What Every Transplant Patient Needs to Know About Dental Care
|
|
|
- Spencer Jordan
- 8 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 What Every Transplant Patient Needs to Know About Dental Care
2 Should patients have a dental exam before having a transplant? Transplant candidates should have a dental check-up as part of the pretransplant evaluation. It is helpful to have an examination by your dentist when you are being evaluated for transplant to check the health of your teeth and gums. This is important because some medications that you take after transplant may cause you to develop infections more easily. Maintaining your dental health as best as you can while waiting for an organ will help you do better after your transplant. Dental Care after Transplant As you recover from transplant surgery, you will learn a lot about how to take care of yourself and your healthy organ. You will learn many new things about medications, rejection, and infection. But there are also many routine care needs that still need to be done. Taking care of your teeth and gums (oral hygiene) is important for everyone. For people who are waiting for an organ transplant and for those who have received organ transplants, maintaining healthy teeth and gums is an essential area of care. This booklet will discuss many issues about dental care and the best ways to take care of your teeth and gums. Why could I have problems with my teeth and gums? There are several reasons why you might have problems with your teeth or gums before and after transplant. When you were waiting for transplant, you may not have thought a lot about caring for your teeth. This may have been because you were ill or unable to take care of yourself as well as when you were healthier. Patients who are very ill before transplant often cannot visit their dentist for regular check-ups and dental care. It is hard for them to care for their teeth and gums each day because they don t feel well. So some patients already have dental problems before they receive a transplant. After transplant, you may have been more concerned about problems like rejection, infection, or side effects of your medications. Because you are now taking medicines to suppress your immune system, you could have an increased risk of dental health problems. All of these factors can add to dental problems following transplant. What are the most common dental problems that transplant recipients have? The types of dental problems seen in transplant patients are similar to those in the general population. Gum disease, tooth decay, mouth ulcers, dry mouth, and dental infections can occur. Some dental problems are side effects of medications you take after transplant. Also, you can develop infections more easily because your immune system is suppressed. 2 Gum Disease (Gingivitis) What is gum disease and how is this treated? Gum disease, or gingivitis, is an infection of the tissue that surrounds your teeth. Infection can develop in the gap between the tooth and the gum, just below the gum line. The infection can cause the tissue to break down. As this tissue breaks down, a pocket develops within the gap between the tooth and gum. The pocket will develop into a more serious type of gum infection called periodontal disease. Some transplant medications can increase your risk of gum disease. Diabetes and smoking or chewing tobacco can speed up the progress of gum disease. Symptoms of gum disease (gingivitis) include: Red, swollen, and/or tender gums Gums that bleed easily Symptoms of gum disease and/or periodontal disease include: Gums that have pulled away from the teeth Bad breath (halitosis) or a bad taste in the mouth that does not go away Loosening of the teeth Wider separations between your teeth Changes in the way your teeth fit together when you bite
3 Gum overgrowth Gum Overgrowth (Gingival Hypertrophy) Another condition of the gums that can occur in patients after transplant is gum enlargement or overgrowth. This is caused by several medications, including some anti-rejection medications. These medications can cause the gums to grow over their usual borders. As the gums enlarge, they cover part of the teeth. This gum overgrowth is called gingival hypertrophy. When the gums are enlarged, the overgrown gums interfere with brushing and flossing. Bleeding and infection can occur. If you are concerned about gum overgrowth or have enlarged gums: Call your transplant coordinator to discuss this medication side effect. Ask if you are taking any of the medications that can cause gum overgrowth. Observe your gums for any fullness and growth over the usual gumtooth border when you brush. Visit your dentist regularly for a dental exam and cleaning. Provide your dentist with a list of your current medications. Brush according to your dentist s or hygienist s guidelines if you have gum overgrowth. A very soft toothbrush is recommended to avoid bleeding gums. Discuss any problems you are having because of gum overgrowth with your transplant physician. In some cases, it may be possible to change to another type of antirejection medication that does not have this side effect. If the medication cannot be changed, sometimes the level or dose of the medication can be lowered. Gum surgery can reduce gum tissue if your gums have become severely overgrown. This will help maintain good gum health and decrease the risk of infection. Plaque deposits on teeth Dental Decay (Dental Caries) What is plaque and how does it lead to tooth decay? Plaque is a sticky layer of bits of food and bacteria that is always forming on teeth. After you eat or drink foods that contain sugar or starch, the bacteria in plaque make acids that attack the hard enamel covering of the tooth. The enamel can break down over time from repeated attacks of this acid. When the enamel breaks down, that area of the tooth decays, forming a cavity. Plaque can also build up around the base of the teeth. Plaque hardens and is more difficult to remove if you do not brush and floss daily or get routine cleanings. Plaque irritates the gums, causing them to become swollen and bleed. This can progress to periodontal disease. The tissue can also become infected. To prevent plaque build up and further complications: Brush at least twice a day with fluoride toothpaste, especially after meals or snacks. Always brush your teeth before going to sleep at night. Clean between your teeth by flossing once a day. Discuss the best method for brushing and flossing your teeth with your hygienist or dentist. Visit your dentist and dental hygienist at least every 6 months or more often if necessary for a professional examination and cleaning. The hygienist will be able to remove any hard plaque on your gum line or between your teeth. Eat a well-balanced diet. Limit between meal snacks and sweets. Limit high sugar foods and sugarcontaining drinks, particularly if they are in prolonged contact with your teeth. Call your dentist if you notice any chips or rough areas on your teeth, if your teeth become sensitive to cold or hot foods and drinks, or if you develop any tooth pain. Have cavities treated as soon as possible to avoid the progression of decay and infection. 3
4 What other oral problems can occur? Thrush (candidiasis) is an infection caused by a fungus that normally lives in your mouth and does not cause any problems. But because you are taking medicines to suppress your immune system, this fungus can cause an infection. You are at a greater risk of developing thrush during times when you are receiving higher levels of immunosuppression to treat rejection. Thrush appears as white patchy areas in your mouth. The areas can be reddened and may be sore. It commonly forms on the lining of the mouth (oral mucosa), tongue, and throat. If you have thrush, it might be uncomfortable to eat and your mouth might be dry. Thrush is treated with a medicine that can be taken as a lozenge, pill or oral rinse. Your doctor will prescribe this medication for you after transplant to prevent thrush, particularly if you are on high levels of anti-rejection medications, including prednisone (corticosteroids). Smoking, dry mouth, diabetes, and having dentures increase the risk of getting a thrush infection in your mouth. Thrush (candidiasis) Dry mouth (xerostomia) occurs when you do not have enough saliva to keep your mouth moist. This happens when the salivary glands are not working well and can occur as a side effect of some medications. Many over-the-counter medications, such as antihistamines and decongestants, cause dry mouth. Some of the medications that you are prescribed after transplant cause dry mouth. Dry mouth is often seen in older adults. Common symptoms of dry mouth include: thick, stringy saliva, a constant sore throat, mouth/tongue burning, bad breath, and difficulty chewing, tasting, and swallowing. It is also difficult to talk when you have dry mouth. Tooth decay and gum disease progress faster when there is not enough saliva to wash away the acids produced by the bacteria in plaque. Dry mouth is harmful to the transplant recipient because the dryness can irritate the soft tissue in the mouth. Mouth sores or ulcers can develop. Having these open sores in your mouth can increase the risk of infection. If you have dry mouth, discuss this side effect with your transplant physician and/or dentist. Ask if this is a side effect of any of the medications you are taking. Your dentist can recommend some ways to increase the moisture in your mouth. You can improve the symptoms of dry mouth by: sucking on sugar-free candy to stimulate saliva chewing sugar-free gum using artificial saliva or an over-thecounter oral moisturizer rinsing frequently with alcoholfree oral rinses such as normal saline, 3% hydrogen peroxide, club soda, or Biotene avoiding alcohol, salty foods, and caffeine drinking water frequently sucking on ice chips Mouth ulcer Mouth ulcers or sores can develop in the soft tissue lining the mouth (oral mucosa). These sores appear for many reasons, as in the general population. Transplant recipients can also get mouth ulcers as a result of some anti-rejection medications. Ulcers also occur by accidentally biting the inside of your lip or when your mouth is irritated from dental braces or dentures. The ulcers wear away the mucosa resulting in a shallow sore with a red border and a yellow or white center. The area is usually swollen and painful. Having mouth ulcers can cause problems with chewing, swallowing, and even talking. Eating soft, mild foods that are easy to swallow such as creamed soups, cottage cheese, and yogurt can help relieve the pain. Drinking cold fluids will also help. There are some over-the-counter medicines that can be applied to the ulcer and surrounding area to decrease pain. Patients who have ulcers that are very painful may find relief with a medicine that numbs the area (anesthetic). This medication is sprayed or applied to the irritated area. Ask your dentist about the product that is best for you. Mouth ulcers usually heal within 1 to 3 weeks. Call your doctor or dentist if you have mouth ulcers that are not healing or if the area around the ulcers has increasing redness, swelling, or pain. 4
