Lab 7.4.1: Basic DHCP and NAT Configuration
|
|
|
- Mabel Randall
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask S0/0/ R1 Fa0/ Fa0/ S0/0/ R2 S0/0/ Fa0/ ISP S0/0/ Scenario In this lab, you will configure the DHCP and NAT IP services. One router is the DHCP server. The other router forwards DHCP requests to the server. You will also configure both static and dynamic NAT configurations, including NAT overload. When you have completed the configurations, verify the connectivity between the inside and outside addresses. All contents are Copyright Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 1 of 9
2 Task 1: Prepare the Network Step 1: Cable a network that is similar to the one in the topology diagram. Step 2: Clear all existing configurations on the routers. Task 2: Perform Basic Router Configurations Configure the R1, R2, and ISP routers according to the following guidelines: Configure the device hostname. Disable DNS lookup. Configure a privileged EXEC mode password. Configure a message-of-the-day banner. Configure a password for the console connections. Configure a password for all vty connections. Configure IP addresses on all routers. The PCs receive IP addressing from DHCP later in the lab. Enable OSPF with process ID 1 on R1 and R2. Do not advertise the /27 network. Note: Instead of attaching a server to R2, you can configure a loopback interface on R2 to use the IP address /24. If you do this, you do not need to configure the Fast Ethernet interface. Task 3: Configure PC1 and PC2 to receive an IP address through DHCP On a Windows PC go to Start -> Control Panel -> Network Connections -> Local Area Connection. Right mouse click on the Local Area Connection and select Properties. Make sure the button is selected that says Obtain an IP address automatically. Once this has been done on both PC1 and PC2, they are ready to receive an IP address from a DHCP server. All contents are Copyright Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 2 of 9
3 Task 4: Configure a Cisco IOS DHCP Server Cisco IOS software supports a DHCP server configuration called Easy IP. The goal for this lab is to have devices on the networks /24 and /24 request IP addresses via DHCP from R2. Step 1: Exclude statically assigned addresses. The DHCP server assumes that all IP addresses in a DHCP address pool subnet are available for assigning to DHCP clients. You must specify the IP addresses that the DHCP server should not assign to clients. These IP addresses are usually static addresses reserved for the router interface, switch management IP address, servers, and local network printer. The ip dhcp excluded-address command prevents the router from assigning IP addresses within the configured range. The following commands exclude the first 10 IP addresses from each pool for the LANs attached to R1. These addresses will not be assigned to any DHCP clients. R2(config)#ip dhcp excluded-address R2(config)#ip dhcp excluded-address Step 2: Configure the pool. Create the DHCP pool using the ip dhcp pool command and name it R1Fa0. R2(config)#ip dhcp pool R1Fa0 Specify the subnet to use when assigning IP addresses. DHCP pools automatically associate with an interface based on the network statement. The router now acts as a DHCP server, handing out addresses in the /24 subnet starting with R2(dhcp-config)#network Configure the default router and domain name server for the network. Clients receive these settings via DHCP, along with an IP address. R2(dhcp-config)#dns-server R2(dhcp-config)#default-router Note: There is not a DNS server at You are configuring the command for practice only. Because devices from the network /24 also request addresses from R2, a separate pool must be created to serve devices on that network. The commands are similar to the commands shown above: R2(config)#ip dhcp pool R1Fa1 R2(dhcp-config)#network R2(dhcp-config)#dns-server R2(dhcp-config)#default-router Step 3: Test DHCP On PC1 and PC2 test whether each has received an IP address automatically. On each PC go to Start - > Run -> cmd -> ipconfig -all What are the results of your test? Why are these the results? All contents are Copyright Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 3 of 9
4 Step 4: Configure a helper address. Network services such as DHCP rely on Layer 2 broadcasts to function. When the devices providing these services exist on a different subnet than the clients, they cannot receive the broadcast packets. Because the DHCP server and the DHCP clients are not on the same subnet, configure R1 to forward DHCP broadcasts to R2, which is the DHCP server, using the ip helper-address interface configuration command. Notice that ip helper-address must be configured on each interface involved. R1(config)#interface fa0/0 R1(config-if)#ip helper-address R1(config)#interface fa0/1 R1(config-if)#ip helper-address Step 5: Release and Renew the IP addresses on PC1 and PC2 Depending upon whether your PCs have been used in a different lab, or connected to the internet, they may already have learned an IP address automatically from a different DHCP server. We need to clear this IP address using the ipconfig /release and ipconfig /renew commands. Step 6: Verify the DHCP configuration. You can verify the DHCP server configuration in several different ways. Issue the command ipconfig on PC1 and PC2 to verify that they have now received an IP address dynamically. You can then issue commands on the router to get more information. The show ip dhcp binding command provides information on all currently assigned DHCP addresses. For instance, the following output shows that the IP address has been assigned to MAC address e The IP lease expires on September 14, 2007 at 7:33 p.m. R1#show ip dhcp binding Bindings from all pools not associated with VRF: IP address Client-ID/ Lease expiration Type Hardware address/ User name f.2d30. Sep :33 PM Automatic e e d.566c. 31 All contents are Copyright Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 4 of 9
5 The show ip dhcp pool command displays information on all currently configured DHCP pools on the router. In this output, the pool R1Fa0 is configured on R1. One address has been leased from this pool. The next client to request an address will receive R2#show ip dhcp pool Pool R1Fa0 : Utilization mark (high/low) : 100 / 0 Subnet size (first/next) : 0 / 0 Total addresses : 254 Leased addresses : 1 Pending event : none 1 subnet is currently in the pool : Current index IP address range Leased addresses The debug ip dhcp server events command can be extremely useful when troubleshooting DHCP leases with a Cisco IOS DHCP server. The following is the debug output on R1 after connecting a host. Notice that the highlighted portion shows DHCP giving the client an address of and mask of *Sep 13 21:04:18.072: DHCPD: Sending notification of DISCOVER: *Sep 13 21:04:18.072: DHCPD: htype 1 chaddr 001c.57ec.0640 *Sep 13 21:04:18.072: DHCPD: remote id 020a0000c0a80b *Sep 13 21:04:18.072: DHCPD: circuit id *Sep 13 21:04:18.072: DHCPD: Seeing if there is an internally specified pool class: *Sep 13 21:04:18.072: DHCPD: htype 1 chaddr 001c.57ec.0640 *Sep 13 21:04:18.072: DHCPD: remote id 020a0000c0a80b *Sep 13 21:04:18.072: DHCPD: circuit id *Sep 13 21:04:18.072: DHCPD: there is no address pool for *Sep 13 21:04:18.072: DHCPD: Sending notification of DISCOVER: R1# *Sep 13 21:04:18.072: DHCPD: htype 1 chaddr 001c.57ec.0640 *Sep 13 21:04:18.072: DHCPD: remote id 020a0000c0a80a *Sep 13 21:04:18.072: DHCPD: circuit id *Sep 13 21:04:18.072: DHCPD: Seeing if there is an internally specified pool class: *Sep 13 21:04:18.072: DHCPD: htype 1 chaddr 001c.57ec.0640 *Sep 13 21:04:18.072: DHCPD: remote id 020a0000c0a80a *Sep 13 21:04:18.072: DHCPD: circuit id R1# *Sep 13 21:04:20.072: DHCPD: Adding binding to radix tree ( ) *Sep 13 21:04:20.072: DHCPD: Adding binding to hash tree *Sep 13 21:04:20.072: DHCPD: assigned IP address to client f.2d e e d.566c.31. *Sep 13 21:04:20.072: DHCPD: Sending notification of ASSIGNMENT: *Sep 13 21:04:20.072: DHCPD: address mask *Sep 13 21:04:20.072: DHCPD: htype 1 chaddr 001c.57ec.0640 *Sep 13 21:04:20.072: DHCPD: lease time remaining (secs) = *Sep 13 21:04:20.076: DHCPD: Sending notification of ASSIGNMENT: *Sep 13 21:04:20.076: DHCPD: address mask R1# *Sep 13 21:04:20.076: DHCPD: htype 1 chaddr 001c.57ec.0640 *Sep 13 21:04:20.076: DHCPD: lease time remaining (secs) = All contents are Copyright Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 5 of 9
