Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus (MRSA) 2010 Alberta Health and Wellness Report
|
|
|
- Allan Sherman
- 3 years ago
- Views:
From this document you will learn the answers to the following questions:
Which health zone had the highest rate of MRSA?
How many people were exposed to MRSA in South Calgary?
Transcription
1 Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus (MRSA) 21 Alberta Health and Wellness Report
2 211 Government of Alberta ISBN October 211 Alberta Health and Wellness, Surveillance and Assessment Send inquiries to:
3 Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus (MRSA) 21 AHW Report October 211 Executive Summary Methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) is one of a number of nosocomial infections found in acute care settings, but also in other facilities and in the community. MRSA first came under lab surveillance in Alberta in June 25. Since then, Alberta Health and Wellness (AHW), in partnership with Alberta Health Services, has developed guidelines and standards to both manage and prevent infections like MRSA, and continues to monitor infection activity through lab surveillance of first clinical isolates. In summary: Total MRSA cases and rates in Alberta have been steady for the last four years. Rates of infection are highest in the elderly (7 years and older) and in babies (under 1 year). Rates for those under 2 years of age have more than doubled between 26 and 21 (26 cases per 1, to 68 cases per 1,). In 21, those who were 5 years and older made up the largest proportion of cases in the South, Calgary and Central health zones, while 2 to 49 year olds were the largest age group in the Edmonton and North zones. In 21, MRSA rates in the Central and North health zones were higher than the provincial average of cases per 1, persons. MRSA can be further typed by the lab to the strain level: CMRSA 1 through CMRSA 1 o The majority of cases reported have been typed as CMRSA 1 since 26, and this increased sharply between 26 and 27. o Since 26, cases of CMRSA 7 and CMRSA 8 have increased, while CMRSA 3 & 6 have decreased. o In 21, rates of CMRSA 7 and CMRSA 1 were highest for those under 1 year of age (31.5 cases per 1, and 84.6 cases per 1,, respectively); CMRSA 2 was highest in those 7 years and older (228.2 cases per 1,). 1 Government of Alberta
4 Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus (MRSA) 21 AHW Report October 211 Background Staphylococcus aureus is a bacterium, which commonly lives in the nose and on the skin of healthy people. Many people that harbour these bacteria have no symptoms but some develop infections and need treatment. MRSA is the term for Staphylococcus aureus (S.A.) bacteria that have become resistant to semi-synthetic penicillins such as cloxacillin and methicillin. It can also acquire resistance to other classes of antibiotics. MRSA infections can be more difficult to treat and drugs commonly used for treatment of other strains of S.A are not always effective. The S.A bacteria are spread primarily through direct person-to-person contact with a colonized or clinically infected individual (see Glossary in the Appendix). Traditionally, MRSA is seen in people who are taking antibiotics and those individuals who are receiving medical care. MRSA, like S.A, may also live on the skin, in the nose, or around the rectum of a person. More recently, MRSA has been found in people who have no contact with the health care system. This is referred to as community-associated MRSA (CA-MRSA). In the community, MRSA most commonly causes skin and soft tissue infections (e.g. boils or abscesses on arms, legs or elsewhere). These are treatable with drainage and antibiotics. In rare cases, MRSA can cause severe invasive infections such as pneumonia and bloodstream infections such as septicemia. These severe infections require urgent medical treatment. Infection occurs when bacteria get past normal body defences and cause disease. MRSA were first reported in the hospital in 1961 by bacteriologist professor Patricia Jevons in England 1. In America, the first reports of MRSA were in hospitals in Boston in In Canada, in 1981, MRSA acquired in the community was first reported by Low et al 2. The preliminary results from a Canadian Nosocomial Infection Surveillance Program (CNISP) study on MRSA between January 1995 and December 1999 found 4,57 patients infected or colonized with MRSA from the 22 to 34 hospital sites participating. Through this study, the rate of MRSA was found to have increased from.46 per 1, admissions in 1995 to 4.12 per 1, admissions in 1999 (p <.5) 3. Colonization occurs when bacteria are present on or in the body without causing illness. An updated CNISP report included data up to and including 23 from 38 hospital sites (mostly tertiary-care teaching hospitals; and a few community hospitals) involved in the MRSA surveillance program in nine Canadian provinces. The results found that MRSA rates continued to increase from 4.12 cases per 1, admissions in 1999 to 5.1 cases per 1, admissions in 23, a significant increase (p=.2) 4. In 27, a preliminary surveillance report on MRSA in patients from 47 Canadian acute-care sentinel hospitals found that the MRSA rate was 8.62 per 1, admissions 5. A 24 investigation of an outbreak of MRSA (Canadian strain type, CMRSA 1) in the Calgary Health Region found that the highest risk was for people with histories of illicit drug use, homelessness or recent incarceration 6. Factors that contribute to transmission of MRSA include environmental (e.g., overcrowded living conditions), social (e.g., belong to specific drug using networks, limited health care access), individual (e.g. pre-existing cut, abrasion or wound) and 2 Government of Alberta
5 Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus (MRSA) 21 AHW Report October 211 behavioural (e.g., sharing drug paraphernalia). The transmission factors have been termed the five C s : cleanliness, crowding, contact, sharing contaminated items, and compromised skin 7. Later, an Alberta report of the Provincial Outbreak Investigation between June 1, 25 and February 28, 26 (EI ) found that the majority of patients infected with MRSA were infected with the typically healthcare-associated strain CMRSA 2 (38.5 per cent) or the usually community-associated strain CMRSA 1 (36.7 per cent) 8. Alberta Health and Wellness provides information on prevention and management of community associated MRSA 7 and Provincial MRSA IPC Guidelines and Standards for Prevention and Management of MRSA on their public website 9. In Alberta, the Provincial Public Health Laboratory (ProvLab) has collected lab information on MRSA cases since June 25. These MRSA cases are reported to AHW weekly. In February 21, to enhance surveillance of MRSA, ProvLab changed typing procedures; ProvLab replaced pulsedfield gel electrophoresis (PFGE) with spa typing the internationally preferred method for MRSA typing as the primary molecular typing method of first clinical isolates of MRSA. The first clinical isolate is an under-estimation of the number of MRSA cases in Alberta, as colonized individuals are not captured. 3 Government of Alberta
6 Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus (MRSA) 21 AHW Report October 211 SUMMARY - MRSA in Alberta, This section presents an annual overview of MRSA in Alberta for the years 26 to 21. The source of all data is the AHW MRSA dataset based on first clinical isolates identified through Provincial Public Health Laboratory (ProvLab) and reported weekly to AHW. Population figures used in the denominators are from the AHW Interactive Health Data Application. Figure 1 7, 6, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1, Number and Crude Rate (per 1,) of MRSA in Alberta (n=19,31) (January 1st, 26 - December 31st, 21) ,533 3,711 4,269 4,219 4,299 Rate Rates (per 1, persons) The number of reported MRSA cases had increased from 2,533 cases (rate of 74 cases per 1, persons) in 26 to 4,269 cases (118 cases per 1, persons) in 28. From 27 to 21, MRSA rates remained at similar levels. In 21, there were 4,299 cases at a rate of 116 cases per 1, persons (Figure 1). Figure 2 Number and Crude Rate (per 1,) of MRSA in Alberta by Sex (January 1st, 26 - December 31st, 21) 3,2 2,8 2,4 2, 1,6 1, Female 1,62 1,46 1,743 1,798 1,944 Male 1,47 2,246 2,523 2,418 2,353 Female Rates Male Rates Rates (per 1, persons) 4 Government of Alberta
7 Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus (MRSA) 21 AHW Report October 211 The MRSA rate for males continues to be higher than those for females for the past five years. In 26, the MRSA male rate was 89 cases per 1, males, increasing to 145 cases per 1, males in 28, and then decreasing to 126 cases per 1, males in 21. The MRSA female rate continued to increase from 64 cases per 1, females in 26 to 15 cases per 1, females in 21 (Figure 2). Overall, MRSA rates for the age group of 7 years and older were the highest. Their rates increased from 277 cases per 1, persons in 26 to 333 cases per 1, persons in 21. The lowest MRSA rates were in the one to nine years of age group, ranging from 19 cases per 1, children in 26 to 61 cases per 1, children in 21 (Figure 3). Figure 3 1,5 1,35 Number and Crude Rate (per 1,) MRSA in Alberta by Age Group (January 1st, 26 - December 31st, 21) ,2 1, < Rate Rate Rate Rate Rate Rate (per 1, persons) Children under 1 year of age had the second highest MRSA rates with 132 and 151 cases per 1, in 29 and 21, respectively. From 26 to 21, MRSA rates for persons under 2 years of age have more than doubled between 26 and 21, increasing from 26 to 68 cases per 1,, respectively. MRSA rates in 5 Government of Alberta
