MAKING IT HAPPEN DEVELOPING TALENT IN THE WORKPLACE
|
|
|
- Alexander Day
- 9 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 MANAGING MAKING IT HAPPEN DEVELOPING IN THE WORKPLACE How do you effectively identify talent potential? Rita McGee offers guidance on developing and executing a successful policy on talent management, with a range of useful checklists and key questions to build a practical approach. Human resource (HR) professionals and the finance department are often thought to be diametrically opposed when it comes to addressing HR matters. The traditional perception is that finance tends only to see the figures, whereas HR tends to focus on the qualitative benefits. However, talent management provides a framework which can be seen as the creation of a language which can unite finance and HR. There is a logic to talent management which means that functions outside HR embrace it. Talent and potential Talent management is the process by which an organisation identifies, attracts, manages, develops and engages people to meet current and future business needs. There is contention about the terms talent and potential. These terms create emotive responses from normally rational people. The organisation could fall foul of legislation, confuse, de-motivate and at worst lose people if there is a lack of clarity about what the organisation means when it refers to talent or potential. Whilst there can be little argument that most people have potential, when managing talent you need to be able to differentiate between people on the basis of that potential. One mindset is based on the assumption that there is potential in each and every person, and any approach should try and release that. Another is that an organisation must identify its top potential and leverage their capabilities. Both are equally valid approaches. In addition, there are certain key competences an organisation requires for sustainable competitive advantage. The aim is to identify, retain and nurture them. This article covers: A framework for developing a talent management strategy What follows is a checklist of the things you should consider when you are preparing to write a talent management strategy. It is long but it is not exhaustive; while there will be variation from company to company, this checklist will allow you to focus on the relevant issues. You may already have much of this in place for your strategic planning process, in which case this list is an aide memoire. You can also use the list as a guide covering the areas that need your attention. Talent management provides a framework which can be seen as a language to unite finance and HR MAKING IT HAPPEN guidance on creating the strategy; information about the different terms; an explanation of the talent/potential matrix; suggestions for identifying high potentials ; checklists to help you think about how to attract the best talent; and a list of the problems you may encounter. I offer some questions to prompt thinking and, finally, some suggestions on how to evaluate your success. Rita McGee is director of RMG Consulting Rita@rmgconsulting.com 9
2 MANAGING September 2008 SPECIAL REPORT Building a clear picture Demand the current demand for skills in your sector/profession/industry; the expected future demand for skills; and your possible future demand (from scenario planning). Supply the current make up of the workforce; numbers employed, grade, length of service, time in role, performance ratings, readiness for promotion, likely promotion, average age, average tenure, % eligible for retirement in next year, diversity metrics: gender, race, disability; labour turnover (wastage) rates, including retirements, resignations); overall size of departments, grade levels and groupings of jobs; performance levels, and the level of likely dismissals due to non-performance; availability of skills externally; recruitment data eg numbers applying for roles, why people reject your offers and go elsewhere, offer rejection rates, time to fill positions; and promotion rates. Gaps You should now have a very clear picture of the talent gaps and may want to present them under the following headings: specific skills; specific levels; and demographic profiles. First start by asking yourself this question: Why am I creating this strategy now? You may also want to consider your timeframe what period is the talent management strategy focusing on eg the next three to five years? The six areas to consider are set out below. 1. Understand the current and future business context. It can be helpful to pull all of this information together in one document to help you contextualise the later steps: identify the current changes taking place externally that impact on your organisation; look at the internal drivers for change; explore the possible future scenarios that face your organisation; recognise the organisation s core competencies things which truly differentiate you from the competition and which need to be protected; state any constraints; consider significant organisational goals; make clear the implications of business goals for management; and identify any specific capabilities that your organisation will require to meet future business needs. Actions needed to meet the talent gaps Offshore/outsource identify activities which are core to your business and which can be offshored or outsourced. Succession plan which roles need to be earmarked for succession? how will you identify the successors? what percentage of key roles will have successors identified? what are the essential roles for which you must have a supply of successors ready at different times? what steps are you taking to ensure people on our succession plans understand their place on the plan and what they need to do to stay on it? Create specific talent pools technical; leadership; general; and other? Acquire talent: recruitment are there any roles that need to be targeted to be filled form outside of the organisation? Why? what percentage do you want to appoint internally/externally? what sources will you use? where will you most likely find the people you need? Develop talent: training, re-deployment, reassigning what support can you offer to train, re-deploy or reassign people? are there any generic training needs? is there a leadership development need? development ladders provide a focused approach to learning they offer training programmes at different levels, and this helps people to progress. what are the specific training needs? what steps are you recommending? Manage talent are current people accurately assessed? what steps can you take to improve the assessment of the existing talent pools? (Options include: building line management; and ensuring that your processes are robust, using stretch assessment rather than anecdotal evidence or questionnaires) what steps do you need to take to move people forward? how good are managers at segmenting their talent pool? how about giving feedback, could more be done to improve performance? Exit talent what strategy do you need to have in place to remove the people who do not demonstrate the talents you need for the future? are there any people/areas that need to be removed completely? If so, why? 10
3 MANAGING 2. Build a clear picture of the demand and supply for talent. This section requires that you interrogate your database or HR system to unearth information. You will also need to gain access to data from other sources eg recruiters, industry reports, benchmark reports. You are trying to create as clear a picture as possible about the demand and supply for talent in your area. You can pick from the headings in the box to the left ( Building a clear picture ). 3. Consider the budget. Yes, the budget is the third step! Do not let it limit your thinking too early. Before you prioritise is the right time to do a reality check about what is affordable. If you have spotted a gap that is critical but outside of the budget, it may be time to build the business case. 4. Decide the priority for addressing gaps. This is the hardest step. Everything may seem urgent but, having worked through step three you will probably find that it is not all possible. Sacrifices will need to be made. In this step you tackle the tough issues of prioritising the gaps that you will seek to fill. As a minimum use these headings: the priority order for addressing current talent management gaps; rationale for selecting the order and/or what might impact the order; and gaps that will not be addressed as priorities and why. 5. Identify the actions or interventions needed to meet the gaps. A list of possible actions or interventions, with questions to help you, is shown in the box below ( Actions needed to meet the talent gaps ). 6. The implementation plan. The implementation plan consists of the following: outline the principles and the philosophy that should underpin the talent management strategy; summarise the key priorities moving forward; provide an overview of the plan; and allocate responsibilities and accountability for delivery. What type of talent pool do you need to develop? Before you move to attracting your talent, you need to be clear what you are looking for, in most organisations the search for talent is for a specific reason. Below are three types of talent pools. General talent pool Most people are familiar with the graduate intake or the apprentice scheme where a group of, normally young, people are recruited into the organisation and developed according to specific needs. This is one type of talent pool and it is not uncommon for large accounting, consulting and legal firms to recruit a much larger pool than they will eventually need. This works on the basis that attrition is good for business. People who find careers elsewhere will become future Before you move to attracting talent, you need to be clear about what you are looking for in most organisations, the search is for a specific reason clients and the firm can pick the very best talent from the pool to retain. With the increasing costs of attraction, retention and development of talent, firms are reconsidering their approach. General talent pool Allows for people with various skills to enter the pool. People are included based on intellectual capability eg degree; graduate schemes may be general pools. People enter based on certain criteria eg general competencies. People can be rotated in the organisation without specific training or skills. Training time is short for the various roles. There are other types of talent pools and the emergence of the whole talent management agenda has been strongly linked to the development of leadership talent pools. Leadership talent pool The civil service also operates on the basis of creating talent pools. Civil servants can apply to join the Senior Civil Service (SCS), which means they are subjected to rigorous interviews and participate in an assessment centre. They are then classified as a member of the SCS, but it may be some time before they are appointed to a specific leadership role. Leadership talent pool The organisation has specific leadership competencies. People are selected for the pool if they either currently demonstrate the competency or are seen as someone with future potential to meet the competency. People are moved into leadership roles based on demonstration of skill either on the job or in an assessment centre. 11
