Approximately two thirds of adults in the United
|
|
|
- Marjorie Phelps
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Change in Body Mass Index Over 1 Year in a Family Medicine Clinic: A Retrospective Analysis of Medical Records James E. Rohrer, PhD, Gregory A. Bartel, MD, Steven C. Adamson, MD, Joseph Furst, MD, and Todd Wade, MD Abstract Objective: To determine if baseline body mass index (BMI) is a predictor of weight loss after 1 year in adult family medicine patients who are overweight or obese. Design: Retrospective chart review. Setting and participants: 598 overweight or obese (BMI, 25 kg/m 2 ) adult patients treated in family medicine practices in Rochester, MN, between January 2006 and June Results: Over 40% of patients lost weight after 1 year, and 13% lost at least 5% of BMI. The percentage of patients losing weight was highest in those with a BMI between 30 and 34.9 kg/m 2 at baseline. Multiple logistic regression analysis revealed that compared with patients with a BMI between 25 and 29.9 kg/m 2, those with BMI of 30 kg/m 2 or more had a higher adjusted odds ratio (OR) for losing any weight (OR, 2.1, 2.2, and 2.0 for BMI ranges , , and 45 kg/m 2, respectively). Adjusted ORs for losing at least 5% of BMI were significantly higher for patients with a BMI of kg/m 2 and kg/m 2 (OR, 1.9 and 2.5, respectively). Conclusion: Overweight and obese patients can be advised that avoiding weight gain and losing a small amount of weight are achievable goals. Approximately two thirds of adults in the United States are overweight or obese [1]. This epidemic may seem inexorable to primary care providers who treat the sequelae of obesity in their clinics. Many individuals attempt to lose weight each year using sensible self-help strategies [2 5]. Although the efficacy of various diet plans has been established for patients who adhere to them [6 8], the likelihood that free-living family medicine patients will be able to control their weight is not widely known. Of special interest is the degree to which baseline obesity affects the odds of being able to lose weight. Weight control is more urgent for heavier patients, and referral to a specialized program may be indicated if the chances of losing weight independently are unacceptably low. The objective of this study was to test the hypothesis that baseline body mass index (BMI) is a predictor of weight loss after 1 year in adult family medicine patients who are overweight or obese at baseline (BMI 25 kg/m 2 ). If higher BMI levels independently reduce the odds of losing weight, referral to weight management programs might be indicated. Methods We analyzed a convenience sample of adult patients who were treated in our family medicine clinics in Rochester, MN, and referred for any type of specialist consultation between January 2006 and June Our sampling frame included 1009 patients with BMI 25 and for whom age, gender, marital status, and comorbidity information were recorded in the medical record. We used a data set that was originally assembled originally for a study of referred patients. Medical records were the sole source of information used in this study. Two trained medical secretaries were used as abstractors. Data collection was approved by the institutional review board. Independent variables included BMI at the index date, age, gender, marital status (yes/no), and comorbidity (none, low, moderate). BMI was categorized as 25 to 29.9, 30 to 34.9, 35 to 44.9, and 45 or greater. Age was divided into 5 categories: 18 to 35, 36 to 45, 46 to 55, 56 to 65, and 66 to 100. The Charlson index was used to score comorbidity [9,10]. An index visit was defined as the visit in which a specialist consultation was ordered. The dependent variables in this study were any weight lost after 1 year (yes/no) and 5% or more of BMI lost after 1 year (yes/no). Percentage weight change was computed as BMI after 1 year BMI at baseline divided by BMI at baseline. A negative number indicated weight loss. A 3-month window was used around both the index date and the 1-year follow-up date. When BMI was recorded more than 1 time during the interval, the value closest to the desired date was chosen. From the Mayo Clinic, Rochester, MN. 66 JCOM February 2008 Vol. 15, No. 2
2 original Research Table 1. Descriptive Statistics: Continuous Variables Mean Standard Deviation Minimum Median Maximum BMI at index visit, kg/m BMI at 1 year post index visit, kg/m Change in BMI after 1 year, kg/m Percentage change in BMI BMI = body mass index. Each predictor variable was compared with the 2 weight loss variables using chi-square tests. A difference was considered statistically significant if P was less than Multiple logistic regression analyses were performed to identify associations between the independent variables and whether BMI declined. All of the independent variables were included in the multiple logistic regression models. Statistical analysis was performed using Epi Info version (Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Atlanta, GA). Results Six patients were removed from our sampling frame because they received bariatric surgery. Of the remaining 1003, BMI after 1 year was recorded for 598. Incomplete cases (ie, cases missing BMI measurements at 1 year; n = 405) were not different from complete cases in regard to marital status or gender. However, patients with incomplete data were more likely to be younger (mean age, 50.9 years vs years for patients with complete data; P < 0.01) and tended to weigh less at baseline (mean BMI, 31.7 kg/m 2 vs kg/m 2 for patients with complete data; P = 0.02). Median BMI was 30.1 kg/m 2 and 31.0 kg/m 2 for incomplete and complete cases, respectively. Table 1 reports descriptive statistics for continuous variables. Mean BMI at baseline and after 1 year was 32.2 kg/m 2 (median, 30.9 kg/m 2 ) and 32.3 kg/m 2 (median, 31.0 kg/m 2 ). The mean change in BMI after 1 year was 0.15 kg/m 2 (median, 0.2 kg/m 2 ). The mean percentage change in BMI was 0.7 (median, 0.8). However, this apparent stability is misleading; over 40% of patients in our sample achieved some weight loss. Table 2 demonstrates that patients with higher baseline BMI lost slightly more weight on average after 1 year. Mean changes were small, with patients in the BMI category 40 kg/m 2 or greater losing an average of 0.71 kg/m 2 (median, 0.11 kg/m 2 ). The trend was significant at P < The mean percentage change was 1.5 (median, 0.3) for baseline BMI of 40 kg/m 2 and over. Over 40% of patients lost at least some weight after 1 year (Table 3), and over 13% lost at least 5% of baseline BMI. The typical patient was female, married, and older than 45 years. Over 40% of patients had a BMI between 25 and Table 2. Body Mass Index Change at 1 Year BMI at Baseline, kg/m 2 Mean BMI Change (Median) P Value* Mean Percentage Change (Median) P Value* (0.42) 2.0 (1.5) (0.09) 0.1 (0.3) ( 0.01) (0.04) ( 0.11) 1.5 ( 0.3) *Kruskal-Wallis test kg/m 2 at the index date. Almost 50% of patients were scored in the lowest comorbidity category. Univariate tests of the association also are shown in Table 3. Gender, being married, and comorbidity were unrelated to either measure of weight loss. Older patients (P = 0.04) and patients with a BMI between 30 and 35 kg/m 2 (P < 0.01) were more likely to have lost some weight than younger patients and patients with the highest and lowest baseline BMI. BMI at baseline was not related to losing 5% of body weight in the univariate analyses. Multiple logistic regression analysis was performed to determine the independent effects of BMI category on weight loss (Table 4). Being married, gender, and comorbidity were not associated with either measure of weight loss. Patients aged 34 to 56 years were less likely to lose some weight as compared with adults younger than 35 years. Patients aged between 35 and 66 years were less likely to lose at least 5% of BMI as compared with patients younger than 35 years. The odds of some losing weight were greater for patients whose baseline BMI was 30 kg/m 2 or greater compared with those whose BMIs were less than 30 kg/m 2. Adjusted ORs were 2.08, 2.16, and 2.03 for BMI 30 to 35 kg/m 2 (P < 0.01), 35 to 45 kg/m 2 (P < 0.01), and 45 kg/m 2 or greater (P = 0.03), respectively. The odds of losing 5% or more of BMI were greater for patients with a BMI 30 to 35 kg/m 2 and 35 to 45 kg/m 2 at baseline (OR, 1.89 [P =0.03] and 2.45 [P = 0.02], respectively). Vol. 15, No. 2 February 2008 JCOM 67
