Prostate Cancer Gene 3 (PCA3) the first highly specific genetic test* improves the diagnosis of prostate cancer. * CE marked
|
|
|
- Leona Shepherd
- 8 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Prostate Cancer Gene 3 (PCA3) the first highly specific genetic test* improves the diagnosis of prostate cancer * CE marked
2 Introduction Prostate biopsy dilemma Prostate cancer (PCa) is the most commonly diagnosed malignancy and the second leading cause of cancer death in (American) men. One in 6 men will be diagnosed with PCa at some point in his life, but only one in 5 will die from PCa. In other words, the prevalence of PCa is very high, but the aggressiveness of the malignancy varies so much that more men will die with PCa than because of PCa. In the diagnosis of PCa the challenge is to detect clinically signi cant PCa that still can be cured. In most patients with PCa, symptoms do not develop when the tumour is still localised. Currently the early detection of PCa relies primarily on the serum prostate speci c antigen (PSA) concentration and digital rectal examination (DRE). The outcome of both tests can result in a prostate biopsy to con rm the diagnosis of PCa. The dilemmas when using DRE, PSA and prostate biopsy in the diagnosis of prostate cancer DRE dilemma DRE is a standard tool in the diagnosis of PCa. Nevertheless, the exam by itself has a very low positive predictive value (PPV) in identifying PCa. In a study in 986 men undergoing biopsy for an abnormal / suspicious DRE with low PSA levels (< 4. ng/ml), only 8.8% of the patients had PCa [1]. Other studies have reported PPVs of 1-19% in this patient population [1]. The DRE reproducibility is poor and inter-examiner variability high [1]. Transrectal ultrasound (TRUS)-guided biopsy provides the de nitive diagnosis of PCa. However, because of the lack of speci city of DRE and serum PSA, an increasing number of men will undergo an unnecessary initial biopsy (around 65% for serum PSA levels between 4. ng/ml and 1 ng/ml) [5]. This number will continue to grow due to increased screening and use of lower serum PSA thresholds. In a recent survey among 139 urologists in Belgium, France, Germany, the Netherlands and the UK almost two thirds of respondents indicated at least 41% of initial biopsies were negative. Whereas for one in ve of the respondents this percentage was even greater with at least 61% of negative biopsy results. Since only a small fraction (around 1%) of total prostate tissue is obtained during biopsy, a negative result does not imply that the patient does not have PCa. Approximately 1-25% of men with PCa remain undiagnosed after a single sextant biopsy [5] and in one study 11% of men with a negative biopsy developed PCa within 7 years [6]. Therefore, an initial negative biopsy will frequently trigger repeat biopsies to con rm that PCa is not present. The high percentage of initial negative and repeat biopsies will continue to increase health care costs while diminishing patients quality of life. Biopsies induce anxiety because of the fear of having PCa and they cause discomfort and pain. The patient can also have complications after the procedure. The incidence of discomfort, pain and complications (haematuria, haematospermia and rectal bleeding) are shown in Table 1. Table 1: Percent of patients reporting complications following a 6-12 core prostate biopsy (range reported in prospective studies involving at least 1 patients) [5-13] PSA dilemma PSA is a protein produced by the prostate and is not PCa-speci c. Serum PSA levels increase as the prostate gland enlarges due to benign prostatic diseases such as lower urinary tract symptoms suggestive of benign prostatic hyperplasia (LUTS/BPH) and prostatitis. The European Randomized Study of Screening for Prostate Cancer (ERSPC) [2] and the Prostate Cancer Prevention Trial (PCPT) [3] have shown that no certain serum PSA level can accurately separate malignant from benign cases. Therefore, the PPV of serum PSA, even at a level of up to 1 ng/ml, is low (-3%) [4,5]. COMPLICATION % OF PATIENTS Discomfort 34-7% Pain 5-7% Haematuria 1-74% Haematospermia 1-78% Rectal bleeding 1-% 1
3 Complications requiring hospitalisation (such as severe haematuria or septicaemia) occur in approximately 1% of patients, despite antibiotics being administered prophylactically. One study showed that 1 in 1 patients would refuse repeat prostate biopsy or would require sedation / analgesia [6] which indicates that biopsies are indeed painful and bothersome for patients. Taking all these factors into consideration, there is obviously a need for an additional diagnostic test that has an improved speci city for PCa and can better identify patients who will have a positive biopsy. This will reduce the number of initial and repeat biopsies. Current dilemmas in the diagnosis of PCa PCA3 and its role in improving the diagnosis of prostate cancer Introduction to PCA3 The PCA3 Assay (Prostate Cancer Gene 3; in the past referred to as PCA3 DD3 or DD3 PCA3 ) is the rst genetic diagnostic test to help solve the mentioned clinical dilemmas associated with the diagnosis of PCa. In contrast to serum PSA, PCA3 is not only prostate-speci c but also PCa-speci c (Figure 1) [14]. Messenger RNA (mrna) of the PCA3 gene is highly over-expressed (median 66-fold) in > 95% of PCa tissue compared to normal or benign prostate tissue of the same patients [14,15]. An increased serum PSA concentration and an abnormal / suspicious DRE are both triggers to perform a prostate biopsy The PPV of both DRE (< %) and serum PSA (< 3% at levels below 1 ng/ml) is far from optimal Approximately two thirds of the initial biopsies are Figure 1: PCA3 (DD3) mrna is over-expressed in prostatic tumour (T and M) compared to benign (B) or normal (N) tissue, in contrast to PSA mrna [14] negative Since only approximately 1% of tissue is obtained during a biopsy, the fear that PCa may have been missed, when the initial biopsy is negative, can lead to repeat biopsies Prostate biopsy is not only costly but also causes distress, pain and discomfort for the patient and can Using the PCA3 Assay in clinical practice The Gen-Probe PCA3 Assay [16] detects the presence of PCA3 mrna from urine (Figure 2): lead to (sometimes severe) complications There is need for an additional diagnostic test I. Perform a DRE (3 strokes per lobe) to release a suf cient number of prostate cells into the urine to better predict biopsy outcome and reduce II. After the DRE, collect -3 ml rst-catch urine from unnecessary biopsies III. the patient Transfer 2 ml of urine to the transport tube IV. Store the transport tube with the urine at or below 8ºC (may be frozen) and ship the transport tube as soon as possible to the laboratory. Note: The transport tubes can be obtained from a PCA3 testing laboratory. 2
4 BASE LEFT LOBE RIGHT LOBE APEX DRE (3 STROKES PER LOBE) FIRST CATCH URINE SPECIMEN (-3 ml) TRANSPORT TUBE WITH URINE (2 ml) SENT IN COLD PACK ( 8 C) DIRECTLY TO LABORATORY Using the PCA3 Assay result for improving the diagnosis of prostate cancer Calculation of the PCA3 Score In order to be sure that a suf cient number of prostate cells / prostate RNA is present in the urine specimen and in order to normalise the PCA3 amount, the laboratory also measures mrna of PSA in the urine sample. Using transcription-mediated ampli cation technology, PCA3 and PSA mrna molecules are ampli ed and the PCA3 Score is calculated. The PCA3 Score = 1 x [mrna PCA3] / [mrna PSA]. PCA3 Score in men with serum PSA 2.5 ng/ml and 1 negative prostate biopsy The PCA3 Score was determined in 233 men (mean age 64 years) with serum PSA 2.5 ng/ml (mean 7.4 ng/ml) and at least one negative biopsy [17]. In 226 urine samples (97%), there was suf cient mrna present for analysis. Repeat biopsies were positive for men (27%). It appeared that the higher the PCA3 Score, the higher the percentage of men with a positive biopsy (Figure 3). A patient with a PCA3 Score 35 has a high probability of having PCa and repeat biopsy is advisable. If the outcome is negative (PCA3 Score < 35), the patient has a lower probability of having PCa and repeat biopsy might be delayed with active surveillance / follow-up of the patient including monitoring of serum PSA. Figure 2: % of men with a positive repeat biopsy The PCA3 urine specimen collection procedure Apply pressure on the prostate, enough to depress the surface approximately 1 cm, from the base to the apex and from the lateral to the median line for each lobe and repeat this 3 times PCA3 Score < > 1 (N = 26) (N = 73) (N = 45) (N = 22) (N = 42) (N = 18) Figure 3: The higher the PCA3 Score, the higher the percentage of men with a positive repeat biopsy [17] 3