6 Task 5: Configure Static and Default Routing ISP uses static routing to reach all networks beyond R2. However, R2 translates private addresses into public addresses before sending traffic to ISP. Therefore, ISP must be configured with the public addresses that are part of the NAT configuration on R2. Enter the following static route on ISP: ISP(config)#ip route serial 0/0/1 This static route includes all addresses assigned to R2 for public use. Configure a default route on R2 and propagate the route in OSPF. R2(config)#ip route R2(config)#router ospf 1 R2(config-router)#default-information originate Allow a few seconds for R1 to learn the default route from R2 and then check the R1 routing table. Alternatively, you can clear the routing table with the clear ip route * command. A default route pointing to R2 should appear in the R1 routing table. From R1, ping the serial 0/0/1 interface on ISP ( ). The pings should be successful. Troubleshoot if the pings fail. Task 6: Configure Static NAT Step 1: Statically map a public IP address to a private IP address. The inside server attached to R2 is accessible by outside hosts beyond ISP. Statically assign the public IP address as the address for NAT to use to map packets to the private IP address of the inside server at R2(config)#ip nat inside source static Step 2: Specify inside and outside NAT interfaces. Before NAT can work, you must specify which interfaces are inside and which interfaces are outside. R2(config)#interface serial 0/0/1 R2(config-if)#ip nat outside R2(config-if)#interface fa0/0 R2(config-if)#ip nat inside Note: If using a simulated inside server, assign the ip nat inside command to the loopback interface. Step 3: Verify the static NAT configuration. From ISP, ping the public IP address Task 7: Configure Dynamic NAT with a Pool of Addresses While static NAT provides a permanent mapping between an internal address and a specific public address, dynamic NAT maps private IP addresses to public addresses. These public IP addresses come from a NAT pool. Step 1: Define a pool of global addresses. Create a pool of addresses to which matched source addresses are translated. The following command creates a pool named MY-NAT-POOL that translates matched addresses to an available IP address in the range. R2(config)#ip nat pool MY-NAT-POOL netmask All contents are Copyright Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 6 of 9
7 Step 2: Create an extended access control list to identify which inside addresses are translated. R2(config)#ip access-list extended NAT R2(config-ext-nacl)#permit ip any R2(config-ext-nacl)#permit ip any Step 3: Establish dynamic source translation by binding the pool with the access control list. A router can have more than one NAT pool and more than one ACL. The following command tells the router which address pool to use to translate hosts that are allowed by the ACL. R2(config)#ip nat inside source list NAT pool MY-NAT-POOL Step 4: Specify inside and outside NAT interfaces. You have already specified the inside and outside interfaces for your static NAT configuration. Now add the serial interface linked to R1 as an inside interface. R2(config)#interface serial 0/0/0 R2(config-if)#ip nat inside Step 5: Verify the configuration. Ping ISP from PC1 or the Fast Ethernet interface on R1 using extended ping. Then use the show ip nat translations and show ip nat statistics commands on R2 to verify NAT. R2#show ip nat translations Pro Inside global Inside local Outside local Outside global icmp : : : : R2#show ip nat statistics Total active translations: 2 (1 static, 1 dynamic; 0 extended) Outside interfaces: Serial0/0/1 Inside interfaces: Serial0/0/0, Loopback0 Hits: 23 Misses: 3 CEF Translated packets: 18, CEF Punted packets: 0 Expired translations: 3 Dynamic mappings: -- Inside Source [Id: 1] access-list NAT pool MY-NAT-POOL refcount 1 pool MY-NAT-POOL: netmask start end type generic, total addresses 6, allocated 1 (16%), misses 0 Queued Packets: 0 To troubleshoot issues with NAT, you can use the debug ip nat command. Turn on NAT debugging and repeat the ping from PC1. R2#debug ip nat IP NAT debugging is on R2# *Sep 13 21:15:02.215: NAT*: s= > , d= [25] *Sep 13 21:15:02.231: NAT*: s= , d= > [25] *Sep 13 21:15:02.247: NAT*: s= > , d= [26] *Sep 13 21:15:02.263: NAT*: s= , d= > [26] All contents are Copyright Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 7 of 9
8 *Sep 13 21:15:02.275: NAT*: s= > , d= [27] *Sep 13 21:15:02.291: NAT*: s= , d= > [27] *Sep 13 21:15:02.307: NAT*: s= > , d= [28] *Sep 13 21:15:02.323: NAT*: s= , d= > [28] *Sep 13 21:15:02.335: NAT*: s= > , d= [29] *Sep 13 21:15:02.351: NAT*: s= , d= > [29] R2# Task 8: Configure NAT Overload In the previous example, what would happen if you needed more than the six public IP addresses that the pool allows? By tracking port numbers, NAT overloading allows multiple inside users to reuse a public IP address. In this task, you will remove the pool and mapping statement configured in the previous task. Then you will configure NAT overload on R2 so that all internal IP addresses are translated to the R2 S0/0/1 address when connecting to any outside device. Step 1: Remove the NAT pool and mapping statement. Use the following commands to remove the NAT pool and the map to the NAT ACL. R2(config)#no ip nat inside source list NAT pool MY-NAT-POOL R2(config)#no ip nat pool MY-NAT-POOL netmask If you receive the following message, clear your NAT translations. %Pool MY-NAT-POOL in use, cannot destroy R2#clear ip nat translation * Step 2: Configure PAT on R2 using the serial 0/0/1 interface public IP address. The configuration is similar to dynamic NAT, except that instead of a pool of addresses, the interface keyword is used to identify the outside IP address. Therefore, no NAT pool is defined. The overload keyword enables the addition of the port number to the translation. Because you already configured an ACL to identify which inside IP addresses to translate as well as which interfaces are inside and outside, you only need to configure the following: R2(config)#ip nat inside source list NAT interface S0/0/1 overload Step 3: Verify the configuration. Ping ISP from PC1 or the Fast Ethernet interface on R1 using extended ping. Then use the show ip nat translations and show ip nat statistics commands on R2 to verify NAT. R2#show ip nat translations Pro Inside global Inside local Outside local Outside global icmp : : : : R2#show ip nat statistics Total active translations: 2 (1 static, 1 dynamic; 1 extended) Outside interfaces: Serial0/0/1 Inside interfaces: All contents are Copyright Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 8 of 9
9 Serial0/0/0, Loopback0 Hits: 48 Misses: 6 CEF Translated packets: 46, CEF Punted packets: 0 Expired translations: 5 Dynamic mappings: -- Inside Source [Id: 2] access-list NAT interface Serial0/0/1 refcount 1 Queued Packets: 0 Note: In the previous task, you could have added the keyword overload to the ip nat inside source list NAT pool MY-NAT-POOL command to allow for more than six concurrent users. Task 9: Clean Up Erase the configurations and reload the routers. Disconnect and store the cabling. For PC hosts that are normally connected to other networks, such as the school LAN or the Internet, reconnect the appropriate cabling and restore the TCP/IP settings. All contents are Copyright Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 9 of 9
Lab 5-5 Configuring the Cisco IOS DHCP Server
 Lab 5-5 Configuring the Cisco IOS DHCP Server Learning Objectives Configure and verify the operation of the Cisco IOS DHCP server Configure an IP Helper address Review the EIGRP configuration Topology
Lab 5-5 Configuring the Cisco IOS DHCP Server Learning Objectives Configure and verify the operation of the Cisco IOS DHCP server Configure an IP Helper address Review the EIGRP configuration Topology
Lab 5.3.7 Configuring DHCP with SDM and the Cisco IOS CLI
 Lab 5.3.7 Configuring DHCP with SDM and the Cisco IOS CLI Device Host Name Interface IP Address Subnet Mask R1 Customer Serial 0/0/1 (DTE) 209.165.200.225 255.255.255.224 Fast Ethernet 0/0 192.168.1.1
Lab 5.3.7 Configuring DHCP with SDM and the Cisco IOS CLI Device Host Name Interface IP Address Subnet Mask R1 Customer Serial 0/0/1 (DTE) 209.165.200.225 255.255.255.224 Fast Ethernet 0/0 192.168.1.1
Note: This case study utilizes Packet Tracer. Please see the Chapter 5 Packet Tracer file located in Supplemental Materials.
