New Acid Etched Titanium Dental Implant Surface
|
|
|
- Martin Davis
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Stomatologija, Baltic Dental and Maxillofacial Journal, 5: , 2003 New Acid Etched Titanium Dental Implant Surface Gintaras Juodzbalys, Marija Sapragoniene, Ann Wennerberg SUMMARY The purpose of this investigation was to create an acid etched implant surface that results in a surface similar to that gained by using sandblasting combined with acid etching and to compare it with surfaces of commercially available screw-type implants. Titanium grade V discs were machined in preparation for acid etching. Tests were carried out using different acids and their combinations with variable time exposures. All etched surfaces were scanned with electron microscope (JEOL JSM-5600, Japan) and digital images were made for visual evaluation and description of the surfaces. The etched surfaces were evaluated for surface morphology (combination of micro roughness and waviness) and were best attained by a combination of sulphuric and hydrochloric acids. The etched titanium discs were fixed in resin (two were cut and polished and two scored and fractured) and the surface profile was examined in. The second part of the investigation used screw-shaped titanium implants. Twenty-eight screwshaped implants that were manufactured from commercially available titanium grade V, were selected and divided into two groups: 3 implants as controls (machined surface) and 25 implants processed using the etching methods used in the first part of the investigation. Magnifications of 27, 200 and 2000 were used to analyse the first two consecutive crests of threads, flanks and root of threads of each implant with the treated surface. A three-dimensional optical interferometer (Micro- Xam, Phase-Shift, USA) was used to characterize the surface roughness of both control and test groups. Three screws were selected from each group and measured at 9 sites: 3 measurements each on the crest, root and flank of the threads. To describe the surface roughness in numbers, the following parameters were used: the average height deviation (Sa), the developed interfacial area ratio (Sdr), the fastest decay autocorrelation length (Sal) and the density of summits (Sds). Surfaces of 5 commercially available screw-type implants and the experimental ones were comparatively analyzed. It was concluded that the new experimental etched titanium surface had features of a roughened titanium surface with glossily micro-roughness and large waviness. In general, the experimental surface was significantly rougher than the selected commercially available implants and similar to SLA treated surface (top Sa 2,08µm (SD 0,36); Sdr 1,34µm (SD 0,3); valley 1,16µm (SD 0,1) and 0,68µm (SD 0,1); flank 2,24µm (SD 0,8) and 1,27µm (SD 0,1) respectively). Key words: commercial titanium, titanium dental implants, endosseous integration, surface texture, acid etching. INTRODUCTION Brånemark et al. (1) started the new era of implantology when they published the findings about titanium dental implants in Since then this method still remains popular and reliable, with only shape and surface of the titanium implants having changed. Excellent titanium biocompatibility assures good tissue integration (2, 3). Baier et al. (4) discussed what features play the most significant role in early acceptance and immobilization of the implant in the tissue bed. Texture, charge and chemistry of the surface as well as cleanliness were considered to be the most important requirements for the implant material (5). Predecki et al (6) observed rapid bone growth and good mechanical adherence with an implant that had an irregular surface. Bowers et al. (7) Gintaras Juodzbalys - D.D.S., PhD, assoc. prof., Clinic of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Kaunas Medical University, Lithuania. Marija Sapragoniene PhD, assoc.prof., Department of Analytic and Toxicologic Chemistry, Kaunas Medical University, Lithuania. Ann Wennerberg - PhD, assoc.prof., Department of Biomaterials, Handicap Research and Department of Prosthetic Dentistry, Dental Material Science, Goteborg University, Sweden. Address correspondence to Gintaras Juodzbalys: Clinic of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Eiveniu 2, Kaunas, Lithuania. confirmed these findings in a histological study. Many researchers have been working during the last decade on the development of new surface textures in order to improve initial implant stability and bone healing (8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14). Characteristics of titanium implant surfaces have been modified by additive methods (e.g. titanium plasma spray) to increase the surface area and provide a more complex surface macro-topography. Subtractive methods (e.g. blasting, acid etching) have also been used to increase the surface area and to alter its micro-topography or texture (15). Buser et al. (16) analyzed the percentage of direct boneimplant contact for different surface modifications: sandblasted, hydroxyapatite, titanium plasma-sprayed and acid etched. The highest percentage of bone-implant contact was recorded with the sandblasted surface treated by acid etching (hydrochloric and sulphuric acids). Acid etching of titanium is of particular interest because it creates a microtextured surface (fine rough surface with micro pits of 1-3µm and larger pits of approximately 6-10µm) that appears to enhance early endosseous integration and stability of the implant (17). This may be related to a change in surface roughness and/or chemical composition (13). It has also been shown in rabbits that implants with macro-textured surface (significant waviness with large elements of 10-30µm Stomatologija, Baltic Dental and Maxillofacial Journal, 2003, Vol. 5., N
2 G.Juodzbalys, M.Sapragoniene, A.Wennerberg and peaks of different size) ensured better endosseous integration (15). A sandblasted and acid etched surface (SLA) provides both a microroughness and waviness that seems to enhance bone contact with the implant surface. The titanium surface was first sandblasted with large particles creating a grossly rough surface followed by acid etching, forming a micro rough surface (18). The purpose of this investigation was to create implant surface using acid etching only, which would result in a surface similar to that gained by using sandblasting combined with acid etching. The experimental surface would then be compared with surfaces of commercially available screw-type implants. MATERIAL AND METHODS Acid etching procedure Titanium grade V discs (8mm in diameter and 2mm in height) were machined in preparation for acid etching. All discs were etched using pure acids or in combination (Table 1). A series of etching processes were performed changing the exposure duration and acid combination. Exposure times were as follows: 12 hours initial exposure followed by 6 h increments until 72h of exposure was reached. The titanium discs were etched with 4 different pure acids or their combination at 11 different exposure times at +20 o C, thus forming 44 experimental groups with 5 samples in each group for a total of 220 discs. Topographical evaluation of the titanium discs All surfaces were scanned with scanning electron microscope (SEM) (JEOL JSM-5600, Japan) using 27, 200 and 2000 magnification and digital images were made for visual examination of the surfaces. The machined implant surfaces were first characterized using the SEM. The surfaces were oriented in the direction of the machine grooves and the surface was rated on the degree of etching. Surface orientation was unidirectional where the machining grooves were still present. When the machining grooves could not be distinguished, the surface was characterized as complex one. Another important indicator was regularity of etching. If the surface was etched unequally and had intact areas, it was characterized as irregular surface. Equally etched surface was characterized as regular or uniformly etched surface. Digital photos were evaluated on the principle that darker spots represented pits and lighter ones peaks. Pits were measured in diameter without estimating their depth. Micro pits of 1-3µm and bigger elements of approximately 6-10µm formed the microtexture of the surface. Microtexture characterized the roughness of titanium surface while macrotexture consisted of large elements of 10-30µm it s and was characterized as waviness. From these results, the etching method that achieved a surface most similar to a SLA surface was selected as the most acceptable. The profile of the selected surface was additionally evaluated visually. Prepared titanium discs were fixed in resin. Two were cut and polished and two scored and fractured without polishing and a detailed examination of the surface profile was performed. Both profiles appeared to have significant roughness. Table 1. Application of different pure acids / their combination in the test groups. Group Acids I HCl II HCl and H 2 III H 2 /HCl and H 3 PO 4 IV H 2 and HCl Screw shaped titanium implants Thereafter we investigated the screw-shaped titanium implants. Twenty-eight screw-shaped implants with 4 threads were manufactured from commercially available titanium grade V (3,5mm in diameter and 6mm in length). Three of them were chosen as control (machined surface) and 25 implants were etched using the method, which was created by the authors on the titanium discs. Five series of surface etching process were performed on 5 implants in each series. Exposition and temperature of etching process were controlled for creation of new standardized implant surface. Topographical evaluation of the screw shaped titanium implants Implants were ultrasonically cleaned prior to examination. Implants with the experimental surface were examined with electron microscope (JEOL JSM-5600, Japan) using 27, 200 and 2000 magnification and digital images were made for visual evaluation according to the previously stated principles. The first two consecutive crest of threads, flanks and roots of threads of each implant were analyzed. A three-dimensional optical interferometer Micro-Xam, Phase-Shift, USA was used to characterize the surface roughness of both control and test group implants. The surfaces of three implants were analyzed topographically according to the method proposed by Wennerberg (19). Three screws were selected from each group and each screw was measured at 9 sites: 3 times on the thread crest, root and flank. Each measured area was 200X200µm. Gaussian filter of 50X50µm size was used to distinguish between roughness and form or undulations in accordance of the requirements of the standard (SS-ISO 11562:1996). To describe the surface roughness in numbers, the following parameters were used: the average height deviation (Sa), the developed interfacial area ratio (Sdr), the fastest decay autocorrelation length (Sal) and the density of summits (Sds). Statistics Statistical analyses were performed using the SPSS/ PC+ version program (SPSS Inc., Chicago, Illinois, USA). Standard deviations of the means were calculated. RESULTS Topographical evaluation of the titanium discs The test titanium discs were examined visually is described as follows: The control group (machined surface) had regular unidirectional grooves with some irregular shallow roughness (Fig.1a); Group I (etched with HCl) had a microtexture that was poor without evidence of micropits (Fig.1b); Group II (etched with HCl and H2SO4) yielding a rather rough surface but the microtexture was poor with few micro pits and smooth waviness (Fig.1c). The length of time that Group I and II were subjected to their respective acids did not change the surface texture. Group III (etched with H2SO4/ HCl and H3PO4) yielded an interesting surface hsowing distinct waviness without microtexture (Fig.1d); Group IV (etched with H2SO4 for 72h and HCl for 30h) showed significant surface roughness with micro pits of 1-10µm and large valleys of 20-30µm with peaks of different sizes (Fig.1e). The waviness and roughness of the surface was regular and without intact areas. This acid etching method was selected for further investigation with screw shaped titanium implants. Evaluation of the surface profile in the cut and polished (Fig.2a) and scored and broken (Fig 2b) groups showed the surface to be rough with small depressions and prominences of 1 to 10µm in size, visible in the profile. Wide trenches of 30µm could be seen (Fig. 2). 102 Stomatologija, Baltic Dental and Maxillofacial Journal, 2003, Vol. 5., N. 3.
