Lung cancer is the number one cancer cause of mortality
|
|
|
- Beverly Carroll
- 8 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Prognostic Factors for Survival in Extensive Stage Small Cell Lung Cancer (ED-SCLC) The Importance of Smoking History, Socioeconomic and Marital Statuses, and Sai-Hong Ignatius Ou, MD, PhD,* Argyrios Ziogas, PhD, and Jason A. Zell, DO, MPH* Background: We investigated whether independent prognostic factors for overall survival (OS) in non-small cell lung cancer such as ethnicity, smoking history, socioeconomic, and marital statuses are also applicable to extensive stage small cell lung cancer (ED- SCLC). Methods: SCLC patients diagnosed from 1991 to 2005 from 3 Southern California counties were identified. Prognostic factors for ED-SCLC patients were evaluated by univariate and multivariate analysis. Results: Of the 4782 SCLC patients analyzed, only 2.5% of the patients were never-smokers and 71.7% of patients presented with ED-SCLC. By multivariate analysis, a positive smoking status was a statistically significant poor prognostic factor for OS in ED-SCLC patients (versus never-smoker; hazard ratio [HR] 1.310; p ), in addition low socioeconomic status (SES) (from the lowest to the highest SES score; p trend ) and being unmarried (versus married; HR 1.179; p ). Asian ethnicity was a favorable prognostic factor in ED-SCLC (versus Caucasian; HR *Chao Family Comprehensive Cancer Center, Division of Hematology/ Oncology, Department of Medicine, University of California Irvine Medical Center, Orange, California; Department of Epidemiology, School of Medicine, and Genetic Epidemiology Research Institute, University of California Irvine, Irvine, California. Disclosure: The authors declare no conflicts of interest. Disclaimer: The collection of cancer incidence data used in this study was supported by the California Department of Public Health as part of the statewide cancer reporting program mandated by California Health and Safety Code Section ; the National Cancer Institute s Surveillance, Epidemiology and End Results Program under contract N01-PC awarded to the Northern California Cancer Center, contract N01-PC awarded to the University of Southern California, and contract N01-PC awarded to the Public Health Institute; and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention s National Program of Cancer Registries, under agreement 1U58DP awarded to the Public Health Institute. The ideas and opinions expressed herein are those of the author(s) and endorsement by the State of California, Department of Public Health the National Cancer Institute, and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention or their Contractors and Subcontractors is not intended nor should be inferred. Address for correspondence: Sai-Hong Ignatius Ou, MD, PhD, Chao Family Comprehensive Cancer Center, University of California Irvine Medical Center, 101 The City Drive South, Bldg 56, Rm 241, RT 81, Orange, CA ignatius.ou@uci.edu Copyright 2008 by the International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer ISSN: /09/ ; p ). Female gender was another independent favorable prognostic factor (versus male; HR 0.823; p ). Conclusions: A positive history of smoking, low SES, and being unmarried are independent unfavorable prognostic factors for OS in ED-SCLC while Asian ethnicity and female gender are independent favorable prognostic factors for OS in ED-SCLC by multivariate analysis. Key Words: Extensive stage small cell lung cancer (ED-SCLC), Asian ethnicity, Smoking status, Female gender, Socioeconomic status, Marital status, California Cancer Registry, Prognostic factors. (J Thorac Oncol. 2009;4: 37 43) Lung cancer is the number one cancer cause of mortality worldwide. 1 Small cell lung cancer (SCLC) used to account for 20 to 25% of all lung cancer but the incidence of SCLC has been decreasing in the United States. 2 SCLC has been highly associated with smoking among the four major lung cancer histologies. 3 It is now recognized that patients with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) who are life-long nonsmokers constitute a distinct clinical entity. 4,5 These patients tend to be found in women from East Asia and they tend to have better survival. 5,6 We previously performed a retrospective population-based study of NSCLC patients in three Southern California counties and found that never-smoking status is a favorable prognostic factor in NSCLC. In addition, Asian ethnicity is another favorable prognostic factor in NSCLC patients independent of smoking status. 7 Other independent favorable prognostic factors identified are high socioeconomic status (SES) and being married. 7 In this report we investigated the proportion of never-smokers with SCLC and whether smoking status is an independent prognostic factor in SCLC similar to NSCLC. We further investigated whether Asian ethnicity, SES, and marital status are independent prognostic factors similar to our findings in NSCLC patients. PATIENTS AND METHODS Population This is a retrospective study involving analysis of data from the Cancer Surveillance Programs of Orange, San Diego and Imperial counties in southern California covering an area Journal of Thoracic Oncology Volume 4, Number 1, January
2 Ou et al. Journal of Thoracic Oncology Volume 4, Number 1, January 2009 with estimated population of 6.2 million. SCLC patients diagnosed between 1991 to 2005 who had complete follow-up data were included in the study. Tumor site was abstracted as previously described. 8 The ICD-O-3 histology codes 8041 to 8045 were designated as SCLC. 9 Limited disease (LD-SCLC) is defined as local and regional disease stage and extensive disease (ED-SCLC) is defined as distant disease stage according to Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER) summary staging. Patients with unknown or missing staging information were excluded in the analysis. Patient demographic data were abstracted using SEER codes. The measurement of SES used in this analysis was a composite measure using California Cancer Registry (CCR) and census data as previously described. 10 therapy and surgical techniques were abstracted using SEER codes. Chemotherapy given during the first course of therapy was ascertained using CCR codes. Smoking status was abstracted by examining text files of individual patient database as previously described. 8 Patients with any documented history of smoking were classified as smokers. Patients with documentation of no smoking history were classified as never-smokers. Patients lacking documented information on smoking history were listed as unknown. Statistical Analyses Comparisons of demographic, clinical, and pathologic variables were made for SCLC patients, using Pearson 2 statistic or Fisher s exact test for nominal variables and Student t test for continuous variables. Univariate survival rate analyses were estimated using the Kaplan and Meier method, with comparisons made between groups by the log-rank test. Cox proportional hazards modeling using time since diagnosis were performed. All statistical analyses were conducted using SAS 9.1 statistical software (SAS Institute, Inc., Cary, NC). Statistical significance was assumed for a two-tailed p value less than Ethical Considerations This research study was approved by the University of California Irvine Institutional Review Board (# and # ). RESULTS Characteristic of SCLC Patients Between 1991 and 2005 a total of 4782 SCLC patients whose staging status were available were analyzed of which 71.7% of these patients presented with ED-SCLC. Only 2.5% of the patients (n 120) were never-smokers. The median time of follow-up for LD-SCLC patients was 12 months (95% confidence interval: 1 77 months) and 5 months for ED-SCLC patients (95% CI: 0 25 months). We only performed analysis of prognostic factors in ED-SCLC patients because of the limited numbers of LD-SCLC patients. The clinical, pathologic, and demographic characteristics of ED- SCLC patients are shown in Table 1. TABLE 1. Clinicopathologic Characteristics of the Extensive Stage Small-Cell Lung Cancer Patients (ED-SCLC) Extensive Disease (ED-SCLC) (%) n 3428 Median age 68 Smoking status Yes 2539 (74.1) No 93 (2.7) Unknown 796 (23.2) Caucasian 2958 (86.3) Hispanic 234 (6.8) Asian 144 (4.2) African American 85 (2.5) Other 7 (0.2) Male 1830 (53.4) Female 1598 (46.6) Age (0.6) (3.9) (17.1) (33.5) (33.8) (11.1) Socioeconomic status (SES) SES1 353 (10.3) SES2 614 (17.9) SES3 828 (24.2) SES4 894 (26.1) SES5 739 (21.6) Marital status Married 1854 (54.1) Unmarried 1503 (43.8) Unknown 71 (2.1) Chemotherapy Yes 2359 (68.8) No 1061 (31.0) Unknown 8 (0.2) Yes 1204 (35.1) No 2224 (64.9) Lobectomy 5 (0.1) Other surgeries 31 (0.9) No 3390 (98.9) Unknown 2 (0.1) ED-SCLC, extensive stage small-cell lung cancer patients; SES, socioeconomic status; n, number. Age at Diagnosis The median age of diagnosis of smokers with ED- SCLC was 68 years compared with 73 years for neversmokers with ED-SCLC (p ). 38 Copyright 2008 by the International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer
