Class/Nursing Education 29
|
|
|
- Howard Jones
- 8 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Class/Nursing Education 29
2 Possible Liver Solutions In 2009, 1,470 patients died in the United States while waiting for a liver transplant. Another 1,001 patients became too ill to receive their transplant. As of September 2010 there were 16,051 people awaiting a liver transplant from a deceased donor in the United States. Unfortunately, in 2009 only 6,320 liver transplants were performed in the United States, of which 6,101 were from deceased donors and 219 were from living donors. Because of the severe national organ shortage, alternative solutions to using deceased donors have been sought. Advances in liver transplantation have provided new techniques that increase the number of livers available for transplantation. Some of those advances are explained here. Deceased Donors Whole Liver: The majority of livers become available through deceased donors. Most donated livers are allocated to one recipient. Split Liver: In some clinical situations it is possible to split a donated liver into two segments; allowing transplants for two recipients. High-Risk Donors Some donors have been determined by the Centers for Disease Control (CDC) to have an increased risk to transmit some viral infections, including HIV, Hepatitis C, and Hepatitis B because of certain donor behaviors such as IV drug abuse, being in jail, or certain sexual behavior (e.g., prostitution). These donors are referred to as, CDC high-risk donors. All donors, whether they are high-risk, or not, are tested for a number of transmissible diseases including hepatitis C, hepatitis B, and HIV infection. These tests can detect a donor infection that may have been acquired as recently as one to two weeks prior to donation. The results of these tests are usually back before the organs are donated. High-risk donors who test negative for transmissible diseases carry a very low risk of transmission of infection and are therefore used as liver donors. The true risk of transmission is not known but is probably much less than 1 percent. Because the risk of dying on the waiting list before receiving a liver transplant is between percent, it is reasonable to consider receiving a liver transplant from a CDC high-risk donor under certain circumstances. 30 Class/Nursing Education
3 In addition, some donors have been previously exposed to the hepatitis B virus and have positive antibody tests. In many instances, these donor organs are fully functional and work as well as donor organs from individuals not previously exposed to hepatitis B. Your doctor may recommend that you consider receiving an organ from a donor who previously had a hepatitis B infection. If you receive an organ from a donor who was previously exposed to hepatitis B you will be given an additional medication following the transplant to prevent reactivation of the virus. Your doctor and the transplant surgeon on call will explain this to you in more detail should you have questions. In general, we recommend liver candidates on the waiting list keep all of their options open. The on-call transplant surgeon will always discuss with you if the donor organ carries a risk of transmitting a hepatitis B or C infection and will obtain your permission and willingness to receive such an organ before using it. Donation After Cardiac Death (DCD) DCD occurs after a person has experienced a devastating medical event from which recovery is not possible. With the family s approval, the patient is withdrawn from life support and cardiac death will occur prior to donation. If cardiac death does not occur within a designated time frame following the withdrawal from life support, the organ recovery will not occur. Living Donors Living liver donation is one of the solutions to the severe national organ shortage that has proven successful. In some clinical situations a recipient is identified as a potential candidate for a segmental or partial liver. A living donor liver transplant is considered when: a) the recipient is a candidate for a living donor, b) the recipient has an individual willing to donate, and c) the potential donor is healthy enough and deemed to be a suitable donor for that recipient. In this process the donor donates a portion of their liver to the recipient. Because of the liver s amazing capacity to regenerate, the liver is restored to its original size in the donor, and grows to a comparable size in the recipient in approximately four weeks. Although it is relatively safe, the operation does involve certain risks, including death. Living liver Class/Nursing Education 31
4 donation will be discussed in detail, including the risks and social issues, with patients who may be a suitable candidate or donor for this program. Potential donors are very carefully screened prior to acceptance as a suitable donor. Living Liver Coordinator/Donation Potential living donors will work with a nurse who will coordinate their care through the evaluation process. Who Can Donate? It is important for living liver donors to have a substantial emotional relationship with the person they are donating to. Parents, children, siblings, other relatives as well as in-laws and close friends can be considered. A potential donor must have no chronic illnesses, such as diabetes, heart disease or high blood pressure. A living liver donor must have personal health insurance, be between the ages of 18 and 59, and have a body mass index (BMI) of less than 35. The donor and recipient must have compatible blood types. Smokers must be willing to quit prior to donation. Prescreening If your blood type is compatible, you will be asked a series of questions regarding your health. If these screening questions don t turn up a medical reason why you should not donate, an appointment will be made for you to come to the transplant clinic to meet with the transplant team. The members of the team include a hepatologist, a surgeon, a social worker, a medical doctor as your donor advocate, a financial counselor and a nurse. 32 Class/Nursing Education
5 Evaluation At your evaluation appointment you will learn more about the donor surgery, potential complications, post operative recovery and expectations for returning to work. To determine whether you would be an appropriate candidate to donate a portion of your liver you will need to have some medical tests. The tests include an EKG, chest X-ray, a variety of lab tests, a CT scan, and an MRA, MRV or MRCP. You will also need to attend a Patient Education Class. History and Physical All living donors must have an appointment for a history and physical just prior to surgery. Since it is imperative you be healthy at the time of the surgery, your surgery may have to be rescheduled if you are not in good health at the time of your appointment. Operation A living donor liver transplant actually involves two overlapping operations between you, the healthy donor and the recipient. The right lobe of your liver is removed with its blood supply intact in one operating room. While this is happening, the patient s diseased liver is being completely removed in another operating room. The healthy portion of your liver is then taken into the adjacent operating room where it is then sewn into place in the recipient. The donor operation usually takes between four and eight hours. The right lobe of the liver is about 60% of the liver, thus leaving 40% of a normal liver in the donor. Because of its amazing capacity to regenerate, your liver is restored to its original size and grows to a comparable size in the patient in approximately four weeks. You can expect to stay in the hospital from five to ten days and be out of work for six to eight weeks after surgery. Class/Nursing Education 33
6 Post Operative Follow-Up Care Your post operative care relationship with the Transplant Center will be at least two years following your operation. You will have an appointment in the Transplant Clinic one week after discharge. You will have an on-going schedule for lab work to monitor your blood levels. Initially you will have lab work done at UMHS at seven to 14 days after donation and then 30 days. Appointments and blood work done at six months, one year, two years can be done locally with your internist or family physician, although the results need to be made available to the Liver Transplant Coordinator. Arrival for Transplant/Once in the Room Nurse Presenter s Name After you have checked in at the nursing desk, you will be placed in a room and will begin to prepare for surgery. History and Physical: A resident will ask about your history, perform a physical exam, will order chest X-rays and an EKG. These are done prior to surgery to verify that there are no significant changes in the patient s heart or lungs. 34 Class/Nursing Education
7 Blood Draw: Blood will be drawn for a variety of lab tests prior to surgery. Shower: You will be asked to take a shower with an antimicrobial soap prior to surgery. IV Started: An IV will be started in your arm. Transplant Research Team: A representative from the Clinical Research Team will meet with you to review the various clinical research studies available. Potential Cancellations or Delays After the offer call comes and you have arrived at the hospital, there are still several factors that can either cancel or delay the transplant. The surgery may be delayed for many hours after you arrive at the hospital for reasons such as coordinating processes between hospitals and surgical teams. The team will proceed as quickly as possible. Your Health Condition You must be healthy before an operation. The transplant cannot proceed if you have any heart or lung problems or any infections in your body. Since you will be taking medications that suppress the immune system, your body will not be able to actively fight an infection at the time of transplant. Class/Nursing Education 35
8 Changes in the Condition of the Donor The medical condition of the donor can impact the availability of the donated liver. If the donor becomes unstable, the liver may not be retrievable. Another situation that can occur is that the surgeon may determine that the donated organ is not suitable for transplant. When the organ isn t suitable for transplant the reason is often some anatomical detail that isn t apparent until the organ is visible to the surgeon. Sometimes patients come to the hospital ready for their transplant, only to be sent back home for reasons beyond their control and when it does it can be disappointing and frustrating. It may help to remember the reasons for canceling a transplant are in your best interest by either avoiding a potential health risk or waiting until a suitable organ becomes available. Family Responsibilities You are taken to the operating room approximately two hours before the start of the operation. Family members are allowed to walk with you to the operating room. Waiting After you are taken to the operating room, your family will be asked to check in at the reception desk in the surgery family waiting room. Be Available Families are asked to tell the receptionist in the surgery family waiting room where they will be if they choose to wait somewhere other than the waiting room. Following surgery, the surgeon will go to the surgery waiting room to speak with your family. If they are not present and cannot be located, they may miss the opportunity to speak with the surgeon immediately following your surgery. Rest Families are encouraged to use the waiting time to rest. Some families use the time to get something to eat or to arrange for lodging. Whatever activity the family engages in during this time, the surgery waiting room must be aware of how to find the family. 36 Class/Nursing Education
