A Key to Classroom Management: Teacher Reflection
|
|
|
- Mae Mason
- 10 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 A Key to Classroom Management: Teacher Reflection A presentation by and Dönercan Dönük, Mersin University, and Dr. Fehmi Sendan, Çucurova University Introduction Unlike in the past, when language education was mostly in the scope of applied linguistics, and basically theoretical, today language teacher education (LTE) mostly relies on practice, classroom centered education and other teaching practices such as materials development, and curriculum development. Thus, LTE as part of the teacher education (TE) has made a shift from theory to practice, and this has an impact on the curricula designed for LTE programs. These programs now rely heavily on more humanistic aspects, seeing the person as a whole. This enables researchers to focus more on the cognitive aspects of teaching practice. Such aspects brings about some basic changes in the concept of TE as a more general term, and the trend is towards a more process oriented, constructivist approach to bottom up practices, in which teachers can practice and understand the nature of teaching by more intellectual means. Traditional teacher education views teachers as passive takers more than active givers, and it does not allow for any space for change or any opportunity to think and make decisions. The role of reflection has come at a stage when the basic competences of the teacher began to be considered as more creative, humanistic and problem solving. A shift to a constructivist perspective on teaching and teacher learning makes teachers a primary source of knowledge about teaching, and the role of reflection in teacher development and the importance of teacher inquiry and research throughout teacher education and development programs have begun to be the major issues in LTE. Teacher roles place the teacher somewhere between the classroom and the student. This relative space varies according to the paradigm that the teacher feels he or she best fits. The changing attitude and theories towards the learner and the way of learning according to different schools of thought have brought about different teacher paradigms: While Zeichner (1983) classifies teachers according to behavioristic, personalistic, traditional craft, and inquiry norms, Wallace (1991) underlines different paradigms of teachers according to the craft model, the applied science model, and the reflective model (cited in Roberts, 1998). That LTE programs do not adequately prepare the teachers for the realities of the teaching world, and that there is not a smooth transition from school theory to classroom practice, has begun to be a major concern for education authorities. Input from novice teachers also confirms the fact that theory remains somewhere at the very top, superficial, and rather far from the reality of classroom settings. The unpredictability of classroom practice (Nunan, 1996) unfolds another picture before the novice teacher. This sometimes makes the situation unbearable and acts as a deterrent from the teaching profession. This study aims to throw light upon the fact that there is a gap between the curricula of LTE programs, and real classroom application. The reality is that the novice teacher suffers some classroom management problems. Books giving ideas for strategy in classroom management can help the teacher to a certain extent, but in some cases remain de-contextualized. The Page 1 1
2 study has its roots in the conversations that the mentor had with student teachers already doing their practice teaching, and novice teachers with four years of professional experience at most. Related research on teacher reflection Research in the area of LTE and teacher reflection makes a clear-cut distinction between the definitions of teacher education, training and development. Teacher education, training and development For Widdowson (1997), teacher training implies that teachers are to be given specific instruction in practical techniques to cope with predictable events, while teacher education is problem-oriented, with the implication of a broader intellectual awareness of theoretical principles underlying particular practices (1997:121). On the other hand, Wallace (1991) highlights the distinction stating that training or education is something which can be presented or managed by others; whereas development is something that can be done only by and for oneself (1991:3). The basic distinction is that, once self and cognition merges with the profession, then the language teacher begins a life-long process based on constructivism. Out of the four perspectives of teacher learning (model based, person focused, reflectiveexperiential, social constructivist), social constructivism includes the interaction and interrelation of all the concepts that arise from all sources in society. Therefore, a social constructivist teacher needs to combine such activities as access to new information, self awareness activities, direct personal experience, opportunities for private reflection on the inputs and experiences he or she has, with the development of skills and attitudes which enable him or her to get the most out of the other activities. The social dimension of language teaching is gaining more and more recognition, which builds up the distinction between the social constructivist and the reflective teacher. (Roberts, 1998: 46), The social constructivist as a reflective practitioner In terms of teacher reflection in teacher education, there are different views. Dewey (1910) highlights such concepts as the value of self-determination, individual responsibility, citizenship in a democracy, and points out that, Reflection is a disciplined, explicit, conscious and critical thought which contributes to the intellectual and moral development of a person. Reflection is an active, persistent and careful consideration of any belief or supposed form of knowledge in the light of the grounds that support it, and the further conclusions to which it tends.( Dewey, 1910:6, cited in Roberts, 1998) Moreover, Schön (1987) states that teachers develop their sense of teaching through continuous reflections on their practice teaching and their interaction with the class. By questioning, discovering, reflecting, teachers reframe the understanding of themselves as teachers. Schön defines reflection as professional artistry to describe the kinds of competence practitioners display in unique, uncertain and conflicted situations of practice. He mentions two dimensions of reflection: reflection on action, and reflection in action. Reflection on action is looking back upon an action some time after or before it has taken Page 2 2
3 place. Teachers use this type of reflection before teaching when they plan their teaching along with the anticipated problems and solutions to them. After they have had their class, they think about any possible problems and weaknesses of the lesson and take some decisions for the classes to be held in the future. Reflection in action means thinking over an action while dealing with it. Teachers pass through this period when they teach. They think about their practice, monitor the class and students, and when needed, adapt the lesson plan according to the need that arises while teaching. It is to some extent conscious; one can consider the does not fit situation and what might have led to this through reflection-in-action. Such reflection questions the assumptions underlying the routine that has become disrupted, and leads to the restructuring of the strategies of action. This type of action leads to on-the-spot experimentation. Schön rejects the idea that objective knowledge about the world is an adequate guide for action, but views the core of professional expertise as a capacity for rapid and creative problem-solving. Schön and Arygris et.al., ( 1985) have argued that the most effective method of developing in the profession is through the ability to reflect on one s own professional practice, which assumes that trainees can be coached in this ability. Such reflective practitioners will be able to continue to develop their professional expertise by using theory mediated within their ongoing practice. As long as teachers as practitioners reflect on their classroom performance and see classrooms as laboratories, they can see the relationship between theory and practice; thus, they can understand whether there is a gap between how they are teaching and how they should be teaching. Loughran (1996) adds another dimension to teacher reflection stating that, reflection does not occur by only training the student-teachers, but rather by probing, inquiring, and challenging when they are experiencing how to teach. The model Loughran suggests has three different time layers. Anticipatory reflection occurs when the teacher plans the lesson, during the teaching process contemporaneous reflection takes its place, and retrospective reflection comes after the lesson has been taught. Through these three layers, teachers are expected to be reflective in their preparation for teaching processes. Thus, it can be said that reflection does not have a specific time layer; it is multilayered and may cover a longer period. As Schön (1983) suggests, a lawyer in a court case can be likened to a teacher in the classroom. The reflective practitioner, and classroom management However rich the theoretical knowledge in terms of teacher reflection may be, the decontextualized behavior cliché the teacher is asked to mould into does not always match the real context. The books related to classroom management can help the teacher to a certain extent. They cannot go any further than prescribe solutions: If in doubt, ask for advice from more experienced teachers. The problem may be a common one for which a solution exists (Gower & Walters, 1983). Page 3 3
