THE FUTURE OF STEM CELLS IN MEDICINE BY AGNES MILNER KATIE CLARK. Pass with Merit
|
|
|
- Georgia Garrison
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 THE FUTURE OF STEM CELLS IN MEDICINE BY AGNES MILNER KATIE CLARK Pass with Merit RESEARCH PAPER BASED ON PATHOLOGY LECTURES AT MEDLINK
2 Abstract Embryonic stem cell research offers great promise for understanding basic mechanisms of human development and differentiation, as well as the hope for new treatments for diseases such as diabetes, spinal cord injury, Parkinson's disease, and myocardial infarction. However, embryonic stem cell research also raises severe ethical and political controversies. The reprogramming of human adult cells to produce induced pluripotent stem cells (ips) avoids the ethical problems specific to embryonic stem cell research. In any stem cell research, however, difficult dilemmas arise regarding consent to donate materials for research, early clinical trials of therapies, and oversight of research. These ethical issues need to be discussed along with scientific challenges to ensure that stem cell research is carried out in an ethically appropriate manner. This paper provides a critical analysis of these issues and how they are addressed in current policies. Discussion Since 1908, when the term stem cell was first proposed for scientific use by the Russian histologist Alexander Maksimov at congress of hematologic society in Berlin, there has been a copious amount of research carried out on stem cells and in particular embryonic stem cells for medical purposes. Stem cells are undifferentiated cells that can, with the right stimuli, transform into many other cell types found in the human body, serving as a possible repair system for the body. They can theoretically divide without limit to replenish other cells. When a stem cell divides, each new cell has the potential to either remain a stem cell or become another type of cell with a more specialised function, such as a muscle cell, a red blood cell or a brain cell. In 1998, Dr. James Thomson at the University of Wisconsin, isolated cells from blastocysts and developed the first embryonic stem cell lines, this was one of the first major steps into the scientific research of embryonic stem cells. Much of the research carried out since 1908 has led scientists to deduce that stem cells, if grown in the correct conditions, can be used to treat such diseases as leukaemia and other malignant illnesses, as well as repair spinal chord and brain tissue. Figure 1: The human embryonic stem cells cultured at the University of Wisconsin - Madison have been observed to randomly differentiate in culture into a variety of different cell types, including (A) gut, (B) neural cells, (C) bone marrow cells, (D) cartilage, (E) muscle and (F) kidney cells 2
3 In October 2010 the first clinical trial on humans with recent spinal cord damage was carried out, the company Geron had injected stem cells into the spines of a small number of patients with spinal cord injuries, in the hope that these stem cells would differentiate into specialised nerve cells. However these trials were halted in October 2011 due to insufficient funding, therefore the outcome of these investigations is unknown. Prior to these clinical trials on humans the same experiment was conducted on paralysed rats. These rats regained some movement due to improvement in their locomoter recovery, which suggests that similar outcomes may be achieved in humans. In 2008 researchers in Kyoto (Japan), Wisconsin and California (USA) recorded that they had successfully reprogrammed human skin cells to become pluripotent, almost identical to embryonic stem cells. In this process, the researchers identified four essential regulator genes and have called the cells induced pluripotent stem cells (ips cells). If such cells can be safely developed from any individuals own skin cells and used to generate the 200+ different cell types found in a human, the technique could replace the more controversial nuclear transfer method used by scientists working on therapeutic cloning, in which a differentiated cell from an adult animal can be taken, and its nucleus placed in an egg cell which has had its own nucleus removed. The egg then goes through the stages of development using genetic information from the inserted nucleus; the first animal cloned by this method was Dolly the sheep in Using genetic reprogramming with protein transcription factors, pluripotent stem cells become equivalent to embryonic stem cells, which have been derived from human adult skin tissue. 3
4 Figure 2: Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell (ips) Pathway As the researchers in Kyoto, Wisconsin and California have successfully reprogrammed specialised adult cells to give rise to cells with pluripotent capabilities we therefore are potentially able to manipulate the signals of a differentiated cell into a pluripotent cell. This pluripotent cell can then become specialised and there is the capability of ultimately developing tissues and possibly organs from an individual s own skin cells therefore providing an alternative to organ transplants. ips cells retain a memory of their tissue of origin, for example ips cells made from blood are easier to turn back into blood. This can become problematic when using ips cells made from skin cells in transplants for other cell types. It may be possible to fade the memory of the ips cells, but only through many rounds of cell division. Today, donated organs and tissues are often used to replace those that are diseased or destroyed. Unfortunately, the number of people needing a transplant far exceeds the number of organs available for transplantation. The ips method is also believed to eliminate the implications of organ donor transplants as there is no possibility for organ rejection due to immunogenic responses as the organ is grown from the recipient s own cells. Every day, 18 people die while waiting for a transplant of a vital organ. Therefore hopefully, with the introduction of the ips method, this number of deaths due to the lack of organ donors will be greatly reduced. Current research is being carried out by Dr. Thanassi Athanassopoulos at the Stem Cell Research Laboratory and National Blood Service, Oxford, on whether tissue engineered skin created with endothelial progenitor cells can provide the solution to many of the limitations associated with the use of skin grafts particularly in patients with major burns. Although stem cells are rare in the peripheral blood, there is strong evidence that suggests that endothelial progenitor cells are present in the circulation. In laboratory-controlled investigations, blood was cultured over a period of eight weeks and colonies of endothelial precursors were grown from the umbilical chord and adult peripheral blood samples. The stem cell nature of these endothelial progenitor cells was confirmed by a technique named flow cytometry, which allows accurate determination of the expression of a cells surface markers. These progenitor cells were able to integrate into mature capillaries, mimicking the process of vascular repair and the progenitor cells were capable of forming capillary like tubes in artificial skin substitutes. This research is continuing with the assessment of the safety of these cells for human use and further development of the microcirculation in skin substitutes. Burn injuries are devastating for the victims and living artificial skin offers improved reconstruction and quality of life stated Dr. Athanassopoulos. Skin grafts are one of the many conditions that embryonic stem cells have the potential of treating. In the USA alone, stem cell research offers hope for 2 million diabetics, 1.5 million Parkinson disease sufferers and 250,000 people with spinal cord injuries. 4
5 Figure 3: The development of capillaries over two weeks from stem cells derived from blood samples However there are many major ethical implications of using embryonic stem cells to treat any medical human conditions. The foremost issue is that the process of obtaining the cells destroys the human embryo. Many patients may object to receiving treatment due to the fact that they believe that life begins at conception and the destruction of the embryo is the termination of a human life. In an address to an international congress in September 2006, Pope Benedict XVI stated: The destruction of human embryos to harvest stem cells is "not only devoid of the light of God but is also devoid of humanity" and "does not truly serve humanity." The notion that an embryo in a petri dish has the same moral status as a person can be challenged on further grounds. Taking the stance that the embryo is regarded on the same grounds as a human life rules out all possibilities for artificial conception and other embryonic stem cell research. For instance, defenders of in vitro fertilization point out that embryo loss in assisted reproduction is less frequent than in natural pregnancy and therefore, the natural loss of embryos can be seen as no worse than the obliteration in the aid of future medical advancements. It can be viewed that the loss of the human embryo is far outweighed by the much-needed developments in medical treatments. Already, there are companies who currently specialise in culturing and engineering stem cells, which scientists use in an array of therapies from wound healing to reconstructive surgeries. Dr. Zain Kadri, a plastic surgeon and medical director of Invitrx Therapeutics, has explained that, the stem cells are programmed to look for damaged tissue. They come and attach to the damaged area, divide and multiply, and they repair the area. However, a danger of embryonic stem cell research into the repairing of damaged skin cells is that the results of a successful technique could be exploited and abused for cosmetic reasons. For instance, stem cells could be injected into the skin of the aged to revitalise and rejuvenate their face and body. The cells injected are able to self-renew and differentiate into mature adipocytes (a type of fat cell, also known as lipocytes). These cells act as soft-tissue filler and this provides the appearance of more youthful skin. This new method has been highly successful in animal trials and avoids the drawbacks of current technology. However as these trials have only been conducted on animals, it is 5