4 MANAGING September 2008 SPECIAL REPORT Technical talent pool Various pharmaceutical and other research organisations are grappling with the need to provide dual career ladders. Scientists often do not want to take on leadership responsibility but have critical talents the business needs to retain. These organisations must engage their top scientific talent and use talent pools or career ladders. Technical talent pool Specific technical skills are identified as essential to the organisation s future. Access to the pool is through demonstration of performance or potential in technical skill only. A common definition of talent is someone who demonstrates both high performance and high potential Building your brand to attract talent How is the organisation seen externally? by your customers? by other stakeholders? Is the company name recognised by consumers? Is the company name recognised by prospective employees? How well do you know the needs and interests of your target talent? are there any geographical differences in need? are there any gender differences? what about any age differences? Do you have clearly defined consumer brand values? are these the same as your employee brand values? is there a mismatch? is there a healthy overlap of core values? How good are you at targeting the different segments? Is the psychological contract between the organisation and the employee in balance ie working to the benefit of both. Some organisations have multiple talent pools operating at any one time. In order for success in talent management it is essential to decide what type of pools you need and why you might need them. It is also important to manage people through the pool. The pool itself should be evaluated to see if it provides the right talent for the organisation s current and future needs. You may also hear the following terms being used, so here is a quick explanation: bench strength this is a term taken from sport, substitutes are sitting on a bench ready to play. Your team is strong because you always have someone in reserve. Some companies talk about having adequate bench strength; the ones that will succeed are those with the fittest and best players ready for substitution as required. Just as a team will have a pool of extra talent ready in case of injury or another eventuality, then organisations need their own pools; and talent pipelines this refers to organisations having people at different levels of readiness for succession or to step into roles at a higher level. In essence, this means that you are coordinating the flow of talent into your organisation. It requires considerable concerted effort and great line management skills to identify, attract, manage, develop, retain and exit talent when needed. Talent management for high potential There are several components you need to consider when creating a definition of talent; most will include a measure of current performance, outputs or results. There are several that include potential and indeed a common definition of talent is someone who demonstrates both high performance and high potential. There is, however, a backlash to the use of the term potential. It is difficult to measure and there are issues about the labelling and withdrawal of coveted labels eg high potential. So many organisations focus on promotability rating their top talent as those who are both high performers and highly promotable. Another way of defining talent is to consider inputs or competencies. Where the organisation has well defined competencies or capabilities, then people who demonstrate high output and high input are regarded as the top talent. Your organisation may need to have several definitions to address different talent needs. It would be good to have one neat solution but this will have little value within the organisation. In my view it is better to have an untidy model that truly reflects the myriad of talent needs, both for now and the future, and one that has currency with the existing and future workforce. A final point to remember is that the definition can lose currency quickly and therefore must be regularly reviewed to see how effective it is in communicating to employees the talents that are valued and needed. 12
5 MANAGING The performance/potential matrix The matrix below is often used as the basis for organisations to create their own model. PERFORMANCE Performance/potential matrix HIGH Solid citizen Plateau-ed Well placed Workhorses Future may be elsewhere Needs remedial action High potentials (HiPos) Stars Future potential Giving people a task which is outside their current experience this will test their tipping point. You must ensure support is in place LOW LOW Deadwood POTENTIAL Talent spotting High potentials tend to be the top 10%-20% of people in the organisation who consistently deliver high performance and demonstrate to you that they have much further to go or more to give. So what does a high potential look like? It is very difficult to quantify this and your definition will be unique to your own organisation. In terms of personal attributes you may be looking for some of the following: has the respect and trust of peers; consistently produces measurable results above expectations; has a bias for action and is a proactive catalyst for change; ensures that team goals are achieved within ethical and cultural guidelines; self-manages in a manner that fosters learning and high-performance; thinks and solves problems creatively; is open to constructive criticism and feedback; has a good understanding of your business and his/her role in delivering its goals; strives to deliver and exceed customers needs; and has a well developed network of people who help him/her achieve their goals. How do you gather data on high potentials? The list below provides some of the ways different organisations gather data about an individual s potential. Which of these are you currently using? Which should you consider? acting up giving people a trial in a role eg maternity leave or sickness cover;? HIGH promoting early taking a risk with someone who is nearly there but who you believe still has room to move; showcasing giving people an opportunity to demonstrate to you/the board their capability either through presentations or working on a project; assessment centres a tried and tested approach that is highly successful in assessing current capability and competence; talent scouts/managers build a network of people who understand your needs, and are good at assessing others; stretch assignments give people a task which you know is outside their current experience and which could result in them failing. This will really test their tipping point. You must ensure support is in place; secondments where employees need to have exposure to different settings, give them an opportunity to work with other organisations to see how they succeed eg public to private sector; and psychometrics these tests are regarded as being - better at assessing ability than potential. Attracting the best talent Critical questions include: Why would people of outstanding talent want to join this organisation? Why should talent stay with this organisation? If you cannot answer them then you need to do work to build the employer brand. The employer brand will have an impact on whether you are seen as an employer of choice. There are numerous things for you to consider; and a few are listed in the box opposite. Your organisation needs to represent a place where people want to work and to do their best. The teams and roles they work in need to be challenging, supportive and engaging. Finally, but most importantly, the line manager must be a great manager. 13
6 MANAGING September 2008 SPECIAL REPORT Issues Possible problems Some questions to prompt thinking Currency of the talent management plan and maintaining top management engagement Tracking people Resources Keeping talented people on track Measuring performance accurately Staying legal Managing people remotely Other employees Talent management is static. Talent plan is out of sync with business reality. People fall out of view. Information is out of date. Information is not shared. Too much information is available. No resources available. Managers have no time for talent management activities. Not able to make the business case. Talented people can derail for many reasons, eg by failing to deliver on promises, to adapt, or to read the impact on others etc. Not receiving timely feedback may mean the problem escalates. ganisations find it difficult to calibrate performance. Line managers do not like to give feedback. Line managers avoid conflict. The talent management process may use assumptions that are inherently discriminatory, eg must have 10 years continuous service. Risks may not be identified early enough. The data on which you base decisions may not be current. Lack of visibility means that you cannot observe their performance. Employees outside talent pool become disengaged. Is talent management on the executive board s agenda on a regular basis? Can you ensure that each business planning review is followed by a talent plan review? How will you decide what data to collect? (See measuring the success of your programme on page x) How will you collect it? What information will be shared widely? What will be withheld and why? Can managers be trained to provide adequate data in a timely manner? What resources can be made available? How can you create time for managers? Is talent management a real priority for the business? Do you have an early identification system in place? How skilled are your line managers in giving feedback? How robust is the performance management system? How do you track performance improvements demonstrated on development activities? How is this data linked back into the talent management tracking system? Is one group favoured over others? Are your talent lists or pools representative of the organisational demographic? Are your selection processes fair? Are your development processes fair? Are you good at identifying and managing the risks? Do you have managers who are skilled in managing remote workers? Do your systems support them? Are the criteria for entering and leaving the talent pool transparent? Your issues Make your notes here 14
