Seeing, Thinking, and Doing in Infancy
|
|
|
- Avis Poole
- 9 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Seeing, Thinking, and Doing in Infancy How Children Develop Chapter 5
2 Infant Development Perception Action Learning Cognition
3 Motor Development Reflexes Motor Milestones Current Views of Motor Development The Expanding World of the Infant
4 Infancy: Motor Development Newborns neonates are surprisingly capable. Which capacities are innate? Which require maturation? Which develop through interaction? Are there discontinuities?
5 Newborn Reflexes A reflex is The Organized Newborn Often used to judge neurological damage early in life SURVIVAL REFLEXES: Serve obvious physical needs breathing sucking eyeblink rooting swallowing pupillary
6 Newborn Reflexes A reflex is The Organized Newborn Often used to judge neurological damage early in life PRIMITIVE REFLEXES: Serve no obvious physical needs; may be vestiges of important reflex behaviors at earlier stages of human evolution moro tonic neck stepping Palmar Babinski swimming
7 Reflex Procedure/response Does what? Rooting Stroke cheek near mouth baby turns head Sucking Finger in infant s mouth infant sucks Moro More specifics on reflexes Palmar grasp
8 Adaptive Value of Reflexes Many have survival value: Sucking crucial to eating. Others protect infants: Eye blink protects from stimulus. Others encourage gratifying interaction: Sucking for feeding, Palmar for physical contact. Some no longer needed: Moro reflex helps baby cling to mother - but in West babies not carried all day.
9 Reflexes and motor skills Disappear by 6 months as voluntary control increases. Issue: Are reflexes building blocks for voluntary control? 1. Babies adapt reflexes: Palmar changes depending on how palm is stimulated. 2. Some reflexes disappear but return later: swimming & stepping.
10 How do reflexes contribute to motor control? Zelazo (1983): Practice stepping increases spontaneous stepping movements. Hence, exercising reflex helps develop area of cortex related to movement. No exercise, reflex disappears. Thelen (1983): Weight gain not matched by leg strength. Exercise builds muscles reflex retained.
11 The Fish Tank Experiment (Thelen, Fisher, & Ridley-Johnson, 1984)
12 The Fish Tank Experiment (Thelen, Fisher, & Ridley-Johnson, 1984) 25 Average Steps per Minute Out-of-Water In-Water
13 Weighting the Legs (Thelen, Fisher, & Ridley-Johnson, 1984) 25 Average Steps per Minute Without Weights Weights Added
14 How do reflexes contribute to motor control? Zelazo (1983): Practice stepping increases spontaneous stepping movements. Hence, exercising reflex helps develop area of cortex related to movement. No exercise, reflex disappears. Thelen (1983): Weight gain not matched by leg strength. Exercise builds muscles reflex retained. So, should parents encourage walking reflex?
15 Motor Development The organization and sequence of motor development 1. Gross motor development: actions that help infant get around crawling, standing, walking. 2. Fine motor development: smaller movements reaching & grasping.
16 Milestones of Motor Development
17 Infancy Differentiation and integration in Postural Control, Locomotion, and Manual Control leads to: Improvements in timing, balance, and coordination Motor advances lead to:
18 Infancy Differentiation and integration in Postural Control, Locomotion, and Manual Control leads to: Improvements in timing, balance, and coordination Motor advances lead to: 1. opportunities for 2. better understanding 3. more accurate judgments 4. more interaction
19 The developmental sequence of motor skills is quite uniform. But, large individual differences in rate of development: Motor skill Average age Range (90% infants) Grasps cube 3 months 3 weeks 2-7 months Crawls Walks alone Often, a baby is slow on some motor skills but advanced on others. We are concerned only if slow on many skills.
20 Developmental norms imply maturation: a hard-wired sequence directed by motor development genes But: Interaction of multiple factors, each of which may be influenced by genes and experience
21 Psychologists ignored motor development for 40 years because of maturationist assumptions: Early pioneers Arnold Gesell and Myrtle McGraw believed that motor skills were determined mainly by neurological maturation of the brain. (Perspective = Nature, Passive Child)
22 Motor Skills as Dynamic Systems (Thelen, Pick, Smith) Dynamic systems theory (DNS) views motor development as acquiring ever more complex systems of action Not just development of independent skills: 1. head and chest control combine into sitting with support 2. crawling, standing, and stepping combine for walking.
23 Dynamic Systems Approach New forms emerge through processes of self-organization patterns and order emerge from the interactions of the multiple components of a complex system without explicit instructions from organism or environment
24 Extraordinarily complex structural patterns can emerge from very simple initial conditions in dynamic systems During development, living things with particular properties spontaneously organize themselves into patterns Movie: Baby body sense
25 Evidence for DS Microgenetic research (Thelen, 1994) Attach mobile to 3-month-olds legs. Infants usually kick with one leg or two in alternation. Attach mobile so that two legged kick works best Infants soon learn, and start to use, two legged kick.
26 Locomotion At around 8 months of age, infants become capable of selflocomotion for the first time as they begin to crawl Infants begin walking independently at around 13 to 14 months of age, using a toddling gait
27 Integration in locomotion
28 Locomotion Karen Adolph and her colleagues have found that infants do not transfer what they learned about crawling down slopes to walking down them
29 Back-Lying and Locomotion The campaign to get parents to put babies to sleep on their backs to reduce the risk of SIDS seems to make infants less likely to roll over on schedule It may be that the better view of the world from their backs results in less motivation to roll over It may also be that spending less time on their tummies causes arm strength to develop more slowly By 18 months of age there were no differences in the development of infant crawling
30 Fine Motor Development: Voluntary Reaching Reaching plays big role in infant cognitive development. Grasping allows exploration of new things. Newborns reach out for objects prereaching poorly coordinated. Voluntary reaching begins at 3 months infants reach in dark and light just as well. Hence, does not require visual guidance instead proprioception allows vision to focus on other things.
31 Nature of grasp varies: After reflex comes ulnar grasp fingers close against palm. By months, use pincer grasp with thumb and index finger. By 12 months or so, reaching & grasping executed smoothly.