4 The teacher should try to understand or analyze the physiological, physical or psycho-social factors that may contribute to misbehavior. You can evaluate the severity of the misbehavior by factors such as appropriateness, magnitude, intent, etc. (Burden, 1999:15) The teacher is the primary custodian of the classroom and decides when and how to intervene into the flow of activities to repair disorder (Burden, 1999: 24). It is helpful to discuss with the student to clarify it both from novice teacher s perspective and the student s and to consider the possible interventions (Burden, 1999 :26). As is clear, each teacher is faced with a unique situation, and has to tailor his or her own teaching to it, which means having some reflective way to create his or her own means. Some writers on teacher education suggest a further model of the teacher as researcher, an orientation to action research, which implies that trainees should be trained in research methods so that, as teachers, they can become their own researchers. This kind of research is different from other types of research in that it is directly and immediately related to professional action in some way. As Chaudron (1988) states, the fundamental goal of research has been to determine which variables best lead to academic achievement. This study takes its starting point from such a point of view. The researcher has already pinpointed a problem, and intends to suggest ways in which the novice teachers can participate in the action to reach a solution. Research Method The participants in this research are selected from fifty novice teachers (twenty have been included in this study) currently employed at schools. The majority of them have been engaged in the profession for at least one year, and are already familiar with the conditions of classroom settings. The background of the research is based on personal communications with the novice teachers, who sometimes ask for a course of action in cases of classroom management. The problems these teachers encountered were the true indicators of lack of classroom experience, and the solutions suggested served as the contextualized knowledge that normally do not appear in books. As Nunan (1996) states, the novice teacher tries to make sense of the real world by reconsidering and reformulating these problems to avoid new difficulties. Therefore, these teachers needed a helping hand in order to solve present problems to prevent others. The study relies on two research tools: 1. Hypothetical classroom management situations that elicit possible responses from teachers in the classroom 2. A scale consisting of items aimed at identifying the explicit beliefs of the participants in terms of classroom management, as well as an alternative scale for triangulation purposes. Both research tools have been developed on the basis of data elicited from the participants by means of an opinion sheet given to the novice teachers asking about their classroom management procedures. Page 4 4
5 The qualitative data have been analyzed using content analysis procedures, and as categories of analysis, using the teacher paradigms proposed by Roth (1991) and Wallace (1991). As well as teacher reflection, the research tool for checking consistency in terms of beliefs and attitudes is based on the argument by Argyris and Schön (1974): when someone is asked how he (or she) would behave under certain circumstances, the answer given is usually his espoused theory of action for that situation. This is the theory of action to which he gives allegiance, and which, upon request, he communicates to others. However, the theory that actually governs his actions is this theory-in-use ( p: 7). Preliminary findings, discussion and educational implications The bottom-up data generated by the research tool used to ask for teachers beliefs, attitudes and action towards classroom management issues, reveals that novice teachers sometimes experience difficulties when managing the class: 1. This may be because the espoused theory is in conflict with the theory in use: 1.1. When given the following item in the attitude scale: I think a teacher should ignore potential individual differences while teaching, the teacher disagrees with the idea. This can be interpreted as a belief that every student is an individual, and should be dealt with individually But when the same teacher is given the following question: What would you do in the following situation - would you deal with the problem on the spot, or later? - You have a student who is a constant source of disturbance for you and class members. While you are teaching something important, he/she pulls the hair of the girl in front, and she cries. All the children are distracted, and the lesson is violated, the teacher s response to the situation is: I would punish the student with a harsh word or action (as can be seen, the teacher s espoused theory and theory in-use do not coincide). 2. The teacher, though a novice, can use creative means of management if given the chance: 2.1. What would you do in the following situation; would you deal with the problem on the spot, or later? - You want your students to keep their notebooks neatly, but a teenage boy shows a messy notebook to you rather rudely The teacher s response to the situation is: I would hang a paper on the bulletin board in the class so that everybody can see the marks and I would write the students names on that paper, and would give high marks to those whose notebooks are really neat. 3. The novice teacher asks for outside help to settle problems in the classroom: 3.1. The teachers ask for help form the school administration: What would you do in the following situation; would you deal with the problem on the spot, or later? You are writing on the board. Upon finishing, you see a noisy group at the back of the class throwing pieces of chalk at each other. You stare at them, but they do not care. Page 5 5
6 3.2. The teacher s response to the situation is: I would deal with the problem on the spot, I cannot ignore such behavior. I cannot tolerate that. I would certainly report it to the principal and the discipline committee The teachers ask for help from families: the teacher s response to the situation is: I would not let a problem get so serious, but in this situation, I would want the students to inform their parents about that event and would ask the parents to visit the school The teachers ask for help from other disciplines: the teacher s response to the situation above is I would deal with the problem on the spot. I m afraid I would send him to the counseling service. 4. The novice teacher considers experience, which she yet lacks, as a significant teacher competency. 5. Most teachers are aware of teacher reflection, but it is not multilayered as Loughran (1996) suggests. In addition, in terms of reflection, many skip reflection on action, which makes it difficult for them to identify long lasting and effective solutions, which they can have on their agenda in the coming years. 6. The novice teacher may not be aware of the underlying beliefs that might change the root attitudes. The novice teacher might need a confrontation to develop an awareness of their espoused theory and the theory-in-use. This confrontation could be achieved by challenging the trainees through exposing them to alternative practices so as to mirror to them that there is a conflict between the espoused theory and the theory-in use. This challenge can be best realized at real classroom contexts during the teaching practice experience, where candidate teachers will obtain more chance of observation, practice, discussion and reflection. Conclusion Research conducted by teacher educators or teachers themselves allows for a new situation in which teachers can reshape and reformulate their assumptions, and enhance their practices to increase the standard of their professionalism. As Chaudron (1988) states, careful evaluation of results can lead to well-informed decision making at all levels of educational planning: development of the curriculum, preparation of materials, training of teachers, preference for classroom teaching activities and techniques, decisions about individualization of instruction, and even teacher s modifications of speech in explanations. Research based on collaboration between novice teachers and two teacher trainers is expected to yield results which will both help to improve the reflective practices of the participants as teachers, and will have its implications for the other teachers who consider teaching as a lifelong, constructivist profession. Teacher reflection in broader terms will serve as a key for many classroom applications, for it will free the teacher of dependency on some other authority to find solutions for the daily problems that she encounters in the classroom; in addition, the teacher will become more autonomous in decision making and will contribute to the administration of their schools. For this reason, the programs of in-service teacher education (ITE) need to be revised with such a solution as the objective. The curriculum of ITE should be based on courses that will invest in the teacher as an independent agent. School practice lessons need to include such issues as teacher roles and the reflection of these roles in the school environment. 6 Page 6
