Treating Clostridium difficile infection (CDI) the second time around
|
|
|
- Louise Pearson
- 8 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Treating Clostridium difficile infection (CDI) the second time around Ciarán P. Kelly, MD Professor of Medicine Harvard Medical School. Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Boston
2 The difficult Clostridium Objectives: CDI - More difficult than ever Who gets recurrent CDI? How do we manage recurrent CDI? What s new in CDI therapy? Spore
3 Difficulties with CDI Increasing disease incidence Increasing disease severity Low cure rate (<70%) 10% of patients don t respond to days of treatment 4% of patients die from CDI 25% have recurrence Overall cure rate < 70%
4 Pathogenesis of Clostridium difficile infection (CDI) Antibiotic therapy Disturbed colonic microflora (loss of colonization resistance) C. difficile exposure & colonization Toxin A & Toxin B Diarrhea & colitis Kelly & LaMont N Engl J Med 2008
5 C. difficile toxin-induced Pseudomembranous colitis C. difficile toxins induce a marked acute Inflammatory response with intestinal injury
6 Antimicrobials Predisposing to CDI Very Commonly Related Clindamycin Ampicillin Amoxicillin Cephalosporins Fluoroquinolones Less Commonly Related Other penicillins Sulfonamides Trimethoprim Cotrimoxazole Macrolides Uncommonly Related Aminoglycosides Bacitracin Metronidazole Teicoplanin Rifampin Chloramphenicol Tetracyclines Carbapenems Daptomycin Tigecycline Bouza E, et al. Med Clin North Am. 2006;90: Loo VG, et al. N Engl J Med. 2005;353:
7 Nosocomial C. difficile infection & asymptomatic carriage are common Hospital Hospital patients patients (Acute (Acute medical medical ward) ward) LOS LOS > 2 days days Receiving Receiving antibiotic antibiotic enrolled Colonized by by C. C. difficile (31%) Hospital-acquired Hospital-acquired (17%) (17%) Colonized Colonized at at Admission Admission (14%) (14%) CDI case 28 (10%) Carrier 19 (7%) CDI case 19 (7%) Carrier 18 (7%) Kyne et al N Engl J Med 2000;342:390
8 Asymptomatic carriers of C. difficile have high serum IgG anti-toxin A Carriers Non-colonized Cases IgG anti-toxin A P=0.06 P=0.002 P=0.001 P=0.005 Admission Admission Colonization Colonization 3 3 days days after after Colonization Colonization Discharge Discharge Kyne et al N Engl J Med 2000;342:390
9 Rates of CDI Tripled in US Hospitals between 2000 and 2005 Discharges per 100,000 population x x Any diagnosis Primary diagnosis x x x x Year x x ~x2 x x ~x3 x McDonald LC, et al. Emerg Infect Dis. 2006;12: , and unpublished CDC data.
10 C. difficile-related deaths have increased in the US 25 Age adjusted death rate per million % increase from 1999 to 2004 In 2004 CDI-related deaths: 4 those attributed to MRSA infection 6 those attributed to all other intestinal IDs combined Redelings et al. Emerg Infect Dis. 2007;13:
11 C. difficile-related Deaths Are Also Increasing in the UK UK Clostridium death difficile certifications Deaths increase in 2005 UK deaths 2006: CDAD 6,480 MRSA 1,652 US deaths (age adjusted): per million per million MRSA=methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Death certificates mentioning C. difficile and recording C. difficile as the underlying cause of death (England and Wales). Source: UK Office of National Statistics. Redelings et al. Emerg Infect Dis. 2007;13:
12 CDI outbreak in Estrie (Quebec) 2003 vs 2002: x 4 CDI cases x 20 CDI deaths > 80% NAP1 strain >64 yr Total yr <17 yr Pepin et al. Can Med Assoc J 2004; 171:
13 Epidemic Strain Strain typed BI/NAP1/027 1,2 Is highly resistant to fluoroquinolones 2,4 Binary toxin genes are present Produces large quantities of toxins A and B 1,3 Has a tcdc gene deletion 1 1. Warny M, et al. Lancet. 2005;366: Hubert B, et al. Clin Infect Dis. 2007;44: CDC Fact Sheet. July McDonald LC, et al. N Engl J Med. 2005;353: Adapted from McDonald LC, et al. N Engl J Med. 2005;353: ; with permission.
14 Recurrent C. difficile diarrhea Common (~25% of treated patients) Mechanisms of recurrence: NOT due to resistance to metronidazole or vancomycin Metronidazole or vancomycin therapy perpetuate loss of colonization resistance Either: Relapse - Persisting infection Re-infection - New inoculum different strain in ~50% of recurrent CDAD cases Wilcox et al. J Hosp Infect. 1998;38:
15 Recurrent C. difficile diarrhea (contd) Risk factors: Age > 65 years Severe underlying illness Concommitant antibiotic use Prior recurrent CDAD ~ 20% risk after first CDAD episode ~ 40% risk after first recurrence > 60% risk after 2 or more recurrences Lack of protective immunity Kyne et al. Lancet 2001;357:189-93
16 Prospective derivation and validation of a clinical prediction rule for recurrent C. difficile infection Gastroenterology 2009;136: Hu MY, Katchar K, Kyne L, Maroo S, Tummala S, Dreisbach V, Xu H, Leffler DA, Kelly CP. Risk factors: Age > 65 years = 1 point Severe illness (Horn s Index) = 1 point Concommitant antibiotic use = 1 point Score Recurrent CDI in validation cohort 0 0% 1 17% 2 31% 3 67%
17 AGA Institute Late-Breaking Abstract Session: May 4, 2010, 2:15 PM Randomized Clinical Trial (RCT) in Clostridium difficile Infection (CDI) Confirms Superiority of Fidaxomicin over Vancomycin S Johnson, DW Crook, OA Cornely, KP High, M Miller, SL Gorbach Concomitant antibiotics (CAs) to treat other infections in 59% of patients during CDI treatment. Lower initial response rate with CAs 86.1% with CAs vs 98.4% without (P=<.001) Higher recurrence rate with CAs 23.9% with CAs vs 8.1% without (P=<.001) Lower global cure rate with CAs 59.8% with CAs vs 90.3% without (P=<.001).
18 Treatment of First Episode of CDI Mild CDI Discontinue other antibacterial agents if possible Request stool testing Monitor course of disease Moderate or persisting CDI (or patients who must continue antibacterial therapy) As for mild plus: Oral metronidazole 500 mg TID for days or 250 mg QID for days Gerding DN, et al. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol. 1995;16: Poutanen SM, Simor AE. Can Med Assoc J. 2004;171:51-58.
