Treatment of psoriatic arthritis and psoriasis vulgaris with the tumor necrosis factor inhibitor infliximab
|
|
|
- Lydia Bennett
- 8 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Rheumatol Int (2002) 22: DOI /s ORIGINAL ARTICLE Edmund Cauza Æ Marita Spak Æ Karla Cauza Ursula Hanusch-Enserer Æ Attila Dunky Æ Ernst Wagner Treatment of psoriatic arthritis and psoriasis vulgaris with the tumor necrosis factor inhibitor infliximab Received: 2 February 2002 / Accepted: 14 August 2002 / Published online: 4 September 2002 Ó Springer-Verlag 2002 Abstract Objective The aim was to evaluate the efficacy and safety of multiple infusions with achimeric, antitumor necrosis factor (TNF)a monoclonal antibody (infliximab) in patients with psoriatic arthritis (PsA) and psoriasis vulgaris. Methods Over 22 weeks, nine patients with both active psoriasis and PsA received five infusions of 3 mg/kg infliximab. The endpoints included changes in the swollen and tender joints counts, American College of Rheumatology (ACR) preliminary criteria for improvement response rates 20, 50, and 70, and improvement in the psoriasis area and severity index (PASI). Results The swollen count (SJC) and tender joint count (TJC) fell from means of 5.33±2.22 and 17.80±4.21 to 1.44±1.09 and 9.77±0.92, respectively, by week 2 (P=0.02, P=0.02). This benefit was sustained through week 22 (2.00±1.12/7.77±3.68, P=0.05/ P=0.002). The ACR 20/50/70 response was achieved in 89%/56%/22% of cases. The mean PASI score improved from 19.04±5.41 to 4.91±2.51 (P=0.002). Conclusion Multiple infusions of infliximab were effective and well tolerated in patients with active psoriasis and PsA. Keywords Infliximab Æ Psoriatic arthritis Æ Psoriasis vulgaris Æ Tumor necrosis factor E. Cauza (&) Æ M. Spak Æ U. Hanusch-Enserer A. Dunky Æ E. Wagner Department of Internal Medicine V, Department of Rheumatology, Wilhelminenspital, Montleartstrasse 37, 1160 Vienna, Austria edmund.cauza@akh-wien.ac.at Tel.: Fax: K. Cauza Department of Dermatology, University of Vienna, Vienna, Austria Introduction A new era in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) started with the development of anti-tumor necrosis factor a (TNFa) agents. This TNFa is a key cytokine in the activation of the inflammatory cascade within the rheumatoid synovium and is therefore a useful target for specific biological therapy in RA [1, 2, 3]. Dramatic and sustained responses following administration of TNFablocking agents have been reported in RA [4, 5]. Infliximab is a human-mouse chimeric monoclonal antibody that binds and inhibits the activity of TNFa [6]. It has proven efficacious in patients with RA who are unresponsive to conventional disease-modifying antirheumatic drug (DMARD) therapy [7]. Intravenous infliximab administration has been shown to reduce expression of interleukins, chemokines, and adhesion molecules in patients with RA [8] and produced sustained clinical response by ACR response criteria in 45 80% of patients with treatment-resistant, active RA [4, 5, 9, 10]. Psoriatic arthritis (PsA) is one of the spondylarthropathy group of inflammatory joint diseases in which a somewhat different set of genetic factors, trauma, and infections may play a role. Recent studies demonstrate that the disease may be as severe as RA [11, 12]. Conventional antirheumatic DMARDs and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) serve as a first line of therapy for controlling inflammation [13], however, DMARD therapy alone or in combination with NSA- IDs sometimes fails [14, 15] or is associated with toxicity and intolerance [16, 17, 18]. To date, only limited experience on the treatment of psoriasis and PsA with anti- TNFa agents exists. Dechant [19] observed dramatic responses in clinical activity evaluation of patients with severe PsA after treatment with infliximab, and three out of ten were able to discontinue therapy due to remission of the disease. Furthermore, in a pilot study, van den Bosch treated patients suffering from different types of spondylarthropathies, including PsA, with infliximab
2 228 and observed a marked decrease in the activity of arthritis and skin involvement (assessed by the psoriasis area severity index, or PASI, score), as early as 2 weeks after treatment initiation [20]. Ogilvie [21] observed a rapid clearing of psoriatic skin lesions resistant to methotrexate after anti-tnfa treatment of patients with PsA. The first open trials of anti-tnfa agents in patients with spondylarthropathies including PsA give rise to justified hopes in the treatment of otherwise resistant forms [22, 23, 24, 25]. Etanercept, another anti-tnfa agent that has been successful in the treatment of resistant RA, was studied in a placebo-controlled trial in 60 patients with PsA for 6 months [26]. It proved efficacious in ameliorating arthritic signs and symptoms as well as skin lesions. The role of TNFa in psoriatic lesions and in the synovium of joints in patients with PsA has been described by several authors [27, 28, 29, 30]. In this study, the objective was to assess the effects of long-term administration of infliximab, a TNFa-blocking agent, in patients with active psoriasis and PsA. Materials and methods Study design and patients Over a period of 22 weeks, nine consecutive patients (five men, four women, mean age 57.3 years, mean duration of PsA and psoriasis 17.2 years and 18.1 years, respectively) who had both active psoriasis and PsA were included in this study. Six patients (66%) had failed standard DMARD therapy including methotrexate, other cytotoxic drugs, retinoids, and psoralen-ultraviolet A irradiation (PUVA). All patients with PsA fulfilled the currently accepted criteria for psoriatic arthritis [12, 31]. Rheumatologists of our division diagnosed PsA, and one or more dermatologists additionally examined each individual. To minimize interobserver variation, the same persons assessed each patient s disease activity throughout the study. The percent change from baseline to week 22 in SJC and TJC was the primary measure of efficacy for PsA. Another primary endpoint for the assessment of psoriatic arthritis was the proportion of patients meeting the American College of Rheumatology (ACR) preliminary criteria for improvement (score of 20) designed for assessment of RA [32] at week 22. This definition requires that the patient improve by at least 20% in both tender and swollen counts and also by at least 20% in three of five other core set parameters (patient global assessment, physician global assessment, self-reported physical disability, acute phase reactant, and patient pain assessment). The scores ACR 50 and ACR 70 were also assessed (defined in a similar manner as ACR 20, but the patient must have improved at least 50% or 70% in the individual measures). The