sounds arriving to the auditory canal or eardrum (transfer function of the auditory canal does not vary along with direction)! In practice left: microphone in the ear of a test subject, OR right: head and torso simulator! Experimenting with sinusoidal tones helps to understand the localization of more complex sounds! Angle-of-arrival perception for sinusoids below 750 Hz is based mainly on interaural time difference Localizing a sinusoidal Hearing Localizing complex sounds Hearing 36! Interaural time difference is useful only up to 750 Hz Above that, the time difference is ambiguous, since there are several wavelengths within the time difference Moving the head (or source movement) helps: can be done up to 1500 Hz! At higher frequencies (> 750 Hz) the auditory system utilizes interaural intensity difference Head causes and acoustic shadow (sound level is lower behind the head) Works especially at high frequencies! Complex sounds refer to sounds that involve a number of different frequency components and vary over time! Localizing sound sources is typically a result of combining all the above-described mechanisms 1. Interaural time difference (most important) 2. Interaural intensity difference 3. HRTFs! Wideband noise: directional hearing works well
10 7.4 Lateralization in headphone listening Hearing 37! When listening with headphones, the sounds are often localized inside the head, on the axis between the ears Sound does not seem to come from outside the head because the diffraction caused by pinnae and head is missing If the sounds are processed with HRTFs carefully, they move outside the head
The Design and Implementation of Multimedia Software
 Chapter 10 Auditory Content The Design and Implementation of Multimedia Software David Bernstein Jones and Bartlett Publishers www.jbpub.com David Bernstein (jbpub.com) Multimedia Software Jones and Bartlett
Chapter 10 Auditory Content The Design and Implementation of Multimedia Software David Bernstein Jones and Bartlett Publishers www.jbpub.com David Bernstein (jbpub.com) Multimedia Software Jones and Bartlett
Lecture 4: Jan 12, 2005
 EE516 Computer Speech Processing Winter 2005 Lecture 4: Jan 12, 2005 Lecturer: Prof: J. Bilmes University of Washington Dept. of Electrical Engineering Scribe: Scott Philips
EE516 Computer Speech Processing Winter 2005 Lecture 4: Jan 12, 2005 Lecturer: Prof: J. Bilmes University of Washington Dept. of Electrical Engineering Scribe: Scott Philips
What Audio Engineers Should Know About Human Sound Perception. Part 2. Binaural Effects and Spatial Hearing
 What Audio Engineers Should Know About Human Sound Perception Part 2. Binaural Effects and Spatial Hearing AES 112 th Convention, Munich AES 113 th Convention, Los Angeles Durand R. Begault Human Factors
What Audio Engineers Should Know About Human Sound Perception Part 2. Binaural Effects and Spatial Hearing AES 112 th Convention, Munich AES 113 th Convention, Los Angeles Durand R. Begault Human Factors
Hearing and Deafness 1. Anatomy & physiology
 Hearing and Deafness 1. Anatomy & physiology Chris Darwin Web site for lectures, lecture notes and filtering lab: http://www.lifesci.susx.ac.uk/home/chris_darwin/ safari 1 Outer, middle & inner ear Capture;
Hearing and Deafness 1. Anatomy & physiology Chris Darwin Web site for lectures, lecture notes and filtering lab: http://www.lifesci.susx.ac.uk/home/chris_darwin/ safari 1 Outer, middle & inner ear Capture;
Your Hearing ILLUMINATED
 Your Hearing ILLUMINATED INFORMATION FROM YOUR HEARING CARE PROFESSIONAL REDISCOVER your hearing and reconnect 1 with the important things you might have been missing. Your sense of hearing is a vital
Your Hearing ILLUMINATED INFORMATION FROM YOUR HEARING CARE PROFESSIONAL REDISCOVER your hearing and reconnect 1 with the important things you might have been missing. Your sense of hearing is a vital
AP Psychology ~ Ms. Justice
 AP Psychology ~ Ms. Justice 8: What are the characteristics of air pressure waves that we hear as sound? Audition Audition, or hearing, is highly adaptive. We hear a wide range of sounds, but we hear best
AP Psychology ~ Ms. Justice 8: What are the characteristics of air pressure waves that we hear as sound? Audition Audition, or hearing, is highly adaptive. We hear a wide range of sounds, but we hear best
A diagram of the ear s structure. The outer ear includes the portion of the ear that we see the pinna/auricle and the ear canal.
 A diagram of the ear s structure THE OUTER EAR The outer ear includes the portion of the ear that we see the pinna/auricle and the ear canal. The pinna or auricle is a concave cartilaginous structure,
A diagram of the ear s structure THE OUTER EAR The outer ear includes the portion of the ear that we see the pinna/auricle and the ear canal. The pinna or auricle is a concave cartilaginous structure,
Sound Perception. Sensitivity to Sound. Sensitivity to Sound 1/9/11. Not physically sensitive to all possible sound frequencies Range
 Sound Perception Similarities between sound and light perception Characteristics of sound waves Wavelength = Pitch Purity = Timbre Amplitude = loudness Sensitivity to Sound Not physically sensitive to
Sound Perception Similarities between sound and light perception Characteristics of sound waves Wavelength = Pitch Purity = Timbre Amplitude = loudness Sensitivity to Sound Not physically sensitive to
The Effects of Ultrasonic Sound Generated by Ultrasonic Cleaning Systems on Human Hearing and Physiology
 The Effects of Ultrasonic Sound Generated by Ultrasonic Cleaning Systems on Human Hearing and Physiology Questions about the effects of ultrasonic energy on hearing and other human physiology arise from
The Effects of Ultrasonic Sound Generated by Ultrasonic Cleaning Systems on Human Hearing and Physiology Questions about the effects of ultrasonic energy on hearing and other human physiology arise from
What are the causes of presbycusis? What can be done? How can I communicate with someone who has a hearing loss? How does hearing work?