3 G.Juodzbalys, M.Sapragoniene, A.Wennerberg SCIENTIFIC ARTICLES Fig. 1. Scanning electron microscopy images of titanium discs. (a) Disc with machined surface. Regular machining grows apparent on the surface. X2000 mag. (b) Disc with acid etched (HCl) surface with poor microtexture without micropits. (c) Disc with acid etched (HCl and H 2 ) surface. Poor microtexture with few micropits and smooth waveness (d) Disc with acid etched (H 2 /HCl and H 3 PO 4 ) surface. Clear expressed surface waveness without microtexture. (e) Disk with acid etched (H 2 and HCl) surface with 1-10 µm micropits, large µm valleys and different size peaks. Fig. 2. Scanning electron microscopy images of titanium discs profile. (a) Cut incised-polished disc surface. (b) Cut-fractured disc surface. Both surface profiles exhibited expressed roughness. Fig. 3. Digital images from the topographical measurement. (a) Machined surface with clear direction of the surface topography. (b) Acid etched (H 2 and HCl) surface with the regular distribution expressed peaks and valleys. Topographical evaluation of the screw shaped titanium implants. Digital topographical images (Fig. 3) were performed in order to compare machined and acid etched surfaces on screw shaped titanium surfaces. The surfaces of the machined titanium implants were examined and shown that these implants had mainly unidirectional machining grooves and ridges (Fig.3a). The acid treated titanium implants showed roughness and waviness that was evenly spread over the entire surface (Fig.3b). Surface texture was characterized by regularly distributed on the peaks and valleys. Electron microscopy scans of the machined surface of a control implant had grooves, which were more expressed on thread crests than at the root or flanks of the thread (Fig. 4 a1). The unidirection of deep grooves and ridges remained from the machining process. The implant surface treated with sulphuric and hydrochloric acids was found to have a very complex surface without any intact areas. But the rough- Table 2. Surface roughness measured with optical interferometer at different sites of thread on machined and experimental etched thread Title Sa (SD) (µm) Sal (SD) (µm) Sds (SD) (/µm2) Sdr (SD) (%) etched flank 2,24 (0,81)* 5,44 (1,19) 0,06 (0,00) 127,06 (10,80)* top 2,08 (0,36)** 7,85 (2,14) 0,07 (0,00) 134,45 (29,10)** valley 1,16 (0,08)+ 6,37 (0,90) 0,07 (0,00) 67,78 (5,31)+ machined flank 1,29 (0,98)* 8,01 (8,99) 0,12 (0,01) 29,75 (10,88)* top 1,28 (0,70)** 10,12 (6,67) 0,11 (0,01) 31,76 (16,85)** valley 0,62 (0,09)+ 6,66 (1,91) 0,09 (0,01) 20,83 (3,79) + *,**,+p<0,04 *,**,+p<0,001 Sa - the average height deviation, Sal - the fastest decay autocorrelation length, Sds - the density of summits, Sdr - the developed interfacial area ratio, SD - the standard deviation. Stomatologija, Baltic Dental and Maxillofacial Journal, 2003, Vol. 5., N
4 G.Juodzbalys, M.Sapragoniene, A.Wennerberg Fig. 4. Scanning electron microscopy images of experimental titanium implants. (a) Implant with machined surface. X27 mag. Clear direction of grooves and ridges as remnants from the machining process. (a1) Machined thread top with deep irregular grooves and ridges. X2000 mag. (a2) A machined thread valley with less distinct ridges and grooves. X2000 mag. (a3) A machined thread flank with distinct ridges and grooves. X2000 mag. (b) implant with acid etched surface X27 mag. Regular distribution of surface texture. (b1) Acid etched thread top with 1-10 µm micropits and large features of approximately 30 µm and different size peaks. X2000 mag. (b2) Acid etched valley with 1-20 µm micropits and small peaks. X2000 mag. (b3) Acid etched flank with clear expressed 1-10 µm micropits, large features of approximately 30 µm and different size peaks. X2000 mag. ness of the surface was more expressed at the crests and flanks (Fig. 4 b1 and b3) than in the root areas (Fig. 4 b2). Measurements with an optical interferometer established that the following parameters - height deviation of acid etched surface (Sa), the surface enlargement (Sdr), the fastest decay autocorrelation length (Sal) and the density of summits (Sds), were significantly bigger than of machined surfaces (Table 2). It is worth noting that common roughness of surface was significant but the roots were again smoother than the crests or the flanks. The surfaces of 5 commercially produced screw-shaped implants (18) and the implant with the experimental surface were comparatively analyzed taking measurements at the same sites (Table 3). Results showed that all commercially available implants had the smoothest surface at the flanks, while flanks of the experimental implants were the roughest Sa 2.24µm (SD 0.8). It is worth noting that the experimental implant screws were generally rougher when compared to other commercially available implants. However the surface enlargement (Sdr) was rather similar to the implant with SLA surface. DISCUSSION Commercially available implants are available with several surface texture types. This study resulted in the development of a surface texture using acid etching technology. It has been shown that finely pitted (micro pits of 1-3µm and larger elements of approximately 6-10µm in size) surfaces had an early enhancement implant and bone integration (15). Studies by Wenneberg et al. (11, 19, 20, 21) demon- Table 3. Comparison of surface roughness measured at 5 different sites on commercially produced screw-type implants and the experimental implant with optical profilometry. Implant /manufacturer Sa (SD) Sdr (SD) Nobel Biocare (Goteborg, Sweden) top 0,99 (0,5) 1,29 (0,2) valley 0,60 (0,3) 1,17 (0,1) flank 0,65 (0,1) 1,26 (0,1) TiOblast (Astra Tech AB, Molndal,Sweden) top 1,27 (0,2) 1,32 (0,1) valley 1,15 (0,2) 1,31 (0,1) flank 0,84 (0,1) 1,25 (0,0) Osseotite (3i, Palm Beach Gardens, FL) top 1,97 (1,0) 1,42 (0,2) valley 0,69 (0,1) 1,12 (0,0) flank 0,54 (0,1) 1,13 (0,0) SLA (Institut Straumann AG, Waldenburg, Switzerland) top 1,79 (0,2) 1,42 (0,1) valley 1,32 (0,1) 1,27 (0,0) flank 1,23 (0,1) 1,30 (0,1) Bonefit (Institut Straumann AG) top 2,08 (0,1) 1,79 (0,0) valley 2,12 (0,7) 1,91 (0,4) flank 2,09 (0,2) 1,88 (1,1) Experimental implant top 2,08 (0,4) 1,34 (0,3) valley 1,16 (0,1) 0,68 (0,1) flank 2,24 (0,8) 1,27 (0,1) Sa - the average height deviation, Sdr - the developed interfacial area ratio, SD - the standard deviation. 104 Stomatologija, Baltic Dental and Maxillofacial Journal, 2003, Vol. 5., N. 3.