6 too early to establish whether they would make the perfect tissue filler. The use of embryonic stem cells in cosmetic techniques is regarded as an extremely narcissistic justification for the discarding of human embryos by a large collection of individuals. Figure 4: The specific focus of stem cell research in New York State in 2008 Another future possibility of using embryonic stem cells, is in sex reassignment surgery, in which the sex organs can be reconstructed, providing people with the opportunity to become transsexual. If the use of embryonic stem cells to construct the exterior sex organs artificially becomes successful, then it may also be possible to grow the interior sex organs such as the uterus, enabling transsexuals to conceive a child and allow the pregnancy to become full term, with no need for immunosuppressant drugs. However, in many religious views, sex reassignment surgery is seen as defiling the wishes of God. In Abrahamic religions there are creation stories in which God creates people, male and female. This is sometimes interpreted as the fact that each gender is a divine mandate and gender variance is strictly prohibited. Although the ethical implications are extensive, the scientific implications are also as devastating and potentially fatal. These implications include the unregulated differentiation of cells, thus leading to the formation of teratomas and teratocarcinomas, these are tumours composed of tissues that are not normally present at the site of formation and consist of all three germ layers, unlike most cancerous tumours, the embryonic stem cell tumours originate from a group of apparently normal cells. Teratomas are potentially dangerous as the cells from which they arise are pluripotent and so can differentiate into a number of different types of tissue, such a teeth, bone and hair. These dangers of developing a teratoma from embryonic stem cell treatments in clinical trials, implicates the extent to which research can be carried out. Conclusion To conclude, the colossal advances in embryonic stem cell research since their discovery in 1908, has led to the development of critical medical achievements, which have the capability to save many human lives and improve the quality of living for countless patients. The use of embryonic stem cells in the treatment of leukaemia, spinal chord damage and other malignant conditions has only been made possible through the 6
7 extensive amount of research, which has been carried out in recent years. Barack Obama stated in an address to the congress in 2009 that; "Medical miracles do not happen simply by accident. They result from painstaking and costly research, from years of lonely trial and error, much of which never bears fruit, and from a government willing to support that work, which demonstrates the extreme importance of the continuation of research into key scientific areas such as embryonic stem cells. Although the extreme importance of research into embryonic stem cells is recognised, an alternative to their use has recently been discovered with research into induced pluripotent stem cells (ips). Many scientists are in favour of using these ips cells instead of embryonic stem cells as they bypass many controversial issues, hoping to bridge the gap between science and religion. However two independent teams of scientists have reported that these ips cells do not behave exactly like the stem cells found in early human embryos. These two research teams both effectively found that the ips cells were not completely reprogrammed back to the early embryonic stage of development, which could cause problems if they were to be used in transplant operations. Dr. George Daley of the Children s Hospital in Boston stated that these findings cut across all clinical applications people are pursuing and whatever disease they are modelling Everyone working with these cells has to think about the tissues of origin and how that affects reprogramming. As the large majority of medical treatments using embryonic stem cells are only at a developing stage, precautions must be taken along with numerous clinical trials to ensure our understanding of any possible detrimental side effects. Embryonic stem cell treatments suggest huge advancements in the medical field, however there are arguments that suggest it may be unsuccessful, such as the formation of teratomas. Research into embryonic stem cells is highly controversial and raises many ethical debates, however we believe that the advancements in medicine, which require the continuation of research, far outweigh the resulting disadvantages, hopefully improving the quality of life for many individuals. There is no doubt that embryonic stem cell research is cutting edge and that the benefits are huge, however in the contemporary economic situation many of the stem cell research companies are in competition with each other for funding, resulting in the overhyping of the achievements of each individual company s research. This exaggeration gives false hope to many and provides a false sense of security to those funding the individual research projects. This hype does however give a realistic interpretation of the future achievements in medicine, which can only be made possible through embryonic stem cell research, causing us to ponder the following questions; Will this research discover a cure for cancer? and Could this research extend our lifespan beyond the best interest of our species?. 7
8 References Athanassopoulos, T. (2010) Tissue Engineering with Endothelial Progenitor Cells, in the Surgical Research Report 2011 online, The Royal College of Surgeons of England, RCSENG, page Stem Cells and Diseases, Bethesda, MD. (2012) National Institutes of Health, U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. 8
9 Bowser, BA. Obama Lifts Restrictions on Funding Human Stem Cell Research (2009), report by PBS Newshour. Connor, S. (Tuesday 20 July 2010) Plan for non-embryo stem cell technique suffers setback, The Independent. Devitt, T. (1998) Wisconsin scientists culture elusive embryonic stem cells in a report by University of Wisconsin Stem Cell and Regenerative Medicine Centre. Kennedy, P and Sochacki, F. (2008) AS OCR Biology, Heinemann Publishers. Page Facts About Organ Donation and Transplantation (2012) National Kidney Foundation, Inc. Stem cells for stroke (2012) online report by NewsChannel5. The use of stem cells in innovative research, report by The State of VA Research Committee. Figure on Cover Sheet. Figure 1: Wisconsin scientists culture elusive embryonic stem cells photograph in a report by University of Wisconsin Stem Cell and Regenerative Medicine Centre. Figure 2: Sigma Aldrich online, Embryonic and Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells. 9
10 Figure 3: Athanassopoulos, T. (2010) Tissue Engineering with Endothelial Progenitor Cells, in the Surgical Research Report 2011 online, The Royal College of Surgeons of England, RCSENG, page Figure 4: Stem Cell Research in New York State, (2008), in a report by New York State Stem Cell Science, 10
STEM CELL FACTS. The ISSCR is an independent, nonproft organization providing a global forum for stem cell research and regenerative medicine.
 STEM CELL FACTS The ISSCR is an independent, nonproft organization providing a global forum for stem cell research and regenerative medicine. WHAT ARE STEM CELLS? Stem cells are the foundation cells for
STEM CELL FACTS The ISSCR is an independent, nonproft organization providing a global forum for stem cell research and regenerative medicine. WHAT ARE STEM CELLS? Stem cells are the foundation cells for
Stem Cell Quick Guide: Stem Cell Basics
 Stem Cell Quick Guide: Stem Cell Basics What is a Stem Cell? Stem cells are the starting point from which the rest of the body grows. The adult human body is made up of hundreds of millions of different
Stem Cell Quick Guide: Stem Cell Basics What is a Stem Cell? Stem cells are the starting point from which the rest of the body grows. The adult human body is made up of hundreds of millions of different
guides BIOLOGY OF AGING STEM CELLS An introduction to aging science brought to you by the American Federation for Aging Research
 infoaging guides BIOLOGY OF AGING STEM CELLS An introduction to aging science brought to you by the American Federation for Aging Research WHAT ARE STEM CELLS? Stem cells are cells that, in cell cultures
infoaging guides BIOLOGY OF AGING STEM CELLS An introduction to aging science brought to you by the American Federation for Aging Research WHAT ARE STEM CELLS? Stem cells are cells that, in cell cultures
15 Stem Cell Research
 15 Stem Cell Research t a l k it o v e r 1 c l a s s se s s i o n Overview Students read about current scientific research on and the social controversy over embryonic stem cells. On a KWL literacy strategy
15 Stem Cell Research t a l k it o v e r 1 c l a s s se s s i o n Overview Students read about current scientific research on and the social controversy over embryonic stem cells. On a KWL literacy strategy
tem ells /background /information Stem cell research Copyright 2007 MRC Centre for Regenerative Medicine, Institute for Stem Cell Research
 tem ells /background /information Stem cell research Copyright 2007 MRC Centre for Regenerative Medicine, Institute for Stem Cell Research /02 /information Table of contents Page 01. What are stem cells?
tem ells /background /information Stem cell research Copyright 2007 MRC Centre for Regenerative Medicine, Institute for Stem Cell Research /02 /information Table of contents Page 01. What are stem cells?