3 Journal of Thoracic Oncology Volume 4, Number 1, January 2009 Factors for Survival in ED-SCLC TABLE 2. Distribution of SES Quintiles Among ED-SCLC Patients SES1 (%) SES2 (%) SES3 (%) SES4 (%) SES5 (%) p n Smoking status Yes 257 (72.8) 449 (73.1) 616 (74.4) 660 (73.8) 557 (75.4) No 6 (1.7) 13 (2.1) 25 (3.0) 29 (3.2) 20 (2.7) Unknown 90 (25.5) 152 (24.8) 187 (23.5) 205 (22.9) 162 (21.9) Male 206 (58.4) 315 (51.3) 450 (54.3) 474 (53.0) 385 (52.1) Female 147 (41.6) 299 (48.7) 378 (45.7) 420 (47.0) 254 (47.9) African American 34 (9.6) 21 (3.4) 21 (2.5) 6 (0.7) 3 (0.4) Asian 20 (5.7) 29 (4.7) 48 (5.8) 25 (2.8) 22 (3.0) Caucasian 219 (62.0) 507 (82.6) 717 (86.6) 825 (92.3) 690 (93.4) Hispanic 78 (22.1) 54 (8.8) 40 (4.8) 38 (4.3) 24 (3.3) Other/unknown 2 (0.6) 3 (0.5) 2 (0.2) 0 (0.0) 0 (0.0) Age of diagnosis (0.0) 3 (0.5) 7 (0.8) 6 (0.7) 3 (0.4) (4.2) 29 (4.7) 23 (2.8) 38 (4.3) 29 (3.9) (17.6) 105 (17.1) 133 (16.1) 163 (18.2) 124 (16.8) (34.3) 207 (33.7) 302 (36.5) 275 (30.8) 244 (33.0) (34.8) 201 (32.7) 278 (33.6) 306 (34.2) 250 (33.8) (9.1) 69 (11.2) 85 (10.3) 106 (11.9) 89 (12.0) Marital status Married 150 (42.5) 310 (50.5) 415 (50.1) 529 (59.2) 450 (60.9) Unmarried 195 (55.2) 289 (47.1) 393 (47.5) 349 (39.0) 277 (37.5) Unknown 8 (2.3) 15 (2.4) 20 (2.4) 16 (1.8) 12 (1.6) Chemistry Yes 231 (65.4) 417 (67.9) 556 (67.2) 634 (70.9) 521 (70.5) No 121 (34.3) 196 (31.9) 272 (32.9) 258 (28.9) 214 (29.0) Unknown 1 (0.3) 1 (0.2) 0 (0.0) 2 (0.2) 4 (0.5) Yes 115 (32.6) 200 (32.6) 281 (33.9) 320 (35.8) 288 (39.0) No 238 (67.4) 414 (67.4) 547 (66.1) 574 (64.2) 451 (61.0) Yes 2 (0.6) 9 (1.5) 8 (1.0) 12 (1.3) 5 (0.7) No 351 (99.4) 605 (98.5) 820 (99.0) 880 (98.4) 734 (99.3) Unknown 0 (0.0) 0 (0.0) 0 (0.0) 2 (0.2) 0 (0.0) ED-SCLC, extensive stage small-cell lung cancer patients; SES, socioeconomic status; n, number. Socioeconomic Status (SES) The distribution of clinicopathologic characteristics of ED-SCLC patients among the five SES quintiles is shown in Table 2. There were significantly more Hispanic, African American, and unmarried patients in the lower SES quintiles. Marital Status The distribution of clinicopathologic characteristics of ED-SCLC according to marital status is shown in Table 3. There were significantly more females, more African Americans, more patients 80 years old, less treatment received (chemotherapy, radiation, surgery), and with lower SES in ED-SCLC patients who are unmarried. Univariate Survival Analysis Stage The 1-year, 2-year, and median overall survival (OS) for LD-SCLC patients were 51.9%, 23.9%, and 13 months which was significantly better than the corresponding values for ED- SCLC patients (20.3%, 5.7%, and 5 months; p ). Smoking Status There was no statistical significant difference in the 1-year, 2-year, and median OS of never-smokers with ED- SCLC (21.9%, 6.9%, and 6 months respectively) when compared with the 1-year, 2-year, and median OS of smokers with ED-SCLC (20.9%, 5.5%, and 6 months respectively; p ). Copyright 2008 by the International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer 39
4 Ou et al. Journal of Thoracic Oncology Volume 4, Number 1, January 2009 TABLE 3. Patients Distribution of Marital Status Among ED-SCLC Married (%) Unmarried (%) Unknown (%) p n Smoking status Yes 1367 (73.7) 1122 (74.7) 50 (70.4) No 56 (3.0) 37 (2.5) 0 (0.0) Unknown 431 (23.2) 344 (22.9) 21 (29.6) Male 1204 (64.9) 597 (39.7) 29 (40.8) Female 650 (35.1) 906 (60.3) 42 (59.2) African American 34 (1.8) 50 (3.3) 1 (1.4) Asian 99 (5.3) 42 (2.8) 3 (4.2) Caucasian 1591 (85.8) 1308 (87.0) 59 (83.1) Hispanic 126 (6.8) 102 (6.8) 6 (8.5) Other/unknown 4 (0.2) 1 (0.1) 2 (2.8) Age of diagnosis (0.5) 10 (0.7) 0 (0.0) (3.8) 60 (4.0) 4 (5.6) (17.6) 245 (16.3) 15 (21.1) (37.6) 435 (28.9) 17 (23.9) (33.2) 519 (34.5) 23 (32.4) (7.3) 234 (15.6) 12 (16.9) Socioeconomic status (SES) SES1 150 (8.1) 195 (13.0) 8 (11.3) SES2 310 (16.7) 289 (19.2) 15 (21.1) SES3 415 (22.4) 393 (26.2) 20 (28.2) SES4 529 (28.5) 349 (23.2) 16 (22.5) SES5 450 (24.3) 277 (18.4) 12 (16.9) Chemistry Yes 1365 (73.6) 956 (63.6) 38 (53.5) No 485 (26.2) 543 (36.1) 33 (46.5) Unknown 4 (0.2) 4 (0.3) 0 (0.0) Yes 717 (38.7) 467 (31.1) 20 (28.2) No 1137 (61.3) 1036 (68.9) 51 (71.8) Yes 21 (1.1) 12 (0.8) 3 (4.2) No 1833 (98.9) 1489 (99.1) 68 (95.8) Unknown 0 (0.0) 2 (0.1) 0 (0.0) ED-SCLC, extensive stage small-cell lung cancer patients; SES, socioeconomic status; n, number. The 1-year, 2-year, and median OS for female ED- SCLC patients were 22.7%, 6.8%, and 6 months respectively were statistically significant better than the corresponding numbers for male ED-SCLC patients (18.2%, 4.8%, and 5 months respectively; p ). The OS of Asian ED-SCLC patients was statistically significant better than African American, Caucasian, and Hispanic ED-SCLC patients (p ) (Figure 1). The survival of ED-SCLC patients who received surgical interventions did not differ significantly from ED-SCLC patients who did not receive surgical interventions (p ) as only 31 ED-SCLC patients received surgeries (0.9%) and only 5 of 3428 ED-SCLC patients received lobectomy (0.1%). Chemotherapy The 1-year, 2-year, and median OS of ED-SCLC patients who received chemotherapy were 27.4%, 7.7%, and 8 months and were significantly better than ED-SCLC patients who did not receive chemotherapy (4.3%, 1.1%, and 1 month respectively; p ). The 1-year, 2-year, and median OS of ED-SCLC patients who received radiation were 27.8%, 9.3%, and 8 months and were significantly better than ED-SCLC patients who did not receive radiation (16.2%, 3.8%, and 4 months respectively; p ). Socioeconomic Status (SES) The 1-year, 2-year, and median OS for ED-SCLC patients in the highest SES quintile (SES5) were 28.0%, 6.2%, and 7 months. For ED-SCLC patients in the SES4 quintile, the corresponding values were 17.7%, 5.1%, and 6 months respectively. For ED-SCLC patients in the SES3 quintile, the values were 17.8%, 5.8%, and 5 months respectively. For ED-SCLC patients in the SES2 quintile, the values were 18.7%, 5.0%, and 5 months respectively. For ED-SCLC patients in the lowest SES quintile (SES1), the values were 19.2%, 7.0%, and 4 months respectively. The difference in survival of ED-SCLC patients among the 5 SES quintiles is statistically significant (p ). Marital Status The 1-year, 2-year, and median OS for ED-SCLC patients who were married were 23.1%, 6.7%, and 7 months respectively were statistically significant improved than ED- SCLC patients who were not married (16.8%, 4.4%, and 4 months respectively; p ). Multivariate Survival Analysis A positive history of smoking (versus never-smoker, hazard ratio [HR] 1.310; p ) was a significant independent unfavorable prognostic factor for OS in ED- SCLC. Being unmarried (versus married, HR 1.179; p ) was another independent unfavorable prognostic factor. Low SES was another significant unfavorable prognostic factor (from lowest to highest SES score; HR 0.965; p trend ). However, Asian ethnicity was an independent favorable prognostic factor (versus Caucasian; HR 0.785; p ). Other favorable prognostic factors were female gender, younger age of diagnosis, and treatment (radiation, chemotherapy) (Table 4). 40 Copyright 2008 by the International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer
5 Journal of Thoracic Oncology Volume 4, Number 1, January 2009 Factors for Survival in ED-SCLC FIGURE 1. Overall survival curves of 4 major ethnicities with extensive stage small cell lung cancer (ED-SCLC). TABLE 4. Cox Multivariate Analysis of ED-SCLC Patients Variable HR 95% CI p Smoking No 1.00 Yes ( ) Unknown ( ) Caucasian 1.00 African American ( ) Asian ( ) Hispanic ( ) Other ( ) Male 1.00 Female ( ) Age ( ) Socioeconomic status (SES) a ( ) Marital status b Married Unmarried c ( ) Chemotherapy b No Yes ( ) No Yes ( ) b No Yes ( ) a Analyzed as a continuous variable from the lowest to the highest SES score. b Unknown included in Cox proportional hazards model but not shown. c Unmarried (single, separated, divorced, widowed). HR, hazard ratio; CI, confidence interval; SES, socioeconomic status; ED-SCLC, extensive stage small-cell lung cancer patients. DISCUSSION In this report, we confirmed that SCLC is highly associated with tobacco smoking as only 2.5% of the patients in the study were never-smokers. We found that never-smokers with SCLC were statistically significant older than smokers with SCLC. Additionally, a positive smoking history is an independent poor prognostic factor for OS in ED-SCLC patients by multivariate analysis despite a 5-year increase in the median age of diagnosis for never-smokers. Wolf et al. 11 have also shown that never-smokers had higher median survival (13.6 months versus 9.9 months) and 2-year survival rate (17% versus 7%) than smokers with SCLC, and that positive history is an independent unfavorable prognostic factor for both male and female SCLC patients by Cox regression analysis. The study included a substantial number of never-smokers (n 63; 8.3%), 11 in contrast the lack of a prognostic effect of smoking history in SCLC reported by others are likely due to the small numbers of never-smokers: 7 (9.2%), (9.1%), 13 and 5 (6.6%) respectively. 14 Lassen et al. 15 reported that only 1 of 1714 SCLC patients was a never-smoker and of the 60 long-term survivors ( 5 years) none were never-smokers. Smoking causes many more genetic disruptions in smokers 16 and likely result in more comorbidities in patients. Given the very low percentage of never-smokers with SCLC further studies are required to distinguish whether SCLC in never-smokers is a distinct clinical entity as in the case of NSCLC 4,5 or as a result of passive exposure to tobacco. Second, we showed that Asian ethnicity is a favorable prognostic factor in ED-SCLC by both univariate and multivariate analyses. There is paucity in the literature about the significance of ethnicity in the survival outcome in SCLC. Albain et al. 17 using Southwest Oncology Group (SWOG) database reported that Caucasian is an independent favorable prognostic factor in survival in LD-SCLC but the significance Copyright 2008 by the International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer 41
