basic BGP in Huawei CLI
|
|
|
- Raymond McCarthy
- 9 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
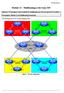
1 basic BGP in Huawei CLI BGP stands for Border Gateway Protocol. It is widely used among Internet Service Providers to make core routing decisions on the Internet. The current BGP version is BGP-4 defined in RFC BGP uses TCP port 179 as its underlying delivery mechanism to increase the reliability of the peer connection. BGP is called a path vector routing protocol. It uses a list of AS numbers through which the packet must pass in order to reach the destination. This list of AS numbers is associated with a BGP route and is called the AS_Path attribute. AS_Path is one of several path attributes associated with each BGP route. How does a BGP select best path to a destination network, you can read at how does BGP select routes. I do not want to describe BGP in details, as this is out of the scope of this article. What I want to do is to show you, how to configure basic BGP features using Huawei CLI. Especially I want to show you how to: run BGP protocol configure IBGP peering sessions using peer groups configure EBGP peering advertise networks. Let s assume that we have three Autonomous Systems (see topology below): AS50 with only one BGP router, terminating EBGP peering with AS100 AS100 with three routers forming IBGP full mesh using peer group AS55 where labnarior5 router will form two EBGP peering sessions with AS100. LabnarioR1 in AS50 will be advertising three prefixes, which will pass through AS100 to AS55. I want labnarior5 router to be able to receive these three routes and reach them (be able to ping them).
2 So let s start with BGP configuration. First I want to configure labnarior1 router to run BGP AS50 and form EBGP peering session with labnarior2 router in AS100 (interface IP addressing configuration is omitted): [labnarior1]bgp 50 [labnarior1-bgp]undo synchronization [labnarior1-bgp]undo summary automatic [labnarior1-bgp]peer as-number 100 Now I can configure AS100. I want my three routers to form an IBGP full mesh. I will use physical interfaces to establish peering sessions for simplicity. Usually it is better to use loopback interfaces when multiple physical links exist inside AS. First I will configure EBGP session to AS50: [labnarior2]bgp 100 [labnarior2-bgp]undo synchronization [labnarior2-bgp]undo summary automatic [labnarior2-bgp]peer as-number 50 Let s check if our EBGP session between AS50 and AS100 is established: [labnarior2-bgp]display bgp peer BGP local router ID : Local AS number : 100 Total number of peers : 1 Peers in established state : 1 Peer V AS MsgRcvd MsgSent OutQ Up/Down State PrefRcv :51:01 Established 0 EBGP session between AS50 and 100 is established, so I can start configuring my IBGP peering sessions in AS100. I will do that using a peer group named ibgp. Of course it is possible to specify every single peer and assign BGP specific parameters to it, but I want to use a peer group, where every BGP parameter will be assigned to it, including peering routers. [labnarior2-bgp]bgp 100 [labnarior2-bgp] group ibgp internal [labnarior2-bgp] peer ibgp next-hop-local [labnarior2-bgp] peer group ibgp [labnarior2-bgp] peer group ibgp As you see above, my ibgp peer group definition includes group type internal. When configuring peer group type internal, there is no need to assign AS number to this group. Every peer belonging to a group type internal, inherits AS number of the local AS. It is also possible to define a peer group type external. Let s check BGP configuration on labnarior2 router: bgp 100 peer as-number 50 group ibgp internal peer as-number 100 peer group ibgp peer as-number 100 peer group ibgp
3 ipv4-family unicast undo synchronization peer enable peer ibgp enable peer ibgp next-hop-local peer enable peer group ibgp peer enable peer group ibgp All the ibgp group parameters are assigned to peering routers. Now labnarior3 and labnarior4 routers can be configured in the same way. Both also should be configured to peer with AS55 and labnarior5 router: [labnarior3]bgp 100 [labnarior3-bgp] undo synchronization [labnarior3-bgp] undo summary automatic [labnarior3-bgp] group ibgp internal [labnarior3-bgp] peer ibgp next-hop-local [labnarior3-bgp] peer group ibgp [labnarior3-bgp] peer group ibgp [labnarior3-bgp] peer as-number 55 [labnarior4]bgp 100 [labnarior4-bgp] undo synchronization [labnarior4-bgp] undo summary automatic [labnarior4-bgp] group ibgp internal [labnarior4-bgp] peer ibgp next-hop-local [labnarior4-bgp] peer group ibgp [labnarior4-bgp] peer group ibgp [labnarior4-bgp] peer as-number 55 Let s check BGP configuration and IBGP peering sessions on labnarior3 and labnarior4: [labnarior3-bgp]dis this bgp 100 peer as-number 55 group ibgp internal peer as-number 100 peer group ibgp peer as-number 100 peer group ibgp ipv4-family unicast undo synchronization peer enable peer ibgp enable peer ibgp next-hop-local peer enable peer group ibgp peer enable peer group ibgp return [labnarior3-bgp]dis bgp peer BGP local router ID : Local AS number : 100
4 Total number of peers : 3 Peers in established state : 3 Peer V AS MsgRcvd MsgSent OutQ Up/Down State PrefRcv :00:16 Idle :37:50 Established :32:49 Established 0 [labnarior4-bgp]dis this bgp 100 peer as-number 55 group ibgp internal peer as-number 100 peer group ibgp peer as-number 100 peer group ibgp ipv4-family unicast undo synchronization peer enable peer ibgp enable peer ibgp next-hop-local peer enable peer group ibgp peer enable peer group ibgp return [labnarior4-bgp]dis bgp peer BGP local router ID : Local AS number : 100 Total number of peers : 3 Peers in established state : 3 Peer V AS MsgRcvd MsgSent OutQ Up/Down State PrefRcv :00:17 Idle :43:39 Established :38:38 Established 0 Of course to have EBGP session established, labnarior5 should be configured first ;). [labnarior5]bgp 55 [labnarior5-bgp] undo summary automatic [labnarior5-bgp] undo synchronization [labnarior5-bgp] peer as-number 100 [labnarior5-bgp] peer as-number 100 [labnarior5-bgp] [labnarior5-bgp]dis bgp peer BGP local router ID : Local AS number : 55 Total number of peers : 2 Peers in established state : 2 Peer V AS MsgRcvd MsgSent OutQ Up/Down State PrefRcv :43:55 Established :43:54 Established 0
5 All my BGP peering sessions are configured now. As the next step I want my AS50 to advertise some prefixes. These prefixes should pass to AS55. I will use loopback interfaces to simulate some networks: [labnarior1]interface LoopBack0 [labnarior1-loopback0] ip address [labnarior1-loopback0] interface LoopBack1 [labnarior1-loopback1] ip address [labnarior1-loopback1] interface LoopBack2 [labnarior1-loopback2] ip address [labnarior1]bgp 50 [labnarior1-bgp] network [labnarior1-bgp] network [labnarior1-bgp] network Remember to use the same network mask under the BGP process and the corresponding interface. Let s check if labnarior1 is advertising my prefixes: [labnarior1]dis bgp routing-table BGP Local router ID is Status codes: * - valid, > - best, d - damped, h - history, i - internal, s - suppressed, S - Stale Origin : i - IGP, e - EGP,? - incomplete Total Number of Routes: 3 Network NextHop MED LocPrf PrefVal Path/Ogn *> / i *> / i *> / i LabnarioR1 now advertises three prefixes. These prefixes should pass through AS100 to AS55. Let s check labnarior5 BGP table: [labnarior5]dis bgp routing-table BGP Local router ID is Status codes: * - valid, > - best, d - damped, h - history, i - internal, s - suppressed, S - Stale Origin : i - IGP, e - EGP,? - incomplete Total Number of Routes: 6 Network NextHop MED LocPrf PrefVal Path/Ogn *> / i * i *> / i * i *> / i * i
6 LabnarioR5 router has all three prefixes in its BGP table. It prefers labnarior3 router as its next hop to reach these prefixes. Does this mean that labnarior5 can ping these networks? Let s check: <labnarior5>ping PING : 56 data bytes, press CTRL_C to break ping statistics packet(s) transmitted 0 packet(s) received % packet loss Why is it like that? Read my next article about BGP.
