Wound healing is a complex process with
|
|
|
- Duane Francis
- 10 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 RECONSTRUCTIVE Antimicrobial Activity of Clinically Used Antiseptics and Wound Irrigating Agents in Combination with s Tobias Hirsch, M.D. Simin Limoochi-Deli, M.S. Armin Lahmer, M.D. Frank Jacobsen, Ph.D. Ole Goertz, M.D. Hans-Ulrich Steinau, M.D. Hans-Martin Seipp, M.D., Ph.D. Lars Steinstraesser, M.D. Bochum and Giessen, Background: A primary strategy for preventing and treating wound infection in chronic wounds is the use of topical antiseptics and wound irrigating agents. However, their interaction with commonly used wound dressings has not yet been investigated. In this study, the authors analyzed the antimicrobial of antiseptics and wound irrigating agents used with commercially available wound dressings. Methods: Five clinically used antiseptics and wound irrigating agents (Prontosan, Lavasept, Braunol, Octenisept, and Betaisodona) were tested in the presence or absence of 42 wound dressings against Staphylococcus aureus. The determination of antibacterial was performed by disk diffusion assay. Results: Povidone-iodine based products showed sufficient antimicrobial in 64 to 78 percent of the combinations assessed (p 0.01). The octenidine derivate Octenisept showed sufficient antimicrobial in 54 percent of combinations. Polyhexamethylene biguanide derivatives demonstrated sufficient antimicrobial in 32 percent of the combinations. Conclusion: This study revealed that commonly used wound dressings dramatically reduce antibacterial of clinically used antiseptics and wound irrigating agents in vitro. (Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 127: 1539, 2011.) From the Department of Plastic Surgery, Ruhr-University Bochum, and the Department of Environmental Engineering and Biotechnology, Fachhochschule Giessen-Friedberg. Received for publication June 1, 2010; accepted October 26, Copyright 2011 by the American Society of Plastic Surgeons DOI: /PRS.0b013e318208d00f Wound healing is a complex process with many potential factors that can delay healing. 1 Chronic wounds are a critically important global health care issue, with treatment costs of at least $7.2 billion per year, according to the Frost & Sullivan Market Research Report Wound infection is a major reason for delayed and complicated wound healing: open wounds, particularly in diabetic and immunosuppressed patients, present an attractive environment for bacterial infection, and over 80 percent of leg ulcers are colonized by bacteria. 2,3 Staphylococcus aureus is the most common cause of skin and soft-tissue infections, in addition to invasive infections acquired within the hospital environment. 4 6 S. aureus is the most common single isolate (76 percent) in both diabetic and chronic wounds. 4 Treatment of severe S. aureus infections is still challenging The progressive reduction of therapeutic efficacies of the available antibiotics emphasizes the need for the development of new therapeutic strategies for the treatment of infected wounds. 9 Optimal management of wound infections is essential not only to promote a good healing response, but also because of the significant morbidity and mortality associated with wound infections. The search for the optimal treatment for chronic and infected wounds is an ongoing challenge for health care professionals because of the lack of evidence-based studies. Health care professionals often use wound irrigating agents and/or antiseptics for wound therapy. Antiseptics are agents that destroy or inhibit the growth and development of microorganisms in or on living tissue. Antiseptics have long and commonly been used on wounds to prevent or treat infection Local antiseptics can reduce local infection without inducing systemic negative side effects of antibiotics. In contrast to antibiotics that act selectively on a specific target, antiseptics Disclosure: This study was funded in part by B. Braun Melsungen AG, Melsungen,
2 Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery April 2011 have multiple targets and a broader spectrum of that includes bacteria, fungi, viruses, protozoa, and even prions. 15 The selection and duration of appropriate therapy is still performed on empirical grounds in many cases, and further work is required to ensure such drugs are used efficiently and effectively. The ideal antiseptic should have broad antimicrobial efficacy against a wide range of Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria, no development of bacterial resistance, no protein error, minimal toxicity toward host tissue, and rapid onset; be long acting; and have minimal interference with materials and products used for wound coverage. Optimal therapy may involve the combined application of local antiseptics, wound irrigating agents, and wound dressings. There are no data yet available on the antimicrobial of antiseptics and wound irrigating agents used in combination with wound dressings. Therefore, the aim of this study is to investigate the antimicrobial of clinically used, commercially available wound dressings with local antiseptics and wound irrigating agents. MATERIALS AND METHODS Antiseptics and Wound Irrigating Agents Five commonly used antiseptics and wound irrigating agents that are commercially available to health care providers were analyzed in combination with different commercially available wound dressings and tested for their antimicrobial : the octenidine product Octenisept (0.1 g of octenidine dihydrochloride and 2 g of phenoxyethanol in aqueous solution; Schuelke & Mayr, Norderstedt, ), the polyhexamethylene biguanide solutions Lavasept (200 mg/ml polyhexanidium and 10 mg/ml macrogol 4000 in aqueous solution; B. Braun Melsungen AG, Melsungen, ) and Protosan (0.1% undecylenamidopropyl-betaine and 0.1% polyhexanide in aqueous solution; B. Braun Melsungen), and the povidone-iodine solutions Braunol (7.5 g of povidone-iodine/100 ml in aqueous solution; Ratiopharm, Ulm, ) and Betaisodona (10 g povidone-iodine/100 ml in aqueous solution; Mundipharma, Limburg/ Lahn, ). The antiseptic solutions were analyzed in undiluted concentrations (Table 1). Assessment of Activity by Standardized Bacterial Disk Diffusion Assay Determination of bacterial inhibition was performed by a standardized disk diffusion assay. The Table 1. Commercially Available and Clinically Used s Assessed in This Study Dressings Alginate Algisite M Askina Sorb DracoAlgin Kaltostat Melgisorb SeaSorb Sorbalgon Plus Suprasorb A Trionic Urgosorb Charcoal CarboFlex Hyalogran Foam Allevyn Adhesive Allevyn Thin Askina Foam Askina Transorbent Biatain Cellosorb Mepilex PermaFoam PolyMem 4x4 Suprasorb P Tegaderm Foam Tielle Max V.A.C black V.A.C white PolyMem WIC Hydroactive Aquacel Cutinova Hydro Promogran Suprasorb H TenderWet 24 Hydrogel Algoplaque Alione Hydrocap NH CombiDERM Comfeel Plus Plaque Comfeel Plus Transparent Hydrocoll Traumasive Plus Varihesive E Other Metalline Hyalofill-R Manufacturer B. Braun Melsungen AG, Melsungen, Dr. Ausbüttel, Witten, ConvaTec, Munich, Mölnlycke Healthcare, Erkrath, Coloplast, Hamburg, Paul Hartmann, Heidenheim, Johnson & Johnson, Düsseldorf, Urgo Medical, Sulzbach, ConvaTec, Munich, ConvaTec, Munich, B. Braun Melsungen AG, Melsungen, B. Braun Melsungen AG, Melsungen, Coloplast, Hamburg, Urgo, Sulzbach, Mölnlycke Healthcare, Erkrath, Paul Hartmann, Heidenheim, PolyMem, Burr Ridge, Ill. 3M Healthcare, Neuss, Johnson & Johnson, Düsseldorf, KCI, Wiesbaden, KCI, Wiesbaden, PolyMem, Burr Ridge, Ill. ConvaTec, Munich, Johnson & Johnson, Düsseldorf, Paul Hartmann, Heidenheim, Urgo, Sulzbach, Coloplast, Hamburg, ConvaTec, Munich, Coloplast, Hamburg, Coloplast, Hamburg, Paul Hartmann, Heidenheim, Hexal AG, Holzkirchen, ConvaTec, Munich, ConvaTec, Munich, 1540
3 Volume 127, Number 4 Antiseptics and s solutions, in the presence or absence of wound dressings, were tested against S. aureus (American Type Culture Collection 6538). Bacterial inhibition testing was performed according to Clinical and Laboratory Standards, National Committee for Clinical Laboratory Standards, and Deutsches Institut fuer Normung (58940 Part 3) as described elsewhere Sixty microliters of the antiseptic solutions was added to each well. The plates were incubated at 37 C and read at 24 hours. Zone diameters were read at the point where growth abruptly decreased. In a first setup, undiluted solutions were evaluated for their in a standardized bacterial inhibition assay. In a second procedure, 75 percent by weight (4.75 g) of each solution was incubated with dressings at 37 C on a roll mixer (RM5-40; Zipperer GmbH, Staufen, ). After 24 hours, 60 l of the incubated solutions was added to each well, and the disk diffusion assay was performed as described above. The resulting inhibition of bacterial growth expressed as zone diameter was correlated with the results from the solutions in the absence of wound dressings and expressed as percentage of deviation. All experiments were repeated on at least four occasions on different dates. Analysis was performed in a blinded fashion. Statistical Analysis Results are presented as mean SEM. A significant difference of p 0.01 was determined as severe loss in antibacterial of the solutions in combination with the wound dressings assessed. The Levene test was used for determination of equal or unequal variance. The t test for equal or unequal variance was used