Tjocklek (mm) T 25 a 25 < t 50 b t >50 S235 till S355 (1.1, 1.2, 1.4) G N O c. S420 till S700 (1.3, 2, 3) O O O. Austenitiska rostfria stål G N O
|
|
|
- Bryan Freeman
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 EN 1090 hänvisar till EN för krav på svetsansvarigs kompetens. Kompetensnivåerna beror av utförandeklass, plåttjocklek och stålsort och delas in i nivåerna G-grundläggande, N-normal och O- omfattande, se tabell nedan. Utförandeklass EXC 2 Stålsort Tjocklek (mm) T 25 a 25 < t 50 b t >50 S235 till S355 (1.1, 1.2, 1.4) G N O c S420 till S700 (1.3, 2, 3) N O d O Austenitiska rostfria stål G N O Austenit-ferritiska rostfria stål N O O S235 till S355 (1.1, 1.2, 1.4) N O O EXC 3 S420 till S700 (1.3, 2, 3) O O O Austenitiska rostfria stål N O O Austenit-ferritiska rostfria stål O O O EXC 4 O O O a Fotplåtar och ändplåtar 50 mm b Fotplåtar och ändplåtar 75 c För stål upp till och med S275 räcker N d För stål N, NL, M och ML räcker kunskapsnivå N Kravet för nivå G och N anses uppfyllt om svetsansvarig innehar diplom från genomgången IWSutbildning. Om detta saknas kan kompetensen hyras in och ingå i företagets FPC. Om företaget har en person som anses uppfylla kompetenskraven utan att ha genomgått en IWS-utbildning kommer en muntlig utfrågning att ske av en svetsexpert vid företagets revision för certifiering enligt EN EWF, European Federation for Welding, Joining and Cutting har skrivit en vägledning med krav på kursinnehåll för kurser som syftar till att utbilda svetsansvariga för nivå G (grundläggande och nivå N (normal) enligt EN Efter varje kursavsnitt ges en sammanfattning av vilken kunskap som förväntas av deltagarna efter genomgånget kursmoment. Nedan följer en sammanställning av den kunskap som en svetsansvarig förväntas ha för nivå G respektive N enligt EWF s guideline.
2 Competence requirements for Responsible Welding Coordinators level B () and level S () according to EN 1090 Welding personnel having an IWS diploma are accepted. If not, knowledge of the following has to be confirmed. 1. Welding processes and equipment. 1.1 General introduction to welding technology Outline the major differences between each main type of welding process, e.g. fusion arc, resistance, flame, forge etc. Differentiate between processes and reference to standards Recognize a welding process by the common abbreviation 1.2 The arc Describe an electric arc; its main areas and their importance to welding and arc stability Outline the generation of heat in the arc Give examples of the influence of magnetic fields on the electric arc Outline appropriate solutions to solve magnetic deflection problems Describe arc characteristics for DC and AC 1.3 Power sources for arc welding Outline how each type of welding power source works (AC and DC) including the most common devices used. Describe for each type of arc welding power source the static characteristic, operation point and control of arc stability Outline the meaning of open circuit voltage, arc voltage short circuit current, duty cycle of a power source, voltage losses and current to cable relationship Be able to select the appropriate power sources för a given welding process. Recognize the various settings and switches on different power sources and their effects. Outline the major differences between each main type of welding process, e.g. fusion arc, resistance, flame, forge etc. Differentiate between processes and reference to standards Recognize a welding process by the common abbreviation Describe an electric arc; its main areas and their importance to welding and arc stability Outline the generation of heat in the arc Give examples of the influence of magnetic fields on the electric arc Outline appropriate solutions to solve magnetic deflection problems Describe arc characteristics for DC and AC Outline how each type of welding power source works (AC and DC) including the most common devices used. Describe for each type of arc welding power source the static characteristic, operation point and control of arc stability Outline the meaning of open circuit voltage, arc voltage short circuit current, duty cycle of a power source, voltage losses and current to cable relationship Be able to select the appropriate power sources för a given welding process. Recognize the various settings and switches on different power sources and their effects.
3 1.4 TIG Welding Outline TIG welding including arc ignition methods and their most common applications. Give examples of the most common application for each type of current, polarity and electrode type. Give examples of the most important applications and select the appropriate values for welding parameters. Know how to use and care for the equipment and accessories. Read given standards for consumables. Give examples of TIG applications, joint preparation and potential problems to Outline potential hazards and methods of safe MIG/MAG Welding Describe and compare the principles of MIG/MAG welding including metal transfer modes and applications. Identify the most common applications for each type of current, polarity and electrode. Identify the range of application, appropriate joint preparations and potential problems to be Identify the influence of the welding parameters on the weld bead and be able to outline welding parameters for particular application. Describe potential hazards and methods of safe Outline the various functions of the main components of the equipment and accessories. Demonstrate the use of appropriate standards for consumables. Give examples on how consumables should be selected. Know how to use and care for the equipment and accessories. Describe and compare the principles of TIG welding including arc ignition methods and their application. Explain the selection of appropriate type of current, polarity, shielding gas and electrode type according to application. Identify the range of application appropriate joint preparations and potential problems to be Identify an appropriate range of welding parameters for particular applications. Explain the purpose and functions of each component of the equipment an accessories. Interpret the use of appropriate standards. Describe potential hazards and methods of safe Describe and compare the principles of MIG/MAG welding including metal transfer modes and applications. Identify the most common applications for each type of current, polarity and electrode. Identify the range of application, appropriate joint preparations and potential problems to be Identify the influence of the welding parameters on the weld bead and be able to outline welding parameters for particular application. Describe potential hazards and methods of safe Outline the various functions of the main components of the equipment and accessories. Demonstrate the use of appropriate standards for consumables. Give examples on how consumables should be selected. Know how to use and care for the equipment and accessories.
4 1.5.2 Flux Cored Arc Welding Describe the principles of Flux Cored Arc welding including their applications. Identify the most common applications for each type of current, polarity and electrode. Identify the range of application, appropriate joint preparations and potential problems to be Identify the influence of the appropriate welding parameters on the weld bead and be able to outline welding parameters for particular applications. Describe potential hazards and methods of safe Outline the various functions of the main components of the equipment and accessories. Demonstrate the use of appropriate standards for consumables. Give examples on how consumables should be selected. Know how to use and care for the equipment and accessories. Describe the principles of Flux Cored Arc welding including their applications. Identify the most common applications for each type of current, polarity and electrode. Identify the range of application, appropriate joint preparations and potential problems to be Identify the influence of the appropriate welding parameters on the weld bead and be able to outline welding parameters for particular applications. Describe potential hazards and methods of safe Outline the various functions of the main components of the equipment and accessories. Demonstrate the use of appropriate standards for consumables. Give examples on how consumables should be selected. Know how to use and care for the equipment and accessories. 1.6 MMA Welding Outline the principles of MMA welding Describe the principles of MMA welding Outline how to select the appropriate type of Describe how to select the appropriate type of current, polarity and electrode according to current, polarity and electrode according to application. application. Identify the range of application, appropriate Identify the range of application, appropriate joint preparations and potential problems to be joint preparations and potential problems to be Identify an appropriate range of welding Identify an appropriate range of welding parameters for particular applications parameters for particular applications List potential hazards and methods of safe Describe potential hazards and methods of safe Outline the purpose and functions of each Outline the purpose and functions of each component of the equipment and accessories. component of the equipment and accessories. List the appropriate methods of handling, control Describe the appropriate methods of handling, and storage of the various types of electrodes. control and storage of the various types of electrodes. Demonstrate the use of appropriate standards. Demonstrate the use of appropriate standards. - Describe the influence of electrode coating on droplet transfer and weld material properties.
5 1.7 Submerged Arc Welding Explain the principle of the SAW process including arc striking methods and their applications. Explain the criteria for evaluating the applicable welding parameters. Identify the application range, joint edge preparation and potential problems to Clarify the procedures for the set-up of power sources. Explain the criteria for the selection of flux-wire combinations. Interpret appropriate standards and welding procedures. Define welding instructions for welders and operators. Define potential hazards and methods of safe 1.8 Stud welding Describe the principles of Stud welding and its application. Name some common applications of the processes in the different industrial fields. Define potential hazards and methods of safe Know how to use and care for the equipment and accessories. Explain the principle of the SAW process including arc striking methods and their applications. Explain the criteria for evaluating the applicable welding parameters. Identify the application range, joint edge preparation and potential problems to Clarify the procedures for the set-up of power sources. Explain the criteria for the selection of flux-wire combinations. Interpret appropriate standards and welding procedures. Define welding instructions for welders and operators. Define potential hazards and methods of safe Describe the principles of Stud welding and its application. Name some common applications of the processes in the different industrial fields. Define potential hazards and methods of safe Know how to use and care for the equipment and accessories. 1.9 Cutting, Drilling and other edge preparation processes Describe the principles of: mechanical, flame arc, Describe the principles of: mechanical, flame arc, laser and plasma cutting. laser and plasma cutting. Identify the characteristic parameters for the Identify the characteristic parameters for the above mentioned processes. above mentioned processes. Make a comparison among different edge Make a comparison among different edge preparation processes, considering technical and preparation processes, considering technical and economic aspects. economic aspects. List potential risks and hazards related with edge preparation processes. List potential risks and hazards related with edge preparation processes.
