BLADDER CANCER GLOSSARY OF TERMS
|
|
|
- Erick Wilson
- 8 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 BLADDER CANCER GLOSSARY OF TERMS Abdomen: The part of the body that contains the pancreas, stomach, intestines, kidneys, urinary bladder, liver, gallbladder, and other organs. Anesthesia: Loss of feeling or awareness. Local anesthetics cause loss of feeling in a part of the body. General anesthetics put the person to sleep. Anterior exenteration: The standard operation to remove the bladder cancer in female patients, which involves not only the removal of the bladder and urethra but also the removal of the uterus, cervix, ovaries, and the anterior or front wall of the vagina. This operation has recently been modified so the urethra can be preserved in select cases. In addition, patients of childbearing age may wish to discuss with their surgeon techniques for preserving the uterus and cervix during cystectomy. Arsenic: A poisonous chemical used to kill weeds and pests. It has also been associated with increased risk of developing bladder cancer. Bacteria: A large group of single-cell microorganisms. Some cause infections and disease in animals and humans. The singular of bacteria is bacterium. BCG solution: A form of biological immunotherapy for non-muscle invasive bladder cancer. A catheter is used to place the BCG solution into the bladder. The solution contains live, weakened bacteria (Bacillus Calmette-Guerin) that activate the immune system. The BCG solution used for bladder cancer is not the same thing as BCG vaccine, a vaccine for tuberculosis. Normally six weekly treatments are given. BCG maintenance is a series of treatments following the initial six treatments. These treatments usually are a series of 3 treatments and usually will be given every 6 months for a 3 year period (Lamm protocol). Benign: Not cancerous; does not invade nearby tissue or spread to other parts of the body. Biological therapy: Treatment to stimulate or restore the ability of the body (e.g. immune system) to fight infection and disease and used to lessen side effects that may be caused by some cancer treatments. Also may be known as immunotherapy, biotherapy, or biological response modifier (BRM) therapy. Biopsy: The removal of cells or tissues for examination under a microscope. When only a sample of tissue is removed, the procedure is called an incision biopsy or core biopsy. When an entire tumor or lesion is removed, the procedure is called an excisional biopsy. When a sample of tissue or fluid is removed with a needle, the procedure is called a needle biopsy or fineneedle aspiration. Bladder: The organ that stores urine. Bone scan: A technique to identify metastasis in bone which creates images of bones on a computer screen or on film. A small amount of radioactive material is injected into a blood vessel and travels through the bloodstream; it collects in the bones and is detected by a scanner.
2 Cancer: A term for diseases in which abnormal cells divide without control. Cancer cells can invade nearby tissues and can spread through the bloodstream and lymphatic system to other parts of the body. Carcinogen: Any substance that causes cancer. Carcinoma in situ: Cancer that involves only the cells in which it began and that has not spread to neighboring tissues. Chemotherapy: Treatment with anticancer drugs. Neoadjuvant chemotherapy is given prior to surgery while adjuvant chemotherapy is given after surgery. Chlorine: A chemical used to disinfect water and as a bleach. Clinical trial: A research study that tests how well new medical treatments or other interventions work in people. Each study is designed to test new methods of screening, prevention, diagnosis, or treatment of a disease. Continence: The ability to control the flow of urine from the bladder to the outside of the body. This capability is normally due to muscular structures called sphincters, which wrap around the base of the bladder and urethra. Removal of or damage to the urinary sphincters can result in an inability to control the flow of urine normally. Continent catheterizable reconstruction: One of a group of internal reservoirs or new bladders (neobladders) that are not attached to the urethra. Instead, it is emptied through catheterization, usually through a special attachment to the skin that is similar to but smaller than the stoma for an ileal conduit. The continent reservoir is formed from a piece of small intestine to hold urine after the bladder has been removed. Continent reconstructions are often referred to by names given to them at the institution where the particular type of reconstruction was developed, e.g. Indiana Pouch. CT scan: Computed tomography scan. A series of detailed pictures of areas inside the body taken from different angles; the pictures are created by a computer linked to an x-ray machine. Also called computerized tomography and computerized axial tomography (CAT) scan. Cystectomy: Surgery to remove all or part of the bladder. Cystoscope: A thin, lighted instrument used to look inside the bladder and remove tissue samples or small tumors. Cystoscopy: Examination of the bladder and urethra using a thin, lighted instrument (called a cytoscope) inserted into the urethra. Tissue samples can be removed and examined under a microscope to determine whether disease is present. Enterostomal therapist: A health professional trained in the care of persons with urostomies and other stomas. Erectile dysfunction (ED): A sexual dysfunction characterized by the inability to develop or maintain an erection of the penis during sexual performance. External radiation: Radiation therapy that uses a machine to aim high-energy rays at the cancer, and also called external-beam radiation.
3 Fallopian tubes: Part of the female reproductive tract. Fulguration: Destroying tissue using an electric current. Gene: The functional and physical unit of heredity passed from parent to offspring. Genes are pieces of DNA, and most genes contain the information for making a specific protein. Grade: The grade of a tumor depends on how abnormal the cancer cells look under a microscope and how quickly the tumor is likely to grow and spread. Grading systems are different for each type of cancer. Hematuria: Blood in the urine. Hematuria is either gross, meaning that the blood can be seen with the naked eye, or microscopic, meaning that blood can only be detected in the urine if the urine is examined under a microscope. Ileal conduit: A simple form of urinary tract reconstruction which utilizes a small piece of intestine called the ileum. The ureters are implanted into this small segment of intestine, one end is closed with sutures, and the other is brought out to the skin to create a small opening, or mouth, called a stoma. Urine drains into a small pouch that fits over the stoma and attaches to the skin with an adhesive. Imaging: tests that produce pictures of areas inside the body. Immune system: The complex group of organs and cells that defends the body against infection or disease. Impotent: Unable to have an erection adequate for sexual intercourse. Incision: A cut made in the body during surgery. Indiana Pouch: A surgically created urinary diversion used to create a way for the body to store and eliminate urine for patients who have had their urinary bladders removed as a result of bladder cancer, pelvic exenteration, bladder exstrophy or who are not continent due to a congenital, neurogenic bladder. This particular urinary diversion results in a continent reservoir that the patient must catheterize regularly to empty urine. Internal radiation: A procedure in which radioactive material sealed in needles, seeds, wires, or catheters is placed directly into or near the tumor, also called brachytherapy, implant radiation, or interstitial radiation therapy. Intravenous: IV into a vein. Intravenous pyelogram (IVP): A series of x-rays of the kidneys, ureters, and bladder. The x- rays are taken after a dye is injected into a blood vessel. The dye is concentrated in the urine, which outlines the kidneys, ureters, and bladder on the x-rays. Intravesical: Within the bladder. Invasive bladder cancer: A bladder cancer that invades the structures that lie beneath the lining cells. These tumors have characteristically worse biological behavior and are capable of spreading to other parts of the body without much warning. Accordingly, physicians are constantly on the lookout for evidence of disease spread in patients with invasive bladder carcinomas. Muscle invasive cancers are less common than superficial ones, but they
4 unfortunately spread to other parts of the body in about half of the patients who have this invasive disease. Invasive cancer: Cancer that has spread beyond the layer of tissue in which it developed and is growing into surrounding, healthy tissues. Interferon: Interferon alpha2b is a BCG enhancer used as a treatment added to BCG in the case of refractory BCG. Kidneys: A pair of organs in the abdomen that remove waste from the blood (as urine), produce erythropoietin (a substance that stimulates red blood cell production), and play a role in blood pressure regulation. Lamina propria: A specialized layer of blood vessels and cells that separates the transitional epithelium from the actual muscle wall of the bladder. Local therapy: Treatment that affects cells in the tumor and the area close to it. Lymph node: A rounded mass of lymphatic tissue that is surrounded by a capsule of connective tissue. Lymph nodes are spread out along lymphatic vessels and contain many lymphocytes, which filter the lymphatic fluid (lymph). Lymphatic system: The tissues and organs that produce, store, and carry white blood cells that fight infection and other diseases. This system includes the bone marrow, spleen, thymus, lymph nodes, and network of thin tubes that carry lymph and white blood cells. These tubes branch, like blood vessels, into all the tissues of the body. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). A procedure in which a magnet linked to a computer is used to create detailed pictures of areas inside the body. Malignant: Cancerous; a growth with a tendency to invade and destroy nearby tissue and spread to other parts of the body. Medical oncologist: A doctor who specializes in diagnosing and treating cancer using chemotherapy, hormonal therapy, and biological therapy. A medical oncologist often serves as the main caretaker of someone who has advanced cancer and coordinates treatment provided by other specialists. Metastasis: The spread of cancer from one part of the body to another. Tumors formed from cells that have spread are called secondary tumors and contain cells that are like those in the original (primary) tumor. The plural is metastases. Metastasize: To spread from one part of the body to another. When cancer cells metastasize and form secondary tumors, the cells in the metastatic tumor are like those in the original (primary) tumor. Neobladder: A new bladder usually constructed out of a piece of intestine and attached to the urethra. This is placed in the position that had been occupied by the bladder before it was removed because of disease. Oncogene: A specific type of cancer-causing gene which, when it mutates, leads to abnormal stimulation of cell growth.