5 G.Juodzbalys, M.Sapragoniene, A.Wennerberg SCIENTIFIC ARTICLES strated optimal surface roughness of particles of 75µm made surface more resistant to torque and greater bone-to-metal contact than small (25µm) or coarse (250µm) particles. The optimal surface had an average height deviation of about 1.5µm resulting in a surface enlargement of 50%. Implants with macrotextured surfaces, e.g., plasma sprayed or hydroxyapatite coated, had more enhanced bone to implant contact at late osseointegration period (15). Some authors have reported erosion of the hydroxyapatite layer (22) and peri-implant bone loss resulting in a higher failure rate (12, 23) for implants with hydroxyapatite surface. On the other hand, Buser et al. (16) showed that implants with sandblasted and acid etched surfaces had higher bone to implant contact percentages than implants with titanium plasma sprayed surfaces. This confirms presumption that significantly roughened surface itself (titanium plasma sprayed surface) does not stimulate early bone and implant integration. The titanium surface was sandblasted at first with large particles creating a significantly rough surface, which afterwards was acid etched, forming a finely rough surface. This surface texture improved the initial implant stability in bone of low-density and increased the quality of the bone to implant interface (18). It should be emphasized REFERENCES 1. Brånemark P.-I., Breine B.E., Adell R et al. Intraosseous anchorage of dental prostheses. I. Experimental studies // Scand. J. Plastic Reconstr. Surg. 1969, vol. 3, p Keller J.C., Stanfort C.M., Wightman J.P. et al. Characterizations of titanium implant surfaces. III // J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 1994, vol. 18, p Quirynen M., Bollen C.M., Papaioannou W. et al. The influence of titanium abutmentsurface roughness on plaque accumulation and gingivitis: short-term observation // Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implants 1996, vol. 11, p Barier R. F., Natiella J.R., Meyer A. E., Carter J.M. Importance of implantsurface preparation for biomaterials with different intrinsic properties // Tissue integration in oral and maxillofacial reconstruction / Ed. D. Steenberghe, T. Albrektsson, P.I.Brånemark.- Amsterdam: Excerpta Medica, 1985, p Lucchini J.-P., Aurelle J.-L., Therin M. et al. A pilot study comparing screw-shaped implants. Surface analysis and histologic evaluation of bone healing // Clin. Oral Implants Res. 1996, vol. 7, p Predecki P., Auslaender B.A.& Stephan J.E. Attachment of bone to threated implants by ingrowth and mechanical interlocking // J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 1972, vol. 6, p Bowers K.T., Keller J.C., Randolph B.A. et al. Optimization of surface micromorphology for enhanced osteoblast responses in vitro // Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implants 1992, vol. 7, p Hayashi K., Inadome T., Tsumura H. et al. Effect of surface roughness of hydroxyapatite-coated titanium on the bone-implant interface shear stregth // Biomaterials 1994, vol. 15, p Wong M., Eulenberger J., Schenk R., Hunzinker E. Effect of surface topology on the osseointegration of implant materials in trabecular bone // J. Biomed. Mater. Res , vol. 29, p Chehroudi B.M., McDonnell D., Brunette D.M. The effects of micromachined surfaces on formation of bonelike tissue on subcutaneous implants as assessed by radiography and computer image processing // J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 1997, vol. 34, p Wennerberg A., Hallgren C., Johansson C., Danelli S. A histomorphometric evaluation of screw-shaped implants each prepared with two surfaces roughnesses // Clin. Oral Implants Res. 1998, vol. 9, p that this titanium surface was gained using two methods of processing sandblasting and acid etching. Probability of surface contamination and of micro-particle dissemination into the surrounding tissues is extremely low (24). In our study we used one method acid etching to create a new titanium surface combining all the aforementioned surface texture features. The present study showed that precise acid selection and the sequence of processing played the main role in preparation of the rough titanium surface. The surface was poorer if it was etched with hydrochloric acid and then with sulphuric one. The very similar results were demonstrated processing implants only with hydrochloric acid or with sulphuric/hydrochloric acids and phosphoric one. Sulphuric and hydrochloric acids in sequence and time showed the best results. The newly created titanium surface according its topography was very much alike to a SLA surface. It combines the main properties of roughened titanium surface: glossily micro rough and large waviness. In general, the experimental surface was rougher when compared to commercially available implants. Although the implant surface created using specific acid etching methods resembles an SLA created surface, further research is necessary to study the biological response to it. 12. Piatelli A., Cosci F., Scarano A., Trisi P. Localized chronic suppurative bone infection as a sequel of peri-implantitis in a hydroxyapatite-coated dental implant // Biomaterials 1995, vol. 16, p Lazzara R., Testori T., Trisi P., Porter S. A human histologic analysis of Osseotite and machined surface using implants with 2 opposing surfaces // Int. J. Periodontics Restorative Dent. 1999, vol. 19, p Martinez H., Davarpanah M., Missika P., Celleti R., Lazzara R. Optimal implant stabilization in low density bone / / Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2001, vol. 12, p Klokkevold P., Johnson P., Dadgostari S et al. Early andosseous integration enhanced by dual acid etching of titanium: a torque removal study in the rabbit // Clin. Oral Implants Res , vol. 12, p Buser D., Schenk R.K., Steinemann S. et al. Influence of surface characteristics on bone integration of titanium implants. A histomorphometric study in miniature pigs (see comments) // J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 1991, vol. 25, p Davies J.E. Mechanisms of endosseous integration // Int. J. Prosthodont. 1998, vol. 11, p Wennerberg A., Albrektsson T. Suggested Guidelines for the Topographic Evaluation of implant surfaces // Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implants 2000, vol. 15, p Wennerberg A., Albrektsson T. Andersson B.,Krol J.J. A histomorphometric and removal torque study of screw-shaped titanium implants with three different surface topographies // Clin. Oral Implants Res. 1985, vol. 6, p Wennerberg A., Albrektsson T. Andersson B. Bone tissue response to commercially pure titanium implants blasted with fine and coarse particles of aluminium oxide // Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implants. 1996, vol. 11, p Cheang P., Khor K.A. Addressing processing problems associated with plasma spraying of hydrxyapatite coatings // Biomaterials 1996, vol. 17, p Weehler S.L. Eight-year clinical retrospective study of titanium plasma-sprayed and hydroxyapatite-coated cylinder implants // Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implants 1996, vol. 11, p Wilke H.J., Claes L., Steinemann S. The influence of various titanium surfaces on the interface shear strength between implants and bone. Clinical Implant Materials // Advances in Biomaterials / Ed. M. Heimke, U. Solstesz, A.J.C.Lee.- Amsterdam: Elsvier Sci. Publ.,1990, p Lacefield W.R. Abrasion of dental implant surfaces inserted into bone: Test Results / University of Alabama at Birmingham, Biomaterials Testing Lab., Received: Accepted for publishing: Stomatologija, Baltic Dental and Maxillofacial Journal, 2003, Vol. 5., N
BCP Surface Treatment
 BCP Surface Treatment Bibliography Pure like nature 2 anthogyr The BCP surface treatment available with anthogyr implants supports rapid and effective osseointegration. Its potential in terms of osteoconduction
BCP Surface Treatment Bibliography Pure like nature 2 anthogyr The BCP surface treatment available with anthogyr implants supports rapid and effective osseointegration. Its potential in terms of osteoconduction
The Surface and Material of Dental Implants
 The Surface and Material of Dental Implants Conrado Aparicio, PhD Minnesota Dental Research Center for Biomaterials and Biomechanics Dpt. of Restorative Sciences. School of Dentistry University of Minnesota
The Surface and Material of Dental Implants Conrado Aparicio, PhD Minnesota Dental Research Center for Biomaterials and Biomechanics Dpt. of Restorative Sciences. School of Dentistry University of Minnesota
Quality from Switzerland 01.01.2014
 Quality from Switzerland 01.01.2014 TRI Dental Implants: An example of the highest standards of quality We deliver quality We supply quality. From patent to patient Modern production Compliance with the
Quality from Switzerland 01.01.2014 TRI Dental Implants: An example of the highest standards of quality We deliver quality We supply quality. From patent to patient Modern production Compliance with the
Contact: Steve Hurson VP, R & D Nobel Biocare 22715 Savi Ranch Pkwy Yorba Linda, CA 92887 (714) 282-5072 steve.hurson@nobelbiocare.
 Use of CP Titanium and Titanium alloys for Dental Implants Steve Hurson, Nobel Biocare U.S.A. Yorba Linda CA Abstract Professor Per Ingvar Branemark of Sweden published his results on 15 years of research
Use of CP Titanium and Titanium alloys for Dental Implants Steve Hurson, Nobel Biocare U.S.A. Yorba Linda CA Abstract Professor Per Ingvar Branemark of Sweden published his results on 15 years of research
Dental Implant Options in Atrophic Jaws
 Dental Implant Options in Atrophic Jaws Orthopedic Application Jay B. Reznick, D.M.D., M.D. Diplomate, American Board of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery Tarzana, CA Endopore Dental Implant System Screw-Type
Dental Implant Options in Atrophic Jaws Orthopedic Application Jay B. Reznick, D.M.D., M.D. Diplomate, American Board of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery Tarzana, CA Endopore Dental Implant System Screw-Type
Standard Internal Hex
 Standard Internal Hex Touareg TM -OS Touareg TM -S Swell TM Touareg -S Touareg -OS Swell About ADIN Adin Dental Implant Systems Ltd., designs, manufactures and markets state of the art, technologically
Standard Internal Hex Touareg TM -OS Touareg TM -S Swell TM Touareg -S Touareg -OS Swell About ADIN Adin Dental Implant Systems Ltd., designs, manufactures and markets state of the art, technologically
Porous surface of extraoral implants: report of two cases rehabilitated with a new Brazilian extraoral implant
 Braz J Oral Sci. October/December 2004 - Vol. 3 - Number 11 Luciano Lauria Dib 1 Joaquim Augusto Piras de Oliveira 2 Renata Lazari Sandoval 3 Ulf Nannmark 4 1 Professor of Stomatology at UNIP, São Paulo,
Braz J Oral Sci. October/December 2004 - Vol. 3 - Number 11 Luciano Lauria Dib 1 Joaquim Augusto Piras de Oliveira 2 Renata Lazari Sandoval 3 Ulf Nannmark 4 1 Professor of Stomatology at UNIP, São Paulo,
Supervisors: Dr. Farhan Raza Khan
 1 Presenter: Dr. Sana Ehsen Supervisors: Dr. Farhan Raza Khan 2 A dental implant (also known as an endosseous implant or fixture) is a surgical component that interfaces with the bone of the jaw to support
1 Presenter: Dr. Sana Ehsen Supervisors: Dr. Farhan Raza Khan 2 A dental implant (also known as an endosseous implant or fixture) is a surgical component that interfaces with the bone of the jaw to support
Ridge Reconstruction for Implant Placement
 Volume 1, No. 5 July/August 2009 The Journal of Implant & Advanced Clinical Dentistry Ridge Reconstruction for Implant Placement 2 Hours of CE Credit Oral Implications of Cancer Chemotherapy Immediate
Volume 1, No. 5 July/August 2009 The Journal of Implant & Advanced Clinical Dentistry Ridge Reconstruction for Implant Placement 2 Hours of CE Credit Oral Implications of Cancer Chemotherapy Immediate
ALL-CERAMIC DENTAL IMPLANT SOLUTIONS
 ALL-CERAMIC DENTAL IMPLANT SOLUTIONS Scientific Evidence Bone-to-implant contact of 78% at 3 months. One piece implant = no prosthetic connections References 1. One-year follow-up of first consecutive
ALL-CERAMIC DENTAL IMPLANT SOLUTIONS Scientific Evidence Bone-to-implant contact of 78% at 3 months. One piece implant = no prosthetic connections References 1. One-year follow-up of first consecutive
For citation purposes, the electronic version is the definitive version of this article: www.cda-adc.ca/jcda/vol-73/issue-9/821.
