Surgery for Morbid Obesity (Formerly Severe Obesity) (70147) Effective October 1, 2008
|
|
|
- Piers Joshua Manning
- 8 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Protocol Surgery for Morbid Obesity (Formerly Severe Obesity) (70147) Effective October 1, 2008 The following protocol contains medical necessity criteria for Surgery for Morbid Obesity services rendered on or after October 1, 2008 for HealthNow New York Inc. (HealthNow) contracts. If these criteria are not met, reimbursement will be denied and the patient cannot be billed. Prior approval is required. Please note that payment for covered services is subject to the limitations noted in the above-referenced contracts and the patient's eligibility at the time the services are rendered. Description Morbid obesity is defined as a body mass index (BMI) greater than 40 kg/m 2 or a BMI greater than 35 kg/m 2 with associated complications including, but not limited to diabetes, hypertension, or obstructive sleep apnea, and has prevalence in the United States of 6% for women and 2% for men. Morbid obesity results in a very high risk for weight-related complications, such as diabetes, hypertension, obstructive sleep apnea, and various types of cancers (for men: colon, rectum, and prostate; for women: breast, uterus, and ovaries), and a shortened life span. A morbidly obese man at age 20 can expect to live 13 years less than his counterpart with a normal BMI, which equates to a 22% reduction in life expectancy. The first treatment of morbid obesity is dietary and lifestyle changes. Although this strategy may be effective in some patients, only a few morbidly obese individuals can reduce and control weight through diet and exercise. The majority of patients find it difficult to comply with these lifestyle modifications on a long-term basis. When conservative measures 1 fail, some patients may consider surgical approaches. A 1991 National Institutes of Health (NIH) Consensus Conference defined surgical candidates as those patients with a BMI* of greater than 40 kg/m 2, or greater than 35 kg/m 2 in conjunction with severe comorbidities such as cardiopulmonary complications or severe diabetes. (*See Guidelines on how to calculate BMI) Surgery for morbid obesity, termed bariatric surgery, falls into 2 general categories: 1) gastric-restrictive procedures that create a small gastric pouch, resulting in weight loss by producing early satiety and thus decreasing dietary intake; and 2) malabsorptive procedures, which produce weight loss due to malabsorption by altering the normal transit of ingested food through the intestinal tract. Some bariatric procedures may include both a restrictive and a malabsorptive component. The following summarizes the different restrictive and malabsorptive procedures. Gastric Restrictive Procedures 1. Vertical-Banded Gastroplasty Vertical-banded gastroplasty was formerly one of the most common gastric restrictive procedures performed in this country but has more recently declined in popularity. In this procedure, the stomach is segmented along its vertical axis. To create a durable reinforced and rate-limiting stoma at the distal end of the pouch, a plug of stomach is removed, and a propylene collar is placed through this hole and then stapled to itself. Because the normal flow of food is preserved, metabolic complications are uncommon. Complications include esophageal reflux, dilation, or obstruction of the stoma, with Page 1 of 8
2 the latter 2 requiring reoperation. Dilation of the stoma is a common reason for weight regain. Vertical-banded gastroplasty may be performed using an open or laparoscopic approach. 2. Adjustable Gastric Banding (laparoscopy, surgical, gastric restrictive procedure; placement of adjustable gastric band [gastric band and subcutaneous port components]) Adjustable gastric banding involves placing a gastric band around the exterior of the stomach. The band is attached to a reservoir that is implanted subcutaneously in the rectus sheath. Injecting the reservoir with saline will alter the diameter of the gastric band; therefore, the rate-limiting stoma in the stomach can be progressively narrowed to induce greater weight loss, or expanded if complications develop. Because the stomach is not entered, the surgery and any revisions, if necessary, are relatively simple. Complications include slippage of the external band or band erosion through the gastric wall. Adjustable gastric banding has been widely used in Europe; currently, 1 such device is approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for marketing in the United States, Lap- Band (BioEnterics, Carpentiera, CA). The labeled indications for this device are as follows: "The Lap-Band system is indicated for use in weight reduction for severely obese patients with a body mass index (BMI) of at least 40 or a BMI of at least 35 with one or more severe comorbid conditions, or those who are 100 lbs. or more over their estimated ideal weight according to the 1983 Metropolitan Life Insurance Tables (use the midpoint for medium frame). It is indicated for use only in severely obese adult patients who have failed more conservative 1 weight-reduction alternatives, such as supervised diet, exercise and behavior modification programs. Patients who elect to have this surgery must make the commitment to accept significant changes in their eating habits for the rest of their lives." A second adjustable gastric banding device was approved by the FDA through the PMA process in September 2007, the REALIZE model (Ethicon Endo-Surgery, Cincinnati, OH). Labeled indications for this device are as listed below: The [REALIZE] device is indicated for weight reduction for morbidly obese patients and is indicated for individuals with a BMI of at least 40 kg/m2, or a BMI or at least 35 kg/m2 with one or more comorbid conditions. The band is indicated for use only in morbidly obese adult patients who have failed more conservative weight-reduction alternatives, such as supervised diet, exercise, and behavior modification programs. 3. Open Gastric Bypass (gastric restrictive procedure, with gastric bypass for morbid obesity; with short limb [150 cm or less] Roux-en-Y gastroenterostomy) The original gastric bypass surgeries were based on the observation that post-gastrectomy patients tended to lose weight. The current procedure involves both a restrictive and a malabsorptive component, with horizontal or vertical partition of the stomach performed in association with a Rouxen-Y procedure (i.e., a gastrojejunal anastomosis). Thus, the flow of food bypasses the duodenum and proximal small bowel. The procedure may also be associated with an unpleasant dumping syndrome, in which a large osmotic load delivered directly to the jejunum from the stomach produces abdominal pain and/or vomiting. The dumping syndrome may further reduce intake, particularly in sweets eaters. Operative complications include leakage and marginal ulceration at the anastomotic site. Because the normal flow of food is disrupted, there are more metabolic complications compared to other gastric restrictive procedures, including iron deficiency anemia, vitamin B-12 deficiency, and hypocalcemia, all of which can be corrected by oral supplementation. Another concern is the ability to evaluate the blind bypassed portion of the stomach. Gastric bypass may be performed with either an open or laparoscopic technique. 4. Laparoscopic Gastric Bypass (laparoscopy, surgical, gastric restrictive procedure; with gastric bypass and Roux-en-Y gastroenterostomy [roux limb 150 cm or less]) Essentially describes the same procedure as No. 3, but performed laparoscopically. 5. Mini-Gastric Bypass Recently, a variant of the gastric bypass, called the mini-gastric bypass, has been popularized. Using a laparoscopic approach, the stomach is segmented, similar to a traditional gastric bypass, but instead of creating a Roux-en-Y anastomosis, the jejunum is anastomosed directly to the stomach, similar to a Billroth II procedure. This unique aspect of this procedure is not based on its laparoscopic approach but rather the type of anastomosis used. Page 2 of 8