5 How can I avoid these dental problems? You can have healthy teeth, gums and mouth tissue after transplant with good oral hygiene. It s easy to forget about this part of your health with all the other responsibilities you have as a new transplant recipient. Here are some important guidelines for good dental health: 3 Brush at least twice a day, particularly after meals and before going to sleep. 3 Floss between teeth daily to remove food particles and plaque. 3 Use a toothbrush that has a small head with soft or ultra soft bristles. Soft toothbrushes will provide a safe and gentle action to remove trapped plaque and food. Automatic (rotary) toothbrushes are also recommended. 3 Brush for about 3 minutes. Power toothbrushes will automatically do this. 3 Replace your toothbrush at least every 3 months. 3 Rinse with a mouthwash to help decrease bacteria, freshen your breath, and reduce plaque. 3 Visit your dentist and hygienist for regular check-ups and cleanings every 6 months. If you develop problems, you should have a checkup every 3 or 4 months. 3 Eat a balanced diet and avoid sweets. As a transplant patient, you should also: 3 Remind your dentist and hygienist that you have had a transplant. 3 Always take all your medications as prescribed by your transplant team. 3 Get your labs drawn regularly as instructed. 3 Make sure your dentist knows what medicines you are taking. 3 Examine your mouth regularly and call your physician and/or dentist if you have any chipped or cracked teeth, tooth pain, swelling, red or swollen gums, bleeding, sores in your mouth, or white patches on your tongue or the lining of your mouth. 3 Remember that your dentist and hygienist are a part of your transplant team. How should I brush my teeth? Discuss the best way to brush and floss your teeth with your dentist and hygienist. If you are having any dental problems, they can advise you about the best method. Generally, the following steps will lead to a thorough cleaning: Choose toothpaste that is approved by your dental association (ADA approved, CDA approved). Choose a toothbrush as recommended by your dentist. A soft bristle brush is usually the best. Your dentist may also recommend an automatic (rotary) toothbrush. Hold the brush at a 45 degree angle against your teeth so that the bristles of the brush reach into the space between your teeth and gums. Gently brush the outside and insides of your teeth on the top and bottom using a short back-and-forth motion or a small circular motion. Brush behind the upper and lower front teeth. Hold your brush vertically (straight up instead of sideways) and use the bristles at the top of the brush. Brush the surfaces of the back teeth. Rinse thoroughly. How should I floss? Wrap the floss comfortably around your fingers so that you can control it as you floss. Gently ease and glide the floss back and forth between your teeth making a C shape around the tooth with the floss. Be careful to move the floss up and down the side of the tooth so that you are thoroughly cleaning between the teeth and between each tooth and the gum. If it is difficult to get the floss between your teeth, try using dental tape. It is slightly thicker than floss and may be helpful. 5
6 Do I have to do anything special before having a dental procedure since my immune system is suppressed? Transplant recipients may have a greater risk for developing an oral infection when the gums or the lining of the mouth are injured through a procedure because their immune system is suppressed. Bacteria that are commonly in the mouth can cause infection. This can become more serious if the infection spreads into the bloodstream. Infection may be more of a risk if the levels of anti-rejection medications are high, as during treatment for rejection. If you are seeing your dentist for a routine examination, no special treatment is needed before your appointment. If you are having a cleaning or any procedure that may injure the gum, like having a tooth pulled, taking an antibiotic before the procedure to prevent any problems with infection may be recommended by some transplant centers. This is called infection prophylaxis. Your dentist will prescribe the appropriate antibiotic and will tell you how to take it. Please contact your transplant coordinator about your center s protocol for infection prevention before dental procedures. What should I do if I have a dental emergency? If you have an emergency situation, such as a cracked or broken tooth, pain, or swelling, contact your dentist immediately. Tell your dentist what medications you are taking or show him your current medication list. Your dentist may prescribe an antibiotic if there is concern about infection before any procedure is begun. Do not ignore any dental pain or delay treatment. It is important to have injured teeth repaired quickly to avoid further complications. How does my diet affect my dental health? The types of food that you eat and your eating habits affect the health of your teeth and gums. Some foods promote and maintain healthy teeth and gums. Other foods cause plaque and tooth decay to develop. Good nutrition is important to maintain 6 healthy teeth and gums: Vitamin C and folic acid help maintain healthy gums. Many fruits and vegetables provide good sources of these nutrients. Iron and B Vitamins, which are important for your blood, are found in whole grains. Breads high in fiber, whole grain cereals, and rice are good sources. Protein is important for wound healing and tissue growth and repair. Good sources of protein include lean meat, fish, poultry, and beans. Fruits and vegetables high in fiber can contribute to good dental health by increasing the flow of saliva which lowers acid levels and helps clean the teeth. Chewing these foods can also help clean your teeth. It is also helpful to drink water throughout the day. Water will help decrease the growth of plaque and can also help rinse food particles from your teeth. Eat a diet that includes the appropriate amounts of these foods based on your health needs. Do not take additional vitamins or supplements unless prescribed by your physician. Carbohydrates can add to tooth decay by feeding the bacteria in plaque. Foods such as pasta, white bread, whole milk, cakes, and cookies can cause the bacteria to release acids leading to decay. Some of this acid can be rinsed away by drinking or rinsing your mouth with water, the rinsing action of your saliva, and of course, by brushing your teeth. Foods that stick to your teeth can be more harmful because the plaque acids will continue to attack the enamel even after you
7 have stopped eating. Other sticky foods include raisins and other dried fruits, candy, and chewing gum. Remember that drinks such as fruit juices, iced tea, sports drinks and carbonated drinks contain sugar, unless they are diet drinks. All these products have a high acid content that can promote tooth decay. What is fluoride and why is it important for my teeth? Fluoride is a mineral that is usually added to the drinking water in many cities. It has been proven to be safe and effective in reducing tooth decay. Fluoride helps strengthen teeth by repairing the areas in the enamel where acid from foods and the bacteria in plaque has begun to break it down. Teeth exposed to fluoride are more resistant to acid attacks that increase tooth decay. If you drink fluoridated water the fluoride will also be in your saliva, which continually washes your teeth. This applies to the general population as well as transplant recipients. Thanks to water fluoridation, the incidence of tooth decay has decreased significantly. Fluoride can also be applied to the tooth surfaces. This is the fluoride treatment applied to your teeth by your dentist or hygienist. Most toothpastes contain fluoride. Fluoride mouth rinses are also available either over-the-counter or by prescription. Adding topical fluoride treatments to your dental care routine helps teeth resist the development of tooth decay. The American Dental Association (ADA), Canadian Dental Association, and the British Dental Health Foundation recommend the appropriate use of fluorides through fluoride toothpaste in adults and children over the age of 2 years, in mouth rinses with fluoride for adults and children over the age of 6 years, and through applications of fluoride by a dentist or dental hygienist during routine dental visits. I know I should visit my dentist regularly, but I m really frightened about having any dental work. What should I do? Being worried and even scared about visiting the dentist is a common fear. There s even a name for it! It s called dental anxiety. The best way to overcome your fear of going to the dentist is to make an appointment to discuss your concerns. As your dentist and the dental staff get to know you better, they will be able to work with you on ways to reduce your fear. Choose a time for your visit when you are not rushed. An early appointment might be helpful so you don t worry all day. Many dentists can use a variety of relaxation therapies, music, and other distraction techniques to help their anxious patients. Try bringing a portable CD player or radio with a headset so you can listen to your favorite music or talk radio. Listening may help distract you during the procedure. Dental treatments have become more comfortable over the years, so you may be worrying unnecessarily. Talk to your dentist about your fears. If you continue to have severe dental anxiety, medications can be used to help you relax. There are some medications that can put you into a light sleep or a deep sleep, if necessary. If this type of medication is needed, your dentist and transplant physician will consider your overall health status, any ongoing problems, the type of dental procedure, your level of anxiety, and your current medications. 7
8 My insurance does not cover any dental care. What options do I have for care? Dental health plans and coverage for dental care varies widely. Some patients pay only a small co-payment while others have very little coverage or must pay out-of-pocket for all dental care. If you do not have insurance coverage for dental care, discuss this with your transplant social worker or insurance case worker. Your social worker may be able to help you get an appointment at a free dental clinic through a dental school or at a community health clinic. Some dental clinics may offer a sliding scale for payment based on your income. You may also be able to set up a payment schedule with your dentist. I wear dentures. Do I still have to be concerned about mouth care? If you have lost some of your teeth and have partial dentures, you should follow the same guidelines that have been described for patients who have their natural teeth. Some organ transplant recipients will have lost all their natural teeth. They may or may not choose to use dentures. Having healthy gums is just as important for these patients. You are also at risk for some of the conditions that have been described in this booklet, including infection with a mouth fungus (thrush), dry mouth, and mouth ulcers. The methods for the prevention and treatment of these problems will be the same as for patients who have teeth. You should keep your mouth and dentures clean and rinse both after eating. Dentures should not be worn at night. Weight gain or loss before or after transplant surgery can cause changes in how your dentures fit. This should be corrected as soon as possible so that poor-fitting dentures do not interfere with eating and maintaining a healthy diet. If you develop a sore spot, a lump, or an ulcer in your mouth that does not heal within 2 weeks, schedule an appointment to see your dentist as soon as possible. Denture wearers should have their mouths examined by a dentist at least once a year. This examination should include a screening for mouth cancer. Can transplant patients develop cancer of the mouth? Cancers of the mouth (oral cancer) tend to develop in older people, especially if they have smoked. This also applies to patients who have received transplants. Mouth cancers tend to grow slowly and patients are usually not aware that cancer has developed in their mouth until the tumors have become advanced. This is another reason why you should have a regular check-up with your dentist. Dentists should include an oral cancer screening at routine check-ups every six months, or every year for denture wearers. Your dentist will carefully inspect all areas in your mouth including your gums, the inside of your cheeks, the tissue under your tongue, and your tongue surfaces. Some mouth cancers develop from pre-cancerous lesions, or patches in the mouth. These are painless white patches (leukoplakia) or red patches (erythroplakia). These lesions should be examined by a dentist immediately, particularly if they develop on the sides or under your tongue. A biopsy of these abnormal areas will be taken to see if the cells of the lesion are benign (not cancerous), pre-cancerous, or malignant (have cancer cells). Your dentist may perform the biopsy or refer you to an oral surgeon or an ear, nose, and throat (ENT) specialist for this procedure. 8 If you develop a lump, sore, or ulcer anywhere in your mouth, or a lump in your neck that lasts for more than two weeks, you should see your doctor or dentist for an examination.