6 2. Materials and their behavior during welding 2.1 Structure and properties of metals. - List pure metals and alloys. - Outline basic mechanical properties of metals. - Outline effect of loading conditions on metals properties. 2.2 Phase diagrams and Alloys - Identify solidification structure and segregation on relevant examples. - Outline the principles of strengthening mechanisms with appropriate examples. - Interpret the relationship between microstructure and phase diagrams. - Describe alloys and phase diagrams. 2.3 Iron Carbon Alloys Special items of the Fe-C diagram (types of Fe-C alloys) Influence of cooling rate, hardenability. TTT and CCT diagrams. Classification of heat treatment Fe-C alloys Influence of cooling rate, hardenability. Prevention of coarse structure Classification of heat treatment 2.4 Classification of steels - Properties of steel semi-products - Types of steel, particularly structural steels. - Use of standards for steel designation and standards on rolling products. - Knowledge of types of inspection documents. 2.5 Behaviour of structural steels in fusion welding Special items of the Fe-C diagram (types of Fe-C Explain the temperature distribution in welds alloys) and the microstructure formed as a result for a single pass weld versus a multi-pass weld. Influence of cooling rate, hardenability. Interpret the effects of heat input, cooling rate and multi-pass operation on weld metal solidification and the microstructure formed for a single pass weld versus a multi-pass weld. TTT and CCT diagrams. Explain the effects of the weld protection, the type of consumables on the microstructure of the weld metal and on its properties for a single pass weld versus a multi-pass weld.
7 Classification of heat treatment Draw areas of HAZ, the reasons for grain size and microstructure changes and their effects on properties for a single pass weld versus a multipass weld. Discuss the various aspects of weldability. 2.6 Heat treatment of base materials and welded joints Describe the major heat treatments and their Explain each of the major heat treatments and objectives. their objectives. Discuss the necessity to perform heat treatment Describe code requirements for heat treatment after welding depending of the type and thickness of steel, the application and the code - Predict the necessity to perform heat treatment after welding depending of the type and thickness of steel, the application and the code 2.7 Structural Steels Having knowledge of: Unalloyed structural steels Filler materials Determination of welding technology Application of standards for filler materials. Having knowledge of: Unalloyed structural steels Filler materials Determination of welding technology Application of standards for filler materials. 2.8 High Strength Steels List the different methods to obtain fine-grained Explain the different methods to obtain finegrained steels steels Explain the relationship between grain Explain the relationship between grain refinement and mechanical properties. refinement and mechanical properties. Interpret the relationship between grade and Outline appropriate applications weldability. Identify applicable welding processes and Interpret the relationship between grade and potential problems. weldability. Name the effects of heat treatment after welding Identify applicable welding processes and and deduce the conditions of such treatment. potential problems. - Name the effects of heat treatment after welding and deduce the conditions of such treatment. - Use the appropriate filler material. 2.9 Cracking Phenomena in welded joints Compare the metallurgical mechanisms for each of the major types of cracking. Appraise the susceptibility to cracking and suggest appropriate precautions to avoid cracking. Name the type of cracking and the reason for its occurrence. Compare the metallurgical mechanisms for each of the major types of cracking. Describe the effects of chemical and physical variables for each of the major types of cracking. Appraise the susceptibility to cracking and suggest appropriate precautions to avoid
8 List alternatives, which will reduce or eliminate the occurrence of lamellar tearing in welded construction /fabrication. Name the effects of heat treatment after welding and deduce the conditions of such treatment. cracking. Name the type of cracking and the reason for its occurrence from study of fractured material and its history. Choose suitable tests which will assist in finding solution of cracking problems. Propose alternatives which will reduce or eliminate the occurrence of lamellar tearing in welded construction/fabrication Stainless steels Outline the structures of the various stainless Outline the structures of the various stainless steels. steels and explain their behavior during welding. Outline welding processes and consumables for State the rules and principles governing each type of steel. corrosion phenomena. Outline the different treatment after welding. Indicate the choice of welding process and consumables for each type of steel using different diagrams. - Describe the different treatment after welding Testing of materials and welded joints Discuss the reasons for destructive testing Discuss the objective of each destructive test and the limitations of the data generated. Outline each of the major testing methods and the parameters to be measured. State when and why special testing should be specified. Describe the major testing methods and the parameters to be measured. Classify competence in carrying out testing to a given schedule. - Show competence in carrying out testing to a given schedule. 3. Construction and design 3.1 theory of structural systems - Understande in general the composition of forces. - Understand in general the resolution of forces. - Name the conditions of equilibrium. - Understand in general the equilibrium of structural systems. - Name bearing, constraints and the basic types of connections.
9 3.2 Fundamentals of the strength of materials - Understand in general the different types of stresses (normal stress, shear stresses) - Understand in general the different types of deformation (axial strain, shear strain etc). - Understand in general the stress-strain relationships. - Understand in general the stresses resulting from internal forces and moments. 3.3 Joint design for Welding Describe different types of welded joints. Identify different types of welded joints. Know how to apply each type of joint in function Apply (EN-) ISO 9692 according to the given of material, thickness and welding process. conditions. Explain the symbolic representation of welded Identify and use appropriate weld symbols. joints on drawings. - Explain the symbolic representation of welded joints in drawings. 3.4 s of weld design - Understand in general the different types of stresses in welded joints (nominal stress, hot spot stress, notch stress). - Understand simple welded joints (internal forces) - Understand cross-sections for welded joints. 3.5 Behaviour of welded structures under different types of loading. - Understand the requirements for the construction according to different types of loading and temperatures. - Identify globally groups of materials which meet strength requirements. - Identify the various types of fracture. 3.6 Design of welded structures predominantly static loading Understand the requirements for the Understand the requirements for the construction according to different types of construction according to different types of loading and temperatures. loading and temperatures. Identify globally groups of materials which meet Identify globally groups of materials which meet strength requirements. strength requirements. Identify the various types of fracture. Identify the various types of fracture.
10 4. Fabrication, applications engineering 4.1 Introduction to quality assurance in welded fabrication Outline of knowledge in: Main difference between quality assurance, quality control and inspection systems and their usage for welded fabrication. Goals for quality assurance and quality control. Writing quality control procedures. Recognition of some factors related to personnel Interpretation of standards (e.g. ISO 3834) and equipment, which influence the quality of a welded construction. Role of the Welding Coordinator in the fabrication industry. factors related to personnel and equipment, which influence the quality of a welded construction. - Role of the Welding Coordinator in the fabrication industry. 4.2 Quality control during manufacture Outline of knowledge in: Purpose of the WPS, and the advantages to the quality of the welded construction. Recognition of the main variables for a certain WPS qualification and its range of approval. Welder qualification purpose, and the advantages to the quality of the welded construction. Recognition of the EN and ISO/other valid standard for a welder qualification, and outline the main variables for a certain welder qualification and its range of approval. Traceability requirements for materials procedures and certificates and give examples. Main purpose of a WPS/WPQR/pWPS and the advantages to the quality of welded fabrication. Compile and review WPss for welded components in accordance with national and international standards. Interpretation of the standard for the qualification of a WPS, determine the main variables for a particular WPS qualification and its range of qualification in accordance with National and/or International standards. Main purpose of a welder qualification and the main advantages to the quality of welded fabrication. Interpretation of the standard for a welder qualification, determine the main variables for a particular welder qualification and its range of qualification. Main purpose of a welding operator qualification and the main advantages to the quality of welded fabrication. - Interpretation of the standard for a welding operator qualification, determine the main variables for a particular welding operator qualification and its range of qualification. - Definition of traceability requirements for material procedures and certificates and give examples.