 This e-book will answer the following questions: What is presbycusis? What are the symptoms of presbycusis? What are the causes of presbycusis? What can be done? How can I communicate with someone who
This e-book will answer the following questions: What is presbycusis? What are the symptoms of presbycusis? What are the causes of presbycusis? What can be done? How can I communicate with someone who
Convention Paper Presented at the 112th Convention 2002 May 10 13 Munich, Germany
 Audio Engineering Society Convention Paper Presented at the 112th Convention 2002 May 10 13 Munich, Germany This convention paper has been reproduced from the author's advance manuscript, without editing,
Audio Engineering Society Convention Paper Presented at the 112th Convention 2002 May 10 13 Munich, Germany This convention paper has been reproduced from the author's advance manuscript, without editing,
PURE TONE AUDIOMETRY Andrew P. McGrath, AuD
 PURE TONE AUDIOMETRY Andrew P. McGrath, AuD Pure tone audiometry is the standard behavioral assessment of an individual s hearing. The results of pure tone audiometry are recorded on a chart or form called
PURE TONE AUDIOMETRY Andrew P. McGrath, AuD Pure tone audiometry is the standard behavioral assessment of an individual s hearing. The results of pure tone audiometry are recorded on a chart or form called
Dr. Abdel Aziz Hussein Lecturer of Physiology Mansoura Faculty of Medicine
 Physiological Basis of Hearing Tests By Dr. Abdel Aziz Hussein Lecturer of Physiology Mansoura Faculty of Medicine Introduction Def: Hearing is the ability to perceive certain pressure vibrations in the
Physiological Basis of Hearing Tests By Dr. Abdel Aziz Hussein Lecturer of Physiology Mansoura Faculty of Medicine Introduction Def: Hearing is the ability to perceive certain pressure vibrations in the
Noise. CIH Review PDC March 2012
 Noise CIH Review PDC March 2012 Learning Objectives Understand the concept of the decibel, decibel determination, decibel addition, and weighting Know the characteristics of frequency that are relevant
Noise CIH Review PDC March 2012 Learning Objectives Understand the concept of the decibel, decibel determination, decibel addition, and weighting Know the characteristics of frequency that are relevant
Anatomy and Physiology of Hearing (added 09/06)
 Anatomy and Physiology of Hearing (added 09/06) 1. Briefly review the anatomy of the cochlea. What is the cochlear blood supply? SW 2. Discuss the effects of the pinna, head and ear canal on the transmission
Anatomy and Physiology of Hearing (added 09/06) 1. Briefly review the anatomy of the cochlea. What is the cochlear blood supply? SW 2. Discuss the effects of the pinna, head and ear canal on the transmission
Trigonometric functions and sound
 Trigonometric functions and sound The sounds we hear are caused by vibrations that send pressure waves through the air. Our ears respond to these pressure waves and signal the brain about their amplitude
Trigonometric functions and sound The sounds we hear are caused by vibrations that send pressure waves through the air. Our ears respond to these pressure waves and signal the brain about their amplitude
Tonal Detection in Noise: An Auditory Neuroscience Insight
 Image: http://physics.ust.hk/dusw/ Tonal Detection in Noise: An Auditory Neuroscience Insight Buddhika Karunarathne 1 and Richard H.Y. So 1,2 1 Dept. of IELM, Hong Kong University of Science & Technology,
Image: http://physics.ust.hk/dusw/ Tonal Detection in Noise: An Auditory Neuroscience Insight Buddhika Karunarathne 1 and Richard H.Y. So 1,2 1 Dept. of IELM, Hong Kong University of Science & Technology,
Nature of the Sound Stimulus. Sound is the rhythmic compression and decompression of the air around us caused by a vibrating object.
 Sound and Hearing Nature of the Sound Stimulus Sound is the rhythmic compression and decompression of the air around us caused by a vibrating object. Applet Applet2 Frequency measured in cycles/sec = Hertz
Sound and Hearing Nature of the Sound Stimulus Sound is the rhythmic compression and decompression of the air around us caused by a vibrating object. Applet Applet2 Frequency measured in cycles/sec = Hertz
Estimation of Loudness by Zwicker's Method
 Estimation of Loudness by Zwicker's Method Loudness is one category in the list of human perceptions of sound. There are many methods of estimating Loudness using objective measurements. No method is perfect.
Estimation of Loudness by Zwicker's Method Loudness is one category in the list of human perceptions of sound. There are many methods of estimating Loudness using objective measurements. No method is perfect.
TECHNICAL LISTENING TRAINING: IMPROVEMENT OF SOUND SENSITIVITY FOR ACOUSTIC ENGINEERS AND SOUND DESIGNERS
 TECHNICAL LISTENING TRAINING: IMPROVEMENT OF SOUND SENSITIVITY FOR ACOUSTIC ENGINEERS AND SOUND DESIGNERS PACS: 43.10.Sv Shin-ichiro Iwamiya, Yoshitaka Nakajima, Kazuo Ueda, Kazuhiko Kawahara and Masayuki
TECHNICAL LISTENING TRAINING: IMPROVEMENT OF SOUND SENSITIVITY FOR ACOUSTIC ENGINEERS AND SOUND DESIGNERS PACS: 43.10.Sv Shin-ichiro Iwamiya, Yoshitaka Nakajima, Kazuo Ueda, Kazuhiko Kawahara and Masayuki
Presbycusis. What is presbycusis? What are the symptoms of presbycusis?