6 Ou et al. Journal of Thoracic Oncology Volume 4, Number 1, January 2009 disappears if only more recent clinical trials were included. Blackstock et al. 18 have previously showed that African American patients had similar survival as non-african American patients in ED-SCLC. There were only 12 Hispanic and 8 Asian patients in that study thus the contribution of Asian or Hispanic ethnicity cannot be adequately determined. Our conclusion is strengthened by the inclusion of SES and marital status in the Cox multivariate analysis. We have previously shown in stage one NSCLC lung cancer that African American and Hispanic patients had poorer survival as compared with Caucasians but this survival disadvantage disappeared after SES and marital status were factored in the Cox proportional hazards model. 19 Studies of SCLC patients from Asian countries indicated Asian SCLC patient had similar clinicopathologic characteristics and survival outcome as Western SCLC patients, however, there were no direct comparison. 12,20 A potential explanation is the ethnic variability in the genetic polymorphism of drug metabolizing genes. Irinotecan in combination with platinum had been shown to confer superior OS in the treatment of first line ED-SCLC from randomized trials performed in Japan 21 but not in the United States. 22,23 The active metabolite of irinotecan, SN-38, is inactivated by glucuronidation by the enzyme UGT1A1. There is well known racial variability in the UGT1A1 promoter from single nucleotide polymorphism leading to varying level of expression of the enzyme and resultant toxicities and potential efficacies from irinotecan. 24,25 Our results should be considered as preliminary and hypothesis-generating and will require validation from other population-based epidemiologic and molecular studies and/or clinical trials. Third, this is the first report to show SES is an independent prognostic factor in ED-SCLC. There were significantly more Hispanic and African American patients in the lower SES quintiles, and significantly more unmarried patients in the lower SES with 55.2% of patients in the lowest SES quintile (SES1) being unmarried compared with only 37.5% of the patients in the highest SES quintile (SES5) (Table 2). Our report also showed that marital status is an independent prognostic factor in ED-SCLC. Comparing to married patients, unmarried patients consisted of significantly more females, more African Americans, more patients who were 80 years old, and more patients in the lower SES. Also fewer unmarried patients received chemotherapy or radiation for the treatment of their ED-SCLC and this observation may partially account for the poorer survival for patients who were unmarried as SCLC are very responsive to chemotherapy and/or radiation. All these prognostic factors were included in the Cox multivariate model but SES and marital status remained as independent prognostic factors. This observation is similar to our report on stage one NSCLC where SES and marital status remained as independent prognostic factors after inclusion in multivariate analysis. 11 Further studies will be needed to investigate and understand the role of these two social factors in determining the survival outcome in ED-SCLC. Finally, we identified female gender, younger age at diagnosis, radiation, and chemotherapy treatment as favorable prognostic factors in ED-SCLC. It has been well-established that female SCLC patients survived longer than male SCLC patients 18,26 33 and it has been shown that female SCLC patients had higher complete and overall response rates to chemotherapy 12,26,30 33 though females also developed more treatment-related toxicities. 32 Limitations of this study include there was no central pathologic review and about 40% patients had incomplete TNM staging data. The time period included in this study is over 15 years but there is essentially no major change in the treatment of ED-SCLC. There was also no information in CCR on the tumor marker lactate dehydrogenase 16,18,31,33 35 or performance status 16,26 35 which has been shown to be an independent important prognostic factor in many studies. Moreover, the site and number of metastasis in ED-SCLC is not coded thus we are not able to include the number of metastatic sites into the Cox model as both brain metastasis and the number of metastatic sites have been shown to be prognostic. 18,26,27,31,35 Thus, the independence of Asian ethnicity, SES, and marital status as prognostic factors are significant but hypothesis-generating and should be validated in future studies where lactate dehydrogenase, performance status, and number of metastatic sites are also incorporated in the multivariate analysis. Lastly, we were unable to determine whether patients had received any prophylactic cranial irradiation which has been shown to increase OS in LD-SCLC 36 and ED-SCLC. 37 In summary, we have shown that a positive history of smoking is an unfavorable prognostic factor for OS in ED-SCLC. Other independent prognostic factors identified in this study such as Asian ethnicity, SES, and marital status will require future validation and investigations. REFERENCES 1. Parkin DM, Bray FJ, Ferlay L, Pissani P. Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin 2002;55: Govindan R, Page N, Morgensztern D, et al. Changing epidemiology of small-cell lung cancer in the United States over the 30 years: analysis of the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results database. J Clin Oncol 2006;24: Khuder SA. Effect of cigarette smoking on major histological types of lung cancer: a meta-analysis. Lung Cancer 2001;31: Toh CK, Gao F, Lim WT, et al. Never-smokers with lung cancer: epidemiologic evidence of a distinct disease entity. J Clin Oncol 2006; 24: Sun S, Schiller JH, Gazdar AF. Lung cancer in never smokers - a different disease. Nature 2007;7: Subramanian J, Govindan R. Lung cancer in never-smokers: a review. J Clin Oncol 2007;25: Ou S-HI, Ziogas A, Zell JA. Epidemiology study of never-smokers with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC): high percentages of Asian and Hispanic female never-smokers and the significance of Asian ethnicity. J Clin Oncol 2008;26 (May 20 suppl; abstr 8004). 8. Zell JA, Ou S-HI, Ziogas A, Anton-Culver H. Epidemiology of bronchioloalveolar carcinoma: improvement in survival after release of the 1999 WHO classification of lung tumors. J Clin Oncol 2005;23: International classification of diseases for oncology (ICD-O). In A Fritz, et al. (Eds.), 3rd Ed. Geneva: World Health Organization, Yost K, Perkins C, Cohen R, Morris C, Wright W. Socioeconomic status and breast cancer incidence in California for different race/ethnic groups. Cancer Causes Control 2001;12: Wolf M, Holle R, Hans K, Drings P, Havemann K. Analysis of prognostic factors in 766 patients with small cell lung cancer (SCLC): the role of sex as a predictor of survival. Br J Cancer 1991;63: Copyright 2008 by the International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer
7 Journal of Thoracic Oncology Volume 4, Number 1, January 2009 Factors for Survival in ED-SCLC 12. Mohan A, Goyal A, Singh S, et al. Survival in small cell lung cancer in India: prognostic utility of clinical features, laboratory parameters and response to treatment. Indian J Cancer 2006;43: Micke P, Faldum A, Metz T, et al. Staging small cell lung cancer: Veterans Administration Lung Cancer Study Group versus International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer-what limits limited disease. Lung Cancer 2002;37: Perng RP, Chen CY, Chang GC, et al. Revisit of 1997 TNM staging system-survival analysis of 1112 lung cancer patients in Taiwan. Jpn J Clin Oncol 2007;37: Lassen U, Osterlind K, Hansen M, Dombernowsky P, Bergman B, Hansen HH. Long-term survival in small-cell lung cancer: posttreatment characteristics in patients surviving 5 to 18 years an analysis of 1,714 consecutive patients. J Clin Oncol 1995;13: Hecht SS. Tobacco carcinogens, their biomarkers, and tobacco-induced cancer. Nature Rev Cancer 2003;3: Albain KS, Crowley JJ, Leblanc M, Livingston R. Determinants of improved outcome in small-cell lung cancer: an analysis of the patient Southwest oncology group data base. J Clin Oncol 1990;8: Blackstock AW, Herdon II JE, Paskett ED, et al. Similar outcomes between African-American and non-african American patients with extensive-stage small cell lung carcinoma: report from the Cancer and Leukemia Group B. J Clin Oncol 2006;24: Ou S-HI, Zell JA, Ziogas A, Anton-Culver H. Low socioeconomic status is a poor prognostic factor for survival in stage I non-small-cell lung cancer and is independent of surgical treatment, race, and marital status. Cancer 2008;112: Toh CK, Hee SW, Lim WT, et al. Survival of small-cell lung cancer and its determinants of outcome in Singapore. Ann Acad Med Singapore 2007;36: Noda K, Nishiwaki Y, Kawahara M, et al. Irinotecan plus cisplatin compared with etoposide plus cisplatin for extensive small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med 2002;346: Hanna N, Bunn PA Jr, Langer C, et al. Randomized phase III trial comparing irinotecan/cisplatin with etoposide/cisplatin in patients with previously untreated extensive-stage disease small cell lung cancer. J Clinc Oncol 2006;24: Natalie RB, Lara PN, Chansky K, et al. S0124: A randomized phase III trial comparing irinotecan/cisplatin (IP) with etoposide/cisplatin (EP) in patients (pts) with previously untreated extensive stage small cell lung cancer (E-SCLC). J Clin Oncol 2008;26:(May 20 suppl: abstract 7512). 24. Beutler E, Gelbert T, Demina A. Racial variability in the UDP-glucuronosyltransferase 1 (UGT1A1) promoter: a balanced polymorphism for regulation of bilirubin metabolism. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 1998;95: Undevia SD, Gomez-Abuin G, Ratain MJ. Pharmacokinetic variability of anticancer agents. Nature Rev Cancer 2005;5: Spiegelman D, Maurer LH, Ware JH, et al. Prognostic factors in small-cell carcinoma of the lung: an analysis of 1521 patients. J Clin Oncol 1989;7: Albain KS, Crowley JJ, Livingston RB. Long-term survival and toxicity in small cell lung cancer. Expanded Southwest Oncology Group experience. Chest 1991;99: Osterlind K, Hansen HH, Hansen M, Dombernowsky P, Andersen PK. Long-term disease-free survival in small-cell carcinoma of the lung: a study of clinical determinants. J Clin Oncol 1986;4: Osterlind K, Andersen PK. Prognostic factors in small cell lung cancer: multivariate model based on 778 patients treated with chemotherapy with or without irradiation. Cancer Res 1986;46: Paesmans M, Sculier P, Lecomte J, et al. Prognostic factors for patients with small cell lung carcinoma: analysis of a series of 763 patients included in 4 consecutive prospective trials with a minimum follow-up of 5 years. Cancer 2000;89: Bremnes RM, Sundstrom S, Aasebo U, et al. The value of prognostic factors in small cell lung cancer: results from a randomized multicenter study with minimum 5 years follow-up. Lung Cancer 2003;39: Singh S, Parulekar W, Murray N, et al. Influence of sex and toxicity and treatment outcome in small cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol 2005;43: Christodolou C, Pavlidis N, Samantas E, et al. Prognostic factors in Greek patients with small lung cancer (SCLC). A Hellenic cooperative oncology group study. Anticancer Res 2002;22: Sagman U, Feld R, Evans WK, et al. The prognostic significance of pretreatment serum lactate dehydrogenase in patients with small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol 1991;9: Sagman U, Maki E, Evans WK, et al. Small-cell carcinoma of the lung: derivation of a prognostic staging system. J Clin Oncol 1991;9: Auperin A, Arriagada R, Pignon JP, et al. Prophylactic Cranial Irradiation Overview Collaboration Group. Prophylactic cranial irradiation for patients with small-cell lung cancer in complete remission. N Eng J Med 1999;341: Slotman B, Faivre-Finn C, Kramer G, et al. EORTC Oncology Group and Lung Cancer Group. Prophylactic cranial irradiation in extensive small-cell lung cancer. N Eng J Med 2007;357: Copyright 2008 by the International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer 43