3 Table 3. Descriptive Statistics: Categorical Variables % of Sample Lost Weight Did Not Lose Any Weight P Value Lost 5% Total sample (n = 598) Age, yr P = Gender Female P = 0.56 Male Married No P = 0.99 Yes Comorbidity None Low P = Moderate BMI at index visit, kg/m P = BMI = body mass index. Did Not Lose 5% of Weight P Value P = 0.08 P = 0.20 P = 0.22 P = 0.54 P = 0.06 Discussion Over 40% of the patients in our sample lost weight after 1 year, and more than 13% lost 5% of BMI or more. This result is similar to findings reported by Crawford et al [4], in which 11.2% of patients lost 5% of BMI after 1 year. Patients in the Crawford et al study had lower BMI at baseline and were younger (aged years), and fewer men were included. In addition, it was a population sample drawn from an urban setting, targeting a university community. In both our study and the study by Crawford et al, weights were measured rather than self-reported. We found that family medicine patients with a BMI between 30 and 45 kg/m 2 at baseline were more likely to experience a decline in BMI than those with a BMI between 25 and 30 kg/m 2 at baseline. Because this relationship was independent of comorbidity, obese patients with a BMI of 30 to 45 kg/m 2 may have reason to be optimistic about their chances of losing small amounts of weight compared with patients who are merely overweight. This is useful information for a group of patients who may have given up hope because of previous failures or because the magnitude of the challenge they face. It is not surprising that those with higher BMI were more likely to lose weight, since concerned friends, family, and health care providers are likely to mobilize support for heavier patients. Obese patients are also more likely to have comorbidities (eg, hypertension, dyslipidemia, hyperglycemia or diabetes, degenerative joint disease) or symptoms such as shortness of breath, fatigue, and joint pains, all of which can at least temporarily motivate the patient. Although it may not lower BMI to the normal range, losing 5% of body weight is still clinically beneficial. The clinical implications of small amounts of weight loss have been well documented. As early as 1992, evidence has shown that for every kilogram of body weight lost, a mmol/l increase in high-density lipoprotein cholesterol is expected [11]. Clinical experience suggests direct correlations in other risk factor parameters, such as glucose and blood pressure. The findings of this study may aid in clarifying recommendations for weight management in primary care. Many primary care practices have no standard decision rules about referral of obese patients to weight loss programs [12 15]. Because many primary care patients are at an advanced stage of readiness to adopt weight control behaviors [16], timely advice and appropriate referrals could precipitate change. The consensus among researchers is that intentional 68 JCOM February 2008 Vol. 15, No. 2
4 original Research Table 4. Multiple Logistic Regression Analysis of Any Weight Loss and Weight Loss of at Least 5% of BMI (n = 598) Any Weight Loss At Least 5% BMI Adjusted OR (95% CI) P Value Adjusted OR (95% CI) P Value BMI at baseline, kg/m Reference Reference ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) 0.06 Age, yr Reference Reference ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) 0.07 Male vs. female 0.85 ( ) ( ) 0.27 Married vs. not married 0.20 ( ) ( ) 0.84 Comorbidity None Reference Reference Low 0.99 ( ) ( ) 0.69 Moderate 1.26 ( ) ( ) log likelihood BMI = body mass index; CI = confidence interval; OR = odds ratio. dieting is modestly successful over the short term, and employing more strategies persistently can lead to positive results over longer periods [2,5]. A variety of approaches can be effective, including commercial programs [6]. Additional research is needed to test the various low-cost interventions available to free-living primary care patients. More information is also needed about repeated weight loss attempts, since re-starts are well-accepted in smoking cessation and problem drinking. Certainly, 1 failed diet is not proof-positive that nonsurgical approaches will never work. Our study has several limitations. First, patients were not randomly selected and thus may not constitute a representative sample. However, since most randomized studies rely on volunteers, some selection bias may influence the findings reported. Another limitation is that methods of weight control (if any) used by the study patients are unknown. Our sample may suffer from selection bias as well, since it was not random, included pregnant women, and was limited to patients who were referred to specialists for any reason. Nevertheless, referral to specialists is common in our system and this is unlikely to substantially bias our findings, especially because we adjusted for comorbidity in the analysis. Conclusion After finding that only about one third of their sample avoided weight gain and approximately 11% lost more than 5% of BMI, Crawford et al [4] concluded that relatively few people successfully control their weight. We prefer to see the glass as half full. Over 40% of our patients lost some weight, and more than 13% lost at least 5% of BMI. The degree of weight control we observed is promising, given that the alternative would have been weight gain. Optimism about the chances of weight control is important in clinical settings. Obesity may be ignored by patients and their doctors in the false belief that weight loss attempts are guaranteed to fail. In our sample, patients lost small amounts of weight and were more likely to lose weight if their starting BMI was between 30 and 45 kg/m 2. Patients can reasonably be offered encouragement and practical information about weight loss. If they fail, restarting is reasonable and should entail no stigma. Additional research is needed to test the relative effectiveness of different low-cost, patient-driven approaches to weight management that might be used by patients with a BMI between 30 and 45 kg/m 2. Unknown are the number and length of visits required to help patients lose weight, the types of providers who can most cost-effectively provide the service (nurses, health educators, or counselors), and the best modalities for losing weight (internet, group classes, or personal health services). Regardless of the availability of systematic and objective evidence, patients should be encouraged to use common sense and employ an experimental attitude, buoyed Vol. 15, No. 2 February 2008 JCOM 69
5 by the knowledge that some degree of weight control is not only possible, it is achieved by many people every year. Acknowledgments: Julie Maxson and Kelly Amunrud abstracted medical records for the project. Corresponding author: James Rohrer, PhD, Mayo Clinic, 200 First St. SW, Rochester, MN 55905, Funding/support: This study was funded by the Department of Family Medicine, Mayo Clinic, Rochester, MN. Financial disclosures: None. Author contributions: conception and design, JER, JF; analysis and interpretation of data, JER, GAB, SCA, TW; drafting of the article, JER, GAB, SCA, JF, TW; critical revision of the article, JER. References 1. Ogden CL, Carroll MD, Curtin LR, et al. Prevalence of overweight and obesity in the United States, JAMA 2006;295: Linde JA, Erickson DJ, Jeffery RW, et al. The relationship between prevalence and duration of weight loss strategies and weight loss among overweight managed care organization members enrolled in a weight loss trial. Int J Behav Nutr Phys Act 2006;3:3. 3. Bish CL, Blanck HM, Serdula MK, et al. Diet and physical activity behaviors among Americans trying to lose weight: 2000 Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System. Obes Res 2005;13: Crawford D, Jeffery RW, French SA. Can anyone successfully control their weight? Findings of a three year communitybased study of men and women. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 2000;24: French SA, Jeffery RW, Murray D. Is dieting good for you?: Prevalence, duration and associated weight and behaviour changes for specific weight loss strategies over four years in US adults. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 1999;23: Truby H, Baic S, delooy A, et al. Randomised controlled trial of four commercial weight loss programmes in the UK: initial findings from the BBC diet trials [published erratum appears in BMJ 2006;332:1418]. BMJ 2006;332: Gardner CD, Kiazand A, Alhassan S, et al. Comparison of the Atkins, Zone, Ornish, and LEARN diets for change in weight and related risk factors among overweight premenopausal women: the A TO Z Weight Loss Study: a randomized trial [published erratum appears in JAMA 2007;298: 178]. JAMA 2007;297: Dansinger MK, Gleason JA, Griffith JL, et al. Comparison of the Atkins, Ornish, Weight Watchers, and Zone diets for weight loss and heart disease risk reduction: a randomized trial. JAMA 2005;293: Chaudhry S, Jin L, Meltzer D. Use of a self-report-generated Charlson Comorbidity Index for predicting mortality. Med Care 2005;43: Rohrer JE, Rasmussen N, Adamson S. Illness severity and total visits in family medicine. J Eval Clin Prac. In press Dattilo AM, Kris-Etherton PM. Effects of weight reduction on blood lipids and lipoproteins: a meta-analysis. Am J Clin Nutr 1992;56: Rohrer JE, Merry SP, Lopez-Jimenez F, et al. A patientcentered decision rule for referral of patients to weight-loss programs. Qual Manag Health Care 2007;16: Lavin JH, Avery A, Whitehead SM, et al. Feasibility and benefits of implementing a Slimming on Referral service in primary care using a commercial weight management partner. Public Health 2006;120: Fontaine KR, Barofsky I, Bartlett SJ, et al. Weight loss and health-related quality of life: results at 1-year follow-up. Eat Behav 2004;5: Fontaine KR, Haaz S, Bartlett SJ. Are overweight and obese adults with arthritis being advised to lose weight? J Clin Rheumatol 2007;13: Wee CC, Davis RB, Phillips RS. Stage of readiness to control weight and adopt weight control behaviors in primary care. J Gen Intern Med 2005;20: Copyright 2008 by Turner White Communications Inc., Wayne, PA. All rights reserved. 70 JCOM February 2008 Vol. 15, No. 2
DIET AND EXERCISE STRATEGIES FOR WEIGHT LOSS AND WEIGHT MAINTENANCE
 DIET AND EXERCISE STRATEGIES FOR WEIGHT LOSS AND WEIGHT MAINTENANCE 40 yo woman, BMI 36. Motivated to begin diet therapy. Which of the following is contraindicated: Robert B. Baron MD MS Professor and
DIET AND EXERCISE STRATEGIES FOR WEIGHT LOSS AND WEIGHT MAINTENANCE 40 yo woman, BMI 36. Motivated to begin diet therapy. Which of the following is contraindicated: Robert B. Baron MD MS Professor and
Recommendations for Prescribing Exercise to Overweight and Obese Patients
 10 Recommendations for Prescribing Exercise to Overweight and Obese Patients 10 10 Recommendations for Prescribing Exercise to Overweight and Obese Patients Effects of Exercise The increasing prevalence
10 Recommendations for Prescribing Exercise to Overweight and Obese Patients 10 10 Recommendations for Prescribing Exercise to Overweight and Obese Patients Effects of Exercise The increasing prevalence
The Prevalence and Determinants of Undiagnosed and Diagnosed Type 2 Diabetes in Middle-Aged Irish Adults
 The Prevalence and Determinants of Undiagnosed and Diagnosed Type 2 Diabetes in Middle-Aged Irish Adults Seán R. Millar, Jennifer M. O Connor, Claire M. Buckley, Patricia M. Kearney, Ivan J. Perry Email:
The Prevalence and Determinants of Undiagnosed and Diagnosed Type 2 Diabetes in Middle-Aged Irish Adults Seán R. Millar, Jennifer M. O Connor, Claire M. Buckley, Patricia M. Kearney, Ivan J. Perry Email:
2016 PQRS OPTIONS FOR INDIVIDUAL MEASURES: CLAIMS, REGISTRY
 Measure #128 (NQF 0421): Preventive Care and Screening: Body Mass Index (BMI) Screening and Follow-Up Plan National Quality Strategy Domain: Community/Population Health 2016 PQRS OPTIONS F INDIVIDUAL MEASURES:
Measure #128 (NQF 0421): Preventive Care and Screening: Body Mass Index (BMI) Screening and Follow-Up Plan National Quality Strategy Domain: Community/Population Health 2016 PQRS OPTIONS F INDIVIDUAL MEASURES:
A Multi-locus Genetic Risk Score for Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm
 A Multi-locus Genetic Risk Score for Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Zi Ye, 1 MD, Erin Austin, 1,2 PhD, Daniel J Schaid, 2 PhD, Iftikhar J. Kullo, 1 MD Affiliations: 1 Division of Cardiovascular Diseases and
A Multi-locus Genetic Risk Score for Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Zi Ye, 1 MD, Erin Austin, 1,2 PhD, Daniel J Schaid, 2 PhD, Iftikhar J. Kullo, 1 MD Affiliations: 1 Division of Cardiovascular Diseases and
The association between health risk status and health care costs among the membership of an Australian health plan
 HEALTH PROMOTION INTERNATIONAL Vol. 18, No. 1 Oxford University Press 2003. All rights reserved Printed in Great Britain The association between health risk status and health care costs among the membership
HEALTH PROMOTION INTERNATIONAL Vol. 18, No. 1 Oxford University Press 2003. All rights reserved Printed in Great Britain The association between health risk status and health care costs among the membership
Cohort Studies. Sukon Kanchanaraksa, PhD Johns Hopkins University
 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike License. Your use of this material constitutes acceptance of that license and the conditions of use of materials on this
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike License. Your use of this material constitutes acceptance of that license and the conditions of use of materials on this
Obesity and hypertension among collegeeducated black women in the United States
 Journal of Human Hypertension (1999) 13, 237 241 1999 Stockton Press. All rights reserved 0950-9240/99 $12.00 http://www.stockton-press.co.uk/jhh ORIGINAL ARTICLE Obesity and hypertension among collegeeducated
Journal of Human Hypertension (1999) 13, 237 241 1999 Stockton Press. All rights reserved 0950-9240/99 $12.00 http://www.stockton-press.co.uk/jhh ORIGINAL ARTICLE Obesity and hypertension among collegeeducated
NICE made the decision not to commission a cost effective review, or de novo economic analysis for this guideline for the following reasons:
 Maintaining a healthy weight and preventing excess weight gain in children and adults. Cost effectiveness considerations from a population modelling viewpoint. Introduction The Centre for Public Health
Maintaining a healthy weight and preventing excess weight gain in children and adults. Cost effectiveness considerations from a population modelling viewpoint. Introduction The Centre for Public Health
Body Mass Index Measurement in Schools BMI. Executive Summary
 Body Mass Index Measurement in Schools BMI = BMI weight(kg) {height(m)} 2 Executive Summary Centers for Disease Control and Prevention National Center for Chronic Disease Prevention and Health Promotion
Body Mass Index Measurement in Schools BMI = BMI weight(kg) {height(m)} 2 Executive Summary Centers for Disease Control and Prevention National Center for Chronic Disease Prevention and Health Promotion
Psoriasis Co-morbidities: Changing Clinical Practice. Theresa Schroeder Devere, MD Assistant Professor, OHSU Dermatology. Psoriatic Arthritis
 Psoriasis Co-morbidities: Changing Clinical Practice Theresa Schroeder Devere, MD Assistant Professor, OHSU Dermatology Psoriatic Arthritis Psoriatic Arthritis! 11-31% of patients with psoriasis have psoriatic
Psoriasis Co-morbidities: Changing Clinical Practice Theresa Schroeder Devere, MD Assistant Professor, OHSU Dermatology Psoriatic Arthritis Psoriatic Arthritis! 11-31% of patients with psoriasis have psoriatic
WEIGHT LOSS SURGERY. Pre-Clinic Conference Jennifer Kinley, MD 12/15/2010
 WEIGHT LOSS SURGERY Pre-Clinic Conference Jennifer Kinley, MD 12/15/2010 EDUCATIONAL OBJECTIVES: Discuss the available pharmaceutical options for weight loss and risks of these medications Explain the
WEIGHT LOSS SURGERY Pre-Clinic Conference Jennifer Kinley, MD 12/15/2010 EDUCATIONAL OBJECTIVES: Discuss the available pharmaceutical options for weight loss and risks of these medications Explain the
Preservation and Incorporation of Valuable Endoscopic Innovations (PIVI)
 Preservation and Incorporation of Valuable Endoscopic Innovations (PIVI) The American Society for Gastrointestinal Endoscopy PIVI on Endoscopic Bariatric Procedures (short form) Please see related White
Preservation and Incorporation of Valuable Endoscopic Innovations (PIVI) The American Society for Gastrointestinal Endoscopy PIVI on Endoscopic Bariatric Procedures (short form) Please see related White
Bariatric Surgery. OHTAC Recommendation. Bariatric Surgery
 OHTAC Recommendation Bariatric Surgery January 21, 2005 1 The Ontario Health Technology Advisory Committee (OHTAC) met on January 21, 2005 and reviewed bariatric surgery for morbid obesity. Obesity is
OHTAC Recommendation Bariatric Surgery January 21, 2005 1 The Ontario Health Technology Advisory Committee (OHTAC) met on January 21, 2005 and reviewed bariatric surgery for morbid obesity. Obesity is
The Link Between Obesity and Diabetes The Rapid Evolution and Positive Results of Bariatric Surgery
 The Link Between Obesity and Diabetes The Rapid Evolution and Positive Results of Bariatric Surgery Michael E. Farkouh, MD, MSc Peter Munk Chair in Multinational Clinical Trials Director, Heart and Stroke
