Engaging Staff as Problem Solvers Leads to Continuous Improvement at Allina Health
|
|
|
- Eustace Sparks
- 8 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Engaging Staff as Problem Solvers Leads to Continuous Improvement at Allina Health GREGORY CLANCY AND MARK GRABAN In a Kaizen endeavor at Allina Health a nonprofit health system in the Midwestern United States with more than 26,000 employees nurses, doctors, dietitians, engineers, housekeepers, and all other staff in four units were encouraged to contribute ideas to solve the problems they encountered on the job. Managers at all levels used effective communication, constructive feedback, and supportive delegation to coach their efforts rather than dictate solutions from above. The results led to a wide range of process improvements that cut costs and enhanced safety, efficiency, patient satisfaction, quality, and morale. Over time, the initiative will be rolled out system-wide toward the formation of an organizational culture that empowers every staff member to improve the flow and outcome of their daily responsibilities. C 2014 Wiley Periodicals, Inc. As recently as 2013, if a nurse at an Allina Health inpatient medical unit needed to start an intravenous infusion for a patient, she would have to walk to the dressing cart for tape and small bandages, then into another room to obtain the catheters and tubing, and, finally, to the medication cart to get a bag of saline. This multistep endeavor could take five to ten minutes assuming she was not interrupted along the way, which often was likely. The nurses had become accustomed to this time-consuming process, until one of them suggested a better way. Thanks to a new Kaizen program implemented by Allina Health, that nurse and her peers now have a systematic way to identify and address workplace problems, for the benefit of patients and staff members alike. A Japanese word that means good change, Kaizen is usually used in the context of continuous improvement in a manufacturing facility. The Kaizen experiences of Toyota, where all employees are empowered to improve their work environment, have been well documented, and the suggestions and improvements made by that company s team members have been described as the cornerstone of Toyota s success (Graban & Swartz, 2012). Over the years, many other organizations outside the manufacturing sector, including health care facilities, have realized the value of engaging staff members in quality improvement. Successful implementation of Kaizen, which encourages staff members at all levels to contribute ideas to solve the problems they encounter, transforms passive acceptance of faulty workflows into a culture of continuous process improvement. In a health care setting, nurses, doctors, dietitians, engineers, housekeepers, and all other staff become active participants in this work, with the active support of leaders at all levels. This results in a wide range of benefits, including cost reduction and improvements in safety, efficiency, patient satisfaction, and quality. These benefits are good for the patients and staff, and lower costs by improving operational efficiency throughout the organization. Writing in Academic Emergency Medicine, the official journal for the Society of Academic Emergency Medicine, Jacobson, McCoin, Lescallette, Russ, and Slovis (2009) described how the Kaizen approach C 2014 Wiley Periodicals, Inc. Published online in Wiley Online Library (wileyonlinelibrary.com) Global Business and Organizational Excellence DOI: /joe September/October
2 could be successfully applied in a health care setting to promote leadership that engages staff to create a culture of positive change. In such an environment, all ideas are addressed shortly after being introduced by staff, and a dialogue is initiated that clarifies the issues and formulates an initial response. Jacobson and his coauthors also emphasized these key points: The greatest benefits from Kaizen occur when efforts are focused on common-sense, low-cost, and low-risk improvements, rather than major innovations. Kaizen starts a process of multiple small changes in the patient care environment that add up to a major change in the work and positive culture change. A major aim of Kaizen is making the daily work of the staff easier. Kaizen incorporates the principles of staff empowerment, shared decision making, self-direction, and shared governance. Though simple, the approach is not consistent with traditional management styles, however. If the nurse s manager in the opening scenario had told her that it would not be possible to move the cart supplies, then she and her fellow nurses would be less likely to bring any other problems forward or offer suggestions. But when staff members are invited to provide suggestions for changing how the work is done, and changes based on their suggestions actually occur, staff members begin to feel greater ownership of their work. This leads to a positive cycle of good ideas engendering other good ideas toward continuous improvement. Typically hired because of their clinical skills and willingness to work long hours, many health care managers have limited leadership education (having learned management skills on the job) and rarely have any experience in the basic skills necessary for continuous improvement. Kaizen is predicated on managers use of effective communication, constructive feedback, and supportive delegation. As the following example shows, for Kaizen to be successful, managers must see themselves as coaches, and not as top-down activity directors who have all the answers. Angela is a new manager of a busy adult medical surgical unit. One day, Fred, a staff member, notes that he has been having difficulty in contacting other staff in different departments in a timely manner. Angela creates a form on which she types in the various departmental names and phone numbers in neat rows. She laminates several copies and tapes them to the unit s computers for ready access. Angela remarks that this took several hours and she hopes it solves the problem. But did it? Kaizen is predicated on managers use of effective communication, constructive feedback, and supportive delegation. Rather than discussing the problem with the staff member, Angela took action and jumped to a solution. Fred, however, felt that his problem was not solved. The real problem was not that Fred did not have access to the numbers he needed but, rather, that most of his phone calls were not answered, which meant all he could do was to leave messages and hope for a call back. Had Angela clarified the full scope of the problem with Fred, she might have been able to lead her staff in devising a way to more effectively support them. To ensure that proposed solutions to workday problems are both effective and long lasting, it is important for managers to consider their broader implications. For instance, when staff members in another surgical unit realized that patients in the next room could hear an IV pump alarm, they initially thought to solve the problem by simply turning down the volume of the alarm. But then they realized that medical personnel might not respond promptly to a quieter alarm. Once the manager recognized that the actual problem was alarm fatigue (which occurs when 36 September/October 2014 DOI: /joe Global Business and Organizational Excellence
3 equipment beeps or rings frequently because of extraneous, noncritical causes, like a bent arm causing a temporary interruption in IV flow), she was able to coach the staff member to help identify the real cause of the problem and subsequently develop meaningful solutions. Implementing Kaizen Daily Improvement at Allina Health s Hospitals Consisting of 13 hospitals, 57 community and 23 hospital-based clinics, 15 retail pharmacy sites, and 3 ambulatory care centers, Allina Health is a notfor-profit health system located in central Minnesota and western Wisconsin. The organization employs more than 26,000 staff members, and 5,000 physicians are associated with its health system. Striving for continuous quality improvement, Allina Health s Performance Improvement Department selected the Kaizen method to enhance organizational effectiveness, and it was endorsed by the Nurse Executive Committee. This methodology is consistent with the Performance Improvement Department goals of engaging front-line staff in quality improvement efforts that address problems that are within the realm of their hospital or clinical care unit. Problems addressed by continuous quality improvement may include workflow barriers, such as not having the right supplies at the right time and location. The scope of problems addressed with continuous quality improvement methodology can be considered as the bottom rung of a continuum of increasingly complex problems addressed by multiple performance improvement tools. The middle rungs of complexity are problems that occur across multiple units, such as implementing a hospital-wide procedure for isolating patients with a suspected communicable disease. A performance improvement methodology for addressing problems at this middle level of complexity is the Rapid Process Improvement Workshop (RPIW). It brings together staff from various clinical units and professions to analyze and improve a complex, common problem. Striving for continuous quality improvement, Allina Health s Performance Improvement Department selected the Kaizen method to enhance organizational effectiveness, and it was endorsed by the Nurse Executive Committee. Problems associated with implementing major change throughout the organization constitute the highest rung of complexity. Examples of complex changes include implementing a new electronic health record or initiating a new patient care service. Such problems require a robust performance improvement methodology. At Allina Health this methodology is the 10-Step model. It incorporates methodologies from Six Sigma and Lean into a linear, structured process that begins with problem identification; moves on to stakeholder engagement, data analysis, and implementation; and ends with evaluation. This 10-Step process has been used to address such complex problems as standardizing discharge planning, reducing preventable readmission to the hospital, and improving the efficiency of care for high-risk populations. The nurse executives selected several hospital units in which to pilot the Kaizen methodology, and funds were provided for consulting services to initiate this. The Allina Health Performance Improvement Department staff also participated in learning about this methodology during a morning conference session and subsequent hospital site visits. In October 2013, Allina s executives decided to initiate Kaizen projects at four pilot sites: a large adult/pediatrics unit in a rural community north of Minneapolis, a cardiovascular unit in suburban Minneapolis, the emergency department at a large hospital in Minneapolis, and a cardiovascular unit at Global Business and Organizational Excellence DOI: /joe September/October