7 MANAGEMENT If you want to win the war for talent (see this reports first article) you must have good management and leadership in place. The manager needs to be someone who can clearly define what is expected of each person in the team. They must be able to give constructive feedback and to coach people to deliver more. They must be good at assessing each individual s capacity and helping to ensure the role fits. Finally they must be people who genuinely care about people. The role of the manager is so critical that I would encourage you to link reward with this capability. Some organisations use engagement statistics, broken down by department or team, to assess a line managers skill in this area. Problems you may encounter Listed in the box on the previous page are a few of the problems that you may encounter. This list is not exhaustive but it should prompt your thinking and can be used to help identify organisational specific issues. How to evaluate the success of your programme Several factors should be taken into account. There is always a danger inherent in any system of measurement or approach. We focus on those things that are obvious or easy to do while neglecting qualitative issues which are harder to assess. In the box (right), we have listed some quantitative and qualitative measures. The bottom line For some talent management is a leap of faith. In my opinion it is too complex and too expensive to be approached in this manner. The best organisations gather their data and build the case, they constantly evaluate progress and they link significant measures such as employee engagement and talent management and they reward success. When talent management is approached appropriately and consistently the benefits are undeniable. Ultimately, not everything can be measured or justified with hard data. The manager of the 21st century will need to make decisions based on best judgement formed from all the data available. However, those who choose to ignore talent management in a world where knowledge is increasingly the driver of so many organisations and indeed economies, do so at their peril. For more information, see Talent Management and Succession Planning, which was co-authored by Rita McGee, see CorporateAndHRStrategy/ htm Measuring the success of your programme The case for talent management Measures that could be used to evaluate your success include: percentage of roles with possible successors identified; vacancies as a percentage of posts; time taken to fill outstanding vacancies; turnover of star performers; cost of acquisition vs the cost of development; and talent budget vs competitors for labour (many firms talk to competitors through reward groups or networks, and use surveys plus anecdotal evidence and recruitment agency information). In time, a measure of return on investment might be attempted based on correlating the change in the investment in talent management with the change in organisational performance. Areas to consider: assess the value of key employees and the impact their departure would have on your business, eg contracts won by them, their relationships and skill sets, replacement cost, disruption and management time, etc; vulnerability what if key roles are not filled or key individuals not retained? The greater the vulnerabilities the greater the justification for investing in talent management; critical talent the greater the business relies on people that are difficult to find in the market place, the greater the justification for investing in talent management; lead times for correcting problems where people are on short notice and are easily mobile, there is a greater justification for investing in planning and strategies to cover key positions quickly; ensure that knowledge is shared across the organisation; and treat mistakes as learning opportunities rather than as a basis for apportioning blame, creating a learning organisation. 15
Talent Management Glossary
 Talent Management Glossary Employer Toolkit February 2013 0 About Asset Skills Asset Skills is one of 21 Sector Skills Councils (SSCs) that have been established to tackle skills needs and support improvements
Talent Management Glossary Employer Toolkit February 2013 0 About Asset Skills Asset Skills is one of 21 Sector Skills Councils (SSCs) that have been established to tackle skills needs and support improvements
Applies from 1 April 2007 Revised April 2008. Core Competence Framework Guidance booklet
 Applies from 1 April 2007 Revised April 2008 Core Competence Framework Guidance booklet - Core Competence Framework - Core Competence Framework Core Competence Framework Foreword Introduction to competences
Applies from 1 April 2007 Revised April 2008 Core Competence Framework Guidance booklet - Core Competence Framework - Core Competence Framework Core Competence Framework Foreword Introduction to competences
DFID CORE COMPETENCY FRAMEWORK
 DFID CORE COMPETENCY FRAMEWORK DFID s Core Competency Framework presents competencies in three clusters as shown below. The red cluster groups the work-related competencies, the green has peoplerelated
DFID CORE COMPETENCY FRAMEWORK DFID s Core Competency Framework presents competencies in three clusters as shown below. The red cluster groups the work-related competencies, the green has peoplerelated
Talent Management Framework
 Talent Management Framework A simple definition of Talent Management is: The systematic attraction, identification, development, engagement/retention and deployment of those individuals who are of particular
Talent Management Framework A simple definition of Talent Management is: The systematic attraction, identification, development, engagement/retention and deployment of those individuals who are of particular
Solutions overview. Inspiring talent management. Solutions insight. Inspiring talent management
 Solutions overview Inspiring talent management Solutions insight Inspiring talent management Inspiring talent management Intuitive technology that people love to use Lumesse is the only global company
Solutions overview Inspiring talent management Solutions insight Inspiring talent management Inspiring talent management Intuitive technology that people love to use Lumesse is the only global company
Succession Planning and Leader Development
 Succession Planning and Leader Development Reducing the Risk of Wrong Choices and Poor Investment Decisions Unleash Capability Reduce Risk Gain Competitive Advantage The New Normal Once reserved for the
Succession Planning and Leader Development Reducing the Risk of Wrong Choices and Poor Investment Decisions Unleash Capability Reduce Risk Gain Competitive Advantage The New Normal Once reserved for the
CHARLES STURT UNIVERSITY WORKFORCE PLANNING FRAMEWORK 2007 2011
 CHARLES STURT UNIVERSITY WORKFORCE PLANNING FRAMEWORK 2007 2011 1. DEFINITION... 1 2. CONTEXT... 1 3. STRATEGIC ALIGNMENT AND DRIVERS... 1 4. VALUES... 2 5. PRINCIPLES OF PRACTICE... 2 6. PERFORMANCE INDICATORS...
CHARLES STURT UNIVERSITY WORKFORCE PLANNING FRAMEWORK 2007 2011 1. DEFINITION... 1 2. CONTEXT... 1 3. STRATEGIC ALIGNMENT AND DRIVERS... 1 4. VALUES... 2 5. PRINCIPLES OF PRACTICE... 2 6. PERFORMANCE INDICATORS...
A new era for HR. Trinity College Dublin Human Resources Strategy 2014 to 2019
 A new era for HR Trinity College Dublin Human Resources Strategy 2014 to 2019 Introduction This revised HR strategy is a response from the HR function in College to the new College Strategy 2014-2019,
A new era for HR Trinity College Dublin Human Resources Strategy 2014 to 2019 Introduction This revised HR strategy is a response from the HR function in College to the new College Strategy 2014-2019,
OFFICE ANGELS. Office Angels Employers guide office-angels.com
 OFFICE ANGELS Employers Guide Office Angels Employers guide office-angels.com From attracting the best talent, to getting the most out of your people, we know that being an employer isn t always easy.
OFFICE ANGELS Employers Guide Office Angels Employers guide office-angels.com From attracting the best talent, to getting the most out of your people, we know that being an employer isn t always easy.
Learning & Development Framework for the Civil Service
 Learning & Development Framework for the Civil Service 2011-2014 Table of Contents 1. Introduction & Background... 1 2. Key Objectives and Actions arising... 3 3. Framework Objectives... 4 3.1 Prioritise
Learning & Development Framework for the Civil Service 2011-2014 Table of Contents 1. Introduction & Background... 1 2. Key Objectives and Actions arising... 3 3. Framework Objectives... 4 3.1 Prioritise
Workforce Management Plan 2013-2017
 Workforce Management Plan 2013-2017 Adopted on Wednesday 19 June 2013 Contents Message from the General Manager 5 city Plan: Cascade of Plans 6 our Vision, Mission and Community Outcomes 7 Introduction
Workforce Management Plan 2013-2017 Adopted on Wednesday 19 June 2013 Contents Message from the General Manager 5 city Plan: Cascade of Plans 6 our Vision, Mission and Community Outcomes 7 Introduction
Middlesbrough Manager Competency Framework. Behaviours Business Skills Middlesbrough Manager
 Middlesbrough Manager Competency Framework + = Behaviours Business Skills Middlesbrough Manager Middlesbrough Manager Competency Framework Background Middlesbrough Council is going through significant
Middlesbrough Manager Competency Framework + = Behaviours Business Skills Middlesbrough Manager Middlesbrough Manager Competency Framework Background Middlesbrough Council is going through significant
Will regional talent management practices keep up with the global pace?
 Will regional talent management practices keep up with the global pace? A STUDY BY It s through employees that the organisation learns fast to turn around challenges and unpredictability into opportunities
Will regional talent management practices keep up with the global pace? A STUDY BY It s through employees that the organisation learns fast to turn around challenges and unpredictability into opportunities
Employee Value Proposition (EVP)
 FACTSHEET Employee Value Proposition () What it is and why it is important Employee Value Proposition () is the jargon commonly used to describe the characteristics and appeal of working for an organisation.