11 4.3 Residual Stresses and Distortion State: The origin, influencing factors and magnitude of residual stress and distortion in welded fabrications. Relationships between the material at a certain temperature and its mechanical characteristics. Distribution of the residual stresses at weld (parallel to the weld axis, perpendicular, and through thickness, influence of the material thickness) Predict contraction and distortion in joints and structures. Develop procedures to minimize distortion and stress. How residual stresses may affect the behavior of a structure in service. 4.4 Plant facilities, welding jigs and fixtures Outline of knowledge in: The layout importance to achieve a higher and easier production Recognize the advantages of using fixtures, jigs and positioners. Recognize the type of fixture, jig and positioned to be used in a certain welded construction. Recognize the necessary characteristics for the auxiliary equipment to be used in a certain welded construction, cables, heat treatment equipment and temperature control. Outline the general precautions related to joint fit up and tack welding. 4.5 Health and safety The risk factors associated with welding from electricity, gases, fumes, fire, radiation and noise. The interpretation of Health and Safety regulations with respect of the above hazards. Select the appropriate methods to reduce each type of welding risk factors. The health effects of grinding and hazards regarding the heat. Safe working procedures to ensure the requirements are met. Using of protective cloting. Oxygen environment enrichment. The origin, influencing factors and magnitude of residual stress and distortion in welded fabrications. Relationships between the material at a certain temperature and its mechanical characteristics. Distribution of the residual stresses at weld (parallel to the weld axis, perpendicular, and through thickness, influence of the material thickness) Predict contraction and distortion in joints and structures. Develop procedures to minimize distortion and stress. How residual stresses may affect the behavior of a structure in service. Explain: Principles for improved productivity, safety and comfort. The advantages of using fixtures, jigs and positioners. Select the type of fixture, jig and positioned to be used in a certain welded construction. Select the type of auxiliary equipment to be used in a certain welded construction, cables, heat treatment equipment and temperature control equipment. The special requirements related to joint fit up and tack welding. The risk factors associated with welding from electricity, gases, fumes, fire, radiation and noise. The interpretation of Health and Safety regulations with respect of the above hazards. Select the appropriate methods to reduce each type of welding risk factors. The health effects of grinding and hazards regarding the heat. Safe working procedures to ensure the requirements are met. Using of protective cloting. Oxygen environment enrichment.
12 4.6 Measurement, Control and Recording in Welding. Explain: The methods iof measurement used in the The methods iof measurement used in the control of welding. control of welding. Working procedures for the measurement of Working procedures for the measurement of welding parameters. welding parameters. - Working procedures for the measurement and control of heat treatment operations. Procedures for the calibration, validation and monitoring of welding operations. 4.7 Non Destructive testing. State: The modes of operation of the principal NDT methods, their advantages and disadvantages when applied to welded fabrications. Weld imperfections, their causes and methods of detection. Interpretation of acceptance standards for weld imperfections. Identification of the principles of NDT interpretation. Selection of weld configurations and design to allow adequate application of NDT methods. Identification of the qualification of NDT personnel. Recognition of safety aspects. 4.8 Economics and Productivity State: The make up of costs associated with welding Welding and handling procedures including mechanization and automation to minimize production costs. Welding processes operation factor 4.9 Repair Welding Problems of making repair welds. Possible hazards likely to occur in making repair welds particularly for in-service repairs. Comprehensive procedures to be applied to weld repairs. The modes of operation of the principal NDT methods, their advantages and disadvantages when applied to welded fabrications. Weld imperfections, their causes and methods of detection. Interpretation of acceptance standards for weld imperfections. Identification of the principles of NDT interpretation. Selection of weld configurations and design to allow adequate application of NDT methods. Identification of the qualification of NDT personnel. Recognition of safety aspects. Elements of costs associated with welding. Costs of welding operations Select welding and handling procedures including mechanization and automation to minimize production costs. Problems of making repair welds. Possible hazards likely to occur in making repair welds particularly for in-service repairs. Comprehensive procedures to be applied to weld repairs.
13 Procedural and operator qualifications to be applied to repair welds. 5. Background of the EN Explain how En 1090 should control manufacturing of steel construction products. 6. Review of requirements, technical review Illustrate the potential hazards of a contract Translate the appropriate standards to working documents. Evaluating the (sub)contractor s ability for manufacturing. Being capable of providing a professional judgement on subcontracting. 7. Welding personnel Decide about the quality of a welder s qualification test performed. Decide on the validity of a welders performance qualification. Compile a list with welding personnel qualified for the project. 8. Equipment Safe and economic use of weld related equipment 9. Production planning To follow up a total production planning and proceed accordingly. Capable of making adjustments if necessary. To administer production data. 10. Qualification of the welding procedures. Compile a list with welding procedure qualification available/necessary for the project. Procedural and operator qualifications to be applied to repair welds. Explain how En 1090 should control manufacturing of steel construction products. Illustrate the potential hazards of a contract Translate the appropriate standards to working documents. Evaluating the (sub)contractor s ability for manufacturing. Being capable of providing a professional judgement on subcontracting. Decide about the quality of a welder s qualification test performed. Decide on the validity of a welders performance qualification. Compile a list with welding personnel qualified for the project. Safe and economic use of weld related equipment To follow up a total production planning and proceed accordingly. Capable of making adjustments if necessary. To administer production data. Compile a list with welding procedure qualification available/necessary for the project. 11. Welding procedure specifications and work instructions To set-up and using welding procedures To set-up and using welding procedures Setting up and organizing toolbox meetings. Setting up and organizing toolbox meetings.
14 12. Welding consumables Correct use of the appropriate welding consumables. 13. Materials Recognize essential differences in material certificates. Ordering the aoolied materials in fabrication manuals Correct use of the appropriate welding consumables. Recognize essential differences in material certificates. Ordering the aoolied materials in fabrication manuals 14. Inspection and testing before, during and after welding. Setting up and organizing welding inspection plans and response appropriate in case of deviations. deviations. To follow up and the interpretation of welding inspection plan and response appropriate in case of deviations. Incorporation into fabrication manuals. Setting up and organizing welding inspection plans and response appropriate in case of To follow up and the interpretation of welding inspection plan and response appropriate in case of deviations. Incorporation into fabrication manuals. 15. Non-conformance, corrective actions and quality records The correct assigning and processing of NCR c The correct assigning and processing of NCR c Oredering the applied materials in fabrication manuals. Oredering the applied materials in fabrication manuals. To set-up a fabrication manual. To set-up a fabrication manual. 16. Calibration and validation of measuring, inspection and testing equipment. The application of and/or the evaluation of the The application of and/or the evaluation of the correct use of testing equipment. correct use of testing equipment.
