The PreFACE. Roberta J. Honigman, MSW,* Alun C. Jackson, PhD, and Nicki A. Dowling, PhD
|
|
|
- Delilah Anderson
- 8 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 AESTHETIC SURGERY The PreFACE A Preoperative Psychosocial Screen for Elective Facial Cosmetic Surgery and Cosmetic Dentistry Patients Roberta J. Honigman, MSW,* Alun C. Jackson, PhD, and Nicki A. Dowling, PhD Background: Currently no brief and objective screening protocol exists to assist surgeons and dentists in the identification of patients who are likely to report unsatisfactory outcomes after cosmetic surgery interventions. The aims of this study were to (1) investigate the relationship between postoperative dissatisfaction and preoperative characteristics (psychiatric disturbance, anxiety, depression, self-esteem, dysmorphic concern, and body image), and (2) empirically derive a preoperative psychosocial screening instrument to identify patients who may require preoperative assessment or counseling. Methods: The sample composed of 84 patients (69 women and 15 men) undergoing elective cosmetic facial surgery or cosmetic dentistry. Before surgery, a self-report questionnaire was administered to the patients, which comprised questions designed to evaluate many of the psychosocial characteristics thought to be associated with unsatisfactory outcomes. Six months after surgery, a questionnaire was administered to the patients, which included items evaluating postoperative satisfaction. Results: The findings revealed that preoperative psychiatric disturbance, anxiety, depression, low appearance evaluation, and body areas dissatisfaction are psychosocial risk factors that indicate an increased likelihood of patient dissatisfaction with surgical outcomes. The PreFACE (Pre-operative FAcial Cosmetic surgery Evaluation), a brief objective preoperative screening questionnaire that can be easily and efficiently administered to elective facial cosmetic surgery and cosmetic dentistry patients, was empirically derived. It is able to identify most patients who are likely to express dissatisfaction and minimizes the selection of those who will express satisfaction. The PreFACE is recommended for validation using other cosmetic surgery populations. Conclusions: The routine use of PreFACE is recommended for identification of patients who may benefit from preoperative counseling. Key Words: plastic surgery, cosmetic surgery, screening, assessment (Ann Plast Surg 2010;65: ) Although most individuals who seek cosmetic surgical and dental procedures appear psychologically healthy, some patients will experience a poor subjective outcome despite a technically good result. The literature has consistently revealed that 10% to 20% of patients undergoing cosmetic interventions report postoperative dissatisfaction. 1,2 Poor perceived patient outcomes can create problems for both practitioner and patient because they can result in depression, anxiety, Received October 7, 2009, and accepted for publication, after revision, January 19, From the *St. Vincent s Hospital Mental Health Service; Melbourne Graduate School of Education, The University of Melbourne, Australia; and Centre on Behavioural Health, University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong. Supported by the HCF Health and Medical Research Foundation, Australia. Reprints: Alun C. Jackson, PhD, Melbourne Graduate School of Education, University of Melbourne, Parkville, Victoria, 3010, Australia. aluncj@unimelb.edu.au. Copyright 2010 by Lippincott Williams & Wilkins ISSN: /10/ DOI: /SAP.0b013e3181d50e54 social isolation, self-injurious behaviors, including suicide, workplace absenteeism, familial dysfunction, poor general health, demands for further surgery, increased litigation, complaints to Health Regulatory bodies, and even violence towards the treating physician. 3 7 Selecting appropriate patients for cosmetic surgery can not only decrease the proportion of patients who are dissatisfied with the surgical outcome, but can also reduce patient management difficulties. 7,8 Surgeons and dentists performing cosmetic procedures can improve the quality of care for patients and enhance the perception of the ultimate outcome of surgery by evaluating psychosocial risk factors 9 12 and referring the small proportion of patients with risk factors for more extensive preoperative psychologic assessment and intervention. 12 Despite its apparent importance, there is little data available to assist practitioners in the selection of inappropriate patients for surgery. Preoperative characteristics of patients who are dissatisfied with the result of cosmetic interventions are generally derived from clinical experience and almost no methodologically robust empirical research has been conducted. An exception was Napoleon s study 13 of the impact of personality disorders in elective cosmetic surgery patients, which found that personality type was significantly related to satisfaction, with borderline and narcissistic personality types being less likely to report being satisfied with the surgical outcome. Despite the paucity of empirical investigation, it is generally agreed that factors associated with unsatisfactory outcomes include male sex, young age, preoperative depression and anxiety, body dysmorphic disorder or concern, dissatisfaction with previous surgeries, low self-esteem and body image, and unrealistic patient expectations of the outcome. 2,6,7,9,12 21 In an attempt to provide a framework for evaluation, Lavell and Lewis 8 derived the SAFE guide from their analysis of 55 patients undergoing facial regenerative surgical procedures. They suggested that 4 patient characteristics need to be considered in determining suitability of candidates for surgery: Self evaluation of attractiveness (positive self-image), Anxiety (conscious awareness of generalized distress), Fear (excessive involvement in detailed preparation for surgery), and Expectation (unrealistic anticipation of postsurgical life changes). Honigman et al 6 reviewed the factors identified in the literature that may indicate a need for preoperative counseling for elective cosmetic surgery patients. The literature is also not particularly useful in guiding the practitioner in how to identify patients who will report poor outcomes. Current techniques for preoperatively evaluating patient characteristics include observation of the patient and conducting a patient interview, inclusive of personality assessment by an attending psychologist. 6 8,13,14,12,22 For example, Lavell and Lewis 8 suggested that assessment of the SAFE patient characteristics can be accomplished by patient observation and the use of open-ended questioning techniques. Others have identified several reliable and valid patient self-administered questionnaires, such as the Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale (HADS), which can be used to screen for each psychosocial risk factor. 6,9,12,19,22 Anderson and Johnson 23 have devised the only presurgical screening questionnaire for cosmetic surgery patients. This questionnaire (rather than screen ) comprises 161 nonempirically derived items evaluating surgical history and motiva- Annals of Plastic Surgery Volume 65, Number 12, December
2 Honigman et al Annals of Plastic Surgery Volume 65, Number 12, December 2010 tion, medication and general medical history, and psychologic states. Although these can facilitate a comprehensive evaluation, a common obstacle to conducting a preoperative assessment is limited time. 8,12 Currently, there exists no brief and objective screening protocol to help identify patients who are contraindicated for surgery or who require more detailed preoperative psychosocial assessment or more intensive pre and postoperative psychologic support. It is important to note this distinction between a screen and an assessment. A screening protocol should be short, able to be administered by a nonspecialist in psychosocial assessment, and should serve to raise red flags, which may then be explored in a more thorough psychosocial assessment. Such screening should not replace clinical judgment, but is a time-efficient aid to such judgment. Study Aims This study aimed to investigate the preoperative characteristics of patients who were dissatisfied with the result of elective cosmetic facial surgery and cosmetic dentistry. Specifically, it was hypothesized that postoperative dissatisfaction would be associated with higher levels of preoperative psychiatric disturbance, anxiety, depression, low selfesteem, dysmorphic concern, and low body image. This study also aimed to empirically derive a presurgery screening instrument to identify elective cosmetic facial surgery and cosmetic dentistry patients who may require preoperative counseling. METHODS Participants Facial surgery and cosmetic dentistry were selected as the focus for the study because the face tends to attract more attention than any other feature and because physical appeal is determined largely by the face. 24,25 Patients undergoing elective facial cosmetic surgery or cosmetic dentistry were administered a questionnaire before surgery and at 6 months after surgery. Overall, 84 (43%) of 194 patients completing the preoperative survey also completed the postoperative survey. These 84 patients (69 women and 15 men) aged between 19 and 71 years (M 42.4, SD 12.2). The patients who completed the postoperative questionnaire were compared on preoperative demographic information and psychologic functioning measures using a series of independent sample t tests and 2 analyses. No significant differences between those who did or did not complete the preoperative questionnaire on any demographic characteristic or type of surgical procedure were found. The type of procedure undertaken by these patients is reported in Table 1. TABLE 1. Procedures Undertaken by the Cosmetic Surgery and Cosmetic Dentistry Sample Procedure Classification n % Rhinoplasty only Cosmetic dentistry Facial surgery only (eg, facelift, cheek and chin implants) Facial surgery and blepharoplasty Blepharoplasty only Facial surgery and rhinoplasty Rhinoplasty and blepharoplasty Otoplasty Facial surgery, blepharoplasty, and rhinoplasty Measures The self-report preoperative questionnaire comprised several well-validated standardized measures of psychosocial dysfunction to evaluate many of the psychosocial characteristics thought to be associated with dissatisfactory outcomes after cosmetic surgery (Table 2). These measures have been extensively used in research and clinical practice, and there is substantial evidence to support their psychometric properties. They have also been used in a number of studies evaluating psychologic factors in cosmetic