5 Ostomy: An operation to create an opening (a stoma) from an area inside the body to the outside. Colostomy and urostomy are types of ostomies. Ovaries: The pair of female reproductive glands in which the ova, or eggs, are formed. The ovaries are located in the pelvis, one on each side of the uterus. P53: A particularly notable tumor-suppressor gene that is thought to play a central role in normal cells' growth regulation. Mutation of the P53 tumor suppressor gene has been shown to occur in up to 40 percent of invasive bladder carcinomas. Some scientists believe that P53 mutation may be a marker of the presence of a dangerous type of tumor which could require multiple therapies to cure. Pathologist: A doctor who identifies diseases by studying cells and tissues under a microscope. Pelvis: The lower part of the abdomen, located between the hip bones. Photodynamic therapy: Treatment with drugs that become active when exposed to light. These drugs kill cancer cells. Primary tumor: The original tumor. Prostate: A gland in the male reproductive system just below the bladder. It surrounds part of the urethra, the canal that empties the bladder, and produces a fluid that forms part of semen. Quality of life: The overall enjoyment of life. Many clinical trials measure aspects of an individual s sense of well-being and ability to perform various tasks to assess the effects of cancer and its treatment on the quality of life. Radiation oncologist: A doctor who specializes in using radiation to treat cancer. Radiation therapy: The use of high-energy radiation from x-rays, gamma rays, neutrons, and other sources to kill cancer cells and shrink tumors. Radiation may come from a machine outside the body (external-beam radiation therapy), or it may come from radioactive material placed in the body in the area near cancer cells (internal radiation therapy, implant radiation, or brachytherapy). Systemic radiation therapy uses a radioactive substance, such as a radio labeled monoclonal antibody that circulates throughout the body, also called radiotherapy. Radical cystectomy: Surgery to remove the bladder as well as nearby tissues and organs. Radioactive: Giving off radiation. Rectal: By or having to do with the rectum. The rectum is the last 8-10 inches of the large intestine and ends at the anus. Recur: To occur again. Recurrence is the return of cancer, at the same site as the original (primary) tumor or in another location, after the tumor had disappeared. Risk factor: A habit, trait, condition, or genetic alteration that increases a person s chance of developing a disease. Segmental cystectomy: The removal of the cancer as well as some of the bladder tissue around the tumor sometimes called a partial cystectomy.
6 Side effects: Problems that occur when treatment affects healthy cells. Common side effects of cancer treatment are fatigue, nausea, vomiting, decreased blood cell counts, hair loss, and mouth sores. Small intestine: The part of the digestive tract that is located between the stomach and the large intestine. Sonogram: A computer picture of areas inside the body created by bouncing sound waves off organs and other tissues, also called ultra sonogram or ultrasound. Sphincter muscle: A specialized circular muscle that effectively cuts off the flow of urine when contracted. Men have two such sphincter mechanisms, one at the junction of the prostate and bladder and the other just below the prostate in the upper part of the urethra. The second sphincter, which wraps around the urethra, is the one that is thought to be responsible for continence in females. Squamous cell carcinoma: Cancer that begins in squamous cells, which are thin, flat cells resembling fish scales. Squamous cells are found in the tissue that forms the surface of the skin, the lining of the hollow organs of the body, and the passages of the respiratory and digestive tracts. Also call epidermoid carcinoma. Squamous cells: Flat cells that look like fish scales under a microscope. These cells cover internal and external surfaces of the body. Stage: The extent of a cancer, especially whether the disease has spread from the original site to other parts of the body. Staging: Performing exams and tests to learn the extent of the cancer within the body, especially whether the disease has spread from the original site to other parts of the body. Stoma: A surgically created opening from an area inside the body to the outside. Superficial: affecting cells on the surface. Not invasive. Superficial bladder cancer: Tumors arising from the lining of the bladder that do not invade the muscle wall. The majority of bladder cancers are superficial, and, though these may progress in only a minority of patients, they do usually recur. Surgeon: A doctor who removes or repairs a part of the body by operating on the patient. Surgery: A procedure to remove or repair a part of the body or to find out whether disease is present. Symptom: An indication that a person has a condition or disease. Some examples of symptoms are headache, fever, fatigue, nausea, vomiting, and pain. Systemic therapy: Treatment that uses substances that travel through the bloodstream, reaching and affecting cells all over the body. Tissue: A group or layer of cells that are alike in type and work together to perform a specific function.
7 Transitional cell carcinoma: The most common type of cancer that develops in the lining of the bladder, ureter, or renal pelvis, also referred to as urothelial cell carcinoma. Transitional cells: Cells that vary in shape depending on whether the tissue is being stretched. The cells may be stretched without breaking apart. They line hollow organs such as the bladder. Transurethral resection of bladder tumor: Surgery performed with a special instrument inserted through the urethra, also called a TURBT. Trigone: The floor of the bladder, where the ureters and urethra connect to the interior of the bladder. Tumor: An abnormal mass of tissue that results from excessive cell division. Tumors perform no useful body function. They may be benign (not cancerous) or malignant (cancerous). Tumor suppressor gene: A member of a category of genes that are thought to be active during embryonic development. These genes have normal functions during embryonic stages that are suppressed when development is complete. If these functions are somehow reactivated during adult life, uncontrolled growth can result. This growth can sometimes lead to the development of certain cancers. Ureter: The tube that carries urine from the kidney to the bladder. Urethra: The tube through which urine leaves the body. It empties urine from the bladder. Urine: Fluid containing water and waste products. Urine is made by the kidneys, stored in the bladder, and leaves the body through the urethra. Urine Cytology: Urine cytology evaluates this urinary sediment for the presence of cancerous cells from the lining of the urinary tract. Urologic oncologist: a doctor who specializes in treating cancers of the urinary system. Urologist: A doctor who specializes in diseases of the urinary organs in females and the urinary and sex organs in males. Urostomy: An operation to create an opening from inside the body to the outside, making a new way to pass urine. Uterus: The small, hollow, pear-shaped organ in a woman s pelvis. This is the organ in which a fetus develops, also called the womb. Vagina: The muscular canal extending from the uterus to the exterior of the body, also called the birth canal. Vaginal: Of or having to do with the vagina, the birth canal. Note: This glossary was compiled by Bladder Cancer Canada and has been reviewed by the Chair of the Bladder Cancer Canada Medical Advisory Board. This glossary is for patients and caregivers to use as a reference only and is not meant to be an exhaustive list, nor is it meant to replace advice from your doctor. Should you have other terms that need to be explained to you or require further clarification on any of the above terms please contact your doctor.