 Note: This case study utilizes Packet Tracer. Please see the Chapter 5 Packet Tracer file located in Supplemental Materials. CHAPTER 5 OBJECTIVES Configure a router with an initial configuration. Use the
Note: This case study utilizes Packet Tracer. Please see the Chapter 5 Packet Tracer file located in Supplemental Materials. CHAPTER 5 OBJECTIVES Configure a router with an initial configuration. Use the
Topic 7 DHCP and NAT. Networking BAsics.
 Topic 7 DHCP and NAT Networking BAsics. 1 Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) IP address assignment Default Gateway assignment Network services discovery I just booted. What network is this? What
Topic 7 DHCP and NAT Networking BAsics. 1 Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) IP address assignment Default Gateway assignment Network services discovery I just booted. What network is this? What
Skills Assessment Student Training Exam
 Skills Assessment Student Training Exam Topology Assessment Objectives Part 1: Initialize Devices (8 points, 5 minutes) Part 2: Configure Device Basic Settings (28 points, 30 minutes) Part 3: Configure
Skills Assessment Student Training Exam Topology Assessment Objectives Part 1: Initialize Devices (8 points, 5 minutes) Part 2: Configure Device Basic Settings (28 points, 30 minutes) Part 3: Configure
Lab 3.1.2 Creating a Logical Network Diagram
 Lab 3.1.2 Creating a Logical Network Diagram Objectives Use router and switch commands to obtain information about an existing network. Use Cisco Network Assistant to obtain information about an existing
Lab 3.1.2 Creating a Logical Network Diagram Objectives Use router and switch commands to obtain information about an existing network. Use Cisco Network Assistant to obtain information about an existing
Lab 5.3.5 Configuring Basic Router Settings with the Cisco IOS CLI
 Lab 5.3.5 Configuring Basic Router Settings with the Cisco IOS CLI Device Host Name Interface IP address Subnet mask R1 R1 Serial 0/0/0 (DCE) 172.17.0.1 255.255.0.0 FastEthernet 0/0 172.16.0.1 255.255.0.0
Lab 5.3.5 Configuring Basic Router Settings with the Cisco IOS CLI Device Host Name Interface IP address Subnet mask R1 R1 Serial 0/0/0 (DCE) 172.17.0.1 255.255.0.0 FastEthernet 0/0 172.16.0.1 255.255.0.0
Lab 8.4.3a Managing Cisco IOS Images with TFTP
 Lab 8.4.3a Managing Cisco IOS Images with TFTP Host Device Name Interface IP Address Subnet Mask R1 R1 Fast Ethernet 0/0 172.17.0.1 255.255.0.0 Objectives Analyze the Cisco IOS image and router flash memory.
Lab 8.4.3a Managing Cisco IOS Images with TFTP Host Device Name Interface IP Address Subnet Mask R1 R1 Fast Ethernet 0/0 172.17.0.1 255.255.0.0 Objectives Analyze the Cisco IOS image and router flash memory.
Lab 5.3.9b Managing Router Configuration Files Using TFTP
 Lab 5.3.9b Managing Router Configuration Files Using TFTP Device Host Name Interface IP Address Subnet Mask R1 R1 Fast Ethernet 0/0 172.17.0.1 255.255.0.0 Objectives Download and install TFTP server software.
Lab 5.3.9b Managing Router Configuration Files Using TFTP Device Host Name Interface IP Address Subnet Mask R1 R1 Fast Ethernet 0/0 172.17.0.1 255.255.0.0 Objectives Download and install TFTP server software.
Lab 4.5.4 Diagramming External Traffic Flows
 Lab 4.5.4 Diagramming External Traffic Flows Device Designation Device Name Address Subnet Mask Discovery Server Business Services 172.17.1.1 255.255.0.0 R1 R2 R3 FC-CPE-1 FC-CPE-2 ISP Fa0/1 172.17.0.1
Lab 4.5.4 Diagramming External Traffic Flows Device Designation Device Name Address Subnet Mask Discovery Server Business Services 172.17.1.1 255.255.0.0 R1 R2 R3 FC-CPE-1 FC-CPE-2 ISP Fa0/1 172.17.0.1
Sample Configuration Using the ip nat outside source list C
 Sample Configuration Using the ip nat outside source list C Table of Contents Sample Configuration Using the ip nat outside source list Command...1 Introduction...1 Before You Begin...1 Conventions...1
Sample Configuration Using the ip nat outside source list C Table of Contents Sample Configuration Using the ip nat outside source list Command...1 Introduction...1 Before You Begin...1 Conventions...1
Lab: Basic Router Configuration
 Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Def. Gateway R1 Fa0/0 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S0/0/0 192.168.2.1 255.255.255.0 N/A R2 Fa0/0 192.168.3.1 255.255.255.0 N/A
Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Def. Gateway R1 Fa0/0 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S0/0/0 192.168.2.1 255.255.255.0 N/A R2 Fa0/0 192.168.3.1 255.255.255.0 N/A
Lab 4.5.2 Diagramming Intranet Traffic Flows
 Lab 4.5.2 Diagramming Intranet Traffic Flows Objective Device Designation Device Name Address Subnet Mask Discovery Server Business Services 172.17.1.1 255.255.0.0 R1 FC-CPE-1 Fa0/1 172.17.0.1 Fa0/0 10.0.0.1
Lab 4.5.2 Diagramming Intranet Traffic Flows Objective Device Designation Device Name Address Subnet Mask Discovery Server Business Services 172.17.1.1 255.255.0.0 R1 FC-CPE-1 Fa0/1 172.17.0.1 Fa0/0 10.0.0.1
Lab - Using IOS CLI with Switch MAC Address Tables
 Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/1 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S1 VLAN 1 192.168.1.11 255.255.255.0 192.168.1.1 S2 VLAN 1 192.168.1.12
Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/1 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S1 VLAN 1 192.168.1.11 255.255.255.0 192.168.1.1 S2 VLAN 1 192.168.1.12
Sample Configuration Using the ip nat outside source static
 Sample Configuration Using the ip nat outside source static Table of Contents Sample Configuration Using the ip nat outside source static Command...1 Introduction...1 Before You Begin...1 Conventions...1
Sample Configuration Using the ip nat outside source static Table of Contents Sample Configuration Using the ip nat outside source static Command...1 Introduction...1 Before You Begin...1 Conventions...1
Lab 5.3.5 Configuring Basic Router Settings with the Cisco IOS CLI
 Lab 5.3.5 Configuring Basic Router Settings with the Cisco IOS CLI Device Host Name Interface IP Address Subnet Mask R1 R1 Serial 0/0/0 (DCE) 172.17.0.1 255.255.0.0 FastEthernet 0/0 172.16.0.1 255.255.0.0
Lab 5.3.5 Configuring Basic Router Settings with the Cisco IOS CLI Device Host Name Interface IP Address Subnet Mask R1 R1 Serial 0/0/0 (DCE) 172.17.0.1 255.255.0.0 FastEthernet 0/0 172.16.0.1 255.255.0.0
LAB Configuring NAT. Objective. Background/Preparation
 LAB Configuring NAT Objective Configure a router to use network address translation (NAT) to convert internal IP addresses, typically private addresses, into outside public addresses. Configure static
LAB Configuring NAT Objective Configure a router to use network address translation (NAT) to convert internal IP addresses, typically private addresses, into outside public addresses. Configure static
Configuring Static and Dynamic NAT Simultaneously
 Configuring Static and Dynamic NAT Simultaneously Document ID: 13778 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configuring NAT Related Information Introduction In some
Configuring Static and Dynamic NAT Simultaneously Document ID: 13778 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configuring NAT Related Information Introduction In some