surgery (eg, Refs. 18, 26 29). Cronbach s, or the scale reliability coefficient for the measures is provided in the right-hand column. Several other questions evaluating other psychosocial characteristics thought to be associated with poor outcomes were included in the preoperative questionnaire to develop the screening instrument (Fig. 1). The postoperative survey included 4 different items evaluating postoperative satisfaction, linked to preoperative expectations (Fig. 2). Procedure The study was approved by the University of Melbourne Health Sciences Human Ethics Sub-Committee (project ). Recruitment of participants was undertaken initially by approaching surgeons who specialized in elective facial cosmetic procedures and dentists (including general dentists, specialist prosthodontists, and prosthetists) who provide elective cosmetic dental procedures in Melbourne and Sydney, Australia. Cosmetic dental procedures included procedures intended to modify or improve appearance rather than function and included noninvasive procedures, such as bleaching, veneers, restoration of crowns, and bridge work. Chair-based procedures only were included. Medicare-rebateable orthognathic procedures performed in hospital and orthodontic procedures were excluded. Preoperative questionnaires were distributed to a sample of prospective patients aged 18 years and over, presenting with requests for elective facial cosmetic surgery or dentistry to a variety of practitioners operating in Victoria and New South Wales, Australia (30 sites). These were supplied to patients on booking in for surgery or dental procedures and were returned in a self-addressed envelope to the investigators after completion. Postoperative questionnaires were completed 6 months after completion of the surgical or dental procedure. Consistent with ethical approval, participants were provided with plain language statements and return of the questionnaire was taken to imply consent. RESULTS Association Between Preoperative Psychosocial Dysfunction and Postoperative Dissatisfaction There was some variation in the response of patients on the different measures of postoperative dissatisfaction. Overall, 24.1% of patients reported worse than expected outcomes on item 1, 25.3% scored 1 to 6 on item 2, 16.9% reported dissatisfaction with the outcome of surgery on item 3, and 12.0% reported worse than expected experience of surgery and recovery on item 4. Because of this variability, the association between the preoperative scores on the standardized psychosocial measures and postoperative dissatisfaction was evaluated for all 4 items. Each variable was checked for violations of the assumption of normal distribution. Variables that were normally distributed were analyzed using parametric statistical tests (independent samples t tests), whereas variables that violated the assumption of normality were analyzed using nonparametric statistical tests (Mann-Whitney U tests, Spearman bivariate correlations). Bonferroni adjustments were used to control for multiple comparisons. Trends were also reported at the significance level of 0.05 and effect sizes were reported Lippincott Williams & Wilkins
3 Annals of Plastic Surgery Volume 65, Number 12, December 2010 PreFACE: A Preoperative Psychosocial Screen TABLE 2. Standardized Measures of Psychosocial Dysfunction Used in the Study Name Description Item Response Scale for This Study General Health Questionnaire-30 (GHQ-30: 32, 33) Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale (HADS: 34) Rosenberg Self-Esteem Scale (RSE: 35) Dysmorphic Concerns Questionnaire (DCQ: 36, 37) Multidimensional Body-Self Relations Questionnaire (MBSRQ: 38) 30-item self-report measure of psychiatric disturbance often used in general practice and other communitybased clinical settings 4-point response scale (from 0 to 3) 0.91 Measure of generalized anxiety and depression. 4-point response scale (from 0 to 3) Subscales: Anxiety (7 items) 0.87 Depression (7 items) item measure of global self-esteem 4-point response scale (from 0 to 3) item measure of the extent of concern with physical appearance 4-point response scale (from 0 to 3) 0.85 Measure of body image 5-point response scale (from 1 to 5) Subscales used in the current study: Appearance evaluation: feelings of physical attractiveness 0.87 and satisfaction with one s looks (7 items) Appearance orientation: extent of investment in one s 0.84 appearance (12 items) Body areas satisfaction: satisfaction with discrete aspects 0.79 of one s appearance (9 items) FIGURE 1. Other variables included in preoperative questionnaire to derive screening instrument. Item 1 A series of independent t tests and Mann-Whitney analyses with Bonferroni adjustments for multiple comparisons (P 0.006) revealed that none of the variables were significantly related to item 1 dissatisfaction (Table 3). There were, however, trends (P 0.05) for the patients reporting worse than expected outcomes to report higher General Health Questionnaire (GHQ)-30, HADS anxiety, and HADS depression scores, and lower Multidimensional Body-Self Relations Questionnaire (MBSRQ) Appearance Evaluation scores before surgery. These variables display small to moderate effect sizes Lippincott Williams & Wilkins 3
4 Honigman et al Annals of Plastic Surgery Volume 65, Number 12, December 2010 FIGURE 2. Four items evaluating postoperative dissatisfaction. TABLE 3. Comparison of Preoperative Psychologic Variables for Satisfaction and Dissatisfaction on Item 4 Variable Better Than or as Expected (n 73) Worse Than Expected (n 10) M SD M SD Mean Difference (95% CI) Statistic P Effect Size ( 2 p ) GHQ (1.2 to 12.5) t(81) * HADS anxiety ( 0.4 to 5.0) t(81) HADS depression (0.1 to 3.5) U RSE ( 1.6 to 4.7) t(79) DCQ ( 0.3 to 5.0) t(81) MBSRQ appearance evaluation (0.0 to 0.9) U * MBSRQ appearance orientation ( 0.3 to 0.5) t(77) Body areas satisfaction (0.2 to 1.0) t(80) *P P Item 2 A series of Spearman bivariate correlations revealed significant weak positive correlations between item 2 dissatisfaction analyzed as a continuous variable and GHQ-30 scores, r (N 83) 0.23, P 0.04 and HADS anxiety scores, r (N 83) 0.38, P 0.001, and significant weak negative correlations between item 2 dissatisfaction and MBSRQ Appearance Evaluation scores, r (N 81) 0.25, P 0.02, and MBSRQ Body Areas Satisfaction scores, r (N 82) 0.26, P They also revealed a significant moderate correlation between item 2 dissatisfaction and HADS depression scores, r (N 82) 0.43, P There were no significant correlations between item 2 dissatisfaction and DCQ scores, r (N 83) 0.16, P 0.15, RSE scores, r (N 81) 0.14, P 0.23, and Appearance Orientation scores, r (N 79) 0.11, P Lippincott Williams & Wilkins
5 Annals of Plastic Surgery Volume 65, Number 12, December 2010 PreFACE: A Preoperative Psychosocial Screen Item 3 A series of independent t tests and Mann-Whitney analyses with Bonferroni adjustments for multiple comparisons (P 0.006) revealed that none of the variables were significantly related to item 3 dissatisfaction. Item 4 A series of independent t tests and Mann-Whitney analyses with Bonferroni adjustments for multiple comparisons (P 0.006) revealed that patients reporting that their experience of surgery and recovery was worse than expected reported lower MBSRQ Body Areas Satisfaction scores than patients reporting better than or as expected experiences (Table 3). None of the remaining variables were significantly related to item 4 postoperative dissatisfaction. There were, however, trends (P 0.05) for patients reporting worse than expected experiences to report higher GHQ-30 and lower MBSRQ Appearance Evaluation scores before surgery. These variables display small to moderate effect sizes. 30 Development of the PreFACE The screening tool was developed using item 1 of postoperative dissatisfaction ( Compared with your expectations, what was the overall result of the surgery? ) because it was one of the most inclusive measures of dissatisfaction and evaluated outcome satisfaction within the context of patient expectations. The screening was then validated using the remaining items of postoperative dissatisfaction. The screening instrument was named the PreFACE: Preoperative FAcial Cosmetic surgery Evaluation. Selection of PreFACE Items The patients reporting better than or as expected and worse than expected results on item 1 were compared on each item in the preoperative questionnaire (including the items of the standardized measures). Each item was checked for violations of the assumption of normal distribution and the appropriate statistical analyses (independent samples t tests, Mann-Whitney U tests, and 2 analyses) were used. Table 4 displays the 9 items displaying statistical significance (P 0.01) that were selected for inclusion in the screening tool. Entering these variables into a binary logistic regression revealed that they significantly predicted group membership on item 1 postoperative dissatisfaction, 2 (23, N 73) 65.62, P The model was able to correctly classify 92% of those who reported worse than expected outcomes and 100% of those who reported better than or as expected outcomes, for an overall success rate of 99%. The 9 items were then validated on the remaining items of postoperative dissatisfaction. A multiple linear regression revealed that the 9 items significantly predicted scores on the item 2 (scores of 1 to 10), adjusted R , F(9,63) 3.98, P 0.001, and a series of binary logistic regressions revealed that they also significantly predicted group membership on item 2 (scores of 1 6 and scores of 7 10), 2 (23, N 73) 54.84, P 0.001, item 3, 2 (23, N 73) 35.13, P 0.05, and item 4, 2 (23, N 73) 41.48, P Deriving PreFACE Scores The original scoring procedures for some of the 9 items were transformed so that higher scores represented higher levels of the construct being measured. Minor changes were made to the wording of some questions to make them uniform across the screening instrument. The items of the PreFACE are displayed in the Appendix (Supplementary Digital Content; available at ). Scores for the PreFACE were derived from adding the scores of the items listed in the Appendix. These scores were significantly higher for those patients reporting worse than expected results on item 1 than those reporting better than or as expected results. PreFACE scores were validated on the remaining items of postoperative dissatisfaction. Independent samples t tests revealed that scores were significantly higher for patients who reported dissatisfaction on the remaining items of postoperative dissatisfaction (Table 5). The scores were also highly correlated with scores on item 2, Spearman r (N 73) 0.36, P Deriving the PreFACE Cut-off