19 Vancomycin is more effective than metronidazole in treating severe CDI Prospective, RCT (172 enrolled, 150 completed) Vancomycin 125 mg QID x 10d vs Metronidazole 250 mg QID x 10d Stratified for disease severity 2 points = SEVERE 1 point: Age: > 60 years Temp: > 101 F [38.3 C] Albumin: < 2.5 mg/dl WBC > 15,000 cells/mm 3 2 points: PMC at colonoscopy ICU patient Response Vancomycin 100% 90% 80% 70% 60% 50% 98% P=0.4 90% Mild / Moderate Metronidazole 97% Severe 76% P=0.02 Zar et al. Clin Infect Dis 2007;45:302-7
20 Management of Severe CDI Early recognition Initiate therapy as soon as diagnosis is suspected Oral vancomycin (125 mg QID for 10 to 14 days) as initial treatment If patient is unable to tolerate oral medication iv metronidazole consider intracolonic vancomycin instillation (by enema) g vancomycin (IV formulation) in ml normal saline via rectal (or Foley) catheter Clamp for 60 minutes Repeat every 4 12 hours Gerding DN, et al. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol. 1995;16: Zar FA, et al. Clin Infect Dis. 2007;45: Louie T, et al. 47th Annual ICAAC Meeting, 2007, Abstract k-425-a. Apisarnthanarak A, et al. Clin Infect Dis. 2002;35:
21 Markers of Severe CDI Severe diarrhea (> 10 BM/day) Marked leukocytosis >15,000 assoc. severe CDI >25,000 assoc. increased fatality Rising serum creatinine Falling serum albumin Colonic thickening on CT scan Ascites on CT scan Pseudomembranes on endoscopy Hemodynamic instability Severe abdominal distension, pain 2 points points = SEVERE 1 point: point: Age: Age: > years years Temp: Temp: > 101 F 101 F [38.3 C] [38.3 C] Albumin: Albumin: < mg/dl mg/dl WBC WBC > 15,000 15,000 cells/mm cells/mm points: points: PMC PMC at at colonoscopy colonoscopy ICU ICU patient patient Zar Zaret et al. al. Clin Clin Infect Infect Dis Dis
22 Colonic distension and small bowel ileus in fulminant Clostridium difficile colitis Severe / fulminant CDI may present as an acute abdomen and/or mimic acute colonic pseudo-obstruction Abdominal pain & distension Little or no diarrhea Kelly & LaMont. Gastrointestinal Pharmacotherapy, W. B. Saunders 1993;
23 Sigmoidoscopic appearance of severe CDI with PMC Immediate bedside diagnosis in severe, complicated CDI Guides surgical management Perforation rare - death usually results from SIDS
24 Management of fulminant or refractory CDI Vancomycin 500 mg qid po If ileus: Metronidazole 500 mg iv tid plus Vancomycin 500 mg qid via n/g tube or by enema If progressive or refractory: Early surgery evaluation/consultation Consider IVIG 400 mg/kg Monitor for progression WBC > 20,000 Creatinine >1.5 baseline Rising lactate (5.0)
25 First recurrence: An approach to treating recurrent CDI - Treat based on disease severity - Metronidazole or Vancomycin x10-14 days Second recurrence: Oral vancomycin taper & pulsed dosing Kelly NEJM 2008
26 Treatment of Multiple Recurrent CDAD Non-randomized study* Vancomycin N Recurrence, n (%) P-Value Medium dose (1g to <2 g/day) (71) Low dose (<1 g/day) (54) High dose ( 2 g/day) 21 9 (43) Tapering dose 29 9 (31) 0.01 Pulse dosing 7 1 (14) 0.02 Other 6 2 (33) All (46) Metronidazole N Recurrence, n (%) Low dose ( 1 g/day) (45) Medium dose (1.5 g/day) 5 2 (40) Other 4 1 (25) All (42) Total (45) * Placebo/antibiotic cohort from 2 clinical trials of Saccharomyces boulardii as adjunctive treatment. Includes vancomycin and rifampin (n=3) and vancomycin and metronidazole (n=3). Includes high dose (2 g/day), taper, or pulse dosing. McFarland LV, et al. Am J Gastroenterol. 2002:97:
27 An approach to treating recurrent CDI Rx Rx Vancomycin Taper & Pulsed First recurrence: dosing: - Metronidazole or Vancomycin x10-14 days Second recurrence: Oral vancomycin taper & pulsed dosing Third recurrence Week Week 1 Week Week 2 Week Week 3 Week Week 4 Week Week mg mg qid qid mg mg bid bid mg mg daily daily mg mg qod qod mg mg q3d q3d Vancomycin 125 mg qid for 14 days followed by Rifaximin 400 mg twice daily for 14 days Subsequent recurrences Intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) (400 mg/kg & repeat after 3 weeks) Vancomycin plus Probiotic? Lactobacillus spp, Saccharomyces boulardii Fecal transplantation / bacteriotherapy Kelly NEJM 2008
28 New treatment approaches for Recurrent C. difficile associated diarrhea Probiotics Antibiotic therapy C. difficile colonization Toxin production Diarrhea Recurrent diarrhea
29 S. boulardii for prevention of CDI: Inconsistent study results Placebo S. boulardii 100% 80% 65% 60% 40% 24% 19% 35% 47% 44% 20% 0% 1st episode CDI (A) P=0.04 Recurrent CDI (A) Recurrent CDI (B) Sb 500 mg bid x 4 weeks A. McFarland. JAMA. 1994;271: B. Surawicz et al. Clin Infect Dis. 2000;31:
30 New treatment approaches for Recurrent C. difficile associated diarrhea Probiotics Antibiotics Antibiotic therapy C. difficile colonization Toxin production Diarrhea Recurrent diarrhea
31 Fidaxomicin in CDI Minimal absorption from human GI tract Selective anti-c. difficile antibiotic Preserves colonization resistance?? 30% Fidaxomicin Vanco 24% 629 adults with CDI treated for 10 days with: * P= mg OPT-80 bid 78% Cured * 125 mg vancomycin qid 67% Cured * 20% 10% 0% 8% 10% Treatment Failure 13% P = NS P = Recurrence
32 New treatment approaches for Recurrent C. difficile associated diarrhea Probiotics Antibiotics Antibiotic therapy C. difficile colonization Toxin production Toxin binder Diarrhea Recurrent diarrhea
33 High serum IgG anti-toxin A levels are associated with a lower risk for recurrent C. difficile diarrhea Recurrent C. difficile diarrhea (%) For a level < 1.29 Odds ratio = 48 (95% CI, ) 0 < >1.28 Serum IgG anti-toxin A Day 12 Kyne et al. Lancet 2001;357:189-93
34 New treatment approaches for Recurrent C. difficile associated diarrhea Probiotics Antibiotics Toxin binder Antibiotic therapy C. difficile colonization Toxin production Diarrhea memory primary Active Active Immunization: Immunization: Toxoid Toxoidvaccine Anti-toxin immune response Passive: Passive: IVIG, IVIG, HuMAbs, HuMAbs, Hyperimmune Hyperimmune globulin globulin Recurrent diarrhea Protection
35 Intravenous immunoglobulin therapy for recurrent C. difficile diarrhea Serum IgG anti-toxin A (Optical Density units) P = 0.03 P = 0.01 Adult Pediatric Pre-IVIG Post-IVIG Healthy controls Children with recurrent C. difficile diarrhea Leung DY, Kelly CP et al J Pediatr 1993 Wilcox. J Antimicrob Chemother 2004;53:882-4.
36 25% 7% Recurrent CDI
37 A C. difficile Toxoid Vaccine (Toxoids A and B) Induces High Serum IgG Anti-Toxin A Response Patients Vaccine recipients Aboudola S, et al. Infect Immun. 2003;71:
38 Take home: C. difficile: more difficult than ever More prevalent More severe ( morbidity & mortality) NAP-1 epidemic strain widely prevalent in US CDI management is changing: Vancomycin 1 st line for severe CDI & possibly for multiple recurrent CDI (taper / pulse) New antibiotic and non-antibiotic approaches to therapy needed & being
39 The difficult Clostridium Aslam S et al. Lancet Infect Dis. 2005;5:
Antibiotic-Associated Diarrhea, Clostridium difficile- Associated Diarrhea and Colitis
 Antibiotic-Associated Diarrhea, Clostridium difficile- Associated Diarrhea and Colitis ANTIBIOTIC-ASSOCIATED DIARRHEA Disturbance of the normal colonic microflora Leading to alterations in bacterial degradation
Antibiotic-Associated Diarrhea, Clostridium difficile- Associated Diarrhea and Colitis ANTIBIOTIC-ASSOCIATED DIARRHEA Disturbance of the normal colonic microflora Leading to alterations in bacterial degradation
Clostridium Difficile Colitis. Presented by Mark Skains August 2003
 Clostridium Difficile Colitis Presented by Mark Skains August 2003 What is Clostridium Difficile Gram positive rod Produces spores (hang out in diverticula) Forms Endotoxin A + B which cause diarrhea.
Clostridium Difficile Colitis Presented by Mark Skains August 2003 What is Clostridium Difficile Gram positive rod Produces spores (hang out in diverticula) Forms Endotoxin A + B which cause diarrhea.