3 6. Sleeve Gastrectomy A sleeve gastrectomy is an alternative approach to gastrectomy that can be performed on its own, or in combination with malabsorptive procedures (most commonly biliopancreatic diversion with duodenal switch). In this procedure, the greater curvature of the stomach is resected from the angle of His to the distal antrum, resulting in a stomach remnant shaped like a tube or sleeve. The pyloric sphincter is preserved, resulting in a more physiologic transit of food from the stomach to the duodenum, and avoiding the dumping syndrome (overly rapid transport of food through stomach into intestines) that is seen with distal gastrectomy. This procedure is relatively simple to perform, and can be done by the open or laparoscopic technique. Some surgeons have proposed this as the first in a 2-stage procedure for very high-risk patients. Weight loss following sleeve gastrectomy may improve a patient s overall medical status, and thus reduce the risk of a subsequent more extensive malabsorptive procedure, such as biliopancreatic diversion. Malabsorptive Procedures There are multiple variants of malabsorptive procedures, which differ in the lengths of the alimentary limb, the biliopancreatic limb, and the common limb, in which the alimentary and biliopancreatic limbs are anastomosed. These procedures also may include an element of a restrictive surgery based on the size of the stomach pouch. The degree of malabsorption is related to the length of the alimentary and common limbs. For example, a shorter alimentary limb (i.e., the greater the amount of intestine that is excluded from the nutrient flow) will be associated with malabsorption of a variety of nutrients, while a short common limb (i.e., the biliopancreatic juices are allowed to mix with nutrients for only a short segment) will primarily limit absorption of fat. 1. Biliopancreatic Bypass Procedure (also known as the Scopinaro procedure) (gastric restrictive procedure, with gastric bypass for morbid obesity; with small intestine reconstruction to limit absorption) Biliopancreatic bypass (BPB) procedure, developed and used extensively in Italy, was designed to address some of the drawbacks of the original intestinal bypass procedures that have been abandoned due to unacceptable metabolic complications. Many of the complications were thought to be related to bacterial overgrowth and toxin production in the blind, bypassed segment. In contrast, BPB consists of a subtotal gastrectomy and diversion of the biliopancreatic juices into the distal ileum by a long Roux-en-Y procedure. The procedure consists of the following components. a. A distal gastrectomy functions to induce a temporary early satiety and/or the dumping syndrome in the early postoperative period, both of which limit food intake. b. A 200-cm long alimentary tract consists of 200 cm of ileum connecting the stomach to a common distal segment. c. A 300- to 400-cm biliary tract, which connects the duodenum, jejunum, and remaining ileum to the common distal segment. d. A 50- to 100-cm common tract, where food from the alimentary tract mixes with biliopancreatic juices from the biliary tract. Food digestion and absorption, particularly of fats and starches, are therefore limited to this small segment of bowel, i.e., creating a selective malabsorption. The length of the common segment will influence the degree of malabsorption. e. Because of the high incidence of cholelithiasis associated with the procedure, patients typically undergo an associated cholecystectomy. f. Many potential metabolic complications are related to biliopancreatic bypass, including most prominently iron deficiency anemia, protein malnutrition, hypocalcemia, and bone demineralization. Protein malnutrition may require treatment with total parenteral nutrition. In addition, there have been several case reports of liver failure resulting in death or liver transplant. 2. Biliopancreatic Bypass with Duodenal Switch (gastric restrictive procedure with partial gastrectomy, pylorus-preserving duodenoileostomy and ileoileostomy [50 to 100 cm common channel] to limit absorption [biliopancreatic diversion with duodenal switch]) The duodenal switch procedure is essentially a variant of the biliopancreatic bypass described here. In this procedure, instead of performing a distal gastrectomy, a sleeve gastrectomy is performed Page 3 of 8
4 along the vertical axis of the stomach, preserving the pylorus and initial segment of the duodenum, which is then anastomosed to a segment of the ileum, similar to the biliopancreatic bypass, to create the alimentary limb. Preservation of the pyloric sphincter is intended to ameliorate the dumping syndrome and decrease the incidence of ulcers at the duodenoileal anastomosis by providing a more physiologic transfer of stomach contents to the duodenum. The sleeve gastrectomy also decreases the volume of the stomach and decreases the parietal cell mass. However, the basic principle of the procedure is similar to that of the biliopancreatic bypass, i.e., producing selective malabsorption by limiting the food digestion and absorption to a short common ileal segment. 3. Long-Limb Gastric Bypass (i.e., >150 cm) (Gastric restrictive procedure with gastric bypass for morbid obesity; with small intestine reconstruction to limit absorption) Recently, variations of gastric bypass procedures have been described, consisting primarily of longlimb Roux-en-Y procedures, which vary in the length of the alimentary and common limbs. For example, the stomach may be divided with a long segment of the jejunum (instead of ileum) anastomosed to the proximal gastric stump, creating the alimentary limb. The remaining pancreaticobiliary limb, consisting of stomach remnant, duodenum, and length of proximal jejunum is then anastomosed to the ileum, creating a common limb of variable length in which the ingested food mixes with the pancreaticobiliary juices. While the long alimentary limb permits absorption of most nutrients, the short common limb primarily limits absorption of fats. The stomach may be bypassed in a variety of ways, i.e., either by resection or stapling along the horizontal or vertical axis. Unlike the traditional gastric bypass, which is essentially a gastric restrictive procedure, these very long-limb Roux-en-Y gastric bypasses combine gastric restriction with some element of malabsorptive procedure, depending on the location of the anastomoses. 4. Laparoscopic Malabsorptive Procedure (Laparoscopy, surgical, gastric restrictive procedure; with gastric bypass and small intestine reconstruction to limit absorption) Other non specific malabsorptive procedures. Corporate Medical Guideline 1. Gastric Restrictive Procedures Open gastric bypass using a Roux-en-Y anastomosis with an alimentary or Roux limb of 150 cm or less, or vertical-banded gastroplasty, may be considered medically appropriate in the treatment of morbid obesity that has not responded to conservative measures 1. Further, bariatric surgery should be performed in appropriately selected patients, by surgeons who are adequately trained and experienced in the specific techniques used, and in institutions that support a comprehensive bariatric surgery program, including long-term monitoring and follow-up post-surgery. Laparoscopic gastric bypass using a Roux-en-Y anastomosis is considered medically appropriate in the treatment of morbid obesity that has not responded to conservative measures 1. Further, bariatric surgery should be performed in appropriately selected patients, by surgeons who are adequately trained and experienced in the specific techniques used, and in institutions that support a comprehensive bariatric surgery program, including long-term monitoring and follow-up post-surgery. Adjustable gastric banding, consisting of an adjustable external band placed around the stomach, is considered medically appropriate in the treatment of morbid obesity that has not responded to conservative measures 1. Further, bariatric surgery should be performed in appropriately selected patients, by surgeons who are adequately trained and experienced in the specific techniques used, and in institutions that support a comprehensive bariatric surgery program, including long-term monitoring and follow-up post-surgery. Gastric bypass using a Billroth II type of anastomosis, popularized as the mini-gastric bypass, is considered investigational as a treatment of morbid obesity because it is not proven as effective as established alternatives. Sleeve gastrectomy, either as the sole procedure or as one step in a staged procedure, is considered investigational as a treatment for morbid obesity because it is not proven as effective as established alternatives. Page 4 of 8
5 2. Malabsorptive Procedures Biliopancreatic bypass (i.e., the Scopinaro procedure), biliopancreatic bypass with duodenal switch, or long-limb gastric bypass procedure (i.e., >150 cm) is considered investigational as a treatment of morbid obesity because it is not proven as effective as established alternatives. 3. Endoscopic Procedures for Weight Gain after Bariatric Surgery Endoscopic procedures (e.g., insertion of the StomaphyX device) to treat weight gain after bariatric surgery to remedy large gastric stoma or large gastric pouches are considered investigational because they are unproven outside the investigational setting. For explanation of experimental and investigational refer to the Technology Assessment Protocol. Policy Guideline *Patient Selection Criteria This policy does not apply to patients under the age of 18 years. There is very limited evidence on which to assess the long-term impacts of bariatric surgery for these patients. The FDA premarket approval for the LAP-BAND System indicates it is for use only in severely obese adult patients. (The clinical study that was submitted to the FDA for the LAP-BAND approval was restricted to adults ages years.) Patients with BMI greater than or equal to 50 kg/m 2 need a bariatric procedure to achieve greater weight loss. Thus, use of adjustable gastric banding, which results in less weight loss, should be most useful as one of the procedures used for patients with BMI less than 50 kg/m 2. Morbid obesity is defined as a body mass index (BMI) greater than 40 kg/m 2 or a BMI greater than 35pass kg/m 2 with associated complications including, but not limited to, diabetes, hypertension, or obstructive sleep apnea. BMI is calculated by dividing a patient s weight (in kilograms) by height (in meters) squared. To convert pounds to kilograms, multiply pounds by To convert inches to meters, multiply inches by Prior approval is required. HealthNow fully expects that only appropriate and medically necessary services will be rendered. HealthNow reserves the right to conduct prepayment and postpayment reviews to assess the medical appropriateness of the above-referenced procedures. conservative or conservative measures hyperlink wording: 1 Conservative measures are defined as non-surgical treatment including dietary counseling and some amount of exercise under the supervision of a physician. (If, in the opinion of the physician, the patient s condition precludes the ability to exercise this will be taken into consideration under individual medical director review on a case by case basis.) Conservative measures need to be documented as refractory for at least 6 months. There should be a failure to sustain a 5-10% or more reduction in body weight prior to consultation for bariatric surgery. The patient should be screened carefully by the appropriate mental health professional with regard to their ability to follow up with post op requirements. There should be no evidence of alcohol or drug abuse and it is strongly recommended that the bariatric surgeon urge the patient to remain nicotine free for 6 weeks prior to surgery. References 1. National Institutes of Health. Consensus Development Conference Panel. Gastrointestinal surgery for severe obesity. Ann Intern Med 1991; 115(12): Santry HP, Gillen DL, Lauderdale DS. Trends in bariatric surgery procedures. JAMA 2005, 294(15): MacLean LD, Rhode BM, Forse RA. Late results of vertical banded gastroplasty for morbid and super obesity. Surgery 1990; 107(1):20-7. Page 5 of 8