Score An attempt was made to derive an appropriate cut-off score on the PreFACE to identify those patients who may benefit from preoperative counseling. The score distributions for patients reporting better than or as expected and worse than expected outcomes on dissatisfaction item 1 were examined. The cut-off score of 11 was selected because it maximized the identification of patients reporting worse than expected results (85%) and minimized the selection of patients reporting better than or as expected results (22%) (Table 6). Examination of Table 6 reveals that the cut-off score also maximized the identification of patients reporting dissatisfaction (70% 83%) and minimized the selection of patients reporting satisfaction (25% 28%) on the remaining items of postoperative dissatisfaction. Scoring of the PreFACE Scores on the PreFACE can range from 0 to 28. Higher scores indicate a higher potential for postoperative dissatisfaction. Preoperative counseling is recommended for facial cosmetic surgery or cosmetic dentistry patients scoring 11 or more on the PreFACE. The PreFACE may be used without permission. Please notify the authors of any studies using the PreFACE by ing prefacescreen@bigpond.com. TABLE 4. Items Selected for Inclusion in the PreFACE No. Measure Item No. Question Statistic P Effect Size ( 2 p ) 1 GHQ-30 1 General health t(81) GHQ Feeling constantly under strain t(81) GHQ Finding everything getting on top of oneself t(81) GHQ Losing confidence in oneself t(81) HADS-Depression 2 Lack of anhedonia U 385.0, z DCQ 6 Worrying about appearance defect t(81) MBSRQ Appearance Orientation 7 Time spent getting ready t(81) MBSRQ Body Areas Satisfaction 26 Face (facial features, complexion) satisfaction t(40.20) Dissatisfaction with previous cosmetic surgical procedures 2 (1, N 77) Lippincott Williams & Wilkins 5
6 Honigman et al Annals of Plastic Surgery Volume 65, Number 12, December 2010 TABLE 5. Comparison of PreFACE Scores for Patients Reporting Satisfaction and Dissatisfaction on the Postoperative Dissatisfaction Items Satisfied Dissatisfied M SD M SD Mean Difference (95% CI) Statistic P Effect Size ( 2 p ) Item ( ) t (71) Item ( ) t (71) Item ( ) t (71) Item ( ) t (71) TABLE 6. Proportion of Patients Reporting Dissatisfaction and Satisfaction on the Postoperative Dissatisfaction Items Identified Using the PreFACE Cut-off Score Dissatisfied (%) Satisfied (%) Item Item Item Item DISCUSSION The first aim of this study was to determine the relationship between preoperative psychosocial dysfunction and postoperative dissatisfaction. The findings revealed that postoperative dissatisfaction was associated with higher levels (significantly or trend) of preoperative psychiatric disturbance and lower levels of appearance evaluation on 3 of the 4 dissatisfaction items. In addition, postoperative dissatisfaction was associated with higher levels (significantly or trend) of preoperative anxiety and depression and lower levels of body areas satisfaction on 2 of the 4 dissatisfaction items. The effect size and correlation coefficients, which revealed small to moderate relationships, 30 suggest that the use of larger samples with larger numbers of individuals reporting dissatisfaction would increase the likelihood of identifying statistically significant relationships between these psychosocial characteristics and postoperative dissatisfaction. The finding that postoperative dissatisfaction is associated with higher levels of preoperative psychiatric disturbance, anxiety, and depression is consistent with recommendations from previous clinically oriented literature that these indicators of psychologic dysfunction are important when considering preoperative counseling. 2,8,12,13,20,23 Interestingly, although lower levels of appearance evaluation and body areas satisfaction were associated with postoperative dissatisfaction, dysmorphic concerns, self-esteem, and appearance orientation were not. Taken together, these findings suggest that worse postoperative outcomes are associated with a general unhappiness with physical appearance and unhappiness with the size or appearance of several body areas, rather than the extent of concern with physical appearance, global self-esteem, or the extent of investment in appearance. These findings contrast with the more specifically body area-focused facial cosmetic surgery patients identified as poor candidates for surgery in previous literature. 31,32 It is evident that further empirical investigation is required to investigate the relationship between these appearance-related characteristics and unsatisfactory outcomes for facial cosmetic surgery. We note that there is no objective measure of surgical outcome against which to rate the patient s perceived unsatisfactory outcome, but suggest that the point of a measure such as this is to identify precisely this population, that is, patients who are likely to be dissatisfied with the outcome, even if they have objectively achieved the most realistically attainable outcome possible. This study also aimed to empirically derive a preoperative screening for elective facial cosmetic surgery and cosmetic dentistry patients, rather than relying solely on anecdotal or nonsystematic evidence for determining such items of concern. This screen, named the PreFACE, was validated on 4 separate measures of postoperative dissatisfaction. The PreFACE is able to identify most patients who are likely to express dissatisfaction with the cosmetic procedure and minimizes the selection of those who will express satisfaction. It is a brief objective self-report screening questionnaire that can be easily and efficiently administered to patients. Practitioners can improve the quality of care provided to patients through the routine use of the PreFACE and by referring the small proportion of patients scoring 11 or more to preoperative counseling. They should explain that referral for preoperative counseling is recommended because it may increase the likelihood of increased patient satisfaction after the intervention. 12 It is not, per se, a device for excluding people from consideration as cosmetic surgery patients. When considering the practical implications of the findings, it is important to note several methodologic limitations. First, a more robust analysis would result from a larger sample of patients expressing postoperative dissatisfaction, although the study incorporated one of the largest samples (194) obtained in this type of study. Second, this study specifically examined elective facial cosmetic surgery and cosmetic dentistry patients, and the characteristics associated with postoperative dissatisfaction may, therefore, not be generalizable to other cosmetic surgery populations. Third, for reasons of practicality, not all possible precursor factors for dissatisfaction were included in the developmental study. Other areas such as preexisting anger and neuroticism may be included in further studies to build on the items contained in the PreFACE. Finally, as a screening tool, the PreFACE does not attempt to measure the existence or extent of other elements that may influence satisfaction, such as the quality of the physician-patient relationship. We recommend that the PreFACE, having now been developed, be validated using other larger samples, if possible, of elective cosmetic facial surgery patients. Although the PreFACE was developed for use with elective facial cosmetic surgery and cosmetic dentistry patients, attempting to use a screening procedure with other cosmetic surgery populations may also be important, given suggestions that the nature and degree of surgical change are likely to be important predictors of outcome. 33 In adapting the PreFACE for different cosmetic surgery populations, some items, such as item 8, may require modification. For breast augmentation or reduction procedures, it would be appropriate to replace item 8 with question 30 of the MBSRQ (ie, How dissatisfied or satisfied are you with your upper torso chest or breasts, shoulders, arms? ). Similarly, for liposuction and abdominoplasty procedures, it would be appropriate to replace item 8 with question 28 of the MBSRQ (ie, How dissatisfied or satisfied are you with your lower torso buttocks, hips, thighs, legs? ) or question 29 of the MBSRQ (ie, How dissatisfied Lippincott Williams & Wilkins
7 Annals of Plastic Surgery Volume 65, Number 12, December 2010 PreFACE: A Preoperative Psychosocial Screen or satisfied are you with your mid torso waist, stomach? ). To maintain scoring consistency, however, we recommend maintaining the same rating scale. It is also important for future empirical research in this area to note that there are multiple ways to measure dissatisfaction, all of which produce slightly different cohorts that are more and less inclusive. REFERENCES 1. Glatt BS, Sarwer DB, O Hara DE, et al. A retrospective study of changes in physical symptoms and body image after reduction mammoplasty. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1999;103: Castle DJ, Honigman RJ, Phillips KA. Does cosmetic surgery improve psychosocial wellbeing? Med J Aust. 2002;176: Olbourne N. Cosmetic surgery: NSW award of exemplary damages. Australian Health Law Bulletin. 1999;7: Cotterill JA. Body dysmorphic disorder. Dermatol Clin. 1996;14: Phillips KA, McElroy SL, Lion JR. Body dysmorphic disorder in cosmetic surgery patients letter. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1992;90: Honigman RJ, Phillips KA, Castle DJ. A review of psychosocial outcomes for patients seeking cosmetic surgery. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2004;113: Blackburn VF, Blackburn AV. Taking a history in aesthetic surgery: SAGA the surgeon s tool for patient selection. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2008;61: Lavell S, Lewis CM. SAFE: a practical guide to psychological factors in selecting patients for facial cosmetic surgery. Ann Plast Surg. 1984;12: Dowrick C. Advances in psychiatric treatment in primary care. Adv Psych Treat. 2001;7: Pruzinsky T. Psychological factors in cosmetic plastic surgery: recent developments in patient care. Plast Surg Nurs. 1993;13: Spencer KW. Selection and pre-operative preparation of plastic surgery patient. Nurs Clin North Am. 1994;29: Turner JA, Dworkin SF. Screening for psychosocial risk factors in patients with chronic orofacial pain: recent advances. J Am Dent Assoc. 2004;135: Napoleon A. The presentation of personalities in plastic surgery. Ann Plast Surg. 1993;31: Sonmez A, Biskin N, Bayramicli M, et al. Comparison of preoperative anxiety in reconstructive and cosmetic surgery patients. Ann Plast Surg. 2005;54: de Jongh A, Adair P. Mental disorders in dental practice: a case report of body dysmorphic disorder. Special Care Dentistry. 