coprimary endpoint was the change in psoriatic plaques of the skin as assessed by the PASI. Methods Treatment-resistant patients with active disease who fulfilled the diagnostic criteria received infusions of 3 mg/kg infliximab at weeks 0, 2, 6, 14, and 22. At baseline and weeks 2, 6, 14, and 22, the following variables were evaluated: patient assessment of pain using the 100-mm visual analog scale (VAS), duration of morning stiffness (MGST), erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR), and C-reactive protein (CRP) count. All blood samples were collected in the morning. For ESR, the Westergren method was used (normal range 0 10 mm/h). C-reactive protein was determined by nephelometry (normal level 0 12mg/l). Evaluation of the duration of MGST (in min) was made by the patients, and SJC (0 66) and TJC (0 68) were assessed by a rheumatologist. All patients had plaque-type psoriasis and had not been treated topically or systemically for at least 1 month before enrollment. The evaluation of psoriasis activity included the PASI [33]. Statistical analysis Paired Student s t-tests were used to evaluate significant differences in all main parameters (PASI, MGST, SJC, TJC, ESR, VAS, and CRP) at baseline and after 2 and 22 weeks. P values below 0.05 were considered statistically significant. All continuous variables are expressed as means ± standard deviation (SD). Results The demographic data of patients before treatment are summarized in Table 1. Eight of the nine patients enrolled completed the study. Only one patient withdrew (after receiving four infusions) due to a mild injection site reaction (erythema plus discomfort) potentially related to anti-tnfa therapy. No side effects were observed in any other patients and no major abnormalities in hematology values were noted during or after the study. Vital signs remained within normal ranges during and 2 h after infusions. Infliximab proved efficacious as judged by all the criteria used. In all patients, the response was rapid: 90% of the patients achieved a 50% or more decrease from baseline in SJC, TJC, and PASI score at the first evaluation point of 2 weeks and all eight patients at the 6-week evaluation point. Thereafter, following a small increase in TJC and PASI, total response rates were sustained up to the 22-week endpoint at levels of 50 70% improvement in SJC and TJC. All efficacy parameters are summarized in Table 2. One patient was maintained on infliximab for the duration of 1 year (given an infusion every 8 weeks from week 22). In this patient, all significant improvements in clinical and laboratory parameters were sustained throughout the entire treatment period. Efficacy of infliximab in psoriasis Evaluation of skin lesions as judged by objective criteria (PASI) demonstrates a significant response to infliximab therapy. The mean index of all patients was 19.04±5.41 (range ) at baseline. After a single infusion with infliximab, the index decreased significantly to 7.41±2.51 (range ) at week 2 (P=0.007). At study end (week 22), the mean PASI value had further Table 1. Demographics of all patients receiving infliximab N patients 9 Male/female 5/4 Mean age (years) 57 (range 46 76) Duration of psoriasis (years) 18.1 Duration of arthritis (years) 17.2
3 229 Table 2. Values (mean±sd) of the main parameters in the nine patients before treatment (T0), after 2 weeks (T2), after 6 weeks (T6), after 14 weeks (T14), and after 22 weeks (T22) and statistical significance (P values) as determined by paired Student s t-test of the change from baseline (P<0.05). PASI psoriasis area and severity index, MGST morning stiffness in min, SJC swollen joint count 0 66, TJC tender joint count 0 68, CRP C-reactive protein <10 mg/l, ESR erythrocyte sedimentation rate <10 mm/h, VAS visual analog scale pain assessment 0 10 cm T0 T2 T6 T14 T22 P value PASI 19.04± ± ± ± ± MGST 52.77± ± ± ± ± SJC. 5.33± ± ± ± ± TJC 17.8± ± ± ± ± CRP 16.04± ± ± ± ± ESR 34.44± ± ± ± ± VAS 5.88± ± ± ± ± decreased to 4.91±2.51 (range ) and remained significantly lower than baseline (P=0.002) (Fig. 1). Improvements in joints Mean joint activity at baseline for all patients was 18 tender joints and five swollen joints. The results show that infliximab therapy has a favorable effect on articular signs directly after the first infusion. The joint activity after 2 weeks of treatment reduced to ten tender joints (P=0.02) and one swollen joint (P=0.02) and was maintained up to week 22 for eight tender (P=0.002) and two swollen joints (P=0.05)). In addition, 6/9 patients (67%) at 2 weeks and 5/9 (56%) at 22 weeks had no swollen joints, while 2/9 (22%) at 2 weeks and 3/9 (33%) at 22 weeks had no tender joints (Fig. 2). after five infusions: mean CRP dropped to 3.53±1.00 (P=0.04) and mean ESR decreased to 11.55±3.86 (P=0.01) (Fig. 3). Response of visual analog scale and morning stiffness Consistent with the previous clinical parameters (SJC and TJC), significant improvements in MGST and VAS values were observed after 22 weeks of therapy: MGST changed from a mean of 52.77±17.0 at baseline to 24.44±11.06 at the end of the study (P=0.01), while VAS improved from a mean 5.88±0.63 at baseline to 3.33±0.66 at week 22 (P=0.01) (Fig. 4, Fig. 5). Effect of infliximab on ESR and CRP The patients presented with slightly increased CRP levels (16.04±5.43) and elevated ESR (34.44±6.34) at the beginning of the study. There was a significant correlation between drops in CRP and ESR levels over the duration of therapy with infliximab. Two weeks after the first infusion, the mean CRP value dropped to 7.8±4.09 (P=0.024), while mean ESR decreased to 14.66±3.96 (P=0.01). Similar results were achieved at the study end Fig. 2. Effects on the mean SJC (dotted line) and mean TJC before, during, and after 22 weeks of infliximab treatment Fig. 1. Effect of infliximab on skin lesions. Mean PASI Fig. 3. Measurement of mean CRP (dotted line) and ESR before, during, and after 22 weeks of treatment with infliximab
