Atypical Heel Pain CLINICALLY SPEAKING. Hyperparathyroidism-Induced Stress Fracture of the Calcaneus WILLIAM D. FISHCO, DPM, MS* RICHARD G.
|
|
|
- Ernest Mason
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CLINICALLY SPEAKING Atypical Heel Pain Hyperparathyroidism-Induced Stress Fracture of the Calcaneus WILLIAM D. FISHCO, DPM, MS* RICHARD G. STILES, MD The authors present a case of atypical heel pain masquerading as plantar fasciitis. The patient was subsequently diagnosed with hyperparathyroidism-induced stress fracture of the calcaneus. The clinical entity of hyperparathyroidism and its manifestations in the skeletal system are presented, as well as a review of stress fractures and pertinent imaging studies. (J Am Podiatr Med Assoc 89(8): , 1999) Heel pain is one of the most common complaints encountered by foot and ankle specialists. In most cases, plantar heel pain is attributed to heel spur syndrome or plantar fasciitis. In the case of recalcitrant heel pain that does not respond to traditional therapy, one should suspect an atypical cause of heel pain. Examples of these atypical causes include infection, fracture, vascular disease, tumor, systemic arthropathy, crystalline arthropathy, metabolic bone disease, entrapment neuropathy (first branch of the lateral plantar nerve), and lumbar radiculopathy. 1 Metabolic bone disease is a general term used to describe metabolic disorders that result in pathology of the skeleton, regardless of the cause. Hyperparathyroidism is a common metabolic disorder. The parathyroid gland secretes parathyroid hormone, which regulates calcium, phosphate, and vitamin D homeostasis. Parathyroid hormone stimulates the kidney to excrete phosphate, retain calcium, and promote synthesis of 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D from 25 (OH) vitamin D. The influence of parathyroid hormone causes resorption of calcium from its bone reservoir. When the parathyroid gland is functioning properly, elevated levels of calcium will result in a negative-feedback mechanism, which inhibits the release of parathyroid hormone. In pathologic states, *Associate, American College of Foot and Ankle Surgeons; private practice, 1515 E Cedar Ave, Ste A-2, Flagstaff, AZ Private practice, Atlanta, GA. parathyroid hormone can be secreted in either excessively low or high amounts. In hyperparathyroidism, excess production of parathyroid hormone causes calcium to be leached from its bone reservoir. The hypercalcemic state results in failure to inhibit parathyroid secretion, creating a vicious cycle. 2 Clinical features of hyperparathyroidism may include gastrointestinal distress, mental changes, recurrent nephrolithiasis, back pain, and nonspecific complaints of anorexia, malaise, fatigue, and depression. Hypercalcemia is often the first finding that raises suspicion of hyperparathyroidism. There are many causes of hypercalcemia, including hyperparathyroidism, malignancy, infection, vitamin A and D intoxication, immobilization, drug-related effects, and renal failure. The most common cause of hyperparathyroidism is a solitary, benign glandular adenoma. Less common causes include a group of metabolic disorders called multiple endocrine neoplasia syndromes. In cases of hyperparathyroidism, incidental radiographic findings of a washed-out appearance of bone may cause one to suspect osteoporosis. The terms osteoporosis, osteomalacia, and osteopenia are often confused. Osteoporosis describes diseases that cause a decrease in bone mass per unit volume. 3 Osteomalacia is a disorder of the osteoid matrix of bone and cartilage in which there is inadequate mineralization. Osteopenia describes reduced bone density or calcification due to inadequate osteoid synthesis. In the patient with hyper- Volume 89 Number 8 August
2 Table 1. Medical Conditions Associated with Insufficiency Stress Fractures Senile/postmenopausal osteoporosis Drug-induced osteoporosis (alcohol, steroids, heparin) Disuse/immobilization-induced osteoporosis Idiopathic juvenile osteoporosis Osteogenesis imperfecta Hyperparathyroidism Hypoparathyroidism Pseudohypoparathyroidism Pseudopseudohypoparathyroidism Paget s disease Rickets/osteomalacia Nutritional deficiencies Chronic liver disease Anemic states Neoplasms Glycogen storage diseases Diabetes mellitus parathyroidism, osteoporosis is a common finding because of the leaching of calcium from the skeleton. Lower-extremity stress fractures are well-documented entities. They are commonly associated with an abrupt increase in activity level and repetitive loading, particularly in new armed-services recruits and exercise enthusiasts. 4 Stress fractures, however, may also occur without changes in physical activity, and may be related to the bone quality of the patient. Stress fractures are classified as either fatigue or insufficiency fractures. Fatigue stress fractures involve abnormal or repetitive forces exerted on normal bone. Insufficiency stress fractures occur when normal forces are applied to abnormal bone, causing a cortical break. 5 In either case, the result is an incomplete fracture that can cause pain and disability. Several studies have documented the incidence, frequency, sex distribution, risk factors, and other parameters of fatigue fractures in large military recruit populations. 4, 6-8 While insufficiency stress fractures have not been studied as extensively in large populations, they have been associated with numerous medical conditions (Table 1). 9 Stress fractures have been reported to occur in several lower-extremity bones, including the metatarsals, midfoot bones, calcaneus, tibia, fibula, and femur. 10 Pedal stress fractures commonly involve the metatarsals and calcaneus; less commonly, they involve the navicular and other tarsal bones. 8 Tarsal stress fractures may present a diagnostic challenge; in particular, the calcaneal stress fracture may be difficult to diagnose because it may mimic several other conditions, including plantar fasciitis. Diagnosis of calcaneal stress fractures involves the correlation of clinical and imaging findings. Gradual onset and progressive and generalized heel pain with or without antecedent changes in activity are common findings. Historical and physical aspects of calcaneal stress fractures may be similar to those of plantar fasciitis, but the physical findings more often reveal the diagnosis. Physically, pericalcaneal edema is common and maximal pain is usually elicited with side-to-side compression of the calcaneal body. Other reported findings include heel pain when the patient is toe walking and with muscle testing of ankle plantar flexors. 11 Calcaneal stress fractures are believed to be initiated by the normal physiologic action of the Achilles tendon. Characteristically, the fracture pattern begins posterior to the subtalar joint at the superior aspect of the calcaneal body and extends inferiorly. Initial radiographs are commonly interpreted as negative because of the radiographic lag time for new bone formation. Serial radiographs for up to 4 to 6 weeks may be required to make the diagnosis, with positive radiographs revealing a sclerotic band at the stress fracture site. When initial radiographs are reevaluated, a small cortical break may be detectable at the superior aspect of the calcaneus. Imaging modalities for further evaluating stress fractures are bone scans, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), and computed tomography. 12 Conservative treatment is effective in the management of stress fractures. This treatment involves antiinflammatory medications, protected weightbearing, radiographic monitoring of the stress fracture, and prevention of fracture progression. When metabolic bone disease is suspected, a referral to a specialist is warranted to identify the cause of the fracture. Case Report On July 7, 1994, a 56-year-old woman presented with a chief complaint of left heel pain. Her medical history was significant for dysphonia, recurrent nephrolithiasis, multiple spinal fractures, gastrointestinal disease (delayed gastric emptying, gastritis, and esophagitis), and asthma. Her surgical history included a splenectomy, an esophagogastroduodenoscopy, and multiple spinal fusions in 1983, 1986, and She had no known drug allergies. On her initial visit, she stated that she had pain located on the bottom of her left heel. She described symptoms typical of plantar fasciitis. Neurovascular and dermatologic findings were unremarkable. Palpation revealed pain 414 Journal of the American Podiatric Medical Association