8 Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus (MRSA) 21 AHW Report October 211 the 2 to 69 years age group increased from 1,613 cases (74 cases per 1,) in 26 to 2,885 cases (125 cases per 1,) in 28, then decreased to 2,723 cases (19 cases per 1,) in 21. For persons from 7 and older, in the same period of time, their MRSA rates have increased slowly from 691 cases or 277 cases per 1, persons in 26 to 923 cases or 333 cases per 1, persons in 21. Figure 4 4,5 4, Number and Crude Rate (per 1,) MRSA in Alberta by Health Zone (January 1st, 26 - December 31st, 21) ,5 3, 2,5 2, 1,5 1, 5 South Calgary Central Edmonton North Alberta , , , , , , , , , , , , , ,299 Rate Rate Rate Rate Rate Rate (per 1, persons) Figure 4 shows that the rate of MRSA has continued to change within the province by health zone in the past five years (26-21). The MRSA rates in the North health zone have increased from 57 cases per 1, persons in 26 to 155 cases per 1, persons in 21, or increasing 2.7 times within five years. Also, its rate was the highest MRSA rate in the province in 21. The second highest MRSA rate in 21 was 139 cases per 1, persons in the Central health zone. In these two health zones, North and Central, the rates of MRSA in 21 were higher than the provincial rate (116 cases per 1,). The MRSA rates for the Edmonton health zone more than doubled from 56 cases per 1, persons in 26 to 123 cases per 1, persons in 28. In the Calgary health zone, the MRSA rates increased from 97 cases per 1, persons in 26 to 13 cases in 27 then decreased to 19 cases per 1, persons in Government of Alberta
9 Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus (MRSA) 21 AHW Report October 211 Edmonton, Calgary, and South health zones, had lower MRSA rates than the provincial rate in 21. Figure 5 breaks down the reported MRSA cases in Alberta from 26 to 21 into the following CMRSA types: Figure 5 CMRSA 1 to CMRSA 6 strains are typical healthcare-associated MRSA with multi-drug resistant phenotypes. CMRSA 7 to CMRSA 1 are typically labelled community-associated strains and have been associated with community-related outbreaks in Canada. CMRSA 7 has caused community outbreaks in aboriginal populations. Community-associated MRSA strains are generally more susceptible to many classes of antimicrobials and often carry a toxin (Panton-Valentine leukocidin, PVL) not typically found in healthcare-associated MRSA strains. 5, Number of MRSA and Rates per 1, in Alberta by Selected Type (January 1st, 26 - December 31st, 21) 4, 3, 2,172 (rate 63.7) 2,587 (rate 74.) 2,489 (rate 68.8) 2,398 (rate 64.5) 2, 1,23 (rate 36.5) 1, (rate 24.4) (rate 26.) 889 (rate 25.4) 92 (rate 24.9) 42 1,13 (rate 29.7) 26 (n=2,533) 27 (n=3,711) 28 (n=4,269) 29 (n=4,219) 21 (n=4,299) CMRSA 2 CMRSA 3/6 CMRSA 7 CMRSA 8 CMRSA 1 NOT ASSIGNED Other CMRSA Not all MRSA strains typed in Alberta will have an assigned PFGE profile using the National Microbiology Laboratory (NML)/CNISP nomenclature. The non-assigned profiles refer to strains with new PFGE patterns, i.e., unique profiles that are not the same as any of the NML prototype strains. 1 The classification of community-associated MRSA and healthcare-associated MRSA is imprecise as it is often impossible to accurately identify the point of transmission. As hospital strains move into 7 Government of Alberta
10 Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus (MRSA) 21 AHW Report October 211 the community and community strains spread within hospitals it may be increasingly difficult to define strains as healthcare-associated MRSA or community MRSA. Figure 5 shows two CMRSA types which stood out among cases since 26: CMRSA 2 cases made up 31.8 per cent of total cases in 26, then decreased to 2.8 per cent in 28 and rose to 25.7 per cent in 21. The CMRSA 2 rates varied from 24 cases per 1, persons in 26 to 26 cases per 1, in 21. CMRSA 1 cases were higher, starting with 47.5 per cent of total cases in 26, then increased to 6.6 per cent in 28, then decreased to 55.8 per cent in 21. The CMRSA 1 rates increased from 37 cases in 26 to 74 cases per 1, in 28. Figure 6 1,8 1,6 1,4 1,2 1, Number of MRSA in Alberta by Selected Type and Sex (January 1st, 26 - December 31st, 21) Female Male Female Male Female Male Female Male Female Male 26 (n=2,533) 27 (n=3,711) 28 (n=4,269) 29 (n=4,219) 21 (n=4,299) CMRSA CMRSA 3/ CMRSA CMRSA CMRSA , , , ,412 NOT ASSIGNED Other CMRSA Overall, Figure 6 shows that females had fewer cases reported than those for males in almost all CMRSA types from 26 to 21 except CMRSA 2. 8 Government of Alberta
11 Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus (MRSA) 21 AHW Report October 211 MRSA in Alberta, 21 This section examines MRSA in Alberta in greater detail for the 21calendar year. In 21, the lowest MRSA infection rate was 61 cases per 1, children aged one to nine years, and the highest rate of MRSA was 333 cases per 1, among persons aged 7 years and older. Children less than one year of age had the second highest MRSA rate with 151 cases per 1, babies (Figure 7). Figure 7 Age-Specific Rate (per 1,) and Counts of MRSA in Alberta (n=4,299) (January 1st - December 31st, 21) 1,5 35 1, < Rate Rates (per 1, persons) Figure 8 Age-Specific Rate (per 1,) and Counts of MRSA in Alberta by Sex (January 1st - December 31st, 21) < Female Male Female Rates Male Rates Rates (per 1, persons) In 21, overall, MRSA rates for males were higher than those for females, except children 1 to 19 years. In that age group, the MRSA rate for males was 54 cases per 1, males compared to 88 9 Government of Alberta
12 Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus (MRSA) 21 AHW Report October 211 cases per 1, females. Both males and females aged 7 years or older had MRSA rates about double or more compared to those from other age groups (Figure 8). Figure 9 1,8 Number and Crude Rate (per 1,) MRSA by Alberta Health Zone (n=4,299) (January 1st - December 31st, 21) 18 1,5 1, South Calgary Central Edmonton North 273 1, , Rate Rates (per 1, persons) In 21, MRSA rates differed among health zones. The North zone had the highest rate (155 cases per 1, persons) while the South zone had the lowest rate with 96 cases per 1, persons. The MRSA rates in Calgary and Edmonton health zones were similar to each other (19 cases vs. 15 cases per 1, persons, respectively) (Figure 9). Figure 1 Number and Crude Rate (per 1,) MRSA by Alberta Health Zone and Sex (n=4,299) (January 1st - December 31st, 21) South Calgary Central Edmonton North Female Male Female Rates Male Rates Rates (per 1, persons) The was also a discrepancy of MRSA rates between females and males in Calgary and Edmonton health zones (female rate was about 76 per cent of male rate Figure 1) which was not apparent in the other zones. 1 Government of Alberta
13 Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus (MRSA) 21 AHW Report October 211 Figure 11 showed that within health zones in 21, the number of MRSA cases increased with age. There were more cases for the South, Calgary, and Central zones, but not for Edmonton and North zones. The highest proportions of MRSA cases for South, Central, and Calgary health zones were in those 5 years of age and older (Figure 11). The highest proportions of MRSA infection for Edmonton and North zones were in the age group of 2 to 49 years with 51 per cent (627/1,223 cases) and 45 per cent (33/679 cases), respectively. The North zone had 28 per cent of cases younger than 2 years of age. Figure 11 MRSA Proportion by Health Zone and Age Group in Alberta (January 1st - December 31st, 21) 1 Proportion of South (n=273) Calgary (n=1,52) Central (n=622) Edmonton (n=1,223) North (n=679) 7+ years 39.6% 25.4% 33.6% 13.2% 9.6% 5-69 yrs 17.9% 22.6% 21.1% 21.8% 18.1% 2-49 yrs 34.1% 39.% 33.3% 51.3% 44.6% <2 years 8.4% 13.1% 12.1% 13.7% 27.7% Of the 4,299 MRSA cases in 21, CMRSA 2 (typically Hospital Associated) accounted for 26 per cent (1,13/4,299 cases), CMRSA 1 (typically Community Associated) 56 per cent (2,398 /4,299 cases), and the other MRSA strains made up the remaining 18 per cent of cases. For CMRSA 2, those 7 years and older had the highest rate and percentage of CMRSA 2 cases (228/1, or 71.7 per cent). Among these cases, with information gathered from patient location codes there were: 83.3 per cent (659/791 cases) from healthcare settings (i.e. clinic, drop in centre, hospital, emergency, inpatient, outpatient, dialysis, and IV therapy), 13.4 per cent (16/791 cases) from long term care, 3.3 per cent from other or unknown. In 21, the break down of 93 CMRSA 2 cases from long term care showed that just over half of the cases (55/16 cases) were from the major cities in southern Alberta. The distributions were as follows: 32.3 per cent (3/93 cases) in Calgary, 17.2 per cent (15/93 cases) in Lethbridge, 1.8 per cent (1/93 cases) in Medicine Hat, and 39.7 per cent (37/93 cases) in 21 other municipalities of Alberta. 11 Government of Alberta