Clostridium Difficile Colitis: Treatments, Guidelines, and Challenges
 Clostridium Difficile Colitis: Treatments, Guidelines, and Challenges Brian S. Zuckerbraun, MD, FACS Henry T. Bahnson Professor of Surgery University of Pittsburgh Chief, Trauma and Acute Care Surgery
Clostridium Difficile Colitis: Treatments, Guidelines, and Challenges Brian S. Zuckerbraun, MD, FACS Henry T. Bahnson Professor of Surgery University of Pittsburgh Chief, Trauma and Acute Care Surgery
Develop an understanding of the differential diagnosis of pseudomembranous colitis
 Update on Clostridium difficile Colitis Clostridium difficile infection has recently emerged in populations without any known risk factors. This presentation will focus on the historical background, diagnosis,
Update on Clostridium difficile Colitis Clostridium difficile infection has recently emerged in populations without any known risk factors. This presentation will focus on the historical background, diagnosis,
Treatments, Tapers, and Transplants: Guidelines and Options for Complicated C. diff Patients MIA A. TAORMINA, DO, FACOI
 Treatments, Tapers, and Transplants: Guidelines and Options for Complicated C. diff Patients MIA A. TAORMINA, DO, FACOI DUPAGE MEDICAL GROUP INFECTIOUS DISEASE Objectives To discuss the epidemiology and
Treatments, Tapers, and Transplants: Guidelines and Options for Complicated C. diff Patients MIA A. TAORMINA, DO, FACOI DUPAGE MEDICAL GROUP INFECTIOUS DISEASE Objectives To discuss the epidemiology and
Treatment and Prevention Options for Clostridium difficile Infection (CDI)
 Treatment and Prevention Options for Clostridium difficile Infection (CDI) Dale N. Gerding, MD Professor of Medicine Loyola University Chicago Stritch School of Medicine Research Physician Hines VA Hospital
Treatment and Prevention Options for Clostridium difficile Infection (CDI) Dale N. Gerding, MD Professor of Medicine Loyola University Chicago Stritch School of Medicine Research Physician Hines VA Hospital
Clostridium Difficile colitismore virulent than ever ECHO- Sept 17, 2015
 Clostridium Difficile colitismore virulent than ever ECHO- Sept 17, 2015 Charles Krasner, M.D. UNR School of Medicine Sierra NV Veterans Affairs Hospital Growing problem of pseudomembranous colitis MMWR-
Clostridium Difficile colitismore virulent than ever ECHO- Sept 17, 2015 Charles Krasner, M.D. UNR School of Medicine Sierra NV Veterans Affairs Hospital Growing problem of pseudomembranous colitis MMWR-
Clostridium difficile colitis
 Iranian Journal of Clinical Infectious Diseases 2007;2(3):161-166 2007 IDTMRC, Infectious Diseases and Tropical Medicine Research Center REVIEW ARTICLE Clostridium difficile colitis Stephen B. Calderwood
Iranian Journal of Clinical Infectious Diseases 2007;2(3):161-166 2007 IDTMRC, Infectious Diseases and Tropical Medicine Research Center REVIEW ARTICLE Clostridium difficile colitis Stephen B. Calderwood
TITLE: CLOSTRIDIUM DIFFICILE INFECTION (CDI): GUIDELINES FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF ADULT PATIENTS
 Page 1 of 6 TITLE: CLOSTRIDIUM DIFFICILE INFECTION (CDI): GUIDELINES FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF ADULT PATIENTS POLICY/GUIDELINES: Diagnosis of Clostridium difficile disease is based on clinical symptoms in
Page 1 of 6 TITLE: CLOSTRIDIUM DIFFICILE INFECTION (CDI): GUIDELINES FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF ADULT PATIENTS POLICY/GUIDELINES: Diagnosis of Clostridium difficile disease is based on clinical symptoms in
growing problem By: Jena Cummins, Doctor of Pharmacy Candidate
 Clostridium difficile: A growing problem By: Jena Cummins, Doctor of Pharmacy Candidate Introduction The word difficile il is Latin for the word difficult. Clostridium difficile, affectionately known as
Clostridium difficile: A growing problem By: Jena Cummins, Doctor of Pharmacy Candidate Introduction The word difficile il is Latin for the word difficult. Clostridium difficile, affectionately known as
Title: Vancomycin for C.difficile Pseudomembranous Colitis: Guidelines and a Clinical Effectiveness Review
 Title: Vancomycin for C.difficile Pseudomembranous Colitis: Guidelines and a Clinical Effectiveness Review Date: 29 February 2008 Context and policy issues: Clostridium difficile is a bacterial enteric
Title: Vancomycin for C.difficile Pseudomembranous Colitis: Guidelines and a Clinical Effectiveness Review Date: 29 February 2008 Context and policy issues: Clostridium difficile is a bacterial enteric
Antimicrobial Stewardship for Hospital Acquired Infection Prevention: Focus on C. difficile infection
 Antimicrobial Stewardship for Hospital Acquired Infection Prevention: Focus on C. difficile infection Emi Minejima, PharmD Assistant Professor of Clinical Pharmacy USC School of Pharmacy minejima@usc.edu
Antimicrobial Stewardship for Hospital Acquired Infection Prevention: Focus on C. difficile infection Emi Minejima, PharmD Assistant Professor of Clinical Pharmacy USC School of Pharmacy minejima@usc.edu
C. diff 10/12/2014. Objectives. My name is but I go by. Treatment of Clostridium difficile: Is metronidazole good enough for your mother?
 Treatment of Clostridium difficile: Is metronidazole good enough for your mother? Daniel M. Rackham, PharmD, BCPS Clinical Assistant Professor Oregon State University College of Pharmacy Clinical Pharmacist
Treatment of Clostridium difficile: Is metronidazole good enough for your mother? Daniel M. Rackham, PharmD, BCPS Clinical Assistant Professor Oregon State University College of Pharmacy Clinical Pharmacist
European Society of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases (ESCMID): treatment guidance document for Clostridium difficile infection (CDI)
 GUIDELINES 10.1111/j.1469-0691.2009.03099.x European Society of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases (ESCMID): treatment guidance document for Clostridium difficile infection (CDI) M. P. Bauer
GUIDELINES 10.1111/j.1469-0691.2009.03099.x European Society of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases (ESCMID): treatment guidance document for Clostridium difficile infection (CDI) M. P. Bauer
Probiotics for the Treatment of Adult Gastrointestinal Disorders
 Probiotics for the Treatment of Adult Gastrointestinal Disorders Darren M. Brenner, M.D. Division of Gastroenterology Northwestern University, Feinberg School of Medicine Chicago, Illinois What are Probiotics?
Probiotics for the Treatment of Adult Gastrointestinal Disorders Darren M. Brenner, M.D. Division of Gastroenterology Northwestern University, Feinberg School of Medicine Chicago, Illinois What are Probiotics?
Clostridium difficile Infection (CDI) Gail Bennett, RN, MSN, CIC
 Clostridium difficile Infection (CDI) Gail Bennett, RN, MSN, CIC 1 Clostridium difficile (C.difficile) Antibiotic induced diarrhea Can cause pseudomembranous colitis Most common cause of acute infectious
Clostridium difficile Infection (CDI) Gail Bennett, RN, MSN, CIC 1 Clostridium difficile (C.difficile) Antibiotic induced diarrhea Can cause pseudomembranous colitis Most common cause of acute infectious
Running head: CLOSTRIDIUM DIFFICILE COLITIS 1. Clostridium Difficile Colitis: One Woman's Journey
 Running head: CLOSTRIDIUM DIFFICILE COLITIS 1 Clostridium Difficile Colitis: One Woman's Journey Winde R. Chambers, APRN, FNP-BC, Jennifer K. Pemberton, RN, BSN, and Susan Chaney, EdD, RN, FNP-C, FAANP
Running head: CLOSTRIDIUM DIFFICILE COLITIS 1 Clostridium Difficile Colitis: One Woman's Journey Winde R. Chambers, APRN, FNP-BC, Jennifer K. Pemberton, RN, BSN, and Susan Chaney, EdD, RN, FNP-C, FAANP
Clostridium difficile Colitis
 Clostridium difficile Colitis Philip A. Efron, MD, John E. Mazuski, MD, PhD* KEYWORDS Clostridium difficile Colitis Diarrhea Infection Clostridium difficile is an anaerobic, gram-positive, spore-forming
Clostridium difficile Colitis Philip A. Efron, MD, John E. Mazuski, MD, PhD* KEYWORDS Clostridium difficile Colitis Diarrhea Infection Clostridium difficile is an anaerobic, gram-positive, spore-forming
CADTH Technology Report
 Canadian Agency for Drugs and Technologies in Health Agence canadienne des médicaments et des technologies de la santé CADTH Technology Report Issue 136 January 2011 Vancomycin or Metronidazole for Treatment