5 PCA3 Score distinguishes normal men and men with LUTS/BPH from men with PCa The PCA3 Score also discriminates normal men (aged < 45 years with no known PCa risk factors) from men with LUTS/BPH, untreated PCa and PCa treated with radical prostatectomy. There was no overlap in the 95% con dence intervals (CIs) between the groups (P <.1) (Figure 4) [18]. PCA3 Score is independent of prostate volume In the same population of men scheduled for (initial or repeat) biopsy or prostatectomy, the mean serum PSA concentration increased with larger prostate volumes whereas the mean PCA3 Score was not in uenced by prostate volume (Figure 6) [] NORMAL LUTS/BPH PCa * P <.1 between groups * Mean PSA (ng/ml) Mean PCA3 Score 1 8 * * Post-radical Normal LUTS/BPH PCa (N = ) (N = 54) (N = 55) (N = 16) Mean PCA3 Score. 1 8 <3 3-5 >5 (N = 127) (N = 229) (N = 1) Prostate Volume (ml) Figure 4: The PCA3 Score seems to be able to discriminate between normal / benign vs. malignant prostate tissue[18] <3 3-5 >5 (N = 127) (N = 229) (N = 1) Prostate Volume (ml) PCA3 Score in men scheduled for initial or repeat prostate biopsy The PCA3 Score was also determined in 529 men who were scheduled for (initial or repeat) biopsy or prostatectomy [19]. In total 18 men (34%) had a positive biopsy. Also in these men it was shown that the higher the mean PCA3 Score, the higher the percentage of patients with a positive biopsy (Figure 5). Figure 6: Serum PSA (mean ± 95% CI) clearly increases with prostate volume; the PCA3 Score (mean ± 95% CI) is independent of prostate volume [] % of men with a positive biopsy 8 PCA3 Score < > 1 (N = 58) (N = 85) (N = 14) (N = 97) (N = 57) (N = 86) (N = 42) Figure 5: The higher the PCA3 Score, the higher the percentage of men with a positive biopsy [19] 4
6 The PCA3 Assay: a highly speci c genetic test to improve the diagnosis of prostate cancer The PCA3 Assay is a genetic test which is highly PCa-speci c The PCA3 Assay uses urine to measure the PCA3 and PSA mrna concentration and calculate the PCA3 Score The PCA3 Score is not in uenced by prostate volume The probability of a positive biopsy increases with higher PCA3 Scores A PCA3 Score of 35 in men with a PSA 2.5 ng/ml and at least one negative biopsy may indicate that repeat biopsy is advisable; for those with a PCA3 Score < 35, biopsy might be delayed based on active surveillance / follow-up of the patient The PCA3 Score may also be used to determine the need for an initial biopsy in men with an elevated serum PSA ( 2 ng/ml) or with a low serum PSA but suspicious DRE; current research in these patient populations is addressing this question The PCA3 Assay can identify patients who have a high probability of having PCa The PCA3 Assay is a useful test for improving the diagnosis of PCa and reducing the number of unnecessary biopsies Reference List [1] Bozeman CB, Carver BS, Caldito G, Venable DD, Eastham JA. Prostate cancer in patients with an abnormal digital rectal examination and serum prostate-speci c antigen less than 4. ng/ml. Urology 5;66: [2] Postma R, Schröder FH. Screening for prostate cancer. Eur J Cancer 5;41: [3] Thompson IM, Pauler DK, Goodman PJ, Tangen CM, Lucia MS, Parnes HL et al. Prevalence of prostate cancer among men with a prostate-speci c antigen level 4. ng per milliliter. N Engl J Med 4;35: [4] Vollmer RT. Predictive probability of serum prostate-speci c antigen for prostate cancer: an approach using Bayes rule. Am J Clin Pathol 6;125: [5] Seitz C, Palermo S, Djavan B. Prostate biopsy. Minerva Urol Nefrol 3;55: [6] Raja J, Ramachandran N, Munneke G, Patel U. Current status of transrectal ultrasound-guided prostate biopsy in the diagnosis of prostate cancer. Clin Radiol 6;61: [7] Autorino R, De Sio M, Di Lorenzo G, Damiano R, Perdonà S, Cindolo L et al. How to decrease pain during transrectal ultrasound guided prostate biopsy: a look at the literature. J Urol 5;174: [8] Raaijmakers R, Kirkels WJ, Roobol MJ, Wildhagen MF, Schröder FH. Complication rates and risk factors of 582 transrectal ultrasound-guided sextant biopsies of the prostate within a population-based screening program. Urology 2;: [9] Ghani KR, Dundas D, Patel U. Bleeding after transrectal ultrasonographyguided prostate biopsy: a study of 7-day morbidity after a six-, eight- and 12-core biopsy protocol. BJU Int 4;94: [1] Peyromaure M, Ravery V, Messas A, Toublanc M, Boccon-Gibod L, Boccon-Gibod L. Pain and morbidity of an extensive prostate 1-biopsy protocol: a prospective study in 289 patients. J Urol 2;167: [12] Djavan B, Waldert M, Zlotta A, Dobronski P, Seitz C, Remzi M et al. Safety and morbidity of rst and repeat transrectal ultrasound guided prostate needle biopsies: results of a prospective European prostate cancer detection study. J Urol 1;166: [13] Naughton CK, Ornstein DK, Smith DS, Catalona WJ. Pain and morbidity of transrectal ultrasound guided prostate biopsy: a prospective randomized trial of 6 versus 12 cores. J Urol ;163: [14] Bussemakers MJ, van Bokhoven A, Verhaegh GW, Smit FP, Karthaus HF, Schalken JA et al. DD3: a new prostate-speci c gene, highly overexpressed in prostate cancer. Cancer Res 1999;59: [15] Hessels D, Klein Gunnewiek JM, van Oort I, Karthaus HF, van Leenders GJ, van Balken B et al. DD3 PCA3 -based molecular urine analysis for the diagnosis of prostate cancer. Eur Urol 3;44: [16] Groskopf J, Aubin SM, Deras IL, Blase A, Bodrug S, Clark C et al. APTIMA PCA3 molecular urine test: development of a method to aid in the diagnosis of prostate cancer. Clin Chem 6;52: [17] Marks LS, Fradet Y, Deras IL, Blase A, Mathis J, Aubin SMJ et al. PCA3 molecular urine assay for prostate cancer in men undergoing repeat biopsy. Urology 6: Submitted. [18] Groskopf J, Aubin SM, Deras IL, Blase A, Bodrug S, Brentano S et al. Speci city of the APTIMA PCA3 assay for prostate cancer. Eur Urol Suppl 6;5: 2 (abs. 87). Poster presented at EAU 6. [19] Gen-Probe Incorporated data on le; Label CE Mark. 6. [] Marks LS, Aubin SMJ, Deras IL, Brentano S, Blase A, Bodrug S et al. Speci city of the APTIMA PCA3 assay for prostate cancer. J Urol 6;175(4 Suppl): (abs. 5). Poster presented at AUA 6. [11] Mäkinen T, Auvinen A, Hakama M, Stenman UH, Tammela TL. Acceptability and complications of prostate biopsy in population-based PSA screening versus routine clinical practice: a prospective, controlled study. Urology 2;:
1. What is the prostate-specific antigen (PSA) test?
 1. What is the prostate-specific antigen (PSA) test? Prostate-specific antigen (PSA) is a protein produced by the cells of the prostate gland. The PSA test measures the level of PSA in the blood. The doctor
1. What is the prostate-specific antigen (PSA) test? Prostate-specific antigen (PSA) is a protein produced by the cells of the prostate gland. The PSA test measures the level of PSA in the blood. The doctor
BJUI. Study Type Diagnosis (exploratory cohort) Level of Evidence 2b OBJECTIVE
 . 2010 BJU INTERNATIONAL Urological Oncology FREE-TO-TOTAL PSA RATIO AND PCA3 SCORE IN PREDICTING POSITIVE BIOPSIES PLOUSSARD ET AL. BJUI BJU INTERNATIONAL The prostate cancer gene 3 (PCA3) urine test
. 2010 BJU INTERNATIONAL Urological Oncology FREE-TO-TOTAL PSA RATIO AND PCA3 SCORE IN PREDICTING POSITIVE BIOPSIES PLOUSSARD ET AL. BJUI BJU INTERNATIONAL The prostate cancer gene 3 (PCA3) urine test
PSA Testing 101. Stanley H. Weiss, MD. Professor, UMDNJ-New Jersey Medical School. Director & PI, Essex County Cancer Coalition. weiss@umdnj.