9 Liver Transplant Surgery Length of the Operation The length of time you spend in the operating room varies, but generally it is between four and 12 hours. Communicating with the Surgeon During and After the Operation Families should not expect updates from the operating room while the operation is taking place. Following the surgery, the surgeon will look for the family in the waiting room. During the evening, weekends and holidays when a receptionist may not be available to assist with communications, it is important to have a family representative available in the surgery waiting room to speak with the surgeon following the operation. Central Lines Just prior to or during surgery, the physician will place many tubes and equipment to assist in your monitoring. Since many of these lines will be in place the first time your family visits you, it is helpful if they are aware and expect to see the equipment. Central lines are inserted into the internal jugular vein in the side of the neck or the subclavian vein in the upper chest. A special catheter (called a Swan-Ganz) is inserted into a large blood vessel. It s a special monitoring IV used to measure circulatory pressure and fluid volume. Class/Nursing Education 37
10 A catheter is placed in an artery at your wrist, elbow or groin area to measure constant blood pressure, and to act as a source for future blood draws. A ventilator or respirator is used to help you breathe. The ventilation tube is inserted through the mouth into the lungs and is attached to a machine. This allows for optimal anesthesia, relaxation and sedation. A nasogastric tube (NGT) is placed through your nasal cavity into the stomach and is used to keep the stomach empty. A foley catheter is placed into your bladder to monitor urine output. A biliary drainage tube may be placed during the surgery into the common bile duct or the cystic duct. It is used to monitor the bile output and protect the connections made during surgery. The tube stays in place for six weeks or longer, depending upon when the problem is resolved. After Surgery Following a liver transplant you will be admitted directly to the Surgical Intensive Care Unit (SICU) on 5D, without going to the Recovery Room. Family members won t be able to visit you for one to two hours after you arrive at the SICU. While you are in the SICU, you will remain connected to many lines, tubes and monitoring devices. Many patients retain fluids, gain fluid weight and appear swollen following surgery. It may take days to weeks before the fluid retention is resolved. SICU Visiting Hours Visitation for patients in the SICU is somewhat more restrictive than the general care floor to allow the patients the rest necessary to recover. 38 Class/Nursing Education
11 Visitation is: Arranged through the charge nurse by calling the desk from the waiting room Available from 9 a.m. to 10 p.m., without specified time periods Limited to one or two visitors at a time Not recommended for individuals who are ill. Sick individuals should not have direct contact with any patient. To be coordinated between your family and your nurse for children. Patients usually stay in the SICU for one to three days following liver transplantation and then are moved to the transplant general care floor, 5C. Length of Stay The overall average length of stay for a liver transplant patient is between eight and 15 days. The following chart reflects the most usual course of stay for our patients. Location Low Average High Average Surgical Intensive Care Unit (SICU), taken there immediately following the operation. 1 day 3 days General care transplant floor (5C), taken there when the equipment is removed and the patient is mobile. 7 days 12 days Class/Nursing Education 39
12 Respirator Patients generally wake up one to two hours after arriving in the SICU and usually awaken with the respirator (commonly known as a ventilator) still in place. Because the ventilator tube goes through the vocal cords, the patient will not be able to talk while the ventilator is in place. Until the ventilator tube is removed, usually within 24 hours, you will have to communicate by writing or non-verbal communications. The time spent on a ventilator varies by patient, but a patient who smokes is usually on a ventilator somewhat longer than a non-smoking patient. Since patients still have anesthesia and pain medication in their system from the operation, they often do not recall much from the first several days following surgery even though they appear awake. Sometimes restraints are needed to remind the patient they have tubes and lines in place. The patient s wrists may be tied down to prevent them from trying to pull the tubes and lines out. Preventing Pneumonia As you improve, equipment is removed and you are encouraged to become more active. Coughing and deep breathing are exercises to help prevent pneumonia by keeping the air sacks open. You will be encouraged to take deep breaths and use your incentive spirometer 10 times each hour while you are awake. You will work to breathe deeply as the incision is close to the diaphragm and you may experience some discomfort. You will be provided a pillow to splint your incision area to reduce discomfort. 40 Class/Nursing Education
13 Mobility Increasing mobility is very important for you to prevent pneumonia, reduce the potential for blood clots, and to increase strength and conditioning. The day after surgery, you will be out of bed and sitting up in a chair. While the removal of lines and tubes is a factor, you will be encouraged to increase your mobility each day. When you move from the ICU to the general care floor, you will be encouraged to progressively increase your walking. Some patients may need the assistance of physical therapy or rehab, either while they are in the hospital or when they return home. Diet and Nutrition You will have a nasogastric tube in place until the function of your intestines resumes. The nasogastric tube may make your throat sore. While the tube is in place you may have ice chips for your throat. Once the tube has been removed, you can begin with a clear liquid diet as tolerated. You will proceed to an advanced diet which could be a heart healthy diet, as you are able to tolerate it. You may be on a diet, restricting salt, protein and fluids. Some patients who cannot eat may require a feeding tube (Dobhoff ). This is uncommon, but it could occur. Class/Nursing Education 41
14 Abdominal Incision There are several types of abdominal incisions for a liver transplant; the Mercedes-Benz or the humped incision. The type of incision is dependent on the surface area the surgeon needs to remove the old liver and transplant the new liver. The incisions are made and closed in the layers of tissue. The outer layer of the abdomen will be closed using staples or sutures. The abdominal incision may look similar to a railroad track. The staples remain in place for approximately three weeks and will be removed during an office visit. You may shower using a mild soap while the staples are in place. Absorbable sutures may be used to close the skin layer and do not need to be removed. Patients may experience fluid drainage from their incision due to ascites. Drainage due to ascites can take several months to resolve. Types of Incisions The humped incision includes one long incision across the upper abdomen which is higher in the midsection than the sides. The Mercedes-Benz incision includes the humped incision in addition to a vertical midline incision at the top of the hump. The Mercedes-Benz incision is used most often. Both incisions are very extensive, usually from one side to the other. The incision is close to the diaphragm, which is under the rib cage. A modified Mercedes-Benz incision is often used on the living liver donor and some recipients. 42 Class/Nursing Education
15 Photos of Mercedes-Benz Incision and Right Subcoastal Incision with Midline Extension (Hockey Stick) The photo on the left shows the Mercedes-Benz incision across the upper abdomen with a midline vertical incision at the top of the hump. This incision is used for the liver transplant. The patient pictured also had a kidney transplant. The lower incision is a result of the kidney transplant. The tube shown in the lower left is a bile tube placed during surgery and used to monitor the bile output. The other photo is the right subcoastal incision with midline extension. Similar to the Mercedes-Benz incision, it is closed in layers. However, final closure is with a suture called Quill that is under the skin and absorbs over time. Post-Operative Pain Our goal is to keep our patients comfortable following a liver transplant, but we cannot eliminate all pain. Pain tolerance differs significantly from person to person. Some patients experience back or rib pain. Some patients experience some numbness following surgery which is helpful with pain in the area of their incision. Pain related to pre-transplant conditions may not go away. Class/Nursing Education 43
16 Post-Operative Pain Medication You will receive pain medications through an IV while you are in the ICU. Some patients have a PCA (Patient Controlled Analgesia) pump that allows them to selfadminister pain medications within prescribed limits. Pain medications cannot eliminate all pain. You will be given oral medications for pain prior to being discharged from the hospital. Some patients may need to be referred to the pain clinic for chronic pain management. Possible Symptoms Pre- and/or Post-Transplant Surgery Following liver transplant surgery you may experience encephalopathy or ascites similar to symptoms experienced before surgery. Encephalopathy is a condition of the brain that is demonstrated as confusion and can be experienced by any patient following transplant. Confusion is caused by toxins not being filtered out of the blood by the liver and may be related to the impaired liver function, sleep deprivation, pain medications or prednisone. Patients may need to be restrained during periods of confusion. Confusion also can be caused by either sleep deprivation or the use of pain medications, or it can be aggravated by the use of steroids. Confusion from these causes is usually relieved by treatment of the cause. For instance, allowing more time for sleep, and decreasing pain medications or steroids at the direction of your physician. Usually the confusion after surgery is caused by a combination of these factors. 44 Class/Nursing Education