14 Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus (MRSA) 21 AHW Report October 211 The rates of MRSA per 1, persons by age groups and MRSA types for 21 are shown below in Figure 12. Figure 12 Rates per 1, population Rates of MRSA in Alberta by Selected Type & Age Group (January 1st - December 31st, 21). < CMRSA CMRSA 3/ CMRSA CMRSA CMRSA For the 2,398 CMRSA 1 cases, the highest proportion was in the 3 to 39 years age group with 19 per cent (455/2,398), followed by the second highest of the 18.5 per cent (455/2,398) in 4 to 49 year olds. The provincial rate for CMRSA 1 was 65 cases per 1, persons. Children between one and nine years of age had the lowest rate (35 cases per 1, persons). The highest rate was 85 cases per 1, persons in those less than one year (Figure 13). Figure MRSA Rate in Alberta by Selected Type and Age Group (January 1st - December 31st, 21) Rates (per 1, persons) < All ages CMRSA 2 CMRSA 7 CMRSA 1 12 Government of Alberta
15 Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus (MRSA) 21 AHW Report October 211 In 21, the provincial rate for CMRSA 2 was 3 cases per 1, persons. All groups of patients aged less than 6 years had rates below its provincial rate, the rate of the age group of 6 to 69 was higher, while the age group of 7 and older was significantly higher. Persons 7 years of age and older had the highest rate of 228 cases per 1, persons, which was 7.7 times greater than the provincial rate (228.2 vs cases) or almost 71.3 times greater than the lowest rate of CMRSA 2 in the age group 1 years to 19 years (228.2 vs. 3.2). In other words, people aged 7 years or more, have a much higher risk of the CMRSA 2 infection than younger people. In comparison, younger persons had higher rates of CMRSA 7 than older people. For people younger than 3 years, the rates of CMRSA 7 were higher than the provincial average rate (17.1 cases vs. 1.8 cases). Figure and Rates of MRSA in Alberta by Selected Type and Health Zone (January 1st - December 31st, 21) South (n=273) Calgary (n=1,52) Central (n=622) Edmonton (n=1,223) North (n=679) CMRSA 2 CMRSA 3/6 CMRSA 7 CMRSA 8 CMRSA 1 Rate CMRSA 2 Rate CMRSA 3/6 Rate CMRSA 7 Rate CMRSA 8 Rate CMRSA 1 Rate per 1, In 21, the rates and number of cases of CMRSA by types differed among the health zones (see Figure 14 and Table 1). The highest rate of CMRSA 2 was 67 cases per 1, persons in Central. The highest rate of CMRSA 1 was 18 cases per 1, persons in North. CMRSA 7 was highest in North with about 26 cases per 1, persons. Table 1: MRSA Rates (per 1,) in Alberta by Selected Type and Health Zone, 21 Health Zone CMRSA 2 CMRSA 3/6 CMRSA 7 CMRSA 8 CMRSA 1 NOT ASSIGNED OTHER CMRSA All TYPES South Calgary Central Edmonton North ALBERTA Government of Alberta
16 Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus (MRSA) 21 AHW Report October 211 Figure 15 OTHER CMRSA (n=33) NOT ASSIGNED (n=233) Number of MRSA in Alberta by Selected Type and Patient Location at DiagnosisTime (January 1st - December 31st, 21) CMRSA 1 (n=2,398) 458 1, CMRSA 8 (n=9) CMRSA 7 (n=42) 313 CMRSA 3/6 (n=4) CMRSA 2 (n=1,13) , 1,25 1,5 1,75 2, 2,25 2,5 Emergency Inpatient Outpatient Long term care Correctional Center Other locations Unknown/Missing Figure 15 and Table 2 show the patient locations of MRSA infected cases in 21 (n=4,299): 64.3 per cent outpatients, 26.4 per cent inpatients (includes emergency), 3.4 per cent from long term care, and 5.9 per cent from other patient locations (includes correctional centres). The break down of MRSA cases by type and the four groups of patient locations at time of diagnosis (inpatient & emergency, outpatient, long term care, and others) is shown below in Table 2. Table 2: MRSA Proportions in Alberta by Selected Type and Patient Location, 21 Patient Location Inpatient & Emergency CMRSA 2 (n=1,13) CMRSA 3/6 (n=4) CMRSA 7 (n=42) CMRSA 8 (n=9) CMRSA 1 (n=2,398) NOT ASSIGNED (n=233) OTHER CMRSA (n=33) ALL CMRSA (n=4,299) 44.4% 32.5% 15.4% 32.2% 2.2% 18.% 36.4% 26.4% Outpatient 42.2% 62.5% 77.9% 51.1% 71.6% 78.1% 45.5% 64.3% Long term care 1.% 2.5%.% 8.9%.9% 1.3% 12.1% 3.4% Others 3.4% 2.5% 6.7% 7.8% 7.3% 2.6% 6.1% 5.9% TOTAL 1.% 1.% 1.% 1.% 1.% 1.% 1.% 1.% 14 Government of Alberta
17 Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus (MRSA) 21 AHW Report October 211 Figure 16 shows the majority of MRSA infections were found in the skin and soft tissue specimens (88.8 per cent or 3,816/4,299 cases). Urine specimens accounted for the next largest proportion of cases (6.2 per cent or 267/4,299 cases). Other specimen sources included blood (2.3 per cent or 97/4,299 cases), respiratory (1.4 per cent or 59/4,299 cases), and other specimens/unknown (1.4 per cent). Figure 16 MRSA in Alberta by Selected Type & Specimen Sources (n=4,299) (January 1st - December 31st, 21) OTHER CMRSA NOT ASSIGNED 216 CMRSA 1 2,298 CMRSA 8 7 CMRSA CMRSA 3/6 CMRSA , 1,25 1,5 1,75 2, 2,25 2,5 Blood Respiratory Skin & soft tissue Urine Other/Unknown/Missing 15 Government of Alberta
18 Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus (MRSA) 21 AHW Report October 211 APPENDIX Glossary Carrier: An individual who is found to be persistently colonized (culture positive) for a particular organism, at one or more body sites, but has no symptoms of infection. Colonization: Occurs when bacteria are present on or in the body without causing illness. MRSA can colonize the nose, skin and moist areas of the body. Infection: Occurs when bacteria get past the person s normal defenses and cause disease (e.g., skin bacteria getting into the bloodstream via an intravenous catheter). Infections with MRSA may be minor, such as pimples and boils, but serious infections may also occur, such as surgical wound infections and pneumonia. Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus aureus: Staphylococcus aureus isolates that carry the meca gene, or that produce PBP 2a (the meca gene product), should be reported as oxacillin / methicillin resistant. If MIC tests are performed, isolates with an oxacillin MIC > 4 μg/ml are resistant to oxacillin / methicillin. References 1. MRSA Action UK (4/4/211) 2. Low DE, Garcia M, Calley S, et al. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus Ontario. Can Dis Weekly Report 1981;7: Simor EA. et al. - The Evolution of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aurenus in Canadain Hospital: 5 years of National Surveillance. Canadian Medical Association Journal 21;165(1): (8/3/211) 4. Public Health Agency of Canada. Surveillance for MRSA in Canadian Hospital - A Report Update from Canadian Nosocomial Infection Surveillance Program. CCDR 25; (8/2/211) 5. Public Health Agency of Canada. Canadian Nosomial Infection Surveillance Program (CNISP) Surveillance for Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) in Patients Hospitalized in Canadian Acute-Care Hospitals Participanting in CNISP Preliminary Results. (8/5/211) 6. Gilbert M. et al. Outbreak in Alberta of community-acquired (USA3) methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in people with a history of drug use, homelessness or incarceration (8/8/211) 7. Alberta Health and Wellness. MRSA (Community Associated). health-info/mrsa.html (8/8/211) 16 Government of Alberta
19 Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus (MRSA) 21 AHW Report October Alberta Health and Wellness. Community Acquired Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus aureus (CA MRSA) in Alberta (EI) #286 Provincial Outbreak Investigation June 1, 25 February 28, 26. Public Health Division October Alberta Health and Wellness. MRSA Standards. MRSA-Standards-28.pdf. (8/8/211) 1. Alberta Health and Wellness. MRSA IPC Guidelines. IPC- MRSA-Guidelines-27.pdf (8/8/211) 17 Government of Alberta
METHICILLIN-RESISTANT STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS (MRSA) COMMUNITY ACQUIRED vs. HEALTHCARE ASSOCIATED
 METHICILLIN-RESISTANT STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS (MRSA) COMMUNITY ACQUIRED vs. HEALTHCARE ASSOCIATED Recently, there have been a number of reports about methicillin-resistant Staph aureus (MRSA) infections
METHICILLIN-RESISTANT STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS (MRSA) COMMUNITY ACQUIRED vs. HEALTHCARE ASSOCIATED Recently, there have been a number of reports about methicillin-resistant Staph aureus (MRSA) infections
EAST CAROLINA UNIVERSITY INFECTION CONTROL POLICY. Methicillin-resistant Staph aureus: Management in the Outpatient Setting
 EAST CAROLINA UNIVERSITY INFECTION CONTROL POLICY Methicillin-resistant Staph aureus: Management in the Outpatient Setting Date Originated: Date Reviewed: Date Approved: Page 1 of Approved by: Department
EAST CAROLINA UNIVERSITY INFECTION CONTROL POLICY Methicillin-resistant Staph aureus: Management in the Outpatient Setting Date Originated: Date Reviewed: Date Approved: Page 1 of Approved by: Department
Introduction to Infection Control
 CHAPTER 3 Introduction to Infection Control George Byrns and Mary Elkins Learning Objectives 1 Define terms used in infection control. 2. Review significant risk factors for infection. 3. Identify the
CHAPTER 3 Introduction to Infection Control George Byrns and Mary Elkins Learning Objectives 1 Define terms used in infection control. 2. Review significant risk factors for infection. 3. Identify the
MRSA, Hand Hygiene and Contact Precautions
 MRSA, Hand Hygiene and Contact Precautions Wesley Medical Center Department of Education May 2007 Authors: Lois Rahal, RN, BSN, CIC Brandy Jackson, RN, BSN Hope Helferich, RNC, BSN 1 Objectives Upon completion
MRSA, Hand Hygiene and Contact Precautions Wesley Medical Center Department of Education May 2007 Authors: Lois Rahal, RN, BSN, CIC Brandy Jackson, RN, BSN Hope Helferich, RNC, BSN 1 Objectives Upon completion