Stem Cell Research: Adult or Somatic Stem Cells
 Chiang 1 Stem Cell Research: Adult or Somatic Stem Cells Abstract Kelly Chiang Cluster 7 Dr. LeFebvre 07/26/10 Over the past few decades, stem cells have been a controversial topic in the scientific field.
Chiang 1 Stem Cell Research: Adult or Somatic Stem Cells Abstract Kelly Chiang Cluster 7 Dr. LeFebvre 07/26/10 Over the past few decades, stem cells have been a controversial topic in the scientific field.
What are Stem Cells? How can they be used in medicine?
 What are Stem Cells? How can they be used in medicine? What is a stem cell????... What is a stem cell????......a cell with the ability to differentiate into specialized cells and renew to become more stem
What are Stem Cells? How can they be used in medicine? What is a stem cell????... What is a stem cell????......a cell with the ability to differentiate into specialized cells and renew to become more stem
Guidance For Research Involving Human Embryonic Stem Cells, Germ Cells, And Cells Obtained From Cord Blood
 Guidance For Research Involving Human Embryonic Stem Cells, Germ Cells, And Cells Obtained From Cord Blood Supreme Council of Health Department of Research Guidance Regarding Research Involving Human Embryonic
Guidance For Research Involving Human Embryonic Stem Cells, Germ Cells, And Cells Obtained From Cord Blood Supreme Council of Health Department of Research Guidance Regarding Research Involving Human Embryonic
The Types of stem cells: Totipotent Pluripotent Multipotent
 Stem Cells is the main material for building and regeneration of the body Stem cells are not differentiated and can transform to any cell of organism Stem cells are capable of indefinite renewal through
Stem Cells is the main material for building and regeneration of the body Stem cells are not differentiated and can transform to any cell of organism Stem cells are capable of indefinite renewal through
Differentiation = Making specialized cells
 Differentiation = Making specialized cells What is a stem cell? Screws: JM www.logodesignweb.com/stockphoto Differentiation = Making specialized cells What is a stem cell? What the photo shows A lump of
Differentiation = Making specialized cells What is a stem cell? Screws: JM www.logodesignweb.com/stockphoto Differentiation = Making specialized cells What is a stem cell? What the photo shows A lump of
Stem cells and motor neurone disease
 Stem cells and motor neurone disease F Stem cell research has fuelled hope of a treatment for a variety of conditions. This information sheet explains what these cells are and includes details of the current
Stem cells and motor neurone disease F Stem cell research has fuelled hope of a treatment for a variety of conditions. This information sheet explains what these cells are and includes details of the current
Stem cells possess 2 main characteristics: Sources of pluripotent stem cells: -Long-term self renewal. -The inner cell mass of the blastocyst.
 Stem cells possess 2 main characteristics: -Long-term self renewal. - They give rise to all types of differentiate cells. Sources of pluripotent stem cells: -The inner cell mass of the blastocyst. - Fetal
Stem cells possess 2 main characteristics: -Long-term self renewal. - They give rise to all types of differentiate cells. Sources of pluripotent stem cells: -The inner cell mass of the blastocyst. - Fetal
Stem Cells and Hope for Patients
 Stem Cells and Hope for Patients by Maureen Condic, Ph.D. Most Americans know someone afflicted with an incurable medical condition. The possibility of stem cell cures has given hope to many who face such
Stem Cells and Hope for Patients by Maureen Condic, Ph.D. Most Americans know someone afflicted with an incurable medical condition. The possibility of stem cell cures has given hope to many who face such
Unit 1 Higher Human Biology Summary Notes
 Unit 1 Higher Human Biology Summary Notes a. Cells tissues organs body systems Division of labour occurs in multicellular organisms (rather than each cell carrying out every function) Most cells become
Unit 1 Higher Human Biology Summary Notes a. Cells tissues organs body systems Division of labour occurs in multicellular organisms (rather than each cell carrying out every function) Most cells become
Should Stem Cells Be Used To Treat Human Diseases?
 SAMPLE ESSAY C Should Stem Cells Be Used To Treat Human Diseases? Stem cells can be defined as undifferentiated cells that are generated during the development of the embryo. There are two functions ascribed
SAMPLE ESSAY C Should Stem Cells Be Used To Treat Human Diseases? Stem cells can be defined as undifferentiated cells that are generated during the development of the embryo. There are two functions ascribed
How To Treat Leukaemia With Cord Blood Stem Cell
 Cord blood for the treatment of acute lymphoblastic leukemia in young children By Caitlin McGreevy Kiara Paramjothy Pass with Merit RESEARCH PAPER BASED ON PATHOLOGY LECTURES AT MEDLINK 2011 1 Abstract:
Cord blood for the treatment of acute lymphoblastic leukemia in young children By Caitlin McGreevy Kiara Paramjothy Pass with Merit RESEARCH PAPER BASED ON PATHOLOGY LECTURES AT MEDLINK 2011 1 Abstract:
THE PROMISE OF STEM CELL RESEARCH
 THE PROMISE OF STEM CELL RESEARCH MALIGNANT OSTEOPETROSIS AUTOSOMAL RECESSIVE DENSE SCLEROTIC SKELETON HEMATOLOGIC ABNORMALITIES NEUROLOGIC ABNOMALITIES DEATH IN INFANCY OR EARLY CHILDHOOD SUCCESS RATE
THE PROMISE OF STEM CELL RESEARCH MALIGNANT OSTEOPETROSIS AUTOSOMAL RECESSIVE DENSE SCLEROTIC SKELETON HEMATOLOGIC ABNORMALITIES NEUROLOGIC ABNOMALITIES DEATH IN INFANCY OR EARLY CHILDHOOD SUCCESS RATE
Stem Cells. Part 1: What is a Stem Cell?