to detect significance. RESULTS Povidone-Iodine Solutions Betaisodona was tested in combination with a total of 42 wound dressings. Twenty-seven (64.28 percent) of the combinations assessed showed sufficient antimicrobial (Table 2). However, 14 (33 percent) of the combinations with wound dressings showed significant loss of antimicrobial, starting with Suprasorb P with percent compared with Betaisodona alone (p 0.005). Hyalogran showed the weakest performance, with percent (p ). To confirm these findings, a second broadly used povidone-iodine product was assessed, Braunol, was tested against 14 wound dressings. Table 2. Povidone-Iodine Detergent Betaisodona Incubated with 42 Different s and Analyzed for Their Activity Compared with the Genuine Efficacy* DracoAlgin Kaltostat Prisma Alione Hydrocap HN Aquacel TenderWet Sorbalgon Plus Trionic SeaSorb Urgosorb CombiDERM V.A.C. white Comfeel Plus Transparent Varihesive Metalline Hydrocoll Comfeel Plus Plaque Physiotulle PolyMem 4x Mepilex Hyalofill R TAMP PlyMem WIC Allevyn Non-Adhesive Allevyn Adhesive Cutinova Hydro Biatain Foam Melgisorb Suprasorb P Tielle Max Cellosorb Tielle Allevyn Thin V.A.C. black Perma Foam Traumasive Plus Foam Suprasorb H Algoplaque CarboFlex Algisite Suprasorb A Hyalogran *Sixty-four percent of the combinations assessed showed sufficient antibacterial. was determined as p 0.01 versus Betaisodona or Braunol in the absence of wound covers. This study showed a result of sufficient antimicrobial in 78.5 percent of wound dressings (11 of 14) (Table 3). All wound dressing tested above p 0.01 were also evaluated positively in the Betaisodona study, except for Suprasorb H, which showed a value of p 0.01 when combined with Braunol ( percent). Incubated with Betaisodona, a reduction to percent 1541
4 Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery April 2011 Table 3. Antimicrobial Activity of Braunol Combined with 14 Different s Previously Analyzed with Betaisodona* Comfeel Plus Plaque Kaltostat CombiDERM V.A.C. white Comfeel Plus Transparent Urgosorb Varihesive Suprasorb H Mepilex PolyMem 4x Prisma Suprasorb P Tielle V.A.C. black *Braunol combined with 14 different wound dressings, previously analyzed with Betaisodona, showed sufficient antimicrobial in 78.5 percent or 11 wound dressings. antibacterial efficacy was determined as p 0.01 versus Betaisodona or Braunol in the absence of wound covers. occurred (p ). All three antiseptics with significant antibacterial reduction in the Braunol study (Suprasorb P, Tielle, and V.A.C. black) were also significantly hampered when incubated with Betaisodona. Thus, both agents showed similar results. Octenidine Octenisept showed sufficient antimicrobial in a total of 23 of 42 of wound dressings (54.76 percent) ranging from Suprasorb P and Mepilex ( percent, p 0.06; and percent, p 0.017, respectively) to Aquacel ( percent, p 0.01). All other wound dressings tested showed significant loss of antibacterial [19 of 42 (45.2 percent)]. The lowest performer in this group (Cutinova Hydro) showed only percent of the initial of Octenisept (p ) (Table 4). Table 4. Efficacy of Octenidine Alone and in Combination with s* Suprasorb P Mepilex Tielle Suprasorb A V.A.C. black Metalline Biatain Foam Perma Foam PolyMem 4x Hyalogran Traumasive Plus Suprasorb H Comfeel Plus Plaque Hyalofill R TAMP CombiDERM V.A.C. white Alione Hydrocap HN Cellosorb PolyMem WIC Trionic SeaSorb Foam Aquacel Algisite Physiotulle Comfeel Plus Transparent Allevyn Non-Adhesive Varihesive Algoplaque Allevyn Adhesive Hydrocoll Sorbalgon Plus Tielle Max Dracoalgin Melgisorb Urgosorb Kaltostat Promogran Carboflex Allevyn Thin TenderWet Cutinova Hydro *Octenidine (Octenisept) showed comparable compared with Octenisept alone (54 percent of the wound dressings assessed in this group) in 23 of 42 wound dressings. The cut-off line was determined to be p 0.01 versus octenidine in the absence of wound covers. Polyhexamethylene Biguanide Derivatives Prontosan, a wound irrigation solution, was incubated with a total of 42 wound dressings. These combinations showed sufficient antimicrobial in 13 of 42 of combinations assessed (32.5 percent): Suprasorb P, V.A.C. black, and V.A.C. white foam, Allevyn Non-Adhesive showed no reduction of (100 percent, p 0.01) followed by Mepilex, Tielle, Metalline, Allevyn Adhesive, Perma Foam, Varihesive, Cellosorb, Algoplaque, and Physiotulle (between 97.6 and 87.8 percent, p 0.01) (Table 5). Thirtytwo combinations assessed showed a significant reduction of. Twelve wound dressings tested even reduced of Prontosan by more than 50 percent of its initial efficacy (Table 5). 1542
5 Volume 127, Number 4 Antiseptics and s Table 5. Efficacy of the Polyhexamethylene Biguanide Detergent Prontosan* Suprasorb P V.A.C. black Allevyn Non-Adhesive V.A.C. white Mepilex Tielle Metalline Allevyn Adhesive Perma Foam Varihesive Cellosorb Algoplaque Physiotulle Biatain foam Hydrocoll Comfeel Plus plaque Traumasive Plus Comfeel Plus Transparent Suprasorb H Hyalogran Tielle Max Melgisorb SeaSorb PolyMem 4s PolyMem WIC Sorbalgon Plus Aquacel Dracoalgin Hyalofill R TAMP Promogran TenderWet Prisma Trionic Suprasorb A Algisite Urgosorb Carboflex Kaltostat Allevyn Thin Foam Alione Hydrocap HN CombiDERM * was determined as p 0.01 versus Lavasept or Prontosan in the absence of wound covers. The polyhexamethylene biguanide detergent Prontosan proved to have sufficient antimicrobial with wound dressings in terms of maintained in 32.5 percent (13 of 42 wound dressings). In the Lavasept group, 41.6 percent (five of 12) of the wound dressings allowed antibacterial efficacy above a value of p 0.01 compared with Lavasept alone (Table 6): Metalline, V.A.C. black and V.A.C. white, Hydrocoll, and Suprasorb P (between and percent, p 0.01). These findings confirmed the results for the Prontosan study: all combinations being not significant in the Table 6. Efficacy of Lavasept When Incubated with s Metallmine V.A.C. black V.A.C. white Hydrocoll Suprasorb P Trionic Suprasorb H Kaltostat Algisite M Promogran CarboFlex Tenderwet *Lavasept was severely hampered in its when incubated with seven of 12 wound dressings. was determined as p 0.01 versus Lavasept or Prontosan in the absence of wound covers. Lavasept study were found to be not significant in the Prontosan study as well. Furthermore, we detected the same results for the significantly different combinations. DISCUSSION This study demonstrated that many broadly used wound dressings significantly decreased antibacterial of local wound antiseptics. Other studies have shown that modern wound dressings show no significant improvement in wound healing. A Cochrane meta-analysis analyzing the topical treatment of wounds with silver as the antimicrobial agent identified three randomized controlled clinical trials comprising a total of 847 participants. One trial compared silver-containing foam (Contreet) with hydrocellular foam (Allevyn) in patients with leg ulcers, the second trial compared a silver-containing alginate (Silvercel) with an alginate alone (Algosteril), and the third trial compared the silver-containing foam Contreet with best local practice in patients with chronic wounds. The data from these three trials demonstrated that silver-containing foam dressings did not significantly increase complete ulcer healing as compared with standard foam dressings or best local practice after up to 4 weeks of followup, although a greater reduction of ulcer size was observed with the silver-containing foam. The authors stated that there is insufficient evidence to recommend the use of silver-containing dressings for the treatment of infected or contaminated 1543
6 Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery April 2011 chronic wounds. 19 In a meta-analysis by Nelson and Bradley investigating dressings and topical agents for arterial leg ulcers to determine whether topical agents and wound dressings affect the rate of healing in arterial ulcers, only one trial met the inclusion criteria. This small trial compared ketanserin ointment with vehicle alone. The trial was too small and far too short a follow-up period to be able to determine whether there was any difference in healing rates. 