3 Figure 1. Note the significant degree of edema of the left foot and ankle that was apparent upon admission to the hospital. located at the plantar medial tubercle of the calcaneus. Plain film radiographs of the foot were taken and were unremarkable. The diagnosis of plantar fasciitis was made and the patient was given a cortisone injection. The patient returned 5 months later. On her return visit, she complained of acute exacerbation of pain of the same heel and received another cortisone injection. The patient returned to the office 3 months later stating that her heel was doing substantially better; however, now the right heel was exquisitely tender. The diagnosis of plantar fasciitis was made and she was given a cortisone injection in her right heel. The patient presented again several times during the subsequent 18 months complaining of bilateral heel pain. Three days after receiving a cortisone injection in her left heel at the 18-month mark, the patient returned to the office concerned about increased pain, swelling, and redness. At this time, plain film radiographs were taken of the left foot and were read as normal. On clinical examination, there appeared to be slight edema over the medial aspect of the left foot and ankle. There was mild erythema and increased skin temperature. The diagnosis was a postinjection steroid flare. The patient was then started on dicloxacillin, 250 mg orally every 6 hours. She was instructed to return to the office in 1 week. Clinically, the patient was not improving and the edema and erythema were worsening. The patient was admitted to the hospital because of cellulitis of the left foot and leg (Fig. 1). Parenteral antibiotics were ordered. An MRI study was obtained that revealed bony destruction of the left calcaneus. The differential diagnosis was stress fracture or osteomyelitis. In light of the significant cellulitis, a bone biopsy was ordered; the results were consistent with healing fracture. No evidence of infection was seen. The patient was discharged from the hospital in a nonweightbearing below-the-knee cast. Approximately 2 months later, the patient was seen because of identical pain, swelling, and erythema of the right foot and leg. Radiographs were consistent with stress fracture of the calcaneus. For academic purposes, an MRI study was performed on the right foot; it yielded classic images of a calcaneal stress fracture. Because bilateral stress fractures of the calcaneus are uncommon, a referral to a metabolic bone disease specialist was made. Blood tests were performed and, in spite of a normal calcium level of 9.7 mg/dl (normal range, 8.5 to 10.3 mg/dl), parathyroid hormone was significantly elevated at 100 pg/ml (normal range, 10 to 65 pg/ml). 25-Hydroxyvitamin D was mildly decreased at 9 ng/ml (normal range, 10 to 55 ng/ml). The remaining elements of a blood chemistry profile, thyroid panel, and urine analysis were essentially unremarkable. Bone-densitometry studies were performed and revealed osteoporosis. In May 1997, the patient underwent a tetracycline-labeled bone biopsy of the iliac crest. Results of the biopsy revealed highturnover osteoporosis without osteomalacia, consistent with hyperparathyroid-induced lesions. Imaging The key to this diagnosis was a careful review of the chronology of imaging studies. The first study was from the initial presentation on July 7, 1994, and included lateral radiographic views; it was essentially normal (Fig. 2). Several studies were then performed of the left foot on October 24, The lateral plain film radiograph is underexposed, making it difficult to interpret. However, upon critical examination, the image shows a classic stress fracture of the calcaneal tuberosity (Fig. 3). An MRI study of the feet was performed on November 22, 1996, and showed the left calcaneus to be abnormal. The sagittal T1-weighted images show diffuse low-signal pattern in the calcaneal tuberosity, replacing the normal marrow fat. Also, a very important finding is a curvilinear low-signal line that can be differentiated from the surrounding low-signal edema in the marrow (Fig. 4). The T2-weighted images show a diffuse low signal in the left calcaneal tuberosity, which represents the actual fracture. The decreased signal intensity on the T1-weighted image is consistent with increased water content from the inflammatory reaction. There Volume 89 Number 8 August
4 Figure 2. The lateral radiograph of the left foot at initial presentation was read as essentially normal. Figure 3. Although the lateral radiograph is underexposed, a stress fracture is visible in the posterior calcaneus. is also surrounding soft-tissue swelling and edema. Again, a crucial observation is the presence of a curvilinear line in the posterior aspect of the calcaneal tuberosity, which is a low signal on the T2-weighted images and also a low signal on the T1-weighted images (Fig. 5). The magnetic resonance pattern described previously is classic for a calcaneal stress fracture; however, it does not permit differentiation between a fatigue and an insufficiency stress fracture. When the curvilinear line is present, it is important not to allow the degree of surrounding edema to dissuade one from making a definitive diagnosis of a stress fracture. The degree of edema present can cause one to think of infection or tumerous conditions. However, again, when the curvilinear line is present, and no marginated mass is seen, a stress fracture should be diagnosed. It is unusual for osteomyelitis to produce a curvilinear fracture line. The low-signal line about the stress fracture is thought to be related to the actual fracture line and the type of cells present. Of course, the edema is related to the inflammatory response or healing response to the fracture. Marrow edema by itself is generally nonspecific and can be seen in many different abnormalities in- Figure 4. The sagittal T1-weighted image shows the characteristic curvilinear low-signal line consistent with stress fracture. Also note the diffuse low-signal pattern in the calcaneus. Figure 5. The frontal T2-weighted image shows a high signal intensity consistent with edema and hemorrhage. This T2-weighted image also reveals a lowsignal-intensity curvilinear fracture line, similar to that in the T1-weighted image. 416 Journal of the American Podiatric Medical Association
5 cluding infection, infarction, injury (acute or chronic), and response to tumor. The challenge is to evaluate findings related to the edema to attempt to determine the cause. This is not always possible. However, when a curvilinear line is present in a site such as the calcaneus or other sites at risk for stress fractures, then this diagnosis can be made confidently. In the absence of this curvilinear line, other diagnoses should be entertained. Tumors will generally have a discretely marginated mass with or without associated cortical destruction. The pattern of marrow edema is usually surrounding the mass. In cases of infection, the curvilinear line is generally not present. It may be possible to have a pathologic fracture in an infected bone, although this is rare. In order for infection to cause such extensive destruction of bone, the infection would have to be severe and of several weeks duration. Infarctions may also demonstrate a type of curvilinear line, but the pattern is different from that seen in this case. Generally speaking, one can demonstrate the so-called double-line sign, which is characteristic of infarction. The patient had postoperative radiographs of the left foot on December 2, 1996, that showed the characteristic sclerotic curvilinear pattern in the tuberosity consistent with an insufficiency fracture, now with a core biopsy site at the site of the sclerosis (Fig. 6). Upright lateral views of both feet were obtained on January 20, 1997, again showing the stress fracture and biopsy pattern on the left side. No definite radiographic abnormality was seen on the right side. An MRI study of the right calcaneus on February 10, 1997, again shows characteristic findings of a stress fracture with a low-signal curvilinear line in the right calcaneal tuberosity just posterior to the posterior subtalar joint corresponding to the sclerotic line seen radiographically. The right calcaneal MRI scan shows the same pattern as previously seen on the left calcaneus, except in a slightly different location. These patterns include the low-signal fracture line on T1- and T2-weighted sequences with surrounding edema. The degree of edema about this stress fracture is slightly less than that seen on the other fracture on the left side (Fig. 7). Subsequent radiographs from September 9, 1997, continue to show the pattern of insufficiency fracture on the right side. However, they also show development of a second sclerotic band in the left calcaneal tuberosity, consistent with an additional stress fracture (Fig. 8). This demonstrates the healing of multiple, bilateral stress fractures. Discussion This case exemplifies how atypical heel pain can be misinterpreted as heel spur syndrome. Making an accurate diagnosis is difficult, especially when concomitant disease processes are present. The authors believe that in this case the original diagnosis of heel spur syndrome or plantar fasciitis was accurate, and the patient later developed an insufficiency stress fracture of the calcaneus that should have been diagnosed earlier. This case demonstrated classic findings of both hyperparathyroid disease and the evolution of stress fractures of the calcaneus. Stress fractures of the calcaneus are not uncommon among active people, such as athletes, sports enthusiasts, and military personnel. When insufficiency Figure 6. Note the trephine-core biopsy site through the sclerotic band in the posterior calcaneus that is clearly visible on the lateral radiograph of the left foot. Figure 7. The sagittal T1-weighted MR image of the right foot displays classic findings of stress fracture. Volume 89 Number 8 August