APNIC elearning: BGP Basics. Contact: [email protected]. erou03_v1.0
 erou03_v1.0 APNIC elearning: BGP Basics Contact: [email protected] Overview What is BGP? BGP Features Path Vector Routing Protocol Peering and Transit BGP General Operation BGP Terminology BGP Attributes
erou03_v1.0 APNIC elearning: BGP Basics Contact: [email protected] Overview What is BGP? BGP Features Path Vector Routing Protocol Peering and Transit BGP General Operation BGP Terminology BGP Attributes
APNIC elearning: BGP Attributes
 APNIC elearning: BGP Attributes Contact: [email protected] erou04_v1.0 Overview BGP Attributes Well-known and Optional Attributes AS Path AS Loop Detection ibgp and ebgp Next Hop Next Hop Best Practice
APNIC elearning: BGP Attributes Contact: [email protected] erou04_v1.0 Overview BGP Attributes Well-known and Optional Attributes AS Path AS Loop Detection ibgp and ebgp Next Hop Next Hop Best Practice
Understanding Route Aggregation in BGP
 Understanding Route Aggregation in BGP Document ID: 5441 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Network Diagram Aggregate Without the as set Argument Aggregate with
Understanding Route Aggregation in BGP Document ID: 5441 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Network Diagram Aggregate Without the as set Argument Aggregate with
Lab 10: Confi guring Basic Border Gateway Protocol
 Lab 10: Objective Confi gure P1R1 for basic Exterior Border Gateway Protocol (EBGP). Confi gure P1R1 and P1R2 for Interior Border Gateway Protocol (IBGP). Confi rm BGP connectivity. Lab Topology For this
Lab 10: Objective Confi gure P1R1 for basic Exterior Border Gateway Protocol (EBGP). Confi gure P1R1 and P1R2 for Interior Border Gateway Protocol (IBGP). Confi rm BGP connectivity. Lab Topology For this
BGP Router Startup Message Flow
 LEG: Brief BGP Router Startup Message Flow This sequence diagram was generated with EventStudio System Designer (http://www.eventhelix.com/eventstudio). The Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) is an inter-autonomous
LEG: Brief BGP Router Startup Message Flow This sequence diagram was generated with EventStudio System Designer (http://www.eventhelix.com/eventstudio). The Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) is an inter-autonomous
Border Gateway Protocol (BGP)
 Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) Petr Grygárek rek 1 Role of Autonomous Systems on the Internet 2 Autonomous systems Not possible to maintain complete Internet topology information on all routers big database,
Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) Petr Grygárek rek 1 Role of Autonomous Systems on the Internet 2 Autonomous systems Not possible to maintain complete Internet topology information on all routers big database,
BGP Terminology, Concepts, and Operation. Chapter 6 2007 2010, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public
 BGP Terminology, Concepts, and Operation 1 IGP versus EGP Interior gateway protocol (IGP) A routing protocol operating within an Autonomous System (AS). RIP, OSPF, and EIGRP are IGPs. Exterior gateway
BGP Terminology, Concepts, and Operation 1 IGP versus EGP Interior gateway protocol (IGP) A routing protocol operating within an Autonomous System (AS). RIP, OSPF, and EIGRP are IGPs. Exterior gateway
BGP Basics. BGP Uses TCP 179 ibgp - BGP Peers in the same AS ebgp - BGP Peers in different AS's. 64512-65535 Private BGP ASN. BGP Router Processes
 BGP Basics BGPv4 - RFC 4271 - IPv6 support Path vector routing protocol EGP Routing between AS'es Classless Transit Area - Area used to reach other areas. Requires full routing table (no default routes).
BGP Basics BGPv4 - RFC 4271 - IPv6 support Path vector routing protocol EGP Routing between AS'es Classless Transit Area - Area used to reach other areas. Requires full routing table (no default routes).
Border Gateway Protocol BGP4 (2)
 Border Gateway Protocol BGP4 (2) Professor Richard Harris School of Engineering and Advanced Technology (SEAT) Presentation Outline Border Gateway Protocol - Continued Computer Networks - 1/2 Learning
Border Gateway Protocol BGP4 (2) Professor Richard Harris School of Engineering and Advanced Technology (SEAT) Presentation Outline Border Gateway Protocol - Continued Computer Networks - 1/2 Learning
BGP overview BGP operations BGP messages BGP decision algorithm BGP states
 BGP overview BGP operations BGP messages BGP decision algorithm BGP states 1 BGP overview Currently in version 4. InterAS (or Interdomain) routing protocol for exchanging network reachability information
BGP overview BGP operations BGP messages BGP decision algorithm BGP states 1 BGP overview Currently in version 4. InterAS (or Interdomain) routing protocol for exchanging network reachability information
How To Understand Bg
 Table of Contents BGP Case Studies...1 BGP4 Case Studies Section 1...3 Contents...3 Introduction...3 How Does BGP Work?...3 ebgp and ibgp...3 Enabling BGP Routing...4 Forming BGP Neighbors...4 BGP and
Table of Contents BGP Case Studies...1 BGP4 Case Studies Section 1...3 Contents...3 Introduction...3 How Does BGP Work?...3 ebgp and ibgp...3 Enabling BGP Routing...4 Forming BGP Neighbors...4 BGP and
Module 7. Routing and Congestion Control. Version 2 CSE IIT, Kharagpur
 Module 7 Routing and Congestion Control Lesson 4 Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) Specific Instructional Objectives On completion of this lesson, the students will be able to: Explain the operation of the
Module 7 Routing and Congestion Control Lesson 4 Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) Specific Instructional Objectives On completion of this lesson, the students will be able to: Explain the operation of the
Using the Border Gateway Protocol for Interdomain Routing
 CHAPTER 12 Using the Border Gateway Protocol for Interdomain Routing The Border Gateway Protocol (BGP), defined in RFC 1771, provides loop-free interdomain routing between autonomous systems. (An autonomous
CHAPTER 12 Using the Border Gateway Protocol for Interdomain Routing The Border Gateway Protocol (BGP), defined in RFC 1771, provides loop-free interdomain routing between autonomous systems. (An autonomous
BGP Attributes and Path Selection
 BGP Attributes and Path Selection ISP Workshops Last updated 29 th March 2015 1 BGP Attributes BGP s policy tool kit 2 What Is an Attribute?... Next Hop AS Path MED...... p Part of a BGP Update p Describes
BGP Attributes and Path Selection ISP Workshops Last updated 29 th March 2015 1 BGP Attributes BGP s policy tool kit 2 What Is an Attribute?... Next Hop AS Path MED...... p Part of a BGP Update p Describes
BSCI Module 6 BGP. Configuring Basic BGP. BSCI Module 6
 Configuring Basic BGP BSCI Module 6 BSCI Module 6 2006 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 1 BSCI Module 6 BGP An AS is a collection of networks under a single technical administration.