 Stem Cells Part 1: What is a Stem Cell? Stem cells differ from other kinds of cells in the body. When a stem cell divides by mitosis, each new cell has the potential to either remain a stem cell or become
Stem Cells Part 1: What is a Stem Cell? Stem cells differ from other kinds of cells in the body. When a stem cell divides by mitosis, each new cell has the potential to either remain a stem cell or become
Introducing stem cells Stem cells in the news
 Introducing stem cells Stem cells in the news Stem cells: Therapeutic Value 16+ year olds February 2010, updated 2012 Objective: Understand the therapeutic value of stem cells About tissue stem cells Stem
Introducing stem cells Stem cells in the news Stem cells: Therapeutic Value 16+ year olds February 2010, updated 2012 Objective: Understand the therapeutic value of stem cells About tissue stem cells Stem
Human stem cell research: a novel technology that will benefit patients Information and Position Paper
 October 2003 Human stem cell research: a novel technology that will benefit patients Information and Position Paper EuropaBio, the European Association for Bio-industries, has 35 corporate members operating
October 2003 Human stem cell research: a novel technology that will benefit patients Information and Position Paper EuropaBio, the European Association for Bio-industries, has 35 corporate members operating
Debate Motion. This house proposes that the procurement and use of embryonic stem cells for scientific research is unethical. Stem Cell Research
 Stem Cell Research Debate Motion Stem Cell Research This house proposes that the procurement and use of embryonic stem cells for scientific research is unethical. The dominant view in the scientific community
Stem Cell Research Debate Motion Stem Cell Research This house proposes that the procurement and use of embryonic stem cells for scientific research is unethical. The dominant view in the scientific community
Stem Cells and Inner Ear Cell Regeneration. Stefan Heller Stanford University School of Medicine
 Stem Cells and Inner Ear Cell Regeneration Stefan Heller Stanford University School of Medicine Embryonic stem cells Induced pluripotent stem cells Somatic stem cells 50 µm Derived from the inner cell
Stem Cells and Inner Ear Cell Regeneration Stefan Heller Stanford University School of Medicine Embryonic stem cells Induced pluripotent stem cells Somatic stem cells 50 µm Derived from the inner cell
Stem cells and motor neurone disease
 Stem cells and motor neurone disease F Stem cell research has fuelled hope of a treatment for a variety of conditions. This information sheet explains what these cells are and how they may be used to create
Stem cells and motor neurone disease F Stem cell research has fuelled hope of a treatment for a variety of conditions. This information sheet explains what these cells are and how they may be used to create
PART I. SECTION 1. The legislature finds that an estimated. 128,000,000 Americans suffer from the crippling economic and
 HOUSE OF REPRESENTATIVES TWENTY-FOURTH LEGISLATURE, 2007 STATE OF HAWAII A BILL FOR AN ACT RELATING TO MEDICAL RESEARCH. BE IT ENACTED BY THE LEGISLATURE OF THE STATE OF HAWAII: PART I SECTION 1. The legislature
HOUSE OF REPRESENTATIVES TWENTY-FOURTH LEGISLATURE, 2007 STATE OF HAWAII A BILL FOR AN ACT RELATING TO MEDICAL RESEARCH. BE IT ENACTED BY THE LEGISLATURE OF THE STATE OF HAWAII: PART I SECTION 1. The legislature
STEM CELLS FROM THE UMBLICAL CORD BLOOD AND UMBLICAL CORD TISSUE
 STEM CELLS FROM THE UMBLICAL CORD BLOOD AND UMBLICAL CORD TISSUE What are Stem Cells? Stem cells are the basic building blocks of all the cells, tissues and organs in the human body. The role of the stem
STEM CELLS FROM THE UMBLICAL CORD BLOOD AND UMBLICAL CORD TISSUE What are Stem Cells? Stem cells are the basic building blocks of all the cells, tissues and organs in the human body. The role of the stem
Stem cell research ACADEMY STATEMENT. progress, hopes and concerns ACADEMY STATEMENT 16 JANUARY 2013
 ACADEMY STATEMENT 16 JANUARY 2013 ACADEMY STATEMENT Stem cell research progress, hopes and concerns KUNGL. VETENSKAPSAKADEMIEN, BOX 50005, SE-104 05 STOCKHOLM, SWEDEN TEL +46 8 673 95 00, FAX +46 8 15
ACADEMY STATEMENT 16 JANUARY 2013 ACADEMY STATEMENT Stem cell research progress, hopes and concerns KUNGL. VETENSKAPSAKADEMIEN, BOX 50005, SE-104 05 STOCKHOLM, SWEDEN TEL +46 8 673 95 00, FAX +46 8 15
your complete stem cell bank
 your complete stem cell bank HYDERABAD - 88985 000 888, WARANGAL - 8297 256 777 VISAKHAPATNAM - 7799 990 774 VIJAYAWADA AND GUNTUR - 7799 990 771 NELLORE - 7799 990 772, KADAPA - 8297 256 700 RAJAHMUNDRY
your complete stem cell bank HYDERABAD - 88985 000 888, WARANGAL - 8297 256 777 VISAKHAPATNAM - 7799 990 774 VIJAYAWADA AND GUNTUR - 7799 990 771 NELLORE - 7799 990 772, KADAPA - 8297 256 700 RAJAHMUNDRY
Stem Cell Research. Debate motion
 Stem Cell Research Debate motion This house proposes that the potential benefits of using embryonic stem cells to develop new medical treatments mean we have a moral obligation to support this type of
Stem Cell Research Debate motion This house proposes that the potential benefits of using embryonic stem cells to develop new medical treatments mean we have a moral obligation to support this type of
Differentiation = Making specialized cells. Your body needs stem cells. What is a stem cell?
 Differentiation = Making specialized cells What is a stem cell? What the photo shows A lump of metal and lots of different kinds of screws. Things to think about Lumps of metal that start off the same
Differentiation = Making specialized cells What is a stem cell? What the photo shows A lump of metal and lots of different kinds of screws. Things to think about Lumps of metal that start off the same
Chapter 16 Reproductive Technology, Gene Therapy, and Stem Cells (modified)
 Chapter 16 Reproductive Technology, Gene Therapy, and Stem Cells (modified) Assisted Reproductive Technologies (ART) Artificial insemination (AI) In vitro fertilization (IVF) Gamete intrafallopian transfer
Chapter 16 Reproductive Technology, Gene Therapy, and Stem Cells (modified) Assisted Reproductive Technologies (ART) Artificial insemination (AI) In vitro fertilization (IVF) Gamete intrafallopian transfer
Class Time: 30 minutes. Other activities in the Stem Cells in the Spotlight module can be found at: http://gslc.genetics.utah.edu/teachers/tindex/
 Teacher Guide: Color-Label-Learn: Creating Stem Cells for Research ACTIVITY OVERVIEW Abstract: Students color and label images on a worksheet and answer questions about the on-line content featured in
Teacher Guide: Color-Label-Learn: Creating Stem Cells for Research ACTIVITY OVERVIEW Abstract: Students color and label images on a worksheet and answer questions about the on-line content featured in
Stem Cell Information
 Stem Cell Information The official National Institutes of Health resource for stem cell research Stem Cell Basics Stem cells have the remarkable potential to develop into many different cell types in the
Stem Cell Information The official National Institutes of Health resource for stem cell research Stem Cell Basics Stem cells have the remarkable potential to develop into many different cell types in the
Briefing on the second reading of the Human Fertilisation and Embryology Bill, Monday 19 November 2007.