 Presbycusis What is presbycusis? Presbycusis is the loss of hearing that gradually occurs in most individuals as they grow older. Hearing loss is a common disorder associated with aging. About 30-35 percent
Presbycusis What is presbycusis? Presbycusis is the loss of hearing that gradually occurs in most individuals as they grow older. Hearing loss is a common disorder associated with aging. About 30-35 percent
So, how do we hear? outer middle ear inner ear
 The ability to hear is critical to understanding the world around us. The human ear is a fully developed part of our bodies at birth and responds to sounds that are very faint as well as sounds that are
The ability to hear is critical to understanding the world around us. The human ear is a fully developed part of our bodies at birth and responds to sounds that are very faint as well as sounds that are
Copyright 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Addison-Wesley.
 Chapter 20. Traveling Waves You may not realize it, but you are surrounded by waves. The waviness of a water wave is readily apparent, from the ripples on a pond to ocean waves large enough to surf. It
Chapter 20. Traveling Waves You may not realize it, but you are surrounded by waves. The waviness of a water wave is readily apparent, from the ripples on a pond to ocean waves large enough to surf. It
The loudness war is fought with (and over) compression
 The loudness war is fought with (and over) compression Susan E. Rogers, PhD Berklee College of Music Dept. of Music Production & Engineering 131st AES Convention New York, 2011 A summary of the loudness
The loudness war is fought with (and over) compression Susan E. Rogers, PhD Berklee College of Music Dept. of Music Production & Engineering 131st AES Convention New York, 2011 A summary of the loudness
Lecture 2, Human cognition
 Human Cognition An important foundation for the design of interfaces is a basic theory of human cognition The information processing paradigm (in its most simple form). Human Information Processing The
Human Cognition An important foundation for the design of interfaces is a basic theory of human cognition The information processing paradigm (in its most simple form). Human Information Processing The
T-61.184. Automatic Speech Recognition: From Theory to Practice
 Automatic Speech Recognition: From Theory to Practice http://www.cis.hut.fi/opinnot// September 27, 2004 Prof. Bryan Pellom Department of Computer Science Center for Spoken Language Research University
Automatic Speech Recognition: From Theory to Practice http://www.cis.hut.fi/opinnot// September 27, 2004 Prof. Bryan Pellom Department of Computer Science Center for Spoken Language Research University
Light wear for a powerful hearing. Bone Conduction Headset
 Light wear for a powerful hearing Bone Conduction Headset 2 Light wear for a powerful hearing Melody Flex, the new bone conduction headset is AUTEL s solution to improve hearing quality of those affected
Light wear for a powerful hearing Bone Conduction Headset 2 Light wear for a powerful hearing Melody Flex, the new bone conduction headset is AUTEL s solution to improve hearing quality of those affected
5th Congress of Alps-Adria Acoustics Association NOISE-INDUCED HEARING LOSS
 5th Congress of Alps-Adria Acoustics Association 12-14 September 2012, Petrčane, Croatia NOISE-INDUCED HEARING LOSS Davor Šušković, mag. ing. el. techn. inf. [email protected] Abstract: One of
5th Congress of Alps-Adria Acoustics Association 12-14 September 2012, Petrčane, Croatia NOISE-INDUCED HEARING LOSS Davor Šušković, mag. ing. el. techn. inf. [email protected] Abstract: One of
Noise: Impact on Hearing; Regulation
 Noise: Impact on Hearing; Regulation EOH 466A Fall 2008 Mechanism of Hearing Sound waves collected, focused by the outer ear. Humans have little control over muscles in outer ear. Many animals have the
Noise: Impact on Hearing; Regulation EOH 466A Fall 2008 Mechanism of Hearing Sound waves collected, focused by the outer ear. Humans have little control over muscles in outer ear. Many animals have the
Basic Concepts of Sound. Contents: Definitions db Conversion Sound Fields db ± db
 Basic Concepts of Sound Contents: Definitions db Conversion Sound Fields db ± db BA 7666-11, 1 Abstract This lecture introduces sound and sound measurements by describing sound pressure, sound level and
Basic Concepts of Sound Contents: Definitions db Conversion Sound Fields db ± db BA 7666-11, 1 Abstract This lecture introduces sound and sound measurements by describing sound pressure, sound level and
Pure Tone Hearing Screening in Schools: Revised Notes on Main Video. IMPORTANT: A hearing screening does not diagnose a hearing loss.
 Pure Tone Hearing Screening in Schools: Revised Notes on Main Video (Notes are also available for Video segments: Common Mistakes and FAQs) IMPORTANT: A hearing screening does not diagnose a hearing loss.
Pure Tone Hearing Screening in Schools: Revised Notes on Main Video (Notes are also available for Video segments: Common Mistakes and FAQs) IMPORTANT: A hearing screening does not diagnose a hearing loss.
The Sonometer The Resonant String and Timbre Change after plucking
 The Sonometer The Resonant String and Timbre Change after plucking EQUIPMENT Pasco sonometers (pick up 5 from teaching lab) and 5 kits to go with them BK Precision function generators and Tenma oscilloscopes
The Sonometer The Resonant String and Timbre Change after plucking EQUIPMENT Pasco sonometers (pick up 5 from teaching lab) and 5 kits to go with them BK Precision function generators and Tenma oscilloscopes
Welcome to the United States Patent and TradeMark Office
 Welcome to the United States Patent and TradeMark Office an Agency of the United States Department of Commerce United States Patent 5,159,703 Lowery October 27, 1992 Silent subliminal presentation system
Welcome to the United States Patent and TradeMark Office an Agency of the United States Department of Commerce United States Patent 5,159,703 Lowery October 27, 1992 Silent subliminal presentation system
Mathematical Harmonies Mark Petersen
 1 Mathematical Harmonies Mark Petersen What is music? When you hear a flutist, a signal is sent from her fingers to your ears. As the flute is played, it vibrates. The vibrations travel through the air
1 Mathematical Harmonies Mark Petersen What is music? When you hear a flutist, a signal is sent from her fingers to your ears. As the flute is played, it vibrates. The vibrations travel through the air
AP1 Waves. (A) frequency (B) wavelength (C) speed (D) intensity. Answer: (A) and (D) frequency and intensity.