6 4. Willbanks OL. Long-term results of silicone elastomer ring vertical gastroplasty for the treatment of morbid obesity. Surgery 1987; 101(5): Brolin RE. Results of obesity surgery. Gastroenterol Clin North Am 1987; 16(2): Kolanowski J. Gastroplasty for morbid obesity: the internist s view. Int J Obes Metab Disord 1995; 19 (suppl 3):S Melissas J, Christodoulakis M, Spyridakis M, et al. Disorders associated with clinically severe obesity: significant improvement after surgical weight reduction. South Med J 1998; 91(12): Hall JC, Watts JM, O'Brien PE, et al. Gastric surgery for morbid obesity. The Adelaide Study. Ann Surg 1990; 211(4): Hall JC, Watts JM, O'Brien PE, et al. Gastric surgery for morbid obesity. The Adelaide Study. Ann Surg 1990; 211(4): Sugerman HJ, Starkey JV, Birkenhauer R. A randomized prospective trial of gastric bypass versus vertical banded gastroplasty for morbid obesity and their effects on sweets versus non-sweets eaters. Ann Surg 1987; 205(6): Griffen WO. Gastric bypass. In: Surgical Management of Morbid Obesity. Griffen WO, Printen KJ (eds.). New York: Marcel Dekker, Inc; pp Pories WJ, Swanson MS, MacDonald KG, et al. Who would have thought it? An operation proves to be the most effective therapy for adult-onset diabetes mellitus. Ann Surg 1995; 222(3): Flickinger EG, Sinar DR, Swanson M. Gastric bypass. Gastroenterol Clin North Am 1987; 16(2): Cowan GS, Buffington CK. Significant changes in blood pressure, glucose and lipids with gastric bypass surgery. World J Surg 1998; 22(9): Rutledge R. The mini-gastric bypass: experience with the first 1,274 cases. Obes Surg 2001; 11(3): Lap-Band Adjustable Gastric Banding System, BioEnterics Corporation, Carpinteria, CA. Package insert. 16. Moon Han S, Kim WW, Oh JH. Results of laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy (LSG) at 1 year in morbidly obese Korean patients. Obes Surg 2005; 15(10): Langer FB, Bohdjalian A, Felberbauer FX, et al. Does gastric dilatation limit the success of sleeve gastrectomy as sole operation for morbid obesity? Obes Surg 2006; 16(2): Regan JP, Inabnet WB, Gagner M, et al. Early experience with two-stage laparoscopic Roux-en-Y gastric bypass as an alternative in the super-super obese patient. Obes Surg 2003; 13(6): Mognol P, Chosidow D, Marmuse JP. Laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy as an initial bariatric procedure for high-risk patients: initial results in 10 patients. Obes Surg 2005; 15(7): Scopinaro N, Gianetta E, Adami GF, et al. Biliopancreatic diversion for obesity at eighteen years. Surgery 1996; 119(3): Slater GH, Ren CJ, Siegel N, et al. Serum fat-soluble vitamin deficiency and abnormal calcium metabolism after malabsorptive bariatric surgery. J Gastrointest Surg 2004; 8(1): Dolan K, Hatzifotis M, Newbury L, et al. A clinical and nutritional comparison of biliopancreatic diversion with and without duodenal switch. Ann Surg 2004; 240(1): Murr MM, Balsiger BM, Kennedy FP, et al. Malabsorptive procedures for severe obesity: comparison of pancreaticobiliary bypass and very, very long limb Roux-en-Y gastric bypass. J Gastrointest Surg 1999; 3(6): Grimm IS, Schindler W, Haluszka O. Steatohepatitis and fatal hepatic failure after biliopancreatic diversion. Am J Gastrenterol 1992; 87(6): Langdon DE, Leffingwell T, Rank D. Hepatic failure after biliopancreatic diversion. Am J Gastroenterol 1993; 88(2):321. Page 6 of 8
7 26. Marceau P, Hould FS, Simard S, et al. Biliopancreatic diversion with duodenal switch. World J Surg 1998; 22(9): Hess DS, Hess DW. Biliopancreatic diversion with a duodenal switch. Obes Surg 1998; 8(3): Baltasar A, del Rio J, Escriva C, et al. Preliminary results of the duodenal switch. Obes Surg 1997; 7(6): Sugerman HJ, Kellum JM, DeMaria EJ. Conversion of proximal to distal gastric bypass for failed gastric bypass for superobesity. J Gastrointest Surg 1997; 1(6): Inabnet WB, Quinn T, Gagner M, et al. Laparoscopic Roux-en-Y gastric bypass in patients with BMI <50: a prospective randomized trial comparing short and long limb lengths. Obes Surg 2005; 15(1): Choban PS, Flancbaum L. The effect of Roux limb lengths on outcome after Roux-en-Y gastric bypass: a prospective, randomized clinical trial. Obes Surg 2002; 12(4): Brolin RE, LaMarca LB, Kenler HA, et al. Malabsorptive gastric bypass in patients with superobesity. J Gastrointest Surg 2002; 6(2): MacLean LD, Rhode BM, Nohr CW. Long- or short-limb gastric bypass? J Gastrointest Surg 2001; 5(5): Mason EE, Tang S, Renquist KE, et al. A decade of change in obesity surgery. National Bariatric Surgery Registry (NBSR) Contributors. Obes Surg 1997; 7(3): Nguyen NT, Paya M, Stevens CM. The relationship between hospital volume and outcome in bariatric surgery at academic medical centers. Ann Surg 2004, 240(4): Liu JH, Zingmond D, Etzioni DA, et al. Characterizing the performance and outcomes of obesity surgery in California. Am Surg 2003; 69(10): Courcoulas A, Schuchert M, Gatti G, et al. The relationship of surgeon and hospital volume to outcome after gastric bypass surgery in Pennsylvania: a 3-year summary. Surgery 2003; 134(4): Bowne WB, Julliard K, Castro AE, et al. Laparoscopic gastric bypass is superior to adjustable gastric band in super morbidly obese patients: a prospective, comparative analysis. Arch Srug 2006; 141(7): Parikh MS, Shen R, Weiner M, et al. Laparoscopic bariatric surgery in super-obese patients (BMI>50) is safe and effective: a review of 332 patients. Obes Surg 2005; 15(6); Myers JA, Sarker S, Shayani V. Treatment of massive super-obesity with laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding. Surg Obes Relat Dis. 2006; 2(1): Montgomery KF, Watkins BM, Ahroni JH, et al. Outpatient laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding in super-obese patients. Obes Surg (6): Mognol P, Chosidow D, Marmuse JP. Laparoscopic gastric bypass versus laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding in the super-obese: a comparative study of 290 patients. Obes Surg 2005; 15(1): Morton JM. Weight gain after bariatric surgery as a result of large gastric stoma: endotherapy with sodium morrhuate to induce stomal stenosis may prevent the need for surgical revision (editorial). Gastrointest Endosc 2007; 66(2): Catalano MF, Rudic G, Anderson AJ, et al. Weight gain after bariatric surgery as a result of a large gastric stoma: endotherapy with sodium morrhuate may prevent the need for surgical revision. Gastrointest Endosc 2007; 66(2): Herron DM, Birkett DH, Thompson CC, et al. Gastric bypass pouch and stoma reduction using a transoral endoscopic anchor placement system: a feasibility study. Surg Endosc 2007 Nov 20 [e-pub ahead of print]. Page 7 of 8
8 47. Thompson CC, Slattery J, Bundga ME, et al. Peroral endoscopic reduction of dilated gastrojejunal anastomoses after Roux-en-Y gastric bypass: a possible new option for patients with weight regain. Surg Endosc 2006; 20(11): Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services. Decision memo for bariatric surgery for the treatment of morbid obesity (CAG-00250R). accessed 3/27/ Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services. Minutes of 11/4/04 MCAC meeting for bariatric surgery. 3/27/ UMD LCD L14089, Bariatric Surgery, effective 1/1/07. Last Review Date Reviewed with literature search/may 2008 Next Review Date Review with literature search/may 2009 Page 8 of 8
d EFFECTIVE DATE: 11 5 2014 POLICY LAST UPDATED: 5 29 2015
 Medical Coverage Policy Bariatric Surgery-Not medically necessary procedures d EFFECTIVE DATE: 11 5 2014 POLICY LAST UPDATED: 5 29 2015 OVERVIEW Surgery for obesity, termed bariatric surgery, is a treatment
Medical Coverage Policy Bariatric Surgery-Not medically necessary procedures d EFFECTIVE DATE: 11 5 2014 POLICY LAST UPDATED: 5 29 2015 OVERVIEW Surgery for obesity, termed bariatric surgery, is a treatment
2. The condition of morbid/clinically severe obesity must be of at least five years duration.
 COVERAGE: Prior to determining the coverage for surgical treatment of obesity, conservative treatment options must have been tried and have failed. The screening criteria listed below should be used: 1.
COVERAGE: Prior to determining the coverage for surgical treatment of obesity, conservative treatment options must have been tried and have failed. The screening criteria listed below should be used: 1.