6 nosed frequently because of the MRI technology. Injuries that are frequently radiographically occult, especially in the early phases, can be glaringly obvious on MRI scans. Conclusion Figure 8. Note the two sclerotic bands in the lateral radiograph of the right foot consistent with two healing stress fracture sites. stress fractures are diagnosed, one should rule out an underlying metabolic bone disease. The overview of this patient s imaging studies demonstrates bilateral insufficiency fractures. The MRI and plain film radiographic findings are characteristic of this diagnosis; on the basis of these images alone, the diagnosis would be straightforward. From an imaging standpoint, one of the most important points is that the marrow edema seen on MRI scans surrounding a stress fracture can be quite prominent and somewhat disconcerting. As described here, one must look for the low-signal curvilinear band of fracture line that helps confirm that the edema is related to a fracture. The degree of edema should not dissuade one from making this diagnosis confidently if the other features are present. Finally, although MRI is more sensitive than plain film radiography, it is not superior to radiography or radionucleotide imaging for the diagnosis of this condition. Assuming that the patient does not have overt signs of infection, it is safe to treat the patient for a stress fracture in such cases, and obtain follow-up radiography in a few days. Typically, the follow-up radiographs show a classic pattern of stress fracture. If the characteristic curvilinear lines are not present, or if the characteristic sclerotic band is not formed on subsequent radiographs, then tissue diagnosis may be required. The authors categorize these types of abnormalities as occult injury. This pattern of abnormality is relatively new to imaging, but is now diag- Plantar heel pain is usually consistent with plantar fasciitis or heel spur syndrome. When historical or physical findings are unusual or routine treatment proves ineffective, one should suspect an atypical cause of the heel pain. The authors have presented a case of insufficiency stress fractures of both calcanei in a patient who was subsequently diagnosed with hyperparathyroidism. References 1. GROVES MJ: Atypical Heel Pain, in Reconstructive Surgery of the Foot and Leg: Update 97, ed by NS Vickers, SJ Miller, KT Mahan, et al, p 220, The Podiatry Institute, Tucker, GA, POTTS JT: Diseases of the Parathyroid Gland and Other Hyper- and Hypocalcemic Disorders, in Harrison s Principles of Internal Medicine, Vol 2, ed by AS Fauci, E Braunwald, KJ Isselbacher, et al, p 2227, McGraw- Hill, New York, KRANE SM, HOLICK MF: Metabolic Bone Disease, in Harrison s Principles of Internal Medicine, Vol 2, ed by AS Fauci, E Braunwald, KJ Isselbacher, et al, p 2247, McGraw-Hill, New York, ORAVA S, PURANEN J, ALA-KETOLA L: Stress fractures caused by physical exercise. Acta Orthop Scand 49: 19, MORRIS JM, BLICKENSTAFF LD: Fatigue Fractures: A Clinical Study, Charles C Thomas, Springfield, IL, DAFFNER RH: Stress fractures: current concepts. Skeletal Radiol 2: 221, GILBERT RS, JOHNSON HA: Stress fractures in military recruits: a review of twelve years experience. Mil Med 131: 716, HOPSON CN, PERRY DR: Stress fractures of the calcaneus in women marine recruits. Clin Orthop 128: 159, RESNICK D, NIWAYAMA G: Osteoporosis, in Diagnosis of Bone and Joint Disorders, Vol 2, ed by D Resnick, G Niwayama, p 1638, WB Saunders, Philadelphia, PENTECOST RL, MURRAY JM, BRINDLEY HH: Fatigue, insufficiency, and pathologic fractures. JAMA 187: 1001, DUDDY RK, DUGGAN RJ, VISSER HJ, ET AL: Diagnosis, treatment, and rehabilitation of injuries to the lower leg and foot. Clin Sports Med 8: 961, PRATHER JL, NUSYNOWITZ ML, SNOWDY HA, ET AL: Scintigraphic findings in stress fractures. J Bone Joint Surg Am 59: 869, Journal of the American Podiatric Medical Association
The Diagnosis and Management of Heel Pain in Active People
 The Diagnosis and Management of Heel Pain in Active People Perry Julien, D.P.M. Past President, American Academy of Podiatric Sports Medicine Podiatry Coordinator, 1996 Summer Olympic Games Atlanta Georgia
The Diagnosis and Management of Heel Pain in Active People Perry Julien, D.P.M. Past President, American Academy of Podiatric Sports Medicine Podiatry Coordinator, 1996 Summer Olympic Games Atlanta Georgia
Objectives Learn the anatomy of the foot. Identify key terms associated with plantar fasciitis. Determine the causes of plantar fasciitis and understa
 Plantar Fasciitis Objectives Learn the anatomy of the foot. Identify key terms associated with plantar fasciitis. Determine the causes of plantar fasciitis and understand why it occurs. Recognize the injury
Plantar Fasciitis Objectives Learn the anatomy of the foot. Identify key terms associated with plantar fasciitis. Determine the causes of plantar fasciitis and understand why it occurs. Recognize the injury
Heel Pain: Heal! Amie C. Scantlin, DPM, MS, FACFAS Glencoe Regional Health Services (320) 864-3121 ext. 1933
 Heel Pain: Heal! Amie C. Scantlin, DPM, MS, FACFAS Glencoe Regional Health Services (320) 864-3121 ext. 1933 www.grhsonline.org Important Notice The information contained in this document is for informational
Heel Pain: Heal! Amie C. Scantlin, DPM, MS, FACFAS Glencoe Regional Health Services (320) 864-3121 ext. 1933 www.grhsonline.org Important Notice The information contained in this document is for informational
.org. Metastatic Bone Disease. Description
 Metastatic Bone Disease Page ( 1 ) Cancer that begins in an organ, such as the lungs, breast, or prostate, and then spreads to bone is called metastatic bone disease (MBD). More than 1.2 million new cancer
Metastatic Bone Disease Page ( 1 ) Cancer that begins in an organ, such as the lungs, breast, or prostate, and then spreads to bone is called metastatic bone disease (MBD). More than 1.2 million new cancer
.org. Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction. Anatomy. Cause. Symptoms
 Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction Page ( 1 ) Posterior tibial tendon dysfunction is one of the most common problems of the foot and ankle. It occurs when the posterior tibial tendon becomes inflamed
Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction Page ( 1 ) Posterior tibial tendon dysfunction is one of the most common problems of the foot and ankle. It occurs when the posterior tibial tendon becomes inflamed
Case Report Calcaneal Insufficiency Fracture Secondary to Celiac Disease Induced Osteomalacia A Rare Cause of Heel Pain
 583310FASXXX10.1177/1938640015583310Foot & Ankle SpecialistFoot & Ankle Specialist research-articlexxxx vol. XX / no. X Foot & Ankle Specialist 1 Case Report Calcaneal Insufficiency Fracture Secondary
583310FASXXX10.1177/1938640015583310Foot & Ankle SpecialistFoot & Ankle Specialist research-articlexxxx vol. XX / no. X Foot & Ankle Specialist 1 Case Report Calcaneal Insufficiency Fracture Secondary
Osteoarthritis progresses slowly and the pain and stiffness it causes worsens over time.
 Arthritis of the Foot and Ankle Arthritis is the leading cause of disability in the United States. It can occur at any age, and literally means "pain within a joint." As a result, arthritis is a term used
Arthritis of the Foot and Ankle Arthritis is the leading cause of disability in the United States. It can occur at any age, and literally means "pain within a joint." As a result, arthritis is a term used
Heel Pain Syndromes DELLON INSTITUTES FOR PERIPHERAL NERVE SURGERY
 Heel Pain s 5 3333 N CALVERT ST, SUITE 370, BALTIMORE, MD 21218 T410 467 5400 F410 366 9826 delloninstitutes.com your complaints are Pain, numbness or burning in your heel. The timing of this pain and
Heel Pain s 5 3333 N CALVERT ST, SUITE 370, BALTIMORE, MD 21218 T410 467 5400 F410 366 9826 delloninstitutes.com your complaints are Pain, numbness or burning in your heel. The timing of this pain and
.org. Lisfranc (Midfoot) Injury. Anatomy. Description
 Lisfranc (Midfoot) Injury Page ( 1 ) Lisfranc (midfoot) injuries result if bones in the midfoot are broken or ligaments that support the midfoot are torn. The severity of the injury can vary from simple
Lisfranc (Midfoot) Injury Page ( 1 ) Lisfranc (midfoot) injuries result if bones in the midfoot are broken or ligaments that support the midfoot are torn. The severity of the injury can vary from simple
Corporate Medical Policy
 Corporate Medical Policy File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: testing_serum_vitamin_d_levels 9/2015 2/2016 2/2017 2/2016 Description of Procedure or Service Vitamin D,
Corporate Medical Policy File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: testing_serum_vitamin_d_levels 9/2015 2/2016 2/2017 2/2016 Description of Procedure or Service Vitamin D,
Plantar Fasciitis. Plantar Fascia
 Plantar Fasciitis Introduction Plantar fasciitis is an inflammation of the thick band of tissue that connects your heel bone to your toes. This thick band of tissue is called the plantar fascia. Plantar
Plantar Fasciitis Introduction Plantar fasciitis is an inflammation of the thick band of tissue that connects your heel bone to your toes. This thick band of tissue is called the plantar fascia. Plantar
6/3/2011. High Prevalence and Incidence. Low back pain is 5 th most common reason for all physician office visits in the U.S.