 1. A fire truck is moving at a fairly high speed, with its siren emitting sound at a specific pitch. As the fire truck recedes from you which of the following characteristics of the sound wave from the
1. A fire truck is moving at a fairly high speed, with its siren emitting sound at a specific pitch. As the fire truck recedes from you which of the following characteristics of the sound wave from the
Acoustic Terms, Definitions and General Information
 Acoustic Terms, Definitions and General Information Authored by: Daniel Ziobroski Acoustic Engineer Environmental and Acoustic Engineering GE Energy Charles Powers Program Manager Environmental and Acoustic
Acoustic Terms, Definitions and General Information Authored by: Daniel Ziobroski Acoustic Engineer Environmental and Acoustic Engineering GE Energy Charles Powers Program Manager Environmental and Acoustic
Veterans UK Leaflet 10. Notes about War Pension claims for deafness
 Veterans UK Leaflet 10 Notes about War Pension claims for deafness 1 About this leaflet About this leaflet This leaflet tells you how claims for deafness are decided and gives you some information about
Veterans UK Leaflet 10 Notes about War Pension claims for deafness 1 About this leaflet About this leaflet This leaflet tells you how claims for deafness are decided and gives you some information about
CHAPTER 6 PRINCIPLES OF NEURAL CIRCUITS.
 CHAPTER 6 PRINCIPLES OF NEURAL CIRCUITS. 6.1. CONNECTIONS AMONG NEURONS Neurons are interconnected with one another to form circuits, much as electronic components are wired together to form a functional
CHAPTER 6 PRINCIPLES OF NEURAL CIRCUITS. 6.1. CONNECTIONS AMONG NEURONS Neurons are interconnected with one another to form circuits, much as electronic components are wired together to form a functional
Check Your Hearing - http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=mmu6npeidoy
 The Science of Hearing The human hearing range is between 20 to 20,000 Hz. There is considerable variation in the hearing range between individuals. Most young people can hear up to 18,000 Hz. Our ability
The Science of Hearing The human hearing range is between 20 to 20,000 Hz. There is considerable variation in the hearing range between individuals. Most young people can hear up to 18,000 Hz. Our ability
BONE-CONDUCTION HEARING AIDS
 BONE-CONDUCTION HEARING AIDS Introduction Conventional hearing aids fit in the ear canal and amplify sounds, which the hearing aid user then hears in the normal way. However, these hearing aids are not
BONE-CONDUCTION HEARING AIDS Introduction Conventional hearing aids fit in the ear canal and amplify sounds, which the hearing aid user then hears in the normal way. However, these hearing aids are not
Lecture 1-6: Noise and Filters
 Lecture 1-6: Noise and Filters Overview 1. Periodic and Aperiodic Signals Review: by periodic signals, we mean signals that have a waveform shape that repeats. The time taken for the waveform to repeat
Lecture 1-6: Noise and Filters Overview 1. Periodic and Aperiodic Signals Review: by periodic signals, we mean signals that have a waveform shape that repeats. The time taken for the waveform to repeat
Guideline for Hearing Conservation and Noise Control
 EVERYONE'S RESPONSIBILITY Guideline for Hearing Conservation and Noise Control February 2007 Guideline for Hearing Conservation and Noise Control Workplace Safety & Health Division 200 401 York Avenue
EVERYONE'S RESPONSIBILITY Guideline for Hearing Conservation and Noise Control February 2007 Guideline for Hearing Conservation and Noise Control Workplace Safety & Health Division 200 401 York Avenue
Hearing Conservation Procedures
 Hearing Conservation Procedures Purpose The University of Regina is committed to providing a safe and healthy work and educational environment for all members of the University community by ensuring that
Hearing Conservation Procedures Purpose The University of Regina is committed to providing a safe and healthy work and educational environment for all members of the University community by ensuring that
AN1200.04. Application Note: FCC Regulations for ISM Band Devices: 902-928 MHz. FCC Regulations for ISM Band Devices: 902-928 MHz
 AN1200.04 Application Note: FCC Regulations for ISM Band Devices: Copyright Semtech 2006 1 of 15 www.semtech.com 1 Table of Contents 1 Table of Contents...2 1.1 Index of Figures...2 1.2 Index of Tables...2
AN1200.04 Application Note: FCC Regulations for ISM Band Devices: Copyright Semtech 2006 1 of 15 www.semtech.com 1 Table of Contents 1 Table of Contents...2 1.1 Index of Figures...2 1.2 Index of Tables...2
Comparative study of the commercial software for sound quality analysis
 TECHNICAL REPORT #2008 The Acoustical Society of Japan Comparative study of the commercial software for sound quality analysis Sung-Hwan Shin Department of Electrical and Mechanical Engineering, Seikei
TECHNICAL REPORT #2008 The Acoustical Society of Japan Comparative study of the commercial software for sound quality analysis Sung-Hwan Shin Department of Electrical and Mechanical Engineering, Seikei
MICROPHONE SPECIFICATIONS EXPLAINED
 Application Note AN-1112 MICROPHONE SPECIFICATIONS EXPLAINED INTRODUCTION A MEMS microphone IC is unique among InvenSense, Inc., products in that its input is an acoustic pressure wave. For this reason,