9 Dental Care for Children with an Organ Transplant My child has received a transplant. How should I start caring for his teeth? If your child is a transplant recipient, caring for your child s teeth and gums includes the same care routines as for any child. The first step in taking care of an infant s teeth is to get him used to the feeling of cleaning his teeth and gums. Dentists call this desensitizing the mouth. You can begin to desensitize your child s mouth by touching or rubbing his mouth and gums with your clean fingers. You can use a washcloth, a rubber stimulator (in the baby section of your pharmacy or supermarket), or a toothette sponge (like a toothbrush, but with a small sponge on the end) to massage and clean the gums and any new teeth. Use water to clean an infant s teeth and gums. You should rinse your baby s mouth with water or clean it with a moist toothette or clean cloth after breast or bottle-feeding. Avoid soothing your child to sleep with breast or bottle feedings or a sippy cup. Tooth decay develops around the teeth where the milk has settled. This pattern of decay is called baby bottle mouth. Saliva, which helps rinse and protect the teeth, decreases when sleeping which adds to the development of tooth decay. As your child gets older, it is important to have him brush twice daily, especially before going to bed. Place a pea-sized amount of toothpaste on his toothbrush. Teach your child to brush each section of his mouth: the upper and lower teeth on each side, and the top and bottom front teeth. After brushing, he should swish and spit, then rinse. Learning to swish and spit is difficult for a small child, but he will improve in time. Rotary (automatic) toothbrushes can be helpful for young children learning to hold and position the toothbrush in their mouths. Flossing between your child s teeth is important to remove plaque and food debris. Your child will need help with this for a while, particularly if they have tightly arranged teeth. Individual dental flossers are easy to use when flossing your child s teeth. These are available in the dental section of your pharmacy or supermarket. What are my child s risks for dental problems after transplant? Children, like adults, are at risk for gum problems, tooth decay, mouth ulcers, and infection. Gum overgrowth can also occur as a side effect of some medications. What can I do to help my child have healthy teeth and gums? There are several things you can do to help your child maintain good dental health. 3 Remind, supervise, and help your child brush his teeth and floss. 3 Examine your child s mouth regularly for gum swelling, redness or overgrowth. Check for mouth ulcers and signs of infection including red, swollen gums and/or white patches (thrush). As your child gets older, teach him how to check for these oral health problems. 3 Provide healthy snacks for your child and avoid high sugar snacks, soft drinks, and treats that can contribute to tooth decay. 3 Schedule visits to your child s dentist and dental hygienist at least every 6 months for an examination and cleaning. 3 Call your dentist with any problems or complaints and have dental problems treated promptly. 3 Ask your dentist about sealants. A sealant is a protective coating that can be applied to the surface of the back teeth where cavities often develop. 9
10 3 Be sure your child is getting the right amount of calcium, vitamin D, and phosphorus. These nutrients help build strong teeth as well as bones and are found in dairy products such as milk, cheese, and yogurt. Talk to your pediatrician or transplant dietician about food choices for your child. Do not give additional vitamins or food supplements unless instructed to do so by your physician. 3 Fluoride is important for children because it strengthens the teeth as they develop - even before the teeth appear. Your child can absorb fluoride through drinking water that is fluoridated or by taking vitamins that have fluoride. Fluoride can also be given as drops, tablets, or lozenges if you do not have fluoridated water. How can I talk to my teenager about the risks of oral piercing? Piercing the tongue and lips has become popular in some groups of adolescents and young adults as a form of self-expression. Many serious complications have been associated with this practice. Teens should be given advice about the serious complications that can arise from oral piercing. There are many risks associated with oral piercing. Injuries, tongue bleeding or swelling, nerve damage, and transmission of infections can occur. These pieces of metal can crack or chip teeth and can lead to gum injury and recession of the gums. The jewelry can also be a choking hazard if it becomes loose in the mouth. Oral jewelry can affect speech, cause problems with chewing and swallowing food, and stimulate excessive saliva. Oral jewelry will interfere with good tooth brushing and flossing. Infection is a common side effect of oral piercing. With all the bacteria in the mouth, infections can easily develop in injured tissues. Transplant patients are at an even higher risk of infection since their immune system is suppressed. Transplant patients should never consider oral piercing. How can I find a dentist? The best plan for most patients is to have your regular dentist continue to treat you after transplant. That person will be familiar with your mouth and will be able to determine if you are developing problems that were not present before you had your transplant. Providing dental care for transplant recipients is not much different than treating other patients. However, dentists may relocate or retire. Your regular dentist may not be comfortable treating you after transplant. If this is the case, you can start by asking your local physician for a referral to a dentist in your area who is comfortable with caring for patients with transplants or has experience with these patients. Friends, family, or co-workers can be a referral source. You can also get a listing of dentists through professional organizations in your country by contacting your local dental society. 10 Before you arrange an appointment with a dentist for your first check-up, ask for some time to discuss your dental care as a transplant recipient. Asking questions before your checkup can help you feel comfortable with your dentist s care. It is important that your dentist spends enough time with you to answer your questions and discuss your concerns. Some questions to ask when choosing a dentist: Do you have any experience in providing dental care for transplant recipients? If not, are you comfortable treating patients who are immunosuppressed? Do you think it is important to take antibiotics before any invasive dental procedure since I m immunosuppressed? If so, will you give me a prescription for the medication or should I ask my transplant physician for the prescription? How often would you like to see me for routine check-ups and cleanings? Are procedures for sterilizing your dental instruments appropriate for patients who are immunosuppressed? What types of procedures are done in your office? What types of procedures will be referred to another specialist? What should be done in case of a dental emergency? Is there an office emergency line, emergency contact, or answering service? Dental health is an important aspect of care for everyone. As a transplant patient, it is essential that you take care of your teeth and gums by routinely brushing and flossing. Be sure to see your dentist and dental hygienist every 6 months. Remember, your dental care practitioners are part of your transplant team!