 PSA Testing 101 Stanley H. Weiss, MD Professor, UMDNJ-New Jersey Medical School Director & PI, Essex County Cancer Coalition weiss@umdnj.edu September 23, 2010 Screening: 3 tests for PCa A good screening
PSA Testing 101 Stanley H. Weiss, MD Professor, UMDNJ-New Jersey Medical School Director & PI, Essex County Cancer Coalition weiss@umdnj.edu September 23, 2010 Screening: 3 tests for PCa A good screening
Role of MRI in the Diagnosis of Prostate Cancer, A Proposal
 Clinical and Experimental Medical Sciences, Vol. 1, 2013, no. 3, 111 116 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com Role of MRI in the Diagnosis of Prostate Cancer, A Proposal W. Akhter Research Fellow Urology, Bartshealth
Clinical and Experimental Medical Sciences, Vol. 1, 2013, no. 3, 111 116 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com Role of MRI in the Diagnosis of Prostate Cancer, A Proposal W. Akhter Research Fellow Urology, Bartshealth
PSA Screening for Prostate Cancer Information for Care Providers
 All men should know they are having a PSA test and be informed of the implications prior to testing. This booklet was created to help primary care providers offer men information about the risks and benefits
All men should know they are having a PSA test and be informed of the implications prior to testing. This booklet was created to help primary care providers offer men information about the risks and benefits
DECISION AID TOOL PROSTATE CANCER SCREENING WITH PSA TESTING
 DECISION AID TOOL PROSTATE CANCER SCREENING WITH PSA TESTING This booklet is what is often called a decision aid. The goals of a decision aid are to help people better understand their medical choices
DECISION AID TOOL PROSTATE CANCER SCREENING WITH PSA TESTING This booklet is what is often called a decision aid. The goals of a decision aid are to help people better understand their medical choices
PCA3 Score and Prostate Cancer Diagnosis at Repeated Saturation Biopsy. Which cut-off: 20 or 35?
 ORIGINAL Article Vol. 38 (4): 489-495, July - August, 2012 PCA3 Score and Prostate Cancer Diagnosis at Repeated Saturation Biopsy. Which cut-off: 20 or 35? Pietro Pepe, Filippo Fraggetta, Antonio Galia,
ORIGINAL Article Vol. 38 (4): 489-495, July - August, 2012 PCA3 Score and Prostate Cancer Diagnosis at Repeated Saturation Biopsy. Which cut-off: 20 or 35? Pietro Pepe, Filippo Fraggetta, Antonio Galia,
Prostate Cancer Screening Guideline
 Prostate Cancer Screening Guideline Contents Prevention 2 Screening Recommendations 2 Shared Decision Making 2 Test Recommendations 3 Follow-up/Referral 3 Treatment Overview 4 Evidence Summary 4 References
Prostate Cancer Screening Guideline Contents Prevention 2 Screening Recommendations 2 Shared Decision Making 2 Test Recommendations 3 Follow-up/Referral 3 Treatment Overview 4 Evidence Summary 4 References
Advances in Diagnostic and Molecular Testing in Prostate Cancer
 Advances in Diagnostic and Molecular Testing in Prostate Cancer Ashley E. Ross MD PhD Assistant Professor Urology, Oncology, Pathology Johns Hopkins School of Medicine September 24, 2015 1 Disclosures
Advances in Diagnostic and Molecular Testing in Prostate Cancer Ashley E. Ross MD PhD Assistant Professor Urology, Oncology, Pathology Johns Hopkins School of Medicine September 24, 2015 1 Disclosures
Advice to patients about the PSA (prostate-specific antigen) blood test: frequently-asked questions
 Advice to patients about the PSA (prostate-specific antigen) blood test: frequently-asked questions What is the PSA blood test? If you want more information before deciding to have this test, it is important
Advice to patients about the PSA (prostate-specific antigen) blood test: frequently-asked questions What is the PSA blood test? If you want more information before deciding to have this test, it is important
Screening for Prostate Cancer
 Screening for Prostate Cancer It is now clear that screening for Prostate Cancer discovers the disease at an earlier and more curable stage. It is not yet clear whether this translates into reduced mortality
Screening for Prostate Cancer It is now clear that screening for Prostate Cancer discovers the disease at an earlier and more curable stage. It is not yet clear whether this translates into reduced mortality
MEDICAL POLICY SUBJECT: PROSTATE CANCER SCREENING, DETECTION AND MONITORING
 MEDICAL POLICY PAGE: 1 OF: 8 If the member's subscriber contract excludes coverage for a specific service it is not covered under that contract. In such cases, medical policy criteria are not applied.
MEDICAL POLICY PAGE: 1 OF: 8 If the member's subscriber contract excludes coverage for a specific service it is not covered under that contract. In such cases, medical policy criteria are not applied.
PCA3 DETECTION TEST FOR PROSTATE CANCER DO YOU KNOW YOUR RISK OF HAVING CANCER?
 PCA3 DETECTION TEST FOR PROSTATE CANCER DO YOU KNOW YOUR RISK OF HAVING CANCER? PCA3 DETECTION TEST FOR PROSTATE CANCER There is a range of methods available to your healthcare professional to verify the
PCA3 DETECTION TEST FOR PROSTATE CANCER DO YOU KNOW YOUR RISK OF HAVING CANCER? PCA3 DETECTION TEST FOR PROSTATE CANCER There is a range of methods available to your healthcare professional to verify the
The 4Kscore blood test for risk of aggressive prostate cancer
 The 4Kscore blood test for risk of aggressive prostate cancer Prostate cancer tests When to use the 4Kscore Test? Screening Prior to 1 st biopsy Prior to negative previous biopsy Prognosis in Gleason 6
The 4Kscore blood test for risk of aggressive prostate cancer Prostate cancer tests When to use the 4Kscore Test? Screening Prior to 1 st biopsy Prior to negative previous biopsy Prognosis in Gleason 6
Diagnosis of Prostate Cancer: Repeated Transrectal Prostate Biopsy or Transurethral Resection
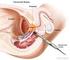 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Diagnosis of Prostate Cancer: Repeated Transrectal Prostate Biopsy or Transurethral Resection Chih-Chieh Lin 1, William J.S. Huang 1,3 *, Li-Ju Wu 2, Yen-Hwa Chang 1,3, Alex T.L. Lin 1,3,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Diagnosis of Prostate Cancer: Repeated Transrectal Prostate Biopsy or Transurethral Resection Chih-Chieh Lin 1, William J.S. Huang 1,3 *, Li-Ju Wu 2, Yen-Hwa Chang 1,3, Alex T.L. Lin 1,3,
Screening for Prostate Cancer
 Screening for Prostate Cancer Review against programme appraisal criteria for the UK National Screening Committee (UK NSC) Version 1: This document summarises the work of ScHARR 1 2 and places it against
Screening for Prostate Cancer Review against programme appraisal criteria for the UK National Screening Committee (UK NSC) Version 1: This document summarises the work of ScHARR 1 2 and places it against
APTIMA PCA3 Molecular Urine Test: Development of a Method to Aid in the Diagnosis of Prostate Cancer
 Clinical Chemistry 52:6 1089 1095 (2006) Cancer Diagnostics APTIMA PCA3 Molecular Urine Test: Development of a Method to Aid in the Diagnosis of Prostate Cancer Jack Groskopf, 1* Sheila M.J. Aubin, 1 Ina
Clinical Chemistry 52:6 1089 1095 (2006) Cancer Diagnostics APTIMA PCA3 Molecular Urine Test: Development of a Method to Aid in the Diagnosis of Prostate Cancer Jack Groskopf, 1* Sheila M.J. Aubin, 1 Ina
Prostate cancer is the most common cause of death from cancer in men over age 75. Prostate cancer is rarely found in men younger than 40.