Lab ID Events MRSA Bloodstream Infection and C. difficile
 Lab ID Events MRSA Bloodstream Infection and C. difficile MDRO and CDI Module Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus (MRSA), Vancomycinresistant Enterococcus(VRE), certain gram negative bacilli, Clostridium
Lab ID Events MRSA Bloodstream Infection and C. difficile MDRO and CDI Module Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus (MRSA), Vancomycinresistant Enterococcus(VRE), certain gram negative bacilli, Clostridium
Methicillin resistant staphylococcus aureus (MRSA)
 Methicillin resistant staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) Patient information Service: Infection Control Team Divison: Intergrated Medical and Rehabiltitation Services Infectioncontrol@homerton.nhs.uk Telephone
Methicillin resistant staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) Patient information Service: Infection Control Team Divison: Intergrated Medical and Rehabiltitation Services Infectioncontrol@homerton.nhs.uk Telephone
Interim Guidelines for the Management of Community-Associated Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Infections in Primary Care February 2006
 Table of Contents 1. Background... 2 2. Diagnosis... 2 3. Susceptibility Patterns of MRSA... 3 4. Management... 3 5. Decolonization of the Patient... 4 6. Prevention and Control... 5 7. Information for
Table of Contents 1. Background... 2 2. Diagnosis... 2 3. Susceptibility Patterns of MRSA... 3 4. Management... 3 5. Decolonization of the Patient... 4 6. Prevention and Control... 5 7. Information for
Solid Organ Transplantation
 Solid Organ Transplantation Infection Prevention And Control Transplant Atlantic 2011 October 13/2011 Kathy Hart Introduction In the past several years, the drugs that we use, the surgeries themselves,
Solid Organ Transplantation Infection Prevention And Control Transplant Atlantic 2011 October 13/2011 Kathy Hart Introduction In the past several years, the drugs that we use, the surgeries themselves,
Nursing college, Second stage Microbiology Dr.Nada Khazal K. Hendi L14: Hospital acquired infection, nosocomial infection
 L14: Hospital acquired infection, nosocomial infection Definition A hospital acquired infection, also called a nosocomial infection, is an infection that first appears between 48 hours and four days after
L14: Hospital acquired infection, nosocomial infection Definition A hospital acquired infection, also called a nosocomial infection, is an infection that first appears between 48 hours and four days after
Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) in Tasmanian Rural Hospitals and Non Acute Health Settings
 Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) in Tasmanian Rural Hospitals and Non Acute Health Settings Guidance for the management of patients with MRSA in Tasmania's rural hospitals and non acute
Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) in Tasmanian Rural Hospitals and Non Acute Health Settings Guidance for the management of patients with MRSA in Tasmania's rural hospitals and non acute
Black Hills Healthcare System
 Black Hills Healthcare System Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcal Aureus (MRSA) Patient and Family Information What is MRSA? Staphylococcus Aureus, often referred to simply as staph, is a bacteria commonly
Black Hills Healthcare System Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcal Aureus (MRSA) Patient and Family Information What is MRSA? Staphylococcus Aureus, often referred to simply as staph, is a bacteria commonly
Antibiotic resistance does it matter in paediatric clinical practice? Jette Bangsborg Department of Clinical Microbiology Herlev Hospital
 Antibiotic resistance does it matter in paediatric clinical practice? Jette Bangsborg Department of Clinical Microbiology Herlev Hospital Background The Department of Clinical Microbiology at Herlev Hospital
Antibiotic resistance does it matter in paediatric clinical practice? Jette Bangsborg Department of Clinical Microbiology Herlev Hospital Background The Department of Clinical Microbiology at Herlev Hospital
Hospital Superbugs, Infection Control and Cleaning
 Superbugs The cleaning work of CUPE members may prove to be even more important in the near future as hospital management scramble to find solutions to the spread of Superbugs. Superbugs are infecting
Superbugs The cleaning work of CUPE members may prove to be even more important in the near future as hospital management scramble to find solutions to the spread of Superbugs. Superbugs are infecting
 Skin and Soft tissue Infections: new bugs, old drugs Disclosure Statement Sponsor: Goodman Photographic Presented by: Dr. Kristopher Wiebe, MD, CCFP (EM) Presented to: BC Chapter, Canadian Society of Hospital
Skin and Soft tissue Infections: new bugs, old drugs Disclosure Statement Sponsor: Goodman Photographic Presented by: Dr. Kristopher Wiebe, MD, CCFP (EM) Presented to: BC Chapter, Canadian Society of Hospital
GUIDELINES FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF PVL ASSOCIATED STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS INFECTIONS IN THE HOSPITAL ENVIRONMENT
 GUIDELINES FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF PVL ASSOCIATED STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS INFECTIONS IN THE HOSPITAL ENVIRONMENT Post holder responsible for Policy: Directorate/Department responsible for Policy: Lead Nurse
GUIDELINES FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF PVL ASSOCIATED STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS INFECTIONS IN THE HOSPITAL ENVIRONMENT Post holder responsible for Policy: Directorate/Department responsible for Policy: Lead Nurse
Massachusetts Department of Developmental Services MRSA, VRE, and C. Diff Management Protocol
 Massachusetts Department of Developmental Services MRSA, VRE, and C. Diff Management Protocol PURPOSE: To provide guidance for personnel in order to prevent the spread of Antibiotic Resistant Microorganisms
Massachusetts Department of Developmental Services MRSA, VRE, and C. Diff Management Protocol PURPOSE: To provide guidance for personnel in order to prevent the spread of Antibiotic Resistant Microorganisms
Report by the Comptroller and Auditor General. The Management and Control of Hospital Acquired Infection in Acute NHS Trusts in England
 Report by the Comptroller and Auditor General The Management and Control of Hospital Acquired Infection in Acute NHS Trusts in England HC 230 Session 1999-00 17 February 2000 Report by the Comptroller
Report by the Comptroller and Auditor General The Management and Control of Hospital Acquired Infection in Acute NHS Trusts in England HC 230 Session 1999-00 17 February 2000 Report by the Comptroller
Advice for those affected by MRSA outside of hospital
 Advice for those affected by MRSA outside of hospital If you have MRSA this leaflet provides information and advice for managing your day-to-day life. 1 About MRSA There are lots of different types or
Advice for those affected by MRSA outside of hospital If you have MRSA this leaflet provides information and advice for managing your day-to-day life. 1 About MRSA There are lots of different types or
Provincial Infectious Diseases Advisory Committee (PIDAC)
 Provincial Infectious Diseases Advisory Committee (PIDAC) Best Practices For Infection Prevention and Control of Resistant Staphylococcus aureus and Enterococci Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus
Provincial Infectious Diseases Advisory Committee (PIDAC) Best Practices For Infection Prevention and Control of Resistant Staphylococcus aureus and Enterococci Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus
Pre-operative M.R.S.A. Screening Information for Patients
 Infection Prevention and Control Pre-operative M.R.S.A. Screening Information for Patients This information is designed for patients undergoing MRSA screening before coming into hospital for a planned
Infection Prevention and Control Pre-operative M.R.S.A. Screening Information for Patients This information is designed for patients undergoing MRSA screening before coming into hospital for a planned
VANCOMYCIN-RESISTANT ENTEROCOCCI INFECTIONS IN CANADIAN ACUTE-CARE HOSPITALS
 INFECTIOUS DISEASE PREVENTION AND CONTROL VANCOMYCIN-RESISTANT ENTEROCOCCI INFECTIONS IN CANADIAN ACUTE-CARE HOSPITALS SURVEILLANCE REPORT JANUARY 1, 1999 TO DECEMBER 31, 2011 PROTECTI NG C ANADIANS FROM
INFECTIOUS DISEASE PREVENTION AND CONTROL VANCOMYCIN-RESISTANT ENTEROCOCCI INFECTIONS IN CANADIAN ACUTE-CARE HOSPITALS SURVEILLANCE REPORT JANUARY 1, 1999 TO DECEMBER 31, 2011 PROTECTI NG C ANADIANS FROM
Addressing the challenge of healthcare associated infections (HCAIs) in Europe
 POSITION PAPER 05 January 2011 Addressing the challenge of healthcare associated infections (HCAIs) in Europe A Call for Action Page 1 of 8 A holistic approach to combating HCAIs in Europe We must rise
POSITION PAPER 05 January 2011 Addressing the challenge of healthcare associated infections (HCAIs) in Europe A Call for Action Page 1 of 8 A holistic approach to combating HCAIs in Europe We must rise
2013 Indiana Healthcare Provider and Hospital Administrator Multi-Drug Resistant Organism Survey
 2013 Indiana Healthcare Provider and Hospital Administrator Multi-Drug Resistant Organism Survey Antibiotic resistance is a global issue that has significant impact in the field of infectious diseases.