2004;22: Phillips KA, Grant J, Siniscalchi J, et al. Surgical and non-psychiatric medical treatment of patients with Body Dysmorphic Disorder. Psychosomatics. 2001;42: Veale D, De Haro L, Lambrou C. Rhinoplasty in body dysmorphic disorder. Br J Plast Surg. 2003;56: Castle DJ, Molton M, Hoffman K, et al. Correlates of dysmorphic concern in people seeking cosmetic enhancement. AustNZJPsychiatry. 2004;38: Juggins KJ, Feinmann C, Shute J, et al. Psychological support for orthognathic patients: what do orthodontists want? J Orthod. 2006;33: Sclafani AP, Choe KS. Psychological aspects of plastic surgery. emedicine. Accessed on July 11, 2010 from overview. 21. Beale S, Hambert G, Lisper H, et al. Augmentation mammaplasty: the surgical and psychological effects of the operation and prediction of the result. Ann Plast Surg. 1985;14: Silverman S, Silverman SI, Silverman B, et al. Self-image and its relation to denture acceptance. J Prosthet Dent. 1976;35: Anderson JR, Johnson CM. A self-administered history questionnaire for cosmetic facial surgery candidates. Arch Otolaryngol. 1978;104: Eriksen HM, Dimitrov V. Ecology of oral health: a complexity perspective. Eur J Oral Sci. 2003;111: Samarodnitzky-Neveh GR, Geiger SB, Levin L. Patients satisfaction with dental esthetics. J Am Dent Assoc. 2007;138: Cunningham SJ, Feinmann C. Psychological assessment of patients requesting orthognathic surgery and the relevance of body dysmorphic disorder. Br J Orthod. 1998;25: Figueroa-Haas CL. Effect of breast augmentation mammoplasty on self-esteem and sexuality: a quantitative analysis. Plast Surg Nurs. 2007;27: Kisely S, Morkell D, Allbrok B, et al. Factors associated with dysmorphic concern and psychiatric morbidity in plastic surgery outpatients. Aust N Z J Psychiatry. 2002;36: von Soest T, Kvalem IL, Skolleborg KC, et al. Psychosocial factors predicting the motivation to undergo cosmetic surgery. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2006;117: Cohen J. Statistical Power Analysis for the Behavioral Sciences. 2nd ed. Hillside, NJ: Lawrence Earlbaum; Grossbart TA, Sarwer DB. Psychosocial issues and their relevance to the cosmetic surgery patient. Semin Cutan Med Surg. 2003;22: Sarwer DB, Crerand CE. Body image and cosmetic medical treatments. Body Image. 2004;1: Sarwer DB, Wadden TA, Pertschuk MJ, et al. The psychology of cosmetic surgery: a review and reconceptualisation. Clin Psychol Rev. 1998;18: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins 7
A Survey Study on Professional Women s Perception toward Cosmetic Surgery: 4 Year Comparison
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE http://dx.doi.org/10.14730/.2015.21.2.70 Arch Aesthetic Plast Surg 2015;21(2):70-74 pissn: 2234-0831 eissn: 2288-9337 A Survey Study on Pressional Women s Perception toward Cosmetic Surgery:
ORIGINAL ARTICLE http://dx.doi.org/10.14730/.2015.21.2.70 Arch Aesthetic Plast Surg 2015;21(2):70-74 pissn: 2234-0831 eissn: 2288-9337 A Survey Study on Pressional Women s Perception toward Cosmetic Surgery:
Psychopathology symptoms in a sample of female cosmetic surgery patients
 Journal of Plastic, Reconstructive & Aesthetic Surgery (2012) 65, 321e327 Psychopathology symptoms in a sample of female cosmetic surgery patients Sandra Mulkens a, *, Arjan E.R. Bos a, Richard Uleman
Journal of Plastic, Reconstructive & Aesthetic Surgery (2012) 65, 321e327 Psychopathology symptoms in a sample of female cosmetic surgery patients Sandra Mulkens a, *, Arjan E.R. Bos a, Richard Uleman
Plastic Surgery - Exceptional Referrals Patient Pathway April 2005
 Patient Presentation Patient seeks exceptional procedure Clinical assessment: Psychology criteria (see Appendix 1) Exceptional physical criteria (see Appendix 2) Patient meets criteria Patient does not
Patient Presentation Patient seeks exceptional procedure Clinical assessment: Psychology criteria (see Appendix 1) Exceptional physical criteria (see Appendix 2) Patient meets criteria Patient does not
Motivations, preoperative, and postoperative wellbeing associated with cosmetic surgery
 The University of Toledo The University of Toledo Digital Repository Master s and Doctoral Projects 2008 Motivations, preoperative, and postoperative wellbeing associated with cosmetic surgery Jennifer
The University of Toledo The University of Toledo Digital Repository Master s and Doctoral Projects 2008 Motivations, preoperative, and postoperative wellbeing associated with cosmetic surgery Jennifer
Cognitive Investigation Study of Patients Admitted for Cosmetic Surgery: Information, Expectations, and Consent for Treatment
 Cognitive Investigation Study of Patients Admitted for Cosmetic Surgery: Information, Expectations, and Consent for Treatment Original Article Mauro Barone 1, Annalisa Cogliandro 1, Giuseppe La Monaca
Cognitive Investigation Study of Patients Admitted for Cosmetic Surgery: Information, Expectations, and Consent for Treatment Original Article Mauro Barone 1, Annalisa Cogliandro 1, Giuseppe La Monaca
The popularity of plastic surgery as a socially COSMETIC. Interest in Cosmetic Surgery and Body Image: Views of Men and Women across the Lifespan
 COSMETIC Interest in Cosmetic Surgery and Body Image: Views of Men and Women across the Lifespan David A. Frederick, M.A. Janet Lever, Ph.D. Letitia Anne Peplau, Ph.D. Los Angeles, Calif. Background: Little
COSMETIC Interest in Cosmetic Surgery and Body Image: Views of Men and Women across the Lifespan David A. Frederick, M.A. Janet Lever, Ph.D. Letitia Anne Peplau, Ph.D. Los Angeles, Calif. Background: Little
It has been recommended that the assessment of. COSMETIC Outcomes Article
 COSMETIC Outcomes Article Psychosocial Characteristics of Young Norwegian Women Interested in Liposuction, Breast Augmentation, Rhinoplasty, and Abdominoplasty: A Population-Based Study Iiná Márjá Javo
COSMETIC Outcomes Article Psychosocial Characteristics of Young Norwegian Women Interested in Liposuction, Breast Augmentation, Rhinoplasty, and Abdominoplasty: A Population-Based Study Iiná Márjá Javo
How To Improve Your Looks with Plastic Surgery
 How To Improve Your Looks with Plastic Surgery By Daniel Becker Plastic surgery is a special type of surgery that involves both a person's appearance and his or her ability to function. Plastic surgeons
How To Improve Your Looks with Plastic Surgery By Daniel Becker Plastic surgery is a special type of surgery that involves both a person's appearance and his or her ability to function. Plastic surgeons
Breast Augmentation Amsterdam Plastic Surgery Breast Augmentation Overview
 Breast Augmentation Amsterdam Plastic Surgery Breast Augmentation Overview The long-lasting results of breast augmentation are not limited to just physical changes as data documents that many patients
Breast Augmentation Amsterdam Plastic Surgery Breast Augmentation Overview The long-lasting results of breast augmentation are not limited to just physical changes as data documents that many patients
Treatment Satisfaction among patients attending a private dental school in Vadodara, India
 J. Int Oral Health 2010 Case Report All right reserved Treatment Satisfaction among patients attending a private dental school in Vadodara, India Thanveer K* Ajith Krishnan** Sudheer Hongal*** *M.D.S,
J. Int Oral Health 2010 Case Report All right reserved Treatment Satisfaction among patients attending a private dental school in Vadodara, India Thanveer K* Ajith Krishnan** Sudheer Hongal*** *M.D.S,
What factors determine poor functional outcome following Total Knee Replacement (TKR)?
 Specific Question: What factors determine poor functional outcome following Total Knee Replacement ()? Clinical bottom line All groups derived benefit from undergoing a, reviews suggests that the decision
Specific Question: What factors determine poor functional outcome following Total Knee Replacement ()? Clinical bottom line All groups derived benefit from undergoing a, reviews suggests that the decision
indicates that the relationship between psychosocial distress and disability in patients with CLBP is not uniform.
 Chronic low back pain (CLBP) is one of the most prevalent health problems in western societies. The prognosis of CLBP is poor, as indicated by very low rate of resolution, even with treatment. In CLBP,
Chronic low back pain (CLBP) is one of the most prevalent health problems in western societies. The prognosis of CLBP is poor, as indicated by very low rate of resolution, even with treatment. In CLBP,
Executive Summary. 1. What is the temporal relationship between problem gambling and other co-occurring disorders?
 Executive Summary The issue of ascertaining the temporal relationship between problem gambling and cooccurring disorders is an important one. By understanding the connection between problem gambling and
Executive Summary The issue of ascertaining the temporal relationship between problem gambling and cooccurring disorders is an important one. By understanding the connection between problem gambling and
Suicidal. Caring For The Person Who Is. Why might a person be suicidal?
 Caring For The Person Who Is Suicidal For further information see also the following MIND Essentials resource Conducting a suicide risk assessment. Suicidal thoughts and behaviours are not unique to mental
Caring For The Person Who Is Suicidal For further information see also the following MIND Essentials resource Conducting a suicide risk assessment. Suicidal thoughts and behaviours are not unique to mental
info@asurgerycommitment.com
 info@asurgerycommitment.com 1 What is it? Remedial cover from the 29th day up to 24 months post surgery. Who is the insured person? You the surgeon are the insured person. How do I apply? You may apply
info@asurgerycommitment.com 1 What is it? Remedial cover from the 29th day up to 24 months post surgery. Who is the insured person? You the surgeon are the insured person. How do I apply? You may apply
How Labia Minora Appearance and Reduction Influences the Female Perceptions
 Special Topic INTERNATIONAL CONTRIBUTION Female Attitudes Regarding Labia Minora Appearance and Reduction With Consideration of Media Influence Merel Koning, MD; Ingeborg A. Zeijlmans, PhD; Theo K. Bouman,
Special Topic INTERNATIONAL CONTRIBUTION Female Attitudes Regarding Labia Minora Appearance and Reduction With Consideration of Media Influence Merel Koning, MD; Ingeborg A. Zeijlmans, PhD; Theo K. Bouman,
ProFiles PUTTING ASSESSMENTS TO WORK. Psychologists Offer Important Support to the Bariatric Treatment Team QOLI TEST. Patient Selection and Education
 ProFiles PUTTING ASSESSMENTS TO WORK QOLI TEST Psychologists Offer Important Support to the Bariatric Treatment Team Some bariatric surgeons require a preoperative psychological evaluation of all surgery