 High Prevalence and Incidence Prevalence 85% of Americans will experience low back pain at some time in their life. Incidence 5% annual Timothy C. Shen, M.D. Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation Sub-specialty
High Prevalence and Incidence Prevalence 85% of Americans will experience low back pain at some time in their life. Incidence 5% annual Timothy C. Shen, M.D. Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation Sub-specialty
Treatment of Recalcitrant Intermetatarsal Neuroma With 4% Sclerosing Alcohol Injection: A Pilot Study
 Treatment of Recalcitrant Intermetatarsal Neuroma With 4% Sclerosing Alcohol Injection: A Pilot Study Christopher F. Hyer, DPM,' Lynette R. Mehl, DPM,2 Alan J. Block, DPM, MS, FACFAS,3 and Robert B. Vancourt,
Treatment of Recalcitrant Intermetatarsal Neuroma With 4% Sclerosing Alcohol Injection: A Pilot Study Christopher F. Hyer, DPM,' Lynette R. Mehl, DPM,2 Alan J. Block, DPM, MS, FACFAS,3 and Robert B. Vancourt,
CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES FOR MANAGEMENT OF LOW BACK PAIN
 CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES FOR MANAGEMENT OF LOW BACK PAIN Low back pain is very common, up to 90+% of people are affected by back pain at some time in their lives. Most often back pain is benign and
CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES FOR MANAGEMENT OF LOW BACK PAIN Low back pain is very common, up to 90+% of people are affected by back pain at some time in their lives. Most often back pain is benign and
Radiologic Diagnosis of Spinal Metastases
 September 2002 Radiologic Diagnosis of Spinal Metastases Natalie J. M. Dailey, Harvard Medical Student Year III Our Patient s Presenting Story 70 year old male Presents to the hospital for laparascopic
September 2002 Radiologic Diagnosis of Spinal Metastases Natalie J. M. Dailey, Harvard Medical Student Year III Our Patient s Presenting Story 70 year old male Presents to the hospital for laparascopic
Plantar fasciitis is a common foot problem that occurs in 10%
 Review Article Plantar Fasciitis Heel Pain: Part 1 a Practical Management Plantar fasciitis is a common foot problem that occurs in 10% of the population. 1,2 The most involved age group is 40-50 3,4 Actually,
Review Article Plantar Fasciitis Heel Pain: Part 1 a Practical Management Plantar fasciitis is a common foot problem that occurs in 10% of the population. 1,2 The most involved age group is 40-50 3,4 Actually,
Calcaneus (Heel Bone) Fractures
 Copyright 2010 American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Calcaneus (Heel Bone) Fractures Fractures of the heel bone, or calcaneus, can be disabling injuries. They most often occur during high-energy collisions
Copyright 2010 American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Calcaneus (Heel Bone) Fractures Fractures of the heel bone, or calcaneus, can be disabling injuries. They most often occur during high-energy collisions
Plantar fascia. Plantar Fasciitis (pain in the heel of the foot)
 ! Plantar fascia Plantar Fasciitis (pain in the heel of the foot) Plantar Fasciitis is the most common foot problem seen in runners and is often associated with an increase in running mileage. Typically
! Plantar fascia Plantar Fasciitis (pain in the heel of the foot) Plantar Fasciitis is the most common foot problem seen in runners and is often associated with an increase in running mileage. Typically
.org. Ankle Fractures (Broken Ankle) Anatomy
 Ankle Fractures (Broken Ankle) Page ( 1 ) A broken ankle is also known as an ankle fracture. This means that one or more of the bones that make up the ankle joint are broken. A fractured ankle can range
Ankle Fractures (Broken Ankle) Page ( 1 ) A broken ankle is also known as an ankle fracture. This means that one or more of the bones that make up the ankle joint are broken. A fractured ankle can range
A Guide to Heel Pain
 The Society of Chiropodists and Podiatrists A Guide to Heel Pain The Society of Chiropodists and Podiatrists Heel pain may be caused by a number of different problems; for effective treatment you need
The Society of Chiropodists and Podiatrists A Guide to Heel Pain The Society of Chiropodists and Podiatrists Heel pain may be caused by a number of different problems; for effective treatment you need
Approach to Lower Extremity Osteomyelitis. A radiologic tour of a patient encounter
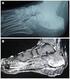 Approach to Lower Extremity Osteomyelitis A radiologic tour of a patient encounter David Guo,, HMS III Gillian Lieberman, MD BIDMC, October 2009 Our learning goals Review lower extremity anatomy Discuss
Approach to Lower Extremity Osteomyelitis A radiologic tour of a patient encounter David Guo,, HMS III Gillian Lieberman, MD BIDMC, October 2009 Our learning goals Review lower extremity anatomy Discuss
.org. Plantar Fasciitis and Bone Spurs. Anatomy. Cause
 Plantar Fasciitis and Bone Spurs Page ( 1 ) Plantar fasciitis (fashee-eye-tiss) is the most common cause of pain on the bottom of the heel. Approximately 2 million patients are treated for this condition
Plantar Fasciitis and Bone Spurs Page ( 1 ) Plantar fasciitis (fashee-eye-tiss) is the most common cause of pain on the bottom of the heel. Approximately 2 million patients are treated for this condition
PLANTAR FASCITIS (Heel Spur Syndrome)
 PLANTAR FASCITIS (Heel Spur Syndrome) R. Amadeus Mason MD Description Plantar fascitis is characterized by stiffness and inflammation of the main fascia (fibrous connective [ligament-like] tissue) on the
PLANTAR FASCITIS (Heel Spur Syndrome) R. Amadeus Mason MD Description Plantar fascitis is characterized by stiffness and inflammation of the main fascia (fibrous connective [ligament-like] tissue) on the
Imaging of Lisfranc Injury
 November 2011 Imaging of Lisfranc Injury Greg Cvetanovich, Harvard Medical School Year IV Agenda Case Presentation Introduction Anatomy Lisfranc Injury Classification Imaging Treatment 2 Case Presentation
November 2011 Imaging of Lisfranc Injury Greg Cvetanovich, Harvard Medical School Year IV Agenda Case Presentation Introduction Anatomy Lisfranc Injury Classification Imaging Treatment 2 Case Presentation
Temple Physical Therapy
 Temple Physical Therapy A General Overview of Common Neck Injuries For current information on Temple Physical Therapy related news and for a healthy and safe return to work, sport and recreation Like Us
Temple Physical Therapy A General Overview of Common Neck Injuries For current information on Temple Physical Therapy related news and for a healthy and safe return to work, sport and recreation Like Us
How To Treat Heel Pain
 Plantar Fasciitis, Heel Spurs, Heel Pain The Plantar Fasciitis Organization is dedicated to the understanding of Plantar Fasciitis, Heel Spurs, and all other forms of Heel Pain. Welcome to the Plantar
Plantar Fasciitis, Heel Spurs, Heel Pain The Plantar Fasciitis Organization is dedicated to the understanding of Plantar Fasciitis, Heel Spurs, and all other forms of Heel Pain. Welcome to the Plantar
Rheumatoid Arthritis of the Foot and Ankle
 Copyright 2011 American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Rheumatoid Arthritis of the Foot and Ankle Rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic disease that attacks multiple joints throughout the body. It most often
Copyright 2011 American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Rheumatoid Arthritis of the Foot and Ankle Rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic disease that attacks multiple joints throughout the body. It most often
Spine University s Guide to Transient Osteoporosis
 Spine University s Guide to Transient Osteoporosis 2 Introduction The word osteoporosis scares many people because they ve heard about brittle bone disease. They may know someone who has had it or seen
Spine University s Guide to Transient Osteoporosis 2 Introduction The word osteoporosis scares many people because they ve heard about brittle bone disease. They may know someone who has had it or seen
Anatomy: The sella is a depression in the sphenoid bone that makes up part of the skull base located behind the eye sockets.
 Pituitary Tumor Your doctor thinks you may have a pituitary tumor. Pituitary tumors are benign (non-cancerous) overgrowth of cells that make up the pituitary gland (the master gland that regulates other
Pituitary Tumor Your doctor thinks you may have a pituitary tumor. Pituitary tumors are benign (non-cancerous) overgrowth of cells that make up the pituitary gland (the master gland that regulates other
Commonly Missed Fractures in the Emergency Department
 Commonly Missed Fractures in the Emergency Department Taylor Sittler MS IV - UMASS Images courtesy of Jim Wu, MD, Sanjay Shetty, MD and Mary Hochman, MD Diagnostic Errors in the ED Taylor Sittler, MS IV
Commonly Missed Fractures in the Emergency Department Taylor Sittler MS IV - UMASS Images courtesy of Jim Wu, MD, Sanjay Shetty, MD and Mary Hochman, MD Diagnostic Errors in the ED Taylor Sittler, MS IV
Disability Evaluation Under Social Security
 Disability Evaluation Under Social Security Revised Medical Criteria for Evaluating Endocrine Disorders Effective June 7, 2011 Why a Revision? Social Security revisions reflect: SSA s adjudicative experience.
Disability Evaluation Under Social Security Revised Medical Criteria for Evaluating Endocrine Disorders Effective June 7, 2011 Why a Revision? Social Security revisions reflect: SSA s adjudicative experience.