17 Ascites is an accumulation of fluid in the abdominal cavity and may occur following liver transplant surgery. Ascites is generally managed with medication, usually Lasix or Aldactone. Patients who experience difficulty breathing due to ascites, may need to have an abdominal tap (Paracentesis). Biliary Drainage Tubes External biliary drainage tubes (also called biliary stents) are occasionally placed during the transplant operation to protect the bile duct where it was sutured and to monitor bile output. The tubes are left open to a bag while you are in the hospital, but by the time you are discharged the tube is usually capped off. These tubes are usually removed during an outpatient visit six to 10 weeks following surgery. An internal biliary stent is placed during the transplant operation from the bile duct to the small bowel. It usually passes on its own through the digestive tract. If you do not pass the stent in four to six weeks an X-ray is taken to confirm the placement. If the stent is still present, an EGD is performed to remove it. An internal/external biliary stent (PTC) is used when the problem is high in the liver. A JP drain is used in the abdominal cavity when there is a need for drainage from that area. Class/Nursing Education 45
18 Bile Duct and Vascular Complications Serious complications can result from the delayed diagnosis of a problem in the bile duct anatomy. Labs are the first step in diagnosis and early intervention of a bile duct problem. All procedures should be performed at the University of Michigan during the early followup period. Abnormal laboratory tests, and presenting signs and symptoms will determine the management of a problem. The liver has a dual blood supply from the portal vein and the hepatic artery. If the hepatic artery develops thrombosis (clot), it may progress to liver failure rapidly. If the portal vein develops thrombosis (clot), the patient may develop variceal bleeding, abdominal pain and ascites. Vena cava obstruction can cause the liver to enlarge leading to ascites and lower extremity edema (swelling). A procedure to open the obstruction may include dilation or stent placement. Bile drains from the liver through the bile ducts. Bile duct obstruction or leaks can make you very sick. Obstructions and leaks are treated with a temporary stent like a T-Tube, ERCP or PTC stent. The stents are changed every four to six weeks until the obstruction or leak is resolved. Sometimes the obstructions can be treated with dilation until the issue is resolved. The gall bladder is removed from the recipient and from the donor during transplant. Discharge Criteria Before you can be discharged from the hospital following a liver transplant there are specific criteria you must meet. You must be able to eat and drink. Your lab values must show increasingly stable liver 46 Class/Nursing Education
19 functions. You must be able to walk to and from the bathroom safely. You must be able to perform basic self care tasks, with some help. You must demonstrate your knowledge of the signs and symptoms of infection and rejection. You must be able to take your anti-rejection medications properly, with the help of your caregiver. You must have your caregiver and support system in place, and it is important to have a secondary support system. Prior to discharge you will need to take and pass a written test to demonstrate your knowledge in these areas. Follow-Up Care For Life! Each liver transplant patient will have an individualized care plan for on-going follow-up care. Weekly clinic visits are necessary for the first four weeks after transplant, followed by bi-weekly clinic visits. Patients, depending upon the services they need, are sometimes seen in the Transplant Ambulatory Care Unit. Eventually you will become sufficiently stable to allow visits once or twice a year. Lab work is necessary to check your blood for anti-rejection drug levels. Lab work will be needed every week for the first few months following transplant, and then may decrease in frequency. It is important to understand that the need for lab work will never go away. Lab work will be needed forever. Transplant Ambulatory Care Unit (TACU) The TACU is an outpatient unit within the hospital that specializes in the handling of transplant-related issues. Patients are frequently seen in this unit for outpatient infusions, treatment of rejection, administering antibiotics, medication and lab monitoring, and evaluation of an acute problem. Class/Nursing Education 47
20 Since the TACU is an outpatient unit, patients are not provided accommodations such as meals. For this reason, you would need to have someone stay with you while you are in the TACU. If your treatment there spans a period of time, they may need to stay in the Med Inn or at a local hotel during your treatment period. Transplant Specialty Pharmacy Services The University of Michigan has a Transplant Specialty Pharmacy whose only focus is to serve patients, ensuring they have ongoing and timely access to their medications. The specialty pharmacy makes available financial counseling and support services to assist transplant patients in navigating through the complexities of insurance coverage and allows patients to obtain answers to questions regarding their medication regimen and medication side effects. A representative from the Transplant Specialty Pharmacy will meet with you while you are in the hospital to review the program and discuss your pharmacy options. If you have questions about the UMHS Transplant Specialty Pharmacy, please call (866) Anti-Rejection Medications Anti-rejection medications are a fact of life for patients following a liver transplant. Immunosuppressive drugs reduce the strength of the body s immune system, but it does not eliminate the immune system. Immediately following transplant, you will take many medications in high dosages. Different combinations of medications and smaller dosages are used to develop a balance between providing enough immunosuppression to avoid rejection and as little as necessary to minimize side effects. While you will always be on some immunosuppressive medication, the dosages may be reduced over time. 48 Class/Nursing Education
21 Side Effects of Anti-Rejection Drugs The immunosuppressive medications necessary following a transplant have side effects that you may find troublesome. Over time the Transplant Team will work with you to find the right balance of medications and dosages to prevent rejection and minimize side effects. The most common side effects for the three major drug types following transplant are shown here. Post-Transplant Complications The most common complications you may experience after a liver transplant are infections, bile duct problems, rejection or blood flow problems. Infections that occur at the wound site are generally treated by opening the wound to allow it to drain and by keeping clean dressings on the wound. An abscess is a pocket of infection that may require a drainage tube in your side. A viral infection, such as cytomegalovirus (CMV), may require medications for a period of one to three months. An acute rejection episode would generally occur early on following transplant and would be treated by increasing immunosuppressive drugs usually administered through an IV. Chronic rejection usually occurs a period of time after the transplant and reoccurs on multiple occasions. Vanishing Bile Duct Syndrome or long-term chronic rejection could result in needing a second transplant. Class/Nursing Education 49
22 The bile duct system is similar to a tree. The bile ducts are a common problem for liver transplant patients. Bile duct problems, such as leaking or a stricture, generally occur at the location of the stitching. Often a stent can be inserted through an EGD to treat a bile duct problem. After a period of time, prolonged damage can affect the new liver. The liver is dependent on blood for survival. The hepatic artery is the main artery that feeds the liver. If the hepatic artery is damaged you could suffer liver damage with eventual liver failure. The portal vein carries blood away from the liver. If there are problems with the portal vein the patient usually suffers ascites and fluid accumulation in their lower extremities. Blood flow problems in the hepatic artery or the portal vein are generally apparent soon after surgery and, if severe, need to be corrected surgically. Potential Medical Complications Following liver transplant some medical complications may appear or re-appear. Diabetes: Acute illness and a lengthy pre-clinical stage can put a patient at risk for developing diabetes. When multiple factors are present (obesity, hyper-lipidemia and age) the risk increases for the patient to need long-term management. After surgery while on high dose steroid and anti-rejection medication, the patient s blood glucose would become unstable requiring insulin intervention. Sometimes a lowering of the medication helps but often it does not. If the patient becomes a diabetic, they must commit to a diabetic regimen that includes self care, development of a treatment plan with their physician and honest communication with a medical team. It is important to note that being a diabetic is a lifestyle change that requires intervention and education for life. 50 Class/Nursing Education
23 Renal Failure: Kidney disease is common in patients with liver disease. While the body is under stress a significant number of patients will undergo a temporary insufficiency related to the surgery. The kidneys usually recover as the patient recovers but sometimes they do not. If the patient s kidneys do not recover they may have to go on hemodialysis temporarily, or for life. Renal failure is associated with poorer transplant and patient outcomes. Anti-rejection medications can cause a decline in kidney function over time with a significant number of liver transplant recipients developing chronic kidney disease. Chronic kidney disease is associated with increased mortality and an increase in cardiovascular risk. Treatment plans for renal failure are hemodialysis which is usually scheduled three times a week and/or a kidney transplant from a living donor or cadaver donor. It is important to note that hemodialysis is a major lifestyle change. Skin Cancer: Skin cancer is a greater risk due to the immunosuppressive medications. Patients are encouraged to use safety precautions in the sun. Limiting sun exposure and the use of a hat and sun block are encouraged. In addition, routine skin observation for foreign moles, spots and lesions is advised. Hypertension and Increased Cholesterol/Lipids: Hypertension and increased cholesterol/ lipid levels may occur. The hypertension is treated with medication, diet and lifestyle changes. While these increases may be temporary, some patients require on-going medications to maintain healthy levels. Your primary care physician will monitor your blood pressure and lipid levels following the transplant admission. Recurrence of Disease Transplant may not cure the underlying disease process that damaged your liver. However, since many of these diseases take years to result in damage to a liver it is hopeful you will not experience liver failure a second time as a result of recurring disease. Class/Nursing Education 51