20 In another Cochrane review, the authors performed an extensive literature search in the field of dressings for healing venous leg ulcers. Fortytwo randomized controlled studies were identified that met the inclusion criteria. The main dressing types that were evaluated were hydrocolloids (n 23), foams (n 6), alginates (n 4), hydrogel dressings (n 6), and a group of miscellaneous dressings (n 3). There was no evidence that any particular dressing type was better than any others in terms of number of ulcers healed. At present, the evidence base does not suggest that hydrocolloids are more effective than simple low adherent dressings used beneath compression. For other comparisons, there was insufficient evidence. In our study, different wound dressings incubated with a povidone-iodine detergent (Betaisodona) showed sufficient antimicrobial in 64 percent of the combinations assessed (27 of 42). These findings were confirmed by a second povidone-iodine derivative, Braunol, which was not significantly impaired by 78 percent of the wound dressings assessed (11 of 14). The antibacterial effect of the octenidine solution Octenisept was significantly reduced when incubated with the wound dressings analyzed in this study: only 23 of 42 of the wound dressings assessed (54 percent) allowed for sufficient antibacterial of octenidine. Thus, the antibacterial was reduced to 35 percent when incubated with a wound dressing consisting of a polyurethane matrix with embedded superabsorbers (Cutinova Hydro, p ). The third group (polyhexamethylene biguanide solutions) revealed the lowest number of sufficient antimicrobial for Prontosan: incubated with 42 different wound covers, this combination showed sufficient antimicrobial in only 13 combinations assessed (32.5 percent). Twelve wound dressings even reduced the of more than 50 percent. Thus, to confirm this finding, a second polyhexamethylene biguanide derivative, Lavasept, was analyzed: 41.6 percent of the wound dressings (five of 12) had sufficient. The weaker results obtained with octenidine and polyhexamethylene biguanide containing agents may be explained by taking into account that both ingredients show strong cationic character and therefore immanently have limited compatibility with anionic matrices that can be present in certain wound dressing materials. These data show that commonly used, commercially available wound dressing products reduce the antibacterial efficacy of clinically used local antiseptics in vitro. In a previously published study, we investigated the potential cytotoxicity of the antiseptics and wound irrigation solution used in this study. Interestingly, this study showed that polyhexamethylene biguanide detergents are the least toxic to skin cells, whereas octenidine showed significant toxicity to keratinocytes and fibroblasts and povidone-iodine based agents showed severe toxicity even at low concentrations. 21 In daily health care routine, antiseptic solutions are often used in advance of the respective wound dressing, overlapping with the wound coverage, and are used at the same time. Furthermore, companies have recently developed vacuum wound dressing systems that are designed to rinse the foams applied to the wound with antiseptics during vacuum application. Other manufacturers are currently advertising wound dressings combined with polyhexamethylene biguanide releasing products. The data from this study show significant reduction of antimicrobial of certain antiseptics in combination with clinically used wound dressings. These findings clearly demonstrate that health care professionals need to be prudent in choosing the appropriate material for wound treatment, with special regard to potential interference and toxicity in the wound environment. Furthermore, commercial suppliers need to analyze product interactions and ensure that products and patients will not suffer chemical interactions and negative side effects. Further research is warranted to observe and optimize the innovative but confusing wound product market. Several limitations of this study should be discussed. First, all agents were tested against S. aureus only. However, for testing of the antimicrobial, the most prevalent Gram-positive bacteria strain S. aureus was chosen. Second, important factors of the wound environment, such as wound fluid, proteins, proteases, and debriding effects of the agents, were excluded from this in vitro study. Furthermore, not all of the solutions used are antiseptics. Prontosan is used as a wound irrigating agent, and whether the results obtained have an influence on the wound cleansing as well 1544
7 Volume 127, Number 4 Antiseptics and s was not investigated. Finally and most importantly, it is difficult to estimate how the results of bacterial inhibition testing reflect clinical practice. Evidence-based medicine has had an increasing impact on patient care over the past few years, and these results give cause for concern and indicate a need to review management of these wounds. The selection and duration of therapy is empirical in many cases, and further research by both manufacturers and health care professionals is required to ensure the effective and efficient combined use of antiseptics and dressings. Wound dressings present a huge and fast-growing market. Furthermore, products change frequently in ingredients and brand names. Thus, there is an urgent need for routine compatibility testing of wound care products. Further research is needed to assess the antibacterial of wound antiseptics and wound irrigating solutions in combination with wound dressings in the clinical setting with a variety of potentially pathogenic microorganisms. Lars Steinstraesser, M.D. Department of Plastic Surgery Burn Center BG University Hospital Bergmannsheil Ruhr University Bochum Buerkle-de-la Camp Platz Bochum, [email protected] REFERENCES 1. Hirsch T, Spielmann M, Zuhaili B, et al. Enhanced susceptibility to infections in a diabetic wound healing model. BMC Surg. 2008;8:5. 2. Brook I, Frazier EH. Aerobic and anaerobic microbiology of infection after trauma. Am J Emerg Med. 1998;16: Harker J. The effect of bacteria on leg ulcer healing. Br J Community Nurs. 2001;6: Goldstein EJ, Citron DM, Nesbit CA. Diabetic foot infections: Bacteriology and of 10 oral antimicrobial agents against bacteria isolated from consecutive cases. Diabetes Care 1996;19: Diekema DJ, Pfaller MA, Schmitz FJ, et al. Survey of infections due to Staphylococcus species: Frequency of occurrence and antimicrobial susceptibility of isolates collected in the United States, Canada, Latin America, Europe, and the Western Pacific region for the SENTRY Antimicrobial Surveillance Program, Clin Infect Dis. 2001;32(Suppl 2):S114 S Fridkin SK, Hageman JC, Morrison M, et al. Methicillinresistant Staphylococcus aureus disease in three communities. N Engl J Med. 2005;352: Archer GL. Staphylococcus aureus: A well-armed pathogen. Clin Infect Dis. 1998;26: Clark NC, Weigel LM, Patel JB, Tenover FC. Comparison of Tn1546-like elements in vancomycin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus isolates from Michigan and Pennsylvania. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2005;49: Hirsch T, Jacobsen F, Steinau HU, Steinstraesser L. Host defense peptides and the new line of defence against multiresistant infections. Protein Pept Lett. 2008;15: Cosgrove SE, Sakoulas G, Perencevich EN, Schwaber MJ, Karchmer AW, Carmeli Y. Comparison of mortality associated with methicillin-resistant and methicillin-susceptible Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia: A meta-analysis. Clin Infect Dis. 2003;36: Chambers HF. The changing epidemiology of Staphylococcus aureus? Emerg Infect Dis. 2001;7: Whitney J, Phillips L, Aslam R, et al. Guidelines for the treatment of pressure ulcers. Wound Repair Regen. 2006;14: Steed DL, Attinger C, Colaizzi T, et al. Guidelines for the treatment of diabetic ulcers. Wound Repair Regen. 2006;14: Hopf HW, Ueno C, Aslam R, et al. Guidelines for the treatment of arterial insufficiency ulcers. Wound Repair Regen. 2006;14: McDonnell G, Russell AD. Antiseptics and disinfectants: Activity, action, and resistance. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1999; 12: Cotter G, Adley CC. Comparison and evaluation of antimicrobial susceptibility testing of enterococci performed in accordance with six national committee standardized disk diffusion procedures. J Clin Microbiol. 2001;39: National Committee for Clinical Laboratory Standards. Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Disk Susceptibility Tests. Approved standard M2-A6. Wayne, Pa: National Committee for Clinical Laboratory Standards; National Committee for Clinical Laboratory Standards. Methods for Dilution Antimicrobial Susceptibility Tests for Bacteria That Grow Aerobically. Document M7-A4. 4th ed. Wayne, Pa: National Committee for Clinical Laboratory Standards; Vermeulen H, van Hattem JM, Storm-Versloot MN, Ubbink DT. Topical silver for treating infected wounds. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2007;(1):CD Nelson EA, Bradley MD. Dressings and topical agents for arterial leg ulcers. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2007;(1): CD Hirsch T, Koerber A, Jacobsen F, et al. Evaluation of toxic side effects of clinically used skin antiseptics in vitro. J Surg Res. 2010;164:
Post-surgical V.A.C. VeraFlo Therapy with Prontosan Instillation on Inpatient Infected Wounds * COLLECTION OF CASE STUDIES
 COLLECTION OF CASE STUDIES Post-surgical V.A.C. VeraFlo Therapy with Prontosan Instillation on Inpatient Infected Wounds * *All patients were treated with systemic antibiotics Post-surgical V.A.C. VeraFlo
COLLECTION OF CASE STUDIES Post-surgical V.A.C. VeraFlo Therapy with Prontosan Instillation on Inpatient Infected Wounds * *All patients were treated with systemic antibiotics Post-surgical V.A.C. VeraFlo
Certofix protect More certainty, more safety, more success
 Certofix protect More certainty, more safety, more success Highly effective, long-term protection against catheter infection Central Venous Catheters Antimicrobial modified hydrophilic surface We help
Certofix protect More certainty, more safety, more success Highly effective, long-term protection against catheter infection Central Venous Catheters Antimicrobial modified hydrophilic surface We help
List of dressings etc on wound formulary (as described on vision system)
 List of dressings etc on wound formulary (as described on vision system) Acticoat dressing 5cm x 5cm (5 per box) Acticoat dressing 10cm x 10cm (5 or 12 per box) Actiocoat dressing 10cm x 20cm (12 per box)