4 230 Fig. 4. Effect of infliximab on mean MGST (in min) before and after treatment Fig. 5. Values for the patients assessments of pain on the mean VAS before, during, and after treatment Improvements in ACR 20, 50, and 70 from baseline to week 22 The results at 22 weeks demonstrated big improvements in the ACR response rate, and in eight patients (89%), ACR 20 was achieved. The percentage of patients at the ACR 50 levels who improved was 56% (five patients), and this dropped to 22% (two patients) using the ACR 70 definition. Discussion The hypothesis that TNFa inhibition could result in efficacious treatment of PsA was generated after several studies reporting increased expression of monocyte-derived cytokines (including TNFa) in synovial fluid (SF) and synovial tissue (ST) of patients with PsA. Histologic studies [34] on multiple biopsy samples obtained from patients with PsA found infiltration of T cells and macrophages and increased vascularity in ST. The same authors demonstrated the presence of the cytokines TNF-a, IL-1b, IL-1a, IL-10, and IL-15 in ST. In addition, the expression of the p65 subunit of the transcription factor nuclear factor jb was localized and immunohistochemically quantified in ST. In 1998, Ritchlin [29] observed the release of elevated levels of the cytokines IL-1b, IL-2, IL-10, IFN-c, and TNF-a in supernatants from synovial and dermal explant cultures, while Nishibu [35] later described an increased production of proinflammatory cytokines, namely IL-1b, IL-6, and IL-8, by freshly isolated peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Similarly, Elkayam [36] found higher serum levels of the cytokines IL-10, IL-6, IL-1ra, and sil-2r than in healthy volunteers. Interestingly, sil-2r correlated with PASI score but not with clinical parameters of joint severity, while IL-1ra correlated with the numbers of tender and swollen joints. Furthermore, Partsch [27] found increased levels of TNF-a, IL-1, IL-6, and IL-8 in SF of patients with PsA. Lastly, inflammatory markers, namely the soluble TNF receptors p55 and p75 as well as sil-2r, are increased in SF of patients with PsA [37]. All these findings support the assumption that, similar to RA, macrophage-derived cytokines drive joint inflammation and cutaneous lesions of PsA. Like RA, PsA is suspected to be an immunologically mediated disease, in that several immunogenetic studies link PsA to certain HLA class I and class II types. Familial clustering confirms the genetic background of PsA [38]. Although the question of whether PsA is an antigendriven disease remains to be answered, substantial insight into the pathophysiologic process of the disease was achieved recently. T lymphocytes and increased vascularity are predominant in synovial tissue of individuals affected by PsA, and T lymphocytes have been identified to be important for T cell extravasation in the skin [39]. Summarizing the immunological findings, it has been confirmed that several proinflammatory cytokines are locally and systemically upregulated in psoriasis and PsA and that TNFa plays a major role. This resembles exactly the situation in RA. These findings gave rise to the application of a novel, therapeutic modality, namely anti-tnfa agents, in the treatment of PsA. Few publications have highlighted the effects of anti- TNFa treatment in PsA. Mease [26] reported dramatic effects on joint symptoms and PASI score in a double blind study of etanercept in PsA. Dechant [19] found remission-inducing properties of infliximab in patients with PsA, and Bosch [20] treated patients with various spondylarthropathies including PsA with a loading dose of infliximab and arrived at similar results, reductions in the number of active joints and PASI scores. Clearing of psoriatic lesions by infliximab was observed by Ogilvie [21] and Oh [40]. Therefore infliximab was employed, a chimeric monoclonal antibody to TNFa proven to be efficacious in active and fistulizing Crohn s disease [41] and RA [1]. Therapy with infliximab produced significant improvements in all measures of articular disease activity. The swollen joint count decreased in five out of six patients with swollen joints at the start of the observation period. This improvement was apparent by the end of
5 231 week 2 and most pronounced at the end of treatment (at 22 weeks). Infliximab not only proved effective in treatment of the signs and symptoms of PsA but also in diminishing psoriatic skin lesions. All treated patients experienced significant decreases in PASI scores. The therapeutic method used in our study was identical to the treatment dosage and time schedule approved for RA. Duration of treatment was originally scheduled for 22 weeks, with extension beyond this time in case of good response. Five patients have now been treated for 1 year and included in the results. Overall, five patients remaining on infliximab were successfully treated over 1 year, with no cutaneous flare reported. Here we report the interim data of a treatment period of 22 weeks. Our objective is to assess the effect of long-term treatment with infliximab. At present we do not consider discontinuation of treatment or a change in treatment regimen (dosage and administration intervals), even for patients with very good response, also taking into consideration that one patient on maintenance treatment for 1 year has sustained remission. Our observations concerning articular disease activity and cutaneous involvement confirm those reported by van den Bosch [20] and Dechant [19], who reported 3/9 patients to be in remission after 5, 7, and 8 months of treatment, respectively, leading to discontinuation of treatment with infliximab. The clinical response of the arthritic component to infliximab occurred within 2 weeks from treatment start, reaching a maximum level of improvement at week 6 and remaining stable through week 22. This trial showed that infliximab provides a clinically high benefit to patients with PsA. Of infliximab patients, nearly 90% achieved ACR 20, more than 50% ACR 50, and 22% ACR 70 response rates after week 22. These findings were superior to the beneficial effects found by Mease et al. using etanercept in the treatment of PsA [26]. Our results in joint counts are similar to those observed in RA, suggesting similar pathogenetic mechanisms. Both cutaneous and articular remissions imply a substantial involvement of TNFa in the pathogenesis of skin lesions and articular inflammation in psoriasis. The response to infliximab was not dependent on concomitant treatment with a DMARD. Patients who had stopped DMARD treatment due to intolerable side effects or inefficacy more than 3 months before starting infliximab responded to monotherapy with infliximab. Cutaneous lesions healed in eight patients, whereby remission occurred rapidly and led to a nearly complete normalization of the skin in all but one case. An interesting finding was the cutaneous flare of one patient after 22 weeks of continuous treatment and following a viral infection that occurred in the early autumn, perhaps seasonally triggered. The recurrence was presented by an exanthematous-type psoriasis. This incidence points toward the necessity of carefully controlled, regular clinical investigations in psoriasis patients treated with infliximab. Since TNFa is found in SF of PsA as well as in cutaneous lesions of psoriasis patients, the hypothesis that an anti-tnfa agent would ameliorate the signs and symptoms of both psoriasis and PsA has been proposed. The results of our observational trial verified this concept and indicated that infliximab may be the treatment of choice