FACTSHEET Employee Value Proposition () What it is and why it is important Employee Value Proposition () is the jargon commonly used to describe the characteristics and appeal of working for an organisation.
D 1. Working with people Develop productive working relationships with colleagues. Unit Summary. effective performance.
 1 Develop productive working relationships with colleagues Unit Summary What is the unit about? This unit is about developing working relationships with colleagues, within your own organisation and within
1 Develop productive working relationships with colleagues Unit Summary What is the unit about? This unit is about developing working relationships with colleagues, within your own organisation and within
KPMG 2013 / 2014 HR & Reward Practices Survey. kpmg.com/ng
 KPMG 2013 / 2014 HR & Reward Practices Survey kpmg.com/ng 2 KPMG 2013 / 2014 HR & Reward Practices Survey Executive Overview Human capital is one of the most critical assets of any business. Many organisations
KPMG 2013 / 2014 HR & Reward Practices Survey kpmg.com/ng 2 KPMG 2013 / 2014 HR & Reward Practices Survey Executive Overview Human capital is one of the most critical assets of any business. Many organisations
Skills Gap Analysis. Employer Toolkit. February 2013
 Skills Gap Analysis Employer Toolkit February 2013 0 About Asset Skills Asset Skills is one of 21 Sector Skills Councils (SSCs) that have been established to tackle skills needs and support improvements
Skills Gap Analysis Employer Toolkit February 2013 0 About Asset Skills Asset Skills is one of 21 Sector Skills Councils (SSCs) that have been established to tackle skills needs and support improvements
THE HR GUIDE TO IDENTIFYING HIGH-POTENTIALS
 THE HR GUIDE TO IDENTIFYING HIGH-POTENTIALS What makes a high-potential? Quite possibly not what you think. The HR Guide to Identifying High-Potentials 1 Chapter 1 - Introduction If you agree people are
THE HR GUIDE TO IDENTIFYING HIGH-POTENTIALS What makes a high-potential? Quite possibly not what you think. The HR Guide to Identifying High-Potentials 1 Chapter 1 - Introduction If you agree people are
Guide on Developing a HRM Plan
 Guide on Developing a HRM Plan Civil Service Branch June 1996 Table of Contents Introduction What is a HRM Plan? Critical Success Factors for Developing the HRM Plan A Shift in Mindset The HRM Plan in
Guide on Developing a HRM Plan Civil Service Branch June 1996 Table of Contents Introduction What is a HRM Plan? Critical Success Factors for Developing the HRM Plan A Shift in Mindset The HRM Plan in
How HR Software Can Help Deliver a Competitive Advantage
 How HR Software Can Help Deliver a Competitive Advantage whitepaper Content 3 4 6 9 12 Executive Summary What is competitive advantage? How can HR contribute to your competitive advantage? Key HR Software
How HR Software Can Help Deliver a Competitive Advantage whitepaper Content 3 4 6 9 12 Executive Summary What is competitive advantage? How can HR contribute to your competitive advantage? Key HR Software
HR Fast Stream Graduate Programme
 HR Fast Stream Graduate Programme 02 Contents Welcome p.03 What is the HR Fast Stream Graduate Programme? p.04 What are we looking for? p.07 Your Fast Stream career path p.08 Location p.09 Profiles p.10
HR Fast Stream Graduate Programme 02 Contents Welcome p.03 What is the HR Fast Stream Graduate Programme? p.04 What are we looking for? p.07 Your Fast Stream career path p.08 Location p.09 Profiles p.10
CareNZ Job Description GENERAL MANAGER HUMAN RESOURCES
 CareNZ Job Description GENERAL MANAGER HUMAN RESOURCES Responsible to: Responsible for: Chief Executive HR and Payroll Administrator HR Interns and Volunteers Dimensions Location of work Other information
CareNZ Job Description GENERAL MANAGER HUMAN RESOURCES Responsible to: Responsible for: Chief Executive HR and Payroll Administrator HR Interns and Volunteers Dimensions Location of work Other information
Competency Based Recruitment and Selection
 Competency Based Recruitment and Selection A Handbook for Managers 2010 March 2010 v2 1 March 2010 v2 2 Table of Contents Introduction...4 1. What are competencies?...4 2. Why use competencies for recruitment
Competency Based Recruitment and Selection A Handbook for Managers 2010 March 2010 v2 1 March 2010 v2 2 Table of Contents Introduction...4 1. What are competencies?...4 2. Why use competencies for recruitment
HR certification: basic course
 HR certification: basic course What makes the program unique: It is a modular program covering all major areas of the integrated talent It combines theoretical and practical training components Trainings
HR certification: basic course What makes the program unique: It is a modular program covering all major areas of the integrated talent It combines theoretical and practical training components Trainings
Talent management: an overview
 Homepage > HR Resources > Factsheets > Talent management: an overview Talent management: an overview Revised August 2012 In this factsheet What is talent management? The changing context and business case
Homepage > HR Resources > Factsheets > Talent management: an overview Talent management: an overview Revised August 2012 In this factsheet What is talent management? The changing context and business case
PERFORMANCE MANAGEMENT
 5 PERFORMANCE MANAGEMENT 59 CHAPTER 5 1. INTRODUCTION As a result of the continual change brought about by the dynamic business landscape, companies have been evolving their performance management systems
5 PERFORMANCE MANAGEMENT 59 CHAPTER 5 1. INTRODUCTION As a result of the continual change brought about by the dynamic business landscape, companies have been evolving their performance management systems
AS BUSINESS Paper 2 Specimen Assessment Material. Mark scheme
 AS BUSINESS Paper 2 Specimen Assessment Material Mark scheme Mark schemes are prepared by the Lead Assessment Writer and considered, together with the relevant questions, by a panel of subject teachers.
AS BUSINESS Paper 2 Specimen Assessment Material Mark scheme Mark schemes are prepared by the Lead Assessment Writer and considered, together with the relevant questions, by a panel of subject teachers.
Author: Lydia Cillie-Schmidt Page 1
 Talent Management: An integrated framework for implementation L Cillie-Schmidt: Talent Management: An integrated framework for implementation, Management Today, February 2009 Companies like to promote
Talent Management: An integrated framework for implementation L Cillie-Schmidt: Talent Management: An integrated framework for implementation, Management Today, February 2009 Companies like to promote
State of Louisiana s Workforce Planning Model Right People, Right Skills, Right Jobs, Right Time
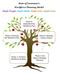 State of Louisiana s Workforce Planning Model Right People, Right Skills, Right Jobs, Right Time Table of Contents Introduction 2 What is Workforce Planning?...3 Why is Workforce Planning Important?.....3
State of Louisiana s Workforce Planning Model Right People, Right Skills, Right Jobs, Right Time Table of Contents Introduction 2 What is Workforce Planning?...3 Why is Workforce Planning Important?.....3
to selection. If you have any questions about these results or In the second half of 2014 we carried out an international
 Candidate Experience Survey RESULTS INTRODUCTION As an HR consultancy, we spend a lot of time talking We ve set out this report to focus on the findings of to our clients about how they can make their
Candidate Experience Survey RESULTS INTRODUCTION As an HR consultancy, we spend a lot of time talking We ve set out this report to focus on the findings of to our clients about how they can make their
Talent Management. What is it and how can you do it?