 A.D.A.M. Medical Encyclopedia. Prostate cancer Cancer - prostate; Biopsy - prostate; Prostate biopsy; Gleason score Last reviewed: October 2, 2013. Prostate cancer is cancer that starts in the prostate
A.D.A.M. Medical Encyclopedia. Prostate cancer Cancer - prostate; Biopsy - prostate; Prostate biopsy; Gleason score Last reviewed: October 2, 2013. Prostate cancer is cancer that starts in the prostate
PSA: Prostate Cancer Screening
 PSA: Prostate Cancer Screening 42 nd Annual Convention of the Philippines College of Physicians May 7, 2012, SMX Convention Center Jose Albert Cruz Reyes III, MD, FPCS, FPUA, DPBU Institute of Urology
PSA: Prostate Cancer Screening 42 nd Annual Convention of the Philippines College of Physicians May 7, 2012, SMX Convention Center Jose Albert Cruz Reyes III, MD, FPCS, FPUA, DPBU Institute of Urology
Prostate Cancer Screening. Dr. J. McCracken, Urologist
 Prostate Cancer Screening Dr. J. McCracken, Urologist USPSTF Lifetime risk for diagnosis currently estimated at 15.9% Llifetime risk of dying of prostate cancer is 2.8% Seventy percent of deaths due to
Prostate Cancer Screening Dr. J. McCracken, Urologist USPSTF Lifetime risk for diagnosis currently estimated at 15.9% Llifetime risk of dying of prostate cancer is 2.8% Seventy percent of deaths due to
PSA screening in asymptomatic men the debate continues www.bpac.org.nz keyword: psa
 PSA screening in asymptomatic men the debate continues www.bpac.org.nz keyword: psa Key messages: PSA is present in the benign and malignant prostate There is currently no national screening programme
PSA screening in asymptomatic men the debate continues www.bpac.org.nz keyword: psa Key messages: PSA is present in the benign and malignant prostate There is currently no national screening programme
Historical Basis for Concern
 Androgens After : Are We Ready? Mohit Khera, MD, MBA Assistant Professor of Urology Division of Male Reproductive Medicine and Surgery Scott Department of Urology Baylor College of Medicine Historical
Androgens After : Are We Ready? Mohit Khera, MD, MBA Assistant Professor of Urology Division of Male Reproductive Medicine and Surgery Scott Department of Urology Baylor College of Medicine Historical
4/8/13. Pre-test Audience Response. Prostate Cancer 2012. Screening and Treatment of Prostate Cancer: The 2013 Perspective
 Pre-test Audience Response Screening and Treatment of Prostate Cancer: The 2013 Perspective 1. I do not offer routine PSA screening, and the USPSTF D recommendation will not change my practice. 2. In light
Pre-test Audience Response Screening and Treatment of Prostate Cancer: The 2013 Perspective 1. I do not offer routine PSA screening, and the USPSTF D recommendation will not change my practice. 2. In light
Saturation Biopsy for Diagnosis and Staging of Prostate Cancer. Original Policy Date
 MP 7.01.101 Saturation Biopsy for Diagnosis and Staging of Prostate Cancer Medical Policy Section Surgery Issue 12/2013 Original Policy Date 12/2013 Last Review Status/Date /12/2013 Return to Medical Policy
MP 7.01.101 Saturation Biopsy for Diagnosis and Staging of Prostate Cancer Medical Policy Section Surgery Issue 12/2013 Original Policy Date 12/2013 Last Review Status/Date /12/2013 Return to Medical Policy
Early Prostate Cancer: Questions and Answers. Key Points
 CANCER FACTS N a t i o n a l C a n c e r I n s t i t u t e N a t i o n a l I n s t i t u t e s o f H e a l t h D e p a r t m e n t o f H e a l t h a n d H u m a n S e r v i c e s Early Prostate Cancer:
CANCER FACTS N a t i o n a l C a n c e r I n s t i t u t e N a t i o n a l I n s t i t u t e s o f H e a l t h D e p a r t m e n t o f H e a l t h a n d H u m a n S e r v i c e s Early Prostate Cancer:
CLINICAL PRACTICE. Clinical Practice. The PSA Test
 Clinical Practice This Journal feature begins with a case vignette highlighting a common clinical problem. Evidence supporting various strategies is then presented, followed by a review of formal guidelines,
Clinical Practice This Journal feature begins with a case vignette highlighting a common clinical problem. Evidence supporting various strategies is then presented, followed by a review of formal guidelines,
Technologies To Detect Prostate Cancer
 CHAPTER 3 Technologies To Detect Prostate Cancer he most commonly used technologies for detecting and diagnosing prostate cancer are digital rectal examination (DRE), prostate-specific antigen (PSA) measurement,
CHAPTER 3 Technologies To Detect Prostate Cancer he most commonly used technologies for detecting and diagnosing prostate cancer are digital rectal examination (DRE), prostate-specific antigen (PSA) measurement,
Prostate Cancer Screening: Are We There Yet? March 2010 Andrew M.D. Wolf, MD University of Virginia School of Medicine
 Prostate Cancer Screening: Are We There Yet? March 2010 Andrew M.D. Wolf, MD University of Virginia School of Medicine Case #1 A 55 yo white man with well-controlled hypertension presents for his annual
Prostate Cancer Screening: Are We There Yet? March 2010 Andrew M.D. Wolf, MD University of Virginia School of Medicine Case #1 A 55 yo white man with well-controlled hypertension presents for his annual
Prostate-Specific Antigen Based Screening: Controversy and Guidelines
 Prostate-Specific Antigen Based Screening: Controversy and Guidelines Eric H. Kim and Gerald L. Andriole Institutional Address: Washington University School of Medicine 4960 Children's Place Campus Box
Prostate-Specific Antigen Based Screening: Controversy and Guidelines Eric H. Kim and Gerald L. Andriole Institutional Address: Washington University School of Medicine 4960 Children's Place Campus Box
The PSA Controversy: Defining It, Discussing It, and Coping With It
 The PSA Controversy: Defining It, Discussing It, and Coping With It 11 TH ANNUAL SYMPOSIUM ON MEN S HEALTH June 12, 2013 The PSA Controversy Defining It, Discussing It and Coping With It As of May 2012,
The PSA Controversy: Defining It, Discussing It, and Coping With It 11 TH ANNUAL SYMPOSIUM ON MEN S HEALTH June 12, 2013 The PSA Controversy Defining It, Discussing It and Coping With It As of May 2012,
Prostate Cancer Screening. A Decision Guide for African Americans
 Prostate Cancer Screening A Decision Guide for African Americans This booklet was developed by the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Published
Prostate Cancer Screening A Decision Guide for African Americans This booklet was developed by the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Published
Official reprint from UpToDate www.uptodate.com 2013 UpToDate
 Official reprint from UpToDate www.uptodate.com 2013 UpToDate The content on the UpToDate website is not intended nor recommended as a substitute for medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek
Official reprint from UpToDate www.uptodate.com 2013 UpToDate The content on the UpToDate website is not intended nor recommended as a substitute for medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek
Update on Prostate Cancer: Screening, Diagnosis, and Treatment Making Sense of the Noise and Directions Forward
 Update on Prostate Cancer: Screening, Diagnosis, and Treatment Making Sense of the Noise and Directions Forward 33 rd Annual Internal Medicine Update December 5, 2015 Ryan C. Hedgepeth, MD, MS Chief of
Update on Prostate Cancer: Screening, Diagnosis, and Treatment Making Sense of the Noise and Directions Forward 33 rd Annual Internal Medicine Update December 5, 2015 Ryan C. Hedgepeth, MD, MS Chief of
7. Prostate cancer in PSA relapse
 7. Prostate cancer in PSA relapse A patient with prostate cancer in PSA relapse is one who, having received a primary treatment with intent to cure, has a raised PSA (prostate-specific antigen) level defined
7. Prostate cancer in PSA relapse A patient with prostate cancer in PSA relapse is one who, having received a primary treatment with intent to cure, has a raised PSA (prostate-specific antigen) level defined
Screening for Prostate Cancer
 Cancer Expert Working Group on Cancer Prevention and Screening Screening for Prostate Cancer Information for men and their families 1 What is the prostate? 2 What is prostate cancer? prostate The prostate
Cancer Expert Working Group on Cancer Prevention and Screening Screening for Prostate Cancer Information for men and their families 1 What is the prostate? 2 What is prostate cancer? prostate The prostate
Prostate Cancer Screening. A Decision Guide
 Prostate Cancer Screening A Decision Guide This booklet was developed by the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Is screening right for you?