Application Note AN-1112 MICROPHONE SPECIFICATIONS EXPLAINED INTRODUCTION A MEMS microphone IC is unique among InvenSense, Inc., products in that its input is an acoustic pressure wave. For this reason,
SPATIAL IMPULSE RESPONSE RENDERING: A TOOL FOR REPRODUCING ROOM ACOUSTICS FOR MULTI-CHANNEL LISTENING
 SPATIAL IMPULSE RESPONSE RENDERING: A TOOL FOR REPRODUCING ROOM ACOUSTICS FOR MULTI-CHANNEL LISTENING VILLE PULKKI AND JUHA MERIMAA Laboratory of Acoustics and Audio Signal Processing, Helsinki University
SPATIAL IMPULSE RESPONSE RENDERING: A TOOL FOR REPRODUCING ROOM ACOUSTICS FOR MULTI-CHANNEL LISTENING VILLE PULKKI AND JUHA MERIMAA Laboratory of Acoustics and Audio Signal Processing, Helsinki University
physics 1/12/2016 Chapter 20 Lecture Chapter 20 Traveling Waves
 Chapter 20 Lecture physics FOR SCIENTISTS AND ENGINEERS a strategic approach THIRD EDITION randall d. knight Chapter 20 Traveling Waves Chapter Goal: To learn the basic properties of traveling waves. Slide
Chapter 20 Lecture physics FOR SCIENTISTS AND ENGINEERS a strategic approach THIRD EDITION randall d. knight Chapter 20 Traveling Waves Chapter Goal: To learn the basic properties of traveling waves. Slide
Hearcentres Guide to Hearing Aid Terminology
 Hearcentres Guide to Hearing Aid Terminology Sophisticated modern hearing aids use a number of complicated technologies and techniques to ensure great improvements in hearing. Not only are the terms used
Hearcentres Guide to Hearing Aid Terminology Sophisticated modern hearing aids use a number of complicated technologies and techniques to ensure great improvements in hearing. Not only are the terms used
Interference to Hearing Aids by Digital Mobile Telephones Operating in the 1800 MHz Band.
 Interference to Hearing Aids by Digital Mobile Telephones Operating in the 1800 MHz Band. Reference: EB968 Date: January 2008 Author: Eric Burwood (National Acoustic Laboratories) Collaborator: Walter
Interference to Hearing Aids by Digital Mobile Telephones Operating in the 1800 MHz Band. Reference: EB968 Date: January 2008 Author: Eric Burwood (National Acoustic Laboratories) Collaborator: Walter
HEARING. With Your Brain
 HEARING With Your Brain Better Hearing with Both Ears Experience A NEW FREEDOM Your brain is responsible for processing everything you hear and needs accurate sound information from both ears. When you
HEARING With Your Brain Better Hearing with Both Ears Experience A NEW FREEDOM Your brain is responsible for processing everything you hear and needs accurate sound information from both ears. When you
Hearing Tests And Your Child
 HOW EARLY CAN A CHILD S HEARING BE TESTED? Most parents can remember the moment they first realized that their child could not hear. Louise Tracy has often told other parents of the time she went onto
HOW EARLY CAN A CHILD S HEARING BE TESTED? Most parents can remember the moment they first realized that their child could not hear. Louise Tracy has often told other parents of the time she went onto
Schindler 3300 / Schindler 5300 Information on noise and vibration.
 Schindler 3300 / Schindler 5300. Content Introduction 1. Ride quality Jerk Car acceleration Vertical car vibration Lateral car vibration Sound in the car 2. Sound basics 3. Vibration basics 4. Structure-borne
Schindler 3300 / Schindler 5300. Content Introduction 1. Ride quality Jerk Car acceleration Vertical car vibration Lateral car vibration Sound in the car 2. Sound basics 3. Vibration basics 4. Structure-borne
Noise at work a guide for health and safety representatives
 Noise at work a guide for health and safety representatives Hearing problems caused by noise at work are far too common. The HSE estimates that 170,000 people in the UK suffer deafness, tinnitus or other
Noise at work a guide for health and safety representatives Hearing problems caused by noise at work are far too common. The HSE estimates that 170,000 people in the UK suffer deafness, tinnitus or other
Sound Pressure Measurement
 Objectives: Sound Pressure Measurement 1. Become familiar with hardware and techniques to measure sound pressure 2. Measure the sound level of various sizes of fan modules 3. Calculate the signal-to-noise
Objectives: Sound Pressure Measurement 1. Become familiar with hardware and techniques to measure sound pressure 2. Measure the sound level of various sizes of fan modules 3. Calculate the signal-to-noise
Audiometry and Hearing Loss Examples
 Audiometry and Hearing Loss Examples An audiogram shows the quietest sounds you can just hear. The red circles represent the right ear and the blue crosses represent the left ear. Across the top, there
Audiometry and Hearing Loss Examples An audiogram shows the quietest sounds you can just hear. The red circles represent the right ear and the blue crosses represent the left ear. Across the top, there
Understanding Hearing Loss 404.591.1884. www.childrensent.com
 Understanding Hearing Loss 404.591.1884 www.childrensent.com You just found out your child has a hearing loss. You know what the Audiologist explained to you, but it is hard to keep track of all the new
Understanding Hearing Loss 404.591.1884 www.childrensent.com You just found out your child has a hearing loss. You know what the Audiologist explained to you, but it is hard to keep track of all the new
PLEASE DO NOT WRITE ON THE TEST. PLACE ALL MULTIPLE CHOICE ANSWERS ON THE SCANTRON. (THANK YOU FOR SAVING A TREE.)
