Treatment of Injuries to the Ulnar Side of the Wrist Occuring with Distal Radial Fractures
|
|
|
- Allyson Pierce
- 8 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Hand Clin 21 (2005) Treatment of Injuries to the Ulnar Side of the Wrist Occuring with Distal Radial Fractures Tommy Lindau, MD, PhD a,b, * a Department of Orthopedics, Hospital of A ngelholm, S A ngelholm, Sweden b The Pulvertaft Centre Derbyshire Royal Infirmary, London Road, Derby, DE1 2QY, UK Frykman first emphasized in 1967 [1] the importance of the disturbance of the distal radioulnar joint. This article is not remembered for its important emphasis on methods for the prevention of reflex sympathetic dystrophy, but rather for its classification, which implied an increased severity if the ulnar styloid was fractured. Frykman, as well as many other authors, recognized that the most frequent complaint after distal radial fractures was ulnar-sided wrist pain [1 5]. It is present in every fifth patient after distal radius fracture [1] and affects the end result adversely [1,6,7]. Ulnar-sided wrist pain has mainly been attributed to malunion of the distal radius [1,6,8 14], creating an imbalance distally, which might lead to ulno-carpal abutment [15], incongruency [16], and osteoarthrosis of the distal radio-ulnar joint (DRUJ) [17]. Wrist arthroscopy has revealed that the common distal radial fracture often is complicated by ligamentous injuries [18 20]. These injuries can lead to laxity of the DRUJ and subsequent worse outcome [21], so that if we want to better understand the fracture and its sequel, we must have a complete diagnosis that includes ligament injuries. This may partly explain way the Frykman classification does not correlate with the outcome [22] and why there is still insufficient knowledge regarding treatment of the fracture and its associated ligament injuries [23]. However, by analyzing recent literature [24], we can recognize the different problems and plan a strategy to address the acute fracture and ligament injuries and later secondary problems related to malunion, instability, and pain. * The Pulvertaft Centre Derbyshire Royal Infirmary, London Road, Derby, DE1 2QY, UK. address: tommy.lindau@telia.com Functional anatomydligaments are important stabilizers The radius rotates around the ulnar head during pronation and supination of the forearm through the DRUJ (Fig. 1) [25,26]. This joint is also connected to the carpus with a ligament apparatus (see Fig. 1) and thus transmits forces to and from the hand [26]. The stability of the DRUJ is achieved by bony congruity between the sigmoid notch of the radius and the ulnar head, which are held together by ligaments (see Fig. 1) [15,26,27]. The bony stability can easily deteriorate after trauma as only approximately 60% of the joint surfaces are in contact in neutral forearm position and 10% in full pronation and supination [27 30]. The major stabilizer of the DRUJ are the ulnoradial ligaments, which represent the transverse, peripheral part of the triangular fibro-cartilage complex (TFCC) [15,26,27,31 34]. The ligaments run from the fovea of the ulnar head and the base of the ulnar styloid to the dorsal and palmar edges of the distal radius [31 35]. The periphery is wellvascularized [35,36], which implies that peripheral tears might heal. The TFCC also includes a central articular disc and the ulno-carpal ligament (see Fig. 1). Secondary stability is achieved through different degrees of contribution from the extensor carpi ulnaris tendon [27], the pronator quadratus muscle [29], and the radio-ulnar interosseous membrane [37]. The fracture must be congruently fixed Ulnar fragments of the distal radius create a problem, because they represent a possible risk of a double joint incongruency [38]; ie, in both /05/$ - see front matter Ó 2005 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. doi: /j.hcl hand.theclinics.com
2 418 LINDAU Fig. 1. Ligaments are important stabilizers. (A) Schematic drawing showing the triangular fibrocartilage complex (TFCC), which is the major stabilizer of the DRUJ. (B) The TFCC is cut open to show that the central disc is membranous and adds no stability between ulna and radius. A = the ulno-carpal ligament, which is the palmar, distal part of the TFCC arising from the fovea of the ulna and inserting at the palmar aspect of triquetrum. B = the central articular disc. C = the dorsal and palmar ulno-radial ligaments, which stabilize the DRUJ. the obvious radio-carpal and the DRUJ. There are several options, decisions, and questions that must be addressed in treating these fractures, and every surgeon has a preference of addressing such an incongruency by means of closed, minimally invasive, or open reduction techniques. It is comforting to know that only a few and provisional conclusions relating to clinical management can be drawn from the available randomized trials, which do not provide robust nor sufficient evidence for most of the decisions necessary in the management of these fractures [23]. Careful analysis has not demonstrated differences of outcome results from treatment of intra-articular incongruencies when comparing medullary pinning with external fixation [39] or percutaneous pinning with external fixation [40,41]. However, it has been shown that a 1 4 tubular plate may be somewhat better than a pi-plate [42] and that arthroscopy-assisted reduction with pinning supported by an external fixator is superior to open reduction and plate fixation [43]. These results agree with nonrandomized studies in which arthroscopy-assisted reduction has been found to realign pre-operative incongruity with good accuracy and give an excellent or good outcome in about 90% of patients [44 47]. Bearing this in mind, there is evidence that arthroscopy should be considered when addressing ulnar-sided injuries, because it combines the possibility of securing the bony congruity with complete diagnosis and treatment of ulnar-sided and intercarpal-associated injuries [38,48]. Arthroscopic reduction and percutaneous pinning Arthroscopy is performed under upright [38,48] or horizontal [49] traction, which can help reduce some fragments by way of ligamentotaxis. Most often, however, the fragments have to be mobilized before reduction, which is done either with a probe within the joint or with an elevator through a separate skin incision over the fracture. This is well described in the article by Geissler elsewhere in this issue. However, in the specific treatment of ulnarsided fragments, I prefer to start the realignment at the ulnar border of the radius, thereby reducing the double joint incongruency of both the radiocarpal joint and the DRUJ (Fig. 2), then add further fragments to the ulnar platform. Finally, the extra-articular fracture component, the cancellous defect, and associated injuries have to be evaluated, and additional procedures have to be considered. Ligamentous (triangular fibro-cartilage complex) injuries are underestimated The TFCC is the most involved associated injury with distal radial fractures (80%) [19].
3 INJURIES TO THE ULNAR SIDE OF THE WRIST 419 Fig. 2. Realignment of the incongruency from the ulnar side. Fragment reduction with arthroscopy-assisted technique should reconstruct the double incongruency of both the DRUJ and the radio-carpal joints, hereby minimizing the risk for instability as well as posttraumatic secondary osteoarthritis. The next step is to realign the other fragments (3) to the ulnar platform. This laxity was not correlated to malunion [21,51], but instead correlated to these peripheral tears of the TFCC. Only a few uncontrolled studies have reported results after acute management of DRUJ injuries; in these studies, reasonably good results have been reported with both open and arthroscopic treatment in selected patients [45,52]. On the other hand, the natural course of untreated peripheral TFCC tears has been found by some authors to end with fairly good results [21]. Hence, the recommendations given here are based upon the authors opinions from what is currently known about these conditions. Keep in mind, though, that there are still no randomized studies that merit surgical treatment regarding these associated injuries, and that surgery itself adds trauma and possible morbidity. Because the TFCC is a combination of structures that make up the ligamentous support of the DRUJ and the ulno-carpal joint, I prefer to describe these injuries not entirely according to Palmer s classification [34], but rather as either central perforation tears, tears of the ulno-radial ligament (ie, peripheral tears), or tears of the ulnocarpal ligament [50]. This facilitates the functional understanding and importance of the different tears, namely as representing possibly destabilizing tears of the DRUJ or not [50], as we have found that tears to the ulno-radial ligament caused laxity and a subsequent worse outcome [21]. Arthroscopic management Central perforation tears are located parallel to the sigmoid notch of the radius with a 2-mm rim of membranous substance left between the sigmoid notch and the perforation (Fig. 3A). These tears are stable and can be debrided with a suction punch (Fig. 3B). Care should be taken not to be too aggressive, thus jeopardizing the stability by debriding the important palmar and dorsal ulnoradial ligaments. The edges are then smoothened with a motorized shaver or vaporizer. Tears of the ulno-radial ligament can be either avulsion tears from the insertion of the dorsal and Fig. 3. Central perforations in the articular disc are stable. (A) Radio-carpal arthroscopy shows a stable central perforation tear in the central articular disc of the TFCC (dorsum of the wrist to the right). The lunate facet of the radius (R) is in the foreground with the probe (1 mm thick) lifting the torn ligament about 2 mm from its insertion in the sigmoid notch of the radius. (B) The tear without healing capacity is best treated with debridement (eg, with a suction punch).
4 420 LINDAU palmar edge of the sigmoid notch of the radius or ulnar avulsion tears (Fig. 4). They can sometimes be hidden behind a capsular blood clot. Hence, debride the area with the shaver to fully examine the ulno-radial ligament. As previously stated, these tears are associated with late clinical instability of the DRUJ [21] and worse outcome [21,51]. Consequently, they probably have to be repaired. Radial avulsion tears are often caused by dorso-ulnar fracture fragments, but may be true avulsions from the insertion site of the ulno-radial ligament. Fragments should be anatomically reduced to both give bony congruity of the sigmoid notch as well as fixate the ligament insertion. A true avulsion at the insertion probably has to be reinserted, either with drill holes through the radius [52,53] or with a suture anchor. An ulnar avulsion tear (Fig. 4A) is preferably repaired with two or three 2-0 absorbable (PDS) sutures through a drill hole of the fovea in the distal ulna (Fig. 4B D) rather than the previously recommended technique through the dorsoulnar capsule and extensor carpi ulnaris tendon sheath. The repair is protected from supination and pronation for 4 weeks, followed by 2 to 4 weeks in a short arm cast or splint. Tears of the ulno-carpal ligament are rare [19]. Treatment may be considered with a palmar open reinsertion technique. Degenerative tears with secondary cartilage changes on the ulnar head and the lunate may be found, en passent, together with the fracture. Sometimes there may be acute tears superimposed on the degenerative tears [19]. The degenerative changes are probably best left alone, as they most Fig. 4. Peripheral TFCC tears cause laxity of the DRUJ. (A) An arthroscopic view of a dorsal ulnar avulsion tear of the ulno-radial ligament of the TFCC (right wrist with dorsal to the right). The lunate is on top with a chondral flake hanging down. The dorso-ulnar peripheral tear (arrows) creates a rough longitudinal line from the lunate facet of the radius in the bottom going all the way toward the ulnar styloid, which is not visible arthroscopically. There is synovium with hematoma to the right and a cloud of blood over the central disc. (B) A drill hole is made to the fovea of the ulnar head. (C) The suture is retrieved after it has been inserted through the extensor carpi ulnaris subsheath with the instrument. (D) The suture is tied after the arm is taken from the traction and with the forearm in neutral.