The Link Between Obesity and Diabetes The Rapid Evolution and Positive Results of Bariatric Surgery Michael E. Farkouh, MD, MSc Peter Munk Chair in Multinational Clinical Trials Director, Heart and Stroke
Diabetes Prevention in Latinos
 Diabetes Prevention in Latinos Matthew O Brien, MD, MSc Assistant Professor of Medicine and Public Health Northwestern Feinberg School of Medicine Institute for Public Health and Medicine October 17, 2013
Diabetes Prevention in Latinos Matthew O Brien, MD, MSc Assistant Professor of Medicine and Public Health Northwestern Feinberg School of Medicine Institute for Public Health and Medicine October 17, 2013
CHAPTER V DISCUSSION. normal life provided they keep their diabetes under control. Life style modifications
 CHAPTER V DISCUSSION Background Diabetes mellitus is a chronic condition but people with diabetes can lead a normal life provided they keep their diabetes under control. Life style modifications (LSM)
CHAPTER V DISCUSSION Background Diabetes mellitus is a chronic condition but people with diabetes can lead a normal life provided they keep their diabetes under control. Life style modifications (LSM)
Are Mortality Benefits from Bariatric Surgery Observed in a Nontraditional Surgical Population? Evidence from a VA Dataset
 Are Mortality Benefits from Bariatric Surgery Observed in a Nontraditional Surgical Population? Evidence from a VA Dataset Arterburn DE, Olsen MK, Smith VA, et al. Association between bariatric surgery
Are Mortality Benefits from Bariatric Surgery Observed in a Nontraditional Surgical Population? Evidence from a VA Dataset Arterburn DE, Olsen MK, Smith VA, et al. Association between bariatric surgery
Jill Malcolm, Karen Moir
 Evaluation of Fife- DICE: Type 2 diabetes insulin conversion Article points 1. Fife-DICE is an insulin conversion group education programme. 2. People with greater than 7.5% on maximum oral therapy are
Evaluation of Fife- DICE: Type 2 diabetes insulin conversion Article points 1. Fife-DICE is an insulin conversion group education programme. 2. People with greater than 7.5% on maximum oral therapy are
Colorectal Cancer Screening Behaviors among American Indians in the Midwest
 JOURNAL OF HD RP Journal of Health Disparities Research and Practice Volume 4, Number 2, Fall 2010, pp. 35 40 2010 Center for Health Disparities Research School of Community Health Sciences University
JOURNAL OF HD RP Journal of Health Disparities Research and Practice Volume 4, Number 2, Fall 2010, pp. 35 40 2010 Center for Health Disparities Research School of Community Health Sciences University
CARE MANAGEMENT FOR LATE LIFE DEPRESSION IN URBAN CHINESE PRIMARY CARE CLINICS
 CARE MANAGEMENT FOR LATE LIFE DEPRESSION IN URBAN CHINESE PRIMARY CARE CLINICS Dept of Public Health Sciences February 6, 2015 Yeates Conwell, MD Dept of Psychiatry, University of Rochester Shulin Chen,
CARE MANAGEMENT FOR LATE LIFE DEPRESSION IN URBAN CHINESE PRIMARY CARE CLINICS Dept of Public Health Sciences February 6, 2015 Yeates Conwell, MD Dept of Psychiatry, University of Rochester Shulin Chen,
Medical Costs of Childhood Obesity in Maine November 2012 MEDICAL COSTS OF CHILDHOOD OBESITY IN MAINE. SOE Staff Paper 603 November 2012
 MEDICAL COSTS OF CHILDHOOD OBESITY IN MAINE SOE Staff Paper 603 November 2012 Todd Gabe* Professor of Economics School of Economics, University of Maine Executive Summary: The purpose of this study is
MEDICAL COSTS OF CHILDHOOD OBESITY IN MAINE SOE Staff Paper 603 November 2012 Todd Gabe* Professor of Economics School of Economics, University of Maine Executive Summary: The purpose of this study is
Trends in Bariatric Surgery for Morbid Obesity in Wisconsin
 Trends in Bariatric Surgery for Morbid Obesity in Wisconsin Jennifer L. Erickson, BA; Patrick L. Remington, MD, MPH; Paul E. Peppard, PhD ABSTRACT Background: Obesity is a national epidemic with rates
Trends in Bariatric Surgery for Morbid Obesity in Wisconsin Jennifer L. Erickson, BA; Patrick L. Remington, MD, MPH; Paul E. Peppard, PhD ABSTRACT Background: Obesity is a national epidemic with rates
overview of weight bias in health care settings Selected research studies on health care utilization and preventive services by obese patients
 Selected research studies on health care utilization and preventive services by obese patients The following list of references and abstracts provides a selection of peer-reviewed articles that address
Selected research studies on health care utilization and preventive services by obese patients The following list of references and abstracts provides a selection of peer-reviewed articles that address
Dr. Paul Naughton, Teagasc Dr. Sinéad McCarthy, Teagasc Dr. Mary McCarthy, UCC
 Healthy s and healthy living: An examination of the relationship between attitudes, food choices and lifestyle behaviours in a representative sample of Irish adults Dr. Paul Naughton, Teagasc Dr. Sinéad
Healthy s and healthy living: An examination of the relationship between attitudes, food choices and lifestyle behaviours in a representative sample of Irish adults Dr. Paul Naughton, Teagasc Dr. Sinéad
Improving cardiometabolic health in Major Mental Illness
 Improving cardiometabolic health in Major Mental Illness Dr. Adrian Heald Consultant in Endocrinology and Diabetes Leighton Hospital, Crewe and Macclesfield Research Fellow, Manchester University Metabolic
Improving cardiometabolic health in Major Mental Illness Dr. Adrian Heald Consultant in Endocrinology and Diabetes Leighton Hospital, Crewe and Macclesfield Research Fellow, Manchester University Metabolic
Smoking in the United States Workforce
 P F I Z E R F A C T S Smoking in the United States Workforce Findings from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) 1999-2002, the National Health Interview Survey (NHIS) 2006, and
P F I Z E R F A C T S Smoking in the United States Workforce Findings from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) 1999-2002, the National Health Interview Survey (NHIS) 2006, and
BACKGROUND. ADA and the European Association recently issued a consensus algorithm for management of type 2 diabetes
 BACKGROUND More than 25% of people with diabetes take insulin ADA and the European Association recently issued a consensus algorithm for management of type 2 diabetes Insulin identified as the most effective
BACKGROUND More than 25% of people with diabetes take insulin ADA and the European Association recently issued a consensus algorithm for management of type 2 diabetes Insulin identified as the most effective
Low diabetes numeracy predicts worse glycemic control
 Low diabetes numeracy predicts worse glycemic control Kerri L. Cavanaugh, MD MHS, Kenneth A. Wallston, PhD, Tebeb Gebretsadik, MPH, Ayumi Shintani, PhD, MPH, Darren DeWalt, MD MPH, Michael Pignone, MD
Low diabetes numeracy predicts worse glycemic control Kerri L. Cavanaugh, MD MHS, Kenneth A. Wallston, PhD, Tebeb Gebretsadik, MPH, Ayumi Shintani, PhD, MPH, Darren DeWalt, MD MPH, Michael Pignone, MD
Clinical Research on Lifestyle Interventions to Treat Obesity and Asthma in Primary Care Jun Ma, M.D., Ph.D.
 Clinical Research on Lifestyle Interventions to Treat Obesity and Asthma in Primary Care Jun Ma, M.D., Ph.D. Associate Investigator Palo Alto Medical Foundation Research Institute Consulting Assistant
Clinical Research on Lifestyle Interventions to Treat Obesity and Asthma in Primary Care Jun Ma, M.D., Ph.D. Associate Investigator Palo Alto Medical Foundation Research Institute Consulting Assistant
Summary Evaluation of the Medicare Lifestyle Modification Program Demonstration and the Medicare Cardiac Rehabilitation Benefit
 The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services' Office of Research, Development, and Information (ORDI) strives to make information available to all. Nevertheless, portions of our files including charts,
The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services' Office of Research, Development, and Information (ORDI) strives to make information available to all. Nevertheless, portions of our files including charts,
Critical Appraisal of Article on Therapy
 Critical Appraisal of Article on Therapy What question did the study ask? Guide Are the results Valid 1. Was the assignment of patients to treatments randomized? And was the randomization list concealed?
Critical Appraisal of Article on Therapy What question did the study ask? Guide Are the results Valid 1. Was the assignment of patients to treatments randomized? And was the randomization list concealed?