2013 Indiana Healthcare Provider and Hospital Administrator Multi-Drug Resistant Organism Survey Antibiotic resistance is a global issue that has significant impact in the field of infectious diseases.
Briefing. Healthcare-associated infections STEMMING THE RISE OF THE SUPERBUG? What are healthcare-associated infections? JULY 2008
 Briefing JULY 2008 Healthcare-associated infections STEMMING THE RISE OF THE SUPERBUG? Healthcare-associated infections are a major concern to patients and the public as a result of both high rates of
Briefing JULY 2008 Healthcare-associated infections STEMMING THE RISE OF THE SUPERBUG? Healthcare-associated infections are a major concern to patients and the public as a result of both high rates of
Planning for an Influenza Pandemic
 Overview It is unlikely that a new pandemic influenza strain will first emerge within Elgin County. The World Health Organization (WHO) uses a series of six phases, as outlined below, of pandemic alert
Overview It is unlikely that a new pandemic influenza strain will first emerge within Elgin County. The World Health Organization (WHO) uses a series of six phases, as outlined below, of pandemic alert
Hialeah Nursing and Rehabilitation Center Combines Technology and Best Practices to Improve Infection Control Specific to C.diff
 RESEARCH ARTICLE Page 1 of 5 Hialeah Nursing and Rehabilitation Center Combines Technology and Best Practices to Improve Infection Control Specific to C.diff ABSTRACT RB Health Partners, Inc., June 24,
RESEARCH ARTICLE Page 1 of 5 Hialeah Nursing and Rehabilitation Center Combines Technology and Best Practices to Improve Infection Control Specific to C.diff ABSTRACT RB Health Partners, Inc., June 24,
Annex A: Screening, Testing and Surveillance for Antibiotic-Resistant Organisms (AROs)
 Annex A: Screening, Testing and Surveillance for Antibiotic-Resistant Organisms (AROs) In All Health Care Settings Provincial Infectious Diseases Advisory Committee (PIDAC) Revised: February 2013 The Ontario
Annex A: Screening, Testing and Surveillance for Antibiotic-Resistant Organisms (AROs) In All Health Care Settings Provincial Infectious Diseases Advisory Committee (PIDAC) Revised: February 2013 The Ontario
Living With Diabetes. March 5, 2009 in Columbia, SC. Contact Ramsey Makhuli at 803-737-3823 or at RMakhuli@eip.sc.gov. Website: www.eip.sc.
 State Health Plan Prevention Partners Employee Insurance Program Mission The mission of The State Health Plan Prevention Partners is to provide activities, programs and services that encourage health promotion,
State Health Plan Prevention Partners Employee Insurance Program Mission The mission of The State Health Plan Prevention Partners is to provide activities, programs and services that encourage health promotion,
GCSE BITESIZE Examinations
 GCSE BITESIZE Examinations General Certificate of Secondary Education AQA SCIENCE A Unit Biology B1a AQA BIOLOGY Unit Biology B1a BLY1A (Human Biology) (Human Biology) FOUNDATION TIER Specimen Paper Time
GCSE BITESIZE Examinations General Certificate of Secondary Education AQA SCIENCE A Unit Biology B1a AQA BIOLOGY Unit Biology B1a BLY1A (Human Biology) (Human Biology) FOUNDATION TIER Specimen Paper Time
ALBERTA S HEALTH SYSTEM PERFORMANCE MEASURES
 ALBERTA S HEALTH SYSTEM PERFORMANCE MEASURES 1.0 Quality of Health Services: Access to Surgery Priorities for Action Acute Care Access to Surgery Reduce the wait time for surgical procedures. 1.1 Wait
ALBERTA S HEALTH SYSTEM PERFORMANCE MEASURES 1.0 Quality of Health Services: Access to Surgery Priorities for Action Acute Care Access to Surgery Reduce the wait time for surgical procedures. 1.1 Wait
Management of Extended Spectrum Beta- Lactamase (ESBL) Producing Enterobacteriaceae in health care settings
 Management of Extended Spectrum Beta- Lactamase (ESBL) Producing Enterobacteriaceae in health care settings Dr. Mary Vearncombe PIDAC-IPC February 2012 Objectives: To provide an overview of the RP/AP Annex
Management of Extended Spectrum Beta- Lactamase (ESBL) Producing Enterobacteriaceae in health care settings Dr. Mary Vearncombe PIDAC-IPC February 2012 Objectives: To provide an overview of the RP/AP Annex
Highlights of the Revised Official ICD-9-CM Guidelines for Coding and Reporting Effective October 1, 2008
 Highlights of the Revised Official ICD-9-CM Guidelines for Coding and Reporting Effective October 1, 2008 Please refer to the complete ICD-9-CM Official Guidelines for Coding and Reporting posted on this
Highlights of the Revised Official ICD-9-CM Guidelines for Coding and Reporting Effective October 1, 2008 Please refer to the complete ICD-9-CM Official Guidelines for Coding and Reporting posted on this
PRIORITY RESEARCH TOPICS
 PRIORITY RESEARCH TOPICS Understanding all the issues associated with antimicrobial resistance is probably impossible, but it is clear that there are a number of key issues about which we need more information.
PRIORITY RESEARCH TOPICS Understanding all the issues associated with antimicrobial resistance is probably impossible, but it is clear that there are a number of key issues about which we need more information.
35-40% of GBS disease occurs in the elderly or in adults with chronic medical conditions.
 What is Group B Strep (GBS)? Group B Streptococcus (GBS) is a type of bacteria that is found in the lower intestine of 10-35% of all healthy adults and in the vagina and/or lower intestine of 10-35% of
What is Group B Strep (GBS)? Group B Streptococcus (GBS) is a type of bacteria that is found in the lower intestine of 10-35% of all healthy adults and in the vagina and/or lower intestine of 10-35% of
DHS: SENIORS AND PEOPLE WITH DISABILITIES DIVISION
 DHS: SENIORS AND PEOPLE WITH DISABILITIES DIVISION Nurse to Nurse Oregon s community-based care nursing newsletter Winter 2009 Vol. 6 No. 1 Infection control Standard Precautions are measures used to protect
DHS: SENIORS AND PEOPLE WITH DISABILITIES DIVISION Nurse to Nurse Oregon s community-based care nursing newsletter Winter 2009 Vol. 6 No. 1 Infection control Standard Precautions are measures used to protect
Orientation Program for New Infection Control Professionals
 Orientation Program for New Infection Control Professionals Module 1: Introduction and Four-Week Schedule Table of Contents Module 1: Introduction... 2 Note to Managers... 2 IPC Orientation Program...
Orientation Program for New Infection Control Professionals Module 1: Introduction and Four-Week Schedule Table of Contents Module 1: Introduction... 2 Note to Managers... 2 IPC Orientation Program...
Streptococcal Infections
 Streptococcal Infections Introduction Streptococcal, or strep, infections cause a variety of health problems. These infections can cause a mild skin infection or sore throat. But they can also cause severe,
Streptococcal Infections Introduction Streptococcal, or strep, infections cause a variety of health problems. These infections can cause a mild skin infection or sore throat. But they can also cause severe,
Policy for Screening Patients for MRSA Colonisation
 Policy for Screening Patients for MRSA Colonisation To whom this document applies: All staff in Colchester Hospital University Foundation Trust screening Patients for MRSA Procedural Documents Approval
Policy for Screening Patients for MRSA Colonisation To whom this document applies: All staff in Colchester Hospital University Foundation Trust screening Patients for MRSA Procedural Documents Approval
National Antimicrobial Resistance Monitoring System - Enteric Bacteria. A program to monitor antimicrobial resistance in humans and animals
 National Antimicrobial Resistance Monitoring System - Enteric Bacteria A program to monitor antimicrobial resistance in humans and animals Antimicrobial resistance in foodborne pathogens is an important
National Antimicrobial Resistance Monitoring System - Enteric Bacteria A program to monitor antimicrobial resistance in humans and animals Antimicrobial resistance in foodborne pathogens is an important
PREVENTING THE SPREAD OF CONTAGIOUS ILLNESS
 PREVENTING THE SPREAD OF CONTAGIOUS ILLNESS This easy-to-use Leader s Guide is provided to assist in conducting a successful presentation. Featured are: INTRODUCTION: A brief description of the program
PREVENTING THE SPREAD OF CONTAGIOUS ILLNESS This easy-to-use Leader s Guide is provided to assist in conducting a successful presentation. Featured are: INTRODUCTION: A brief description of the program
Infection Prevention
 Infection Prevention Dear HSS Patient: The Hospital for Special Surgery is committed to patient safety and quality patient care and is proud to have achieved one of the lowest infection rates in New York
Infection Prevention Dear HSS Patient: The Hospital for Special Surgery is committed to patient safety and quality patient care and is proud to have achieved one of the lowest infection rates in New York
New Brunswick Health Indicators
 New Brunswick Health Indicators Issue 8, July 2013 A population health bulletin published by the Office of the Chief Medical Officer of Health Youth Sexual Health Sexual health is an important aspect of
New Brunswick Health Indicators Issue 8, July 2013 A population health bulletin published by the Office of the Chief Medical Officer of Health Youth Sexual Health Sexual health is an important aspect of
Health Care Worker s Role in Preventing the Transmission of Communicable Diseases
 Health Care Worker s Role in Preventing the Transmission of Communicable Diseases Réka Gustafson, MD FRCPC Medical Health Officer Director of Communicable Disease Control Vancouver Infection Control 101
Health Care Worker s Role in Preventing the Transmission of Communicable Diseases Réka Gustafson, MD FRCPC Medical Health Officer Director of Communicable Disease Control Vancouver Infection Control 101
Tuberculosis Exposure Control Plan for Low Risk Dental Offices
 Tuberculosis Exposure Control Plan for Low Risk Dental Offices A. BACKGROUND According to the CDC, approximately one-third of the world s population, almost two billion people, are infected with tuberculosis.