5 INJURIES TO THE ULNAR SIDE OF THE WRIST 421 often have been asymptomatic before the fracture. However, an acute component may need treatment as recommended above. The ulnar styloid fracture is unimportant Ulnar styloid fractures have been associated with worse outcome [1,7,10,54], which was part of the reason for Frykman s classification [1]. This classification pointed out that each fracture type (extra-articular = I, radio-carpal = III, radioulnar = V, radio-carpal and radio-ulnar = VII) had a worse counterpart when the ulnar styloid was fractured (type II, IV, VI, and VIII) [1]. However, the usefulness of his classification has been questioned [55], because others have not found a correlation between this classification and outcome [22]. Furthermore, several studies have not found any correlation between ulnar styloid fractures and end result [14,21,51,56 58]. This controversy might be explained by the previously stated findings of acute TFCC tears without ulnar styloid fractures [38,48]. Furthermore, there has been no correlation between ulnar styloid fractures at the time of trauma and development of late DRUJ instability [21,51]. Consequently, the outcome is more correlated with the other ulnarsided injuries than the fracture of the ulnar styloid itself. This is probably the reason why no studies have shown any benefits with repair of ulnar styloid fractures [38,57]. Even if operative treatment cannot be advocated, I strongly recommend arthroscopic evaluation if a subluxation or dislocation is present on normal radiography. After complete diagnosis, I then recommend a combined repair of both the TFCC tear (as described above) and the styloid fracture, preferably with a tension band wiring technique. Late DRUJ-related problems are often misunderstood There are many possible causes of ulnar-sided wrist pain after distal radial fractures (Box 1) [24]. Patients who have symptomatic malunion of the distal radius mainly have symptoms secondary to the relatively longer ulna, causing an ulna abutment syndrome. By performing a radial osteotomy with bone graft [17,28,59], the distal radius can be realigned regarding both axial shortening as well as radial and dorsal angulation. The lengthening osteotomy rebalances the load distribution in the wrist, thereby decompressing the Box 1. Verified and suggested causes of distal radio-ulnar joint related symptoms after distal radial fractures Verified causes Ulno-carpal abutment DRUJ laxity Tears of the TFCC Radiographic osteoarthrosis of the DRUJ Incongruency of the sigmoid notch Nonunion of hypertrophic ulnar styloid Arthrofibrosis Suggested causes Tenosynovitis of the extensor carpi ulnaris Adapted from Lindau T, Aspenberg P. The radioulnar joint in distal radial fractures. A review. Acta Orthop Scand 2002;73:583. ulna abutment. The techniques of this are addressed in Stevanovic s article on extra-articular distal radial fracture malunion. The ulna abutment might also be decompressed with ulnar shortening osteotomies [15,60], with Sauve - Kapandji arthrodesis of the DRUJ [61 64], or with an ulnar head resection arthroplasty [65]. The arthroplasty might in turn be performed as an arthroscopic [60,66] or open [60] procedure. The radial osteotomy for malunion also alters the sigmoid notch, which might give both better range of pro-supination motion and create bony stability of the DRUJ [17,59]. However, this osteotomy alone does not yield stability in all cases. Some authors have considered additional ligament stabilizing procedures to be necessary in almost half the patients [17,67,68], while af Ekenstam and colleagues [28] did not find this advantageous. Because ulnar styloid fixation was seen as a ligament-stabilizing procedure, these contradictory results might be explained by the findings that the stabilizing ulno-radial ligaments might be torn without an ulnar styloid fracture [19]. Furthermore, ligament rupture alone can give laxity of the DRUJ even without malunion [21]. Consequently, we should not only reinsert the ulnar styloid when we attempt to stabilize the DRUJ in conjunction with a radial osteotomy, but also need to address the soft-tissue problem completely.
6 422 LINDAU Fig. 5. Ligament reconstruction is sometimes the final solution. (A) The most appealing reconstruction technique uses a tendon graft (most often palmaris longus), which is passed in a tunnel parallel to the sigmoid notch of the radius and reinserted in the fovea [1]. (B) After reconstruction, the graft is pulled firmly and tied with the forearm in neutral rotation. Thereafter, the capsule is closed. Authors preferred assessment of posttraumatic ulnar wrist pain Every patient with ulnar sided wrist pain after distal radial fractures should be examined with a stability test of the DRUJ [50], including ulnocarpal stress test, and assessment of radiographic signs of malunion. In cases with obviuos axial, radial and dorsal malunion, I do a straightforward lengthening osteotomy of the radius with bone graft. If congruity and stability of the DRUJ is not achieved, there is a clear indication to add arthroscopy to evaluate the status of the TFCC and continue with a reattachment of its ulnar insertion in the fovea of the ulnar head, sometimes combined with reinsertion of the ulnar styloid. In cases with only axial shortening malunion, I always start with an arthroscopic evaluation of the ulno-carpal complex and grade the findings according to Palmer [34] (as opposed to the acute tears were I follow my previous recommendations for classification). A shortening osteotomy of the ulna is done if there is an ulnar variance of 1 to 2 mm or more, while I do an arthroscopic partial ulnar head resection (wafer) if the ulnar variance is less than 1 to 2 mm, bearing in mind that the full circumference of the ulnar head must be resected. However, in cases with additional wear of the luno-triquetral ligament [34], I always do an ulnar shortening osteotomy to stabilize the entire ulno-carpal complex. In cases with laxity of the DRUJ without malunion of the radius, I perform an arthroscopy to see if there is an option to arthroscopically reinsert the ligament to the fovea, as previously described. However, in many cases it is necessary to do a reconstruction procedure, where a tendon graft I used to constrain the joint by passing the graft in a tunnel parallel to the sigmoid notch of the radius and reinserting both ends in the fovea through a tunnel of the ulnar head [69] (Fig. 5). This pulls the radius toward the ulna like the reigns of a horse. Summary We still do not know how to best treat the DRUJ condition that was recognized 200 years ago by Abraham Colles and later addressed in Frykman s classic thesis [18]. To improve the outcome, we must recognize the differences between osteoporotic and other fractures and understand the importance of ligament injuries, especially in patients under the osteoporotic age [39]. However, our current problem is that neither the initial ligament injury nor the posttraumatic laxity is detectable with radiographic methods, which creates future challenges regarding diagnosis and treatment. We therefore have to critically analyze each fracture in each patient and be aware of the complexity of the entire injury to the wrist. References [1] Frykman G. Fracture of the distal radius including sequele, shoulder-hand-finger syndrome, disturbance in the distal radio-ulnar joint and impairment of nerve function. Acta Orthop Scand 1967;38(Suppl 108):83 8. [2] Altissimi M, Antenucci R, Fiacca C, et al. Longterm results of conservative treatment of fractures
7 INJURIES TO THE ULNAR SIDE OF THE WRIST 423 of the distal radius. Clin Orthop 1986;206: [3] Cooney WP, Dobyns JH, Linscheid RL. Complications of Colles fractures. J Bone Joint Surg 1980; 62A:613. [4] Solgaard S. Function after distal radius fracture. Acta Orthop Scand 1988;59: [5] Tsukazaki T, Takagi K, Iwasaki K. Poor correlation between functional results and radiographic findings in Colles fracture. J Hand Surg 1993;18B: [6] Hollingsworth R, Morris J. The importance of the ulnar side of the wrist in fractures of the distal end of the radius. Injury 1976;7: [7] Stoffelen D, De Smet L, Broos P. The importance of the distal radioulnar joint in distal radial fractures. J Hand Surg 1998;23B: [8] Hove LM, Fjeldsgaard K, Skjeie R, et al. Anatomical and functional results five years after remanipulated Colles fracture. Scand J Plast Reconstr Hand Surg 1995;29: [9] Kopylov P, Johnell O, Redlundh-JohnelI, et al. Fractures of the distal end of the radius in young adults: a 30-year follow-up. J Hand Surg 1993;18B: [10] Lidström A. Fractures of the distal end of the radius. A clinical and statistical study of the end results. Acta Orthop Scand 1959;(Suppl 41). [11] van der Linden W, Ericson R. Colles fracture. How should its desplacement be measured and how should it be immobilized? J Bone Joint Surg 1981; 63A: [12] Stoffelen D. Fractures of the distal radius: an experimental