Medical Coverage Policy Bariatric Surgery
 Medical Coverage Policy Bariatric Surgery Device/Equipment Drug Medical Surgery Test Other Effective Date: 9/1/2011 Policy Last Updated: 11/01/2011 Prospective review is recommended/required. Please check
Medical Coverage Policy Bariatric Surgery Device/Equipment Drug Medical Surgery Test Other Effective Date: 9/1/2011 Policy Last Updated: 11/01/2011 Prospective review is recommended/required. Please check
Overview of Bariatric Surgery
 Overview of Bariatric Surgery To better understand how weight loss surgery works, it is helpful to know how the normal digestive process works. As food moves along the digestive tract, special digestive
Overview of Bariatric Surgery To better understand how weight loss surgery works, it is helpful to know how the normal digestive process works. As food moves along the digestive tract, special digestive
BARIATRIC SURGERY. Prerequisites. Authorization, Notification and Referral
 BARIATRIC SURGERY Policy NHP reimburses participating providers for specific types of medically necessary bariatric surgery when needed to either alleviate or correct medical problems caused by severe
BARIATRIC SURGERY Policy NHP reimburses participating providers for specific types of medically necessary bariatric surgery when needed to either alleviate or correct medical problems caused by severe
Types of Bariatric Procedures. Tejal Brahmbhatt, MD General Surgery Teaching Conference April 18, 2012
 Types of Bariatric Procedures Tejal Brahmbhatt, MD General Surgery Teaching Conference April 18, 2012 A Brief History of Bariatric Surgery First seen in pts with short bowel syndrome weight loss First
Types of Bariatric Procedures Tejal Brahmbhatt, MD General Surgery Teaching Conference April 18, 2012 A Brief History of Bariatric Surgery First seen in pts with short bowel syndrome weight loss First
POLICY PRODUCT VARIATIONS DESCRIPTION/BACKGROUND RATIONALE DEFINITIONS BENEFIT VARIATIONS DISCLAIMER CODING INFORMATION REFERENCES POLICY HISTORY
 Original Issue Date (Created): 8/9/2002 Most Recent Review Date (Revised): 3/24/2015 Effective Date: 8/1/2015 POLICY PRODUCT VARIATIONS DESCRIPTION/BACKGROUND RATIONALE DEFINITIONS BENEFIT VARIATIONS DISCLAIMER
Original Issue Date (Created): 8/9/2002 Most Recent Review Date (Revised): 3/24/2015 Effective Date: 8/1/2015 POLICY PRODUCT VARIATIONS DESCRIPTION/BACKGROUND RATIONALE DEFINITIONS BENEFIT VARIATIONS DISCLAIMER
Medical Coverage Policy Bariatric Surgery
 Medical Coverage Policy Bariatric Surgery-Not medically necessary procedures EFFECTIVE DATE: 11 04 2014 POLICY LAST UPDATED: 02 24 2016 OVERVIEW Surgery for obesity, termed bariatric surgery, is a treatment
Medical Coverage Policy Bariatric Surgery-Not medically necessary procedures EFFECTIVE DATE: 11 04 2014 POLICY LAST UPDATED: 02 24 2016 OVERVIEW Surgery for obesity, termed bariatric surgery, is a treatment
BARIATRIC SURGERY AND OTHER INVASIVE TREATMENTS FOR OBESITY
 Coverage for services, procedures, medical devices and drugs are dependent upon benefit eligibility as outlined in the member's specific benefit plan. This Medical Coverage Guideline must be read in its
Coverage for services, procedures, medical devices and drugs are dependent upon benefit eligibility as outlined in the member's specific benefit plan. This Medical Coverage Guideline must be read in its
BARIATRIC SURGERY FOR MORBID OBESITY Corporate Medical Policy
 BARIATRIC SURGERY FOR MORBID OBESITY Corporate Medical Policy File name: Bariatric Surgery for Morbid Obesity File code: UM.SURG.01 Origination: 7/2008 Last Review: 04/2013 Next Review: 04/2014 Effective
BARIATRIC SURGERY FOR MORBID OBESITY Corporate Medical Policy File name: Bariatric Surgery for Morbid Obesity File code: UM.SURG.01 Origination: 7/2008 Last Review: 04/2013 Next Review: 04/2014 Effective
Protocol. Bariatric Surgery
 Protocol Bariatric Surgery (70147) Medical Benefit Effective Date: 04/01/14 Next Review Date: 01/15 Preauthorization Yes Review Dates: 04/07, 05/08, 05/09, 03/10, 03/11, 07/11, 07/12, 9/12, 05/13, 01/14
Protocol Bariatric Surgery (70147) Medical Benefit Effective Date: 04/01/14 Next Review Date: 01/15 Preauthorization Yes Review Dates: 04/07, 05/08, 05/09, 03/10, 03/11, 07/11, 07/12, 9/12, 05/13, 01/14
Morbid obesity is a chronic condition that
 COSMETIC A Review of Bariatric Surgery Procedures Morbid obesity is a chronic condition that is extremely difficult to treat. In addition to unhealthy food choices and lifestyles, effective treatment for
COSMETIC A Review of Bariatric Surgery Procedures Morbid obesity is a chronic condition that is extremely difficult to treat. In addition to unhealthy food choices and lifestyles, effective treatment for
BARIATRIC SURGERY FOR MORBID OBESITY Corporate Medical Policy
 BARIATRIC SURGERY FOR MORBID OBESITY Corporate Medical Policy File name: Bariatric Surgery for Morbid Obesity File code: UM.SURG.01 Origination: 7/2008 Last Review: 06/2015 Next Review: 06/2016 Effective
BARIATRIC SURGERY FOR MORBID OBESITY Corporate Medical Policy File name: Bariatric Surgery for Morbid Obesity File code: UM.SURG.01 Origination: 7/2008 Last Review: 06/2015 Next Review: 06/2016 Effective
Some of the diseases and conditions associated with obesity include:
 WEIGHT-LOSS SURGERY facts about obesity Obesity is rapidly becoming the nation s number-one health problem. Of the 97 million Americans who are overweight, 10 million are considered morbidly obese. Obesity
WEIGHT-LOSS SURGERY facts about obesity Obesity is rapidly becoming the nation s number-one health problem. Of the 97 million Americans who are overweight, 10 million are considered morbidly obese. Obesity
IEHP UM Subcommittee Approved Authorization Guidelines Bariatric Surgery for Morbid Obesity
 According to the National Institutes of Health (NIH) Consensus Development Conference on Gastrointestinal Surgery for Severe Obesity, the risk for morbidity and mortality accompanying obesity increases
According to the National Institutes of Health (NIH) Consensus Development Conference on Gastrointestinal Surgery for Severe Obesity, the risk for morbidity and mortality accompanying obesity increases
Gastric Surgery for Clinically Severe (Morbid) Obesity
 Origination: 03/28/01 Revised: 01/16/15 Annual Review: 11/12/15 Purpose: The Medical Technology Assessment Committee will review published scientific literature and information from appropriate government
Origination: 03/28/01 Revised: 01/16/15 Annual Review: 11/12/15 Purpose: The Medical Technology Assessment Committee will review published scientific literature and information from appropriate government
Surgical Weight Loss. Mission Bariatrics
 Surgical Weight Loss Mission Bariatrics Obesity is a major health problem in the United States, with more than one in every three people suffering from this chronic condition. Obese adults are at an increased
Surgical Weight Loss Mission Bariatrics Obesity is a major health problem in the United States, with more than one in every three people suffering from this chronic condition. Obese adults are at an increased
Corporate Medical Policy
 Corporate Medical Policy File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: surgery_for_morbid_obesity 5/1983 5/2012 5/2013 5/2012 Description of Procedure or Service Surgery for morbid
Corporate Medical Policy File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: surgery_for_morbid_obesity 5/1983 5/2012 5/2013 5/2012 Description of Procedure or Service Surgery for morbid
d EFFECTIVE DATE: 11 04 14 POLICY LAST UPDATED: 08 03 2015
 Medical Coverage Policy Bariatric Surgery-Not medically necessary procedures d EFFECTIVE DATE: 11 04 14 POLICY LAST UPDATED: 08 03 2015 OVERVIEW Surgery for obesity, termed bariatric surgery, is a treatment
Medical Coverage Policy Bariatric Surgery-Not medically necessary procedures d EFFECTIVE DATE: 11 04 14 POLICY LAST UPDATED: 08 03 2015 OVERVIEW Surgery for obesity, termed bariatric surgery, is a treatment
Bariatric Surgery. Policy Number: 7.01.47 Last Review: 3/2016 Origination: 10/1988 Next Review: 12/2016
 Bariatric Surgery Policy Number: 7.01.47 Last Review: 3/2016 Origination: 10/1988 Next Review: 12/2016 Policy Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Kansas City (Blue KC) will provide coverage for bariatric surgery
Bariatric Surgery Policy Number: 7.01.47 Last Review: 3/2016 Origination: 10/1988 Next Review: 12/2016 Policy Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Kansas City (Blue KC) will provide coverage for bariatric surgery
Weight Loss Surgery Info for Physicians
 Weight Loss Surgery Info for Physicians As physicians, we see it every day when we see our patients more and more people are obese, and it s affecting their health. It s estimated that at least 2/3 of
Weight Loss Surgery Info for Physicians As physicians, we see it every day when we see our patients more and more people are obese, and it s affecting their health. It s estimated that at least 2/3 of
IHCP bulletin INDIANA HEALTH COVERAGE PROGRAMS BT201420 APRIL 29, 2014
 IHCP bulletin INDIANA HEALTH COVERAGE PROGRAMS BT201420 APRIL 29, 2014 IHCP to cover sleeve gastrectomy surgery The Indiana Health Coverage Programs (IHCP) covers bariatric surgery for individuals with
IHCP bulletin INDIANA HEALTH COVERAGE PROGRAMS BT201420 APRIL 29, 2014 IHCP to cover sleeve gastrectomy surgery The Indiana Health Coverage Programs (IHCP) covers bariatric surgery for individuals with
Bariatric surgery for morbid obesity: Why, who, when, how, where, and then what?
 REVIEW PATRICIA SMITH CHOBAN, MD Bariatric Treatment Center of Ohio, and the Department of Human Nutrition, The Ohio State University, Columbus BENITA JACKSON, MD, MPH School of Public Health, The Ohio
REVIEW PATRICIA SMITH CHOBAN, MD Bariatric Treatment Center of Ohio, and the Department of Human Nutrition, The Ohio State University, Columbus BENITA JACKSON, MD, MPH School of Public Health, The Ohio
BARIATRIC SURGERY MAY CURE TYPE 2 DIABETES IN SOME PATIENTS
 BARIATRIC SURGERY MAY CURE TYPE 2 DIABETES IN SOME PATIENTS Thomas Rogula MD, Stacy Brethauer MD, Bipand Chand MD, and Philip Schauer, MD. "Gastric bypass surgery has become a popular option for obese
BARIATRIC SURGERY MAY CURE TYPE 2 DIABETES IN SOME PATIENTS Thomas Rogula MD, Stacy Brethauer MD, Bipand Chand MD, and Philip Schauer, MD. "Gastric bypass surgery has become a popular option for obese
Bariatric Surgery MM.06.003 09/11/2001. HMO; PPO; QUEST Integration 09/26/2014 Section: Surgery Place(s) of Service: Outpatient; Inpatient
 Bariatric Surgery Policy Number: Original Effective Date: MM.06.003 09/11/2001 Line(s) of Business: Current Effective Date: HMO; PPO; QUEST Integration 09/26/2014 Section: Surgery Place(s) of Service:
Bariatric Surgery Policy Number: Original Effective Date: MM.06.003 09/11/2001 Line(s) of Business: Current Effective Date: HMO; PPO; QUEST Integration 09/26/2014 Section: Surgery Place(s) of Service:
Gastric Bypass and Other Bariatric Surgical Procedures*
 Subject: Gastric Bypass and Other Bariatric Surgical Procedures* Updated: February 24, 2009 Department(s): Policy: Objective: Utilization Management Medically necessary bariatric surgical procedures are
Subject: Gastric Bypass and Other Bariatric Surgical Procedures* Updated: February 24, 2009 Department(s): Policy: Objective: Utilization Management Medically necessary bariatric surgical procedures are