32
33 The Impact of Culture Mothers in Mali believe it is important to exercise their infants to promote their physical and motor development The maneuvers shown here do not harm the babies and do hasten their early motor skills
34 The Impact of Culture Mothers in Mali believe it is important to exercise their infants to promote their physical and motor development The maneuvers shown here do not harm the babies and do hasten their early motor skills
35 Summary of influences on Motor Development Biological Contributions 1. Twins develop motor control at similar rates 2. Blind and disabled children acquire motor skills though later Experiential Contributions 1. Twins study from video 2. Practice accelerates motor development 3. Cultural effects
Infant reflexes and stereotypies are very important in the process of development
 Infant Reflexes and Stereotypies Infant reflexes and stereotypies are very important in the process of development 2007 McGraw-Hill Higher Education. All rights reserved. Importance of Infant Reflexes
Infant Reflexes and Stereotypies Infant reflexes and stereotypies are very important in the process of development 2007 McGraw-Hill Higher Education. All rights reserved. Importance of Infant Reflexes
Neonatal Reflexes. By Courtney Plaster
 Neonatal Reflexes By Courtney Plaster Neonatal Reflexes Neonatal reflexes are inborn reflexes which are present at birth and occur in a predictable fashion. A normally developing newborn should respond
Neonatal Reflexes By Courtney Plaster Neonatal Reflexes Neonatal reflexes are inborn reflexes which are present at birth and occur in a predictable fashion. A normally developing newborn should respond
Chapter 7 Physical Development of the Infant
 Chapter 7 Physical Development of the Infant Mason is 10 months old. Although he is large for his age, his motor skills lag far behind those of other children his age. For example, Mason has trouble sitting
Chapter 7 Physical Development of the Infant Mason is 10 months old. Although he is large for his age, his motor skills lag far behind those of other children his age. For example, Mason has trouble sitting
The Developing Person Through the Life Span 8e by Kathleen Stassen Berger
 The Developing Person Through the Life Span 8e by Kathleen Stassen Berger Chapter 4 Prenatal Development and Birth PowerPoint Slides developed by Martin Wolfger and Michael James Ivy Tech Community College-Bloomington
The Developing Person Through the Life Span 8e by Kathleen Stassen Berger Chapter 4 Prenatal Development and Birth PowerPoint Slides developed by Martin Wolfger and Michael James Ivy Tech Community College-Bloomington
Understanding Growth and Development Patterns of Infants
 Understanding Growth and Development Patterns of Infants publication 350-055 Novella J. Ruffin, Ph.D., Assistant Professor and Extension Specialist, Child Development, Virginia State University, Virginia
Understanding Growth and Development Patterns of Infants publication 350-055 Novella J. Ruffin, Ph.D., Assistant Professor and Extension Specialist, Child Development, Virginia State University, Virginia
Normal and Abnormal Development in the Infant and Pre-School Child
 Normal and Abnormal Development in the Infant and Pre-School Child Steven Bachrach, M.D. Co-Director, Cerebral Palsy Program A.I. dupont Hospital for Children Development in the Infant and Child A newborn
Normal and Abnormal Development in the Infant and Pre-School Child Steven Bachrach, M.D. Co-Director, Cerebral Palsy Program A.I. dupont Hospital for Children Development in the Infant and Child A newborn
Clumsy Child Syndrome/ Academic Difficulties for the School Age Child
 Clumsy Child Syndrome/ Academic Difficulties for the School Age Child Gross motor proficiencies in a baby provide a foundation for success in school.. School Age Problems Children may be identified as
Clumsy Child Syndrome/ Academic Difficulties for the School Age Child Gross motor proficiencies in a baby provide a foundation for success in school.. School Age Problems Children may be identified as
Child Development. Caseworker Core Training Module VII: Child Development: Implications for Family-Centered Child Protective Services
 Child Development P R E - T R A I N I N G A S S I G N M E N T Caseworker Core Training Module VII: Child Development: Implications for Family-Centered Child Protective Services Developed by the Institute
Child Development P R E - T R A I N I N G A S S I G N M E N T Caseworker Core Training Module VII: Child Development: Implications for Family-Centered Child Protective Services Developed by the Institute
Stationary (St)--This subtest measures a child's ability to sustain control of the body within its center of gravity and retain equilibrium.
 Peabody Developmental Motor Scales Second Edition (PDMS-2) Summary Report Section I. Identifying Information Name: Jane Doe Date of Testing: 9/13/2006 Date of Birth: 4/8/2003 Prematurity Adjustment: 0
Peabody Developmental Motor Scales Second Edition (PDMS-2) Summary Report Section I. Identifying Information Name: Jane Doe Date of Testing: 9/13/2006 Date of Birth: 4/8/2003 Prematurity Adjustment: 0
Infants: (0-18 months)
 Handout: Developmental Milestones Infants: (0-18 months) Developmental Milestones : 0-3 months Sucking, grasping reflexes Lifts head when held at shoulder Moves arms actively Is able to follow objects
Handout: Developmental Milestones Infants: (0-18 months) Developmental Milestones : 0-3 months Sucking, grasping reflexes Lifts head when held at shoulder Moves arms actively Is able to follow objects
Jump Around: Motor Development for Babies and Toddlers
 Jump Around: Motor Development for Babies and Toddlers Danielle King: Branch Manager Lauren Mathur: Branch Librarian Debra Winslow: Youth Program Specialist Overview The Orange County Library System created
Jump Around: Motor Development for Babies and Toddlers Danielle King: Branch Manager Lauren Mathur: Branch Librarian Debra Winslow: Youth Program Specialist Overview The Orange County Library System created
WHAT IS CEREBRAL PALSY?
 WHAT IS CEREBRAL PALSY? Cerebral Palsy is a dysfunction in movement resulting from injury to or poor development of the brain prior to birth or in early childhood. Generally speaking, any injury or disease
WHAT IS CEREBRAL PALSY? Cerebral Palsy is a dysfunction in movement resulting from injury to or poor development of the brain prior to birth or in early childhood. Generally speaking, any injury or disease
CHAPTER 7: PHYSICAL ACTIVITY IN INFANCY
 CHAPTER 7: PHYSICAL ACTIVITY IN INFANCY Physical activity, defined as any bodily movement produced by skeletal muscles resulting in energy expenditure, is an important part of overall health and maintenance
CHAPTER 7: PHYSICAL ACTIVITY IN INFANCY Physical activity, defined as any bodily movement produced by skeletal muscles resulting in energy expenditure, is an important part of overall health and maintenance
Cerebral Palsy. In order to function, the brain needs a continuous supply of oxygen.