 Briefing on the second reading of the Human Fertilisation and Embryology Bill, Monday 19 November 2007. Prepared by the Medical Research Council, Royal Society and Wellcome Trust The Medical Research Council,
Briefing on the second reading of the Human Fertilisation and Embryology Bill, Monday 19 November 2007. Prepared by the Medical Research Council, Royal Society and Wellcome Trust The Medical Research Council,
STEM CELL FELLOWSHIP
 Module I: The Basic Principles of Stem Cells 1. Basics of Stem Cells a. Understanding the development of embryonic stem cells i. Embryonic stem cells ii. Embryonic germ cells iii. Differentiated stem cell
Module I: The Basic Principles of Stem Cells 1. Basics of Stem Cells a. Understanding the development of embryonic stem cells i. Embryonic stem cells ii. Embryonic germ cells iii. Differentiated stem cell
Stem Cells: Scientific Progress and Future Research Directions
 2001 Terese Winslow Stem Cells: Scientific Progress and Future Research Directions STEM CELLS: SCIENTIFIC PROGRESS AND FUTURE RESEARCH DIRECTIONS June 2001 This page intentionally left blank TABLE OF CONTENTS
2001 Terese Winslow Stem Cells: Scientific Progress and Future Research Directions STEM CELLS: SCIENTIFIC PROGRESS AND FUTURE RESEARCH DIRECTIONS June 2001 This page intentionally left blank TABLE OF CONTENTS
An Introduction to Stem Cells
 By Kirstin Matthews, Ph.D. An Introduction to Stem Cells Overview Stem cells are cells that have the potential to replicate themselves for indefinite periods and to divide, producing one of themselves
By Kirstin Matthews, Ph.D. An Introduction to Stem Cells Overview Stem cells are cells that have the potential to replicate themselves for indefinite periods and to divide, producing one of themselves
Stem cell research and Parkinson's
 Parkinson's research Stem cell research and Parkinson's T his information sheet looks at what stem cells are and why they are important for research into a cure for Parkinson s. It also discusses where
Parkinson's research Stem cell research and Parkinson's T his information sheet looks at what stem cells are and why they are important for research into a cure for Parkinson s. It also discusses where
Stem Cells for Life. (301) 654-7070 www.facialart.com
 Stem Cells for Life Dr. H. Ryan Kazemi Board Certified Oral & Maxillofacial Surgeon (301) 654-7070 www.facialart.com 4825 Bethesda Ave., #310 Bethesda, MD 20814 Researchers feel that stem cells could have
Stem Cells for Life Dr. H. Ryan Kazemi Board Certified Oral & Maxillofacial Surgeon (301) 654-7070 www.facialart.com 4825 Bethesda Ave., #310 Bethesda, MD 20814 Researchers feel that stem cells could have
San Diego Stem Cell Treatment Center Frequently Asked Questions
 San Diego Stem Cell Treatment Center Frequently Asked Questions What is a Stem Cell? A stem cell is basically any cell that can replicate and differentiate. This means the cell can not only multiply, but
San Diego Stem Cell Treatment Center Frequently Asked Questions What is a Stem Cell? A stem cell is basically any cell that can replicate and differentiate. This means the cell can not only multiply, but
Introducing stem cells
 Introducing stem cells 1 Dear speaker This presentation is intended as a flexible tool for scientists, science communicators and educators. Not all the slides will be useful for any one occasion. Choose
Introducing stem cells 1 Dear speaker This presentation is intended as a flexible tool for scientists, science communicators and educators. Not all the slides will be useful for any one occasion. Choose
Chapter 2 The different types of stem cells
 Chapter 2 The different types of stem cells This chapter investigates the two main types of stem cells, each with their own subcategories: 1. Pluripotent stem cells can become any cell type in the body.
Chapter 2 The different types of stem cells This chapter investigates the two main types of stem cells, each with their own subcategories: 1. Pluripotent stem cells can become any cell type in the body.
An Introduction to Stem Cell Biology. Michael L. Shelanski, MD,PhD Professor of Pathology and Cell Biology Columbia University
 An Introduction to Stem Cell Biology Michael L. Shelanski, MD,PhD Professor of Pathology and Cell Biology Columbia University Figures adapted from ISSCR. Presentations of Drs. Martin Pera (Monash University),
An Introduction to Stem Cell Biology Michael L. Shelanski, MD,PhD Professor of Pathology and Cell Biology Columbia University Figures adapted from ISSCR. Presentations of Drs. Martin Pera (Monash University),
Patient Handbook on Stem Cell Therapies
 Patient Handbook on Stem Cell Therapies Appendix I of the Guidelines for the Clinical Translation of Stem Cells www.isscr.org 2008, International Society for Stem Cell Research 2 Introduction We have all
Patient Handbook on Stem Cell Therapies Appendix I of the Guidelines for the Clinical Translation of Stem Cells www.isscr.org 2008, International Society for Stem Cell Research 2 Introduction We have all
The ethics of stem cell research and treatment
 The ethics of stem cell research and treatment Bernard Lo, M.D. March 12, 2009 1 hesc: ethical controversies Moral status of embryo? Clearly a potential person Some believe a person with rights Is hesc
The ethics of stem cell research and treatment Bernard Lo, M.D. March 12, 2009 1 hesc: ethical controversies Moral status of embryo? Clearly a potential person Some believe a person with rights Is hesc
47/CNECV/05 STEM CELL RESEARCH
 CONSELHO NACIONAL DE ÉTICA PARA AS CIÊNCIAS DA VIDA NATIONAL COUNCIL OF ETHICS FOR THE LIFE SCIENCES 47/CNECV/05 OPINION Nº 47 OF THE NATIONAL COUNCIL OF ETHICS FOR THE LIFE SCIENCES STEM CELL RESEARCH
CONSELHO NACIONAL DE ÉTICA PARA AS CIÊNCIAS DA VIDA NATIONAL COUNCIL OF ETHICS FOR THE LIFE SCIENCES 47/CNECV/05 OPINION Nº 47 OF THE NATIONAL COUNCIL OF ETHICS FOR THE LIFE SCIENCES STEM CELL RESEARCH
Genetics, Ethics &Meaning. Module 4
 Genetics, Ethics &Meaning INItiative (GEMINI) Life Sciences and Society @University of Michigan Module 4 Myths versus Facts The University of Michigan s Stem Cell Research Environment A Case Study MYTH:
Genetics, Ethics &Meaning INItiative (GEMINI) Life Sciences and Society @University of Michigan Module 4 Myths versus Facts The University of Michigan s Stem Cell Research Environment A Case Study MYTH:
Roche Position on Human Stem Cells
 Roche Position on Human Stem Cells Background Stem cells and treating diseases. Stem cells and their applications offer an enormous potential for the treatment and even the cure of diseases, along with
Roche Position on Human Stem Cells Background Stem cells and treating diseases. Stem cells and their applications offer an enormous potential for the treatment and even the cure of diseases, along with
Stem Cells. What Are Stem Cells? Sources for Stem Cells. Stem cells. Medical Ethics 1. Cells able to develop into nearly any other type of cell.
 Stem Cells What Are Stem Cells? Cells able to develop into nearly any other type of cell. Adult stem cells found in skin, gut, blood Embryonic stem cells found in very early development of embryo (when
Stem Cells What Are Stem Cells? Cells able to develop into nearly any other type of cell. Adult stem cells found in skin, gut, blood Embryonic stem cells found in very early development of embryo (when
CONSENT FORM TEMPLATE. Derivation and Distribution of Induced Pluripotent Stem (ips) Cell Lines Created from Donor Specimens
 CONSENT FORM TEMPLATE Derivation and Distribution of Induced Pluripotent Stem (ips) Cell Lines Created from Donor Specimens INTRODUCTION We invite you to take part in a research study at [name of research
CONSENT FORM TEMPLATE Derivation and Distribution of Induced Pluripotent Stem (ips) Cell Lines Created from Donor Specimens INTRODUCTION We invite you to take part in a research study at [name of research
5 Frequently Asked Questions About Adult Stem Cell Research
 5 Frequently Asked Questions About Adult Stem Cell Research Stem cells are often referred to in the sociopolitical realm with some level of controversy and beyond that, some level of confusion. Many researchers
5 Frequently Asked Questions About Adult Stem Cell Research Stem cells are often referred to in the sociopolitical realm with some level of controversy and beyond that, some level of confusion. Many researchers
Top Ten Things to Know About Stem Cell Treatments
 Top Ten Things to Know About Stem Cell Treatments Many clinics that are offering stem cell treatments make claims about what stem cells can and cannot do that are not supported by our understanding of
Top Ten Things to Know About Stem Cell Treatments Many clinics that are offering stem cell treatments make claims about what stem cells can and cannot do that are not supported by our understanding of
It s not something you want to think about, but it s something you want to prepare for.
 It s not something you want to think about, but it s something you want to prepare for. StemCyte cord blood banking offers your family a new lifesaving treatment alternative Why Bank Take the once-in-alifetime
It s not something you want to think about, but it s something you want to prepare for. StemCyte cord blood banking offers your family a new lifesaving treatment alternative Why Bank Take the once-in-alifetime
Expert Advice on Stem Cells (for Beginners)...