5. Conversion Procedures that change from an index procedure to a different type of procedure.
 Benefit Coverage Covered Benefit for lines of business including Health Benefits Exchange (HBE), Rite Care (MED), Children with Special Needs (CSN), Substitute Care (SUB), Rhody Health Partners (RHP),
Benefit Coverage Covered Benefit for lines of business including Health Benefits Exchange (HBE), Rite Care (MED), Children with Special Needs (CSN), Substitute Care (SUB), Rhody Health Partners (RHP),
Transmittal 54 Date: APRIL 28, 2006. SUBJECT: Bariatric Surgery for Treatment of Morbid Obesity
 CMS Manual System Pub 100-03 Medicare National Coverage Determinations Department of Health & Human Services (DHHS) Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) Transmittal 54 Date: APRIL 28, 2006 Change
CMS Manual System Pub 100-03 Medicare National Coverage Determinations Department of Health & Human Services (DHHS) Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) Transmittal 54 Date: APRIL 28, 2006 Change
MEDICAL COVERAGE POLICY. SERVICE: Bariatric (Weight Loss) Surgery Policy Number: 053 Effective Date: 5/27/2014 Last Review: 4/24/2014
 Page 1 of 6 MEDICAL COVERAGE POLICY Important note Even though this policy may indicate that a particular service or supply is considered covered, this conclusion is not necessarily based upon the terms
Page 1 of 6 MEDICAL COVERAGE POLICY Important note Even though this policy may indicate that a particular service or supply is considered covered, this conclusion is not necessarily based upon the terms
Protocol. Bariatric Surgery
 Protocol Bariatric Surgery (70147) Medical Benefit Effective Date: 01/01/16 Next Review Date: 11/16 Preauthorization Yes Review Dates: 04/07, 05/08, 05/09, 03/10, 03/11, 07/11, 07/12, 9/12, 05/13, 01/14,
Protocol Bariatric Surgery (70147) Medical Benefit Effective Date: 01/01/16 Next Review Date: 11/16 Preauthorization Yes Review Dates: 04/07, 05/08, 05/09, 03/10, 03/11, 07/11, 07/12, 9/12, 05/13, 01/14,
White Paper: Treating Clinical Obesity: When is Bariatric Surgery or Bariatric Surgery Revision Medically Necessary?
 White Paper: Treating Clinical Obesity: When is Bariatric Surgery or Bariatric Surgery Revision Medically Necessary? For Health Plans, Medical Management Organizations and TPAs Introduction More than one
White Paper: Treating Clinical Obesity: When is Bariatric Surgery or Bariatric Surgery Revision Medically Necessary? For Health Plans, Medical Management Organizations and TPAs Introduction More than one
Vertical Sleeve Gastrectomy (VSG) - Also known as Sleeve Gastrectomy, Vertical Gastrectomy
 Vertical Sleeve Gastrectomy (VSG) - Also known as Sleeve Gastrectomy, Vertical Gastrectomy The Vertical Sleeve Gastrectomy procedure (also called Sleeve Gastrectomy, Vertical Gastrectomy, Greater Curvature
Vertical Sleeve Gastrectomy (VSG) - Also known as Sleeve Gastrectomy, Vertical Gastrectomy The Vertical Sleeve Gastrectomy procedure (also called Sleeve Gastrectomy, Vertical Gastrectomy, Greater Curvature
Weight Gain After Short- and Long-Limb Gastric Bypass in Patients Followed for Longer Than 10 Years
 ORIGINAL ARTICLES Weight Gain After Short- and Long-Limb Gastric Bypass in Patients Followed for Longer Than 10 Years Nicolas V. Christou, MD, PhD, Didier Look, MD, and Lloyd D. MacLean, MD, PhD Objective:
ORIGINAL ARTICLES Weight Gain After Short- and Long-Limb Gastric Bypass in Patients Followed for Longer Than 10 Years Nicolas V. Christou, MD, PhD, Didier Look, MD, and Lloyd D. MacLean, MD, PhD Objective:
MEDICAL POLICY No. 91595-R2 SURGICAL TREATMENT OF OBESITY
 SURGICAL TREATMENT OF OBESITY Effective Date: October 1, 2015 Review Dates: 8/11, 12/11, 2/12, 2/13, 2/14, 11/14, 2/15 Date Of Origin: August 10, 2011 Status: Current Note: This medical policy does not
SURGICAL TREATMENT OF OBESITY Effective Date: October 1, 2015 Review Dates: 8/11, 12/11, 2/12, 2/13, 2/14, 11/14, 2/15 Date Of Origin: August 10, 2011 Status: Current Note: This medical policy does not
Subject: Obesity: Surgical Management
 Page 1 of 5 Approved: Robert Neal Mills, MD Date: 7/12/2012 (This criteria is for plans that provide an obesity surgery benefit and do NOT have their own specific criteria.) (Please refer to the member
Page 1 of 5 Approved: Robert Neal Mills, MD Date: 7/12/2012 (This criteria is for plans that provide an obesity surgery benefit and do NOT have their own specific criteria.) (Please refer to the member
Surgical Treatment of Obesity: A Surgeon s View
 Surgical Treatment of Obesity: A Surgeon s View Jenny J. Choi, MD Director of Bariatrics Associate Director of Clinical Affairs Assistant Professor of Surgery Albert Einstein School of Medicine Montefiore
Surgical Treatment of Obesity: A Surgeon s View Jenny J. Choi, MD Director of Bariatrics Associate Director of Clinical Affairs Assistant Professor of Surgery Albert Einstein School of Medicine Montefiore
Technical Aspects of Bariatric Surgical Procedures. Robert O. Carpenter, MD, MPH, FACS Department of Surgery Scott & White Memorial Hospital
 Technical Aspects of Bariatric Surgical Procedures Robert O. Carpenter, MD, MPH, FACS Department of Surgery Scott & White Memorial Hospital Disclosures Allergan, Inc. (Past) Faculty Member Educational
Technical Aspects of Bariatric Surgical Procedures Robert O. Carpenter, MD, MPH, FACS Department of Surgery Scott & White Memorial Hospital Disclosures Allergan, Inc. (Past) Faculty Member Educational
Obesity When to Recommend Surgery. Lily Chang, MD September 27, 2013
 Obesity When to Recommend Surgery Lily Chang, MD September 27, 2013 Obesity BMI >30 Trends Among U.S. Adults Source: Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System, CDC, 2012 Obesity Related Co-Morbidities
Obesity When to Recommend Surgery Lily Chang, MD September 27, 2013 Obesity BMI >30 Trends Among U.S. Adults Source: Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System, CDC, 2012 Obesity Related Co-Morbidities
Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass
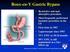 Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass Restrictive and malabsorptive procedure Most frequently performed bariatric procedure in the US First done in 1967 Laparoscopic since 1993 75% EWL in 18-24 months 50% EWL is still
Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass Restrictive and malabsorptive procedure Most frequently performed bariatric procedure in the US First done in 1967 Laparoscopic since 1993 75% EWL in 18-24 months 50% EWL is still
biliopancreatic bypass; a surgical procedure involving a gastric restriction diverting bile and pancreatic juice into the distal ileum.