List of dressings etc on wound formulary (as described on vision system) Acticoat dressing 5cm x 5cm (5 per box) Acticoat dressing 10cm x 10cm (5 or 12 per box) Actiocoat dressing 10cm x 20cm (12 per box)
Antimicrobial activities of silver dressings: an in vitro comparison
 Journal of Medical Microbiology (2006), 55, 59 63 DOI 10.1099/jmm.0.46124-0 Antimicrobial activities of silver dressings: an in vitro comparison Margaret Ip, 1 Sau Lai Lui, 1 Vincent K. M. Poon, 2 Ivan
Journal of Medical Microbiology (2006), 55, 59 63 DOI 10.1099/jmm.0.46124-0 Antimicrobial activities of silver dressings: an in vitro comparison Margaret Ip, 1 Sau Lai Lui, 1 Vincent K. M. Poon, 2 Ivan
Clinical Wound Assessment - A Pocket Guide
 Clinical Wound Assessment - A Pocket Guide Developed by Professor Finn Gottrup, Denmark Dr. Robert Kirsner, US Dr. Sylvie Meaume, France Dr. Christian Münter, Germany Professor Gary Sibbald, Canada The
Clinical Wound Assessment - A Pocket Guide Developed by Professor Finn Gottrup, Denmark Dr. Robert Kirsner, US Dr. Sylvie Meaume, France Dr. Christian Münter, Germany Professor Gary Sibbald, Canada The
Use of a Pressure Ulcer Protocol: Benefits and Recommendations
 Use of a Pressure Ulcer Protocol: Benefits and Recommendations Elizabeth L. Enriquez RN,BSN,MPH,CWOCN Wound Care Specialist/Infection Control Morningiside House 1000 Pellham Parkway, Bronx, NY 10461 Wound
Use of a Pressure Ulcer Protocol: Benefits and Recommendations Elizabeth L. Enriquez RN,BSN,MPH,CWOCN Wound Care Specialist/Infection Control Morningiside House 1000 Pellham Parkway, Bronx, NY 10461 Wound
Development of a Next- Generation Antimicrobial Wound Dressing- Results Count
 Development of a Next- Generation Antimicrobial Wound Dressing- Results Count Phil Bowler, MPhil, FIBMS Science & Technology, ConvaTec 24 th November 2015 /TM all trade marks are the property of their
Development of a Next- Generation Antimicrobial Wound Dressing- Results Count Phil Bowler, MPhil, FIBMS Science & Technology, ConvaTec 24 th November 2015 /TM all trade marks are the property of their
ORTHOPAEDIC INFECTION PREVENTION AND CONTROL: AN EMERGING NEW PARADIGM
 ORTHOPAEDIC INFECTION PREVENTION AND CONTROL: AN EMERGING NEW PARADIGM AMERICAN ACADEMY OF ORTHOPAEDIC SURGEONS 77th Annual Meeting March 9-12, 2010 New Orleans, Louisiana COMMITTEE ON PATIENT SAFETY PREPARED
ORTHOPAEDIC INFECTION PREVENTION AND CONTROL: AN EMERGING NEW PARADIGM AMERICAN ACADEMY OF ORTHOPAEDIC SURGEONS 77th Annual Meeting March 9-12, 2010 New Orleans, Louisiana COMMITTEE ON PATIENT SAFETY PREPARED
MEDIZINISCHE PUBLIKATIONEN
 Re Print MEDIZIN & PRAXIS Spezial Infected Wounds Has Cutisorb Sorbact proved its practical value as an antibacterial dressing? B. v. Hallern, Copyright 2005 by Verlag für MEDIZINISCHE PUBLIKATIONEN Bernd
Re Print MEDIZIN & PRAXIS Spezial Infected Wounds Has Cutisorb Sorbact proved its practical value as an antibacterial dressing? B. v. Hallern, Copyright 2005 by Verlag für MEDIZINISCHE PUBLIKATIONEN Bernd
Stop painful dressing changes!*
 Stop painful dressing changes!* Apply it, leave it,* help heal it * AQUACEL Ag BURN and AQUACEL BURN dressings provide a comfortable environment while the dressing is in situ or upon removal. Although
Stop painful dressing changes!* Apply it, leave it,* help heal it * AQUACEL Ag BURN and AQUACEL BURN dressings provide a comfortable environment while the dressing is in situ or upon removal. Although
Opticell Wound Dressings. Powerful Yet Gentle Moisture Management
 Wound Dressings Powerful Yet Gentle Moisture Management 1 Exclusive Forzagel TM Technology s unique gelling attributes are the result of Forzagel technology. When moistened, the absorbent fibers of the
Wound Dressings Powerful Yet Gentle Moisture Management 1 Exclusive Forzagel TM Technology s unique gelling attributes are the result of Forzagel technology. When moistened, the absorbent fibers of the
TAKING CARE OF WOUNDS KEY FIGURE:
 Chapter 9 TAKING CARE OF WOUNDS KEY FIGURE: Gauze Wound care represents a major area of concern for the rural health provider. This chapter discusses the treatment of open wounds, with emphasis on dressing
Chapter 9 TAKING CARE OF WOUNDS KEY FIGURE: Gauze Wound care represents a major area of concern for the rural health provider. This chapter discusses the treatment of open wounds, with emphasis on dressing
Dressings for superficial and partial thickness burns (Review)
 Wasiak J, Cleland H, Campbell F, Spinks A This is a reprint of a Cochrane review, prepared and maintained by The Cochrane Collaboration and published in The Cochrane Library 2013, Issue 3 http://www.thecochranelibrary.com
Wasiak J, Cleland H, Campbell F, Spinks A This is a reprint of a Cochrane review, prepared and maintained by The Cochrane Collaboration and published in The Cochrane Library 2013, Issue 3 http://www.thecochranelibrary.com
PRIORITY RESEARCH TOPICS
 PRIORITY RESEARCH TOPICS Understanding all the issues associated with antimicrobial resistance is probably impossible, but it is clear that there are a number of key issues about which we need more information.
PRIORITY RESEARCH TOPICS Understanding all the issues associated with antimicrobial resistance is probably impossible, but it is clear that there are a number of key issues about which we need more information.
healthcare associated infection 1.2
 healthcare associated infection A C T I O N G U I D E 1.2 AUSTRALIAN SAFETY AND QUALITY GOALS FOR HEALTH CARE What are the goals? The Australian Safety and Quality Goals for Health Care set out some important
healthcare associated infection A C T I O N G U I D E 1.2 AUSTRALIAN SAFETY AND QUALITY GOALS FOR HEALTH CARE What are the goals? The Australian Safety and Quality Goals for Health Care set out some important
wound care ...wound healing devices, wound care products, adhesive, non-adhesive bandages, dressings, wound cleansers... Contents Infection Control
 113 wound care Nursing Wound Ostomy...wound healing devices, wound care products, adhesive, non-adhesive bandages, dressings, wound cleansers... 113 114 Wound Cross Reference - Chart 1 Nursing Wound Ostomy
113 wound care Nursing Wound Ostomy...wound healing devices, wound care products, adhesive, non-adhesive bandages, dressings, wound cleansers... 113 114 Wound Cross Reference - Chart 1 Nursing Wound Ostomy
Hydrosorb Comfort. Hydrosorb comfort features its own adhesive film border. 4.5 x 6.5cm HTM900702 Box/5 $ 7.5 x 10cm HTM900706 Box/5.
 202 / HYDROGEL Hydrosorb Hydrosorb is a transparent, solid hydrogel sheet with a semi-permeable outer layer. The dressing provides a moist wound environment for optimal healing. The dressing s 60% water
202 / HYDROGEL Hydrosorb Hydrosorb is a transparent, solid hydrogel sheet with a semi-permeable outer layer. The dressing provides a moist wound environment for optimal healing. The dressing s 60% water
The compatibility of INTRASITE Gel and ACTICOAT : An In-Vivo and In-Vitro assessment
 *smith&nephew The compatibility of INTRASITE Gel and ACTICOAT : An In-Vivo and In-Vitro assessment 1 Trade Marks of Smith & Nephew An In-Vivo and In-Vitro assessment of the compatibility of ACTICOAT and
*smith&nephew The compatibility of INTRASITE Gel and ACTICOAT : An In-Vivo and In-Vitro assessment 1 Trade Marks of Smith & Nephew An In-Vivo and In-Vitro assessment of the compatibility of ACTICOAT and
Surveillance cultures PRO. Kurt Espersen ICU 4131 Rigshospitalet Copenhagen
 Kurt Espersen ICU 4131 Rigshospitalet Copenhagen Difficult to Diagnose Systemic Candidal Infection Immunsuppression in critically ill patients Frequent manifestation of fungus in ICU Fungi were isolated
Kurt Espersen ICU 4131 Rigshospitalet Copenhagen Difficult to Diagnose Systemic Candidal Infection Immunsuppression in critically ill patients Frequent manifestation of fungus in ICU Fungi were isolated
An Essential Tool For The Care DFUs
 Adjunct HBO 2 Therapy: March 16, 2016 William Tettelbach, MD, FACP, FIDSA System Medical Director of Wound & Hyperbaric Medicine Services An Essential Tool For The Care DFUs Fedorko, L., et al., Hyperbaric
Adjunct HBO 2 Therapy: March 16, 2016 William Tettelbach, MD, FACP, FIDSA System Medical Director of Wound & Hyperbaric Medicine Services An Essential Tool For The Care DFUs Fedorko, L., et al., Hyperbaric
Treatment of skin and soft tissue infections due to methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in adults
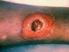 1 of 6 9/24/2010 11:16 AM Official reprint from UpToDate www.uptodate.com 2010 UpToDate Treatment of skin and soft tissue infections due to methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in adults Author
1 of 6 9/24/2010 11:16 AM Official reprint from UpToDate www.uptodate.com 2010 UpToDate Treatment of skin and soft tissue infections due to methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in adults Author
No. prev. doc.: 9392/08 SAN 77 DENLEG 48 VETER 5 Subject: EMPLOYMENT, SOCIAL POLICY, HEALTH AND CONSUMER AFFAIRS COUNCIL MEETING ON 9 AND 10 JUNE 2008
 COUNCIL OF THE EUROPEAN UNION Brussels, 22 May 2008 9637/08 SAN 88 DENLEG 52 VETER 7 NOTE from: Committee of Permanent Representatives (Part 1) to: Council No. prev. doc.: 9392/08 SAN 77 DENLEG 48 VETER
COUNCIL OF THE EUROPEAN UNION Brussels, 22 May 2008 9637/08 SAN 88 DENLEG 52 VETER 7 NOTE from: Committee of Permanent Representatives (Part 1) to: Council No. prev. doc.: 9392/08 SAN 77 DENLEG 48 VETER
Val Robson University Hospital Aintree. Liverpool U.K.