 Cerebral Palsy Introduction Cerebral palsy, or CP, can cause serious neurological symptoms in children. Up to 5000 children in the United States are diagnosed with cerebral palsy every year. This reference
Cerebral Palsy Introduction Cerebral palsy, or CP, can cause serious neurological symptoms in children. Up to 5000 children in the United States are diagnosed with cerebral palsy every year. This reference
Creative Curriculum Developmental Continuum Checklist
 Social/Emotional Development: Prosocial Behavior Curriculum Objective: 13 Uses thinking skills to resolve conflicts Accepts adult solution to resolve a conflict Seeks adult assistance to resolve a conflict
Social/Emotional Development: Prosocial Behavior Curriculum Objective: 13 Uses thinking skills to resolve conflicts Accepts adult solution to resolve a conflict Seeks adult assistance to resolve a conflict
www.icommunicatetherapy.com
 icommuni cate SPEECH & COMMUNICATION THERAPY Milestones of speech, language and communication development 0-12 Months The rate of children's speech and language development can vary, depending on the child.
icommuni cate SPEECH & COMMUNICATION THERAPY Milestones of speech, language and communication development 0-12 Months The rate of children's speech and language development can vary, depending on the child.
Child Psychology MODULE 1 MAJOR DEVELOPMENTAL ISSUES
 Child Psychology MODULE 1 MAJOR DEVELOPMENTAL ISSUES 1 Home Learning College 2 Child Psychology Unit One The First Years of Life Aims The aim of this unit is to enable you to: distinguish between innate
Child Psychology MODULE 1 MAJOR DEVELOPMENTAL ISSUES 1 Home Learning College 2 Child Psychology Unit One The First Years of Life Aims The aim of this unit is to enable you to: distinguish between innate
Chapter 2. Cognitive Development COGNITIVE DEVELOPMENT
 Chapter 2 Cognitive Development COGNITIVE DEVELOPMENT Cognitive development is a field of study in neuroscience and psychology focusing on a child's development in terms of information processing, conceptual
Chapter 2 Cognitive Development COGNITIVE DEVELOPMENT Cognitive development is a field of study in neuroscience and psychology focusing on a child's development in terms of information processing, conceptual
OVERALL PERFORMANCE. Pediatrics In-Training History and Physical Examination (HPE) Assessment
 OVERALL PERFORMANCE Pediatrics In-Training History and Physical Examination (HPE) Assessment Name: University: This resident completed the standardized assessment of history -taking, physical examination
OVERALL PERFORMANCE Pediatrics In-Training History and Physical Examination (HPE) Assessment Name: University: This resident completed the standardized assessment of history -taking, physical examination
Cerebral Palsy. 1995-2014, The Patient Education Institute, Inc. www.x-plain.com nr200105 Last reviewed: 06/17/2014 1
 Cerebral Palsy Introduction Cerebral palsy, or CP, can cause serious neurological symptoms in children. Thousands of children are diagnosed with cerebral palsy every year. This reference summary explains
Cerebral Palsy Introduction Cerebral palsy, or CP, can cause serious neurological symptoms in children. Thousands of children are diagnosed with cerebral palsy every year. This reference summary explains
Purpose: To develop physical and motor skills and promote health and well-being
 Purpose: To develop physical and motor skills and promote health and well-being The physical and motor development domain includes the physical and motor skills and abilities that emerge during the infant
Purpose: To develop physical and motor skills and promote health and well-being The physical and motor development domain includes the physical and motor skills and abilities that emerge during the infant
IDAHO EARLY LEARNING EGUJDELINES
 IDAHO EARLY LEARNING EGUJDELINES Sus-DOMAIN: MOTOR DEVELOPMENT Goal 17: Goal 18: Goal19: Children demonstrate strength and coordination of large motor muscles. Children demonstrate strength and coordination
IDAHO EARLY LEARNING EGUJDELINES Sus-DOMAIN: MOTOR DEVELOPMENT Goal 17: Goal 18: Goal19: Children demonstrate strength and coordination of large motor muscles. Children demonstrate strength and coordination
Brachial Plexus Palsy
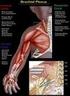 Patient and Family Education Brachial Plexus Palsy A Therapy Guide for Your Baby Brachial Plexus Palsy is caused by trauma to the nerves of the arm. This trauma may have caused muscle weakness, lack of
Patient and Family Education Brachial Plexus Palsy A Therapy Guide for Your Baby Brachial Plexus Palsy is caused by trauma to the nerves of the arm. This trauma may have caused muscle weakness, lack of
Table 7. Infant Behaviors. The ability of infants to lessen their response to repeated stimuli
 Perinatal Nursing Education Understanding the Behavior of Term Infants Infant behavior is influenced by state, temperament and the ability of the infant to self-regulate. The manner in which infants respond
Perinatal Nursing Education Understanding the Behavior of Term Infants Infant behavior is influenced by state, temperament and the ability of the infant to self-regulate. The manner in which infants respond
If baby was born 3 or more weeks prematurely, # of weeks premature: Last name: State/ Province: Home telephone number:
 Ages & Stages Questionnaires 2 1 month 0 days through 2 months 30 days Month Questionnaire Please provide the following information. Use black or blue ink only and print legibly when completing this form.
Ages & Stages Questionnaires 2 1 month 0 days through 2 months 30 days Month Questionnaire Please provide the following information. Use black or blue ink only and print legibly when completing this form.
Learn the steps to identify pediatric muscle weakness and signs of neuromuscular disease.
 Learn the steps to identify pediatric muscle weakness and signs of neuromuscular disease. Guide for therapists/specialists Questions and comments to: [email protected] Surveillance and Referral
Learn the steps to identify pediatric muscle weakness and signs of neuromuscular disease. Guide for therapists/specialists Questions and comments to: [email protected] Surveillance and Referral
CLASS OBJECTIVE: What factors influence prenatal development? Test Your Knowledge! True or False? Is the prenatal environment that important??
 Life Span Development I Chapter 9 CLASS OBJECTIVE: What factors influence prenatal development? 1 Test Your Knowledge! True or False? Most babies are born healthy and most hazards can be avoided. TRUE!
Life Span Development I Chapter 9 CLASS OBJECTIVE: What factors influence prenatal development? 1 Test Your Knowledge! True or False? Most babies are born healthy and most hazards can be avoided. TRUE!
