hip replacement t h e p r e p a r a t i o n, t h e h o s p i t a l s t a y a n d t h e r e c o v e r y
|
|
|
- Hilary Jones
- 8 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 hip replacement t h e p r e p a r a t i o n, t h e h o s p i t a l s t a y a n d t h e r e c o v e r y CENTER FOR MINIMALLY INVASIVE JOINT SURGERY th Street South Fargo ND
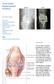
2 HIP IMPLANTS for a Total Hip replacement. The Implants are sometimes called prosthesis or components. XRAY: Replaced hip and a normal hip
3 what to expect: the patient s guide to the direct anterior approach (DAA) Contents Questions Page Number General/Overview Risks Getting Ready for Surgery Who Provides Your Care After Surgery Follow-Up
4 General/Overview What is the hip joint?... 3 What is cartilage?...3 What is arthritis?...3 What types of arthritis are there?... 4 Does arthritis progress or does it heal itself?... 4 Are there any alternatives to surgery for my hip arthritis?... 4 Why are x-rays required?... 5 When should I have my hip replaced?... 5 Facts about Total Hip Replacements in the U.S Can I put off surgery?...6 How long does a hip replacement last?...7 What is Minimally Invasive Surgery (MIS) for Hip Replacement...8 What is revision surgery?...9 Why are second and third time operations (revisions) not as good as the first time?...9 By putting off surgery, does my hip deteriorate?... 9 Is there any medication that can be injected or taken by mouth that can re-grow cartilage?... 9 Is there any medications that can help with my arthritis?... 9 How many Cortisone injections can I have a year?...10 Are there different types of hip injections?...10 Should I try to lose weight before surgery?
5 The Hip Joint and Arthritis What is the hip joint? The hip joint forms where the top of the femur (thigh bone) meets the socket of the pelvic bone. The top of the femur is ball-shaped and fits snugly in the socket formed by the acetabulum (The hollow, cuplike portion of the pelvis into which the head of the thigh bone (femur) fits). A layer of smooth, shiny cartilage that cushions and protects the bones while allowing easy motion covers the bones of the hip joint. Surrounding the hip joint is the synovial lining, which produces a moisturizing lubricant. Tough fibers, called ligaments, connect the bones of the joint and hold them in place, while adding strength and elasticity for movement. Muscles and tendons also play an important role in keeping the joint stable. What is cartilage? Normal hip function requires a smooth gliding surface on the ends of the bones. This surface is made of a thin layer of slippery, tough tissue called hyaline cartilage. This cartilage also acts to distribute force during repetitive pounding-like movements such as jumping or running. The hyaline cartilage is also referred to as articular cartilage. Drawing of a NORMAL and an ARTHRITIC hip joint. There is normally a well defined space between the socket and the femoral head (ball). What is arthritis? Arthritis is a term that includes a group of disorders that affect the joints. The word arthritis literally means, joint inflammation that is, a joint that is painful, warm to the touch, possibly red, swollen, and associated with a loss of function. Arthritis symptoms include joint pain, inflammation and limited movement of joints. Surrounding each joint is a protective capsule holding a lubricating fluid to aid in motion. 3
6 With joint arthritis, the cartilage may be damaged, narrowed and lost by a degenerative process (see diagram on page 3) or by inflammation, making movement painful. Because of arthritis symptoms, many people will experience some difficulty with activities at home or work. The following may all be impaired to some degree by arthritis pain and joint stiffness: getting out of bed in the morning fastening buttons writing sewing meal preparation dressing sleeping walking climbing stairs arising from a chair or a toilet seat personal hygiene Many people find that loss of mobility is more distressing to them than arthritis pain. For most people, arthritis pain and inflammation cannot be avoided as the body ages. In fact, most people over the age of 50 show some signs of arthritis. Joints naturally degenerate over time. Fortunately, arthritis can be managed through a combination of medication, exercise, rest, weight-management, nutrition, and, in some cases, surgery. Treatments often change over time and medication may be adjusted. What types of arthritis are there? Arthritis is not a single ailment. In fact, more than 100 different conditions can affect the joints and their adjacent bones, muscles, and tissues. The conditions are classified into various types of arthritis based on: Inflammation (ex. Rheumatoid arthritis) Non inflammatory (ex. Osteoarthritis) Post-Traumatic Arthritis: occurring after a major injury to the joint surface Infection of the joint(s) Recurrent bleeding into a joint due to a blood disorder All of these types of arthritis are completely different, with different presentations, symptoms and treatment. Does arthritis progress or does it heal itself? Unfortunately, damaged cartilage cannot heal to become normal again, though tremendous research is taking place on developing methods to restore damaged cartilage. Generally arthritis gets worse with age. The hip becomes more painful and the good days start to become fewer and fewer. Are there any surgical alternatives to hip replacement for the treatment of hip arthritis? Although there is no cure and little prevention for osteoarthritis, there are ways to help relieve the pain and to keep active and productive. In younger patients, the hip may be painful but the arthritis may be minimal. Sometimes the hip has developed abnormally (DYSPLASIA) and surgery other than a replacement may be needed. This procedure is called an osteotomy (Periacetabular Osteotomy or Ganz 4
7 Osteotomy). This procedure is done to alleviate the pain and retain the natural hip in younger patients (generally less than 50) that have dysplasia. Alternative surgical options for young patients are discussed in other handouts. Please see material on surface hip replacement hip, hip arthroscopy and surgical dislocation of the hip for femoroacetubalar impingement syndrome (FIA). Why are x-rays required before hip surgery? An x-ray of the hip joint usually shows a space between the ball and the socket. In the normal hip this joint space is approximately 1/8 inch wide and fairly even in outline. X-rays are used to determine the extent of degeneration to the cartilage or bone and may suggest a cause for the degeneration of the hip joint. X-rays can also help determine if there are any areas of the hip that may have developed abnormally. JOINT SPACE NORMAL HIP XRAY ABNORMAL HIP XRAY: loss of joint space and pistol grip deformity. Cysts noted on the head. When should I have my hip replaced? The decision to have a hip replacement is usually up to you and your family. A hip replacement can commonly be avoided as long as you are willing to put up with a moderate degree of pain and minimal disability. Most people have a hip replacement when they experience significant and persistent pain, need a cane at least part of the time, are having sleep problems and are taking nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medication (NSAIDs) often. In general a total hip replacement (THR) is indicated when the hip discomfort has progressed to intolerable pain and significantly interferes with daily living. 5
8 DISCOMFORT: patient seeks medical advice Start medication EPISODES OF PAIN and DISCOMFORT: Activity modification Medication adjustment PAIN EVERYDAY & DISRUPTS LIFESTYLE Consider surgery T H R If the hip problem is only minor and only occasionally bothersome (causing discomfort) then non-operative treatments are more reasonable than surgery. There is almost never urgency or an emergency situation for hip replacement. You may choose to have a hip replacement because of the desire to have a more active lifestyle such has taking part in recreational activities, traveling, and taking part in regular day-to-day exercise routines. If cardiovascular fitness is being compromised due to hip pain, then surgery should be considered. Also, prolonged use of narcotic medication (codeine, hydrocodone, oxycontin, Darvocet) is not recommended for the treatment of arthritis. If the hip disease is so bad that walking requires crutches and/or a wheelchair or there is a significant limp, most orthopedists would recommend a hip replacement, assuming that you are physically able to tolerate the surgery. In summary, hip arthritis and the pain it causes will usually progress. It progresses from tolerable discomfort that is managed with anti-inflammatory medication and activity modification to persistent pain causing limitations in the amount you can walk and sleep disturbance. Most people decide to have a hip replacement when the pain becomes this severe. FACTS ABOUT TOTAL HIP REPLACEMENT: Approximately 300,000 hip replacements are performed in the U.S. each year. 64 percent of hip replacement patients are women. 34 percent of hip replacement patients are between 40 and 64 years of age. 90 to 95 percent of hip replacements are successful for up to 10 years. Younger, more active patients are now receiving hip replacements and are demanding high-technology implants that will last longer and support their active lifestyles. Can I put off surgery? There are some advantages to putting off surgery. The technology is always improving; however, improved technology needs to be tested with medical studies to prove that it is better than a previous technique. Orthopedists encourage young people to hold off with joint replacement surgery as long as possible. The problem with joint replacements is how long they will last. If you are undergoing hip replacement surgery for the first time in your early 40s, you may require two additional 6
9 surgical procedures over your lifetime. You may benefit delaying surgery if your lifestyle is not compromised due to the pain and you have manageable hip discomfort. The disadvantages of waiting are the pain, discomfort, loss of motion, disability, the possible loss of muscle and strength around the hip due to inactivity. It is because of the loss of muscle strength that some orthopedists recommend undergoing a hip replacement if you have a persistent and noticeable limp. How long does a hip replacement last? This depends on several factors: your age the disease of your hip the type of total hip prosthesis implanted The longevity of the hip replacement depends on how well you take care of your total hip replacement and also how well it was put in. A vast majority of total hip replacements can be expected to last fifteen to twenty years. A high level of activity and increased weight may decrease the longevity of a total hip replacement. There are many factors involved; it s not unlike asking how long your car will last or how long the tires will wear. Your mileage will vary, but these are the controlling factors: With the polyethylene liners, wear of the liner is a function of use. Less use gives you more time before it wears through. For the hard bearing surfaces (metal-on-metal and ceramic-on-ceramic), the wear rate is so small it is not expected that wear-through will be the limited factor however, the wear debris (tiny particles that gradually wear off of the artificial joint surfaces and are absorbed by the surrounding tissues) can cause problems. Age is a factor. Younger people are harder on their joints and walk more steps per day. Males are usually harder on their joints and statistically put on more miles. Response of your body to the prosthesis used in your hip. This table shows 25-year results of a conventional, cemented, polyethylene on metal prosthesis. Consequently, the prosthesis model and the operation technique are 25 years old. This data is from a study out of the Mayo clinic. The table shows the percentage of total hips still in function after 25 years for patients of different age categories. AGE AT OPERATION Percent of TH still in function 25 years later < 50 years 63 % years 76 % years 87 % years 93 % > 79 years 96 % 7