 Talent Management What is it and how can you do it? MTD Training, 5 Orchard Court, Binley Business Park, Coventry, CV3 2TQ Web: www.mtdtraining.com Phone: 0800 849 6732 Email: info@mtdtraining.com What
Talent Management What is it and how can you do it? MTD Training, 5 Orchard Court, Binley Business Park, Coventry, CV3 2TQ Web: www.mtdtraining.com Phone: 0800 849 6732 Email: info@mtdtraining.com What
Recruit the Right Talent To Increase Sales Effectiveness. ManpowerGroup Solutions Recruitment Process Outsourcing
 Recruit the Right Talent To Increase Sales Effectiveness ManpowerGroup Solutions Recruitment Process Outsourcing Executive Summary The most successful sales professionals are often promoted to leadership
Recruit the Right Talent To Increase Sales Effectiveness ManpowerGroup Solutions Recruitment Process Outsourcing Executive Summary The most successful sales professionals are often promoted to leadership
Afro Ant Conversation. Change Management Return on Investment 3 April 2014
 Afro Ant Conversation Change Management Return on Investment 3 April 2014 Overview This report documents the information gathered at the Afro Ant Conversation held on the 3 rd of April 2014 on the topic
Afro Ant Conversation Change Management Return on Investment 3 April 2014 Overview This report documents the information gathered at the Afro Ant Conversation held on the 3 rd of April 2014 on the topic
Organisational Development Improvement Strategy 2009-2011 Delivering results through our people
 Organisational Development Improvement Strategy 2009-2011 Delivering results through our people 1 Index Page No Foreword 3 What is Organisational Development? 4 Organisational Development- Driving change
Organisational Development Improvement Strategy 2009-2011 Delivering results through our people 1 Index Page No Foreword 3 What is Organisational Development? 4 Organisational Development- Driving change
SKILLED, ENGAGED & MOTIVATED STAFF
 Leadership and Management Capability Flexibility of Staff SKILLED, ENGAGED & MOTIVATED STAFF Skills Assurance Reward and Recognition Scottish Court Service People Strategy 2012 2015 1 Why have a People
Leadership and Management Capability Flexibility of Staff SKILLED, ENGAGED & MOTIVATED STAFF Skills Assurance Reward and Recognition Scottish Court Service People Strategy 2012 2015 1 Why have a People
Human Resources Report 2014 and People Strategy
 24 February 2015 Council 5 To consider Human Resources Report 2014 and People Strategy Issue 1 The annual report on Human Resources issues and a proposed People Strategy. Recommendations 2 Council is asked
24 February 2015 Council 5 To consider Human Resources Report 2014 and People Strategy Issue 1 The annual report on Human Resources issues and a proposed People Strategy. Recommendations 2 Council is asked
CEM+ Snapshot. Introduction
 Defining Your Customer Experience JOURNEY Many organisations seek to differentiate through customer experience, yet few have a systematic process for doing so. Different executives have different ideas
Defining Your Customer Experience JOURNEY Many organisations seek to differentiate through customer experience, yet few have a systematic process for doing so. Different executives have different ideas
Relationship Manager (Banking) Assessment Plan
 1. Introduction and Overview Relationship Manager (Banking) Assessment Plan The Relationship Manager (Banking) is an apprenticeship that takes 3-4 years to complete and is at a Level 6. It forms a key
1. Introduction and Overview Relationship Manager (Banking) Assessment Plan The Relationship Manager (Banking) is an apprenticeship that takes 3-4 years to complete and is at a Level 6. It forms a key
STRATEGIC WORKFORCE PLANNING LATEST TRENDS AND LEADING PRACTICE EXAMPLES
 STRATEGIC WORKFORCE PLANNING LATEST TRENDS AND LEADING PRACTICE EXAMPLES BERLIN, 21 MAY 2015 Julia Howes Mercer Workforce Analytics & Planning A WORKFORCE TSUNAMI IS APPROACHING COPYRIGHT MERCER 2015 STRATEGIC
STRATEGIC WORKFORCE PLANNING LATEST TRENDS AND LEADING PRACTICE EXAMPLES BERLIN, 21 MAY 2015 Julia Howes Mercer Workforce Analytics & Planning A WORKFORCE TSUNAMI IS APPROACHING COPYRIGHT MERCER 2015 STRATEGIC
Talent Management Essential Toolkit
 Talent Management Essential Toolkit Talent Management Essential Toolkit This presentation has been prepared to to provide the reader with an initial overview of five talent management tools that can assist
Talent Management Essential Toolkit Talent Management Essential Toolkit This presentation has been prepared to to provide the reader with an initial overview of five talent management tools that can assist
Best in Class Customer Retention
 Take your business to the next level Best in Class Customer Retention A 5% Improvement Can Double Your Bottom Line Profits Free Sales and Marketing Audit Call 410-977-7355 Lead Scoring, Prioritization,
Take your business to the next level Best in Class Customer Retention A 5% Improvement Can Double Your Bottom Line Profits Free Sales and Marketing Audit Call 410-977-7355 Lead Scoring, Prioritization,
as a key driver of their financial performance, can be influential in realizing on that objective. SMART HR Manager By : Irene
 SMART HR Manager By : Irene Dhanavathi Abstract: Human resource management (HRM), the management of work and people towards desired ends, is a fundamental activity in any organization in which human beings
SMART HR Manager By : Irene Dhanavathi Abstract: Human resource management (HRM), the management of work and people towards desired ends, is a fundamental activity in any organization in which human beings
Hiring for Retention Get It Right, Right Out of the Gate
 Hiring for Retention Get It Right, Right Out of the Gate By Russell M. Klosk, SPHR, GPHR Unrelenting Hiring Pressures Global workforces, maturing workforces, baby-boomer retirement waves you don t have
Hiring for Retention Get It Right, Right Out of the Gate By Russell M. Klosk, SPHR, GPHR Unrelenting Hiring Pressures Global workforces, maturing workforces, baby-boomer retirement waves you don t have
1 Executive Onboarding Reward vs. Risk
 1 Executive Onboarding Reward vs. Risk Gerard F. McDonough and Becky Choi, J.D. LEADFIRST LEARNING SYSTEMS, LLC Challenging Transitions It would seem that as professionals become more advanced in their
1 Executive Onboarding Reward vs. Risk Gerard F. McDonough and Becky Choi, J.D. LEADFIRST LEARNING SYSTEMS, LLC Challenging Transitions It would seem that as professionals become more advanced in their
workforce planning toolkit a guide for workforce planning in small to medium sized victorian public sector organisations
 1 workforce planning toolkit a guide for workforce planning in small to medium sized victorian public sector organisations workforce planning toolkit a guide for workforce planning in small to medium
1 workforce planning toolkit a guide for workforce planning in small to medium sized victorian public sector organisations workforce planning toolkit a guide for workforce planning in small to medium
Employee Engagement Drives Client Satisfaction and Employee Success in Professional Services
 Employee Engagement Drives Client Satisfaction and Employee Success in In professional services, business success is achieved through employee success. Organizations that prioritize top talent gain competitive
Employee Engagement Drives Client Satisfaction and Employee Success in In professional services, business success is achieved through employee success. Organizations that prioritize top talent gain competitive
October 17, 2011. HRBP Version Preparing for Talent Review: Updating imap Succession
 October 17, 2011 HRBP Version Preparing for Talent Review: Updating imap Succession FY12 Timeline for Succession / Talent Calibration Objective: Identify successors and high potential employees in the
October 17, 2011 HRBP Version Preparing for Talent Review: Updating imap Succession FY12 Timeline for Succession / Talent Calibration Objective: Identify successors and high potential employees in the
DESCRIBING OUR COMPETENCIES. new thinking at work
 DESCRIBING OUR COMPETENCIES new thinking at work OUR COMPETENCIES - AT A GLANCE 2 PERSONAL EFFECTIVENESS Influencing Communicating Self-development Decision-making PROVIDING EXCELLENT CUSTOMER SERVICE
DESCRIBING OUR COMPETENCIES new thinking at work OUR COMPETENCIES - AT A GLANCE 2 PERSONAL EFFECTIVENESS Influencing Communicating Self-development Decision-making PROVIDING EXCELLENT CUSTOMER SERVICE
A-LEVEL BUSINESS Paper 3 Specimen Assessment Material. Mark scheme
 A-LEVEL BUSINESS Paper 3 Specimen Assessment Material Mark scheme Mark schemes are prepared by the Lead Assessment Writer and considered, together with the relevant questions, by a panel of subject teachers.