4 a hospital in downtown St. Paul. The formal kickoff began with a daylong conference during which managers and selected staff were given an overview of the process. The conference leaders also discussed the role of managers in engaging and empowering staff, and how to move new ideas through the process to completion. In addition, the program involved role-playing that demonstrated various tactics for engaging staff and leaders in continuous quality improvement. Leaders asked managers to describe Kaizen to staff, discussed empowering strategies, and asked staff to participate directly. Leaders also discussed ways to encourage staff members to use Kaizen, including rewarding and recognizing staff members participation, sharing their ideas, and promoting the benefits. In October 2013, Allina s executives decided to initiate Kaizen projects at four pilot sites: a large adult/pediatrics unit in a rural community north of Minneapolis, a cardiovascular unit in suburban Minneapolis, the emergency department at a large hospital in Minneapolis, and a cardiovascular unit at a hospital in downtown St. Paul. Leaders answered questions and had the managers (or their designees) describe their plans for implementation within their specific unit. After the conference, two advisors visited each site two times to review the unit s descriptions of its goals and progress, tour the facility, and address any questions from managers and staff about the Kaizen process. They coached managers to demonstrate their techniques for inviting staff suggestions for workplace improvement. Since many of the hospitals staff members were not familiar with the term Kaizen, it was combined with the words daily improvement to make the goal of continuous improvement more readily understood as the approach spread. Visual Display of Goals Guides Actions The first practical step was mounting a Kaizen Visual Idea Board in each pilot unit, where it would be highly visible to staff members. These bulletin boards were placed in break rooms or staff lounges at three of the pilot sites. One facility, however, placed its Idea Board at the end of a public hallway leading to the staff lockers, where patients and their families could see it. The hospital received feedback that patients appreciated seeing that staff members were making efforts to improve their work and the patient care environment. Each Idea Board is divided into four sections under the headings New Ideas, To Do, Doing, and Done. This board is a key communications tool, as managers and staff are asked to huddle around the board for ten minutes each day to review newly submitted ideas and discuss the progress of ideas that are being worked on. To submit a project for consideration, staff members use preprinted cards containing spaces to write down the problem, an idea (if they have one), the expected benefits, their name, and the date. Blank cards are kept near the board for ready access, so when an idea occurs to a staff member, he or she can quickly write it down during the course of their work. Some managers keep cards in their jacket pockets or desk drawers, so ideas that pop up can be immediately captured before they are forgotten in the midst of a busy day. Staff members attach each new card to the board under the New Ideas column. Managers or specifically delegated staff review the recently submitted cards during the daily huddle and contact each staff member who submitted an idea. After the problem is clarified, the idea is discussed and implementation planned. Then the card is moved to the To Do column. The ideas may be prioritized if there are many ideas at once. 38 September/October 2014 DOI: /joe Global Business and Organizational Excellence
5 During the daily huddle, staff and managers determine which ideas are ready to be addressed, and assign or delegate the work to staff members. When someone begins working on an idea, its respective idea card is moved to the Doing column. Idea cards in the Doing column are also reviewed during the daily huddle. Progress is recorded in the Implementation section on the back of the card. For example, when the staff at one hospital suggested the use of numbing spray prior to IV needle insertion to reduce patient pain, they learned that obtaining the anesthetic spray for the emergency unit required pharmacy approval. The status of the request was recorded on the idea card and updated over time to keep all staff members informed of progress. During the daily huddle, staff and managers determine which ideas are ready to be addressed, and assign or delegate the work to staff members. Once an idea has been implemented, its card is moved to the Done column. Staff members are able to review the recently completed work and make comments, either on the card itself, or as one hospital did, on a clipboard mounted to the board. Since many staff members work night or weekend shifts, they may not have a chance to discuss ideas or ask questions during the daily huddle. The manager and staff found that written notes on the clipboard facilitated two-way communication and identified educational gaps, in addition to providing details about the completed ideas. The final column on the board is for Completed ideas, which are highlighted during the daily huddle and celebrated. Staff members who submitted the idea or helped in some way to implement it are recognized. A brief summary report, created by the manager, may include a before and after picture or a description of how the idea solved a problem and its benefits. Highlighting completed projects and recognizing those involved in them encourages staff members to submit more ideas. One completed project addressed the lack of suitable supplies for finger sticks used to check blood sugar levels. Originally, the supply box contained only small needles used to puncture the skin for a drop of blood. Since nonsterile dry pads were not available, the staff needed to find something to absorb extra leakage. Some used convenient items like tissues, which were not appropriate. Others used more expensive sterile pads, which added unnecessary cost. The idea card submitted by a staff member suggested placing nonsterile pads, the most appropriate supply to use, in the box. After discussing this issue with the manger, the staff member who submitted the idea was asked to contact the hospital supply department to coordinate a regular daily delivery of the new stock item. She also modified and labeled space in the supply box for the pads. This completed project was celebrated during the daily huddle because it improved quality and safety and reduced cost. How Problems and Ideas Are Tracked As the Kaizen method came to be used daily, managers monitored the number of new ideas submitted and their progress through completion. An Excel spreadsheet tracking the various initiatives was placed in a computer folder shared system-wide. Completed ideas were categorized by patient safety, patient satisfaction, operations efficiency, or staff satisfaction. Reviewing the projects by date of submission prompted managers to seek feedback from the staff assigned to the work or who had submitted the idea. It also encouraged them to consider the possibility of assigning newly available staff members, such as a temporarily reassigned nurse or a student, to a particular effort. Global Business and Organizational Excellence DOI: /joe September/October
6 All managers reported that the Kaizen approach improved staff morale and delivery of care. They were not interested, however, in quantifying the exact value, financial or otherwise, of each idea. They felt that their time would be better spent supporting other improvements. Another manager of a cardiovascular inpatient unit delegated the Kaizen work to a unit-based committee of six staff members who were familiar with performance improvement. Staff members had previous experience with TCAB (Transforming Care at the Bedside), a national quality-improvement initiative sponsored by the Institute for Healthcare Improvement. Because of this previous experience, many projects in this unit were more complex than in others. Problems that were addressed included standardizing patient handoffs to the next care provider and improving the timeliness of test result communications to the patient. Obstacles to Successful Kaizen Two main obstacles were encountered during the implementation of Kaizen in the Allina Health facilities. The first was a lack of time for managers and staff to work on ideas. The second was managers limited ability to coach employees in this method. Managers worried about not having enough time to review the Kaizen Daily Improvement Board, plan initiatives, discuss barriers, and evaluate progress during daily huddles. They recognized the fact that successfully sustaining Kaizen would require strategies to incorporate the management of the Kaizen activities into existing processes and delegate it to influential and reliable staff members. Two of the four pilot sites organized unit-based committees whose members could take on this role. For example, the manager at one hospital delegated responsibility for encouraging colleagues to submit ideas for solving problems they encountered to four senior staff nurses who worked varying shifts. Every other week, any staff member who had been assigned work to implement the ideas was allotted two to four hours for doing so. During this time, they contacted different stakeholders for assistance, updated the idea cards, or completed documentation on the Kaizen board. Kaizen tended to be most successfully implemented and sustained in the Allina Health units when senior staff members were delegated responsibility and managers had good coaching skills. The unit s manager assigned the quality committee to work on submitted ideas. In addition to giving the committee time to meet, the manager also allots two to four hours every other week for individuals to work on Kaizen ideas. Staff members communicate their progress using , newsletters, and updates written on the cards. The manager, who monitors progress on the Idea Board, is available to help address any barriers. Having learned to accept and promote the suggestions submitted by staff members, she describes her role as that of a coach. Kaizen tended to be most successfully implemented and sustained in the Allina Health units when senior staff members were delegated responsibility and managers had good coaching skills. These units generated more ideas, completed more projects, and successfully engaged staff members to create a positive work environment. Directors and peers provide support for managers coaching during implementation. Support from top executives is also necessary for setting a positive tone throughout the organization and can facilitate the system-wide spread of applicable improvements. Concerned that staff would become cynical if solutions to identified problems were not implemented immediately, managers realized the need to provide a supportive coaching environment by 40 September/October 2014 DOI: /joe Global Business and Organizational Excellence