 SURGERY FOR MORBID OBESITY SUR716.003 COVERAGE: Surgical procedures which may be eligible for coverage for the treatment of morbid or clinically severe obesity are: 1. Vertical banded gastroplasty (gastric
SURGERY FOR MORBID OBESITY SUR716.003 COVERAGE: Surgical procedures which may be eligible for coverage for the treatment of morbid or clinically severe obesity are: 1. Vertical banded gastroplasty (gastric
Changes to Bariatric Surgery Prior Authorization Guidelines
 Update August 2011 No. 2011-44 Affected Programs: BadgerCare Plus, Medicaid To: Hospital Providers, Physician Assistants, Physician Clinics, Physicians, HMOs and Other Managed Care Programs Changes to
Update August 2011 No. 2011-44 Affected Programs: BadgerCare Plus, Medicaid To: Hospital Providers, Physician Assistants, Physician Clinics, Physicians, HMOs and Other Managed Care Programs Changes to
Bariatric Surgery. Beth A. Ryder, MD FACS. Assistant Professor of Surgery The Miriam Hospital Warren Alpert Medical School of Brown University
 Bariatric Surgery Beth A. Ryder, MD FACS Assistant Professor of Surgery The Miriam Hospital Warren Alpert Medical School of Brown University April 30, 2013 Why surgery? Eligibility criteria Most commonly
Bariatric Surgery Beth A. Ryder, MD FACS Assistant Professor of Surgery The Miriam Hospital Warren Alpert Medical School of Brown University April 30, 2013 Why surgery? Eligibility criteria Most commonly
Consumer summary Laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding for the treatment of obesity (Update and re-appraisal)
 ASERNIP S Australian Safety and Efficacy Register of New Interventional Procedures Surgical Consumer summary Laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding for the treatment of obesity (Update and re-appraisal)
ASERNIP S Australian Safety and Efficacy Register of New Interventional Procedures Surgical Consumer summary Laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding for the treatment of obesity (Update and re-appraisal)
Bariatric Surgery. Overview of Procedural Options
 Bariatric Surgery Overview of Procedural Options The Obesity Epidemic In 1991, NO state had an obesity rate above 20% 1 As of 2010, more than two-thirds of states (38) now have adult obesity rates above
Bariatric Surgery Overview of Procedural Options The Obesity Epidemic In 1991, NO state had an obesity rate above 20% 1 As of 2010, more than two-thirds of states (38) now have adult obesity rates above
Morbid obesity is defined as a body mass index (BMI) >40 kg/m2 (normal BMI range: 19-25 kg/m2)
 Medical Policy Manual Topic: Bariatric Surgery Date of Origin: January 1996 Section: Surgery Last Reviewed Date: January 2014 Policy No: 58 Effective Date: July 1, 2014 IMPORTANT REMINDER Medical Policies
Medical Policy Manual Topic: Bariatric Surgery Date of Origin: January 1996 Section: Surgery Last Reviewed Date: January 2014 Policy No: 58 Effective Date: July 1, 2014 IMPORTANT REMINDER Medical Policies
Obesity Affects Quality of Life
 Obesity Obesity is a serious health epidemic. Obesity is a condition characterized by excessive body fat, genetic and environmental factors. Obesity increases the likelihood of certain diseases and other
Obesity Obesity is a serious health epidemic. Obesity is a condition characterized by excessive body fat, genetic and environmental factors. Obesity increases the likelihood of certain diseases and other
Weight loss surgery more than just a gastric band
 Weight loss surgery more than just a gastric band Presented by Ms Beth Murgatroyd Honorary Bariatric Nurse Practitioner Mr Ameet G Patel Consultant Surgeon Director of Bariatric Surgery at King s College
Weight loss surgery more than just a gastric band Presented by Ms Beth Murgatroyd Honorary Bariatric Nurse Practitioner Mr Ameet G Patel Consultant Surgeon Director of Bariatric Surgery at King s College
NHRMC General Surgery Specialists. Minimally Invasive Gastrointestinal Surgery Phone: 910-662-9300 Fax: 910-662-9303
 Minimally Invasive Gastrointestinal Surgery Phone: 910-662-9300 Fax: 910-662-9303 W. Borden Hooks III, MD 1725 New Hanover Medical Park Drive Wilmington, NC 28403 Thank you for choosing NHRMC General Surgery
Minimally Invasive Gastrointestinal Surgery Phone: 910-662-9300 Fax: 910-662-9303 W. Borden Hooks III, MD 1725 New Hanover Medical Park Drive Wilmington, NC 28403 Thank you for choosing NHRMC General Surgery
Treatment for Severely Obese Patients
 Treatment for Severely Obese Patients Associate Professor Jimmy So Senior Consultant Surgeon Director, Centre for Obesity Management and Surgery (COMS) National University Hospital Obesity Shortens Lives
Treatment for Severely Obese Patients Associate Professor Jimmy So Senior Consultant Surgeon Director, Centre for Obesity Management and Surgery (COMS) National University Hospital Obesity Shortens Lives
The Evolution of Bariatric Surgery. History of the Development of a Successful Bariatric Program at the University of Iowa Hospitals & Clinics
 The Evolution of Bariatric Surgery History of the Development of a Successful Bariatric Program at the University of Iowa Hospitals & Clinics It s a BIG Problem & it s Getting Worse Obesity is now a disease
The Evolution of Bariatric Surgery History of the Development of a Successful Bariatric Program at the University of Iowa Hospitals & Clinics It s a BIG Problem & it s Getting Worse Obesity is now a disease
Weight Loss Surgery Information Session. WFBH Bariatric Surgery Program
 Weight Loss Surgery Information Session WFBH Bariatric Surgery Program What makes us different? Center of Excellence (COE) High volume center > 1000 procedures since 2003 Less complications than non-coe
Weight Loss Surgery Information Session WFBH Bariatric Surgery Program What makes us different? Center of Excellence (COE) High volume center > 1000 procedures since 2003 Less complications than non-coe
Comparison of Nutritional Deficiencies after Rouxen-Y Gastric Bypass and after Biliopancreatic Diversion with Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass
 Obesity Surgery, 12, 551-558 Comparison of Nutritional Deficiencies after Rouxen-Y Gastric Bypass and after Biliopancreatic Diversion with Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass George Skroubis, MD 1 ; George Sakellaropoulos,
Obesity Surgery, 12, 551-558 Comparison of Nutritional Deficiencies after Rouxen-Y Gastric Bypass and after Biliopancreatic Diversion with Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass George Skroubis, MD 1 ; George Sakellaropoulos,
WEIGHT LOSS SURGERY. Pre-Clinic Conference Jennifer Kinley, MD 12/15/2010
 WEIGHT LOSS SURGERY Pre-Clinic Conference Jennifer Kinley, MD 12/15/2010 EDUCATIONAL OBJECTIVES: Discuss the available pharmaceutical options for weight loss and risks of these medications Explain the
WEIGHT LOSS SURGERY Pre-Clinic Conference Jennifer Kinley, MD 12/15/2010 EDUCATIONAL OBJECTIVES: Discuss the available pharmaceutical options for weight loss and risks of these medications Explain the
Morbid obesity is defined as a body mass index (BMI) >40 kg/m2 (normal BMI range: 19-25 kg/m2)
 Medical Policy Manual Topic: Bariatric Surgery Date of Origin: January 1996 Section: Surgery Last Reviewed Date: May 2016 Policy No: 58 Effective Date: June 1, 2016 IMPORTANT REMINDER Medical Policies
Medical Policy Manual Topic: Bariatric Surgery Date of Origin: January 1996 Section: Surgery Last Reviewed Date: May 2016 Policy No: 58 Effective Date: June 1, 2016 IMPORTANT REMINDER Medical Policies
Corporate Medical Policy
 Corporate Medical Policy File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: surgery_for_morbid_obesity 5/1983 5/2015 5/2016 5/2015 Description of Procedure or Service Surgery for morbid
Corporate Medical Policy File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: surgery_for_morbid_obesity 5/1983 5/2015 5/2016 5/2015 Description of Procedure or Service Surgery for morbid
Bariatric Surgery. OHTAC Recommendation. Bariatric Surgery
 OHTAC Recommendation Bariatric Surgery January 21, 2005 1 The Ontario Health Technology Advisory Committee (OHTAC) met on January 21, 2005 and reviewed bariatric surgery for morbid obesity. Obesity is
OHTAC Recommendation Bariatric Surgery January 21, 2005 1 The Ontario Health Technology Advisory Committee (OHTAC) met on January 21, 2005 and reviewed bariatric surgery for morbid obesity. Obesity is
Morbid obesity is defined as a body mass index (BMI) >40 kg/m2 (normal BMI range: 19-25 kg/m2)
 Medical Policy Manual Topic: Bariatric Surgery Date of Origin: January 1996 Section: Surgery Last Reviewed Date: August 2015 Policy No: 58 Effective Date: September 1, 2015 IMPORTANT REMINDER Medical Policies
Medical Policy Manual Topic: Bariatric Surgery Date of Origin: January 1996 Section: Surgery Last Reviewed Date: August 2015 Policy No: 58 Effective Date: September 1, 2015 IMPORTANT REMINDER Medical Policies
Why a loop and new approach makes sense!
 IP: tomach Intestinal Pylorus paring urgery Why a loop and new approach makes sense! Mitchell Roslin, MD, FAC Chief of Bariatric and Metabolic urgery Lenox Hill Hospital Northern Westchester Hospital Center
IP: tomach Intestinal Pylorus paring urgery Why a loop and new approach makes sense! Mitchell Roslin, MD, FAC Chief of Bariatric and Metabolic urgery Lenox Hill Hospital Northern Westchester Hospital Center
Section 2. Overview of Obesity, Weight Loss, and Bariatric Surgery
 Section 2 Overview of Obesity, Weight Loss, and Bariatric Surgery What is Weight Loss? How does surgery help with weight loss? Short term versus long term weight loss? Conditions Improved with Weight Loss
Section 2 Overview of Obesity, Weight Loss, and Bariatric Surgery What is Weight Loss? How does surgery help with weight loss? Short term versus long term weight loss? Conditions Improved with Weight Loss
Acute Abdominal Pain following Bariatric Surgery. Disclosure. Objectives 8/17/2015. I have nothing to disclose
 Acute Abdominal Pain following Bariatric Surgery Kathy J. Morris, DNP, APRN, FNP C, FAANP University of Nebraska Medical Center College of Nursing Disclosure I have nothing to disclose Objectives Pathophysiology
Acute Abdominal Pain following Bariatric Surgery Kathy J. Morris, DNP, APRN, FNP C, FAANP University of Nebraska Medical Center College of Nursing Disclosure I have nothing to disclose Objectives Pathophysiology
Subject: Weight Loss Surgery Policy. Effective Date: 1/00 Revision Date: 10/15
 Subject: Weight Loss Surgery Policy Effective Date: 1/00 Revision Date: 10/15 DESCRIPTION OSU Health Plans supports covered members with a spectrum of service for obesity and weight loss attempts. The
Subject: Weight Loss Surgery Policy Effective Date: 1/00 Revision Date: 10/15 DESCRIPTION OSU Health Plans supports covered members with a spectrum of service for obesity and weight loss attempts. The
Bariatric Weight Loss Surgery
 BARIATRIC SURGERY Bariatric Weight Loss Surgery The heart and science of medicine. Weight loss surgery, also known as bariatric surgery, was developed as a tool to help people with morbid obesity reduce
BARIATRIC SURGERY Bariatric Weight Loss Surgery The heart and science of medicine. Weight loss surgery, also known as bariatric surgery, was developed as a tool to help people with morbid obesity reduce
The weight of the world.