Canadian Agency for Drugs and Technologies in Health Agence canadienne des médicaments et des technologies de la santé CADTH Technology Report Issue 136 January 2011 Vancomycin or Metronidazole for Treatment
Clostridium difficile associated Diarrhea: Brief Review and Update of Medical Management
 內 科 學 誌 013:4:309-316 Clostridium difficile associated Diarrhea: Brief Review and Update of Medical Management Shih-Ta Shang 1,, Sheng-Kang Chiu, Ning-Chi Wang, and Jung-Chung Lin 1 Division of Infectious
內 科 學 誌 013:4:309-316 Clostridium difficile associated Diarrhea: Brief Review and Update of Medical Management Shih-Ta Shang 1,, Sheng-Kang Chiu, Ning-Chi Wang, and Jung-Chung Lin 1 Division of Infectious
Clostridium Difficile Colitis. Anton Sharapov, PGY 5
 Clostridium Difficile Colitis Anton Sharapov, PGY 5 Outline Case Introduction Diagnosis Treatment New risk factor Clostridium sp. 60 species, most saprophytic four major problems intestinal deep tissue
Clostridium Difficile Colitis Anton Sharapov, PGY 5 Outline Case Introduction Diagnosis Treatment New risk factor Clostridium sp. 60 species, most saprophytic four major problems intestinal deep tissue
CONSUMERS UNION POLICY BRIEF HOSPITAL-ACQUIRED C. DIFFICILE INFECTIONS (CDI) 11-08
 CONSUMERS UNION POLICY BRIEF HOSPITAL-ACQUIRED C. DIFFICILE INFECTIONS (CDI) 11-08 The growth of infections caused by Clostridium difficile (C.diff) is a highly alarming trend in hospitals today. In 1993
CONSUMERS UNION POLICY BRIEF HOSPITAL-ACQUIRED C. DIFFICILE INFECTIONS (CDI) 11-08 The growth of infections caused by Clostridium difficile (C.diff) is a highly alarming trend in hospitals today. In 1993
Guidelines for Diagnosis, Treatment, and Prevention of Clostridium difficile Infections
 478 PRACTICE GUIDELINES nature publishing group CME Guidelines for Diagnosis, Treatment, and Prevention of Clostridium difficile Infections Christina M. Surawicz, MD 1, L aw renc e J. Br andt, M D 2, David
478 PRACTICE GUIDELINES nature publishing group CME Guidelines for Diagnosis, Treatment, and Prevention of Clostridium difficile Infections Christina M. Surawicz, MD 1, L aw renc e J. Br andt, M D 2, David
MAJOR ARTICLE. Antibiotic treatment is often associated with diarrhea and symptoms ranging from mild abdominal
 MAJOR ARTICLE Efficacy of Fidaxomicin Versus Vancomycin as Therapy for Clostridium difficile Infection in Individuals Taking Concomitant Antibiotics for Other Concurrent Infections Kathleen M. Mullane,
MAJOR ARTICLE Efficacy of Fidaxomicin Versus Vancomycin as Therapy for Clostridium difficile Infection in Individuals Taking Concomitant Antibiotics for Other Concurrent Infections Kathleen M. Mullane,
Clostridium Difficile Colitis: Epidemiology, Diagnosis, Treatment and Modalities
 Osteopathic Family Physician (2014)5, 13-18 Clostridium Difficile Colitis: Epidemiology, Diagnosis, Treatment and Modalities Vincenzo A. Barbato, DO 1 ; Robert Hasty, DO, FACOI 2 ; Ilya Fonarov, DO 3 ;
Osteopathic Family Physician (2014)5, 13-18 Clostridium Difficile Colitis: Epidemiology, Diagnosis, Treatment and Modalities Vincenzo A. Barbato, DO 1 ; Robert Hasty, DO, FACOI 2 ; Ilya Fonarov, DO 3 ;
Clostridium difficile is an important cause of diarrhea
 Clostridium difficile-associated diarrhea in a region of Quebec from 1991 to 2003: a changing pattern of disease severity Research Recherche Jacques Pépin, Louis Valiquette, Marie-Eve Alary, Philippe Villemure,
Clostridium difficile-associated diarrhea in a region of Quebec from 1991 to 2003: a changing pattern of disease severity Research Recherche Jacques Pépin, Louis Valiquette, Marie-Eve Alary, Philippe Villemure,
Treatment of antibiotic-associated diarrhea caused by Clostridium difficile
 Official reprint from UpToDate www.uptodate.com Print Back Treatment of antibiotic-associated diarrhea caused by Clostridium difficile Authors Ciarán P Kelly, MD J Thomas LaMont, MD Section Editor Stephen
Official reprint from UpToDate www.uptodate.com Print Back Treatment of antibiotic-associated diarrhea caused by Clostridium difficile Authors Ciarán P Kelly, MD J Thomas LaMont, MD Section Editor Stephen
MDCH SHARP NHSN USERS CONFERENCE CALL Wednesday, March 25 th, 2015
 MDCH SHARP NHSN USERS CONFERENCE CALL Wednesday, March 25 th, 2015 Thank you to those who were able to join our bi-monthly NHSN users conference call. If you were unable to participate on this call, we
MDCH SHARP NHSN USERS CONFERENCE CALL Wednesday, March 25 th, 2015 Thank you to those who were able to join our bi-monthly NHSN users conference call. If you were unable to participate on this call, we
What Is Clostridium Difficile (C. Diff)? CLOSTRIDIUM DIFFICILE (C. DIFF)
 What Is Clostridium Difficile (C. Diff)? Clostridium difficile, or C. diff for short, is an infection from a bacterium, or bug, that can grow in your intestines and cause bad GI symptoms. The main risk
What Is Clostridium Difficile (C. Diff)? Clostridium difficile, or C. diff for short, is an infection from a bacterium, or bug, that can grow in your intestines and cause bad GI symptoms. The main risk
Original Article: http://www.mayoclinic.com/health/c-difficile/ds00736
 MayoClinic.com reprints This single copy is for your personal, noncommercial use only. For permission to reprint multiple copies or to order presentation-ready copies for distribution, use the reprints
MayoClinic.com reprints This single copy is for your personal, noncommercial use only. For permission to reprint multiple copies or to order presentation-ready copies for distribution, use the reprints
Recent changes in Clostridium difficile infection
 REVIEW Recent changes in Clostridium difficile infection Recentes mudanças da infecção por Clostridium difficile Moacyr Silva Júnior 1 ABSTRACT Clostridium difficile is the main cause of nosocomial diarrhea.
REVIEW Recent changes in Clostridium difficile infection Recentes mudanças da infecção por Clostridium difficile Moacyr Silva Júnior 1 ABSTRACT Clostridium difficile is the main cause of nosocomial diarrhea.
Clostridium difficile Infections in Solid Organ Transplantation
 American Journal of Transplantation 2013; 13: 42 49 Wiley Periodicals Inc. Special Article C Copyright 2013 The American Society of Transplantation and the American Society of Transplant Surgeons doi:
American Journal of Transplantation 2013; 13: 42 49 Wiley Periodicals Inc. Special Article C Copyright 2013 The American Society of Transplantation and the American Society of Transplant Surgeons doi:
Fecal Bacteriotherapy for the Treatment of Recurrent Clostridium Difficile Infection in Adults
 Pacific University CommonKnowledge School of Physician Assistant Studies Theses, Dissertations and Capstone Projects 8-14-2010 Fecal Bacteriotherapy for the Treatment of Recurrent Clostridium Difficile
Pacific University CommonKnowledge School of Physician Assistant Studies Theses, Dissertations and Capstone Projects 8-14-2010 Fecal Bacteriotherapy for the Treatment of Recurrent Clostridium Difficile
R e s i d e n t G r a n d R o u n d s. Clostridium difficile Associated Diarrhea and Colitis in the Hospitalized Patient
 R e s i d e n t G r a n d R o u n d s Series Editor: Mark A. Perazella, MD Clostridium difficile Associated Diarrhea and Colitis in the Hospitalized Patient Ravi K. Mallavarapu, MD Harold P. Katner, MD
R e s i d e n t G r a n d R o u n d s Series Editor: Mark A. Perazella, MD Clostridium difficile Associated Diarrhea and Colitis in the Hospitalized Patient Ravi K. Mallavarapu, MD Harold P. Katner, MD
Fecal Microbiota Transplantation for Clostridium Difficile Infection: A Systematic Review of the Evidence
 4 Department of Veterans Affairs Health Services Research & Development Service Fecal Microbiota Transplantation for Clostridium Difficile Infection: A Systematic Review of the Evidence July 2014 Prepared
4 Department of Veterans Affairs Health Services Research & Development Service Fecal Microbiota Transplantation for Clostridium Difficile Infection: A Systematic Review of the Evidence July 2014 Prepared
Clostridium difficile Not So Easy To Treat?