in moderate-to-severe, treatment-resistant PsA. However, larger, controlled studies are needed for establishing the treatment of PsA with infliximab. Finally, these results may additionally support the idea of a pathogenetic link between skin and joint in psoriatic patients with arthritis, since the clinical manifestations of both diseases were effectively controlled with infliximab therapy. References 1. Elliott MJ, Maini RN, Feldmann M, Long-Fox A, Charles P, Katsikis P, Brennan FM, Walker J, Bijl H, Ghrayeb J (1993) Treatment of rheumatoid arthritis with chimeric monoclonal antibodies to tumor necrosis factor a. Arthritis Rheum 36: Feldmann M, Brennan FM, Maini RN (1996) Role of cytokines in rheumatoid arthritis. Annu Rev Immunol 14: Szekanecz Z, Koch AE, Kunkel SL, Strieter RM (1998) Cytokines in rheumatoid arthritis: potential targets for pharmacological intervention. Drugs Aging 12: Maini R, St Clair EW, Breedveld F, Furst D, Kalden J, Weisman M, Smolen J, Emery P, Harriman G, Feldmann M, Lipsky P (1999) Infliximab (chimeric anti-tumour necrosis factor alpha monoclonal antibody) versus placebo in rheumatoid arthritis patients receiving concomitant methotrexate: a randomized phase III trial. ATTRACT Study Group. Lancet 354: Lipsky PE, van der Heijde DM, St Clair EW, Furst DE, Breedveld FC, Kalden JR, Smolen JS, Weisman M, Emery P, Feldmann M, Harriman GR, Maini RN (2000) Infliximab and methotrexate in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Anti-Tumor Necrosis Factor Trial in Rheumatoid Arthritis with Concomitant Therapy Study Group. N Engl J Med 343: Scallon BJ, Moore MA, Trinh H, Knight DM, Ghrayeb J (1995) Chimeric anti-tnf a monoclonal antibody ca2 binds recombinant transmembrane TNFa and activates immune effector functions. Cytokine 7: Maini RN, Breedveld FC, Kalden JR, Smolen JS, Davis D, Macfarlane JD, Antoni C, Leeb B, Elliott MJ, Woody JN, Schaible TF, Feldmann M (1998) Therapeutic efficacy of multiple intravenous infusions of anti-tumor necrosis factor (alpha) monoclonal antibody combined with low-dose weekly methotrexate in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 41: Lorenz HM, Antoni C, Valerius T, Repp R, Grunke M, Schwerdtner N, Nusslein H, Woody J, Kalden JR, Manger B (1996) In vivo blockade of TNFa by iv infusion of a chimeric monoclonal TNFa antibody in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: short term cellular and molecular effects. J Immunol 156: Elliott MJ, Maini RN, Feldmann M, Kalden JR, Antoni C, Smolen JS, Leeb B, Breedveld FC, Macfarlane JD, Bijl H (1994) Randomised double blind comparison of chimeric monoclonal antibody to tumour necrosis factor-a (ca2) versus placebo in rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet 344: Elliott MJ, Maini RN, Feldmann M, Long-Fox A, Charles P, Bijl H, Woody JN (1994) Repeated therapy with monoclonal antibody to tumour necrosis factor-a (ca2) in a patient with rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet 344:
6 Gladmann DD (1994) Natural history of psoriatic arthritis. In: Wright V, Helliwell P (eds) Psoriatic arthritis. Bailliere s clinical rheumatology international practice and research, vol 8. Bailliere Tindall, London, p Gladman DD, Shuckett R, Russell ML, Thorne JC, Schachter RK (1987) Psoriatic arthritis analysis of 220 patients. QJM 62: Gomez-Vaquero C, Rodriguez-Moreno J, Ros S, Marcos R, Fiter J, Roig-Escofet D (1996) Termination of disease-modifying drugs in psoriatic arthritis: study of 109 courses of treatment. Br J Rheumatol 35: Abu-Shakra M, Gladman DD, Thorne JC, Long J, Gough J, Farewell VT (1995) Long term methotrexate therapy in psoriatic arthritis. Clinical and radiologic outcome. J Rheumatol 22: Wolfe F, Cathey MA (1991) The assessment and prediction of functional disability in rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol 18: Wolfe F, Hawley DJ, Cathey MA (1990) Termination of slow acting antirheumatic therapy in rheumatoid arthritis: a 14-year prospective evaluation of 1017 consecutive starts. J Rheumatol 17: Morand EF, McCloud PI, Littlejohn GO (1992) Life table analysis of 879 treatment episodes with slow acting antirheumatic drugs in community rheumatology practice. J Rheumatol 19: McKendry RJR, Dale P (1993) Adverse effects of low dose methotrexate therapy in rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol 20: Dechant C, Antoni C, Wendler J (2000) One year outcome of patients with severe psoriatic arthritis treated with infliximab. Arthritis Rheum 43[Suppl]: Van den Bosch F, Kruithof E, Baeten D, De Keyser F, Mielants H, Veys EM (2000) Effects of a loading dose regimen of three infusions of chimeric monoclonal antibody to tumour necrosis factor alpha (infliximab) in spondyloarthropathy: an open pilot study. Ann Rheum Dis 59: Ogilvie AL, Antoni C, Dechant C, Manger B, Kalden JR, Schuler G, Luftl M (2001) Treatment of psoriatic arthritis with anti tumour necrosis factor-alpha antibody clears skin lesions of psoriasis resistant to treatment with methotrexate. Br J Dermatol 144: Braun J, Sieper J (2000) Anti-TNF alpha: a new dimension in the pharmacotherapy of the spondylarthropathies? Ann Rheum Dis 59: Braun J, de Keyser F, Brandt J, Mielants H, Sieper J, Veys E (2001) New treatment options in spondyloarthropathies: increasing evidence for significant efficacy of anti-tumor necrosis factor therapy. Curr Opin Rheumatol 13: Zabraniecki L, Fournie B (2001) TNF alpha inhibition in psoriatic arthritis: cause for hope. Joint Bone Spine 68: De Keyser FD, Mielants H, Veys EM (2001) Current use of biologicals for the treatment of spondyloarthropathies. Expert Opin Pharmacother 2: Mease PJ, Goffe BS, Metz J, Vanderstoep A, Finck B, Burge DJ (2000) Etanercept in the treatment of psoriatic arthritis and psoriasis: a randomised trial. Lancet 356: Partsch G, Steiner G, Leeb BF, Dunky A, Bro ll H, Smolen JS (1997) Highly increased levels of tumor necrosis factor a and other proinflammatory cytokines in psoriatic arthritis synovial fluid. J Rheumatol 24: Ackermann L, Harvima IT (1998) Mast cells of psoriatic and atopic dermatitis skin are positive for TNFa and their degranulation is associated with expression of ICAM1 in the epidermis. Arch Derm Res 290: Ritchlin C, Haas-Smith SA, Hicks D, Cappuccio J, Osterland CK, Looney RJ (1998) Patterns of cytokine production in psoriatic synovium. J Rheumatol 25: Ettehadi P, Greaves MW, Wallach D, Aderka D, Camp RDR (1994) Elevated tumor necrosis factor alpha and biological activity in psoriatic skin lesions. Clin Exp Immun 96: Gladman D, Farewell VT, Nadeau C (1995) Clinical indicators of progression in psoriatic arthritis: multivariate relative risk model. J Rheumatol 22: Felson D, Anderson J, Lange M, Wells G, Lavalley M (1998) Should improvement in rheumatoid arthritis clinical trails be defined as fifty