A-LEVEL BUSINESS Paper 3 Specimen Assessment Material Mark scheme Mark schemes are prepared by the Lead Assessment Writer and considered, together with the relevant questions, by a panel of subject teachers.
Optimizing Rewards and Employee Engagement
 Optimizing Rewards and Employee Engagement Improving employee motivation and engagement, and identifying the right total rewards strategy to influence workforce effectiveness. Kevin Aselstine, Towers Perrin
Optimizing Rewards and Employee Engagement Improving employee motivation and engagement, and identifying the right total rewards strategy to influence workforce effectiveness. Kevin Aselstine, Towers Perrin
Trust Board Meeting: Wednesday 11 March 2015 TB2015.33. Oxford University Hospitals Trust Nursing and Midwifery Strategy 2015-2018
 Trust Board Meeting: Wednesday 11 March 2015 Title Oxford University Hospitals Trust Nursing and Midwifery Strategy 2015-2018 Status History This is a new paper Presented to the Trust Management Executive
Trust Board Meeting: Wednesday 11 March 2015 Title Oxford University Hospitals Trust Nursing and Midwifery Strategy 2015-2018 Status History This is a new paper Presented to the Trust Management Executive
Succession Planning Guide
 Succession Planning Guide The realities of succession planning and the future sale of your business Succession Planning Guide 1 Introduction Contents In New Zealand it is estimated 24% of small business
Succession Planning Guide The realities of succession planning and the future sale of your business Succession Planning Guide 1 Introduction Contents In New Zealand it is estimated 24% of small business
Workforce Planning, Succession Planning and Capability Planning. 13
 Report title Agenda item Workforce Planning, Succession Planning and Capability Planning. 13 Meeting Human Resources, Health & Safety and Equalities Panel 13 November 2008 Date Report by Document Number
Report title Agenda item Workforce Planning, Succession Planning and Capability Planning. 13 Meeting Human Resources, Health & Safety and Equalities Panel 13 November 2008 Date Report by Document Number
Talent management. Khamis 2 hb Jun 2011 1-2 petang
 Talent management Khamis 2 hb Jun 2011 1-2 petang TALENT MANAGEMENT(TM) NEED FOR EFFECTIVE TM PROCESS: Provide a focus for investment Place subject of talent high in the corporate agenda Desirable objective
Talent management Khamis 2 hb Jun 2011 1-2 petang TALENT MANAGEMENT(TM) NEED FOR EFFECTIVE TM PROCESS: Provide a focus for investment Place subject of talent high in the corporate agenda Desirable objective
ENHANCING PERFORMANCE MANAGEMENT: THE VALUE OF STAFF APPRAISALS A BUSINESS INSIGHT REPORT BY KAPLAN
 ENHANCING PERFORMANCE MANAGEMENT: THE VALUE OF STAFF APPRAISALS A BUSINESS INSIGHT REPORT BY KAPLAN 1 INTRODUCTION In 2014, leading global education and training provider Kaplan carried out a survey among
ENHANCING PERFORMANCE MANAGEMENT: THE VALUE OF STAFF APPRAISALS A BUSINESS INSIGHT REPORT BY KAPLAN 1 INTRODUCTION In 2014, leading global education and training provider Kaplan carried out a survey among
Workforce Planning Benefits
 Workforce Planning Benefits Seven Ways Workforce Planning Can Help Your Organization While surveys show that upwards of 90-percent of companies aren t getting the results they expected from a talent management
Workforce Planning Benefits Seven Ways Workforce Planning Can Help Your Organization While surveys show that upwards of 90-percent of companies aren t getting the results they expected from a talent management
Employing Military Spouses
 Employing Military Spouses A guide for employers Incorporating: 1. Introduction The UK has approximately 100,000 military spouses 1 with the important job of supporting a partner in the armed forces, which
Employing Military Spouses A guide for employers Incorporating: 1. Introduction The UK has approximately 100,000 military spouses 1 with the important job of supporting a partner in the armed forces, which
Consulting Performance, Rewards & Talent. Making Employee Engagement Happen: Best Practices from Best Employers
 Consulting Performance, Rewards & Talent Making Employee Engagement Happen: Best Practices from Best Employers The Challenge Companies across the globe are taking the initiative to administer and manage
Consulting Performance, Rewards & Talent Making Employee Engagement Happen: Best Practices from Best Employers The Challenge Companies across the globe are taking the initiative to administer and manage
Promotion, Transfer and Termination attachment one Developing and Implementing Succession Plans
 Promotion, Transfer and Termination attachment one Developing and Implementing Succession Plans Contents WGEA Tool: Developing Succession Plans 3 Introduction 3 Developing and Implementing Succession Plans
Promotion, Transfer and Termination attachment one Developing and Implementing Succession Plans Contents WGEA Tool: Developing Succession Plans 3 Introduction 3 Developing and Implementing Succession Plans
Recruitment and Selection
 Recruitment and Selection The recruitment and selection belongs to value added HR Processes. The recruitment is about: the ability of the organization to source new employees, to keep the organization
Recruitment and Selection The recruitment and selection belongs to value added HR Processes. The recruitment is about: the ability of the organization to source new employees, to keep the organization
BUILDING A SUCCESSFUL BUSINESS CASE FOR TALENT MANAGEMENT TECHNOLOGY By Kelly McCombs and Tim Welsh, AON Hewitt
 BUILDING A SUCCESSFUL BUSINESS CASE FOR TALENT MANAGEMENT TECHNOLOGY By Kelly McCombs and Tim Welsh, AON Hewitt Introduction Human Resources today sits smack-dab in the middle of the most compelling and
BUILDING A SUCCESSFUL BUSINESS CASE FOR TALENT MANAGEMENT TECHNOLOGY By Kelly McCombs and Tim Welsh, AON Hewitt Introduction Human Resources today sits smack-dab in the middle of the most compelling and
Passing the Torch Corporate Succession Planning
 Passing the Torch Corporate Succession Planning AUTHORS: Carroll Thatcher, CFM, IFMA Fellow Meredith Thatcher, CFM, IFMA Fellow, LEED AP The successful passage of the leadership role is one of the most
Passing the Torch Corporate Succession Planning AUTHORS: Carroll Thatcher, CFM, IFMA Fellow Meredith Thatcher, CFM, IFMA Fellow, LEED AP The successful passage of the leadership role is one of the most
Succession Management/Planning Talent Management
 Succession Management/Planning Talent Management Objectives Upon completing this workshop you will be able to: Utilize a basic framework for building a comprehensive succession plan. Understand the need
Succession Management/Planning Talent Management Objectives Upon completing this workshop you will be able to: Utilize a basic framework for building a comprehensive succession plan. Understand the need
Future-proofing employee engagement 5 areas of focus for 2015
 Future-proofing employee engagement 5 areas of focus for 2015 Employer Branding Experience 5 th November 2014 1 By way of introduction Thanks for having me Employee engagement is for life 4 An important
Future-proofing employee engagement 5 areas of focus for 2015 Employer Branding Experience 5 th November 2014 1 By way of introduction Thanks for having me Employee engagement is for life 4 An important
V1.0. Business. Specimen Assessment Material AS-level Paper 1 7131/1 Mark scheme. June 2014. Version 2.0
 V1.0 AS Business Specimen Assessment Material AS-level Paper 1 7131/1 Mark scheme June 2014 Version 2.0 Mark schemes are prepared by the Principal Examiner and considered, together with the relevant questions,
V1.0 AS Business Specimen Assessment Material AS-level Paper 1 7131/1 Mark scheme June 2014 Version 2.0 Mark schemes are prepared by the Principal Examiner and considered, together with the relevant questions,
VISION FOR LEARNING AND DEVELOPMENT
 VISION FOR LEARNING AND DEVELOPMENT As a Council we will strive for excellence in our approach to developing our employees. We will: Value our employees and their impact on Cardiff Council s ability to
VISION FOR LEARNING AND DEVELOPMENT As a Council we will strive for excellence in our approach to developing our employees. We will: Value our employees and their impact on Cardiff Council s ability to
The Human Capital Management Systems Business Case A Checklist to assist agencies developing a business case