 Clostridium difficile Not So Easy To Treat? Manish Rungta, MD Bay Area Gastroenterology, PA Clinical Assistant Professor, UTMB Clinical Assistant Professor, Baylor College of Medicine Vice Chief of Staff,
Clostridium difficile Not So Easy To Treat? Manish Rungta, MD Bay Area Gastroenterology, PA Clinical Assistant Professor, UTMB Clinical Assistant Professor, Baylor College of Medicine Vice Chief of Staff,
C. difficile Infections
 C. difficile Infections Introduction C. difficile is a type of bacteria that can cause diarrhea and infection of the colon. This bacterium is more likely to infect patients at hospitals and other healthcare
C. difficile Infections Introduction C. difficile is a type of bacteria that can cause diarrhea and infection of the colon. This bacterium is more likely to infect patients at hospitals and other healthcare
Clostridium difficile infections in elderly patients
 Clostridium difficile infections in elderly patients Review articles Ángela Blanco Pérez, MD, 1 Óscar Ruiz Morales, MD, 2 William Otero Regino, MD, 3 Martín Gómez Zuleta, MD. 4 1 Third year resident in
Clostridium difficile infections in elderly patients Review articles Ángela Blanco Pérez, MD, 1 Óscar Ruiz Morales, MD, 2 William Otero Regino, MD, 3 Martín Gómez Zuleta, MD. 4 1 Third year resident in
Clostridium difficile infection: How to deal with the problem
 Clostridium difficile infection: How to deal with the problem DH INFORMATION RE ADER B OX Policy HR / Workforce Management Planning / Clinical Estates Commissioning IM & T Finance Social Care / Partnership
Clostridium difficile infection: How to deal with the problem DH INFORMATION RE ADER B OX Policy HR / Workforce Management Planning / Clinical Estates Commissioning IM & T Finance Social Care / Partnership
Intra-abdominal abdominal Infections
 Intra-abdominal abdominal Infections Marnie Peterson, Pharm.D., BCPS Dept. of Pediatric Infectious Diseases Medical School University of Minnesota Intra-abdominal abdominal Infections Intra-abdominal abdominal
Intra-abdominal abdominal Infections Marnie Peterson, Pharm.D., BCPS Dept. of Pediatric Infectious Diseases Medical School University of Minnesota Intra-abdominal abdominal Infections Intra-abdominal abdominal
EVIDENCE BASED TREATMENT OF CROHN S DISEASE. Dr E Ndabaneze
 EVIDENCE BASED TREATMENT OF CROHN S DISEASE Dr E Ndabaneze PLAN 1. Case presentation 2. Topic on Evidence based Treatment of Crohn s disease - Introduction pathology aetiology - Treatment - concept of
EVIDENCE BASED TREATMENT OF CROHN S DISEASE Dr E Ndabaneze PLAN 1. Case presentation 2. Topic on Evidence based Treatment of Crohn s disease - Introduction pathology aetiology - Treatment - concept of
Clostridium difficile (CDI) Infections Toolkit
 Clostridium difficile (CDI) Infections Toolkit Activity C: ELC Prevention Collaboratives Carolyn Gould, MD MSCR Cliff McDonald, MD, FACP Division of Healthcare Quality Promotion Centers for Disease Control
Clostridium difficile (CDI) Infections Toolkit Activity C: ELC Prevention Collaboratives Carolyn Gould, MD MSCR Cliff McDonald, MD, FACP Division of Healthcare Quality Promotion Centers for Disease Control
Diagnosis and Management of Clostridium difficile Infection
 31 Diagnosis and Management of Clostridium difficile Infection Tony M. Korman, MBBS, FRACP, FRCPA 1 1 Monash Infectious Diseases, Monash Health, Monash University, Clayton, Victoria, Australia Semin Respir
31 Diagnosis and Management of Clostridium difficile Infection Tony M. Korman, MBBS, FRACP, FRCPA 1 1 Monash Infectious Diseases, Monash Health, Monash University, Clayton, Victoria, Australia Semin Respir
Practice Parameters for the Management of Clostridium difficile Infection
 PRACTICE PARAMETERS Practice Parameters for the Management of Clostridium difficile Infection Scott R. Steele, M.D. James McCormick, D.O. Genevieve B. Melton, M.D. Ian Paquette, M.D. David E. Rivadeneira,
PRACTICE PARAMETERS Practice Parameters for the Management of Clostridium difficile Infection Scott R. Steele, M.D. James McCormick, D.O. Genevieve B. Melton, M.D. Ian Paquette, M.D. David E. Rivadeneira,
Received 4 July 2010; returned 10 August 2010; revised 27 September 2010; accepted 30 September 2010
 J Antimicrob Chemother 2011; 66: 205 209 doi:10.1093/jac/dkq404 Advance Access publication 8 November 2010 Sustained reduction in antimicrobial use and decrease in methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus
J Antimicrob Chemother 2011; 66: 205 209 doi:10.1093/jac/dkq404 Advance Access publication 8 November 2010 Sustained reduction in antimicrobial use and decrease in methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus
Vancomycin, Metronidazole, or Tolevamer for Clostridium difficile Infection: Results From Two Multinational, Randomized, Controlled Trials
 MAJOR ARTICLE Vancomycin, Metronidazole, or Tolevamer for Clostridium difficile Infection: Results From Two Multinational, Randomized, Controlled Trials Stuart Johnson, 1 Thomas J. Louie, 2 Dale N. Gerding,
MAJOR ARTICLE Vancomycin, Metronidazole, or Tolevamer for Clostridium difficile Infection: Results From Two Multinational, Randomized, Controlled Trials Stuart Johnson, 1 Thomas J. Louie, 2 Dale N. Gerding,
Updated guidance on the management and treatment of Clostridium difficile infection
 Updated guidance on the management and treatment of Clostridium difficile infection About Public Health England We are a new national executive agency formed in 2013 from a number of expert organisations
Updated guidance on the management and treatment of Clostridium difficile infection About Public Health England We are a new national executive agency formed in 2013 from a number of expert organisations
Inhibit terminal acid secretion from parietal cells by blocking H + /K + - ATPase pump
 Chris J. Taylor, Pharm.D., BCPS Clinical Pharmacist Phoenix VA Health Care System Review pharmacology of PPIs Discuss possible association between PPI use and development of the following: Pneumonia (community-acquired
Chris J. Taylor, Pharm.D., BCPS Clinical Pharmacist Phoenix VA Health Care System Review pharmacology of PPIs Discuss possible association between PPI use and development of the following: Pneumonia (community-acquired
Urinary Tract Infections
 Urinary Tract Infections Overview A urine culture must ALWAYS be interpreted in the context of the urinalysis and patient symptoms. If a patient has no signs of infection on urinalysis, no symptoms of
Urinary Tract Infections Overview A urine culture must ALWAYS be interpreted in the context of the urinalysis and patient symptoms. If a patient has no signs of infection on urinalysis, no symptoms of
Treatment of skin and soft tissue infections due to methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in adults
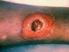 1 of 6 9/24/2010 11:16 AM Official reprint from UpToDate www.uptodate.com 2010 UpToDate Treatment of skin and soft tissue infections due to methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in adults Author
1 of 6 9/24/2010 11:16 AM Official reprint from UpToDate www.uptodate.com 2010 UpToDate Treatment of skin and soft tissue infections due to methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in adults Author
www.australiandoctor.com.au Clostridium difficileassociated of deaths. This has been the case for both hospital- and communityacquired
 How to Treat PULL-OUT SECTION www.australiandoctor.com.au Complete How to Treat quizzes online (www.australiandoctor.com.au/cpd) to earn CPD or PDP points. inside Epidemiology Risk factors Presentation
How to Treat PULL-OUT SECTION www.australiandoctor.com.au Complete How to Treat quizzes online (www.australiandoctor.com.au/cpd) to earn CPD or PDP points. inside Epidemiology Risk factors Presentation
New Treatments for Stroke Prevention in Atrial Fibrillation. John C. Andrefsky, MD, FAHA NEOMED Internal Medicine Review course May 5 th, 2013
 New Treatments for Stroke Prevention in Atrial Fibrillation John C. Andrefsky, MD, FAHA NEOMED Internal Medicine Review course May 5 th, 2013 Classification Paroxysmal atrial fibrillation (AF) Last < 7
New Treatments for Stroke Prevention in Atrial Fibrillation John C. Andrefsky, MD, FAHA NEOMED Internal Medicine Review course May 5 th, 2013 Classification Paroxysmal atrial fibrillation (AF) Last < 7
CME. Clostridium difficile associated colitis. Mark W. Hull, MD. Paul L. Beck, MD, PHD, FRCPC
 CME Clostridium difficile associated colitis Mark W. Hull, MD Paul L. Beck, MD, PHD, FRCPC ABSTRACT OBJECTIVE To review the basic microbiology, pathogenesis of disease, and diagnosis of the nosocomial
CME Clostridium difficile associated colitis Mark W. Hull, MD Paul L. Beck, MD, PHD, FRCPC ABSTRACT OBJECTIVE To review the basic microbiology, pathogenesis of disease, and diagnosis of the nosocomial
Recurrent Clostridium difficile Colitis: Case Series Involving 18 Patients Treated with Donor Stool Administered via a Nasogastric Tube
 MAJOR ARTICLE Recurrent Clostridium difficile Colitis: Case Series Involving 18 Patients Treated with Donor Stool Administered via a Nasogastric Tube Johannes Aas, 1 Charles E. Gessert, 2 and Johan S.