ProFiles PUTTING ASSESSMENTS TO WORK QOLI TEST Psychologists Offer Important Support to the Bariatric Treatment Team Some bariatric surgeons require a preoperative psychological evaluation of all surgery
Correlates of Referral Practices of General Surgeons to Plastic Surgeons for Mastectomy Reconstruction
 1715 Correlates of Referral Practices of General Surgeons to Plastic Surgeons for Mastectomy Reconstruction Amy K. Alderman, MD, MPH 1,2 Sarah T. Hawley, PhD 2,3 Jennifer Waljee, MD 4 Monica Morrow, MD
1715 Correlates of Referral Practices of General Surgeons to Plastic Surgeons for Mastectomy Reconstruction Amy K. Alderman, MD, MPH 1,2 Sarah T. Hawley, PhD 2,3 Jennifer Waljee, MD 4 Monica Morrow, MD
Motiva Implant Matrix Silicone Breast Implants Summary of Clinical Data 4-Year Follow Up
 Motiva Implant Matrix Silicone Breast Implants Summary of Clinical Data 4-Year Follow Up October 2010 - March 2015 Motiva Implant Matrix Silicone Breast Implants Prospective Clinical Evaluation: 4-Year
Motiva Implant Matrix Silicone Breast Implants Summary of Clinical Data 4-Year Follow Up October 2010 - March 2015 Motiva Implant Matrix Silicone Breast Implants Prospective Clinical Evaluation: 4-Year
PARC Service Evaluation Project Update
 PARC Service Evaluation Project Update Adam Zimmermann & Lisa Thompson October 2012 2 PARCS Evaluation Project Update October 2012 1. STUDY AIMS The Prevention and Recovery Care (PARC) service is a relatively
PARC Service Evaluation Project Update Adam Zimmermann & Lisa Thompson October 2012 2 PARCS Evaluation Project Update October 2012 1. STUDY AIMS The Prevention and Recovery Care (PARC) service is a relatively
HEALTH AND COMMUNITY EMPLOYEES PSYCHOLOGISTS (STATE) AWARD
 IRC No 423 of 2015 Walton P New Award effective 1 July 2015 IRC IIIRCSCC HEALTH AND COMMUNITY EMPLOYEES PSYCHOLOGISTS (STATE) AWARD INDUSTRIAL RELATIONS COMMISSION OF NEW SOUTH WALES Arrangement Clause
IRC No 423 of 2015 Walton P New Award effective 1 July 2015 IRC IIIRCSCC HEALTH AND COMMUNITY EMPLOYEES PSYCHOLOGISTS (STATE) AWARD INDUSTRIAL RELATIONS COMMISSION OF NEW SOUTH WALES Arrangement Clause
1 Risk Factors for Prolonged Disability After Whiplash Injury: A Prospective Study. Spine: Volume 30(4), February 15, 2005, pp 386-391
 1 Risk Factors for Prolonged Disability After Whiplash Injury: A Prospective Study Spine: Volume 30(4), February 15, 2005, pp 386-391 Gun, Richard Townsend MB, BS; Osti, Orso Lorenzo MD, PhD; O'Riordan,
1 Risk Factors for Prolonged Disability After Whiplash Injury: A Prospective Study Spine: Volume 30(4), February 15, 2005, pp 386-391 Gun, Richard Townsend MB, BS; Osti, Orso Lorenzo MD, PhD; O'Riordan,
CLINICAL GOALS OF PATIENT CARE AND CLINIC MANAGEMENT. Philosophical Basis of the Patient Care System. Patient Care Goals
 University of Washington School of Dentistry CLINICAL GOALS OF PATIENT CARE AND CLINIC MANAGEMENT Philosophical Basis of the Patient Care System The overall mission of the patient care system in the School
University of Washington School of Dentistry CLINICAL GOALS OF PATIENT CARE AND CLINIC MANAGEMENT Philosophical Basis of the Patient Care System The overall mission of the patient care system in the School
Patient outcomes of refractive surgery
 articles Patient outcomes of refractive surgery The Refractive Status and Vision Profile Oliver D. Schein, MD, MPH, Susan Vitale, PhD, MHS, Sandra D. Cassard, ScD, Earl P. Steinberg, MD, MPP ABSTRACT Purpose:
articles Patient outcomes of refractive surgery The Refractive Status and Vision Profile Oliver D. Schein, MD, MPH, Susan Vitale, PhD, MHS, Sandra D. Cassard, ScD, Earl P. Steinberg, MD, MPP ABSTRACT Purpose:
COURSE APPROVAL GUIDELINES APS COLLEGE OF SPORT PSYCHOLOGISTS
 COURSE APPROVAL GUIDELINES APS COLLEGE OF SPORT PSYCHOLOGISTS Updated October 2000 Page 2 1. General Introduction and Principles The following principles provide the bases and framework for the development
COURSE APPROVAL GUIDELINES APS COLLEGE OF SPORT PSYCHOLOGISTS Updated October 2000 Page 2 1. General Introduction and Principles The following principles provide the bases and framework for the development
National Mental Health Survey of Doctors and Medical Students Executive summary
 National Mental Health Survey of Doctors and Medical Students Executive summary www.beyondblue.org.au 13 22 4636 October 213 Acknowledgements The National Mental Health Survey of Doctors and Medical Students
National Mental Health Survey of Doctors and Medical Students Executive summary www.beyondblue.org.au 13 22 4636 October 213 Acknowledgements The National Mental Health Survey of Doctors and Medical Students
General practitioners psychosocial resources, distress, and sickness absence: a study comparing the UK and Finland
 Family Practice, 2014, Vol. 31, No. 3, 319 324 doi:10.1093/fampra/cmt086 Advance Access publication 30 January 2014 General practitioners psychosocial resources, distress, and sickness absence: a study
Family Practice, 2014, Vol. 31, No. 3, 319 324 doi:10.1093/fampra/cmt086 Advance Access publication 30 January 2014 General practitioners psychosocial resources, distress, and sickness absence: a study
The Psychologists Board of Western Australia
 The Psychologists Board of Western Australia APPLICANT S PROGRAMME - CLINICAL NEUROPSYCHOLOGY and Knowledge INTRODUCTION Psychologists entering supervision for registration of the specialist title, Clinical
The Psychologists Board of Western Australia APPLICANT S PROGRAMME - CLINICAL NEUROPSYCHOLOGY and Knowledge INTRODUCTION Psychologists entering supervision for registration of the specialist title, Clinical
Quality of Life and Illness Perception in Adult EB Clinic Patients
 Quality of Life and Illness Perception in Adult EB Clinic Patients Diane Beattie, Psychologist in Clinical Training Jacinta Kennedy, Principal Clinical Psychologist Katherine Sweeney, Clinical Nurse Specialist
Quality of Life and Illness Perception in Adult EB Clinic Patients Diane Beattie, Psychologist in Clinical Training Jacinta Kennedy, Principal Clinical Psychologist Katherine Sweeney, Clinical Nurse Specialist
Trends in psychosocial working conditions 2001-2008: Evidence of narrowing inequalities?
 Trends in psychosocial working conditions 2001-2008: Evidence of narrowing inequalities? Anthony LaMontagne, Lauren Krnjacki, Anne Kavanagh & Rebecca Bentley Centre for Women s Health, Gender & Society
Trends in psychosocial working conditions 2001-2008: Evidence of narrowing inequalities? Anthony LaMontagne, Lauren Krnjacki, Anne Kavanagh & Rebecca Bentley Centre for Women s Health, Gender & Society
A one-year survey of dental malpractice claims in Riyadh Wafa Al Ammar*, BDS E. Ernest Guile*, DMD, MPH
 95 A one-year survey of dental malpractice claims in Riyadh Wafa Al Ammar*, BDS E. Ernest Guile*, DMD, MPH Malpractice is an increasing problem related to dental treatment around the world. The present
95 A one-year survey of dental malpractice claims in Riyadh Wafa Al Ammar*, BDS E. Ernest Guile*, DMD, MPH Malpractice is an increasing problem related to dental treatment around the world. The present
UNILATERAL VS. BILATERAL FIRST RAY SURGERY: A PROSPECTIVE STUDY OF 186 CONSECUTIVE CASES COMPLICATIONS, PATIENT SATISFACTION, AND COST TO SOCIETY
 UNILATERAL VS. BILATERAL FIRST RAY SURGERY: A PROSPECTIVE STUDY OF 186 CONSECUTIVE CASES COMPLICATIONS, PATIENT SATISFACTION, AND COST TO SOCIETY Robert Fridman DPM, Jarrett Cain DPM, Lowell Weil Jr. DPM,
UNILATERAL VS. BILATERAL FIRST RAY SURGERY: A PROSPECTIVE STUDY OF 186 CONSECUTIVE CASES COMPLICATIONS, PATIENT SATISFACTION, AND COST TO SOCIETY Robert Fridman DPM, Jarrett Cain DPM, Lowell Weil Jr. DPM,
Faculty of General Dental Practice (UK) Response to HEE Call for Evidence on Non-Surgical Cosmetic Interventions. February 2014
 Faculty of General Dental Practice (UK) Response to HEE Call for Evidence on Non-Surgical Cosmetic Interventions February 2014 About the FGDP(UK) The Faculty of General Dental Practice (UK) is based at
Faculty of General Dental Practice (UK) Response to HEE Call for Evidence on Non-Surgical Cosmetic Interventions February 2014 About the FGDP(UK) The Faculty of General Dental Practice (UK) is based at
A Manual Therapy and Exercise Approach to Breast Cancer Rehabilitation Course
 2014 Annual Breast Cancer Rehabilitation Healthcare Provider Event A Manual Therapy and Exercise Approach to Breast Cancer Rehabilitation Course November 7 th and 8 th, 2014 Mercer University, Atlanta,
2014 Annual Breast Cancer Rehabilitation Healthcare Provider Event A Manual Therapy and Exercise Approach to Breast Cancer Rehabilitation Course November 7 th and 8 th, 2014 Mercer University, Atlanta,
The First Page is the Selection Criteria List. The pages that follow is an example of how to address the criteria.
 The First Page is the Selection Criteria List. The pages that follow is an example of how to address the criteria. Selection Criteria List For Counsellor Role ESSENTIAL 1. Four year degree and/or postgraduate
The First Page is the Selection Criteria List. The pages that follow is an example of how to address the criteria. Selection Criteria List For Counsellor Role ESSENTIAL 1. Four year degree and/or postgraduate
Chapter 24. Evolution of Procedures
 Chapter 24 BREAST SURGERY KEY FIGURES: Saline implant reconstruction Latissimus dorsi reconstruction Free TRAM reconstruction In the developed world, breast reconstruction after mastectomy and breast reduction
Chapter 24 BREAST SURGERY KEY FIGURES: Saline implant reconstruction Latissimus dorsi reconstruction Free TRAM reconstruction In the developed world, breast reconstruction after mastectomy and breast reduction
Evaluation of Female Patients Motivating Factors for Aesthetic Surgery
 6 Original Article Evaluation of Female Patients Motivating Factors for Aesthetic Surgery Seyed Mehdi Moosavizadeh, Feizollah Niazi, Abdoljalil Kalantar-Hormozi. Department of Plastic Surgery, 5 th Khordad
6 Original Article Evaluation of Female Patients Motivating Factors for Aesthetic Surgery Seyed Mehdi Moosavizadeh, Feizollah Niazi, Abdoljalil Kalantar-Hormozi. Department of Plastic Surgery, 5 th Khordad
Objectives. Significant Costs Of Chronic Pain. Pain Catastrophizing. Pain Catastrophizing. Pain Catastrophizing
 Effectiveness of a Comprehensive Pain Rehabilitation Program in the Reduction of Pain Catastrophizing Michele Evans, MS, APRN-C, CNS, March 27, 2007 Mayo Foundation for Medical Education and Research (MFMER).
Effectiveness of a Comprehensive Pain Rehabilitation Program in the Reduction of Pain Catastrophizing Michele Evans, MS, APRN-C, CNS, March 27, 2007 Mayo Foundation for Medical Education and Research (MFMER).