Lab 5.5.3 Developing ACLs to Implement Firewall Rule Sets
 Lab 5.5.3 Developing ACLs to Implement Firewall Rule Sets All contents are Copyright 1992 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 1 of 8 Device Interface
Lab 5.5.3 Developing ACLs to Implement Firewall Rule Sets All contents are Copyright 1992 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 1 of 8 Device Interface
Lab 9.1.1 Organizing CCENT Objectives by OSI Layer
 Lab 9.1.1 Organizing CCENT Objectives by OSI Layer Objectives Organize the CCENT objectives by which layer or layers they address. Background / Preparation In this lab, you associate the objectives of
Lab 9.1.1 Organizing CCENT Objectives by OSI Layer Objectives Organize the CCENT objectives by which layer or layers they address. Background / Preparation In this lab, you associate the objectives of
Objectives. Background. Required Resources. CCNA Security
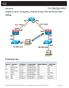 Chapter 8 Lab B, Configuring a Remote Access VPN Server and Client Topology IP Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway Switch Port R1 FA0/1 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A
Chapter 8 Lab B, Configuring a Remote Access VPN Server and Client Topology IP Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway Switch Port R1 FA0/1 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A
Lab 5.3.8 Configuring PAT with SDM and Static NAT using Cisco IOS Commands
 Lab 5.3.8 Configuring PAT with SDM and Static NAT using Cisco IOS Commands Device Host Name Interface IP Address Subnet Mask R1 CustomerRouter Serial 0/0/0 (DTE) 209.165.200.225 255.255.255.224 Fast Ethernet
Lab 5.3.8 Configuring PAT with SDM and Static NAT using Cisco IOS Commands Device Host Name Interface IP Address Subnet Mask R1 CustomerRouter Serial 0/0/0 (DTE) 209.165.200.225 255.255.255.224 Fast Ethernet
Lab 8.5.3 Configuring the PIX Firewall as a DHCP Server
 Lab 8.5.3 Configuring the PIX Firewall as a DHCP Server Objective Scenario Estimated Time: 15 minutes Number of Team Members: Two teams with four students per team. In this lab, students will learn the
Lab 8.5.3 Configuring the PIX Firewall as a DHCP Server Objective Scenario Estimated Time: 15 minutes Number of Team Members: Two teams with four students per team. In this lab, students will learn the
Lab 7.2.9 Load Balancing Across Multiple Paths
 Lab 7.2.9 Load Balancing Across Multiple Paths Objective Configure Load balance across multiple paths. Observe the load balancing process. Background/Preparation Cable a network similar to the one in the
Lab 7.2.9 Load Balancing Across Multiple Paths Objective Configure Load balance across multiple paths. Observe the load balancing process. Background/Preparation Cable a network similar to the one in the
Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway
 Felix Rohrer Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 99 192.168.99.11 255.255.255.0 192.168.99.1 S2 VLAN 99 192.168.99.12 255.255.255.0 192.168.99.1
Felix Rohrer Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 99 192.168.99.11 255.255.255.0 192.168.99.1 S2 VLAN 99 192.168.99.12 255.255.255.0 192.168.99.1
CCNA / CCNP Tutorial: Introduction To NAT
 CCNA / CCNP Tutorial: Introduction To NAT By Chris Bryant, CCIE #12933 A Free Excerpt From The Bryant Advantage Ultimate CCNA Study Guide Network Address Translation (NAT) is not only an important topic
CCNA / CCNP Tutorial: Introduction To NAT By Chris Bryant, CCIE #12933 A Free Excerpt From The Bryant Advantage Ultimate CCNA Study Guide Network Address Translation (NAT) is not only an important topic
Computer Networks I Laboratory Exercise 1
 Computer Networks I Laboratory Exercise 1 The lab is divided into two parts where the first part is a basic PC network TCP/IP configuration and connection to the Internet. The second part is building a
Computer Networks I Laboratory Exercise 1 The lab is divided into two parts where the first part is a basic PC network TCP/IP configuration and connection to the Internet. The second part is building a
CCT vs. CCENT Skill Set Comparison
 Operation of IP Data Networks Recognize the purpose and functions of various network devices such as Routers, Switches, Bridges and Hubs Select the components required to meet a given network specification
Operation of IP Data Networks Recognize the purpose and functions of various network devices such as Routers, Switches, Bridges and Hubs Select the components required to meet a given network specification
Lab 8.4.2 Configuring Access Policies and DMZ Settings
 Lab 8.4.2 Configuring Access Policies and DMZ Settings Objectives Log in to a multi-function device and view security settings. Set up Internet access policies based on IP address and application. Set
Lab 8.4.2 Configuring Access Policies and DMZ Settings Objectives Log in to a multi-function device and view security settings. Set up Internet access policies based on IP address and application. Set
DHCP Server Port-Based Address Allocation
 The feature provides port-based address allocation support on the Cisco IOS Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) server for the Ethernet platform. The DHCP server provides address assignment support
The feature provides port-based address allocation support on the Cisco IOS Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) server for the Ethernet platform. The DHCP server provides address assignment support
Lab 4.5.3 Diagramming Traffic Flows to and from Remote Sites
 Lab 4.5.3 Diagramming Traffic Flows to and from Remote Sites Objective Device Designation Device Name Address Subnet Mask Discovery Server Business Services 172.17.1.1 255.255.0.0 R1 R2 R3 FC-CPE-1 FC-CPE-2
Lab 4.5.3 Diagramming Traffic Flows to and from Remote Sites Objective Device Designation Device Name Address Subnet Mask Discovery Server Business Services 172.17.1.1 255.255.0.0 R1 R2 R3 FC-CPE-1 FC-CPE-2
Chapter 8 Lab B: Configuring a Remote Access VPN Server and Client
 Chapter 8 Lab B: Configuring a Remote Access VPN Server and Client Topology Note: ISR G2 devices have Gigabit Ethernet interfaces instead of FastEthernet Interfaces. All contents are Copyright 1992 2012
Chapter 8 Lab B: Configuring a Remote Access VPN Server and Client Topology Note: ISR G2 devices have Gigabit Ethernet interfaces instead of FastEthernet Interfaces. All contents are Copyright 1992 2012
Lab 4.1.2 Characterizing Network Applications
 Lab 4.1.2 Characterizing Network Applications Objective Device Designation Device Name Address Subnet Mask Discovery Server Business Services 172.17.1.1 255.255.0.0 R1 FC-CPE-1 Fa0/1 172.17.0.1 Fa0/0 10.0.0.1
Lab 4.1.2 Characterizing Network Applications Objective Device Designation Device Name Address Subnet Mask Discovery Server Business Services 172.17.1.1 255.255.0.0 R1 FC-CPE-1 Fa0/1 172.17.0.1 Fa0/0 10.0.0.1
100-101: Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Part 1 v2.0 (ICND1)
 100-101: Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Part 1 v2.0 (ICND1) Course Overview This course provides students with the knowledge and skills to implement and support a small switched and routed network.