percent or seventy percent improvement in core set measures, rather than twenty percent? Arthritis Rheum 41: Christophers E, Sterry W (1993) Psoriasis. In: Fitzpatrick TB, Eisen AZ, Wolff K, Freedberg IM, Austen KF (eds) Dermatology in general medicine. McGraw-Hill, New York, pp Danning CL, Illei GG, Hitchon C, Greer MR, Boumpas DT, McInnes IB (2000) Macrophage-derived cytokine and nuclear factor jb p65 expression in synovial membrane and skin of patients with psoriatic arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 43: Nishibu A, Han GW, Iwatsuki K, Matsui T, Inoue M, Akiba H, Kaneko R, Kaneko F (1999) Overexpression of monocytederived cytokines in active psoriasis: a relation to coexistent arthropathy. J Dermatol Sci 21: Elkayam O, Yaro I, Shirazi I, Yaron M, Caspi D (2000) Serum levels of IL-10, IL-6, IL-1ra, and sil-2r in patients with psoriatic arthritis. Rheumatol Int 19: Partsch G, Wagner E, Leeb BF, Dunky A, Steiner G, Smolen J (1998) Upregulation of cytokine receptors TNF-R55, stnf- R75, and sil-2r in psoriatic arthritis synovial fluid. J Rheumatol 25: Moll JMH, Wright V (1973) Familial occurrence of psoriatic arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 32: Pitzalis C, Pipitone N (2000) Psoriatic arthritis. J R Soc Med 93: Oh CJ, Das KM, Gottlieb AB (2000) Treatment with antitumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-alpha) monoclonal antibody dramatically decreases the clinical activity of psoriasis lesions. J Am Acad Dermatol 42: Van Deventer SJH (1997) Tumor necrosis factor and Crohn s disease. Gut 40:
1. Title 2. Background
 1. Title EARLY PsA Effectiveness of early Adalimumab therapy in psoriatic arthritis patients from Reuma.pt, the Rheumatic Diseases Portuguese Register, Portuguese RheumatoLogy SocietY (SPR) 2. Background
1. Title EARLY PsA Effectiveness of early Adalimumab therapy in psoriatic arthritis patients from Reuma.pt, the Rheumatic Diseases Portuguese Register, Portuguese RheumatoLogy SocietY (SPR) 2. Background
påçííáëü=jéçáåáåéë=`çåëçêíáìã==
 påçííáëü=jéçáåáåéë=`çåëçêíáìã== adalimumab 40mg pre-filled syringe for subcutaneous injection (Humira ) No. (218/05) Abbott New indication: treatment of active and progressive psoriatic arthritis in adults
påçííáëü=jéçáåáåéë=`çåëçêíáìã== adalimumab 40mg pre-filled syringe for subcutaneous injection (Humira ) No. (218/05) Abbott New indication: treatment of active and progressive psoriatic arthritis in adults
BEDFORDSHIRE AND LUTON JOINT PRESCRIBING COMMITTEE (JPC)
 BEDFORDSHIRE AND LUTON JOINT PRESCRIBING COMMITTEE (JPC) September 2014 Review date: September 2017 Bulletin 203: Tocilizumab (subcutaneous) in combination with methotrexate or as monotherapy for the treatment
BEDFORDSHIRE AND LUTON JOINT PRESCRIBING COMMITTEE (JPC) September 2014 Review date: September 2017 Bulletin 203: Tocilizumab (subcutaneous) in combination with methotrexate or as monotherapy for the treatment
ustekinumab 45mg solution for injection in pre-filled syringe (Stelara ) SMC No. (944/14) Janssen-Cilag Ltd
 ustekinumab 45mg solution for injection in pre-filled syringe (Stelara ) SMC No. (944/14) Janssen-Cilag Ltd 07 February 2014 The Scottish Medicines Consortium (SMC) has completed its assessment of the
ustekinumab 45mg solution for injection in pre-filled syringe (Stelara ) SMC No. (944/14) Janssen-Cilag Ltd 07 February 2014 The Scottish Medicines Consortium (SMC) has completed its assessment of the
New Evidence reports on presentations given at EULAR 2012. Rituximab for the Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis
 New Evidence reports on presentations given at EULAR 2012 Rituximab for the Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis Report on EULAR 2012 presentations Long-term safety of rituximab: 10-year follow-up in the
New Evidence reports on presentations given at EULAR 2012 Rituximab for the Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis Report on EULAR 2012 presentations Long-term safety of rituximab: 10-year follow-up in the
Patient Input Information Clinical Trials Outcomes Common Drug Review
 CDEC FINAL RECOMMENDATION USTEKINUMAB (Stelara Janssen Inc.) Indication: Psoriatic Arthritis Recommendation: The Canadian Drug Expert Committee (CDEC) recommends that ustekinumab not be listed at the submitted
CDEC FINAL RECOMMENDATION USTEKINUMAB (Stelara Janssen Inc.) Indication: Psoriatic Arthritis Recommendation: The Canadian Drug Expert Committee (CDEC) recommends that ustekinumab not be listed at the submitted
Biologic Treatments for Rheumatoid Arthritis
 Biologic Treatments Rheumatoid Arthritis (also known as cytokine inhibitors, TNF inhibitors, IL 1 inhibitor, or Biologic Response Modifiers) Description Biologics are new class of drugs that have been
Biologic Treatments Rheumatoid Arthritis (also known as cytokine inhibitors, TNF inhibitors, IL 1 inhibitor, or Biologic Response Modifiers) Description Biologics are new class of drugs that have been
Immune modulation in rheumatology. Geoff McColl University of Melbourne/Australian Rheumatology Association
 Immune modulation in rheumatology Geoff McColl University of Melbourne/Australian Rheumatology Association A traditional start to a presentation on biological agents in rheumatic disease is Plasma cell
Immune modulation in rheumatology Geoff McColl University of Melbourne/Australian Rheumatology Association A traditional start to a presentation on biological agents in rheumatic disease is Plasma cell
A New Era in Rheumatoid Arthritis Treatment
 A New Era in Rheumatoid Arthritis Treatment Jill C. Costello, MD; Paul B. Halverson, MD ABSTRACT Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) is a systemic autoimmune disease that primarily manifests as a chronic symmetric
A New Era in Rheumatoid Arthritis Treatment Jill C. Costello, MD; Paul B. Halverson, MD ABSTRACT Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) is a systemic autoimmune disease that primarily manifests as a chronic symmetric
SYNOPSIS. 2-Year (0.5 DB + 1.5 OL) Addendum to Clinical Study Report
 Name of Sponsor/Company: Bristol-Myers Squibb Name of Finished Product: Abatacept () Name of Active Ingredient: Abatacept () Individual Study Table Referring to the Dossier (For National Authority Use
Name of Sponsor/Company: Bristol-Myers Squibb Name of Finished Product: Abatacept () Name of Active Ingredient: Abatacept () Individual Study Table Referring to the Dossier (For National Authority Use
Etanercept (Enbrel ) in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis with Recent Onset Versus Established Disease: Improvement in Disability
 Etanercept (Enbrel ) in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis with Recent Onset Versus Established Disease: Improvement in Disability SCOTT W. BAUMGARTNER, ROY M. FLEISCHMANN, LARRY W. MORELAND, MICHAEL H.