 Applied R e s e a r c h Survival and Success of Sandblasted, Large- Grit, Acid-Etched and Titanium Plasma-Sprayed Implants: A Retrospective Study Murray L. Arlin, DDS, FRCD(C) ABSTRACT Contact Author Dr.
Applied R e s e a r c h Survival and Success of Sandblasted, Large- Grit, Acid-Etched and Titanium Plasma-Sprayed Implants: A Retrospective Study Murray L. Arlin, DDS, FRCD(C) ABSTRACT Contact Author Dr.
Clinical and Laboratory Procedures for Fixed Margin Implant Abutments
 Clinical and Laboratory Procedures for Fixed Margin Implant Abutments Dr. Carl Drago DDS, MS, American Board of Prosthodontics Director, Dental Research BIOMET 3i, Adjunct Faculty Department of Prosthodontics,
Clinical and Laboratory Procedures for Fixed Margin Implant Abutments Dr. Carl Drago DDS, MS, American Board of Prosthodontics Director, Dental Research BIOMET 3i, Adjunct Faculty Department of Prosthodontics,
Curriculum Vitae Frank L. Higginbottom, D.D.S.
 Curriculum Vitae Frank L. Higginbottom, D.D.S. Education Oklahoma University B.S. 1967 Baylor College of Dentistry D.D.S. 1971 Practice Staff Appointments Private Practice of Esthetics, Restorative, and
Curriculum Vitae Frank L. Higginbottom, D.D.S. Education Oklahoma University B.S. 1967 Baylor College of Dentistry D.D.S. 1971 Practice Staff Appointments Private Practice of Esthetics, Restorative, and
Life Table Analysis for Evaluating Curative-effect of One-stage Non-submerged Dental Implant in Taiwan
 Journal of Data Science 6(2008), 591-599 Life Table Analysis for Evaluating Curative-effect of One-stage Non-submerged Dental Implant in Taiwan Miin-Jye Wen 1, Chuen-Chyi Tseng 2 and Cheng K. Lee 3 1 National
Journal of Data Science 6(2008), 591-599 Life Table Analysis for Evaluating Curative-effect of One-stage Non-submerged Dental Implant in Taiwan Miin-Jye Wen 1, Chuen-Chyi Tseng 2 and Cheng K. Lee 3 1 National
Implants Placed in Immediate Extraction Sites: A Report of Histologic and Histometric Analyses of Human Biopsies
 Implants Placed in Immediate Extraction Sites: A Report of Histologic and Histometric Analyses of Human Biopsies Thomas G. Wilson, Jr, DDS*/Robert Schenk, MD, Prof Dr Med**/ Daniel Buser, DMD, Prof Dr
Implants Placed in Immediate Extraction Sites: A Report of Histologic and Histometric Analyses of Human Biopsies Thomas G. Wilson, Jr, DDS*/Robert Schenk, MD, Prof Dr Med**/ Daniel Buser, DMD, Prof Dr
Dental Implant System Design and the Potential Impact on Long-Term Aesthetics: A Review of the 3i T3 Tapered Implant
 Dental Implant System Design and the Potential Impact on Long-Term Aesthetics: A Review of the 3i T3 Tapered Implant Richard J. Lazzara, DMD, MScD Published by Dental Implant System Design and the Potential
Dental Implant System Design and the Potential Impact on Long-Term Aesthetics: A Review of the 3i T3 Tapered Implant Richard J. Lazzara, DMD, MScD Published by Dental Implant System Design and the Potential
Surface Characterization of Titanium Based Dental Implants
 00 Brazilian Journal of Physics, vol. 6, no. B, September, 006 Surface Characterization of Titanium Based Dental Implants Guilherme A. A. Castilho, Maximiliano D. Martins, and Waldemar A. A. Macedo Laboratório
00 Brazilian Journal of Physics, vol. 6, no. B, September, 006 Surface Characterization of Titanium Based Dental Implants Guilherme A. A. Castilho, Maximiliano D. Martins, and Waldemar A. A. Macedo Laboratório
Implant materials. Learning outcomes. Implant materials in trauma. How to use this handout? Functions of implants. Types of materials
 Implant materials How to use this handout? The left column is the information as given during the lecture. The column at the right gives you space to make personal notes. Learning outcomes At the end of
Implant materials How to use this handout? The left column is the information as given during the lecture. The column at the right gives you space to make personal notes. Learning outcomes At the end of
The SATURN implant by Cortex Dental Industries
 The SATURN implant by Cortex Dental Industries By Dr. Zvi Laster DMD W e P r o v e I t E v e r y D a y A case report using a newly designed implant specifically designed for immediate post-extraction loading
The SATURN implant by Cortex Dental Industries By Dr. Zvi Laster DMD W e P r o v e I t E v e r y D a y A case report using a newly designed implant specifically designed for immediate post-extraction loading
Factors Influencing the Resonance Frequency of Dental Implants
 SCIENTIFIC ARTICLES J Oral Maxillofac Surg 61:1184-1188, 2003 Factors Influencing the Resonance Frequency of Dental Implants Haw-Ming Huang, MS,* Ching-Lai Chiu, DDS, MS, Ching-Ying Yeh, PhD, and Sheng-Yang
SCIENTIFIC ARTICLES J Oral Maxillofac Surg 61:1184-1188, 2003 Factors Influencing the Resonance Frequency of Dental Implants Haw-Ming Huang, MS,* Ching-Lai Chiu, DDS, MS, Ching-Ying Yeh, PhD, and Sheng-Yang
Zimmer Trabecular Metal Dental Implant
 Zimmer Trabecular Metal Dental Implant TRABECULAR METAL MATERIAL: Designed to Enhance Secondary Stability Through Bone Ingrowth. Artistic Rendering osseoincorporation TRABECULAR METAL MATERIAL Designed
Zimmer Trabecular Metal Dental Implant TRABECULAR METAL MATERIAL: Designed to Enhance Secondary Stability Through Bone Ingrowth. Artistic Rendering osseoincorporation TRABECULAR METAL MATERIAL Designed
Dental Implant Surface Roughness and Topography: A Review of the Literature
 J. Gifu. Dent. Soc Vol.,No., February, Dental Implant Surface Roughness and Topography Dental Implant Surface Roughness and Topography: A Review of the Literature ISABEL de MONSERRAT OSORIO BERNAL,ITO
J. Gifu. Dent. Soc Vol.,No., February, Dental Implant Surface Roughness and Topography Dental Implant Surface Roughness and Topography: A Review of the Literature ISABEL de MONSERRAT OSORIO BERNAL,ITO
IMPLANT DENTISTRY EXAM BANK
 IMPLANT DENTISTRY EXAM BANK 1. Define osseointegration. (4 points, 1/4 2. What are the critical components of an acceptable clinical trial? (10 points) 3. Compare the masticatory performance of individuals
IMPLANT DENTISTRY EXAM BANK 1. Define osseointegration. (4 points, 1/4 2. What are the critical components of an acceptable clinical trial? (10 points) 3. Compare the masticatory performance of individuals
BIOACTIVE COATINGS ON 316L STAINLESS STEEL IMPLANTS
 Trends Biomater. Artif. Organs. Vol. 17(2) pp 43-47 (2004) http//www.sbaoi.org BIOACTIVE COATINGS ON 316L STAINLESS STEEL IMPLANTS N. Ramesh Babu*,+, Sushant Manwatkar*, K. Prasada Rao* and T. S. Sampath
Trends Biomater. Artif. Organs. Vol. 17(2) pp 43-47 (2004) http//www.sbaoi.org BIOACTIVE COATINGS ON 316L STAINLESS STEEL IMPLANTS N. Ramesh Babu*,+, Sushant Manwatkar*, K. Prasada Rao* and T. S. Sampath
Histologic comparison of biologic width around teeth versus implants: The effect on bone preservation
 Clinical Histologic comparison of biologic width around teeth versus implants: The effect on bone preservation Kazuto Makigusa 1 Abstract Histological analysis of the biological width surrounding primate
Clinical Histologic comparison of biologic width around teeth versus implants: The effect on bone preservation Kazuto Makigusa 1 Abstract Histological analysis of the biological width surrounding primate
Amajor limitation in the use of most
 Volume 75 Number 6 A Targeted Review of Study Outcomes With Short ( 7 mm) Endosseous Dental Implants Placed in Partially Edentulous Patients D. Hagi,* D.A. Deporter,* R.M. Pilliar,* and T. Arenovich Background:
Volume 75 Number 6 A Targeted Review of Study Outcomes With Short ( 7 mm) Endosseous Dental Implants Placed in Partially Edentulous Patients D. Hagi,* D.A. Deporter,* R.M. Pilliar,* and T. Arenovich Background:
Anatomic limitations in the maxilla provide challenges
 Osteotome Single-Stage Dental Implant Placement With and Without Sinus Elevation: A Clinical Report Orest G. Komarnyckyj, DDS*/Robert M. London, DDS** Forty-three sites in 16 patients were selected for
Osteotome Single-Stage Dental Implant Placement With and Without Sinus Elevation: A Clinical Report Orest G. Komarnyckyj, DDS*/Robert M. London, DDS** Forty-three sites in 16 patients were selected for
Don t Let Life Pass You By Because Of Missing Teeth
 Don t Let Life Pass You By Because Of Missing Teeth Ask For Dental Implant Solutions From BIOMET 3i Scan With Your Smartphone! In order to scan QR codes, your mobile device must have a QR code reader installed.