7 REFERENCES 1. Argyris, C. & Schön, D.(1974). Theory into Practice, San Francisco: Jossey-Bass. 2. Burden, P, Evertson, Emmer Et. C, Worsham Me. (2000). Classroom Management For Secondary Teachers, Ally And Bacon Fifth Edition 3. Chaudron, Craig. (1988). Second Language Classrooms, Cambridge University Press 4. Gower, R. And Walters, S. (1983). Teaching Practice Handbook, Heinemann Educational Books Ltd 5. Nunan, David. (1999). Second Language Teaching& Learning, Heinle& Heinle Publishers 6. Roberts, Jon. (1998). Language Teacher Education, Eatsbourne: Anthony Rowe Ltd., 7. Loughran, J., Russell, T.( 1996). Teaching About Teaching, Routledge 8. Schön, D.A. (1983). The Reflective Practitioner: How Professionals Think in Action, London: Temple Smith. 9. Widdowson, H.G. (1990). Aspects of Language Teaching, Oxford University Press 10. Zeichner, Kennett M. (1983). Alternative Paradigms of Teacher Education, May-June Volume Number 3/3 Page 7 7
A KEY TO CLASSROOM MANAGEMENT: TEACHER REFLECTION
 ISSN: 2342-0251 Volume 2/2 Summer 2014 p. 165/181 A KEY TO CLASSROOM MANAGEMENT: TEACHER REFLECTION Sınıf Yönetimi İçin Bir Anahtar: Yansıtıcı Düşünme 1 Fehmi Can Sendan 2 & Dönercan Dönük 3 Abstract Voices
ISSN: 2342-0251 Volume 2/2 Summer 2014 p. 165/181 A KEY TO CLASSROOM MANAGEMENT: TEACHER REFLECTION Sınıf Yönetimi İçin Bir Anahtar: Yansıtıcı Düşünme 1 Fehmi Can Sendan 2 & Dönercan Dönük 3 Abstract Voices
LEARNING MUSIC IN FORMAL, NON-FORMAL AND INFORMAL CONTEXTS
 LEARNING MUSIC IN FORMAL, NON-FORMAL AND INFORMAL CONTEXTS By Peter Mak, member of the team of knowledge experts of the lectorate Lifelong Learning in Music (North Netherlands Conservatoire Groningen and
LEARNING MUSIC IN FORMAL, NON-FORMAL AND INFORMAL CONTEXTS By Peter Mak, member of the team of knowledge experts of the lectorate Lifelong Learning in Music (North Netherlands Conservatoire Groningen and
TOOL KIT for RESIDENT EDUCATOR and MENT OR MOVES
 Get to Know My RE Observe Collect Evidence Mentor Moments Reflect Review Respond Tailor Support Provide Provide specific feedback specific Feedback What does my RE need? Practice Habits Of Mind Share Data
Get to Know My RE Observe Collect Evidence Mentor Moments Reflect Review Respond Tailor Support Provide Provide specific feedback specific Feedback What does my RE need? Practice Habits Of Mind Share Data
English Teacher Education: The Need for a New Perspective
 Revista Alicantina de Estudios Ingleses 4 (1991): 71-76 English Teacher Education: The Need for a New Perspective Celia Floren Serrano Universidad de Zaragoza ABSTRACT The paper explores the drawbacks
Revista Alicantina de Estudios Ingleses 4 (1991): 71-76 English Teacher Education: The Need for a New Perspective Celia Floren Serrano Universidad de Zaragoza ABSTRACT The paper explores the drawbacks
Crosswalk of the New Colorado Principal Standards (proposed by State Council on Educator Effectiveness) with the
 Crosswalk of the New Colorado Principal Standards (proposed by State Council on Educator Effectiveness) with the Equivalent in the Performance Based Principal Licensure Standards (current principal standards)
Crosswalk of the New Colorado Principal Standards (proposed by State Council on Educator Effectiveness) with the Equivalent in the Performance Based Principal Licensure Standards (current principal standards)
Novice Experienced Expert a. Understands the importance of ABE, ASE, and ESOL at the personal and program level. X X X
 Complete Draft 1 through 5 Rhode Island Adult Education Practitioner Standards for Instructors 9-12-12 Definitions: Expert Teachers Expert teachers have the capacity to teach from the heart as well as
Complete Draft 1 through 5 Rhode Island Adult Education Practitioner Standards for Instructors 9-12-12 Definitions: Expert Teachers Expert teachers have the capacity to teach from the heart as well as
DEEPER LEARNING COMPETENCIES April 2013
 DEEPER LEARNING COMPETENCIES April 2013 Deeper learning is an umbrella term for the skills and knowledge that students must possess to succeed in 21 st century jobs and civic life. At its heart is a set
DEEPER LEARNING COMPETENCIES April 2013 Deeper learning is an umbrella term for the skills and knowledge that students must possess to succeed in 21 st century jobs and civic life. At its heart is a set
IDOL Outcomes and Competencies (ibstpi) 2
 Instructional Design for Online Learning (IDOL) Specialization Outcomes and Specialization Competencies Updated January 2008 Table of Contents Outcomes-based curricula at Capella University...3 IDOL MS
Instructional Design for Online Learning (IDOL) Specialization Outcomes and Specialization Competencies Updated January 2008 Table of Contents Outcomes-based curricula at Capella University...3 IDOL MS
ABA. History of ABA. Interventions 8/24/2011. Late 1800 s and Early 1900 s. Mentalistic Approachs
 ABA Is an extension of Experimental Analysis of Behavior to applied settings Is not the same as modification Uses cognition in its approach Focuses on clinically or socially relevant s Is used in many
ABA Is an extension of Experimental Analysis of Behavior to applied settings Is not the same as modification Uses cognition in its approach Focuses on clinically or socially relevant s Is used in many
ASU College of Education Course Syllabus ED 4972, ED 4973, ED 4974, ED 4975 or EDG 5660 Clinical Teaching
 ASU College of Education Course Syllabus ED 4972, ED 4973, ED 4974, ED 4975 or EDG 5660 Clinical Teaching Course: ED 4972, ED 4973, ED 4974, ED 4975 or EDG 5660 Credit: 9 Semester Credit Hours (Undergraduate),
ASU College of Education Course Syllabus ED 4972, ED 4973, ED 4974, ED 4975 or EDG 5660 Clinical Teaching Course: ED 4972, ED 4973, ED 4974, ED 4975 or EDG 5660 Credit: 9 Semester Credit Hours (Undergraduate),
Alignment Table School Counseling. Austin Peay State University Professional Educational Standards, CACREP STANDARDS, and NCATE Standards
 Alignment Table School Counseling Austin Peay State University Professional Educational Standards, CACREP STANDARDS, and NCATE Standards Austin Peay State University Professional Educational Standards
Alignment Table School Counseling Austin Peay State University Professional Educational Standards, CACREP STANDARDS, and NCATE Standards Austin Peay State University Professional Educational Standards
College of Psychology and Humanistic Studies (PHS) Curriculum Learning Goals and PsyD Program Learning Goals, Objectives and Competencies (GOCs)
 College of Psychology and Humanistic Studies (PHS) Curriculum Learning Goals and PsyD Program Learning Goals, Objectives and Competencies (GOCs) College of PHS Learning Goals PsyD Program Learning Goals
College of Psychology and Humanistic Studies (PHS) Curriculum Learning Goals and PsyD Program Learning Goals, Objectives and Competencies (GOCs) College of PHS Learning Goals PsyD Program Learning Goals
EA 597 School Planning and Facilities Management (3)
 EA 581 Basic Concepts of Educational Administration (3) An introduction to the basic concepts underlying school building administration. The theory and practice of educational administration is analyzed
EA 581 Basic Concepts of Educational Administration (3) An introduction to the basic concepts underlying school building administration. The theory and practice of educational administration is analyzed
NEW TSPC SPECIALIZATION: AUTISM SPECTRUM DISORDER. Q and A. May 24, 2012
 NEW TSPC SPECIALIZATION: AUTISM SPECTRUM DISORDER 1. What is a TSPC "Specialization"? Q and A May 24, 2012 This is a new specialization on a license now offered by TSPC. The first TSPC "specialization"
NEW TSPC SPECIALIZATION: AUTISM SPECTRUM DISORDER 1. What is a TSPC "Specialization"? Q and A May 24, 2012 This is a new specialization on a license now offered by TSPC. The first TSPC "specialization"
DOCTOR OF PHILOSOPHY DEGREE. Educational Leadership Doctor of Philosophy Degree Major Course Requirements. EDU721 (3.