Tuberculosis Exposure Control Plan for Low Risk Dental Offices A. BACKGROUND According to the CDC, approximately one-third of the world s population, almost two billion people, are infected with tuberculosis.
Methicillin-resistant S taphylococcus
 Nevio Cimolai, MD, FRCPC Community-acquired MRSA infection: An emerging trend The use of culture as backup to empiric treatment of staphylococcal infection can help deal with widespread antibiotic resistance.
Nevio Cimolai, MD, FRCPC Community-acquired MRSA infection: An emerging trend The use of culture as backup to empiric treatment of staphylococcal infection can help deal with widespread antibiotic resistance.
4.06. Infection Prevention and Control at Long-term-care Homes. Chapter 4 Section. Background. Follow-up on VFM Section 3.06, 2009 Annual Report
 Chapter 4 Section 4.06 Infection Prevention and Control at Long-term-care Homes Follow-up on VFM Section 3.06, 2009 Annual Report Background Long-term-care nursing homes and homes for the aged (now collectively
Chapter 4 Section 4.06 Infection Prevention and Control at Long-term-care Homes Follow-up on VFM Section 3.06, 2009 Annual Report Background Long-term-care nursing homes and homes for the aged (now collectively
Introduction. 1 Centres for Disease Control. Overview of healthcare related MRSA 2 Invasive Methicillin-Resistant Staphyloccus aureus
 An Alternative Approach in The Treatment of Methicillin- Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus (MRSA), using Classical Homeopathy. Pierre Fontaine RSHom CCH. Introduction MRSA (Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus
An Alternative Approach in The Treatment of Methicillin- Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus (MRSA), using Classical Homeopathy. Pierre Fontaine RSHom CCH. Introduction MRSA (Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus
CLINICAL GUIDELINE FOR
 CLINICAL GUIDELINE FOR the investigation and management of inpatients with discitis (vertebral osteomyelitis) 1. Aim/Purpose of this Guideline 1.1.This guideline applies to clinical staff managing patients
CLINICAL GUIDELINE FOR the investigation and management of inpatients with discitis (vertebral osteomyelitis) 1. Aim/Purpose of this Guideline 1.1.This guideline applies to clinical staff managing patients
Safety FIRST: Infection Prevention Tips
 Reading Hospital Safety FIRST: Infection Prevention Tips Reading Hospital is committed to providing high quality care to our patients. Your healthcare team does many things to help prevent infections.
Reading Hospital Safety FIRST: Infection Prevention Tips Reading Hospital is committed to providing high quality care to our patients. Your healthcare team does many things to help prevent infections.
Wound Care on the Field. Objectives
 Wound Care on the Field Brittany Witte, PT, DPT Cook Children s Medical Center Objectives Name 3 different types of wounds commonly seen in sports and how to emergently provide care for them. Name all
Wound Care on the Field Brittany Witte, PT, DPT Cook Children s Medical Center Objectives Name 3 different types of wounds commonly seen in sports and how to emergently provide care for them. Name all
ANNUAL REPORT ON STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS BACTERAEMIA CASES IN DENMARK 2009 (part I)
 ANNUAL REPORT ON STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS BACTERAEMIA CASES IN DENMARK 2009 (part I) STAPHYLOCOCCUS LABORATORY, STATENS SERUM INSTITUT 1 Staphylococcus aureus Bacteraemia Annual Report, Part I The annual
ANNUAL REPORT ON STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS BACTERAEMIA CASES IN DENMARK 2009 (part I) STAPHYLOCOCCUS LABORATORY, STATENS SERUM INSTITUT 1 Staphylococcus aureus Bacteraemia Annual Report, Part I The annual
Enteric Septicemia of Catfish
 Enteric Septicemia of Catfish Jesse Chappell Extension Fisheries Specialist Revised 2008 Enteric Septicemia of Catfish (ESC) has become one of the two most significant diseases of economic significance
Enteric Septicemia of Catfish Jesse Chappell Extension Fisheries Specialist Revised 2008 Enteric Septicemia of Catfish (ESC) has become one of the two most significant diseases of economic significance
Frequently Asked Questions
 Guidelines for Testing and Treatment of Gonorrhea in Ontario, 2013 Frequently Asked Questions Table of Contents Background... 1 Treatment Recommendations... 2 Treatment of Contacts... 4 Administration
Guidelines for Testing and Treatment of Gonorrhea in Ontario, 2013 Frequently Asked Questions Table of Contents Background... 1 Treatment Recommendations... 2 Treatment of Contacts... 4 Administration
Controlling MRSA in England: what we have done and what we think worked. Professor Barry Cookson
 Controlling MRSA in England: what we have done and what we think worked Professor Barry Cookson Depts. of Health Policy & Tropical & Infectious Disease, London School of Hygiene & Tropical Medicine. Dept
Controlling MRSA in England: what we have done and what we think worked Professor Barry Cookson Depts. of Health Policy & Tropical & Infectious Disease, London School of Hygiene & Tropical Medicine. Dept
3.0 Treatment of Infection
 3.0 Treatment of Infection Antibiotics and Medicine National Curriculum Link SCN 3-13b SCN 3-20b HWB 3-15a HWB 3-16a HWB 3-17a Learning Outcomes All students will know: Most common infections will get
3.0 Treatment of Infection Antibiotics and Medicine National Curriculum Link SCN 3-13b SCN 3-20b HWB 3-15a HWB 3-16a HWB 3-17a Learning Outcomes All students will know: Most common infections will get
Open and Honest Care in your Local Hospital
 Open and Honest Care in your Local Hospital The Open and Honest Care: Driving Improvement Programme aims to support organisations to become more transparent and consistent in publishing safety, experience
Open and Honest Care in your Local Hospital The Open and Honest Care: Driving Improvement Programme aims to support organisations to become more transparent and consistent in publishing safety, experience
Treatment of skin and soft tissue infections due to methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in adults
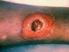 1 of 6 9/24/2010 11:16 AM Official reprint from UpToDate www.uptodate.com 2010 UpToDate Treatment of skin and soft tissue infections due to methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in adults Author
1 of 6 9/24/2010 11:16 AM Official reprint from UpToDate www.uptodate.com 2010 UpToDate Treatment of skin and soft tissue infections due to methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in adults Author
Canadian Public Health Laboratory Network. Core Functions of Canadian Public Health Laboratories
 Canadian Public Health Laboratory Network Core Functions of Canadian Public Health Laboratories Canadian Public Health Laboratory Network The CPHLN Core Functions of Canadian Public Health Laboratories
Canadian Public Health Laboratory Network Core Functions of Canadian Public Health Laboratories Canadian Public Health Laboratory Network The CPHLN Core Functions of Canadian Public Health Laboratories
Annual Report on Staphylococcus aureus Bacteraemia Cases 2006
 Annual Report on Staphylococcus aureus Bacteraemia Cases 2006 STAPHYLOCOCCUS LABORATORY, STATENS SERUM INSTITUT, 2006 Members of the Danish Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia group Thomas Benfield, Dr. med.
Annual Report on Staphylococcus aureus Bacteraemia Cases 2006 STAPHYLOCOCCUS LABORATORY, STATENS SERUM INSTITUT, 2006 Members of the Danish Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia group Thomas Benfield, Dr. med.
Arizona Department of Health Services State Healthcare-Associated Infection Plan
 Executive Summary Healthcare-associated infections (HAI) are an emerging public health issue and have received increasing public attention. Arizona healthcare facilities and infection preventionists at
Executive Summary Healthcare-associated infections (HAI) are an emerging public health issue and have received increasing public attention. Arizona healthcare facilities and infection preventionists at
Staphylococcus aureus Bloodstream Infection Treatment Guideline
 Staphylococcus aureus Bloodstream Infection Treatment Guideline Purpose: To provide a framework for the evaluation and management patients with Methicillin- Susceptible (MSSA) and Methicillin-Resistant
Staphylococcus aureus Bloodstream Infection Treatment Guideline Purpose: To provide a framework for the evaluation and management patients with Methicillin- Susceptible (MSSA) and Methicillin-Resistant
MRSA. Living with. Acknowledgements. (Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus)
 How can I keep myself healthy? Hand washing and use of an alcohol-based hand sanitizer are the primary way to prevent acquiring or transmitting bacteria. If you get a cut or scrape, wash it well with soap
How can I keep myself healthy? Hand washing and use of an alcohol-based hand sanitizer are the primary way to prevent acquiring or transmitting bacteria. If you get a cut or scrape, wash it well with soap
Whooping Cough. The Lungs Whooping cough is an infection of the lungs and breathing tubes, both of which are parts of the respiratory system.