Don t Let Life Pass You By Because Of Missing Teeth Ask For Dental Implant Solutions From BIOMET 3i Scan With Your Smartphone! In order to scan QR codes, your mobile device must have a QR code reader installed.
Advances in implant designs, biomaterials, and surgical techniques have
 Immediate Loading of Dental Implants in the Edentulous Mandible: A Preliminary Case Report From an International Prospective Multicenter Study Abstract: The ability to predictably achieve long-term osseointegration
Immediate Loading of Dental Implants in the Edentulous Mandible: A Preliminary Case Report From an International Prospective Multicenter Study Abstract: The ability to predictably achieve long-term osseointegration
Straumann Dental Implant System. Implant Selection Guide.
 Straumann Dental Implant System. Implant Selection Guide. STRAUMANN's IMPLANT PORTFOLIO The Straumann Dental Implant System offers two implant lines with diverse body and neck designs ranging from the
Straumann Dental Implant System. Implant Selection Guide. STRAUMANN's IMPLANT PORTFOLIO The Straumann Dental Implant System offers two implant lines with diverse body and neck designs ranging from the
WHAT YOU NEED TO KNOW ABOUT SELECTING A DENTAL IMPLANT SYSTEM
 the CONFIDENt choice WHT YOU NEED TO KNOW BOUT SELECTING DENTL IMPLNT SYSTEM WHEN CHOOSING DENTL IMPLNT SYSTEM There are many factors when choosing an implant system How much will it cost and will it RELLY
the CONFIDENt choice WHT YOU NEED TO KNOW BOUT SELECTING DENTL IMPLNT SYSTEM WHEN CHOOSING DENTL IMPLNT SYSTEM There are many factors when choosing an implant system How much will it cost and will it RELLY
Implant Systems MAX LOGIC MONO. Today s name in tomorrow s implant technology
 Implant Systems MAX LOGIC MONO Today s name in tomorrow s implant technology Implant Systems Etgar Medical Implant Systems brings to the market an entire spectrum of dental implant products based on its
Implant Systems MAX LOGIC MONO Today s name in tomorrow s implant technology Implant Systems Etgar Medical Implant Systems brings to the market an entire spectrum of dental implant products based on its
3M ESPE MDI. Mini Dental Implants. Literature Review. Espertise. Scientific Facts
 3M ESPE MDI Mini Dental Implants Literature Review Espertise Scientific Facts 3M ESPE MDI Mini Dental Implant Denture Stabilization Literature Review June 2009 Objective: To review the published literature
3M ESPE MDI Mini Dental Implants Literature Review Espertise Scientific Facts 3M ESPE MDI Mini Dental Implant Denture Stabilization Literature Review June 2009 Objective: To review the published literature
Photofunctionalization
 Photofunctionalization One and only technology to overcome the biological aging of titanium Scientific brochure of photofunctionalization Volume 1, Issue 1, 2013 published by Global Network for Photofunctionalized
Photofunctionalization One and only technology to overcome the biological aging of titanium Scientific brochure of photofunctionalization Volume 1, Issue 1, 2013 published by Global Network for Photofunctionalized
Implants of high-performance ceramic. vk-lange 12.03.2007 14:44 Uhr Seite 1. One-piece precision implant. Made in Germany
 OMNIS Implants of high-performance ceramic vk-lange 12.03.2007 14:44 Uhr Seite 1 One-piece precision implant C M Y CM MY CY CMY K Dieter Lange Verkaufsleiter Labor Made in Germany creamed nge 12.03.2007
OMNIS Implants of high-performance ceramic vk-lange 12.03.2007 14:44 Uhr Seite 1 One-piece precision implant C M Y CM MY CY CMY K Dieter Lange Verkaufsleiter Labor Made in Germany creamed nge 12.03.2007
Outcomes of Placing Short Dental Implants in the Posterior Mandible: A Retrospective Study of 124 Cases
 DENTAL IMPLANTS J Oral Maxillofac Surg 67:713-717, 2009 Outcomes of Placing Short Dental in the Posterior Mandible: A Retrospective Study of 124 Cases Bao-Thy N. Grant, DDS,* Franklin X. Pancko, DDS, and
DENTAL IMPLANTS J Oral Maxillofac Surg 67:713-717, 2009 Outcomes of Placing Short Dental in the Posterior Mandible: A Retrospective Study of 124 Cases Bao-Thy N. Grant, DDS,* Franklin X. Pancko, DDS, and
platform shifting Nobel Biocare is shifting gingival beauty to the next level
 platform shifting Nobel Biocare is shifting gingival beauty to the next level Nobel Biocare is shifting gingival beauty to the next level Platform Shifting is the latest in Nobel Biocare s offering of
platform shifting Nobel Biocare is shifting gingival beauty to the next level Nobel Biocare is shifting gingival beauty to the next level Platform Shifting is the latest in Nobel Biocare s offering of
The Impact of Oral Implants Past and Future, 1966 2042. Tomas Albrektsson, MD, PhD, ODhc Ann Wennerberg, DDS, PhD
 P R O F E S S I O N A L I S S U E S The Impact of Oral Implants Past and Future, 1966 202 Tomas Albrektsson, MD, PhD, ODhc Ann Wennerberg, DDS, PhD A b s t r a c t This paper traces the history of oral
P R O F E S S I O N A L I S S U E S The Impact of Oral Implants Past and Future, 1966 202 Tomas Albrektsson, MD, PhD, ODhc Ann Wennerberg, DDS, PhD A b s t r a c t This paper traces the history of oral
Straumann Dental Implant System. Fax Order Form Collection.*
 Straumann Dental Implant System. Fax Order Form Collection.* * The NNC Fax Order Form is still a stand alone document due to the unique restorative portfolio Straumann Roxolid SLActive Tissue Level Implants
Straumann Dental Implant System. Fax Order Form Collection.* * The NNC Fax Order Form is still a stand alone document due to the unique restorative portfolio Straumann Roxolid SLActive Tissue Level Implants
Eliminating effect of Er, Cr: YSGG laser irradiation on the smear layer of dentin
 Eliminating effect of Er, Cr: YSGG laser irradiation on the smear layer of dentin Jingtao Yu, MD, DDS, and Lu Yan, MD, DDS College of Stomatology, China Medical University, Shenyang, P. R. China Purpose:
Eliminating effect of Er, Cr: YSGG laser irradiation on the smear layer of dentin Jingtao Yu, MD, DDS, and Lu Yan, MD, DDS College of Stomatology, China Medical University, Shenyang, P. R. China Purpose:
Information on the product
 Information on the product Information on the product -Implantat.doc Page 1 of 15 This document composes of the following items 1. Name of the product 2. Raw materials 3. Structure and dimensions 3.1.
Information on the product Information on the product -Implantat.doc Page 1 of 15 This document composes of the following items 1. Name of the product 2. Raw materials 3. Structure and dimensions 3.1.
Plastic Film Texture Measurement With 3D Profilometry
 Plastic Film Texture Measurement With 3D Profilometry Prepared by Jorge Ramirez 6 Morgan, Ste156, Irvine CA 92618 P: 949.461.9292 F: 949.461.9232 nanovea.com Today's standard for tomorrow's materials.
Plastic Film Texture Measurement With 3D Profilometry Prepared by Jorge Ramirez 6 Morgan, Ste156, Irvine CA 92618 P: 949.461.9292 F: 949.461.9232 nanovea.com Today's standard for tomorrow's materials.