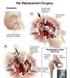
10 What is Minimally Invasive Surgery (MIS) for Hip Replacement? Minimally invasive hip replacement surgery allows the surgeon to perform the hip replacement through a smaller skin incision. Traditional hip replacement surgery involves making a 10- to 12-inch incision on the side of the hip. With MIS the hip replacement is performed through a 3-4 inch incision or some techniques require two small incisions. After the skin incision the muscles are split or detached from the hip, allowing the hip to be dislocated. Most surgeons today are performing MIS hip replacement using a smaller skin incision. This may provide for a more pleasing scar; however the muscles below the skin are still split and detached from the bone. Therefore the recovery and the pain after certain techniques of MIS hip replacement may be the same as a traditional hip replacement. The concept of muscle preserving hip replacement has continued to evolve. The only true way to preserve all the muscles and tendons around the hip during a hip replacement is to use a technique to access the hip from the front or also know as anterior, sometimes called the Direct Anterior Approach (DAA). Unlike performing hip surgery from the side (lateral) or the buttock (posterior) of the hip, the DAA takes advantage of going between the long thin muscles that go across the hip joint. These muscles are not detached and therefore the recovery may be faster. Also beneficial to the patient is the lack of hip precautions that are frequently required after a hip replacement. With a side or buttock incision, important muscles are detached and frequently your doctor will impose certain restrictions that need to be placed on the hip while the muscles heal. Minimally invasive surgery is performed by most doctors, however not all MIS techniques are the same. To learn more about the Direct Anterior Approach by Dr. Matthys, please review the patient education material provided in another handout: Direct Anterior Approach for Total Hip Replacement. General Technique for MIS hip surgery: The artificial implants used for the minimally invasive hip replacement procedures are the same as those used for traditional hip replacement. Specially designed instruments are needed to prepare the socket and femur and to place the implants properly. The surgical procedure is similar, but there is less soft-tissue dissection. A single minimally invasive hip incision may measure only 3 to 4 inches. It depends on the size of the patient and the difficulty of the procedure. The incision is placed over the front of the hip. The muscles and tendons are NOT split or detached during the DAA. With MIS approaches through the side or buttock, the muscle detachment may be to a lesser extent than in the traditional hip replacement operation. The muscles are routinely repaired after the surgeon places the implants. Benefits of DAA: Reported benefits of less invasive hip replacement include: Less pain More cosmetic incisions No muscle detachment No muscles are split Rehabilitation is faster No hip restrictions Fewer implant dislocations Hospital stays are shorter For traditional hip replacement, hospital stays average 4 to 5 days. Many patients need extensive rehabilitation afterward. With less-invasive procedures, the hospital stay may be as short as 2 or 3 days. It is very unlikely to expect to go home on the day of or the day after surgery. 8
11 What is revision surgery? Hip replacements may fail after 25 years, or sooner. The parts may come loose, wear out or break. Loose, worn or broken parts may need to be replaced. The surgery to replace or repair the components is called revision surgery. Why are second and third time operations (revisions) not as good as the first time? Bone availability. The more times a joint is replaced, the less bone there is for the surgeon to work with. Special implants are required. The surgery is more extensive. Muscle weakness. The hip recovers from surgery less predictably with more operations. A weak hip or pelvis puts the patient at risk for dislocation and walking with a persistent limp. Higher complication rate. These complex revision operations are much riskier than the first time a hip is replaced. All the risks associated with first-time hip replacements are present, but the chances of complications occurring are increased. If I put off surgery, will my hip deteriorate? The surgical procedure in general is not any more difficult if surgery is delayed. Deterioration of the bone is rare, but can occur. The surrounding joints, such as the back, knees, and the other hip are not compromised and will not be damaged; however, the added stress may irritate these areas due to limp or weak hip muscles. If there is a significant delay and muscle weakness and loss of strength has occurred, recovery may take a longer period of time. Is there any medication that can be injected or taken by mouth that can re-grow cartilage? There are no scientific studies reporting regeneration of cartilage tissue with any medications prescribed by doctors or supplements provided by health food stores such as shark cartilage. Glucosamine and chondroitin sulfate, generally taken together, have demonstrated decreased pain, but there have been no studies to support regeneration of cartilage or slowing of cartilage loss due to the arthritis. Most researchers feel that the pain relief from glucosamine and chondroitin sulfate is more of an anti-inflammatory effect. Is there any medications that can help with my arthritis? Arthritis medications, sometimes called non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDS), help in decreasing the pain and inflammation. The effect of these medications vary from one patient to the other. NSAIDs are available both over-the-counter and as a prescription. It is very important to understand that while there are differences between prescription and non-prescription NSAIDs, these differences are not the strength or potential relief of symptoms. Many patients find their best response from over-the-counter NSAIDs. 9
12 Aspirin (Anacin, Ascriptin, Bayer, Bufferin, Ecotrin, Excedrin) Choline and magnesium salicylates (CMT, Tricosal, Trilisate) Choline salicylate (Arthropan) Celecoxib (Celebrex) Diclofenac potassium (Cataflam) Diclofenac sodium (Voltaren, Voltaren XR) Diclofenac sodium with misoprostol (Arthrotec) Diflunisal (Dolobid) Etodolac (Lodine, Lodine XL) Fenoprofen calcium (Nalfon) Flurbiprofen (Ansaid) Ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin, Motrin IB, Nuprin) Indomethacin (Indocin, Indocin SR) Ketoprofen (Actron, Orudis, Orudis KT, Oruvail) Magnesium salicylate (Arthritab, Bayer Select, Doan's Pills, Magan, Mobidin, Mobogesic) Meclofenamate sodium (Meclomen) Mefenamic acid (Ponstel) Meloxicam (Mobic) Nabumetone (Relafen) Naproxen (Naprosyn, Naprelan*) Naproxen sodium (Aleve, Anaprox) Oxaprozin (Daypro) Piroxicam (Feldene) Rofecoxib (Vioxx) Salsalate (Amigesic, Anaflex 750, Disalcid, Marthritic, Mono-Gesic, Salflex, Salsitab) Sodium salicylate (various generics) Sulindac (Clinoril) Tolmetin sodium (Tolectin) Valdecoxib (Bextra) Some products, such as Excedrin, are combination drugs (Excedrin is acetaminophen, aspirin, and caffeine). Note that acetaminophen (Paracetamol; Tylenol) is not on this list. Acetaminophen belongs to a class of drugs called analgesics (pain relievers) and antipyretics (fever reducers). The exact mechanism of action of acetaminophen is not known. Acetaminophen relieves pain by elevating the pain threshold, that is, by requiring a greater amount of pain to develop before it is felt by a person. It reduces fever through its action on the heat-regulating center of the brain. Specifically, it tells the center to lower the body's temperature when the temperature is elevated. Acetaminophen relieves pain in mild arthritis but has no effect on the underlying inflammation, redness and swelling of the joint. Table of NSAIDs How many Cortisone injections can I have a year? In general most doctors do not recommend more than four per year. The injections can lose effectiveness the more times they are performed. This is generally because arthritis progresses and becomes more painful. Injections are indicated for patients with mild or moderate arthritis. The more severe the disease, the less likely an injection will be helpful. Are there different types of hip injections? Yes, injections can be placed on the side of the hip and are generally placed in the soft tissue bursa sac. This is generally used to alleviate pain that is outside the joint and is originating from the trochanteric bursa. Bursa are located throughout the body and are generally located over a 10
13 bony prominence. The function of the bursa is to decrease friction between the bone and a tendon or muscle. The bursa can swell and become inflamed and painful. The other injection usually involves placing the medication into the joint under the guidance of X-ray. This generally requires an appointment with a radiologist. Here the needle is directed into the small joint space while using an X-ray to determine the location of the needle. This injection is intended to alleviate pain that is originating from the hip joint. Trochanteric Bursa (Bursitis) McKesson Health Solutions Should I try to lose weight before surgery? If you are overweight, your extra weight will increase the hip pain. Weight loss will make you more comfortable, but is unlikely to completely relieve the pain. It may also be beneficial in allowing you to delay surgery, especially an advantage for younger people. It is important to understand that one pound of weight loss decreases the hip stress by three pounds. Obesity can also make surgical treatment more challenging. However, a hip replacement on heavier patients is commonly performed and does not usually prevent the surgeon from operating. It is documented in the medical literature that obese patients have a higher complication rate. This increased risk is rarely of a degree to make replacement impossible. Certain techniques of minimally invasive total hip replacement are not used in obese people. The Direct Anterior approach can be used since the surgery is performed in the front part of the hip between the trunk and the upper leg, where fatty tissue is less. In summary, it is desirable to lose weight if you feel that you are overweight, however, we rarely insist upon it prior to surgery. We do recognize the difficulty with weight loss, especially when arthritis pain can cause a person to be less active. 11
14 Risks and Complications Are there risks to the surgery? What are some of the risks of the operation to replace my hip? What are the four most common complications after joint replacement? What measures are taken to reduce the rate of dislocation? What measures are taken to reduce blood clots? What measures are taken to help prevent an infection after surgery? Will there be a difference in the length of my legs after the hip replacement?...15 What measures are used to make my leg lengths as equal as possible?...16 What if my leg feels longer after surgery, but the x-rays show that they are equal?...16 Are most patients satisfied with Total Hip Replacement?