 Val Robson University Hospital Aintree. Liverpool U.K. Results of a Randomised Controlled Trial Comparing Antibacterial Honey (Medihoney ) to conventional treatment in wound care and the problems arising
Val Robson University Hospital Aintree. Liverpool U.K. Results of a Randomised Controlled Trial Comparing Antibacterial Honey (Medihoney ) to conventional treatment in wound care and the problems arising
Technological platforms
 Advitech Advitech is a life sciences & technology company Its mission is to discover and commercialize proprietary and evidence-based natural health products Focus on milk, whey and bovine colostrum R&D,
Advitech Advitech is a life sciences & technology company Its mission is to discover and commercialize proprietary and evidence-based natural health products Focus on milk, whey and bovine colostrum R&D,
Silver Antimicrobial Dressings in Wound Management: A Comparison of Antibacterial, Physical, and Chemical Characteristics
 Original Research Silver Antimicrobial Dressings in Wound Management: A Comparison of Antibacterial, Physical, and Chemical Characteristics David Parsons, PhD; Philip G. Bowler, MPhil; Viv Myles, MSc;
Original Research Silver Antimicrobial Dressings in Wound Management: A Comparison of Antibacterial, Physical, and Chemical Characteristics David Parsons, PhD; Philip G. Bowler, MPhil; Viv Myles, MSc;
A Pocket Guide. Application and Cutting Guide
 A Pocket Guide Application and Cutting Guide Developed by Pia Carlsen, RN, Denmark Jacqui Fletcher, Principal Lecturer, MSc BSc (Hons) PG Dip (ED) RN ILT, UK Maria Mousley, AHP, Consultant Podiatrist,
A Pocket Guide Application and Cutting Guide Developed by Pia Carlsen, RN, Denmark Jacqui Fletcher, Principal Lecturer, MSc BSc (Hons) PG Dip (ED) RN ILT, UK Maria Mousley, AHP, Consultant Podiatrist,
Rafael Carrion, MD Associate Professor of Urology University of South Florida School of Medicine
 Rafael Carrion, MD Associate Professor of Urology University of South Florida School of Medicine Prosthetics Most catastrophic complication is infection Original estimates were calculated: Virgin 3-5%
Rafael Carrion, MD Associate Professor of Urology University of South Florida School of Medicine Prosthetics Most catastrophic complication is infection Original estimates were calculated: Virgin 3-5%
Addressing the challenge of healthcare associated infections (HCAIs) in Europe
 POSITION PAPER 05 January 2011 Addressing the challenge of healthcare associated infections (HCAIs) in Europe A Call for Action Page 1 of 8 A holistic approach to combating HCAIs in Europe We must rise
POSITION PAPER 05 January 2011 Addressing the challenge of healthcare associated infections (HCAIs) in Europe A Call for Action Page 1 of 8 A holistic approach to combating HCAIs in Europe We must rise
The true cost of wounds. And how to reduce it
 The true cost of wounds And how to reduce it Wounds are a growing challenge Wounds have been called the silent epidemic. In a typical hospital setting today, between 25% and 40% of beds will be occupied
The true cost of wounds And how to reduce it Wounds are a growing challenge Wounds have been called the silent epidemic. In a typical hospital setting today, between 25% and 40% of beds will be occupied
METHICILLIN-RESISTANT STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS (MRSA) COMMUNITY ACQUIRED vs. HEALTHCARE ASSOCIATED
 METHICILLIN-RESISTANT STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS (MRSA) COMMUNITY ACQUIRED vs. HEALTHCARE ASSOCIATED Recently, there have been a number of reports about methicillin-resistant Staph aureus (MRSA) infections
METHICILLIN-RESISTANT STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS (MRSA) COMMUNITY ACQUIRED vs. HEALTHCARE ASSOCIATED Recently, there have been a number of reports about methicillin-resistant Staph aureus (MRSA) infections
WOUND MANAGEMENT PROTOCOLS WOUND CLEANSING: REMOVING WOUND DEBRIS FROM WOUND BASE
 WOUND MANAGEMENT PROTOCOLS PURPOSE: Provide nursing personnel with simple guidance regarding appropriate dressing selection in the absence of wound specialist expertise Identify appropriate interventions
WOUND MANAGEMENT PROTOCOLS PURPOSE: Provide nursing personnel with simple guidance regarding appropriate dressing selection in the absence of wound specialist expertise Identify appropriate interventions
Managing cavity wounds Journal of Community Nursing March 1998 Author: Rosemary Pudner
 Managing cavity wounds Journal of Community Nursing March 1998 Author: Rosemary Pudner It has been seen in recent years, that an increasing number of patients are being discharged early into the community,
Managing cavity wounds Journal of Community Nursing March 1998 Author: Rosemary Pudner It has been seen in recent years, that an increasing number of patients are being discharged early into the community,
Hialeah Nursing and Rehabilitation Center Combines Technology and Best Practices to Improve Infection Control Specific to C.diff
 RESEARCH ARTICLE Page 1 of 5 Hialeah Nursing and Rehabilitation Center Combines Technology and Best Practices to Improve Infection Control Specific to C.diff ABSTRACT RB Health Partners, Inc., June 24,
RESEARCH ARTICLE Page 1 of 5 Hialeah Nursing and Rehabilitation Center Combines Technology and Best Practices to Improve Infection Control Specific to C.diff ABSTRACT RB Health Partners, Inc., June 24,
Nursing college, Second stage Microbiology Dr.Nada Khazal K. Hendi L14: Hospital acquired infection, nosocomial infection
 L14: Hospital acquired infection, nosocomial infection Definition A hospital acquired infection, also called a nosocomial infection, is an infection that first appears between 48 hours and four days after
L14: Hospital acquired infection, nosocomial infection Definition A hospital acquired infection, also called a nosocomial infection, is an infection that first appears between 48 hours and four days after
Fungal Infection in Total Joint Arthroplasty. Dr.Wismer Dr.Al-Sahan
 Fungal Infection in Total Joint Arthroplasty Dr.Wismer Dr.Al-Sahan Delayed Reimplantation Arthroplasty for Candidal Prosthetic Joint Infection: A Report of 4 Cases and Review of the Literature David M.
Fungal Infection in Total Joint Arthroplasty Dr.Wismer Dr.Al-Sahan Delayed Reimplantation Arthroplasty for Candidal Prosthetic Joint Infection: A Report of 4 Cases and Review of the Literature David M.