FIT Child Development Audio Conference Journal Date: March 10, 2010 Topic: 24 30 months Participants: 6 New information:
 FIT Child Development Audio Conference Journal Date: March 10, 2010 Topic: 24 30 months Participants: 6 New information: ~ In the area of gross motor/movement development, babies are, with support, walking
FIT Child Development Audio Conference Journal Date: March 10, 2010 Topic: 24 30 months Participants: 6 New information: ~ In the area of gross motor/movement development, babies are, with support, walking
Follow-up Form B3: Evaluation Form Unified Parkinson s Disease Rating Scale (UPDRS 1 ) Motor Exam
 phone: (206) 543-8637; fax: (206) 616-5927 e-mail: [email protected] website: www.alz.washington.edu NACC Uniform Data Set (UDS) Follow-up Form B3: Evaluation Form Unified Parkinson s Disease Rating
phone: (206) 543-8637; fax: (206) 616-5927 e-mail: [email protected] website: www.alz.washington.edu NACC Uniform Data Set (UDS) Follow-up Form B3: Evaluation Form Unified Parkinson s Disease Rating
Four Areas of Development: Infancy to Toddler
 Four Areas of Development: Infancy to Toddler Copyright Copyright Texas Education Agency, 2012. These Materials are copyrighted and trademarked as the property of the Texas Education Agency (TEA) and may
Four Areas of Development: Infancy to Toddler Copyright Copyright Texas Education Agency, 2012. These Materials are copyrighted and trademarked as the property of the Texas Education Agency (TEA) and may
1. What is Cerebral Palsy?
 1. What is Cerebral Palsy? Introduction Cerebral palsy refers to a group of disorders that affect movement. It is a permanent, but not unchanging, physical disability caused by an injury to the developing
1. What is Cerebral Palsy? Introduction Cerebral palsy refers to a group of disorders that affect movement. It is a permanent, but not unchanging, physical disability caused by an injury to the developing
Primitive Reflexes. What are Primitive Reflexes? What happens if Primitive Reflexes don t go away? Causes of retained Primitive Reflexes
 What are Primitive Reflexes? Primitive reflexes are automatic stereotypic movements directed from the brainstem and require no cortical involvement (thought). They are needed for survival and development
What are Primitive Reflexes? Primitive reflexes are automatic stereotypic movements directed from the brainstem and require no cortical involvement (thought). They are needed for survival and development
Neurological Assessment of the School Age Child
 O U T R E A C H E D U C A T I O N Neurological Assessment of the School Age Child April 3, 2008 Program Handouts This information is provided as a courtesy by Children's Health Care System and its related
O U T R E A C H E D U C A T I O N Neurological Assessment of the School Age Child April 3, 2008 Program Handouts This information is provided as a courtesy by Children's Health Care System and its related
Physical Activity Developmental Chapters
 Physical Activity Developmental Chapters Infancy 0 11 Months INFANCY 0 11 MONTHS The first year of life is marked by dramatic changes in the amount and type of physical activity displayed. Infants spend
Physical Activity Developmental Chapters Infancy 0 11 Months INFANCY 0 11 MONTHS The first year of life is marked by dramatic changes in the amount and type of physical activity displayed. Infants spend
INFANT REFLEXES AND ADULT DEVELOPMENT
 INFANT REFLEXES AND ADULT DEVELOPMENT Sensory Integration through Movement By Eve Kodiak, M.M., Licensed Brain Gym Consultant Reprinted from the Newsletter of the Boston Institute for the Development of
INFANT REFLEXES AND ADULT DEVELOPMENT Sensory Integration through Movement By Eve Kodiak, M.M., Licensed Brain Gym Consultant Reprinted from the Newsletter of the Boston Institute for the Development of
Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorder
 Workshop F5: Fetal Alcohol Syndrome/Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorder: The Invisible Disability FAS/FASD Handout: Therapies that Help Children with Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorder Presenters Jerry Larson,
Workshop F5: Fetal Alcohol Syndrome/Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorder: The Invisible Disability FAS/FASD Handout: Therapies that Help Children with Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorder Presenters Jerry Larson,
Human Growth and Reproduction
 Human Growth and Reproduction Sperm reach ovum and cluster around it Only one sperm is allowed to penetrate egg When the sperm penetrates the egg, the egg immediately releases a chemical creating a hard
Human Growth and Reproduction Sperm reach ovum and cluster around it Only one sperm is allowed to penetrate egg When the sperm penetrates the egg, the egg immediately releases a chemical creating a hard
James is a five year old boy and spends his days at the. spends time with each individually. One of activities James loves is to sit down on the
 Sarah Neuhalfen Case Study Child Development May 12, 2006 James is a five year old boy and spends his days at the Manchester Early Learning Center. He is the average size for his age and has blond hair
Sarah Neuhalfen Case Study Child Development May 12, 2006 James is a five year old boy and spends his days at the Manchester Early Learning Center. He is the average size for his age and has blond hair
Check List for identifying Special Needs Children among School age children. Cerebral Palsy
 Check List for identifying Special Needs Children among School age children Cerebral Palsy Sl. 1. The child has drooling? 2. The child has problems in controlling voluntary movements? 3. The child has
Check List for identifying Special Needs Children among School age children Cerebral Palsy Sl. 1. The child has drooling? 2. The child has problems in controlling voluntary movements? 3. The child has
Introduction to Motor Development, Control, & Motor Learning. Chapter 1
 Introduction to Motor Development, Control, & Motor Learning Chapter 1 What is motor learning? Emphasizes the acquisition of motor skills, the performance enhancement of learned or highly experienced motor
Introduction to Motor Development, Control, & Motor Learning Chapter 1 What is motor learning? Emphasizes the acquisition of motor skills, the performance enhancement of learned or highly experienced motor
Cerebral palsy, neonatal death and stillbirth rates Victoria, 1973-1999
 Cerebral Palsy: Aetiology, Associated Problems and Management Lecture for FRACP candidates July 2010 Definitions and prevalence Risk factors and aetiology Associated problems Management options Cerebral
Cerebral Palsy: Aetiology, Associated Problems and Management Lecture for FRACP candidates July 2010 Definitions and prevalence Risk factors and aetiology Associated problems Management options Cerebral
PSYCHOLOGY OF CHILDHOOD REVIEW QUESTIONS
 PSYCHOLOGY OF CHILDHOOD REVIEW QUESTIONS These review questions are designed to help you assess your grasp of the facts and definitions covered in your textbook. Knowing facts and definitions is necessary
PSYCHOLOGY OF CHILDHOOD REVIEW QUESTIONS These review questions are designed to help you assess your grasp of the facts and definitions covered in your textbook. Knowing facts and definitions is necessary
IMM 5738. Developmental milestones. Subject. Chart of early childhood development. Goal/Objective. Instructions. Additional Investigation
 Developmental milestones Chart of early childhood development IMM 5738 Subject Instructions for evaluating and reporting of developmental milestones of infants as well as children and completing of the
Developmental milestones Chart of early childhood development IMM 5738 Subject Instructions for evaluating and reporting of developmental milestones of infants as well as children and completing of the
If baby was born 3 or more weeks prematurely, # of weeks premature: Last name: State/ Province: Home telephone number:
 Ages & Stages Questionnaires 8 7 months 0 days through 8 months 30 days Month Questionnaire Please provide the following information. Use black or blue ink only and print legibly when completing this form.