 Expert Advice on Stem Cells (for Beginners)... Thanks to http://www.explorestemcells.co.uk/ Contents Why are Stem Cells Important?... 3 Adult vs. Embryonic Stem Cells... 4 Stem Cell Controversy... 5 Religion
Expert Advice on Stem Cells (for Beginners)... Thanks to http://www.explorestemcells.co.uk/ Contents Why are Stem Cells Important?... 3 Adult vs. Embryonic Stem Cells... 4 Stem Cell Controversy... 5 Religion
Testimony of. Before The Subcommittee on Labor, Health and Human Services and Education of the Committee on Appropriations United States Senate
 Testimony of James F. Childress, Ph.D. Commissioner, National Bioethics Advisory Commission and Kyle Professor of Religious Studies Professor of Medical Education University of Virginia Charlottesville,
Testimony of James F. Childress, Ph.D. Commissioner, National Bioethics Advisory Commission and Kyle Professor of Religious Studies Professor of Medical Education University of Virginia Charlottesville,
Running head: STEM CELL RESEARCH 1
 Running head: STEM CELL RESEARCH 1 NOTE: This paper is an actual senior project paper that scored highproficient or advanced in the spring of 2010. It is not a perfect paper, but it does represent high
Running head: STEM CELL RESEARCH 1 NOTE: This paper is an actual senior project paper that scored highproficient or advanced in the spring of 2010. It is not a perfect paper, but it does represent high
National Academy of Sciences National Academy of Engineering Institute of Medicine National Research Council
 National Academy of Sciences National Academy of Engineering Institute of Medicine National Research Council IN THIS BOOKLET... WHAT IS A STEM CELL? 3 TYPES OF STEM CELLS 4 WORKING WITH STEM CELLS 9 WHY
National Academy of Sciences National Academy of Engineering Institute of Medicine National Research Council IN THIS BOOKLET... WHAT IS A STEM CELL? 3 TYPES OF STEM CELLS 4 WORKING WITH STEM CELLS 9 WHY
Policy statement. Stem cell research
 Policy statement Stem cell research Introduction For some people who survive a heart attack, the damage to their heart muscle can lead to debilitating heart failure, for which there is no cure. Nearly
Policy statement Stem cell research Introduction For some people who survive a heart attack, the damage to their heart muscle can lead to debilitating heart failure, for which there is no cure. Nearly
Cloning and the Church's Position on Stem Cells
 Stem Cell Research & Human Cloning Topics for Discussion Clarify the scientific and moral definition of cloning Discuss the facts about stem cells, therapies, and cures Learn the truth about the Church
Stem Cell Research & Human Cloning Topics for Discussion Clarify the scientific and moral definition of cloning Discuss the facts about stem cells, therapies, and cures Learn the truth about the Church
Marc Welc. Y1 Writes: A Collection of Student Essays 270
 Y1 Writes: A Collection of Student Essays 270 Marc Welc Marc Welc graduated from Hiawatha High School, where he was actively involved in basketball, student council, National Honors Society, yearbook,
Y1 Writes: A Collection of Student Essays 270 Marc Welc Marc Welc graduated from Hiawatha High School, where he was actively involved in basketball, student council, National Honors Society, yearbook,
4. All cord blood banks should be subject to the same standards, regulations and accreditation requirements.
 WMDA Policy Statement on the Utility of Autologous or Family Cord Blood Unit Storage The WMDA Board adopted this policy on 25 th of May 2006. Policy updated _April 2011 The Cord Blood Working Group and
WMDA Policy Statement on the Utility of Autologous or Family Cord Blood Unit Storage The WMDA Board adopted this policy on 25 th of May 2006. Policy updated _April 2011 The Cord Blood Working Group and
Stem cells will change medicine as we know it. Are you ready? STEM CELL BANKING
 Stem cells will change medicine as we know it. Are you ready? STEM CELL BANKING Stem cell banking with Store-A-Tooth is a unique investment in the health of your family. WHY BANK STEM CELLS? YOU PLAN FOR
Stem cells will change medicine as we know it. Are you ready? STEM CELL BANKING Stem cell banking with Store-A-Tooth is a unique investment in the health of your family. WHY BANK STEM CELLS? YOU PLAN FOR
Background Information
 Background Information 1. What are stem cells? 2. What might stem cell research achieve? 3. Why we need to continue research using embryonic stem cells? 4. Time taken for discoveries 5. Examples of stem
Background Information 1. What are stem cells? 2. What might stem cell research achieve? 3. Why we need to continue research using embryonic stem cells? 4. Time taken for discoveries 5. Examples of stem
 CAMBRIDGE UNIVERSITY CENTRE FOR BRAIN REPAIR A layman's account of our scientific objectives What is Brain Damage? Many forms of trauma and disease affect the nervous system to produce permanent neurological
CAMBRIDGE UNIVERSITY CENTRE FOR BRAIN REPAIR A layman's account of our scientific objectives What is Brain Damage? Many forms of trauma and disease affect the nervous system to produce permanent neurological
Support structure for genetic material
 Support structure for genetic material 1 Making proteins in the RER Making copies of humans 2 Making copies of cells Making copies of genetic material 3 Making copies of genetic material Making copies
Support structure for genetic material 1 Making proteins in the RER Making copies of humans 2 Making copies of cells Making copies of genetic material 3 Making copies of genetic material Making copies
Stem Cell Therapy. Treat your pain, improve your lifestyle and look after your wellbeing. What are stem cells?
 (02) 9824 3044 LIVERPOOL NSW 2170 Stem Cell Therapy Treat your pain, improve your lifestyle and look after your wellbeing What are stem cells? Stem cells are cells that can differentiate into other types
(02) 9824 3044 LIVERPOOL NSW 2170 Stem Cell Therapy Treat your pain, improve your lifestyle and look after your wellbeing What are stem cells? Stem cells are cells that can differentiate into other types
How To Support Umbilical Cord Blood Stem Cell Research
 Cauley O. Gieb Advanced Health Law HLP Article Umbilical Cord Blood Stem Cell Research: The Proof is in the Cord Today advances in science seem to gain the most recognition and support when the subject
Cauley O. Gieb Advanced Health Law HLP Article Umbilical Cord Blood Stem Cell Research: The Proof is in the Cord Today advances in science seem to gain the most recognition and support when the subject
DNA Fingerprinting. Unless they are identical twins, individuals have unique DNA
 DNA Fingerprinting Unless they are identical twins, individuals have unique DNA DNA fingerprinting The name used for the unambiguous identifying technique that takes advantage of differences in DNA sequence
DNA Fingerprinting Unless they are identical twins, individuals have unique DNA DNA fingerprinting The name used for the unambiguous identifying technique that takes advantage of differences in DNA sequence