 Whooping Cough Introduction Whooping cough is a serious bacterial infection of the lungs and breathing tubes. It is also called pertussis. About 16 million cases of whooping cough happen worldwide each
Whooping Cough Introduction Whooping cough is a serious bacterial infection of the lungs and breathing tubes. It is also called pertussis. About 16 million cases of whooping cough happen worldwide each
State of Kuwait Ministry of Health Infection Control Directorate. Guidelines for Prevention of Surgical Site Infection (SSI)
 State of Kuwait Ministry of Health Infection Control Directorate Guidelines for Prevention of Surgical Site Infection (SSI) September 1999 Updated 2007 Surgical Wound: According to 1998 Kuwait National
State of Kuwait Ministry of Health Infection Control Directorate Guidelines for Prevention of Surgical Site Infection (SSI) September 1999 Updated 2007 Surgical Wound: According to 1998 Kuwait National
MN HAI Prevention Plan 1
 Healthcare Associated Infections Plan Minnesota Department of Health Healthcare Associated Infections Program Introduction In response to the increasing concerns about the public health impact of healthcare-associated
Healthcare Associated Infections Plan Minnesota Department of Health Healthcare Associated Infections Program Introduction In response to the increasing concerns about the public health impact of healthcare-associated
ORTHOPAEDIC INFECTION PREVENTION AND CONTROL: AN EMERGING NEW PARADIGM
 ORTHOPAEDIC INFECTION PREVENTION AND CONTROL: AN EMERGING NEW PARADIGM AMERICAN ACADEMY OF ORTHOPAEDIC SURGEONS 77th Annual Meeting March 9-12, 2010 New Orleans, Louisiana COMMITTEE ON PATIENT SAFETY PREPARED
ORTHOPAEDIC INFECTION PREVENTION AND CONTROL: AN EMERGING NEW PARADIGM AMERICAN ACADEMY OF ORTHOPAEDIC SURGEONS 77th Annual Meeting March 9-12, 2010 New Orleans, Louisiana COMMITTEE ON PATIENT SAFETY PREPARED
NURSING SKILLS FAIR GAME QUESTIONS
 NURSING SKILLS FAIR GAME QUESTIONS FOR UNLICENSED NURSING STAFF The questions contained in this document are intended to be used during a long-term care facility (LTCF) nursing education or skills fair
NURSING SKILLS FAIR GAME QUESTIONS FOR UNLICENSED NURSING STAFF The questions contained in this document are intended to be used during a long-term care facility (LTCF) nursing education or skills fair
Advice about MRSA for people not in hospital. If you have MRSA, this leaflet tells you about things you should do in your everyday life.
 Advice about MRSA for people not in hospital If you have MRSA, this leaflet tells you about things you should do in your everyday life. Easy read This booklet is about a germ called MRSA. It is an Easy
Advice about MRSA for people not in hospital If you have MRSA, this leaflet tells you about things you should do in your everyday life. Easy read This booklet is about a germ called MRSA. It is an Easy
9 Expenditure on breast cancer
 9 Expenditure on breast cancer Due to the large number of people diagnosed with breast cancer and the high burden of disease related to it, breast cancer is associated with substantial health-care costs.
9 Expenditure on breast cancer Due to the large number of people diagnosed with breast cancer and the high burden of disease related to it, breast cancer is associated with substantial health-care costs.
healthcare associated infection 1.2
 healthcare associated infection A C T I O N G U I D E 1.2 AUSTRALIAN SAFETY AND QUALITY GOALS FOR HEALTH CARE What are the goals? The Australian Safety and Quality Goals for Health Care set out some important
healthcare associated infection A C T I O N G U I D E 1.2 AUSTRALIAN SAFETY AND QUALITY GOALS FOR HEALTH CARE What are the goals? The Australian Safety and Quality Goals for Health Care set out some important
Manitoba Guidelines for the Prevention and Control of Antibiotic Resistant Organisms (AROs)
 Manitoba Guidelines for the Prevention and Control of Antibiotic Resistant Organisms (AROs) January 2007 COMMUNICABLE DISEASE CONTROL Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus (MRSA) Infection Control
Manitoba Guidelines for the Prevention and Control of Antibiotic Resistant Organisms (AROs) January 2007 COMMUNICABLE DISEASE CONTROL Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus (MRSA) Infection Control
FACULTY OF MEDICAL SCIENCE
 Doctor of Philosophy Program in Microbiology FACULTY OF MEDICAL SCIENCE Naresuan University 171 Doctor of Philosophy Program in Microbiology The time is critical now for graduate education and research
Doctor of Philosophy Program in Microbiology FACULTY OF MEDICAL SCIENCE Naresuan University 171 Doctor of Philosophy Program in Microbiology The time is critical now for graduate education and research
OPERATIONAL DIRECTIVE
 OPERATIONAL DIRECTIVE Enquiries to: Healthcare Associated Infection Unit OD number: 0478/13 Phone number: 08 9388 4868 Date: 15 November 2013 Supersedes: OP 1922/05 (24/02/2005) OP 1854/04 (14/10/2004)
OPERATIONAL DIRECTIVE Enquiries to: Healthcare Associated Infection Unit OD number: 0478/13 Phone number: 08 9388 4868 Date: 15 November 2013 Supersedes: OP 1922/05 (24/02/2005) OP 1854/04 (14/10/2004)
Tobacco Use in Canada: Patterns and Trends. 2012 Edition
 Tobacco Use in Canada: Patterns and Trends 212 Edition Tobacco Use in Canada: Patterns and Trends 212 Edition This report was prepared by Jessica Reid, MSc, and David Hammond, PhD. Data analysis was completed
Tobacco Use in Canada: Patterns and Trends 212 Edition Tobacco Use in Canada: Patterns and Trends 212 Edition This report was prepared by Jessica Reid, MSc, and David Hammond, PhD. Data analysis was completed
Educational Module for Nursing Assistants in Long-term Care Facilities: Antibiotic Use and Antibiotic Resistance
 Educational Module for Nursing Assistants in Long-term Care Facilities: Antibiotic Use and Antibiotic Resistance Antibiotic resistance is an increasing concern for everyone. This module: Defines antibiotic
Educational Module for Nursing Assistants in Long-term Care Facilities: Antibiotic Use and Antibiotic Resistance Antibiotic resistance is an increasing concern for everyone. This module: Defines antibiotic
Core Functions and Capabilities. Laboratory Services
 Core Functions and Capabilities British Columbia Centre for Disease Control Laboratory Services Understanding the role and value of British Columbia s public health laboratory in protecting our community
Core Functions and Capabilities British Columbia Centre for Disease Control Laboratory Services Understanding the role and value of British Columbia s public health laboratory in protecting our community
Catheter-Associated Urinary Tract Infection (CAUTI) Prevention. Basics of Infection Prevention 2 Day Mini-Course 2013
 Catheter-Associated Urinary Tract Infection (CAUTI) Prevention Basics of Infection Prevention 2 Day Mini-Course 2013 2 Objectives Define the scope of healthcare-associated urinary tract infections (UTI)
Catheter-Associated Urinary Tract Infection (CAUTI) Prevention Basics of Infection Prevention 2 Day Mini-Course 2013 2 Objectives Define the scope of healthcare-associated urinary tract infections (UTI)
Hepatitis C Virus Infection: Prevalence Report, 2003 Data Source: Minnesota Department of Health HCV Surveillance System
 Hepatitis C Virus Infection: Prevalence Report, 2003 Data Source: Minnesota Department of Health HCV Surveillance System P.O. Box 9441 Minneapolis, MN 55440-9441 612-676-5414, 1-877-676-5414 www.health.state.mn.us/immunize
Hepatitis C Virus Infection: Prevalence Report, 2003 Data Source: Minnesota Department of Health HCV Surveillance System P.O. Box 9441 Minneapolis, MN 55440-9441 612-676-5414, 1-877-676-5414 www.health.state.mn.us/immunize
H1N1 Flu in Manitoba MANITOBA S RESPONSE LESSONS LEARNED
 H1N1 Flu in Manitoba MANITOBA S RESPONSE LESSONS LEARNED F A L L 2 0 1 0 H1N1 Report Fall 2010 On June 11, 2009, the World Health Organization (WHO) declared the novel H1N1 influenza virus a pandemic
H1N1 Flu in Manitoba MANITOBA S RESPONSE LESSONS LEARNED F A L L 2 0 1 0 H1N1 Report Fall 2010 On June 11, 2009, the World Health Organization (WHO) declared the novel H1N1 influenza virus a pandemic
Answers to Frequently Asked Questions on Reporting in NHSN
 Answers to Frequently Asked Questions on Reporting in NHSN 1. With multiple infection sites, if you are unsure of the primary site of the infection, what should you do? If more than one NHSN operative
Answers to Frequently Asked Questions on Reporting in NHSN 1. With multiple infection sites, if you are unsure of the primary site of the infection, what should you do? If more than one NHSN operative
TB CARE EARLY DETECTION AND PREVENTION OF TUBERCULOSIS (TB) IN CHILDREN. Risk factors in children acquiring TB:
 EARLY DETECTION AND PREVENTION OF TUBERCULOSIS (TB) IN CHILDREN Risk factors in children acquiring TB: Children living in the same household as a lung TB patient (especially children under 5) Children
EARLY DETECTION AND PREVENTION OF TUBERCULOSIS (TB) IN CHILDREN Risk factors in children acquiring TB: Children living in the same household as a lung TB patient (especially children under 5) Children
Recommendations for Metrics for Multidrug-Resistant Organisms in Healthcare Settings: SHEA/HICPAC Position Paper
 infection control and hospital epidemiology october 2008, vol. 29, no. 10 shea/hicpac position paper Recommendations for Metrics for Multidrug-Resistant Organisms in Healthcare Settings: SHEA/HICPAC Position
infection control and hospital epidemiology october 2008, vol. 29, no. 10 shea/hicpac position paper Recommendations for Metrics for Multidrug-Resistant Organisms in Healthcare Settings: SHEA/HICPAC Position
Clinical description 2 Laboratory test for diagnosis 3. Incubation period 4 Mode of transmission 4 Period of communicability 4
 Tuberculosis Contents Epidemiology in New Zealand 2 Case definition 2 Clinical description 2 Laboratory test for diagnosis 3 Case classification 3 Spread of infection 4 Incubation period 4 Mode of transmission
Tuberculosis Contents Epidemiology in New Zealand 2 Case definition 2 Clinical description 2 Laboratory test for diagnosis 3 Case classification 3 Spread of infection 4 Incubation period 4 Mode of transmission
The Disease is a commonly diagnosed infectious disease that affects all equidae worldwide. Caused by the bacterium Streptococcus equi (S.equi), this d
 ADVICE ON The Disease is a commonly diagnosed infectious disease that affects all equidae worldwide. Caused by the bacterium Streptococcus equi (S.equi), this disease is highly contagious and is spread
ADVICE ON The Disease is a commonly diagnosed infectious disease that affects all equidae worldwide. Caused by the bacterium Streptococcus equi (S.equi), this disease is highly contagious and is spread
PERTUSSIS SURVEILLANCE AND RESPONSE PROTOCOL
 PERTUSSIS SURVEILLANCE AND RESPONSE PROTOCOL Public Health Action 1. Educate the public, particularly parents of infants, about the dangers of whooping cough and the advantages of initiating immunization
PERTUSSIS SURVEILLANCE AND RESPONSE PROTOCOL Public Health Action 1. Educate the public, particularly parents of infants, about the dangers of whooping cough and the advantages of initiating immunization
Living healthy with MRSA
 Stamford Health System Having MRSA means what? Living healthy with MRSA Discharge information for patients and families WASHING YOUR HANDS IS THE KEY!!! Staph aureus is a bacteria that lives on your skin
Stamford Health System Having MRSA means what? Living healthy with MRSA Discharge information for patients and families WASHING YOUR HANDS IS THE KEY!!! Staph aureus is a bacteria that lives on your skin
The National Antimicrobial Resistance Monitoring System (NARMS)
 The National Antimicrobial Resistance Monitoring System (NARMS) Strategic Plan 2012-2016 Table of Contents Background... 2 Mission... 3 Overview of Accomplishments, 1996-2011... 4 Strategic Goals and Objectives...