Smoking and misuse of certain pain medicines can affect the risk of developing renal cell cancer.
 Renal cell cancer Renal cell cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in tubules of the kidney. Renal cell cancer (also called kidney cancer or renal adenocarcinoma) is a disease in which
Renal cell cancer Renal cell cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in tubules of the kidney. Renal cell cancer (also called kidney cancer or renal adenocarcinoma) is a disease in which
A bladder cancer glossary
 A bladder cancer glossary We ve put together a list of the medical terms you might hear people use when they talk about bladder cancer. Abdomen The middle part of your body that contains your stomach,
A bladder cancer glossary We ve put together a list of the medical terms you might hear people use when they talk about bladder cancer. Abdomen The middle part of your body that contains your stomach,
Radiation Therapy for Prostate Cancer
 Radiation Therapy for Prostate Cancer Introduction Cancer of the prostate is the most common form of cancer that affects men. About 240,000 American men are diagnosed with prostate cancer every year. Your
Radiation Therapy for Prostate Cancer Introduction Cancer of the prostate is the most common form of cancer that affects men. About 240,000 American men are diagnosed with prostate cancer every year. Your
Thymus Cancer. This reference summary will help you better understand what thymus cancer is and what treatment options are available.
 Thymus Cancer Introduction Thymus cancer is a rare cancer. It starts in the small organ that lies in the upper chest under the breastbone. The thymus makes white blood cells that protect the body against
Thymus Cancer Introduction Thymus cancer is a rare cancer. It starts in the small organ that lies in the upper chest under the breastbone. The thymus makes white blood cells that protect the body against
Benign (beh-nine): Not cancerous. Benign tumors may grow larger but do not spread to other parts of the body.
 Cancer Glossary Source: National Cancer Institute: What You Need to Know About Cancer Adenoma (ad-in-oh-ma): A noncancerous tumor. Adjuvant therapy (AD-joo-vant): Treatment given after the primary treatment
Cancer Glossary Source: National Cancer Institute: What You Need to Know About Cancer Adenoma (ad-in-oh-ma): A noncancerous tumor. Adjuvant therapy (AD-joo-vant): Treatment given after the primary treatment
Small cell lung cancer
 Small cell lung cancer Small cell lung cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of the lung. The lungs are a pair of cone-shaped breathing organs that are found within
Small cell lung cancer Small cell lung cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of the lung. The lungs are a pair of cone-shaped breathing organs that are found within
General Information About Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
 General Information About Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Non-small cell lung cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of the lung. The lungs are a pair of cone-shaped breathing
General Information About Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Non-small cell lung cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of the lung. The lungs are a pair of cone-shaped breathing
Frequently Asked Questions About Ovarian Cancer
 Media Contact: Gerri Gomez Howard Cell: 303-748-3933 gerri@gomezhowardgroup.com Frequently Asked Questions About Ovarian Cancer What is ovarian cancer? Ovarian cancer is a cancer that forms in tissues
Media Contact: Gerri Gomez Howard Cell: 303-748-3933 gerri@gomezhowardgroup.com Frequently Asked Questions About Ovarian Cancer What is ovarian cancer? Ovarian cancer is a cancer that forms in tissues
Introduction Breast cancer is cancer that starts in the cells of the breast. Breast cancer happens mainly in women. But men can get it too.
 Male Breast Cancer Introduction Breast cancer is cancer that starts in the cells of the breast. Breast cancer happens mainly in women. But men can get it too. Many people do not know that men can get breast
Male Breast Cancer Introduction Breast cancer is cancer that starts in the cells of the breast. Breast cancer happens mainly in women. But men can get it too. Many people do not know that men can get breast
Your bladder cancer diary. WA Cancer and Palliative Care Network
 Your bladder cancer diary WA Cancer and Palliative Care Network Patient information and persons to contact Your Name Date of Birth URMN (Patient Hospital Unit Number) Address Phone Mobile GP Name Phone
Your bladder cancer diary WA Cancer and Palliative Care Network Patient information and persons to contact Your Name Date of Birth URMN (Patient Hospital Unit Number) Address Phone Mobile GP Name Phone
Cancer of the Cervix
 Cancer of the Cervix WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 A woman's cervix (the opening of the uterus) is lined with cells. Cancer of the cervix occurs when those cells change,
Cancer of the Cervix WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 A woman's cervix (the opening of the uterus) is lined with cells. Cancer of the cervix occurs when those cells change,
Lung Cancer. This reference summary will help you better understand lung cancer and the treatment options that are available.
 Lung Cancer Introduction Lung cancer is the number one cancer killer of men and women. Over 165,000 people die of lung cancer every year in the United States. Most cases of lung cancer are related to cigarette
Lung Cancer Introduction Lung cancer is the number one cancer killer of men and women. Over 165,000 people die of lung cancer every year in the United States. Most cases of lung cancer are related to cigarette
Understanding. Pancreatic Cancer
 Understanding Pancreatic Cancer Understanding Pancreatic Cancer The Pancreas The pancreas is an organ that is about 6 inches long. It s located deep in your belly between your stomach and backbone. Your
Understanding Pancreatic Cancer Understanding Pancreatic Cancer The Pancreas The pancreas is an organ that is about 6 inches long. It s located deep in your belly between your stomach and backbone. Your
BLADDER HEALTH. Non-Muscle Invasive Bladder Cancer: A Patient Guide
 BLADDER HEALTH Non-Muscle Invasive Bladder Cancer: A Patient Guide What is the Bladder? What is Cancer? The bladder is a balloon-shaped organ in your pelvic* area that stores urine and is made up of four
BLADDER HEALTH Non-Muscle Invasive Bladder Cancer: A Patient Guide What is the Bladder? What is Cancer? The bladder is a balloon-shaped organ in your pelvic* area that stores urine and is made up of four
Bladder Cancer Overview
 Bladder Cancer Overview This overview is based on the more detailed information in our document, Bladder Cancer: Detailed Guide. What is bladder cancer? Cancer starts when cells in the body begin to grow
Bladder Cancer Overview This overview is based on the more detailed information in our document, Bladder Cancer: Detailed Guide. What is bladder cancer? Cancer starts when cells in the body begin to grow
M6-1 NOTE. Each major learning point is clearly identified by boldface type throughout the guide and emphasized in the PowerPoint presentation.
 Basics of Cancer Treatment Module 6 Basics of Cancer Treatment Target Audience: Community members Staff of Indian health programs, including Community Health Representatives Contents of Learning Module:
Basics of Cancer Treatment Module 6 Basics of Cancer Treatment Target Audience: Community members Staff of Indian health programs, including Community Health Representatives Contents of Learning Module:
AFTER DIAGNOSIS: PROSTATE CANCER Understanding Your Treatment Options
 AFTER DIAGNOSIS: PROSTATE CANCER Understanding Your Treatment Options INTRODUCTION This booklet describes how prostate cancer develops, how it affects the body and the current treatment methods. Although
AFTER DIAGNOSIS: PROSTATE CANCER Understanding Your Treatment Options INTRODUCTION This booklet describes how prostate cancer develops, how it affects the body and the current treatment methods. Although
Multiple Myeloma. This reference summary will help you understand multiple myeloma and its treatment options.