ABThera Open Abdomen Negative Pressure Therapy for Active Abdominal Therapy. Case Series
 ABThera Open Abdomen Negative Pressure Therapy for Active Abdominal Therapy Case Series Summary of Cases: USER EXPERIENCE The ABThera OA NPT system was found by surgeons to be a convenient and effective
ABThera Open Abdomen Negative Pressure Therapy for Active Abdominal Therapy Case Series Summary of Cases: USER EXPERIENCE The ABThera OA NPT system was found by surgeons to be a convenient and effective
Title Older people s participation and engagement in falls prevention interventions: Comparing rates and settings
 Title Older people s participation and engagement in falls prevention interventions: Comparing rates and settings Keywords: patient adherence; falls, accidental; intervention studies; patient participation;
Title Older people s participation and engagement in falls prevention interventions: Comparing rates and settings Keywords: patient adherence; falls, accidental; intervention studies; patient participation;
C-Difficile Infection Control and Prevention Strategies
 C-Difficile Infection Control and Prevention Strategies Adrienne Mims, MD MPH VP, Chief Medical Officer [email protected] 1/18/2016 1 Disclosure This educational activity does not have commercial
C-Difficile Infection Control and Prevention Strategies Adrienne Mims, MD MPH VP, Chief Medical Officer [email protected] 1/18/2016 1 Disclosure This educational activity does not have commercial
University of Huddersfield Repository
 University of Huddersfield Repository Atkin, Leanne and Shirlow, K. Understanding and applying compression therapy Original Citation Atkin, Leanne and Shirlow, K. (2014) Understanding and applying compression
University of Huddersfield Repository Atkin, Leanne and Shirlow, K. Understanding and applying compression therapy Original Citation Atkin, Leanne and Shirlow, K. (2014) Understanding and applying compression
EAST CAROLINA UNIVERSITY INFECTION CONTROL POLICY. Methicillin-resistant Staph aureus: Management in the Outpatient Setting
 EAST CAROLINA UNIVERSITY INFECTION CONTROL POLICY Methicillin-resistant Staph aureus: Management in the Outpatient Setting Date Originated: Date Reviewed: Date Approved: Page 1 of Approved by: Department
EAST CAROLINA UNIVERSITY INFECTION CONTROL POLICY Methicillin-resistant Staph aureus: Management in the Outpatient Setting Date Originated: Date Reviewed: Date Approved: Page 1 of Approved by: Department
Vacuum-Assisted Wound Closure ISSN: 0002-936X American Journal of Nursing
 Vacuum-Assisted Wound Closure ISSN: 0002-936X American Journal of Nursing Author(s): Chua Patel, Christy T. MS, RN; Kinsey, Gail C. MS, RN, CNS; Koperski-Moen, Kelley J. ADN, RN; Bungum, Lisa D. BSN, RN
Vacuum-Assisted Wound Closure ISSN: 0002-936X American Journal of Nursing Author(s): Chua Patel, Christy T. MS, RN; Kinsey, Gail C. MS, RN, CNS; Koperski-Moen, Kelley J. ADN, RN; Bungum, Lisa D. BSN, RN
Environmental Management of Staph and MRSA in Community Settings July 2008
 Page 1 of 7 Environmental Management of Staph and MRSA in Community Settings July 2008 Questions addressed on this page What are Staph and MRSA? How is Staph and MRSA spread? What is the role of the environment
Page 1 of 7 Environmental Management of Staph and MRSA in Community Settings July 2008 Questions addressed on this page What are Staph and MRSA? How is Staph and MRSA spread? What is the role of the environment
Wound Healing Community Outreach Service
 Wound Healing Community Outreach Service Wound Management Education Plan January 2012 December 2012 Author: Michelle Gibb Nurse Practitioner Wound Management Wound Healing Community Outreach Service Institute
Wound Healing Community Outreach Service Wound Management Education Plan January 2012 December 2012 Author: Michelle Gibb Nurse Practitioner Wound Management Wound Healing Community Outreach Service Institute
Introduction to Wound Management
 EWMA Educational Development Programme Curriculum Development Project Education Module: Introduction to Wound Management Latest revision: October 2012 ABOUT THE EWMA EDUCATIONAL DEVELOPMENT PROGRAMME The
EWMA Educational Development Programme Curriculum Development Project Education Module: Introduction to Wound Management Latest revision: October 2012 ABOUT THE EWMA EDUCATIONAL DEVELOPMENT PROGRAMME The
Develop an understanding of the differential diagnosis of pseudomembranous colitis
 Update on Clostridium difficile Colitis Clostridium difficile infection has recently emerged in populations without any known risk factors. This presentation will focus on the historical background, diagnosis,
Update on Clostridium difficile Colitis Clostridium difficile infection has recently emerged in populations without any known risk factors. This presentation will focus on the historical background, diagnosis,
WHY IS THIS IMPORTANT?
 CHAPTER 1 WHAT IS MICROBIOLOGY AND WHY IS IT IMPORTANT? WHO / TDR / Crump WHY IS THIS IMPORTANT? Microbiology is more relevant than ever in today s world. Infectious diseases are a leading health-related
CHAPTER 1 WHAT IS MICROBIOLOGY AND WHY IS IT IMPORTANT? WHO / TDR / Crump WHY IS THIS IMPORTANT? Microbiology is more relevant than ever in today s world. Infectious diseases are a leading health-related
WOUND MANAGEMENT PRODUCTS FORMULARY
 Tissue Viability Service WOUND MANAGEMENT PRODUCTS FORMULARY Version: April 2014 Tissue Viability Service: Pia Obank, Julie Sturges, Ann Fowler, Sam Goodman 01/04/2014 Introduction The first choice dressing
Tissue Viability Service WOUND MANAGEMENT PRODUCTS FORMULARY Version: April 2014 Tissue Viability Service: Pia Obank, Julie Sturges, Ann Fowler, Sam Goodman 01/04/2014 Introduction The first choice dressing
2013 Indiana Healthcare Provider and Hospital Administrator Multi-Drug Resistant Organism Survey
 2013 Indiana Healthcare Provider and Hospital Administrator Multi-Drug Resistant Organism Survey Antibiotic resistance is a global issue that has significant impact in the field of infectious diseases.
2013 Indiana Healthcare Provider and Hospital Administrator Multi-Drug Resistant Organism Survey Antibiotic resistance is a global issue that has significant impact in the field of infectious diseases.
The present study reports on the application of silver anode in root canals for disinfection of
 Murat AYDIN *, The antibacterial effect of silver anode in root canals Oral Microbiol Immunol Abstract The present study reports on the application of silver anode in root canals for disinfection of infected
Murat AYDIN *, The antibacterial effect of silver anode in root canals Oral Microbiol Immunol Abstract The present study reports on the application of silver anode in root canals for disinfection of infected
What dressing for what wound. Prudence Lennox National Clinical Leader Healthcare Rehabilitation Ltd
 What dressing for what wound Prudence Lennox National Clinical Leader Healthcare Rehabilitation Ltd Wound assessment Accurate wound assessment is a prerequisite to planning appropriate care & should adopt
What dressing for what wound Prudence Lennox National Clinical Leader Healthcare Rehabilitation Ltd Wound assessment Accurate wound assessment is a prerequisite to planning appropriate care & should adopt
CHAPTER 13. Quality Control/Quality Assurance
 CHAPTER 13 Quality Control/Quality Assurance Quality Control/Quality Assurance (QC/QA) can be defined as the set of planned and systematic activities focused on providing confidence that quality requirements
CHAPTER 13 Quality Control/Quality Assurance Quality Control/Quality Assurance (QC/QA) can be defined as the set of planned and systematic activities focused on providing confidence that quality requirements
FUNCTIONS OF THE SKIN
 FUNCTIONS OF THE SKIN Skin is the largest organ of the body. The average adult has 18 square feet of skin which account for 16% of the total body weight. Skin acts as a physical barrier for you to the
FUNCTIONS OF THE SKIN Skin is the largest organ of the body. The average adult has 18 square feet of skin which account for 16% of the total body weight. Skin acts as a physical barrier for you to the
Strep Throat. Group Members: Rebecca Okinczyc
 Strep Throat Group Members: Rebecca Okinczyc Andrew Miclat Joshua Savage Introduction It is the purpose of this paper to present a comprehensive and exhaustive description of the disease Streptococcal
Strep Throat Group Members: Rebecca Okinczyc Andrew Miclat Joshua Savage Introduction It is the purpose of this paper to present a comprehensive and exhaustive description of the disease Streptococcal
MRSA Positive. An information guide
 TO PROVIDE THE VERY BEST CARE FOR EACH PATIENT ON EVERY OCCASION MRSA Positive An information guide MRSA Positive What is MRSA? Staphylococcus aureus is a germ often found on the skin and up the nose of
TO PROVIDE THE VERY BEST CARE FOR EACH PATIENT ON EVERY OCCASION MRSA Positive An information guide MRSA Positive What is MRSA? Staphylococcus aureus is a germ often found on the skin and up the nose of
Urinary Tract Infections
 Urinary Tract Infections Leading cause of morbidity and health care expenditures in persons of all ages. An estimated 50 % of women report having had a UTI at some point in their lives. 8.3 million office