Mental Health Smartphone Application A New Initiative for Mental Health Care Providers
 Mental Health Smartphone Application A New Initiative for Mental Health Care Providers Dr. Melvyn Zhang MBBS (S pore), DCP(Ireland), MRCPsych(UK) Psychiatry Resident in Training Department of Psychological
Mental Health Smartphone Application A New Initiative for Mental Health Care Providers Dr. Melvyn Zhang MBBS (S pore), DCP(Ireland), MRCPsych(UK) Psychiatry Resident in Training Department of Psychological
Update: Psychosocial status of pediatric patients undergoing bariatric surgery
 Update: Psychosocial status of pediatric patients undergoing bariatric surgery Preventive Medicine Sabine.herget@medizin.uni-leipzig.de Outline Epidemiology of pediatric obesity Psychopathology and bariatric
Update: Psychosocial status of pediatric patients undergoing bariatric surgery Preventive Medicine Sabine.herget@medizin.uni-leipzig.de Outline Epidemiology of pediatric obesity Psychopathology and bariatric
Archive of SID. Awareness of Consumer Protection Act among Doctors in Udaipur City, India. www.sid.ir. K. Singh 1
 Original Article Awareness of Consumer Protection Act among Doctors in Udaipur City, India K. Singh 1, S. Shetty 2, N. Bhat 3, A. Sharda 4, A. Agrawal 1, H. Chaudhary 1 1 Postgraduate Student, Department
Original Article Awareness of Consumer Protection Act among Doctors in Udaipur City, India K. Singh 1, S. Shetty 2, N. Bhat 3, A. Sharda 4, A. Agrawal 1, H. Chaudhary 1 1 Postgraduate Student, Department
CAGE. AUDIT-C and the Full AUDIT
 CAGE In the past have you ever: C tried to Cut down or Change your pattern of drinking or drug use? A been Annoyed or Angry because of others concern about your drinking or drug use? G felt Guilty about
CAGE In the past have you ever: C tried to Cut down or Change your pattern of drinking or drug use? A been Annoyed or Angry because of others concern about your drinking or drug use? G felt Guilty about
Delivering Appropriate Emergency Care Services - Protocol Development and Design
 Delivering Appropriate Emergency Care Services - Protocol Development and Design Sherrill Evans, Karen Evans, Peter Huxley, Helen Snooks, Ian Russell et al Mental Health Research Team, College of Human
Delivering Appropriate Emergency Care Services - Protocol Development and Design Sherrill Evans, Karen Evans, Peter Huxley, Helen Snooks, Ian Russell et al Mental Health Research Team, College of Human
Mental Health Referral Practices and Diabetic Management at Community Medical Alliance Clinic (Bell Site) Northeast Community Clinic (NECC)
 Mental Health Referral Practices and Diabetic Management at Community Medical Alliance Clinic (Bell Site) Northeast Community Clinic (NECC) MaryAnn Garcia, SUNY Downstate Medical College NMF PCLP Scholar
Mental Health Referral Practices and Diabetic Management at Community Medical Alliance Clinic (Bell Site) Northeast Community Clinic (NECC) MaryAnn Garcia, SUNY Downstate Medical College NMF PCLP Scholar
Date Submitted: 7/15/2011. Unit: Counseling and Career Services at Oxford. Contact Person: Joe Moon and Sandra Schein
 EMORY UNIVERSITY 2010-2011 Assessment Report for Administrative and Educational Support Units Assessment Period Covered: September 1, 2010-August 31, 2011 Unit: Counseling and Career Services at Oxford
EMORY UNIVERSITY 2010-2011 Assessment Report for Administrative and Educational Support Units Assessment Period Covered: September 1, 2010-August 31, 2011 Unit: Counseling and Career Services at Oxford
Patient Satisfaction with Dental Hygiene Providers in US Military Clinics
 Source: Journal of Dental Hygiene, Vol. 81, No. 1, January 2007 Patient Satisfaction with Dental Hygiene Providers in US Military Clinics Jeffrey G Chaffin, DDS, MPH, MBA, CHE, Sherry D Chaffin, RDH, A
Source: Journal of Dental Hygiene, Vol. 81, No. 1, January 2007 Patient Satisfaction with Dental Hygiene Providers in US Military Clinics Jeffrey G Chaffin, DDS, MPH, MBA, CHE, Sherry D Chaffin, RDH, A
International Journal of Economics, Commerce and Management United Kingdom Vol. II, Issue 2, 2014
 International Journal of Economics, Commerce and Management United Kingdom Vol. II, Issue 2, 2014 http://ijecm.co.uk/ ISSN 2348 0386 HEALTHCARE MANAGEMENT AND PSYCHOLOGICAL WELL-BEING IN PATIENTS WITH
International Journal of Economics, Commerce and Management United Kingdom Vol. II, Issue 2, 2014 http://ijecm.co.uk/ ISSN 2348 0386 HEALTHCARE MANAGEMENT AND PSYCHOLOGICAL WELL-BEING IN PATIENTS WITH
CARE MANAGEMENT FOR LATE LIFE DEPRESSION IN URBAN CHINESE PRIMARY CARE CLINICS
 CARE MANAGEMENT FOR LATE LIFE DEPRESSION IN URBAN CHINESE PRIMARY CARE CLINICS Dept of Public Health Sciences February 6, 2015 Yeates Conwell, MD Dept of Psychiatry, University of Rochester Shulin Chen,
CARE MANAGEMENT FOR LATE LIFE DEPRESSION IN URBAN CHINESE PRIMARY CARE CLINICS Dept of Public Health Sciences February 6, 2015 Yeates Conwell, MD Dept of Psychiatry, University of Rochester Shulin Chen,
P.O. Box 31001 Abu Dhabi, Tel: +971 2 22 22 616 Fax: +971 2 22 22 717 E-mail: info@davincidental.ae. www.davincidental.ae.
 P.O. Box 31001 Abu Dhabi, Tel: +971 2 22 22 616 Fax: +971 2 22 22 717 E-mail: info@davincidental.ae www.davincidental.ae /DavinciDental1 ADental care you deserve! We give you more of what you want the
P.O. Box 31001 Abu Dhabi, Tel: +971 2 22 22 616 Fax: +971 2 22 22 717 E-mail: info@davincidental.ae www.davincidental.ae /DavinciDental1 ADental care you deserve! We give you more of what you want the
The relationship between mental wellbeing and financial management among older people
 The relationship between mental wellbeing and financial management among older people An analysis using the third wave of Understanding Society January 2014 www.pfrc.bris.ac.uk www.ilcuk.org.uk A working
The relationship between mental wellbeing and financial management among older people An analysis using the third wave of Understanding Society January 2014 www.pfrc.bris.ac.uk www.ilcuk.org.uk A working
Case-management by the GP of domestic violence
 Case-management by the GP of domestic violence an example of results from a sentinel network of general practitioners Nathalie Bossuyt Sentinel network of general practitioners Outline Introduction Research
Case-management by the GP of domestic violence an example of results from a sentinel network of general practitioners Nathalie Bossuyt Sentinel network of general practitioners Outline Introduction Research
4: Complexity and maintenance - a report from the Adult Dental Health Survey 2009
 4: Complexity and maintenance - a report from the Adult Dental Health Survey 2009 Copyright 2011, The Health and Social Care Information Centre. All Rights Reserved. 1 The NHS Information Centre is England
4: Complexity and maintenance - a report from the Adult Dental Health Survey 2009 Copyright 2011, The Health and Social Care Information Centre. All Rights Reserved. 1 The NHS Information Centre is England
Quality of Life of Children
 Quality of Life of Children with Mental Illness Martha J. Molly Faulkner, PhD, CNP, LISW University of New Mexico Health Sciences Center Children s Psychiatric Center Outpatient Services Objectives History
Quality of Life of Children with Mental Illness Martha J. Molly Faulkner, PhD, CNP, LISW University of New Mexico Health Sciences Center Children s Psychiatric Center Outpatient Services Objectives History
MENTAL HEALTH COUNSELING CONCENTRATION PRACTICUM/INTERNSHIP HANDBOOK
 WILLIAM PATERSON UNIVERSITY COLLEGE OF EDUCATION DEPARTMENT OF SPECIAL EDUCATION AND COUNSELING MENTAL HEALTH COUNSELING CONCENTRATION PRACTICUM/INTERNSHIP HANDBOOK Prepared April, 2000 by Paula Danzinger,
WILLIAM PATERSON UNIVERSITY COLLEGE OF EDUCATION DEPARTMENT OF SPECIAL EDUCATION AND COUNSELING MENTAL HEALTH COUNSELING CONCENTRATION PRACTICUM/INTERNSHIP HANDBOOK Prepared April, 2000 by Paula Danzinger,
The ACC 50 th Annual Scientific Session
 Special Report The ACC 50 th Annual Scientific Session Part Two From March 18 to 21, 2001, physicians from around the world gathered to learn, to teach and to discuss at the American College of Cardiology
Special Report The ACC 50 th Annual Scientific Session Part Two From March 18 to 21, 2001, physicians from around the world gathered to learn, to teach and to discuss at the American College of Cardiology
Emotional dysfunction in psychosis.
 Early intervention Service Emotional dysfunction in psychosis. 2. Depression In First Episode Psychosis (DIPS) study: The role of awareness and appraisal Max Birchwood and Rachel Upthegrove Background:
Early intervention Service Emotional dysfunction in psychosis. 2. Depression In First Episode Psychosis (DIPS) study: The role of awareness and appraisal Max Birchwood and Rachel Upthegrove Background:
Educational Psychology. Dr Vicki McKenzie
 Educational Psychology Dr Vicki McKenzie Educational and developmental psychology is concerned with wellbeing across the lifespan, in particular, the developmental and learning processes that people experience
Educational Psychology Dr Vicki McKenzie Educational and developmental psychology is concerned with wellbeing across the lifespan, in particular, the developmental and learning processes that people experience
COURSE APPROVAL GUIDELINES APS COLLEGE OF CLINICAL NEUROPSYCHOLOGISTS
 Page 1 COURSE APPROVAL GUIDELINES APS COLLEGE OF CLINICAL NEUROPSYCHOLOGISTS Updated October 2000 Page 2 1. General Introduction and Principles Clinical neuropsychology is a division of psychology concerned
Page 1 COURSE APPROVAL GUIDELINES APS COLLEGE OF CLINICAL NEUROPSYCHOLOGISTS Updated October 2000 Page 2 1. General Introduction and Principles Clinical neuropsychology is a division of psychology concerned
Earlier research on this group intervention Presentation of the study: Acceptance and Commitment Therapy (ACT), To prevent stress and promote health
 Acceptance and Commitment Therapy ACT To prevent stress and promote health Psychological TreatmentofYouth under Stressful Conditions A Pilot Evaluation of the Impact of ACT in an Adolescent Group Emma
Acceptance and Commitment Therapy ACT To prevent stress and promote health Psychological TreatmentofYouth under Stressful Conditions A Pilot Evaluation of the Impact of ACT in an Adolescent Group Emma
Cosmetic Dentistry. State of the Industry. Survey 2013. American Academy of Cosmetic Dentistry www.aacd.com
 Cosmetic Dentistry State of the Industry Survey 2013 American Academy of Cosmetic Dentistry www.aacd.com Page 2 Table of Contents About This Study... 4 FINDINGS: Respondent Demographics... 5 AACD Member
Cosmetic Dentistry State of the Industry Survey 2013 American Academy of Cosmetic Dentistry www.aacd.com Page 2 Table of Contents About This Study... 4 FINDINGS: Respondent Demographics... 5 AACD Member
Stress and wellbeing in Australia survey 2013
 Stress and wellbeing in Australia survey 2013 The state of the nation two years on, and Special feature on working Australians October 2013 Lynne Casey PhD MAPS National Psychology Week is an initiative
Stress and wellbeing in Australia survey 2013 The state of the nation two years on, and Special feature on working Australians October 2013 Lynne Casey PhD MAPS National Psychology Week is an initiative
Data from a total of 1,391 plastic surgeons were compiled for this survey.