 Multiple Myeloma Introduction Multiple myeloma is a type of cancer that affects white blood cells. Each year, thousands of people find out that they have multiple myeloma. This reference summary will help
Multiple Myeloma Introduction Multiple myeloma is a type of cancer that affects white blood cells. Each year, thousands of people find out that they have multiple myeloma. This reference summary will help
2008 All rights reserved.
 BCAN provides this information as a service. Publication of this information is not intended to take the place of medical care or the advice of your doctor. BCAN strongly suggests consulting your doctor
BCAN provides this information as a service. Publication of this information is not intended to take the place of medical care or the advice of your doctor. BCAN strongly suggests consulting your doctor
Understanding Your Diagnosis of Endometrial Cancer A STEP-BY-STEP GUIDE
 Understanding Your Diagnosis of Endometrial Cancer A STEP-BY-STEP GUIDE Introduction This guide is designed to help you clarify and understand the decisions that need to be made about your care for the
Understanding Your Diagnosis of Endometrial Cancer A STEP-BY-STEP GUIDE Introduction This guide is designed to help you clarify and understand the decisions that need to be made about your care for the
Early Prostate Cancer: Questions and Answers. Key Points
 CANCER FACTS N a t i o n a l C a n c e r I n s t i t u t e N a t i o n a l I n s t i t u t e s o f H e a l t h D e p a r t m e n t o f H e a l t h a n d H u m a n S e r v i c e s Early Prostate Cancer:
CANCER FACTS N a t i o n a l C a n c e r I n s t i t u t e N a t i o n a l I n s t i t u t e s o f H e a l t h D e p a r t m e n t o f H e a l t h a n d H u m a n S e r v i c e s Early Prostate Cancer:
Mesothelioma. 1995-2013, The Patient Education Institute, Inc. www.x-plain.com ocft0101 Last reviewed: 03/21/2013 1
 Mesothelioma Introduction Mesothelioma is a type of cancer. It starts in the tissue that lines your lungs, stomach, heart, and other organs. This tissue is called mesothelium. Most people who get this
Mesothelioma Introduction Mesothelioma is a type of cancer. It starts in the tissue that lines your lungs, stomach, heart, and other organs. This tissue is called mesothelium. Most people who get this
PATIENT GUIDE. Localized Prostate Cancer
 PATIENT GUIDE Localized Prostate Cancer The prostate* is part of the male reproductive system. It is about the same size as a walnut and weighs about an ounce. As pictured in Figure 1, the prostate is
PATIENT GUIDE Localized Prostate Cancer The prostate* is part of the male reproductive system. It is about the same size as a walnut and weighs about an ounce. As pictured in Figure 1, the prostate is
Lung Cancer: Diagnosis, Staging and Treatment
 PATIENT EDUCATION patienteducation.osumc.edu Lung Cancer: Diagnosis, Staging and Treatment Cancer begins in our cells. Cells are the building blocks of our tissues. Tissues make up the organs of the body.
PATIENT EDUCATION patienteducation.osumc.edu Lung Cancer: Diagnosis, Staging and Treatment Cancer begins in our cells. Cells are the building blocks of our tissues. Tissues make up the organs of the body.
Treating Localized Prostate Cancer A Review of the Research for Adults
 Treating Localized Prostate Cancer A Review of the Research for Adults Is this information right for me? Yes, this information is right for you if: Your doctor * said all tests show you have localized
Treating Localized Prostate Cancer A Review of the Research for Adults Is this information right for me? Yes, this information is right for you if: Your doctor * said all tests show you have localized
Report series: General cancer information
 Fighting cancer with information Report series: General cancer information Eastern Cancer Registration and Information Centre ECRIC report series: General cancer information Cancer is a general term for
Fighting cancer with information Report series: General cancer information Eastern Cancer Registration and Information Centre ECRIC report series: General cancer information Cancer is a general term for
Breast Cancer. Sometimes cells keep dividing and growing without normal controls, causing an abnormal growth called a tumor.
 Breast Cancer Introduction Cancer of the breast is the most common form of cancer that affects women but is no longer the leading cause of cancer deaths. About 1 out of 8 women are diagnosed with breast
Breast Cancer Introduction Cancer of the breast is the most common form of cancer that affects women but is no longer the leading cause of cancer deaths. About 1 out of 8 women are diagnosed with breast
A Woman s Guide to Prostate Cancer Treatment
 A Woman s Guide to Prostate Cancer Treatment Supporting the man in your life Providing prostate cancer support and resources for women and families WOMEN AGAINST PROSTATE CANCER A Woman s Guide to Prostate
A Woman s Guide to Prostate Cancer Treatment Supporting the man in your life Providing prostate cancer support and resources for women and families WOMEN AGAINST PROSTATE CANCER A Woman s Guide to Prostate
Bladder Cancer What is bladder cancer?
 Bladder Cancer What is bladder cancer? Bladder cancer begins when cells in the urinary bladder start to grow uncontrollably. As more cancer cells develop, they can form a tumor and spread to other areas
Bladder Cancer What is bladder cancer? Bladder cancer begins when cells in the urinary bladder start to grow uncontrollably. As more cancer cells develop, they can form a tumor and spread to other areas
WHEN PROSTATE CANCER RETURNS: ADVANCED PROSTATE CANCER. How Will I Know If My Prostate Cancer Returns?
 WHEN PROSTATE CANCER RETURNS: ADVANCED PROSTATE CANCER (The following information is based on the general experiences of many prostate cancer patients. Your experience may be different.) How Will I Know
WHEN PROSTATE CANCER RETURNS: ADVANCED PROSTATE CANCER (The following information is based on the general experiences of many prostate cancer patients. Your experience may be different.) How Will I Know
Adjuvant Therapy for Breast Cancer: Questions and Answers
 CANCER FACTS N a t i o n a l C a n c e r I n s t i t u t e N a t i o n a l I n s t i t u t e s o f H e a l t h D e p a r t m e n t o f H e a l t h a n d H u m a n S e r v i c e s Adjuvant Therapy for Breast
CANCER FACTS N a t i o n a l C a n c e r I n s t i t u t e N a t i o n a l I n s t i t u t e s o f H e a l t h D e p a r t m e n t o f H e a l t h a n d H u m a n S e r v i c e s Adjuvant Therapy for Breast
CMScript. Member of a medical scheme? Know your guaranteed benefits! Issue 7 of 2014
 Background CMScript Member of a medical scheme? Know your guaranteed benefits! Issue 7 of 2014 Prostate cancer is second only to lung cancer as the leading cause of cancer-related deaths in men. It is
Background CMScript Member of a medical scheme? Know your guaranteed benefits! Issue 7 of 2014 Prostate cancer is second only to lung cancer as the leading cause of cancer-related deaths in men. It is
dedicated to curing BREAST CANCER
 dedicated to curing BREAST CANCER When you are diagnosed with breast cancer, you need a team of specialists who will share their knowledge of breast disease and the latest treatments available. At Cancer
dedicated to curing BREAST CANCER When you are diagnosed with breast cancer, you need a team of specialists who will share their knowledge of breast disease and the latest treatments available. At Cancer
CEU Update. Pancreatic Cancer
 CEU Update A semi-annual publication of the National Association for Health Professionals June 2015 Issue #0615 Pancreatic Cancer The Pancreatic Cancer Action Network, Inc. (PanCAN), established in 1999,
CEU Update A semi-annual publication of the National Association for Health Professionals June 2015 Issue #0615 Pancreatic Cancer The Pancreatic Cancer Action Network, Inc. (PanCAN), established in 1999,
Acute myeloid leukemia (AML)
 Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) Adult acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is a type of cancer in which the bone marrow makes abnormal myeloblasts (a type of white blood cell), red blood cells, or platelets. Adult
Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) Adult acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is a type of cancer in which the bone marrow makes abnormal myeloblasts (a type of white blood cell), red blood cells, or platelets. Adult
An Introduction to PROSTATE CANCER
 An Introduction to PROSTATE CANCER Being diagnosed with prostate cancer can be a life-altering experience. It requires making some very difficult decisions about treatments that can affect not only the
An Introduction to PROSTATE CANCER Being diagnosed with prostate cancer can be a life-altering experience. It requires making some very difficult decisions about treatments that can affect not only the
Colorectal Cancer Care A Cancer Care Map for Patients
 Colorectal Cancer Care A Cancer Care Map for Patients Understanding the process of care that a patient goes through in the diagnosis and treatment of colorectal cancer in BC. Colorectal Cancer Care Map
Colorectal Cancer Care A Cancer Care Map for Patients Understanding the process of care that a patient goes through in the diagnosis and treatment of colorectal cancer in BC. Colorectal Cancer Care Map
The causes of kidney cancer are unknown. However, there are several factors that may increase your risk including:
 Kidney cancer Summary Kidney cancer is more common in people over the age of 55 years. Most kidney cancers are found when the doctor is checking for something else. A person is usually able to live quite
Kidney cancer Summary Kidney cancer is more common in people over the age of 55 years. Most kidney cancers are found when the doctor is checking for something else. A person is usually able to live quite
Colorectal Cancer Treatment
 Scan for mobile link. Colorectal Cancer Treatment Colorectal cancer overview Colorectal cancer, also called large bowel cancer, is the term used to describe malignant tumors found in the colon and rectum.