100-101: Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Part 1 v2.0 (ICND1) Course Overview This course provides students with the knowledge and skills to implement and support a small switched and routed network.
Routing Protocols and Concepts Chapter 2 Conceitos de protocolos de Encaminhamento Cap 2
 Static Routing Routing Protocols and Concepts Chapter 2 1 1 Objectives Define the general role a router plays in networks. Describe the directly connected networks, different router interfaces Examine
Static Routing Routing Protocols and Concepts Chapter 2 1 1 Objectives Define the general role a router plays in networks. Describe the directly connected networks, different router interfaces Examine
Lab 4.2.3 Analyzing Network Traffic
 Lab 4.2.3 Analyzing Network Traffic Objective Device Designation Device Name Address Subnet Mask Discovery Server Network Services 172.17.1.1 255.255.0.0 R1 FC-CPE-1 Fa0/1 172.17.0.1 Fa0/0 10.0.0.1 255.255.0.0
Lab 4.2.3 Analyzing Network Traffic Objective Device Designation Device Name Address Subnet Mask Discovery Server Network Services 172.17.1.1 255.255.0.0 R1 FC-CPE-1 Fa0/1 172.17.0.1 Fa0/0 10.0.0.1 255.255.0.0
PC/POLL SYSTEMS Version 7 Polling SPS2000 Cash Register TCP/IP Communications
 PC/POLL SYSTEMS Version 7 Polling SPS2000 Cash Register TCP/IP Communications PC/POLL SYSTEMS supports native TCP/IP polling for the SPS2000 cash register. It is recommended users have the register updated
PC/POLL SYSTEMS Version 7 Polling SPS2000 Cash Register TCP/IP Communications PC/POLL SYSTEMS supports native TCP/IP polling for the SPS2000 cash register. It is recommended users have the register updated
Basic Wireless Configuration
 Basic Wireless Configuration Topology Diagram Learning Objectives Configure options in the Linksys Setup tab. Configure options in the Linksys Wireless tab. Configure options in the Linksys Administration
Basic Wireless Configuration Topology Diagram Learning Objectives Configure options in the Linksys Setup tab. Configure options in the Linksys Wireless tab. Configure options in the Linksys Administration
1 PC to WX64 direction connection with crossover cable or hub/switch
 1 PC to WX64 direction connection with crossover cable or hub/switch If a network is not available, or if it is desired to keep the WX64 and PC(s) completely separated from other computers, a simple network
1 PC to WX64 direction connection with crossover cable or hub/switch If a network is not available, or if it is desired to keep the WX64 and PC(s) completely separated from other computers, a simple network
Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices 1 Course, Class Outline
 www.etidaho.com (208) 327-0768 Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices 1 Course, Class Outline 5 Days Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices, Part 1 (ICND1) v2.0 is a five-day, instructorled training course
www.etidaho.com (208) 327-0768 Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices 1 Course, Class Outline 5 Days Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices, Part 1 (ICND1) v2.0 is a five-day, instructorled training course
Expert Reference Series of White Papers. The Basics of Configuring and Using Cisco Network Address Translation
 Expert Reference Series of White Papers The Basics of Configuring and Using Cisco Network Address Translation 1-800-COURSES www.globalknowledge.com The Basics of Configuring and Using Cisco Network Address
Expert Reference Series of White Papers The Basics of Configuring and Using Cisco Network Address Translation 1-800-COURSES www.globalknowledge.com The Basics of Configuring and Using Cisco Network Address
3.1 Connecting to a Router and Basic Configuration
 3.1 Connecting to a Router and Basic Configuration Objective This lab will focus on the ability to connect a PC to a router in order to establish a console session and observe the user interface. A console
3.1 Connecting to a Router and Basic Configuration Objective This lab will focus on the ability to connect a PC to a router in order to establish a console session and observe the user interface. A console
Packet Tracer 3 Lab VLSM 2 Solution
 Packet Tracer 3 Lab VLSM 2 Solution Objective Create a simulated network topology using Packet Tracer Design an IP addressing scheme using a Class B subnetwork address and VLSM Apply IP addresses to the
Packet Tracer 3 Lab VLSM 2 Solution Objective Create a simulated network topology using Packet Tracer Design an IP addressing scheme using a Class B subnetwork address and VLSM Apply IP addresses to the
ICND1-100-101 IOS CLI Study Guide (CCENT)
 ICND1-100-101 IOS CLI Study Guide (CCENT) Hostname: 2. hostname SW1 SWITCH CONFIGURATION Mgmt IP: 2. interface vlan 1 3. ip address 10.0.0.2 4. no shut Gateway: 2. ip default-gateway 10.0.0.1 Local User/Pwd:
ICND1-100-101 IOS CLI Study Guide (CCENT) Hostname: 2. hostname SW1 SWITCH CONFIGURATION Mgmt IP: 2. interface vlan 1 3. ip address 10.0.0.2 4. no shut Gateway: 2. ip default-gateway 10.0.0.1 Local User/Pwd:
Objectives. Router as a Computer. Router components and their functions. Router components and their functions
 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public Objectives Introduction to Routing and Packet Forwarding Routing Protocols and Concepts Chapter 1 Identify a router as a computer with an OS and
2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public Objectives Introduction to Routing and Packet Forwarding Routing Protocols and Concepts Chapter 1 Identify a router as a computer with an OS and
Configure ISDN Backup and VPN Connection
 Case Study 2 Configure ISDN Backup and VPN Connection Cisco Networking Academy Program CCNP 2: Remote Access v3.1 Objectives In this case study, the following concepts are covered: AAA authentication Multipoint
Case Study 2 Configure ISDN Backup and VPN Connection Cisco Networking Academy Program CCNP 2: Remote Access v3.1 Objectives In this case study, the following concepts are covered: AAA authentication Multipoint
Cisco - Configure the 1721 Router for VLANs Using a Switch Module (WIC-4ESW)
 Page 1 of 20 Configure the 1721 Router for VLANs Using a Switch Module (WIC-4ESW) Document ID: 50036 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Network Diagram The Role of Switched
Page 1 of 20 Configure the 1721 Router for VLANs Using a Switch Module (WIC-4ESW) Document ID: 50036 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Network Diagram The Role of Switched
IOS NAT Load Balancing for Two ISP Connections
 IOS NAT Load Balancing for Two ISP Connections Document ID: 100658 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure Network Diagram Configurations Verify Troubleshoot
IOS NAT Load Balancing for Two ISP Connections Document ID: 100658 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure Network Diagram Configurations Verify Troubleshoot
Lab 4.2.4 Advanced Telnet Operations
 Lab 4.2.4 Advanced Telnet Operations Objective Use the telnet command to remotely access other routers. Verify that the application layer between the source and the destination is working properly. Suspend
Lab 4.2.4 Advanced Telnet Operations Objective Use the telnet command to remotely access other routers. Verify that the application layer between the source and the destination is working properly. Suspend
Cisco Certified Network Associate Exam. Operation of IP Data Networks. LAN Switching Technologies. IP addressing (IPv4 / IPv6)
 Cisco Certified Network Associate Exam Exam Number 200-120 CCNA Associated Certifications CCNA Routing and Switching Operation of IP Data Networks Operation of IP Data Networks Recognize the purpose and
Cisco Certified Network Associate Exam Exam Number 200-120 CCNA Associated Certifications CCNA Routing and Switching Operation of IP Data Networks Operation of IP Data Networks Recognize the purpose and
INTERCONNECTING CISCO NETWORK DEVICES PART 1 V2.0 (ICND 1)
 INTERCONNECTING CISCO NETWORK DEVICES PART 1 V2.0 (ICND 1) COURSE OVERVIEW: Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices, Part 1 (ICND1) v2.0 is a five-day, instructor-led training course that teaches learners