24 Hepatitis B affects 1.2 million Americans and can reoccur following transplant. We follow a protocol to treat and monitor patients following liver transplant. Hepatitis C affects four million Americans. Patients may require anti-viral medications to treat a recurrence of hepatitis C. Autoimmune hepatitis usually affects young women and the cause in unknown. With autoimmune hepatitis your body attacks your own liver. Primary biliary cirrhosis (PBC) is a chronic cholestatic liver disease characterized by immune destruction of interlobular and septal bile ducts. PBC occurs most often in women. Primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC) is a chronic cholestatic syndrome characterized by immune diffuse fibrosing inflammation of the intra and extra hepatic bile ducts. PSC occurs most often in men. There is a close association with inflammatory bowel disease, especially ulcerative colitis. Substance abuse is an issue the patient must control. If the patient avoids using drugs or alcohol, they will not experience a recurrence of liver disease as a result of substance abuse. Cholangiocarcinoma and Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cholangiocarcinoma is a cancer that starts in the bile ducts. When it is at the branch points of the right and left bile ducts, it is called hilar cholangiocarcinoma. In some patients, hilar cholangiocarcinoma may be cured by combining chemotherapy and radiation followed by liver transplantation. Hepatocellular Carcinoma is a cancer that starts in the liver cells and is often associated with cirrhosis. A liver transplant may cure this cancer in some patients by removing all of the cancer along with all of the old liver and replacing the old liver with a new one. Lifetime Commitment It is important to recognize that a liver transplant is more than a single surgical event. Liver transplant is not a cure for liver disease; it is a treatment. A successful liver 52 Class/Nursing Education
25 transplant is a group effort that requires a lifetime commitment by the patient to adhere to a healthy lifestyle and receive on-going medical care. The following areas are examples that require an on-going commitment. Medications to suppress the immune system will be required for life. The types of medications and the dosages may change over time, but some level of medication will always be needed. Generally, the number of medications and the dosages are highest immediately following the transplant. Lab work will be required on a regular and on-going basis. Lab tests are required to monitor the level of medications and the functions of the liver. Medical procedures will be needed on an on-going basis generally they are most frequent following the transplant surgery or during a rejection episode. The members of the group needed for a successful liver transplant include the transplant professionals, the patient, the patient s family or caregiver, and the patient s primary care physician. Liver transplant patients must establish a relationship with a primary care physician who will manage their non-transplant health issues. The support you receive from your family and caregiver team is crucial to your success. The support will be needed on an on-going basis. Class/Nursing Education 53
26 54 Class/Nursing Education
Saint Francis Kidney Transplant Program Issue Date: 6/9/15
 Kidney Transplant Candidate Informed Consent Education Here are educational materials about Kidney Transplant. Please review and read these before your evaluation visit. The RN Transplant Coordinator will
Kidney Transplant Candidate Informed Consent Education Here are educational materials about Kidney Transplant. Please review and read these before your evaluation visit. The RN Transplant Coordinator will
CORONARY ARTERY BYPASS GRAFT & HEART VALVE SURGERY
 CORONARY ARTERY BYPASS GRAFT & HEART VALVE SURGERY www.cpmc.org/learning i learning about your health What to Expect During Your Hospital Stay 1 Our Team: Our cardiac surgery specialty team includes nurses,
CORONARY ARTERY BYPASS GRAFT & HEART VALVE SURGERY www.cpmc.org/learning i learning about your health What to Expect During Your Hospital Stay 1 Our Team: Our cardiac surgery specialty team includes nurses,
Living Donor Liver Transplantation. The Normal Liver
 Living Donor Liver Transplantation This information is for those individuals who are considering donating a portion of their liver to a family member or close friend. This information should supplement
Living Donor Liver Transplantation This information is for those individuals who are considering donating a portion of their liver to a family member or close friend. This information should supplement
Endovascular Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Repair Surgery
 Endovascular Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Repair Surgery You are scheduled for an admission to Cooper University Hospital for Endovascular Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm surgery (EVAR). Please read this handout,
Endovascular Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Repair Surgery You are scheduled for an admission to Cooper University Hospital for Endovascular Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm surgery (EVAR). Please read this handout,
LIVING DONATION. What You Need to Know. www.kidney.org
 LIVING DONATION What You Need to Know www.kidney.org 2 NATIONAL KIDNEY FOUNDATION TABLE OF CONTENTS About Living Donation.... 4 The Evaluation Process.... 6 Surgery and Recovery.... 12 After Donation....
LIVING DONATION What You Need to Know www.kidney.org 2 NATIONAL KIDNEY FOUNDATION TABLE OF CONTENTS About Living Donation.... 4 The Evaluation Process.... 6 Surgery and Recovery.... 12 After Donation....
Urinary Diversion: Ileovesicostomy/Ileal Loop/Colon Loop
 Urinary Diversion: Ileovesicostomy/Ileal Loop/Colon Loop Why do I need this surgery? A urinary diversion is a surgical procedure that is performed to allow urine to safely pass from the kidneys into a
Urinary Diversion: Ileovesicostomy/Ileal Loop/Colon Loop Why do I need this surgery? A urinary diversion is a surgical procedure that is performed to allow urine to safely pass from the kidneys into a
Laparoscopic Colectomy. What do I need to know about my laparoscopic colorectal surgery?
 Laparoscopic Colectomy What do I need to know about my laparoscopic colorectal surgery? Traditionally, colon & rectal surgery requires a large, abdominal and/or pelvic incision, which often requires a
Laparoscopic Colectomy What do I need to know about my laparoscopic colorectal surgery? Traditionally, colon & rectal surgery requires a large, abdominal and/or pelvic incision, which often requires a
Becoming a living kidney donor. Question and Answer Pamphlet UCSF Medical Center Transplant Service
 Becoming a living kidney donor Question and Answer Pamphlet UCSF Medical Center Transplant Service 1 What You Need to Know about Kidney Living Donor Kidney Transplantation At UCSF Medical Center, the majority
Becoming a living kidney donor Question and Answer Pamphlet UCSF Medical Center Transplant Service 1 What You Need to Know about Kidney Living Donor Kidney Transplantation At UCSF Medical Center, the majority
Inferior Vena Cava filter and removal
 Inferior Vena Cava filter and removal What is Inferior Vena Cava Filter Placement and Removal? An inferior vena cava filter placement procedure involves an interventional radiologist (a specialist doctor)
Inferior Vena Cava filter and removal What is Inferior Vena Cava Filter Placement and Removal? An inferior vena cava filter placement procedure involves an interventional radiologist (a specialist doctor)
YTTRIUM 90 MICROSPHERES THERAPY OF LIVER TUMORS
 YTTRIUM 90 MICROSPHERES THERAPY OF LIVER TUMORS The information regarding placement of Yttrium 90 microsphres for the management of liver tumors on the next several pages includes questions commonly asked
YTTRIUM 90 MICROSPHERES THERAPY OF LIVER TUMORS The information regarding placement of Yttrium 90 microsphres for the management of liver tumors on the next several pages includes questions commonly asked
INTRAPERITONEAL HYPERTHERMIC CHEMOTHERAPY (IPHC) FOR PERITONEAL CARCINOMATOSIS AND MALIGNANT ASCITES. INFORMATION FOR PATIENTS AND FAMILY MEMBERS
 INTRAPERITONEAL HYPERTHERMIC CHEMOTHERAPY (IPHC) FOR PERITONEAL CARCINOMATOSIS AND MALIGNANT ASCITES. INFORMATION FOR PATIENTS AND FAMILY MEMBERS Description of Treatment A major difficulty in treating
INTRAPERITONEAL HYPERTHERMIC CHEMOTHERAPY (IPHC) FOR PERITONEAL CARCINOMATOSIS AND MALIGNANT ASCITES. INFORMATION FOR PATIENTS AND FAMILY MEMBERS Description of Treatment A major difficulty in treating
PATIENT CONSENT TO PROCEDURE - ROUX-EN-Y GASTRIC BYPASS
 As a patient you must be adequately informed about your condition and the recommended surgical procedure. Please read this document carefully and ask about anything you do not understand. Please initial
As a patient you must be adequately informed about your condition and the recommended surgical procedure. Please read this document carefully and ask about anything you do not understand. Please initial
Bile Duct Diseases and Problems
 Bile Duct Diseases and Problems Introduction A bile duct is a tube that carries bile between the liver and gallbladder and the intestine. Bile is a substance made by the liver that helps with digestion.
Bile Duct Diseases and Problems Introduction A bile duct is a tube that carries bile between the liver and gallbladder and the intestine. Bile is a substance made by the liver that helps with digestion.
KIDNEY PRE-TRANSPLANT EDUCATION BOOK
 KIDNEY PRE-TRANSPLANT EDUCATION BOOK This book is to give information to you and your family about kidney transplant. Please keep this book handy in order to look back at it as you have questions. At the
KIDNEY PRE-TRANSPLANT EDUCATION BOOK This book is to give information to you and your family about kidney transplant. Please keep this book handy in order to look back at it as you have questions. At the
You will be having surgery to remove a tumour(s) from your liver.