Prostate Cancer Screening A Decision Guide This booklet was developed by the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Is screening right for you?
ERSPC and PLCO Prostate Cancer Screening Studies: What Are the Differences?
 EUROPEAN UROLOGY 58 (2010) 46 52 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.europeanurology.com Editorial ERSPC and PLCO Prostate Cancer Screening Studies: What Are the Differences? Fritz
EUROPEAN UROLOGY 58 (2010) 46 52 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.europeanurology.com Editorial ERSPC and PLCO Prostate Cancer Screening Studies: What Are the Differences? Fritz
Prostate Specific Antigen (PSA) Blood Test
 TO PROVIDE THE VERY BEST CARE FOR EACH PATIENT ON EVERY OCCASION Prostate Specific Antigen (PSA) Blood Test An information guide Prostate Specific Antigen (PSA) Blood Test Prostate Specific Antigen (PSA)
TO PROVIDE THE VERY BEST CARE FOR EACH PATIENT ON EVERY OCCASION Prostate Specific Antigen (PSA) Blood Test An information guide Prostate Specific Antigen (PSA) Blood Test Prostate Specific Antigen (PSA)
An Introduction to PROSTATE CANCER
 An Introduction to PROSTATE CANCER Being diagnosed with prostate cancer can be a life-altering experience. It requires making some very difficult decisions about treatments that can affect not only the
An Introduction to PROSTATE CANCER Being diagnosed with prostate cancer can be a life-altering experience. It requires making some very difficult decisions about treatments that can affect not only the
Guidelines for Cancer Prevention, Early detection & Screening. Prostate Cancer
 Guidelines for Cancer Prevention, Early detection & Screening Prostate Cancer Intervention Comments & Recommendations For primary prevention, it has been suggested that diets low in meat & other fatty
Guidelines for Cancer Prevention, Early detection & Screening Prostate Cancer Intervention Comments & Recommendations For primary prevention, it has been suggested that diets low in meat & other fatty
Key Messages for Healthcare Providers
 Cancer Care Ontario: Prostate Cancer Screening with the Prostate- Specific Antigen (PSA) Test Key Messages for Healthcare Providers Considerations for men at average risk Avoid prostate-specific antigen
Cancer Care Ontario: Prostate Cancer Screening with the Prostate- Specific Antigen (PSA) Test Key Messages for Healthcare Providers Considerations for men at average risk Avoid prostate-specific antigen
Update on Prostate Cancer Screening Guidelines
 www.medscape.com Update on Prostate Cancer Screening Guidelines Christine Gonzalez, PharmD, CHHC US Pharmacist Abstract and Introduction Introduction In the United States, prostate cancer is the most common
www.medscape.com Update on Prostate Cancer Screening Guidelines Christine Gonzalez, PharmD, CHHC US Pharmacist Abstract and Introduction Introduction In the United States, prostate cancer is the most common
An Empirical Evaluation of Guidelines on Prostate-specific Antigen Velocity in Prostate Cancer Detection
 DOI: 10.1093/jnci/djr028 ARTICLE JNCI djr028 MA JOURNAL NAME Art. No. CE Code The Author 2011. Published by Oxford University Press. All rights reserved. For Permissions, please e-mail: journals.permissions@oup.com.
DOI: 10.1093/jnci/djr028 ARTICLE JNCI djr028 MA JOURNAL NAME Art. No. CE Code The Author 2011. Published by Oxford University Press. All rights reserved. For Permissions, please e-mail: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Use Of Testosterone In Men With Prostate Cancer. Traditional view: T is dangerous for PCa
 Use Of Testosterone In Men With Prostate Cancer Abraham Morgentaler, MD, FACS Director, Men s s Health Boston Associate Clinical Professor of Urology Harvard Medical School Boston, USA Traditional view:
Use Of Testosterone In Men With Prostate Cancer Abraham Morgentaler, MD, FACS Director, Men s s Health Boston Associate Clinical Professor of Urology Harvard Medical School Boston, USA Traditional view:
The role of urine prostate cancer antigen 3 mrna levels in the diagnosis of prostate cancer among Hong Kong Chinese patients
 O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E The role of urine prostate cancer antigen 3 mrna levels in the diagnosis of prostate cancer among Hong Kong Chinese patients CF Ng Rachel Yeung Peter KF Chiu NY Lam Joseph
O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E The role of urine prostate cancer antigen 3 mrna levels in the diagnosis of prostate cancer among Hong Kong Chinese patients CF Ng Rachel Yeung Peter KF Chiu NY Lam Joseph
PROSTATE CANCER. Normal-risk men: No family history of prostate cancer No history of prior screening Not African-American
 PROSTATE CANCER 1. Guidelines for Screening Risk Factors Normal-risk men: No family history of prostate cancer No history of prior screening Not African-American High-risk men: Family history of prostate
PROSTATE CANCER 1. Guidelines for Screening Risk Factors Normal-risk men: No family history of prostate cancer No history of prior screening Not African-American High-risk men: Family history of prostate
Prostate Cancer. Patient Information
 Prostate Cancer Patient Information 1 The Prostate & Prostate Cancer The prostate is a small gland in the male reproductive system, approximately the size and shape of a walnut. It is located directly
Prostate Cancer Patient Information 1 The Prostate & Prostate Cancer The prostate is a small gland in the male reproductive system, approximately the size and shape of a walnut. It is located directly
How prostate cancer is diagnosed
 How prostate cancer is diagnosed This information is an extract from the booklet Having tests for prostate cancer. You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you a free copy see page 7. Contents
How prostate cancer is diagnosed This information is an extract from the booklet Having tests for prostate cancer. You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you a free copy see page 7. Contents
FAQ About Prostate Cancer Treatment and SpaceOAR System
 FAQ About Prostate Cancer Treatment and SpaceOAR System P. 4 Prostate Cancer Background SpaceOAR Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) 1. What is prostate cancer? The vast majority of prostate cancers develop
FAQ About Prostate Cancer Treatment and SpaceOAR System P. 4 Prostate Cancer Background SpaceOAR Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) 1. What is prostate cancer? The vast majority of prostate cancers develop
Tumor Markers for Prostate Cancer: Update for 2012 IAD-Cechtuma 2012 Conference Usti nad Labem, Czech Republic April 1-3, 2012
 Tumor Markers for Prostate Cancer: Update for 2012 IAD-Cechtuma 2012 Conference Usti nad Labem, Czech Republic April 1-3, 2012 Herbert A. Fritsche, Ph.D. Health Discovery Corporaton Houston, Texas hfritsche@healthdiscoverycorp.com
Tumor Markers for Prostate Cancer: Update for 2012 IAD-Cechtuma 2012 Conference Usti nad Labem, Czech Republic April 1-3, 2012 Herbert A. Fritsche, Ph.D. Health Discovery Corporaton Houston, Texas hfritsche@healthdiscoverycorp.com
Prostate Cancer Screening: Phantom menace to society. Folusho Ogunfiditimi, DM, MPH, PA-C Vattikuti Urology Institute Henry Ford Health System
 Prostate Cancer Screening: Phantom menace to society Folusho Ogunfiditimi, DM, MPH, PA-C Vattikuti Urology Institute Henry Ford Health System Objectives USPTF Recommendations on PSA testing Justification
Prostate Cancer Screening: Phantom menace to society Folusho Ogunfiditimi, DM, MPH, PA-C Vattikuti Urology Institute Henry Ford Health System Objectives USPTF Recommendations on PSA testing Justification
TO SCREEN OR NOT TO SCREEN: THE PROSTATE CANCER