 DOCTOR OF PHILOSOPHY DEGREE Educational Leadership Doctor of Philosophy Degree Major Course Requirements EDU710 (3.0 credit hours) Ethical and Legal Issues in Education/Leadership This course is an intensive
DOCTOR OF PHILOSOPHY DEGREE Educational Leadership Doctor of Philosophy Degree Major Course Requirements EDU710 (3.0 credit hours) Ethical and Legal Issues in Education/Leadership This course is an intensive
Master s in Educational Leadership Ed.S. in Administration and Supervision
 Master s in Educational Leadership Ed.S. in Administration and Supervision Austin Peay State University Professional Educational Standards, TILS Standards, and NCATE Standards Austin Peay State University
Master s in Educational Leadership Ed.S. in Administration and Supervision Austin Peay State University Professional Educational Standards, TILS Standards, and NCATE Standards Austin Peay State University
Towards Reflective Teaching
 The Teacher Trainer Back Articles Saved from: http://www.tttjournal.co.uk Towards Reflective Teaching by Jack C. Richards Department of English, City Polytechnic of Hong Kong Most teachers develop their
The Teacher Trainer Back Articles Saved from: http://www.tttjournal.co.uk Towards Reflective Teaching by Jack C. Richards Department of English, City Polytechnic of Hong Kong Most teachers develop their
Leeds Metropolitan University Repository
 Leeds Metropolitan University Repository http://repository.leedsmet.ac.uk/ Citation: Chapman, F., Clegg, P. (2007) Bridging the theory practice gap: an innovative approach to praxis in professional education.
Leeds Metropolitan University Repository http://repository.leedsmet.ac.uk/ Citation: Chapman, F., Clegg, P. (2007) Bridging the theory practice gap: an innovative approach to praxis in professional education.
Australian Professional Standard for Principals
 AITSL is funded by the Australian Government Australian Professional Standard for Principals July 2011 Formerly the National Professional Standard for Principals 2011 Education Services Australia as the
AITSL is funded by the Australian Government Australian Professional Standard for Principals July 2011 Formerly the National Professional Standard for Principals 2011 Education Services Australia as the
School-Based Teacher Educators Take On New Roles In Professional Development Schools. Richard E. Ishler University of South Carolina
 School-Based Teacher Educators Take On New Roles In Professional Development Schools Richard E. Ishler University of South Carolina Ann L. Ishler Columbia College We are grateful for the loyal support
School-Based Teacher Educators Take On New Roles In Professional Development Schools Richard E. Ishler University of South Carolina Ann L. Ishler Columbia College We are grateful for the loyal support
A reflective teaching practice experience: a case study
 A reflective teaching practice experience: a case study Bertha Paredes Zepeda Hilda Hidalgo Avilés Universidad Autónoma del Estado de Hidalgo Abstract This paper aims to share an experience of how students,
A reflective teaching practice experience: a case study Bertha Paredes Zepeda Hilda Hidalgo Avilés Universidad Autónoma del Estado de Hidalgo Abstract This paper aims to share an experience of how students,
Analysing Technological Pedagogic Content Knowledge of Science Teacher Candidates According to Various Variables
 Analysing Technological Pedagogic Content Knowledge of Science Teacher Candidates According to Various Variables 1 Mehmet Barış Horzum, 2 Murat Demirbaş, 1 Mustafa Bayrakcı 1 Sakarya University Education
Analysing Technological Pedagogic Content Knowledge of Science Teacher Candidates According to Various Variables 1 Mehmet Barış Horzum, 2 Murat Demirbaş, 1 Mustafa Bayrakcı 1 Sakarya University Education
MASTER OF EDUCATION (LEADERSHIP AND MANAGEMENT) Abbreviated as M Ed (Leadership and Management) CURRICULUM
 MASTER OF EDUCATION (LEADERSHIP AND MANAGEMENT) Abbreviated as M Ed (Leadership and Management) CURRICULUM Revised Version of Master of Education (Educational Management)-2007 Endorsed By Academic Council,
MASTER OF EDUCATION (LEADERSHIP AND MANAGEMENT) Abbreviated as M Ed (Leadership and Management) CURRICULUM Revised Version of Master of Education (Educational Management)-2007 Endorsed By Academic Council,
School of Clinical Psychology LIOS Masters in Psychology: Counseling Specialization Course Descriptions 2013-2014
 School of Clinical Psychology LIOS Masters in Psychology: Counseling Specialization Course Descriptions 2013-2014 Courses for: Fall 2013 Entry Cohort Spring 2014 Entry Cohort Counseling professional courses:
School of Clinical Psychology LIOS Masters in Psychology: Counseling Specialization Course Descriptions 2013-2014 Courses for: Fall 2013 Entry Cohort Spring 2014 Entry Cohort Counseling professional courses:
The Teacher Educator Standards
 The Teacher Educator Standards From the Association of Teacher Educators Winter Conference Standards Clinic New Orleans, LA February, 2008 Facilitators: Dr. Robert Fisher Dr. Barbara Short Dr. Robin McBee
The Teacher Educator Standards From the Association of Teacher Educators Winter Conference Standards Clinic New Orleans, LA February, 2008 Facilitators: Dr. Robert Fisher Dr. Barbara Short Dr. Robin McBee
Teaching Framework. Framework components
 Teaching Framework Framework components CE/3007b/4Y09 UCLES 2014 Framework components Each category and sub-category of the framework is made up of components. The explanations below set out what is meant
Teaching Framework Framework components CE/3007b/4Y09 UCLES 2014 Framework components Each category and sub-category of the framework is made up of components. The explanations below set out what is meant
ROLES AND RESPONSIBILITIES The roles and responsibilities expected of teachers at each classification level are specified in the Victorian Government
 ROLES AND RESPONSIBILITIES The roles and responsibilities expected of teachers at each classification level are specified in the Victorian Government Schools Agreement 2004: Leading teacher Leading teachers
ROLES AND RESPONSIBILITIES The roles and responsibilities expected of teachers at each classification level are specified in the Victorian Government Schools Agreement 2004: Leading teacher Leading teachers
Illinois Professional Teaching Standards
 Illinois Professional Teaching Standards Preamble: We believe that all students have the potential to learn rigorous content and achieve high standards. A well-educated citizenry is essential for maintaining
Illinois Professional Teaching Standards Preamble: We believe that all students have the potential to learn rigorous content and achieve high standards. A well-educated citizenry is essential for maintaining
Evgenia Theodotou Metropolitan College, Athens, Greece. Abstract. Introduction. Motivation to learn: the theoretical framework
 Vol.4, No.1. April 2014 pp. 17 21. Early years education: are young students intrinsically or extrinsically motivated towards school activities? A discussion about the effects of rewards on young children
Vol.4, No.1. April 2014 pp. 17 21. Early years education: are young students intrinsically or extrinsically motivated towards school activities? A discussion about the effects of rewards on young children
EDUCATIONAL FOUNDATIONS (EDF)
 Interim Head of the Department: Assistant Professor Slaton Professors: Bitner, Nauman Associate Professors: Armenta Assistant Professors: Adams, DeVaney, Duplantier, Echols, Ennis, Stader, Watson-Mathews