15 Risks and Complications Are there risks to the surgery? Yes, total joint replacement surgery is a major operation and there are some risks. The risks are rare due to experience and expertise in the field. According to the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons, approximately 300,000 hip replacement operations are performed each year in the United States and less than 10 percent require further surgery. New technology and advances in surgical techniques have greatly reduced the risks involved with hip replacements. Numerous measures are undertaken to reduce the chance of a complication. What are some of the risks of the operation to replace my hip? To achieve the benefits that total hip replacement can offer you, you must accept certain limitations and be aware of possible risks. In most circumstances these risks can be avoided, prevented or corrected. Complications occur in approximately 3% of all cases. Possible risks and complications include: 1. Infection Occurs in 3% of cases despite using sterile techniques. If infection occurs early (less than 6 weeks after surgery), then a revision surgery that is less extensive may be all that is needed. However, if the infection occurs after this time period the implants will have to be removed and the infection treated before the implants are put back in. 2. Blood clots 3. Leg length differences 4. Fracture of the bone 5. Dislocation 6. Excess bone formation around the hip socket This is rare, but can occur. It is also called heterotopic ossification. In rare circumstances it would require surgery to remove the extra bone that has formed. 7. Early loosening/early failure of the implant 8. Blood loss requiring a transfusion of blood products 9. Nerve damage 10. Continued pain/thigh pain This is due to bone ingrowth in a cementless prosthesis. It usually improves with time. 11. Stress related conditions The stress of surgery can increase the risk of heart attack or stroke. 12. Late complication: loosening due to osteolysis The most common later complication of hip replacement surgery is an inflammatory reaction to tiny particles that gradually wear off of the artificial joint surfaces and are absorbed by the surrounding tissues. The inflammation may trigger the action of special cells that eat away some of the bone, causing the implant to loosen. To treat this complication, the doctor may use anti-inflammatory medications or recommend revision surgery (replacement of an artificial joint). Medical scientists are experimenting with new materials that last longer and cause less inflammation. 13
16 What are the four most common complications after joint replacement? Dislocation What measures are taken to reduce the rate of dislocation? Dislocation occurs when the ball comes out of the socket. Just like your real hip, an artificial hip can dislocate. There is a greater risk of dislocation right after surgery, before the muscles and tendons around the new joint have healed. Hip dislocation causes pain and the hip will need to be put back in place in an emergency room or the operating room. If dislocation happens, it usually happens only once. Approximately 20% of patients will dislocate a second time. If the hip continues to dislocate it may require revision surgery. The artificial hip is held in the socket by the muscles and other soft tissues around the hip. There is a low rate of dislocation with the direct anterior approach (DAA) because there is no disruption of the muscles and tendons around the hip Blood clots/deep vein thrombosis (DVT) What measures are taken to reduce blood clots? Blood clots result from several factors including; being less active after surgery, use of oral contraception, history of DVT, history of cancer, use of tobacco and damage to the blood vessels. Blood clots may be suspected if pain and swelling develop in your calf or thigh (unrelated to your incision), tenderness or redness in your calf, and swelling of your thigh, calf, ankle or foot. Warning signs that a blood clot has traveled to your lung include shortness of breath or chest pain, particularly with breathing. This is called a pulmonary embolism. This can be a fatal condition if not treated. Consult your doctor immediately if you experience any of the above symptoms. Several measures are used to reduce the possibility of blood clots, including: Mayo Foundation Blood thinning medications (anticoagulants). Elastic stockings. Exercise to increase blood flow in the leg muscles. Plastic boots that inflate with air to compress the muscles in your legs. Infection What measures are taken to help prevent an infection after surgery? Infection can be a serious complication. Despite using precautions, the infection rate after a total hip replacement is 3%, and may be higher in patients that have other medical problems such as diabetes, chronic use of prednisone, obesity or chronic tobacco use. Multiple precautions are taken which include use of special surgical gowns, use of antibiotics and a sterile surgical environment. If an infection occurs, treatment is based on how severe it is and also how long ago the surgery was performed. 14
17 This table demonstrates the general guidelines for treatment of post-operative infection in joint replacement. This does not apply to every patient. Infection Infection involving only the skin (cellulitis). Deep infection involving the joint, less than six weeks after surgery. Deep infection involving the joint, later than six weeks after surgery. Treatment Oral or intravenous antibiotics. I.V. antibiotics, surgery requiring the hip to be opened up and irrigated, possible removal of all or some of the implant device. I.V. antibiotics, surgery requiring the hip to be opened up and irrigated with removal of all of the implant device and two to three months of antibiotics. A second surgery required to replace the hip with new parts. Leg Length Differences Will there be a difference in the length of my legs after the hip replacement? The surgeon s goal at the time of the surgery is to restore the normal anatomy and length of the leg, as well as provide a stable hip that does not dislocate. However, sometimes either due your unique anatomy or weakness in the muscles and soft tissues in the hip area, it may be necessary to lengthen the leg at the time of the surgery. Most commonly, the limbs can be restored to within 1/4" to the length of the leg before surgery. Usually, patients already have a difference in length of their two legs before surgery. This is due to the loss of cartilage and thus shortening of the leg. If the leg requiring hip replacement surgery is shorter than the other leg, it can be lengthened with a goal of making it the same length as your other leg. If you have arthritis and shortening of both legs, then the leg lengths will be made equal at the time the second hip replacement is performed. If the leg to be operated on is already longer than the other leg, there is little that can be done to shorten the leg at the time of hip replacement surgery. To do so will very commonly lead to a looseness or laxity in the soft tissues, which will result in dislocation of the total hip replacement. In other words, if the leg that is being operated on is longer (which is rare) than your other leg, then it may be that way after surgery. 15
18 What measures are used to make my leg lengths as equal as possible? Leg length is checked during surgery using x-rays. Hip replacement using the DAA is performed with you lying on your back flat on the table. Most surgeons perform hip replacement with you lying on your side. One major advantage of having you on your back is that leg lengths can be checked by x-raying both hips and printing a transparent image. These two images can then be overlaid to decide if the leg is long or short and make changes as needed. Although all surgeons try to get the leg length correct at the time of the operation, it is common to be off by 5mm (one quarter of an inch), usually on the longer side. Most people usually adjust to this difference. This difference is naturally common in patients without hip disease. If you have questions regarding the length of your legs before surgery, please ask your doctor about this. What if my leg feels longer after surgery, but the x-rays show that they are equal? Usually, the cause is the muscles and tissues that keep the pelvis slanting to the operated hip side after surgery. As the muscle contracture gradually disappears, the apparent leg length difference will disappear too. It takes one or two months to train your muscles to adapt after surgery. Are most patients satisfied with total hip replacement? Yes. About 90% of all patients are satisfied with their new hip. This is a very high figure, actually, compared with other kinds of surgery. Yet, about 10% of all patients operated on with the total hip replacement have been dissatisfied with the result of the operation. These are results of a national survey. Dissatisfied patients in this group: Remaining pain in the joint that interferes with sleep (about 5%) unequal leg length (about 1%) instability in the new hip joint (about 5% with traditional approaches and 0.02% for the Direct Anterior Approach) 16
19 Getting Ready for Surgery Once it is decided that I will undergo total hip replacement surgery, how long will it take before it is done? Are there any medications I should stop taking before my surgery? Are there other things I need to do before sugery?...18 Will I need blood? Should I donate my own blood before surgery? What are the risks of receiving blood? What type of anesthesia will I receive?
20 Getting Ready For Surgery Once it is decided that I will undergo total hip replacement surgery, how long will it take before it is done? Usually it takes about four to six weeks to get everything ready for your surgery. You will be asked to have a medical exam by your own doctor (family practice or internal medicine) before your operation to make sure you are physically fit to undergo major surgery. This is called a pre-op history and physical.. If you have any infection (teeth, bladder, kidney, for example), it should be treated and cleared up before joint surgery is done. An ample amount of time must be set aside for any special testing that needs to be done. Any dental and colonoscopy procedures that are needed should be done before undergoing a total hip procedure. Are there any medications I should stop taking before my surgery? Stop taking NSAIDs, aspirin and all anti-inflammatories prior to surgery. (Motrin, Advil, Aleve, Naprosyn, Celebrex, Ultram, etc) should be stopped 7 days before the date of your surgery. This includes aspirin and aspirin-containing medication such as Anacin and Bufferin. Medications that thin the blood (coumadin, lovenox, heparin, plavix) must be stopped 7 days before surgery. Please consult with your internist or family practice doctor before you stop these medications. Discontinue all herbal supplements 7 days before surgery. Because of the potential increase in bleeding during surgery, these medications must be stopped or adjusted. If they have not been discontinued properly, your surgery will need to be postponed. Are there other things I need to do before surgery? If you smoke, stop or at least cut down significantly. Smoking can delay the healing process. Have any gum or tooth problems treated before surgery to reduce the risk of infection. Always inform your doctor of any medical procedures being done before surgery regardless of how minor they may be. Lose weight if you re overweight. It will help take some of the stress off your new joints. Continue to exercise; it will help with your post-op recovery. Report any infections (even a cold), as surgery cannot be performed if present. Eat a well-balanced diet, supplemented with iron and a multivitamin. 18
21 Will I need blood? Most patients require a blood transfusion after surgery. The blood may be from the blood bank (community donated) or blood that you donated prior to surgery (autologous). Should I donate my own blood before surgery? You may choose to donate your own blood before surgery, or if you are unable to give blood, a family member or friend with the same blood type may donate instead (directed donation). Every effort will be made to help reduce the amount of blood lost during surgery. To cut down on bleeding your blood pressure is lowered and blood vessels that are cut are cauterized. A specialized drain is used after surgery that will collect the blood that commonly leaks out after surgery. This blood that is collected can then be placed back into your body through an I.V. Donating your own blood before surgery depletes your red blood cell supply, which can make you weak and anemic before surgery. Please speak to Dr. Matthys regarding donating your own blood and blood loss if you have any questions. You may donate at the blood bank of the hospital at which you will have your surgery. If you live far from that hospital, or out of state, you may elect to donate blood at a major hospital near your home. It will be transferred to the hospital before surgery. Blood can also be donated at any American Red Cross blood collection facility. Please call (800) to locate the center nearest your home. What are the risks of receiving blood? If a blood transfusion is indicated during a surgical procedure or other medical treatment, the risks of NOT receiving blood far outweigh the risks of transfusion. Risks of transfusion are low, but include: Some people may experience minor changes in the body s immune system after a transfusion, causing mild symptoms, such as fever, chills or hives, which typically require little or no treatment. A small number of people may also react to donated blood by developing antibodies (immune reactions). The transmission of disease and the destruction of red blood cells can occur rarely. This seldom threatens life. All donated blood in the United States is tested. When you consider the risks of transfusion, it may be helpful to know that many common activities carry far greater risks for example, smoking cigarettes, driving a car or being pregnant. Anesthesia What type of anesthesia will I receive? This choice is between the anesthesia staff and you, unless they feel that a particular type of anesthesia is right for you. Modern anesthesia is very safe. While spinal anesthesia is preferred for total joint replacement, some patients may not be able to have it. Spinal anesthesia can be more difficult in patients that have had lower back fusions (surgery). 19
22 General anesthesia is an excellent alternative. Just before surgery, the anesthesiologist will review your medical history and briefly examine you. The anesthesiologist will talk to you about which anesthesia he or she feels is best for you. The technique most patients are familiar with is general anesthesia. With general anesthesia, the patient is unconscious during the procedure. The anesthesiologist may administer a variety of drugs and gases to keep you unconscious during the operation. This type of anesthesia requires a machine to breathe for you during the operation. Another anesthetic technique is spinal anesthesia. With this technique, a small needle is used to inject an anesthetic solution into your lower back, near the spinal canal. This numbs the body from the waist down, but you are still awake. You will also be given other medications that make you sleepy throughout the surgery. An additional option may be the epidural technique. This technique is similar to the spinal anesthesia and involves an injection into the lower spine. A small catheter is placed through the epidural needle to add more analgesic-anesthetic solution during the operation. After surgery, small amounts of medication may be infused through the catheter for one or two days for pain relief. Your anesthesiologist may suggest a modification or combination of any of these techniques and will be glad to explain the pros and cons of each type of anesthetic technique to you. If you or your family have had an abnormal reaction to anesthesia, it is important that you tell Dr. Matthys and the anesthesiologist. 20
23 WHO PROVIDES YOUR CARE THE TOTAL JOINT TEAM: WHO ARE THEY AND WHAT DO THEY DO? Joint replacement is a joint effort! The total joint team works together to help you along the way, making sure you know what to expect and assist you towards the best recovery. THE PATIENT AND FAMILY You, your spouse, family or significant other are the most essential members of this team. Taking the time to learn about your health and your surgery helps with your recovery. ORTHOPAEDIC SURGEON Your orthopedic surgeon is the leader of the team. In addition to planning and performing your surgery, your surgeon will work with the other team members to assure your complete and rapid recovery. Feel free to discuss any aspect of your care with your surgeon. Your complete satisfaction is your surgeon s and the team s goal. OTHER MEDICAL DOCTORS To care for all your medical needs, other doctors may be involved in your care. These doctors are internal medicine physicians and manage medical conditions such as high blood pressure, diabetes, heart disease and many more ailments. CLINICAL STAFF Donna is the coordinator for Dr. Matthys clinic. Donna can answer any questions or help with any problems you or your loved ones have while preparing for your surgery. Jane is the clinic manager and can try to answer any questions regarding insurance or finance. Both can be reached at or NURSING STAFF During your hospital stay, registered nurses and other skilled workers will care for you. Nurses attending to you after your surgery are specialists in orthopedic care. Each morning you and your nurse will develop a plan for the day, and coordinate your care accordingly. The nurse will monitor your condition throughout your stay. The nursing staff will assist you with personal care activities, such as bathing and changing positions in bed. The nurse will assist you with pain management, medication administration, care of your surgical site, bowel and bladder function, walking, and other aspects of your recovery. PHYSICAL THERAPIST The physical therapist focuses on developing your independence by increasing your ability to move with ease. He/she will evaluate your mobility and strength. Your therapist will tailor an exercise plan to increase your strength and endurance. You will be shown special ways to walk and move to ensure your safety and protect the new joint as it heals. He/she will also give you exercises to increase your strength and improve your hip s range of motion. 21
24 OCCUPATIONAL THERAPIST The occupational therapist provides training and recommends equipment for independence in your daily activities at home. The therapist assesses your physical capabilities and limitations to determine your needs for equipment such as a raised toilet seat, hand rails, a tub bench, etc. The therapist will also show you how to use this equipment effectively. Not every patient will be seen by the occupational therapist, only those with special needs. DISCHARGE PLANNERS AND SOCIAL WORKERS The discharge planners will assist you with your discharge from the hospital. They may help plan outpatient physical therapy, home health care, or a short stay in a nursing care facility, if necessary After Surgery What can I expect right after surgery? Can you tell me something about the pain from the surgery? How long does it take to recover from surgery? When will I begin physical therapy? When will I be able to go home? Will I need to stay longer in a rehab unit or a nursing home? Will I need to use a special pillow (abduction pillow) between my legs to help prevent dislocation? Are there any special hip positions that I must avoid? When can I resume normal sexual activity? Do I need to follow any special precautions or use a special chair after my surgery? Will I need to use a cane long term after surgery? When will I be able to go back to work? What do I have to look out for when I get home? When can I be shower or take a bath? Will I receive physical therapy at home? I have difficulty putting on a sock and tying a shoe before surgery. Will I be able to do this after surgery? When do I need to return for follow-up visits? When can I drive after surgery? My new joint feels great! How soon can I start my daily walking?