Etanercept (Enbrel ) in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis with Recent Onset Versus Established Disease: Improvement in Disability SCOTT W. BAUMGARTNER, ROY M. FLEISCHMANN, LARRY W. MORELAND, MICHAEL H.
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE. Health Technology Appraisal
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE Health Technology Appraisal Adalimumab, etanercept, infliximab, rituximab and abatacept for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis after the failure
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE Health Technology Appraisal Adalimumab, etanercept, infliximab, rituximab and abatacept for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis after the failure
DISEASE COURSE IN EARLY RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS: AN OBSERVATIONAL STUDY
 ORIGINAL ARTICLES DISEASE COURSE IN EARLY RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS: AN OBSERVATIONAL STUDY Teodora Serban 1,2, Iulia Satulu 2, Oana Vutcanu 2, Mihaela Milicescu 1,2, Carina Mihai 1,2, Mihai Bojinca 1,2, Victor
ORIGINAL ARTICLES DISEASE COURSE IN EARLY RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS: AN OBSERVATIONAL STUDY Teodora Serban 1,2, Iulia Satulu 2, Oana Vutcanu 2, Mihaela Milicescu 1,2, Carina Mihai 1,2, Mihai Bojinca 1,2, Victor
Efficacy and safety of leflunomide in psoriatic arthritis
 Original Article Efficacy and safety of leflunomide in psoriatic arthritis ATM Asaduzzaman*, Akramullah Sikder*, Md. Mostaque Mahmud**, Harashit Kumar Paul*, Md. Nazrul Islam* *Department of Dermatology
Original Article Efficacy and safety of leflunomide in psoriatic arthritis ATM Asaduzzaman*, Akramullah Sikder*, Md. Mostaque Mahmud**, Harashit Kumar Paul*, Md. Nazrul Islam* *Department of Dermatology
Beyond methotrexate: biologic therapy in rheumatoid arthritis
 from patients with ankylosing spondylitis. Arthritis Rheum 1995;38:499 505. 6 Braun J, Brandt J, Listing J, Zink A et al. Treatment of active ankylosing spondylitis with infliximab: a randomised controlled
from patients with ankylosing spondylitis. Arthritis Rheum 1995;38:499 505. 6 Braun J, Brandt J, Listing J, Zink A et al. Treatment of active ankylosing spondylitis with infliximab: a randomised controlled
MEDICAL ASSISTANCE HANDBOOK PRIOR AUTHORIZATION OF PHARMACEUTICAL SERVICES `I. Requirements for Prior Authorization of Cytokine and CAM Antagonists
 MEDICAL ASSISTANCE HBOOK `I. Requirements for Prior Authorization of Cytokine and CAM Antagonists A. Prescriptions That Require Prior Authorization All prescriptions for Cytokine and CAM Antagonists must
MEDICAL ASSISTANCE HBOOK `I. Requirements for Prior Authorization of Cytokine and CAM Antagonists A. Prescriptions That Require Prior Authorization All prescriptions for Cytokine and CAM Antagonists must
Effect of Methotrexate on Serum Levels of IL-1α and IL-8 in Rheumatoid Arthritis
 THE RHEUMATOID IRAQI POSTGRADUATE ARTHRITIS MEDICAL JOURNAL VOL.12, NO. 3,2013 Effect of Methotrexate on Serum Levels of IL-1α and IL-8 in Rheumatoid Arthritis Ahmed A. Al-Hassan*, Mohammed O. Hamzah**,
THE RHEUMATOID IRAQI POSTGRADUATE ARTHRITIS MEDICAL JOURNAL VOL.12, NO. 3,2013 Effect of Methotrexate on Serum Levels of IL-1α and IL-8 in Rheumatoid Arthritis Ahmed A. Al-Hassan*, Mohammed O. Hamzah**,
COMMITTEE FOR MEDICINAL PRODUCTS FOR HUMAN USE (CHMP) DRAFT
 European Medicines Agency Evaluation of Medicines for Human Use London, 23 June 2005 COMMITTEE FOR MEDICINAL PRODUCTS FOR HUMAN USE (CHMP) DRAFT GUIDELINE ON CLINICAL INVESTIGATION OF MEDICINAL PRODUCTS
European Medicines Agency Evaluation of Medicines for Human Use London, 23 June 2005 COMMITTEE FOR MEDICINAL PRODUCTS FOR HUMAN USE (CHMP) DRAFT GUIDELINE ON CLINICAL INVESTIGATION OF MEDICINAL PRODUCTS
Effectiveness and Drug Adherence in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients on Biologic Monotherapy: A prospective observational study in Southern Sweden
 Effectiveness and Drug Adherence in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients on Biologic Monotherapy: A prospective observational study in Southern Sweden Collaborators: Primary investigators Dr Lars Erik Kristensen,
Effectiveness and Drug Adherence in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients on Biologic Monotherapy: A prospective observational study in Southern Sweden Collaborators: Primary investigators Dr Lars Erik Kristensen,
The Most Common Autoimmune Disease: Rheumatoid Arthritis. Bonita S. Libman, M.D.