 TO SCREEN OR NOT TO SCREEN: THE PROSTATE CANCER DILEMMA Thomas J Stormont MD January 2012 http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=8jd 7bAHVp0A&feature=related related INTRODUCTION A government health panel (the
TO SCREEN OR NOT TO SCREEN: THE PROSTATE CANCER DILEMMA Thomas J Stormont MD January 2012 http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=8jd 7bAHVp0A&feature=related related INTRODUCTION A government health panel (the
PSA Testing for Prostate Cancer An information sheet for men considering a PSA Test
 PSA Testing for Prostate Cancer An information sheet for men considering a PSA Test What is the aim of this leaflet? Prostate cancer is a serious condition. The PSA test, which can give an early indication
PSA Testing for Prostate Cancer An information sheet for men considering a PSA Test What is the aim of this leaflet? Prostate cancer is a serious condition. The PSA test, which can give an early indication
PSA TESTING FOR PROSTATE CANCER A CRICO/RMF DECISION SUPPORT TOOL
 PSA TESTING FOR PROSTATE CANCER A CRICO/RMF DECISION SUPPORT TOOL Created: 2008 Updated: 2009 PROSTATE-SPECIFIC ANTIGEN TESTING FOR PROSTATE CANCER A DECISION SUPPORT TOOL Prostate Cancer and Medical Malpractice
PSA TESTING FOR PROSTATE CANCER A CRICO/RMF DECISION SUPPORT TOOL Created: 2008 Updated: 2009 PROSTATE-SPECIFIC ANTIGEN TESTING FOR PROSTATE CANCER A DECISION SUPPORT TOOL Prostate Cancer and Medical Malpractice
Prostate Cancer Screening in Taiwan: a must
 Prostate Cancer Screening in Taiwan: a must 吳 俊 德 基 隆 長 庚 醫 院 台 灣 醫 學 會 105 th What is the PSA test? The blood level of PSA is often elevated in men with prostate cancer, and the PSA test was originally
Prostate Cancer Screening in Taiwan: a must 吳 俊 德 基 隆 長 庚 醫 院 台 灣 醫 學 會 105 th What is the PSA test? The blood level of PSA is often elevated in men with prostate cancer, and the PSA test was originally
Cancer in Primary Care: Prostate Cancer Screening. How and How often? Should we and in which patients?
 Cancer in Primary Care: Prostate Cancer Screening How and How often? Should we and in which patients? PLCO trial (Prostate, Lung, Colorectal and Ovarian) Results In the screening group, rates of compliance
Cancer in Primary Care: Prostate Cancer Screening How and How often? Should we and in which patients? PLCO trial (Prostate, Lung, Colorectal and Ovarian) Results In the screening group, rates of compliance
PSA screening: Controversies and Guidelines
 PSA screening: Controversies and Guidelines John Phillips, MD, FACS Department of Urology Urology Center of Westchester New York Medical College Historical PerspecGve Cancer of the prostate, although rare,
PSA screening: Controversies and Guidelines John Phillips, MD, FACS Department of Urology Urology Center of Westchester New York Medical College Historical PerspecGve Cancer of the prostate, although rare,
The PSA Test for Prostate Cancer Screening:
 For more information, please contact your local VA Medical Center or Health Clinic. U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs Veterans Health Administration Patient Care Services Health Promotion and Disease
For more information, please contact your local VA Medical Center or Health Clinic. U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs Veterans Health Administration Patient Care Services Health Promotion and Disease
PSA Screening and the USPSTF Understanding the Controversy
 PSA Screening and the USPSTF Understanding the Controversy Peter C. Albertsen Division of Urology University of Connecticut Farmington, CT, USA USPSTF Final Report 1 Four Key Questions 1. Does PSA based
PSA Screening and the USPSTF Understanding the Controversy Peter C. Albertsen Division of Urology University of Connecticut Farmington, CT, USA USPSTF Final Report 1 Four Key Questions 1. Does PSA based
Specificity of PCA3 determination in urine for prostate cancer detection in Mexican patients
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE of PCA3 determination in urine for prostate cancer detection in Mexican patients Dorian V. Saavedra-Briones, 1 Mauricio Rodríguez-Dorantes, 2 Jorge G Morales Montor, 1 Iván Salido-Guadarrama,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE of PCA3 determination in urine for prostate cancer detection in Mexican patients Dorian V. Saavedra-Briones, 1 Mauricio Rodríguez-Dorantes, 2 Jorge G Morales Montor, 1 Iván Salido-Guadarrama,
New targets for molecular diagnosis of prostate cancer: beyond the era of PSA
 Review articles New targets for molecular diagnosis of prostate cancer: beyond the era of PSA Maciej Salagierski 1,2, Grégoire Robert 3, Marek Sosnowski 2, Jack A. Schalken 1 1 Department of Urology, Radboud
Review articles New targets for molecular diagnosis of prostate cancer: beyond the era of PSA Maciej Salagierski 1,2, Grégoire Robert 3, Marek Sosnowski 2, Jack A. Schalken 1 1 Department of Urology, Radboud
PATIENT GUIDE. Localized Prostate Cancer
 PATIENT GUIDE Localized Prostate Cancer The prostate* is part of the male reproductive system. It is about the same size as a walnut and weighs about an ounce. As pictured in Figure 1, the prostate is
PATIENT GUIDE Localized Prostate Cancer The prostate* is part of the male reproductive system. It is about the same size as a walnut and weighs about an ounce. As pictured in Figure 1, the prostate is
The 4Kscore blood test for risk of aggressive prostate cancer
 The 4Kscore blood test for risk of aggressive prostate cancer Early detection of aggressive prostate cancer Challenges Serum PSA has a high false positive rate Over 1 million prostate biopsies performed
The 4Kscore blood test for risk of aggressive prostate cancer Early detection of aggressive prostate cancer Challenges Serum PSA has a high false positive rate Over 1 million prostate biopsies performed
Prostate cancer. Christopher Eden. The Royal Surrey County Hospital, Guildford & The Hampshire Clinic, Old Basing.
 Prostate cancer Christopher Eden The Royal Surrey County Hospital, Guildford & The Hampshire Clinic, Old Basing. Screening Screening men for PCa (prostate cancer) using PSA (Prostate Specific Antigen blood
Prostate cancer Christopher Eden The Royal Surrey County Hospital, Guildford & The Hampshire Clinic, Old Basing. Screening Screening men for PCa (prostate cancer) using PSA (Prostate Specific Antigen blood
AFTER DIAGNOSIS: PROSTATE CANCER Understanding Your Treatment Options
 AFTER DIAGNOSIS: PROSTATE CANCER Understanding Your Treatment Options INTRODUCTION This booklet describes how prostate cancer develops, how it affects the body and the current treatment methods. Although
AFTER DIAGNOSIS: PROSTATE CANCER Understanding Your Treatment Options INTRODUCTION This booklet describes how prostate cancer develops, how it affects the body and the current treatment methods. Although
Prostate cancer screening. It s YOUR decision!
 Prostate cancer screening It s YOUR decision! For many years now, a test has been available to screen for. The test is called the prostate-specific antigen blood test (or PSA test). It is used in combination
Prostate cancer screening It s YOUR decision! For many years now, a test has been available to screen for. The test is called the prostate-specific antigen blood test (or PSA test). It is used in combination
HEALTH NEWS PROSTATE CANCER THE PROSTATE
 HEALTH NEWS PROSTATE CANCER THE PROSTATE Prostate comes from the Greek meaning to stand in front of ; this is very different than prostrate which means to lie down flat. The prostate is a walnut-sized
HEALTH NEWS PROSTATE CANCER THE PROSTATE Prostate comes from the Greek meaning to stand in front of ; this is very different than prostrate which means to lie down flat. The prostate is a walnut-sized
There are many different types of cancer and sometimes cancer is diagnosed when in fact you are not suffering from the disease at all.