25 After Surgery What can I expect right after surgery? Right after surgery you will go to the recovery room until you are awake and alert. You may have chills and nausea which are normal side effects of the anesthesia. You may also notice: Drainage tubes and catheters. A drainage tube and catheter may be in place and is usually removed the second day after surgery. White elastic stockings. You may be fitted with elastic surgical stockings that help prevent blood clots and improve circulation. You will wear these stockings for 18 hours a day, every day for six weeks following surgery. Can you tell me something about the pain after the surgery? You will experience some pain, but we are prepared to handle it with various methods. You will be given pain medication to control the pain after surgery. You may be treated with a PCA (patient-controlled analgesia) device that you use to administer your own pain medication through an IV. This device allows you to press a button on the PCA pump and get a predetermined amount of pain medicine injected into your IV. The pump is set to prevent against an overdose. After the IV is removed, your pain medication will be given in pill form. How long does it take to recover from surgery? Recovery varies with each person and goes in different stages. Recovery is faster with the direct anterior approach. However, the time it takes for you is dependent on your: Age Activity level before surgery Complexity of any other medical problems you have How well you can tolerate pain When will I begin physical therapy? Generally, you begin physical therapy the day after surgery. You may be walking on the day of surgery. Once home, you may use a walker for 2-4 weeks to protect the new joint while it heals. It is usually two to four weeks before you are able to drive. Most people gradually increase their activities during the next six to eight weeks; some play golf, doubles tennis or go bowling in 12 weeks. You and Dr. Matthys will determine your activity level. Recovery is affected by the condition that your joint was in before surgery. It is natural that some weakness had developed around the joint that has been painful. Therefore the recovery phase is dependent on the condition your joint was in before the operation. When will I be able to go home? Although this depends largely on the avoidance of complications while in the hospital and how active you were before surgery, most stays are 2-5 days after routine, uncomplicated total hip 23
26 surgery for the primary or first time total hip patients. See table below for some examples. Patient Demographics Average Hospital Stay Rehab or Skilled Nursing Young patients or elderly patients that are active (walk greater than six blocks) and have few medical problems Patients with stable medical problems (heart, lung), less active patients, patients using a walker or cane for less than three months Elderly patients living independently. Patients using a cane for greater than three months who use a wheelchair for longer distances. Elderly patients with multiple steps in their living quarters, patients having both hips replaced. Two to four days Four to six days Four to seven days Not required May not be required Four to ten days *This table is only a guide. Your length of stay will be decided by you and Dr. Matthys. Will I need to stay longer in a rehab unit or a nursing home? On occasion, patients may be admitted to a rehabilitation or skilled nursing facility after being discharged from the hospital. This depends on your activity level and general medical condition before undergoing hip replacement surgery. Most of our patients return home without an extended care facility stay or requiring a live-in companion. Will I need to use a special pillow (abduction pillow) between my legs to help prevent dislocation? This is not required with the direct anterior approach. With traditional surgery there is usually a wedge shaped pillow that patients sleep with for up to three months. Are there any special hip positions that I must avoid? With traditional hip replacement surgery there are usually restrictions that are required. These restrictions are called hip precautions. These usually involve restricting the amount of bending that can be done at the waist and hip. There are usually restrictions on sitting in low chairs and crossing one leg over the other. These restrictions are necessary so that the muscles/tendons that were detached have time to repair themselves. Because there are no muscles that are cut from the bone with the DAA, there are no special hip or trunk positions that must be avoided. 24
27 When can I resume normal sexual activity? There are no restrictions for patients undergoing THR with the DAA. Sexual activity can be safe as soon as two weeks after surgery. The major limitations in most activity after the surgery are due to pain and discomfort. Therefore if the pain in the hip is tolerable, there are no restrictions. Do I need to follow any special precautions or use a special chair after my surgery? No. There are no specific precautions to prevent hip dislocation. Hip dislocation with the direct anterior approach is very low. There is no requirement for a special chair or special toilet seat. Will I need to use a cane long term after surgery? No. Many patients are able to walk with a completely normal gait after hip replacement surgery. Very few patients require a cane for long term use after hip replacement surgery. Normally, the reasons for needing a cane are due to problems with balance, arthritis, or other disabling conditions in other joints of the lower extremities. When will I be able to go back to work? One to two weeks for a desk-type job is typical; up to three months for moderately physical work. Examples: Student, secretary, and computer operator: one to two weeks. Landscaper, airline baggage attendant: two months (with restricted work duties). Construction worker, delivery personnel: up to three months. Many patients will choose to go back to work earlier on light duty. Your employer and Dr. Matthys will help you decide when it is appropriate. What do I have to look out for when I get home? It is normal for you to have some discomfort. You will probably receive a prescription for pain medication before you go home. If a refill is needed, please call your doctor s nurse a few days before you run out of pills. Contact your doctor if you develop any of the following: Changes around your incision: Drainage and/or foul odor coming from the incision. Fever (temperature about 101 degrees F or 38 degrees C) for two days. Excessive swelling of your operated leg and foot. It usually develops during the first few weeks after surgery. The collected blood in the tissues around the hip will settle down to the knee and even to the ankle area and the swelling may take a bluish color. Usually, this wound healing disturbance will resolve without special treatment. Use of special stockings will reduce the edema. 25
Hip Replacement. Department of Orthopaedic Surgery Tel: 01473 702107
 Information for Patients Hip Replacement Department of Orthopaedic Surgery Tel: 01473 702107 DMI ref: 0134-08.indd(RP) Issue 3: February 2008 The Ipswich Hospital NHS Trust, 2005-2008. All rights reserved.
Information for Patients Hip Replacement Department of Orthopaedic Surgery Tel: 01473 702107 DMI ref: 0134-08.indd(RP) Issue 3: February 2008 The Ipswich Hospital NHS Trust, 2005-2008. All rights reserved.