5. All cord blood banks should be subject to the same standards, regulations and accreditation requirements.
 WMDA Policy Statement for the Utility of Autologous or Family Cord Blood Unit Storage (This policy statement has been approved and adopted by the WMDA board on the 25 th of May 2006) The Cord Blood Registries
WMDA Policy Statement for the Utility of Autologous or Family Cord Blood Unit Storage (This policy statement has been approved and adopted by the WMDA board on the 25 th of May 2006) The Cord Blood Registries
New Issues in Stem cells and Regenerative Medicine
 New Issues in Stem cells and Regenerative Medicine Bioethics and Biological Sciences Working Group Conference of European Churches Church and Society Commission 8, rue du Fossé des Treize, FR - 67000 Strasbourg,
New Issues in Stem cells and Regenerative Medicine Bioethics and Biological Sciences Working Group Conference of European Churches Church and Society Commission 8, rue du Fossé des Treize, FR - 67000 Strasbourg,
the future in your hands imagine
 the future in your hands imagine The promise of hope Carrie and Wilf s story... Quinn weighed in at a healthy 4397g at birth. His parents, Carrie and Wilf, had decided to store the umbilical cord blood
the future in your hands imagine The promise of hope Carrie and Wilf s story... Quinn weighed in at a healthy 4397g at birth. His parents, Carrie and Wilf, had decided to store the umbilical cord blood
Rationale: Revisions enhanced current content by shortening it through deletions of language
 Total Number of Pages: 1 of 4 Rationale: Revisions enhanced current content by shortening it through deletions of language that occurs in other resolutions, such as 3182 Human Cloning. Amend Delete last
Total Number of Pages: 1 of 4 Rationale: Revisions enhanced current content by shortening it through deletions of language that occurs in other resolutions, such as 3182 Human Cloning. Amend Delete last
I. The Basic Science and Current Context
 I. The Basic Science and Current Context Stem cells, or "master cells," are cells in the human body that have not yet differentiated into a particular type of tissue. As such, they seem to have the potential
I. The Basic Science and Current Context Stem cells, or "master cells," are cells in the human body that have not yet differentiated into a particular type of tissue. As such, they seem to have the potential
CURRENT STATUS OF STEM CELL TREATMENTS FOR CEREBRAL PALSY: A GUIDE FOR PATIENTS, FAMILIES AND CAREGIVERS
 SPRING, 2011 CURRENT STATUS OF STEM CELL TREATMENTS FOR CEREBRAL PALSY: A GUIDE FOR PATIENTS, FAMILIES AND CAREGIVERS *Crystal Ruff, *Jared Wilcox, Michael G. Fehlings Krembil Neuroscience Centre, Toronto
SPRING, 2011 CURRENT STATUS OF STEM CELL TREATMENTS FOR CEREBRAL PALSY: A GUIDE FOR PATIENTS, FAMILIES AND CAREGIVERS *Crystal Ruff, *Jared Wilcox, Michael G. Fehlings Krembil Neuroscience Centre, Toronto
Assignment Discovery Online Curriculum
 Assignment Discovery Online Curriculum Lesson title: In Vitro Fertilization Grade level: 9-12, with adaptation for younger students Subject area: Life Science Duration: Two class periods Objectives: Students
Assignment Discovery Online Curriculum Lesson title: In Vitro Fertilization Grade level: 9-12, with adaptation for younger students Subject area: Life Science Duration: Two class periods Objectives: Students
The Controversy Over Stem Cell Research
 The Controversy Over Stem Cell Research Ray Bohlin What Are Stem Cells and Why Are They Important? President Bush recently decided to allow the use of federal funds to research the therapeutic properties
The Controversy Over Stem Cell Research Ray Bohlin What Are Stem Cells and Why Are They Important? President Bush recently decided to allow the use of federal funds to research the therapeutic properties
International Policies on Stem Cell Research
 International Policies on Stem Cell Research Prof. Reza Nassiri Director, Institute of International Health Associate Dean of Global Health Programs College of Osteopathic Medicine Michigan State University
International Policies on Stem Cell Research Prof. Reza Nassiri Director, Institute of International Health Associate Dean of Global Health Programs College of Osteopathic Medicine Michigan State University
Religious Attitudes to Matters of Life
 Religious Attitudes to Matters of Life Sanctity of Life Life is a sacred God-given gift. It is only for God to decide when it starts and ends. It is extremely precious and should be treated with the utmost
Religious Attitudes to Matters of Life Sanctity of Life Life is a sacred God-given gift. It is only for God to decide when it starts and ends. It is extremely precious and should be treated with the utmost
Research: Stem Cells. What are Stem Cells?
 What are Stem Cells? Have you ever thought about where you come from? How you were made? How did you grow from two tiny cells from your mother and father into a human mass of cells all performing independent
What are Stem Cells? Have you ever thought about where you come from? How you were made? How did you grow from two tiny cells from your mother and father into a human mass of cells all performing independent
AP BIOLOGY 2012 SCORING GUIDELINES
 AP BIOLOGY 2012 SCORING GUIDELINES Question 1 Note: At least 1 point must be earned from each of parts (a), (b), (c), and (d) in order to earn a maximum score of 10. The ability to reproduce is a characteristic
AP BIOLOGY 2012 SCORING GUIDELINES Question 1 Note: At least 1 point must be earned from each of parts (a), (b), (c), and (d) in order to earn a maximum score of 10. The ability to reproduce is a characteristic
34 Stem Cell Research and Applications: Monitoring the Frontiers of Biomedical Research
 34 Stem Cell Research and Applications: Monitoring the Frontiers of Biomedical Research Audrey R. Chapman, Mark S. Frankel and Michele S. Garfinkel In the face of extraordinary advances in the prevention,
34 Stem Cell Research and Applications: Monitoring the Frontiers of Biomedical Research Audrey R. Chapman, Mark S. Frankel and Michele S. Garfinkel In the face of extraordinary advances in the prevention,
RESEARCH PAPER BASED ON PATHOLOGY LECTURES AT MEDLINK 2014
 THE DEVELOPMENT OF STEM CELL RESEARCH AND TREATMENTS WITHIN MEDICINE BY JENNA BUXTON Grade awarded: Pass with Merit RESEARCH PAPER BASED ON PATHOLOGY LECTURES AT MEDLINK 2014 ABSTRACT This paper discusses
THE DEVELOPMENT OF STEM CELL RESEARCH AND TREATMENTS WITHIN MEDICINE BY JENNA BUXTON Grade awarded: Pass with Merit RESEARCH PAPER BASED ON PATHOLOGY LECTURES AT MEDLINK 2014 ABSTRACT This paper discusses
CORD BLOOD BANKING FAQ
 CORD BLOOD BANKING FAQ Cord Blood & Stem Cells Q: What is umbilical cord blood (UCB)? A: Bone marrow, peripheral blood and UCB constitute the three primary sources of stem cells. Cord blood, which, until
CORD BLOOD BANKING FAQ Cord Blood & Stem Cells Q: What is umbilical cord blood (UCB)? A: Bone marrow, peripheral blood and UCB constitute the three primary sources of stem cells. Cord blood, which, until
Please visit this site for the current GESCR procedures info: http://www.research.ucsf.edu/chr/stemcell/scprocedures.asp
 GESCR PROCEDURES: REVIEW PROCESS AND LEVELS OF REVIEW Office of Origin: Human Research Protection Program Effective Date: January 2012 I. Introduction The Human Gamete, Embryo and Stem Cell Research (GESCR)
GESCR PROCEDURES: REVIEW PROCESS AND LEVELS OF REVIEW Office of Origin: Human Research Protection Program Effective Date: January 2012 I. Introduction The Human Gamete, Embryo and Stem Cell Research (GESCR)
An Overview of Cells and Cell Research
 An Overview of Cells and Cell Research 1 An Overview of Cells and Cell Research Chapter Outline Model Species and Cell types Cell components Tools of Cell Biology Model Species E. Coli: simplest organism
An Overview of Cells and Cell Research 1 An Overview of Cells and Cell Research Chapter Outline Model Species and Cell types Cell components Tools of Cell Biology Model Species E. Coli: simplest organism
Biotechnology. Srivatsan Kidambi, Ph.D.