 Liver surgery You will be having surgery to remove a tumour(s) from your liver. This handout will help you learn about the surgery, how to prepare for surgery and your care after surgery. Surgery can be
Liver surgery You will be having surgery to remove a tumour(s) from your liver. This handout will help you learn about the surgery, how to prepare for surgery and your care after surgery. Surgery can be
Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy
 Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy Gallbladder removal is one of the most commonly performed surgical procedures in the United States. Today,gallbladder surgery is performed laparoscopically. The medical name
Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy Gallbladder removal is one of the most commonly performed surgical procedures in the United States. Today,gallbladder surgery is performed laparoscopically. The medical name
X-Plain Preparing For Surgery Reference Summary
 X-Plain Preparing For Surgery Reference Summary Introduction More than 25 million surgical procedures are performed each year in the US. This reference summary will help you prepare for surgery. By understanding
X-Plain Preparing For Surgery Reference Summary Introduction More than 25 million surgical procedures are performed each year in the US. This reference summary will help you prepare for surgery. By understanding
Informed Consent for Laparoscopic Vertical Sleeve Gastrectomy. Patient Name
 Informed Consent for Laparoscopic Vertical Sleeve Gastrectomy Patient Name Please read this form carefully and ask about anything you may not understand. I consent to have a laparoscopic Vertical Sleeve
Informed Consent for Laparoscopic Vertical Sleeve Gastrectomy Patient Name Please read this form carefully and ask about anything you may not understand. I consent to have a laparoscopic Vertical Sleeve
Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy
 Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy Removal of Gall Bladder Page 12 Patient Information Further Information We endeavour to provide an excellent service at all times, but should you have any concerns please,
Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy Removal of Gall Bladder Page 12 Patient Information Further Information We endeavour to provide an excellent service at all times, but should you have any concerns please,
MANAGEMENT OF LIVER CIRRHOSIS
 MANAGEMENT OF LIVER CIRRHOSIS Information Leaflet Your Health. Our Priority. Page 2 of 6 What is cirrhosis? Cirrhosis is a result of long-term, continuous damage to the liver and may be due to many different
MANAGEMENT OF LIVER CIRRHOSIS Information Leaflet Your Health. Our Priority. Page 2 of 6 What is cirrhosis? Cirrhosis is a result of long-term, continuous damage to the liver and may be due to many different
TheraSphere A Radiation Treatment Option for Liver Cancer
 TheraSphere A Radiation Treatment Option for Liver Cancer TheraSphere is a treatment which is done in the Interventional Radiology Clinic. If you have more questions after reading this handout, you can
TheraSphere A Radiation Treatment Option for Liver Cancer TheraSphere is a treatment which is done in the Interventional Radiology Clinic. If you have more questions after reading this handout, you can
Kidney Transplantation
 ilearning about your health Kidney Transplantation www.cpmc.org/learning What is Kidney Failure? Normally, kidneys filter waste products from your blood, control the balance of salt and water in your body,
ilearning about your health Kidney Transplantation www.cpmc.org/learning What is Kidney Failure? Normally, kidneys filter waste products from your blood, control the balance of salt and water in your body,
Surgery and cancer of the pancreas
 Surgery and cancer of the pancreas This information is an extract from the booklet Understanding cancer of the pancreas. You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you a free copy see page 8. Introduction
Surgery and cancer of the pancreas This information is an extract from the booklet Understanding cancer of the pancreas. You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you a free copy see page 8. Introduction
Colon Cancer Surgery and Recovery. A Guide for Patients and Families
 Colon Cancer Surgery and Recovery A Guide for Patients and Families This Booklet You are receiving this booklet because you will be having surgery shortly. This booklet tells you what to do before, during,
Colon Cancer Surgery and Recovery A Guide for Patients and Families This Booklet You are receiving this booklet because you will be having surgery shortly. This booklet tells you what to do before, during,
Laparoscopic Gallbladder Removal (Cholecystectomy) Patient Information from SAGES
 Laparoscopic Gallbladder Removal (Cholecystectomy) Patient Information from SAGES Gallbladder removal is one of the most commonly performed surgical procedures. Gallbladder removal surgery is usually performed
Laparoscopic Gallbladder Removal (Cholecystectomy) Patient Information from SAGES Gallbladder removal is one of the most commonly performed surgical procedures. Gallbladder removal surgery is usually performed
Treating your abdominal aortic aneurysm by open repair (surgery)
 Patient information Abdominal aortic aneurysm open surgery Treating your abdominal aortic aneurysm by open repair (surgery) Introduction This leaflet tells you about open repair of abdominal aortic aneurysm,
Patient information Abdominal aortic aneurysm open surgery Treating your abdominal aortic aneurysm by open repair (surgery) Introduction This leaflet tells you about open repair of abdominal aortic aneurysm,
Liver Transarterial Chemoembolization (TACE) Cancer treatment
 Patient Education Liver Transarterial Chemoembolization (TACE) Cancer treatment This handout explains what liver transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) is and what to expect with this cancer treatment.
Patient Education Liver Transarterial Chemoembolization (TACE) Cancer treatment This handout explains what liver transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) is and what to expect with this cancer treatment.
Liver Resection. Patient Information Booklet. Delivering the best in care. UHB is a no smoking Trust
 Liver Resection Patient Information Booklet Delivering the best in care UHB is a no smoking Trust To see all of our current patient information leaflets please visit www.uhb.nhs.uk/patient-information-leaflets.htm
Liver Resection Patient Information Booklet Delivering the best in care UHB is a no smoking Trust To see all of our current patient information leaflets please visit www.uhb.nhs.uk/patient-information-leaflets.htm
Excision of Vaginal Mesh
 What is excision of vaginal mesh? This procedure is done to remove mesh from the vagina. When is this surgery used? If mesh has eroded into the vagina, bladder, urethra, or bowel If there is pain associated
What is excision of vaginal mesh? This procedure is done to remove mesh from the vagina. When is this surgery used? If mesh has eroded into the vagina, bladder, urethra, or bowel If there is pain associated
Quality Measures for Long-stay Residents Percent of residents whose need for help with daily activities has increased.
 Quality Measures for Long-stay Residents Percent of residents whose need for help with daily activities has increased. This graph shows the percent of residents whose need for help doing basic daily tasks
Quality Measures for Long-stay Residents Percent of residents whose need for help with daily activities has increased. This graph shows the percent of residents whose need for help doing basic daily tasks
The Whipple Procedure. Sally Hodges, Ph.D.(c) Given the length and difficulty of the procedure, regardless of the diagnosis, certain
 The Whipple Procedure Sally Hodges, Ph.D.(c) Preoperative procedures Given the length and difficulty of the procedure, regardless of the diagnosis, certain assurances must occur prior to offering a patient
The Whipple Procedure Sally Hodges, Ph.D.(c) Preoperative procedures Given the length and difficulty of the procedure, regardless of the diagnosis, certain assurances must occur prior to offering a patient
LIVER CANCER AND TUMOURS
 LIVER CANCER AND TUMOURS LIVER CANCER AND TUMOURS Healthy Liver Cirrhotic Liver Tumour What causes liver cancer? Many factors may play a role in the development of cancer. Because the liver filters blood
LIVER CANCER AND TUMOURS LIVER CANCER AND TUMOURS Healthy Liver Cirrhotic Liver Tumour What causes liver cancer? Many factors may play a role in the development of cancer. Because the liver filters blood
Subtotal Colectomy. Delivering the best in care. UHB is a no smoking Trust
 Subtotal Colectomy Delivering the best in care UHB is a no smoking Trust To see all of our current patient information leaflets please visit www.uhb.nhs.uk/patient-information-leaflets.htm This leaflet
Subtotal Colectomy Delivering the best in care UHB is a no smoking Trust To see all of our current patient information leaflets please visit www.uhb.nhs.uk/patient-information-leaflets.htm This leaflet
What You Need to know about Your Pet s Upcoming Dentistry and Periodontal Treatment
 What You Need to know about Your Pet s Upcoming Dentistry and Periodontal Treatment We are sending this packet of information in anticipation of your pet s upcoming dental procedure. Many people have questions
What You Need to know about Your Pet s Upcoming Dentistry and Periodontal Treatment We are sending this packet of information in anticipation of your pet s upcoming dental procedure. Many people have questions
Nursing college, Second stage Microbiology Dr.Nada Khazal K. Hendi L14: Hospital acquired infection, nosocomial infection
 L14: Hospital acquired infection, nosocomial infection Definition A hospital acquired infection, also called a nosocomial infection, is an infection that first appears between 48 hours and four days after
L14: Hospital acquired infection, nosocomial infection Definition A hospital acquired infection, also called a nosocomial infection, is an infection that first appears between 48 hours and four days after
Weight Loss before Hernia Repair Surgery
 Weight Loss before Hernia Repair Surgery What is an abdominal wall hernia? The abdomen (commonly called the belly) holds many of your internal organs. In the front, the abdomen is protected by a tough
Weight Loss before Hernia Repair Surgery What is an abdominal wall hernia? The abdomen (commonly called the belly) holds many of your internal organs. In the front, the abdomen is protected by a tough
Ureteroscopy with Laser Lithotripsy
 Ureteroscopy with Laser Lithotripsy Introduction Kidney stones are fairly common. Although kidney stones can be very painful, they are treatable, and in many cases preventable. Your doctor may recommend
Ureteroscopy with Laser Lithotripsy Introduction Kidney stones are fairly common. Although kidney stones can be very painful, they are treatable, and in many cases preventable. Your doctor may recommend
Yttrium-90 Radiotherapy Treatment for liver tumors
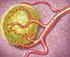 Patient Education Yttrium-90 Radiotherapy Treatment for liver tumors This handout explains what Yttrium-90 radiotherapy is and what to expect when you have it done. Why do I need this treatment? Your doctors
Patient Education Yttrium-90 Radiotherapy Treatment for liver tumors This handout explains what Yttrium-90 radiotherapy is and what to expect when you have it done. Why do I need this treatment? Your doctors
Gallbladder Surgery with an Incision (Cholecystectomy)
 Gallbladder Surgery with an Incision (Cholecystectomy) It is normal to have questions about your surgery. This handout gives you information about what will happen to you before, during and after your
Gallbladder Surgery with an Incision (Cholecystectomy) It is normal to have questions about your surgery. This handout gives you information about what will happen to you before, during and after your
SOD (Sphincter of Oddi Dysfunction)
 SOD (Sphincter of Oddi Dysfunction) SOD refers to the mechanical malfunctioning of the Sphincter of Oddi, which is the valve muscle that regulates the flow of bile and pancreatic juice into the duodenum.