 The weight of the world. SONY ANTHONY Obesity Derived from the Latin word obesus to devour Definition: having a very high amount of body fat in relation to lean body mass Classifications using Body Mass
The weight of the world. SONY ANTHONY Obesity Derived from the Latin word obesus to devour Definition: having a very high amount of body fat in relation to lean body mass Classifications using Body Mass
Medical Policy Bariatric Surgery
 Medical Policy Bariatric Surgery Document Number: 001 Commercial MassHealth and Qualified Health Plans Authorization required X X Notification within 24 hours of service or next business day No notification
Medical Policy Bariatric Surgery Document Number: 001 Commercial MassHealth and Qualified Health Plans Authorization required X X Notification within 24 hours of service or next business day No notification
Endoscopic therapy for obesity and complications of bariatric surgery
 Endoscopic therapy for obesity and complications of bariatric surgery Jacques Devière, MD, PhD Erasme University Hospital Brussels Belgium jacques.deviere@erasme.ulb.ac.be Obesity Affects 300 millions
Endoscopic therapy for obesity and complications of bariatric surgery Jacques Devière, MD, PhD Erasme University Hospital Brussels Belgium jacques.deviere@erasme.ulb.ac.be Obesity Affects 300 millions
BARIATRIC SURGERY (SURGERY FOR THE TREATMENT OF OBESITY)
 BARIATRIC SURGERY (SURGERY FOR THE TREATMENT OF OBESITY) WHAT IS OBESITY? Obesity is the condition whereby the individual sustains the body weight that is significantly higher than ideal body weight for
BARIATRIC SURGERY (SURGERY FOR THE TREATMENT OF OBESITY) WHAT IS OBESITY? Obesity is the condition whereby the individual sustains the body weight that is significantly higher than ideal body weight for
Understanding Obesity
 Your Guide to Understanding Obesity As your partner in health for your life s journey, we want you to be as informed and confident as possible regarding the disease or medical issue you may be facing.
Your Guide to Understanding Obesity As your partner in health for your life s journey, we want you to be as informed and confident as possible regarding the disease or medical issue you may be facing.
The Role of Obesity in Bariatric Surgery - Part 1
 MORBID OBESITY: The Role of Bariatric Surgery Rajan V. Nair, MD Medical Director Salem Hospital Bariatric Surgery Program ICL Willamette University Tuesday November 27, 2012 DISCLOSURES Medical Director,
MORBID OBESITY: The Role of Bariatric Surgery Rajan V. Nair, MD Medical Director Salem Hospital Bariatric Surgery Program ICL Willamette University Tuesday November 27, 2012 DISCLOSURES Medical Director,
GASTRIC SLEEVE SURGERY FOR WEIGHT LOSS. www.carepointhealth.org GASTRIC SLEEVE SURGERY FOR WEIGHT LOSS. 201-795-8175 CarePointHealth.
 www.carepointhealth.org GASTRIC SLEEVE SURGERY FOR WEIGHT LOSS 201-795-8175 CarePointHealth.org 1 CONTENTS What is sleeve gastrectomy? Why choose sleeve gastrectomy? Health risks associated with excess
www.carepointhealth.org GASTRIC SLEEVE SURGERY FOR WEIGHT LOSS 201-795-8175 CarePointHealth.org 1 CONTENTS What is sleeve gastrectomy? Why choose sleeve gastrectomy? Health risks associated with excess
PATIENT CONSENT TO PROCEDURE - ROUX-EN-Y GASTRIC BYPASS
 As a patient you must be adequately informed about your condition and the recommended surgical procedure. Please read this document carefully and ask about anything you do not understand. Please initial
As a patient you must be adequately informed about your condition and the recommended surgical procedure. Please read this document carefully and ask about anything you do not understand. Please initial
Endoluminal Bariatric Revision. Todd David Wilson, MD
 Endoluminal Bariatric Revision Todd David Wilson, MD Surgical Endoscopy and the Bariatric Surgeon Preoperative Endoscopy Postoperative Endoscopy Revisional Endoscopy Primary Endoluminal Bariatrics Preoperative
Endoluminal Bariatric Revision Todd David Wilson, MD Surgical Endoscopy and the Bariatric Surgeon Preoperative Endoscopy Postoperative Endoscopy Revisional Endoscopy Primary Endoluminal Bariatrics Preoperative
Bariatric Surgery: What the Internist Needs to Know
 Bariatric Surgery: What the Internist Needs to Know Richard Stahl, MD, FACS Assistant Professor of Surgery Medical Director of Bariatric Surgery Disclosures None (sadly) Objectives Describe several myths
Bariatric Surgery: What the Internist Needs to Know Richard Stahl, MD, FACS Assistant Professor of Surgery Medical Director of Bariatric Surgery Disclosures None (sadly) Objectives Describe several myths
BARIATRIC SURGERY PATIENT GUIDE
 You the patient play a critical role in the long term success of surgery. You will need to: Commit to improving your health. Discuss your health history with your surgeon. Discuss any questions or concerns
You the patient play a critical role in the long term success of surgery. You will need to: Commit to improving your health. Discuss your health history with your surgeon. Discuss any questions or concerns
Weight Loss Surgery. Malabsorptive: Your intestines are rearranged to reduce the amount of food absorbed into the system
 The Region s Leader Weight Loss Surgery Table of Contents About Weight Loss Surgery 1 Laparoscopic Procedures 2 Adjustable Gastric Band 2 Biliopancreatic Diversion With Duodenal Switch 3 Rou-en-Y (RNY)
The Region s Leader Weight Loss Surgery Table of Contents About Weight Loss Surgery 1 Laparoscopic Procedures 2 Adjustable Gastric Band 2 Biliopancreatic Diversion With Duodenal Switch 3 Rou-en-Y (RNY)
GASTRIC SLEEVE SURGERY FOR WEIGHT LOSS. www.malleysurgical.com GASTRIC SLEEVE SURGERY FOR WEIGHT LOSS
 GASTRIC SLEEVE SURGERY FOR WEIGHT LOSS www.malleysurgical.com GASTRIC SLEEVE SURGERY FOR WEIGHT LOSS 1 CONTENTS What is sleeve gastrectomy? Why choose sleeve gastrectomy? Health risks associated with excess
GASTRIC SLEEVE SURGERY FOR WEIGHT LOSS www.malleysurgical.com GASTRIC SLEEVE SURGERY FOR WEIGHT LOSS 1 CONTENTS What is sleeve gastrectomy? Why choose sleeve gastrectomy? Health risks associated with excess
2013 RN.ORG, S.A., RN.ORG, LLC
 Obesity: Bariatric Surgical Options WWW.RN.ORG Reviewed September, 2013, Expires September, 2015 Provider Information and Specifics available on our Website Unauthorized Distribution Prohibited 2013 RN.ORG,
Obesity: Bariatric Surgical Options WWW.RN.ORG Reviewed September, 2013, Expires September, 2015 Provider Information and Specifics available on our Website Unauthorized Distribution Prohibited 2013 RN.ORG,
The GaBP Ring for Banding the Pouch in Gastric Bypass and Sleeve Gastrectomy Operations BARIATEC.COM
 The GaBP Ring for Banding the Pouch in Gastric Bypass and Sleeve Gastrectomy Operations BARIATEC.COM GaBP Ring The GaBP Ring is a prefabricated, caliberated and sterilized silicone coated implantable device
The GaBP Ring for Banding the Pouch in Gastric Bypass and Sleeve Gastrectomy Operations BARIATEC.COM GaBP Ring The GaBP Ring is a prefabricated, caliberated and sterilized silicone coated implantable device
MORTALITY RISK FACTORS IN PATIENTS UNDERGOING GASTRIC BYPASS SURGERY
 Where Do We Stand? Alan M. Brader, MD Lancaster General Bariatrics Introduction The management of a patient with extreme obesity is a challenging task for most health care givers. Unfortunately, there
Where Do We Stand? Alan M. Brader, MD Lancaster General Bariatrics Introduction The management of a patient with extreme obesity is a challenging task for most health care givers. Unfortunately, there
Surgical Weight Loss Program for Teens
 Surgical Weight Loss Program for Teens Surgical Weight Loss Program for Teens The Surgical Weight Loss Program team understands the impact that being severely overweight can have on your life. Our guiding
Surgical Weight Loss Program for Teens Surgical Weight Loss Program for Teens The Surgical Weight Loss Program team understands the impact that being severely overweight can have on your life. Our guiding
If you are morbidly obese, you should remember these important points:
 What is Morbid Obesity? Morbid obesity is a serious medical condition. If you are morbidly obese, it means that you are severely overweight, usually by at least 100 pounds. It also means that you have
What is Morbid Obesity? Morbid obesity is a serious medical condition. If you are morbidly obese, it means that you are severely overweight, usually by at least 100 pounds. It also means that you have
Considering Bariatric Surgery? Learn about minimally invasive da Vinci Surgery
 Considering Bariatric Surgery? Learn about minimally invasive da Vinci Surgery The Condition: Obesity Obesity is defined as having a body mass index (BMI) of 30 or greater. Obesity is a serious medical
Considering Bariatric Surgery? Learn about minimally invasive da Vinci Surgery The Condition: Obesity Obesity is defined as having a body mass index (BMI) of 30 or greater. Obesity is a serious medical
The University of Hong Kong Department of Surgery Division of Esophageal and Upper Gastrointestinal Surgery