Chapter 5 - Aircraft Welding
 Chapter 5 - Aircraft Welding Chapter 5 Section A Study Aid Questions Fill in the Blanks 1. There are 3 types of welding:, and, welding. 2. The oxy acetylene flame, with a temperature of Fahrenheit is produced
Chapter 5 - Aircraft Welding Chapter 5 Section A Study Aid Questions Fill in the Blanks 1. There are 3 types of welding:, and, welding. 2. The oxy acetylene flame, with a temperature of Fahrenheit is produced
Welding. ArcelorMittal Europe Flat Products. Definitions of welding and weldability. Consequences of welding
 ArcelorMittal Europe Flat Products Welding Definitions of welding and weldability Welding of metal parts is a joining process designed to ensure metallic continuity across the joint. This continuity is
ArcelorMittal Europe Flat Products Welding Definitions of welding and weldability Welding of metal parts is a joining process designed to ensure metallic continuity across the joint. This continuity is
www.klmtechgroup.com TABLE OF CONTENT
 Page : 1 of 45 Project Engineering Standard www.klmtechgroup.com KLM Technology #03-12 Block Aronia, Jalan Sri Perkasa 2 Taman Tampoi Utama 81200 Johor Bahru Malaysia TABLE OF CONTENT 1.0 SCOPE 2 2.0 CONFLICTS
Page : 1 of 45 Project Engineering Standard www.klmtechgroup.com KLM Technology #03-12 Block Aronia, Jalan Sri Perkasa 2 Taman Tampoi Utama 81200 Johor Bahru Malaysia TABLE OF CONTENT 1.0 SCOPE 2 2.0 CONFLICTS
Duplex Stainless Steel Fabrication. Gary M. Carinci TMR Stainless Consultant for International Molybdenum Association
 Duplex Stainless Steel Fabrication Gary M. Carinci TMR Stainless Consultant for International Molybdenum Association 1 Promoting molybdenum - as a material with superior properties and performance in a
Duplex Stainless Steel Fabrication Gary M. Carinci TMR Stainless Consultant for International Molybdenum Association 1 Promoting molybdenum - as a material with superior properties and performance in a
WORD DEFINITION WORD (NATIONAL LANGUAGE)
 WELDING GLOSSARY The Glossary has been created as part of the Migration for Development in the Western Balkans (MIDWEB) project, which received financial assistance from the European Commission IPA 2009
WELDING GLOSSARY The Glossary has been created as part of the Migration for Development in the Western Balkans (MIDWEB) project, which received financial assistance from the European Commission IPA 2009
Weld Cracking. An Excerpt from The Fabricators' and Erectors' Guide to Welded Steel Construction. The James F. Lincoln Arc Welding Foundation
 Weld Cracking An Excerpt from The Fabricators' and Erectors' Guide to Welded Steel Construction The James F. Lincoln Arc Welding Foundation Weld Cracking Several types of discontinuities may occur in welds
Weld Cracking An Excerpt from The Fabricators' and Erectors' Guide to Welded Steel Construction The James F. Lincoln Arc Welding Foundation Weld Cracking Several types of discontinuities may occur in welds
WELDING TECHNOLOGY DEGREES AND CERTIFICATES. Welding Technology Degree. Shielded Metal Arc Plate and Pipe (270 hours) Certificate
 Area: Technical Education Dean: Dr. Trish Caldwell Phone: (916) 484-8354 Counseling: (916) 484-8572 www.arc.losrios.edu/~welding/ The American Welding Society (AWS) nationally accredits American River
Area: Technical Education Dean: Dr. Trish Caldwell Phone: (916) 484-8354 Counseling: (916) 484-8572 www.arc.losrios.edu/~welding/ The American Welding Society (AWS) nationally accredits American River
INDIAN STANDARDS (BIS) ON WELDING
 ** IS 82:957 Glossary of terms relating to welding and cutting of Sep 2008 metals 2 IS 83:986 Scheme of symbols for welding (revised) Sep 2008 3 IS 84:2004 Covered electrodes for manual metal arc welding
** IS 82:957 Glossary of terms relating to welding and cutting of Sep 2008 metals 2 IS 83:986 Scheme of symbols for welding (revised) Sep 2008 3 IS 84:2004 Covered electrodes for manual metal arc welding
STANDARDS FOR THE MATERIALS
 STANDARDILUETTELO 1(15) Kpl Standardin numero STANDARDS FOR THE MATERIALS 1 EN 10204 2004-10 Metallic products.types of inspection documents 2 EN 10079 1992-10 Definition of steel products 3 EN 10027-1
STANDARDILUETTELO 1(15) Kpl Standardin numero STANDARDS FOR THE MATERIALS 1 EN 10204 2004-10 Metallic products.types of inspection documents 2 EN 10079 1992-10 Definition of steel products 3 EN 10027-1
Copper. Consumables. Copper and Copper Alloys. Welding Processes
 Consumables and Alloys is a metal with some very important properties, the main ones being its high electrical conductivity, its high thermal conductivity, its excellent resistance to corrosion, and its
Consumables and Alloys is a metal with some very important properties, the main ones being its high electrical conductivity, its high thermal conductivity, its excellent resistance to corrosion, and its
SMARTY 160 POWER page 4-5 SMARTY 180 / 220 XL page 4-6 SMARTY TX 250 page 4-7. SMARTY TX 160 Alu page 4-8 SMARTY TX 220 Alu page 4-9
 CHAPTER TIG welding Introduction pages - & - WELDING POWER SOURCES DC power sources SMARTY 60 POWER page -5 SMARTY 80 / 0 XL page -6 SMARTY TX 50 page -7 AC/DC power sources SMARTY TX 60 Alu page -8 SMARTY
CHAPTER TIG welding Introduction pages - & - WELDING POWER SOURCES DC power sources SMARTY 60 POWER page -5 SMARTY 80 / 0 XL page -6 SMARTY TX 50 page -7 AC/DC power sources SMARTY TX 60 Alu page -8 SMARTY
High-strength and ultrahigh-strength. Cut sheet from hot-rolled steel strip and heavy plate. voestalpine Steel Division www.voestalpine.
 High-strength and ultrahigh-strength TM steels Cut sheet from hot-rolled steel strip and heavy plate Josef Elmer, Key account manager voestalpine Steel Division www.voestalpine.com/steel Weight savings
High-strength and ultrahigh-strength TM steels Cut sheet from hot-rolled steel strip and heavy plate Josef Elmer, Key account manager voestalpine Steel Division www.voestalpine.com/steel Weight savings
EN 13445-4:2002 (E) Issue 1 (2002-05)
 Issue 1 (2002-05) 8.4.4 Impact test...26 8.4.5 Bend test...26 8.4.6 Macro examination...27 8.4.7 Micro examination...27 8.4.8 Hardness test...27 8.4.9 Retests...27 8.4.10 Test report...28 9 Forming of
Issue 1 (2002-05) 8.4.4 Impact test...26 8.4.5 Bend test...26 8.4.6 Macro examination...27 8.4.7 Micro examination...27 8.4.8 Hardness test...27 8.4.9 Retests...27 8.4.10 Test report...28 9 Forming of
WJM Technologies excellence in material joining
 Girish P. Kelkar, Ph.D. (562) 743-7576 girish@welding-consultant.com www.welding-consultant.com Weld Cracks An Engineer s Worst Nightmare There are a variety of physical defects such as undercut, insufficient
Girish P. Kelkar, Ph.D. (562) 743-7576 girish@welding-consultant.com www.welding-consultant.com Weld Cracks An Engineer s Worst Nightmare There are a variety of physical defects such as undercut, insufficient
Alternative Steel Materials to BS 5950
 BC 1: 2008 Design Guide on Use of Alternative Steel Materials to BS 5950 BCA Sustainable Construction Series 3 The education and research arm of the Building and Construction Authority 200 Braddell Road
BC 1: 2008 Design Guide on Use of Alternative Steel Materials to BS 5950 BCA Sustainable Construction Series 3 The education and research arm of the Building and Construction Authority 200 Braddell Road
QSTE... hot-rolled high strength cold forming sheet steel as per EN 10 149
 QSTE... hot-rolled high strength cold forming sheet steel as per QStE hot-rolled high strength cold forming sheet steel Steels labelled QStE are a class of fine grain micro-alloyed thermo-mechanically
QSTE... hot-rolled high strength cold forming sheet steel as per QStE hot-rolled high strength cold forming sheet steel Steels labelled QStE are a class of fine grain micro-alloyed thermo-mechanically
Typical TIG-plasma solutions
 Typical -plasma solutions 2228-005 2003-670 Boilers maker solutions 2004-257 1210-064 1210-067 64 3638-008 2008-400 1415-014 2000-169 2003-204 1467-003 2000-343 2000-160 Pipework solutions or plasma welded
Typical -plasma solutions 2228-005 2003-670 Boilers maker solutions 2004-257 1210-064 1210-067 64 3638-008 2008-400 1415-014 2000-169 2003-204 1467-003 2000-343 2000-160 Pipework solutions or plasma welded
جامعة البلقاء التطبيقية
 AlBalqa Applied University تا سست عام 997 The curriculum of associate degree in Air Conditioning, Refrigeration and Heating Systems consists of (7 credit hours) as follows: Serial No. Requirements First
AlBalqa Applied University تا سست عام 997 The curriculum of associate degree in Air Conditioning, Refrigeration and Heating Systems consists of (7 credit hours) as follows: Serial No. Requirements First
TIG torches... 3-2 to 3-5 Tungsten electrodes... 3-6 to 3-7 TIG consumables... 3-8 Miscellaneous... 3-9
 3- welding torches........................................................... 3-2 to 3-5 Tungsten electrodes........................................ 3-6 to 3-7 consumables........................................................
3- welding torches........................................................... 3-2 to 3-5 Tungsten electrodes........................................ 3-6 to 3-7 consumables........................................................