Non-response bias in a lifestyle survey
 Journal of Public Health Medicine Vol. 19, No. 2, pp. 203-207 Printed in Great Britain Non-response bias in a lifestyle survey Anthony Hill, Julian Roberts, Paul Ewings and David Gunnell Summary Background
Journal of Public Health Medicine Vol. 19, No. 2, pp. 203-207 Printed in Great Britain Non-response bias in a lifestyle survey Anthony Hill, Julian Roberts, Paul Ewings and David Gunnell Summary Background
The Cross-Sectional Study:
 The Cross-Sectional Study: Investigating Prevalence and Association Ronald A. Thisted Departments of Health Studies and Statistics The University of Chicago CRTP Track I Seminar, Autumn, 2006 Lecture Objectives
The Cross-Sectional Study: Investigating Prevalence and Association Ronald A. Thisted Departments of Health Studies and Statistics The University of Chicago CRTP Track I Seminar, Autumn, 2006 Lecture Objectives
The Use of an Electronic Medical Record to Improve Documentation and Treatment of Obesity
 274 April 2007 Family Medicine Practice Management The Use of an Electronic Medical Record to Improve Documentation and Treatment of Obesity Richard Bordowitz, MD, MPH; Kimberly Morland, PhD; Douglas Reich,
274 April 2007 Family Medicine Practice Management The Use of an Electronic Medical Record to Improve Documentation and Treatment of Obesity Richard Bordowitz, MD, MPH; Kimberly Morland, PhD; Douglas Reich,
Oncology Nursing Society Annual Progress Report: 2008 Formula Grant
 Oncology Nursing Society Annual Progress Report: 2008 Formula Grant Reporting Period July 1, 2011 June 30, 2012 Formula Grant Overview The Oncology Nursing Society received $12,473 in formula funds for
Oncology Nursing Society Annual Progress Report: 2008 Formula Grant Reporting Period July 1, 2011 June 30, 2012 Formula Grant Overview The Oncology Nursing Society received $12,473 in formula funds for
Factors in Women Aged 35-57 Years in Khuzestan. Province of Iran
 Advanced Studies in Biology, Vol., 0, no., 7 6 Prevalence of Overweight, Obesity and the Related Factors in Women Aged -7 Years in Khuzestan Province of Iran S. Nouhjah*, M. Nadi-baghu, M. Salehi and H.
Advanced Studies in Biology, Vol., 0, no., 7 6 Prevalence of Overweight, Obesity and the Related Factors in Women Aged -7 Years in Khuzestan Province of Iran S. Nouhjah*, M. Nadi-baghu, M. Salehi and H.
C. The null hypothesis is not rejected when the alternative hypothesis is true. A. population parameters.
 Sample Multiple Choice Questions for the material since Midterm 2. Sample questions from Midterms and 2 are also representative of questions that may appear on the final exam.. A randomly selected sample
Sample Multiple Choice Questions for the material since Midterm 2. Sample questions from Midterms and 2 are also representative of questions that may appear on the final exam.. A randomly selected sample
A Study to Predict No Show Probability for a Scheduled Appointment at Free Health Clinic
 A Study to Predict No Show Probability for a Scheduled Appointment at Free Health Clinic Report prepared for Brandon Slama Department of Health Management and Informatics University of Missouri, Columbia
A Study to Predict No Show Probability for a Scheduled Appointment at Free Health Clinic Report prepared for Brandon Slama Department of Health Management and Informatics University of Missouri, Columbia
II. DISTRIBUTIONS distribution normal distribution. standard scores
 Appendix D Basic Measurement And Statistics The following information was developed by Steven Rothke, PhD, Department of Psychology, Rehabilitation Institute of Chicago (RIC) and expanded by Mary F. Schmidt,
Appendix D Basic Measurement And Statistics The following information was developed by Steven Rothke, PhD, Department of Psychology, Rehabilitation Institute of Chicago (RIC) and expanded by Mary F. Schmidt,
NHS Diabetes Prevention Programme (NHS DPP) Non-diabetic hyperglycaemia. Produced by: National Cardiovascular Intelligence Network (NCVIN)
 NHS Diabetes Prevention Programme (NHS DPP) Non-diabetic hyperglycaemia Produced by: National Cardiovascular Intelligence Network (NCVIN) Date: August 2015 About Public Health England Public Health England
NHS Diabetes Prevention Programme (NHS DPP) Non-diabetic hyperglycaemia Produced by: National Cardiovascular Intelligence Network (NCVIN) Date: August 2015 About Public Health England Public Health England
The weight of the world.
 The weight of the world. SONY ANTHONY Obesity Derived from the Latin word obesus to devour Definition: having a very high amount of body fat in relation to lean body mass Classifications using Body Mass
The weight of the world. SONY ANTHONY Obesity Derived from the Latin word obesus to devour Definition: having a very high amount of body fat in relation to lean body mass Classifications using Body Mass
Am I at Risk for type 2 Diabetes? Taking Steps to Lower the Risk of Getting Diabetes NATIONAL DIABETES INFORMATION CLEARINGHOUSE
 NATIONAL DIABETES INFORMATION CLEARINGHOUSE Am I at Risk for type 2 Diabetes? Taking Steps to Lower the Risk of Getting Diabetes U.S. Department of Health and Human Services National Institutes of Health
NATIONAL DIABETES INFORMATION CLEARINGHOUSE Am I at Risk for type 2 Diabetes? Taking Steps to Lower the Risk of Getting Diabetes U.S. Department of Health and Human Services National Institutes of Health
The relationship between socioeconomic status and healthy behaviors: A mediational analysis. Jenn Risch Ashley Papoy.
 Running head: SOCIOECONOMIC STATUS AND HEALTHY BEHAVIORS The relationship between socioeconomic status and healthy behaviors: A mediational analysis Jenn Risch Ashley Papoy Hanover College Prior research
Running head: SOCIOECONOMIC STATUS AND HEALTHY BEHAVIORS The relationship between socioeconomic status and healthy behaviors: A mediational analysis Jenn Risch Ashley Papoy Hanover College Prior research
What factors determine poor functional outcome following Total Knee Replacement (TKR)?
 Specific Question: What factors determine poor functional outcome following Total Knee Replacement ()? Clinical bottom line All groups derived benefit from undergoing a, reviews suggests that the decision
Specific Question: What factors determine poor functional outcome following Total Knee Replacement ()? Clinical bottom line All groups derived benefit from undergoing a, reviews suggests that the decision
THE NHS HEALTH CHECK AND INSURANCE FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS
 THE NHS HEALTH CHECK AND INSURANCE FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS Introduction The following document has been produced by the Department of Health in partnership with the Association of British Insurers,
THE NHS HEALTH CHECK AND INSURANCE FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS Introduction The following document has been produced by the Department of Health in partnership with the Association of British Insurers,
Appendix: Description of the DIETRON model
 Appendix: Description of the DIETRON model Much of the description of the DIETRON model that appears in this appendix is taken from an earlier publication outlining the development of the model (Scarborough
Appendix: Description of the DIETRON model Much of the description of the DIETRON model that appears in this appendix is taken from an earlier publication outlining the development of the model (Scarborough
Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass
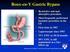 Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass Restrictive and malabsorptive procedure Most frequently performed bariatric procedure in the US First done in 1967 Laparoscopic since 1993 75% EWL in 18-24 months 50% EWL is still
Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass Restrictive and malabsorptive procedure Most frequently performed bariatric procedure in the US First done in 1967 Laparoscopic since 1993 75% EWL in 18-24 months 50% EWL is still
Impromy Weight Loss 2014
 Impromy Weight Loss 2014 Impromy Member Number: Client Details Name: Address: Mobile #: Initial Consultation Email: Age Range: Gender: Welcome to the Impromy Program Introduce yourself (mention that you
Impromy Weight Loss 2014 Impromy Member Number: Client Details Name: Address: Mobile #: Initial Consultation Email: Age Range: Gender: Welcome to the Impromy Program Introduce yourself (mention that you
Complementary and alternative medicine use in Chinese women with breast cancer: A Taiwanese survey