 The Human Capital Management Systems Business Case A Checklist to assist agencies developing a business case Final version for release Human Capital Management See more at psc.nsw.gov.au/hcm Index - Business
The Human Capital Management Systems Business Case A Checklist to assist agencies developing a business case Final version for release Human Capital Management See more at psc.nsw.gov.au/hcm Index - Business
Considerations for Outsourcing
 Considerations for Outsourcing Chris Luxford, Director Contact Centre Technology Practice, 3D Networks Save 90% of your operational labour costs!!! Improve your bottom line ten fold!!! Dramatically reduce
Considerations for Outsourcing Chris Luxford, Director Contact Centre Technology Practice, 3D Networks Save 90% of your operational labour costs!!! Improve your bottom line ten fold!!! Dramatically reduce
White Paper. Executing Organizational. Strategy: Achieving. Success through Talent. Management
 White Paper Executing Organizational Strategy: Achieving Success through Talent Management April 2007 Table of Contents Factors Impacting Business Value and Execution 4 The Solution: Business Execution
White Paper Executing Organizational Strategy: Achieving Success through Talent Management April 2007 Table of Contents Factors Impacting Business Value and Execution 4 The Solution: Business Execution
We HAVE to do Performance Reviews We GET to do Career Development
 We HAVE to do Performance Reviews We GET to do Career Development Engaging Employees through Career Development NCCI 2014 Conference Presentation Dr. Kathy Burkgren Chris Halladay Employee Engagement:
We HAVE to do Performance Reviews We GET to do Career Development Engaging Employees through Career Development NCCI 2014 Conference Presentation Dr. Kathy Burkgren Chris Halladay Employee Engagement:
Technical Review Coversheet
 Status: Submitted Last Updated: 8/6/1 4:17 PM Technical Review Coversheet Applicant: Seattle Public Schools -- Strategic Planning and Alliances, (S385A1135) Reader #1: ********** Questions Evaluation Criteria
Status: Submitted Last Updated: 8/6/1 4:17 PM Technical Review Coversheet Applicant: Seattle Public Schools -- Strategic Planning and Alliances, (S385A1135) Reader #1: ********** Questions Evaluation Criteria
Effectiveness or Efficiency? Is your firm tracking the right Real Estate Metrics? TENANT PERSPECTIVES. The Challenge of Real Estate Management
 Effectiveness or Efficiency? Is your firm tracking the right Real Estate Metrics? By Joseph Hamilton, SVP, Cornish & Carey Client Solutions The Challenge of Real Estate Management Managing real estate
Effectiveness or Efficiency? Is your firm tracking the right Real Estate Metrics? By Joseph Hamilton, SVP, Cornish & Carey Client Solutions The Challenge of Real Estate Management Managing real estate
CHANGE MANAGEMENT POLICY AND PROCEDURE
 CHANGE MANAGEMENT POLICY AND PROCEDURE This Change Management Policy and Procedure contains guidance to managers and staff who are involved in the development and implementation of changes in working arrangements
CHANGE MANAGEMENT POLICY AND PROCEDURE This Change Management Policy and Procedure contains guidance to managers and staff who are involved in the development and implementation of changes in working arrangements
Applicant Tracking Technology The Business Case for Investment. Prepared by: John Cridland in co-operation with Chris Keeling
 Applicant Tracking Technology The Business Case for Investment Prepared by: John Cridland in co-operation with Chris Keeling 1 Applicant tracking technology the business case for investment Contents Introduction
Applicant Tracking Technology The Business Case for Investment Prepared by: John Cridland in co-operation with Chris Keeling 1 Applicant tracking technology the business case for investment Contents Introduction
Interview Guide for Hiring Executive Directors. April 2008
 Interview Guide for Hiring Executive Directors April 2008 Introduction This interview guide has been developed to help the Board of Directors of Big Brothers Big Sisters agencies interview candidates for
Interview Guide for Hiring Executive Directors April 2008 Introduction This interview guide has been developed to help the Board of Directors of Big Brothers Big Sisters agencies interview candidates for
MANAGING & REWARDING EMPLOYEE S PERFORMANCE
 262 ABSTRACT MANAGING & REWARDING EMPLOYEE S PERFORMANCE S. SUBRAMANIAM* *Assistant Professor, Datta Meghe Institute of Management Studies, Rashtrasant Tukadoji Maharaj Nagpur University, SDMP Campus,
262 ABSTRACT MANAGING & REWARDING EMPLOYEE S PERFORMANCE S. SUBRAMANIAM* *Assistant Professor, Datta Meghe Institute of Management Studies, Rashtrasant Tukadoji Maharaj Nagpur University, SDMP Campus,
A guide to strategic human resource planning
 A guide to strategic human resource planning By Workinfo.com, www.workinfo.com 1. Introduction A comprehensive Human Resource Strategy plays a vital role in the achievement of an organisation's overall
A guide to strategic human resource planning By Workinfo.com, www.workinfo.com 1. Introduction A comprehensive Human Resource Strategy plays a vital role in the achievement of an organisation's overall
Recruiting in a Competitive Market
 Recruiting in a Competitive Market MAURA DYER 15 YEARS Online Talent Acquisition Director, Rogers Facilitating the recruitment, engagement, and development of top talent at leading Canadian organizations
Recruiting in a Competitive Market MAURA DYER 15 YEARS Online Talent Acquisition Director, Rogers Facilitating the recruitment, engagement, and development of top talent at leading Canadian organizations
Addressing the challenges of Performance Management. part of our We think series
 Addressing the challenges of Performance Management part of our We think series Contents Contents 2 The Return on Investment in Performance Management 3 The challenges of effective Performance Management
Addressing the challenges of Performance Management part of our We think series Contents Contents 2 The Return on Investment in Performance Management 3 The challenges of effective Performance Management
McLAREN ASSOCIATES LIMITED
 McLAREN ASSOCIATES LIMITED JOB TITLE: Recruitment Consultant REPORTS TO: Directors EFFECTIVE DATE: January 2015 PURPOSE OF POSITION To develop McLaren Associates Limited business in order to both maintain
McLAREN ASSOCIATES LIMITED JOB TITLE: Recruitment Consultant REPORTS TO: Directors EFFECTIVE DATE: January 2015 PURPOSE OF POSITION To develop McLaren Associates Limited business in order to both maintain
Managing Staff Retention
 Managing Staff Retention Stephen Bevan, Institute for Employment Studies It wasn t so long ago that UK employers were worried about labour surpluses. Inevitably, as recession turns into boom, concern about
Managing Staff Retention Stephen Bevan, Institute for Employment Studies It wasn t so long ago that UK employers were worried about labour surpluses. Inevitably, as recession turns into boom, concern about
WHITE PAPER: How to Tackle Industry Challenges?
 WHITE PAPER: How to Tackle Industry Challenges? Introduction Human Resources (HR) teams came into existence, during the industrial revolution, for the purpose of manpower planning. HR professionals have
WHITE PAPER: How to Tackle Industry Challenges? Introduction Human Resources (HR) teams came into existence, during the industrial revolution, for the purpose of manpower planning. HR professionals have
The HR Director s Talent Challenge: Research report on Motivation and Engagement of staff in Higher Education institutions
 The HR Director s Talent Challenge: Research report on Motivation and Engagement of staff in Higher Education institutions Fierce competition for funding and the need to differentiate from other institutions
The HR Director s Talent Challenge: Research report on Motivation and Engagement of staff in Higher Education institutions Fierce competition for funding and the need to differentiate from other institutions
Insight paper. Succession Management: Assessment report
 Insight paper Succession Management: Assessment report Understanding the business impact of career and succession management To support your career and succession planning, this concise report presents
Insight paper Succession Management: Assessment report Understanding the business impact of career and succession management To support your career and succession planning, this concise report presents
APPENDIX I. Best Practices: Ten design Principles for Performance Management 1 1) Reflect your company's performance values.