Scan for mobile link. Colorectal Cancer Treatment Colorectal cancer overview Colorectal cancer, also called large bowel cancer, is the term used to describe malignant tumors found in the colon and rectum.
National Cancer Institute
 National Cancer Institute What You Need To Know About Prostate Cancer U.S. DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES National Institutes of Health National Cancer Institute Services This booklet is only
National Cancer Institute What You Need To Know About Prostate Cancer U.S. DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES National Institutes of Health National Cancer Institute Services This booklet is only
PERIPHERAL STEM CELL TRANSPLANT INTRODUCTION
 PERIPHERAL STEM CELL TRANSPLANT INTRODUCTION This booklet was designed to help you and the important people in your life understand the treatment of high dose chemotherapy with stem cell support: a procedure
PERIPHERAL STEM CELL TRANSPLANT INTRODUCTION This booklet was designed to help you and the important people in your life understand the treatment of high dose chemotherapy with stem cell support: a procedure
Kidney Cancer. Understanding your diagnosis
 Kidney Cancer Understanding your diagnosis Kidney Cancer Understanding your diagnosis When you first hear that you have cancer, you may feel alone and afraid. You may be overwhelmed by the large amount
Kidney Cancer Understanding your diagnosis Kidney Cancer Understanding your diagnosis When you first hear that you have cancer, you may feel alone and afraid. You may be overwhelmed by the large amount
Palm Beach Obstetrics & Gynecology, PA
 Palm Beach Obstetrics & Gynecology, PA 4671 S. Congress Avenue, Lake Worth, FL 33461 561.434.0111 4631 N. Congress Avenue, Suite 102, West Palm Beach, FL 33407 Urinary Tract Infection About one of every
Palm Beach Obstetrics & Gynecology, PA 4671 S. Congress Avenue, Lake Worth, FL 33461 561.434.0111 4631 N. Congress Avenue, Suite 102, West Palm Beach, FL 33407 Urinary Tract Infection About one of every
Mesothelioma: Questions and Answers
 CANCER FACTS N a t i o n a l C a n c e r I n s t i t u t e N a t i o n a l I n s t i t u t e s o f H e a l t h D e p a r t m e n t o f H e a l t h a n d H u m a n S e r v i c e s Mesothelioma: Questions
CANCER FACTS N a t i o n a l C a n c e r I n s t i t u t e N a t i o n a l I n s t i t u t e s o f H e a l t h D e p a r t m e n t o f H e a l t h a n d H u m a n S e r v i c e s Mesothelioma: Questions
Prostate Cancer Guide. A resource to help answer your questions about prostate cancer
 Prostate Cancer Guide A resource to help answer your questions about prostate cancer Thank you for downloading this guide to prostate cancer treatment. We know that all the information provided online
Prostate Cancer Guide A resource to help answer your questions about prostate cancer Thank you for downloading this guide to prostate cancer treatment. We know that all the information provided online
National Cancer Institute. What You Need TM. To Know About. Ovarian Cancer. U.S. DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES National Institutes of Health
 National Cancer Institute What You Need TM To Know About Ovarian Cancer U.S. DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES National Institutes of Health Contents About This Booklet 1 The Ovaries 2 Understanding
National Cancer Institute What You Need TM To Know About Ovarian Cancer U.S. DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES National Institutes of Health Contents About This Booklet 1 The Ovaries 2 Understanding
Cervical Cancer. Cervical smear test. The cervix. Dysplasia. Cervical cancer. The female reproductive system
 INFORMATION SHEET Cervical Cancer This information sheet has been written to provide you with information about cervical cancer (cancer of the cervix). The sheet has information about the different types
INFORMATION SHEET Cervical Cancer This information sheet has been written to provide you with information about cervical cancer (cancer of the cervix). The sheet has information about the different types
Gallbladder Diseases and Problems
 Gallbladder Diseases and Problems Introduction Your gallbladder is a pear-shaped organ under your liver. It stores bile, a fluid made by your liver to digest fat. There are many diseases and problems that
Gallbladder Diseases and Problems Introduction Your gallbladder is a pear-shaped organ under your liver. It stores bile, a fluid made by your liver to digest fat. There are many diseases and problems that
Bladder reconstruction (neo-bladder)
 Bladder reconstruction (neo-bladder) We have written this leaflet to help you understand about your operation. It is designed to help you answer any questions you may have. The leaflet contains the following
Bladder reconstruction (neo-bladder) We have written this leaflet to help you understand about your operation. It is designed to help you answer any questions you may have. The leaflet contains the following
Prostate Cancer. There is no known association with an enlarged prostate or benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH).
 Prostate Cancer Definition Prostate cancer is cancer that starts in the prostate gland. The prostate is a small, walnut-sized structure that makes up part of a man's reproductive system. It wraps around
Prostate Cancer Definition Prostate cancer is cancer that starts in the prostate gland. The prostate is a small, walnut-sized structure that makes up part of a man's reproductive system. It wraps around
Prostate Cancer. What is prostate cancer?
 Scan for mobile link. Prostate Cancer Prostate cancer is a tumor of the prostate gland, which is located in front of the rectum and below the bladder. Your doctor may perform a physical exam, prostate-specific
Scan for mobile link. Prostate Cancer Prostate cancer is a tumor of the prostate gland, which is located in front of the rectum and below the bladder. Your doctor may perform a physical exam, prostate-specific
1400 Telegraph Bloomfield Hills, MI 48302 248-334-6877-Phone number/248-334-6877-fax Number CANCER TREATMENT
 1400 Telegraph Bloomfield Hills, MI 48302 248-334-6877-Phone number/248-334-6877-fax Number CANCER TREATMENT Learning that your pet has a diagnosis of cancer can be overwhelming. We realize that your pet
1400 Telegraph Bloomfield Hills, MI 48302 248-334-6877-Phone number/248-334-6877-fax Number CANCER TREATMENT Learning that your pet has a diagnosis of cancer can be overwhelming. We realize that your pet
Introduction Ovarian cysts are a very common female condition. An ovarian cyst is a fluid-filled sac on an ovary in the female reproductive system.