Surface modification of Ti dental implants by Nd:YVO 4 laser irradiation
 Applied Surface Science 253 (2007) 9203 9208 www.elsevier.com/locate/apsusc Surface modification of Ti dental implants by Nd:YVO 4 laser irradiation Francisco J.C. Braga a, Rodrigo F.C. Marques b, Edson
Applied Surface Science 253 (2007) 9203 9208 www.elsevier.com/locate/apsusc Surface modification of Ti dental implants by Nd:YVO 4 laser irradiation Francisco J.C. Braga a, Rodrigo F.C. Marques b, Edson
All-on-4 treatment concept with NobelSpeedy Groovy
 All-on-4 treatment concept with NobelSpeedy Groovy Product overview Immediate Function for high patient satisfaction Immediately loaded fixed provisional prosthesis on the day of surgery. Immediate improvement
All-on-4 treatment concept with NobelSpeedy Groovy Product overview Immediate Function for high patient satisfaction Immediately loaded fixed provisional prosthesis on the day of surgery. Immediate improvement
Implant therapy using osseointegrated implants has
 Natural Tooth Intrusion Phenomenon With Implants: A Survey Lily T. Garcia, DDS, MS*/Larry J. Oesterle, DDS, MS** A common assumption when planning for treatment for a fixed partial denture potentially
Natural Tooth Intrusion Phenomenon With Implants: A Survey Lily T. Garcia, DDS, MS*/Larry J. Oesterle, DDS, MS** A common assumption when planning for treatment for a fixed partial denture potentially
Restoration of the Edentulous Maxilla: The Case for the Zygomatic Implants
 CLINICAL CONTROVERSIES IN ORAL AND MAXILLOFACIAL SURGERY: PART ONE J Oral Maxillofac Surg 62:1418-1422, 2004 Restoration of the Edentulous Maxilla: The Case for the Zygomatic Implants Eric D. Ferrara,
CLINICAL CONTROVERSIES IN ORAL AND MAXILLOFACIAL SURGERY: PART ONE J Oral Maxillofac Surg 62:1418-1422, 2004 Restoration of the Edentulous Maxilla: The Case for the Zygomatic Implants Eric D. Ferrara,
Early loading (4 weeks) of dental implants Impladent in maxilla and mandible - monitoring of the healing process using resonance frequency analysis
 Early loading (4 weeks) of dental implants Impladent in maxilla and mandible - monitoring of the healing process using resonance frequency analysis 1 2 2 A. Štěpánek, J. Strnad, Z. Strnad Quintessenz Vol.14,
Early loading (4 weeks) of dental implants Impladent in maxilla and mandible - monitoring of the healing process using resonance frequency analysis 1 2 2 A. Štěpánek, J. Strnad, Z. Strnad Quintessenz Vol.14,
Dentistry Fatigue test for endosseous dental implants. Report No.: 1 ASTRA System Ti Design
 Dentistry Fatigue test for endosseous dental implants Report No.: 1 ASTRA System Ti Design Client: NT - Trading Time of execution: Mai 2011 Subject of work: - - S - 24285 Abutment Ti DesignTM - RESULTS
Dentistry Fatigue test for endosseous dental implants Report No.: 1 ASTRA System Ti Design Client: NT - Trading Time of execution: Mai 2011 Subject of work: - - S - 24285 Abutment Ti DesignTM - RESULTS
Modern Tooth Replacement Strategies & Digital Workflow
 Modern Tooth Replacement Strategies & Digital Workflow Case Studies by Dr Maurice Salama, DMD AS PUBLISHED BY Dentistry Today, June 2014 Complete Implant Restoration System FACTS: Implant Dentistry Has
Modern Tooth Replacement Strategies & Digital Workflow Case Studies by Dr Maurice Salama, DMD AS PUBLISHED BY Dentistry Today, June 2014 Complete Implant Restoration System FACTS: Implant Dentistry Has
ATLANTIS ISUS the benchmark for CAD/CAM suprastructures. For all major implant systems
 ATLANTIS ISUS the benchmark for CAD/CAM suprastructures For all major implant systems Patient satisfaction meets clinical benefits ATLANTIS delivers leading CAD/CAM patient-specific restorative solutions
ATLANTIS ISUS the benchmark for CAD/CAM suprastructures For all major implant systems Patient satisfaction meets clinical benefits ATLANTIS delivers leading CAD/CAM patient-specific restorative solutions
Surface Treatment of Titanium
 Surface Treatment of Titanium Christiane Jung KKS Ultraschall AG, Steinen SZ The Tribology of Precision Swiss Tribology Meeting SBB Centre Löwenberg in Murten, Switzerland 16. November 2007 1 Outline:
Surface Treatment of Titanium Christiane Jung KKS Ultraschall AG, Steinen SZ The Tribology of Precision Swiss Tribology Meeting SBB Centre Löwenberg in Murten, Switzerland 16. November 2007 1 Outline:
Comparison of Peri-Implant Bone Loss
 Original Article Comparison of Peri-Implant Bone Loss and Survival of Maxillary Intrasinus and Extrasinus Implants After 2 Years AR. Rokn 1,2, AAR. Rasouli Ghahroudi 3,4, S. Hemati 5, A. Soolari 6 1 Associate
Original Article Comparison of Peri-Implant Bone Loss and Survival of Maxillary Intrasinus and Extrasinus Implants After 2 Years AR. Rokn 1,2, AAR. Rasouli Ghahroudi 3,4, S. Hemati 5, A. Soolari 6 1 Associate
Don t Let Life Pass You By Because Of Oral Bone Loss
 Don t Let Life Pass You By Because Of Oral Bone Loss Ask For Dental Implant Solutions From BIOMET 3i Scan With Your Smartphone! In order to scan QR codes, your mobile device must have a QR code reader
Don t Let Life Pass You By Because Of Oral Bone Loss Ask For Dental Implant Solutions From BIOMET 3i Scan With Your Smartphone! In order to scan QR codes, your mobile device must have a QR code reader
ISSN 2307-5295, Published by the POSEIDO Organization & Foundation
 POSEIDO. 2014;2(1) ISIS identification cards of 62 implant surfaces. Part 2 23 Research article Identification card and codification of the chemical and morphological characteristics of 62 dental implant
POSEIDO. 2014;2(1) ISIS identification cards of 62 implant surfaces. Part 2 23 Research article Identification card and codification of the chemical and morphological characteristics of 62 dental implant
NARROW DIAMETER implant
 ND NARROW DIAMETER implant TABLE OF CONTENTS ND - NARROW DIAMETER implant Implant characteristics page 04 Dental implant page 05 Open Tray Impression Transfer page 06 Titanium Abutments page 07 O-Ball
ND NARROW DIAMETER implant TABLE OF CONTENTS ND - NARROW DIAMETER implant Implant characteristics page 04 Dental implant page 05 Open Tray Impression Transfer page 06 Titanium Abutments page 07 O-Ball
education Although demographic factors and growing patient awareness of the benefits of dental implants
 education Increasing implant dentistry in undergraduate education using new technology: A pilot project Hugo De Bruyn, MDS, MsC, PhD ± & Stefan Vandeweghe, DDS Although demographic factors and growing
education Increasing implant dentistry in undergraduate education using new technology: A pilot project Hugo De Bruyn, MDS, MsC, PhD ± & Stefan Vandeweghe, DDS Although demographic factors and growing
SPECIAL SUPPLEMENT. Inside this issue: 2014 No. 2. Abstracts from Selected Publications and Poster Presentations BIOMET 3i T3 Implants
 www.jird.com SPECIAL SUPPLEMENT Inside this issue: s from Selected Publications and Poster Presentations BIOMET 3i T3 Implants Official Publication of 2014 No. 2 The Institute for Implant and Reconstructive
www.jird.com SPECIAL SUPPLEMENT Inside this issue: s from Selected Publications and Poster Presentations BIOMET 3i T3 Implants Official Publication of 2014 No. 2 The Institute for Implant and Reconstructive
The predictability of attaining osseointegration
 ITI Implant Use in Private Practice: Clinical Results with 5,526 Implants Followed Up to 72+ Months in Function Paul A. Fugazzotto, DDS 1 /James Vlassis, DDS 2 /Bobby Butler, DDS 3 Purpose: To evaluate
ITI Implant Use in Private Practice: Clinical Results with 5,526 Implants Followed Up to 72+ Months in Function Paul A. Fugazzotto, DDS 1 /James Vlassis, DDS 2 /Bobby Butler, DDS 3 Purpose: To evaluate
Osstell ISQ. The objective way to measure implant stability. www.osstell.com
 Osstell ISQ. The objective way to measure implant stability. www.osstell.com Three reasons why you need With a success rate above 95%, who needs diagnostics? Implant treatment is one of the most predictable
Osstell ISQ. The objective way to measure implant stability. www.osstell.com Three reasons why you need With a success rate above 95%, who needs diagnostics? Implant treatment is one of the most predictable
Previous studies have shown that
 RESEARCH Early Human Bone Response to Laser Metal Sintering Surface Topography: A Histologic Report Carlo Mangano, MD, DDS 1 Adriano Piattelli, MD, DDS 2 Susana d Avila, DDS, MS, PhD 3 Giovanna Iezzi,
RESEARCH Early Human Bone Response to Laser Metal Sintering Surface Topography: A Histologic Report Carlo Mangano, MD, DDS 1 Adriano Piattelli, MD, DDS 2 Susana d Avila, DDS, MS, PhD 3 Giovanna Iezzi,
Redesign of a fixture mount to be used as an impression coping and a provisional abutment as well
 Redesign of a fixture mount to be used as an impression coping and a provisional abutment as well Glenn Hsuan-Chen Chang, Chen Tian 1, Yuen-Siang Hung 2 Abstract Purpose: An integrated fixture mount/impression
Redesign of a fixture mount to be used as an impression coping and a provisional abutment as well Glenn Hsuan-Chen Chang, Chen Tian 1, Yuen-Siang Hung 2 Abstract Purpose: An integrated fixture mount/impression
COMPLETE CHOICE GUIDE
 COMPLETE CHOICE GUIDE The widest range of dental implants to satisfy all surgical needs With professionals, for professionals. This is how btk creates its medical devices. The extremely wide range of btk