HEADER TOTAL HIP REPLACEMENT SURGERY FROM PREPARATION TO RECOVERY
 HEADER TOTAL HIP REPLACEMENT SURGERY FROM PREPARATION TO RECOVERY ABOUT THE HIP JOINT The hip joint is a ball and socket joint that connects the body to the legs. The leg bone is called the femur. The
HEADER TOTAL HIP REPLACEMENT SURGERY FROM PREPARATION TO RECOVERY ABOUT THE HIP JOINT The hip joint is a ball and socket joint that connects the body to the legs. The leg bone is called the femur. The
Anterior Hip Replacement
 Disclaimer This movie is an educational resource only and should not be used to manage Orthopaedic health. All decisions about the management of hip replacement and arthritis management must be made in
Disclaimer This movie is an educational resource only and should not be used to manage Orthopaedic health. All decisions about the management of hip replacement and arthritis management must be made in
X-Plain Hip Replacement Surgery - Preventing Post Op Complications Reference Summary
 X-Plain Hip Replacement Surgery - Preventing Post Op Complications Reference Summary Introduction Severe arthritis in the hip can lead to severe pain and inability to walk. To relieve the pain and improve
X-Plain Hip Replacement Surgery - Preventing Post Op Complications Reference Summary Introduction Severe arthritis in the hip can lead to severe pain and inability to walk. To relieve the pain and improve
ARTHROSCOPIC HIP SURGERY
 ARTHROSCOPIC HIP SURGERY Hip Arthroscopy is a relatively simple procedure whereby common disorders of the hip can be diagnosed and treated using keyhole surgery. Some conditions, which previously were
ARTHROSCOPIC HIP SURGERY Hip Arthroscopy is a relatively simple procedure whereby common disorders of the hip can be diagnosed and treated using keyhole surgery. Some conditions, which previously were
Your Practice Online
 P R E S E N T S Your Practice Online Disclaimer This information is an educational resource only and should not be used to make a decision on Revision Hip Replacement or arthritis management. All decisions
P R E S E N T S Your Practice Online Disclaimer This information is an educational resource only and should not be used to make a decision on Revision Hip Replacement or arthritis management. All decisions
Total Hip Replacement Surgery Home Care Instructions
 Total Hip Replacement Surgery Home Care Instructions Surgery: Date: Doctor: This handout will review the care you need to follow once you are home. If you have any questions or concerns, please ask your
Total Hip Replacement Surgery Home Care Instructions Surgery: Date: Doctor: This handout will review the care you need to follow once you are home. If you have any questions or concerns, please ask your
Further information You can get more information and share your experience at www.aboutmyhealth.org
 OS01 Total Hip Replacement Further information You can get more information and share your experience at www.aboutmyhealth.org Local information You can get information locally from: Taunton and Somerset
OS01 Total Hip Replacement Further information You can get more information and share your experience at www.aboutmyhealth.org Local information You can get information locally from: Taunton and Somerset
Hip Replacement Surgery Understanding the Risks
 Hip Replacement Surgery Understanding the Risks Understanding the Risks of Hip Replacement Surgery Introduction This booklet is designed to help your doctor talk to you about the most common risks you
Hip Replacement Surgery Understanding the Risks Understanding the Risks of Hip Replacement Surgery Introduction This booklet is designed to help your doctor talk to you about the most common risks you
Total Knee Replacement
 Total Knee Replacement Contents Introduction Total Knee Replacement Preparing for surgery Pre-op visit Day of surgery After surgery (In Hospital) After surgery (In Rehab) Exercise Program and Physical
Total Knee Replacement Contents Introduction Total Knee Replacement Preparing for surgery Pre-op visit Day of surgery After surgery (In Hospital) After surgery (In Rehab) Exercise Program and Physical
Y O U R S U R G E O N S. choice of. implants F O R Y O U R S U R G E R Y
 Y O U R S U R G E O N S choice of implants F O R Y O U R S U R G E R Y Y O U R S U R G E O N S choice of implants F O R Y O U R S U R G E R Y Your Surgeon Has Chosen the C 2 a-taper Acetabular System The
Y O U R S U R G E O N S choice of implants F O R Y O U R S U R G E R Y Y O U R S U R G E O N S choice of implants F O R Y O U R S U R G E R Y Your Surgeon Has Chosen the C 2 a-taper Acetabular System The
Level 1, 131-135 Summer Street ORANGE NSW 2800 Ph: 02 63631688 Fax: 02 63631865
 Write questions or notes here: Level 1, 131-135 Summer Street ORANGE NSW 2800 Ph: 02 63631688 Fax: 02 63631865 Document Title: Total Knee Replacement Further Information and Feedback: Tell us how useful
Write questions or notes here: Level 1, 131-135 Summer Street ORANGE NSW 2800 Ph: 02 63631688 Fax: 02 63631865 Document Title: Total Knee Replacement Further Information and Feedback: Tell us how useful
HIP JOINT REPLACEMENT
 HIP JOINT REPLACEMENT Information for Patients WHAT IS HIP JOINT REPLACEMENT? The hip joint is a ball-and-socket joint formed by the upper part of the thigh bone (femoral head) and a part of the pelvis
HIP JOINT REPLACEMENT Information for Patients WHAT IS HIP JOINT REPLACEMENT? The hip joint is a ball-and-socket joint formed by the upper part of the thigh bone (femoral head) and a part of the pelvis
Procedure Information Guide
 Procedure Information Guide Total hip replacement Brought to you in association with EIDO and endorsed by the The Royal College of Surgeons of England Discovery has made every effort to ensure that the
Procedure Information Guide Total hip replacement Brought to you in association with EIDO and endorsed by the The Royal College of Surgeons of England Discovery has made every effort to ensure that the
Lumbar or Thoracic Fusion +/- Decompression
 Lumbar or Thoracic Fusion +/- Decompression PLEASE DO NOT TAKE ANY NON-STEROIDAL ANTI-INFLAMMATORY DRUGS (NSAIDs like Advil, Celebrex, Ibuprofen, Motrin, Vioxx, Naprosyn, Aleve, etc) OR ASPIRIN PRODUCTS
Lumbar or Thoracic Fusion +/- Decompression PLEASE DO NOT TAKE ANY NON-STEROIDAL ANTI-INFLAMMATORY DRUGS (NSAIDs like Advil, Celebrex, Ibuprofen, Motrin, Vioxx, Naprosyn, Aleve, etc) OR ASPIRIN PRODUCTS
Total Hip Replacement
 Please contactmethroughthegoldcoasthospitaswityouhaveanyproblemsafteryoursurgery. Dr. Benjamin Hewitt Orthopaedic Surgeon Total Hip Replacement The hip joint is a ball and socket joint that connects the
Please contactmethroughthegoldcoasthospitaswityouhaveanyproblemsafteryoursurgery. Dr. Benjamin Hewitt Orthopaedic Surgeon Total Hip Replacement The hip joint is a ball and socket joint that connects the
Procedure Information Guide
 Procedure Information Guide Resurfacing hip replacement Brought to you in association with EIDO and endorsed by the The Royal College of Surgeons of England Discovery has made every effort to ensure that
Procedure Information Guide Resurfacing hip replacement Brought to you in association with EIDO and endorsed by the The Royal College of Surgeons of England Discovery has made every effort to ensure that
Lumbar or Thoracic Decompression and Fusion
 Lumbar or Thoracic Decompression and Fusion DO NOT TAKE ANY ASPIRIN PRODUCTS OR NON-STEROIDAL ANTI- INFLAMMATORY DRUGS (ie NSAIDs, Advil, Celebrex, Ibuprofen, Motrin, Naprosyn, Aleve, etc) FOR 2 WEEKS
Lumbar or Thoracic Decompression and Fusion DO NOT TAKE ANY ASPIRIN PRODUCTS OR NON-STEROIDAL ANTI- INFLAMMATORY DRUGS (ie NSAIDs, Advil, Celebrex, Ibuprofen, Motrin, Naprosyn, Aleve, etc) FOR 2 WEEKS
Arthritis of the hip. Normal hip In an x-ray of a normal hip, the articular cartilage (the area labeled normal joint space ) is clearly visible.
 Arthritis of the hip Arthritis of the hip is a condition in which the smooth gliding surfaces of your hip joint (articular cartilage) have become damaged. This usually results in pain, stiffness, and reduced
Arthritis of the hip Arthritis of the hip is a condition in which the smooth gliding surfaces of your hip joint (articular cartilage) have become damaged. This usually results in pain, stiffness, and reduced
Choosing Pain Medicine for Osteoarthritis. A Guide for Consumers
 Choosing Pain Medicine for Osteoarthritis A Guide for Consumers Fast Facts on Pain Relievers Acetaminophen (Tylenol ) works on mild pain and has fewer risks than other pain pills. Prescription (Rx) pain
Choosing Pain Medicine for Osteoarthritis A Guide for Consumers Fast Facts on Pain Relievers Acetaminophen (Tylenol ) works on mild pain and has fewer risks than other pain pills. Prescription (Rx) pain
Anterior Approach. to Hip Replacement Surgery
 Anterior Approach to Hip Replacement Surgery Introduction When debilitating pain and stiffness in your hip limits your daily activities, you may need a total hip replacement. The development of total hip
Anterior Approach to Hip Replacement Surgery Introduction When debilitating pain and stiffness in your hip limits your daily activities, you may need a total hip replacement. The development of total hip
Treatment with Rivaroxaban
 UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Treatment with Rivaroxaban Xarelto This handout explains the medicine rivaroxaban, a drug that helps prevent blood clots. What is rivaroxaban? Rivaroxaban (brand name Xarelto)
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Treatment with Rivaroxaban Xarelto This handout explains the medicine rivaroxaban, a drug that helps prevent blood clots. What is rivaroxaban? Rivaroxaban (brand name Xarelto)
.org. Arthritis of the Hand. Description
 Arthritis of the Hand Page ( 1 ) The hand and wrist have multiple small joints that work together to produce motion, including the fine motion needed to thread a needle or tie a shoelace. When the joints
Arthritis of the Hand Page ( 1 ) The hand and wrist have multiple small joints that work together to produce motion, including the fine motion needed to thread a needle or tie a shoelace. When the joints
Total Knee Replacement Surgery
 Total Knee Replacement Surgery On this page: Overview Reasons for Surgery Evaluation Preparing for Surgery Your Surgery Risks Expectations after Surgery Convalescence Also: Partial Knee Replacement Overview
Total Knee Replacement Surgery On this page: Overview Reasons for Surgery Evaluation Preparing for Surgery Your Surgery Risks Expectations after Surgery Convalescence Also: Partial Knee Replacement Overview
Total hip replacement
 Patient Information to be retained by patient What is a total hip replacement? In a total hip replacement both the ball (femoral or thigh bone) side of the hip joint and the socket (acetabular or pelvic
Patient Information to be retained by patient What is a total hip replacement? In a total hip replacement both the ball (femoral or thigh bone) side of the hip joint and the socket (acetabular or pelvic
YOUR GUIDE TO TOTAL HIP REPLACEMENT
 A Partnership for Better Healthcare A Partnership for Better Healthcare YOUR GUIDE TO TOTAL HIP REPLACEMENT PEI Limited M50 Business Park Ballymount Road Upper Ballymount Dublin 12 Tel: 01-419 6900 Fax:
A Partnership for Better Healthcare A Partnership for Better Healthcare YOUR GUIDE TO TOTAL HIP REPLACEMENT PEI Limited M50 Business Park Ballymount Road Upper Ballymount Dublin 12 Tel: 01-419 6900 Fax:
ANTERIOR CERVICAL DECOMPRESSION AND FUSION
 ANTERIOR CERVICAL DECOMPRESSION AND FUSION NOTE: PLEASE DO NOT TAKE ANY NON-STEROIDAL ANTI-INFLAMMATORY DRUGS (NSAIDs like Advil, Celebrex, Ibuprofen, Motrin, Vioxx, etc) OR ASPIRIN PRODUCTS FOR 2 WEEKS
ANTERIOR CERVICAL DECOMPRESSION AND FUSION NOTE: PLEASE DO NOT TAKE ANY NON-STEROIDAL ANTI-INFLAMMATORY DRUGS (NSAIDs like Advil, Celebrex, Ibuprofen, Motrin, Vioxx, etc) OR ASPIRIN PRODUCTS FOR 2 WEEKS
Selective Nerve Root Block
 Selective Nerve Root Block What is a selective nerve root block? Selective nerve root blocks is similar to epidural injections, as the preparation and approach is identical. Epidural refers to the space
Selective Nerve Root Block What is a selective nerve root block? Selective nerve root blocks is similar to epidural injections, as the preparation and approach is identical. Epidural refers to the space
Level 1, 131-135 Summer Street ORANGE NSW 2800 Ph: 02 63631688 Fax: 02 63631865
 Write questions or notes here: Level 1, 131-135 Summer Street ORANGE NSW 2800 Ph: 02 63631688 Fax: 02 63631865 Document Title: Revision Total Hip Replacement Further Information and Feedback: Tell us how
Write questions or notes here: Level 1, 131-135 Summer Street ORANGE NSW 2800 Ph: 02 63631688 Fax: 02 63631865 Document Title: Revision Total Hip Replacement Further Information and Feedback: Tell us how
PERIACETABULAR OSTEOTOMY SURGERY
 1 PERIACETABULAR OSTEOTOMY SURGERY It is important to us that all of our patients know what to expect before surgery, during their hospitalization and after surgery. Office Visits Planning begins with
1 PERIACETABULAR OSTEOTOMY SURGERY It is important to us that all of our patients know what to expect before surgery, during their hospitalization and after surgery. Office Visits Planning begins with
PALM BEACH ORTHOPAEDIC INSTITUTE, P.A. FAQ: OUT-PATIENT SURGERY
 DISCLAIMER This information is a general guideline for most out-patient surgeries. Since every case is unique, your surgeon may give you further or differing instructions. Please follow his or her guidelines.