Ages & Stages Questionnaires 8 7 months 0 days through 8 months 30 days Month Questionnaire Please provide the following information. Use black or blue ink only and print legibly when completing this form.
Motor Planning Organizing Yourself to Move
 Motor Planning Organizing Yourself to Move What is motor planning? Praxis: It s actually a component of praxis although the terms are often used interchangeably. the ability to conceive of, organize, and
Motor Planning Organizing Yourself to Move What is motor planning? Praxis: It s actually a component of praxis although the terms are often used interchangeably. the ability to conceive of, organize, and
What is cerebral palsy?
 What is cerebral palsy? This booklet will help you to have a better understanding of the physical and medical aspects of cerebral palsy. We hope it will be a source of information to anyone who wishes
What is cerebral palsy? This booklet will help you to have a better understanding of the physical and medical aspects of cerebral palsy. We hope it will be a source of information to anyone who wishes
Nikki White Children s Occupational Therapist Barnet Community Services
 Nikki White Children s Occupational Therapist Barnet Community Services What is Occupational Therapy (OT)? An occupation is anything you do in your daily life. Anything meaningful or purposeful Eg. Getting
Nikki White Children s Occupational Therapist Barnet Community Services What is Occupational Therapy (OT)? An occupation is anything you do in your daily life. Anything meaningful or purposeful Eg. Getting
Parkinson's s disease - a
 Parkinson's Disease Parkinson's s disease - a progressive disorder of the nervous system that affects movement. The most common perception of Parkinson s is the patient having tremors. Hands shaking, inability
Parkinson's Disease Parkinson's s disease - a progressive disorder of the nervous system that affects movement. The most common perception of Parkinson s is the patient having tremors. Hands shaking, inability
Autism and Intellectual Disabilities
 Autism and Intellectual Disabilities (DSM IV & V) Accessibility Politecnico di Milano Autism (I) A total of six (or more) items from (A), (B), and (C), with at least two from (A), and one each from (B)
Autism and Intellectual Disabilities (DSM IV & V) Accessibility Politecnico di Milano Autism (I) A total of six (or more) items from (A), (B), and (C), with at least two from (A), and one each from (B)
CORTICAL VISUAL IMPAIRMENT
 Idaho Project for Children and Youth with Deaf-Blindness Fact Sheet CORTICAL VISUAL IMPAIRMENT Definition: Cortical Visual Impairment (CVI) is a temporary or permanent visual impairment caused by the disturbance
Idaho Project for Children and Youth with Deaf-Blindness Fact Sheet CORTICAL VISUAL IMPAIRMENT Definition: Cortical Visual Impairment (CVI) is a temporary or permanent visual impairment caused by the disturbance
PARENT/CARER QUESTIONNAIRE 0 18 months
 PARENT/CARER QUESTIONNAIRE 0 18 months We appreciate the time taken to complete this questionnaire, which allows us to gain vital information regarding your child s development. This information will be
PARENT/CARER QUESTIONNAIRE 0 18 months We appreciate the time taken to complete this questionnaire, which allows us to gain vital information regarding your child s development. This information will be
STAGES OF PRENATAL DEVELOPMENT
 STAGES OF PRENATAL DEVELOPMENT College of William and Mary Students for Life 2013 Germinal Period From conception to implantation Terms to Know Conception: the first stage in human development in which
STAGES OF PRENATAL DEVELOPMENT College of William and Mary Students for Life 2013 Germinal Period From conception to implantation Terms to Know Conception: the first stage in human development in which
Activities for the Young Baby
 31 Chapter 5 Activities for the Young Baby (Birth to 6 Months) A new baby does not usually look as though she is doing very much. She spends most of her time eating, sleeping, and resting. But even though
31 Chapter 5 Activities for the Young Baby (Birth to 6 Months) A new baby does not usually look as though she is doing very much. She spends most of her time eating, sleeping, and resting. But even though
Babies From Birth to 12 Months:
 Babies From Birth to 12 Months: Becoming Aware of the World Around Them 2004, ZERO TO THREE. All rights reserved. Contact ZERO TO THREE for all uses: www.zerotothree.org Key Ideas Look for toys and games
Babies From Birth to 12 Months: Becoming Aware of the World Around Them 2004, ZERO TO THREE. All rights reserved. Contact ZERO TO THREE for all uses: www.zerotothree.org Key Ideas Look for toys and games
Jellow. for the Cerebral Palsy. Antara Hazarika, Kumar Anchal, Priti Thankar, Samraat Sardesai. a study by
 Jellow for the Cerebral Palsy a study by Antara Hazarika, Kumar Anchal, Priti Thankar, Samraat Sardesai Index Understanding the world of CP Modes of communication The need for the product ( product rational)
Jellow for the Cerebral Palsy a study by Antara Hazarika, Kumar Anchal, Priti Thankar, Samraat Sardesai Index Understanding the world of CP Modes of communication The need for the product ( product rational)
If baby was born 3 or more weeks prematurely, # of weeks premature: Last name: State/ Province: Home telephone number:
 Ages & Stages Questionnaires 6 5 months 0 days through 6 months 30 days Month Questionnaire Please provide the following information. Use black or blue ink only and print legibly when completing this form.
Ages & Stages Questionnaires 6 5 months 0 days through 6 months 30 days Month Questionnaire Please provide the following information. Use black or blue ink only and print legibly when completing this form.
Montessori House. Curriculum for Toddlers. 18 Months to 2 1/2 Years of Age
 Montessori House Curriculum for Toddlers 18 Months to 2 1/2 Years of Age www.mymontessorihouse.com Copyright @2010 Montessori House, Inc. Contents By the Time Your Child is Three... 4 Montessori Fundamentals
Montessori House Curriculum for Toddlers 18 Months to 2 1/2 Years of Age www.mymontessorihouse.com Copyright @2010 Montessori House, Inc. Contents By the Time Your Child is Three... 4 Montessori Fundamentals
Tracks of a Panda by Nick Dowson, Illustrated by Yu Rong Scripted for Readers Theater by Karen Antikajian
 Tracks of a Panda by Nick Dowson, Illustrated by Yu Rong Scripted for Readers Theater by Karen Antikajian Narrator 1: Narrator 6: Narrator 2: Narrator 7: Narrator 3: Narrator 8: Narrator 4: Fact Announcer
Tracks of a Panda by Nick Dowson, Illustrated by Yu Rong Scripted for Readers Theater by Karen Antikajian Narrator 1: Narrator 6: Narrator 2: Narrator 7: Narrator 3: Narrator 8: Narrator 4: Fact Announcer
0 3 Months Sensory Motor Checklist
 0 3 Months Sensory Motor Checklist Enjoys playful face-to-face interaction with people Coos in response to playful interaction Notices and responds to sounds Moves legs and arms off of surface when excited
0 3 Months Sensory Motor Checklist Enjoys playful face-to-face interaction with people Coos in response to playful interaction Notices and responds to sounds Moves legs and arms off of surface when excited
A Baby Polar Bear Grows Up
 A Baby Polar Bear Grows Up Polar bears live in ice and snow. A polar bear baby is a cub. A cub is born with its eyes closed. It does not have much hair. A cub drinks its mother s milk. The mother keeps
A Baby Polar Bear Grows Up Polar bears live in ice and snow. A polar bear baby is a cub. A cub is born with its eyes closed. It does not have much hair. A cub drinks its mother s milk. The mother keeps
Baby Signing. Babies are born with an inherent body language that is common to all cultures.