 ISAPS International Survey on Aesthetic/Cosmetic Procedures Performed in 2014 Methodology: Survey participants completed a single-page questionnaire that focused on the number of specific surgical and
ISAPS International Survey on Aesthetic/Cosmetic Procedures Performed in 2014 Methodology: Survey participants completed a single-page questionnaire that focused on the number of specific surgical and
Early Intervention Programs CAN YOU AFFORD NOT TO?
 Early Intervention Programs CAN YOU AFFORD NOT TO? NT Safe Work Week (26/10/2014 to 1/11/2014) Rachel Cassar Current member of NT Workers Compensation Advisory Council Certificate IV TAE Graduate Certificate
Early Intervention Programs CAN YOU AFFORD NOT TO? NT Safe Work Week (26/10/2014 to 1/11/2014) Rachel Cassar Current member of NT Workers Compensation Advisory Council Certificate IV TAE Graduate Certificate
Improving Health for People with Compensable Injuries. Ian Cameron University of Sydney
 Improving Health for People with Compensable Injuries Ian Cameron University of Sydney Summary Definitions Two stories Hypothesis 1 People with compensable injuries have worse health (than people without
Improving Health for People with Compensable Injuries Ian Cameron University of Sydney Summary Definitions Two stories Hypothesis 1 People with compensable injuries have worse health (than people without
Cosmetic Interventions - Survey of Scottish Population HEALTH AND SOCIAL CARE. social. research
 Cosmetic Interventions - Survey of Scottish Population HEALTH AND SOCIAL CARE social research Cosmetic Interventions Survey of Scottish Population YouGov Gavin Ellison Laura Piggott Contents Contents...
Cosmetic Interventions - Survey of Scottish Population HEALTH AND SOCIAL CARE social research Cosmetic Interventions Survey of Scottish Population YouGov Gavin Ellison Laura Piggott Contents Contents...
Emotionally unstable? It spells trouble for work, relationships and life
 Emotionally unstable? It spells trouble for work, relationships and life Rob Bailey and Tatiana Gulko, OPP Ltd Summary This presentation explores a range of studies of resilience using the 16PF questionnaire,
Emotionally unstable? It spells trouble for work, relationships and life Rob Bailey and Tatiana Gulko, OPP Ltd Summary This presentation explores a range of studies of resilience using the 16PF questionnaire,
DENT IMPLANT restoring qualit S: of LIfE
 DENTAL IMPLANTS: restoring quality of life Dental Implants: A Better Treatment Option. What are dental implants? Dental implants are a safe, esthetic alternative to traditional crowns, bridgework, and
DENTAL IMPLANTS: restoring quality of life Dental Implants: A Better Treatment Option. What are dental implants? Dental implants are a safe, esthetic alternative to traditional crowns, bridgework, and
RESIDENT TRAINING GOALS AND OBJECTIVES STATEMENTS
 RESIDENT TRAINING GOALS AND OBJECTIVES STATEMENTS Evaluation and treatment of dental emergencies Recognize, anticipate and manage emergency problems related to the oral cavity. Differentiate between those
RESIDENT TRAINING GOALS AND OBJECTIVES STATEMENTS Evaluation and treatment of dental emergencies Recognize, anticipate and manage emergency problems related to the oral cavity. Differentiate between those
Applied Psychology. Course Descriptions
 Applied Psychology s AP 6001 PRACTICUM SEMINAR I 1 CREDIT AP 6002 PRACTICUM SEMINAR II 3 CREDITS Prerequisites: AP 6001: Successful completion of core courses. Approval of practicum site by program coordinator.
Applied Psychology s AP 6001 PRACTICUM SEMINAR I 1 CREDIT AP 6002 PRACTICUM SEMINAR II 3 CREDITS Prerequisites: AP 6001: Successful completion of core courses. Approval of practicum site by program coordinator.
Adherence to Sport Injury Rehabilitation: Implications for Athletic Training. Britton W. Brewer Springfield College Springfield, MA USA
 Adherence to Sport Injury Rehabilitation: Implications for Athletic Training Britton W. Brewer Springfield College Springfield, MA USA Acknowledgements Allen E. Cornelius, Judy L. Van Raalte, Albert J.
Adherence to Sport Injury Rehabilitation: Implications for Athletic Training Britton W. Brewer Springfield College Springfield, MA USA Acknowledgements Allen E. Cornelius, Judy L. Van Raalte, Albert J.
Body Dysmorphic Disorder and Cosmetic Dentistry
 Course Number: 171 Body Dysmorphic Disorder and Cosmetic Dentistry Diagnostic, Management, and Ethical Issues Authored by Willie J. Winfree, DDS, MPA; Leo E. Rouse, DDS; and Ronald S. Brown, DDS, MS Upon
Course Number: 171 Body Dysmorphic Disorder and Cosmetic Dentistry Diagnostic, Management, and Ethical Issues Authored by Willie J. Winfree, DDS, MPA; Leo E. Rouse, DDS; and Ronald S. Brown, DDS, MS Upon
D. Main Section of the proposal
 D. Main Section of the proposal The purpose of this project is to improve health outcomes for treatment of tobacco dependence among the Arizona behavioral health population. This will be accomplished through
D. Main Section of the proposal The purpose of this project is to improve health outcomes for treatment of tobacco dependence among the Arizona behavioral health population. This will be accomplished through
IBADAN STUDY OF AGEING (ISA): RATIONALE AND METHODS. Oye Gureje Professor of Psychiatry University of Ibadan Nigeria
 IBADAN STUDY OF AGEING (ISA): RATIONALE AND METHODS Oye Gureje Professor of Psychiatry University of Ibadan Nigeria Introduction The Ibadan Study of Ageing consists of two components: Baseline cross sectional
IBADAN STUDY OF AGEING (ISA): RATIONALE AND METHODS Oye Gureje Professor of Psychiatry University of Ibadan Nigeria Introduction The Ibadan Study of Ageing consists of two components: Baseline cross sectional
High School Psychology and its Impact on University Psychology Performance: Some Early Data
 High School Psychology and its Impact on University Psychology Performance: Some Early Data John Reece Discipline of Psychology School of Health Sciences Impetus for This Research Oh, can you study psychology
High School Psychology and its Impact on University Psychology Performance: Some Early Data John Reece Discipline of Psychology School of Health Sciences Impetus for This Research Oh, can you study psychology
Better Access to Medicare Mental Health Items and Psychology Providers
 Better Access to Medicare Mental Health Items and Psychology Providers The issue of ease of access by the community to the new mental health items is central to its success. This paper attempts to examine
Better Access to Medicare Mental Health Items and Psychology Providers The issue of ease of access by the community to the new mental health items is central to its success. This paper attempts to examine
Stress Assessment questionnaire
 MySkillsProfile Report Stress Assessment questionnaire Dave Smith myskillsprofile.com around the globe Report The SAQ questionnaires are copyright MySkillsProfile.com. MySkillsProfile.com developed and
MySkillsProfile Report Stress Assessment questionnaire Dave Smith myskillsprofile.com around the globe Report The SAQ questionnaires are copyright MySkillsProfile.com. MySkillsProfile.com developed and
STATE OF OHIO. DEPARTMENT OF REHABILITATION RELATED ACA STANDARDS: EFFECTIVE DATE: AND CORRECTION February 19, 2011 I. AUTHORITY
 STATE OF OHIO SUBJECT: PAGE 1 OF 7. Specialized Assessments and Screenings NUMBER: 67-MNH-16 RULE/CODE REFERENCE: SUPERSEDES: AR 5120-11-03, 07, 21 67-MNH-16 dated 01/13/10 ORC 5120.031; 5120.032; 5120.033
STATE OF OHIO SUBJECT: PAGE 1 OF 7. Specialized Assessments and Screenings NUMBER: 67-MNH-16 RULE/CODE REFERENCE: SUPERSEDES: AR 5120-11-03, 07, 21 67-MNH-16 dated 01/13/10 ORC 5120.031; 5120.032; 5120.033
Attitudes About Cosmetic Surgery: Gender and Body Experience
 McNair Scholars Journal Volume 6 Issue 1 Article 3 2002 Attitudes About Cosmetic Surgery: Gender and Body Experience Jennifer Bazner Grand Valley State University Follow this and additional works at: http://scholarworks.gvsu.edu/mcnair
McNair Scholars Journal Volume 6 Issue 1 Article 3 2002 Attitudes About Cosmetic Surgery: Gender and Body Experience Jennifer Bazner Grand Valley State University Follow this and additional works at: http://scholarworks.gvsu.edu/mcnair
The Unhappy total knee replacement patient whose X rays look fine. Can we predict, prevent and treat. Myles RJ Coolican and Kunal Dhurve
 The Unhappy total knee replacement patient whose X rays look fine Introduction: Can we predict, prevent and treat Myles RJ Coolican and Kunal Dhurve Total knee replacement (TKR) is an effective treatment
The Unhappy total knee replacement patient whose X rays look fine Introduction: Can we predict, prevent and treat Myles RJ Coolican and Kunal Dhurve Total knee replacement (TKR) is an effective treatment
3D Analysis of Breast Augmentation Defines Operative Changes and Their Relationship to Implant Dimensions
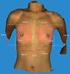 NORTHEASTERN SOCIETY OF PLASTIC SURGEONS 3D Analysis of Breast Augmentation Defines Operative Changes and Their Relationship to Implant Dimensions Oren M. Tepper, MD, Kevin H. Small, MD, Jacob G. Unger,
NORTHEASTERN SOCIETY OF PLASTIC SURGEONS 3D Analysis of Breast Augmentation Defines Operative Changes and Their Relationship to Implant Dimensions Oren M. Tepper, MD, Kevin H. Small, MD, Jacob G. Unger,
Quick Facts about Breast Augmentation with IDEAL IMPLANT Saline-filled Breast Implants
 Quick Facts about Breast Augmentation with IDEAL IMPLANT Saline-filled Breast Implants Important Factors Breast Augmentation Patients Should Consider October 2015 Caution: Federal law restricts this device
Quick Facts about Breast Augmentation with IDEAL IMPLANT Saline-filled Breast Implants Important Factors Breast Augmentation Patients Should Consider October 2015 Caution: Federal law restricts this device
University of Michigan Dearborn Graduate Psychology Assessment Program
 University of Michigan Dearborn Graduate Psychology Assessment Program Graduate Clinical Health Psychology Program Goals 1 Psychotherapy Skills Acquisition: To train students in the skills and knowledge
University of Michigan Dearborn Graduate Psychology Assessment Program Graduate Clinical Health Psychology Program Goals 1 Psychotherapy Skills Acquisition: To train students in the skills and knowledge
Celebrity worship and incidence of elective cosmetic surgery: evidence of a link among young adults.