 PLEASE DO NOT WRITE ON THE TEST. PLACE ALL MULTIPLE CHOICE ANSWERS ON THE SCANTRON. (THANK YOU FOR SAVING A TREE.) Sound Waves Test -- each multiple choice question is worth 3 points. 1. Sound waves are
PLEASE DO NOT WRITE ON THE TEST. PLACE ALL MULTIPLE CHOICE ANSWERS ON THE SCANTRON. (THANK YOU FOR SAVING A TREE.) Sound Waves Test -- each multiple choice question is worth 3 points. 1. Sound waves are
Sound absorption and acoustic surface impedance
 Sound absorption and acoustic surface impedance CHRISTER HEED SD2165 Stockholm October 2008 Marcus Wallenberg Laboratoriet för Ljud- och Vibrationsforskning Sound absorption and acoustic surface impedance
Sound absorption and acoustic surface impedance CHRISTER HEED SD2165 Stockholm October 2008 Marcus Wallenberg Laboratoriet för Ljud- och Vibrationsforskning Sound absorption and acoustic surface impedance
Noise and Hearing Protection
 Noise and Hearing Protection Noise and Hearing Safety Training This training module is designed to teach you about the purpose and benefits of a hearing conservation program. After completing the training,
Noise and Hearing Protection Noise and Hearing Safety Training This training module is designed to teach you about the purpose and benefits of a hearing conservation program. After completing the training,
The Role of the Efferent System in Auditory Performance in Background Noise
 The Role of the Efferent System in Auditory Performance in Background Noise Utah Speech-Language Hearing Association, 2015 Skyler G. Jennings Ph.D., Au.D. CCC-A Outline Hearing in a noisy background Normal
The Role of the Efferent System in Auditory Performance in Background Noise Utah Speech-Language Hearing Association, 2015 Skyler G. Jennings Ph.D., Au.D. CCC-A Outline Hearing in a noisy background Normal
Workshop Perceptual Effects of Filtering and Masking Introduction to Filtering and Masking
 Workshop Perceptual Effects of Filtering and Masking Introduction to Filtering and Masking The perception and correct identification of speech sounds as phonemes depends on the listener extracting various
Workshop Perceptual Effects of Filtering and Masking Introduction to Filtering and Masking The perception and correct identification of speech sounds as phonemes depends on the listener extracting various
Hearing Tests And Your Child
 How Early Can A Child s Hearing Be Tested? Most parents can remember the moment they first realized that their child could not hear. Louise Tracy has often told other parents of the time she went onto
How Early Can A Child s Hearing Be Tested? Most parents can remember the moment they first realized that their child could not hear. Louise Tracy has often told other parents of the time she went onto
Advanced Speech-Audio Processing in Mobile Phones and Hearing Aids
 Advanced Speech-Audio Processing in Mobile Phones and Hearing Aids Synergies and Distinctions Peter Vary RWTH Aachen University Institute of Communication Systems WASPAA, October 23, 2013 Mohonk Mountain
Advanced Speech-Audio Processing in Mobile Phones and Hearing Aids Synergies and Distinctions Peter Vary RWTH Aachen University Institute of Communication Systems WASPAA, October 23, 2013 Mohonk Mountain
HEAD acoustics. Standards on Audio Quality - from a system-level view. H. W. Gierlich HEAD acoustics GmbH. www.head-acoustics.
 HEAD acoustics Standards on Audio Quality - from a system-level view H. W. Gierlich HEAD acoustics GmbH www.head-acoustics.de 27-Mar-03 #1 Overview Reference Points and Equalization free field-/diffuse
HEAD acoustics Standards on Audio Quality - from a system-level view H. W. Gierlich HEAD acoustics GmbH www.head-acoustics.de 27-Mar-03 #1 Overview Reference Points and Equalization free field-/diffuse
Introduction to Digital Audio
 Introduction to Digital Audio Before the development of high-speed, low-cost digital computers and analog-to-digital conversion circuits, all recording and manipulation of sound was done using analog techniques.
Introduction to Digital Audio Before the development of high-speed, low-cost digital computers and analog-to-digital conversion circuits, all recording and manipulation of sound was done using analog techniques.
The Calculation of G rms
 The Calculation of G rms QualMark Corp. Neill Doertenbach The metric of G rms is typically used to specify and compare the energy in repetitive shock vibration systems. However, the method of arriving
The Calculation of G rms QualMark Corp. Neill Doertenbach The metric of G rms is typically used to specify and compare the energy in repetitive shock vibration systems. However, the method of arriving
Building Design for Advanced Technology Instruments Sensitive to Acoustical Noise
 Building Design for Advanced Technology Instruments Sensitive to Acoustic Noise Michael Gendreau Colin Gordon & Associates Presentation Outline! High technology research and manufacturing instruments respond
Building Design for Advanced Technology Instruments Sensitive to Acoustic Noise Michael Gendreau Colin Gordon & Associates Presentation Outline! High technology research and manufacturing instruments respond
This document is downloaded from DR-NTU, Nanyang Technological University Library, Singapore.