 Complementary and alternative medicine use in Chinese women with breast cancer: A Taiwanese survey Dr Fang-Ying (Sylvia) Chu Department of Nursing, Tzu Chi College of Technology, Hua Lien, Taiwan 1 BACKGROUND
Complementary and alternative medicine use in Chinese women with breast cancer: A Taiwanese survey Dr Fang-Ying (Sylvia) Chu Department of Nursing, Tzu Chi College of Technology, Hua Lien, Taiwan 1 BACKGROUND
Excessive alcohol consumption increases the likelihood of accidental injury. This
 Abstract Excessive alcohol consumption increases the likelihood of accidental injury. This pilot study reports on the prevalence of hazardous drinkers presenting to a Minor Injuries Unit. The proportion
Abstract Excessive alcohol consumption increases the likelihood of accidental injury. This pilot study reports on the prevalence of hazardous drinkers presenting to a Minor Injuries Unit. The proportion
Robert Okwemba, BSPHS, Pharm.D. 2015 Philadelphia College of Pharmacy
 Robert Okwemba, BSPHS, Pharm.D. 2015 Philadelphia College of Pharmacy Judith Long, MD,RWJCS Perelman School of Medicine Philadelphia Veteran Affairs Medical Center Background Objective Overview Methods
Robert Okwemba, BSPHS, Pharm.D. 2015 Philadelphia College of Pharmacy Judith Long, MD,RWJCS Perelman School of Medicine Philadelphia Veteran Affairs Medical Center Background Objective Overview Methods
Louisiana Report 2013
 Louisiana Report 2013 Prepared by Louisiana State University s Public Policy Research Lab For the Department of Health and Hospitals State of Louisiana December 2015 Introduction The Behavioral Risk Factor
Louisiana Report 2013 Prepared by Louisiana State University s Public Policy Research Lab For the Department of Health and Hospitals State of Louisiana December 2015 Introduction The Behavioral Risk Factor
1.0 Abstract. Title: Real Life Evaluation of Rheumatoid Arthritis in Canadians taking HUMIRA. Keywords. Rationale and Background:
 1.0 Abstract Title: Real Life Evaluation of Rheumatoid Arthritis in Canadians taking HUMIRA Keywords Rationale and Background: This abbreviated clinical study report is based on a clinical surveillance
1.0 Abstract Title: Real Life Evaluation of Rheumatoid Arthritis in Canadians taking HUMIRA Keywords Rationale and Background: This abbreviated clinical study report is based on a clinical surveillance
Nutrition for Family Living
 Susan Nitzke, Nutrition Specialist; susan.nitzke@ces.uwex.edu Sherry Tanumihardjo, Nutrition Specialist; sherry.tan@ces.uwex.edu Amy Rettammel, Outreach Specialist; arettamm@facstaff.wisc.edu Betsy Kelley,
Susan Nitzke, Nutrition Specialist; susan.nitzke@ces.uwex.edu Sherry Tanumihardjo, Nutrition Specialist; sherry.tan@ces.uwex.edu Amy Rettammel, Outreach Specialist; arettamm@facstaff.wisc.edu Betsy Kelley,
The Arguments: T2DM - tremendous economic burden globally Lifestyle / Pharm Rx:
 James Cromie The Arguments: T2DM - tremendous economic burden globally Lifestyle / Pharm Rx: INEFFECTIVE and UNSUSTAINED Bariatric surgery is an Effective and Durable treatment option Well established
James Cromie The Arguments: T2DM - tremendous economic burden globally Lifestyle / Pharm Rx: INEFFECTIVE and UNSUSTAINED Bariatric surgery is an Effective and Durable treatment option Well established
Chronic diseases in low and middle income countries: more research or more action? Shah Ebrahim London School of Hygiene & Tropical Medicine
 Chronic diseases in low and middle income countries: more research or more action? Shah Ebrahim London School of Hygiene & Tropical Medicine More action needed Overview Growing burden of chronic diseases
Chronic diseases in low and middle income countries: more research or more action? Shah Ebrahim London School of Hygiene & Tropical Medicine More action needed Overview Growing burden of chronic diseases
Predictors of Physical Therapy Use in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis
 Predictors of Physical Therapy Use in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis Maura Iversen,, PT, DPT, SD, MPH 1,2,3 Ritu Chhabriya,, MSPT 4 Nancy Shadick, MD 2,3 1 Department of Physical Therapy, Northeastern
Predictors of Physical Therapy Use in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis Maura Iversen,, PT, DPT, SD, MPH 1,2,3 Ritu Chhabriya,, MSPT 4 Nancy Shadick, MD 2,3 1 Department of Physical Therapy, Northeastern
2015 Michigan Department of Health and Human Services Adult Medicaid Health Plan CAHPS Report
 2015 State of Michigan Department of Health and Human Services 2015 Michigan Department of Health and Human Services Adult Medicaid Health Plan CAHPS Report September 2015 Draft Draft 3133 East Camelback
2015 State of Michigan Department of Health and Human Services 2015 Michigan Department of Health and Human Services Adult Medicaid Health Plan CAHPS Report September 2015 Draft Draft 3133 East Camelback
Fatigue and TSH Levels in Hypothyroid Patients Abstract Background Methods Results Conclusions Introduction
 in Hypothyroid Patients Boutros El-Haddad, M.D. 1, Issam El Bizri, M.D. 2, K. James Kallail, Ph.D. 1, Rosalee E. Zackula, M.A. 3, and Jan M. Hoffman, M.D. 1,4 1 University of Kansas School of Medicine-Wichita
in Hypothyroid Patients Boutros El-Haddad, M.D. 1, Issam El Bizri, M.D. 2, K. James Kallail, Ph.D. 1, Rosalee E. Zackula, M.A. 3, and Jan M. Hoffman, M.D. 1,4 1 University of Kansas School of Medicine-Wichita
Listen to your heart: Good Cardiovascular Health for Life
 Listen to your heart: Good Cardiovascular Health for Life Luis R. Castellanos MD, MPH Assistant Clinical Professor of Medicine University of California San Diego School of Medicine Sulpizio Family Cardiovascular
Listen to your heart: Good Cardiovascular Health for Life Luis R. Castellanos MD, MPH Assistant Clinical Professor of Medicine University of California San Diego School of Medicine Sulpizio Family Cardiovascular
Obesity in the United States Workforce. Findings from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys (NHANES) III and 1999-2000
 P F I Z E R F A C T S Obesity in the United States Workforce Findings from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys (NHANES) III and 1999-2000 p p Obesity in The United States Workforce One
P F I Z E R F A C T S Obesity in the United States Workforce Findings from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys (NHANES) III and 1999-2000 p p Obesity in The United States Workforce One
New Cholesterol Guidelines: Carte Blanche for Statin Overuse Rita F. Redberg, MD, MSc Professor of Medicine
 New Cholesterol Guidelines: Carte Blanche for Statin Overuse Rita F. Redberg, MD, MSc Professor of Medicine Disclosures & Relevant Relationships I have nothing to disclose No financial conflicts Editor,
New Cholesterol Guidelines: Carte Blanche for Statin Overuse Rita F. Redberg, MD, MSc Professor of Medicine Disclosures & Relevant Relationships I have nothing to disclose No financial conflicts Editor,
relates to utilization of conventional preventive services and health care satisfaction among health plan members.
 Complementary and Alternative Medicine Use among Health Plan Members A Cross-Sectional Survey CONTEXT. Many health plans have started to cover the cost of complementary and alternative medicine (CAM).
Complementary and Alternative Medicine Use among Health Plan Members A Cross-Sectional Survey CONTEXT. Many health plans have started to cover the cost of complementary and alternative medicine (CAM).
Summary of health effects
 Review of Findings on Chronic Disease Self- Management Program (CDSMP) Outcomes: Physical, Emotional & Health-Related Quality of Life, Healthcare Utilization and Costs Summary of health effects The major
Review of Findings on Chronic Disease Self- Management Program (CDSMP) Outcomes: Physical, Emotional & Health-Related Quality of Life, Healthcare Utilization and Costs Summary of health effects The major
TYPE 2 DIABETES MELLITUS: NEW HOPE FOR PREVENTION. Robert Dobbins, M.D. Ph.D.
 TYPE 2 DIABETES MELLITUS: NEW HOPE FOR PREVENTION Robert Dobbins, M.D. Ph.D. Learning Objectives Recognize current trends in the prevalence of type 2 diabetes. Learn differences between type 1 and type
TYPE 2 DIABETES MELLITUS: NEW HOPE FOR PREVENTION Robert Dobbins, M.D. Ph.D. Learning Objectives Recognize current trends in the prevalence of type 2 diabetes. Learn differences between type 1 and type
on a daily basis. On the whole, however, those with heart disease are more limited in their activities, including work.