DOCUMENT CS/1: SCHEME DESCRIPTION AND BENEFITS
 WELDING FABRICATOR CERTIFICATION SCHEME DOCUMENT CS/1: SCHEME DESCRIPTION AND BENEFITS 6 th Edition July 2012 Issued under the authority of the Governing Board for Certification All correspondence should
WELDING FABRICATOR CERTIFICATION SCHEME DOCUMENT CS/1: SCHEME DESCRIPTION AND BENEFITS 6 th Edition July 2012 Issued under the authority of the Governing Board for Certification All correspondence should
Application of Welding Standards in Hong Kong. S. K. Babu Laboratory Manager - Foundation Techniques Ltd
 Application of Welding Standards in Hong Kong S. K. Babu Laboratory Manager - Foundation Techniques Ltd Introduction: This paper summarizes the current welding standards practiced in Hong Kong & also outlines
Application of Welding Standards in Hong Kong S. K. Babu Laboratory Manager - Foundation Techniques Ltd Introduction: This paper summarizes the current welding standards practiced in Hong Kong & also outlines
Wear-resistant steels. Technical terms of delivery for heavy plates. voestalpine Grobblech GmbH www.voestalpine.com/grobblech
 Wear-resistant steels Technical terms of delivery for heavy plates voestalpine Grobblech GmbH www.voestalpine.com/grobblech Wear-resistant steels durostat durostat 400 durostat 450 durostat 500 durostat
Wear-resistant steels Technical terms of delivery for heavy plates voestalpine Grobblech GmbH www.voestalpine.com/grobblech Wear-resistant steels durostat durostat 400 durostat 450 durostat 500 durostat
FLAME CuTTIng te la P is utting B c
 FLAME CUTTING Both Oxy-LPG and Oxy-acetylene processes are acceptable for sectioning all thicknesses of BISPLATE. With these processes, the following techniques are recommended: Gas pressure to be the
FLAME CUTTING Both Oxy-LPG and Oxy-acetylene processes are acceptable for sectioning all thicknesses of BISPLATE. With these processes, the following techniques are recommended: Gas pressure to be the
www.ruukki.com WELDING. GENERAL HOT-ROLLED STEEL SHEETS, PLATES AND COILS
 www.ruukki.com WELDING. GENERAL HOT-ROLLED STEEL SHEETS, PLATES AND COILS Selecting the welding process The choice of the welding process must include the consideration of any steel-specific limitations
www.ruukki.com WELDING. GENERAL HOT-ROLLED STEEL SHEETS, PLATES AND COILS Selecting the welding process The choice of the welding process must include the consideration of any steel-specific limitations
Handbook on the Ultrasonic Examination. Austenitic Welds
 Handbook on the Ultrasonic Examination Austenitic Welds The International Institute of Welding Edition Handbook On the Ultrasonic Examination of Austenitic Welds Compiled by COMMISSION V Testing, Measurement,
Handbook on the Ultrasonic Examination Austenitic Welds The International Institute of Welding Edition Handbook On the Ultrasonic Examination of Austenitic Welds Compiled by COMMISSION V Testing, Measurement,
ASTM A860/A860M-09 Standard Specification for Wrought High Strength. Ferritic Steel Butt Welding Fittings. 1. Scope :- 2. Reference Documents :-
 Standard Specification for Wrought High Strength Ferritic Steel Butt Welding Fittings 1. Scope :- 1.1 This specification covers wrought high strength ferritic steel butt-welding fitting of seamless and
Standard Specification for Wrought High Strength Ferritic Steel Butt Welding Fittings 1. Scope :- 1.1 This specification covers wrought high strength ferritic steel butt-welding fitting of seamless and
Overview on Welding and Ergonomics
 Jannuary, 30-2014 Overview on Welding and Ergonomics Luca Costa srl, Italy luca.costa@iisprogress.it Approaching ergonomics in welding fabrication Welding fabrication involves several operations which
Jannuary, 30-2014 Overview on Welding and Ergonomics Luca Costa srl, Italy luca.costa@iisprogress.it Approaching ergonomics in welding fabrication Welding fabrication involves several operations which
European Welding Standards
 European Welding Standards John Dyson 15 th March 2004 European Standards Harmonised Standards Not all EN Standards are Harmonised, only those that are considered to satisfy relevant ESRs in product directives.
European Welding Standards John Dyson 15 th March 2004 European Standards Harmonised Standards Not all EN Standards are Harmonised, only those that are considered to satisfy relevant ESRs in product directives.
DOCUMENT CAESAS/1: SCHEME DESCRIPTION AND BENEFITS
 CONFORMITY ASSESSMENT FOR THE EXECUTION OF STEEL & ALUMINIUM STRUCTURES DOCUMENT CAESAS/1: SCHEME DESCRIPTION AND BENEFITS 2nd Edition July 2012 Issued under the authority of the Governing Board for Certification
CONFORMITY ASSESSMENT FOR THE EXECUTION OF STEEL & ALUMINIUM STRUCTURES DOCUMENT CAESAS/1: SCHEME DESCRIPTION AND BENEFITS 2nd Edition July 2012 Issued under the authority of the Governing Board for Certification
North American Stainless
 North American Stainless Flat Products Stainless Steel Grade Sheet 310S (S31008)/ EN 1.4845 Introduction: SS310 is a highly alloyed austenitic stainless steel designed for elevated-temperature service.
North American Stainless Flat Products Stainless Steel Grade Sheet 310S (S31008)/ EN 1.4845 Introduction: SS310 is a highly alloyed austenitic stainless steel designed for elevated-temperature service.
8.2 FUSION WELDING. Types of welding processes. Oxyfuel gas welding
 Valery Marino, Manufacturing Technology Fusion Welding 153 8.2 FUSION WELDING Types of welding processes Welding is a material joining process for a permanent combining of two (or more) parts that inoles
Valery Marino, Manufacturing Technology Fusion Welding 153 8.2 FUSION WELDING Types of welding processes Welding is a material joining process for a permanent combining of two (or more) parts that inoles
Problems in Welding of High Strength Aluminium Alloys
 Singapore Welding Society Newsletter, September 1999 Problems in Welding of High Strength Aluminium Alloys Wei Zhou Nanyang Technological University, Singapore E-mail: WZhou@Cantab.Net Pure aluminium has
Singapore Welding Society Newsletter, September 1999 Problems in Welding of High Strength Aluminium Alloys Wei Zhou Nanyang Technological University, Singapore E-mail: WZhou@Cantab.Net Pure aluminium has
SERIES NG 1800 STRUCTURAL STEELWORK
 MANUAL OF CONTRACT DOCUMENTS FOR HIGHWAY WORKS VOLUME 2 NOTES FOR GUIDANCE ON THE SPECIFICATION FOR HIGHWAY WORKS SERIES NG 1800 STRUCTURAL STEELWORK Contents Clause Title Page NG 1800 (08/14) General
MANUAL OF CONTRACT DOCUMENTS FOR HIGHWAY WORKS VOLUME 2 NOTES FOR GUIDANCE ON THE SPECIFICATION FOR HIGHWAY WORKS SERIES NG 1800 STRUCTURAL STEELWORK Contents Clause Title Page NG 1800 (08/14) General
Autogenous Laser Welding of Aluminum
 Hans Leidich OEM Laser Specialist Laser Technology Center TRUMPF Inc. Why Autogenous Simpler Less hardware Easier process Faster speed Should be first approach (if doesn t work, then go to the next step)
Hans Leidich OEM Laser Specialist Laser Technology Center TRUMPF Inc. Why Autogenous Simpler Less hardware Easier process Faster speed Should be first approach (if doesn t work, then go to the next step)
North American Stainless
 North American Stainless Flat Products Stainless Steel Sheet T409 INTRODUCTION NAS 409 is an 11% chromium, stabilized ferritic stainless steel. It is not as resistant to corrosion or high-temperature oxidation
North American Stainless Flat Products Stainless Steel Sheet T409 INTRODUCTION NAS 409 is an 11% chromium, stabilized ferritic stainless steel. It is not as resistant to corrosion or high-temperature oxidation
Non- Carbon Fiber Electrical Heating Textile Introduction:
 Non- Carbon Fiber Electrical Heating Introduction: This Heating is a new generation electrical heating system which is specially designed for mobile heating, energy saving and safety orientated requirements
Non- Carbon Fiber Electrical Heating Introduction: This Heating is a new generation electrical heating system which is specially designed for mobile heating, energy saving and safety orientated requirements
Surveillance Report. Bascule span to the Railway bridge Jernbanebroen over Limfjorden
 Transportudvalget 2013-14 TRU Alm.del endeligt svar på spørgsmål 192 Offentligt Surveillance Report Package / Item: Bascule span to the Railway bridge Jernbanebroen over Limfjorden Supplier: Purpose of
Transportudvalget 2013-14 TRU Alm.del endeligt svar på spørgsmål 192 Offentligt Surveillance Report Package / Item: Bascule span to the Railway bridge Jernbanebroen over Limfjorden Supplier: Purpose of
LASER CUTTING OF STAINLESS STEEL
 LASER CUTTING OF STAINLESS STEEL Laser inert gas cutting is the most applicable process type used for cutting of stainless steel. Laser oxygen cutting is also applied in cases where the cut face oxidation
LASER CUTTING OF STAINLESS STEEL Laser inert gas cutting is the most applicable process type used for cutting of stainless steel. Laser oxygen cutting is also applied in cases where the cut face oxidation
Materials Joining Technology
 Materials Joining Technology Technical Competency Profile (TCP) This information has been created as part of a National Science Foundation (NSF) grant initiative by Lorain County Community College and
Materials Joining Technology Technical Competency Profile (TCP) This information has been created as part of a National Science Foundation (NSF) grant initiative by Lorain County Community College and
Structural welding is a process by which the parts that are to be connected are heated and
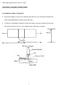 CHAPTER 6. WELDED CONNECTIONS 6.1 INTRODUCTORY CONCEPTS Structural welding is a process by which the parts that are to be connected are heated and fused, with supplementary molten metal at the joint. A
CHAPTER 6. WELDED CONNECTIONS 6.1 INTRODUCTORY CONCEPTS Structural welding is a process by which the parts that are to be connected are heated and fused, with supplementary molten metal at the joint. A
3.3 Welding and welded connections