A Patient s Guide to Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH)
 A Patient s Guide to Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH) Introduction Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH) is a phenomenon that more commonly affects older males. It is associated
A Patient s Guide to Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH) Introduction Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH) is a phenomenon that more commonly affects older males. It is associated
DIAGNOSING SCAPHOID FRACTURES. Anthony Hewitt
 DIAGNOSING SCAPHOID FRACTURES Anthony Hewitt Introduction Anatomy of the scaphoid Resembles a deformed peanut Articular cartilage covers 80% of the surface It rests in a plane 45 degrees to the longitudinal
DIAGNOSING SCAPHOID FRACTURES Anthony Hewitt Introduction Anatomy of the scaphoid Resembles a deformed peanut Articular cartilage covers 80% of the surface It rests in a plane 45 degrees to the longitudinal
Plantar Fascia Release
 Plantar Fascia Release Introduction Plantar fasciitis is a common condition that causes pain around the heel. It may be severe enough to affect regular activities. If other treatments are unsuccessful,
Plantar Fascia Release Introduction Plantar fasciitis is a common condition that causes pain around the heel. It may be severe enough to affect regular activities. If other treatments are unsuccessful,
Open the Flood Gates Urinary Obstruction and Kidney Stones. Dr. Jeffrey Rosenberg Dr. Emilio Lastarria Dr. Richard Kasulke
 Open the Flood Gates Urinary Obstruction and Kidney Stones Dr. Jeffrey Rosenberg Dr. Emilio Lastarria Dr. Richard Kasulke Nephrology vs. Urology Nephrologist a physician who has been trained in the diagnosis
Open the Flood Gates Urinary Obstruction and Kidney Stones Dr. Jeffrey Rosenberg Dr. Emilio Lastarria Dr. Richard Kasulke Nephrology vs. Urology Nephrologist a physician who has been trained in the diagnosis
.org. Achilles Tendinitis. Description. Cause. Achilles tendinitis is a common condition that causes pain along the back of the leg near the heel.
 Achilles Tendinitis Page ( 1 ) Achilles tendinitis is a common condition that causes pain along the back of the leg near the heel. The Achilles tendon is the largest tendon in the body. It connects your
Achilles Tendinitis Page ( 1 ) Achilles tendinitis is a common condition that causes pain along the back of the leg near the heel. The Achilles tendon is the largest tendon in the body. It connects your
November 2012 Case Study. Authors: Kyle Nagle, MD, MPH; Karl Fry, PT, DPT, OCS; David Bernhardt, MD
 CC: Right foot pain November 2012 Case Study Authors: Kyle Nagle, MD, MPH; Karl Fry, PT, DPT, OCS; David Bernhardt, MD HPI: A 17 year old female cross country runner presents with right foot pain. At a
CC: Right foot pain November 2012 Case Study Authors: Kyle Nagle, MD, MPH; Karl Fry, PT, DPT, OCS; David Bernhardt, MD HPI: A 17 year old female cross country runner presents with right foot pain. At a
Measure Title X RAY PRIOR TO MRI OR CAT SCAN IN THE EVAULATION OF LOWER BACK PAIN Disease State Back pain Indicator Classification Utilization
 Client HMSA: PQSR 2009 Measure Title X RAY PRIOR TO MRI OR CAT SCAN IN THE EVAULATION OF LOWER BACK PAIN Disease State Back pain Indicator Classification Utilization Strength of Recommendation Organizations
Client HMSA: PQSR 2009 Measure Title X RAY PRIOR TO MRI OR CAT SCAN IN THE EVAULATION OF LOWER BACK PAIN Disease State Back pain Indicator Classification Utilization Strength of Recommendation Organizations
C H A P T E R 3 5. Thomas J. Merrill, DPM Riquel Gonzalez, DPM INTRODUCTION CASE REPORT
 C H A P T E R 3 5 CORTICOSTEROID INDUCED AVASCULAR NECROSIS OF THE RIGHT MEDIAL CUNEIFORM TREATED WITH TRINITY EVOLUTION BONE GRAFT AND ARTHRODESIS: Case Report and Review of the Literature Thomas J. Merrill,
C H A P T E R 3 5 CORTICOSTEROID INDUCED AVASCULAR NECROSIS OF THE RIGHT MEDIAL CUNEIFORM TREATED WITH TRINITY EVOLUTION BONE GRAFT AND ARTHRODESIS: Case Report and Review of the Literature Thomas J. Merrill,
Clinical guidance for MRI referral
 MRI for cervical radiculopathy Referral by a medical practitioner (excluding a specialist or consultant physician) for a scan of spine for a patient 16 years or older for suspected: cervical radiculopathy
MRI for cervical radiculopathy Referral by a medical practitioner (excluding a specialist or consultant physician) for a scan of spine for a patient 16 years or older for suspected: cervical radiculopathy
The Ankle Sprain That Won t Get Better. By: George E. Quill, Jr., M.D. With springtime in Louisville upon us, the primary care physician and the
 The Ankle Sprain That Won t Get Better By: George E. Quill, Jr., M.D. With springtime in Louisville upon us, the primary care physician and the orthopaedist alike can expect to see more than his or her
The Ankle Sprain That Won t Get Better By: George E. Quill, Jr., M.D. With springtime in Louisville upon us, the primary care physician and the orthopaedist alike can expect to see more than his or her
MRI of Bone Marrow Radiologic-Pathologic Correlation
 MRI of Bone Marrow Radiologic-Pathologic Correlation Marilyn J. Siegel, M.D. Mallinckrodt Institute of Radiology Washington University School of Medicine St. Louis, MO and Visiting Scientist, AFIP, Washington,
MRI of Bone Marrow Radiologic-Pathologic Correlation Marilyn J. Siegel, M.D. Mallinckrodt Institute of Radiology Washington University School of Medicine St. Louis, MO and Visiting Scientist, AFIP, Washington,
CMS Limitations Guide Mammograms and Bone Density Radiology Services
 CMS Limitations Guide Mammograms and Bone Density Radiology Services Starting July 1, 2008, CMS has placed numerous medical necessity limits on tests and procedures. This reference guide provides you with
CMS Limitations Guide Mammograms and Bone Density Radiology Services Starting July 1, 2008, CMS has placed numerous medical necessity limits on tests and procedures. This reference guide provides you with
Common Foot & Ankle Sports Injuries
 Common Foot & Ankle Sports Injuries Symptoms Related to Abnormal Foot Biomechanics & their Differential Diagnosis Daniel Pang BSc (Hon) P&O, Cped Certified Pedorthist (USA) Only 10% of foot having structure
Common Foot & Ankle Sports Injuries Symptoms Related to Abnormal Foot Biomechanics & their Differential Diagnosis Daniel Pang BSc (Hon) P&O, Cped Certified Pedorthist (USA) Only 10% of foot having structure
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS OF LOW BACK PAIN. Arnold J. Weil, M.D., M.B.A. Non-Surgical Orthopaedics, P.C. Atlanta, GA
 DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS OF LOW BACK PAIN Arnold J. Weil, M.D., M.B.A. Non-Surgical Orthopaedics, P.C. Atlanta, GA MEDICAL ALGORITHM OF REALITY LOWER BACK PAIN Yes Patient will never get better until case
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS OF LOW BACK PAIN Arnold J. Weil, M.D., M.B.A. Non-Surgical Orthopaedics, P.C. Atlanta, GA MEDICAL ALGORITHM OF REALITY LOWER BACK PAIN Yes Patient will never get better until case
Page 2 of 6 plantar fascia. This is called the windlass mechanism. Later, we'll discuss how this mechanism is used to treat plantar fasciitis with str
 Page 1 of 6 Plantar Fasciitis (Heel Pain) Plantar fasciitis is a painful condition affecting the bottom of the foot. It is a common cause of heel pain and is sometimes called a heel spur. Plantar fasciitis
Page 1 of 6 Plantar Fasciitis (Heel Pain) Plantar fasciitis is a painful condition affecting the bottom of the foot. It is a common cause of heel pain and is sometimes called a heel spur. Plantar fasciitis
ADVANCEMENTS IN PLANTAR FASCIA SURGERY
 C H A P T E R 3 3 ADVANCEMENTS IN PLANTAR FASCIA SURGERY James L. Bouchard, DPM Andrea Cass, DPM INTRODUCTION It has been estimated that 90% of patients with plantar fasciitis and heel spur syndrome get
C H A P T E R 3 3 ADVANCEMENTS IN PLANTAR FASCIA SURGERY James L. Bouchard, DPM Andrea Cass, DPM INTRODUCTION It has been estimated that 90% of patients with plantar fasciitis and heel spur syndrome get
Endoscopic Plantar Fasciotomy
 Endoscopic Plantar Fasciotomy Introduction Plantar fasciitis is a common condition that causes pain centralized around the heel. It may be severe enough to affect regular activities. Health care providers
Endoscopic Plantar Fasciotomy Introduction Plantar fasciitis is a common condition that causes pain centralized around the heel. It may be severe enough to affect regular activities. Health care providers
RHEUMATOLOGY ICD-10 CROSSWALK
 RHEUMATOLOGY ICD-10 CROSSWALK ICD is revised periodically and is currently in its tenth edition and will be implemented in the United States on October 1, 2015. There is an annual minor update and three-yearly
RHEUMATOLOGY ICD-10 CROSSWALK ICD is revised periodically and is currently in its tenth edition and will be implemented in the United States on October 1, 2015. There is an annual minor update and three-yearly
The role of bone scintigraphy in determining the etiology of heel pain
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Annals of Nuclear Medicine Vol. 16, No. 6, 395 401, 2002 The role of bone scintigraphy in determining the etiology of heel pain Hakan ÖZDEMI%R,* Aysun ÖZDEMI%R,** Yetkin SOYUNCU* and Mustafa
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Annals of Nuclear Medicine Vol. 16, No. 6, 395 401, 2002 The role of bone scintigraphy in determining the etiology of heel pain Hakan ÖZDEMI%R,* Aysun ÖZDEMI%R,** Yetkin SOYUNCU* and Mustafa
Posttraumatic medial ankle instability
 Posttraumatic medial ankle instability Alexej Barg, Markus Knupp, Beat Hintermann Orthopaedic Department University Hospital of Basel, Switzerland Clinic of Orthopaedic Surgery, Kantonsspital Baselland
Posttraumatic medial ankle instability Alexej Barg, Markus Knupp, Beat Hintermann Orthopaedic Department University Hospital of Basel, Switzerland Clinic of Orthopaedic Surgery, Kantonsspital Baselland
Outline. The Agony of the Foot: Disclosure. Plantar Fasciitis. Top 5 Foot and Ankle Problems in Primary Care. Daniel Thuillier, M.D.