 This document is downloaded from DR-NTU, Nanyang Technological University Library, Singapore. Title to improve 3D audio playback Author(s) Sunder, Kaushik; Tan, Ee-Leng; Gan, Woon-Seng Citation Sunder,
This document is downloaded from DR-NTU, Nanyang Technological University Library, Singapore. Title to improve 3D audio playback Author(s) Sunder, Kaushik; Tan, Ee-Leng; Gan, Woon-Seng Citation Sunder,
Convention Paper Presented at the 118th Convention 2005 May 28 31 Barcelona, Spain
 Audio Engineering Society Convention Paper Presented at the 118th Convention 25 May 28 31 Barcelona, Spain 6431 This convention paper has been reproduced from the author s advance manuscript, without editing,
Audio Engineering Society Convention Paper Presented at the 118th Convention 25 May 28 31 Barcelona, Spain 6431 This convention paper has been reproduced from the author s advance manuscript, without editing,
Lecture 1-10: Spectrograms
 Lecture 1-10: Spectrograms Overview 1. Spectra of dynamic signals: like many real world signals, speech changes in quality with time. But so far the only spectral analysis we have performed has assumed
Lecture 1-10: Spectrograms Overview 1. Spectra of dynamic signals: like many real world signals, speech changes in quality with time. But so far the only spectral analysis we have performed has assumed
Expanding Performance Leadership in Cochlear Implants. Hansjuerg Emch President, Advanced Bionics AG GVP, Sonova Medical
 Expanding Performance Leadership in Cochlear Implants Hansjuerg Emch President, Advanced Bionics AG GVP, Sonova Medical Normal Acoustic Hearing High Freq Low Freq Acoustic Input via External Ear Canal
Expanding Performance Leadership in Cochlear Implants Hansjuerg Emch President, Advanced Bionics AG GVP, Sonova Medical Normal Acoustic Hearing High Freq Low Freq Acoustic Input via External Ear Canal
Section 4. Hearing loss and hearing tests
 Section 4 Hearing loss and hearing tests How we hear Outer Ear Middle Ear Inner Ear 4. 7. 8. 1. 3. 6. 2. 5. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Ear canal Ear drum Middle ear cavity Middle ear bones the malleus, incus,
Section 4 Hearing loss and hearing tests How we hear Outer Ear Middle Ear Inner Ear 4. 7. 8. 1. 3. 6. 2. 5. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Ear canal Ear drum Middle ear cavity Middle ear bones the malleus, incus,
Decibel Table Loudness Comparison Chart
 Deutsche Version Decibel Table Loudness Comparison Chart Table of Sound Levels (db Scale) and the corresponding Units of Sound Pressure and Sound Intensity (Examples) To get a feeling for decibels, look
Deutsche Version Decibel Table Loudness Comparison Chart Table of Sound Levels (db Scale) and the corresponding Units of Sound Pressure and Sound Intensity (Examples) To get a feeling for decibels, look
Unlocking. Potential. Using The Listening Program to Help Individuals with Autism Spectrum Disorders Improve Auditory Processing
 Unlocking Potential Using The Listening Program to Help Individuals with Autism Spectrum Disorders Improve Auditory Processing Children with autism spectrum disorders can recover. A bold statement perhaps
Unlocking Potential Using The Listening Program to Help Individuals with Autism Spectrum Disorders Improve Auditory Processing Children with autism spectrum disorders can recover. A bold statement perhaps
Help maintain homeostasis by capturing stimuli from the external environment and relaying them to the brain for processing.
 The Sense Organs... (page 409) Help maintain homeostasis by capturing stimuli from the external environment and relaying them to the brain for processing. Ex. Eye structure - protected by bony ridges and
The Sense Organs... (page 409) Help maintain homeostasis by capturing stimuli from the external environment and relaying them to the brain for processing. Ex. Eye structure - protected by bony ridges and
Basic Acoustics and Acoustic Filters
 Basic CHAPTER Acoustics and Acoustic Filters 1 3 Basic Acoustics and Acoustic Filters 1.1 The sensation of sound Several types of events in the world produce the sensation of sound. Examples include doors
Basic CHAPTER Acoustics and Acoustic Filters 1 3 Basic Acoustics and Acoustic Filters 1.1 The sensation of sound Several types of events in the world produce the sensation of sound. Examples include doors
Room Acoustic Reproduction by Spatial Room Response
 Room Acoustic Reproduction by Spatial Room Response Rendering Hoda Nasereddin 1, Mohammad Asgari 2 and Ayoub Banoushi 3 Audio Engineer, Broadcast engineering department, IRIB university, Tehran, Iran,
Room Acoustic Reproduction by Spatial Room Response Rendering Hoda Nasereddin 1, Mohammad Asgari 2 and Ayoub Banoushi 3 Audio Engineer, Broadcast engineering department, IRIB university, Tehran, Iran,
Overview. Dolby PC Entertainment Experience v4
 Dolby PC Entertainment Experience v4 Overview From humble beginnings as a productivity device, the personal computer has evolved into an entertainment hub for the digital lifestyle. People are increasingly
Dolby PC Entertainment Experience v4 Overview From humble beginnings as a productivity device, the personal computer has evolved into an entertainment hub for the digital lifestyle. People are increasingly
Figure1. Acoustic feedback in packet based video conferencing system
 Real-Time Howling Detection for Hands-Free Video Conferencing System Mi Suk Lee and Do Young Kim Future Internet Research Department ETRI, Daejeon, Korea {lms, dyk}@etri.re.kr Abstract: This paper presents
Real-Time Howling Detection for Hands-Free Video Conferencing System Mi Suk Lee and Do Young Kim Future Internet Research Department ETRI, Daejeon, Korea {lms, dyk}@etri.re.kr Abstract: This paper presents
Voice Communication Package v7.0 of front-end voice processing software technologies General description and technical specification
 Voice Communication Package v7.0 of front-end voice processing software technologies General description and technical specification (Revision 1.0, May 2012) General VCP information Voice Communication
Voice Communication Package v7.0 of front-end voice processing software technologies General description and technical specification (Revision 1.0, May 2012) General VCP information Voice Communication
Speech Signal Processing: An Overview
 Speech Signal Processing: An Overview S. R. M. Prasanna Department of Electronics and Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Guwahati December, 2012 Prasanna (EMST Lab, EEE, IITG) Speech
Speech Signal Processing: An Overview S. R. M. Prasanna Department of Electronics and Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Guwahati December, 2012 Prasanna (EMST Lab, EEE, IITG) Speech
PROTECT YOUR HEARING
 PROTECT YOUR HEARING Original idea from David Carlisle Aviation can be a noisy business that can assault tour ears and chip away at your ability to hear clearly. Prevention is your only effective defense.