and clinical approach [thesis]. Leuven (Belgium): University of Leuven; [13] Villar RN, Marsh D, Rushton N, et al. Three years after Colles fracture. J Bone Joint Surg 1987;69B: [14] Warwick D, Prothero D, Field J, et al. Radiological measurement of radial shortening in Colles fracture. J Hand Surg 1993;18B:50 2. [15] Trankle M, van Schoonhoven J, Krimmer H, et al. Indication and results of ulna shortening osteotomy in ulnocarpal wrist joint pain. Unfallchirurg 2000; 103: [16] Kihara H, Short WH, Werner FW, et al. The stabilising mechanism of the distal radioulnar joint during pronation and supination. J Hand Surg 1995;20A: [17] Fernandez DL. Distal radius fractures: reconstructive procedures for malunion and traumatic arthritis. Orthop Clin North Am 1993;24: [18] Geissler WB, Freeland AE, Savoie FH, et al. Intracarpal soft tissue lesions associated with an intraarticular fracture of the distal end of the radius. J Bone Joint Surg 1996;78A: [19] Lindau T, Arner M, Hagberg L. Chondral and ligamentous wrist lesions in young adults with distal radius fractures. A descriptive, arthroscopic study in 50 patients. J Hand Surg [Br] 1997;22B: [20] Richards RS, Bennett JD, Roth JH, et al. Arthroscopic diagnosis of intra-articular soft tissue injuries associated with distal radial fractures. J Hand Surg 1997;22A: [21] Lindau T, Adlercreutz C, Aspenberg P. Peripheral TFCC tears and instability of the distal radioulnar joint after distal radial fractures. J Hand Surg 2000;25A: [22] Flinkkilä T, Raatikainen T, Ha mäläinen M. AO and Frykman s classifications of Colles fracture. No prognostic value in 652 patients evaluated after 5 years. Acta Ortop Scand 1998;69: [23] Handoll HHG, Madhok R. Surgical interventions for treating distal radial fractures in adults (Cochrane Review). In: The Cochrane Library. Issue 3. Chichester (UK): John Wiley & Sons, Ltd; [24] Lindau T, Aspenberg P. The radioulnar joint in distal radial fractures. A review. Acta Orthop Scand 2002;73: [25] Hagert CG. The distal radioulnar joint in raletion to the whole forearm. Clin Orthop 1992;275: [26] Hagert CG. Current concepts of the functional anatomy of the distal radioulnar joint, including the ulnocarpal junction. In: Bu chler U, editor. Wrist instability. London, UK: Martin Dunitz Ltd; p [27] Garcia-Elias M. Soft-tissue anatomy and relationships about the distal ulna. Hand Clin 1998;14: [28] af Ekenstam F, Hagert CG, Engkvist O, et al. Corrective osteotomy of malunited fractures of the distal end of the radius. Scand J Plast Reconstr Surg 1985; 19: [29] Johnson RK, Shrewsbury MM. The pronator quadratus in motions and in stabilisation of the radius and ulna at the distal radioulnar joint. J Hand Surg [Am] 1976;1: [30] Tolat AR, Stanley JK, Trail IA. A cadaveric study of the anatomy and stability of the distal radioulnar joint in the coronal and transverse planes. J Hand Surg 1996;21B:587. [31] af Ekenstam F, Hagert CG. The distal radio ulnar joint. The influence of geometry and ligament on simulated Colles fracture. An experimental study. Scand J Plast Reconstr Surg 1985;19: [32] af Ekenstam F, Hagert CG. Anatomical studies on the geometry and stability of the distal radio ulnar joint. Scand J Plast Reconstr Surg 1985;19: [33] Palmer AK, Werner FW. The triangular fibrocartilage complex of the wristdanatomy and function. J Hand Surg [Am] 1981;6: [34] Palmer AK. Triangular fibrocartilage complex lesions: a classification. J Hand Surg 1989;14A:
8 424 LINDAU [35] Chidgey LK, Dell PC, Bitar ES, et al. Histologic anatomy of the triangular fibrocartilage. J Hand Surg 1991;16A: [36] Bednar MS, Arnoczky SP, Weiland AJ. The microvasculature of the triangular fibrocartilage complex: its clinical significance. J Hand Surg 1991;16A: [37] Hotchkiss RN, An KN, Sowa DT, et al. An anatomic and mechanical study of the interosseous membrane of the forearm: pathomechanics of proximal migration of the radius. J Hand Surg 1989;14A: [38] Lindau T. Wrist arthroscopy in distal radial fractures. In: Geissler W, editor. Wrist arthroscopy. New York: Springer Verlag; [39] Pritchett JW. External fixation or closed medullary pinning for unstable Colles fractures? J Bone Joint Surg Br 1995;77: [40] Ludvigsen TC, Johansen S, Svenningsen S, et al. External fixation versus percutaneous pinning for unstable Colles fracture. Equal outcome in a randomized study of 60 patients. Acta Orthop Scand 1997;68: [41] Neumann K, Clarius M, Gutsfeld P. External fixation or percutaneous pin fixation in distal intraarticular radius fractures in elderly patients. Langenbecks Archiv fur Chirurgie 1996; 113(Suppl 2): [42] Hahnloser D, Platz A, Amgwerd M, et al. Internal fixation of distal radius fractures with dorsal dislocation: pi-plate or two 1/4 tube plates? A prospective randomized study. J Trauma 1999; 47: [43] Doi K, Hattori Y, Otsuka K, et al. Intra-articular fractures of the distal aspect of the radius: arthroscopically assisted reduction compared with open reduction and internal fixation. J Bone Joint Surg Am 1999;81: [44] Adolfsson L, Jo rgsholm P. Arthroscopicallyassisted reduction of intra-articular fractures of the distal radius. J Hand Surg [Br] 1998;23: [45] Geissler WB, Freeland AE. Arthroscopically assisted reduction of intraarticular distal radial fractures. Clin Orthop 1996; [46] Mehta JA, Bain GI, Heptinstall RJ. Anatomical reduction of intra-articular fractures of the distal radius. An arthroscopically-assisted approach. J Bone Joint Surg Br 2000;82: [47] Wolfe SW, Easterling KJ, Yoo HH. Arthroscopicassisted reduction of distal radius fractures. Arthroscopy 1995;11: [48] Lindau T. The role of wrist arthroscopy in distal radial fractures. Atlas of the Hand Clinics 2001;6: [49] Lindau T. Wrist arthroscopy in distal radial fractures with a modified horizontal technique. Arthroscopy 2001;e5:1 6. [50] Lindau T. Distal radial fractures and effects of associated ligament injuries [thesis]. Lund (Sweden): University of Lund; [51] Lindau T, Aspenberg P, Adlercreutz C, et al. Instability of the distal radioulnar joint is an independent worsening factor after distal radial fractures. Clin Orthop 2000;375: [52] Fellinger M, Peicha G, Seibert FJ, et al. Radial avulsion of the triangular fibrocartilage complex in acute wrist trauma: a new technique for arthroscopic repair. Arthroscopy 1997;13: [53] Sagerman SD, Short W. Arthroscopic repair of radial-sided triangular fibrocartilage complex tears. Arthroscopy 1996;12: [54] Stewart HD, Innes AR, Burke FD. Factors affecting the outcome of Colles fractures: an anatomical and functional study. Injury 1985;16: [55] Andersen DJ, Blair WF, Steyers CM, et al. Classification of distal radius fractures: an analysis of interobserver reliability and intraobserver reproducibility. J Hand Surg 1996;21A: [56] Aro HT, Koivonen T. Minor acts of shortening of the radius affects the outcome of Colles fracture treatment. J Hand Surg 1991;16A: [57] af Ekenstam F, Jacobsson OP, Wadin K. Repair of the triangular ligament in Colles fracture. No effect in a prospective randomized study. Acta Orthop Scand 1989;60: [58] Tsukazaki T, Iwasaki K. Ulnar wrist pain after Colles fracture. 109 fractures followed for 4 years. Acta Orthop Scand 1993;64: [59] Fernandez DL. Correction of posttraumatic wrist deformity in adults by osteotomy, bone grafting and internal fixation. J Bone Joint Surg 1982;64A: [60] Geissler W, Fernandez D, Lamey D. Distal radioulnar joint injuries associated with fracture of the distal radius. Clin Orthop 1996;327: [61] Kapandji IA. The Kapandji-Sauve operation. Its techniques and indications in non rheumatoid diseases. Ann Chir Main 1986;5: [62] Mikkelsen SS, Lindblad BE, Larsen ER, et al. Sauve-Kapandji operation for disorders of the distal radioulnar joint after Colles fracture. Good results in 12 patients followed for years. Acta Orthop Scand 1997;68:64 6. [63] Preisser P, Buck-Gramcko D, Hess J. Distal radio-ulnar arthrodesis and Kapandji ulna segment resection in treatment of limited forearm rotation. Handchir Mikrochir Plast Chir 1991;23: [64] Zilch H, Kauschke T. Kapandji corrective operation of post-traumatic disorder of the distal radio-ulnar joint. Unfallchirurg 1996;99: [65] Imbriglia JE, Matthews D. Treatment of chronic post-traumatic dorsal subluxation of the distal ulna by hemiresection-interposition arthroplasty. J Hand Surg 1993;18:
9 INJURIES TO THE ULNAR SIDE OF THE WRIST 425 [66] Osterman AL, Bora FW, Maitin E. Arthroscopic débridement of the triangular fibrocartilage complex tears. Arthroscopy 1990;6: [67] Hove LM, Molster AO. Surgery for posttraumatic wrist deformity. Radial osteotomy and/or ulnar shortening in 16 Colles fractures. Acta Orthop Scand 1994;65: [68] Posner MA, Ambrose L. Malunited Colles fractures: correction with a biplanar closing wedge osteotomy. J Hand Surg [Am] 1991;16: [69] Adams BD. Anatomic reconstruction of the distal radioulnar ligaments for DRUJ instability. Tech Hand Upper Extrem Surg 2000;4:
INJURIES OF THE HAND AND WRIST By Derya Dincer, M.D.