 APPENDIX I Best Practices: Ten design Principles for Performance Management 1 1) Reflect your company's performance values. Identify the underlying priorities that should guide decisions about performance.
APPENDIX I Best Practices: Ten design Principles for Performance Management 1 1) Reflect your company's performance values. Identify the underlying priorities that should guide decisions about performance.
The Future of HR in Europe Key Challenges Through 2015
 The Future of HR in Europe Key Challenges Through 2015 The Future of HR in Europe 1 Executive Summary Companies in Europe will face five particularly critical HR challenges in the near future: managing
The Future of HR in Europe Key Challenges Through 2015 The Future of HR in Europe 1 Executive Summary Companies in Europe will face five particularly critical HR challenges in the near future: managing
Effective Workforce Development Starts with a Talent Audit
 Effective Workforce Development Starts with a Talent Audit By Stacey Harris, VP Research September, 2012 Introduction In a recent survey of CEO s, one in four felt they were unable to pursue a market opportunity
Effective Workforce Development Starts with a Talent Audit By Stacey Harris, VP Research September, 2012 Introduction In a recent survey of CEO s, one in four felt they were unable to pursue a market opportunity
Equality and Diversity Policy. Deputy Director of HR Version Number: V.2.00 Date: 27/01/11
 Equality and Diversity Policy Author: Deputy Director of HR Version Number: V.2.00 Date: 27/01/11 Approval and Authorisation Completion of the following signature blocks signifies the review and approval
Equality and Diversity Policy Author: Deputy Director of HR Version Number: V.2.00 Date: 27/01/11 Approval and Authorisation Completion of the following signature blocks signifies the review and approval
Talent Management / Development Framework 2011-2013: Maximising Potential of Organisations Assistant Director of OD
 AGENDA ITEM 4.5 Talent Management / Development Framework 2011-2013: Maximising Potential of Organisations Report of Paper prepared by Purpose of Paper Assistant Director of OD Senior LED Manager Leadership
AGENDA ITEM 4.5 Talent Management / Development Framework 2011-2013: Maximising Potential of Organisations Report of Paper prepared by Purpose of Paper Assistant Director of OD Senior LED Manager Leadership
BEAT THE ELITE HOW TO USE CRM TO OUT COMPETE YOUR RIVALS.
 BEAT THE ELITE HOW TO USE CRM TO OUT COMPETE YOUR RIVALS. 1 CONTENTS INTRODUCTION 2 ACHIEVE TARGETED MARKETING 6 CUSTOMER SERVICE AND SATISFACTION 3 EMPOWER STAFF WITH MOBILE CRM 7 DON T RELY ON SPREAD
BEAT THE ELITE HOW TO USE CRM TO OUT COMPETE YOUR RIVALS. 1 CONTENTS INTRODUCTION 2 ACHIEVE TARGETED MARKETING 6 CUSTOMER SERVICE AND SATISFACTION 3 EMPOWER STAFF WITH MOBILE CRM 7 DON T RELY ON SPREAD
HCPC 2015 Employee Exit Interview Report
 HCPC 2015 Employee Exit Interview Report Section Page 1. Introduction 3 2. Scope 3 3. Employee turnover rates 3 4. Summary of findings 3 5. Analysis of data 4 6. Conclusions and actions 11 2 1. Introduction
HCPC 2015 Employee Exit Interview Report Section Page 1. Introduction 3 2. Scope 3 3. Employee turnover rates 3 4. Summary of findings 3 5. Analysis of data 4 6. Conclusions and actions 11 2 1. Introduction
Human Capital Management: Leveraging Your Human Assets
 Human Capital Management: Leveraging Your Human Assets Executive Summary Managers have always intuitively believed that their employees generate value for the organization but today, intuition is no longer
Human Capital Management: Leveraging Your Human Assets Executive Summary Managers have always intuitively believed that their employees generate value for the organization but today, intuition is no longer
MODULE 10 CHANGE MANAGEMENT AND COMMUNICATION
 MODULE 10 CHANGE MANAGEMENT AND COMMUNICATION PART OF A MODULAR TRAINING RESOURCE Commonwealth of Australia 2015. With the exception of the Commonwealth Coat of Arms and where otherwise noted all material
MODULE 10 CHANGE MANAGEMENT AND COMMUNICATION PART OF A MODULAR TRAINING RESOURCE Commonwealth of Australia 2015. With the exception of the Commonwealth Coat of Arms and where otherwise noted all material
CUPA HR Strengthen Leadership Development and Succession Planning Practices
 CUPA HR Strengthen Leadership Development and Succession Planning Practices April 11, 2013 Prepared by Consulting Performance, Reward & Talent The Higher Ed Leadership Development Challenge Strength Board
CUPA HR Strengthen Leadership Development and Succession Planning Practices April 11, 2013 Prepared by Consulting Performance, Reward & Talent The Higher Ed Leadership Development Challenge Strength Board
Career development planning and the changing workforce. Why the transition between different generations of workers makes it more important than ever
 Career development planning and the changing workforce Why the transition between different generations of workers makes it more important than ever 1 Table of contents Executive summary 3 The skill gap
Career development planning and the changing workforce Why the transition between different generations of workers makes it more important than ever 1 Table of contents Executive summary 3 The skill gap
Requirements for implementing a succession management system
 Requirements for implementing a succession management system David Berke T here s not much information around on how to put effective succession management into practice. Which makes the following step-by-step
Requirements for implementing a succession management system David Berke T here s not much information around on how to put effective succession management into practice. Which makes the following step-by-step
hrpa.ca/ac2016 #HRPA2016 Recruiting in a Competitive Market 1
 hrpa.ca/ac2016 #HRPA2016 Recruiting in a Competitive Market 1 MAURA DYER 15 YEARS Online Senior Director of Talent Acquisition, Rogers Facilitating the recruitment, engagement, and development of top talent
hrpa.ca/ac2016 #HRPA2016 Recruiting in a Competitive Market 1 MAURA DYER 15 YEARS Online Senior Director of Talent Acquisition, Rogers Facilitating the recruitment, engagement, and development of top talent
Leadership Development Best Practices. By Russel Horwitz
 Leadership Development Best Practices By Russel Horwitz 1 December 2014 Contents The case for leadership development 4 Creating a strategy 4 Best practices 5 1. Align to organizational strategy 5 Begin
Leadership Development Best Practices By Russel Horwitz 1 December 2014 Contents The case for leadership development 4 Creating a strategy 4 Best practices 5 1. Align to organizational strategy 5 Begin
Project Management Process
 Project Management Process Description... 1 STAGE/STEP/TASK SUMMARY LIST... 2 Project Initiation 2 Project Control 4 Project Closure 5 Project Initiation... 7 Step 01: Project Kick Off 10 Step 02: Project
Project Management Process Description... 1 STAGE/STEP/TASK SUMMARY LIST... 2 Project Initiation 2 Project Control 4 Project Closure 5 Project Initiation... 7 Step 01: Project Kick Off 10 Step 02: Project
Career Management. Succession Planning. Dr. Oyewole O. Sarumi
 Career Management & Succession Planning Dr. Oyewole O. Sarumi Scope of Discourse Introduction/Background Definitions of Terms: Career, Career Path, Career Planning, Career Management. The Career Development
Career Management & Succession Planning Dr. Oyewole O. Sarumi Scope of Discourse Introduction/Background Definitions of Terms: Career, Career Path, Career Planning, Career Management. The Career Development