11 For additional information on dental care: The American Dental Association is the professional association of dentists committed to the public s oral health, ethics, science and professional advancement The Australian Dental Association is an organization of dentists whose aim is the encouragement of the health of the public and the promotion of the art and science of dentistry. The American Dental Hygienists Association. Contains consumer information about dental care. August-2005/The-Importance-of-Dental-Care-for- Transplant-Recipients/index.cfm An article on the American Association of Kidney Patients website about dental care pre- and post-transplant. Oral Health Resources through the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Contains information about state- and community-based programs in the US to prevent oral disease, promote oral health, and foster research to enhance oral disease prevention. The British Dental Health Foundation is the leading UK-based independent charity working to bring about improved standards of oral health care. Its goal is to serve the public interest by improving awareness of and access to better oral health. Related Links for More Information ITNS is not responsible or liable for any information received from these websites. These sites are provided as a network resource. Information from the Internet in regard to your transplant should always be discussed with your transplant team. The Hispanic Dental Association is the only national association of dental health professionals dedicated to promoting and improving the oral health of the Hispanic community. The National Institute of Dental and Craniofacial Research (NIDCR). The mission of this organization is to improve oral, dental and craniofacial health through research, research training, and the dissemination of health information. Oral Care India. Information on dental care, emergencies, and dental practitioners in India. Information about dental care from the Columbia University College of Dental Medicine, New York. UK Dental Care Websites. A complete listing of a variety of dental care websites within the UK The Canadian Dental Hygienists Association. The CDHA contributes to the health of the public by leading the development of national positions and encouraging standards related to dental hygiene practice, education, research, and regulation. Information is available on oral health care for the public. 11
12 This project is made possible by ITNS, providing educational endeavors for improving patient care and outcomes. Authors: Leslie Gibson RN, BScN, CDA II Beverly Kosmach-Park MSN, CRNP James Guggenheimer DDS Reviewers: Caroline Tassey MS ARNP CCRN Pat Folk RN, BSN, CCTC Kathy Lawrence MN, RN Darlene Long MS, APRN, BC, ANP, CCTC Cindy Hoekstra RN, BScN, CCTN Lisa L. Bakken RN BSN CCTC The International Transplant Nurses Society was founded in 1992 as the first professional nursing organization to focus on the professional growth and development of the transplant clinician. ITNS is committed to the promotion of excellence in transplant clinical nursing through the provision of educational and professional growth opportunities, interdisciplinary networking and collaborative activities, and transplant nursing research. This educational brochure is designed to enhance patient education as provided by individual transplant centers. Patients should follow their transplant team s specific guidelines for dental care after transplant. Printed in the USA 10/2010 5K
Your child s heart problem and dental care
 Your child s heart problem and dental care Contents p.3 Why is dental health important for my child? p.3 What is tooth decay and what causes it? p.4 How can I prevent this from happening to my child? p.6
Your child s heart problem and dental care Contents p.3 Why is dental health important for my child? p.3 What is tooth decay and what causes it? p.4 How can I prevent this from happening to my child? p.6
Oral health care is vital for seniors
 Oral health care is vital for seniors (NC) Statistics Canada estimates seniors represent the fastest growing segment of the Canadian population, a segment expected to reach 9.2 million by 2041. As more
Oral health care is vital for seniors (NC) Statistics Canada estimates seniors represent the fastest growing segment of the Canadian population, a segment expected to reach 9.2 million by 2041. As more
Dental Care and Chronic Conditions. Respiratory Disease Cardiovascular Disease Diabetes
 Dental Care and Chronic Conditions Respiratory Disease Cardiovascular Disease Diabetes Shape Up Your Smile and Avoid Some Complications of Chronic Diseases When you take good care of your oral health,
Dental Care and Chronic Conditions Respiratory Disease Cardiovascular Disease Diabetes Shape Up Your Smile and Avoid Some Complications of Chronic Diseases When you take good care of your oral health,
Dental health following cancer treatment
 Dental health following cancer treatment Treatment for cancer often increases the risk for dental problems. As a cancer survivor, it is important for you to understand the reasons why dental care is especially
Dental health following cancer treatment Treatment for cancer often increases the risk for dental problems. As a cancer survivor, it is important for you to understand the reasons why dental care is especially
Tooth Decay. What Is Tooth Decay? Tooth decay happens when you have an infection of your teeth.
 Tooth Decay What Is Tooth Decay? Tooth decay happens when you have an infection of your teeth. When you eat food and drink, it is broken down into acid. This acid helps to make plaque (a sticky substance).
Tooth Decay What Is Tooth Decay? Tooth decay happens when you have an infection of your teeth. When you eat food and drink, it is broken down into acid. This acid helps to make plaque (a sticky substance).
Cancer Care Oral Mucositis Managing Oral Care After Radiation or Chemotherapy. May 08
 Cancer Care Oral Mucositis Managing Oral Care After Radiation or Chemotherapy May 08 Halton Region Health Department Mission Statement Together with the Halton community, the Health Department works to
Cancer Care Oral Mucositis Managing Oral Care After Radiation or Chemotherapy May 08 Halton Region Health Department Mission Statement Together with the Halton community, the Health Department works to
Dental care for patients with head and neck cancer
 Dental care for patients with head and neck cancer This leaflet explains why it is important to see a dentist before and after your treatment for head and neck cancer. It also explains what you can expect
Dental care for patients with head and neck cancer This leaflet explains why it is important to see a dentist before and after your treatment for head and neck cancer. It also explains what you can expect
Dental Health and Epilepsy
 Dental Health and Epilepsy Good dental health is important to everyone. But it is especially important for people who take antiepileptic medications. Certain antiepileptic drugs and other medications can
Dental Health and Epilepsy Good dental health is important to everyone. But it is especially important for people who take antiepileptic medications. Certain antiepileptic drugs and other medications can
Your Own Teeth and Gums
 Your Own Teeth and Gums CHAPTER1 Next time you look in a mirror, look at your teeth and the skin (gums) around them. Look in your children s mouths, too. Look at both gums and teeth, because the health
Your Own Teeth and Gums CHAPTER1 Next time you look in a mirror, look at your teeth and the skin (gums) around them. Look in your children s mouths, too. Look at both gums and teeth, because the health
1. Target Keyword: How to care for your toddler's teeth Page Title: How to care for your toddler's teeth
 1. Target Keyword: How to care for your toddler's teeth Page Title: How to care for your toddler's teeth Toddlers are often stubborn when it comes to the essentials of life; as any parent can attest, they
1. Target Keyword: How to care for your toddler's teeth Page Title: How to care for your toddler's teeth Toddlers are often stubborn when it comes to the essentials of life; as any parent can attest, they
Lesson 2: Save your Smile from Tooth Decay
 Lesson 2: Save your Smile from Tooth Decay OVERVIEW Objectives: By the end of the lesson, the Lay Health Worker will be able to: 1. Describe what tooth decay is and how it happens. 2. State the causes
Lesson 2: Save your Smile from Tooth Decay OVERVIEW Objectives: By the end of the lesson, the Lay Health Worker will be able to: 1. Describe what tooth decay is and how it happens. 2. State the causes
U.S. Department of Health and Human Services National Institutes of Health National Institute of Dental and Craniofacial Research
 U.S. Department of Health and Human Services National Institutes of Health National Institute of Dental and Craniofacial Research What do I need to know about dry mouth? Dry mouth is the feeling that
U.S. Department of Health and Human Services National Institutes of Health National Institute of Dental and Craniofacial Research What do I need to know about dry mouth? Dry mouth is the feeling that
[PAGE HEADLINE] Improve your Health and Change Your Smile with Complete Dental Services in One [CITYNAME] Location
![[PAGE HEADLINE] Improve your Health and Change Your Smile with Complete Dental Services in One [CITYNAME] Location [PAGE HEADLINE] Improve your Health and Change Your Smile with Complete Dental Services in One [CITYNAME] Location](/thumbs/31/14971568.jpg) Eddie Stephens//Copywriter Sample: Website copy/internal Dental Services Pages [PAGE HEADLINE] Improve your Health and Change Your Smile with Complete Dental Services in One [CITYNAME] Location [LEAD SENTENCE/PARAGRAPH]
Eddie Stephens//Copywriter Sample: Website copy/internal Dental Services Pages [PAGE HEADLINE] Improve your Health and Change Your Smile with Complete Dental Services in One [CITYNAME] Location [LEAD SENTENCE/PARAGRAPH]
Oxford Centre for Head and Neck Oncology. Sore Mouth or Throat (Mucositis) Dry Mouth (Xerostomia) Oral Thrush (Candida) Information for patients
 Oxford Centre for Head and Neck Oncology Sore Mouth or Throat (Mucositis) Dry Mouth (Xerostomia) Oral Thrush (Candida) Information for patients This leaflet gives you some suggested remedies which previous
Oxford Centre for Head and Neck Oncology Sore Mouth or Throat (Mucositis) Dry Mouth (Xerostomia) Oral Thrush (Candida) Information for patients This leaflet gives you some suggested remedies which previous
Understanding Dental Implants
 Understanding Dental Implants Comfort and Confidence Again A new smile It s no fun when you re missing teeth. You may not feel comfortable eating or speaking. You might even avoid smiling in public. Fortunately,
Understanding Dental Implants Comfort and Confidence Again A new smile It s no fun when you re missing teeth. You may not feel comfortable eating or speaking. You might even avoid smiling in public. Fortunately,
Managing Mouth Sores
 Managing Mouth Sores The following information is based on the general experiences of many prostate cancer patients. Your experience may be different. If you have any questions about what prostate cancer
Managing Mouth Sores The following information is based on the general experiences of many prostate cancer patients. Your experience may be different. If you have any questions about what prostate cancer
Dental care and treatment for patients with head and neck cancer. Department of Restorative Dentistry Information for patients
 Dental care and treatment for patients with head and neck cancer Department of Restorative Dentistry Information for patients i Why have I been referred to the Restorative Dentistry Team? Treatment of
Dental care and treatment for patients with head and neck cancer Department of Restorative Dentistry Information for patients i Why have I been referred to the Restorative Dentistry Team? Treatment of
How to take care of your baby s teeth and gums
 Children s Dental Health In This Issue: } How to take care of your baby s teeth and gums } How to keep your child s teeth healthy } Preparing Kids for Their First Dental Checkup How to take care of your
Children s Dental Health In This Issue: } How to take care of your baby s teeth and gums } How to keep your child s teeth healthy } Preparing Kids for Their First Dental Checkup How to take care of your
HOW TO MAKE SURE YOUR MOUTH MAKES IT THROUGH YOUR TWENTIES.