Urinary Tract Infections Leading cause of morbidity and health care expenditures in persons of all ages. An estimated 50 % of women report having had a UTI at some point in their lives. 8.3 million office
Cutimed PROTECT Medical skin protection. Protect Preserve Prevent
 PROTECT Medical skin protection Protect Preserve Prevent PROTECT Ordering information PROTECT is available in foam applicators and spray bottle PROTECT REF No. Size Unit of Measure HCPCS Spray 7265300
PROTECT Medical skin protection Protect Preserve Prevent PROTECT Ordering information PROTECT is available in foam applicators and spray bottle PROTECT REF No. Size Unit of Measure HCPCS Spray 7265300
APPROPRIATE USE OF SILVER DRESSINGS IN WOUNDS
 INTERNATIONAL CONSENSUS APPROPRIATE USE OF SILVER DRESSINGS IN WOUNDS an expert working group consensus EDITOR: Lisa MacGregor PUBLISHER: Kathy Day PUBLISHED BY: Wounds International Enterprise House 1
INTERNATIONAL CONSENSUS APPROPRIATE USE OF SILVER DRESSINGS IN WOUNDS an expert working group consensus EDITOR: Lisa MacGregor PUBLISHER: Kathy Day PUBLISHED BY: Wounds International Enterprise House 1
Short Report: Failure of Burkholderia pseudomallei to Grow in an Automated Blood Culture System
 Accepted for Publication, Published online October 13, 2014; doi:10.4269/ajtmh.14-0018. The latest version is at http://ajtmh.org/cgi/doi/10.4269/ajtmh.14-0018 In order to provide our readers with timely
Accepted for Publication, Published online October 13, 2014; doi:10.4269/ajtmh.14-0018. The latest version is at http://ajtmh.org/cgi/doi/10.4269/ajtmh.14-0018 In order to provide our readers with timely
Catheter-Associated Urinary Tract Infection (CAUTI) Prevention. Basics of Infection Prevention 2 Day Mini-Course 2013
 Catheter-Associated Urinary Tract Infection (CAUTI) Prevention Basics of Infection Prevention 2 Day Mini-Course 2013 2 Objectives Define the scope of healthcare-associated urinary tract infections (UTI)
Catheter-Associated Urinary Tract Infection (CAUTI) Prevention Basics of Infection Prevention 2 Day Mini-Course 2013 2 Objectives Define the scope of healthcare-associated urinary tract infections (UTI)
{ Rifaximin versus Nonabsorbable Disaccharides for the Treatment of Hepatic Encephalopathy: A Meta Analysis}
 { Rifaximin versus Nonabsorbable Disaccharides for the Treatment of Hepatic Encephalopathy: A Meta Analysis} {Dong Wu, Shu-Mei Wu, Jie Lu, Ying-Qun Zhou, Ling Xu, and Chuan-Yong Guo} Noor Al-Hakami, Pharm
{ Rifaximin versus Nonabsorbable Disaccharides for the Treatment of Hepatic Encephalopathy: A Meta Analysis} {Dong Wu, Shu-Mei Wu, Jie Lu, Ying-Qun Zhou, Ling Xu, and Chuan-Yong Guo} Noor Al-Hakami, Pharm
Technology update: Understanding Hydrofiber Technology
 Technology update: Understanding Hydrofiber Technology Modern wound care clinicians have witnessed the development of a bewildering array of new technologies, many of which have emerged as a result of
Technology update: Understanding Hydrofiber Technology Modern wound care clinicians have witnessed the development of a bewildering array of new technologies, many of which have emerged as a result of
Surgical Site Infection Prevention
 Surgical Site Infection Prevention 1 Objectives 1. Discuss risk factors for SSI 2. Describe evidence-based best practices for SSI prevention 3. State principles of antibiotic prophylaxis 4. Discuss novel
Surgical Site Infection Prevention 1 Objectives 1. Discuss risk factors for SSI 2. Describe evidence-based best practices for SSI prevention 3. State principles of antibiotic prophylaxis 4. Discuss novel
Guidance for Industry Diabetes Mellitus Evaluating Cardiovascular Risk in New Antidiabetic Therapies to Treat Type 2 Diabetes
 Guidance for Industry Diabetes Mellitus Evaluating Cardiovascular Risk in New Antidiabetic Therapies to Treat Type 2 Diabetes U.S. Department of Health and Human Services Food and Drug Administration Center
Guidance for Industry Diabetes Mellitus Evaluating Cardiovascular Risk in New Antidiabetic Therapies to Treat Type 2 Diabetes U.S. Department of Health and Human Services Food and Drug Administration Center
NHS Greater Glasgow and Clyde Wound Formulary 2015/16
 NHS Greater Glasgow and Clyde Wound Formulary 2015/16 rimary Care and Acute Joint Formulary Wound care formulary, product data and prescribing guidance developed by the Wound Formulary and Implementation
NHS Greater Glasgow and Clyde Wound Formulary 2015/16 rimary Care and Acute Joint Formulary Wound care formulary, product data and prescribing guidance developed by the Wound Formulary and Implementation
SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS
 SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS 1. NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT Aknemycin Solution 2. QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION 10 g of solution contains 0.2 g of erythromycin. Structural formula of
SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS 1. NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT Aknemycin Solution 2. QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION 10 g of solution contains 0.2 g of erythromycin. Structural formula of
Urinary Tract Infections
 Urinary Tract Infections Overview A urine culture must ALWAYS be interpreted in the context of the urinalysis and patient symptoms. If a patient has no signs of infection on urinalysis, no symptoms of
Urinary Tract Infections Overview A urine culture must ALWAYS be interpreted in the context of the urinalysis and patient symptoms. If a patient has no signs of infection on urinalysis, no symptoms of
Antimicrobial Therapy in Immunocompromised and Critically Ill Patients: Management and Perspectives Palazzo dei Congressi - LUGANO 29-30 May 2014
 Antimicrobial Therapy in Immunocompromised and Critically Ill Patients: Management and Perspectives Palazzo dei Congressi - LUGANO 29-30 May 2014 BACKGROUND The incidence and diagnosis of viral, bacterial
Antimicrobial Therapy in Immunocompromised and Critically Ill Patients: Management and Perspectives Palazzo dei Congressi - LUGANO 29-30 May 2014 BACKGROUND The incidence and diagnosis of viral, bacterial
CHAPTER V CONCLUSION AND RECOMMENDATIONS. findings are presented, implications for nursing practice and education are discussed,
 CHAPTER V CONCLUSION AND RECOMMENDATIONS In this chapter, a summary of the findings and conclusion drawn from the findings are presented, implications for nursing practice and education are discussed,
CHAPTER V CONCLUSION AND RECOMMENDATIONS In this chapter, a summary of the findings and conclusion drawn from the findings are presented, implications for nursing practice and education are discussed,
Health-Care Associated Infection Rates among Adult Patients in Bahrain Military Hospital: A Cross Sectional Survey
 Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol. 32, No. 1, March 2010 Health-Care Associated Infection Rates among Adult Patients in Bahrain Military Hospital: A Cross Sectional Survey Kelechi Austin Ofurum, M.Sc, B.Sc*,
Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol. 32, No. 1, March 2010 Health-Care Associated Infection Rates among Adult Patients in Bahrain Military Hospital: A Cross Sectional Survey Kelechi Austin Ofurum, M.Sc, B.Sc*,
Use of Packing for Surgical Wounds. Maggie Benson Clinical Problem Solving II
 Use of Packing for Surgical Wounds Maggie Benson Clinical Problem Solving II Purpose Present patient management s/p Incision and Drainage in an outpatient setting Examine evidence for the use of wound
Use of Packing for Surgical Wounds Maggie Benson Clinical Problem Solving II Purpose Present patient management s/p Incision and Drainage in an outpatient setting Examine evidence for the use of wound
Telemedicine - a challenge rather than solution for payers and service providers in EU
 Telemedicine - a challenge rather than solution for payers and service providers in EU K. Dziadek, MAHTA G. Waligora Keywords: adherence, e-health, telemedicine, telemonitoring DOI: 10.7365 / JHPOR.2015.1.1
Telemedicine - a challenge rather than solution for payers and service providers in EU K. Dziadek, MAHTA G. Waligora Keywords: adherence, e-health, telemedicine, telemonitoring DOI: 10.7365 / JHPOR.2015.1.1
Approaches to Infection Control
 Approaches to Infection Control Considerations for PTAs in the Clinic Objectives Describe the basic characteristics of bacteria, viruses, fungi, and parasites. Discuss the locations, advantages, and disadvantages
Approaches to Infection Control Considerations for PTAs in the Clinic Objectives Describe the basic characteristics of bacteria, viruses, fungi, and parasites. Discuss the locations, advantages, and disadvantages
Summary of Recommendations
 Summary of Recommendations *LEVEL OF EVIDENCE Practice Recommendations Assessment 1.1 Conduct a history and focused physical assessment. IV 1.2 Conduct a psychosocial assessment to determine the client
Summary of Recommendations *LEVEL OF EVIDENCE Practice Recommendations Assessment 1.1 Conduct a history and focused physical assessment. IV 1.2 Conduct a psychosocial assessment to determine the client
Long-term urinary catheters: prevention and control of healthcare-associated infections in primary and community care