 05/05/2007 INJURIES OF THE HAND AND WRIST By Derya Dincer, M.D. Hand injuries, especially the fractures of metacarpals and phalanges, are the most common fractures in the skeletal system. Hand injuries
05/05/2007 INJURIES OF THE HAND AND WRIST By Derya Dincer, M.D. Hand injuries, especially the fractures of metacarpals and phalanges, are the most common fractures in the skeletal system. Hand injuries
ASSOCIATED LESIONS COMPLICATIONS OSTEOARTICULAR COMPLICATIONS
 Corrective Osteotomy of Distal Radius Malunion---New Horizons I certify that, to the best of my knowledge, no aspect of my current personal or profession situation might reasonably be expected to affect
Corrective Osteotomy of Distal Radius Malunion---New Horizons I certify that, to the best of my knowledge, no aspect of my current personal or profession situation might reasonably be expected to affect
Distal Radius Fractures. Lee W Hash, MD Affinity Orthopedics and Sports Medicine
 Distal Radius Fractures Lee W Hash, MD Affinity Orthopedics and Sports Medicine The Problem of Distal Radius Fractures Common injury: >450,000/yr. in USA High potential for functional impairment and frequent
Distal Radius Fractures Lee W Hash, MD Affinity Orthopedics and Sports Medicine The Problem of Distal Radius Fractures Common injury: >450,000/yr. in USA High potential for functional impairment and frequent
Ulnar sided Wrist Pain
 Ulnar sided Wrist Pain 1 Susan Cross, 1 Anshul Rastogi, 2 Brian Cohen, 1 Rosy Jalan 1 Dept of Radiology, Barts Health NHS Trust, London, UK 2 London Orthopaedic Centre Contact: susan.cross@bartshealth.nhs.uk
Ulnar sided Wrist Pain 1 Susan Cross, 1 Anshul Rastogi, 2 Brian Cohen, 1 Rosy Jalan 1 Dept of Radiology, Barts Health NHS Trust, London, UK 2 London Orthopaedic Centre Contact: susan.cross@bartshealth.nhs.uk
Fractures around wrist
 Fractures around wrist Colles Fracture Smiths fracture Barton s fracture Chauffer s fracture Scaphoid fracture Lunate dislocation Vivek Pandey Colles fracture Definition: Fracture of the distal end radius
Fractures around wrist Colles Fracture Smiths fracture Barton s fracture Chauffer s fracture Scaphoid fracture Lunate dislocation Vivek Pandey Colles fracture Definition: Fracture of the distal end radius
IFSSH Scientific Committee on Bone and Joint Injuries: Distal Radioulnar Joint Instability
 IFSSH Scientific Committee on Bone and Joint Injuries: Distal Radioulnar Joint Instability Chair: Goo Hyun Baek (Korea) Committee: Hiroyuki Kato (Japan) Leszek Romanowski (Romania) Report submitted November
IFSSH Scientific Committee on Bone and Joint Injuries: Distal Radioulnar Joint Instability Chair: Goo Hyun Baek (Korea) Committee: Hiroyuki Kato (Japan) Leszek Romanowski (Romania) Report submitted November
Systemic condition affecting synovial tissue Hypertrohied synovium destroys. Synovectomy. Tenosynovectomy Tendon Surgery Arthroplasty Arthrodesis
 Surgical Options for Rheumatoid Arthritis of the Wrist Raj Bhatia Consultant Hand & Orthopaedic Surgeon Bristol Royal Infirmary & Avon Orthopaedic Centre Rheumatoid Arthritis Systemic condition affecting
Surgical Options for Rheumatoid Arthritis of the Wrist Raj Bhatia Consultant Hand & Orthopaedic Surgeon Bristol Royal Infirmary & Avon Orthopaedic Centre Rheumatoid Arthritis Systemic condition affecting
Arthroscopy of the Hand and Wrist
 Arthroscopy of the Hand and Wrist Arthroscopy is a minimally invasive procedure whereby a small camera is inserted through small incisions of a few millimeters each around a joint to view the joint directly.
Arthroscopy of the Hand and Wrist Arthroscopy is a minimally invasive procedure whereby a small camera is inserted through small incisions of a few millimeters each around a joint to view the joint directly.
Stable fixation of fractures of the distal radius can
 Fractures of the distal radius treated by internal fixation and early function A PROSPECTIVE STUDY OF 73 CONSECUTIVE PATIENTS M. Jakob, D. A. Rikli, P. Regazzoni From the Kantonsspital, Aarau, Switzerland
Fractures of the distal radius treated by internal fixation and early function A PROSPECTIVE STUDY OF 73 CONSECUTIVE PATIENTS M. Jakob, D. A. Rikli, P. Regazzoni From the Kantonsspital, Aarau, Switzerland
11/18/2009. day 1. 6 weeks
 11/18/2009 from Fractures of the Distal Radius : a practical approach to management DL Fernandez and JB Jupiter, Springer, New York, 1995 SGH, Biel, 2009 FRACTURES OF THE DISTAL RADIUS: do we still indicate
11/18/2009 from Fractures of the Distal Radius : a practical approach to management DL Fernandez and JB Jupiter, Springer, New York, 1995 SGH, Biel, 2009 FRACTURES OF THE DISTAL RADIUS: do we still indicate
Most active and intricate part of the upper extremity Especially vulnerable to injury Do not respond well to serious trauma. Magee, 2008. pg.
 PTA 216 Most active and intricate part of the upper extremity Especially vulnerable to injury Do not respond well to serious trauma Magee, 2008. pg. 396 28 bones Numerous articulations 19 intrinsic muscles
PTA 216 Most active and intricate part of the upper extremity Especially vulnerable to injury Do not respond well to serious trauma Magee, 2008. pg. 396 28 bones Numerous articulations 19 intrinsic muscles
EXTENSOR CARPI ULNARIS TENDINOPATHY. Amanda Cooper
 EXTENSOR CARPI ULNARIS TENDINOPATHY Amanda Cooper OVERVIEW Anatomy Biomechanics Injury Pathology Assessment Treatment Anatomy Origin: Middle third of the posterior border of ulna Lateral epicondyle of
EXTENSOR CARPI ULNARIS TENDINOPATHY Amanda Cooper OVERVIEW Anatomy Biomechanics Injury Pathology Assessment Treatment Anatomy Origin: Middle third of the posterior border of ulna Lateral epicondyle of
The distal radioulnar joint in rheumatoid arthritis
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2006, 72, 381-386 REVIEW ARTICLE The distal radioulnar joint in rheumatoid arthritis Luc DE SMET From the University Hospital Pellenberg, Pellenberg, Belgium Rheumatoid arthritis (RA)
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2006, 72, 381-386 REVIEW ARTICLE The distal radioulnar joint in rheumatoid arthritis Luc DE SMET From the University Hospital Pellenberg, Pellenberg, Belgium Rheumatoid arthritis (RA)
WRIST EXAMINATION. Look. Feel. Move. Special Tests
 WRIST EXAMINATION Look o Dorsum, side, palmar- palmar flex wrist to exacerbate dorsal swellings o Deformity e.g. radial deviation after colles, prominent ulna o Swellings e.g. ganglion o Scars, muscle
WRIST EXAMINATION Look o Dorsum, side, palmar- palmar flex wrist to exacerbate dorsal swellings o Deformity e.g. radial deviation after colles, prominent ulna o Swellings e.g. ganglion o Scars, muscle
Wrist Fractures. Wrist Injuries/Pain. Upper Extremity Care in an Aging Population. Objectives. Jon J. Cherney, M.D. Fractures of the Distal Radius
 Upper Extremity Care in an Aging Population Hand and Upper Extremity Center of Northeast Wisconsin, Ltd. Symposium February 24, 2012 1 2 Objectives Wrist Injuries/Pain by Jon J. Cherney, M.D. Anatomy History/Evaluation
Upper Extremity Care in an Aging Population Hand and Upper Extremity Center of Northeast Wisconsin, Ltd. Symposium February 24, 2012 1 2 Objectives Wrist Injuries/Pain by Jon J. Cherney, M.D. Anatomy History/Evaluation
Wrist Fractures. Wrist Defined: Carpal Bones Distal Radius Distal Ulna
 Wrist Fractures Wrist Fractures Wrist Defined: Carpal Bones Distal Radius Distal Ulna Wrist Fractures Wrist Joints: CMC Intercarpal Radiocarpal DRUJ drudge Wrist Fractures Wrist Fractures: (that we are
Wrist Fractures Wrist Fractures Wrist Defined: Carpal Bones Distal Radius Distal Ulna Wrist Fractures Wrist Joints: CMC Intercarpal Radiocarpal DRUJ drudge Wrist Fractures Wrist Fractures: (that we are
Wrist and Hand. Patient Information Guide to Bone Fracture, Bone Reconstruction and Bone Fusion: Fractures of the Wrist and Hand: Carpal bones
 Patient Information Guide to Bone Fracture, Bone Reconstruction and Bone Fusion: Wrist and Hand Fractures of the Wrist and Hand: Fractures of the wrist The wrist joint is made up of the two bones in your
Patient Information Guide to Bone Fracture, Bone Reconstruction and Bone Fusion: Wrist and Hand Fractures of the Wrist and Hand: Fractures of the wrist The wrist joint is made up of the two bones in your
CLOSED REDUCTION AND PERCUTANEOUS KIRSCHNER WIRE FIXATION OF DISPLACED COLLES FRACTURE IN ADULTS
 Original Article CLOSED REDUCTION AND PERCUTANEOUS KIRSCHNER WIRE FIXATION OF DISPLACED COLLES FRACTURE IN ADULTS M. AKHTER BAIG, KASHIF AHMED, S. MUJAHID HUMAIL Department of Orthopaedics (Unit I), Dow
Original Article CLOSED REDUCTION AND PERCUTANEOUS KIRSCHNER WIRE FIXATION OF DISPLACED COLLES FRACTURE IN ADULTS M. AKHTER BAIG, KASHIF AHMED, S. MUJAHID HUMAIL Department of Orthopaedics (Unit I), Dow
Wrist Fractures: What the Clinician Wants to Know 1
 What the Clinician Wants to Know Charles A. Goldfarb, MD Yuming Yin, MD Louis A. Gilula, MD Andrew J. Fisher, MD Martin I. Boyer, MD Index terms: Bones, CT, 43.1211 Wrist, fractures, 43.41 Wrist, MR, 43.12141,
What the Clinician Wants to Know Charles A. Goldfarb, MD Yuming Yin, MD Louis A. Gilula, MD Andrew J. Fisher, MD Martin I. Boyer, MD Index terms: Bones, CT, 43.1211 Wrist, fractures, 43.41 Wrist, MR, 43.12141,
Pediatric Sports Injuries of the Wrist and Hand. Sunni Alford, OTR/L,CHT Preferred Physical Therapy
 Pediatric Sports Injuries of the Wrist and Hand Sunni Alford, OTR/L,CHT Preferred Physical Therapy Wrist injuries TFCC ECU/ FCU tendonitis Instability Growth Plate Fractures Ulnar abutment syndrome Triangular
Pediatric Sports Injuries of the Wrist and Hand Sunni Alford, OTR/L,CHT Preferred Physical Therapy Wrist injuries TFCC ECU/ FCU tendonitis Instability Growth Plate Fractures Ulnar abutment syndrome Triangular
9 DISTAL RADIUS AND ULNA FRACTURES
 9: DISTAL RADIUS AND ULNA FRACTURES Rockwood and Wilkins Fractures in Children 9 DISTAL RADIUS AND ULNA FRACTURES PETER M. WATERS Classification Anatomy Physeal Injuries Diagnosis Treatment Options Complications