Temporal Trends in Demographics and Overall Survival of Non Small-Cell Lung Cancer Patients at Moffitt Cancer Center From 1986 to 2008
 Special Report Temporal Trends in Demographics and Overall Survival of Non Small-Cell Lung Cancer Patients at Moffitt Cancer Center From 1986 to 2008 Matthew B. Schabath, PhD, Zachary J. Thompson, PhD,
Special Report Temporal Trends in Demographics and Overall Survival of Non Small-Cell Lung Cancer Patients at Moffitt Cancer Center From 1986 to 2008 Matthew B. Schabath, PhD, Zachary J. Thompson, PhD,
Epidemiology, Staging and Treatment of Lung Cancer. Mark A. Socinski, MD
 Epidemiology, Staging and Treatment of Lung Cancer Mark A. Socinski, MD Associate Professor of Medicine Multidisciplinary Thoracic Oncology Program Lineberger Comprehensive Cancer Center University of
Epidemiology, Staging and Treatment of Lung Cancer Mark A. Socinski, MD Associate Professor of Medicine Multidisciplinary Thoracic Oncology Program Lineberger Comprehensive Cancer Center University of
Lung Cancer: More than meets the eye
 Lung Cancer Education Program November 23, 2013 Lung Cancer: More than meets the eye Shantanu Banerji MD, FRCPC Presenter Disclosure Faculty: Shantanu Banerji Relationships with commercial interests: Grants/Research
Lung Cancer Education Program November 23, 2013 Lung Cancer: More than meets the eye Shantanu Banerji MD, FRCPC Presenter Disclosure Faculty: Shantanu Banerji Relationships with commercial interests: Grants/Research
Adjuvant Therapy Non Small Cell Lung Cancer. Sunil Nagpal MD Director, Thoracic Oncology Jan 30, 2015
 Adjuvant Therapy Non Small Cell Lung Cancer Sunil Nagpal MD Director, Thoracic Oncology Jan 30, 2015 No Disclosures Number of studies Studies Per Month 12 10 8 6 4 2 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 1 2 3
Adjuvant Therapy Non Small Cell Lung Cancer Sunil Nagpal MD Director, Thoracic Oncology Jan 30, 2015 No Disclosures Number of studies Studies Per Month 12 10 8 6 4 2 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 1 2 3
Early mortality rate (EMR) in Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML)
 Early mortality rate (EMR) in Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML) George Yaghmour, MD Hematology Oncology Fellow PGY5 UTHSC/West cancer Center, Memphis, TN May,1st,2015 Off-Label Use Disclosure(s) I do not intend
Early mortality rate (EMR) in Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML) George Yaghmour, MD Hematology Oncology Fellow PGY5 UTHSC/West cancer Center, Memphis, TN May,1st,2015 Off-Label Use Disclosure(s) I do not intend
Harmesh Naik, MD. Hope Cancer Clinic HOW DO I MANAGE STAGE 4 NSCLC IN 2012: STATE OF THE ART
 Harmesh Naik, MD. Hope Cancer Clinic HOW DO I MANAGE STAGE 4 NSCLC IN 2012: STATE OF THE ART Goals Discuss treatment options for stage 4 lung cancer: New and old Discuss new developments in personalized
Harmesh Naik, MD. Hope Cancer Clinic HOW DO I MANAGE STAGE 4 NSCLC IN 2012: STATE OF THE ART Goals Discuss treatment options for stage 4 lung cancer: New and old Discuss new developments in personalized
Small Cell Lung Cancer
 Small Cell Lung Cancer Lung Practice Guideline Dr. Brian Dingle MSc, MD, FRCPC Approval Date: April 2007 Revised: November 2008 This guideline is a statement of consensus of the Thoracic Disease Site Team
Small Cell Lung Cancer Lung Practice Guideline Dr. Brian Dingle MSc, MD, FRCPC Approval Date: April 2007 Revised: November 2008 This guideline is a statement of consensus of the Thoracic Disease Site Team
Electronic health records to study population health: opportunities and challenges
 Electronic health records to study population health: opportunities and challenges Caroline A. Thompson, PhD, MPH Assistant Professor of Epidemiology San Diego State University Caroline.Thompson@mail.sdsu.edu
Electronic health records to study population health: opportunities and challenges Caroline A. Thompson, PhD, MPH Assistant Professor of Epidemiology San Diego State University Caroline.Thompson@mail.sdsu.edu
A new score predicting the survival of patients with spinal cord compression from myeloma
 A new score predicting the survival of patients with spinal cord compression from myeloma (1) Sarah Douglas, Department of Radiation Oncology, University of Lubeck, Germany; sarah_douglas@gmx.de (2) Steven
A new score predicting the survival of patients with spinal cord compression from myeloma (1) Sarah Douglas, Department of Radiation Oncology, University of Lubeck, Germany; sarah_douglas@gmx.de (2) Steven
Effect of Risk and Prognosis Factors on Breast Cancer Survival: Study of a Large Dataset with a Long Term Follow-up
 Georgia State University ScholarWorks @ Georgia State University Mathematics Theses Department of Mathematics and Statistics 7-28-2012 Effect of Risk and Prognosis Factors on Breast Cancer Survival: Study
Georgia State University ScholarWorks @ Georgia State University Mathematics Theses Department of Mathematics and Statistics 7-28-2012 Effect of Risk and Prognosis Factors on Breast Cancer Survival: Study
Lung Cancer. Public Outcomes Report. Submitted by Omar A. Majid, MD
 Public Outcomes Report Lung Cancer Submitted by Omar A. Majid, MD Lung cancer is the most common cancer-related cause of death among men and women. It has been estimated that there will be 226,1 new cases
Public Outcomes Report Lung Cancer Submitted by Omar A. Majid, MD Lung cancer is the most common cancer-related cause of death among men and women. It has been estimated that there will be 226,1 new cases
Disparities in Stage at Diagnosis, Survival, and Quality of Cancer Care in California by Source of Health Insurance
 Disparities in Stage at Diagnosis, Survival, and Quality of Cancer Care in California by Source of Health Insurance Acknowledgements and Disclaimer The collection of cancer incidence data used in this
Disparities in Stage at Diagnosis, Survival, and Quality of Cancer Care in California by Source of Health Insurance Acknowledgements and Disclaimer The collection of cancer incidence data used in this
Cesare Gridelli 1, Francesca Casaluce 2, Assunta Sgambato 2, Fabio Monaco 3, Cesare Guida 4
 Editorial Treatment of limited-stage small cell lung cancer in the elderly, chemotherapy vs. sequential chemoradiotherapy vs. concurrent chemoradiotherapy: that s the question Cesare Gridelli 1, Francesca
Editorial Treatment of limited-stage small cell lung cancer in the elderly, chemotherapy vs. sequential chemoradiotherapy vs. concurrent chemoradiotherapy: that s the question Cesare Gridelli 1, Francesca
SMALL CELL LUNG CANCER
 Protocol for Planning and Treatment The process to be followed in the management of: SMALL CELL LUNG CANCER Patient information given at each stage following agreed information pathway 1. DIAGNOSIS New
Protocol for Planning and Treatment The process to be followed in the management of: SMALL CELL LUNG CANCER Patient information given at each stage following agreed information pathway 1. DIAGNOSIS New
Pharmacogenomic markers in EGFR-targeted therapy of lung cancer
 Pharmacogenomic markers in EGFR-targeted therapy of lung cancer Rafal Dziadziuszko, MD, PhD University of Colorado Cancer Center, Aurora, CO, USA Medical University of Gdansk, Poland EMEA Workshop on Biomarkers,
Pharmacogenomic markers in EGFR-targeted therapy of lung cancer Rafal Dziadziuszko, MD, PhD University of Colorado Cancer Center, Aurora, CO, USA Medical University of Gdansk, Poland EMEA Workshop on Biomarkers,
Seton Medical Center Hepatocellular Carcinoma Patterns of Care Study Rate of Treatment with Chemoembolization 2007 2012 N = 50
 General Data Seton Medical Center Hepatocellular Carcinoma Patterns of Care Study Rate of Treatment with Chemoembolization 2007 2012 N = 50 The vast majority of the patients in this study were diagnosed
General Data Seton Medical Center Hepatocellular Carcinoma Patterns of Care Study Rate of Treatment with Chemoembolization 2007 2012 N = 50 The vast majority of the patients in this study were diagnosed
NCCN Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer V.1.2011 Update Meeting 07/09/10
 Guideline Page and Request NSCL-3 Stage IA, margins positive delete the recommendation for chemoradiation. Stage IB, IIA, margins positive delete the recommendation for chemoradiation + Stage IIA, Stage
Guideline Page and Request NSCL-3 Stage IA, margins positive delete the recommendation for chemoradiation. Stage IB, IIA, margins positive delete the recommendation for chemoradiation + Stage IIA, Stage
Survival analysis of 220 patients with completely resected stage II non small cell lung cancer
 窑 Original Article 窑 Chinese Journal of Cancer Survival analysis of 22 patients with completely resected stage II non small cell lung cancer Yun Dai,2,3, Xiao Dong Su,2,3, Hao Long,2,3, Peng Lin,2,3, Jian
窑 Original Article 窑 Chinese Journal of Cancer Survival analysis of 22 patients with completely resected stage II non small cell lung cancer Yun Dai,2,3, Xiao Dong Su,2,3, Hao Long,2,3, Peng Lin,2,3, Jian
Komorbide brystkræftpatienter kan de tåle behandling? Et registerstudie baseret på Danish Breast Cancer Cooperative Group
 Komorbide brystkræftpatienter kan de tåle behandling? Et registerstudie baseret på Danish Breast Cancer Cooperative Group Lotte Holm Land MD, ph.d. Onkologisk Afd. R. OUH Kræft og komorbiditet - alle skal