7 ensuring open communication and prompt feedback. The importance of doing so became apparent when an infectious disease nurse advised against a staff member s idea to purchase fans to circulate the air for patients with breathing difficulty. Thanks to open communication, the nurse explained that the fans might spread germs. Instead of leading to discouragement, the rejection of the idea provided an opportunity to disseminate information about the risks of airborne germs. Progress Toward Continuous Improvement Since Kaizen Daily Performance Improvement was initiated at Allina Health in October 2013, more than 275 ideas have been submitted, with projects associated with 70 percent of them completed within the first six months. As of March 2014, the managers at the four Allina sites that have implemented Kaizen reported ongoing support of and commitment to this process. A breakdown of the efforts at each of the four sites, as of this writing, follows. Adult/Pediatrics Unit: 104 improvement ideas 70 Kaizens Done ; 34 in the Doing phase. The manager of this unit reported that since embarking on Kaizen, employee engagement scores improved in three key areas. The number of employees who agreed with the statement I have resources to do the work increased from 72 percent to 83 percent. Those who agreed with the statement I participate in decision-making increased from 83 percent to 88 percent. And those who said, My job makes good use of my skills/abilities, increased from 76 percent to 83 percent. The manager also reported that patient satisfaction scores increased in the areas of communication with nurses and staff responsiveness. Suburban Cardiovascular Unit: 79 improvement ideas 59 Done (not including 9 that were not able to be implemented); 20 in the Doing phase. The manager of this unit reported that using Kaizens to improve processes was often a challenge because many smaller improvements had already been achieved during other performance improvement initiatives. Current projects include tackling such complex issues as reducing time to access test results and improving patient care handoffs during shift change. Emergency Department: 67 improvement ideas 31 Done ; 17 in the Doing phase; 19 left To Do. The ED manager reported that various types of staff members were involved in submitting ideas for improving this busy department. Staff members noted that they appreciated seeing their ideas quickly implemented to improve operations and workflow. Cardiovascular Unit in St. Paul: 27 improvement ideas 20 Done ; 2 in the Doing phase; 5 left To Do. The manager plans to engage staff members from an adjacent unit to increase the number of submitted ideas. This is because the units share common resources, patient care requirements are similar, and staff may be assigned across the units. These commonalities will support spreading improvement initiatives across the broader work environment. Next Steps for Kaizen at Allina Health The efforts at the four sites currently engaged in Kaizen will be supported via bimonthly telephone calls by the Performance Improvement facilitator and biannual daylong meetings during which staff can share their achievements and progress. These forums have fostered camaraderie and led to the creation of informal networks that staff and managers use to address specific questions or problems regarding Kaizen implementation. A second cohort of sites is now preparing to implement Kaizen. The establishment of a foundation of units successfully using Kaizen eventually will lead to the expansion of this daily improvement strategy throughout each hospital. Staff and managers in the pioneer units will provide support and act as role models to the personnel in other units when problems are encountered. Global Business and Organizational Excellence DOI: /joe September/October
8 As the Kaizen method spreads through the Allina organization, two tactics will be used to help track its value. The first is to use the spreadsheet data available in the shared resource folder to count the number and types of ideas that are implemented. The second is to continue using surveys of patient satisfaction and staff member engagement. These measures will help determine whether Kaizen methods are having a positive impact on both patients and staff. In addition, Allina s executives are investigating a software solution for establishing a more robust feedback mechanism that will further encourage a culture of continuous improvement. Ideally, such a system would allow staff members to enter their ideas directly into it. Ultimately, the ideal system would serve as a repository of descriptions of completed projects that could be searched to help people solve newly submitted problems, in some cases by leveraging what has already been done at other sites. By piloting this process in four units and making plans to disseminate it throughout Allina s system, the organization s leaders have demonstrated their conviction in the power of Kaizen to positively engage staff in continuous improvement. The experiences of Allina Health and other facilities in a variety of industries have proven the effectiveness of this process. Regardless of the size or scope of those organizations, they have found that Kaizen is most successful when managers become coaches who engage staff members in a collaborative way that solves problems by using ideas from those who do the work each day. References Graban, M., & Swartz, J. E. (2012). Healthcare kaizen: Engaging front-line staff in sustainable continuous improvements. New York: Productivity Press. Jacobson, G. H., McCoin, N. S., Lescallette, R., Russ, S., & Slovis, C. M. (2009). Kaizen: A method of process improvement in the emergency department. Academic Emergency Medicine, 16(12), Gregory Clancy, DNP, RN, is a senior performance improvement advisor for Allina Health. Clancy initiates and supports performance improvement projects throughout the health care organization by engaging front-line staff to use performance improvement methods and providing data analysis from the Enterprise Data Warehouse. Clancy has been a nurse in several Midwest hospitals, a nurse manager in a large ICU, and a researcher. Recently, he completed a doctorate in nursing practice with a focus on informatics. Mark Graban, MS, MBA, is the author of the Shingo Awardwinning book Lean Hospitals: Improving Quality, Patient Safety, and Employee Engagement and co-author, with Joe Swartz, of Healthcare Kaizen: Engaging Front-Line Staff in Sustainable Continuous Improvements (which also received a Shingo Award) and The Executive Guide to Healthcare Kaizen. He serves as a consultant to health care organizations through his company, Constancy, Inc., and is also the vice president of innovation and improvement services for the technology company KaiNexus. Graban has a BS in industrial engineering from Northwestern University and an MS in mechanical engineering and an MBA from the Massachusetts Institute of Technology s Leaders for Global Operations Program. 42 September/October 2014 DOI: /joe Global Business and Organizational Excellence
A Doctor s Perspective on Kaizen Making Improvement Easier www.kainexus.com
 A Doctor s Perspective on Kaizen Making Improvement Easier www.kainexus.com Dr. Gregory Jacobson, CEO and Co-Founder 210-601-4564 greg@kainexus.com COPYRIGHT 2012, KAINEXUS LLC Mark Graban, Chief Improvement
A Doctor s Perspective on Kaizen Making Improvement Easier www.kainexus.com Dr. Gregory Jacobson, CEO and Co-Founder 210-601-4564 greg@kainexus.com COPYRIGHT 2012, KAINEXUS LLC Mark Graban, Chief Improvement
Changing the culture of any organization is well known to be a long process,
 Creative Nursing, Volume 18, Issue 4, 2012 Impact of Unit Practice Councils on Culture and Outcomes Susan Wessel, MS, MBA, RN, NEA-BC This article describes positive outcomes in culture, Hospital Consumer
Creative Nursing, Volume 18, Issue 4, 2012 Impact of Unit Practice Councils on Culture and Outcomes Susan Wessel, MS, MBA, RN, NEA-BC This article describes positive outcomes in culture, Hospital Consumer
Pulling it all together
 Pulling it all together How a lean management system and leader standard work can align daily activity with the strategic priorities of a healthcare organization. Executive summary To achieve their strategic
Pulling it all together How a lean management system and leader standard work can align daily activity with the strategic priorities of a healthcare organization. Executive summary To achieve their strategic
Sanford Improvement Making Lean Work in Healthcare
 Sanford Improvement Making Lean Work in Healthcare David Peterson Enterprise Director of Continuous Improvement Outline/Agenda Office of Continuous Improvement Who are we and what do we do? History/Journey
Sanford Improvement Making Lean Work in Healthcare David Peterson Enterprise Director of Continuous Improvement Outline/Agenda Office of Continuous Improvement Who are we and what do we do? History/Journey
Best Practices for Planning and Budgeting. A white paper prepared by PROPHIX Software October 2006
 A white paper prepared by PROPHIX Software October 2006 Executive Summary The continual changes in the business climate constantly challenge companies to find more effective business practices. However,
A white paper prepared by PROPHIX Software October 2006 Executive Summary The continual changes in the business climate constantly challenge companies to find more effective business practices. However,
The lack of depth of women leaders in U.S. healthcare organizations continues to
 C A R E E R S Leveraging Women s Leadership Talent in Healthcare Martha C. Hauser, managing director and Southern Region healthcare practice leader, Diversified Search, Atlanta, Georgia The lack of depth
C A R E E R S Leveraging Women s Leadership Talent in Healthcare Martha C. Hauser, managing director and Southern Region healthcare practice leader, Diversified Search, Atlanta, Georgia The lack of depth
EXECUTIVE BEHAVIORAL INTERVIEW GUIDE
 EXECUTIVE BEHAVIORAL INTERVIEW GUIDE INTERVIEW GUIDE INSTRUCTIONS: This Interview Guide is intended to help hiring executives conduct behavioral interviews for executive classifications covered by the
EXECUTIVE BEHAVIORAL INTERVIEW GUIDE INTERVIEW GUIDE INSTRUCTIONS: This Interview Guide is intended to help hiring executives conduct behavioral interviews for executive classifications covered by the
Shared Governance Models Optimize Outcomes, Adoption and User Perception
 Shared Governance Models Optimize Outcomes, Adoption and User Perception Nicole Martinez BSN, RN DISCLAIMER: The views and opinions expressed in this presentation are those of the author and do not necessarily
Shared Governance Models Optimize Outcomes, Adoption and User Perception Nicole Martinez BSN, RN DISCLAIMER: The views and opinions expressed in this presentation are those of the author and do not necessarily
Eliminating inefficiencies with PerfectServe. SUCCESS STORY Elimination of delays in consultant care. perfectserve.com 866.844.
 perfectserve.com 866.844.5484 @PerfectServe SUCCESS STORY Elimination of delays in consultant care Hospital: Munroe Regional Medical Center Location: Ocala, FL Beds: 421 Key results: Standardized clinical
perfectserve.com 866.844.5484 @PerfectServe SUCCESS STORY Elimination of delays in consultant care Hospital: Munroe Regional Medical Center Location: Ocala, FL Beds: 421 Key results: Standardized clinical
Practice for 2 years. She graduated from the University of Wisconsin Madison with a degree in Industrial Engineering and focus in Healthcare Systems.