INTERCONNECTING CISCO NETWORK DEVICES PART 1 V2.0 (ICND 1) COURSE OVERVIEW: Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices, Part 1 (ICND1) v2.0 is a five-day, instructor-led training course that teaches learners
Lab 2.3.2 Configuring OSPF with Loopback Addresses
 Lab 2.3.2 Configuring OSPF with Loopback Addresses Objective Configure routers with a Class C IP addressing scheme. Observe the election process for designated routers (DR) and backup designated routers
Lab 2.3.2 Configuring OSPF with Loopback Addresses Objective Configure routers with a Class C IP addressing scheme. Observe the election process for designated routers (DR) and backup designated routers
Building a Network in GNS3
 Building a Network in GNS3 In this tutorial, you will create a network in GNS3 between two routers, and each router will have one host connected to it. The ultimate goal is to route data between network
Building a Network in GNS3 In this tutorial, you will create a network in GNS3 between two routers, and each router will have one host connected to it. The ultimate goal is to route data between network
Lab 1.2.3 Review of Basic Router Configuration with RIP. Objective. Background / Preparation. General Configuration Tips
 Lab 1.2.3 Review of Basic Router Configuration with RIP Objective Cable and configure workstations and routers Setup IP addressing scheme using Class B networks Configure Routing Information Protocol (RIP)
Lab 1.2.3 Review of Basic Router Configuration with RIP Objective Cable and configure workstations and routers Setup IP addressing scheme using Class B networks Configure Routing Information Protocol (RIP)
During this lab time you will configure the routing protocol OSPF with IPv4 addresses.
 Lab 2: OSPF During this lab time you will configure the routing protocol OSPF with IPv4 addresses. It is your responsibility to create an appropriate IPv4 subnet plan and address plan. To ensure a timely
Lab 2: OSPF During this lab time you will configure the routing protocol OSPF with IPv4 addresses. It is your responsibility to create an appropriate IPv4 subnet plan and address plan. To ensure a timely
Procedure: You can find the problem sheet on Drive D: of the lab PCs. 1. IP address for this host computer 2. Subnet mask 3. Default gateway address
 Objectives University of Jordan Faculty of Engineering & Technology Computer Engineering Department Computer Networks Laboratory 907528 Lab.4 Basic Network Operation and Troubleshooting 1. To become familiar
Objectives University of Jordan Faculty of Engineering & Technology Computer Engineering Department Computer Networks Laboratory 907528 Lab.4 Basic Network Operation and Troubleshooting 1. To become familiar
Chapter 4 Customizing Your Network Settings
 . Chapter 4 Customizing Your Network Settings This chapter describes how to configure advanced networking features of the Wireless-G Router Model WGR614v9, including LAN, WAN, and routing settings. It
. Chapter 4 Customizing Your Network Settings This chapter describes how to configure advanced networking features of the Wireless-G Router Model WGR614v9, including LAN, WAN, and routing settings. It
Network Protocol Configuration
 Table of Contents Table of Contents Chapter 1 Configuring IP Addressing... 1 1.1 IP Introduction... 1 1.1.1 IP... 1 1.1.2 IP Routing Protocol... 1 1.2 Configuring IP Address Task List... 2 1.3 Configuring
Table of Contents Table of Contents Chapter 1 Configuring IP Addressing... 1 1.1 IP Introduction... 1 1.1.1 IP... 1 1.1.2 IP Routing Protocol... 1 1.2 Configuring IP Address Task List... 2 1.3 Configuring
Chapter 5 Customizing Your Network Settings
 Chapter 5 Customizing Your Network Settings This chapter describes how to configure advanced networking features of the RangeMax NEXT Wireless Router WNR834B, including LAN, WAN, and routing settings.
Chapter 5 Customizing Your Network Settings This chapter describes how to configure advanced networking features of the RangeMax NEXT Wireless Router WNR834B, including LAN, WAN, and routing settings.
Table of Contents. Cisco Using the Cisco IOS Firewall to Allow Java Applets From Known Sites while Denying Others
 Cisco IOS Firewall to Allow Java Applets From Known Sites w Table of Contents Using the Cisco IOS Firewall to Allow Java Applets From Known Sites while Denying Others...1 Introduction...1 To Deny Java
Cisco IOS Firewall to Allow Java Applets From Known Sites w Table of Contents Using the Cisco IOS Firewall to Allow Java Applets From Known Sites while Denying Others...1 Introduction...1 To Deny Java
BASIC ANALYSIS OF TCP/IP NETWORKS
 BASIC ANALYSIS OF TCP/IP NETWORKS INTRODUCTION Communication analysis provides powerful tool for maintenance, performance monitoring, attack detection, and problems fixing in computer networks. Today networks
BASIC ANALYSIS OF TCP/IP NETWORKS INTRODUCTION Communication analysis provides powerful tool for maintenance, performance monitoring, attack detection, and problems fixing in computer networks. Today networks
Lab 3.5.1: Basic VLAN Configuration (Instructor Version)
 (Instructor Version) Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device (Hostname) Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 99 172.17.99.11 255.255.255.0 N/A S2 VLAN 99 172.17.99.12 255.255.255.0
(Instructor Version) Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device (Hostname) Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 99 172.17.99.11 255.255.255.0 N/A S2 VLAN 99 172.17.99.12 255.255.255.0
Lab 6.2.3 Managing the MAC Address Table
 Lab 6.2.3 Managing the MAC Address Table Objective Create a basic switch configuration. Manage the switch MAC table. Background/Preparation Cable a network similar to the one in the diagram. The configuration
Lab 6.2.3 Managing the MAC Address Table Objective Create a basic switch configuration. Manage the switch MAC table. Background/Preparation Cable a network similar to the one in the diagram. The configuration
How To Learn Cisco Cisco Ios And Cisco Vlan
 Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices: Accelerated Course CCNAX v2.0; 5 Days, Instructor-led Course Description Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices: Accelerated (CCNAX) v2.0 is a 60-hour instructor-led
Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices: Accelerated Course CCNAX v2.0; 5 Days, Instructor-led Course Description Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices: Accelerated (CCNAX) v2.0 is a 60-hour instructor-led
Lab Configuring Syslog and NTP (Instructor Version)
 (Instructor Version) Instructor Note: Red font color or Gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only. Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask
(Instructor Version) Instructor Note: Red font color or Gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only. Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask
PT Activity 8.1.2: Network Discovery and Documentation Topology Diagram
 Topology Diagram All contents are Copyright 1992 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 1 of 6 Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet
Topology Diagram All contents are Copyright 1992 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 1 of 6 Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet
CCNA Exploration: Accessing the WAN Chapter 7 Case Study
 Objectives: Mitigate attacks based on DHCP rogue servers. Intro: ChurchBells Inc. is having connectivity issues and needs your help. The Scenario: According to the reports, some user PCs within the company
Objectives: Mitigate attacks based on DHCP rogue servers. Intro: ChurchBells Inc. is having connectivity issues and needs your help. The Scenario: According to the reports, some user PCs within the company
Chapter 4 Customizing Your Network Settings
 Chapter 4 Customizing Your Network Settings This chapter describes how to configure advanced networking features of the RangeMax Dual Band Wireless-N Router WNDR3300, including LAN, WAN, and routing settings.