 About Cancer Cancer is a disease where there is a disturbance in the normal pattern of cell replacement. The cells mutate and become abnormal or grow uncontrollably. Not all tumours are cancerous (i.e.
About Cancer Cancer is a disease where there is a disturbance in the normal pattern of cell replacement. The cells mutate and become abnormal or grow uncontrollably. Not all tumours are cancerous (i.e.
Beyond the PSA: Genomic Testing in Localized Prostate Cancer
 Beyond the PSA: Genomic Testing in Localized Prostate Cancer Kelvin A. Moses, MD, PhD Vanderbilt University Medical Center Wednesday, December 2, 2015 5:00 p.m. ET/2:00 p.m. PT About ZERO ZERO s mission
Beyond the PSA: Genomic Testing in Localized Prostate Cancer Kelvin A. Moses, MD, PhD Vanderbilt University Medical Center Wednesday, December 2, 2015 5:00 p.m. ET/2:00 p.m. PT About ZERO ZERO s mission
Corporate Medical Policy Saturation Biopsy for Diagnosis and Staging of Prostate Cancer
 Corporate Medical Policy Saturation Biopsy for Diagnosis and Staging of Prostate Cancer File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: saturation_biopsy_for_diagnosis_and_staging_of_prostate_cancer
Corporate Medical Policy Saturation Biopsy for Diagnosis and Staging of Prostate Cancer File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: saturation_biopsy_for_diagnosis_and_staging_of_prostate_cancer
Prostate Health Index Literature
 Prostate Health Index Literature Update June 2013 Preoperative Prostate-Specific Antigen Isoform p2psa and Its Derivatives, %p2psa and Prostate Health Index, Predict Pathologic Outcomes in Patients Undergoing
Prostate Health Index Literature Update June 2013 Preoperative Prostate-Specific Antigen Isoform p2psa and Its Derivatives, %p2psa and Prostate Health Index, Predict Pathologic Outcomes in Patients Undergoing
Real Time MRI guided Focal Laser Ablation Therapy for Prostate Cancer
 Real Time MRI guided Focal Laser Ablation Therapy for Prostate Cancer A/Prof Celi Varol and Dr Orit Raz Uro-Oncologist Nepean and Macquarie Hospital Trial at Macquarie University Hospital Ethics board
Real Time MRI guided Focal Laser Ablation Therapy for Prostate Cancer A/Prof Celi Varol and Dr Orit Raz Uro-Oncologist Nepean and Macquarie Hospital Trial at Macquarie University Hospital Ethics board
Us TOO University Presents: Understanding Diagnostic Testing
 Us TOO University Presents: Understanding Diagnostic Testing for Prostate Cancer Patients Today s speaker is Manish Bhandari, MD Program moderator is Pam Barrett, Us TOO International Made possible by
Us TOO University Presents: Understanding Diagnostic Testing for Prostate Cancer Patients Today s speaker is Manish Bhandari, MD Program moderator is Pam Barrett, Us TOO International Made possible by
UKNSC Screening for Prostate Cancer Review 2015 Update
 UKNSC Screening for Prostate Cancer Review 2015 Update Review against programme appraisal criteria for the UK National Screening Committee (UKNSC) November 2015 Prepared by: Dr Karly S Louie Queen Mary
UKNSC Screening for Prostate Cancer Review 2015 Update Review against programme appraisal criteria for the UK National Screening Committee (UKNSC) November 2015 Prepared by: Dr Karly S Louie Queen Mary
Detection and staging of recurrent prostate cancer is still one of the important clinical problems in prostate cancer. A rise in PSA or biochemical
 Summary. 111 Detection and staging of recurrent prostate cancer is still one of the important clinical problems in prostate cancer. A rise in PSA or biochemical recurrence (BCR) is the first sign of recurrent
Summary. 111 Detection and staging of recurrent prostate cancer is still one of the important clinical problems in prostate cancer. A rise in PSA or biochemical recurrence (BCR) is the first sign of recurrent
SIGNPOSTS. Along the Pathway of Prostate Cancer. Understanding Diagnostic Tests and Procedures to Monitor Prostate Cancer
 SIGNPOSTS Along the Pathway of Prostate Cancer Understanding Diagnostic Tests and Procedures to Monitor Prostate Cancer Your journey is unique like you. Signposts along the pathway can show you where you
SIGNPOSTS Along the Pathway of Prostate Cancer Understanding Diagnostic Tests and Procedures to Monitor Prostate Cancer Your journey is unique like you. Signposts along the pathway can show you where you
Prostate Cancer Management and Referral Guidance
 Prostate Cancer Management and Referral Guidance The Prostate Cancer Management and Referral Guidance has been developed to help primary care health professionals manage men with symptoms suggestive of
Prostate Cancer Management and Referral Guidance The Prostate Cancer Management and Referral Guidance has been developed to help primary care health professionals manage men with symptoms suggestive of
For further information on screening and early detection of prostate cancer, see the Section entitled Screening for Prostate Cancer.
 Prostate Cancer For many older men, prostate cancer may be present but never cause symptoms or problems and many men will die with their prostate cancer rather than of their prostate cancer. Yet it remains
Prostate Cancer For many older men, prostate cancer may be present but never cause symptoms or problems and many men will die with their prostate cancer rather than of their prostate cancer. Yet it remains
A New Biomarker in Prostate Cancer Care: Oncotype Dx. David M Albala, MD Chief of Urology Crouse Hospital Syracuse, NY
 A New Biomarker in Prostate Cancer Care: Oncotype Dx David M Albala, MD Chief of Urology Crouse Hospital Syracuse, NY Learning Objectives Review the current challenges in the prediction and prognosis of
A New Biomarker in Prostate Cancer Care: Oncotype Dx David M Albala, MD Chief of Urology Crouse Hospital Syracuse, NY Learning Objectives Review the current challenges in the prediction and prognosis of
Analysis of Prostate Cancer at Easter Connecticut Health Network Using Cancer Registry Data
 The 2014 Cancer Program Annual Public Reporting of Outcomes/Annual Site Analysis Statistical Data from 2013 More than 70 percent of all newly diagnosed cancer patients are treated in the more than 1,500
The 2014 Cancer Program Annual Public Reporting of Outcomes/Annual Site Analysis Statistical Data from 2013 More than 70 percent of all newly diagnosed cancer patients are treated in the more than 1,500
These rare variants often act aggressively and may respond differently to therapy than the more common prostate adenocarcinoma.
 Prostate Cancer OVERVIEW Prostate cancer is the second most common cancer diagnosed among American men, accounting for nearly 200,000 new cancer cases in the United States each year. Greater than 65% of
Prostate Cancer OVERVIEW Prostate cancer is the second most common cancer diagnosed among American men, accounting for nearly 200,000 new cancer cases in the United States each year. Greater than 65% of
Science Highlights. To PSA or not to PSA: That is the Question.