 Presenter Biography: Kate Béténé is currently a Performance Excellence Facilitator at Hennepin County Medical Center (HCMC) in Minneapolis, Minnesota. HCMC has been on its lean journey since 2007, making
Presenter Biography: Kate Béténé is currently a Performance Excellence Facilitator at Hennepin County Medical Center (HCMC) in Minneapolis, Minnesota. HCMC has been on its lean journey since 2007, making
Australian Safety and Quality Framework for Health Care
 Activities for MANAGERS Australian Safety and Quality Framework for Health Care Putting the Framework into action: Getting started Contents Principle: Consumer centred Area for action: 1.1 Develop methods
Activities for MANAGERS Australian Safety and Quality Framework for Health Care Putting the Framework into action: Getting started Contents Principle: Consumer centred Area for action: 1.1 Develop methods
Beyond the Quick Fix: The Medical Director s Role in Quality Assurance Performance Improvement (QAPI) By: Jane Pederson, M.D.
 T O P I C S In Geriatric Medicine and Medical Direction Volume 34 Issue 4 April 2013 A Peer Reviewed Journal of the Minnesota Medical Directors Association Beyond the Quick Fix: The Medical Director s
T O P I C S In Geriatric Medicine and Medical Direction Volume 34 Issue 4 April 2013 A Peer Reviewed Journal of the Minnesota Medical Directors Association Beyond the Quick Fix: The Medical Director s
The Power of Shared Decision Making
 The Power of Shared Decision Making What is Shared Decision Making Point of Service Decision Making - where staff who perform the work participate in decision making affecting their environment A 30 year
The Power of Shared Decision Making What is Shared Decision Making Point of Service Decision Making - where staff who perform the work participate in decision making affecting their environment A 30 year
Health Care. A LexisNexis Company
 Case Study Expanding Opportunities through Analytics: How Successful Implementation of Predictive Analytics Improved Operational and Clinical Effectiveness across a Large Organization. Two full years into
Case Study Expanding Opportunities through Analytics: How Successful Implementation of Predictive Analytics Improved Operational and Clinical Effectiveness across a Large Organization. Two full years into
Alignment of ANCC Forces of Magnitude and TIGER Collaboratives
 Alignment of and I. Transformational Today's health care environment is experiencing unprecedented, intense reformation. Unlike yesterday's leadership requirement for stabilization and growth, today's
Alignment of and I. Transformational Today's health care environment is experiencing unprecedented, intense reformation. Unlike yesterday's leadership requirement for stabilization and growth, today's
Best practices for planning and budgeting. A white paper prepared by Prophix
 A white paper prepared by Prophix Executive summary The continual changes in the business climate constantly challenge companies to find more effective business practices. However, common budgeting limitations
A white paper prepared by Prophix Executive summary The continual changes in the business climate constantly challenge companies to find more effective business practices. However, common budgeting limitations
Nursing Strategic Plan. Fiscal Year 2015. Shaping the Future of UCLA Nursing at Ronald Reagan UCLA Medical Center
 Nursing Strategic Plan Fiscal Year 2015 Shaping the Future of UCLA Nursing at Ronald Reagan UCLA Medical Center The strategic plan of the Ronald Reagan UCLA Medical Center Department of Nursing aligns
Nursing Strategic Plan Fiscal Year 2015 Shaping the Future of UCLA Nursing at Ronald Reagan UCLA Medical Center The strategic plan of the Ronald Reagan UCLA Medical Center Department of Nursing aligns
Leveraging Technology to Power Transformation in Today's Healthcare Environment
 Leveraging Technology to Power Transformation in Today's Healthcare Environment Healthcare executives, staff and clinicians consistently say they are both surprised and impressed at how new technology
Leveraging Technology to Power Transformation in Today's Healthcare Environment Healthcare executives, staff and clinicians consistently say they are both surprised and impressed at how new technology
Building Capability for Success with Lean:
 White Paper Building Capability for Success with Lean: The Critical Competencies When a nation emerges from economic collapse to become the world s second largest economy in thirty years, world economists
White Paper Building Capability for Success with Lean: The Critical Competencies When a nation emerges from economic collapse to become the world s second largest economy in thirty years, world economists
STRATEGIC PLANNING IS A SYSTEMATIC METHOD OF DEVELOPING
 by Rose Seavey, MBA, BS, RN, CNOR, CRCST, CSPDT President/CEO of Seavey Healthcare Consulting STRATEGIC PLANNING PROCESS FOR CENTRAL SERVICE LEARNING OBJECTIVES 1. Discuss the rational for developing a
by Rose Seavey, MBA, BS, RN, CNOR, CRCST, CSPDT President/CEO of Seavey Healthcare Consulting STRATEGIC PLANNING PROCESS FOR CENTRAL SERVICE LEARNING OBJECTIVES 1. Discuss the rational for developing a
UW Health strategic plan Refocus and Renew
 UW Health strategic plan Refocus and Renew 2013-2015 MISSION: Our Reason for Being Advancing health without compromise through: Service Scholarship Science Social Responsibility VISION: Our place in the
UW Health strategic plan Refocus and Renew 2013-2015 MISSION: Our Reason for Being Advancing health without compromise through: Service Scholarship Science Social Responsibility VISION: Our place in the
IMPLEMENTING EMPLOYEE EMPOWERMENT
 61-03-63 IMPLEMENTING EMPLOYEE EMPOWERMENT James A. Ward Total quality management (TQM) is built on the four cornerstones of customer focus, continuous process improvement, management leadership, and employee
61-03-63 IMPLEMENTING EMPLOYEE EMPOWERMENT James A. Ward Total quality management (TQM) is built on the four cornerstones of customer focus, continuous process improvement, management leadership, and employee
Overview of Lean at URMC
 Overview of Lean at URMC Agenda Introduction to Lean at URMC Strategy for Lean at URMC Understanding Waste Introduction to Tools & Techniques 1 Healthcare, As It Is Currently Delivered in The US, is Unsustainable
Overview of Lean at URMC Agenda Introduction to Lean at URMC Strategy for Lean at URMC Understanding Waste Introduction to Tools & Techniques 1 Healthcare, As It Is Currently Delivered in The US, is Unsustainable
Analytic-Driven Quality Keys Success in Risk-Based Contracts. Ross Gustafson, Vice President Allina Performance Resources, Health Catalyst
 Analytic-Driven Quality Keys Success in Risk-Based Contracts March 2 nd, 2016 Ross Gustafson, Vice President Allina Performance Resources, Health Catalyst Brian Rice, Vice President Network/ACO Integration,
Analytic-Driven Quality Keys Success in Risk-Based Contracts March 2 nd, 2016 Ross Gustafson, Vice President Allina Performance Resources, Health Catalyst Brian Rice, Vice President Network/ACO Integration,
Changing Clinical Behaviors to Lower Costs and Reduce Catheter-Associated Urinary Tract Infections (CAUTI)
 Changing Clinical Behaviors to Lower Costs and Reduce Catheter-Associated Urinary Tract Infections (CAUTI) ARKANSAS METHODIST MEDICAL CENTER: How a foley catheter management system combined with education
Changing Clinical Behaviors to Lower Costs and Reduce Catheter-Associated Urinary Tract Infections (CAUTI) ARKANSAS METHODIST MEDICAL CENTER: How a foley catheter management system combined with education
Case Study: Allina Health Giving the Patients a Voice through Patient Advisory Councils (PACs) Allina Health System, Minneapolis, MN
 In 2009, Allina Health embarked on a journey to foundationally change their patients experiences. Allina believes that an important part of making a difference for patients involves bringing forward patients
In 2009, Allina Health embarked on a journey to foundationally change their patients experiences. Allina believes that an important part of making a difference for patients involves bringing forward patients
Peer to Peer Validation. Sarb Randhawa BSN, RN, CNCCP(C) Karen LeComte MSN, RN, CNCCP(C)
 Peer to Peer Validation Sarb Randhawa BSN, RN, CNCCP(C) Karen LeComte MSN, RN, CNCCP(C) Outline Background BCCH Critical Care Program Situation/Problem Search for Solutions Rapid Process Improvement Workshop