Chapter 4 Customizing Your Network Settings This chapter describes how to configure advanced networking features of the RangeMax Dual Band Wireless-N Router WNDR3300, including LAN, WAN, and routing settings.
Welcome to Todd Lammle s CCNA Bootcamp
 Welcome to Todd Lammle s CCNA Bootcamp Todd Lammle Cisco Authorized CCNA Bootcamps are now available, delivered by CCSI instructor, and popular Sybex author Todd Lammle. Todd Lammle CCNA Training Boot
Welcome to Todd Lammle s CCNA Bootcamp Todd Lammle Cisco Authorized CCNA Bootcamps are now available, delivered by CCSI instructor, and popular Sybex author Todd Lammle. Todd Lammle CCNA Training Boot
"Charting the Course...
 Description "Charting the Course... Course Summary Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices: Accelerated (CCNAX), is a course consisting of ICND1 and ICND2 content in its entirety, but with the content
Description "Charting the Course... Course Summary Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices: Accelerated (CCNAX), is a course consisting of ICND1 and ICND2 content in its entirety, but with the content
Network Simulator Lab Study Plan
 The CCNA 640-802 Network Simulator has 300 lab exercises, organized both by type (Skill Builder, Configuration Scenario, Troubleshooting Scenario, and Subnetting Exercise) and by major topic within each
The CCNA 640-802 Network Simulator has 300 lab exercises, organized both by type (Skill Builder, Configuration Scenario, Troubleshooting Scenario, and Subnetting Exercise) and by major topic within each
Configuring WAN Failover with a Cisco 881 Router and an AirLink ES440
 Configuring WAN Failover with a Cisco 881 Router and an AirLink ES440 When the AirLink ES440 is combined with a third-party router, the combined solution supports business continuity by providing primary
Configuring WAN Failover with a Cisco 881 Router and an AirLink ES440 When the AirLink ES440 is combined with a third-party router, the combined solution supports business continuity by providing primary
1 Basic Configuration of Cisco 2600 Router. Basic Configuration Cisco 2600 Router
 1 Basic Configuration of Cisco 2600 Router Basic Configuration Cisco 2600 Router I decided to incorporate the Cisco 2600 into my previously designed network. This would give me two seperate broadcast domains
1 Basic Configuration of Cisco 2600 Router Basic Configuration Cisco 2600 Router I decided to incorporate the Cisco 2600 into my previously designed network. This would give me two seperate broadcast domains
CCNA Discovery 4.0.3.0 Networking for Homes and Small Businesses Student Packet Tracer Lab Manual
 4.0.3.0 Networking for Homes and Small Businesses Student Packet Tracer Lab Manual This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial
4.0.3.0 Networking for Homes and Small Businesses Student Packet Tracer Lab Manual This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial
Chapter 8 Lab A: Configuring a Site-to-Site VPN Using Cisco IOS and SDM
 Chapter 8 Lab A: Configuring a Site-to-Site VPN Using Cisco IOS and SDM Topology IP Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway Switch Port R1 Fa0/1 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0
Chapter 8 Lab A: Configuring a Site-to-Site VPN Using Cisco IOS and SDM Topology IP Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway Switch Port R1 Fa0/1 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0
Lab PC Network TCP/IP Configuration
 Lab PC Network TCP/IP Configuration Objective Identify tools used to discover a computer network configuration with various operating systems. Gather information including connection, host name, Layer
Lab PC Network TCP/IP Configuration Objective Identify tools used to discover a computer network configuration with various operating systems. Gather information including connection, host name, Layer
Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices, Part 1 (ICND1) v3.0
 Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices, Part 1 (ICND1) v3.0 COURSE OVERVIEW: Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices, Part 1 (ICND1) v3.0 is a five-day, instructor-led training course that teaches learners
Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices, Part 1 (ICND1) v3.0 COURSE OVERVIEW: Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices, Part 1 (ICND1) v3.0 is a five-day, instructor-led training course that teaches learners
Savvius Insight Initial Configuration
 The configuration utility on Savvius Insight lets you configure device, network, and time settings. Additionally, if you are forwarding your data from Savvius Insight to a Splunk server, You can configure
The configuration utility on Savvius Insight lets you configure device, network, and time settings. Additionally, if you are forwarding your data from Savvius Insight to a Splunk server, You can configure
1. Hardware Installation
 4 Port 10/100M Internet Broadband Router with USB Printer server Quick Installation Guide #4824904AXZZ0 1. Hardware Installation A. System Requirement Before you getting started, make sure that you meet
4 Port 10/100M Internet Broadband Router with USB Printer server Quick Installation Guide #4824904AXZZ0 1. Hardware Installation A. System Requirement Before you getting started, make sure that you meet
PT Activity: Configure Cisco Routers for Syslog, NTP, and SSH Operations
 PT Activity: Configure Cisco Routers for Syslog, NTP, and SSH Operations Instructor Version Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway Switch Port R1 FA0/1
PT Activity: Configure Cisco Routers for Syslog, NTP, and SSH Operations Instructor Version Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway Switch Port R1 FA0/1
Lab Exercise Configure the PIX Firewall and a Cisco Router
 Lab Exercise Configure the PIX Firewall and a Cisco Router Scenario Having worked at Isis Network Consulting for two years now as an entry-level analyst, it has been your hope to move up the corporate
Lab Exercise Configure the PIX Firewall and a Cisco Router Scenario Having worked at Isis Network Consulting for two years now as an entry-level analyst, it has been your hope to move up the corporate
Configuring a Gateway of Last Resort Using IP Commands
 Configuring a Gateway of Last Resort Using IP Commands Document ID: 16448 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions ip default gateway ip default network Flag a Default
Configuring a Gateway of Last Resort Using IP Commands Document ID: 16448 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions ip default gateway ip default network Flag a Default
Table of Contents. Cisco Configuring IPSec Cisco Secure VPN Client to Central Router Controlling Access
 Table of Contents Configuring IPSec Cisco Secure VPN Client to Central Router Controlling Access...1 Introduction...1 Prerequisites...1 Requirements...1 Components Used...1 Conventions...1 Configure...2
Table of Contents Configuring IPSec Cisco Secure VPN Client to Central Router Controlling Access...1 Introduction...1 Prerequisites...1 Requirements...1 Components Used...1 Conventions...1 Configure...2
Introduction to Network Address Translation
 1 Introduction to Network Address Translation Session 2 Agenda Basic Concept of Network Address Translation (NAT) and PAT Definition, Benefits, Availability and Application Support NAT Concepts and Terminology