 Ovarian Cysts Introduction Ovarian cysts are a very common female condition. An ovarian cyst is a fluid-filled sac on an ovary in the female reproductive system. Most women have ovarian cysts sometime
Ovarian Cysts Introduction Ovarian cysts are a very common female condition. An ovarian cyst is a fluid-filled sac on an ovary in the female reproductive system. Most women have ovarian cysts sometime
GYNECOLOGIC CANCERS Facts to Help Patients Make an Informed Decision
 RADIATION THERAPY FOR GYNECOLOGIC CANCERS Facts to Help Patients Make an Informed Decision TARGETING CANCER CARE AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR RADIATION ONCOLOGY FACTS ABOUT GYNECOLOGIC CANCERS Gynecologic cancers
RADIATION THERAPY FOR GYNECOLOGIC CANCERS Facts to Help Patients Make an Informed Decision TARGETING CANCER CARE AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR RADIATION ONCOLOGY FACTS ABOUT GYNECOLOGIC CANCERS Gynecologic cancers
About the Uterus. Hysterectomy may be done to treat conditions that affect the uterus. Some reasons a hysterectomy may be needed include:
 Hysterectomy removal of the uterus is a way of treating problems that affect the uterus. Many conditions can be cured with hysterectomy. Because it is major surgery, your doctor may suggest trying other
Hysterectomy removal of the uterus is a way of treating problems that affect the uterus. Many conditions can be cured with hysterectomy. Because it is major surgery, your doctor may suggest trying other
Us TOO University Presents: Understanding Diagnostic Testing
 Us TOO University Presents: Understanding Diagnostic Testing for Prostate Cancer Patients Today s speaker is Manish Bhandari, MD Program moderator is Pam Barrett, Us TOO International Made possible by
Us TOO University Presents: Understanding Diagnostic Testing for Prostate Cancer Patients Today s speaker is Manish Bhandari, MD Program moderator is Pam Barrett, Us TOO International Made possible by
Ovarian Cancer. Understanding your diagnosis
 Ovarian Cancer Understanding your diagnosis Ovarian Cancer Understanding your diagnosis When you first hear that you have cancer, you may feel alone and afraid. You may be overwhelmed by the large amount
Ovarian Cancer Understanding your diagnosis Ovarian Cancer Understanding your diagnosis When you first hear that you have cancer, you may feel alone and afraid. You may be overwhelmed by the large amount
Ovarian Cancer. in Georgia, 1999-2003. Georgia Department of Human Resources Division of Public Health
 Ovarian Cancer in Georgia, 1999-23 Georgia Department of Human Resources Division of Public Health Acknowledgments Georgia Department of Human Resources......B. J. Walker, Commissioner Division of Public
Ovarian Cancer in Georgia, 1999-23 Georgia Department of Human Resources Division of Public Health Acknowledgments Georgia Department of Human Resources......B. J. Walker, Commissioner Division of Public
Prostate Cancer Screening. A Decision Guide for African Americans
 Prostate Cancer Screening A Decision Guide for African Americans This booklet was developed by the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Published
Prostate Cancer Screening A Decision Guide for African Americans This booklet was developed by the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Published
Prostate Cancer Treatment
 Scan for mobile link. Prostate Cancer Treatment Prostate cancer is a tumor of the prostate gland, which is located in front of the rectum and below the bladder. Your doctor may perform a physical exam,
Scan for mobile link. Prostate Cancer Treatment Prostate cancer is a tumor of the prostate gland, which is located in front of the rectum and below the bladder. Your doctor may perform a physical exam,
Skin cancer Patient information
 Skin cancer Patient information What is cancer? The human body is made up of billions of cells. In healthy people, cells grow, divide and die. New cells constantly replace old ones in an orderly way. This
Skin cancer Patient information What is cancer? The human body is made up of billions of cells. In healthy people, cells grow, divide and die. New cells constantly replace old ones in an orderly way. This
U.S. DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES
 National Cancer Institute What You Need TM To Know About Prostate Cancer U.S. DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES National Institutes of Health For more publications This is only one of many free booklets
National Cancer Institute What You Need TM To Know About Prostate Cancer U.S. DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES National Institutes of Health For more publications This is only one of many free booklets
Melanoma The Skin Understanding Cancer
 Melanoma A form of cancer that begins in melanocytes (cells that make the pigment melanin). It may begin in a mole (skin melanoma), but can also begin in other pigmented tissues, such as in the eye or
Melanoma A form of cancer that begins in melanocytes (cells that make the pigment melanin). It may begin in a mole (skin melanoma), but can also begin in other pigmented tissues, such as in the eye or
National Cancer Institute. What You Need TM. To Know About. Kidney Cancer. U.S. DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES National Institutes of Health
 National Cancer Institute What You Need TM To Know About Kidney Cancer U.S. DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES National Institutes of Health National Cancer Institute Services This is only one of
National Cancer Institute What You Need TM To Know About Kidney Cancer U.S. DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES National Institutes of Health National Cancer Institute Services This is only one of
INTRAPERITONEAL HYPERTHERMIC CHEMOTHERAPY (IPHC) FOR PERITONEAL CARCINOMATOSIS AND MALIGNANT ASCITES. INFORMATION FOR PATIENTS AND FAMILY MEMBERS
 INTRAPERITONEAL HYPERTHERMIC CHEMOTHERAPY (IPHC) FOR PERITONEAL CARCINOMATOSIS AND MALIGNANT ASCITES. INFORMATION FOR PATIENTS AND FAMILY MEMBERS Description of Treatment A major difficulty in treating
INTRAPERITONEAL HYPERTHERMIC CHEMOTHERAPY (IPHC) FOR PERITONEAL CARCINOMATOSIS AND MALIGNANT ASCITES. INFORMATION FOR PATIENTS AND FAMILY MEMBERS Description of Treatment A major difficulty in treating
Spinal Cord and Bladder Management Male: Intermittent Catheter
 Spinal Cord and Bladder Management Male: Intermittent Catheter The 5 parts of the urinary system work together to get rid of waste and make urine. Urine is made in your kidneys and travels down 2 thin
Spinal Cord and Bladder Management Male: Intermittent Catheter The 5 parts of the urinary system work together to get rid of waste and make urine. Urine is made in your kidneys and travels down 2 thin
X-Plain Chemotherapy for Breast Cancer - Adriamycin, Cytoxan, and Tamoxifen Reference Summary
 X-Plain Chemotherapy for Breast Cancer - Adriamycin, Cytoxan, and Tamoxifen Reference Summary Introduction Breast cancer is a common condition that affects one out of every 11 women. Your doctor has recommended
X-Plain Chemotherapy for Breast Cancer - Adriamycin, Cytoxan, and Tamoxifen Reference Summary Introduction Breast cancer is a common condition that affects one out of every 11 women. Your doctor has recommended
How To Treat A Uterine Sarcoma
 EVERYONE S GUIDE FOR CANCER THERAPY Malin Dollinger, MD, Ernest H. Rosenbaum, MD, Margaret Tempero, MD, and Sean Mulvihill, MD 4 th Edition 2001 Uterus: Uterine Sarcomas Jeffrey L. Stern, MD Uterine sarcomas
EVERYONE S GUIDE FOR CANCER THERAPY Malin Dollinger, MD, Ernest H. Rosenbaum, MD, Margaret Tempero, MD, and Sean Mulvihill, MD 4 th Edition 2001 Uterus: Uterine Sarcomas Jeffrey L. Stern, MD Uterine sarcomas
Disease/Illness GUIDE TO ASBESTOS LUNG CANCER. What Is Asbestos Lung Cancer? www.simpsonmillar.co.uk Telephone 0844 858 3200
 GUIDE TO ASBESTOS LUNG CANCER What Is Asbestos Lung Cancer? Like tobacco smoking, exposure to asbestos can result in the development of lung cancer. Similarly, the risk of developing asbestos induced lung
GUIDE TO ASBESTOS LUNG CANCER What Is Asbestos Lung Cancer? Like tobacco smoking, exposure to asbestos can result in the development of lung cancer. Similarly, the risk of developing asbestos induced lung
These rare variants often act aggressively and may respond differently to therapy than the more common prostate adenocarcinoma.