 3.3 Welding and welded connections Welding is the process of joining two pieces of metal by creating a strong metallurgical bond between them by heating or pressure or both. It is distinguished from other
3.3 Welding and welded connections Welding is the process of joining two pieces of metal by creating a strong metallurgical bond between them by heating or pressure or both. It is distinguished from other
Conceptual Design of Buildings (Course unit code 1C2)
 (Course unit code 1C2) Module C Design of Steel Members J.P. Jaspart (University of Liège) 520121-1-2011-1-CZ-ERA MUNDUS-EMMC Bolts are the main type of fasteners used in steel joints. The main geometrical
(Course unit code 1C2) Module C Design of Steel Members J.P. Jaspart (University of Liège) 520121-1-2011-1-CZ-ERA MUNDUS-EMMC Bolts are the main type of fasteners used in steel joints. The main geometrical
Valve Steel. Valve Steel
 Valve Steel Valve Steel BÖHLER-UDDEHOLM Precision Strip AB is one of the world s leading manufacturers of high quality strip steel. More than a century s experience of cold rolling has given us a unique
Valve Steel Valve Steel BÖHLER-UDDEHOLM Precision Strip AB is one of the world s leading manufacturers of high quality strip steel. More than a century s experience of cold rolling has given us a unique
Standards and projects under the direct responsibility of TC 44 Secretariat
 Standards and projects under the direct responsibility of TC 44 Secretariat ISO 3677:1992 Filler metal for soft soldering, brazing and braze welding -- Designation ISO 5187:1985 Welding and allied processes
Standards and projects under the direct responsibility of TC 44 Secretariat ISO 3677:1992 Filler metal for soft soldering, brazing and braze welding -- Designation ISO 5187:1985 Welding and allied processes
AUSTENITIC STAINLESS DAMASCENE STEEL
 AUSTENITIC STAINLESS DAMASCENE STEEL Damasteel s austenitic stainless Damascene Steel is a mix between types 304L and 316L stainless steels which are variations of the 18 percent chromium 8 percent nickel
AUSTENITIC STAINLESS DAMASCENE STEEL Damasteel s austenitic stainless Damascene Steel is a mix between types 304L and 316L stainless steels which are variations of the 18 percent chromium 8 percent nickel
Qualification of welding procedures for duplex stainless steels
 TIP 0402-29 ISSUED - 2001 2001 TAPPI The information and data contained in this document were prepared by a technical committee of the Association. The committee and the Association assume no liability
TIP 0402-29 ISSUED - 2001 2001 TAPPI The information and data contained in this document were prepared by a technical committee of the Association. The committee and the Association assume no liability
The mechanical properties of metal affected by heat treatment are:
 Training Objective After watching this video and reviewing the printed material, the student/trainee will learn the basic concepts of the heat treating processes as they pertain to carbon and alloy steels.
Training Objective After watching this video and reviewing the printed material, the student/trainee will learn the basic concepts of the heat treating processes as they pertain to carbon and alloy steels.
UNDERWATER WELDING INTRODUCTION
 UNDERWATER WELDING Amit Mukund Joshi (Mechanical Engineer) Junior Research Fellow Mechanical Engineering Department Indian Institute of Technology I.I.T Bombay INTRODUCTION The fact that electric arc could
UNDERWATER WELDING Amit Mukund Joshi (Mechanical Engineer) Junior Research Fellow Mechanical Engineering Department Indian Institute of Technology I.I.T Bombay INTRODUCTION The fact that electric arc could
HEAT TREATMENT OF STEEL
 HEAT TREATMENT OF STEEL Heat Treatment of Steel Most heat treating operations begin with heating the alloy into the austenitic phase field to dissolve the carbide in the iron. Steel heat treating practice
HEAT TREATMENT OF STEEL Heat Treatment of Steel Most heat treating operations begin with heating the alloy into the austenitic phase field to dissolve the carbide in the iron. Steel heat treating practice
EML 2322L MAE Design and Manufacturing Laboratory. Welding
 EML 2322L MAE Design and Manufacturing Laboratory Welding Intro to Welding A weld is made when separate pieces of material to be joined combine and form one piece when heated to a temperature high enough
EML 2322L MAE Design and Manufacturing Laboratory Welding Intro to Welding A weld is made when separate pieces of material to be joined combine and form one piece when heated to a temperature high enough
Gas tungsten arc welding, commonly called TIG (tungsten inert gas), produces an arc between a
 DESIGN CONSIDERATIONS FOR WELDING Apart from resistance spot welding (RSW), three processes are most commonly used for welding metal stampings and fabrications: gas metal arc welding (GMAW) or MIG; gas
DESIGN CONSIDERATIONS FOR WELDING Apart from resistance spot welding (RSW), three processes are most commonly used for welding metal stampings and fabrications: gas metal arc welding (GMAW) or MIG; gas
DX2202 Duplex stainless steel
 Stainless Europe Grade DX22 Duplex stainless steel Chemical Composition Elements C Mn Cr Ni Mo N %.25.3 23. 2.5
Stainless Europe Grade DX22 Duplex stainless steel Chemical Composition Elements C Mn Cr Ni Mo N %.25.3 23. 2.5
NON DESTRUCTIVE TESTING & ASNT WELD INSPECTION & AWS
 NON DESTRUCTIVE TESTING & ASNT WELD INSPECTION & AWS What is ASNT? What is ASNT? The American Society for Nondestructive Testing, Inc. What is ASNT? ASNT is the world's largest technical society for nondestructive
NON DESTRUCTIVE TESTING & ASNT WELD INSPECTION & AWS What is ASNT? What is ASNT? The American Society for Nondestructive Testing, Inc. What is ASNT? ASNT is the world's largest technical society for nondestructive
Reproduced with the permission of the American Welding Society (AWS), Miami, Florida - 09/15/2011. 7. Stud Welding
 7. Stud Welding 7.1 Scope Section 7 contains general requirements for welding steel studs to steel (see 7.2.7 and 1.2.2 for approved steels). In addition, it stipulates specific requirements for the following:
7. Stud Welding 7.1 Scope Section 7 contains general requirements for welding steel studs to steel (see 7.2.7 and 1.2.2 for approved steels). In addition, it stipulates specific requirements for the following:
Copper Alloys COPPER ALLOYS. Weld Tech News VOL 1. NO. 8
 Copper Alloys Weld Tech News VOL 1. NO. 8 WELD TECH NEWS is a newsletter for welders working primarily in maintenance and repair. Each issue contains useful information on materials (cast irons, steels,
Copper Alloys Weld Tech News VOL 1. NO. 8 WELD TECH NEWS is a newsletter for welders working primarily in maintenance and repair. Each issue contains useful information on materials (cast irons, steels,
TRAINING AND DIALOGUE PROGRAMS
 TRAINING AND DIALOGUE PROGRAMS GENERAL INFORMATION ON Human Resource Development for International Welding Engineer. 集 団 研 修 国 際 溶 接 技 術 者 育 成 JFY 2009
TRAINING AND DIALOGUE PROGRAMS GENERAL INFORMATION ON Human Resource Development for International Welding Engineer. 集 団 研 修 国 際 溶 接 技 術 者 育 成 JFY 2009
North American Stainless
 North American Stainless Flat Products Stainless Steel Grade Sheet 430 (S43000)/ EN 1.4016 Introduction: SS430 is a low-carbon plain chromium, ferritic stainless steel without any stabilization of carbon
North American Stainless Flat Products Stainless Steel Grade Sheet 430 (S43000)/ EN 1.4016 Introduction: SS430 is a low-carbon plain chromium, ferritic stainless steel without any stabilization of carbon
A Beginner s Guide to MIG Welding
 A Beginner s Guide to MIG Welding MIG Welding Names MIG welding, or MIG, is an acronym for Metal Inert Gas welding. MIG is a commonly used and accepted slang term that was appropriate when the process
A Beginner s Guide to MIG Welding MIG Welding Names MIG welding, or MIG, is an acronym for Metal Inert Gas welding. MIG is a commonly used and accepted slang term that was appropriate when the process
National Welding Education and Training Center
 Student Learning Outcomes Appropriate for all postsecondary Welding Technician education programs National Welding Education and Training Center Partial support for this work was provided by the National
Student Learning Outcomes Appropriate for all postsecondary Welding Technician education programs National Welding Education and Training Center Partial support for this work was provided by the National
ALLOY 2205 DATA SHEET
 ALLOY 2205 DATA SHEET UNS S32205, EN 1.4462 / UNS S31803 GENERAL PROPERTIES ////////////////////////////////////////////////////// //// 2205 (UNS designations S32205 / S31803) is a 22 % chromium, 3 % molybdenum,
ALLOY 2205 DATA SHEET UNS S32205, EN 1.4462 / UNS S31803 GENERAL PROPERTIES ////////////////////////////////////////////////////// //// 2205 (UNS designations S32205 / S31803) is a 22 % chromium, 3 % molybdenum,
ASME Section IX, 2007 Edition, 2009 Addenda. As published in the Welding Journal, October, 2009. Prepared by
 Summary of Changes in ASME Section IX, 2007 Edition, 2009 Addenda As published in the Welding Journal, October, 2009 Prepared by Walter J. Sperko, P.E. Sperko Engineering Services, Inc 4803 Archwood Drive
Summary of Changes in ASME Section IX, 2007 Edition, 2009 Addenda As published in the Welding Journal, October, 2009 Prepared by Walter J. Sperko, P.E. Sperko Engineering Services, Inc 4803 Archwood Drive
SEMPEO2-54 - SQA Unit Code FP47 04 Carrying out heat treatment of engineering materials
 Overview This standard covers a broad range of basic competences that you need, to apply specified heat treatment processes to engineering materials/components. It will prepare you for entry into the engineering
Overview This standard covers a broad range of basic competences that you need, to apply specified heat treatment processes to engineering materials/components. It will prepare you for entry into the engineering
EN 1090 Guideline. White paper. EN 1090 Guideline.