 The Most Common Autoimmune Disease: Rheumatoid Arthritis Bonita S. Libman, M.D. Disclosures Two googled comics The Normal Immune System Network of cells and proteins that work together Goal: protect against
The Most Common Autoimmune Disease: Rheumatoid Arthritis Bonita S. Libman, M.D. Disclosures Two googled comics The Normal Immune System Network of cells and proteins that work together Goal: protect against
COMMITTEE FOR PROPRIETARY MEDICINAL PRODUCTS (CPMP)
 The European Agency for the Evaluation of Medicinal Products Evaluation of Medicines for Human Use London, 17 December 2003 CPMP/EWP/556/95 rev 1/Final COMMITTEE FOR PROPRIETARY MEDICINAL PRODUCTS (CPMP)
The European Agency for the Evaluation of Medicinal Products Evaluation of Medicines for Human Use London, 17 December 2003 CPMP/EWP/556/95 rev 1/Final COMMITTEE FOR PROPRIETARY MEDICINAL PRODUCTS (CPMP)
Recognizing the Value of Innovation in the Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis
 White Paper March 2013 Recognizing the Value of Innovation in the Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis Catherine Augustyn, Brigham Walker, and Thomas F. Goss, PharmD Boston Healthcare Associates, Inc., Boston,
White Paper March 2013 Recognizing the Value of Innovation in the Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis Catherine Augustyn, Brigham Walker, and Thomas F. Goss, PharmD Boston Healthcare Associates, Inc., Boston,
Rheumatoid arthritis: an overview. Christine Pham MD
 Rheumatoid arthritis: an overview Christine Pham MD RA prevalence Chronic inflammatory disease affecting approximately 0.5 1% of the general population Prevalence is higher in North America (approaching
Rheumatoid arthritis: an overview Christine Pham MD RA prevalence Chronic inflammatory disease affecting approximately 0.5 1% of the general population Prevalence is higher in North America (approaching
Current Rheumatoid Arthritis Treatment Options: Update for Managed Care and Specialty Pharmacists
 Current Rheumatoid Arthritis Treatment Options: Update for Managed Care and Specialty Pharmacists 1. Which of the following matches of biologic targets that contribute to rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and
Current Rheumatoid Arthritis Treatment Options: Update for Managed Care and Specialty Pharmacists 1. Which of the following matches of biologic targets that contribute to rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and
Psoriasis, Incidence, Quality of Life, Psoriatic Arthritis, Prevalence
 1.0 Abstract Title Prevalence and Incidence of Articular Symptoms and Signs Related to Psoriatic Arthritis in Patients with Psoriasis Severe or Moderate with Adalimumab Treatment (TOGETHER). Keywords Psoriasis,
1.0 Abstract Title Prevalence and Incidence of Articular Symptoms and Signs Related to Psoriatic Arthritis in Patients with Psoriasis Severe or Moderate with Adalimumab Treatment (TOGETHER). Keywords Psoriasis,
COMMITTEE FOR MEDICINAL PRODUCTS FOR HUMAN USE (CHMP)
 European Medicines Agency London, 14 December 2006 Doc. Ref. CHMP/EWP/438/04 COMMITTEE FOR MEDICINAL PRODUCTS FOR HUMAN USE (CHMP) GUIDELINE ON CLINICAL INVESTIGATION OF MEDICINAL PRODUCTS FOR THE TREATMENT
European Medicines Agency London, 14 December 2006 Doc. Ref. CHMP/EWP/438/04 COMMITTEE FOR MEDICINAL PRODUCTS FOR HUMAN USE (CHMP) GUIDELINE ON CLINICAL INVESTIGATION OF MEDICINAL PRODUCTS FOR THE TREATMENT
Understanding Rheumatoid Arthritis
 Understanding Rheumatoid Arthritis Understanding Rheumatoid Arthritis What Is Rheumatoid Arthritis? 1,2 Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic autoimmune disease. It causes joints to swell and can result
Understanding Rheumatoid Arthritis Understanding Rheumatoid Arthritis What Is Rheumatoid Arthritis? 1,2 Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic autoimmune disease. It causes joints to swell and can result
Is Monotherapy Treatment of Etanercept Effective Against Plaque Psoriasis?
 Philadelphia College of Osteopathic Medicine DigitalCommons@PCOM PCOM Physician Assistant Studies Student Scholarship Student Dissertations, Theses and Papers 2011 Is Monotherapy Treatment of Etanercept
Philadelphia College of Osteopathic Medicine DigitalCommons@PCOM PCOM Physician Assistant Studies Student Scholarship Student Dissertations, Theses and Papers 2011 Is Monotherapy Treatment of Etanercept
A Genetic Analysis of Rheumatoid Arthritis
 A Genetic Analysis of Rheumatoid Arthritis Introduction to Rheumatoid Arthritis: Classification and Diagnosis Rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic inflammatory disorder that affects mainly synovial joints.
A Genetic Analysis of Rheumatoid Arthritis Introduction to Rheumatoid Arthritis: Classification and Diagnosis Rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic inflammatory disorder that affects mainly synovial joints.