SOD (Sphincter of Oddi Dysfunction) SOD refers to the mechanical malfunctioning of the Sphincter of Oddi, which is the valve muscle that regulates the flow of bile and pancreatic juice into the duodenum.
X-Plain Subclavian Inserted Central Catheter (SICC Line) Reference Summary
 X-Plain Subclavian Inserted Central Catheter (SICC Line) Reference Summary Introduction A Subclavian Inserted Central Catheter, or subclavian line, is a long thin hollow tube inserted in a vein under the
X-Plain Subclavian Inserted Central Catheter (SICC Line) Reference Summary Introduction A Subclavian Inserted Central Catheter, or subclavian line, is a long thin hollow tube inserted in a vein under the
Liver Function Essay
 Liver Function Essay Name: Quindoline Ntui Date: April 20, 2009 Professor: Dr. Danil Hammoudi Class: Anatomy and Physiology 2 Liver function The human body consist of many highly organize part working
Liver Function Essay Name: Quindoline Ntui Date: April 20, 2009 Professor: Dr. Danil Hammoudi Class: Anatomy and Physiology 2 Liver function The human body consist of many highly organize part working
Is a Kidney Transplant Right for Me?
 Is a Kidney Transplant Right for Me? Network 8 Introduction What do singer Natalie Cole, actor Ken Howard, funny men Tracy Morgan and George Lopez and fashion reporter Steven Cojocaru have in common? They
Is a Kidney Transplant Right for Me? Network 8 Introduction What do singer Natalie Cole, actor Ken Howard, funny men Tracy Morgan and George Lopez and fashion reporter Steven Cojocaru have in common? They
Heart transplantation
 Heart transplantation A patient s guide 1 Heart transplantation Heart transplantation has the potential to significantly improve the length and quality of life for patients with severe heart failure.
Heart transplantation A patient s guide 1 Heart transplantation Heart transplantation has the potential to significantly improve the length and quality of life for patients with severe heart failure.
Colon and Rectal Cancer
 Colon and Rectal Cancer What is colon or rectal cancer? Colon or rectal cancer is the growth of abnormal cells in your large intestine, which is also called the large bowel. The colon is the last 5 feet
Colon and Rectal Cancer What is colon or rectal cancer? Colon or rectal cancer is the growth of abnormal cells in your large intestine, which is also called the large bowel. The colon is the last 5 feet
Epidural Continuous Infusion. Patient information Leaflet
 Epidural Continuous Infusion Patient information Leaflet April 2015 Introduction You may already know that epidural s are often used to treat pain during childbirth. This same technique can also used as
Epidural Continuous Infusion Patient information Leaflet April 2015 Introduction You may already know that epidural s are often used to treat pain during childbirth. This same technique can also used as
TA L K I N G A B O U T T R A N S P L A N TAT I O N
 TA L K I N G A B O U T T R A N S P L A N TAT I O N UNITED NETWORK FOR ORGAN SHARING United Network for Organ Sharing (UNOS) is a private non-profit 501(c)(3) organization that operates the Organ Procurement
TA L K I N G A B O U T T R A N S P L A N TAT I O N UNITED NETWORK FOR ORGAN SHARING United Network for Organ Sharing (UNOS) is a private non-profit 501(c)(3) organization that operates the Organ Procurement
Lumbar or Thoracic Decompression and Fusion
 Lumbar or Thoracic Decompression and Fusion DO NOT TAKE ANY ASPIRIN PRODUCTS OR NON-STEROIDAL ANTI- INFLAMMATORY DRUGS (ie NSAIDs, Advil, Celebrex, Ibuprofen, Motrin, Naprosyn, Aleve, etc) FOR 2 WEEKS
Lumbar or Thoracic Decompression and Fusion DO NOT TAKE ANY ASPIRIN PRODUCTS OR NON-STEROIDAL ANTI- INFLAMMATORY DRUGS (ie NSAIDs, Advil, Celebrex, Ibuprofen, Motrin, Naprosyn, Aleve, etc) FOR 2 WEEKS
Department of Surgery
 What is emphysema? 2004 Regents of the University of Michigan Emphysema is a chronic disease of the lungs characterized by thinning and overexpansion of the lung-like blisters (bullae) in the lung tissue.
What is emphysema? 2004 Regents of the University of Michigan Emphysema is a chronic disease of the lungs characterized by thinning and overexpansion of the lung-like blisters (bullae) in the lung tissue.
The degree of liver inflammation or damage (grade) Presence and extent of fatty liver or other metabolic liver diseases
 ilearning about your health Liver Biopsy www.cpmc.org/learning What is a Liver Biopsy? A liver biopsy is a procedure where a specially trained doctor (typically a hepatologist, radiologist, or gastroenterologist)
ilearning about your health Liver Biopsy www.cpmc.org/learning What is a Liver Biopsy? A liver biopsy is a procedure where a specially trained doctor (typically a hepatologist, radiologist, or gastroenterologist)
Surgical removal of fibroids through an abdominal incision-either up and down or bikini cut. The uterus and cervix are left in place.
 What is an abdominal myomectomy? Surgical removal of fibroids through an abdominal incision-either up and down or bikini cut. The uterus and cervix are left in place. When is this surgery used? Treatment
What is an abdominal myomectomy? Surgical removal of fibroids through an abdominal incision-either up and down or bikini cut. The uterus and cervix are left in place. When is this surgery used? Treatment
Multiple Myeloma. This reference summary will help you understand multiple myeloma and its treatment options.
 Multiple Myeloma Introduction Multiple myeloma is a type of cancer that affects white blood cells. Each year, thousands of people find out that they have multiple myeloma. This reference summary will help
Multiple Myeloma Introduction Multiple myeloma is a type of cancer that affects white blood cells. Each year, thousands of people find out that they have multiple myeloma. This reference summary will help
ANESTHESIA. Anesthesia for Ambulatory Surgery
 ANESTHESIA & YOU Anesthesia for Ambulatory Surgery T oday the majority of patients who undergo surgery or diagnostic tests do not need to stay overnight in the hospital. In most cases, you will be well
ANESTHESIA & YOU Anesthesia for Ambulatory Surgery T oday the majority of patients who undergo surgery or diagnostic tests do not need to stay overnight in the hospital. In most cases, you will be well
Presence and extent of fatty liver or other metabolic liver diseases
 UC San Diego Health System Patient Information Sheet: Liver Biopsy What is a Liver Biopsy? A liver biopsy is a procedure where a qualified doctor (typically a hepatologist, radiologist or gastroenterologist)
UC San Diego Health System Patient Information Sheet: Liver Biopsy What is a Liver Biopsy? A liver biopsy is a procedure where a qualified doctor (typically a hepatologist, radiologist or gastroenterologist)
Varicose Veins Operation. Patient information Leaflet
 Varicose Veins Operation Patient information Leaflet 22 nd August 2014 WHAT IS VARICOSE VEIN SURGERY (HIGH LIGATION AND MULTIPLE AVULSIONS) The operation varies from case to case, depending on where the
Varicose Veins Operation Patient information Leaflet 22 nd August 2014 WHAT IS VARICOSE VEIN SURGERY (HIGH LIGATION AND MULTIPLE AVULSIONS) The operation varies from case to case, depending on where the
Patient Information. Lumbar Spine Segmental Decompression. Royal Devon and Exeter NHS Foundation Trust
 Lumbar Spine Segmental Decompression Royal Devon and Exeter NHS Foundation Trust Patient Information Lumbar Spine Segmental Decompression Reference Number: TO 05 004 004 (version date: June 2015) Introduction
Lumbar Spine Segmental Decompression Royal Devon and Exeter NHS Foundation Trust Patient Information Lumbar Spine Segmental Decompression Reference Number: TO 05 004 004 (version date: June 2015) Introduction
Dear Prospective Donor,
 Dear Prospective Donor, Considering organ donation is an extraordinary act of kindness. The decision to actually become a living donor should be based on a clear understanding of the benefits as well as
Dear Prospective Donor, Considering organ donation is an extraordinary act of kindness. The decision to actually become a living donor should be based on a clear understanding of the benefits as well as
The Patient s Guide. Pancreaticoduodenectomy (Whipple) Surgery. Where life shines bright.
 Pancreaticoduodenectomy (Whipple) Surgery The Patient s Guide Where life shines bright. SM Methodist Dallas Medical Center 1441 N. Beckley Ave. Dallas, TX 75203 214-947-8181 MethodistHealthSystem.org Find
Pancreaticoduodenectomy (Whipple) Surgery The Patient s Guide Where life shines bright. SM Methodist Dallas Medical Center 1441 N. Beckley Ave. Dallas, TX 75203 214-947-8181 MethodistHealthSystem.org Find
Hepatic resection (Removal of part of the liver)
 Hepatic resection (Removal of part of the liver) The liver is the largest solid organ in the body and is located in the upper right-quadrant of the abdomen under the rib cage. Functionally it is a major
Hepatic resection (Removal of part of the liver) The liver is the largest solid organ in the body and is located in the upper right-quadrant of the abdomen under the rib cage. Functionally it is a major
Femoral artery bypass graft (Including femoral crossover graft)
 Femoral artery bypass graft (Including femoral crossover graft) Why do I need the operation? You have a blockage or narrowing of the arteries supplying blood to your leg. This reduces the blood flow to
Femoral artery bypass graft (Including femoral crossover graft) Why do I need the operation? You have a blockage or narrowing of the arteries supplying blood to your leg. This reduces the blood flow to
Total Abdominal Hysterectomy
 What is a total abdominal hysterectomy? Is the removal of the uterus and cervix through an abdominal incision (either an up and down or bikini cut). Removal of the ovaries and tubes depends on the patient.