Peer to Peer Validation Sarb Randhawa BSN, RN, CNCCP(C) Karen LeComte MSN, RN, CNCCP(C) Outline Background BCCH Critical Care Program Situation/Problem Search for Solutions Rapid Process Improvement Workshop
Case Study High-Performing Health Care Organization December 2008
 Case Study High-Performing Health Care Organization December 2008 Duke University Hospital: Organizational and Tactical Strategies to Enhance Patient Satisfaction Sha r o n Si l o w-ca r r o l l, M.B.A.,
Case Study High-Performing Health Care Organization December 2008 Duke University Hospital: Organizational and Tactical Strategies to Enhance Patient Satisfaction Sha r o n Si l o w-ca r r o l l, M.B.A.,
Transforming the Healthcare Organization through Process Improvement
 WHITE PAPER Whitepaper Transforming the Healthcare Organization through Process Improvement The movement towards value-based purchasing models has made the concept of process improvement and its methodologies
WHITE PAPER Whitepaper Transforming the Healthcare Organization through Process Improvement The movement towards value-based purchasing models has made the concept of process improvement and its methodologies
pm4dev, 2007 management for development series Project Management Organizational Structures PROJECT MANAGEMENT FOR DEVELOPMENT ORGANIZATIONS
 pm4dev, 2007 management for development series Project Management Organizational Structures PROJECT MANAGEMENT FOR DEVELOPMENT ORGANIZATIONS PROJECT MANAGEMENT FOR DEVELOPMENT ORGANIZATIONS A methodology
pm4dev, 2007 management for development series Project Management Organizational Structures PROJECT MANAGEMENT FOR DEVELOPMENT ORGANIZATIONS PROJECT MANAGEMENT FOR DEVELOPMENT ORGANIZATIONS A methodology
Change Management. SAP Consulting & Thaibev IT Department
 Change Management SAP Consulting & Thaibev IT Department The process of change and adjustment Source: based on Kubler-Ross (1969) Source: based on Satir et al (1991) Critical Points in the Change Process
Change Management SAP Consulting & Thaibev IT Department The process of change and adjustment Source: based on Kubler-Ross (1969) Source: based on Satir et al (1991) Critical Points in the Change Process
The Wisdom Project: Stories from the Field that Inform Leaders. Wendy Harrison, Brenda Hubley, Alison McLaughlin, Kass Rafih, and Darren Sander
 The Wisdom Project: Stories from the Field that Inform Leaders Wendy Harrison, Brenda Hubley, Alison McLaughlin, Kass Rafih, and Darren Sander INTRODUCTION Today s leaders are tasked with affecting meaningful,
The Wisdom Project: Stories from the Field that Inform Leaders Wendy Harrison, Brenda Hubley, Alison McLaughlin, Kass Rafih, and Darren Sander INTRODUCTION Today s leaders are tasked with affecting meaningful,
North Shore Physicians Group Primary Care Redesign
 North Shore Physicians Group Primary Care Redesign Christine Sinsky, MD 12.23.11 The physician cannot do this work alone, notes Lindsay Gainer, Director of Clinical Services and Innovations at North Shore
North Shore Physicians Group Primary Care Redesign Christine Sinsky, MD 12.23.11 The physician cannot do this work alone, notes Lindsay Gainer, Director of Clinical Services and Innovations at North Shore
Physician-Led Emergency Department Optimization Dashboard
 Physician-Led Emergency Department Optimization Dashboard Enhancing Efficiencies in the ED and Beyond ehealth 2015: Making Connections June 1, 2015 Dr. Tony Meriano, Chief Medical Information Officer TransForm
Physician-Led Emergency Department Optimization Dashboard Enhancing Efficiencies in the ED and Beyond ehealth 2015: Making Connections June 1, 2015 Dr. Tony Meriano, Chief Medical Information Officer TransForm
Award-Winning Customer Service Patient Access Services. January 2011
 Award-Winning Customer Service Patient Access Services January 2011 1 Outline Introductions Stanford University Medical Center Stanford Hospital & Clinics (SHC) Service Excellence Program Customer Service
Award-Winning Customer Service Patient Access Services January 2011 1 Outline Introductions Stanford University Medical Center Stanford Hospital & Clinics (SHC) Service Excellence Program Customer Service
Activity Guide Innovation & Growth Nova Scotia Public Service Commission
 TALENT MANAGEMENT Activity Guide This document is protected by copyright. The consent of the copyright owner must be obtained for reproduction. Innovation & Growth Nova Scotia Public Service Commission
TALENT MANAGEMENT Activity Guide This document is protected by copyright. The consent of the copyright owner must be obtained for reproduction. Innovation & Growth Nova Scotia Public Service Commission
Auditing Electronic Medical Record Systems. Mary Jo Flynn, RN, CIA, CCSA Interim Vice President, Audit Services
 Auditing Electronic Medical Record Systems Mary Jo Flynn, RN, CIA, CCSA Interim Vice President, Audit Services Allina Hospitals and Clinics Allina Hospitals & Clinics is a not-for-profit system of hospitals,
Auditing Electronic Medical Record Systems Mary Jo Flynn, RN, CIA, CCSA Interim Vice President, Audit Services Allina Hospitals and Clinics Allina Hospitals & Clinics is a not-for-profit system of hospitals,
TRAINING NEEDS ANALYSIS
 TRAINING NEEDS ANALYSIS WHAT IS A NEEDS ANALYSIS? It is a systematic means of determining what training programs are needed. Specifically, when you conduct a needs analysis, you Gather facts about training
TRAINING NEEDS ANALYSIS WHAT IS A NEEDS ANALYSIS? It is a systematic means of determining what training programs are needed. Specifically, when you conduct a needs analysis, you Gather facts about training
MEDSAFE Annual Conference 2012. Prescribed Strategies for Today s Challenges October 4, 2012
 MEDSAFE Annual Conference 2012 Prescribed Strategies for Today s Challenges October 4, 2012 Carroll Hospital Center Larry Siegel, Pharm.D. Director of Pharmacy 10/4/12 66% of patients surveyed did not
MEDSAFE Annual Conference 2012 Prescribed Strategies for Today s Challenges October 4, 2012 Carroll Hospital Center Larry Siegel, Pharm.D. Director of Pharmacy 10/4/12 66% of patients surveyed did not
Meeting Professionals International (MPI) June 2006, www.mpiweb.org
 1 360º of Teamwork: How Meetings and Travel Professionals Can Build Strategic Synergies to Drive Results A Position Paper from Meeting Professionals International s Global Corporate Circle of Excellence
1 360º of Teamwork: How Meetings and Travel Professionals Can Build Strategic Synergies to Drive Results A Position Paper from Meeting Professionals International s Global Corporate Circle of Excellence
Dermatology Associates of KY, PSC Job Description
 Dermatology Associates of KY, PSC Job Description Job Title: Perioperative R.N. Department: Ambulatory Surgery Center Reports To: ASC Manager FLSA Status: Non-Exempt;Hourly; Full-Time Summary Responsible
Dermatology Associates of KY, PSC Job Description Job Title: Perioperative R.N. Department: Ambulatory Surgery Center Reports To: ASC Manager FLSA Status: Non-Exempt;Hourly; Full-Time Summary Responsible
Optimizing the EMR for Your Orthopedic Practice: A Framework for Clinical Transformation.
 Optimizing the EMR for Your Orthopedic Practice: A Framework for Clinical Transformation. Joseph J. Greene MS ATC Shari Khaja MS ATC Orthopedic practices of all types are being confronted today with how
Optimizing the EMR for Your Orthopedic Practice: A Framework for Clinical Transformation. Joseph J. Greene MS ATC Shari Khaja MS ATC Orthopedic practices of all types are being confronted today with how
Innovative Strategies to Engage Bedside Providers in Quality
 Innovative Strategies to Engage Bedside Providers in Quality Second Annual Summit on Quality October 22, 2010 Liz Carlton, RN MSN CCRN Director: Quality, Safety & Regulatory Compliance The University of
Innovative Strategies to Engage Bedside Providers in Quality Second Annual Summit on Quality October 22, 2010 Liz Carlton, RN MSN CCRN Director: Quality, Safety & Regulatory Compliance The University of
Tips and Strategies on Handoffs
 Tips and Strategies on Handoffs In 2007, the Handoffs & Transitions Learning Network (H&T) was established to support the mid-atlantic healthcare community in tackling the complex problem of handoffs and
Tips and Strategies on Handoffs In 2007, the Handoffs & Transitions Learning Network (H&T) was established to support the mid-atlantic healthcare community in tackling the complex problem of handoffs and
Wellness leadership: culture + strategy = results!