COMPLETE CHOICE GUIDE The widest range of dental implants to satisfy all surgical needs With professionals, for professionals. This is how btk creates its medical devices. The extremely wide range of btk
R J M E Romanian Journal of Morphology & Embryology
 Rom J Morphol Embryol 2014, 55(2):335 341 ORIGINAL PAPER R J M E Romanian Journal of Morphology & Embryology http://www.rjme.ro/ Correlations between cyto-histopathological tissue changes at the dental
Rom J Morphol Embryol 2014, 55(2):335 341 ORIGINAL PAPER R J M E Romanian Journal of Morphology & Embryology http://www.rjme.ro/ Correlations between cyto-histopathological tissue changes at the dental
MISCIBILITY AND INTERACTIONS IN CHITOSAN AND POLYACRYLAMIDE MIXTURES
 MISCIBILITY AND INTERACTIONS IN CHITOSAN AND POLYACRYLAMIDE MIXTURES Katarzyna Lewandowska Faculty of Chemistry Nicolaus Copernicus University, ul. Gagarina 7, 87-100 Toruń, Poland e-mail: reol@chem.umk.pl
MISCIBILITY AND INTERACTIONS IN CHITOSAN AND POLYACRYLAMIDE MIXTURES Katarzyna Lewandowska Faculty of Chemistry Nicolaus Copernicus University, ul. Gagarina 7, 87-100 Toruń, Poland e-mail: reol@chem.umk.pl
Leslie Laing Gibbard, BSc, BEd, MSc, PhD, DDS George Zarb, BChD, DDS, MS, MS, FRCD(C)
 A P P L I E D R E S E A R C H A 5-Year Prospective Study of Implant-Supported Single-Tooth Replacements Leslie Laing Gibbard, BSc, BEd, MSc, PhD, DDS George Zarb, BChD, DDS, MS, MS, FRCD(C) A b s t r a
A P P L I E D R E S E A R C H A 5-Year Prospective Study of Implant-Supported Single-Tooth Replacements Leslie Laing Gibbard, BSc, BEd, MSc, PhD, DDS George Zarb, BChD, DDS, MS, MS, FRCD(C) A b s t r a
CAD/CAM technology supporting successful implant therapy
 CAD/CAM technology supporting successful implant therapy Suheil M. Boutros, DDS, MS, Manuel Fricke, DT Modern implantology opens up new treatment options for individuals with only minimal or no remaining
CAD/CAM technology supporting successful implant therapy Suheil M. Boutros, DDS, MS, Manuel Fricke, DT Modern implantology opens up new treatment options for individuals with only minimal or no remaining
CUSTOMIZED PROVISIONAL ABUTMENT AND PROVISIONAL RESTORATION FOR AN IMMEDIATELY-PLACED IMPLANT
 CONTINUING EDUCATION 1 4 CUSTOMIZED PROVISIONAL ABUTMENT AND PROVISIONAL RESTORATION FOR AN IMMEDIATELY-PLACED IMPLANT Gerard J. Lemongello, Jr, DMD* LEMONGELLO 19 7 AUGUST The use of immediate implant
CONTINUING EDUCATION 1 4 CUSTOMIZED PROVISIONAL ABUTMENT AND PROVISIONAL RESTORATION FOR AN IMMEDIATELY-PLACED IMPLANT Gerard J. Lemongello, Jr, DMD* LEMONGELLO 19 7 AUGUST The use of immediate implant
Replacement of the upper left central incisor with a Straumann Bone Level Implant and a Straumann Customized Ceramic Abutment
 Replacement of the upper left central incisor with a Straumann Bone Level Implant and a Straumann Customized Ceramic Abutment by Dr. Ronald Jung and Master Dental Technician Xavier Zahno Initial situation
Replacement of the upper left central incisor with a Straumann Bone Level Implant and a Straumann Customized Ceramic Abutment by Dr. Ronald Jung and Master Dental Technician Xavier Zahno Initial situation
More than an implant. A sense of trust. Straumann Dental Implant System
 More than an implant. A sense of trust. Straumann Dental Implant System More than an implant. A sense of trust. Patients today are more aware of their options when it comes to tooth replacement. Partner
More than an implant. A sense of trust. Straumann Dental Implant System More than an implant. A sense of trust. Patients today are more aware of their options when it comes to tooth replacement. Partner
Six-Year Survival and Early Failure Rate of 2918 Implants with Hydrophobic and Hydrophilic Enossal Surfaces
 Dent. J. 2015, 3, 15-23; doi:10.3390/dj3010015 Article OPEN ACCESS dentistry journal ISSN 2304-6767 www.mdpi.com/journal/dentistry Six-Year Survival and Early Failure Rate of 2918 Implants with Hydrophobic
Dent. J. 2015, 3, 15-23; doi:10.3390/dj3010015 Article OPEN ACCESS dentistry journal ISSN 2304-6767 www.mdpi.com/journal/dentistry Six-Year Survival and Early Failure Rate of 2918 Implants with Hydrophobic
The rate of success of implants in the edentulous
 Clinical evaluation of single-tooth mini-implant restorations: A five-year retrospective study Paolo Vigolo, Dr Odont, MScD, and Andrea Givani, MD, DDS Vicenza, Italy Statement of problem. Placement of
Clinical evaluation of single-tooth mini-implant restorations: A five-year retrospective study Paolo Vigolo, Dr Odont, MScD, and Andrea Givani, MD, DDS Vicenza, Italy Statement of problem. Placement of
Healing Abutment Selection. Perio Implant Part I. Implant Surface Characteristics. Single Tooth Restorations. Credit and Thanks for Lecture Material
 Healing Abutment Selection Perio Implant Part I Credit and Thanks for Lecture Material Implant Surface Characteristics!CAPT Robert Taft!CAPT Greg Waskewicz!Periodontal Residents NPDS and UMN!Machined Titanium!Tiunite!Osseotite
Healing Abutment Selection Perio Implant Part I Credit and Thanks for Lecture Material Implant Surface Characteristics!CAPT Robert Taft!CAPT Greg Waskewicz!Periodontal Residents NPDS and UMN!Machined Titanium!Tiunite!Osseotite
Fixing Dental Implant Component Failure and Fracture: Retrieving the Fractured Implant Abutment Screw. Charles A. Mastrovich, DDS
 Fixing Dental Implant Component Failure and Fracture: Retrieving the Fractured Implant Abutment Screw Charles A. Mastrovich, DDS cmastrovichdds@gmail.com www.mastrovichdental.com Evaluating component failure
Fixing Dental Implant Component Failure and Fracture: Retrieving the Fractured Implant Abutment Screw Charles A. Mastrovich, DDS cmastrovichdds@gmail.com www.mastrovichdental.com Evaluating component failure
POWER SCALING AIR-FLOW AIR POLISHING SOLUTIONS
 POWER SCALING AIR-FLOW AIR POLISHING SOLUTIONS ADVANCING PROPHYLAXIS PROTOCOL Introducing THE AIR-FLOW TECHNOLOGY AIR-FLOW PERIO units reach into periodontal pockets to remove biofilm. The new PERIO-FLOW
POWER SCALING AIR-FLOW AIR POLISHING SOLUTIONS ADVANCING PROPHYLAXIS PROTOCOL Introducing THE AIR-FLOW TECHNOLOGY AIR-FLOW PERIO units reach into periodontal pockets to remove biofilm. The new PERIO-FLOW
IMMEDIATE OCCLUSAL LOADING
 IMMEDIATE OCCLUSAL LOADING (IOL ) OF DENTAL IMPLANTS: Predictable Results Through DIEM Guidelines Richard J. Lazzara, DMD, MScD * Tiziano Testori, MD, DDS Alan Meltzer, DDS, MScD Craig Misch, DDS, MDS
IMMEDIATE OCCLUSAL LOADING (IOL ) OF DENTAL IMPLANTS: Predictable Results Through DIEM Guidelines Richard J. Lazzara, DMD, MScD * Tiziano Testori, MD, DDS Alan Meltzer, DDS, MScD Craig Misch, DDS, MDS
Forming the Interface Between Doctor and Designing Engineer
 Forming the Interface Between Doctor and Designing Engineer Christine Schoene (&), Philipp Sembdner, Stefan Holzhausen, and Ralph Stelzer Faculty of Mechanical Science and Engineering, Technische Universitaet
Forming the Interface Between Doctor and Designing Engineer Christine Schoene (&), Philipp Sembdner, Stefan Holzhausen, and Ralph Stelzer Faculty of Mechanical Science and Engineering, Technische Universitaet
Photoelastic Comparison of Single Tooth Implant-Abutment-Bone of Platform Switching vs Conventional Implant Designs
 10.5005/jp-journals-10024-1021 Fabiana Rossi et al ORIGINAL RESEARCH Photoelastic Comparison of Single Tooth Implant-Abutment-Bone of Platform Switching vs Conventional Implant Designs Fabiana Rossi, Adriana
10.5005/jp-journals-10024-1021 Fabiana Rossi et al ORIGINAL RESEARCH Photoelastic Comparison of Single Tooth Implant-Abutment-Bone of Platform Switching vs Conventional Implant Designs Fabiana Rossi, Adriana
Rehabilitation of a complex case with zirconium dental implants
 Rehabilitation of a complex case with zirconium dental Authors_Dr Andrea Enrico Borgonovo, Dr Marcello Dolci, Dr Rachele Censi, Dr Oscar Arnaboldi, Dr Virna Vavassori & Prof Carlo Maiorana, Italy _Introduction
Rehabilitation of a complex case with zirconium dental Authors_Dr Andrea Enrico Borgonovo, Dr Marcello Dolci, Dr Rachele Censi, Dr Oscar Arnaboldi, Dr Virna Vavassori & Prof Carlo Maiorana, Italy _Introduction
Surface Engineering Solutions Rebuild, Repair and Protect Industrial Equipment
 Surface Engineering Solutions Rebuild, Repair and Protect Industrial Equipment Whatever You Rebuild, Repair and Protect...... Find the Right Solution! Henkel's Solutions for all Surface Engineering Needs
Surface Engineering Solutions Rebuild, Repair and Protect Industrial Equipment Whatever You Rebuild, Repair and Protect...... Find the Right Solution! Henkel's Solutions for all Surface Engineering Needs
Long-term success of osseointegrated implants
 Against All Odds A No Bone Solution Long-term success of osseointegrated implants depends on the length of the implants used and the quality and quantity of bone surrounding these implants. As surgical
Against All Odds A No Bone Solution Long-term success of osseointegrated implants depends on the length of the implants used and the quality and quantity of bone surrounding these implants. As surgical
World leading in innovative restorative and esthetic dental solutions.