The National Antimicrobial Resistance Monitoring System (NARMS) Strategic Plan 2012-2016 Table of Contents Background... 2 Mission... 3 Overview of Accomplishments, 1996-2011... 4 Strategic Goals and Objectives...
Hospitalizations for Hepatitis A, B, and C, Active Component, U.S. Armed Forces, 1991-2011
 Hospitalizations for Hepatitis A, B, and C, Active Component, U.S. Armed Forces, 1991-2011 lthough genetically quite distinct from one another, hepatitis viruses A, B, and C all cause inflammatory liver
Hospitalizations for Hepatitis A, B, and C, Active Component, U.S. Armed Forces, 1991-2011 lthough genetically quite distinct from one another, hepatitis viruses A, B, and C all cause inflammatory liver
ANNUAL REPORT ON STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS BACTERAEMIA CASES IN DENMARK 2008 (part I)
 ANNUAL REPORT ON STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS BACTERAEMIA CASES IN DENMARK 2008 (part I) STAPHYLOCOCCUS LABORATORY, STATENS SERUM INSTITUT 1 Staphylococcus aureus bacteraemia annual report, part I The format
ANNUAL REPORT ON STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS BACTERAEMIA CASES IN DENMARK 2008 (part I) STAPHYLOCOCCUS LABORATORY, STATENS SERUM INSTITUT 1 Staphylococcus aureus bacteraemia annual report, part I The format
school for boys Persistent streptococcal throat infection in a preparatory BY J. H. D. BRISCOE
 J. Hyg., Camb. (1985), 95, 671-676 671 Printed in Great Britain Persistent streptococcal throat infection in a preparatory school for boys BY J. H. D. BRISCOE Eton Court House, Eton, Windsor, Berkshire
J. Hyg., Camb. (1985), 95, 671-676 671 Printed in Great Britain Persistent streptococcal throat infection in a preparatory school for boys BY J. H. D. BRISCOE Eton Court House, Eton, Windsor, Berkshire
Tuberculosis: FAQs. What is the difference between latent TB infection and TB disease?
 Tuberculosis: FAQs What is TB disease? Tuberculosis (TB) is a disease caused by bacteria (germs) that are spread from person to person through the air. TB usually affects the lungs, but it can also affect
Tuberculosis: FAQs What is TB disease? Tuberculosis (TB) is a disease caused by bacteria (germs) that are spread from person to person through the air. TB usually affects the lungs, but it can also affect
MRSA Positive. An information guide
 TO PROVIDE THE VERY BEST CARE FOR EACH PATIENT ON EVERY OCCASION MRSA Positive An information guide MRSA Positive What is MRSA? Staphylococcus aureus is a germ often found on the skin and up the nose of
TO PROVIDE THE VERY BEST CARE FOR EACH PATIENT ON EVERY OCCASION MRSA Positive An information guide MRSA Positive What is MRSA? Staphylococcus aureus is a germ often found on the skin and up the nose of
Healthcare-associated Infections in Utah
 2013 Healthcare-associated Infections in Utah Utah Department of Health Division of Disease Control and Prevention Published October 2014 2013 Annual Report Prepared by Rebecca L. Ward Division of Disease
2013 Healthcare-associated Infections in Utah Utah Department of Health Division of Disease Control and Prevention Published October 2014 2013 Annual Report Prepared by Rebecca L. Ward Division of Disease
Your Future by Design
 Retirement Research Series Your Future by Design Health, money, retirement: The different needs of men and women This research report is one of several reports in the Your Future by Design Retirement Research
Retirement Research Series Your Future by Design Health, money, retirement: The different needs of men and women This research report is one of several reports in the Your Future by Design Retirement Research
PRIMARY CARE MEASUREMENT INITIATIVE
 PRIMARY CARE MEASUREMENT INITIATIVE March 2014 Promoting and improving patient safety and health service quality across Alberta. TABLE OF CONTENTS EXECUTIVE SUMMARY... 3 INTRODUCTION... 4 Primary care...
PRIMARY CARE MEASUREMENT INITIATIVE March 2014 Promoting and improving patient safety and health service quality across Alberta. TABLE OF CONTENTS EXECUTIVE SUMMARY... 3 INTRODUCTION... 4 Primary care...
Root Cause Analysis following
 Root Cause Analysis following MRSA Bacteraemia: Reviewing the Patient s Journey Sharren Pells Senior Infection Control Nurse NHS Swindon Helen Forrest Infection Control Nurse Specialist NHS Swindon Aims
Root Cause Analysis following MRSA Bacteraemia: Reviewing the Patient s Journey Sharren Pells Senior Infection Control Nurse NHS Swindon Helen Forrest Infection Control Nurse Specialist NHS Swindon Aims
New Jersey State Department of Health and Senior Services Healthcare-Associated Infections Plan 2010
 New Jersey State Department of Health and Senior Services Healthcare-Associated Infections Plan Introduction The State of New Jersey has been proactive in creating programs to address the growing public
New Jersey State Department of Health and Senior Services Healthcare-Associated Infections Plan Introduction The State of New Jersey has been proactive in creating programs to address the growing public
Arizona Department of Health Services Healthcare-Associated Infection Plan Progress Report June 2010
 On December 31 st, 2010, the Arizona Department of Health Services (ADHS) submitted the state healthcare-associated infection (HAI) plan to the United States Department of Health and Human Services. The
On December 31 st, 2010, the Arizona Department of Health Services (ADHS) submitted the state healthcare-associated infection (HAI) plan to the United States Department of Health and Human Services. The
C-Difficile Infection Control and Prevention Strategies
 C-Difficile Infection Control and Prevention Strategies Adrienne Mims, MD MPH VP, Chief Medical Officer Adrienne.Mims@AlliantQuality.org 1/18/2016 1 Disclosure This educational activity does not have commercial
C-Difficile Infection Control and Prevention Strategies Adrienne Mims, MD MPH VP, Chief Medical Officer Adrienne.Mims@AlliantQuality.org 1/18/2016 1 Disclosure This educational activity does not have commercial
North Carolina Statewide Program for Infection Control and Prevention (SPICE) Objectives. Healthcare-Associated Infections: Impact
 North Carolina Statewide Program for Infection Control and Prevention (SPICE) Karen K. Hoffmann, RN, MS, CIC, FSHEA U School of Medicine, Chapel Hill, NC Objectives Describe how and why SPICE was created.
North Carolina Statewide Program for Infection Control and Prevention (SPICE) Karen K. Hoffmann, RN, MS, CIC, FSHEA U School of Medicine, Chapel Hill, NC Objectives Describe how and why SPICE was created.