 Baby Signing Babies are born with an inherent body language that is common to all cultures. Long before the emergence of speech, babies spontaneously communicate with their parents using gestures and sounds
Baby Signing Babies are born with an inherent body language that is common to all cultures. Long before the emergence of speech, babies spontaneously communicate with their parents using gestures and sounds
Wu Ming Qigong for Breast Cancer Treatment and Prevention
 Wu Ming Qigong for Breast Cancer Treatment and Prevention The most powerful tool traditional Chinese medicine has to offer for breast cancer treatment and prevention is qigong (pronounced chee-kung), an
Wu Ming Qigong for Breast Cancer Treatment and Prevention The most powerful tool traditional Chinese medicine has to offer for breast cancer treatment and prevention is qigong (pronounced chee-kung), an
Cognitive Development
 Cognitive Chapter 2 Piaget s Approach to Cognitive Jean Piaget (1896-1980) A Swiss Psychologist credited with one of the most influential theories of cognitive development. Carefully observed children
Cognitive Chapter 2 Piaget s Approach to Cognitive Jean Piaget (1896-1980) A Swiss Psychologist credited with one of the most influential theories of cognitive development. Carefully observed children
Descriptions of the Leg Movements of Infants in an Aquatic Environment
 Descriptions of the Leg Movements of Infants in an Aquatic Environment Czeslaw Wielki and Marielle Houben Catholic University of Louvain, Louvain-La-Neuve, Belgium The majority of research concerning the
Descriptions of the Leg Movements of Infants in an Aquatic Environment Czeslaw Wielki and Marielle Houben Catholic University of Louvain, Louvain-La-Neuve, Belgium The majority of research concerning the
Vestibular Assessment
 Oculomotor Examination A. Tests performed in room light Vestibular Assessment 1. Spontaneous nystagmus 2. Gaze holding nystagmus 3. Skew deviation 4. Vergence 5. Decreased vestibular ocular reflex i. Head
Oculomotor Examination A. Tests performed in room light Vestibular Assessment 1. Spontaneous nystagmus 2. Gaze holding nystagmus 3. Skew deviation 4. Vergence 5. Decreased vestibular ocular reflex i. Head
CEREBRAL PALSY CLASSIFICATION BY SEVERITY LEVEL
 Patient Name: Today s Date: CAUSE OF CEREBRAL PALSY Hypoxic-Ischemic Encephalopathy (HIE) or Intrapartum Asphyxia - Brain injury Lack of oxygen to the brain or asphyxia. Intracranial Hemorrhage (IVH) Brain
Patient Name: Today s Date: CAUSE OF CEREBRAL PALSY Hypoxic-Ischemic Encephalopathy (HIE) or Intrapartum Asphyxia - Brain injury Lack of oxygen to the brain or asphyxia. Intracranial Hemorrhage (IVH) Brain
Self-Range of Motion Exercises for Shoulders, Arms, Wrists, Fingers
 Self-Range of Motion Exercises for Shoulders, Arms, Wrists, Fingers These exercises will help keep your muscles strong and mobile, and your joints flexible. Other benefits of these exercises include: C
Self-Range of Motion Exercises for Shoulders, Arms, Wrists, Fingers These exercises will help keep your muscles strong and mobile, and your joints flexible. Other benefits of these exercises include: C
DEVELOPMENTAL CHECKLIST 1 TO 3 MONTHS (Revised as of 9/04)
 DEVELOPMENTAL CHECKLIST 1 TO 3 MONTHS (Revised as of 9/04) MOVEMENT RAISES HEAD AND CHEST WHEN LYING ON STOMACH (3 MOS.) SUPPORTS UPPER BODY WITH ARMS WHEN LYING ON STOMACH (3 MOS.) STRETCHES LEGS OUT
DEVELOPMENTAL CHECKLIST 1 TO 3 MONTHS (Revised as of 9/04) MOVEMENT RAISES HEAD AND CHEST WHEN LYING ON STOMACH (3 MOS.) SUPPORTS UPPER BODY WITH ARMS WHEN LYING ON STOMACH (3 MOS.) STRETCHES LEGS OUT
EARLY INTERVENTION: COMMUNICATION AND LANGUAGE SERVICES FOR FAMILIES OF DEAF AND HARD-OF-HEARING CHILDREN
 EARLY INTERVENTION: COMMUNICATION AND LANGUAGE SERVICES FOR FAMILIES OF DEAF AND HARD-OF-HEARING CHILDREN Our child has a hearing loss. What happens next? What is early intervention? What can we do to
EARLY INTERVENTION: COMMUNICATION AND LANGUAGE SERVICES FOR FAMILIES OF DEAF AND HARD-OF-HEARING CHILDREN Our child has a hearing loss. What happens next? What is early intervention? What can we do to
Rigid spine syndrome (RSS) (Congenital muscular dystrophy with rigidity of the spine, including RSMD1)
 Rigid spine syndrome (RSS) (Congenital muscular dystrophy with rigidity of the spine, including RSMD1) What is RSMD1? The congenital muscular dystrophies are a group of conditions which share early presentation
Rigid spine syndrome (RSS) (Congenital muscular dystrophy with rigidity of the spine, including RSMD1) What is RSMD1? The congenital muscular dystrophies are a group of conditions which share early presentation
How babies' senses develop
 B2 There is much growth and change that must occur in your baby s body. For babies born full-term (37-40 weeks), this growth and change occurred within the warm, dark, watery womb. For the premature baby,
B2 There is much growth and change that must occur in your baby s body. For babies born full-term (37-40 weeks), this growth and change occurred within the warm, dark, watery womb. For the premature baby,
Physical and Cognitive Development in Infancy
 CHAPTER OUTLINE PHYSICAL GROWTH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFANCY Patterns of Growth Height and Weight The Brain Sleep Nutrition MOTOR DEVELOPMENT The Dynamic Systems View Refl exes Gross Motor Skills Fine Motor
CHAPTER OUTLINE PHYSICAL GROWTH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFANCY Patterns of Growth Height and Weight The Brain Sleep Nutrition MOTOR DEVELOPMENT The Dynamic Systems View Refl exes Gross Motor Skills Fine Motor
Session 2. Brain Development; Ages and Stages; Comfort and Calming. Nature vs. Nurture
 Session 2 Brain Development; Ages and Stages; Comfort and Calming Nature vs. Nurture The debate of whether children are more influenced by their genetics (nature) or the way they are parented (nurture)
Session 2 Brain Development; Ages and Stages; Comfort and Calming Nature vs. Nurture The debate of whether children are more influenced by their genetics (nature) or the way they are parented (nurture)