Komorbide brystkræftpatienter kan de tåle behandling? Et registerstudie baseret på Danish Breast Cancer Cooperative Group Lotte Holm Land MD, ph.d. Onkologisk Afd. R. OUH Kræft og komorbiditet - alle skal
Social inequalities impacts of care management and survival in patients with non-hodgkin lymphomas (ISO-LYMPH)
 Session 3 : Epidemiology and public health Social inequalities impacts of care management and survival in patients with non-hodgkin lymphomas (ISO-LYMPH) Le Guyader-Peyrou Sandra Bergonie Institut Context:
Session 3 : Epidemiology and public health Social inequalities impacts of care management and survival in patients with non-hodgkin lymphomas (ISO-LYMPH) Le Guyader-Peyrou Sandra Bergonie Institut Context:
Post-recurrence survival in completely resected stage I non-small cell lung cancer with local recurrence
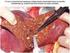 Post- survival in completely resected stage I non-small cell lung cancer with local J-J Hung, 1,2,3 W-H Hsu, 3 C-C Hsieh, 3 B-S Huang, 3 M-H Huang, 3 J-S Liu, 2 Y-C Wu 3 See Editorial, p 185 c A supplementary
Post- survival in completely resected stage I non-small cell lung cancer with local J-J Hung, 1,2,3 W-H Hsu, 3 C-C Hsieh, 3 B-S Huang, 3 M-H Huang, 3 J-S Liu, 2 Y-C Wu 3 See Editorial, p 185 c A supplementary
Underutilization of Radiotherapy for Lung Cancer in New South Wales, Australia
 Underutilization of Radiotherapy for Lung Cancer in New South Wales, Australia Shalini K. Vinod, MBBS, MD, FRANZCR 1 ; Leonardo Simonella, BA, MPH 2 ; David Goldsbury, BSc, MPH 2 ; Geoff P. Delaney, MBBS,
Underutilization of Radiotherapy for Lung Cancer in New South Wales, Australia Shalini K. Vinod, MBBS, MD, FRANZCR 1 ; Leonardo Simonella, BA, MPH 2 ; David Goldsbury, BSc, MPH 2 ; Geoff P. Delaney, MBBS,
Update on Small Cell Lung Cancer
 Welcome to Master Class for Oncologists Session 3: 2:45 PM - 3:30 PM Washington, DC March 28, 2009 Small Cell Lung Cancer: Best Practices & Recent Advances Speaker: Bruce E. Johnson, MD Professor of Medicine,
Welcome to Master Class for Oncologists Session 3: 2:45 PM - 3:30 PM Washington, DC March 28, 2009 Small Cell Lung Cancer: Best Practices & Recent Advances Speaker: Bruce E. Johnson, MD Professor of Medicine,
Big Data and Oncology Care Quality Improvement in the United States
 Big Data and Oncology Care Quality Improvement in the United States Peter P. Yu, MD, FACP, FASCO President, American Society of Clinical Oncology Director of Cancer Research, Palo Alto Medical Foundation
Big Data and Oncology Care Quality Improvement in the United States Peter P. Yu, MD, FACP, FASCO President, American Society of Clinical Oncology Director of Cancer Research, Palo Alto Medical Foundation
L Lang-Lazdunski, A Bille, S Marshall, R Lal, D Landau, J Spicer
 Pleurectomy/decortication, hyperthermic pleural lavage with povidone-iodine and systemic chemotherapy in malignant pleural mesothelioma. A 10-year experience. L Lang-Lazdunski, A Bille, S Marshall, R Lal,
Pleurectomy/decortication, hyperthermic pleural lavage with povidone-iodine and systemic chemotherapy in malignant pleural mesothelioma. A 10-year experience. L Lang-Lazdunski, A Bille, S Marshall, R Lal,
A new score predicting the survival of patients with spinal cord compression from myeloma
 A new score predicting the survival of patients with spinal cord compression from myeloma (1) Sarah Douglas, Department of Radiation Oncology, University of Lubeck, Germany; sarah_douglas@gmx.de (2) Steven
A new score predicting the survival of patients with spinal cord compression from myeloma (1) Sarah Douglas, Department of Radiation Oncology, University of Lubeck, Germany; sarah_douglas@gmx.de (2) Steven
Maintenance therapy in in Metastatic NSCLC. Dr Amit Joshi Associate Professor Dept. Of Medical Oncology Tata Memorial Centre Mumbai
 Maintenance therapy in in Metastatic NSCLC Dr Amit Joshi Associate Professor Dept. Of Medical Oncology Tata Memorial Centre Mumbai Definition of Maintenance therapy The U.S. National Cancer Institute s
Maintenance therapy in in Metastatic NSCLC Dr Amit Joshi Associate Professor Dept. Of Medical Oncology Tata Memorial Centre Mumbai Definition of Maintenance therapy The U.S. National Cancer Institute s
GUIDELINES FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF LUNG CANCER
 GUIDELINES FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF LUNG CANCER BY Ali Shamseddine, MD (Coordinator); as04@aub.edu.lb Fady Geara, MD Bassem Shabb, MD Ghassan Jamaleddine, MD CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES FOR THE TREATMENT
GUIDELINES FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF LUNG CANCER BY Ali Shamseddine, MD (Coordinator); as04@aub.edu.lb Fady Geara, MD Bassem Shabb, MD Ghassan Jamaleddine, MD CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES FOR THE TREATMENT
Treatment of Small Cell Lung Cancer: American Society of Clinical Oncology Endorsement of the American College of Chest Physicians (ACCP) Guideline
 Treatment of Small Cell Lung Cancer: American Society of Clinical Oncology Endorsement of the American College of Chest Physicians (ACCP) Guideline An ASCO Endorsement of Treatment of Small Cell Lung Cancer:
Treatment of Small Cell Lung Cancer: American Society of Clinical Oncology Endorsement of the American College of Chest Physicians (ACCP) Guideline An ASCO Endorsement of Treatment of Small Cell Lung Cancer:
Travel Distance to Healthcare Centers is Associated with Advanced Colon Cancer at Presentation
 Travel Distance to Healthcare Centers is Associated with Advanced Colon Cancer at Presentation Yan Xing, MD, PhD, Ryaz B. Chagpar, MD, MS, Y Nancy You MD, MHSc, Yi Ju Chiang, MSPH, Barry W. Feig, MD, George
Travel Distance to Healthcare Centers is Associated with Advanced Colon Cancer at Presentation Yan Xing, MD, PhD, Ryaz B. Chagpar, MD, MS, Y Nancy You MD, MHSc, Yi Ju Chiang, MSPH, Barry W. Feig, MD, George
Non Small Cell Lung Cancer: Scientific Discoveries and the Pursuit of Progress
 Non Small Cell Lung Cancer: Scientific Discoveries and the Pursuit of Progress Lung Cancer Accounts for 14% of All New Cancer Diagnoses in the United States 1 Lung cancer is the second most common malignancy
Non Small Cell Lung Cancer: Scientific Discoveries and the Pursuit of Progress Lung Cancer Accounts for 14% of All New Cancer Diagnoses in the United States 1 Lung cancer is the second most common malignancy
Is the third-line chemotherapy feasible for non-small cell lung cancer? A retrospective study
 Turkish Journal of Cancer Volume 34, No.1, 2004 19 Is the third-line chemotherapy feasible for non-small cell lung cancer? A retrospective study MUSTAFA ÖZDO AN, MUSTAFA SAMUR, HAKAN BOZCUK, ERKAN ÇOBAN,
Turkish Journal of Cancer Volume 34, No.1, 2004 19 Is the third-line chemotherapy feasible for non-small cell lung cancer? A retrospective study MUSTAFA ÖZDO AN, MUSTAFA SAMUR, HAKAN BOZCUK, ERKAN ÇOBAN,
Decision to Continue the Development of Tecemotide (L-BLP25) in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer to be Announced
 September 27, 2013 ONO PHARMACEUTICAL CO., LTD. Corporate Communications Phone: +81-6-6263-5670 Decision to Continue the Development of Tecemotide (L-BLP25) in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer to be Announced
September 27, 2013 ONO PHARMACEUTICAL CO., LTD. Corporate Communications Phone: +81-6-6263-5670 Decision to Continue the Development of Tecemotide (L-BLP25) in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer to be Announced
Protein kinase C alpha expression and resistance to neo-adjuvant gemcitabine-containing chemotherapy in non-small cell lung cancer
 Protein kinase C alpha expression and resistance to neo-adjuvant gemcitabine-containing chemotherapy in non-small cell lung cancer Dan Vogl Lay Abstract Early stage non-small cell lung cancer can be cured
Protein kinase C alpha expression and resistance to neo-adjuvant gemcitabine-containing chemotherapy in non-small cell lung cancer Dan Vogl Lay Abstract Early stage non-small cell lung cancer can be cured
Lung cancer is not just one disease. There are two main types of lung cancer:
 1. What is lung cancer? 2. How common is lung cancer? 3. What are the risk factors for lung cancer? 4. What are the signs and symptoms of lung cancer? 5. How is lung cancer diagnosed? 6. What are the available
1. What is lung cancer? 2. How common is lung cancer? 3. What are the risk factors for lung cancer? 4. What are the signs and symptoms of lung cancer? 5. How is lung cancer diagnosed? 6. What are the available
Small Cell Lung Cancer
 Small Cell Lung Cancer Types of Lung Cancer Non-small cell carcinoma (NSCC) (87%) Adenocarcinoma (38%) Squamous cell (20%) Large cell (5%) Small cell carcinoma (13%) Small cell lung cancer is virtually
Small Cell Lung Cancer Types of Lung Cancer Non-small cell carcinoma (NSCC) (87%) Adenocarcinoma (38%) Squamous cell (20%) Large cell (5%) Small cell carcinoma (13%) Small cell lung cancer is virtually
Racial Disparities and Barrier to Statin Utilization in Patients with Diabetes in the U.S. School of Pharmacy Virginia Commonwealth University
 Racial Disparities and Barrier to Statin Utilization in Patients with Diabetes in the U.S. School of Pharmacy Virginia Commonwealth University Outline Background Motivation Objectives Study design Results
Racial Disparities and Barrier to Statin Utilization in Patients with Diabetes in the U.S. School of Pharmacy Virginia Commonwealth University Outline Background Motivation Objectives Study design Results
Measures of Prognosis. Sukon Kanchanaraksa, PhD Johns Hopkins University
 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike License. Your use of this material constitutes acceptance of that license and the conditions of use of materials on this
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike License. Your use of this material constitutes acceptance of that license and the conditions of use of materials on this
Disclosure. I have the following relationships with commercial interests:
 Disclosure Electra Paskett, Ph.D., MPH I have the following relationships with commercial interests: Merck Research grant, in-kind donation Pfizer Stock ownership Meridian Bioscience Stock ownership A