 Wellness leadership: culture + strategy = results! Bryce Williams, Vice President, Well-Being Blue Shield of California costs health blueshieldca.com Wellness leadership 2 Employers are the ultimate purchasers
Wellness leadership: culture + strategy = results! Bryce Williams, Vice President, Well-Being Blue Shield of California costs health blueshieldca.com Wellness leadership 2 Employers are the ultimate purchasers
Philips Hospital to Home: redefining healthcare. through innovation in telehealth
 Philips Hospital to Home: redefining healthcare through innovation in telehealth Healthcare costs are at a crisis point, forcing the federal government to make comprehensive changes to healthcare payment
Philips Hospital to Home: redefining healthcare through innovation in telehealth Healthcare costs are at a crisis point, forcing the federal government to make comprehensive changes to healthcare payment
Transitions of Care: The need for collaboration across entire care continuum
 H O T T O P I C S I N H E A L T H C A R E, I S S U E # 2 Transitions of Care: The need for collaboration across entire care continuum Safe, quality Transitions Effective C o l l a b o r a t i v e S u c
H O T T O P I C S I N H E A L T H C A R E, I S S U E # 2 Transitions of Care: The need for collaboration across entire care continuum Safe, quality Transitions Effective C o l l a b o r a t i v e S u c
Management Fundamentals in Healthcare Organizations
 Management Fundamentals in Healthcare Organizations University of Minnesota School of Public Health LEARNING MODEL The learning model underlying the Management Fundamentals Certificate is an application
Management Fundamentals in Healthcare Organizations University of Minnesota School of Public Health LEARNING MODEL The learning model underlying the Management Fundamentals Certificate is an application
Managing a Payroll Department
 Managing a Payroll Department 01/24/2013 1 Topics Basic Management Theory Management Skills Management Issues Management Styles Research Needs Policies and Procedures 01/24/2013 2 Basic Management Theory
Managing a Payroll Department 01/24/2013 1 Topics Basic Management Theory Management Skills Management Issues Management Styles Research Needs Policies and Procedures 01/24/2013 2 Basic Management Theory
5 Steps To Healthcare Change Management: A Roadmap For Success
 Optimizing the business of healthcare 5 Steps To Healthcare Change Management: Table of Contents Overview 1 1. Establishing Change Goals 2 The Change Driver 2 The Importance of Clear Goals and Objectives
Optimizing the business of healthcare 5 Steps To Healthcare Change Management: Table of Contents Overview 1 1. Establishing Change Goals 2 The Change Driver 2 The Importance of Clear Goals and Objectives
System is a not-forprofit
 ABOUT THE PROJECT The Pioneer Employer Initiative is based on the idea that employers who do good, do well. It is an effort to discover and promote the next generation of best practices in workforce management,
ABOUT THE PROJECT The Pioneer Employer Initiative is based on the idea that employers who do good, do well. It is an effort to discover and promote the next generation of best practices in workforce management,
STAAR Issue Brief: Reducing Barriers to Care Across the Continuum - Engaging Physicians
 STAAR Issue Brief: Reducing Barriers to Care Across the Continuum - Engaging Physicians Amy Boutwell, MD, MPP, Vanessa Calderon, MD, MPP, and Ali Khan, MD, MPP Overview: Reducing Avoidable Rehospitalizations
STAAR Issue Brief: Reducing Barriers to Care Across the Continuum - Engaging Physicians Amy Boutwell, MD, MPP, Vanessa Calderon, MD, MPP, and Ali Khan, MD, MPP Overview: Reducing Avoidable Rehospitalizations
Performance Factors and Campuswide Standards Guidelines. With Behavioral Indicators
 Performance Factors and Campuswide Standards Guidelines With Behavioral Indicators Rev. 05/06/2014 Contents PERFORMANCE FACTOR GUIDELINES... 1 Position Expertise... 1 Approach to Work... 2 Quality of Work...
Performance Factors and Campuswide Standards Guidelines With Behavioral Indicators Rev. 05/06/2014 Contents PERFORMANCE FACTOR GUIDELINES... 1 Position Expertise... 1 Approach to Work... 2 Quality of Work...
Biliary Drain. What is a biliary drain?
 Biliary Drain What is a biliary drain? A biliary drain is a tube to drain bile from your liver. It is put in by a doctor called an Interventional Radiologist. The tube or catheter is placed through your
Biliary Drain What is a biliary drain? A biliary drain is a tube to drain bile from your liver. It is put in by a doctor called an Interventional Radiologist. The tube or catheter is placed through your
Reversing OutMigration Michelle Rathman Batschke Impact! Communications
 Energy, Momentum, Motion Changing Community Perception Strategies for Reversing Outmigration Copyright 2012 by, Inc No part of this presentation can be reproduced or distributed without written consent.
Energy, Momentum, Motion Changing Community Perception Strategies for Reversing Outmigration Copyright 2012 by, Inc No part of this presentation can be reproduced or distributed without written consent.
The Next Role in Healthcare
 PART OF VOCERA The Next Role in Healthcare Physician as Chief Experience Officer M. Bridget Duffy, MD, Chief Medical Officer, Vocera Communications, Inc. Co-Founder of Experience Innovation Network 1 Physicians:
PART OF VOCERA The Next Role in Healthcare Physician as Chief Experience Officer M. Bridget Duffy, MD, Chief Medical Officer, Vocera Communications, Inc. Co-Founder of Experience Innovation Network 1 Physicians:
CENTRE FOR LEARNING AND DEVELOPMENT Public Service Secretariat
 CENTRE FOR LEARNING AND DEVELOPMENT Acknowledgements Many people have contributed to the development of this competency model. We extend our appreciation to the individuals who participate in focus groups
CENTRE FOR LEARNING AND DEVELOPMENT Acknowledgements Many people have contributed to the development of this competency model. We extend our appreciation to the individuals who participate in focus groups
ASQ s Healthcare Update:
 Developing a Problem-solving Culture in Healthcare For any healthcare organization embarking on a quality journey, a key element of success involves engaging staff members at all levels and empowering
Developing a Problem-solving Culture in Healthcare For any healthcare organization embarking on a quality journey, a key element of success involves engaging staff members at all levels and empowering
CASE STUDY: Shared Governance Improves Patient Care, Nurse Satisfaction
 CASE STUDY: Shared Governance Improves Patient Care, Nurse Satisfaction The Client A multiple-magnet, large metropolitan hospital. The Challenge Nurses were dissatisfied with the amount of input they were
CASE STUDY: Shared Governance Improves Patient Care, Nurse Satisfaction The Client A multiple-magnet, large metropolitan hospital. The Challenge Nurses were dissatisfied with the amount of input they were
Knowledge is the food of the soul ~Plato. Knowledge Transferred Transferencia del Saber
 Knowledge is the food of the soul ~Plato Knowledge Transferred Transferencia del Saber Unlocking your organization s workforce potential with customized key solutions Saber Academy Capacity Building Program
Knowledge is the food of the soul ~Plato Knowledge Transferred Transferencia del Saber Unlocking your organization s workforce potential with customized key solutions Saber Academy Capacity Building Program
Capturing New Sources of Revenue with a Hospital-Owned Outpatient Pharmacy:
 Capturing New Sources of Revenue with a Hospital-Owned Outpatient Pharmacy: A White Paper Providing Three Best Practices By Tracy W. Becker, PharmD, and Robert Ketchum, RPh, MS ABSTRACT Faced with another
Capturing New Sources of Revenue with a Hospital-Owned Outpatient Pharmacy: A White Paper Providing Three Best Practices By Tracy W. Becker, PharmD, and Robert Ketchum, RPh, MS ABSTRACT Faced with another
Executive Leadership Program. A powerful model for peer-to-peer executive professional development
 Executive Leadership Program A powerful model for peer-to-peer executive professional development By Eileen Lavigne Flug February 2015 Fairfield County s Community Foundation Center for Nonprofit Excellence
Executive Leadership Program A powerful model for peer-to-peer executive professional development By Eileen Lavigne Flug February 2015 Fairfield County s Community Foundation Center for Nonprofit Excellence
DRIVING VALUE IN HEALTHCARE: PERSPECTIVES FROM TWO ACO EXECUTIVES, PART I
 DRIVING VALUE IN HEALTHCARE: PERSPECTIVES FROM TWO ACO EXECUTIVES, PART I A firm understanding of the key components and drivers of healthcare reform is increasingly important within the pharmaceutical,
DRIVING VALUE IN HEALTHCARE: PERSPECTIVES FROM TWO ACO EXECUTIVES, PART I A firm understanding of the key components and drivers of healthcare reform is increasingly important within the pharmaceutical,
WHITE PAPER Wellness that Works
 WHITE PAPER Wellness that Works How program integration can maximize participation and create a culture of total health and wellness Written by the behavioral experts at eni www.eniweb.com Successfully
WHITE PAPER Wellness that Works How program integration can maximize participation and create a culture of total health and wellness Written by the behavioral experts at eni www.eniweb.com Successfully
Supporting Employee Success. A Tool to Plan Accommodations that Support Success at Work
 Supporting Employee A Tool to Plan Accommodations that Support at Work Supporting Employee A Tool to Plan Accommodations that Support at Work Table of Contents Background... Page 1 How the process works...