Challenges of Foster Parents who Care for Infants with Neonatal Abstinence Syndrome
 Challenges of Foster Parents who Care for Infants with Neonatal Abstinence Syndrome All Health Care Providers are required by law to make a referral to the Department of Children s Services (DCS) Child
Challenges of Foster Parents who Care for Infants with Neonatal Abstinence Syndrome All Health Care Providers are required by law to make a referral to the Department of Children s Services (DCS) Child
UK Physical Activity Guidelines for Costs Early of Years (walkers) Physical Inactivity
 UK Physical Activity Guidelines for Costs Early of Years (walkers) Physical Inactivity Information for stakeholders, early years practitioners and health professionals Making physical activity a priority
UK Physical Activity Guidelines for Costs Early of Years (walkers) Physical Inactivity Information for stakeholders, early years practitioners and health professionals Making physical activity a priority
THE HUMAN LIFE CYCLE-
 THE HUMAN LIFE CYCLE- EMBRYO, FETUS, INFANT & CHILD - Arundhati Tambwekar THE LIFE CYCLE THEORY FUNDAMENTAL ASSUMPTIONS: Development occurs in successive, clearly defined stages and the sequence is invariant.
THE HUMAN LIFE CYCLE- EMBRYO, FETUS, INFANT & CHILD - Arundhati Tambwekar THE LIFE CYCLE THEORY FUNDAMENTAL ASSUMPTIONS: Development occurs in successive, clearly defined stages and the sequence is invariant.
Creative Activities & Assignments Toolbox
 Creative Activities & Assignments Toolbox Designed by Sharon Little Topic Activities/Assignments Resources Universal Design & Play Stages of Creative Development Across the Curriculum Creative Development
Creative Activities & Assignments Toolbox Designed by Sharon Little Topic Activities/Assignments Resources Universal Design & Play Stages of Creative Development Across the Curriculum Creative Development
AGES AND STAGES: BREASTFEEDING DURING YOUR BABY S FIRST YEAR
 AGES AND STAGES: BREASTFEEDING DURING YOUR BABY S FIRST YEAR Adapted from Ages and Stages: What to Expect During Breastfeeding by Vicki Schmidt, RN, IBCLC BREASTFEEDING YOUR 1-2 MONTH OLD 2» Turn his head
AGES AND STAGES: BREASTFEEDING DURING YOUR BABY S FIRST YEAR Adapted from Ages and Stages: What to Expect During Breastfeeding by Vicki Schmidt, RN, IBCLC BREASTFEEDING YOUR 1-2 MONTH OLD 2» Turn his head
Continuous vs. Discontinuous Nature vs. Nurture
 Piaget s Theory The first cognitive theory, developed by Jean Piaget beginning about 1920. Piaget observed and described children at different ages. His theory is very broad, from birth adolescence, and
Piaget s Theory The first cognitive theory, developed by Jean Piaget beginning about 1920. Piaget observed and described children at different ages. His theory is very broad, from birth adolescence, and
PARKINSON S DISEASE INTRODUCTION. Parkinson s disease is defined as a disease of the nervous system that affects voluntary movement.
 PARKINSON S DISEASE INTRODUCTION Parkinson s disease is a disorder of the brain and the nervous system. It is one of the more common neurological diseases in people over the age of 60, and it is more common
PARKINSON S DISEASE INTRODUCTION Parkinson s disease is a disorder of the brain and the nervous system. It is one of the more common neurological diseases in people over the age of 60, and it is more common
Parkinson's disease. Definition. Symptoms
 Parkinson's disease Definition Parkinson's disease is a progressive disorder of the nervous system that affects your movement. It develops gradually, sometimes starting with a barely noticeable tremor
Parkinson's disease Definition Parkinson's disease is a progressive disorder of the nervous system that affects your movement. It develops gradually, sometimes starting with a barely noticeable tremor
BABIES BORN TO ADDICTED MOTHERS
 BABIES BORN TO ADDICTED MOTHERS PATRICA M. MESSERLE LICENSED CLINICAL PSYCHOLOGIST, M.A., ABSNP LICENSED SCHOOL PSYCHOLOGIST DIPLOMATE OF THE AMERICAN BOARD OF SCHOOL- NEUROPSYCHOLOGY 1 Signs and Symptoms
BABIES BORN TO ADDICTED MOTHERS PATRICA M. MESSERLE LICENSED CLINICAL PSYCHOLOGIST, M.A., ABSNP LICENSED SCHOOL PSYCHOLOGIST DIPLOMATE OF THE AMERICAN BOARD OF SCHOOL- NEUROPSYCHOLOGY 1 Signs and Symptoms
GUIDELINES AND SERVICES FOR OCCUPATIONAL THERAPY AND PHYSICAL THERAPY
 GUIDELINES AND SERVICES FOR OCCUPATIONAL THERAPY AND PHYSICAL THERAPY Linda Paule, Coordinator San Bernardino City Unified School District Dr. Patty Imbiorski, Director Special Education TABLE OF CONTENTS
GUIDELINES AND SERVICES FOR OCCUPATIONAL THERAPY AND PHYSICAL THERAPY Linda Paule, Coordinator San Bernardino City Unified School District Dr. Patty Imbiorski, Director Special Education TABLE OF CONTENTS
Understanding Pervasive Developmental Disorders. Page 1 of 10 MC5155-09 Pervasive Developmental Disorders
 Understanding Pervasive Developmental Disorders Page 1 of 10 MC5155-09 Pervasive Developmental Disorders Page 2 of 10 MC5155-09 Pervasive Developmental Disorders This information is intended to help you
Understanding Pervasive Developmental Disorders Page 1 of 10 MC5155-09 Pervasive Developmental Disorders Page 2 of 10 MC5155-09 Pervasive Developmental Disorders This information is intended to help you
Ambulatory Outcome in Children with Developmental Delay. Rehab Al-Marzooq, MRCP, Arab Board, DCH*
 Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol 29, No. 2, June 2007 Ambulatory Outcome in Children with Developmental Delay Rehab Al-Marzooq, MRCP, Arab Board, DCH* Objective: To identify early predictors of walking in
Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol 29, No. 2, June 2007 Ambulatory Outcome in Children with Developmental Delay Rehab Al-Marzooq, MRCP, Arab Board, DCH* Objective: To identify early predictors of walking in
HOW YOU CAN HELP YOUR CHILD WITH CEREBRAL PALSY