Disclosure Electra Paskett, Ph.D., MPH I have the following relationships with commercial interests: Merck Research grant, in-kind donation Pfizer Stock ownership Meridian Bioscience Stock ownership A
Collection and Use of Industry and Occupation Data III: Cancer surveillance findings among construction workers
 Collection and Use of Industry and Occupation Data III: Cancer surveillance findings among construction workers Geoffrey M. Calvert, MD, MPH, FACP National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health
Collection and Use of Industry and Occupation Data III: Cancer surveillance findings among construction workers Geoffrey M. Calvert, MD, MPH, FACP National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health
The Blood Cancer Twice As Likely To Affect African Americans: Multiple Myeloma
 The Blood Cancer Twice As Likely To Affect African Americans: Multiple Myeloma 11 th Annual National Leadership Summit on Health Disparities Innovation Towards Reducing Disparities Congressional Black
The Blood Cancer Twice As Likely To Affect African Americans: Multiple Myeloma 11 th Annual National Leadership Summit on Health Disparities Innovation Towards Reducing Disparities Congressional Black
CHILDHOOD CANCER SURVIVOR STUDY Analysis Concept Proposal
 CHILDHOOD CANCER SURVIVOR STUDY Analysis Concept Proposal 1. STUDY TITLE: Longitudinal Assessment of Chronic Health Conditions: The Aging of Childhood Cancer Survivors 2. WORKING GROUP AND INVESTIGATORS:
CHILDHOOD CANCER SURVIVOR STUDY Analysis Concept Proposal 1. STUDY TITLE: Longitudinal Assessment of Chronic Health Conditions: The Aging of Childhood Cancer Survivors 2. WORKING GROUP AND INVESTIGATORS:
Activity of pemetrexed in thoracic malignancies
 Activity of pemetrexed in thoracic malignancies Results of phase III clinical studies of pemetrexed in malignant pleural mesothelioma and non-small cell lung cancer show benefit P emetrexed (Alimta) is
Activity of pemetrexed in thoracic malignancies Results of phase III clinical studies of pemetrexed in malignant pleural mesothelioma and non-small cell lung cancer show benefit P emetrexed (Alimta) is
ORIGINAL ARTICLE THORACIC ONCOLOGY
 Ann Surg Oncol (2013) 20:1934 1940 DOI 10.1245/s10434-012-2800-x ORIGINAL ARTICLE THORACIC ONCOLOGY Predictors for Locoregional Recurrence for Clinical Stage III-N2 Non-small Cell Lung Cancer with Nodal
Ann Surg Oncol (2013) 20:1934 1940 DOI 10.1245/s10434-012-2800-x ORIGINAL ARTICLE THORACIC ONCOLOGY Predictors for Locoregional Recurrence for Clinical Stage III-N2 Non-small Cell Lung Cancer with Nodal
ALCHEMIST (Adjuvant Lung Cancer Enrichment Marker Identification and Sequencing Trials)
 ALCHEMIST (Adjuvant Lung Cancer Enrichment Marker Identification and Sequencing Trials) 3 Integrated Trials Testing Targeted Therapy in Early Stage Lung Cancer Part of NCI s Precision Medicine Effort in
ALCHEMIST (Adjuvant Lung Cancer Enrichment Marker Identification and Sequencing Trials) 3 Integrated Trials Testing Targeted Therapy in Early Stage Lung Cancer Part of NCI s Precision Medicine Effort in
Clinical trial enrollment among older cancer patients
 Clinical trial enrollment among older cancer patients Sharon H. Giordano MD, MPH Professor, Health Services Research Mariana Chavez Mac Gregor MD, MSc Assistant Professor, Breast Medical Oncology Department
Clinical trial enrollment among older cancer patients Sharon H. Giordano MD, MPH Professor, Health Services Research Mariana Chavez Mac Gregor MD, MSc Assistant Professor, Breast Medical Oncology Department
Non-small cell lung cancer, advanced or metastatic, switch-therapy after gemcitabine/carboplatin
 COMPENDIA TRANSPARENCY TRACKING FORM DRUG: Docetaxel INDICATION: Non-small cell lung cancer, advanced or metastatic, switch-therapy after gemcitabine/carboplatin COMPENDIA TRANSPARENCY REQUIREMENTS 1 Provide
COMPENDIA TRANSPARENCY TRACKING FORM DRUG: Docetaxel INDICATION: Non-small cell lung cancer, advanced or metastatic, switch-therapy after gemcitabine/carboplatin COMPENDIA TRANSPARENCY REQUIREMENTS 1 Provide
Management of stage III A-B of NSCLC. Hamed ALHusaini Medical Oncologist
 Management of stage III A-B of NSCLC Hamed ALHusaini Medical Oncologist Global incidence, CA cancer J Clin 2011;61:69-90 Stage III NSCLC Includes heterogeneous group of patients with differences in the
Management of stage III A-B of NSCLC Hamed ALHusaini Medical Oncologist Global incidence, CA cancer J Clin 2011;61:69-90 Stage III NSCLC Includes heterogeneous group of patients with differences in the
Summary of treatment benefits
 Risk Management Plan PEMETREXED Powder for concentrate for Solution for infusion Pemetrexed is also indicated as monotherapy for the maintenance treatment of locally advanced or metastatic non small cell
Risk Management Plan PEMETREXED Powder for concentrate for Solution for infusion Pemetrexed is also indicated as monotherapy for the maintenance treatment of locally advanced or metastatic non small cell
Challenges in assessing disease latency for cancer in environmental epidemiology
 Challenges in assessing disease latency for cancer in environmental epidemiology Peggy Reynolds, Ph.D. Case-only Clustering in Mobile Populations Workshop - November 11-12, 2010 Ann Arbor, Michigan Outline
Challenges in assessing disease latency for cancer in environmental epidemiology Peggy Reynolds, Ph.D. Case-only Clustering in Mobile Populations Workshop - November 11-12, 2010 Ann Arbor, Michigan Outline
Corso Integrato di Clinica Medica ONCOLOGIA MEDICA AA 2010-2011 LUNG CANCER. VIII. THERAPY. V. SMALL CELL LUNG CANCER Prof.
 Corso Integrato di Clinica Medica ONCOLOGIA MEDICA AA 2010-2011 LUNG CANCER. VIII. THERAPY. V. SMALL CELL LUNG CANCER Prof. Alberto Riccardi SMALL CELL LUNG CARCINOMA Summary of treatment approach * limited
Corso Integrato di Clinica Medica ONCOLOGIA MEDICA AA 2010-2011 LUNG CANCER. VIII. THERAPY. V. SMALL CELL LUNG CANCER Prof. Alberto Riccardi SMALL CELL LUNG CARCINOMA Summary of treatment approach * limited
Lung cancer is the leading cause of cancer death in the U.S. for both. Cost-Effectiveness and Lung Cancer Clinical Trials
 1491 Cost-Effectiveness and Lung Cancer Clinical Trials Wei Du, Ph.D. 1,2 Jaxk H. Reeves, Ph.D. 3 Shirish Gadgeel, M.D. 1,2 Judith Abrams, Ph.D. 1,2 William P. Peters, M.D., Ph.D. 1,2 1 Center for Cancer
1491 Cost-Effectiveness and Lung Cancer Clinical Trials Wei Du, Ph.D. 1,2 Jaxk H. Reeves, Ph.D. 3 Shirish Gadgeel, M.D. 1,2 Judith Abrams, Ph.D. 1,2 William P. Peters, M.D., Ph.D. 1,2 1 Center for Cancer
Third-line or fourth-line chemotherapy in non-small-cell lung cancer patients with relatively good performance status
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Journal of the Chinese Medical Association 74 (2011) 209e214 Original Article Third-line or fourth-line chemotherapy in non-small-cell lung cancer patients with
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Journal of the Chinese Medical Association 74 (2011) 209e214 Original Article Third-line or fourth-line chemotherapy in non-small-cell lung cancer patients with
Stage IV Renal Cell Carcinoma. Changing Management in A Comprehensive Community Cancer Center. Susquehanna Health Cancer Center
 Stage IV Renal Cell Carcinoma Changing Management in A Comprehensive Community Cancer Center Susquehanna Health Cancer Center 2000 2009 Warren L. Robinson, MD, FACP January 27, 2014 Introduction 65,150
Stage IV Renal Cell Carcinoma Changing Management in A Comprehensive Community Cancer Center Susquehanna Health Cancer Center 2000 2009 Warren L. Robinson, MD, FACP January 27, 2014 Introduction 65,150
Developments in Biomarker Identification and Validation for Lung Cancer
 Developments in Biomarker Identification and Validation for Lung Cancer Alexandre Passioukov, MD, PhD Alexandre.Passioukov@eortc.be Contents Introduction Lung cancer pathogenesis NSCLC treatment options
Developments in Biomarker Identification and Validation for Lung Cancer Alexandre Passioukov, MD, PhD Alexandre.Passioukov@eortc.be Contents Introduction Lung cancer pathogenesis NSCLC treatment options
Outcome analysis of breast cancer patients who declined evidence-based treatment
 Joseph et al. World Journal of Surgical Oncology 2012, 10:118 WORLD JOURNAL OF SURGICAL ONCOLOGY RESEARCH Open Access Outcome analysis of breast cancer patients who declined evidence-based treatment Kurian
Joseph et al. World Journal of Surgical Oncology 2012, 10:118 WORLD JOURNAL OF SURGICAL ONCOLOGY RESEARCH Open Access Outcome analysis of breast cancer patients who declined evidence-based treatment Kurian
Risk Factors for Alcoholism among Taiwanese Aborigines
 Risk Factors for Alcoholism among Taiwanese Aborigines Introduction Like most mental disorders, Alcoholism is a complex disease involving naturenurture interplay (1). The influence from the bio-psycho-social
Risk Factors for Alcoholism among Taiwanese Aborigines Introduction Like most mental disorders, Alcoholism is a complex disease involving naturenurture interplay (1). The influence from the bio-psycho-social
New Trends & Current Research in the Treatment of Lung Cancer, Pt. II
 New Trends & Current esearch in the Treatment of Lung Cancer, Pt. II Howard (Jack) West, MD President & CEO, GACE Medical Director, Thoracic Oncology Program Swedish Cancer Institute Seattle, WA Cancer
New Trends & Current esearch in the Treatment of Lung Cancer, Pt. II Howard (Jack) West, MD President & CEO, GACE Medical Director, Thoracic Oncology Program Swedish Cancer Institute Seattle, WA Cancer
Lung cancer. A guide for journalists on Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC) and its treatment
 Lung cancer A guide for journalists on Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC) and its treatment Contents Contents 2 3 Section 1: Lung Cancer 4 i. Types of lung cancer 4 ii. Causes and risk factors 5 iii. Symptoms
Lung cancer A guide for journalists on Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC) and its treatment Contents Contents 2 3 Section 1: Lung Cancer 4 i. Types of lung cancer 4 ii. Causes and risk factors 5 iii. Symptoms
If several different trials are mentioned in one publication, the data of each should be extracted in a separate data extraction form.