 EN 1090 Guideline. White paper. EN 1090 Guideline. Date April 2014 02 EN 1090 Guideline ontents. 4 Are you ready for EN 1090? 5 Introduction 13 Holing 13 Execution of holing 13 ut outs 6 Execution classes
EN 1090 Guideline. White paper. EN 1090 Guideline. Date April 2014 02 EN 1090 Guideline ontents. 4 Are you ready for EN 1090? 5 Introduction 13 Holing 13 Execution of holing 13 ut outs 6 Execution classes
Health Care for Pipelines From Cradle to Grave
 Health Care for Pipelines From Cradle to Grave By Jim Costain, GE Inspection Technologies Assuring the mechanical integrity of piping systems, whether they be in exploration, transmission, or process plants
Health Care for Pipelines From Cradle to Grave By Jim Costain, GE Inspection Technologies Assuring the mechanical integrity of piping systems, whether they be in exploration, transmission, or process plants
Structural Steel Welding
 PDH Course S150 Structural Steel Welding Semih Genculu, P.E. 2007 PDH Center 2410 Dakota Lakes Drive Herndon, VA 20171-2995 Phone: 703-478-6833 Fax: 703-481-9535 www.pdhcenter.com An Approved Continuing
PDH Course S150 Structural Steel Welding Semih Genculu, P.E. 2007 PDH Center 2410 Dakota Lakes Drive Herndon, VA 20171-2995 Phone: 703-478-6833 Fax: 703-481-9535 www.pdhcenter.com An Approved Continuing
Submerged Arc Wires & Fluxes
 Submerged Arc Wires & Fluxes Unsurpassed solutions for ambitious tasks www.airliquide.ca www.blueshield.ca 1 of 6 For decades, Air Liquide and Oerlikon have contributed significantly to the development
Submerged Arc Wires & Fluxes Unsurpassed solutions for ambitious tasks www.airliquide.ca www.blueshield.ca 1 of 6 For decades, Air Liquide and Oerlikon have contributed significantly to the development
Job Ready Assessment Blueprint. Welding. Test Code: 4172 / Version: 01. Copyright 2013. All Rights Reserved.
 Job Ready Assessment Blueprint Welding Test Code: 4172 / Version: 01 Copyright 2013. All Rights Reserved. General Assessment Information Blueprint Contents General Assessment Information Written Assessment
Job Ready Assessment Blueprint Welding Test Code: 4172 / Version: 01 Copyright 2013. All Rights Reserved. General Assessment Information Blueprint Contents General Assessment Information Written Assessment
PARTNERS and RESPONSABILITIES
 Location Key Facts Core Business Design and manufacture management of heavy machined steel structures and components for steel mill industry. Sales up to 40 MLN Staff 190 person Area of shops 35.000 m²
Location Key Facts Core Business Design and manufacture management of heavy machined steel structures and components for steel mill industry. Sales up to 40 MLN Staff 190 person Area of shops 35.000 m²
WHAT EVERY ENGINEER SHOULD KNOW ABOUT WELDING
 WHAT EVERY ENGINEER SHOULD KNOW ABOUT WELDING From amperage to preheat, there s more to welding procedures than meets the eye By Duane K. Miller, P.E. WITHIN THE WELDING INDUS- TRY, THE TERM WELDING PROCEDURE
WHAT EVERY ENGINEER SHOULD KNOW ABOUT WELDING From amperage to preheat, there s more to welding procedures than meets the eye By Duane K. Miller, P.E. WITHIN THE WELDING INDUS- TRY, THE TERM WELDING PROCEDURE
TARIFF CODE and updates standard
 TARIFF CODE and updates standard No HS CODE AHTN CODE PRODUCT DESCRIPTION PRODUCT TYPE STANDARDS IDENTIFIED 7207 Semi finished products of iron or non alloy steel Containing by weight less than 0.25% of
TARIFF CODE and updates standard No HS CODE AHTN CODE PRODUCT DESCRIPTION PRODUCT TYPE STANDARDS IDENTIFIED 7207 Semi finished products of iron or non alloy steel Containing by weight less than 0.25% of
Welding. Module 19.2.1
 Welding Module 19.2.1 Hard Soldering Hard soldering is a general term for silver soldering and brazing. These are very similar thermal joining processes to soft soldering in as much that the parent metal
Welding Module 19.2.1 Hard Soldering Hard soldering is a general term for silver soldering and brazing. These are very similar thermal joining processes to soft soldering in as much that the parent metal
Outline of a quality system and standard for the certification of conformity
 Outline of a quality system and standard for the certification of conformity Although still in early steps, novel Additive Manufacturing (AM) processes are growing in expectations as enabling technology
Outline of a quality system and standard for the certification of conformity Although still in early steps, novel Additive Manufacturing (AM) processes are growing in expectations as enabling technology
North American Stainless
 Introduction: North American Stainless Flat Products Stainless Steel Grade Sheet 309S (S30908)/ EN1.4833 SS309 is a highly alloyed austenitic stainless steel used for its excellent oxidation resistance,
Introduction: North American Stainless Flat Products Stainless Steel Grade Sheet 309S (S30908)/ EN1.4833 SS309 is a highly alloyed austenitic stainless steel used for its excellent oxidation resistance,
INTER PLANT STANDARD STEEL INDUSTRY
 INTER PLANT STANDARD STEEL INDUSTRY CODE OF PRACTICE FOR REVAMPING OF EOT CRANES IPSS:3-02-014-03 IPSS Corresponding IS does not exist 0. FOREWORD 0.1 This Inter Plant Standard has been prepared by the
INTER PLANT STANDARD STEEL INDUSTRY CODE OF PRACTICE FOR REVAMPING OF EOT CRANES IPSS:3-02-014-03 IPSS Corresponding IS does not exist 0. FOREWORD 0.1 This Inter Plant Standard has been prepared by the
Drill Pipe Hard-facing
 Drill Pipe Hard-facing GLOBAL PROTECTION AGAINST WEAR AND TEAR Oxyacetylene Rods Flux- and Metal Cored Wires Electrodes PTA - Welding Oxyacetylene Welding and Spray Powders Flame Spraying FLSP Arc Spraying
Drill Pipe Hard-facing GLOBAL PROTECTION AGAINST WEAR AND TEAR Oxyacetylene Rods Flux- and Metal Cored Wires Electrodes PTA - Welding Oxyacetylene Welding and Spray Powders Flame Spraying FLSP Arc Spraying
TERMS AND TERMINOLOGY FOR WELDING PROCESSES AND WELD CONFIGURATIONS
 ECCC ECCC RECOMMENDATIONS - VOLUME 2 Part IIa [Issue 2] TERMS AND TERMINOLOGY FOR WELDING PROCESSES AND WELD CONFIGURATIONS blank page blank page ABSTRACT ECCC Recommendations Volume 2 Part IIa presents
ECCC ECCC RECOMMENDATIONS - VOLUME 2 Part IIa [Issue 2] TERMS AND TERMINOLOGY FOR WELDING PROCESSES AND WELD CONFIGURATIONS blank page blank page ABSTRACT ECCC Recommendations Volume 2 Part IIa presents
Naue GmbH&Co.KG. Quality Control and. Quality Assurance. Manual. For Geomembranes
 Naue GmbH&Co.KG Quality Control and Quality Assurance Manual For Geomembranes July 2004 V.O TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. Introduction 2. Quality Assurance and Control 2.1 General 2.2 Quality management acc. to
Naue GmbH&Co.KG Quality Control and Quality Assurance Manual For Geomembranes July 2004 V.O TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. Introduction 2. Quality Assurance and Control 2.1 General 2.2 Quality management acc. to
FINAL DRAFT PREN ISO 14327 RESISTANCE WELDING PROCEDURES FOR DETERMINING THE WELDABILITY LOBE FOR RESISTANCE SPOT, PROJECTION AND SEAM
 EUROPEAN COMMITTEE FOR STANDARDIZATION COMITÉ EUROPÉEN DE NORMALISATION EUROPÄISCHES KOMITEE FÜR NORMUNG CEN/TC 121 N 1060 FINAL DRAFT PREN ISO 14327 RESISTANCE WELDING PROCEDURES FOR DETERMINING THE WELDABILITY
EUROPEAN COMMITTEE FOR STANDARDIZATION COMITÉ EUROPÉEN DE NORMALISATION EUROPÄISCHES KOMITEE FÜR NORMUNG CEN/TC 121 N 1060 FINAL DRAFT PREN ISO 14327 RESISTANCE WELDING PROCEDURES FOR DETERMINING THE WELDABILITY
Guidance from the Group of Notified Bodies for the Construction Products Directive 89/106/EEC. GNB-CPD position paper from SG17 - EN 1090-1:2009
 GNB-CPD SG17 Guidance from the Group of Notified Bodies for the Construction Products Directive 89/106/EEC NB-CPD/SG17/09/069 Issued: 7 September 2009 APPROVED GUIDANCE GNB-CPD position paper from SG17
GNB-CPD SG17 Guidance from the Group of Notified Bodies for the Construction Products Directive 89/106/EEC NB-CPD/SG17/09/069 Issued: 7 September 2009 APPROVED GUIDANCE GNB-CPD position paper from SG17
SVENSKA.......................................................3 DANSK.........................................................10 NORSK................