 HOW YOU CAN HELP YOUR CHILD WITH CEREBRAL PALSY CBM is one of the world s largest international disability and development organisations, committed to improving the quality of life of persons with disabilities
HOW YOU CAN HELP YOUR CHILD WITH CEREBRAL PALSY CBM is one of the world s largest international disability and development organisations, committed to improving the quality of life of persons with disabilities
A Child s Developmental Milestones
 A Child s Developmental Listens attentively to sounds and voices (by 1 month) Makes some sounds other than crying (by 2 Cries deliberately for assistance (by 1 month) Begins cooing one syllable (by 3 Coordinates
A Child s Developmental Listens attentively to sounds and voices (by 1 month) Makes some sounds other than crying (by 2 Cries deliberately for assistance (by 1 month) Begins cooing one syllable (by 3 Coordinates
Kriya for Positive Mind
 Kriya for Positive Mind Bron: The Ten Light Bodies of Conciousness van Nirvair Singh Khalsa Ego Eliminator (heart center) 6 MINUTES. Sit cross-legged. Lift left arm up to 60 degrees with the palm up. Right
Kriya for Positive Mind Bron: The Ten Light Bodies of Conciousness van Nirvair Singh Khalsa Ego Eliminator (heart center) 6 MINUTES. Sit cross-legged. Lift left arm up to 60 degrees with the palm up. Right
Cerebral palsy can be classified according to the type of abnormal muscle tone or movement, and the distribution of these motor impairments.
 The Face of Cerebral Palsy Segment I Discovering Patterns What is Cerebral Palsy? Cerebral palsy (CP) is an umbrella term for a group of non-progressive but often changing motor impairment syndromes, which
The Face of Cerebral Palsy Segment I Discovering Patterns What is Cerebral Palsy? Cerebral palsy (CP) is an umbrella term for a group of non-progressive but often changing motor impairment syndromes, which
9/14/2015. Innate behavior. Innate behavior. Stimuli that trigger innate behaviors are called releasers.
 & & has a fixed, genetic component. Despite differing environments, the behavior develops in all individuals. Learned behavior is acquired and modified over development. s can be triggered or enhanced
& & has a fixed, genetic component. Despite differing environments, the behavior develops in all individuals. Learned behavior is acquired and modified over development. s can be triggered or enhanced
Week 7. Equipment. None required. Session 19. Total lengths = 48 lengths. Total distance = 1,200m
 Equipment None required Session 19 Total lengths = 48 lengths Total distance = 1,200m Warm up 200m FC (concentrating on push and glide at the start of each length) Main set 1. 100m FC X 4 (pace yourself
Equipment None required Session 19 Total lengths = 48 lengths Total distance = 1,200m Warm up 200m FC (concentrating on push and glide at the start of each length) Main set 1. 100m FC X 4 (pace yourself
Early Intervention Seating in Pediatric Rehab Strollers
 Early Intervention Seating in Pediatric Rehab Strollers Eli Anselmi Product and Education Specialist Convaid University, May 15, 2014 NuMotion Clinical Education Objectives Attendee will be able to describe
Early Intervention Seating in Pediatric Rehab Strollers Eli Anselmi Product and Education Specialist Convaid University, May 15, 2014 NuMotion Clinical Education Objectives Attendee will be able to describe
Parkinson s Disease (PD)
 Parkinson s Disease (PD) Parkinson s disease (PD) is a movement disorder that worsens over time. About 1 in 100 people older than 60 has Parkinson s. The exact cause of PD is still not known, but research
Parkinson s Disease (PD) Parkinson s disease (PD) is a movement disorder that worsens over time. About 1 in 100 people older than 60 has Parkinson s. The exact cause of PD is still not known, but research
Info. from the nurses of the Medical Service. LOWER BACK PAIN Exercise guide
 Info. from the nurses of the Medical Service LOWER BACK PAIN Exercise guide GS/ME 03/2009 EXERCISE GUIDE One of the core messages for people suffering with lower back pain is to REMAIN ACTIVE. This leaflet
Info. from the nurses of the Medical Service LOWER BACK PAIN Exercise guide GS/ME 03/2009 EXERCISE GUIDE One of the core messages for people suffering with lower back pain is to REMAIN ACTIVE. This leaflet
Cognitive Development
 LP 9C Piaget 1 Cognitive Development Piaget was intrigued by the errors in thinking children made. To investigate how these errors and how thinking changes as we grow older, Jean Piaget carefully observed
LP 9C Piaget 1 Cognitive Development Piaget was intrigued by the errors in thinking children made. To investigate how these errors and how thinking changes as we grow older, Jean Piaget carefully observed
Cerebral Palsy. www.teachinngei.org p. 1
 Cerebral Palsy What is cerebral palsy? Cerebral palsy (CP) is a motor disability caused by a static, non-progressive lesion (encephalopathy) in the brain that occurs in early childhood, usually before
Cerebral Palsy What is cerebral palsy? Cerebral palsy (CP) is a motor disability caused by a static, non-progressive lesion (encephalopathy) in the brain that occurs in early childhood, usually before
Magical Milestones for Healthy Baby Development. Dr Melodie de Jager
 1. Milestones- an overview Magical Milestones for Healthy Baby Development Dr Melodie de Jager Motor milestones are beacons of progress; they show moms and dads if their baby s senses of touch, smell,
1. Milestones- an overview Magical Milestones for Healthy Baby Development Dr Melodie de Jager Motor milestones are beacons of progress; they show moms and dads if their baby s senses of touch, smell,
Dr. Enas Elsayed. Brunnstrom Approach
 Brunnstrom Approach Learning Objectives: By the end of this lab, the student will be able to: 1. Demonstrate different reflexes including stimulus and muscle tone response. 2. Demonstrate how to evoke
Brunnstrom Approach Learning Objectives: By the end of this lab, the student will be able to: 1. Demonstrate different reflexes including stimulus and muscle tone response. 2. Demonstrate how to evoke