 General Remarks This template of a data extraction form is intended to help you to start developing your own data extraction form, it certainly has to be adapted to your specific question. Delete unnecessary
General Remarks This template of a data extraction form is intended to help you to start developing your own data extraction form, it certainly has to be adapted to your specific question. Delete unnecessary
Prior Authorization Guideline
 Prior Authorization Guideline Guideline: PS Inj - Alimta Therapeutic Class: Antineoplastic Agents Therapeutic Sub-Class: Antifolates Client: PS Inj Approval Date: 8/2/2004 Revision Date: 12/5/2006 I. BENEFIT
Prior Authorization Guideline Guideline: PS Inj - Alimta Therapeutic Class: Antineoplastic Agents Therapeutic Sub-Class: Antifolates Client: PS Inj Approval Date: 8/2/2004 Revision Date: 12/5/2006 I. BENEFIT
Treatment of Metastatic Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Systematic Review of Comparative Effectiveness and Cost-Effectiveness
 Department of Veterans Affairs Health Services Research & Development Service Treatment of Metastatic Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Systematic Review of Comparative Effectiveness and Cost-Effectiveness
Department of Veterans Affairs Health Services Research & Development Service Treatment of Metastatic Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Systematic Review of Comparative Effectiveness and Cost-Effectiveness
Molecular markers and clinical trial design parallels between oncology and rare diseases?
 Molecular markers and clinical trial design parallels between oncology and rare diseases?, Harriet Sommer Institute for Medical Biometry and Statistics, University of Freiburg Medical Center 6. Forum Patientennahe
Molecular markers and clinical trial design parallels between oncology and rare diseases?, Harriet Sommer Institute for Medical Biometry and Statistics, University of Freiburg Medical Center 6. Forum Patientennahe
Colorectal Cancer Screening Behaviors among American Indians in the Midwest
 JOURNAL OF HD RP Journal of Health Disparities Research and Practice Volume 4, Number 2, Fall 2010, pp. 35 40 2010 Center for Health Disparities Research School of Community Health Sciences University
JOURNAL OF HD RP Journal of Health Disparities Research and Practice Volume 4, Number 2, Fall 2010, pp. 35 40 2010 Center for Health Disparities Research School of Community Health Sciences University
Lung Cancer and Mesothelioma
 Lung Cancer and Mesothelioma Robert Kratzke, M.D. John C. Skoglund Professor of Lung Cancer Research Section of Heme/Onc/Transplant Department of Medicine University of Minnesota Medical School Malignant
Lung Cancer and Mesothelioma Robert Kratzke, M.D. John C. Skoglund Professor of Lung Cancer Research Section of Heme/Onc/Transplant Department of Medicine University of Minnesota Medical School Malignant
4.8 Lung cancer. 4.8.5 In the UK, three fractionation regimens are most commonly used:
 4.8 Lung cancer 4.8.1 In 2005, both NICE (National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence) and SIGN (Scottish Intercollegiate Guidelines Network) published guidelines on the management of lung cancer.
4.8 Lung cancer 4.8.1 In 2005, both NICE (National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence) and SIGN (Scottish Intercollegiate Guidelines Network) published guidelines on the management of lung cancer.
Who may benefit from prophylactic cranial irradiation amongst stage III non-small cell lung cancer patients?
 JBUON 2013; 18(2): 453-458 ISSN: 1107-0625 www.jbuon.com E-mail: info@jbuon.com ORIGINAL ARTICLE Who may benefit from prophylactic cranial irradiation amongst stage III non-small cell lung cancer patients?
JBUON 2013; 18(2): 453-458 ISSN: 1107-0625 www.jbuon.com E-mail: info@jbuon.com ORIGINAL ARTICLE Who may benefit from prophylactic cranial irradiation amongst stage III non-small cell lung cancer patients?
Breast and Lung Cancer Biomarker Research at ASCO: Changing Treatment Patterns
 July 2013 Edition Vol. 7, Issue 7 Breast and Lung Cancer Biomarker Research at ASCO: Changing Treatment Patterns By Julie Katz, MPH, MPhil Biomarkers played a prominent role in the research presented in
July 2013 Edition Vol. 7, Issue 7 Breast and Lung Cancer Biomarker Research at ASCO: Changing Treatment Patterns By Julie Katz, MPH, MPhil Biomarkers played a prominent role in the research presented in
Survival disparities in non-small cell lung cancer patients receiving radiation treatment: An investigation of race and gender
 Journal of Cancer Research and Experimental Oncology Vol. 2(3), pp. 29-34, September 2010 Available online http://www.academicjournals.org/jcreo ISSN 2141-2243 2010 Academic Journals Full Length Research
Journal of Cancer Research and Experimental Oncology Vol. 2(3), pp. 29-34, September 2010 Available online http://www.academicjournals.org/jcreo ISSN 2141-2243 2010 Academic Journals Full Length Research
NEOPLASMS OF KIDNEY (RENAL CELL CARCINOMA) And RENAL PELVIS (TRANSITIONAL CELL CARCINOMA)
 NEOPLASMS OF KIDNEY (RENAL CELL CARCINOMA) And RENAL PELVIS (TRANSITIONAL CELL CARCINOMA) Merat Esfahani, MD Medical Oncologist, Hematologist Cancer Liaison Physician SwedishAmerican Regional Cancer Center
NEOPLASMS OF KIDNEY (RENAL CELL CARCINOMA) And RENAL PELVIS (TRANSITIONAL CELL CARCINOMA) Merat Esfahani, MD Medical Oncologist, Hematologist Cancer Liaison Physician SwedishAmerican Regional Cancer Center
Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma in Singapore
 RESEARCH COMMUNICATION C SP Yip 1, HN Koong 2, CM Loo 3, KW Fong 1* Abstract Aim: To examine the clinical characteristics and outcomes of malignant pleural mesothelioma (MPM) in Singapore. Methods and
RESEARCH COMMUNICATION C SP Yip 1, HN Koong 2, CM Loo 3, KW Fong 1* Abstract Aim: To examine the clinical characteristics and outcomes of malignant pleural mesothelioma (MPM) in Singapore. Methods and
The New International Staging System Lung Cancer
 The New International Staging System Lung Cancer Valerie W. Rusch, MD Chief, Thoracic Surgery Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center Chair, Lung and Esophagus Task Force, American Joint Commission on Cancer
The New International Staging System Lung Cancer Valerie W. Rusch, MD Chief, Thoracic Surgery Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center Chair, Lung and Esophagus Task Force, American Joint Commission on Cancer
Research Article Frequency of Surgery in Black Patients with Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma
 Disease Markers Volume 2015, Article ID 282145, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/282145 Research Article Frequency of Surgery in Black Patients with Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma Emanuela Taioli,
Disease Markers Volume 2015, Article ID 282145, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/282145 Research Article Frequency of Surgery in Black Patients with Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma Emanuela Taioli,
Background. t 1/2 of 3.7 4.7 days allows once-daily dosing (1.5 mg) with consistent serum concentration 2,3 No interaction with CYP3A4 inhibitors 4
 Abstract No. 4501 Tivozanib versus sorafenib as initial targeted therapy for patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma: Results from a Phase III randomized, open-label, multicenter trial R. Motzer, D.
Abstract No. 4501 Tivozanib versus sorafenib as initial targeted therapy for patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma: Results from a Phase III randomized, open-label, multicenter trial R. Motzer, D.
Male. Female. Death rates from lung cancer in USA
 Male Female Death rates from lung cancer in USA Smoking represents an interesting combination of an entrenched industry and a clearly drug-induced cancer Tobacco Use in the US, 1900-2000 5000 100 Per Capita
Male Female Death rates from lung cancer in USA Smoking represents an interesting combination of an entrenched industry and a clearly drug-induced cancer Tobacco Use in the US, 1900-2000 5000 100 Per Capita
Wisconsin Cancer Data Bulletin Wisconsin Department of Health Services Division of Public Health Office of Health Informatics
 Wisconsin Cancer Data Bulletin Wisconsin Department of Health Services Division of Public Health Office of Health Informatics In Situ Breast Cancer in Wisconsin INTRODUCTION This bulletin provides information
Wisconsin Cancer Data Bulletin Wisconsin Department of Health Services Division of Public Health Office of Health Informatics In Situ Breast Cancer in Wisconsin INTRODUCTION This bulletin provides information
Screening Mammography for Breast Cancer: American College of Preventive Medicine Practice Policy Statement
 Screening Mammography for Breast Cancer: American College of Preventive Medicine Practice Policy Statement Rebecca Ferrini, MD, Elizabeth Mannino, MD, Edith Ramsdell, MD and Linda Hill, MD, MPH Burden
Screening Mammography for Breast Cancer: American College of Preventive Medicine Practice Policy Statement Rebecca Ferrini, MD, Elizabeth Mannino, MD, Edith Ramsdell, MD and Linda Hill, MD, MPH Burden
Treatment of Metastatic Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Systematic Review of Comparative Effectiveness and Cost Effectiveness
 Treatment of Metastatic Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Systematic Review of Comparative Effectiveness and Cost Effectiveness Investigators: Paul G. Shekelle, MD, PhD, Director Alicia R. Maher, MD Clinical
Treatment of Metastatic Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Systematic Review of Comparative Effectiveness and Cost Effectiveness Investigators: Paul G. Shekelle, MD, PhD, Director Alicia R. Maher, MD Clinical
Long-term survival of children with cerebral palsy in Okinawa, Japan
 DEVELOPMENTAL MEDICINE & CHILD NEUROLOGY ORIGINAL ARTICLE Long-term survival of children with cerebral palsy in Okinawa, Japan MAYUMI TOUYAMA 1 JUN TOUYAMA 1 YASUO OCHIAI 2 SATOSHI TOYOKAWA 3 YASUKI KOBAYASHI
DEVELOPMENTAL MEDICINE & CHILD NEUROLOGY ORIGINAL ARTICLE Long-term survival of children with cerebral palsy in Okinawa, Japan MAYUMI TOUYAMA 1 JUN TOUYAMA 1 YASUO OCHIAI 2 SATOSHI TOYOKAWA 3 YASUKI KOBAYASHI
Treatment of Small Cell Lung Cancer: American Society of Clinical Oncology. Endorsement of the American College of Chest Physicians (ACCP) Guideline
 Treatment of Small Cell Lung Cancer: American Society of Clinical Oncology Endorsement of the American College of Chest Physicians (ACCP) Guideline Table of Contents Data Supplement 1: Summary of included
Treatment of Small Cell Lung Cancer: American Society of Clinical Oncology Endorsement of the American College of Chest Physicians (ACCP) Guideline Table of Contents Data Supplement 1: Summary of included
Mesothelioma. 1. Introduction. 1.1 General Information and Aetiology
 Mesothelioma 1. Introduction 1.1 General Information and Aetiology Mesotheliomas are tumours that arise from the mesothelial cells of the pleura, peritoneum, pericardium or tunica vaginalis [1]. Most are
Mesothelioma 1. Introduction 1.1 General Information and Aetiology Mesotheliomas are tumours that arise from the mesothelial cells of the pleura, peritoneum, pericardium or tunica vaginalis [1]. Most are
Avastin in Metastatic Breast Cancer
 Non-interventional study Avastin in Metastatic Breast Cancer ML 21165 / 2007 Clinical Study Report Synopsis ROCHE ML21165 / WiSP Project RH09 / V. 1.0 / 24.06.2013 ROCHE ML21165-2 - Name of Sponsor Roche
Non-interventional study Avastin in Metastatic Breast Cancer ML 21165 / 2007 Clinical Study Report Synopsis ROCHE ML21165 / WiSP Project RH09 / V. 1.0 / 24.06.2013 ROCHE ML21165-2 - Name of Sponsor Roche
Metastatic breast cancer, HER2 overexpression, first-line therapy in combination with a taxane and trastuzumab
 COMPENDIA TRANSPARENCY TRACKING FORM DRUG: Carboplatin INDICATION: Metastatic breast cancer, HER2 overexpression, first-line therapy in combination with a taxane and trastuzumab COMPENDIA TRANSPARENCY
COMPENDIA TRANSPARENCY TRACKING FORM DRUG: Carboplatin INDICATION: Metastatic breast cancer, HER2 overexpression, first-line therapy in combination with a taxane and trastuzumab COMPENDIA TRANSPARENCY
Prostatectomy, pelvic lymphadenect. Med age 63 years Mean followup 53 months No other cancer related therapy before recurrence. Negative.