DISCLAIMER This information is a general guideline for most out-patient surgeries. Since every case is unique, your surgeon may give you further or differing instructions. Please follow his or her guidelines.
TOTAL HIP REPLACEMENT
 TOTAL HIP REPLACEMENT 2 Causes of Hip Pain Arthritis is the leading cause of disability in the United States, and the most frequent cause of discomfort and chronic hip pain. In fact, it s estimated that
TOTAL HIP REPLACEMENT 2 Causes of Hip Pain Arthritis is the leading cause of disability in the United States, and the most frequent cause of discomfort and chronic hip pain. In fact, it s estimated that
Total knee replacement
 Patient Information to be retained by patient What is a total knee replacement? In a total knee replacement the cartilage surfaces of the thigh bone (femur) and leg bone (tibia) are replaced. The cartilage
Patient Information to be retained by patient What is a total knee replacement? In a total knee replacement the cartilage surfaces of the thigh bone (femur) and leg bone (tibia) are replaced. The cartilage
Understanding Total Hip Replacement
 Understanding Total Hip Replacement Brian J. White MD Orthopaedic Specialist in Disorders of the Hip Assistant Team Physician Denver Nuggets Western Orthopaedics Denver, Colorado Introduction This is designed
Understanding Total Hip Replacement Brian J. White MD Orthopaedic Specialist in Disorders of the Hip Assistant Team Physician Denver Nuggets Western Orthopaedics Denver, Colorado Introduction This is designed
Shoulder Arthroscopy
 Copyright 2011 American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Shoulder Arthroscopy Arthroscopy is a procedure that orthopaedic surgeons use to inspect, diagnose, and repair problems inside a joint. The word
Copyright 2011 American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Shoulder Arthroscopy Arthroscopy is a procedure that orthopaedic surgeons use to inspect, diagnose, and repair problems inside a joint. The word
Total Hip Arthroplasty (Hip Replacement) PROCEDURAL CONSENT FORM. A. Interpreter / cultural needs. B. Condition and treatment
 The State of Queensland (Queensland Health), 2011 Permission to reproduce should be sought from ip_officer@health.qld.gov.au DO NOT WRITE IN THIS BINDING MARGIN v4.00-04/2011 SW9336 Facility: Total Hip
The State of Queensland (Queensland Health), 2011 Permission to reproduce should be sought from ip_officer@health.qld.gov.au DO NOT WRITE IN THIS BINDING MARGIN v4.00-04/2011 SW9336 Facility: Total Hip
OPERATION:... Proximal tibial osteotomy Distal femoral osteotomy
 AFFIX PATIENT DETAIL STICKER HERE Forename.. Surname NHS Organisation. Responsible surgeon. Job Title Hospital Number... D.O.B.././ No special requirements OPERATION:..... Proximal tibial osteotomy Distal
AFFIX PATIENT DETAIL STICKER HERE Forename.. Surname NHS Organisation. Responsible surgeon. Job Title Hospital Number... D.O.B.././ No special requirements OPERATION:..... Proximal tibial osteotomy Distal
Herniated Lumbar Disc
 Herniated Lumbar Disc North American Spine Society Public Education Series What Is a Herniated Disc? The spine is made up of a series of connected bones called vertebrae. The disc is a combination of strong
Herniated Lumbar Disc North American Spine Society Public Education Series What Is a Herniated Disc? The spine is made up of a series of connected bones called vertebrae. The disc is a combination of strong
Treatment with Apixaban
 UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Treatment with Apixaban Eliquis This handout explains the medicine apixaban, a drug that helps prevent blood clots. What is apixaban? Apixaban (brand name Eliquis) is an anticoagulant
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Treatment with Apixaban Eliquis This handout explains the medicine apixaban, a drug that helps prevent blood clots. What is apixaban? Apixaban (brand name Eliquis) is an anticoagulant
Your Practice Online
 P R E S E N T S Your Practice Online Disclaimer This information is an educational resource only and should not be used to make a decision on Knee replacement or arthritis management. All decisions about
P R E S E N T S Your Practice Online Disclaimer This information is an educational resource only and should not be used to make a decision on Knee replacement or arthritis management. All decisions about
Hip arthroscopy Frequently Asked Questions
 Hip arthroscopy Frequently Asked Questions What is a hip arthroscopy? Hip arthroscopy is key hole surgery. Usually 2-3 small incisions (about 1 cm long) are made on the side of your hip. Through these
Hip arthroscopy Frequently Asked Questions What is a hip arthroscopy? Hip arthroscopy is key hole surgery. Usually 2-3 small incisions (about 1 cm long) are made on the side of your hip. Through these
Laparoscopic Colectomy. What do I need to know about my laparoscopic colorectal surgery?
 Laparoscopic Colectomy What do I need to know about my laparoscopic colorectal surgery? Traditionally, colon & rectal surgery requires a large, abdominal and/or pelvic incision, which often requires a
Laparoscopic Colectomy What do I need to know about my laparoscopic colorectal surgery? Traditionally, colon & rectal surgery requires a large, abdominal and/or pelvic incision, which often requires a
it s time for rubber to meet the road
 your total knee replacement surgery Steps to returning to a Lifestyle You Deserve it s time for rubber to meet the road AGAIN The knee is the largest joint in the body. The knee is made up of the lower
your total knee replacement surgery Steps to returning to a Lifestyle You Deserve it s time for rubber to meet the road AGAIN The knee is the largest joint in the body. The knee is made up of the lower
A Patient s Guide to Arthritis of the Big Toe (Hallux Rigidus) With Discussion on Cheilectomy and Fusion
 A Patient s Guide to Arthritis of the Big Toe (Hallux Rigidus) With Discussion on Cheilectomy and Fusion The foot and ankle unit at the Royal National Orthopaedic Hospital (RNOH) is a multi-disciplinary
A Patient s Guide to Arthritis of the Big Toe (Hallux Rigidus) With Discussion on Cheilectomy and Fusion The foot and ankle unit at the Royal National Orthopaedic Hospital (RNOH) is a multi-disciplinary
Dr. Anseth s Frequently Asked Questions about Knee Replacement Surgery
 Dr. Anseth s Frequently Asked Questions about Knee Replacement Surgery What hospital do you use? Abbott Northwestern Hospital What type of anesthesia do you use? General anesthesia with an additional nerve
Dr. Anseth s Frequently Asked Questions about Knee Replacement Surgery What hospital do you use? Abbott Northwestern Hospital What type of anesthesia do you use? General anesthesia with an additional nerve
Orthopaedic Spine Center. Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion (ACDF) Normal Discs
 Orthopaedic Spine Center Graham Calvert MD James Woodall MD PhD Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion (ACDF) Normal Discs The cervical spine consists of the bony vertebrae, discs, nerves and other structures.
Orthopaedic Spine Center Graham Calvert MD James Woodall MD PhD Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion (ACDF) Normal Discs The cervical spine consists of the bony vertebrae, discs, nerves and other structures.
Total Hip Replacement
 NOTES Total Hip Replacement QUESTIONS DATES PHONE NOS. Compiled by Mr John F Nolan FRCS for The British Hip Society 2009. A patient s information booklet 16 1 Introduction This booklet has been produced
NOTES Total Hip Replacement QUESTIONS DATES PHONE NOS. Compiled by Mr John F Nolan FRCS for The British Hip Society 2009. A patient s information booklet 16 1 Introduction This booklet has been produced
.org. Total Knee Replacement. Anatomy
 Total Knee Replacement Page ( 1 ) If your knee is severely damaged by arthritis or injury, it may be hard for you to perform simple activities, such as walking or climbing stairs. You may even begin to
Total Knee Replacement Page ( 1 ) If your knee is severely damaged by arthritis or injury, it may be hard for you to perform simple activities, such as walking or climbing stairs. You may even begin to
Herniated Cervical Disc
 Herniated Cervical Disc North American Spine Society Public Education Series What Is a Herniated Disc? The backbone, or spine, is composed of a series of connected bones called vertebrae. The vertebrae
Herniated Cervical Disc North American Spine Society Public Education Series What Is a Herniated Disc? The backbone, or spine, is composed of a series of connected bones called vertebrae. The vertebrae
Before Surgery You will likely be asked to see your family physician or an internal medicine doctor for a thorough medical evaluation.