Interim Head of the Department: Assistant Professor Slaton Professors: Bitner, Nauman Associate Professors: Armenta Assistant Professors: Adams, DeVaney, Duplantier, Echols, Ennis, Stader, Watson-Mathews
PERFORMANCE STANDARDS FOR ADVANCED MASTERS PROGRAMS CURRICULUM STUDIES
 1 PERFORMANCE STANDARDS FOR ADVANCED MASTERS PROGRAMS CURRICULUM STUDIES 2 PREAMBLE VINCENTIAN SPIRIT AND URBAN MISSION Given that the School of Education subscribes to the Vincentian spirit and urban
1 PERFORMANCE STANDARDS FOR ADVANCED MASTERS PROGRAMS CURRICULUM STUDIES 2 PREAMBLE VINCENTIAN SPIRIT AND URBAN MISSION Given that the School of Education subscribes to the Vincentian spirit and urban
Reflective Journaling: Building Bridges between Theory and Practice KENNETH GOLDBERG National University [email protected]
 Reflective Journaling: Building Bridges between Theory and Practice KENNETH GOLDBERG National University [email protected] ABSTRACT Assessing practitioner experience as it relates to subject theory can be
Reflective Journaling: Building Bridges between Theory and Practice KENNETH GOLDBERG National University [email protected] ABSTRACT Assessing practitioner experience as it relates to subject theory can be
College of Education GUIDE TO GRADUATE PROGRAMS
 College of Education GUIDE TO GRADUATE PROGRAMS http://education.msu.edu/academics/ Graduate Programs OVERVIEW Graduate programs in the Michigan State University College of Education both on-campus and
College of Education GUIDE TO GRADUATE PROGRAMS http://education.msu.edu/academics/ Graduate Programs OVERVIEW Graduate programs in the Michigan State University College of Education both on-campus and
The Art and Science of Teaching the Common Core State Standards
 The Art and Science of Teaching the Common Core State Standards Author: Robert J. Marzano July 2013 Learning Sciences Marzano Center 3001 PGA Boulevard Palm Beach Gardens, Florida 33410 717.845.6300 MarzanoCenter.com
The Art and Science of Teaching the Common Core State Standards Author: Robert J. Marzano July 2013 Learning Sciences Marzano Center 3001 PGA Boulevard Palm Beach Gardens, Florida 33410 717.845.6300 MarzanoCenter.com
Psy 212- Educational Psychology Practice Test - Ch. 1
 Psy 212- Educational Psychology Practice Test - Ch. 1 1) Use of the "common sense" approach to teaching is viewed by educational psychologists as A) inappropriate unless supported by research. B) the main
Psy 212- Educational Psychology Practice Test - Ch. 1 1) Use of the "common sense" approach to teaching is viewed by educational psychologists as A) inappropriate unless supported by research. B) the main
Strategies That Foster Critical Reading
 Strategies That Foster Critical Reading This guide offers strategies faculty members can use to foster careful reading and critical thinking. Provide Guidance before Each Reading Make Them Curious Professors
Strategies That Foster Critical Reading This guide offers strategies faculty members can use to foster careful reading and critical thinking. Provide Guidance before Each Reading Make Them Curious Professors
College of Education Clinical Faculty Appointment and Promotion Criteria Provost Approved 11/11/11
 Introduction: The Clinical Faculty College of Education Clinical Faculty Appointment and Promotion Criteria Provost Approved 11/11/11 In accordance with University guidelines most professional programs
Introduction: The Clinical Faculty College of Education Clinical Faculty Appointment and Promotion Criteria Provost Approved 11/11/11 In accordance with University guidelines most professional programs
REGULATIONS FOR THE DEGREE OF MASTER OF EDUCATION (MEd)
 215 REGULATIONS FOR THE DEGREE OF MASTER OF EDUCATION (MEd) (See also General Regulations) Any publication based on work approved for a higher degree should contain a reference to the effect that the work
215 REGULATIONS FOR THE DEGREE OF MASTER OF EDUCATION (MEd) (See also General Regulations) Any publication based on work approved for a higher degree should contain a reference to the effect that the work
How To Learn To Teach With A Language Skill
 UNIT I: Knowing the Learner Foundations of Curriculum and Instruction Essential Curriculum Goal 1: Students will review how the needs of children change as they develop. a. Describe typical developmental
UNIT I: Knowing the Learner Foundations of Curriculum and Instruction Essential Curriculum Goal 1: Students will review how the needs of children change as they develop. a. Describe typical developmental
Scientist-practitioner?
 Paper 14-1 PAPER 14 Scientist-practitioner? Bob Dick (1996) Is it time to revise the scientistpractitioner model?. An unpublished discussion paper. Revised in 1996 from an earlier draft. For some years
Paper 14-1 PAPER 14 Scientist-practitioner? Bob Dick (1996) Is it time to revise the scientistpractitioner model?. An unpublished discussion paper. Revised in 1996 from an earlier draft. For some years
JOINT MASTER OF ARTS IN LEADERSHIP AND EDUCATION CHANGE COURSE DESCRIPTIONS
 JOINT MASTER OF ARTS IN LEADERSHIP AND EDUCATION CHANGE COURSE DESCRIPTIONS A. CORE COURSES MALC 801 Perspectives in Educational Leadership Educational leadership is a complex concept, both in theory and
JOINT MASTER OF ARTS IN LEADERSHIP AND EDUCATION CHANGE COURSE DESCRIPTIONS A. CORE COURSES MALC 801 Perspectives in Educational Leadership Educational leadership is a complex concept, both in theory and
Mentoring and Coaching Models
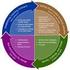 Mentoring and Coaching Models Peer coaching is a of staff development model you can use to help you and your partners develop and try new strategies and determine what does and does not work by critically
Mentoring and Coaching Models Peer coaching is a of staff development model you can use to help you and your partners develop and try new strategies and determine what does and does not work by critically
Section Two: Ohio Standards for the Teaching Profession
 12 Section Two: Ohio Standards for the Teaching Profession 1 Teachers understand student learning and development and respect the diversity of the students they teach. Teachers display knowledge of how
12 Section Two: Ohio Standards for the Teaching Profession 1 Teachers understand student learning and development and respect the diversity of the students they teach. Teachers display knowledge of how
Running Head: FORMULATION OF AN EDUCATIONAL PHILOSOPHY AND AN ORGANIZATIONAL FRAMEWORK. Lauren Jansen. Midwestern State University
 Educational Philosophy 1 Running Head: FORMULATION OF AN EDUCATIONAL PHILOSOPHY AND AN ORGANIZATIONAL FRAMEWORK Lauren Jansen Midwestern State University Educational Philosophy 2 Formulation Of An Educational
Educational Philosophy 1 Running Head: FORMULATION OF AN EDUCATIONAL PHILOSOPHY AND AN ORGANIZATIONAL FRAMEWORK Lauren Jansen Midwestern State University Educational Philosophy 2 Formulation Of An Educational
Essays on Teaching Excellence. The Challenge of Teaching the Introductory-level Course
 Essays on Teaching Excellence Toward the Best in the Academy Volume 1, Number 6, 1989-90 A publication of The Professional & Organizational Development Network in Higher Education (www.podnetwork.org)
Essays on Teaching Excellence Toward the Best in the Academy Volume 1, Number 6, 1989-90 A publication of The Professional & Organizational Development Network in Higher Education (www.podnetwork.org)