 Celebrity worship and incidence of elective cosmetic surgery: evidence of a link among young adults. MALTBY, J and DAY, Liza Available from Sheffield Hallam University Research Archive (SHURA) at: http://shura.shu.ac.uk/6042/
Celebrity worship and incidence of elective cosmetic surgery: evidence of a link among young adults. MALTBY, J and DAY, Liza Available from Sheffield Hallam University Research Archive (SHURA) at: http://shura.shu.ac.uk/6042/
EVALUATION OF THE IMPLEMENTATION OF THE PROSTATE CANCER SPECIALIST NURSE ROLE
 EVALUATION OF THE IMPLEMENTATION OF THE PROSTATE CANCER SPECIALIST NURSE ROLE Julie Sykes, 1 Patsy Yates, 2 Danette Langbecker 2 1. Prostate Cancer Foundation of Australia 2. Queensland University of Technology,
EVALUATION OF THE IMPLEMENTATION OF THE PROSTATE CANCER SPECIALIST NURSE ROLE Julie Sykes, 1 Patsy Yates, 2 Danette Langbecker 2 1. Prostate Cancer Foundation of Australia 2. Queensland University of Technology,
Evaluating a Fatigue Management Training Program For Coaches
 Evaluating a fatigue management training program for coach drivers. M. Anthony Machin University of Southern Queensland Abstract A nonprescriptive fatigue management training program was developed that
Evaluating a fatigue management training program for coach drivers. M. Anthony Machin University of Southern Queensland Abstract A nonprescriptive fatigue management training program was developed that
Job satisfaction of registered dental practitioners
 SCIENTIFIC ARTICLE Australian Dental Journal 2005;50:(3):179-185 Job satisfaction of registered dental practitioners L Luzzi,* AJ Spencer,* K Jones,* D Teusner* Abstract Background: This study was designed
SCIENTIFIC ARTICLE Australian Dental Journal 2005;50:(3):179-185 Job satisfaction of registered dental practitioners L Luzzi,* AJ Spencer,* K Jones,* D Teusner* Abstract Background: This study was designed
Summary chapter 2 chapter 2
 Summary Multiple Sclerosis (MS) is a chronic disease of the brain and the spinal cord. The cause of MS is unknown. MS usually starts in young adulthood. In the course of the disease progression of neurological
Summary Multiple Sclerosis (MS) is a chronic disease of the brain and the spinal cord. The cause of MS is unknown. MS usually starts in young adulthood. In the course of the disease progression of neurological
Health Anxiety and Hypochondriasis in Older Adults: Overlooked Conditions in a Susceptible Population
 Health Anxiety and Hypochondriasis in Older Adults: Overlooked Conditions in a Susceptible Population Presented by: Renée El-Gabalawy, M.A., Ph.D Candidate Collaborators Dr. Corey Mackenzie Associate Professor
Health Anxiety and Hypochondriasis in Older Adults: Overlooked Conditions in a Susceptible Population Presented by: Renée El-Gabalawy, M.A., Ph.D Candidate Collaborators Dr. Corey Mackenzie Associate Professor
Plastic Surgery. Statistics Report. ASPS National Clearinghouse of. Plastic Surgery. Procedural Statistics
 ASPS National Clearinghouse of Procedural Statistics All figures are projected. * Data unavailable in prior year. **77% of total breast implants were silicone; 23% were saline. ***Botulinum Toxin Type
ASPS National Clearinghouse of Procedural Statistics All figures are projected. * Data unavailable in prior year. **77% of total breast implants were silicone; 23% were saline. ***Botulinum Toxin Type
Predictors of recovery and legal representation in a compensation setting 12 months post injury: The Whiplash Outcome Study [WOS]
![Predictors of recovery and legal representation in a compensation setting 12 months post injury: The Whiplash Outcome Study [WOS] Predictors of recovery and legal representation in a compensation setting 12 months post injury: The Whiplash Outcome Study [WOS]](/thumbs/26/7931923.jpg) Predictors of recovery and legal representation in a compensation setting 12 months post injury: The Whiplash Outcome Study [WOS] Petrina Casey [PhD candidate], Rehabilitation Studies Unit, Sydney Medical
Predictors of recovery and legal representation in a compensation setting 12 months post injury: The Whiplash Outcome Study [WOS] Petrina Casey [PhD candidate], Rehabilitation Studies Unit, Sydney Medical
Comorbidity of mental disorders and physical conditions 2007
 Comorbidity of mental disorders and physical conditions 2007 Comorbidity of mental disorders and physical conditions, 2007 Australian Institute of Health and Welfare Canberra Cat. no. PHE 155 The Australian
Comorbidity of mental disorders and physical conditions 2007 Comorbidity of mental disorders and physical conditions, 2007 Australian Institute of Health and Welfare Canberra Cat. no. PHE 155 The Australian
Evaluation of a Self- Management Course Using the Health Education Impact Questionnaire
 Evaluation of a Self- Management Course Using the Health Education Impact Questionnaire Tiffany Gill Jing Wu Anne Taylor Report by Population Research and Outcome Studies, University of Adelaide for Arthritis
Evaluation of a Self- Management Course Using the Health Education Impact Questionnaire Tiffany Gill Jing Wu Anne Taylor Report by Population Research and Outcome Studies, University of Adelaide for Arthritis
The University of Hong Kong Department of Surgery Division of Esophageal and Upper Gastrointestinal Surgery
 Program Overview The University of Hong Kong Department of Surgery Division of Esophageal and Upper Gastrointestinal Surgery Weight Control and Metabolic Surgery Program The Weight Control and Metabolic
Program Overview The University of Hong Kong Department of Surgery Division of Esophageal and Upper Gastrointestinal Surgery Weight Control and Metabolic Surgery Program The Weight Control and Metabolic
Alcohol Disorders in Older Adults: Common but Unrecognised. Amanda Quealy Chief Executive Officer The Hobart Clinic Association
 Alcohol Disorders in Older Adults: Common but Unrecognised Amanda Quealy Chief Executive Officer The Hobart Clinic Association The Hobart Clinic Association Not-for-profit private Mental Health Service
Alcohol Disorders in Older Adults: Common but Unrecognised Amanda Quealy Chief Executive Officer The Hobart Clinic Association The Hobart Clinic Association Not-for-profit private Mental Health Service
2013 Plastic Surgery Statistics Report
 All figures are projected. * Data unavailable in prior year. **72% of total breast implants were silicone; 28% were saline. ***Botulinum toxin type A numbers are of anatomic sites injected. ASPS National
All figures are projected. * Data unavailable in prior year. **72% of total breast implants were silicone; 28% were saline. ***Botulinum toxin type A numbers are of anatomic sites injected. ASPS National
Practice patterns of oral and maxillofacial surgeons in Australia
 Practice patterns of oral and maxillofacial surgeons in Australia ARCPOH Population Oral Health Series NO. 3 KA Singh, DS Brennan, AJ Spencer, AN Goss August 2004 ARCPOH POPULATION ORAL HEALTH SERIES Number
Practice patterns of oral and maxillofacial surgeons in Australia ARCPOH Population Oral Health Series NO. 3 KA Singh, DS Brennan, AJ Spencer, AN Goss August 2004 ARCPOH POPULATION ORAL HEALTH SERIES Number
Running head: SEX DIFFERENCES IN GAMING MACHINE GAMBLING. Sex differences in pathological gambling using gaming machines 1
 Sex Differences in Gaming Machine Gambling 1 Running head: SEX DIFFERENCES IN GAMING MACHINE GAMBLING Sex differences in pathological gambling using gaming machines 1 Keis Ohtsuka, Eric Bruton, Louisa
Sex Differences in Gaming Machine Gambling 1 Running head: SEX DIFFERENCES IN GAMING MACHINE GAMBLING Sex differences in pathological gambling using gaming machines 1 Keis Ohtsuka, Eric Bruton, Louisa
Child Behavior Checklist/4-18 Achenbach, T. M. 1991
 Description of Measure Child Behavior Checklist/4-18 Achenbach, T. M. 1991 Purpose To obtain caregiver report of children's competencies and behavior problems in a standardized format. Conceptual Organization
Description of Measure Child Behavior Checklist/4-18 Achenbach, T. M. 1991 Purpose To obtain caregiver report of children's competencies and behavior problems in a standardized format. Conceptual Organization
Tools for Screening and Assessment of Suicide Risk
 Tools for Screening and Assessment of Suicide Risk Screening 1. High School Questionnaire: Profile of Experiences Leona L. Eggert, Ph.D., R.N., FAAN; Jerald R. Herting, Ph.D., and Elaine A. Thompson Ph.D.,
Tools for Screening and Assessment of Suicide Risk Screening 1. High School Questionnaire: Profile of Experiences Leona L. Eggert, Ph.D., R.N., FAAN; Jerald R. Herting, Ph.D., and Elaine A. Thompson Ph.D.,
NORCOM COMMISSIONING POLICY. Specialist Plastic Surgery Procedures
 NORCOM North Derbyshire, South Yorkshire and Bassetlaw Commissioning Consortium NORCOM COMMISSIONING POLICY Specialist Plastic Surgery Procedures January 2007 Review Date: January 2009 Prepared by Rotherham
NORCOM North Derbyshire, South Yorkshire and Bassetlaw Commissioning Consortium NORCOM COMMISSIONING POLICY Specialist Plastic Surgery Procedures January 2007 Review Date: January 2009 Prepared by Rotherham