Supporting Employee A Tool to Plan Accommodations that Support at Work Supporting Employee A Tool to Plan Accommodations that Support at Work Table of Contents Background... Page 1 How the process works...
Team-Based Primary Care: Convergence of Improving Engagement, Safety, and Enhanced Joy in Practice
 Team-Based Primary Care: Convergence of Improving Engagement, Safety, and Enhanced Joy in Practice Executive Summary Summary The physician leadership in the primary care practices of Bellin Health in Green
Team-Based Primary Care: Convergence of Improving Engagement, Safety, and Enhanced Joy in Practice Executive Summary Summary The physician leadership in the primary care practices of Bellin Health in Green
Accountable Care: Implications for Managing Health Information. Quality Healthcare Through Quality Information
 Accountable Care: Implications for Managing Health Information Quality Healthcare Through Quality Information Introduction Healthcare is currently experiencing a critical shift: away from the current the
Accountable Care: Implications for Managing Health Information Quality Healthcare Through Quality Information Introduction Healthcare is currently experiencing a critical shift: away from the current the
PICCs and Midline Catheters
 Patient Education PICCs and Midline Catheters Patient s guide to PICC (peripherally inserted central catheter) and midline catheters What are PICCs and midline catheters used for? Any medicine given over
Patient Education PICCs and Midline Catheters Patient s guide to PICC (peripherally inserted central catheter) and midline catheters What are PICCs and midline catheters used for? Any medicine given over
Performance from problem solving. An interview with three leaders at MassMutual
 123 Performance from problem solving An interview with three leaders at MassMutual At MassMutual, problem solving leads to higher standards, which in turn mean more problems to solve. The constant cycle
123 Performance from problem solving An interview with three leaders at MassMutual At MassMutual, problem solving leads to higher standards, which in turn mean more problems to solve. The constant cycle
Nursing Committee Structure
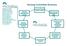 Nursing Nursing Management Council Nursing Coordinating Councils Hospital-Based Service Teams Nursing Area Management Team Nursing Area Shared Governance Councils Nursing Executive Council Unit Shared
Nursing Nursing Management Council Nursing Coordinating Councils Hospital-Based Service Teams Nursing Area Management Team Nursing Area Shared Governance Councils Nursing Executive Council Unit Shared
customer experiences Delivering exceptional Customer Service Excellence
 Delivering exceptional customer experiences Customer Service QA can work with you to create customer experiences that consistently reflect the aims, values and aspirations of your organisation. Every organisation
Delivering exceptional customer experiences Customer Service QA can work with you to create customer experiences that consistently reflect the aims, values and aspirations of your organisation. Every organisation
NCQA INCLUDES ODS PROGRAM IN NATIONAL QUALITY LEADERSHIP PUBLICATION
 NCQA INCLUDES ODS PROGRAM IN NATIONAL QUALITY LEADERSHIP PUBLICATION The National Committee for Quality Assurance (NCQA) invited ODS to submit a case study for publication in its Quality Profiles: The
NCQA INCLUDES ODS PROGRAM IN NATIONAL QUALITY LEADERSHIP PUBLICATION The National Committee for Quality Assurance (NCQA) invited ODS to submit a case study for publication in its Quality Profiles: The
X-Plain Subclavian Inserted Central Catheter (SICC Line) Reference Summary
 X-Plain Subclavian Inserted Central Catheter (SICC Line) Reference Summary Introduction A Subclavian Inserted Central Catheter, or subclavian line, is a long thin hollow tube inserted in a vein under the
X-Plain Subclavian Inserted Central Catheter (SICC Line) Reference Summary Introduction A Subclavian Inserted Central Catheter, or subclavian line, is a long thin hollow tube inserted in a vein under the
Healthcare Interpreting Career Lattice
 Using the Healthcare Interpreting Career Lattice A supplemental guide to the online resource Published October, 2015 by the CATIE Center at St. Catherine University, St. Paul, Minnesota Revised December,
Using the Healthcare Interpreting Career Lattice A supplemental guide to the online resource Published October, 2015 by the CATIE Center at St. Catherine University, St. Paul, Minnesota Revised December,
An Experienced RN s Seven Commandments for Healthcare Project Management Success
 An Experienced RN s Seven Commandments for Healthcare Project Management Success Patti Hope, MSHI BSN RN DISCLAIMER: The views and opinions expressed in this presentation are those of the author and do
An Experienced RN s Seven Commandments for Healthcare Project Management Success Patti Hope, MSHI BSN RN DISCLAIMER: The views and opinions expressed in this presentation are those of the author and do
Fall 2014. Dear Students and Prospective Carpenter Community Nursing Fellows,
 Fall 2014 Dear Students and Prospective Carpenter Community Nursing Fellows, Nurses must create, serve in, and disseminate re-conceptualized roles to bridge whatever gaps remain between coverage and access
Fall 2014 Dear Students and Prospective Carpenter Community Nursing Fellows, Nurses must create, serve in, and disseminate re-conceptualized roles to bridge whatever gaps remain between coverage and access
THE INFORMATION AUDIT AS A FIRST STEP TOWARDS EFFECTIVE KNOWLEDGE MANAGEMENT: AN OPPORTUNITY FOR THE SPECIAL LIBRARIAN * By Susan Henczel
 INSPEL 34(2000)3/4, pp. 210-226 THE INFORMATION AUDIT AS A FIRST STEP TOWARDS EFFECTIVE KNOWLEDGE MANAGEMENT: AN OPPORTUNITY FOR THE SPECIAL LIBRARIAN * By Susan Henczel Introduction Knowledge is universally
INSPEL 34(2000)3/4, pp. 210-226 THE INFORMATION AUDIT AS A FIRST STEP TOWARDS EFFECTIVE KNOWLEDGE MANAGEMENT: AN OPPORTUNITY FOR THE SPECIAL LIBRARIAN * By Susan Henczel Introduction Knowledge is universally
OAHHS LEAN WEBINAR DECEMBER 9, 2014. Purdue Research Foundation
 OAHHS LEAN WEBINAR DECEMBER 9, 2014 1 Overview A3 Improve Key Components Control tools Deeper dive into a tool Questions? 2 DMAIC 3 4 Project Title and Area: Date: Organization: Authors: Pre- Define Measure
OAHHS LEAN WEBINAR DECEMBER 9, 2014 1 Overview A3 Improve Key Components Control tools Deeper dive into a tool Questions? 2 DMAIC 3 4 Project Title and Area: Date: Organization: Authors: Pre- Define Measure
Successful EHR Change Management
 Successful EHR Change Management Roles and responsibilities White paper Table of contents Executive summary... 2 Introduction... 3 Never underestimate the power of the people... 3 People... 4 From resisting
Successful EHR Change Management Roles and responsibilities White paper Table of contents Executive summary... 2 Introduction... 3 Never underestimate the power of the people... 3 People... 4 From resisting
Members respond to help identify what makes RNs unique and valuable to healthcare in Alberta.