 Caddy 150 & Caddy Tig 150 LHQ 150, LTV 150 SVENSKA.......................................................3 DANSK.........................................................10 NORSK.........................................................17
Caddy 150 & Caddy Tig 150 LHQ 150, LTV 150 SVENSKA.......................................................3 DANSK.........................................................10 NORSK.........................................................17
TABLE OF CONTENTS 2 Heavy-Wall Seamless & Welded Carbon Steel Pipe. 4 Alloy Pipe & Tube. 6 Chrome-Moly Pipe. 7 Low-Temp Pipe
 PRODUCT CATALOG TABLE OF CONTENTS 2 Heavy-Wall Seamless & Welded Carbon Steel Pipe 4 Alloy Pipe & Tube 6 Chrome-Moly Pipe 7 Low-Temp Pipe 9 Services amerpipe.com 1.800.316.5737 sales@amerpipe.com 18333
PRODUCT CATALOG TABLE OF CONTENTS 2 Heavy-Wall Seamless & Welded Carbon Steel Pipe 4 Alloy Pipe & Tube 6 Chrome-Moly Pipe 7 Low-Temp Pipe 9 Services amerpipe.com 1.800.316.5737 sales@amerpipe.com 18333
Friction Surfacing of Austenitic Stainless Steel on Low Carbon Steel: Studies on the Effects of Traverse Speed
 , June 30 - July 2, 2010, London, U.K. Friction Surfacing of Austenitic Stainless Steel on Low Carbon Steel: Studies on the Effects of Traverse Speed H. Khalid Rafi, G. D. Janaki Ram, G. Phanikumar and
, June 30 - July 2, 2010, London, U.K. Friction Surfacing of Austenitic Stainless Steel on Low Carbon Steel: Studies on the Effects of Traverse Speed H. Khalid Rafi, G. D. Janaki Ram, G. Phanikumar and
Summary of Changes in. ASME Section IX, 2000 Addenda
 Summary of Changes in ASME Section IX, 2000 Addenda Prepared by Walter J. Sperko, P.E. Sperko Engineering Services, Inc 4803 Archwood Drive Greensboro, NC 27406 USA Voice: 336-674-0600 FAX: 336-674-0600
Summary of Changes in ASME Section IX, 2000 Addenda Prepared by Walter J. Sperko, P.E. Sperko Engineering Services, Inc 4803 Archwood Drive Greensboro, NC 27406 USA Voice: 336-674-0600 FAX: 336-674-0600
ME349 Engineering Design Projects
 ME349 Engineering Design Projects Introduction to Materials Selection The Material Selection Problem Design of an engineering component involves three interrelated problems: (i) selecting a material, (ii)
ME349 Engineering Design Projects Introduction to Materials Selection The Material Selection Problem Design of an engineering component involves three interrelated problems: (i) selecting a material, (ii)
EUROPEAN STANDARDS PERSONAL PROTECTIVE CLOTHING FOR FLAME RESISTANT. Alexander Gstettner, Lenzing AG Austria
 EUROPEAN STANDARDS FOR FLAME RESISTANT PERSONAL PROTECTIVE CLOTHING Alexander Gstettner, Lenzing AG Austria W a t e r How are the standards organized? A 1 Testing Methods Standards specifiying performance
EUROPEAN STANDARDS FOR FLAME RESISTANT PERSONAL PROTECTIVE CLOTHING Alexander Gstettner, Lenzing AG Austria W a t e r How are the standards organized? A 1 Testing Methods Standards specifiying performance
STUDY OF SHIELDING GASES FOR MAG WELDING
 Materials Physics and Mechanics 16 (2013) 126-134 Received: March 14, 2013 STUDY OF SHIELDING GASES FOR MAG WELDING Irina Boiko, Didzis Avisans Riga Technical University, Institute of Mechanical Engineering,
Materials Physics and Mechanics 16 (2013) 126-134 Received: March 14, 2013 STUDY OF SHIELDING GASES FOR MAG WELDING Irina Boiko, Didzis Avisans Riga Technical University, Institute of Mechanical Engineering,
Infrastructure Steel in Norway; Requirements and Specifications
 Madrid 9. December 2013 Infrastructure Steel in Norway; Requirements and Specifications Kjetil Myhre Chairman ECCS/TC9 Manager Norwegian Steel Association Norwegian Steel Association has promoted the use
Madrid 9. December 2013 Infrastructure Steel in Norway; Requirements and Specifications Kjetil Myhre Chairman ECCS/TC9 Manager Norwegian Steel Association Norwegian Steel Association has promoted the use
LABORATORY EXPERIMENTS TESTING OF MATERIALS
 LABORATORY EXPERIMENTS TESTING OF MATERIALS 1. TENSION TEST: INTRODUCTION & THEORY The tension test is the most commonly used method to evaluate the mechanical properties of metals. Its main objective
LABORATORY EXPERIMENTS TESTING OF MATERIALS 1. TENSION TEST: INTRODUCTION & THEORY The tension test is the most commonly used method to evaluate the mechanical properties of metals. Its main objective
X15TN TM. A high hardness, corrosion and fatigue resistance martensitic grade CONTINUOUS INNOVATION RESEARCH SERVICE.
 TM A high hardness, corrosion and fatigue resistance martensitic grade CONTINUOUS METALLURGICAL SPECIAL STEELS INNOVATION RESEARCH SERVICE DEVELOPMENT Enhancing your performance THE INDUSTRIAL ENVIRONMENT
TM A high hardness, corrosion and fatigue resistance martensitic grade CONTINUOUS METALLURGICAL SPECIAL STEELS INNOVATION RESEARCH SERVICE DEVELOPMENT Enhancing your performance THE INDUSTRIAL ENVIRONMENT
WELD - STATIC AND FATIGUE STRENGTH -III
 32 WELD - STATIC AND FATIGUE STRENGTH -III 1.0 INTRODUCTION A component or a structure, which can withstand a single application of load, may fracture if the same load is applied a large number of times.
32 WELD - STATIC AND FATIGUE STRENGTH -III 1.0 INTRODUCTION A component or a structure, which can withstand a single application of load, may fracture if the same load is applied a large number of times.