 The Agony of the Foot: Top 5 Foot and Ankle Problems in Primary Care Daniel Thuillier, M.D. Assistant Professor of Clinical Orthopaedics University of California San Francisco Plantar Fasciitis Achilles
The Agony of the Foot: Top 5 Foot and Ankle Problems in Primary Care Daniel Thuillier, M.D. Assistant Professor of Clinical Orthopaedics University of California San Francisco Plantar Fasciitis Achilles
Preventing Potential Claims of Negligence What Would You Do Settle or Go to Trial?
 Preventing Potential Claims of Negligence What Would You Do Settle or Go to Trial? Ross E. Taubman, DPM PICA President and Chief Medical Officer 2013 APMA YOUNG PHYSICIANS INSTITUTE April 12 14 PICA Headquarters
Preventing Potential Claims of Negligence What Would You Do Settle or Go to Trial? Ross E. Taubman, DPM PICA President and Chief Medical Officer 2013 APMA YOUNG PHYSICIANS INSTITUTE April 12 14 PICA Headquarters
Lower Back Spinal Fusion & Exercise
 & Exercise with Rick Kaselj, MS More FREE Information on Exercise & Injuries $299 Fitness Education Returning the Shoulder Back to Optimal Function Seminar Exercise Modification for the Sensitive Shoulder
& Exercise with Rick Kaselj, MS More FREE Information on Exercise & Injuries $299 Fitness Education Returning the Shoulder Back to Optimal Function Seminar Exercise Modification for the Sensitive Shoulder
Plantar Heel Pain. By: Kevin Kleiner, M.B.S. New York College of Podiatric Medicine
 Plantar Heel Pain By: Kevin Kleiner, M.B.S. New York College of Podiatric Medicine Plantar Heel Pain: - Many Etiologies but few solutions Plantar heel pain more specifically: Heel pain felt in ones rear-foot
Plantar Heel Pain By: Kevin Kleiner, M.B.S. New York College of Podiatric Medicine Plantar Heel Pain: - Many Etiologies but few solutions Plantar heel pain more specifically: Heel pain felt in ones rear-foot
Ankle Injury/Sprains in Youth Soccer Players Elite Soccer Community Organization (ESCO) November 14, 2013
 Ankle Injury/Sprains in Youth Soccer Players Elite Soccer Community Organization (ESCO) November 14, 2013 Jeffrey R. Baker, DPM, FACFAS Weil Foot and Ankle Institute Des Plaines, IL Ankle Injury/Sprains
Ankle Injury/Sprains in Youth Soccer Players Elite Soccer Community Organization (ESCO) November 14, 2013 Jeffrey R. Baker, DPM, FACFAS Weil Foot and Ankle Institute Des Plaines, IL Ankle Injury/Sprains
Heel pain and Plantar fasciitis
 A patient s guide Heel pain and Plantar fasciitis Fred Robinson BSc FRCS FRCS(orth) Consultant Trauma & Orthopaedic Surgeon Alex Wee BSc FRCS(orth) Consultant Trauma & Orthopaedic Surgeon. What causes
A patient s guide Heel pain and Plantar fasciitis Fred Robinson BSc FRCS FRCS(orth) Consultant Trauma & Orthopaedic Surgeon Alex Wee BSc FRCS(orth) Consultant Trauma & Orthopaedic Surgeon. What causes
LATERAL PAIN SYNDROMES OF THE FOOT AND ANKLE
 C H A P T E R 3 LATERAL PAIN SYNDROMES OF THE FOOT AND ANKLE William D. Fishco, DPM The majority of patient encounters with the podiatrist are secondary to pain in the foot and/or ankle. If we draw an
C H A P T E R 3 LATERAL PAIN SYNDROMES OF THE FOOT AND ANKLE William D. Fishco, DPM The majority of patient encounters with the podiatrist are secondary to pain in the foot and/or ankle. If we draw an
A Diagnostic Chest XRay: Multiple Myeloma
 Daniela Marinho Tridente, VI FCMSCSP October 2013 A Diagnostic Chest XRay: Multiple Myeloma Daniela Marinho Tridente, VI FCMSCSP Our Learning Agenda Introduction of our patient His imaging data and findings
Daniela Marinho Tridente, VI FCMSCSP October 2013 A Diagnostic Chest XRay: Multiple Myeloma Daniela Marinho Tridente, VI FCMSCSP Our Learning Agenda Introduction of our patient His imaging data and findings
INJURIES OF THE HAND AND WRIST By Derya Dincer, M.D.
 05/05/2007 INJURIES OF THE HAND AND WRIST By Derya Dincer, M.D. Hand injuries, especially the fractures of metacarpals and phalanges, are the most common fractures in the skeletal system. Hand injuries
05/05/2007 INJURIES OF THE HAND AND WRIST By Derya Dincer, M.D. Hand injuries, especially the fractures of metacarpals and phalanges, are the most common fractures in the skeletal system. Hand injuries
Ankle Sports injuries. Ben Yates
 Ankle Sports injuries Ben Yates Common Extra-articular Conditions Lateral collateral ligament sprains (grades 1,2,3) Functional instability Mechanical instability Achilles tendonopathy (Achillodynia) superficial
Ankle Sports injuries Ben Yates Common Extra-articular Conditions Lateral collateral ligament sprains (grades 1,2,3) Functional instability Mechanical instability Achilles tendonopathy (Achillodynia) superficial
Other Noninfectious Diseases. Chapter 31 Lesson 3
 Other Noninfectious Diseases Chapter 31 Lesson 3 Diabetes Diabetes- a chronic disease that affects the way body cells convert food into energy. Diabetes is the seventh leading cause of death by disease
Other Noninfectious Diseases Chapter 31 Lesson 3 Diabetes Diabetes- a chronic disease that affects the way body cells convert food into energy. Diabetes is the seventh leading cause of death by disease
Spine University s Guide to Vertebral Osteonecrosis (Kummel's Disease)
 Spine University s Guide to Vertebral Osteonecrosis (Kummel's Disease) 2 Introduction Kummel's disease is a collapse of the vertebrae (the bones that make up the spine). It is also called vertebral osteonecrosis.
Spine University s Guide to Vertebral Osteonecrosis (Kummel's Disease) 2 Introduction Kummel's disease is a collapse of the vertebrae (the bones that make up the spine). It is also called vertebral osteonecrosis.