 Science Highlights June 2012 by Ann A. Kiessling, PhD at the To PSA or not to PSA: That is the Question. The current raucous debate over the commonly used PSA blood test to screen for prostate cancer,
Science Highlights June 2012 by Ann A. Kiessling, PhD at the To PSA or not to PSA: That is the Question. The current raucous debate over the commonly used PSA blood test to screen for prostate cancer,
CONTENTS: WHAT S IN THIS BOOKLET
 Q Questions & A & Answers About Your Prostate Having a biopsy test to find out if you may have prostate cancer can bring up a lot of questions. This booklet will help answer those questions. CONTENTS:
Q Questions & A & Answers About Your Prostate Having a biopsy test to find out if you may have prostate cancer can bring up a lot of questions. This booklet will help answer those questions. CONTENTS:
Controversites: Screening for Prostate Cancer in Older Adults
 Controversites: Screening for Prostate Cancer in Older Adults William Dale, MD, PhD University of Chicago Sections of Geriatrics & Palliative Medicine and Hematology/Oncology Director, Specialized Oncology
Controversites: Screening for Prostate Cancer in Older Adults William Dale, MD, PhD University of Chicago Sections of Geriatrics & Palliative Medicine and Hematology/Oncology Director, Specialized Oncology
Cancer research in the Midland Region the prostate and bowel cancer projects
 Cancer research in the Midland Region the prostate and bowel cancer projects Ross Lawrenson Waikato Clinical School University of Auckland MoH/HRC Cancer Research agenda Lung cancer Palliative care Prostate
Cancer research in the Midland Region the prostate and bowel cancer projects Ross Lawrenson Waikato Clinical School University of Auckland MoH/HRC Cancer Research agenda Lung cancer Palliative care Prostate
Gleason Score. Oncotype DX GPS. identified for. about surveillance. time to get sophisticated
 patient: MARK SMITH PSA 6.2 Gleason Score 6 Oncotype DX GPS 8 identified for active surveillance time to get sophisticated about surveillance Accurate prediction of prostate cancer risk is needed at the
patient: MARK SMITH PSA 6.2 Gleason Score 6 Oncotype DX GPS 8 identified for active surveillance time to get sophisticated about surveillance Accurate prediction of prostate cancer risk is needed at the
Tumour Markers. What are Tumour Markers? How Are Tumour Markers Used?
 Dr. Anthony C.H. YING What are? Tumour markers are substances that can be found in the body when cancer is present. They are usually found in the blood or urine. They can be products of cancer cells or
Dr. Anthony C.H. YING What are? Tumour markers are substances that can be found in the body when cancer is present. They are usually found in the blood or urine. They can be products of cancer cells or
PROSTATE CANCER 101 WHAT IS PROSTATE CANCER?
 PROSTATE CANCER 101 WHAT IS PROSTATE CANCER? Prostate cancer is cancer that begins in the prostate. The prostate is a walnut-shaped gland in the male reproductive system located below the bladder and in
PROSTATE CANCER 101 WHAT IS PROSTATE CANCER? Prostate cancer is cancer that begins in the prostate. The prostate is a walnut-shaped gland in the male reproductive system located below the bladder and in
Prostate cancer Multidisciplinary approach: a key to success
 Critical Reviews in Oncology/Hematology 68S (2008) S32 S36 Prostate cancer Multidisciplinary approach: a key to success C. Montagut, J. Albanell, J. Bellmunt Medical Oncology Service, Hospital del Mar
Critical Reviews in Oncology/Hematology 68S (2008) S32 S36 Prostate cancer Multidisciplinary approach: a key to success C. Montagut, J. Albanell, J. Bellmunt Medical Oncology Service, Hospital del Mar
Bard: Prostate Cancer Treatment. Bard: Pelvic Organ Prolapse. Prostate Cancer. An overview of. Treatment. Prolapse. Information and Answers
 Bard: Prostate Cancer Treatment Bard: Pelvic Organ Prolapse Prostate Cancer An overview of Pelvic Treatment Organ Prolapse Information and Answers A Brief Overview Prostate Anatomy The prostate gland,
Bard: Prostate Cancer Treatment Bard: Pelvic Organ Prolapse Prostate Cancer An overview of Pelvic Treatment Organ Prolapse Information and Answers A Brief Overview Prostate Anatomy The prostate gland,
Understanding the PSA test. A guide for men concerned about prostate cancer
 Understanding the PSA test A guide for men concerned about prostate cancer Introduction This booklet is for men who want to know more about having a blood test, called a PSA test, that can help diagnose
Understanding the PSA test A guide for men concerned about prostate cancer Introduction This booklet is for men who want to know more about having a blood test, called a PSA test, that can help diagnose
Saturation Biopsy vs. 3D Spatial Biopsy vs. Free Hand Ultrasound biopsy for Targeted Prostate Cancer Therapies
 Saturation Biopsy vs. 3D Spatial Biopsy vs. Free Hand Ultrasound biopsy for Targeted Prostate Cancer Therapies John F. Ward, MD Assistant Professor University of Texas M. D. Anderson Cancer Center Ablation
Saturation Biopsy vs. 3D Spatial Biopsy vs. Free Hand Ultrasound biopsy for Targeted Prostate Cancer Therapies John F. Ward, MD Assistant Professor University of Texas M. D. Anderson Cancer Center Ablation
Examples of good screening tests include: mammography for breast cancer screening and Pap smears for cervical cancer screening.
 CANCER SCREENING Dr. Tracy Sexton (updated July 2010) What is screening? Screening is the identification of asymptomatic disease or risk factors by history taking, physical examination, laboratory tests
CANCER SCREENING Dr. Tracy Sexton (updated July 2010) What is screening? Screening is the identification of asymptomatic disease or risk factors by history taking, physical examination, laboratory tests
MODULE 8: PROSTATE CANCER: SCREENING & MANAGEMENT
 MODULE 8: PROSTATE CANCER: SCREENING & MANAGEMENT KEYWORDS: Prostate cancer, PSA, Screening, Radical Prostatectomy LEARNING OBJECTIVES At the end of this clerkship, the medical student will be able to:
MODULE 8: PROSTATE CANCER: SCREENING & MANAGEMENT KEYWORDS: Prostate cancer, PSA, Screening, Radical Prostatectomy LEARNING OBJECTIVES At the end of this clerkship, the medical student will be able to:
Medical Tests for Prostate Problems
 Medical Tests for Prostate Problems National Kidney and Urologic Diseases Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH What is the prostate? The
Medical Tests for Prostate Problems National Kidney and Urologic Diseases Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH What is the prostate? The
Prostate cancer screening: clinical applications and challenges
 Urologic Oncology: Seminars and Original Investigations 22 (2004) 353 357 Seminar article Prostate cancer screening: clinical applications and challenges Otis W. Brawley, M.D.* Winship Cancer Institute,
Urologic Oncology: Seminars and Original Investigations 22 (2004) 353 357 Seminar article Prostate cancer screening: clinical applications and challenges Otis W. Brawley, M.D.* Winship Cancer Institute,
What is the goal after hormone therapy: PSA or testosterone? 삼성서울병원 서성일
 What is the goal after hormone therapy: PSA or testosterone? 삼성서울병원 서성일 Huggins & Hodges s study in the 1940s. Testosterone (T) became as a key therapeutic target, and ADT to lower serum T remains standard
What is the goal after hormone therapy: PSA or testosterone? 삼성서울병원 서성일 Huggins & Hodges s study in the 1940s. Testosterone (T) became as a key therapeutic target, and ADT to lower serum T remains standard
Adjuvant radiation therapy for recurrent PSA after radical prostatectomy in T1±T2 prostate cancer
 Adjuvant radiation therapy for recurrent after radical prostatectomy in T1±T2 prostate cancer Prostate Cancer and Prostatic Diseases (1998) 1, 321±325 ß 1998 Stockton Press All rights reserved 1365±7852/98
Adjuvant radiation therapy for recurrent after radical prostatectomy in T1±T2 prostate cancer Prostate Cancer and Prostatic Diseases (1998) 1, 321±325 ß 1998 Stockton Press All rights reserved 1365±7852/98
Prostate Cancer 2014
 Prostate Cancer 2014 Eric A. Klein, M.D. Chairman Glickman Urological and Kidney Institute Professor of Surgery Cleveland Clinic Lerner College of Medicine Incidence rates, US Men Mortality Rates, US Men
Prostate Cancer 2014 Eric A. Klein, M.D. Chairman Glickman Urological and Kidney Institute Professor of Surgery Cleveland Clinic Lerner College of Medicine Incidence rates, US Men Mortality Rates, US Men
PEER REVIEW HISTORY ARTICLE DETAILS TITLE (PROVISIONAL)
 PEER REVIEW HISTORY BMJ Open publishes all reviews undertaken for accepted manuscripts. Reviewers are asked to complete a checklist review form (http://bmjopen.bmj.com/site/about/resources/checklist.pdf)
PEER REVIEW HISTORY BMJ Open publishes all reviews undertaken for accepted manuscripts. Reviewers are asked to complete a checklist review form (http://bmjopen.bmj.com/site/about/resources/checklist.pdf)