1 Introduction to Network Address Translation Session 2 Agenda Basic Concept of Network Address Translation (NAT) and PAT Definition, Benefits, Availability and Application Support NAT Concepts and Terminology
Procedure: You can find the problem sheet on Drive D: of the lab PCs. Part 1: Router & Switch
 University of Jordan Faculty of Engineering & Technology Computer Engineering Department Computer Networks Laboratory 907528 Lab. 2 Network Devices & Packet Tracer Objectives 1. To become familiar with
University of Jordan Faculty of Engineering & Technology Computer Engineering Department Computer Networks Laboratory 907528 Lab. 2 Network Devices & Packet Tracer Objectives 1. To become familiar with
Configuring Static and Dynamic NAT Translation
 This chapter contains the following sections: Network Address Translation Overview, page 1 Information About Static NAT, page 2 Dynamic NAT Overview, page 3 Timeout Mechanisms, page 4 NAT Inside and Outside
This chapter contains the following sections: Network Address Translation Overview, page 1 Information About Static NAT, page 2 Dynamic NAT Overview, page 3 Timeout Mechanisms, page 4 NAT Inside and Outside
CS 326e F2002 Lab 1. Basic Network Setup & Ethereal Time: 2 hrs
 CS 326e F2002 Lab 1. Basic Network Setup & Ethereal Time: 2 hrs Tasks: 1 (10 min) Verify that TCP/IP is installed on each of the computers 2 (10 min) Connect the computers together via a switch 3 (10 min)
CS 326e F2002 Lab 1. Basic Network Setup & Ethereal Time: 2 hrs Tasks: 1 (10 min) Verify that TCP/IP is installed on each of the computers 2 (10 min) Connect the computers together via a switch 3 (10 min)
Lab - Observing DNS Resolution
 Objectives Part 1: Observe the DNS Conversion of a URL to an IP Address Part 2: Observe DNS Lookup Using the nslookup Command on a Web Site Part 3: Observe DNS Lookup Using the nslookup Command on Mail
Objectives Part 1: Observe the DNS Conversion of a URL to an IP Address Part 2: Observe DNS Lookup Using the nslookup Command on a Web Site Part 3: Observe DNS Lookup Using the nslookup Command on Mail
Lab 4.4.8a Configure a Cisco GRE over IPSec Tunnel using SDM
 Lab 4.4.8a Configure a Cisco GRE over IPSec Tunnel using SDM Objective Scenario Topology In this lab, the students will complete the following tasks: Prepare to configure Virtual Private Network (VPN)
Lab 4.4.8a Configure a Cisco GRE over IPSec Tunnel using SDM Objective Scenario Topology In this lab, the students will complete the following tasks: Prepare to configure Virtual Private Network (VPN)
Session Title: Exploring Packet Tracer v5.3 IP Telephony & CME. Scenario
 Session Title: Exploring Packet Tracer v5.3 IP Telephony & CME Scenario With the scheduled release of Packet Tracer v5.3 in the near future, this case study is designed to provide you with an insight into
Session Title: Exploring Packet Tracer v5.3 IP Telephony & CME Scenario With the scheduled release of Packet Tracer v5.3 in the near future, this case study is designed to provide you with an insight into
Configuring a Leased Line
 CHAPTER 4 Configuring a Leased Line The configuration in this chapter describes how to configure a Cisco 1700 router for IP and IPX over a synchronous serial line. Before You Begin The configuration in
CHAPTER 4 Configuring a Leased Line The configuration in this chapter describes how to configure a Cisco 1700 router for IP and IPX over a synchronous serial line. Before You Begin The configuration in
Chapter 11 Network Address Translation
 Chapter 11 Network Address Translation You can configure an HP routing switch to perform standard Network Address Translation (NAT). NAT enables private IP networks that use nonregistered IP addresses
Chapter 11 Network Address Translation You can configure an HP routing switch to perform standard Network Address Translation (NAT). NAT enables private IP networks that use nonregistered IP addresses
Lab 8.4.2 Configuring Access Policies and DMZ Settings
 Lab 8.4.2 Configuring Access Policies and DMZ Settings Objectives Log in to a multi-function device and view security settings. Set up Internet access policies based on IP address and application. Set
Lab 8.4.2 Configuring Access Policies and DMZ Settings Objectives Log in to a multi-function device and view security settings. Set up Internet access policies based on IP address and application. Set
LAN TCP/IP and DHCP Setup
 CHAPTER 2 LAN TCP/IP and DHCP Setup 2.1 Introduction In this chapter, we will explain in more detail the LAN TCP/IP and DHCP Setup. 2.2 LAN IP Network Configuration In the Vigor 2900 router, there are
CHAPTER 2 LAN TCP/IP and DHCP Setup 2.1 Introduction In this chapter, we will explain in more detail the LAN TCP/IP and DHCP Setup. 2.2 LAN IP Network Configuration In the Vigor 2900 router, there are
Configuring the PIX Firewall with PDM
 Configuring the PIX Firewall with PDM Objectives In this lab exercise you will complete the following tasks: Install PDM Configure inside to outside access through your PIX Firewall using PDM Configure
Configuring the PIX Firewall with PDM Objectives In this lab exercise you will complete the following tasks: Install PDM Configure inside to outside access through your PIX Firewall using PDM Configure
Chapter 10 Troubleshooting
 Chapter 10 Troubleshooting This chapter provides troubleshooting tips and information for your ProSafe Dual WAN Gigabit Firewall with SSL & IPsec VPN. After each problem description, instructions are provided
Chapter 10 Troubleshooting This chapter provides troubleshooting tips and information for your ProSafe Dual WAN Gigabit Firewall with SSL & IPsec VPN. After each problem description, instructions are provided
Multi-Homing Security Gateway
 Multi-Homing Security Gateway MH-5000 Quick Installation Guide 1 Before You Begin It s best to use a computer with an Ethernet adapter for configuring the MH-5000. The default IP address for the MH-5000
Multi-Homing Security Gateway MH-5000 Quick Installation Guide 1 Before You Begin It s best to use a computer with an Ethernet adapter for configuring the MH-5000. The default IP address for the MH-5000
Catalyst Layer 3 Switch for Wake On LAN Support Across VLANs Configuration Example
 Catalyst Layer 3 Switch for Wake On LAN Support Across VLANs Configuration Example Document ID: 91672 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Background Information
Catalyst Layer 3 Switch for Wake On LAN Support Across VLANs Configuration Example Document ID: 91672 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Background Information
Lab 8.3.1.2 Configure Basic AP Security through IOS CLI
 Lab 8.3.1.2 Configure Basic AP Security through IOS CLI Estimated Time: 30 minutes Number of Team Members: Students will work in teams of two. Objective In this lab, the student will learn the following
Lab 8.3.1.2 Configure Basic AP Security through IOS CLI Estimated Time: 30 minutes Number of Team Members: Students will work in teams of two. Objective In this lab, the student will learn the following
Configuring DHCP. DHCP Server Overview
 Configuring DHCP This chapter describes how to configure Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP). For a complete description of the DHCP commands listed in this chapter, refer to the DHCP s chapter
Configuring DHCP This chapter describes how to configure Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP). For a complete description of the DHCP commands listed in this chapter, refer to the DHCP s chapter