 Stem Stem Cell Cell Engineering-What, Biology and it Application Why, How?? to Biotechnology Srivatsan Kidambi, Ph.D. Assistant Professor Department of Chemical & Biomolecular Engineering University of
Stem Stem Cell Cell Engineering-What, Biology and it Application Why, How?? to Biotechnology Srivatsan Kidambi, Ph.D. Assistant Professor Department of Chemical & Biomolecular Engineering University of
Saving Cord Tissue for Your Family
 Saving Cord Tissue for Your Family Dear Future Mom and/or Dad, All of us at CorCell would like to give you a big CONGRATULATIONS on your pregnancy! Now that you are expecting, you have probably heard about
Saving Cord Tissue for Your Family Dear Future Mom and/or Dad, All of us at CorCell would like to give you a big CONGRATULATIONS on your pregnancy! Now that you are expecting, you have probably heard about
COLUMBIA UNIVERSITY POLICY ON THE CONDUCT OF RESEARCH WITH HUMAN EMBRYOS AND HUMAN EMBRYONIC STEM CELLS*
 July 7, 2014 COLUMBIA UNIVERSITY POLICY ON THE CONDUCT OF RESEARCH WITH HUMAN EMBRYOS AND HUMAN EMBRYONIC STEM CELLS* A. INTRODUCTION Columbia University believes that human embryonic and human stem cell
July 7, 2014 COLUMBIA UNIVERSITY POLICY ON THE CONDUCT OF RESEARCH WITH HUMAN EMBRYOS AND HUMAN EMBRYONIC STEM CELLS* A. INTRODUCTION Columbia University believes that human embryonic and human stem cell
Vita 34 Parents Guide to umbilical Cord Blood Banking. secure first-class innovative
 Vita 34 Parents Guide to umbilical Cord Blood Banking secure first-class innovative Contents INTRODUCTION 3 THERAPEUTIC USES OF STEM CELLS 4 STEM CELLS IN CANCER TREATMENT STEM CELLS IN THE TREATMENT OF
Vita 34 Parents Guide to umbilical Cord Blood Banking secure first-class innovative Contents INTRODUCTION 3 THERAPEUTIC USES OF STEM CELLS 4 STEM CELLS IN CANCER TREATMENT STEM CELLS IN THE TREATMENT OF
Introduction. Materials
 Lesson 2 Techniques for Obtaining Stem Cells Objectives Students will be able to: Describe scientific techniques (IVF, therapeutic cloning, using cord blood and bone marrow, inducing pluripotent stem cells)
Lesson 2 Techniques for Obtaining Stem Cells Objectives Students will be able to: Describe scientific techniques (IVF, therapeutic cloning, using cord blood and bone marrow, inducing pluripotent stem cells)
Muscular Dystrophy: Stem Cell Therapy
 by Caitlin Pederson Abstract: Genetic disorders affect many people, and muscular dystrophy is a disorder that can greatly decrease the quality of life. Finding treatment to stop or prevent the loss of
by Caitlin Pederson Abstract: Genetic disorders affect many people, and muscular dystrophy is a disorder that can greatly decrease the quality of life. Finding treatment to stop or prevent the loss of
56 MaxPlanckForschung 3 09
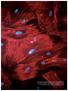 56 MaxPlanckForschung 3 09 One factor is enough for neural stem cells to become pluripotent. They can then be differentiated into smooth muscular cells that are found, for example, in blood and lymph vessels.
56 MaxPlanckForschung 3 09 One factor is enough for neural stem cells to become pluripotent. They can then be differentiated into smooth muscular cells that are found, for example, in blood and lymph vessels.
Donating Life. The Workplace Partnership for Life Program
 The Workplace Partnership for Life Program Every day about 63 people receive an organ transplant, but another 16 people on the waiting list die because not enough organs are available. Approximately 80,000
The Workplace Partnership for Life Program Every day about 63 people receive an organ transplant, but another 16 people on the waiting list die because not enough organs are available. Approximately 80,000
Embryonic Choices. Scientist Toolkit for Public Engagement: Clinical Embryology, Genetics and Haematology
 Embryonic Choices An A-level workshop on Assisted Conception and Saviour Siblings Scientist Toolkit for Public Engagement: Clinical Embryology, Genetics and Haematology Pathology: the science behind the
Embryonic Choices An A-level workshop on Assisted Conception and Saviour Siblings Scientist Toolkit for Public Engagement: Clinical Embryology, Genetics and Haematology Pathology: the science behind the
Save up to 25% off stem cell banking with Netcells Biosciences
 Save up to 25% off stem cell banking with Netcells Biosciences In a unique offering, we have been able to arrange an exclusive offer for medical scheme members with Netcells Biosciences Africa s leading
Save up to 25% off stem cell banking with Netcells Biosciences In a unique offering, we have been able to arrange an exclusive offer for medical scheme members with Netcells Biosciences Africa s leading
The Ethics of Stem Cell Research and Prenatal Genetic Alteration
 The Ethics of Stem Cell Research and Prenatal Genetic Alteration Blake Rodgers, Brandon Peterson Introduction Technological advancements associated with the medical industry create opportunities to conduct
The Ethics of Stem Cell Research and Prenatal Genetic Alteration Blake Rodgers, Brandon Peterson Introduction Technological advancements associated with the medical industry create opportunities to conduct
One of the most important recent developments in cancer treatment has been the ability to harvest stem
 BIOTECHNOLOGY A Patient-Friendly Approach to Human Cell Transplantation One of the most important recent developments in cancer treatment has been the ability to harvest stem cells from bone marrow or
BIOTECHNOLOGY A Patient-Friendly Approach to Human Cell Transplantation One of the most important recent developments in cancer treatment has been the ability to harvest stem cells from bone marrow or
ADULT STEM CELLS: THE ONLY ONES THAT REALLY HELP
 1 ADULT STEM CELLS: THE ONLY ONES THAT REALLY HELP Almost every time we pick up the paper, there is an article on stem cells. It can be very confusing. Here are some simple definitions that can help. Stem
1 ADULT STEM CELLS: THE ONLY ONES THAT REALLY HELP Almost every time we pick up the paper, there is an article on stem cells. It can be very confusing. Here are some simple definitions that can help. Stem
Information for Egg Donors for Research
 Newcastle Fertility Centre at BioScience Centre, International Centre for Life Times Square, Newcastle upon Tyne, NE1 4EP Telephone: 0191 2138213 Fax: 0191 2138124 www.nfc-life.org.uk Information for Egg
Newcastle Fertility Centre at BioScience Centre, International Centre for Life Times Square, Newcastle upon Tyne, NE1 4EP Telephone: 0191 2138213 Fax: 0191 2138124 www.nfc-life.org.uk Information for Egg
THE ETHICAL AND PRACTICAL IMPLICATIONS OF THE USE OF EMBRYONIC STEM CELLS IN MAINSTREAM MEDICINE JAMES AKERS. Grade awarded: Pass with Merit
 THE ETHICAL AND PRACTICAL IMPLICATIONS OF THE USE OF EMBRYONIC STEM CELLS IN MAINSTREAM MEDICINE BY JAMES AKERS Grade awarded: Pass with Merit ABSTRACT RESEARCH PAPER BASED ON PATHOLOGY LECTURES AT MEDLINK
THE ETHICAL AND PRACTICAL IMPLICATIONS OF THE USE OF EMBRYONIC STEM CELLS IN MAINSTREAM MEDICINE BY JAMES AKERS Grade awarded: Pass with Merit ABSTRACT RESEARCH PAPER BASED ON PATHOLOGY LECTURES AT MEDLINK
Reproductive System & Development: Practice Questions #1
 Reproductive System & Development: Practice Questions #1 1. Which two glands in the diagram produce gametes? A. glands A and B B. glands B and E C. glands C and F D. glands E and F 2. Base your answer
Reproductive System & Development: Practice Questions #1 1. Which two glands in the diagram produce gametes? A. glands A and B B. glands B and E C. glands C and F D. glands E and F 2. Base your answer