 Prostate Cancer OVERVIEW Prostate cancer is the second most common cancer diagnosed among American men, accounting for nearly 200,000 new cancer cases in the United States each year. Greater than 65% of
Prostate Cancer OVERVIEW Prostate cancer is the second most common cancer diagnosed among American men, accounting for nearly 200,000 new cancer cases in the United States each year. Greater than 65% of
Esophageal Cancer Treatment
 Scan for mobile link. Esophageal Cancer Treatment What is Esophageal Cancer? Esophageal cancer occurs when cancer cells develop in the esophagus, a long, tube-like structure that connects the throat and
Scan for mobile link. Esophageal Cancer Treatment What is Esophageal Cancer? Esophageal cancer occurs when cancer cells develop in the esophagus, a long, tube-like structure that connects the throat and
Prostate Cancer Screening. A Decision Guide
 Prostate Cancer Screening A Decision Guide This booklet was developed by the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Is screening right for you?
Prostate Cancer Screening A Decision Guide This booklet was developed by the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Is screening right for you?
95% of childhood kidney cancer cases are Wilms tumours. Childhood kidney cancer is extremely rare, with only 90 cases a year in
 James Whale Fund for Kidney Cancer Childhood kidney cancer factsheet Kidney cancer rarely afflicts children and about 90 paediatric cases are diagnosed in the UK each year. About 75% of childhood kidney
James Whale Fund for Kidney Cancer Childhood kidney cancer factsheet Kidney cancer rarely afflicts children and about 90 paediatric cases are diagnosed in the UK each year. About 75% of childhood kidney
Appendix 2. Patient information
 Appendix 2. Patient information Original document: "Comprendre le cancer de la prostate. Guide d information et de dialogue à l'usage des personnes malades et de leurs proches (http://www.sor-cancer.fr),
Appendix 2. Patient information Original document: "Comprendre le cancer de la prostate. Guide d information et de dialogue à l'usage des personnes malades et de leurs proches (http://www.sor-cancer.fr),
Prostate Cancer. Treatments as unique as you are
 Prostate Cancer Treatments as unique as you are UCLA Prostate Cancer Program Prostate cancer is the second most common cancer among men. The UCLA Prostate Cancer Program brings together the elements essential
Prostate Cancer Treatments as unique as you are UCLA Prostate Cancer Program Prostate cancer is the second most common cancer among men. The UCLA Prostate Cancer Program brings together the elements essential
Prostate Cancer. Understanding your diagnosis
 Prostate Cancer Understanding your diagnosis Prostate Cancer Understanding your diagnosis When you first hear that you have cancer, you may feel alone and afraid. You may be overwhelmed by the large amount
Prostate Cancer Understanding your diagnosis Prostate Cancer Understanding your diagnosis When you first hear that you have cancer, you may feel alone and afraid. You may be overwhelmed by the large amount
Cancer of the Uterus. National Cancer Institute. What You Need TM. To Know About
 National Cancer Institute What You Need TM To Know About Cancer of the Uterus U.S. DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES National Institutes of Health National Cancer Institute Services This is only
National Cancer Institute What You Need TM To Know About Cancer of the Uterus U.S. DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES National Institutes of Health National Cancer Institute Services This is only
Brain Cancer. This reference summary will help you understand how brain tumors are diagnosed and what options are available to treat them.
 Brain Cancer Introduction Brain tumors are not rare. Thousands of people are diagnosed every year with tumors of the brain and the rest of the nervous system. The diagnosis and treatment of brain tumors
Brain Cancer Introduction Brain tumors are not rare. Thousands of people are diagnosed every year with tumors of the brain and the rest of the nervous system. The diagnosis and treatment of brain tumors
OBJECTIVES By the end of this segment, the community participant will be able to:
 Cancer 101: Cancer Diagnosis and Staging Linda U. Krebs, RN, PhD, AOCN, FAAN OCEAN Native Navigators and the Cancer Continuum (NNACC) (NCMHD R24MD002811) Cancer 101: Diagnosis & Staging (Watanabe-Galloway
Cancer 101: Cancer Diagnosis and Staging Linda U. Krebs, RN, PhD, AOCN, FAAN OCEAN Native Navigators and the Cancer Continuum (NNACC) (NCMHD R24MD002811) Cancer 101: Diagnosis & Staging (Watanabe-Galloway
Basic Radiation Therapy Terms
 Basic Radiation Therapy Terms accelerated radiation: radiation schedule in which the total dose is given over a shorter period of time. (Compare to hyperfractionated radiation.) adjuvant therapy (add-joo-vunt):
Basic Radiation Therapy Terms accelerated radiation: radiation schedule in which the total dose is given over a shorter period of time. (Compare to hyperfractionated radiation.) adjuvant therapy (add-joo-vunt):
LIvING WITH Prostate Cancer
 Living with Prostate Cancer A Common Cancer in Men If you ve been diagnosed with prostate cancer, it s normal to be concerned about your future. It may help you to know that this disease can often be cured
Living with Prostate Cancer A Common Cancer in Men If you ve been diagnosed with prostate cancer, it s normal to be concerned about your future. It may help you to know that this disease can often be cured
Guide to Understanding Breast Cancer
 An estimated 220,000 women in the United States are diagnosed with breast cancer each year, and one in eight will be diagnosed during their lifetime. While breast cancer is a serious disease, most patients
An estimated 220,000 women in the United States are diagnosed with breast cancer each year, and one in eight will be diagnosed during their lifetime. While breast cancer is a serious disease, most patients
Cervical Cancer The Importance of Cervical Screening and Vaccination
 Cervical Cancer The Importance of Cervical Screening and Vaccination Cancer Cells Cancer begins in cells, the building blocks that make up tissues. Tissues make up the organs of the body. Sometimes, this
Cervical Cancer The Importance of Cervical Screening and Vaccination Cancer Cells Cancer begins in cells, the building blocks that make up tissues. Tissues make up the organs of the body. Sometimes, this
Treating Melanoma S kin Cancer A Quick Guide
 Treating Melanoma Skin Cancer A Quick Guide Contents This is a brief summary of the information on Treating melanoma skin cancer from our website. You will find more detailed information on the website.
Treating Melanoma Skin Cancer A Quick Guide Contents This is a brief summary of the information on Treating melanoma skin cancer from our website. You will find more detailed information on the website.
PROSTATE CANCER 101 WHAT IS PROSTATE CANCER?