MAJOR ARTICLE Recurrent Clostridium difficile Colitis: Case Series Involving 18 Patients Treated with Donor Stool Administered via a Nasogastric Tube Johannes Aas, 1 Charles E. Gessert, 2 and Johan S.
Evidence of Crohn s Disease. Case Presentation
 Witt Wait to Treat tutiled Until Endoscopic Evidence of Crohn s Disease Raymond Cross, MD, MS, AGAF Associate Professor of Medicine Director, IBD Program University of Maryland School of Medicine Co-Director,
Witt Wait to Treat tutiled Until Endoscopic Evidence of Crohn s Disease Raymond Cross, MD, MS, AGAF Associate Professor of Medicine Director, IBD Program University of Maryland School of Medicine Co-Director,
Diabetic Ketoacidosis: When Sugar Isn t Sweet!!!
 Diabetic Ketoacidosis: When Sugar Isn t Sweet!!! W Ricks Hanna Jr MD Assistant Professor of Pediatrics University of Tennessee Health Science Center LeBonheur Children s Hospital Introduction Diabetes
Diabetic Ketoacidosis: When Sugar Isn t Sweet!!! W Ricks Hanna Jr MD Assistant Professor of Pediatrics University of Tennessee Health Science Center LeBonheur Children s Hospital Introduction Diabetes
Management of Extended Spectrum Beta- Lactamase (ESBL) Producing Enterobacteriaceae in health care settings
 Management of Extended Spectrum Beta- Lactamase (ESBL) Producing Enterobacteriaceae in health care settings Dr. Mary Vearncombe PIDAC-IPC February 2012 Objectives: To provide an overview of the RP/AP Annex
Management of Extended Spectrum Beta- Lactamase (ESBL) Producing Enterobacteriaceae in health care settings Dr. Mary Vearncombe PIDAC-IPC February 2012 Objectives: To provide an overview of the RP/AP Annex
Clostridium difficile, an anaerobic, spore-forming, toxin-forming, gram-positive bacillus, has
 Feature Clostridium difficile Infection Clinical Challenges and Management Strategies PAMELA R. WALTERS, RN, MSN, ACNP-BC BRIAN S. ZUCKERBRAUN, MD Clostridium difficile has become the leading cause of
Feature Clostridium difficile Infection Clinical Challenges and Management Strategies PAMELA R. WALTERS, RN, MSN, ACNP-BC BRIAN S. ZUCKERBRAUN, MD Clostridium difficile has become the leading cause of
Clostridium difficile in Long-Term Care Facilities for the Elderly
 696 INFECTION CONTROL AND HOSPITAL EPIDEMIOLOGY November 2002 SHEA Position Paper Clostridium difficile in Long-Term Care Facilities for the Elderly Andrew E. Simor, MD; Suzanne F. Bradley, MD; Larry J.
696 INFECTION CONTROL AND HOSPITAL EPIDEMIOLOGY November 2002 SHEA Position Paper Clostridium difficile in Long-Term Care Facilities for the Elderly Andrew E. Simor, MD; Suzanne F. Bradley, MD; Larry J.
C-Difficile Infection Control and Prevention Strategies
 C-Difficile Infection Control and Prevention Strategies Adrienne Mims, MD MPH VP, Chief Medical Officer Adrienne.Mims@AlliantQuality.org 1/18/2016 1 Disclosure This educational activity does not have commercial
C-Difficile Infection Control and Prevention Strategies Adrienne Mims, MD MPH VP, Chief Medical Officer Adrienne.Mims@AlliantQuality.org 1/18/2016 1 Disclosure This educational activity does not have commercial
Clostridium difficile Infections and their Treatment
 Department of Medicine Division of Infectious diseases and Division of Gastroenterology Helsinki University Central Hospital Helsinki, Finland Clostridium difficile Infections and their Treatment Eero
Department of Medicine Division of Infectious diseases and Division of Gastroenterology Helsinki University Central Hospital Helsinki, Finland Clostridium difficile Infections and their Treatment Eero
Colocutaneous Fistula. Disclosures
 Colocutaneous Fistula Madhulika G. Varma MD Associate Professor Chief, Colorectal Surgery University of California, San Francisco Honoraria Applied Medical Covidien Disclosures 1 Colocutaneous Fistula
Colocutaneous Fistula Madhulika G. Varma MD Associate Professor Chief, Colorectal Surgery University of California, San Francisco Honoraria Applied Medical Covidien Disclosures 1 Colocutaneous Fistula
New Oral Anticoagulants
 New Oral Anticoagulants Tracy Minichiello, MD Associate Professor of Medicine Chief, San FranciscoVA Anticoagulation and Thrombosis Service Ansell, J. Hematology Copyright 2010 American Society of Hematology.
New Oral Anticoagulants Tracy Minichiello, MD Associate Professor of Medicine Chief, San FranciscoVA Anticoagulation and Thrombosis Service Ansell, J. Hematology Copyright 2010 American Society of Hematology.
Clostridium difficile infection in Europe A CDI Europe Report
 Clostridium difficile infection in Europe A CDI Europe Report CONTENTS FOREWORD 5 1. INTRODUCTION: CDI WHAT IS THE PROBLEM? 6 1.1 How does CDI occur? 6 1.2 How common is CDI? 8 1.3 Who is at risk of CDI?
Clostridium difficile infection in Europe A CDI Europe Report CONTENTS FOREWORD 5 1. INTRODUCTION: CDI WHAT IS THE PROBLEM? 6 1.1 How does CDI occur? 6 1.2 How common is CDI? 8 1.3 Who is at risk of CDI?
Early Colonoscopy in Patients with Acute Diverticulitis Simon Bar-Meir, M.D.
 Early Colonoscopy in Patients with Acute Diverticulitis Simon Bar-Meir, M.D. Professor of Medicine Germanis Kaufman Chair of Gastroenterology Director, Dept. of Gastroenterology Chaim Sheba Medical Center,
Early Colonoscopy in Patients with Acute Diverticulitis Simon Bar-Meir, M.D. Professor of Medicine Germanis Kaufman Chair of Gastroenterology Director, Dept. of Gastroenterology Chaim Sheba Medical Center,
Antimicrobial Therapy of Clostridium difficile-associated Diarrhea
 Med Clin N Am 90 (2006) 1141 1163 Antimicrobial Therapy of Clostridium difficile-associated Diarrhea Emilio Bouza, MD, PhD a, *, Almudena Burillo, MD, PhD b, Patricia Mun oz, MD, PhD a a Department of
Med Clin N Am 90 (2006) 1141 1163 Antimicrobial Therapy of Clostridium difficile-associated Diarrhea Emilio Bouza, MD, PhD a, *, Almudena Burillo, MD, PhD b, Patricia Mun oz, MD, PhD a a Department of
Scientific Committee on Enteric Infections and Foodborne Diseases
 Scientific Committee on Enteric Infections and Foodborne Diseases Epidemiology, prevention and control of Clostridium difficile associated outbreaks in Hong Kong Purpose This paper reviews the latest global
Scientific Committee on Enteric Infections and Foodborne Diseases Epidemiology, prevention and control of Clostridium difficile associated outbreaks in Hong Kong Purpose This paper reviews the latest global
- 301-17. SICKLE CELL SCREENING AND SELECT TOPICS IN PREVENTION OF COMPLICATIONS Mark Schuster, M.D., Ph.D.
 - 301-17. SICKLE CELL SCREENING AND SELECT TOPICS IN PREVENTION OF COMPLICATIONS Mark Schuster, M.D., Ph.D. We used the following sources to construct indicators for sickle cell disease screening for newborns
- 301-17. SICKLE CELL SCREENING AND SELECT TOPICS IN PREVENTION OF COMPLICATIONS Mark Schuster, M.D., Ph.D. We used the following sources to construct indicators for sickle cell disease screening for newborns
HSE Health Protection Surveillance Centre. Sample Root Cause Analysis Tool of Hospital-acquired Clostridium difficile Infection
 Clostridium difficile Sub-Committee Health Protection Surveillance Centre Sample Root Cause Analysis Tool of Hospital-acquired Clostridium difficile Infection Version 3, January 2016 This document has
Clostridium difficile Sub-Committee Health Protection Surveillance Centre Sample Root Cause Analysis Tool of Hospital-acquired Clostridium difficile Infection Version 3, January 2016 This document has
CDC 2015 STD Treatment Guidelines: Update for IHS Providers Sharon Adler M.D., M.P.H.