9: DISTAL RADIUS AND ULNA FRACTURES Rockwood and Wilkins Fractures in Children 9 DISTAL RADIUS AND ULNA FRACTURES PETER M. WATERS Classification Anatomy Physeal Injuries Diagnosis Treatment Options Complications
Scaphoid Non-union. Dr. Mandel Dr. Gyomorey. May 3 rd 2006
 Scaphoid Non-union Dr. Mandel Dr. Gyomorey May 3 rd 2006 Introduction Scaphoid fracture incidence: 8-38/100,000 Non-union 5% (0-22%) Adams and Leonard (1928) first described operative treatment of the
Scaphoid Non-union Dr. Mandel Dr. Gyomorey May 3 rd 2006 Introduction Scaphoid fracture incidence: 8-38/100,000 Non-union 5% (0-22%) Adams and Leonard (1928) first described operative treatment of the
Common wrist injuries in sport. Chris Milne Sports Physician Hamilton,NZ
 Common wrist injuries in sport Chris Milne Sports Physician Hamilton,NZ Overview / Classification Acute injuries Simple - wrist sprain Not so simple 1 - Fracture of distal radius/ulna 2 - Scaphoid fracture
Common wrist injuries in sport Chris Milne Sports Physician Hamilton,NZ Overview / Classification Acute injuries Simple - wrist sprain Not so simple 1 - Fracture of distal radius/ulna 2 - Scaphoid fracture
RADIOGRAPHIC EVALUATION
 Jeff Husband MD Objectives Evaluate, diagnose and manage common wrist injuries due to high energy trauma in athletes Appropriately use radiographs, CT scans and MRI Know when to refer patients for additional
Jeff Husband MD Objectives Evaluate, diagnose and manage common wrist injuries due to high energy trauma in athletes Appropriately use radiographs, CT scans and MRI Know when to refer patients for additional
Intercarpal Ligament Injuries Associated with Fractures of the Distal Part of the Radius
 This is an enhanced PDF from The Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery The PDF of the article you requested follows this cover page. Intercarpal Ligament Injuries Associated with Fractures of the Distal Part
This is an enhanced PDF from The Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery The PDF of the article you requested follows this cover page. Intercarpal Ligament Injuries Associated with Fractures of the Distal Part
At the completion of the rotation, the resident will have acquired the following competencies and will function effectively as:
 Goals and Objectives Orthopedic Surgery Residency Program - Memorial University Plastic Surgery DEFINITION Traumatic or acquired problems of the musculoskeletal system frequently have a soft tissue component
Goals and Objectives Orthopedic Surgery Residency Program - Memorial University Plastic Surgery DEFINITION Traumatic or acquired problems of the musculoskeletal system frequently have a soft tissue component
.org. Distal Radius Fracture (Broken Wrist) Description. Cause
 Distal Radius Fracture (Broken Wrist) Page ( 1 ) The radius is the larger of the two bones of the forearm. The end toward the wrist is called the distal end. A fracture of the distal radius occurs when
Distal Radius Fracture (Broken Wrist) Page ( 1 ) The radius is the larger of the two bones of the forearm. The end toward the wrist is called the distal end. A fracture of the distal radius occurs when
Treatment of intra-articular fractures of the distal radius
 Treatment of intra-articular fractures of the distal radius FLUOROSCOPIC OR ARTHROSCOPIC REDUCTION? S. E. Varitimidis, G. K. Basdekis, Z. H. Dailiana, M. E. Hantes, K. Bargiotas, K. Malizos From the University
Treatment of intra-articular fractures of the distal radius FLUOROSCOPIC OR ARTHROSCOPIC REDUCTION? S. E. Varitimidis, G. K. Basdekis, Z. H. Dailiana, M. E. Hantes, K. Bargiotas, K. Malizos From the University
Wrist and Hand Injuries Keep Your Edge: Hockey Sports Medicine 2015 Toronto, Canada August 28-30
 Wrist and Hand Injuries Keep Your Edge: Hockey Sports Medicine 2015 Toronto, Canada August 28-30 Steven E. Rokito, MD Division Chief, Sports Medicine, NSLIJ Associate team orthopedist NY Islanders Wrist
Wrist and Hand Injuries Keep Your Edge: Hockey Sports Medicine 2015 Toronto, Canada August 28-30 Steven E. Rokito, MD Division Chief, Sports Medicine, NSLIJ Associate team orthopedist NY Islanders Wrist
Posttraumatic medial ankle instability
 Posttraumatic medial ankle instability Alexej Barg, Markus Knupp, Beat Hintermann Orthopaedic Department University Hospital of Basel, Switzerland Clinic of Orthopaedic Surgery, Kantonsspital Baselland
Posttraumatic medial ankle instability Alexej Barg, Markus Knupp, Beat Hintermann Orthopaedic Department University Hospital of Basel, Switzerland Clinic of Orthopaedic Surgery, Kantonsspital Baselland
Malleolar fractures Anna Ekman, Lena Brauer
 Malleolar fractures Anna Ekman, Lena Brauer How to use this handout? The left column is the information as given during the lecture. The column at the right gives you space to make personal notes. Learning
Malleolar fractures Anna Ekman, Lena Brauer How to use this handout? The left column is the information as given during the lecture. The column at the right gives you space to make personal notes. Learning
Standard Terminology Wrist Disorders
 Standard Terminology Wrist Disorders Gregory I Bain, Luigi Pederzini, Gary Poehling Corresponding Author Ass Prof G.I.Bain University of Adelaide, Australia www.gregbain.com.au 1. Introduction The aim
Standard Terminology Wrist Disorders Gregory I Bain, Luigi Pederzini, Gary Poehling Corresponding Author Ass Prof G.I.Bain University of Adelaide, Australia www.gregbain.com.au 1. Introduction The aim
Anatomic Percutaneous Ankle Reconstruction of Lateral Ligaments (A Percutaneous Anti ROLL)
 Anatomic Percutaneous Ankle Reconstruction of Lateral Ligaments (A Percutaneous Anti ROLL) Mark Glazebrook James Stone Masato Takao Stephane Guillo Introduction Ankle stabilization is required when a patient
Anatomic Percutaneous Ankle Reconstruction of Lateral Ligaments (A Percutaneous Anti ROLL) Mark Glazebrook James Stone Masato Takao Stephane Guillo Introduction Ankle stabilization is required when a patient
Abdominal Pedicle Flaps To The Hand And Forearm John C. Kelleher M.D., F.A.C.S.
 Abdominal Pedicle Flaps To The Hand And Forearm John C. Kelleher M.D., F.A.C.S. Global-HELP Publications Chapter Eight: TECHNICAL REQUIREMENTS FOR FORMATION OF A TUBED PEDICLE FLAP Creating a tube pedicle
Abdominal Pedicle Flaps To The Hand And Forearm John C. Kelleher M.D., F.A.C.S. Global-HELP Publications Chapter Eight: TECHNICAL REQUIREMENTS FOR FORMATION OF A TUBED PEDICLE FLAP Creating a tube pedicle
How To Fix A Radial Head Plate
 Mayo Clinic CoNGRUENT RADIAL HEAD PLATE Since 1988 Acumed has been designing solutions to the demanding situations facing orthopedic surgeons, hospitals and their patients. Our strategy has been to know
Mayo Clinic CoNGRUENT RADIAL HEAD PLATE Since 1988 Acumed has been designing solutions to the demanding situations facing orthopedic surgeons, hospitals and their patients. Our strategy has been to know
Operative Treatment of Intra-articular Distal Radius Fractures Using the Small AO External Fixation Device
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Operative Treatment of Intra-articular Distal Radius Fractures Using the Small AO External Fixation Device Teng-Le Huang 1,2 *, Ching-Kuei Huang 2,3, Jung-Kuang Yu 2,3, Fang-Yao Chiu 2,3,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Operative Treatment of Intra-articular Distal Radius Fractures Using the Small AO External Fixation Device Teng-Le Huang 1,2 *, Ching-Kuei Huang 2,3, Jung-Kuang Yu 2,3, Fang-Yao Chiu 2,3,
Citation International Orthopaedics, 2011, v. 35 n. 3, p. 389-394. Creative Commons: Attribution 3.0 Hong Kong License
 Title Operative treatment of distal radial fractures with locking plate system - A prospective study Author(s) Kwan, KYH; Lau, TW; Leung, F Citation International Orthopaedics, 2011, v. 35 n. 3, p. 389-394
Title Operative treatment of distal radial fractures with locking plate system - A prospective study Author(s) Kwan, KYH; Lau, TW; Leung, F Citation International Orthopaedics, 2011, v. 35 n. 3, p. 389-394
SHOULDER INSTABILITY. E. Edward Khalfayan, MD
 SHOULDER INSTABILITY E. Edward Khalfayan, MD Instability of the shoulder can occur from a single injury or as the result of repetitive activity such as overhead sports. Dislocations of the shoulder are
SHOULDER INSTABILITY E. Edward Khalfayan, MD Instability of the shoulder can occur from a single injury or as the result of repetitive activity such as overhead sports. Dislocations of the shoulder are
THE WRIST. At a glance. 1. Introduction
 THE WRIST At a glance The wrist is possibly the most important of all joints in everyday and professional life. It is under strain not only in many blue collar trades, but also in sports and is therefore
THE WRIST At a glance The wrist is possibly the most important of all joints in everyday and professional life. It is under strain not only in many blue collar trades, but also in sports and is therefore
Volar Fixation for Dorsally Displaced Fractures of the Distal Radius: A Preliminary Report
 Volar Fixation for Dorsally Displaced Fractures of the Distal Radius: A Preliminary Report Jorge L. Orbay, MD, Miami, FL, Diego L. Fernandez, MD, Berne, Switzerland Using a volar approach to avoid the
Volar Fixation for Dorsally Displaced Fractures of the Distal Radius: A Preliminary Report Jorge L. Orbay, MD, Miami, FL, Diego L. Fernandez, MD, Berne, Switzerland Using a volar approach to avoid the
Bankart Repair using the Smith & Nephew BIORAPTOR 2.9 Suture Anchor
 Shoulder Series Technique Guide *smith&nephew BIORAPTOR 2.9 Suture Anchor Bankart Repair using the Smith & Nephew BIORAPTOR 2.9 Suture Anchor Gary M. Gartsman, M.D. Introduction Arthroscopic studies of
Shoulder Series Technique Guide *smith&nephew BIORAPTOR 2.9 Suture Anchor Bankart Repair using the Smith & Nephew BIORAPTOR 2.9 Suture Anchor Gary M. Gartsman, M.D. Introduction Arthroscopic studies of
Acute Scapholunate and Lunotriquetral Dissociation
 CHAPTER 10 Acute Scapholunate and Lunotriquetral Dissociation Craig M. Rodner, MD Arnold-Peter C. Weiss, MD INTRODUCTION: The scapholunate (SL) and lunotriquetral (LT) ligaments are interosseous carpal