Configuring Basic BGP BSCI Module 6 BSCI Module 6 2006 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 1 BSCI Module 6 BGP An AS is a collection of networks under a single technical administration.
Routing Protocol - BGP
 Routing Protocol - BGP BGP Enterprise Network BGP ISP AS 3000 AS 2000 BGP is using between Autonomous Systems BGP(cont.) RFC 1771(BGPv4) Support CIDR Transfer the AS information to reach destination Using
Routing Protocol - BGP BGP Enterprise Network BGP ISP AS 3000 AS 2000 BGP is using between Autonomous Systems BGP(cont.) RFC 1771(BGPv4) Support CIDR Transfer the AS information to reach destination Using
BGP Best Path Selection Algorithm
 BGP Best Path Selection Algorithm Document ID: 13753 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Why Routers Ignore Paths How the Best Path Algorithm Works Example: BGP
BGP Best Path Selection Algorithm Document ID: 13753 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Why Routers Ignore Paths How the Best Path Algorithm Works Example: BGP
Lecture 18: Border Gateway Protocol"
 Lecture 18: Border Gateway Protocol" CSE 123: Computer Networks Alex C. Snoeren HW 3 due Wednesday! Some figures courtesy Mike Freedman Lecture 18 Overview" Path-vector Routing Allows scalable, informed
Lecture 18: Border Gateway Protocol" CSE 123: Computer Networks Alex C. Snoeren HW 3 due Wednesday! Some figures courtesy Mike Freedman Lecture 18 Overview" Path-vector Routing Allows scalable, informed
Inter-domain Routing Basics. Border Gateway Protocol. Inter-domain Routing Basics. Inter-domain Routing Basics. Exterior routing protocols created to:
 Border Gateway Protocol Exterior routing protocols created to: control the expansion of routing tables provide a structured view of the Internet by segregating routing domains into separate administrations
Border Gateway Protocol Exterior routing protocols created to: control the expansion of routing tables provide a structured view of the Internet by segregating routing domains into separate administrations
CS551 External v.s. Internal BGP
 CS551 External v.s. Internal BGP Bill Cheng http://merlot.usc.edu/cs551-f12 1 Exterior vs. Interior World vs. me EGP vs. IGP Little control vs. complete administrative control BGP (and GGP, Hello, EGP)
CS551 External v.s. Internal BGP Bill Cheng http://merlot.usc.edu/cs551-f12 1 Exterior vs. Interior World vs. me EGP vs. IGP Little control vs. complete administrative control BGP (and GGP, Hello, EGP)
BGP1 Multihoming and Traffic Engineering
 83950 Telecommunications Laboratory Course BGP1 BGP1 Multihoming and Traffic Engineering date & time student # name 1 2 bgp-tyo.tex,v 1.11 2005/04/18 14:09:14 ams Exp 1/17 Part I Home Assignment 1 General
83950 Telecommunications Laboratory Course BGP1 BGP1 Multihoming and Traffic Engineering date & time student # name 1 2 bgp-tyo.tex,v 1.11 2005/04/18 14:09:14 ams Exp 1/17 Part I Home Assignment 1 General
IPv6 over MPLS VPN. Contents. Prerequisites. Document ID: 112085. Requirements
 IPv6 over MPLS VPN Document ID: 112085 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure Network Diagram VRF Configuration Multiprotocol BGP (MP BGP) Configuration
IPv6 over MPLS VPN Document ID: 112085 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure Network Diagram VRF Configuration Multiprotocol BGP (MP BGP) Configuration
E6998-02: Internet Routing
 E6998-02: Internet Routing Lecture 13 Border Gateway Protocol, Part II John Ioannidis AT&T Labs Research [email protected] Copyright 2002 by John Ioannidis. All Rights Reserved. Announcements Lectures
E6998-02: Internet Routing Lecture 13 Border Gateway Protocol, Part II John Ioannidis AT&T Labs Research [email protected] Copyright 2002 by John Ioannidis. All Rights Reserved. Announcements Lectures
How To Set Up Bgg On A Network With A Network On A Pb Or Pb On A Pc Or Ipa On A Bg On Pc Or Pv On A Ipa (Netb) On A Router On A 2
 61200860L1-29.4E March 2012 Configuration Guide Configuring Border Gateway Protocol in AOS for Releases Prior to 18.03.00/R10.1.0 This guide only addresses BGP in AOS data products using AOS firmware prior
61200860L1-29.4E March 2012 Configuration Guide Configuring Border Gateway Protocol in AOS for Releases Prior to 18.03.00/R10.1.0 This guide only addresses BGP in AOS data products using AOS firmware prior
Exterior Gateway Protocols (BGP)
 Exterior Gateway Protocols (BGP) Internet Structure Large ISP Large ISP Stub Dial-Up ISP Small ISP Stub Stub Stub Autonomous Systems (AS) Internet is not a single network! The Internet is a collection
Exterior Gateway Protocols (BGP) Internet Structure Large ISP Large ISP Stub Dial-Up ISP Small ISP Stub Stub Stub Autonomous Systems (AS) Internet is not a single network! The Internet is a collection
BGP Link Bandwidth. Finding Feature Information. Contents
 The BGP (Border Gateway Protocol) Link Bandwidth feature is used to advertise the bandwidth of an autonomous system exit link as an extended community. This feature is configured for links between directly
The BGP (Border Gateway Protocol) Link Bandwidth feature is used to advertise the bandwidth of an autonomous system exit link as an extended community. This feature is configured for links between directly
Analyzing Capabilities of Commercial and Open-Source Routers to Implement Atomic BGP
 Telfor Journal, Vol. 2, No. 1, 2010. 13 Analyzing Capabilities of Commercial and Open-Source Routers to Implement Atomic BGP Aleksandar Cvjetić and Aleksandra Smiljanić Abstract The paper analyzes implementations
Telfor Journal, Vol. 2, No. 1, 2010. 13 Analyzing Capabilities of Commercial and Open-Source Routers to Implement Atomic BGP Aleksandar Cvjetić and Aleksandra Smiljanić Abstract The paper analyzes implementations
Configuring and Testing Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) on Basis of Cisco Hardware and Linux Gentoo with Quagga Package (Zebra)
 Configuring and Testing Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) on Basis of Cisco Hardware and Linux Gentoo with Quagga Package (Zebra) Contents Introduction Used Abbreviations Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) Overview
Configuring and Testing Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) on Basis of Cisco Hardware and Linux Gentoo with Quagga Package (Zebra) Contents Introduction Used Abbreviations Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) Overview
Monitoring and Troubleshooting BGP Neighbor Sessions
 Application Note Monitoring and Troubleshooting BGP Neighbor Sessions Juniper Networks, Inc. 1194 North Mathilda Avenue Sunnyvale, CA 94089 USA 408 745 2000 or 888 JUNIPER www.juniper.net Part Number:
Application Note Monitoring and Troubleshooting BGP Neighbor Sessions Juniper Networks, Inc. 1194 North Mathilda Avenue Sunnyvale, CA 94089 USA 408 745 2000 or 888 JUNIPER www.juniper.net Part Number:
- Border Gateway Protocol -
 1 Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) - Border Gateway Protocol - BGP is a standardized exterior gateway protocol (EGP), as opposed to RIP, OSPF, and EIGRP which are interior gateway protocols (IGP s). BGP Version
1 Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) - Border Gateway Protocol - BGP is a standardized exterior gateway protocol (EGP), as opposed to RIP, OSPF, and EIGRP which are interior gateway protocols (IGP s). BGP Version
Chapter 49 Border Gateway Protocol version 4 (BGP-4)
 Chapter 49 Border Gateway Protocol version 4 (BGP-4) Introduction... 1-3 Overview of BGP-4... 1-3 BGP Operation... 1-5 BGP Attributes... 1-6 BGP Route Selection... 1-8 Classless Inter-domain Routing (CIDR)
Chapter 49 Border Gateway Protocol version 4 (BGP-4) Introduction... 1-3 Overview of BGP-4... 1-3 BGP Operation... 1-5 BGP Attributes... 1-6 BGP Route Selection... 1-8 Classless Inter-domain Routing (CIDR)
BGP Link Bandwidth. Finding Feature Information. Prerequisites for BGP Link Bandwidth
 The Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) Link Bandwidth feature is used to advertise the bandwidth of an autonomous system exit link as an extended community. This feature is configured for links between directly
The Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) Link Bandwidth feature is used to advertise the bandwidth of an autonomous system exit link as an extended community. This feature is configured for links between directly
Internet inter-as routing: BGP
 Internet inter-as routing: BGP BGP (Border Gateway Protocol): the de facto standard BGP provides each AS a means to: 1. Obtain subnet reachability information from neighboring ASs. 2. Propagate the reachability
Internet inter-as routing: BGP BGP (Border Gateway Protocol): the de facto standard BGP provides each AS a means to: 1. Obtain subnet reachability information from neighboring ASs. 2. Propagate the reachability
BGP: Frequently Asked Questions
 BGP: Frequently Asked Questions Document ID: 5816 Contents Introduction How do I configure BGP? How do I configure BGP with the use of a loopback address? What is the order of preference of attributes
BGP: Frequently Asked Questions Document ID: 5816 Contents Introduction How do I configure BGP? How do I configure BGP with the use of a loopback address? What is the order of preference of attributes
Configuring BGP. Cisco s BGP Implementation
 Configuring BGP This chapter describes how to configure Border Gateway Protocol (BGP). For a complete description of the BGP commands in this chapter, refer to the BGP s chapter of the Network Protocols
Configuring BGP This chapter describes how to configure Border Gateway Protocol (BGP). For a complete description of the BGP commands in this chapter, refer to the BGP s chapter of the Network Protocols
Understanding Route Redistribution & Filtering
 Understanding Route Redistribution & Filtering When to Redistribute and Filter PAN-OS 5.0 Revision B 2013, Palo Alto Networks, Inc. www.paloaltonetworks.com Contents Overview... 3 Route Redistribution......
Understanding Route Redistribution & Filtering When to Redistribute and Filter PAN-OS 5.0 Revision B 2013, Palo Alto Networks, Inc. www.paloaltonetworks.com Contents Overview... 3 Route Redistribution......
Chapter 6: Implementing a Border Gateway Protocol Solution for ISP Connectivity
 : Implementing a Border Gateway Protocol Solution for ISP Connectivity CCNP ROUTE: Implementing IP Routing ROUTE v6 1 Objectives Describe basic BGP terminology and operation, including EBGP and IBGP. Configure
: Implementing a Border Gateway Protocol Solution for ISP Connectivity CCNP ROUTE: Implementing IP Routing ROUTE v6 1 Objectives Describe basic BGP terminology and operation, including EBGP and IBGP. Configure
BGP4 Case Studies/Tutorial
 BGP4 Case Studies/Tutorial Sam Halabi-cisco Systems The purpose of this paper is to introduce the reader to the latest in BGP4 terminology and design issues. It is targeted to the novice as well as the
BGP4 Case Studies/Tutorial Sam Halabi-cisco Systems The purpose of this paper is to introduce the reader to the latest in BGP4 terminology and design issues. It is targeted to the novice as well as the
H3C large-scale network routing
 Exam : GB0-380 Title : H3C large-scale network routing Version : DEMO 1 / 9 1.L L L L A. BGP B. RIP-1 C. RIP-2 D. IS-IS Answer: CD 2. EGP A. BGP OSPF B. OSPF RIP C. BGP RIP D. OSPF BGP Answer: A 3. 4 10.0.0.0/24
Exam : GB0-380 Title : H3C large-scale network routing Version : DEMO 1 / 9 1.L L L L A. BGP B. RIP-1 C. RIP-2 D. IS-IS Answer: CD 2. EGP A. BGP OSPF B. OSPF RIP C. BGP RIP D. OSPF BGP Answer: A 3. 4 10.0.0.0/24
Examination. IP routning på Internet och andra sammansatta nät, DD2491 IP routing in the Internet and other complex networks, DD2491
 Examination IP routning på Internet och andra sammansatta nät, DD2491 IP routing in the Internet and other complex networks, DD2491 Date: December 15 2009 14:00 18:00 1. No help material is allowed - You
Examination IP routning på Internet och andra sammansatta nät, DD2491 IP routing in the Internet and other complex networks, DD2491 Date: December 15 2009 14:00 18:00 1. No help material is allowed - You
Application Note. Failover through BGP route health injection
 Application Note Document version: v1.2 Last update: 8th November 2013 Purpose This application note aims to describe how to build a high available platform using BGP routing protocol to choose the best
Application Note Document version: v1.2 Last update: 8th November 2013 Purpose This application note aims to describe how to build a high available platform using BGP routing protocol to choose the best
How To Import Ipv4 From Global To Global On Cisco Vrf.Net (Vf) On A Vf-Net (Virtual Private Network) On Ipv2 (Vfs) On An Ipv3 (Vv
 BGP Support for IP Prefix Import from Global Table into a VRF Table The BGP Support for IP Prefix Import from Global Table into a VRF Table feature introduces the capability to import IPv4 unicast prefixes
BGP Support for IP Prefix Import from Global Table into a VRF Table The BGP Support for IP Prefix Import from Global Table into a VRF Table feature introduces the capability to import IPv4 unicast prefixes
BGP Advanced Routing in SonicOS
 BGP Advanced Routing in SonicOS Document Scope This document provides an overview of SonicWALL s implmenetation of Border Gateway protocol (BGP), how BGP operates, and how to configure BGP for your network.