A. The master of arts, educational studies program will allow students to do the following.
 PROGRAM OBJECTIVES DEPARTMENT OF EDUCATION DEGREES OFFERED MASTER OF ARTS, EDUCATIONAL STUDIES (M.A.); MASTER OF ARTS, SCIENCE EDUCATION (M.S.); MASTER OF ARTS IN GERMAN WITH TEACHING LICENSURE (M.A.);
PROGRAM OBJECTIVES DEPARTMENT OF EDUCATION DEGREES OFFERED MASTER OF ARTS, EDUCATIONAL STUDIES (M.A.); MASTER OF ARTS, SCIENCE EDUCATION (M.S.); MASTER OF ARTS IN GERMAN WITH TEACHING LICENSURE (M.A.);
Essential Ways That Coaching Can Help Executives
 Journal of Excellence Issue No. 8 Witherspoon & White 7 Essential Ways That Coaching Can Help Executives Robert Witherspoon and Randall P. White, USA Robert Witherspoon is the founding principal of Performance
Journal of Excellence Issue No. 8 Witherspoon & White 7 Essential Ways That Coaching Can Help Executives Robert Witherspoon and Randall P. White, USA Robert Witherspoon is the founding principal of Performance
Implementing E-Learning Designed Courses in General Education
 Implementing E-Learning Designed Courses in General Education Prasart Nuangchalerm 1, Krissada Sukkhamduang 2, Suleeporn Uhwa 2, Pacharawit Chansirisira 3 1 Department of Curriculum and Instruction, Faculty
Implementing E-Learning Designed Courses in General Education Prasart Nuangchalerm 1, Krissada Sukkhamduang 2, Suleeporn Uhwa 2, Pacharawit Chansirisira 3 1 Department of Curriculum and Instruction, Faculty
UNIVERSITY OF BELGRADE FACULTY OF PHILOSOPHY. Part two: INFORMATION ON DEGREE PROGRAMS
 Part two: INFORMATION ON DEGREE PROGRAMS Part two: Information on Degree Programs Philosophy Bachelor s Degree Philosophy Master s Degree Philosophy Doctoral Degree Sociology Bachelor s Degree Sociology
Part two: INFORMATION ON DEGREE PROGRAMS Part two: Information on Degree Programs Philosophy Bachelor s Degree Philosophy Master s Degree Philosophy Doctoral Degree Sociology Bachelor s Degree Sociology
Student Leadership Development Through General Classroom Activities
 Student Leadership Development Through General Classroom Activities Ian Hay & Neil Dempster S tudent leadership enhancement involves giving students opportunities to practice leadership skills in a supportive
Student Leadership Development Through General Classroom Activities Ian Hay & Neil Dempster S tudent leadership enhancement involves giving students opportunities to practice leadership skills in a supportive
NUNAN, David (ed.) Practical English Language Teaching International Edition 1 st Edition Singapore: McGraw-Hill, 2003, 342 p.
 Available online at: http://ijrte.eab.org.tr/1/1/ayilmaz_stekir.pdf http://eab.org.tr Educational Research Association The International Journal of Research in Teacher Education 2010, 1(1):65-72 ISSN:
Available online at: http://ijrte.eab.org.tr/1/1/ayilmaz_stekir.pdf http://eab.org.tr Educational Research Association The International Journal of Research in Teacher Education 2010, 1(1):65-72 ISSN:
Instructional Design: A Postcard View. Brian Querry EDTECH 503 Spring 2011
 Instructional Design: A Postcard View Brian Querry EDTECH 503 Spring 2011 List of Postcards SLIDES CONTENT 3-4 The History of Instructional Design 5-6 Definition of "Instructional Design" 7-8 Systematic
Instructional Design: A Postcard View Brian Querry EDTECH 503 Spring 2011 List of Postcards SLIDES CONTENT 3-4 The History of Instructional Design 5-6 Definition of "Instructional Design" 7-8 Systematic
Principles of Adult Learning
 Principles of Adult Learning Adapted from John Goodlad ADULTS PREFER LEARNING SITUATIONS WHICH: 1. ARE PRACTICAL AND PROBLEM-CENTERED, SO... Give overviews, summaries, examples, & use stories to link theory
Principles of Adult Learning Adapted from John Goodlad ADULTS PREFER LEARNING SITUATIONS WHICH: 1. ARE PRACTICAL AND PROBLEM-CENTERED, SO... Give overviews, summaries, examples, & use stories to link theory
Executive Skills Questionnaire. Peg Dawson & Richard Guare
 Executive Skills Questionnaire Peg Dawson & Richard Guare Step I: Read each item below and then rate that item based on the extent to which you agree or disagree with how well it describes you. Use the
Executive Skills Questionnaire Peg Dawson & Richard Guare Step I: Read each item below and then rate that item based on the extent to which you agree or disagree with how well it describes you. Use the
Teacher Rubric with Suggested Teacher and Student Look-fors
 Teacher Rubric with Suggested Teacher and Student Look-fors This document is intended to inform school communities in recognizing the performance levels for key elements defined in the Teacher Rubric and
Teacher Rubric with Suggested Teacher and Student Look-fors This document is intended to inform school communities in recognizing the performance levels for key elements defined in the Teacher Rubric and
2014-15 College-wide Goal Assessment Plans (SoA&S Assessment Coordinator September 24, 2015)
 2014-15 College-wide Goal Assessment Plans (SoA&S Assessment Coordinator September 24, 2015) College-wide Goal 1: Intellectual Engagement PG1 Students will demonstrate the ability to think critically and
2014-15 College-wide Goal Assessment Plans (SoA&S Assessment Coordinator September 24, 2015) College-wide Goal 1: Intellectual Engagement PG1 Students will demonstrate the ability to think critically and
Gifted Intervention Specialist
 Gifted Intervention Specialist Endorsement Grades K-12 2008 Ohio Modified /CEC/NAGC Program Standards An endorsement of a teacher license, valid for teaching the subject or learners named, shall be issued
Gifted Intervention Specialist Endorsement Grades K-12 2008 Ohio Modified /CEC/NAGC Program Standards An endorsement of a teacher license, valid for teaching the subject or learners named, shall be issued
Chapter 1. The primary responsibility for character and citizenship development lies with. Character and Citizenship Education in Alberta Schools
 Character and Citizenship Education in Alberta Schools Chapter 1 it is next to impossible to separate the teaching of values from schooling itself; it is a part of schooling whether people are willing
Character and Citizenship Education in Alberta Schools Chapter 1 it is next to impossible to separate the teaching of values from schooling itself; it is a part of schooling whether people are willing
Running head: PERSONAL STATEMENT ON LEARNING AND INSTRUCTION 1. Personal Statement on Learning and Instruction. Jay A. Bostwick
 Running head: PERSONAL STATEMENT ON LEARNING AND INSTRUCTION 1 Personal Statement on Learning and Instruction Jay A. Bostwick IP&T 620 Principles of Learning PERSONAL STATEMENT ON LEARNING AND INSTRUCTION
Running head: PERSONAL STATEMENT ON LEARNING AND INSTRUCTION 1 Personal Statement on Learning and Instruction Jay A. Bostwick IP&T 620 Principles of Learning PERSONAL STATEMENT ON LEARNING AND INSTRUCTION
Ph.D. in Educational Theory and Practice. Emphasis Areas
 In addition to the shared core courses, doctoral students in ETAP choose an emphasis area. Emphasis areas are overlapping, of course, and should not be considered as exclusive. While the ETAP core provides
In addition to the shared core courses, doctoral students in ETAP choose an emphasis area. Emphasis areas are overlapping, of course, and should not be considered as exclusive. While the ETAP core provides
Dalhousie School of Health Sciences Halifax, Nova Scotia. Curriculum Framework
 Dalhousie School of Health Sciences Halifax, Nova Scotia Approved: June 2001 Revised: May 2006 Reviewed: Sept. 06 Revised/Approved August 2010 Reviewed/Approved by Full Faculty November 2012 Preamble This
Dalhousie School of Health Sciences Halifax, Nova Scotia Approved: June 2001 Revised: May 2006 Reviewed: Sept. 06 Revised/Approved August 2010 Reviewed/Approved by Full Faculty November 2012 Preamble This
Learning Theory and Instructional Design
 Learning Theory and Instructional Design Gregory McLeod Introduction Designing effective instruction goes beyond systematically executing various steps within an instructional design model. Among a host
Learning Theory and Instructional Design Gregory McLeod Introduction Designing effective instruction goes beyond systematically executing various steps within an instructional design model. Among a host
School Psychology Program Goals, Objectives, & Competencies
 RUTGERS SCHOOL PSYCHOLOGY PROGRAM PRACTICUM HANDBOOK Introduction School Psychology is a general practice and health service provider specialty of professional psychology that is concerned with the science
RUTGERS SCHOOL PSYCHOLOGY PROGRAM PRACTICUM HANDBOOK Introduction School Psychology is a general practice and health service provider specialty of professional psychology that is concerned with the science
Critical Inquiry in Educational Research and Professional Practice
 DOCTOR IN EDUCATION COURSE DESCRIPTIONS A. CORE COURSES NEDD 800 Professionalism, Ethics, and the Self This introductory core course will explore and interrogate ideas surrounding professionalism and professionalization.