CHAPTER 10 Acute Scapholunate and Lunotriquetral Dissociation Craig M. Rodner, MD Arnold-Peter C. Weiss, MD INTRODUCTION: The scapholunate (SL) and lunotriquetral (LT) ligaments are interosseous carpal
IFSSH Scientific Committee on. Wrist Biomechanics and Instability
 IFSSH Scientific Committee on Wrist Biomechanics and Instability Chair: Hisao Moritomo (Japan) Committee: Emmanuel Apergis (Greece) Guillaume Herzberg (France) Scott Wolfe (USA) Jose Maria Rotella (Argentina)
IFSSH Scientific Committee on Wrist Biomechanics and Instability Chair: Hisao Moritomo (Japan) Committee: Emmanuel Apergis (Greece) Guillaume Herzberg (France) Scott Wolfe (USA) Jose Maria Rotella (Argentina)
Radial Head Fracture Repair and Rehabilitation
 1 Radial Head Fracture Repair and Rehabilitation Surgical Indications and Considerations Anatomical Considerations: The elbow is a complex joint due to its intricate functional anatomy. The ulna, radius
1 Radial Head Fracture Repair and Rehabilitation Surgical Indications and Considerations Anatomical Considerations: The elbow is a complex joint due to its intricate functional anatomy. The ulna, radius
Distal Radio-Ulnar Joint Instability. Literature Review. And. Case Studies
 Distal Radio-Ulnar Joint Instability Literature Review And Case Studies Email: ShorelinePT@aol.com PO Box 88 East Lyme CT 06333 Phone: 860/739-4497 Fax: 860/739-7256 By Joanne Moore, MS, PT, OCS, MTC In
Distal Radio-Ulnar Joint Instability Literature Review And Case Studies Email: ShorelinePT@aol.com PO Box 88 East Lyme CT 06333 Phone: 860/739-4497 Fax: 860/739-7256 By Joanne Moore, MS, PT, OCS, MTC In
Elbow Injuries and Disorders
 Elbow Injuries and Disorders Introduction Your elbow joint is made up of bone, cartilage, ligaments and fluid. Muscles and tendons help the elbow joint move. There are many injuries and disorders that
Elbow Injuries and Disorders Introduction Your elbow joint is made up of bone, cartilage, ligaments and fluid. Muscles and tendons help the elbow joint move. There are many injuries and disorders that
Malunions of the Distal Radius
 12 Malunions of the Distal Radius Sameer J. Lodha, MD Robert W. Wysocki, MD Mark S. Cohen, MD Fractures of the distal radius are common injuries, comprising approximately 8% to 17% of fractures seen in
12 Malunions of the Distal Radius Sameer J. Lodha, MD Robert W. Wysocki, MD Mark S. Cohen, MD Fractures of the distal radius are common injuries, comprising approximately 8% to 17% of fractures seen in
Arthroscopic Shoulder Procedures. David C. Neuschwander MD. Shoulder Instability. Allegheny Health Network Orthopedic Associates of Pittsburgh
 Arthroscopic Shoulder Procedures David C. Neuschwander MD Allegheny Health Network Orthopedic Associates of Pittsburgh Shoulder Instability Anterior Instability Posterior Instability Glenohumeral Joint
Arthroscopic Shoulder Procedures David C. Neuschwander MD Allegheny Health Network Orthopedic Associates of Pittsburgh Shoulder Instability Anterior Instability Posterior Instability Glenohumeral Joint
Fracture of the distal radius is one of the most common
 112 Complications of Distal Radius Fracture Fixation Vipul P. Patel, M.D., and Nader Paksima, D.O., M.P.H. Fracture of the distal radius is one of the most common injuries in orthopaedics, accounting for
112 Complications of Distal Radius Fracture Fixation Vipul P. Patel, M.D., and Nader Paksima, D.O., M.P.H. Fracture of the distal radius is one of the most common injuries in orthopaedics, accounting for
SOME COMPLICATIONS OF COLLES' FRACTURE AND THEIR TREATMENT
 627 SOME COMPLICATIONS OF COLLES' FRACTURE AND THEIR TREATMENT By W. H. STEPHENSON, F.R.C.S. From the Department of Surgery, Postgraduate Medical School of London, Hammersmith Hospital Though Colles' fracture
627 SOME COMPLICATIONS OF COLLES' FRACTURE AND THEIR TREATMENT By W. H. STEPHENSON, F.R.C.S. From the Department of Surgery, Postgraduate Medical School of London, Hammersmith Hospital Though Colles' fracture
ASSOCIATE PROFESSOR BO POVLSEN Emeritus Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon Guy s & St Thomas Hospitals NHS Trust GMC no. 3579329
 ASSOCIATE PROFESSOR BO POVLSEN Emeritus Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon Guy s & St Thomas Hospitals NHS Trust GMC no. 3579329 Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon London Bridge Hospital Medico-Legal Secretary:
ASSOCIATE PROFESSOR BO POVLSEN Emeritus Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon Guy s & St Thomas Hospitals NHS Trust GMC no. 3579329 Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon London Bridge Hospital Medico-Legal Secretary:
Hand and Upper Extremity Injuries in Outdoor Activities. John A. Schneider, M.D.
 Hand and Upper Extremity Injuries in Outdoor Activities John A. Schneider, M.D. Biographical Sketch Dr. Schneider is an orthopedic surgeon that specializes in the treatment of hand and upper extremity
Hand and Upper Extremity Injuries in Outdoor Activities John A. Schneider, M.D. Biographical Sketch Dr. Schneider is an orthopedic surgeon that specializes in the treatment of hand and upper extremity
Semmelweis University Department of Traumatology Dr. Gál Tamás
 Semmelweis University Department of Traumatology Dr. Gál Tamás Anatomy Ankle injuries DIRECT INDIRECT Vertical Compression (Tibia plafond Pilon) AO 43-A,B,C Suppination (adduction + inversion) AO 44-A
Semmelweis University Department of Traumatology Dr. Gál Tamás Anatomy Ankle injuries DIRECT INDIRECT Vertical Compression (Tibia plafond Pilon) AO 43-A,B,C Suppination (adduction + inversion) AO 44-A
Adult Forearm Fractures
 Adult Forearm Fractures Your forearm is made up of two bones, the radius and ulna. In most cases of adult forearm fractures, both bones are broken. Fractures of the forearm can occur near the wrist at
Adult Forearm Fractures Your forearm is made up of two bones, the radius and ulna. In most cases of adult forearm fractures, both bones are broken. Fractures of the forearm can occur near the wrist at
There are several different causes, both idiopathic
 REVIEW ARTICLE Osteoarthritis of the Wrist Krista E. Weiss, Craig M. Rodner, MD From Harvard College, Cambridge, MA and Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, University of Connecticut Health Center, Farmington,
REVIEW ARTICLE Osteoarthritis of the Wrist Krista E. Weiss, Craig M. Rodner, MD From Harvard College, Cambridge, MA and Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, University of Connecticut Health Center, Farmington,
Syndesmosis Injuries
 Syndesmosis Injuries Dr. Alex Rabinovich Outline Anatomy Injury types and classification Treatment options Nonoperative vs. Operative Indications for operative Operative technique Postoperative management
Syndesmosis Injuries Dr. Alex Rabinovich Outline Anatomy Injury types and classification Treatment options Nonoperative vs. Operative Indications for operative Operative technique Postoperative management
.org. Rotator Cuff Tears: Surgical Treatment Options. When Rotator Cuff Surgery is Recommended. Surgical Repair Options
 Rotator Cuff Tears: Surgical Treatment Options Page ( 1 ) The following article provides in-depth information about surgical treatment for rotator cuff injuries, and is a continuation of the article Rotator
Rotator Cuff Tears: Surgical Treatment Options Page ( 1 ) The following article provides in-depth information about surgical treatment for rotator cuff injuries, and is a continuation of the article Rotator
NOW PLAYING THE WRIST. David Costa, OTR/L October 20, 2007
 NOW PLAYING THE WRIST David Costa, OTR/L October 20, 2007 Starring Radius Ulna Scaphoid Lunate Triquetrum Trapezium Trapezoid Capitate Hamate Pisiform TFCC Transverse Carpal Ligament Scapholunate Ligament
NOW PLAYING THE WRIST David Costa, OTR/L October 20, 2007 Starring Radius Ulna Scaphoid Lunate Triquetrum Trapezium Trapezoid Capitate Hamate Pisiform TFCC Transverse Carpal Ligament Scapholunate Ligament
Elbow, Forearm, Wrist, & Hand. Bony Anatomy. Objectives. Bones. Bones. Bones
 Objectives Elbow, Forearm, Wrist, & Hand Chapter 19 Identify and discuss the functional anatomy of the elbow and forearm Discuss the common injuries associated with these anatomical structures Bones Humerus
Objectives Elbow, Forearm, Wrist, & Hand Chapter 19 Identify and discuss the functional anatomy of the elbow and forearm Discuss the common injuries associated with these anatomical structures Bones Humerus
Scaphoid Fracture of the Wrist
 Page 1 of 6 Scaphoid Fracture of the Wrist Doctors commonly diagnose a sprained wrist after a patient falls on an outstretched hand. However, if pain and swelling don't go away, doctors become suspicious
Page 1 of 6 Scaphoid Fracture of the Wrist Doctors commonly diagnose a sprained wrist after a patient falls on an outstretched hand. However, if pain and swelling don't go away, doctors become suspicious
The Emergent Evaluation and Treatment of Hand and Wrist Injuries
 The Emergent Evaluation and Treatment of Hand and Wrist Injuries Michael K. Abraham, MD, MS a,b, *, Sara Scott, MD a,c KEYWORDS Hand and wrist injuries Emergency physician Emergent evaluation Treatment
The Emergent Evaluation and Treatment of Hand and Wrist Injuries Michael K. Abraham, MD, MS a,b, *, Sara Scott, MD a,c KEYWORDS Hand and wrist injuries Emergency physician Emergent evaluation Treatment
Recognition and Management of Triangular Fibrocartilage Complex Injury
 INJURY EVALUATION AND MANAGEMENT Recognition and Management of Triangular Fibrocartilage Complex Injury Gary E. McIlvain, EdD, LAT, ATC; Neil A. Evans, PT, DPT, OCS, CSCS; and Suzanne M. Konz, PhD, ATC,
INJURY EVALUATION AND MANAGEMENT Recognition and Management of Triangular Fibrocartilage Complex Injury Gary E. McIlvain, EdD, LAT, ATC; Neil A. Evans, PT, DPT, OCS, CSCS; and Suzanne M. Konz, PhD, ATC,
Rotator Cuff Tears in Football
 Disclosures Rotator Cuff Tears in Football Roger Ostrander, MD Consultant: Mitek Consultant: On-Q Research Support: Arthrex Research Support: Breg Research Support: Arthrosurface 2 Anatomy 4 major muscles:
Disclosures Rotator Cuff Tears in Football Roger Ostrander, MD Consultant: Mitek Consultant: On-Q Research Support: Arthrex Research Support: Breg Research Support: Arthrosurface 2 Anatomy 4 major muscles:
Y O U R S U R G E O N S. choice of. implants F O R Y O U R S U R G E R Y
 Y O U R S U R G E O N S choice of implants F O R Y O U R S U R G E R Y Y O U R S U R G E O N S choice of implants F O R Y O U R S U R G E R Y Your Surgeon Has Chosen the C 2 a-taper Acetabular System The
Y O U R S U R G E O N S choice of implants F O R Y O U R S U R G E R Y Y O U R S U R G E O N S choice of implants F O R Y O U R S U R G E R Y Your Surgeon Has Chosen the C 2 a-taper Acetabular System The
A Simplified Approach to Common Shoulder Problems
 A Simplified Approach to Common Shoulder Problems Objectives: Understand the basic categories of common shoulder problems. Understand the common patient symptoms. Understand the basic exam findings. Understand
A Simplified Approach to Common Shoulder Problems Objectives: Understand the basic categories of common shoulder problems. Understand the common patient symptoms. Understand the basic exam findings. Understand
Total Elbow Arthroplasty and Rehabilitation
 Total Elbow Arthroplasty and Rehabilitation Surgical Indications and Considerations Anatomical Considerations: There are three bones and four joint articulations that have a high degree of congruence in
Total Elbow Arthroplasty and Rehabilitation Surgical Indications and Considerations Anatomical Considerations: There are three bones and four joint articulations that have a high degree of congruence in
DIAGNOSING SCAPHOID FRACTURES. Anthony Hewitt
 DIAGNOSING SCAPHOID FRACTURES Anthony Hewitt Introduction Anatomy of the scaphoid Resembles a deformed peanut Articular cartilage covers 80% of the surface It rests in a plane 45 degrees to the longitudinal
DIAGNOSING SCAPHOID FRACTURES Anthony Hewitt Introduction Anatomy of the scaphoid Resembles a deformed peanut Articular cartilage covers 80% of the surface It rests in a plane 45 degrees to the longitudinal
How To Know If You Can Recover From A Knee Injury
 David R. Cooper, M.D. www.thekneecenter.com Wilkes-Barre, Pa. Knee Joint- Anatomy Is not a pure hinge Ligaments are balanced Mechanism of injury determines what structures get damaged Medial meniscus tears
David R. Cooper, M.D. www.thekneecenter.com Wilkes-Barre, Pa. Knee Joint- Anatomy Is not a pure hinge Ligaments are balanced Mechanism of injury determines what structures get damaged Medial meniscus tears
Soft Tissue Complications of Distal Radius Fractures
 Soft Tissue Complications of Distal Radius Fractures Damien I. Davis, MD a, Mark Baratz, MD a,b,c,d,e, * KEYWORDS Distal radius fracture Soft tissue Complications Wrist Distal radius fractures account
Soft Tissue Complications of Distal Radius Fractures Damien I. Davis, MD a, Mark Baratz, MD a,b,c,d,e, * KEYWORDS Distal radius fracture Soft tissue Complications Wrist Distal radius fractures account
The intricate anatomy and compartmentalization of structures
 Radiographic Evaluation of the Wrist: A Vanishing Art Rebecca A. Loredo, MD,* David G. Sorge, MD, Lt. Colonel, and Glenn Garcia, MD The intricate anatomy and compartmentalization of structures in the wrist
Radiographic Evaluation of the Wrist: A Vanishing Art Rebecca A. Loredo, MD,* David G. Sorge, MD, Lt. Colonel, and Glenn Garcia, MD The intricate anatomy and compartmentalization of structures in the wrist
Rehabilitation Guidelines for Knee Arthroscopy
 Rehabilitation Guidelines for Knee Arthroscopy Arthroscopy is a common surgical procedure in which a joint is viewed using a small camera. This technique allows the surgeon to have a clear view of the
Rehabilitation Guidelines for Knee Arthroscopy Arthroscopy is a common surgical procedure in which a joint is viewed using a small camera. This technique allows the surgeon to have a clear view of the
Operative treatment of distal radius fractures
 Operative treatment of distal radius fractures Jarkko Vasenius Dextra Hand Clinic, Helsinki, Finland The incidence of distal radius fractures is increasing together with the average age of population.
Operative treatment of distal radius fractures Jarkko Vasenius Dextra Hand Clinic, Helsinki, Finland The incidence of distal radius fractures is increasing together with the average age of population.
Outcome of distal radius fractures in relation to bone mineral density
 Outcome of distal radius fractures in relation to bone mineral density Nadine HOLLEVOET, René VERDONK The purpose of this study was to determine whether osteoporosis influenced the clinical results of
Outcome of distal radius fractures in relation to bone mineral density Nadine HOLLEVOET, René VERDONK The purpose of this study was to determine whether osteoporosis influenced the clinical results of
Radius and Scaphoid Fractures
 Page 1 of 7 Return to the Table of Contents Site Map Your Account Support About Us Marketplace Offerings: Medscape.com Charts Mobile Logician CBSHealthwatch American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Annual
Page 1 of 7 Return to the Table of Contents Site Map Your Account Support About Us Marketplace Offerings: Medscape.com Charts Mobile Logician CBSHealthwatch American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Annual
Shoulder Arthroscopy
 Copyright 2011 American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Shoulder Arthroscopy Arthroscopy is a procedure that orthopaedic surgeons use to inspect, diagnose, and repair problems inside a joint. The word
Copyright 2011 American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Shoulder Arthroscopy Arthroscopy is a procedure that orthopaedic surgeons use to inspect, diagnose, and repair problems inside a joint. The word
ASOP Exams PO Box 7440 Seminole, FL 33775. The Manual of Fracture Casting & Bracing Exam 80% Passing ID # Name Title. Address. City State Zip.
 The Manual of Fracture Casting & Bracing Exam 80% Passing ID # Name Title Address City State Zip Tel# Email Certification Organization Cert# Mail a copy of your completed exam to: ASOP Exams PO Box 7440
The Manual of Fracture Casting & Bracing Exam 80% Passing ID # Name Title Address City State Zip Tel# Email Certification Organization Cert# Mail a copy of your completed exam to: ASOP Exams PO Box 7440
TOWN CENTER ORTHOPAEDIC ASSOCIATES P.C. Labral Tears
 Labral Tears The shoulder is your body s most flexible joint. It is designed to let the arm move in almost any direction. But this flexibility has a price, making the joint prone to injury. The shoulder
Labral Tears The shoulder is your body s most flexible joint. It is designed to let the arm move in almost any direction. But this flexibility has a price, making the joint prone to injury. The shoulder
Shoulder Instability. Fig 1: Intact labrum and biceps tendon
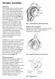 Shoulder Instability What is it? The shoulder joint is a ball and socket joint, with the humeral head (upper arm bone) as the ball and the glenoid as the socket. The glenoid (socket) is a shallow bone
Shoulder Instability What is it? The shoulder joint is a ball and socket joint, with the humeral head (upper arm bone) as the ball and the glenoid as the socket. The glenoid (socket) is a shallow bone
.org. Tennis Elbow (Lateral Epicondylitis) Anatomy. Cause
 Tennis Elbow (Lateral Epicondylitis) Page ( 1 ) Tennis elbow, or lateral epicondylitis, is a painful condition of the elbow caused by overuse. Not surprisingly, playing tennis or other racquet sports can
Tennis Elbow (Lateral Epicondylitis) Page ( 1 ) Tennis elbow, or lateral epicondylitis, is a painful condition of the elbow caused by overuse. Not surprisingly, playing tennis or other racquet sports can
Mini TightRope CMC Surgical Technique
 Mini TightRope CMC Surgical Technique Mini TightRope CMC Mini TightRope CMC Fixation The Mini TightRope provides a unique means to suspend the thumb metacarpal after partial or complete trapezial resection
Mini TightRope CMC Surgical Technique Mini TightRope CMC Mini TightRope CMC Fixation The Mini TightRope provides a unique means to suspend the thumb metacarpal after partial or complete trapezial resection
Elbow Examination. Haroon Majeed
 Elbow Examination Haroon Majeed Key Points Inspection Palpation Movements Neurological Examination Special tests Joints above and below Before Starting Introduce yourself Explain to the patient what the
Elbow Examination Haroon Majeed Key Points Inspection Palpation Movements Neurological Examination Special tests Joints above and below Before Starting Introduce yourself Explain to the patient what the
Wrist Fusion and Back to Work
 Wrist Fusion and Back to Work Marc J. Richard, M.D. Associate Professor Department of Orthopaedic Surgery Durham, North Carolina 42 yo Ironworker, Failed Scope Debridement FUSION ARTHROPLASTY FUSION ARTHROPLASTY
Wrist Fusion and Back to Work Marc J. Richard, M.D. Associate Professor Department of Orthopaedic Surgery Durham, North Carolina 42 yo Ironworker, Failed Scope Debridement FUSION ARTHROPLASTY FUSION ARTHROPLASTY
Wrist Ligaments and Instability
 Wrist Ligaments and Instability The Wrist The wrist or carpus provides a stable support for the hand, allowing for the transmission of grip forces as well as positioning of the hand and digits for fine
Wrist Ligaments and Instability The Wrist The wrist or carpus provides a stable support for the hand, allowing for the transmission of grip forces as well as positioning of the hand and digits for fine
Clarification of Medicare Benefits Schedule rules for the Transport Accident Commission and WorkSafe Victoria
 Clarification of Medicare Benefits Schedule rules for the Transport Accident Commission and WorkSafe Victoria MAY 2013 When paying the reasonable costs of medical services, the TAC and WorkSafe pay in
Clarification of Medicare Benefits Schedule rules for the Transport Accident Commission and WorkSafe Victoria MAY 2013 When paying the reasonable costs of medical services, the TAC and WorkSafe pay in
Technique Guide. 2.4 mm LCP Distal Radius System. A comprehensive plating system to address a variety of fracture patterns.