 World leading in innovative restorative and esthetic dental solutions. Individualized crowns, bridges, veneers and abutments Standardized implants and abutments TiUnite surface At a glance Nobel Biocare
World leading in innovative restorative and esthetic dental solutions. Individualized crowns, bridges, veneers and abutments Standardized implants and abutments TiUnite surface At a glance Nobel Biocare
Straumann Dental Implants Confident smiles
 Straumann Dental Implants Confident smiles STRAUMANN DENTAL IMPLANTS - DESIGNED TO LAST A LIFETIME Dental Implants The decision to replace missing teeth with dental implants is an excellent investment
Straumann Dental Implants Confident smiles STRAUMANN DENTAL IMPLANTS - DESIGNED TO LAST A LIFETIME Dental Implants The decision to replace missing teeth with dental implants is an excellent investment
Lapping and Polishing Basics
 Lapping and Polishing Basics Applications Laboratory Report 54 Lapping and Polishing 1.0: Introduction Lapping and polishing is a process by which material is precisely removed from a workpiece (or specimen)
Lapping and Polishing Basics Applications Laboratory Report 54 Lapping and Polishing 1.0: Introduction Lapping and polishing is a process by which material is precisely removed from a workpiece (or specimen)
Etching effects and the formation of Streaking Defects on Al Extrusions
 Etching effects and the formation of Streaking Defects on Al Extrusions Surface defects such as streaking are often present on anodized extrusions of 6xxx series alloys. The streak defect is the result
Etching effects and the formation of Streaking Defects on Al Extrusions Surface defects such as streaking are often present on anodized extrusions of 6xxx series alloys. The streak defect is the result
Rehabilitation of Endondontically Failed Anterior teeth by Immediate Replacement and Loading of an Implant supported Crown: A Case Report.
 RESEARCH AND REVIEWS: JOURNAL OF DENTAL SCIENCES Rehabilitation of Endondontically Failed Anterior teeth by Immediate Replacement and Loading of an Implant supported Crown: A Case Report. Lalit Kumar 1
RESEARCH AND REVIEWS: JOURNAL OF DENTAL SCIENCES Rehabilitation of Endondontically Failed Anterior teeth by Immediate Replacement and Loading of an Implant supported Crown: A Case Report. Lalit Kumar 1
Trabecular Metal Technology
 Trabecular Metal Technology TM The Best Thing Next To Bone. Introducing Trabecular Metal Material to implant dentistry. trabecular metal technology Trabecular Metal Technology is an innovative material
Trabecular Metal Technology TM The Best Thing Next To Bone. Introducing Trabecular Metal Material to implant dentistry. trabecular metal technology Trabecular Metal Technology is an innovative material
Oftentimes, as implant surgeons, we are
 CLINICAL AVOIDING INJURY TO THE INFERIOR ALVEOLAR NERVE BY ROUTINE USE OF INTRAOPERATIVE RADIOGRAPHS DURING IMPLANT PLACEMENT Jeffrey Burstein, DDS, MD; Chris Mastin, DMD; Bach Le, DDS, MD Injury to the
CLINICAL AVOIDING INJURY TO THE INFERIOR ALVEOLAR NERVE BY ROUTINE USE OF INTRAOPERATIVE RADIOGRAPHS DURING IMPLANT PLACEMENT Jeffrey Burstein, DDS, MD; Chris Mastin, DMD; Bach Le, DDS, MD Injury to the
Prosthetic treatment planning on the basis of scientific evidence.
 Prosthetic treatment planning on the basis of scientific evidence. Pjetursson BE, Lang NP. J Oral Rehabil. 2008 Jan;35 Suppl 1:72-9. Faculty of Odontology, University of Iceland, Reykjavik, Iceland, and
Prosthetic treatment planning on the basis of scientific evidence. Pjetursson BE, Lang NP. J Oral Rehabil. 2008 Jan;35 Suppl 1:72-9. Faculty of Odontology, University of Iceland, Reykjavik, Iceland, and
ARCS Pre-Implantology
 ARCS Pre-Implantology ARCS - Alveolarkamm Reconstruction System The ARCS System meets the requirements of modern implantology. Atrophy of the alveolar crest causes continuous problems during restoration
ARCS Pre-Implantology ARCS - Alveolarkamm Reconstruction System The ARCS System meets the requirements of modern implantology. Atrophy of the alveolar crest causes continuous problems during restoration
Bone response to unloaded and loaded titanium implants with a sandblasted and acid-etched surface: A histometric study in the canine mandible
 Bone response to unloaded and loaded titanium implants with a sandblasted and acid-etched surface: A histometric study in the canine mandible D. L. Cochran, 1 R. K. Schenk, 2 A. Lussi, 3 F. L. Higginbottom,
Bone response to unloaded and loaded titanium implants with a sandblasted and acid-etched surface: A histometric study in the canine mandible D. L. Cochran, 1 R. K. Schenk, 2 A. Lussi, 3 F. L. Higginbottom,
1 The Single Tooth Implant. The Ultimate Aesthetic Challenge
 1 The Single Tooth Implant The Ultimate Aesthetic Challenge by Daniel G. Pompa, D.D.S. 2 Before starting any Maxillary Anterior Single Implant, or any case in the esthetic zone: TAKE A PHOTO OF YOUR PATIENT
1 The Single Tooth Implant The Ultimate Aesthetic Challenge by Daniel G. Pompa, D.D.S. 2 Before starting any Maxillary Anterior Single Implant, or any case in the esthetic zone: TAKE A PHOTO OF YOUR PATIENT
Retention of maxillary implant overdenture bars of different designs
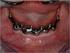 Retention of maxillary implant overdenture bars of different designs Brian H. Williams, DDS, a Kent T. Ochiai, DDS, b Satoru Hojo, DDS, PhD, c Russell Nishimura, DDS, d and Angelo A. Caputo, PhD e School
Retention of maxillary implant overdenture bars of different designs Brian H. Williams, DDS, a Kent T. Ochiai, DDS, b Satoru Hojo, DDS, PhD, c Russell Nishimura, DDS, d and Angelo A. Caputo, PhD e School
Bone remodeling surrounding osseointegrated. Stress Analysis in Platform-Switching Implants: A 3-Dimensional Finite Element Study RESEARCH
 RESEARCH Stress Analysis in Platform-Switching Implants: A 3-Dimensional Finite Element Study Eduardo Piza Pellizzer, DDS, PhD, MSc 1 * Fellippo Ramos Verri, DDS, PhD, MSc 1 Rosse Mary Falcón-Antenucci,
RESEARCH Stress Analysis in Platform-Switching Implants: A 3-Dimensional Finite Element Study Eduardo Piza Pellizzer, DDS, PhD, MSc 1 * Fellippo Ramos Verri, DDS, PhD, MSc 1 Rosse Mary Falcón-Antenucci,
, Yong-Min Kwon 1 ) , Ho-Young Son 1 ) , Jeong-Tak Moon 2 ) Byung-Wook Jeong 2 ) , Kyung-In Kang 2 )
 Effect of Sb Addition in Sn-Ag-Cu Solder Balls on the Drop Test Reliability of BGA Packages with Electroless Nickel Immersion Gold (ENIG) Surface Finish Yong-Sung Park 1 ), Yong-Min Kwon 1 ), Ho-Young
Effect of Sb Addition in Sn-Ag-Cu Solder Balls on the Drop Test Reliability of BGA Packages with Electroless Nickel Immersion Gold (ENIG) Surface Finish Yong-Sung Park 1 ), Yong-Min Kwon 1 ), Ho-Young
Smile Confidently With DIEM 2. Immediate Full Arch Rehabilitation
 Smile Confidently With DIEM 2 Immediate Full Arch Rehabilitation Immediate Full Arch Rehabilitation * Edentulism and failing dentition continue to be major health challenges affecting millions of people
Smile Confidently With DIEM 2 Immediate Full Arch Rehabilitation Immediate Full Arch Rehabilitation * Edentulism and failing dentition continue to be major health challenges affecting millions of people
ORTHODONTIC MINI IMPLANTS Clinical procedure for positioning. Orthodontics and Implantology
 ORTHODONTIC MINI IMPLANTS Clinical procedure for positioning Orthodontics and Implantology 2 All rights are reserved. Any reproduction of the present publication is prohibited in whole or in part and by
ORTHODONTIC MINI IMPLANTS Clinical procedure for positioning Orthodontics and Implantology 2 All rights are reserved. Any reproduction of the present publication is prohibited in whole or in part and by
Titanium versus Zirconium Implants
 Titanium versus Zirconium Implants A dental materials comparison Dr. Gerald Regni, DMD!!" Christian St. Phila. PA 1213" T: (""") %&'-!"#" E: Dr.Gerald_Regni@yahoo.com Titanium versus Zirconium Implants
Titanium versus Zirconium Implants A dental materials comparison Dr. Gerald Regni, DMD!!" Christian St. Phila. PA 1213" T: (""") %&'-!"#" E: Dr.Gerald_Regni@yahoo.com Titanium versus Zirconium Implants
DENTAL FOR EVERYONE SUMMARY OF BENEFITS, LIMITATIONS AND EXCLUSIONS
 DENTAL FOR EVERYONE SUMMARY OF BENEFITS, LIMITATIONS AND EXCLUSIONS DEDUCTIBLE The dental plan features a deductible. This is an amount the Enrollee must pay out-of-pocket before Benefits are paid. The
DENTAL FOR EVERYONE SUMMARY OF BENEFITS, LIMITATIONS AND EXCLUSIONS DEDUCTIBLE The dental plan features a deductible. This is an amount the Enrollee must pay out-of-pocket before Benefits are paid. The
Straumann Dental implant system ONE SYSTEM ONE INSTRUMENT KIT ALL INDICATIONS*
 Straumann Dental implant system ONE SYSTEM ONE INSTRUMENT KIT ALL INDICATIONS* For all indications*! The Straumann Dental Implant System offers you and your patients efficient and esthetic implant-borne
Straumann Dental implant system ONE SYSTEM ONE INSTRUMENT KIT ALL INDICATIONS* For all indications*! The Straumann Dental Implant System offers you and your patients efficient and esthetic implant-borne