 CDC 2015 STD Treatment Guidelines: Update for IHS Providers Sharon Adler M.D., M.P.H. Clinical Faculty, CA Prevention Training Center Disclosure Information Sharon Adler MD, MPH I have no financial relationships
CDC 2015 STD Treatment Guidelines: Update for IHS Providers Sharon Adler M.D., M.P.H. Clinical Faculty, CA Prevention Training Center Disclosure Information Sharon Adler MD, MPH I have no financial relationships
C. difficile infection. Background and guidance for hospitals and clinical labs
 infection Background and guidance for hospitals and clinical labs infection is a serious public health concern First described in 1935 by Hall and O Toole, Clostridium difficile is the gram-positive, spore-forming
infection Background and guidance for hospitals and clinical labs infection is a serious public health concern First described in 1935 by Hall and O Toole, Clostridium difficile is the gram-positive, spore-forming
Intracolonic Vancomycin for Adjunctive Treatment of Severe Clostridium difficile Colitis: Indications and Precautions
 Review Article Intracolonic Vancomycin for Adjunctive Treatment of Severe Clostridium difficile Colitis: Indications and Precautions Anucha Apisarnthanarak, M.D. Linda M. Mundy, M.D. ABSTRACT Treatment
Review Article Intracolonic Vancomycin for Adjunctive Treatment of Severe Clostridium difficile Colitis: Indications and Precautions Anucha Apisarnthanarak, M.D. Linda M. Mundy, M.D. ABSTRACT Treatment
Clostridium difficile is a gram-positive,
 Clostridium difficile Associated Diarrhea MICHAEL S. SCHROEDER, M.D., Kaiser Permanente, Fontana, California Clostridium difficile infection is responsible for approximately 3 million cases of diarrhea
Clostridium difficile Associated Diarrhea MICHAEL S. SCHROEDER, M.D., Kaiser Permanente, Fontana, California Clostridium difficile infection is responsible for approximately 3 million cases of diarrhea
Why Do Some Antibiotics Fail?
 Why Do Some Antibiotics Fail? Patty W. Wright, M.D. April 2010 Objective To outline common reasons why antibiotic therapy is not successful and how this can be avoided. And to teach you a little bit about
Why Do Some Antibiotics Fail? Patty W. Wright, M.D. April 2010 Objective To outline common reasons why antibiotic therapy is not successful and how this can be avoided. And to teach you a little bit about
GLOBAL OVERVIEW OF ANTIMICROBIAL RESISTANCE STD AGENTS
 GLOBAL OVERVIEW OF ANTIMICROBIAL RESISTANCE STD AGENTS IN Dr.P.Bhalla Director Professor and Head Dept. of Microbiology Maulana Azad Medical College New Delhi, INDIA STDs & RTIs l HIV l Gonococcal infections/
GLOBAL OVERVIEW OF ANTIMICROBIAL RESISTANCE STD AGENTS IN Dr.P.Bhalla Director Professor and Head Dept. of Microbiology Maulana Azad Medical College New Delhi, INDIA STDs & RTIs l HIV l Gonococcal infections/
Terapia con farmaci biologici e non nella. Sandro Ardizzone. Azienda Ospedaliera Fatebenefratelli e. Ospedale di Rilievo Nazionale Milan
 Terapia con farmaci biologici e non nella Colite Ulcerosa Severa/Refrattaria Sandro Ardizzone Gastrointestinal Unit Azienda Ospedaliera Fatebenefratelli e Oftalmico Ospedale di Rilievo Nazionale Milan
Terapia con farmaci biologici e non nella Colite Ulcerosa Severa/Refrattaria Sandro Ardizzone Gastrointestinal Unit Azienda Ospedaliera Fatebenefratelli e Oftalmico Ospedale di Rilievo Nazionale Milan
GI Bleed. Steven Lichtenstein, D.O. Chief, Division of Gastroenterology Mercy Health System. Director, Endoscopy/GI Lab Mercy Fitzgerald Hospital
 October 3, 2015 GI Bleed Steven Lichtenstein, D.O. Chief, Division of Gastroenterology Mercy Health System Director, Endoscopy/GI Lab Mercy Fitzgerald Hospital Clinical Associate Professor of Medicine
October 3, 2015 GI Bleed Steven Lichtenstein, D.O. Chief, Division of Gastroenterology Mercy Health System Director, Endoscopy/GI Lab Mercy Fitzgerald Hospital Clinical Associate Professor of Medicine
Bowel Preparation for Colon Resection. Eric Klein, M.D. SUNY Downstate Department of Surgery
 Bowel Preparation for Colon Resection Eric Klein, M.D. SUNY Downstate Department of Surgery Historical Perspective During World War II, failure to treat penetrating colon injuries with diversion could
Bowel Preparation for Colon Resection Eric Klein, M.D. SUNY Downstate Department of Surgery Historical Perspective During World War II, failure to treat penetrating colon injuries with diversion could
shea-idsa guideline executive summary
 infection control and hospital epidemiology may 2010, vol. 31, no. 5 shea-idsa guideline Clinical Practice Guidelines for Clostridium difficile Infection in Adults: 2010 Update by the Society for Healthcare
infection control and hospital epidemiology may 2010, vol. 31, no. 5 shea-idsa guideline Clinical Practice Guidelines for Clostridium difficile Infection in Adults: 2010 Update by the Society for Healthcare
New and Emerging Immunotherapies for Multiple Sclerosis: Oral Agents
 New and Emerging Immunotherapies for Multiple Sclerosis: Oral Agents William Tyor, M.D. Chief, Neurology Atlanta VA Medical Center Professor, Department of Neurology Emory University School of Medicine
New and Emerging Immunotherapies for Multiple Sclerosis: Oral Agents William Tyor, M.D. Chief, Neurology Atlanta VA Medical Center Professor, Department of Neurology Emory University School of Medicine
The Nexus of Poop & Public Health
 The Nexus of Poop & Public Health The Power of Fecal Microbiota Transplantation ti Photo: Katie Scott Chief Medical Officer Zain Kassam MD, MPH, FRCPC ACG/VGS/ODSGNA Post Graduate Course Williamsburg,
The Nexus of Poop & Public Health The Power of Fecal Microbiota Transplantation ti Photo: Katie Scott Chief Medical Officer Zain Kassam MD, MPH, FRCPC ACG/VGS/ODSGNA Post Graduate Course Williamsburg,
Gruppo di lavoro: Malattie Tromboemboliche
 Gruppo di lavoro: Malattie Tromboemboliche 2381 Soluble Recombinant Thrombomodulin Ameliorates Hematological Malignancy-Induced Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation More Promptly Than Conventional Anticoagulant
Gruppo di lavoro: Malattie Tromboemboliche 2381 Soluble Recombinant Thrombomodulin Ameliorates Hematological Malignancy-Induced Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation More Promptly Than Conventional Anticoagulant
ESCMID Online Lecture Library. by author
 Do statins improve outcomes of patients with sepsis and pneumonia? Jordi Carratalà Department of Infectious Diseases Statins for sepsis & community-acquired pneumonia Sepsis and CAP are major healthcare
Do statins improve outcomes of patients with sepsis and pneumonia? Jordi Carratalà Department of Infectious Diseases Statins for sepsis & community-acquired pneumonia Sepsis and CAP are major healthcare
4/18/14. Background. Evaluation of a Morphine Weaning Protocol in Pediatric Intensive Care Patients. Background. Signs and Symptoms of Withdrawal
 Background 1 Evaluation of a Morphine Weaning Protocol in Pediatric Intensive Care Patients Alyssa Cavanaugh, PharmD PGY1 Pharmacy Resident Children s Hospital of Michigan **The speaker has no actual or
Background 1 Evaluation of a Morphine Weaning Protocol in Pediatric Intensive Care Patients Alyssa Cavanaugh, PharmD PGY1 Pharmacy Resident Children s Hospital of Michigan **The speaker has no actual or
Omega-3 fatty acids improve the diagnosis-related clinical outcome. Critical Care Medicine April 2006;34(4):972-9
 Omega-3 fatty acids improve the diagnosis-related clinical outcome 1 Critical Care Medicine April 2006;34(4):972-9 Volume 34(4), April 2006, pp 972-979 Heller, Axel R. MD, PhD; Rössler, Susann; Litz, Rainer