DOCTOR IN EDUCATION COURSE DESCRIPTIONS A. CORE COURSES NEDD 800 Professionalism, Ethics, and the Self This introductory core course will explore and interrogate ideas surrounding professionalism and professionalization.
MASTER OF EDUCATION 1. MASTER OF EDUCATION DEGREE (M.ED.) (845) 575-3028 [email protected]
 MASTER OF EDUCATION 1 MASTER OF EDUCATION DEGREE (M.ED.) (845) 575-3028 [email protected] MISSION AND OBJECTIVES The Teacher Education programs offered by Marist College are integrally linked
MASTER OF EDUCATION 1 MASTER OF EDUCATION DEGREE (M.ED.) (845) 575-3028 [email protected] MISSION AND OBJECTIVES The Teacher Education programs offered by Marist College are integrally linked
What is the impact of multisource learning on History at Key Stage 3?
 What is the impact of multisource learning on History at Key Stage 3? Researchers: Lloyd Brown and Rolf Purvis Date of research: September 2000 August 2001 Contact details: Chesterton Community College,
What is the impact of multisource learning on History at Key Stage 3? Researchers: Lloyd Brown and Rolf Purvis Date of research: September 2000 August 2001 Contact details: Chesterton Community College,
Faculty Member Completing this Form: Melissa Cummings
 Department Name: Science Middle/Secondary Education Date Submitted and Academic Year: Fall 2011 for AY 2011-2012 Department Mission Statement: All SUNY Potsdam education programs are aligned with our conceptual
Department Name: Science Middle/Secondary Education Date Submitted and Academic Year: Fall 2011 for AY 2011-2012 Department Mission Statement: All SUNY Potsdam education programs are aligned with our conceptual
The IBIS Education for Change strategy states the overall objective
 CONCEPT PAPER: TRANSFORMATIVE EDUCATION 1 Concept Paper transformative education Photo: Toke Nyborg The IBIS Education for Change strategy states the overall objective of IBIS work with education as follows:
CONCEPT PAPER: TRANSFORMATIVE EDUCATION 1 Concept Paper transformative education Photo: Toke Nyborg The IBIS Education for Change strategy states the overall objective of IBIS work with education as follows:
LEARNING THEORIES Ausubel's Learning Theory
 LEARNING THEORIES Ausubel's Learning Theory David Paul Ausubel was an American psychologist whose most significant contribution to the fields of educational psychology, cognitive science, and science education.
LEARNING THEORIES Ausubel's Learning Theory David Paul Ausubel was an American psychologist whose most significant contribution to the fields of educational psychology, cognitive science, and science education.
LEVEL 1 LICENSURE PORTFOLIO
 LEVEL 1 LICENSURE PORTFOLIO Part I Purpose Principles to Be Addressed Required Documentation Directions Entry 1: Analyzing the School Counseling Environment Candidates analyze the school counseling environment
LEVEL 1 LICENSURE PORTFOLIO Part I Purpose Principles to Be Addressed Required Documentation Directions Entry 1: Analyzing the School Counseling Environment Candidates analyze the school counseling environment
PRESERVICE. PROFESSIONAL STANDARDS FOR QUEENSLAND TEACHERS (graduate level): A guide for use with preservice teachers QUEENSLAND COLLEGE OF TEACHERS
 PRESERVICE PROFESSIONAL STANDARDS FOR TEACHERS (graduate level): March 2009 INTRODUCTION The Professional Standards for Queensland Teachers underpin all stages of teachers professional learning throughout
PRESERVICE PROFESSIONAL STANDARDS FOR TEACHERS (graduate level): March 2009 INTRODUCTION The Professional Standards for Queensland Teachers underpin all stages of teachers professional learning throughout
1 REVISOR 8710.6400. (2) basic diagnostic classifications and referral mechanisms of the helping
 1 REVISOR 8710.6400 8710.6400 SCHOOL COUNSELOR. Subpart 1. Scope of practice. A school counselor is authorized to provide to kindergarten through grade 12 students school counseling services that focus
1 REVISOR 8710.6400 8710.6400 SCHOOL COUNSELOR. Subpart 1. Scope of practice. A school counselor is authorized to provide to kindergarten through grade 12 students school counseling services that focus
Classroom Management: An Ecological Model Donald F. Perras, Ph.D.
 Classroom Management: An Ecological Model Donald F. Perras, Ph.D. Help Wanted! Teachers prepared to manage students limited behavioral readiness for school. This national dilemma reflects students changing
Classroom Management: An Ecological Model Donald F. Perras, Ph.D. Help Wanted! Teachers prepared to manage students limited behavioral readiness for school. This national dilemma reflects students changing
Although this is a rather dated paper, it provides a straightforward and useful introduction to some of the key theories and theorists of reflection.
 Although this is a rather dated paper, it provides a straightforward and useful introduction to some of the key theories and theorists of reflection. Richard Hawkins & Harvey Woolf Greater Manchester AHP/HCS
Although this is a rather dated paper, it provides a straightforward and useful introduction to some of the key theories and theorists of reflection. Richard Hawkins & Harvey Woolf Greater Manchester AHP/HCS
THE UNIVERSITY OF TENNESSEE AT MARTIN DEPARTMENT OF EDUCATIONAL STUDIES
 THE UNIVERSITY OF TENNESSEE AT MARTIN DEPARTMENT OF EDUCATIONAL STUDIES Instructor: David Dietrich, Ph.D. Office: 219 McWherter, Jackson State Community College, Jackson, TN 38301 Phone: 731.267.2949 or
THE UNIVERSITY OF TENNESSEE AT MARTIN DEPARTMENT OF EDUCATIONAL STUDIES Instructor: David Dietrich, Ph.D. Office: 219 McWherter, Jackson State Community College, Jackson, TN 38301 Phone: 731.267.2949 or
Implementing E-Learning Designed Courses in General Education
 Implementing E-Learning Designed Courses in General Education Prasart Nuangchalerm 1, Krissada Sakkumduang 2, Suleepornn Uhwha 3 and Pacharawit Chansirisira 4 1 Department of Curriculum and Instruction,
Implementing E-Learning Designed Courses in General Education Prasart Nuangchalerm 1, Krissada Sakkumduang 2, Suleepornn Uhwha 3 and Pacharawit Chansirisira 4 1 Department of Curriculum and Instruction,
TEACHING AND LEARNING IN COMPETENCY-BASED EDUCATION
 The Fifth International Conference on e-learning (elearning-2014), 22-23 September 2014, Belgrade, Serbia TEACHING AND LEARNING IN COMPETENCY-BASED EDUCATION NEIL O SULLIVAN Innovative Together Ltd, [email protected]
The Fifth International Conference on e-learning (elearning-2014), 22-23 September 2014, Belgrade, Serbia TEACHING AND LEARNING IN COMPETENCY-BASED EDUCATION NEIL O SULLIVAN Innovative Together Ltd, [email protected]
The Bennington College Plan Process
 The Bennington College Plan Process April 23, 2012 INTRODUCTION OF THE PLAN PROCESS Central to Bennington s founding vision was the belief that a dynamic, relevant education could best be achieved when
The Bennington College Plan Process April 23, 2012 INTRODUCTION OF THE PLAN PROCESS Central to Bennington s founding vision was the belief that a dynamic, relevant education could best be achieved when
CALIFORNIA S TEACHING PERFORMANCE EXPECTATIONS (TPE)