 Program Overview The University of Hong Kong Department of Surgery Division of Esophageal and Upper Gastrointestinal Surgery Weight Control and Metabolic Surgery Program The Weight Control and Metabolic
Program Overview The University of Hong Kong Department of Surgery Division of Esophageal and Upper Gastrointestinal Surgery Weight Control and Metabolic Surgery Program The Weight Control and Metabolic
Sudbury Bariatric Regional Assessment & Treatment Centre
 Sudbury Bariatric Regional Assessment & Treatment Centre Outline Obesity as a Chronic Disease 5 A s of Obesity Management OBN & BRATC Referral Process Obesity Definition BMI Normal Weight 18.5-24.9 Overweight
Sudbury Bariatric Regional Assessment & Treatment Centre Outline Obesity as a Chronic Disease 5 A s of Obesity Management OBN & BRATC Referral Process Obesity Definition BMI Normal Weight 18.5-24.9 Overweight
Preservation and Incorporation of Valuable Endoscopic Innovations (PIVI)
 Preservation and Incorporation of Valuable Endoscopic Innovations (PIVI) The American Society for Gastrointestinal Endoscopy PIVI on Endoscopic Bariatric Procedures (short form) Please see related White
Preservation and Incorporation of Valuable Endoscopic Innovations (PIVI) The American Society for Gastrointestinal Endoscopy PIVI on Endoscopic Bariatric Procedures (short form) Please see related White
Bariatric i Surgery: Optimalizing Outcome Results. Dr. B. Dillemans AZ Sint-Jan AV Brugge-Oostende BARIATRIC SURGERY
 Bariatric i Surgery: Optimalizing i Outcome Results Dr. B. Dillemans AZ Sint-Jan AV Brugge-Oostende THE OBESE PATIENT : A CHALLENGE FOR ANAESTHESIA, Ostend,14/11/09 BARIATRIC SURGERY 50 s : First Reported
Bariatric i Surgery: Optimalizing i Outcome Results Dr. B. Dillemans AZ Sint-Jan AV Brugge-Oostende THE OBESE PATIENT : A CHALLENGE FOR ANAESTHESIA, Ostend,14/11/09 BARIATRIC SURGERY 50 s : First Reported
Colorado Medicaid Benefit Coverage Standard
 BARIATRIC SURGERY Brief Coverage Statement Colorado Medicaid covers bariatric surgery for the treatment of clinically severe obesity, when medically necessary as described in this policy. Bariatric surgery
BARIATRIC SURGERY Brief Coverage Statement Colorado Medicaid covers bariatric surgery for the treatment of clinically severe obesity, when medically necessary as described in this policy. Bariatric surgery
Procedure Type: Metabolic and Malabsorbtion. Procedure Names. Adjustable Gastric Band (LAGB) Realize Band. Vertical Sleeve Gastrectomy (VSG)
 The following table explains and compares the various weight loss surgeries, and their differences. For more information, please also read our compilation of related medical journals & articles below the
The following table explains and compares the various weight loss surgeries, and their differences. For more information, please also read our compilation of related medical journals & articles below the
Surgery for obesity Michael Korenkov a, Stefan Sauerland b and Theodor Junginger a
 Surgery for obesity Michael Korenkov a, Stefan Sauerland b and Theodor Junginger a Purpose of review Bariatric surgery today is the only effective therapy for morbid obesity. Commonly performed procedures
Surgery for obesity Michael Korenkov a, Stefan Sauerland b and Theodor Junginger a Purpose of review Bariatric surgery today is the only effective therapy for morbid obesity. Commonly performed procedures
Surgical & Nutritional Complications of Bariatric Surgery: What Every GI Doc Needs to Know Brian R. Smith, MD, FACS Associate Clinical Professor of
 Surgical & Nutritional Complications of Bariatric Surgery: What Every GI Doc Needs to Know Brian R. Smith, MD, FACS Associate Clinical Professor of Surgery & Associate Residency Program Director UC Irvine
Surgical & Nutritional Complications of Bariatric Surgery: What Every GI Doc Needs to Know Brian R. Smith, MD, FACS Associate Clinical Professor of Surgery & Associate Residency Program Director UC Irvine
Bariatric Surgery 101
 Bariatric Surgery 101 Dr. Brent Bell, MD Bariatric / General Surgeon Medical Conditions Caused By Morbid Obesity Type 2 DM Hypertension Cholesterol Sleep Apnea Fatty Liver Asthma Osteoarthritis Reduced
Bariatric Surgery 101 Dr. Brent Bell, MD Bariatric / General Surgeon Medical Conditions Caused By Morbid Obesity Type 2 DM Hypertension Cholesterol Sleep Apnea Fatty Liver Asthma Osteoarthritis Reduced
The Arguments: T2DM - tremendous economic burden globally Lifestyle / Pharm Rx:
 James Cromie The Arguments: T2DM - tremendous economic burden globally Lifestyle / Pharm Rx: INEFFECTIVE and UNSUSTAINED Bariatric surgery is an Effective and Durable treatment option Well established
James Cromie The Arguments: T2DM - tremendous economic burden globally Lifestyle / Pharm Rx: INEFFECTIVE and UNSUSTAINED Bariatric surgery is an Effective and Durable treatment option Well established
Position Statement Weight Loss Surgery (Bariatric Surgery) and its Use in Treating Obesity or Treating and Preventing Diabetes
 Position Statement Weight Loss Surgery (Bariatric Surgery) and its Use in Treating Obesity or Treating and Preventing Diabetes People with diabetes Losing excess weight will assist in the management of
Position Statement Weight Loss Surgery (Bariatric Surgery) and its Use in Treating Obesity or Treating and Preventing Diabetes People with diabetes Losing excess weight will assist in the management of
Emerging Concepts in Bariatric Surgery
 Emerging Concepts in Bariatric Surgery C Y N T H I A L. L O N G, M D, F A C S S I N A I H O S P I T A L O F B A L T I M O R E D E P A R T M E N T O F S U R G E R Y D I V I S I O N O F M I N I M A L L Y
Emerging Concepts in Bariatric Surgery C Y N T H I A L. L O N G, M D, F A C S S I N A I H O S P I T A L O F B A L T I M O R E D E P A R T M E N T O F S U R G E R Y D I V I S I O N O F M I N I M A L L Y
L.A. Care Health Plan Medical Management Quarterly Technical Bulletin 1Q10 - March 2010
 Medical Management Quarterly Technical Bulletin 1Q10 - March 2010 Editor In-Chief: Z. Joseph Wanski, MD, F.A.C.E. Contributing Editor: L.A. Care Health Plan Lynnette Hutcherson, RN Medical Director, Medical
Medical Management Quarterly Technical Bulletin 1Q10 - March 2010 Editor In-Chief: Z. Joseph Wanski, MD, F.A.C.E. Contributing Editor: L.A. Care Health Plan Lynnette Hutcherson, RN Medical Director, Medical
How To Perform Laparoscopic Bariatric Surgery
 SAGES guideline for clinical application of laparoscopic bariatric surgery (24/03/2553) กร ณาอ านฉบ บเต มได ท http://www.sages.org/publication/id/30/ SAGES guideline for clinical application of laparoscopic
SAGES guideline for clinical application of laparoscopic bariatric surgery (24/03/2553) กร ณาอ านฉบ บเต มได ท http://www.sages.org/publication/id/30/ SAGES guideline for clinical application of laparoscopic
Cleveland Clinic Bariatric and Metabolic Institute. Weight Loss Surgery for Severely Obese Patients
 Cleveland Clinic Bariatric and Metabolic Institute Weight Loss Surgery for Severely Obese Patients life-altering therapy requires close communication Careful patient selection for bariatric surgery is
Cleveland Clinic Bariatric and Metabolic Institute Weight Loss Surgery for Severely Obese Patients life-altering therapy requires close communication Careful patient selection for bariatric surgery is
Weight-Loss Surgery for Adults With Diabetes or Prediabetes Who Are at the Lower Levels of Obesity
 Weight-Loss Surgery for Adults With Diabetes or Prediabetes Who Are at the Lower Levels of Obesity A Review of the Research for Adults With a BMI Between 30 and 35 Is This Information Right for Me? If
Weight-Loss Surgery for Adults With Diabetes or Prediabetes Who Are at the Lower Levels of Obesity A Review of the Research for Adults With a BMI Between 30 and 35 Is This Information Right for Me? If
Weight Loss Surgery Program
 Weight loss surgery helped me lose 112 pounds. Jennifer Weaver Weight Loss Surgery Program baylor university medical center at dallas Follow us on: Facebook.com/BaylorHealth YouTube.com/BaylorHealth When
Weight loss surgery helped me lose 112 pounds. Jennifer Weaver Weight Loss Surgery Program baylor university medical center at dallas Follow us on: Facebook.com/BaylorHealth YouTube.com/BaylorHealth When
BARIATRIC SURGERY. Personalized Weight Loss Program
 BARIATRIC SURGERY Personalized Weight Loss Program Lafayette General Medical Center performs three major operations for weight loss surgery: Adjustable Gastric Band, Laparoscopic Sleeve Gastrectomy and
BARIATRIC SURGERY Personalized Weight Loss Program Lafayette General Medical Center performs three major operations for weight loss surgery: Adjustable Gastric Band, Laparoscopic Sleeve Gastrectomy and
Hyperoxaluria and Bariatric Surgery
 Hyperoxaluria and Bariatric Surgery John R. Asplin Litholink Corporation and University of Chicago, Chicago IL Abstract. Bariatric surgery as a means to treat obesity is becoming increasingly common in
Hyperoxaluria and Bariatric Surgery John R. Asplin Litholink Corporation and University of Chicago, Chicago IL Abstract. Bariatric surgery as a means to treat obesity is becoming increasingly common in