BGP Advanced Routing in SonicOS Document Scope This document provides an overview of SonicWALL s implmenetation of Border Gateway protocol (BGP), how BGP operates, and how to configure BGP for your network.
BGP: Border Gateway Protocol
 LAB 8 BGP: Border Gateway Protocol An Interdomain Routing Protocol OBJECTIVES The objective of this lab is to simulate and study the basic features of an interdomain routing protocol called Border Gateway
LAB 8 BGP: Border Gateway Protocol An Interdomain Routing Protocol OBJECTIVES The objective of this lab is to simulate and study the basic features of an interdomain routing protocol called Border Gateway
BGP-4 Case Studies. Nenad Krajnovic. e-mail: [email protected]
 BGP-4 Case Studies Nenad Krajnovic e-mail: [email protected] Today topics load balancing over multiple links multihoming to a single provider multihoming to different providers following defaults inside
BGP-4 Case Studies Nenad Krajnovic e-mail: [email protected] Today topics load balancing over multiple links multihoming to a single provider multihoming to different providers following defaults inside
BGP Support for Next-Hop Address Tracking
 The feature is enabled by default when a supporting Cisco software image is installed. BGP next-hop address tracking is event driven. BGP prefixes are automatically tracked as peering sessions are established.
The feature is enabled by default when a supporting Cisco software image is installed. BGP next-hop address tracking is event driven. BGP prefixes are automatically tracked as peering sessions are established.
MPLS VPN Route Target Rewrite
 The feature allows the replacement of route targets on incoming and outgoing Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) updates Typically, Autonomous System Border Routers (ASBRs) perform the replacement of route targets
The feature allows the replacement of route targets on incoming and outgoing Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) updates Typically, Autonomous System Border Routers (ASBRs) perform the replacement of route targets
Route Discovery Protocols
 Route Discovery Protocols Columbus, OH 43210 [email protected] http://www.cse.ohio-state.edu/~jain/ 1 Overview Building Routing Tables Routing Information Protocol Version 1 (RIP V1) RIP V2 OSPF
Route Discovery Protocols Columbus, OH 43210 [email protected] http://www.cse.ohio-state.edu/~jain/ 1 Overview Building Routing Tables Routing Information Protocol Version 1 (RIP V1) RIP V2 OSPF
Multihomed BGP Configurations
 Multihomed BGP Configurations lvaro Retana Cisco IOS Deployment and Scalability 1 genda General Considerations Multihomed Networks Best Current Practices 2 The Basics General Considerations 3 General Considerations
Multihomed BGP Configurations lvaro Retana Cisco IOS Deployment and Scalability 1 genda General Considerations Multihomed Networks Best Current Practices 2 The Basics General Considerations 3 General Considerations
Based on Computer Networking, 4 th Edition by Kurose and Ross
 Computer Networks Internet Routing Based on Computer Networking, 4 th Edition by Kurose and Ross Intra-AS Routing Also known as Interior Gateway Protocols (IGP) Most common Intra-AS routing protocols:
Computer Networks Internet Routing Based on Computer Networking, 4 th Edition by Kurose and Ross Intra-AS Routing Also known as Interior Gateway Protocols (IGP) Most common Intra-AS routing protocols:
Border Gateway Protocol Best Practices
 Border Gateway Protocol Best Practices By Clifton Funakura The Internet has grown into a worldwide network supporting a wide range of business applications. Many companies depend on the Internet for day-to-day
Border Gateway Protocol Best Practices By Clifton Funakura The Internet has grown into a worldwide network supporting a wide range of business applications. Many companies depend on the Internet for day-to-day
Configuring MPLS Hub-and-Spoke Layer 3 VPNs
 CHAPTER 23 This chapter describes how to configure a hub-and-spoke topology for Multiprotocol Layer Switching (MPLS) Layer 3 virtual private networks (VPNs) on Cisco NX-OS devices. This chapter includes
CHAPTER 23 This chapter describes how to configure a hub-and-spoke topology for Multiprotocol Layer Switching (MPLS) Layer 3 virtual private networks (VPNs) on Cisco NX-OS devices. This chapter includes
JUNOS Secure BGP Template
 JUNOS Secure BGP Template Version 1.92, 03/30/2005 Stephen Gill E-mail: [email protected] Published: 04/25/2001 Contents Credits... 2 Introduction... 2 Template... 4 References... 10 Credits Rob Thomas
JUNOS Secure BGP Template Version 1.92, 03/30/2005 Stephen Gill E-mail: [email protected] Published: 04/25/2001 Contents Credits... 2 Introduction... 2 Template... 4 References... 10 Credits Rob Thomas
Internet inter-as routing: BGP
 Internet inter-as routing: BGP BGP (Border Gateway Protocol): the de facto standard BGP provides each AS a means to: 1. Obtain subnet reachability information from neighboring ASs. 2. Propagate the reachability
Internet inter-as routing: BGP BGP (Border Gateway Protocol): the de facto standard BGP provides each AS a means to: 1. Obtain subnet reachability information from neighboring ASs. 2. Propagate the reachability
Load balancing and traffic control in BGP
 DD2491 p2 2011 Load balancing and traffic control in BGP Olof Hagsand KTH CSC 1 Issues in load balancing Load balancing: spread traffic on several paths instead of a single. Why? Use resources better Can
DD2491 p2 2011 Load balancing and traffic control in BGP Olof Hagsand KTH CSC 1 Issues in load balancing Load balancing: spread traffic on several paths instead of a single. Why? Use resources better Can
BGP as an IGP for Carrier/Enterprise Networks
 BGP as an IGP for Carrier/Enterprise Networks Presented by: Kevin Myers, SENIOR NETWORK ENGINEER IP ArchiTECHS MANAGED SERVICES Background Kevin Myers 15 + years in IT/Network Engineering Designed and
BGP as an IGP for Carrier/Enterprise Networks Presented by: Kevin Myers, SENIOR NETWORK ENGINEER IP ArchiTECHS MANAGED SERVICES Background Kevin Myers 15 + years in IT/Network Engineering Designed and
Edge-1#show ip route 10.1.2.0. Routing entry for 10.1.2.0/24. Known via "bgp 65001", distance 200, metric 0. Tag 65300, type internal
 Edge-1#show ip route 10.1.2.0 Routing entry for 10.1.2.0/24 Known via "bgp 65001", distance 200, metric 0 Tag 65300, type internal Last update from 172.16.0.22 00:03:31 ago Routing Descriptor Blocks: *
Edge-1#show ip route 10.1.2.0 Routing entry for 10.1.2.0/24 Known via "bgp 65001", distance 200, metric 0 Tag 65300, type internal Last update from 172.16.0.22 00:03:31 ago Routing Descriptor Blocks: *
--BGP 4 White Paper Ver.1.0-- BGP-4 in Vanguard Routers
 BGP-4 in Vanguard Routers 1 Table of Contents Introduction to BGP... 6 BGP terminology... 6 AS (Autonomous system):... 6 AS connection:... 6 BGP Speaker:... 6 BGP Neighbor/Peer:... 7 BGP Session:... 7
BGP-4 in Vanguard Routers 1 Table of Contents Introduction to BGP... 6 BGP terminology... 6 AS (Autonomous system):... 6 AS connection:... 6 BGP Speaker:... 6 BGP Neighbor/Peer:... 7 BGP Session:... 7
Presentation_ID. 2001, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
 1 Session Number BGP Feature Update 12.0S July 2003 Mike Pennington [email protected] Cisco Systems - Denver, CO 2 Overview Overview Definition of Terms BGP Convergence optimization Issues w/ Static peer-groups
1 Session Number BGP Feature Update 12.0S July 2003 Mike Pennington [email protected] Cisco Systems - Denver, CO 2 Overview Overview Definition of Terms BGP Convergence optimization Issues w/ Static peer-groups
Active measurements: networks. Prof. Anja Feldmann, Ph.D. Dr. Nikolaos Chatzis Georgios Smaragdakis, Ph.D.