Worsening thigh pain after blunt trauma
 Images in Radiology Worsening thigh pain after blunt trauma LT Kendall Lane MD MC USN A 19 year-old otherwise healthy male presented with right thigh pain for three weeks after another player s knee struck
Images in Radiology Worsening thigh pain after blunt trauma LT Kendall Lane MD MC USN A 19 year-old otherwise healthy male presented with right thigh pain for three weeks after another player s knee struck
George E. Quill, Jr., M.D. Louisville Orthopaedic Clinic Louisville, KY
 George E. Quill, Jr., M.D. Louisville Orthopaedic Clinic Louisville, KY The Ankle Sprain That Won t Get Better With springtime in Louisville upon us, the primary care physician and the orthopaedist alike
George E. Quill, Jr., M.D. Louisville Orthopaedic Clinic Louisville, KY The Ankle Sprain That Won t Get Better With springtime in Louisville upon us, the primary care physician and the orthopaedist alike
Insufficiency fracture of the tibial plateau : An often missed diagnosis
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2006, 72, 587-591 ORIGINAL STUDY Insufficiency of the tibial plateau : An often missed diagnosis Narayana PRASAD, Judy M. MURRAY, Deepak KUMAR, Stephen G. DAVIES From the Royal Glamorgan
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2006, 72, 587-591 ORIGINAL STUDY Insufficiency of the tibial plateau : An often missed diagnosis Narayana PRASAD, Judy M. MURRAY, Deepak KUMAR, Stephen G. DAVIES From the Royal Glamorgan
Spinal Compression Fractures A Patient's Guide to Spinal Compression Fractures
 Arcata Chiropractic Office Larry J. Kleefeld D.C. Spinal Compression Fractures A Patient's Guide to Spinal Compression Fractures Introduction Compression fractures are the most common type of fracture
Arcata Chiropractic Office Larry J. Kleefeld D.C. Spinal Compression Fractures A Patient's Guide to Spinal Compression Fractures Introduction Compression fractures are the most common type of fracture
Joint Pain: Wrist, Knee, Shoulder, Ankle, Elbow, TMJ
 Joint Pain: Wrist, Knee, Shoulder, Ankle, Elbow, TMJ 6 3333 N CALVERT ST, SUITE 370, BALTIMORE, MD 21218 T410 467 5400 F410 366 9826 delloninstitutes.com your complaints are Your wrist hurts when you bend
Joint Pain: Wrist, Knee, Shoulder, Ankle, Elbow, TMJ 6 3333 N CALVERT ST, SUITE 370, BALTIMORE, MD 21218 T410 467 5400 F410 366 9826 delloninstitutes.com your complaints are Your wrist hurts when you bend
Osteoporosis and Arthritis: Two Common but Different Conditions
 and : Two Common but Different Conditions National Institutes of Health and Related Bone Diseases ~ National Resource Center 2 AMS Circle Bethesda, MD 20892 3676 Tel: 800 624 BONE or 202 223 0344 Fax:
and : Two Common but Different Conditions National Institutes of Health and Related Bone Diseases ~ National Resource Center 2 AMS Circle Bethesda, MD 20892 3676 Tel: 800 624 BONE or 202 223 0344 Fax:
Predislocation syndrome
 Predislocation syndrome Sky Ridge Medical Center, Aspen Building Pre-dislocation syndrome, capsulitis, and metatarsalgia are all similar problems usually at the ball of the foot near the second and third
Predislocation syndrome Sky Ridge Medical Center, Aspen Building Pre-dislocation syndrome, capsulitis, and metatarsalgia are all similar problems usually at the ball of the foot near the second and third
Physician Assistant Post Graduate Orthopaedic Surgery Fellowship Program. Watauga Orthopaedics
 Physician Assistant Post Graduate Orthopaedic Surgery Fellowship Program Watauga Orthopaedics Physician Assistant Post-Graduate Fellowship Program in Orthopaedic Surgery Required Texts: 1. Backache Macnab,
Physician Assistant Post Graduate Orthopaedic Surgery Fellowship Program Watauga Orthopaedics Physician Assistant Post-Graduate Fellowship Program in Orthopaedic Surgery Required Texts: 1. Backache Macnab,
Kidney Cancer OVERVIEW
 Kidney Cancer OVERVIEW Kidney cancer is the third most common genitourinary cancer in adults. There are approximately 54,000 new cancer cases each year in the United States, and the incidence of kidney
Kidney Cancer OVERVIEW Kidney cancer is the third most common genitourinary cancer in adults. There are approximately 54,000 new cancer cases each year in the United States, and the incidence of kidney
Critically evaluate the organization of diabetic foot ulcer services and interdisciplinary team working
 Rationale of Module Accurate nursing assessment is the key to effective diabetic foot ulcer prevention, treatment and management. A comprehensive assessment identifies ulcer aetiology and the factors which
Rationale of Module Accurate nursing assessment is the key to effective diabetic foot ulcer prevention, treatment and management. A comprehensive assessment identifies ulcer aetiology and the factors which
Things You Don t Want to Miss in Multiple Myeloma
 Things You Don t Want to Miss in Multiple Myeloma Sreenivasa Chandana, MD, PhD Attending Hematologist and Medical Oncologist West Michigan Cancer Center Assistant Professor, Western Michigan University
Things You Don t Want to Miss in Multiple Myeloma Sreenivasa Chandana, MD, PhD Attending Hematologist and Medical Oncologist West Michigan Cancer Center Assistant Professor, Western Michigan University
.org. Osteochondroma. Solitary Osteochondroma
 Osteochondroma Page ( 1 ) An osteochondroma is a benign (noncancerous) tumor that develops during childhood or adolescence. It is an abnormal growth that forms on the surface of a bone near the growth
Osteochondroma Page ( 1 ) An osteochondroma is a benign (noncancerous) tumor that develops during childhood or adolescence. It is an abnormal growth that forms on the surface of a bone near the growth
CHARACTERSTIC RADIOGRAPHIC APPEARANCE
 OSTEOLYTIC LESIONS APPROACH AGE Metastatic Neuroblastoma in infant and young child. Metastases and multiple myeloma in middle aged and elderly. Ewing s sarcoma and simple bone cyst in children and teens.
OSTEOLYTIC LESIONS APPROACH AGE Metastatic Neuroblastoma in infant and young child. Metastases and multiple myeloma in middle aged and elderly. Ewing s sarcoma and simple bone cyst in children and teens.
Diabetic Foot Ulcers and Pressure Ulcers. Laurie Duckett D.O. Plastic and Reconstructive Surgeon Oklahoma State University Center for Health Sciences
 Diabetic Foot Ulcers and Pressure Ulcers Laurie Duckett D.O. Plastic and Reconstructive Surgeon Oklahoma State University Center for Health Sciences Lecture Objectives Identify risk factors Initiate appropriate
Diabetic Foot Ulcers and Pressure Ulcers Laurie Duckett D.O. Plastic and Reconstructive Surgeon Oklahoma State University Center for Health Sciences Lecture Objectives Identify risk factors Initiate appropriate
SPINAL STENOSIS Information for Patients WHAT IS SPINAL STENOSIS?
 SPINAL STENOSIS Information for Patients WHAT IS SPINAL STENOSIS? The spinal canal is best imagined as a bony tube through which nerve fibres pass. The tube is interrupted between each pair of adjacent
SPINAL STENOSIS Information for Patients WHAT IS SPINAL STENOSIS? The spinal canal is best imagined as a bony tube through which nerve fibres pass. The tube is interrupted between each pair of adjacent
Podiatry Specialty ICD-10-CM Coding Tip Sheet Overview of Key Chapter Updates for Podiatry and Top 20 codes
 Podiatry Specialty ICD-10-CM Coding Tip Sheet Overview of Key Chapter Updates for Podiatry and Top 20 codes Chapter 1 Certain Infectious and Parasitic Diseases Terminology changes: The term sepsis (ICD-10-CM)
Podiatry Specialty ICD-10-CM Coding Tip Sheet Overview of Key Chapter Updates for Podiatry and Top 20 codes Chapter 1 Certain Infectious and Parasitic Diseases Terminology changes: The term sepsis (ICD-10-CM)
ILIOTIBIAL BAND SYNDROME
 ILIOTIBIAL BAND SYNDROME Description The iliotibial band is the tendon attachment of hip muscles into the upper leg (tibia) just below the knee to the outer side of the front of the leg. Where the tendon
ILIOTIBIAL BAND SYNDROME Description The iliotibial band is the tendon attachment of hip muscles into the upper leg (tibia) just below the knee to the outer side of the front of the leg. Where the tendon
Laparoscopic Adrenal Gland Removal (Adrenalectomy) Patient Information from SAGES
 Laparoscopic Adrenal Gland Removal (Adrenalectomy) Patient Information from SAGES What are the Adrenal Glands? The adrenal glands are two small organs, one located above each kidney. They are triangular
Laparoscopic Adrenal Gland Removal (Adrenalectomy) Patient Information from SAGES What are the Adrenal Glands? The adrenal glands are two small organs, one located above each kidney. They are triangular
Acute Low Back Pain. North American Spine Society Public Education Series
 Acute Low Back Pain North American Spine Society Public Education Series What Is Acute Low Back Pain? Acute low back pain (LBP) is defined as low back pain present for up to six weeks. It may be experienced
Acute Low Back Pain North American Spine Society Public Education Series What Is Acute Low Back Pain? Acute low back pain (LBP) is defined as low back pain present for up to six weeks. It may be experienced