 Anterior Hip Replacement - Before and After Surgery Your Hip Evaluation An orthopaedic surgeon specializes in problems affecting bones and joints. The surgeon will ask you many questions about your hip
Anterior Hip Replacement - Before and After Surgery Your Hip Evaluation An orthopaedic surgeon specializes in problems affecting bones and joints. The surgeon will ask you many questions about your hip
A Patient s Guide to PAIN MANAGEMENT. After Surgery
 A Patient s Guide to PAIN MANAGEMENT After Surgery C o m p a s s i o n a n d C o m m i t m e n t A Patient s Guide to Pain Management After Surgery If you re facing an upcoming surgery, it s natural to
A Patient s Guide to PAIN MANAGEMENT After Surgery C o m p a s s i o n a n d C o m m i t m e n t A Patient s Guide to Pain Management After Surgery If you re facing an upcoming surgery, it s natural to
HIP & KNEE SURGERY PATIENTS
 HIP & KNEE HIP & KNEE SURGERY PATIENTS GET ANSWERS TO FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS YOU. IMPROVED. 2001 Vail Ave (N. Caswell St. Entrance) Suite 200A Charlotte, NC 28207 orthocarolina.com GENERAL QUESTIONS
HIP & KNEE HIP & KNEE SURGERY PATIENTS GET ANSWERS TO FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS YOU. IMPROVED. 2001 Vail Ave (N. Caswell St. Entrance) Suite 200A Charlotte, NC 28207 orthocarolina.com GENERAL QUESTIONS
Lumbar Spinal Stenosis
 Lumbar Spinal Stenosis North American Spine Society Public Education Series What Is Lumbar Spinal Stenosis? The vertebrae are the bones that make up the lumbar spine (low back). The spinal canal runs through
Lumbar Spinal Stenosis North American Spine Society Public Education Series What Is Lumbar Spinal Stenosis? The vertebrae are the bones that make up the lumbar spine (low back). The spinal canal runs through
Total Knee Replacement
 Total Knee Replacement The Knee Joint A total knee replacement, also called total knee arthroplasty, is a surgery performed to remove and replace your knee joint. The knee joint, comprised of the femur
Total Knee Replacement The Knee Joint A total knee replacement, also called total knee arthroplasty, is a surgery performed to remove and replace your knee joint. The knee joint, comprised of the femur
Total knee replacement: The enhanced recovery programme
 INFORMATION FOR PATIENTS Total knee replacement: The enhanced recovery programme Aim This leaflet aims to explain the enhanced recovery programme after total knee replacement surgery, and outline what
INFORMATION FOR PATIENTS Total knee replacement: The enhanced recovery programme Aim This leaflet aims to explain the enhanced recovery programme after total knee replacement surgery, and outline what
.org. Herniated Disk in the Lower Back. Anatomy. Description
 Herniated Disk in the Lower Back Page ( 1 ) Sometimes called a slipped or ruptured disk, a herniated disk most often occurs in your lower back. It is one of the most common causes of low back pain, as
Herniated Disk in the Lower Back Page ( 1 ) Sometimes called a slipped or ruptured disk, a herniated disk most often occurs in your lower back. It is one of the most common causes of low back pain, as
This information is for patients who are considering having a hip replacement.
 Directorate of Surgical Care Department of Orthopaedics Hip Replacement: Information for Patients and Carers This information is for patients who are considering having a hip replacement. What is a hip
Directorate of Surgical Care Department of Orthopaedics Hip Replacement: Information for Patients and Carers This information is for patients who are considering having a hip replacement. What is a hip
Total Joint Replacement
 Total Joint Replacement Brinceton M. Phipps MD Animas Orthopedic Associates 575 Rivergate Lane, Suite 105 Durango Colorado 970-259-3020 www.brincetonphippsmd.com www.animasorthopedics.com Frequently Asked
Total Joint Replacement Brinceton M. Phipps MD Animas Orthopedic Associates 575 Rivergate Lane, Suite 105 Durango Colorado 970-259-3020 www.brincetonphippsmd.com www.animasorthopedics.com Frequently Asked
Total Knee Replacement
 Dr C.S. Waller MB BS FRCS(Ed) FRACS FA(Orth)A Specialist Hip and Knee Surgeon Total Knee Replacement If your knee is severely damaged by arthritis or injury, it may be hard for you to perform simple activities
Dr C.S. Waller MB BS FRCS(Ed) FRACS FA(Orth)A Specialist Hip and Knee Surgeon Total Knee Replacement If your knee is severely damaged by arthritis or injury, it may be hard for you to perform simple activities
TOTAL HIP REPLACEMENT
 TOTAL HIP REPLACEMENT Total Hip replacement is usually needed when the normally smooth, slippery soft joint surface cartilage wears down to rough bone (degenerative arthritis or osteoarthritis). One or
TOTAL HIP REPLACEMENT Total Hip replacement is usually needed when the normally smooth, slippery soft joint surface cartilage wears down to rough bone (degenerative arthritis or osteoarthritis). One or
ARTHRITIS INTRODUCTION
 ARTHRITIS INTRODUCTION Arthritis is the most common disease affecting the joints. There are various forms of arthritis but the two that are the most common are osteoarthritis (OA), and rheumatoid arthritis
ARTHRITIS INTRODUCTION Arthritis is the most common disease affecting the joints. There are various forms of arthritis but the two that are the most common are osteoarthritis (OA), and rheumatoid arthritis
Dr. Anseth s Frequently Asked Questions about Hip Replacement
 Dr. Anseth s Frequently Asked Questions about Hip Replacement What hospital do you use? Abbott Northwestern Hospital What type of anesthesia do you use? General anesthesia with sciatic and lumbar plexus
Dr. Anseth s Frequently Asked Questions about Hip Replacement What hospital do you use? Abbott Northwestern Hospital What type of anesthesia do you use? General anesthesia with sciatic and lumbar plexus
Patient Guide. Sacroiliac Joint Pain
 Patient Guide Sacroiliac Joint Pain Anatomy Where is the Sacroiliac Joint? The sacroiliac joint (SIJ) is located at the bottom end of your spine, where the "tailbone" (sacrum) joins the pelvis (ilium).
Patient Guide Sacroiliac Joint Pain Anatomy Where is the Sacroiliac Joint? The sacroiliac joint (SIJ) is located at the bottom end of your spine, where the "tailbone" (sacrum) joins the pelvis (ilium).
Total elbow joint replacement for rheumatoid arthritis: A Patient s Guide
 www.orthop.washington.edu TABLE OF CONTENTS 1 Overview 2 Review of the condition 3 Considering surgery 5 Preparing for surgery 6 About the procedure 8 Recovering from surgery 9 Convalescence and Rehabilitation
www.orthop.washington.edu TABLE OF CONTENTS 1 Overview 2 Review of the condition 3 Considering surgery 5 Preparing for surgery 6 About the procedure 8 Recovering from surgery 9 Convalescence and Rehabilitation
Arthritis www.patientedu.org
 written by Harvard Medical School Arthritis www.patientedu.org Arthritis is the most common chronic disease in the world, and it s the leading cause of disability in the United States. There are more than
written by Harvard Medical School Arthritis www.patientedu.org Arthritis is the most common chronic disease in the world, and it s the leading cause of disability in the United States. There are more than
Should I have a knee replacement?
 Introduction Should I have a knee replacement? Knee replacement is an operation to remove the arthritic parts of the knee and replace them with an artificial joint made of metal and plastic. It can either
Introduction Should I have a knee replacement? Knee replacement is an operation to remove the arthritic parts of the knee and replace them with an artificial joint made of metal and plastic. It can either
Fine jewelry is rarely reactive, but cheaper watches, bracelets, rings, earrings and necklaces often contain nickel.
 BEFORE SURGERY What should I do to prepare for my surgery? Arrange for a family member or friend to accompany you to the hospital on the day of your surgery. Cancel any dental appointments that fall within
BEFORE SURGERY What should I do to prepare for my surgery? Arrange for a family member or friend to accompany you to the hospital on the day of your surgery. Cancel any dental appointments that fall within
Shoulder Joint Replacement
 Shoulder Joint Replacement Many people know someone with an artificial knee or hip joint. Shoulder replacement is less common, but it is just as successful in relieving joint pain. Shoulder replacement
Shoulder Joint Replacement Many people know someone with an artificial knee or hip joint. Shoulder replacement is less common, but it is just as successful in relieving joint pain. Shoulder replacement
Total Hip Replacement
 Total Hip Replacement INTRODUCTION T he following information is a guide to your upcoming surgery. It describes what is likely to happen at the time of surgery. This is a guide only and there may be some
Total Hip Replacement INTRODUCTION T he following information is a guide to your upcoming surgery. It describes what is likely to happen at the time of surgery. This is a guide only and there may be some
X-Plain Preparing For Surgery Reference Summary
 X-Plain Preparing For Surgery Reference Summary Introduction More than 25 million surgical procedures are performed each year in the US. This reference summary will help you prepare for surgery. By understanding
X-Plain Preparing For Surgery Reference Summary Introduction More than 25 million surgical procedures are performed each year in the US. This reference summary will help you prepare for surgery. By understanding
Low Back Surgery. Remember to bring this handout to the hospital with you.
 Remember to bring this handout to the hospital with you. Table of contents Page Why do I need low back surgery?... 1 What kinds of low back surgeries are there?... 2 Before your surgery... 3 After your
Remember to bring this handout to the hospital with you. Table of contents Page Why do I need low back surgery?... 1 What kinds of low back surgeries are there?... 2 Before your surgery... 3 After your
world-class orthopedic care right in your own backyard.
 world-class orthopedic care right in your own backyard. Patient Promise: At Adventist Hinsdale Hospital, our Patient Promise means we strive for continued excellence in everything we do. This means you
world-class orthopedic care right in your own backyard. Patient Promise: At Adventist Hinsdale Hospital, our Patient Promise means we strive for continued excellence in everything we do. This means you
Your Practice Online
 P R E S E N T S Your Practice Online Disclaimer This information is an educational resource only and should not be used to make a decision on Knee Replacement or arthritis management. All decisions about
P R E S E N T S Your Practice Online Disclaimer This information is an educational resource only and should not be used to make a decision on Knee Replacement or arthritis management. All decisions about
Excision of Vaginal Mesh
 What is excision of vaginal mesh? This procedure is done to remove mesh from the vagina. When is this surgery used? If mesh has eroded into the vagina, bladder, urethra, or bowel If there is pain associated
What is excision of vaginal mesh? This procedure is done to remove mesh from the vagina. When is this surgery used? If mesh has eroded into the vagina, bladder, urethra, or bowel If there is pain associated
Lumbar Decompression Surgery Guide
 Lumbar Decompression Surgery Guide TABLE OF CONTENTS: Page 3: Page 5: Page 7: Page 8: Page 9: Page 10: Page 11: Page 12: The Lumbar Spine Lumbar Surgery Before Surgery Medications Day of Surgery Evening
Lumbar Decompression Surgery Guide TABLE OF CONTENTS: Page 3: Page 5: Page 7: Page 8: Page 9: Page 10: Page 11: Page 12: The Lumbar Spine Lumbar Surgery Before Surgery Medications Day of Surgery Evening
Arthritis of the Shoulder
 Arthritis of the Shoulder In 2011, more than 50 million people in the United States reported that they had been diagnosed with some form of arthritis, according to the National Health Interview Survey.
Arthritis of the Shoulder In 2011, more than 50 million people in the United States reported that they had been diagnosed with some form of arthritis, according to the National Health Interview Survey.
Cheltenham Hip Clinic
 Hip surgery At Cheltenham, we treat a wide range of hip conditions. It s important to note that not all hip problems require surgery and we will always look for a non-surgical solution where possible.
Hip surgery At Cheltenham, we treat a wide range of hip conditions. It s important to note that not all hip problems require surgery and we will always look for a non-surgical solution where possible.