 Active measurements: networks Prof. Anja Feldmann, Ph.D. Dr. Nikolaos Chatzis Georgios Smaragdakis, Ph.D. Outline Organization of Internet routing Types of domains Intra- and inter-domain routing Intra-domain
Active measurements: networks Prof. Anja Feldmann, Ph.D. Dr. Nikolaos Chatzis Georgios Smaragdakis, Ph.D. Outline Organization of Internet routing Types of domains Intra- and inter-domain routing Intra-domain
Internet Routing Protocols Lecture 04 BGP Continued
 Internet Routing Protocols Lecture 04 BGP Continued Advanced Systems Topics Lent Term, 008 Timothy G. Griffin Computer Lab Cambridge UK Two Types of BGP Sessions AS External Neighbor (EBGP) in a different
Internet Routing Protocols Lecture 04 BGP Continued Advanced Systems Topics Lent Term, 008 Timothy G. Griffin Computer Lab Cambridge UK Two Types of BGP Sessions AS External Neighbor (EBGP) in a different
GregSowell.com. Mikrotik Routing
 Mikrotik Routing Static Dynamic Routing To Be Discussed RIP Quick Discussion OSPF BGP What is Routing Wikipedia has a very lengthy explanation http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/routing In the context of this
Mikrotik Routing Static Dynamic Routing To Be Discussed RIP Quick Discussion OSPF BGP What is Routing Wikipedia has a very lengthy explanation http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/routing In the context of this
Transitioning to BGP. ISP Workshops. Last updated 24 April 2013
 Transitioning to BGP ISP Workshops Last updated 24 April 2013 1 Scaling the network How to get out of carrying all prefixes in IGP 2 Why use BGP rather than IGP? p IGP has Limitations: n The more routing
Transitioning to BGP ISP Workshops Last updated 24 April 2013 1 Scaling the network How to get out of carrying all prefixes in IGP 2 Why use BGP rather than IGP? p IGP has Limitations: n The more routing
This feature was introduced. This feature was integrated in Cisco IOS Release 12.2(11)T.
 BGP Link Bandwidth The Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) Link Bandwidth feature is used to advertise the bandwidth of an autonomous system exit link as an extended community. This feature is configured for
BGP Link Bandwidth The Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) Link Bandwidth feature is used to advertise the bandwidth of an autonomous system exit link as an extended community. This feature is configured for
Computer Networks Administration Help Manual Sana Saadaoui Jemai Oliver Wellnitz
 Technische Universität Braunschweig Institut für Betriebssysteme und Rechnerverbund Computer Networks Administration Help Manual Sana Saadaoui Jemai Oliver Wellnitz Braunschweig, 27 th March 2007 Contents
Technische Universität Braunschweig Institut für Betriebssysteme und Rechnerverbund Computer Networks Administration Help Manual Sana Saadaoui Jemai Oliver Wellnitz Braunschweig, 27 th March 2007 Contents
Routing in Small Networks. Internet Routing Overview. Agenda. Routing in Large Networks
 Routing in Small Networks Internet Routing Overview AS, IGP,, BGP in small networks distance vector or link state protocols like RIP or OSPF can be used for dynamic routing it is possible that every router
Routing in Small Networks Internet Routing Overview AS, IGP,, BGP in small networks distance vector or link state protocols like RIP or OSPF can be used for dynamic routing it is possible that every router
Border Gateway Protocol (BGP-4)
 Vanguard Applications Ware IP and LAN Feature Protocols Border Gateway Protocol (BGP-4) Notice 2008 Vanguard Networks 25 Forbes Blvd Foxboro, MA 02035 Phone: (508) 964 6200 Fax: (508) 543 0237 All rights
Vanguard Applications Ware IP and LAN Feature Protocols Border Gateway Protocol (BGP-4) Notice 2008 Vanguard Networks 25 Forbes Blvd Foxboro, MA 02035 Phone: (508) 964 6200 Fax: (508) 543 0237 All rights
ECSE-6600: Internet Protocols Exam 2
 ECSE-6600: Internet Protocols Exam 2 Time: 75 min (strictly enforced) Points: 50 YOUR NAME: Be brief, but DO NOT omit necessary detail {Note: Simply copying text directly from the slides or notes will
ECSE-6600: Internet Protocols Exam 2 Time: 75 min (strictly enforced) Points: 50 YOUR NAME: Be brief, but DO NOT omit necessary detail {Note: Simply copying text directly from the slides or notes will
Gateway of last resort is 192.208.10.5 to network 192.208.10.0
 RTB#sh ip bgp BGP table version is 14, local router ID is 203.250.15.10 Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, h history, * valid, > best, i - internal Origin codes: i - IGP, e - EGP,? - incomplete Network
RTB#sh ip bgp BGP table version is 14, local router ID is 203.250.15.10 Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, h history, * valid, > best, i - internal Origin codes: i - IGP, e - EGP,? - incomplete Network
IP Routing Tecnologie e Protocolli per Internet II rev 1
 IP Routing Tecnologie e Protocolli per Internet II rev 1 Andrea Detti Vergata Electronic Engineering dept. E-mail: [email protected] Some sources: Cisco CCNA Routing and Switching ICND1 and ICND2
IP Routing Tecnologie e Protocolli per Internet II rev 1 Andrea Detti Vergata Electronic Engineering dept. E-mail: [email protected] Some sources: Cisco CCNA Routing and Switching ICND1 and ICND2
CS 457 Lecture 19 Global Internet - BGP. Fall 2011
 CS 457 Lecture 19 Global Internet - BGP Fall 2011 Decision Process Calculate degree of preference for each route in Adj-RIB-In as follows (apply following steps until one route is left): select route with
CS 457 Lecture 19 Global Internet - BGP Fall 2011 Decision Process Calculate degree of preference for each route in Adj-RIB-In as follows (apply following steps until one route is left): select route with
Interdomain Routing. Outline
 Interdomain Routing David Andersen 15-744 Spring 2007 Carnegie Mellon University Outline What does the Internet look like? Relationships between providers Enforced by: Export filters and import ranking
Interdomain Routing David Andersen 15-744 Spring 2007 Carnegie Mellon University Outline What does the Internet look like? Relationships between providers Enforced by: Export filters and import ranking
Introduction to Routing
 Introduction to Routing How traffic flows on the Internet Philip Smith [email protected] RIPE NCC Regional Meeting, Moscow, 16-18 18 June 2004 1 Abstract Presentation introduces some of the terminologies used,