PROTECT YOUR HEARING Original idea from David Carlisle Aviation can be a noisy business that can assault tour ears and chip away at your ability to hear clearly. Prevention is your only effective defense.
Getting Started Kei Te Timata
 Getting Started Kei Te Timata AN INTRODUCTION FOR THE FAMILIES AND WHANAU OF CHILDREN DIAGNOSED WITH A HEARING LOSS. THIS IS A JOINT PROJECT BY DEAF EDUCATION AOTEAROA NEW ZEALAND AND THE NATIONAL AUDIOLOGY
Getting Started Kei Te Timata AN INTRODUCTION FOR THE FAMILIES AND WHANAU OF CHILDREN DIAGNOSED WITH A HEARING LOSS. THIS IS A JOINT PROJECT BY DEAF EDUCATION AOTEAROA NEW ZEALAND AND THE NATIONAL AUDIOLOGY
Summary Our science project is an investigation into the varying levels of damage that different types of earphones and mp3 players cause to hearing.
 Meet The Team Ella Lyons is our team leader. Whilst we were doing our experiment Ella was the main operator of the data logging device. Ella took charge in any part of our experiment which involved computers
Meet The Team Ella Lyons is our team leader. Whilst we were doing our experiment Ella was the main operator of the data logging device. Ella took charge in any part of our experiment which involved computers
The Physics of Music: Brass Instruments. James Bernhard
 The Physics of Music: Brass Instruments James Bernhard As a first approximation, brass instruments can be modeled as closed cylindrical pipes, where closed means closed at one end, open at the other Here
The Physics of Music: Brass Instruments James Bernhard As a first approximation, brass instruments can be modeled as closed cylindrical pipes, where closed means closed at one end, open at the other Here
Computer Networks and Internets, 5e Chapter 6 Information Sources and Signals. Introduction
 Computer Networks and Internets, 5e Chapter 6 Information Sources and Signals Modified from the lecture slides of Lami Kaya ([email protected]) for use CECS 474, Fall 2008. 2009 Pearson Education Inc., Upper
Computer Networks and Internets, 5e Chapter 6 Information Sources and Signals Modified from the lecture slides of Lami Kaya ([email protected]) for use CECS 474, Fall 2008. 2009 Pearson Education Inc., Upper
Acoustics: the study of sound waves
 Acoustics: the study of sound waves Sound is the phenomenon we experience when our ears are excited by vibrations in the gas that surrounds us. As an object vibrates, it sets the surrounding air in motion,
Acoustics: the study of sound waves Sound is the phenomenon we experience when our ears are excited by vibrations in the gas that surrounds us. As an object vibrates, it sets the surrounding air in motion,
Paediatric Hearing Assessment
 Information for parents Paediatric Hearing Assessment Hearing assessment of infants is limited by their ability to respond to sounds. This is determined by both the development of the hearing system and
Information for parents Paediatric Hearing Assessment Hearing assessment of infants is limited by their ability to respond to sounds. This is determined by both the development of the hearing system and
application note Directional Microphone Applications Introduction Directional Hearing Aids
 APPLICATION NOTE AN-4 Directional Microphone Applications Introduction The inability to understand speech in noisy environments is a significant problem for hearing impaired individuals. An omnidirectional
APPLICATION NOTE AN-4 Directional Microphone Applications Introduction The inability to understand speech in noisy environments is a significant problem for hearing impaired individuals. An omnidirectional
Big Data in Education
 Big Data in Education Assessment of the New Educational Standards Markus Iseli, Deirdre Kerr, Hamid Mousavi Big Data in Education Technology is disrupting education, expanding the education ecosystem beyond
Big Data in Education Assessment of the New Educational Standards Markus Iseli, Deirdre Kerr, Hamid Mousavi Big Data in Education Technology is disrupting education, expanding the education ecosystem beyond
Ear Disorders and Problems
 Ear Disorders and Problems Introduction Your ear has three main parts: outer, middle and inner. You use all of them to hear. There are many disorders and problems that can affect the ear. The symptoms
Ear Disorders and Problems Introduction Your ear has three main parts: outer, middle and inner. You use all of them to hear. There are many disorders and problems that can affect the ear. The symptoms
Once your baby has good head control and can turn towards something interesting, a more advanced behavioural procedure can be used.
 How do we test the hearing of babies and children? An audiologist will select from a range of different tests to evaluate your child s hearing. The choice of test depends on the information that is needed
How do we test the hearing of babies and children? An audiologist will select from a range of different tests to evaluate your child s hearing. The choice of test depends on the information that is needed
Spectrum Level and Band Level
 Spectrum Level and Band Level ntensity, ntensity Level, and ntensity Spectrum Level As a review, earlier we talked about the intensity of a sound wave. We related the intensity of a sound wave to the acoustic
Spectrum Level and Band Level ntensity, ntensity Level, and ntensity Spectrum Level As a review, earlier we talked about the intensity of a sound wave. We related the intensity of a sound wave to the acoustic
quick guide to hearing protection Oregon OSHA s What you should know and not a word more!
 Oregon OSHA s quick guide to hearing protection What you should know and not a word more! A Division of the Department of Consumer and Business Services About this guide Oregon OSHA quick guides are for
Oregon OSHA s quick guide to hearing protection What you should know and not a word more! A Division of the Department of Consumer and Business Services About this guide Oregon OSHA quick guides are for
Surgery for Conductive Hearing Loss
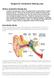 Surgery for Conductive Hearing Loss What is conductive hearing loss Conductive hearing loss is a form of hearing loss due to abnormalities in mobile portions of the ear. Theses are the movable parts (including
Surgery for Conductive Hearing Loss What is conductive hearing loss Conductive hearing loss is a form of hearing loss due to abnormalities in mobile portions of the ear. Theses are the movable parts (including