 Heart Disease A disabling yet preventable condition Number 3 January 2 NATIONAL ACADEMY ON AN AGING SOCIETY Almost 18 million people 7 percent of all Americans have heart disease. More than half of the
Heart Disease A disabling yet preventable condition Number 3 January 2 NATIONAL ACADEMY ON AN AGING SOCIETY Almost 18 million people 7 percent of all Americans have heart disease. More than half of the
The Scottish Health Survey
 The Scottish Health Survey The Glasgow Effect Topic Report A National Statistics Publication for Scotland The Scottish Health Survey The Glasgow Effect Topic Report The Scottish Government, Edinburgh
The Scottish Health Survey The Glasgow Effect Topic Report A National Statistics Publication for Scotland The Scottish Health Survey The Glasgow Effect Topic Report The Scottish Government, Edinburgh
Study Design and Statistical Analysis
 Study Design and Statistical Analysis Anny H Xiang, PhD Department of Preventive Medicine University of Southern California Outline Designing Clinical Research Studies Statistical Data Analysis Designing
Study Design and Statistical Analysis Anny H Xiang, PhD Department of Preventive Medicine University of Southern California Outline Designing Clinical Research Studies Statistical Data Analysis Designing
Maintaining Healthy Body Mass Index (BMI) Through Physical Activity and Diet Pitfalls of Fad Dieting. Julia Sosa, MS,RD,LD ADPH
 Maintaining Healthy Body Mass Index (BMI) Through Physical Activity and Diet Pitfalls of Fad Dieting Julia Sosa, MS,RD,LD ADPH How do you define Healthy? What is Body Mass Index? Body mass index (BMI)
Maintaining Healthy Body Mass Index (BMI) Through Physical Activity and Diet Pitfalls of Fad Dieting Julia Sosa, MS,RD,LD ADPH How do you define Healthy? What is Body Mass Index? Body mass index (BMI)
Scientific Method. 2. Design Study. 1. Ask Question. Questionnaire. Descriptive Research Study. 6: Share Findings. 1: Ask Question.
 Descriptive Research Study Investigation of Positive and Negative Affect of UniJos PhD Students toward their PhD Research Project : Ask Question : Design Study Scientific Method 6: Share Findings. Reach
Descriptive Research Study Investigation of Positive and Negative Affect of UniJos PhD Students toward their PhD Research Project : Ask Question : Design Study Scientific Method 6: Share Findings. Reach
Kansas Behavioral Health Risk Bulletin
 Kansas Behavioral Health Risk Bulletin Kansas Department of Health and Environment November 7, 1995 Bureau of Chronic Disease and Health Promotion Vol. 1 No. 12 Diabetes Mellitus in Kansas Diabetes mellitus
Kansas Behavioral Health Risk Bulletin Kansas Department of Health and Environment November 7, 1995 Bureau of Chronic Disease and Health Promotion Vol. 1 No. 12 Diabetes Mellitus in Kansas Diabetes mellitus
PREOPERATIVE MANAGEMENT FOR BARIATRIC PATIENTS. Adrienne R. Gomez, MD Bariatric Physician St. Vincent Bariatric Center of Excellence
 PREOPERATIVE MANAGEMENT FOR BARIATRIC PATIENTS Adrienne R. Gomez, MD Bariatric Physician St. Vincent Bariatric Center of Excellence BARIATRIC SURGERY Over 200,000 bariatric surgical procedures are performed
PREOPERATIVE MANAGEMENT FOR BARIATRIC PATIENTS Adrienne R. Gomez, MD Bariatric Physician St. Vincent Bariatric Center of Excellence BARIATRIC SURGERY Over 200,000 bariatric surgical procedures are performed
Kansas Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System Local Data, 2009
 Kansas Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System Local Data, 2009 Kansas BRFSS Bureau of Health Promotion Kansas Department of Health and Environment 1000 SW Jackson St., Suite 230 Topeka, Kansas 66612-1274
Kansas Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System Local Data, 2009 Kansas BRFSS Bureau of Health Promotion Kansas Department of Health and Environment 1000 SW Jackson St., Suite 230 Topeka, Kansas 66612-1274
Trends in Australian children traveling to school 1971-2003: burning petrol or carbohydrates?
 1 Trends in Australian children traveling to school 1971-2003: burning petrol or carbohydrates? Hidde P. van der Ploeg 1, Dafna Merom 1, Grace Corpuz 2, Adrian E. Bauman 1 1 Centre for Physical Activity
1 Trends in Australian children traveling to school 1971-2003: burning petrol or carbohydrates? Hidde P. van der Ploeg 1, Dafna Merom 1, Grace Corpuz 2, Adrian E. Bauman 1 1 Centre for Physical Activity
Kansas Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System Local Data, 2009
 Kansas Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System Local Data, 2009 Kansas BRFSS Bureau of Health Promotion Kansas Department of Health and Environment 1000 SW Jackson St., Suite 230 Topeka, Kansas 66612-1274
Kansas Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System Local Data, 2009 Kansas BRFSS Bureau of Health Promotion Kansas Department of Health and Environment 1000 SW Jackson St., Suite 230 Topeka, Kansas 66612-1274
Understanding Obesity
 Your Guide to Understanding Obesity As your partner in health for your life s journey, we want you to be as informed and confident as possible regarding the disease or medical issue you may be facing.
Your Guide to Understanding Obesity As your partner in health for your life s journey, we want you to be as informed and confident as possible regarding the disease or medical issue you may be facing.
Weight Loss Surgery DA participants- 18 months later. By: Caitlyn Patrick and Evan Morgan
 Weight Loss Surgery DA participants- 18 months later By: Caitlyn Patrick and Evan Morgan Outline Background Obesity Comorbidities Treatments Barriers to care Kylee Miller s work PDSA Plan: Systematic follow
Weight Loss Surgery DA participants- 18 months later By: Caitlyn Patrick and Evan Morgan Outline Background Obesity Comorbidities Treatments Barriers to care Kylee Miller s work PDSA Plan: Systematic follow
Main Effect of Screening for Coronary Artery Disease Using CT
 Main Effect of Screening for Coronary Artery Disease Using CT Angiography on Mortality and Cardiac Events in High risk Patients with Diabetes: The FACTOR-64 Randomized Clinical Trial Joseph B. Muhlestein,
Main Effect of Screening for Coronary Artery Disease Using CT Angiography on Mortality and Cardiac Events in High risk Patients with Diabetes: The FACTOR-64 Randomized Clinical Trial Joseph B. Muhlestein,
Competency 1 Describe the role of epidemiology in public health
 The Northwest Center for Public Health Practice (NWCPHP) has developed competency-based epidemiology training materials for public health professionals in practice. Epidemiology is broadly accepted as
The Northwest Center for Public Health Practice (NWCPHP) has developed competency-based epidemiology training materials for public health professionals in practice. Epidemiology is broadly accepted as
UNINSURED ADULTS IN MAINE, 2013 AND 2014: RATE STAYS STEADY AND BARRIERS TO HEALTH CARE CONTINUE
 UNINSURED ADULTS IN MAINE, 2013 AND 2014: RATE STAYS STEADY AND BARRIERS TO HEALTH CARE CONTINUE December 2015 Beginning in January 2014, the federal Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act (ACA) has
UNINSURED ADULTS IN MAINE, 2013 AND 2014: RATE STAYS STEADY AND BARRIERS TO HEALTH CARE CONTINUE December 2015 Beginning in January 2014, the federal Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act (ACA) has
METABOLIC SYNDROME IN A CORRECTIONS POPULATION TREATED WITH ANTIPSYCHOTICS
 METABOLIC SYNDROME IN A CORRECTIONS POPULATION TREATED WITH ANTIPSYCHOTICS Andrew M. Cislo, PhD Megan J. Ehret, PharmD, MS, BCPP Robert L. Trestman, MD, PhD Kirsten Shea, MBA www.uchc.edu Background Metabolic
METABOLIC SYNDROME IN A CORRECTIONS POPULATION TREATED WITH ANTIPSYCHOTICS Andrew M. Cislo, PhD Megan J. Ehret, PharmD, MS, BCPP Robert L. Trestman, MD, PhD Kirsten Shea, MBA www.uchc.edu Background Metabolic
THE CORRELATION BETWEEN PHYSICAL HEALTH AND MENTAL HEALTH
 HENK SWINKELS (STATISTICS NETHERLANDS) BRUCE JONAS (US NATIONAL CENTER FOR HEALTH STATISTICS) JAAP VAN DEN BERG (STATISTICS NETHERLANDS) THE CORRELATION BETWEEN PHYSICAL HEALTH AND MENTAL HEALTH IN THE