Introduction to Routing How traffic flows on the Internet Philip Smith [email protected] RIPE NCC Regional Meeting, Moscow, 16-18 18 June 2004 1 Abstract Presentation introduces some of the terminologies used,
Configuring BGP. The Cisco BGP Implementation
 Configuring BGP This chapter describes how to configure Border Gateway Protocol (BGP). For a complete description of the BGP commands in this chapter, refer to the BGP s chapter of the Cisco IOS IP Reference,
Configuring BGP This chapter describes how to configure Border Gateway Protocol (BGP). For a complete description of the BGP commands in this chapter, refer to the BGP s chapter of the Cisco IOS IP Reference,
> Border Gateway Protocol (BGP-4) Technical Configuration Guide. Ethernet Routing Switch. Engineering
 Ethernet Routing Switch 8600 Engineering > Border Gateway Protocol (BGP-4) Technical Configuration Guide Enterprise Solution Engineering Document Date: November, 2007 Document Number: NN48500-538 Document
Ethernet Routing Switch 8600 Engineering > Border Gateway Protocol (BGP-4) Technical Configuration Guide Enterprise Solution Engineering Document Date: November, 2007 Document Number: NN48500-538 Document
DD2491 p1 2008. Load balancing BGP. Johan Nicklasson KTHNOC/NADA
 DD2491 p1 2008 Load balancing BGP Johan Nicklasson KTHNOC/NADA Dual home When do you need to be dual homed? How should you be dual homed? Same provider. Different providers. What do you need to have in
DD2491 p1 2008 Load balancing BGP Johan Nicklasson KTHNOC/NADA Dual home When do you need to be dual homed? How should you be dual homed? Same provider. Different providers. What do you need to have in
UPDATE = [Withdrawn prefixes (Optional)] + [Path Attributes] + [NLRIs].
![UPDATE = [Withdrawn prefixes (Optional)] + [Path Attributes] + [NLRIs]. UPDATE = [Withdrawn prefixes (Optional)] + [Path Attributes] + [NLRIs].](/thumbs/40/20887550.jpg) Table of Contents Introduction...1 MP-BGP Overview...1 VPNv4 Prefixes and EIGRP Extended Communities...3 VPNv4 Prefixes and Redistribution...4 Race Condition 1: Backdoor Link preferred by EIGRP...8 BGP
Table of Contents Introduction...1 MP-BGP Overview...1 VPNv4 Prefixes and EIGRP Extended Communities...3 VPNv4 Prefixes and Redistribution...4 Race Condition 1: Backdoor Link preferred by EIGRP...8 BGP
Module 12 Multihoming to the Same ISP
 Module 12 Multihoming to the Same ISP Objective: To investigate various methods for multihoming onto the same upstream s backbone Prerequisites: Module 11 and Multihoming Presentation The following will
Module 12 Multihoming to the Same ISP Objective: To investigate various methods for multihoming onto the same upstream s backbone Prerequisites: Module 11 and Multihoming Presentation The following will
Basic Configuration Examples for BGP
 Application Note Basic Configuration Examples for BGP Juniper Networks, Inc. 1194 North Mathilda Avenue Sunnyvale, CA 94089 USA 408 745 2000 or 888 JUNIPER www.juniper.net Part Number: :350008-001 04/02
Application Note Basic Configuration Examples for BGP Juniper Networks, Inc. 1194 North Mathilda Avenue Sunnyvale, CA 94089 USA 408 745 2000 or 888 JUNIPER www.juniper.net Part Number: :350008-001 04/02
no aggregate-address address mask [as-set] [summary-only] [suppress-map map-name] [advertise-map map-name] [attribute-map map-name]
![no aggregate-address address mask [as-set] [summary-only] [suppress-map map-name] [advertise-map map-name] [attribute-map map-name] no aggregate-address address mask [as-set] [summary-only] [suppress-map map-name] [advertise-map map-name] [attribute-map map-name]](/thumbs/37/17757146.jpg) BGP Commands Use the commands in this chapter to configure and monitor Border Gateway Protocol (BGP). For BGP configuration information and examples, refer to the Configuring BGP chapter of the Network
BGP Commands Use the commands in this chapter to configure and monitor Border Gateway Protocol (BGP). For BGP configuration information and examples, refer to the Configuring BGP chapter of the Network
MPLS VPN over mgre. Finding Feature Information. Prerequisites for MPLS VPN over mgre
 The feature overcomes the requirement that a carrier support multiprotocol label switching (MPLS) by allowing you to provide MPLS connectivity between networks that are connected by IP-only networks. This
The feature overcomes the requirement that a carrier support multiprotocol label switching (MPLS) by allowing you to provide MPLS connectivity between networks that are connected by IP-only networks. This
Understanding Virtual Router and Virtual Systems
 Understanding Virtual Router and Virtual Systems PAN- OS 6.0 Humair Ali Professional Services Content Table of Contents VIRTUAL ROUTER... 5 CONNECTED... 8 STATIC ROUTING... 9 OSPF... 11 BGP... 17 IMPORT
Understanding Virtual Router and Virtual Systems PAN- OS 6.0 Humair Ali Professional Services Content Table of Contents VIRTUAL ROUTER... 5 CONNECTED... 8 STATIC ROUTING... 9 OSPF... 11 BGP... 17 IMPORT
Internet Firewall CSIS 4222. Packet Filtering. Internet Firewall. Examples. Spring 2011 CSIS 4222. net15 1. Routers can implement packet filtering
 Internet Firewall CSIS 4222 A combination of hardware and software that isolates an organization s internal network from the Internet at large Ch 27: Internet Routing Ch 30: Packet filtering & firewalls
Internet Firewall CSIS 4222 A combination of hardware and software that isolates an organization s internal network from the Internet at large Ch 27: Internet Routing Ch 30: Packet filtering & firewalls
Bell Aliant. Business Internet Border Gateway Protocol Policy and Features Guidelines
 Bell Aliant Business Internet Border Gateway Protocol Policy and Features Guidelines Effective 05/30/2006, Updated 1/30/2015 BGP Policy and Features Guidelines 1 Bell Aliant BGP Features Bell Aliant offers
Bell Aliant Business Internet Border Gateway Protocol Policy and Features Guidelines Effective 05/30/2006, Updated 1/30/2015 BGP Policy and Features Guidelines 1 Bell Aliant BGP Features Bell Aliant offers
Configuring BGP Services
 Part No. 314721-C Rev 00 May 2004 4655 Great America Parkway Santa Clara, CA 95054 Passport 8000 Series Software Release 3.7 *314721-C Rev 00* 2 Copyright 2003 Nortel Networks All rights reserved. May