loving life YOUR GUIDE TO YOUR THYROID
 loving life YOUR GUIDE TO YOUR THYROID one THE THYROID two HYPOTHYROIDISM three HYPERTHYROIDISM four TREATING HYPERTHYROIDISM five THYROID NODULES AND GOITRES one THE THYROID What is the thyroid? The thyroid
loving life YOUR GUIDE TO YOUR THYROID one THE THYROID two HYPOTHYROIDISM three HYPERTHYROIDISM four TREATING HYPERTHYROIDISM five THYROID NODULES AND GOITRES one THE THYROID What is the thyroid? The thyroid
RUNNING INJURIES: PREVENTION AND REHABILITATION
 RUNNING INJURIES: PREVENTION AND REHABILITATION Topics of Tonight s s Lecture Common Injuries and Treatments Causes of Common Injuries Measures to Avoid Injury Most Common Running Injuries Plantar Fascitis
RUNNING INJURIES: PREVENTION AND REHABILITATION Topics of Tonight s s Lecture Common Injuries and Treatments Causes of Common Injuries Measures to Avoid Injury Most Common Running Injuries Plantar Fascitis
Large L5 S1 Disc Protrusion Treated Successfully With Cox Technic
 Cox Technic Email Case #77 October 2009 by Dr. Greenwood 1 Large L5 S1 Disc Protrusion Treated Successfully With Cox Technic A case study presented to the Part III Hospital Based Training Course for Cox
Cox Technic Email Case #77 October 2009 by Dr. Greenwood 1 Large L5 S1 Disc Protrusion Treated Successfully With Cox Technic A case study presented to the Part III Hospital Based Training Course for Cox
Acute Ankle Injuries, Part 1: Office Evaluation and Management
 t June 08, 2009 Each acute ankle injury commonly seen in the office has associated with it a mechanism by which it can be injured, trademark symptoms that the patient experiences during the injury, and
t June 08, 2009 Each acute ankle injury commonly seen in the office has associated with it a mechanism by which it can be injured, trademark symptoms that the patient experiences during the injury, and
Highlights of the Revised Official ICD-9-CM Guidelines for Coding and Reporting Effective October 1, 2008
 Highlights of the Revised Official ICD-9-CM Guidelines for Coding and Reporting Effective October 1, 2008 Please refer to the complete ICD-9-CM Official Guidelines for Coding and Reporting posted on this
Highlights of the Revised Official ICD-9-CM Guidelines for Coding and Reporting Effective October 1, 2008 Please refer to the complete ICD-9-CM Official Guidelines for Coding and Reporting posted on this
Guide to Claims against General Practitioners (GPs)
 Patients often build up a relationship of trust with their GP over a number of years. It can be devastating when a GP fails in his or her duty to a patient. Our medical negligence solicitors understand
Patients often build up a relationship of trust with their GP over a number of years. It can be devastating when a GP fails in his or her duty to a patient. Our medical negligence solicitors understand
July 2012 Exercise Away Your Knee Pain It seems counterintuitive, but when it hurts to move
 Exercise Away Your Knee Pain It seems counterintuitive, but when it hurts to move your knee, the best thing you can do is move your knee. A 2009 study in the British Medical Journal found that supervised
Exercise Away Your Knee Pain It seems counterintuitive, but when it hurts to move your knee, the best thing you can do is move your knee. A 2009 study in the British Medical Journal found that supervised
Continuing Medical Education Article Imaging of Multiple Myeloma and Related Plasma Cell Dyscrasias JNM, July 2012, Volume 53, Number 7
 Continuing Medical Education Article Imaging of Multiple Myeloma and Related Plasma Cell Dyscrasias JNM, July 2012, Volume 53, Number 7 Authors Ronald C. Walker 1,2, Tracy L. Brown 3, Laurie B. Jones-Jackson
Continuing Medical Education Article Imaging of Multiple Myeloma and Related Plasma Cell Dyscrasias JNM, July 2012, Volume 53, Number 7 Authors Ronald C. Walker 1,2, Tracy L. Brown 3, Laurie B. Jones-Jackson
Musculoskeletal: Acute Lower Back Pain
 Musculoskeletal: Acute Lower Back Pain Acute Lower Back Pain Back Pain only Sciatica / Radiculopathy Possible Cord or Cauda Equina Compression Possible Spinal Canal Stenosis Red Flags Initial conservative
Musculoskeletal: Acute Lower Back Pain Acute Lower Back Pain Back Pain only Sciatica / Radiculopathy Possible Cord or Cauda Equina Compression Possible Spinal Canal Stenosis Red Flags Initial conservative
Return to same game if sx s resolve within 15 minutes. Return to next game if sx s resolve within one week Return to Competition
 Assessment Skills of the Spine on the Field and in the Clinic Ron Burke, MD Cervical Spine Injuries Sprains and strains Stingers Transient quadriparesis Cervical Spine Injuries Result in critical loss
Assessment Skills of the Spine on the Field and in the Clinic Ron Burke, MD Cervical Spine Injuries Sprains and strains Stingers Transient quadriparesis Cervical Spine Injuries Result in critical loss
X-Plain Vertebral Compression Fractures Reference Summary
 X-Plain Vertebral Compression Fractures Reference Summary Introduction Back pain caused by a vertebral compression fracture, or VCF, is a common condition that affects thousands of people every year. A
X-Plain Vertebral Compression Fractures Reference Summary Introduction Back pain caused by a vertebral compression fracture, or VCF, is a common condition that affects thousands of people every year. A
Rotator Cuff Pathophysiology. treatment program that will effectively treat it. The tricky part about the shoulder is that it is a ball and
 Rotator Cuff Pathophysiology Shoulder injuries occur to most people at least once in their life. This highly mobile and versatile joint is one of the most common reasons people visit their health care
Rotator Cuff Pathophysiology Shoulder injuries occur to most people at least once in their life. This highly mobile and versatile joint is one of the most common reasons people visit their health care
Evaluation of an Algorithmic Approach to Pediatric Back Pain
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Evaluation of an Algorithmic Approach to Pediatric Back Pain David S. Feldman, MD, Joseph J. Straight, MD, Mohammad I. Badra, MD, Ahamed Mohaideen, MD, and Sanjeev S. Madan, MD Abstract:
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Evaluation of an Algorithmic Approach to Pediatric Back Pain David S. Feldman, MD, Joseph J. Straight, MD, Mohammad I. Badra, MD, Ahamed Mohaideen, MD, and Sanjeev S. Madan, MD Abstract:
Contents. Introduction 1. Anatomy of the Spine 1. 2. Spinal Imaging 7. 3. Spinal Biomechanics 23. 4. History and Physical Examination of the Spine 33
 Contents Introduction 1. Anatomy of the Spine 1 Vertebrae 1 Ligaments 3 Intervertebral Disk 4 Intervertebral Foramen 5 2. Spinal Imaging 7 Imaging Modalities 7 Conventional Radiographs 7 Myelography 9
Contents Introduction 1. Anatomy of the Spine 1 Vertebrae 1 Ligaments 3 Intervertebral Disk 4 Intervertebral Foramen 5 2. Spinal Imaging 7 Imaging Modalities 7 Conventional Radiographs 7 Myelography 9
Chapter 5. Objectives. Normal Ankle Range of Motion. Lateral Ankle Sprains. Lateral Ankle Sprains. Assessment of Lateral Ankle Sprains
 Objectives Chapter 5 Assessment of Ankle & Lower Leg Injuries Review the following components of injury assessment related to the ankle and lower leg Stress tests Special tests Normal Ankle Range of Motion
Objectives Chapter 5 Assessment of Ankle & Lower Leg Injuries Review the following components of injury assessment related to the ankle and lower leg Stress tests Special tests Normal Ankle Range of Motion
2011 Radiology Diagnosis Coding Update Questions and Answers
 2011 Radiology Diagnosis Coding Update Questions and Answers How can we subscribe to the Coding Clinic for ICD-9 guidelines and updates? The American Hospital Association publishes this quarterly newsletter.
2011 Radiology Diagnosis Coding Update Questions and Answers How can we subscribe to the Coding Clinic for ICD-9 guidelines and updates? The American Hospital Association publishes this quarterly newsletter.
Resorptive Changes of Maxillary and Mandibular Bone Structures in Removable Denture Wearers
 Resorptive Changes of Maxillary and Mandibular Bone Structures in Removable Denture Wearers Dubravka KnezoviÊ-ZlatariÊ Asja»elebiÊ Biserka LaziÊ Department of Prosthodontics School of Dental Medicine University
Resorptive Changes of Maxillary and Mandibular Bone Structures in Removable Denture Wearers Dubravka KnezoviÊ-ZlatariÊ Asja»elebiÊ Biserka LaziÊ Department of Prosthodontics School of Dental Medicine University
Ankle Fractures - OrthoInfo - AAOS. Copyright 2007 American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons. Ankle Fractures
 Copyright 2007 American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Ankle Fractures "I broke my ankle." A broken ankle is also known as an ankle "fracture." This means that one or more of the bones that make up the
Copyright 2007 American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Ankle Fractures "I broke my ankle." A broken ankle is also known as an ankle "fracture." This means that one or more of the bones that make up the