HENK SWINKELS (STATISTICS NETHERLANDS) BRUCE JONAS (US NATIONAL CENTER FOR HEALTH STATISTICS) JAAP VAN DEN BERG (STATISTICS NETHERLANDS) THE CORRELATION BETWEEN PHYSICAL HEALTH AND MENTAL HEALTH IN THE
Trends in Bariatric Surgery for Morbid Obesity. in Wisconsin
 Trends in Bariatric Surgery for Morbid Obesity in Wisconsin Jennifer L. Erickson, B.A. Patrick L. Remington, M.D., M.P.H. Paul E. Peppard, PhD A Working Paper of the Wisconsin Public Health and Health
Trends in Bariatric Surgery for Morbid Obesity in Wisconsin Jennifer L. Erickson, B.A. Patrick L. Remington, M.D., M.P.H. Paul E. Peppard, PhD A Working Paper of the Wisconsin Public Health and Health
Mode and Patient-mix Adjustment of the CAHPS Hospital Survey (HCAHPS)
 Mode and Patient-mix Adjustment of the CAHPS Hospital Survey (HCAHPS) April 30, 2008 Abstract A randomized Mode Experiment of 27,229 discharges from 45 hospitals was used to develop adjustments for the
Mode and Patient-mix Adjustment of the CAHPS Hospital Survey (HCAHPS) April 30, 2008 Abstract A randomized Mode Experiment of 27,229 discharges from 45 hospitals was used to develop adjustments for the
Living a happy, healthy and satisfying life Tineke de Jonge, Christianne Hupkens, Jan-Willem Bruggink, Statistics Netherlands, 15-09-2009
 Living a happy, healthy and satisfying life Tineke de Jonge, Christianne Hupkens, Jan-Willem Bruggink, Statistics Netherlands, 15-09-2009 1 Introduction Subjective well-being (SWB) refers to how people
Living a happy, healthy and satisfying life Tineke de Jonge, Christianne Hupkens, Jan-Willem Bruggink, Statistics Netherlands, 15-09-2009 1 Introduction Subjective well-being (SWB) refers to how people
Losing Weight in Singapore - Public Perception of Obesity
 Singapore Med J 2012; 53(2) : 104 Public perceptions of obesity and bariatric surgery in Singapore: a pilot study Teo EY 1, MBBS, MRCP, Lew PS 2, MBBS, Foo CS 2, FRCS, FAMS Introduction Obesity is a real
Singapore Med J 2012; 53(2) : 104 Public perceptions of obesity and bariatric surgery in Singapore: a pilot study Teo EY 1, MBBS, MRCP, Lew PS 2, MBBS, Foo CS 2, FRCS, FAMS Introduction Obesity is a real
Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
 Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria Inclusion criteria = attributes of subjects that are essential for their selection to participate. Inclusion criteria function remove the influence of specific confounding
Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria Inclusion criteria = attributes of subjects that are essential for their selection to participate. Inclusion criteria function remove the influence of specific confounding
Cardiovascular risk assessment: Audit findings from a nurse clinic a quality improvement initiative
 Cardiovascular risk assessment: Audit findings from a nurse clinic a quality improvement initiative Sarah Waldron RN, PG Dip (Adv Ng); Margaret Horsburgh RN, EdD, MA (Hons), Dip Ed, FCNA(NZ) School of
Cardiovascular risk assessment: Audit findings from a nurse clinic a quality improvement initiative Sarah Waldron RN, PG Dip (Adv Ng); Margaret Horsburgh RN, EdD, MA (Hons), Dip Ed, FCNA(NZ) School of
IMPACT OF DIABETES ON QUALITY OF LIFE OF ELDERLY
 1 Panacea Journal of Health Science IMPACT OF DIABETES ON QUALITY OF LIFE OF ELDERLY Shama Begum, Research Scholar, Roopa K.S. Associate Professor, Department of Human Development and Research Centre,
1 Panacea Journal of Health Science IMPACT OF DIABETES ON QUALITY OF LIFE OF ELDERLY Shama Begum, Research Scholar, Roopa K.S. Associate Professor, Department of Human Development and Research Centre,
Fleet and Marine Corps Health Risk Assessment, 1 January 31 December, 2014
 Fleet and Marine Corps Health Risk Assessment, 1 January 31 December, 2014 Executive Summary The Fleet and Marine Corps Health Risk Appraisal is a 22-question anonymous self-assessment of many of the most
Fleet and Marine Corps Health Risk Assessment, 1 January 31 December, 2014 Executive Summary The Fleet and Marine Corps Health Risk Appraisal is a 22-question anonymous self-assessment of many of the most
Bipolar Disorder and Substance Abuse Joseph Goldberg, MD
 Diabetes and Depression in Older Adults: A Telehealth Intervention Julie E. Malphurs, PhD Asst. Professor of Psychiatry and Behavioral Science Miller School of Medicine, University of Miami Research Coordinator,
Diabetes and Depression in Older Adults: A Telehealth Intervention Julie E. Malphurs, PhD Asst. Professor of Psychiatry and Behavioral Science Miller School of Medicine, University of Miami Research Coordinator,
Minnesota Studies of Health Education and Environmental Approaches to Obesity Treatment and Prevention
 Minnesota Studies of Health Education and Environmental Approaches to Obesity Treatment and Prevention Robert W. Jeffery, Ph.D. University of Minnesota USA Prevalence of Obesity (BMI 30) in US Adults,
Minnesota Studies of Health Education and Environmental Approaches to Obesity Treatment and Prevention Robert W. Jeffery, Ph.D. University of Minnesota USA Prevalence of Obesity (BMI 30) in US Adults,
CAGE. AUDIT-C and the Full AUDIT
 CAGE In the past have you ever: C tried to Cut down or Change your pattern of drinking or drug use? A been Annoyed or Angry because of others concern about your drinking or drug use? G felt Guilty about
CAGE In the past have you ever: C tried to Cut down or Change your pattern of drinking or drug use? A been Annoyed or Angry because of others concern about your drinking or drug use? G felt Guilty about
Obesity and Socioeconomic Status in Children and Adolescents: United States, 2005 2008
 Obesity and Socioeconomic Status in Children and Adolescents: United States, 2005 2008 Cynthia L. Ogden, Ph.D.; Molly M. Lamb, Ph.D.; Margaret D. Carroll, M.S.P.H.; and Katherine M. Flegal, Ph.D. Key findings
Obesity and Socioeconomic Status in Children and Adolescents: United States, 2005 2008 Cynthia L. Ogden, Ph.D.; Molly M. Lamb, Ph.D.; Margaret D. Carroll, M.S.P.H.; and Katherine M. Flegal, Ph.D. Key findings
Fewer people with coronary heart disease are being diagnosed as compared to the expected figures.
 JSNA Coronary heart disease 1) Key points 2) Introduction 3) National picture 4) Local picture of CHD prevalence 5) Mortality from coronary heart disease in Suffolk County 6) Trends in mortality rates
JSNA Coronary heart disease 1) Key points 2) Introduction 3) National picture 4) Local picture of CHD prevalence 5) Mortality from coronary heart disease in Suffolk County 6) Trends in mortality rates
ESCMID Online Lecture Library. by author
 Do statins improve outcomes of patients with sepsis and pneumonia? Jordi Carratalà Department of Infectious Diseases Statins for sepsis & community-acquired pneumonia Sepsis and CAP are major healthcare
Do statins improve outcomes of patients with sepsis and pneumonia? Jordi Carratalà Department of Infectious Diseases Statins for sepsis & community-acquired pneumonia Sepsis and CAP are major healthcare
Outcome of Drug Counseling of Outpatients in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Clinic at Thawangpha Hospital
 Mahidol University Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences 008; 35(14): 81. Original Article Outcome of Drug Counseling of Outpatients in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Clinic at Thawangpha Hospital
Mahidol University Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences 008; 35(14): 81. Original Article Outcome of Drug Counseling of Outpatients in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Clinic at Thawangpha Hospital
Study Designs. Simon Day, PhD Johns Hopkins University
 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike License. Your use of this material constitutes acceptance of that license and the conditions of use of materials on this
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike License. Your use of this material constitutes acceptance of that license and the conditions of use of materials on this