 HOW TO MAKE SURE YOUR MOUTH MAKES IT THROUGH YOUR TWENTIES. By now you ll know that virtually everything you do can be bad for you. While most of us make it through our teens and twenties in one piece,
HOW TO MAKE SURE YOUR MOUTH MAKES IT THROUGH YOUR TWENTIES. By now you ll know that virtually everything you do can be bad for you. While most of us make it through our teens and twenties in one piece,
Periodontal (Gum) Disease: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatments
 Periodontal (Gum) Disease: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatments Introduction If you have been told you have periodontal (gum) disease, you're not alone. An estimated 80 percent of American adults currently
Periodontal (Gum) Disease: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatments Introduction If you have been told you have periodontal (gum) disease, you're not alone. An estimated 80 percent of American adults currently
LANAP. (Laser Assisted New Attachment Procedure)
 LANAP (Laser Assisted New Attachment Procedure) Marcus Hannah, DDS 970 N. Kalaheo Avenue, Suite A305 Kailua, HI 96734 Tel: 808.254.5454 Fax: 808.254.5427 Dental Laser ANAP Informed Consent and Authorization
LANAP (Laser Assisted New Attachment Procedure) Marcus Hannah, DDS 970 N. Kalaheo Avenue, Suite A305 Kailua, HI 96734 Tel: 808.254.5454 Fax: 808.254.5427 Dental Laser ANAP Informed Consent and Authorization
Mouth care during chemotherapy
 Some people having chemotherapy treatment find that their mouth gets sore. This information gives some tips about how you can look after your mouth before and during your chemotherapy treatment. In this
Some people having chemotherapy treatment find that their mouth gets sore. This information gives some tips about how you can look after your mouth before and during your chemotherapy treatment. In this
Oral Health. Steps to a healthy mouth Use good oral hygiene. least twice each day with fluoride toothpaste. (ADA) Seal of Acceptance.
 Oral Health Oral refers to the mouth, which includes the teeth, gums, and supporting tissues. And having a healthy mouth means more than just having nice-looking teeth your whole mouth needs care. It is
Oral Health Oral refers to the mouth, which includes the teeth, gums, and supporting tissues. And having a healthy mouth means more than just having nice-looking teeth your whole mouth needs care. It is
GRADE 6 DENTAL HEALTH
 GRADE 6 DENTAL HEALTH DENTAL HEALTH GRADE: 6 LESSON: 1 THEME: STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION CONCEPT: THE STRUCTURE OF A TOOTH IS RELATED TO ITS FUNCTION PREPARATION: 1. Prepare an overhead transparency of Parts
GRADE 6 DENTAL HEALTH DENTAL HEALTH GRADE: 6 LESSON: 1 THEME: STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION CONCEPT: THE STRUCTURE OF A TOOTH IS RELATED TO ITS FUNCTION PREPARATION: 1. Prepare an overhead transparency of Parts
Best Practices for Oral Health Assessments for School Nurses. Jill Fernandez RDH, MPH. National Association of School Nurses June 22, 2012
 Best Practices for Oral Health Assessments for School Nurses Jill Fernandez RDH, MPH National Association of School Nurses June 22, 2012 Jill Fernandez RDH, MPH Clinical Associate Professor Department
Best Practices for Oral Health Assessments for School Nurses Jill Fernandez RDH, MPH National Association of School Nurses June 22, 2012 Jill Fernandez RDH, MPH Clinical Associate Professor Department
Building Better Oral Health Communities
 Building Better Oral Health Communities Better Oral Health in Home Care Activity 4 answers: Care of natural teeth Building Better Oral Health Communities Better Oral Health in Home Care Prepared by Ms
Building Better Oral Health Communities Better Oral Health in Home Care Activity 4 answers: Care of natural teeth Building Better Oral Health Communities Better Oral Health in Home Care Prepared by Ms
Type 2 Diabetes. Increase of diabetic complications as HAIC increases
 Type 2 Diabetes Diabetes is a disease of too much sugar (glucose) in the blood. Type 2 diabetes is caused by insulin resistance of the cells and abnormal insulin production by the pancreas. Insulin is
Type 2 Diabetes Diabetes is a disease of too much sugar (glucose) in the blood. Type 2 diabetes is caused by insulin resistance of the cells and abnormal insulin production by the pancreas. Insulin is
Learning about Mouth Cancer
 Learning about Mouth Cancer Creation of this material was made possible in part by a pioneering grant from CBCC-USA. Distributed by India Cancer Initiative What is mouth cancer? Our bodies are made up
Learning about Mouth Cancer Creation of this material was made possible in part by a pioneering grant from CBCC-USA. Distributed by India Cancer Initiative What is mouth cancer? Our bodies are made up
For Pediatric Oncology Patients and Families
 Atlantic Provinces Pediatric Hematology Oncology Network Réseau d oncologie et d hématologie pédiatrique des provinces de l Atlantique 5850/5980 University Avenue, PO Box 9700, Halifax, NS, B3K 6R8, 1.902.470.7429,
Atlantic Provinces Pediatric Hematology Oncology Network Réseau d oncologie et d hématologie pédiatrique des provinces de l Atlantique 5850/5980 University Avenue, PO Box 9700, Halifax, NS, B3K 6R8, 1.902.470.7429,
Radiation Treatment and Your Mouth
 Radiation Treatment and Your Mouth Oral Health, Cancer Care, and You Fitting the Pieces Together Oral Health, Cancer Care, and You Fitting the Pieces Together Oral Health, Cancer Care, and You is an awareness
Radiation Treatment and Your Mouth Oral Health, Cancer Care, and You Fitting the Pieces Together Oral Health, Cancer Care, and You Fitting the Pieces Together Oral Health, Cancer Care, and You is an awareness
Post-Transplant Diabetes: What Every Patient Needs to Know
 Post-Transplant Diabetes: What Every Patient Needs to Know International Transplant Nurses Society What is Diabetes? Diabetes is an illness that effects how your body makes and uses a hormone called insulin.
Post-Transplant Diabetes: What Every Patient Needs to Know International Transplant Nurses Society What is Diabetes? Diabetes is an illness that effects how your body makes and uses a hormone called insulin.
Oral Health Risk Assessment
 Oral Health Risk Assessment Paula Duncan, MD Oral Health Initiative January 22, 2011 I have no relevant financial relationships with the manufacturers of any commercial products and/or provider of commercial
Oral Health Risk Assessment Paula Duncan, MD Oral Health Initiative January 22, 2011 I have no relevant financial relationships with the manufacturers of any commercial products and/or provider of commercial
Why Good Oral Health is Important. Poor oral health and dental pain significantly affect residents in a variety of ways, including:
 The Facts... IOWA GERIATRIC EDUCATION CENTER INFO-CONNECT Oral Hygiene Care for Nursing Home Residents with Dementia Oral hygiene care is very difficult for many residents with dementia. Residents with
The Facts... IOWA GERIATRIC EDUCATION CENTER INFO-CONNECT Oral Hygiene Care for Nursing Home Residents with Dementia Oral hygiene care is very difficult for many residents with dementia. Residents with
Suggested Open Ended Questions Suggested Affirming Statements Suggested Nutrition Education Statements
 Suggested Open Ended Questions Suggested Affirming Statements Suggested Nutrition Education Statements Caregiver: How did your baby s last check-up go? Primary Feeding: Tell me about the kind of formula
Suggested Open Ended Questions Suggested Affirming Statements Suggested Nutrition Education Statements Caregiver: How did your baby s last check-up go? Primary Feeding: Tell me about the kind of formula
Cheekbone (zygoma) and/or eye socket (orbit) fracture surgery
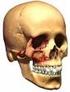 Ambulatory Care & Local Networks Cheekbone (zygoma) and/or eye socket (orbit) fracture surgery Information for patients You have been treated in the Emergency Department for a broken (fractured) cheekbone
Ambulatory Care & Local Networks Cheekbone (zygoma) and/or eye socket (orbit) fracture surgery Information for patients You have been treated in the Emergency Department for a broken (fractured) cheekbone
THE TRUTH. What it is like to provide baby dental care. Beth Noel RDH, BS
 THE TRUTH What it is like to provide baby dental care Beth Noel RDH, BS Oral Health During Pregnancy Good oral health for infants starts during pregnancy 2012 Oral Health Care During Pregnancy : A National
THE TRUTH What it is like to provide baby dental care Beth Noel RDH, BS Oral Health During Pregnancy Good oral health for infants starts during pregnancy 2012 Oral Health Care During Pregnancy : A National
Tooth Replacement Options
 Dr. Jordan Johnson Johnson Dental Associates http://www.beta.mydentalhub.com/ada/test/ (800) 947-4746 Tooth Replacement Options If you re missing one or more teeth, you may be all too aware of their importance
Dr. Jordan Johnson Johnson Dental Associates http://www.beta.mydentalhub.com/ada/test/ (800) 947-4746 Tooth Replacement Options If you re missing one or more teeth, you may be all too aware of their importance
What Dental Implants Can Do For You!
 What Dental Implants Can Do For You! Putting Smiles into Motion About Implants 01. What if a Tooth is Lost and the Area is Left Untreated? 02. Do You Want to Restore Confidence in Your Appearance? 03.
What Dental Implants Can Do For You! Putting Smiles into Motion About Implants 01. What if a Tooth is Lost and the Area is Left Untreated? 02. Do You Want to Restore Confidence in Your Appearance? 03.