 Adjuvante und Salvage Radiotherapie Ludwig Plasswilm Klinik für Radio-Onkologie, KSSG CANCER CONTROL WITH RADICAL PROSTATECTOMY ALONE IN 1,000 CONSECUTIVE PATIENTS 1983 1998 Clinical stage T1 and T2 Mean
Adjuvante und Salvage Radiotherapie Ludwig Plasswilm Klinik für Radio-Onkologie, KSSG CANCER CONTROL WITH RADICAL PROSTATECTOMY ALONE IN 1,000 CONSECUTIVE PATIENTS 1983 1998 Clinical stage T1 and T2 Mean
Treatment of Small Cell Lung Cancer
 Chapter 5 Treatment of Small Cell Lung Cancer Ariel Lopez-Chavez MD, MS Introduction There are two main types of lung cancer, non-small cell lung cancer and small cell lung cancer. 1 It is important that
Chapter 5 Treatment of Small Cell Lung Cancer Ariel Lopez-Chavez MD, MS Introduction There are two main types of lung cancer, non-small cell lung cancer and small cell lung cancer. 1 It is important that
Small Cell Lung Cancer* State-of-the-Art Therapy 1994
 Small Cell Lung Cancer* State-of-the-Art Therapy 1994 Daniel C. Ihde, MD In the United States, small cell lung cancer (SCLC) accounts for about 20% of all cases of lung cancer. Without treatment, tumor
Small Cell Lung Cancer* State-of-the-Art Therapy 1994 Daniel C. Ihde, MD In the United States, small cell lung cancer (SCLC) accounts for about 20% of all cases of lung cancer. Without treatment, tumor
Does chronic lymphocytic leukemia increase the risk of osteoporosis?
 Does chronic lymphocytic leukemia increase the risk of osteoporosis? Amrita Desai, MD Internal Medicine Residency Program Adam Olszewski, MD Department of Hematology and Oncology Memorial Hospital of Rhode
Does chronic lymphocytic leukemia increase the risk of osteoporosis? Amrita Desai, MD Internal Medicine Residency Program Adam Olszewski, MD Department of Hematology and Oncology Memorial Hospital of Rhode
2010 SITE REPORT St. Joseph Hospital PROSTATE CANCER
 2010 SITE REPORT St. Joseph Hospital PROSTATE CANCER Humboldt County is located on the Redwood Coast of Northern California. U.S census data for 2010 reports county population at 134,623, an increase of
2010 SITE REPORT St. Joseph Hospital PROSTATE CANCER Humboldt County is located on the Redwood Coast of Northern California. U.S census data for 2010 reports county population at 134,623, an increase of
Role of taxanes in the treatment of advanced NHL patients: A randomized study of 87 cases
 Role of taxanes in the treatment of advanced NHL patients: A randomized study of 87 cases R. Shraddha, P.N. Pandit Radium Institute, Patna Medical College and Hospital, Patna, India Abstract NHL is a highly
Role of taxanes in the treatment of advanced NHL patients: A randomized study of 87 cases R. Shraddha, P.N. Pandit Radium Institute, Patna Medical College and Hospital, Patna, India Abstract NHL is a highly
Stephen R. Veach, M.D.
 Stephen R. Veach, M.D. Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center International Oncology Programs 160 E. 53 rd Street New York, NY 10022 212-610 610-08780878 - tel 212-308 308-7063 - fax veachs@mskcc.org SCREENING
Stephen R. Veach, M.D. Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center International Oncology Programs 160 E. 53 rd Street New York, NY 10022 212-610 610-08780878 - tel 212-308 308-7063 - fax veachs@mskcc.org SCREENING
Impact of radiation therapy on survival in patients with triple negative breast cancer
 548 Impact of radiation therapy on survival in patients with triple negative breast cancer LAUREN T. STEWARD 1, FENG GAO 2, MARIE A. TAYLOR 3 and JULIE A. MARGENTHALER 1 1 Department of Surgery; 2 Division
548 Impact of radiation therapy on survival in patients with triple negative breast cancer LAUREN T. STEWARD 1, FENG GAO 2, MARIE A. TAYLOR 3 and JULIE A. MARGENTHALER 1 1 Department of Surgery; 2 Division
Lung cancer is a disease of the elderly. National
 Similar Long-term Survival of Elderly Patients With Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Treated With Lobectomy or Wedge Resection Within the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results Database* Carlos M. Mery,
Similar Long-term Survival of Elderly Patients With Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Treated With Lobectomy or Wedge Resection Within the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results Database* Carlos M. Mery,
Conditional Colon Cancer Survival in the United States
 Research Article imedpub Journals http://www.imedpub.com Colorectal Cancer: Open Access Abstract Conditional Colon Cancer Survival in the United States Purpose: As long-term colon cancer survivors increase,
Research Article imedpub Journals http://www.imedpub.com Colorectal Cancer: Open Access Abstract Conditional Colon Cancer Survival in the United States Purpose: As long-term colon cancer survivors increase,
Genomic Medicine The Future of Cancer Care. Shayma Master Kazmi, M.D. Medical Oncology/Hematology Cancer Treatment Centers of America
 Genomic Medicine The Future of Cancer Care Shayma Master Kazmi, M.D. Medical Oncology/Hematology Cancer Treatment Centers of America Personalized Medicine Personalized health care is a broad term for interventions
Genomic Medicine The Future of Cancer Care Shayma Master Kazmi, M.D. Medical Oncology/Hematology Cancer Treatment Centers of America Personalized Medicine Personalized health care is a broad term for interventions
Future Directions in Clinical Research. Karen Kelly, MD Associate Director for Clinical Research UC Davis Cancer Center
 Future Directions in Clinical Research Karen Kelly, MD Associate Director for Clinical Research UC Davis Cancer Center Outline 1. Status of Cancer Treatment 2. Overview of Clinical Research at UCDCC 3.
Future Directions in Clinical Research Karen Kelly, MD Associate Director for Clinical Research UC Davis Cancer Center Outline 1. Status of Cancer Treatment 2. Overview of Clinical Research at UCDCC 3.
National Horizon Scanning Centre. Vandetanib (Zactima) for advanced or metastatic non-small cell lung cancer. December 2007
 Vandetanib (Zactima) for advanced or metastatic non-small cell lung cancer December 2007 This technology summary is based on information available at the time of research and a limited literature search.
Vandetanib (Zactima) for advanced or metastatic non-small cell lung cancer December 2007 This technology summary is based on information available at the time of research and a limited literature search.
Breast Cancer Among the US Male Population June 2015
 Breast Cancer Among the US Male Population June 2015 Centers for Disease Control and Prevention NCCDPHP, DCPC, Cancer Surveillance Branch Background Focus on female breast cancer Few studies on male breast
Breast Cancer Among the US Male Population June 2015 Centers for Disease Control and Prevention NCCDPHP, DCPC, Cancer Surveillance Branch Background Focus on female breast cancer Few studies on male breast
Integrating Chemotherapy and Liver Surgery for the Management of Colorectal Metastases
 I Congresso de Oncologia D Or July 5-6, 2013 Integrating Chemotherapy and Liver Surgery for the Management of Colorectal Metastases Michael A. Choti, MD, MBA, FACS Department of Surgery Johns Hopkins University
I Congresso de Oncologia D Or July 5-6, 2013 Integrating Chemotherapy and Liver Surgery for the Management of Colorectal Metastases Michael A. Choti, MD, MBA, FACS Department of Surgery Johns Hopkins University
Patterns of Care in Palliative Radiotherapy: A Population-Based Study
 Health Care Delivery Original Contribution Patterns of Care in Palliative Radiotherapy: A Population-Based Study By James D. Murphy, MD, MS, Lorene M. Nelson, PhD, Daniel T. Chang, MD, Loren K. Mell, MD,
Health Care Delivery Original Contribution Patterns of Care in Palliative Radiotherapy: A Population-Based Study By James D. Murphy, MD, MS, Lorene M. Nelson, PhD, Daniel T. Chang, MD, Loren K. Mell, MD,
Does Radiation Treatment of Prostate Cancer Increase Risk for Rectal Cancer? The Perfect Storm
 NAACCR Conference, Austin, TX June 13, 2013 In Collaboration with: Does Radiation Treatment of Prostate Cancer Increase Risk for Rectal Cancer? The Perfect Storm John W. Morgan, DrPH, CPH, Brice Jabo,
NAACCR Conference, Austin, TX June 13, 2013 In Collaboration with: Does Radiation Treatment of Prostate Cancer Increase Risk for Rectal Cancer? The Perfect Storm John W. Morgan, DrPH, CPH, Brice Jabo,