Part No. 314721-C Rev 00 May 2004 4655 Great America Parkway Santa Clara, CA 95054 Passport 8000 Series Software Release 3.7 *314721-C Rev 00* 2 Copyright 2003 Nortel Networks All rights reserved. May
BGP Routing. Course Description. Students Will Learn. Target Audience. Hands-On
 Hands-On Course Description This Hands-On course on (Border Gateway Protocol), from the basics of how it works through to advanced issues such as route reflectors, policy, filtering, route selection and
Hands-On Course Description This Hands-On course on (Border Gateway Protocol), from the basics of how it works through to advanced issues such as route reflectors, policy, filtering, route selection and
s@lm@n Juniper Exam JN0-343 Juniper Networks Certified Internet Specialist (JNCIS-ENT) Version: 10.1 [ Total Questions: 498 ]
![s@lm@n Juniper Exam JN0-343 Juniper Networks Certified Internet Specialist (JNCIS-ENT) Version: 10.1 [ Total Questions: 498 ] s@lm@n Juniper Exam JN0-343 Juniper Networks Certified Internet Specialist (JNCIS-ENT) Version: 10.1 [ Total Questions: 498 ]](/thumbs/39/18985711.jpg) s@lm@n Juniper Exam JN0-343 Juniper Networks Certified Internet Specialist (JNCIS-ENT) Version: 10.1 [ Total Questions: 498 ] Topic 1, Volume A Question No : 1 - (Topic 1) How much overhead does the GRE
s@lm@n Juniper Exam JN0-343 Juniper Networks Certified Internet Specialist (JNCIS-ENT) Version: 10.1 [ Total Questions: 498 ] Topic 1, Volume A Question No : 1 - (Topic 1) How much overhead does the GRE
Introduction Inter-AS L3VPN
 Introduction Inter-AS L3VPN 1 Extending VPN services over Inter-AS networks VPN Sites attached to different MPLS VPN Service Providers How do you distribute and share VPN routes between ASs Back- to- Back
Introduction Inter-AS L3VPN 1 Extending VPN services over Inter-AS networks VPN Sites attached to different MPLS VPN Service Providers How do you distribute and share VPN routes between ASs Back- to- Back
Implementing MPLS VPNs over IP Tunnels on Cisco IOS XR Software
 Implementing MPLS VPNs over IP Tunnels on Cisco IOS XR Software The MPLS VPNs over IP Tunnels feature lets you deploy Layer 3 Virtual Private Netwk (L3VPN) services, over an IP ce netwk, using L2TPv3 multipoint
Implementing MPLS VPNs over IP Tunnels on Cisco IOS XR Software The MPLS VPNs over IP Tunnels feature lets you deploy Layer 3 Virtual Private Netwk (L3VPN) services, over an IP ce netwk, using L2TPv3 multipoint
HP Networking BGP and MPLS technology training
 Course overview HP Networking BGP and MPLS technology training (HL046_00429577) The HP Networking BGP and MPLS technology training provides networking professionals the knowledge necessary for designing,
Course overview HP Networking BGP and MPLS technology training (HL046_00429577) The HP Networking BGP and MPLS technology training provides networking professionals the knowledge necessary for designing,
Introduction to TCP/IP
 Introduction to TCP/IP Raj Jain The Ohio State University Columbus, OH 43210 Nayna Networks Milpitas, CA 95035 Email: [email protected] http://www.cis.ohio-state.edu/~jain/ 1 Overview! Internetworking Protocol
Introduction to TCP/IP Raj Jain The Ohio State University Columbus, OH 43210 Nayna Networks Milpitas, CA 95035 Email: [email protected] http://www.cis.ohio-state.edu/~jain/ 1 Overview! Internetworking Protocol
Routing Protocols. Interconnected ASes. Hierarchical Routing. Hierarchical Routing
 Routing Protocols scale: with 200 million destinations: can t store all dest s in routing tables! routing table exchange would swamp links! Hierarchical Routing Our routing study thus far - idealization
Routing Protocols scale: with 200 million destinations: can t store all dest s in routing tables! routing table exchange would swamp links! Hierarchical Routing Our routing study thus far - idealization
Lab 4.2 Challenge Lab: Implementing MPLS VPNs
 Lab 4.2 Challenge Lab: Implementing MPLS VPNs Learning Objectives Configure Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) and Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (EIGRP) on a router Enable MPLS on a router Verify
Lab 4.2 Challenge Lab: Implementing MPLS VPNs Learning Objectives Configure Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) and Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (EIGRP) on a router Enable MPLS on a router Verify
6.263 Data Communication Networks
 6.6 Data Communication Networks Lecture : Internet Routing (some slides are taken from I. Stoica and N. Mckewon & T. Griffin) Dina Katabi [email protected] www.nms.csail.mit.edu/~dina Books Text Book Data Communication
6.6 Data Communication Networks Lecture : Internet Routing (some slides are taken from I. Stoica and N. Mckewon & T. Griffin) Dina Katabi [email protected] www.nms.csail.mit.edu/~dina Books Text Book Data Communication
Increasing Path Diversity using Route Reflector
 International Journal of Engineering Science Invention ISSN (Online): 2319 6734, ISSN (Print): 2319 6726 Volume 2 Issue 5 ǁ May. 2013 ǁ PP.05-09 Increasing Path Diversity using Route Reflector Prasha Dubey
International Journal of Engineering Science Invention ISSN (Online): 2319 6734, ISSN (Print): 2319 6726 Volume 2 Issue 5 ǁ May. 2013 ǁ PP.05-09 Increasing Path Diversity using Route Reflector Prasha Dubey
Can Forwarding Loops Appear when Activating ibgp Multipath Load Sharing?
 Can Forwarding Loops Appear when Activating ibgp Multipath Load Sharing? Simon Balon and Guy Leduc Research Unit in Networking EECS Department- University of Liège (ULg) Institut Montefiore, B28 - B-4000
Can Forwarding Loops Appear when Activating ibgp Multipath Load Sharing? Simon Balon and Guy Leduc Research Unit in Networking EECS Department- University of Liège (ULg) Institut Montefiore, B28 - B-4000
DD2491 p1 2008. Inter-domain routing and BGP part I Olof Hagsand KTH/CSC
 DD2491 p1 2008 Inter-domain routing and BGP part I Olof Hagsand KTH/CSC Inter-domain routing The objective of inter-domain routing is to bind together all the thousands of independent IP networks that
DD2491 p1 2008 Inter-domain routing and BGP part I Olof Hagsand KTH/CSC Inter-domain routing The objective of inter-domain routing is to bind together all the thousands of independent IP networks that