Dental Health Following Childhood Cancer Treatment
 Following Childhood Cancer Treatment Treatment for cancer during childhood often increases the risk for dental problems. As a childhood cancer survivor, it is important for you to understand the reasons
Following Childhood Cancer Treatment Treatment for cancer during childhood often increases the risk for dental problems. As a childhood cancer survivor, it is important for you to understand the reasons
There are three major forms of this disease.
 For more information about diabetes and it s risk factors, visit our website at: doh.sd.gov/diabetes or visit the South Dakota Diabetes Association at: www.sddiabetescoalition.org/ Your body needs insulin
For more information about diabetes and it s risk factors, visit our website at: doh.sd.gov/diabetes or visit the South Dakota Diabetes Association at: www.sddiabetescoalition.org/ Your body needs insulin
Dental Health Tip Cards
 A Parent s Guide Birth to SIX years Dental Health Tip Cards Six Dental Health Tip Cards are available from your local health region that highlight specific topics of interest regarding your child's dental
A Parent s Guide Birth to SIX years Dental Health Tip Cards Six Dental Health Tip Cards are available from your local health region that highlight specific topics of interest regarding your child's dental
Table of Contents. Grades Preschool 1 (Ages 4-7)...3. Grades 2 3 (Ages 7-9)...19. Grades 4 6 (Ages 9-12)...38
 Table of Contents HAPPY TEETH! Grades Preschool 1 (Ages 4-7)...3 A LIFETIME OF HEALTHY HAPPY TEETH! Grades 2 3 (Ages 7-9)...19 TEETH TO TREASURE! Grades 4 6 (Ages 9-12)...38 Legends for A-Maze-ing Message
Table of Contents HAPPY TEETH! Grades Preschool 1 (Ages 4-7)...3 A LIFETIME OF HEALTHY HAPPY TEETH! Grades 2 3 (Ages 7-9)...19 TEETH TO TREASURE! Grades 4 6 (Ages 9-12)...38 Legends for A-Maze-ing Message
Oral Health QUESTIONS
 Oral Health COMPENTENCY The resident should understand the timing of tooth development. The resident should recognize the clinical picture of bottle caries. In addition, the resident should know the current
Oral Health COMPENTENCY The resident should understand the timing of tooth development. The resident should recognize the clinical picture of bottle caries. In addition, the resident should know the current
High blood sugars caused by steroids
 High blood sugars caused by steroids Your blood sugars are high because you are taking a medication called steroids. Steroids are used to: decrease swelling decrease the natural response of your immune
High blood sugars caused by steroids Your blood sugars are high because you are taking a medication called steroids. Steroids are used to: decrease swelling decrease the natural response of your immune
Oral health and MS. Factsheet. How might MS affect my oral health? September 2012
 Factsheet September 2012 Oral health and MS MS (multiple sclerosis) doesn't directly make you more likely to get dental problems than other people. But it might make it harder for you to maintain good
Factsheet September 2012 Oral health and MS MS (multiple sclerosis) doesn't directly make you more likely to get dental problems than other people. But it might make it harder for you to maintain good
Lateral pterygoid muscle Medial pterygoid muscle
 PATIENT INFORMATION BOOKLET Trismus Normal Jaw Function The jaw is a pair of bones that form the framework of the mouth and teeth. The upper jaw is called the maxilla. The lower jaw is called the mandible.
PATIENT INFORMATION BOOKLET Trismus Normal Jaw Function The jaw is a pair of bones that form the framework of the mouth and teeth. The upper jaw is called the maxilla. The lower jaw is called the mandible.
Protocol for the treatment of oral candida at E.M.H.
 Protocol for the treatment of oral candida at E.M.H. Introduction Candidosis and Xerostomia [a dry mouth] are the two most common oral problems found in palliative care. Cancer patients are very susceptible
Protocol for the treatment of oral candida at E.M.H. Introduction Candidosis and Xerostomia [a dry mouth] are the two most common oral problems found in palliative care. Cancer patients are very susceptible
Important Information for Patients Who Receive Radiation Therapy to the Head & Neck Region. Therapeutic Radiation & Oral Heath
 Important Information for Patients Who Receive Radiation Therapy to the Head & Neck Region Therapeutic Radiation & Oral Heath This leaflet should be given to patients attending the Head and Neck Cancer
Important Information for Patients Who Receive Radiation Therapy to the Head & Neck Region Therapeutic Radiation & Oral Heath This leaflet should be given to patients attending the Head and Neck Cancer
FOLFOX Chemotherapy. This handout provides information about FOLFOX chemotherapy. It is sometimes called as FLOX chemotherapy.
 FOLFOX Chemotherapy This handout provides information about FOLFOX chemotherapy. It is sometimes called as FLOX chemotherapy. What is chemotherapy? Chemotherapy is a method of treating cancer by using
FOLFOX Chemotherapy This handout provides information about FOLFOX chemotherapy. It is sometimes called as FLOX chemotherapy. What is chemotherapy? Chemotherapy is a method of treating cancer by using
In-Patient Radioactive Iodine ( 131 I) Treatment
 In-Patient Radioactive Iodine ( 131 I) Treatment Information for patients and families Princess Margaret Read this booklet to learn: what radioactive iodine treatment is what to expect instructions to
In-Patient Radioactive Iodine ( 131 I) Treatment Information for patients and families Princess Margaret Read this booklet to learn: what radioactive iodine treatment is what to expect instructions to
dental care every day
 dental care every day A Caregiver s Guide U.S. DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH National Institute of Dental and Craniofacial Research Contents Getting Started... 2
dental care every day A Caregiver s Guide U.S. DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH National Institute of Dental and Craniofacial Research Contents Getting Started... 2
Take Control of Your Health and Reduce Your Cancer Risk
 Take Control of Your Health and Reduce Your Cancer Risk Creation of this material was made possible in part by a pioneering grant from CBCC-USA. Distributed by India Cancer Initiative Take Control of
Take Control of Your Health and Reduce Your Cancer Risk Creation of this material was made possible in part by a pioneering grant from CBCC-USA. Distributed by India Cancer Initiative Take Control of
Taking Out a Tooth. Before You Begin: Ask Questions! CHAPTER11
 159 CHAPTER11 Taking Out a Tooth Not every painful tooth needs to come out. You must decide how serious the problem is, and then decide if you can treat and save the tooth. Some problems such as root canal
159 CHAPTER11 Taking Out a Tooth Not every painful tooth needs to come out. You must decide how serious the problem is, and then decide if you can treat and save the tooth. Some problems such as root canal
For the Patient: GDP Other names: LYGDP
 1 For the Patient: GDP Other names: LYGDP G D P Gemcitabine Dexamethasone (taken by mouth) CISPlatin Uses: GDP is a drug treatment given for Non-Hodgkins and Hodgkin Lymphoma with the expectation of destroying
1 For the Patient: GDP Other names: LYGDP G D P Gemcitabine Dexamethasone (taken by mouth) CISPlatin Uses: GDP is a drug treatment given for Non-Hodgkins and Hodgkin Lymphoma with the expectation of destroying
4th-5th grade Lesson Plan
 4th-5th grade Lesson Plan Curriculum Guide Objective: The student will be able to explain why sodas, chewing gum, and candy are bad for our teeth. 1) Guiding Questions How and why do cavities form on our
4th-5th grade Lesson Plan Curriculum Guide Objective: The student will be able to explain why sodas, chewing gum, and candy are bad for our teeth. 1) Guiding Questions How and why do cavities form on our
SAMPLE. Your Child s Teeth. Parents. Helpful Tips for Parents and Caregivers W177
 Parents Your Child s Teeth Helpful Tips for Parents and Caregivers Produced in cooperation with the American Academy of Pediatric Dentistry (www.aapd.org) and the American Association of Orthodontists
Parents Your Child s Teeth Helpful Tips for Parents and Caregivers Produced in cooperation with the American Academy of Pediatric Dentistry (www.aapd.org) and the American Association of Orthodontists
Fluoride Products for Oral Health: Professional Information
 Albertans without water fluoridation and without drinking water that has natural fluoride around 0.7 parts per million (ppm) may benefit from other forms of fluoride that prevent tooth decay. This information
Albertans without water fluoridation and without drinking water that has natural fluoride around 0.7 parts per million (ppm) may benefit from other forms of fluoride that prevent tooth decay. This information
Supported by. A seven part series exploring the fantastic world of science.
 Supported by A seven part series exploring the fantastic world of science. Find out about the different types of teeth in your mouth. Milk Teeth As a child you have 20 milk teeth. Your first tooth appears
Supported by A seven part series exploring the fantastic world of science. Find out about the different types of teeth in your mouth. Milk Teeth As a child you have 20 milk teeth. Your first tooth appears
A PARENT S GUIDE. Caring for Children s Teeth. Teething Toddlers to Teens, One Smile at a Time.