What is a total abdominal hysterectomy? Is the removal of the uterus and cervix through an abdominal incision (either an up and down or bikini cut). Removal of the ovaries and tubes depends on the patient.
The main surgical options for treating early stage cervical cancer are:
 INFORMATION LEAFLET ON TOTAL LAPAROSCOPIC RADICAL HYSTERECTOMY (TLRH) FOR EARLY STAGE CERVICAL CANCER (TREATING EARLY STAGE CERVICAL CANCER BY RADICAL HYSTERECTOMY THROUGH KEYHOLE SURGERY) Aim of the leaflet
INFORMATION LEAFLET ON TOTAL LAPAROSCOPIC RADICAL HYSTERECTOMY (TLRH) FOR EARLY STAGE CERVICAL CANCER (TREATING EARLY STAGE CERVICAL CANCER BY RADICAL HYSTERECTOMY THROUGH KEYHOLE SURGERY) Aim of the leaflet
X-Plain Inguinal Hernia Repair Reference Summary
 X-Plain Inguinal Hernia Repair Reference Summary Introduction Hernias are common conditions that affect men and women of all ages. Your doctor may recommend a hernia operation. The decision whether or
X-Plain Inguinal Hernia Repair Reference Summary Introduction Hernias are common conditions that affect men and women of all ages. Your doctor may recommend a hernia operation. The decision whether or
PATIENT HANDBOOK AND JOURNAL DAY OF SURGERY
 PATIENT HANDBOOK AND JOURNAL DAY OF SURGERY PREPARING YOUR SKIN BEFORE SURGERY PRE-OP HIBICLENS BATHING INSTRUCTIONS: General Information: Because the skin is not sterile, it is important to make sure
PATIENT HANDBOOK AND JOURNAL DAY OF SURGERY PREPARING YOUR SKIN BEFORE SURGERY PRE-OP HIBICLENS BATHING INSTRUCTIONS: General Information: Because the skin is not sterile, it is important to make sure
Brachytherapy: Low Dose Rate (LDR) Radiation Interstitial Implant
 Brachytherapy: Low Dose Rate (LDR) Radiation Interstitial Implant Goal of the Procedure Brachytherapy, or internal radiation therapy, is a way of giving a higher dose of radiation to the tumor area while
Brachytherapy: Low Dose Rate (LDR) Radiation Interstitial Implant Goal of the Procedure Brachytherapy, or internal radiation therapy, is a way of giving a higher dose of radiation to the tumor area while
Kidney Disease WHAT IS KIDNEY DISEASE? TESTS TO DETECT OR DIAGNOSE KIDNEY DISEASE TREATMENT STRATEGIES FOR KIDNEY DISEASE
 Kidney Disease WHAT IS KIDNEY DISEASE? Kidney disease is when your kidneys are damaged and not functioning as they should. When kidney disease is not going away it is called chronic kidney disease or CKD.
Kidney Disease WHAT IS KIDNEY DISEASE? Kidney disease is when your kidneys are damaged and not functioning as they should. When kidney disease is not going away it is called chronic kidney disease or CKD.
Smoking and misuse of certain pain medicines can affect the risk of developing renal cell cancer.
 Renal cell cancer Renal cell cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in tubules of the kidney. Renal cell cancer (also called kidney cancer or renal adenocarcinoma) is a disease in which
Renal cell cancer Renal cell cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in tubules of the kidney. Renal cell cancer (also called kidney cancer or renal adenocarcinoma) is a disease in which
X-Plain Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Vascular Surgery Reference Summary
 X-Plain Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Vascular Surgery Reference Summary Ballooning of the aorta, also known as an "abdominal aortic aneurysm," can lead to life threatening bleeding. Doctors may recommend
X-Plain Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Vascular Surgery Reference Summary Ballooning of the aorta, also known as an "abdominal aortic aneurysm," can lead to life threatening bleeding. Doctors may recommend
Sleeve Gastrectomy Surgery & Follow Up Care
 Sleeve Gastrectomy Surgery & Follow Up Care Sleeve Gastrectomy Restrictive surgical weight loss procedure Able to eat a smaller amount of food to feel satiety, less than 6 ounces at a meal Surgery The
Sleeve Gastrectomy Surgery & Follow Up Care Sleeve Gastrectomy Restrictive surgical weight loss procedure Able to eat a smaller amount of food to feel satiety, less than 6 ounces at a meal Surgery The
Is a kidney transplant right for me?
 Is a kidney transplant right for me? Your guide to the transplant process www.esrdncc.org Contents Introduction 3 What is a Transplant Center? 4 What is the Waiting List? 5 What Happens After the Surgery?
Is a kidney transplant right for me? Your guide to the transplant process www.esrdncc.org Contents Introduction 3 What is a Transplant Center? 4 What is the Waiting List? 5 What Happens After the Surgery?
Lumbar Spine Surgery What to Expect
 Lumbar Spine Surgery What to Expect You have been scheduled for lumbar spine surgery and are probably wondering what to expect with your surgical journey. We will discuss pre- operative tasks, the day
Lumbar Spine Surgery What to Expect You have been scheduled for lumbar spine surgery and are probably wondering what to expect with your surgical journey. We will discuss pre- operative tasks, the day
Treating Mesothelioma - A Quick Guide
 Treating Mesothelioma - A Quick Guide Contents This is a brief summary of the information on Treating mesothelioma from CancerHelp UK. You will find more detailed information on the website. In this information
Treating Mesothelioma - A Quick Guide Contents This is a brief summary of the information on Treating mesothelioma from CancerHelp UK. You will find more detailed information on the website. In this information
Gastric Sleeve Surgery
 Gastric Sleeve Surgery Introduction Obesity is associated with many diseases such as diabetes, high blood pressure, heart problems, and degeneration of the joints. These diseases and the obesity itself
Gastric Sleeve Surgery Introduction Obesity is associated with many diseases such as diabetes, high blood pressure, heart problems, and degeneration of the joints. These diseases and the obesity itself
Canine Lymphoma Frequently Asked Questions by Pet Owners
 Canine Lymphoma Frequently Asked Questions by Pet Owners What is lymphoma? The term lymphoma describes a diverse group of cancers in dogs that are derived from white blood cells called lymphocytes. Lymphocytes
Canine Lymphoma Frequently Asked Questions by Pet Owners What is lymphoma? The term lymphoma describes a diverse group of cancers in dogs that are derived from white blood cells called lymphocytes. Lymphocytes
PATIENT INFORMATION INSURANCE INFORMATION
 (mm/dd/yyyy): Have you been to Physicians Urgent Care before? Yes No Arrival Time: If yes, when? Is this a follow-up to a previous visit: Yes No PATIENT INFORMATION Patient s First Name: Middle Name: Last
(mm/dd/yyyy): Have you been to Physicians Urgent Care before? Yes No Arrival Time: If yes, when? Is this a follow-up to a previous visit: Yes No PATIENT INFORMATION Patient s First Name: Middle Name: Last
Before Surgery You will likely be asked to see your family physician or an internal medicine doctor for a thorough medical evaluation.
 Anterior Hip Replacement - Before and After Surgery Your Hip Evaluation An orthopaedic surgeon specializes in problems affecting bones and joints. The surgeon will ask you many questions about your hip
Anterior Hip Replacement - Before and After Surgery Your Hip Evaluation An orthopaedic surgeon specializes in problems affecting bones and joints. The surgeon will ask you many questions about your hip
Recto-vaginal Fistula Repair
 What is a recto-vaginal fistula repair? Rectovaginal fistula repair is a procedure in which the healthy tissue between the rectum and vagina is closed in multiple tissue layers. An incision is made either
What is a recto-vaginal fistula repair? Rectovaginal fistula repair is a procedure in which the healthy tissue between the rectum and vagina is closed in multiple tissue layers. An incision is made either
Surgery for oesophageal cancer
 Surgery for oesophageal cancer This information is an extract from the booklet Understanding oesophageal cancer (cancer of the gullet). You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you a free copy
Surgery for oesophageal cancer This information is an extract from the booklet Understanding oesophageal cancer (cancer of the gullet). You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you a free copy
Diuretics: You may get diuretic medicine to help decrease swelling in your brain. This may help your brain get better blood flow.