 CALIFORNIA S TEACHING PERFORMANCE EXPECTATIONS (TPE) The Teaching Performance Expectations describe the set of knowledge, skills, and abilities that California expects of each candidate for a Multiple
CALIFORNIA S TEACHING PERFORMANCE EXPECTATIONS (TPE) The Teaching Performance Expectations describe the set of knowledge, skills, and abilities that California expects of each candidate for a Multiple
ELL Considerations for Common Core-Aligned Tasks in English Language Arts
 ELL Considerations for Common Core-Aligned Tasks in English Language Arts A substantial body of research clearly indicates that utilizing specific instructional modifications as well as targeted pedagogical
ELL Considerations for Common Core-Aligned Tasks in English Language Arts A substantial body of research clearly indicates that utilizing specific instructional modifications as well as targeted pedagogical
Exam papers from RE 5100, Beginning Readers and Writers. Assessment Summary Sheet from RE 5715, Reading Assessment and Correction
 Name: Angela McCrary Steele IRA Standards Artifacts Rationale Standard 1. Foundational Knowledge. 1.1 Candidates understand major theories and empirical research that describe the cognitive, linguistic,
Name: Angela McCrary Steele IRA Standards Artifacts Rationale Standard 1. Foundational Knowledge. 1.1 Candidates understand major theories and empirical research that describe the cognitive, linguistic,
Source- Illinois State Board of Education (www.isbe.net)
 Wise Ways / Center on Innovation & Improvement CL17 Indicator: Professional development for teachers is determined by data (including classroom observations and review of lesson plans) that demonstrate
Wise Ways / Center on Innovation & Improvement CL17 Indicator: Professional development for teachers is determined by data (including classroom observations and review of lesson plans) that demonstrate
STAFF DEVELOPMENT in SPECIAL EDUCATION
 STAFF DEVELOPMENT in SPECIAL EDUCATION Roles and Responsibilities of the Special Education Teacher AASEP s Staff Development Course Roles and Responsibilities of the Special Education Teacher Copyright
STAFF DEVELOPMENT in SPECIAL EDUCATION Roles and Responsibilities of the Special Education Teacher AASEP s Staff Development Course Roles and Responsibilities of the Special Education Teacher Copyright
(i) The program shall prepare candidates who are familiar with the historical foundations of gifted and talented education;
 Effective May 15, 2014 505-3-.90 GIFTED IN-FIELD EDUCATION ENDORSEMENT PROGRAM (1) Purpose. This rule states field-specific content standards for approving endorsement programs that prepare individuals
Effective May 15, 2014 505-3-.90 GIFTED IN-FIELD EDUCATION ENDORSEMENT PROGRAM (1) Purpose. This rule states field-specific content standards for approving endorsement programs that prepare individuals
Conference "Competencies and Capabilities in Education" Oradea 2009 EDUCAŢIA ANTREPRENORIALĂ - EDUCAŢIE PENTRU VIITOR
 EDUCAŢIA ANTREPRENORIALĂ - EDUCAŢIE PENTRU VIITOR ENTREPRENEURIAL EDUCATION - EDUCATION FOR THE FUTURE Andrada Pandelea 1 Abstract The development of the entrepreneurial spirit among young people is a
EDUCAŢIA ANTREPRENORIALĂ - EDUCAŢIE PENTRU VIITOR ENTREPRENEURIAL EDUCATION - EDUCATION FOR THE FUTURE Andrada Pandelea 1 Abstract The development of the entrepreneurial spirit among young people is a
the general concept down to the practical steps of the process.
 Article Critique Affordances of mobile technologies for experiential learning: the interplay of technology and pedagogical practices C.- H. Lai, J.- C. Yang, F.- C. Chen, C.- W. Ho & T.- W. Chan Theoretical
Article Critique Affordances of mobile technologies for experiential learning: the interplay of technology and pedagogical practices C.- H. Lai, J.- C. Yang, F.- C. Chen, C.- W. Ho & T.- W. Chan Theoretical
Broad and Integrative Knowledge. Applied and Collaborative Learning. Civic and Global Learning
 1 2 3 4 5 Specialized Knowledge Broad and Integrative Knowledge Intellectual Skills Applied and Collaborative Learning Civic and Global Learning The Degree Qualifications Profile (DQP) provides a baseline
1 2 3 4 5 Specialized Knowledge Broad and Integrative Knowledge Intellectual Skills Applied and Collaborative Learning Civic and Global Learning The Degree Qualifications Profile (DQP) provides a baseline
Chapter 2 Conceptualizing Scientific Inquiry
 Chapter 2 Conceptualizing Scientific Inquiry 2.1 Introduction In order to develop a strategy for the assessment of scientific inquiry in a laboratory setting, a theoretical construct of the components
Chapter 2 Conceptualizing Scientific Inquiry 2.1 Introduction In order to develop a strategy for the assessment of scientific inquiry in a laboratory setting, a theoretical construct of the components
UNH Graduate Education Department. Quarterly Assessment Report
 First Quarter Assessment Report UNH Graduate Education Department Quarterly Assessment Report First Quarter i First Quarter Assessment Report Table of Contents Introduction... Section - Purpose of the
First Quarter Assessment Report UNH Graduate Education Department Quarterly Assessment Report First Quarter i First Quarter Assessment Report Table of Contents Introduction... Section - Purpose of the
MASTER OF SCIENCE IN NURSING (MSN) PRACTICUM GUIDELINES
 MASTER OF SCIENCE IN NURSING (MSN) PRACTICUM GUIDELINES Mentor Manual 2011-2012 Table of Contents Philosophy of the Graduate Program... 2 MSN Program Outcomes... 2 Mentor Role Introduction... 3 Mentor
MASTER OF SCIENCE IN NURSING (MSN) PRACTICUM GUIDELINES Mentor Manual 2011-2012 Table of Contents Philosophy of the Graduate Program... 2 MSN Program Outcomes... 2 Mentor Role Introduction... 3 Mentor
School leadership and student outcomes: Identifying what works and why
 School leadership and student outcomes: Identifying what works and why Summary of the the Best Evidence Synthesis (BES) conducted by Viviane Robinson, Margie Hohepa and Claire Lloyd Research Summary December
School leadership and student outcomes: Identifying what works and why Summary of the the Best Evidence Synthesis (BES) conducted by Viviane Robinson, Margie Hohepa and Claire Lloyd Research Summary December
GLOBAL-READY TEACHER COMPETENCY FRAMEWORK: STANDARDS AND INDICATORS
 GLOBAL-READY TEACHER COMPETENCY FRAMEWORK: STANDARDS AND INDICATORS GLOBAL-READY TEACHER COMPETENCY FRAMEWORK All learners whether adult or child acquire the attitudes, skills and knowledge needed for
GLOBAL-READY TEACHER COMPETENCY FRAMEWORK: STANDARDS AND INDICATORS GLOBAL-READY TEACHER COMPETENCY FRAMEWORK All learners whether adult or child acquire the attitudes, skills and knowledge needed for
Special Education Student Learning Outcomes
 Special Education Student Learning Outcomes 1. Foundations. Special educators understand the field as an evolving and changing discipline based on philosophies, evidence-based principles and theories,
Special Education Student Learning Outcomes 1. Foundations. Special educators understand the field as an evolving and changing discipline based on philosophies, evidence-based principles and theories,