Rehabilitation After Your Total Hip Replacement
 1809 E. 13 th Street Suite 200 Tulsa, OK 74104-4243 (918) 582-6800 www.toctulsa.com Rehabilitation After Your Total Hip Replacement Whether you have just begun exploring treatment options or have already
1809 E. 13 th Street Suite 200 Tulsa, OK 74104-4243 (918) 582-6800 www.toctulsa.com Rehabilitation After Your Total Hip Replacement Whether you have just begun exploring treatment options or have already
Total Knee Replacement. Patient Information
 Total Knee Replacement Patient Information Introduction: We would like to thank you for choosing The Institute for Advanced Bone and Joint Surgery at St. Joseph s/ Candler for your Total Joint Replacement
Total Knee Replacement Patient Information Introduction: We would like to thank you for choosing The Institute for Advanced Bone and Joint Surgery at St. Joseph s/ Candler for your Total Joint Replacement
.org. Knee Arthroscopy. Description. Preparing for Surgery. Surgery
 Knee Arthroscopy Page ( 1 ) Arthroscopy is a common surgical procedure in which a joint (arthro-) is viewed (-scopy) using a small camera. Arthroscopy gives doctors a clear view of the inside of the knee.
Knee Arthroscopy Page ( 1 ) Arthroscopy is a common surgical procedure in which a joint (arthro-) is viewed (-scopy) using a small camera. Arthroscopy gives doctors a clear view of the inside of the knee.
THE REVERSE SHOULDER REPLACEMENT
 THE REVERSE SHOULDER REPLACEMENT The Reverse Shoulder Replacement is a newly approved implant that has been used successfully for over ten years in Europe. It was approved by the FDA for use in the U.S.A.
THE REVERSE SHOULDER REPLACEMENT The Reverse Shoulder Replacement is a newly approved implant that has been used successfully for over ten years in Europe. It was approved by the FDA for use in the U.S.A.
This is my information booklet: Introduction
 Hip arthroscopy is a relatively new procedure which allows the surgeon to diagnose and treat hip disorders by providing a clear view of the inside of the hip with very small incisions. This is a more complicated
Hip arthroscopy is a relatively new procedure which allows the surgeon to diagnose and treat hip disorders by providing a clear view of the inside of the hip with very small incisions. This is a more complicated
Shared Decision Making
 Deciding what to do about osteoarthritis of the knee This short decision aid is to help you decide what to do about your knee osteoarthritis. You can use it on your own, or with your doctor, to help you
Deciding what to do about osteoarthritis of the knee This short decision aid is to help you decide what to do about your knee osteoarthritis. You can use it on your own, or with your doctor, to help you
You will be having surgery to remove a tumour(s) from your liver.
 Liver surgery You will be having surgery to remove a tumour(s) from your liver. This handout will help you learn about the surgery, how to prepare for surgery and your care after surgery. Surgery can be
Liver surgery You will be having surgery to remove a tumour(s) from your liver. This handout will help you learn about the surgery, how to prepare for surgery and your care after surgery. Surgery can be
Anterior Cervical Decompression and Fusion or Anterior Cervical Corpectomy and Fusion
 Anterior Cervical Decompression and Fusion or Anterior Cervical Corpectomy and Fusion DO NOT TAKE ANY ASPIRIN PRODUCTS OR NON-STEROIDAL ANTI- INFLAMMATORY DRUGS (ie NSAIDs, Advil, Celebrex, Ibuprofen,
Anterior Cervical Decompression and Fusion or Anterior Cervical Corpectomy and Fusion DO NOT TAKE ANY ASPIRIN PRODUCTS OR NON-STEROIDAL ANTI- INFLAMMATORY DRUGS (ie NSAIDs, Advil, Celebrex, Ibuprofen,
POSTOPERATIVE INSTRUCTION FOR ANTERIOR/POSTERIOR LUMBAR SPINE FUSION
 www.southerarizonaspine.com POSTOPERATIVE INSTRUCTION FOR ANTERIOR/POSTERIOR LUMBAR SPINE FUSION This handout will review the care you need to follow once you are home. If you have any questions or concerns,
www.southerarizonaspine.com POSTOPERATIVE INSTRUCTION FOR ANTERIOR/POSTERIOR LUMBAR SPINE FUSION This handout will review the care you need to follow once you are home. If you have any questions or concerns,
Total Hip Joint Replacement. A Patient s Guide
 Total Hip Joint Replacement A Patient s Guide Don t Let Hip Pain Slow You Down What is a Hip Joint? Your joints are involved in almost every activity you do. Simple movements such as walking, bending,
Total Hip Joint Replacement A Patient s Guide Don t Let Hip Pain Slow You Down What is a Hip Joint? Your joints are involved in almost every activity you do. Simple movements such as walking, bending,
Pain Management after Surgery Patient Information Booklet
 Pain Management after Surgery Patient Information Booklet PATS 509-15-05 Your Health Care Be Involved Be involved in your healthcare. Speak up if you have questions or concerns about your care. Tell a
Pain Management after Surgery Patient Information Booklet PATS 509-15-05 Your Health Care Be Involved Be involved in your healthcare. Speak up if you have questions or concerns about your care. Tell a
SPINAL STENOSIS Information for Patients WHAT IS SPINAL STENOSIS?
 SPINAL STENOSIS Information for Patients WHAT IS SPINAL STENOSIS? The spinal canal is best imagined as a bony tube through which nerve fibres pass. The tube is interrupted between each pair of adjacent
SPINAL STENOSIS Information for Patients WHAT IS SPINAL STENOSIS? The spinal canal is best imagined as a bony tube through which nerve fibres pass. The tube is interrupted between each pair of adjacent
P REPLACEMENT SURGERY
 P REPLACEMENT SURGERY DIRECT ANTERIOR APPROACH M I N I M I Z I N G R E C O V E R Y. M A X I M I Z I N G R E S U L T S. CENTER FOR MINIMAL INVASIVE JOINT SURGERY 2301 25TH STREET SOUTH FARGO ND 58103 701-241-9300
P REPLACEMENT SURGERY DIRECT ANTERIOR APPROACH M I N I M I Z I N G R E C O V E R Y. M A X I M I Z I N G R E S U L T S. CENTER FOR MINIMAL INVASIVE JOINT SURGERY 2301 25TH STREET SOUTH FARGO ND 58103 701-241-9300
Elbow Injuries and Disorders
 Elbow Injuries and Disorders Introduction Your elbow joint is made up of bone, cartilage, ligaments and fluid. Muscles and tendons help the elbow joint move. There are many injuries and disorders that
Elbow Injuries and Disorders Introduction Your elbow joint is made up of bone, cartilage, ligaments and fluid. Muscles and tendons help the elbow joint move. There are many injuries and disorders that
What to Expect from your Hip Arthroscopy Surgery A Guide for Patients
 What to Expect from your Hip Arthroscopy Surgery A Guide for Patients Sources of Information: http://orthoinfo.aaos.org http://dev.aana.org/portals/0/popups/animatedsurgery.htm http://www.isha.net/ http://
What to Expect from your Hip Arthroscopy Surgery A Guide for Patients Sources of Information: http://orthoinfo.aaos.org http://dev.aana.org/portals/0/popups/animatedsurgery.htm http://www.isha.net/ http://
 Total Hip Replacement Hip replacement surgery, or arthroplasty, uses implants to resurface and replace the bones in the joint, re-creating the smooth gliding surfaces that were once intact. Hip replacement
Total Hip Replacement Hip replacement surgery, or arthroplasty, uses implants to resurface and replace the bones in the joint, re-creating the smooth gliding surfaces that were once intact. Hip replacement
Total Knee Arthroplasty (Knee Replacement) PROCEDURAL CONSENT FORM. A. Interpreter / cultural needs. B. Condition and treatment
 The State of Queensland (Queensland Health), 2011 Permission to reproduce should be sought from ip_officer@health.qld.gov.au DO NOT WRITE IN THIS BINDING MARGIN v4.00-04/2011 SW9337 Total Knee Arthroplasty
The State of Queensland (Queensland Health), 2011 Permission to reproduce should be sought from ip_officer@health.qld.gov.au DO NOT WRITE IN THIS BINDING MARGIN v4.00-04/2011 SW9337 Total Knee Arthroplasty
JOINT REPLACEMENT FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS
 Tower Medical Building Elmwood Business Park Sewell Office Cherry Hill Suite 6 Building E-100 Suite B-2 737 Main Street 773 Route 70 East 570 Egg Harbor Road 1004 Haddonfield Road Lumberton, NJ 08048 Marlton,
Tower Medical Building Elmwood Business Park Sewell Office Cherry Hill Suite 6 Building E-100 Suite B-2 737 Main Street 773 Route 70 East 570 Egg Harbor Road 1004 Haddonfield Road Lumberton, NJ 08048 Marlton,
Femoral artery bypass graft (Including femoral crossover graft)
 Femoral artery bypass graft (Including femoral crossover graft) Why do I need the operation? You have a blockage or narrowing of the arteries supplying blood to your leg. This reduces the blood flow to
Femoral artery bypass graft (Including femoral crossover graft) Why do I need the operation? You have a blockage or narrowing of the arteries supplying blood to your leg. This reduces the blood flow to
Baker Rehab Group HomeCare Rehab and Nursing LLC
 Baker Rehab Group HomeCare Rehab and Nursing LLC Introduction So it s time for a joint replacement... Are you worried about the surgery? Are you wondering about the pre and post surgical process? Do you
Baker Rehab Group HomeCare Rehab and Nursing LLC Introduction So it s time for a joint replacement... Are you worried about the surgery? Are you wondering about the pre and post surgical process? Do you
Patient Information for Lumbar Spinal Fusion. What is a lumbar spinal fusion? Page 1 of 5
 Patient Information for Lumbar Spinal Fusion What is a lumbar spinal fusion? You have been offered surgery to the lumbar region of your spine, your lower back. The operation is called a lumbar spinal fusion.
Patient Information for Lumbar Spinal Fusion What is a lumbar spinal fusion? You have been offered surgery to the lumbar region of your spine, your lower back. The operation is called a lumbar spinal fusion.
ILIOTIBIAL BAND SYNDROME
 ILIOTIBIAL BAND SYNDROME Description The iliotibial band is the tendon attachment of hip muscles into the upper leg (tibia) just below the knee to the outer side of the front of the leg. Where the tendon
ILIOTIBIAL BAND SYNDROME Description The iliotibial band is the tendon attachment of hip muscles into the upper leg (tibia) just below the knee to the outer side of the front of the leg. Where the tendon
Total Knee Replacement
 Total Knee Replacement Welcome to the Joint Replacement Center at DMOS. With over forty years of total joint experience, DMOS was the first group of surgeons in Iowa to perform the total joint procedures.
Total Knee Replacement Welcome to the Joint Replacement Center at DMOS. With over forty years of total joint experience, DMOS was the first group of surgeons in Iowa to perform the total joint procedures.