 A PARENT S GUIDE Caring for Children s Teeth. Teething Toddlers to Teens, One Smile at a Time. Oral Care in America THE ISSUE In May 2001, the Office of the Surgeon General released its first ever report
A PARENT S GUIDE Caring for Children s Teeth. Teething Toddlers to Teens, One Smile at a Time. Oral Care in America THE ISSUE In May 2001, the Office of the Surgeon General released its first ever report
How To Care For Older People
 Healthy Mouth, Healthy Ageing ORAL HEALTH GUIDE FOR CAREGIVERS OF OLDER PEOPLE This publication was prepared in conjunction with Healthy Mouth, Healthy Ageing ORAL HEALTH GUIDE FOR CAREGIVERS OF OLDER
Healthy Mouth, Healthy Ageing ORAL HEALTH GUIDE FOR CAREGIVERS OF OLDER PEOPLE This publication was prepared in conjunction with Healthy Mouth, Healthy Ageing ORAL HEALTH GUIDE FOR CAREGIVERS OF OLDER
get more customers who need more, Cigna Dental Oral Health Integration Program
 Cigna Dental Oral Health Integration Program customers who need more, get more For eligible Cigna Dental customers. The Cigna Dental Oral Health Integration Program was first to enhance dental coverage
Cigna Dental Oral Health Integration Program customers who need more, get more For eligible Cigna Dental customers. The Cigna Dental Oral Health Integration Program was first to enhance dental coverage
Take Charge of Your Diabetes
 Take Charge of Your Diabetes A Reinforcement Booklet for People With Diabetes Purpose and Acknowledgments This simplified and shortened overview of CDC s 1997 publication, Take Charge of Your Diabetes,
Take Charge of Your Diabetes A Reinforcement Booklet for People With Diabetes Purpose and Acknowledgments This simplified and shortened overview of CDC s 1997 publication, Take Charge of Your Diabetes,
USE AND CARE INSTRUCTIONS for your Invisalign aligners
 USE AND CARE INSTRUCTIONS for your Invisalign aligners WEARING AND USING YOURINVISALIGN ALIGNERS - ENGLISH Here are some tips to help ensure proper use and avoid damaging your aligners. Always Remember
USE AND CARE INSTRUCTIONS for your Invisalign aligners WEARING AND USING YOURINVISALIGN ALIGNERS - ENGLISH Here are some tips to help ensure proper use and avoid damaging your aligners. Always Remember
Better Breathing with COPD
 Better Breathing with COPD People with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) often benefit from learning different breathing techniques. Pursed Lip Breathing Pursed Lip Breathing (PLB) can be very
Better Breathing with COPD People with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) often benefit from learning different breathing techniques. Pursed Lip Breathing Pursed Lip Breathing (PLB) can be very
Medications to help you quit smoking
 Medications to help you quit smoking How can medication help me quit smoking? Using medications can increase your chances of quitting smoking 2 to 3 times more than quitting without using medications.
Medications to help you quit smoking How can medication help me quit smoking? Using medications can increase your chances of quitting smoking 2 to 3 times more than quitting without using medications.
Injecting Inside the Mouth
 Injecting Inside the Mouth 135 9 CHAPTER It is possible to treat a tooth without pain. You do this with an injection of local anesthetic. You must inject near the nerve, so to give good injections, you
Injecting Inside the Mouth 135 9 CHAPTER It is possible to treat a tooth without pain. You do this with an injection of local anesthetic. You must inject near the nerve, so to give good injections, you
Electronic Medical Record Integration Guide: Pediatric Oral Health in Primary Care Practices
 Electronic Medical Record Integration Guide: Pediatric Oral Health in Primary Care Practices (Documentation, Coding, Charging, Billing & Measurement) The purpose of this document is to guide medical providers
Electronic Medical Record Integration Guide: Pediatric Oral Health in Primary Care Practices (Documentation, Coding, Charging, Billing & Measurement) The purpose of this document is to guide medical providers
IMPLANT CONSENT FORM WHAT ARE DENTAL IMPLANTS?
 IMPLANT CONSENT FORM WHAT ARE DENTAL IMPLANTS? Dental implants are a very successful and accepted treatment option to replace lost or missing teeth. A dental implant is essentially an artificial tooth
IMPLANT CONSENT FORM WHAT ARE DENTAL IMPLANTS? Dental implants are a very successful and accepted treatment option to replace lost or missing teeth. A dental implant is essentially an artificial tooth
Michael Abufaris, DDS, PA 201 N Lakemont Ave, Suite 600 Winter Park, FL 32792 407.629.6400
 Michael Abufaris, DDS, PA 201 N Lakemont Ave, Suite 600 Winter Park, FL 32792 407.629.6400 Oral lichen Oral lichen planus is an inflammatory condition of the mucus membranes (mucosa) and/or skin. The cause
Michael Abufaris, DDS, PA 201 N Lakemont Ave, Suite 600 Winter Park, FL 32792 407.629.6400 Oral lichen Oral lichen planus is an inflammatory condition of the mucus membranes (mucosa) and/or skin. The cause
Taking care of your dental Implants ( By Dr. B. Pulec )
 This article is written and presented by Dr. Boris Pulec MDS Dr. Pulec graduated from the University of Toronto and has been practicing privately for over 27 years. He has been a proponent of patient education
This article is written and presented by Dr. Boris Pulec MDS Dr. Pulec graduated from the University of Toronto and has been practicing privately for over 27 years. He has been a proponent of patient education
Instructions Following Dental Implant Surgery
 Instructions Following Dental Implant Surgery Swelling is to be expected and usually reaches its maximum in 2-3 days. To minimize swelling, cold packs or ice bag wrapped in a towel should be applied to
Instructions Following Dental Implant Surgery Swelling is to be expected and usually reaches its maximum in 2-3 days. To minimize swelling, cold packs or ice bag wrapped in a towel should be applied to
4 Steps to Manage Your Diabetes for Life
 4 Steps to Manage Your Diabetes for Life ENGLISH A program of the National Institutes of Health and the Centers for Disease Control and Preventioni This booklet gives four key steps to help you manage
4 Steps to Manage Your Diabetes for Life ENGLISH A program of the National Institutes of Health and the Centers for Disease Control and Preventioni This booklet gives four key steps to help you manage
Living With Congestive Heart Failure
 Living With Congestive Heart Failure Information for patients and their families Patient information developed by EPICORE Centre, Division of Cardiology, University of Alberta The REACT study: supported
Living With Congestive Heart Failure Information for patients and their families Patient information developed by EPICORE Centre, Division of Cardiology, University of Alberta The REACT study: supported
Guidelines for Surgical Patients
 Guidelines for Surgical Patients Guidelines for Surgical Patients We are pleased that you and your physician have selected us to provide your surgical care. Everyone associated with the hospital is dedicated
Guidelines for Surgical Patients Guidelines for Surgical Patients We are pleased that you and your physician have selected us to provide your surgical care. Everyone associated with the hospital is dedicated
Background (cont) World Health Organisation (WHO) and IDF predict that this number will increase to more than 1,3 million in the next 25 years.
 Diabetes Overview Background What is diabetes Non-modifiable risk factors Modifiable risk factors Common symptoms of diabetes Early diagnosis and management of diabetes Non-medical management of diabetes
Diabetes Overview Background What is diabetes Non-modifiable risk factors Modifiable risk factors Common symptoms of diabetes Early diagnosis and management of diabetes Non-medical management of diabetes
Patient Information. Patient s First and Last name: Preferred Name: Mailing Address: City: State: Zip Code: Date of Birth: Gender:
 Patient Information: Patient Information Patient s First and Last name: Preferred Name: Mailing Address: Date of Birth: Gender: Best Number to Confirm Your Appointments: Alternate Phone Number: Social
Patient Information: Patient Information Patient s First and Last name: Preferred Name: Mailing Address: Date of Birth: Gender: Best Number to Confirm Your Appointments: Alternate Phone Number: Social
Oral Hygiene Aids Áiseanna Shláinteachas Béil
 Oral Hygiene Aids Áiseanna Shláinteachas Béil Older people and those who are dependent or in palliative care may benefit from a range of oral hygiene aids designed to help keep mouth and gums healthy.
Oral Hygiene Aids Áiseanna Shláinteachas Béil Older people and those who are dependent or in palliative care may benefit from a range of oral hygiene aids designed to help keep mouth and gums healthy.
4 Steps to Control Your Diabetes for Life
 4 Steps to Control Your Diabetes for Life Contents Step 1: Learn about diabetes... 6 Step 2: Know your diabetes ABCs... 12 Step 3: Manage your diabetes... 16 Step 4: Get routine care... 22 Notes... 26
4 Steps to Control Your Diabetes for Life Contents Step 1: Learn about diabetes... 6 Step 2: Know your diabetes ABCs... 12 Step 3: Manage your diabetes... 16 Step 4: Get routine care... 22 Notes... 26
Fluoride Strengthens Teeth
 Fluoride Strengthens Teeth Two hard-boiled eggs Fluoride gel or solution, 4 to 6 oz. (from dental office) Three clean plastic containers Several cans of dark soda Water 1. Place a hard-boiled egg in one
Fluoride Strengthens Teeth Two hard-boiled eggs Fluoride gel or solution, 4 to 6 oz. (from dental office) Three clean plastic containers Several cans of dark soda Water 1. Place a hard-boiled egg in one
INFORMATION ON AFTERCARE OF DENTAL IMPLANTS
 INFORMATION ON AFTERCARE OF DENTAL IMPLANTS.132.indd 1 30.11.11 16:0 WHAT DOES AFTERCARE CONSIST OF? Straumann implants are a modern option for tooth replacement when you are missing one or more teeth.