 CARNA - Uniquely RN Members respond to help identify what makes RNs unique and valuable to healthcare in Alberta. RNs have expressed that their role is not always understood by colleagues, employers and
CARNA - Uniquely RN Members respond to help identify what makes RNs unique and valuable to healthcare in Alberta. RNs have expressed that their role is not always understood by colleagues, employers and
BUSINESS CONSULTING SERVICES Comprehensive practice management solutions for independent investment advisors
 BUSINESS CONSULTING SERVICES Comprehensive practice management solutions for independent investment advisors Insights, tools and resources to help you Accelerate Your Growth, Scale Your Business and Elevate
BUSINESS CONSULTING SERVICES Comprehensive practice management solutions for independent investment advisors Insights, tools and resources to help you Accelerate Your Growth, Scale Your Business and Elevate
Case Study: Factors in Defining the Nurse Informatics Specialist Role
 Case Study: Factors in Defining the Nurse Informatics Specialist Role Margaret (Mimi) Hassett, MS, RN, FHIMSS A B S T R A C T Healthcare organizations, consultant groups, vendor companies, and academic
Case Study: Factors in Defining the Nurse Informatics Specialist Role Margaret (Mimi) Hassett, MS, RN, FHIMSS A B S T R A C T Healthcare organizations, consultant groups, vendor companies, and academic
AB Volvo, 405 08 Göteborg, Sweden. Ref No 953810003, August 2009. The Volvo Way
 AB Volvo, 405 08 Göteborg, Sweden Ref No 953810003, August 2009 The Volvo Way index Preface Our mission Customers first Customer focus Clear objectives Quality, safety, environmental care Continuous improvements
AB Volvo, 405 08 Göteborg, Sweden Ref No 953810003, August 2009 The Volvo Way index Preface Our mission Customers first Customer focus Clear objectives Quality, safety, environmental care Continuous improvements
PATIENT EXPERIENCE GRANT PROGRAM SERIES RESEARCH REPORT
 PATIENT EXPERIENCE GRANT PROGRAM SERIES RESEARCH REPORT Impact of a Collaborative Re-structuring of New Hire Hospital Orientation on Employee Engagement Tanya Lott, MSN, RN-BC Winnie Hennessy, PhD, RN,
PATIENT EXPERIENCE GRANT PROGRAM SERIES RESEARCH REPORT Impact of a Collaborative Re-structuring of New Hire Hospital Orientation on Employee Engagement Tanya Lott, MSN, RN-BC Winnie Hennessy, PhD, RN,
The University of Chicago Medicine: Driving Engagement With Interactive Care
 The University of Chicago Medicine: Driving Engagement With Interactive Care 1 Training front-line clinical and administrative staff to encourage patients to use technology, but also reminding them of
The University of Chicago Medicine: Driving Engagement With Interactive Care 1 Training front-line clinical and administrative staff to encourage patients to use technology, but also reminding them of
A Comparison of Leadership Development Interventions: Effects on Nurse and Patient Outcomes
 A Comparison of Leadership Development Interventions: Effects on Nurse and Patient Outcomes Lisa Rowen, DNSc, RN, FAAN Senior Vice President and Chief Nurse Officer Karen Doyle, MBA, MS, RN, NEA-BC Vice
A Comparison of Leadership Development Interventions: Effects on Nurse and Patient Outcomes Lisa Rowen, DNSc, RN, FAAN Senior Vice President and Chief Nurse Officer Karen Doyle, MBA, MS, RN, NEA-BC Vice
Emergency Department Quality Collaborative: Improving Quality in Emergency Departments by Enhancing Flow. Executive Summary
 60 Renfrew Drive, Suite 300 Markham, ON L3R 0E1 Tel: 905 948-1872 Fax: 905 948-8011 Toll Free: 1 866 392-5446 www.centrallhin.on.ca Emergency Department Quality Collaborative: Improving Quality in Emergency
60 Renfrew Drive, Suite 300 Markham, ON L3R 0E1 Tel: 905 948-1872 Fax: 905 948-8011 Toll Free: 1 866 392-5446 www.centrallhin.on.ca Emergency Department Quality Collaborative: Improving Quality in Emergency
Reducing Readmissions with Predictive Analytics
 Reducing Readmissions with Predictive Analytics Conway Regional Health System uses analytics and the LACE Index from Medisolv s RAPID business intelligence software to identify patients poised for early
Reducing Readmissions with Predictive Analytics Conway Regional Health System uses analytics and the LACE Index from Medisolv s RAPID business intelligence software to identify patients poised for early
Leadership and Management Competencies
 Leadership and Management Competencies 0 The Saskatchewan Public Service Vision: The Best Public Service in Canada Our Commitment to Excellence Dedicated to service excellence, we demonstrate innovation,
Leadership and Management Competencies 0 The Saskatchewan Public Service Vision: The Best Public Service in Canada Our Commitment to Excellence Dedicated to service excellence, we demonstrate innovation,
How to Conduct a Physical Inventory. Instructions. Forms. And. Sample Memos
 How to Conduct a Physical Inventory Instructions Forms And Sample Memos Produced for NAILM Audio Conference Program July 20, 2006 CIRCULATING INVENTORY The total amount of linen required to operate a healthcare
How to Conduct a Physical Inventory Instructions Forms And Sample Memos Produced for NAILM Audio Conference Program July 20, 2006 CIRCULATING INVENTORY The total amount of linen required to operate a healthcare
Improving Employee Satisfaction in Healthcare through Effective Employee Performance Management
 Improving Employee Satisfaction in Healthcare through Effective Employee Performance Management Introduction The following quotes are comments made by HR professionals from U.S. healthcare providers who
Improving Employee Satisfaction in Healthcare through Effective Employee Performance Management Introduction The following quotes are comments made by HR professionals from U.S. healthcare providers who
The Evolving Role of Process Automation and the Customer Service Experience
 The Evolving Role of Process Automation and the Customer Service Experience Kyle Lyons Managing Director Ponvia Technology Gina Clarkin Product Manager Interactive Intelligence Table of Contents Executive
The Evolving Role of Process Automation and the Customer Service Experience Kyle Lyons Managing Director Ponvia Technology Gina Clarkin Product Manager Interactive Intelligence Table of Contents Executive
Examples of Quality Improvement Projects in Adult Immunization
 Examples of Quality Improvement Projects in Adult Immunization The following activities are provided to prompt your thinking about what works best for your practice. When designing a project, consider
Examples of Quality Improvement Projects in Adult Immunization The following activities are provided to prompt your thinking about what works best for your practice. When designing a project, consider
Improving ED Flow through the UMLN II
 Improving ED Flow through the UMLN II Thomas Jefferson University Hospital Philadelphia, PA 957 beds, XX ED beds www.jeffersonhospital.org/ Thomas Jefferson s emergency department (ED), located in Center
Improving ED Flow through the UMLN II Thomas Jefferson University Hospital Philadelphia, PA 957 beds, XX ED beds www.jeffersonhospital.org/ Thomas Jefferson s emergency department (ED), located in Center
The NIH Roadmap: Re-Engineering the Clinical Research Enterprise
 NIH BACKGROUNDER National Institutes of Health The NIH Roadmap: Re-Engineering the Clinical Research Enterprise Clinical research is the linchpin of the nation s biomedical research enterprise. Before
NIH BACKGROUNDER National Institutes of Health The NIH Roadmap: Re-Engineering the Clinical Research Enterprise Clinical research is the linchpin of the nation s biomedical research enterprise. Before
Enterprise Analytics Strategic Planning
 Enterprise Analytics Strategic Planning June 5, 2013 1 "The first question a data driven organization needs to ask itself is not "what do we think?" but rather "what do we know? Big Data: The Management
Enterprise Analytics Strategic Planning June 5, 2013 1 "The first question a data driven organization needs to ask itself is not "what do we think?" but rather "what do we know? Big Data: The Management
DATA DRIVEN HEALTH CARE TRANSFORMATION
 DATA DRIVEN HEALTH CARE TRANSFORMATION Population Health Analytics as the Foundation for Primary Care Redesign Sylvia Meltzer, MD, LSSGBC Laura Spurr, MPS, PMP Learning Objectives Organization description
DATA DRIVEN HEALTH CARE TRANSFORMATION Population Health Analytics as the Foundation for Primary Care Redesign Sylvia Meltzer, MD, LSSGBC Laura Spurr, MPS, PMP Learning Objectives Organization description
Centre for Learning and Development
 The Leadership and Management Development Strategy was developed to endorse learning and development opportunities to strengthen the leadership and management capacity of the Newfoundland and Labrador
The Leadership and Management Development Strategy was developed to endorse learning and development opportunities to strengthen the leadership and management capacity of the Newfoundland and Labrador
Organizational agility the ability to react quickly to changing market circumstances is. Agility and Cost. Organizational Design and Key Workflows
 Agility and Cost Organizational Design and Key Workflows Cindy Shelton Organizational agility the ability to react quickly to changing market circumstances is a critical necessity for effective government
Agility and Cost Organizational Design and Key Workflows Cindy Shelton Organizational agility the ability to react quickly to changing market circumstances is a critical necessity for effective government
Looking to Increase Employee Engagement? Consider On-the- Job Coaching
 Looking to Increase Employee Engagement? Consider On-the- Job Coaching By John Barry In healthcare, employees who feel engaged with their work are more likely to provide quality care. Many healthcare organizations
Looking to Increase Employee Engagement? Consider On-the- Job Coaching By John Barry In healthcare, employees who feel engaged with their work are more likely to provide quality care. Many healthcare organizations