 PROSTATE CANCER 101 WHAT IS PROSTATE CANCER? Prostate cancer is cancer that begins in the prostate. The prostate is a walnut-shaped gland in the male reproductive system located below the bladder and in
PROSTATE CANCER 101 WHAT IS PROSTATE CANCER? Prostate cancer is cancer that begins in the prostate. The prostate is a walnut-shaped gland in the male reproductive system located below the bladder and in
The main surgical options for treating early stage cervical cancer are:
 INFORMATION LEAFLET ON TOTAL LAPAROSCOPIC RADICAL HYSTERECTOMY (TLRH) FOR EARLY STAGE CERVICAL CANCER (TREATING EARLY STAGE CERVICAL CANCER BY RADICAL HYSTERECTOMY THROUGH KEYHOLE SURGERY) Aim of the leaflet
INFORMATION LEAFLET ON TOTAL LAPAROSCOPIC RADICAL HYSTERECTOMY (TLRH) FOR EARLY STAGE CERVICAL CANCER (TREATING EARLY STAGE CERVICAL CANCER BY RADICAL HYSTERECTOMY THROUGH KEYHOLE SURGERY) Aim of the leaflet
Pancreatic Cancer Understanding your diagnosis
 Pancreatic Cancer Understanding your diagnosis Let s Make Cancer History 1 888 939-3333 cancer.ca Pancreatic Cancer Understanding your diagnosis When you first hear that you have cancer you may feel alone
Pancreatic Cancer Understanding your diagnosis Let s Make Cancer History 1 888 939-3333 cancer.ca Pancreatic Cancer Understanding your diagnosis When you first hear that you have cancer you may feel alone
Surgery. Wedge resection only part of the lung, not. not a lobe, is removed. Cancer Council NSW
 The treatment you receive will depend on your lung cancer type, for example, whether you have a non-small cell lung cancer Adenocarcinoma or Squamous cell carcinoma, and if this is a sub-type with a mutation.
The treatment you receive will depend on your lung cancer type, for example, whether you have a non-small cell lung cancer Adenocarcinoma or Squamous cell carcinoma, and if this is a sub-type with a mutation.
Prostate Cancer Action Plan: Choosing the treatment that s right for you
 Prostate Cancer Action Plan: Choosing the treatment that s right for you Segment 1: Introduction Trust me, there's a better way to choose a treatment for your prostate cancer. Watching this program is
Prostate Cancer Action Plan: Choosing the treatment that s right for you Segment 1: Introduction Trust me, there's a better way to choose a treatment for your prostate cancer. Watching this program is
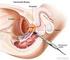
RADIATION THERAPY FOR BLADDER CANCER. Facts to Help Patients Make an Informed Decision TARGETING CANCER CARE AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR RADIATION ONCOLOGY
 RADIATION THERAPY FOR Facts to Help Patients Make an Informed Decision TARGETING CANCER CARE AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR RADIATION ONCOLOGY FACTS ABOUT The bladder is located in the pelvis. It collects and stores
RADIATION THERAPY FOR Facts to Help Patients Make an Informed Decision TARGETING CANCER CARE AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR RADIATION ONCOLOGY FACTS ABOUT The bladder is located in the pelvis. It collects and stores
Cryosurgery in Cancer Treatment: Questions and Answers. Key Points
 CANCER FACTS N a t i o n a l C a n c e r I n s t i t u t e N a t i o n a l I n s t i t u t e s o f H e a l t h D e p a r t m e n t o f H e a l t h a n d H u m a n S e r v i c e s Cryosurgery in Cancer
CANCER FACTS N a t i o n a l C a n c e r I n s t i t u t e N a t i o n a l I n s t i t u t e s o f H e a l t h D e p a r t m e n t o f H e a l t h a n d H u m a n S e r v i c e s Cryosurgery in Cancer
Basics on Treatment for prostate cancer
 Basics on Treatment for prostate cancer SECTION 1: TREATMENTS This pamphlet provides information about different treatments for prostate cancer including what to expect and any risks and side-effects.
Basics on Treatment for prostate cancer SECTION 1: TREATMENTS This pamphlet provides information about different treatments for prostate cancer including what to expect and any risks and side-effects.
PCA3 DETECTION TEST FOR PROSTATE CANCER DO YOU KNOW YOUR RISK OF HAVING CANCER?
 PCA3 DETECTION TEST FOR PROSTATE CANCER DO YOU KNOW YOUR RISK OF HAVING CANCER? PCA3 DETECTION TEST FOR PROSTATE CANCER There is a range of methods available to your healthcare professional to verify the
PCA3 DETECTION TEST FOR PROSTATE CANCER DO YOU KNOW YOUR RISK OF HAVING CANCER? PCA3 DETECTION TEST FOR PROSTATE CANCER There is a range of methods available to your healthcare professional to verify the
A WOMAN S GUIDE foundationforwomenscancer.org
 Understanding Cervical Cancer A WOMAN S GUIDE foundationforwomenscancer.org Contents Introduction...1 Cervical Cancer: An Overview...2 Medical Evaluation...3 WORKING WITH YOUR TREATMENT TEAM...3 TREATMENT...4
Understanding Cervical Cancer A WOMAN S GUIDE foundationforwomenscancer.org Contents Introduction...1 Cervical Cancer: An Overview...2 Medical Evaluation...3 WORKING WITH YOUR TREATMENT TEAM...3 TREATMENT...4
Neuroendocrine Tumors
 Neuroendocrine Tumors Neuroendocrine tumors arise from cells that release a hormone in response to a signal from the nervous system. Neuro refers to the nervous system. Endocrine refers to the hormones.
Neuroendocrine Tumors Neuroendocrine tumors arise from cells that release a hormone in response to a signal from the nervous system. Neuro refers to the nervous system. Endocrine refers to the hormones.
A start to help you understand prostate cancer
 A start to help you understand prostate cancer If you are reading this because you have worries or concerns about yourself or someone you know then the best thing to do is make an appointment with your
A start to help you understand prostate cancer If you are reading this because you have worries or concerns about yourself or someone you know then the best thing to do is make an appointment with your
Quick Facts about Appendix Cancer
 Quick Facts about Appendix Cancer What is the appendix? The appendix is a pouch-like tube attached to the first part of the large intestine (cecum). The appendix is about 10 centimetres long and has no
Quick Facts about Appendix Cancer What is the appendix? The appendix is a pouch-like tube attached to the first part of the large intestine (cecum). The appendix is about 10 centimetres long and has no
Pyelonephritis: Kidney Infection
 Pyelonephritis: Kidney Infection National Kidney and Urologic Diseases Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH What is pyelonephritis? Pyelonephritis
Pyelonephritis: Kidney Infection National Kidney and Urologic Diseases Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH What is pyelonephritis? Pyelonephritis
Spine University s Guide to Cauda Equina Syndrome
 Spine University s Guide to Cauda Equina Syndrome 2 Introduction Your spine is a very complicated part of your body. It s made up of the bones (vertebrae) that keep it aligned, nerves that channel down
Spine University s Guide to Cauda Equina Syndrome 2 Introduction Your spine is a very complicated part of your body. It s made up of the bones (vertebrae) that keep it aligned, nerves that channel down
Colorectal Cancer Facts and Figures In support of the SPECTAcolor Biobank Project
 Colorectal Cancer Facts and Figures In support of the SPECTAcolor Biobank Project ITALY Contact: Mathilde Fenoulhet, Fundraising Project Coordinator EORTC Headquarters mathilde.fenoulhet@eortc.be +32 2
Colorectal Cancer Facts and Figures In support of the SPECTAcolor Biobank Project ITALY Contact: Mathilde Fenoulhet, Fundraising Project Coordinator EORTC Headquarters mathilde.fenoulhet@eortc.be +32 2