INFORMATION ON AFTERCARE OF DENTAL IMPLANTS.132.indd 1 30.11.11 16:0 WHAT DOES AFTERCARE CONSIST OF? Straumann implants are a modern option for tooth replacement when you are missing one or more teeth.
Dental Health Guide. School Nurses
 Dental Health Guide Dental Health for Guide School fornurses School Nurses Missouri Department of Health and Senior Services Missouri Department of Health and Senior Services 2014 Missouri Department of
Dental Health Guide Dental Health for Guide School fornurses School Nurses Missouri Department of Health and Senior Services Missouri Department of Health and Senior Services 2014 Missouri Department of
Healthy Smile Connection for Young Children and Children with Special Health Care Needs
 Healthy Smile Connection for Young Children and Children with Special Health Care Needs Disclosure statement: I have no relevant financial relationships, conflicts of interest, or commercial support to
Healthy Smile Connection for Young Children and Children with Special Health Care Needs Disclosure statement: I have no relevant financial relationships, conflicts of interest, or commercial support to
Dental Care in Scleroderma
 Dental Care in Scleroderma People living with scleroderma face unique challenges while trying to maintain their oral health. They are more likely to be affected by dental conditions such as small mouth,
Dental Care in Scleroderma People living with scleroderma face unique challenges while trying to maintain their oral health. They are more likely to be affected by dental conditions such as small mouth,
Iodine-131 Treatment of Thyroid Cancer Information about your treatment November 2011 Great Staff Great Care Great Future
 Department of Nuclear Medicine Iodine-131 Treatment of Thyroid Cancer Information about your treatment November 2011 Great Staff Great Care Great Future INTRODUCTION This leaflet has been produced to give
Department of Nuclear Medicine Iodine-131 Treatment of Thyroid Cancer Information about your treatment November 2011 Great Staff Great Care Great Future INTRODUCTION This leaflet has been produced to give
SENIOR ORAL HEALTH. Oral Health Care Concerns Preventive Guidelines & Techniques for Seniors and Caregivers
 SENIOR ORAL HEALTH Oral Health Care Concerns Preventive Guidelines & Techniques for Seniors and Caregivers Funded by: United Way of Tucson and Southern Arizona and the Alliance of the American Dental Association
SENIOR ORAL HEALTH Oral Health Care Concerns Preventive Guidelines & Techniques for Seniors and Caregivers Funded by: United Way of Tucson and Southern Arizona and the Alliance of the American Dental Association
Galerie Dental Care. Patient Information. Emergency Contact Relationship: Phone:
 Galerie Dental Care Patient Information Date: Patient Name: Last First Middle Initial (Preferred Name) Gender: Birth Date: Marital/Family Status Address: Street Apartment # City Province Postal Code Phone
Galerie Dental Care Patient Information Date: Patient Name: Last First Middle Initial (Preferred Name) Gender: Birth Date: Marital/Family Status Address: Street Apartment # City Province Postal Code Phone
Oral health and MS. Factsheet
 Factsheet Oral health and MS Multiple sclerosis (MS) does not directly make you any more susceptible to dental diseases than other members of the population. However, people with MS often have difficulties
Factsheet Oral health and MS Multiple sclerosis (MS) does not directly make you any more susceptible to dental diseases than other members of the population. However, people with MS often have difficulties
TrialNet Natural History Study of the Development of Type 1 Diabetes: A Pathway to Prevention
 TrialNet Natural History Study of the Development of Type 1 Diabetes: A Pathway to Prevention Type 1 Diabetes TrialNet Researchers in this study are part of a larger group called Type 1 Diabetes TrialNet.
TrialNet Natural History Study of the Development of Type 1 Diabetes: A Pathway to Prevention Type 1 Diabetes TrialNet Researchers in this study are part of a larger group called Type 1 Diabetes TrialNet.
The Importance of Dental Care. in Huntington Disease
 Huntington s New South Wales The Importance of Dental Care in Huntington Disease Supported by NSW Health 1 2 The Importance of Dental Care in Huntington Disease It should be stated at the outset that the
Huntington s New South Wales The Importance of Dental Care in Huntington Disease Supported by NSW Health 1 2 The Importance of Dental Care in Huntington Disease It should be stated at the outset that the
dental fillings facts About the brochure:
 dental fillings facts About the brochure: Your dentist is dedicated to protecting and improving oral health while providing safe dental treatment. This fact sheet provides information you need to discuss
dental fillings facts About the brochure: Your dentist is dedicated to protecting and improving oral health while providing safe dental treatment. This fact sheet provides information you need to discuss
Dental Health in Teens DENTAL INJURIES & USING MOUTH GUARDS
 Dental Health in Teens DENTAL INJURIES & USING MOUTH GUARDS S h a r e t h e C a r e San Diego County Health and Human Services Agency Statistics on Dental Injuries from Sports More than 5 million teeth
Dental Health in Teens DENTAL INJURIES & USING MOUTH GUARDS S h a r e t h e C a r e San Diego County Health and Human Services Agency Statistics on Dental Injuries from Sports More than 5 million teeth
Frequently Asked Questions
 Frequently Asked Questions Frequently Asked Questions Why Waterlase Dentistry? Doctors have used lasers for years to provide better care for their patients in LASIK vision correction, for removing skin
Frequently Asked Questions Frequently Asked Questions Why Waterlase Dentistry? Doctors have used lasers for years to provide better care for their patients in LASIK vision correction, for removing skin
Unit: Fluoride in Drinking Water/Alternate Source of Fluoride
 Unit: Fluoride in Drinking Water/Alternate Source of Fluoride Understandings: Fluoridated water is safe and helps to prevent tooth decay. Use fluoride toothpaste to brush your teeth. Fluoride toothpaste
Unit: Fluoride in Drinking Water/Alternate Source of Fluoride Understandings: Fluoridated water is safe and helps to prevent tooth decay. Use fluoride toothpaste to brush your teeth. Fluoride toothpaste
Dental services. in Bath and North East Somerset, Bristol, North Somerset and South Gloucestershire
 Dental services in Bath and North East Somerset, Bristol, North Somerset and South Gloucestershire Contents Finding an NHS dentist 1 What can I do to avoid dental disease? 2 Information about sugar 2 Dental
Dental services in Bath and North East Somerset, Bristol, North Somerset and South Gloucestershire Contents Finding an NHS dentist 1 What can I do to avoid dental disease? 2 Information about sugar 2 Dental
MDwise Right Choices Program
 Welcome to the MDwise Right Choices Program Helping you get the right care at the right time at the right place. MDwise Right Choices Program What is the Right Choices program? The Right Choices program
Welcome to the MDwise Right Choices Program Helping you get the right care at the right time at the right place. MDwise Right Choices Program What is the Right Choices program? The Right Choices program
Multiple Myeloma. This reference summary will help you understand multiple myeloma and its treatment options.
 Multiple Myeloma Introduction Multiple myeloma is a type of cancer that affects white blood cells. Each year, thousands of people find out that they have multiple myeloma. This reference summary will help
Multiple Myeloma Introduction Multiple myeloma is a type of cancer that affects white blood cells. Each year, thousands of people find out that they have multiple myeloma. This reference summary will help
Dental Admission Form
 Dental Admission Form PERSONAL HISTORY All of the information which you provide on this form will be held in the strictest confidence. Although some questions may seem unimportant at the time, they may
Dental Admission Form PERSONAL HISTORY All of the information which you provide on this form will be held in the strictest confidence. Although some questions may seem unimportant at the time, they may
WHAT YOU SHOULD KNOW ABOUT. low blood counts.
 WHAT YOU SHOULD KNOW ABOUT low blood counts. 1 INTRODUCTION Overview It is important for you to be aware that cancer, and some treatments for cancer, may affect your blood counts. Radiation therapy and
WHAT YOU SHOULD KNOW ABOUT low blood counts. 1 INTRODUCTION Overview It is important for you to be aware that cancer, and some treatments for cancer, may affect your blood counts. Radiation therapy and
X-Plain Sinus Surgery Reference Summary
 X-Plain Sinus Surgery Reference Summary Introduction Sinus surgery is a very common and safe operation. Your doctor may recommend that you have sinus surgery. The decision whether or not to have sinus
X-Plain Sinus Surgery Reference Summary Introduction Sinus surgery is a very common and safe operation. Your doctor may recommend that you have sinus surgery. The decision whether or not to have sinus
Day Case Unit, Horton General Hospital Advice after dental extractions Information for patients
 Day Case Unit, Horton General Hospital Advice after dental extractions Information for patients page 2 For the first 24 hours after your dental surgery you should avoid: any food or drinks that are very
Day Case Unit, Horton General Hospital Advice after dental extractions Information for patients page 2 For the first 24 hours after your dental surgery you should avoid: any food or drinks that are very