 Long-term urinary catheters: prevention and control of healthcare-associated infections in primary and community care A NICE pathway brings together all NICE guidance, quality standards and materials to
Long-term urinary catheters: prevention and control of healthcare-associated infections in primary and community care A NICE pathway brings together all NICE guidance, quality standards and materials to
Wound Care: The Basics
 Wound Care: The Basics Suzann Williams-Rosenthal, RN, MSN, WOC, GNP Norma Branham, RN, MSN, WOC, GNP University of Virginia May, 2010 What Type of Wound is it? How long has it been there? Acute-generally
Wound Care: The Basics Suzann Williams-Rosenthal, RN, MSN, WOC, GNP Norma Branham, RN, MSN, WOC, GNP University of Virginia May, 2010 What Type of Wound is it? How long has it been there? Acute-generally
Hepatitis C Glossary of Terms
 Acute Hepatitis C A short-term illness that usually occurs within the first six months after someone is exposed to the hepatitis C virus (HCV). 1 Antibodies Proteins produced as part of the body s immune
Acute Hepatitis C A short-term illness that usually occurs within the first six months after someone is exposed to the hepatitis C virus (HCV). 1 Antibodies Proteins produced as part of the body s immune
Wirral University Teaching Hospital NHS Foundation Trust
 Clinical guideline Wound dressings Guidance for Use There are several types of dressings in use at Wirral University Teaching Hospitals (WUTH). These are: 1. Medicated dressings a) Hydrocolloid dressings
Clinical guideline Wound dressings Guidance for Use There are several types of dressings in use at Wirral University Teaching Hospitals (WUTH). These are: 1. Medicated dressings a) Hydrocolloid dressings
Course Curriculum for Master Degree in Clinical Pharmacy
 Course Curriculum for Master Degree in Clinical Pharmacy The Master Degree in Clinical Pharmacy is awarded by the Faculty of Graduate studies at Jordan University of Science and Technology (JUST) upon
Course Curriculum for Master Degree in Clinical Pharmacy The Master Degree in Clinical Pharmacy is awarded by the Faculty of Graduate studies at Jordan University of Science and Technology (JUST) upon
Critically evaluate the organization of diabetic foot ulcer services and interdisciplinary team working
 Rationale of Module Accurate nursing assessment is the key to effective diabetic foot ulcer prevention, treatment and management. A comprehensive assessment identifies ulcer aetiology and the factors which
Rationale of Module Accurate nursing assessment is the key to effective diabetic foot ulcer prevention, treatment and management. A comprehensive assessment identifies ulcer aetiology and the factors which
(Resolutions, recommendations and opinions) RECOMMENDATIONS COUNCIL
 3.7.2009 Official Journal of the European Union C 151/1 I (Resolutions, recommendations and opinions) RECOMMENDATIONS COUNCIL COUNCIL RECOMMENDATION of 9 June 2009 on patient safety, including the prevention
3.7.2009 Official Journal of the European Union C 151/1 I (Resolutions, recommendations and opinions) RECOMMENDATIONS COUNCIL COUNCIL RECOMMENDATION of 9 June 2009 on patient safety, including the prevention
Research Priority Areas
 Research Priority Areas July 2015 Contents About The Wound Management Innovation CRC 4 Executive Summary 5 Research, Core and Development Activities 6 Research Priority Areas 8 Project Application and
Research Priority Areas July 2015 Contents About The Wound Management Innovation CRC 4 Executive Summary 5 Research, Core and Development Activities 6 Research Priority Areas 8 Project Application and
National Quality Forum Safe Practices for Better Healthcare
 National Quality Forum Safe Practices for Better Healthcare UCLA Health System advocates the National Quality Forum (NQF) endorsed safe practices.this set of safe Practices encompasses 34 practices that
National Quality Forum Safe Practices for Better Healthcare UCLA Health System advocates the National Quality Forum (NQF) endorsed safe practices.this set of safe Practices encompasses 34 practices that
Microcyn Technology. Life-Altering Advance in Tissue Care
 Microcyn Technology Life-Altering Advance in Tissue Care The patented Microcyn Technology mimics the same oxychlorine composition as that manufactured by neutrophils in the body s immune system. Neutrophils
Microcyn Technology Life-Altering Advance in Tissue Care The patented Microcyn Technology mimics the same oxychlorine composition as that manufactured by neutrophils in the body s immune system. Neutrophils
Provided by the American Venous Forum: veinforum.org
 CHAPTER 17 SURGICAL THERAPY FOR DEEP VALVE INCOMPETENCE Original author: Seshadri Raju Abstracted by Gary W. Lemmon Introduction Deep vein valvular incompetence happens when the valves in the veins (tubes
CHAPTER 17 SURGICAL THERAPY FOR DEEP VALVE INCOMPETENCE Original author: Seshadri Raju Abstracted by Gary W. Lemmon Introduction Deep vein valvular incompetence happens when the valves in the veins (tubes
Super-absorbent dressing for improving patient care
 BIGGER PACKAGES NOW AVAILABLE! Super-absorbent dressing for improving patient care BRITAIN S No. SUPER-ABSORBENT (IMS May 205) Caring with KerraMax As a woundcare nurse, you ve seen the damage exudate
BIGGER PACKAGES NOW AVAILABLE! Super-absorbent dressing for improving patient care BRITAIN S No. SUPER-ABSORBENT (IMS May 205) Caring with KerraMax As a woundcare nurse, you ve seen the damage exudate
CCME CNE Course Announcement
 CCME CNE Course Announcement Activity Title: NoCVA Pressure Ulcer Webinar The Carolinas Center for Medical Excellence (CCME) is accredited as an approved provider of continuing nursing education by North
CCME CNE Course Announcement Activity Title: NoCVA Pressure Ulcer Webinar The Carolinas Center for Medical Excellence (CCME) is accredited as an approved provider of continuing nursing education by North
C HAPTER 4 O RAL AND M AXILLOFACIAL S URGERY
 C HAPTER 4 O RAL AND M AXILLOFACIAL S URGERY I. TREATMENT PLANNING GUIDELINES As part of informed consent, the clinician should carefully explain the risks and benefits of oral and maxillofacial surgery
C HAPTER 4 O RAL AND M AXILLOFACIAL S URGERY I. TREATMENT PLANNING GUIDELINES As part of informed consent, the clinician should carefully explain the risks and benefits of oral and maxillofacial surgery
Science Highlights. To PSA or not to PSA: That is the Question.
 Science Highlights June 2012 by Ann A. Kiessling, PhD at the To PSA or not to PSA: That is the Question. The current raucous debate over the commonly used PSA blood test to screen for prostate cancer,
Science Highlights June 2012 by Ann A. Kiessling, PhD at the To PSA or not to PSA: That is the Question. The current raucous debate over the commonly used PSA blood test to screen for prostate cancer,
CURRICULUM VITAE. Michele Toby Sasmor, M.D.
 CURRICULUM VITAE NAME: ADDRESS: Michele Toby Sasmor, M.D. Office: RiverSong Plastic Surgery 21 Highland Ave Suite 3-4A Newburyport, Ma. 01950 Tel: (978) 462-8300 Fax: (978) 462-8301 PERSONAL DATA: Born:
CURRICULUM VITAE NAME: ADDRESS: Michele Toby Sasmor, M.D. Office: RiverSong Plastic Surgery 21 Highland Ave Suite 3-4A Newburyport, Ma. 01950 Tel: (978) 462-8300 Fax: (978) 462-8301 PERSONAL DATA: Born:
Open Ventral Hernia Repair
 Ventral Hernias Open Ventral Hernia Repair UCSF Postgraduate Course in General Surgery Maui, HI March 21, 2011 Hobart W. Harris, MD, MPH Ventral Hernias: National Experience Occur following 11-23% of laparotomies,
Ventral Hernias Open Ventral Hernia Repair UCSF Postgraduate Course in General Surgery Maui, HI March 21, 2011 Hobart W. Harris, MD, MPH Ventral Hernias: National Experience Occur following 11-23% of laparotomies,
Compare and Save. Dressings and wound care. www.supplychain.nhs.uk
 Compare and Save Dressings and wound care Today s panelists Stacie Croxton (Chair) Customer Services Director Email: [email protected] Gareth Hudson Dressings and Wound Care Procurement
Compare and Save Dressings and wound care Today s panelists Stacie Croxton (Chair) Customer Services Director Email: [email protected] Gareth Hudson Dressings and Wound Care Procurement
Etiology and treatment of chronic bacterial prostatitis the Croatian experience
 Etiology and treatment of chronic bacterial prostatitis the Croatian experience Višnja Škerk University Hospital for Infectious Diseases "Dr. Fran Mihaljevic" Zagreb Croatia Milano, Malpensa, 14 Nov 2008
Etiology and treatment of chronic bacterial prostatitis the Croatian experience Višnja Škerk University Hospital for Infectious Diseases "Dr. Fran Mihaljevic" Zagreb Croatia Milano, Malpensa, 14 Nov 2008
CODE OF PRACTICE TO MINIMIZE AND CONTAIN ANTIMICROBIAL RESISTANCE CAC/RCP 61-2005
 CAC/RCP 61-2005 Page 1 of 15 CODE OF PRACTICE TO MINIMIZE AND CONTAIN ANTIMICROBIAL RESISTANCE CAC/RCP 61-2005 INTRODUCTION... 2 AIMS AND OBJECTIVES... 2 RESPONSIBILITIES OF THE REGULATORY AUTHORITIES...
CAC/RCP 61-2005 Page 1 of 15 CODE OF PRACTICE TO MINIMIZE AND CONTAIN ANTIMICROBIAL RESISTANCE CAC/RCP 61-2005 INTRODUCTION... 2 AIMS AND OBJECTIVES... 2 RESPONSIBILITIES OF THE REGULATORY AUTHORITIES...