 Hemorrhagic Stroke GENERAL INFORMATION: What is a hemorrhagic stroke? A hemorrhagic stroke happens when a blood vessel in the brain bursts. This may happen if the blood vessel wall is weak, or sometimes
Hemorrhagic Stroke GENERAL INFORMATION: What is a hemorrhagic stroke? A hemorrhagic stroke happens when a blood vessel in the brain bursts. This may happen if the blood vessel wall is weak, or sometimes
Positron Emission Tomography - For Patients
 Positron Emission Tomography - For Patients A physician s written order is required for any PET-CT tests. How should I prepare for my PET-CT? PET-CT is more complicated than most other tests you may be
Positron Emission Tomography - For Patients A physician s written order is required for any PET-CT tests. How should I prepare for my PET-CT? PET-CT is more complicated than most other tests you may be
Degree of Intervention
 Inglewood Care Centre Degree of Intervention Handbook for Residents and Families Index Introduction..................................................... 2 Beliefs, Values, and Wishes.........................................
Inglewood Care Centre Degree of Intervention Handbook for Residents and Families Index Introduction..................................................... 2 Beliefs, Values, and Wishes.........................................
Prevention and Recognition of Obstetric Fistula Training Package. Module 8: Pre-repair Care and Referral for Women with Obstetric Fistula
 Prevention and Recognition of Obstetric Fistula Training Package Module 8: Pre-repair Care and Referral for Women with Obstetric Fistula Early detection and treatment If a woman has recently survived a
Prevention and Recognition of Obstetric Fistula Training Package Module 8: Pre-repair Care and Referral for Women with Obstetric Fistula Early detection and treatment If a woman has recently survived a
restricted to certain centers and certain patients, preferably in some sort of experimental trial format.
 Managing Pancreatic Cancer, Part 4: Pancreatic Cancer Surgery, Complications, & the Importance of Surgical Volume Dr. Matthew Katz, Surgeon, MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, TX I m going to talk a little
Managing Pancreatic Cancer, Part 4: Pancreatic Cancer Surgery, Complications, & the Importance of Surgical Volume Dr. Matthew Katz, Surgeon, MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, TX I m going to talk a little
Radiation Therapy for Prostate Cancer
 Radiation Therapy for Prostate Cancer Introduction Cancer of the prostate is the most common form of cancer that affects men. About 240,000 American men are diagnosed with prostate cancer every year. Your
Radiation Therapy for Prostate Cancer Introduction Cancer of the prostate is the most common form of cancer that affects men. About 240,000 American men are diagnosed with prostate cancer every year. Your
Biliary Stone Disease
 Biliary Stone Disease Delivering the best in care UHB is a no smoking Trust To see all of our current patient information leaflets please visit www.uhb.nhs.uk/patient-information-leaflets.htm You have
Biliary Stone Disease Delivering the best in care UHB is a no smoking Trust To see all of our current patient information leaflets please visit www.uhb.nhs.uk/patient-information-leaflets.htm You have
Femoral Hernia Repair
 Femoral Hernia Repair WHAT IS A FEMORAL HERNIA REPAIR? 2 WHAT CAUSES A FEMORAL HERNIA? 2 WHAT DOES TREATMENT/ MANAGEMENT INVOLVE? 3 DAY SURGERY MANAGEMENT 3 SURGICAL REPAIR 4 WHAT ARE THE RISKS/COMPLICATIONS
Femoral Hernia Repair WHAT IS A FEMORAL HERNIA REPAIR? 2 WHAT CAUSES A FEMORAL HERNIA? 2 WHAT DOES TREATMENT/ MANAGEMENT INVOLVE? 3 DAY SURGERY MANAGEMENT 3 SURGICAL REPAIR 4 WHAT ARE THE RISKS/COMPLICATIONS
Total Vaginal Hysterectomy
 What is a total vaginal hysterectomy? Is the removal of the uterus and cervix through the vagina. Removal of the ovaries and tubes depends on the patient. Why is this surgery used? To treat disease of
What is a total vaginal hysterectomy? Is the removal of the uterus and cervix through the vagina. Removal of the ovaries and tubes depends on the patient. Why is this surgery used? To treat disease of
Recovery plan: radical cystectomy Information for patients
 Recovery plan: radical cystectomy Information for patients Help for you following a bereavement 5 This leaflet will help you know what to expect during your time with us. Please take some time to read
Recovery plan: radical cystectomy Information for patients Help for you following a bereavement 5 This leaflet will help you know what to expect during your time with us. Please take some time to read
PERIPHERAL STEM CELL TRANSPLANT INTRODUCTION
 PERIPHERAL STEM CELL TRANSPLANT INTRODUCTION This booklet was designed to help you and the important people in your life understand the treatment of high dose chemotherapy with stem cell support: a procedure
PERIPHERAL STEM CELL TRANSPLANT INTRODUCTION This booklet was designed to help you and the important people in your life understand the treatment of high dose chemotherapy with stem cell support: a procedure
Introduction. Evaluation
 Introduction Most patients evaluated for kidney transplantation are already on dialysis, but this is not an absolute requirement. The evaluation process for a kidney transplant ensures that the patient
Introduction Most patients evaluated for kidney transplantation are already on dialysis, but this is not an absolute requirement. The evaluation process for a kidney transplant ensures that the patient
Orthopaedic Spine Center. Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion (ACDF) Normal Discs
 Orthopaedic Spine Center Graham Calvert MD James Woodall MD PhD Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion (ACDF) Normal Discs The cervical spine consists of the bony vertebrae, discs, nerves and other structures.
Orthopaedic Spine Center Graham Calvert MD James Woodall MD PhD Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion (ACDF) Normal Discs The cervical spine consists of the bony vertebrae, discs, nerves and other structures.
GASTRIC BYPASS SURGERY CONSENT FORM
 Page 1 of 6 I, have been asked to read carefully all of the (name of patient or substitute decision-maker) information contained in this consent form and to consent to the procedure described below on
Page 1 of 6 I, have been asked to read carefully all of the (name of patient or substitute decision-maker) information contained in this consent form and to consent to the procedure described below on
Procedure Information Guide
 Procedure Information Guide Surgery to remove the pancreas (whipple's procedure) Brought to you in association with EIDO and endorsed by the The Royal College of Surgeons of England Discovery has made
Procedure Information Guide Surgery to remove the pancreas (whipple's procedure) Brought to you in association with EIDO and endorsed by the The Royal College of Surgeons of England Discovery has made
Radical Hysterectomy and Pelvic Lymph Node Dissection
 Radical Hysterectomy and Pelvic Lymph Node Dissection Tena koutou katoa, Kia orana, Talofa lava, Malo e lelei, Fakaalofa lahi atu, Taloha Ni, Ni Sa Bula Vinaka, Greetings and Welcome to National Women's
Radical Hysterectomy and Pelvic Lymph Node Dissection Tena koutou katoa, Kia orana, Talofa lava, Malo e lelei, Fakaalofa lahi atu, Taloha Ni, Ni Sa Bula Vinaka, Greetings and Welcome to National Women's
Elective Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy
 General Surgery Elective Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy This information aims to explain what will happen before, during and after your surgery to remove your gallbladder. It includes information about the
General Surgery Elective Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy This information aims to explain what will happen before, during and after your surgery to remove your gallbladder. It includes information about the
Preparing for your Surgery:
 Preparing for your Surgery: Information for Patients Undergoing a: UHN Minimally Invasive Radical Hysterectomy Possible removal of one or both ovaries and tubes Possible removal of pelvic lymph nodes Patient
Preparing for your Surgery: Information for Patients Undergoing a: UHN Minimally Invasive Radical Hysterectomy Possible removal of one or both ovaries and tubes Possible removal of pelvic lymph nodes Patient
Percutaneous Abdominal or Pelvic Drain What to expect
 Patient Education Percutaneous Abdominal or Pelvic Drain What to expect This handout explains what percutaneous abdominal or pelvic drain is and what to expect when you have one. What is a percutaneous
Patient Education Percutaneous Abdominal or Pelvic Drain What to expect This handout explains what percutaneous abdominal or pelvic drain is and what to expect when you have one. What is a percutaneous
GASTRIC SLEEVE SURGERY FOR WEIGHT LOSS. www.carepointhealth.org GASTRIC SLEEVE SURGERY FOR WEIGHT LOSS. 201-795-8175 CarePointHealth.
 www.carepointhealth.org GASTRIC SLEEVE SURGERY FOR WEIGHT LOSS 201-795-8175 CarePointHealth.org 1 CONTENTS What is sleeve gastrectomy? Why choose sleeve gastrectomy? Health risks associated with excess
www.carepointhealth.org GASTRIC SLEEVE SURGERY FOR WEIGHT LOSS 201-795-8175 CarePointHealth.org 1 CONTENTS What is sleeve gastrectomy? Why choose sleeve gastrectomy? Health risks associated with excess
X-Plain Hip Replacement Surgery - Preventing Post Op Complications Reference Summary
 X-Plain Hip Replacement Surgery - Preventing Post Op Complications Reference Summary Introduction Severe arthritis in the hip can lead to severe pain and inability to walk. To relieve the pain and improve
X-Plain Hip Replacement Surgery - Preventing Post Op Complications Reference Summary Introduction Severe arthritis in the hip can lead to severe pain and inability to walk. To relieve the pain and improve