Omega-3 fatty acids improve the diagnosis-related clinical outcome 1 Critical Care Medicine April 2006;34(4):972-9 Volume 34(4), April 2006, pp 972-979 Heller, Axel R. MD, PhD; Rössler, Susann; Litz, Rainer
HEPATITIS WEB STUDY Acute Hepatitis C Virus Infection: Epidemiology, Clinical Features, and Diagnosis
 HEPATITIS WEB STUDY Acute C Virus Infection: Epidemiology, Clinical Features, and Diagnosis H. Nina Kim, MD Assistant Professor of Medicine Division of Infectious Diseases University of Washington School
HEPATITIS WEB STUDY Acute C Virus Infection: Epidemiology, Clinical Features, and Diagnosis H. Nina Kim, MD Assistant Professor of Medicine Division of Infectious Diseases University of Washington School
Title: Antibiotic Guideline for Acute Pelvic Inflammatory Disease
 Title: Antibiotic Guideline for Acute Pelvic Inflammatory Disease Version 3 Date ratified December 2007 Review date December 2009 Ratified by NUH Antimicrobial Guidelines Committee Gynaecology Directorate
Title: Antibiotic Guideline for Acute Pelvic Inflammatory Disease Version 3 Date ratified December 2007 Review date December 2009 Ratified by NUH Antimicrobial Guidelines Committee Gynaecology Directorate
Lamivudine for Patients with hronic Hepatitis B and Advanced Liver Disease. From : New England Journal of Medicine
 Lamivudine for Patients with hronic Hepatitis B and Advanced Liver Disease From : New England Journal of Medicine Volume 351:1521-1531, Number 15, Oct 7, 2004 馬 偕 紀 念 醫 院 一 般 內 科, 肝 膽 腸 胃 科 新 竹 分 院 陳 重
Lamivudine for Patients with hronic Hepatitis B and Advanced Liver Disease From : New England Journal of Medicine Volume 351:1521-1531, Number 15, Oct 7, 2004 馬 偕 紀 念 醫 院 一 般 內 科, 肝 膽 腸 胃 科 新 竹 分 院 陳 重
Massachusetts Department of Developmental Services MRSA, VRE, and C. Diff Management Protocol
 Massachusetts Department of Developmental Services MRSA, VRE, and C. Diff Management Protocol PURPOSE: To provide guidance for personnel in order to prevent the spread of Antibiotic Resistant Microorganisms
Massachusetts Department of Developmental Services MRSA, VRE, and C. Diff Management Protocol PURPOSE: To provide guidance for personnel in order to prevent the spread of Antibiotic Resistant Microorganisms
Solid Organ Transplantation
 Solid Organ Transplantation Infection Prevention And Control Transplant Atlantic 2011 October 13/2011 Kathy Hart Introduction In the past several years, the drugs that we use, the surgeries themselves,
Solid Organ Transplantation Infection Prevention And Control Transplant Atlantic 2011 October 13/2011 Kathy Hart Introduction In the past several years, the drugs that we use, the surgeries themselves,
POAC CLINICAL GUIDELINE
 POAC CLINICAL GUIDELINE Acute Pylonephritis DIAGNOSIS COMPLICATED PYELONEPHRITIS EXCLUSION CRITERIA: Male Known or suspected renal impairment (egfr < 60) Abnormality of renal tract Known or suspected renal
POAC CLINICAL GUIDELINE Acute Pylonephritis DIAGNOSIS COMPLICATED PYELONEPHRITIS EXCLUSION CRITERIA: Male Known or suspected renal impairment (egfr < 60) Abnormality of renal tract Known or suspected renal
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE. Multiple Technology Appraisal
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Multiple Technology Appraisal Infliximab, adalimumab and golimumab for treating moderately to severely active ulcerative colitis after the failure of conventional
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Multiple Technology Appraisal Infliximab, adalimumab and golimumab for treating moderately to severely active ulcerative colitis after the failure of conventional
Acute abdominal conditions Key Points
 7 Acute abdominal conditions Key Points 7.1 ASSESSMENT AND DIAGNOSIS Referred abdominal pain Fore gut pain (stomach, duodenum, gall bladder) is referred to the upper abdomen Mid gut pain (small intestine,
7 Acute abdominal conditions Key Points 7.1 ASSESSMENT AND DIAGNOSIS Referred abdominal pain Fore gut pain (stomach, duodenum, gall bladder) is referred to the upper abdomen Mid gut pain (small intestine,
Open Ventral Hernia Repair
 Ventral Hernias Open Ventral Hernia Repair UCSF Postgraduate Course in General Surgery Maui, HI March 21, 2011 Hobart W. Harris, MD, MPH Ventral Hernias: National Experience Occur following 11-23% of laparotomies,
Ventral Hernias Open Ventral Hernia Repair UCSF Postgraduate Course in General Surgery Maui, HI March 21, 2011 Hobart W. Harris, MD, MPH Ventral Hernias: National Experience Occur following 11-23% of laparotomies,
Hematologic Malignancies/Stem Cell Transplantation Program Clinical Section UCLA Health System Los Angeles, CA 90095
 Hematologic Malignancies/Stem Cell Transplantation Program Clinical Section UCLA Health System Los Angeles, CA 90095 CS 6.4 DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT OF CYTOMEGALOVIRUS (CMV) INFECTION AND DISEASE Location:
Hematologic Malignancies/Stem Cell Transplantation Program Clinical Section UCLA Health System Los Angeles, CA 90095 CS 6.4 DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT OF CYTOMEGALOVIRUS (CMV) INFECTION AND DISEASE Location:
HOMEOPATHY AS AN ALTERNATIVE TO ANTIBIOTICS
 HOMEOPATHY AS AN ALTERNATIVE TO ANTIBIOTICS Professor Dr. Michael FRASS Medical University of Vienna, Department Medicine I Doctor s Asscociation for Classical Homeopathy www.aekh.at President, Umbrella
HOMEOPATHY AS AN ALTERNATIVE TO ANTIBIOTICS Professor Dr. Michael FRASS Medical University of Vienna, Department Medicine I Doctor s Asscociation for Classical Homeopathy www.aekh.at President, Umbrella
Appendix M: Guidelines for the Prophylaxis and Management of Intraabdominal, Biliary, and Appendiceal Infections
 Appendix M: Guidelines for the Prophylaxis and Management of Intraabdominal, Biliary, and Appendiceal Infections University of Wisconsin Hospital and Clinics Intraabdominal Infections Prophylaxis and Management
Appendix M: Guidelines for the Prophylaxis and Management of Intraabdominal, Biliary, and Appendiceal Infections University of Wisconsin Hospital and Clinics Intraabdominal Infections Prophylaxis and Management
Clinical Study Outcomes and Risk Factors Associated with Clostridium difficile Diarrhea in Hospitalized Adult Patients
 Hindawi Publishing Corporation Gastroenterology Research and Practice Volume 2015, Article ID 346341, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/346341 Clinical Study Outcomes and Risk Factors Associated with
Hindawi Publishing Corporation Gastroenterology Research and Practice Volume 2015, Article ID 346341, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/346341 Clinical Study Outcomes and Risk Factors Associated with
Equine Equine Diarrhea Diarrhea Diarrhea in the Horse: Salmonella and Other Infections Introduction Clinical Signs
 Equine Diarrhea Diarrhea in the Horse: Salmonella and Other Infections Amanda M. House, DVM, DACVIM Assistant Professor Large Animal Clinical Sciences UF College of Veterinary Medicine Introduction Clinical
Equine Diarrhea Diarrhea in the Horse: Salmonella and Other Infections Amanda M. House, DVM, DACVIM Assistant Professor Large Animal Clinical Sciences UF College of Veterinary Medicine Introduction Clinical
Surveillance, Diagnosis and Management of Clostridium difficile Infection in Ireland. National Clinical Guideline No. 3
 Surveillance, Diagnosis and Management of Clostridium difficile Infection in Ireland National Clinical Guideline No. 3 June 2014 National Clinical Effectiveness Committee (NCEC) The National Clinical Effectiveness
Surveillance, Diagnosis and Management of Clostridium difficile Infection in Ireland National Clinical Guideline No. 3 June 2014 National Clinical Effectiveness Committee (NCEC) The National Clinical Effectiveness