 Technique Guide 2.4 mm LCP Distal Radius System. A comprehensive plating system to address a variety of fracture patterns. Table of Contents Introduction 2.4 mm LCP Distal Radius System 2 AO Principles
Technique Guide 2.4 mm LCP Distal Radius System. A comprehensive plating system to address a variety of fracture patterns. Table of Contents Introduction 2.4 mm LCP Distal Radius System 2 AO Principles
Chapter 7 The Wrist and Hand Joints
 Chapter 7 The Wrist and Hand Manual of Structural Kinesiology R.T. Floyd, EdD, ATC, CSCS Many Archery, Relate wrist require sports require precise functioning of flexion, & hand & hand functional combined
Chapter 7 The Wrist and Hand Manual of Structural Kinesiology R.T. Floyd, EdD, ATC, CSCS Many Archery, Relate wrist require sports require precise functioning of flexion, & hand & hand functional combined
UPPER EXTREMITY INJURIES IN SPORTS
 UPPER EXTREMITY INJURIES IN SPORTS Wrist and Hand Injuries in the Athlete Tim L. Uhl, PhD, ATC, PT Philip Blazar, MD Greg Pitts, MS, OTR/L, CHT Kelly Ramsdell, ATC CHAPTER 2 Sports Physical Therapy Section
UPPER EXTREMITY INJURIES IN SPORTS Wrist and Hand Injuries in the Athlete Tim L. Uhl, PhD, ATC, PT Philip Blazar, MD Greg Pitts, MS, OTR/L, CHT Kelly Ramsdell, ATC CHAPTER 2 Sports Physical Therapy Section
.org. Arthritis of the Hand. Description
 Arthritis of the Hand Page ( 1 ) The hand and wrist have multiple small joints that work together to produce motion, including the fine motion needed to thread a needle or tie a shoelace. When the joints
Arthritis of the Hand Page ( 1 ) The hand and wrist have multiple small joints that work together to produce motion, including the fine motion needed to thread a needle or tie a shoelace. When the joints
MR and CT Arthrography of the Wrist
 27 Luis Cerezal, M.D. 1 Juan de Dios Berná-Mestre, M.D., Ph.D. 2 Ana Canga, M.D. 3 Eva Llopis, M.D. 4 Alejandro Rolon, M.D. 5 Xavier Martín-Oliva, M.D. 6 Francisco del Piñal, M.D., Ph.D. 7 1 Department
27 Luis Cerezal, M.D. 1 Juan de Dios Berná-Mestre, M.D., Ph.D. 2 Ana Canga, M.D. 3 Eva Llopis, M.D. 4 Alejandro Rolon, M.D. 5 Xavier Martín-Oliva, M.D. 6 Francisco del Piñal, M.D., Ph.D. 7 1 Department
THE THERAPIST S MANAGEMENT OF THE STIFF ELBOW MARK PISCHKE, OTR/L, CHT NOV, 17, 2014
 THE THERAPIST S MANAGEMENT OF THE STIFF ELBOW MARK PISCHKE, OTR/L, CHT NOV, 17, 2014 ELBOW FUNCTION 1. Required to provide stability for power and precision tasks for both open and closed kinetic chain
THE THERAPIST S MANAGEMENT OF THE STIFF ELBOW MARK PISCHKE, OTR/L, CHT NOV, 17, 2014 ELBOW FUNCTION 1. Required to provide stability for power and precision tasks for both open and closed kinetic chain
Imaging of Lisfranc Injury
 November 2011 Imaging of Lisfranc Injury Greg Cvetanovich, Harvard Medical School Year IV Agenda Case Presentation Introduction Anatomy Lisfranc Injury Classification Imaging Treatment 2 Case Presentation
November 2011 Imaging of Lisfranc Injury Greg Cvetanovich, Harvard Medical School Year IV Agenda Case Presentation Introduction Anatomy Lisfranc Injury Classification Imaging Treatment 2 Case Presentation
1 of 6 1/22/2015 10:06 AM
 1 of 6 1/22/2015 10:06 AM 2 of 6 1/22/2015 10:06 AM This cross-section view of the shoulder socket shows a typical SLAP tear. Injuries to the superior labrum can be caused by acute trauma or by repetitive
1 of 6 1/22/2015 10:06 AM 2 of 6 1/22/2015 10:06 AM This cross-section view of the shoulder socket shows a typical SLAP tear. Injuries to the superior labrum can be caused by acute trauma or by repetitive
SPECT/CT Wrist. Wrist pain 3/27/2012
 Wrist pain Wrist joint - complicated anatomy complex biomechanics Imaging and management of wrist pain presents a significant challenge Significant economic burden SPECT/CT Wrist HK Mohan GSTT London Intra-capsular
Wrist pain Wrist joint - complicated anatomy complex biomechanics Imaging and management of wrist pain presents a significant challenge Significant economic burden SPECT/CT Wrist HK Mohan GSTT London Intra-capsular
3.1. Presenting signs and symptoms; may include some of the following;
 Title: Clinical Protocol for the management of Forearm and Wrist injuries. Document Owner: Deirdre Molloy Document Author: Deirdre Molloy Presented to: Care & Clinical Policies Date: August 2015 Ratified
Title: Clinical Protocol for the management of Forearm and Wrist injuries. Document Owner: Deirdre Molloy Document Author: Deirdre Molloy Presented to: Care & Clinical Policies Date: August 2015 Ratified
August 1st, 2006. Scaphoid Fractures. Dr. Christine Walton, PGY 2 Orthopedics
 August 1st, 2006 Scaphoid Fractures Dr. Christine Walton, PGY 2 Orthopedics Injury Patterns to the Carpal Bones 1) Perilunate pattern injuries 2) Axial pattern injuries 3) Local impaction/avulsion injuries
August 1st, 2006 Scaphoid Fractures Dr. Christine Walton, PGY 2 Orthopedics Injury Patterns to the Carpal Bones 1) Perilunate pattern injuries 2) Axial pattern injuries 3) Local impaction/avulsion injuries
A Systematic Approach To A Painful Wrist
 A Systematic Approach To A Painful Wrist Although wrist injuries are not life threatening, they are of great importance in terms of how they can affect daily functioning. Without an accurate diagnosis,
A Systematic Approach To A Painful Wrist Although wrist injuries are not life threatening, they are of great importance in terms of how they can affect daily functioning. Without an accurate diagnosis,
SHOULDER INSTABILITY IN PATIENTS WITH EDS
 EDNF 2012 CONFERENCE LIVING WITH EDS SHOULDER INSTABILITY IN PATIENTS WITH EDS Keith Kenter, MD Associate Professor Sports Medicine & Shoulder Reconstruction Director, Orthopaedic Residency Program Department
EDNF 2012 CONFERENCE LIVING WITH EDS SHOULDER INSTABILITY IN PATIENTS WITH EDS Keith Kenter, MD Associate Professor Sports Medicine & Shoulder Reconstruction Director, Orthopaedic Residency Program Department
Codes for Qualis Health Rev. updated 12/26/2012. 22532 Arthrodesis lateral extracavitary thoracic. 22533 Arthrodesis lateral extracavitary lumbar
 22532 Arthrodesis lateral extracavitary thoracic 22533 Arthrodesis lateral extracavitary lumbar 22534 Arthrodesis lat extracavitary ea addl thrc/lmbr 22548 Neck spine fusion 22551 Neck spine fuse&remov
22532 Arthrodesis lateral extracavitary thoracic 22533 Arthrodesis lateral extracavitary lumbar 22534 Arthrodesis lat extracavitary ea addl thrc/lmbr 22548 Neck spine fusion 22551 Neck spine fuse&remov
WRIST DISORDERS IN THE YOUNG ATHLETE
 WRIST DISORDERS IN THE YOUNG ATHLETE PETER G. GERBINO, II, MD In the young athlete, forced dorsiflexion causes most wrist injuries. Sudden dorsiflexion from a fall onto the outstretched hand results in
WRIST DISORDERS IN THE YOUNG ATHLETE PETER G. GERBINO, II, MD In the young athlete, forced dorsiflexion causes most wrist injuries. Sudden dorsiflexion from a fall onto the outstretched hand results in