Despite remarkable advances in therapy, rheumatoid
 Use of Biological Agents in the Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis Richard J. Misischia, MD, and Larry W. Moreland, MD Despite remarkable advances in therapy, rheumatoid arthritis (RA) still results in
Use of Biological Agents in the Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis Richard J. Misischia, MD, and Larry W. Moreland, MD Despite remarkable advances in therapy, rheumatoid arthritis (RA) still results in
Rheumatoid Arthritis. Outline. Treatment Goal 4/10/2013. Clinical evaluation New treatment options Future research Discussion
 Rheumatoid Arthritis Robert L. Talbert, Pharm.D., FCCP, BCPS University of Texas at Austin College of Pharmacy University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio Outline Clinical evaluation New treatment
Rheumatoid Arthritis Robert L. Talbert, Pharm.D., FCCP, BCPS University of Texas at Austin College of Pharmacy University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio Outline Clinical evaluation New treatment
Recognizing the Value of Innovation in the Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis
 White Paper March 2013 Recognizing the Value of Innovation in the Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis Catherine Augustyn, Brigham Walker, and Thomas F. Goss, PharmD Boston Healthcare Associates, Inc., Boston,
White Paper March 2013 Recognizing the Value of Innovation in the Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis Catherine Augustyn, Brigham Walker, and Thomas F. Goss, PharmD Boston Healthcare Associates, Inc., Boston,
Etanercept in dermatological practice authors own experience in the treatment of psoriasis vulgaris and psoriatic arthritis
 Original paper Etanercept in dermatological practice authors own experience in the treatment of psoriasis vulgaris and psoriatic arthritis Zygmunt Adamski 1,2, Małgorzata Dudziak 1, Katarzyna Zakrzewska
Original paper Etanercept in dermatological practice authors own experience in the treatment of psoriasis vulgaris and psoriatic arthritis Zygmunt Adamski 1,2, Małgorzata Dudziak 1, Katarzyna Zakrzewska
Etanercept, infliximab and adalimumab for the treatment of psoriatic arthritis
 Etanercept, infliximab and adalimumab for the treatment of Issued: August 2010 guidance.nice.org.uk/ta199 NICE has accredited the process used by the Centre for Health Technology Evaluation at NICE to
Etanercept, infliximab and adalimumab for the treatment of Issued: August 2010 guidance.nice.org.uk/ta199 NICE has accredited the process used by the Centre for Health Technology Evaluation at NICE to
Media Release. Basel, 11 June 2009. RA patients with enhanced response identified
 Media Release Basel, 11 June 2009 New data demonstrate the ability of MabThera to reduce the progression of joint damage when used as a first-line biologic treatment in rheumatoid arthritis RA patients
Media Release Basel, 11 June 2009 New data demonstrate the ability of MabThera to reduce the progression of joint damage when used as a first-line biologic treatment in rheumatoid arthritis RA patients
Chapter 1. Scope and objectives of the thesis
 Chapter 1 Scope and objectives of the thesis Chapter 1 Observational studies: focus on leflunomide The view that randomized controlled trials are the gold standard for evaluation and that observational
Chapter 1 Scope and objectives of the thesis Chapter 1 Observational studies: focus on leflunomide The view that randomized controlled trials are the gold standard for evaluation and that observational
Rheumatoid Arthritis. Disease RA Final.indd 2 15. 6. 10. 11:23
 Rheumatoid Arthritis Disease RA Final.indd 2 15. 6. 10. 11:23 Understanding what to expect can help you prepare for your transition into treatment. Rheumatoid Arthritis What You Need To Know About Rheumatoid
Rheumatoid Arthritis Disease RA Final.indd 2 15. 6. 10. 11:23 Understanding what to expect can help you prepare for your transition into treatment. Rheumatoid Arthritis What You Need To Know About Rheumatoid
Dermatologica Sinica
 DERMATOLOGICA SINICA 31 (2013) 49e53 Contents lists available at SciVerse ScienceDirect Dermatologica Sinica journal homepage: http://www.derm-sinica.com ORIGINAL ARTICLE Efficacy and safety of etanercept
DERMATOLOGICA SINICA 31 (2013) 49e53 Contents lists available at SciVerse ScienceDirect Dermatologica Sinica journal homepage: http://www.derm-sinica.com ORIGINAL ARTICLE Efficacy and safety of etanercept
Biologic treatments in rheumatoid arthritis and juvenile idiopathic arthritis
 Review Article Biologic treatments in rheumatoid arthritis and juvenile idiopathic arthritis Andrew A Borg Abstract A number of biological approaches to the management of inflammtory arthropathies have
Review Article Biologic treatments in rheumatoid arthritis and juvenile idiopathic arthritis Andrew A Borg Abstract A number of biological approaches to the management of inflammtory arthropathies have
Drug Therapy Guidelines: Humira (adalimumab)
 Drug Therapy Guidelines: Humira (adalimumab) Effective Date: 5/1/08 Committee Review Date: 1/6/01, 9/18/01, 1/15/02, 1/7/03, 1/20/04, 1/18/05, 12/7/05, 10/15/06, 7/2/07, 11/5/07, 3/25/08 Policy Statements:
Drug Therapy Guidelines: Humira (adalimumab) Effective Date: 5/1/08 Committee Review Date: 1/6/01, 9/18/01, 1/15/02, 1/7/03, 1/20/04, 1/18/05, 12/7/05, 10/15/06, 7/2/07, 11/5/07, 3/25/08 Policy Statements:
Morgan Schultz 1, Stephanie Keeling 2, Steven Katz 2, Walter Maksymowych 2, Dean Eurich 3, Jill Hall 1 1
 Morgan Schultz 1, Stephanie Keeling 2, Steven Katz 2, Walter Maksymowych 2, Dean Eurich 3, Jill Hall 1 1 Faculty of Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Sciences, 2 Faciluty of Medicine and Dentistry, 3 School
Morgan Schultz 1, Stephanie Keeling 2, Steven Katz 2, Walter Maksymowych 2, Dean Eurich 3, Jill Hall 1 1 Faculty of Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Sciences, 2 Faciluty of Medicine and Dentistry, 3 School
Psoriatic Arthritis. Title. Understanding and Managing. in All the Wrong Places. Clinical Features. Etiology of Psoriatic Arthritis
 Focus on CME at Memorial University Understanding and Managing Title Psoriatic Arthritis in All the Wrong Places Proton Rahman MD, MSc, FRCPC Although Baron Jean-Luis Aubert offered the first case description
Focus on CME at Memorial University Understanding and Managing Title Psoriatic Arthritis in All the Wrong Places Proton Rahman MD, MSc, FRCPC Although Baron Jean-Luis Aubert offered the first case description
Rheumatoid Arthritis
 Rheumatoid Arthritis While rheumatoid arthritis (RA) has long been feared as one of the most disabling types of arthritis, the outlook has dramatically improved for many newly diagnosed patients. Certainly
Rheumatoid Arthritis While rheumatoid arthritis (RA) has long been feared as one of the most disabling types of arthritis, the outlook has dramatically improved for many newly diagnosed patients. Certainly
In the last decade, there have been major changes in the
 233 Promising New Treatments for Rheumatoid Arthritis The Kinase Inhibitors Yusuf Yazici, M.D., and Alexandra L. Regens, B.A. Abstract Three major advances over the last decade have impacted the way we
233 Promising New Treatments for Rheumatoid Arthritis The Kinase Inhibitors Yusuf Yazici, M.D., and Alexandra L. Regens, B.A. Abstract Three major advances over the last decade have impacted the way we
Psoriatic arthritis in practice : How to detect? How to diagnose? Pascal RICHETTE Hôpital Lariboisière, Paris. Copyright
 Psoriatic arthritis in practice : How to detect? How to diagnose? Pascal RICHETTE Hôpital Lariboisière, Paris The patient: a 57 year-old man, with a history of psoriatic nail dystrophy for 10 years Past
Psoriatic arthritis in practice : How to detect? How to diagnose? Pascal RICHETTE Hôpital Lariboisière, Paris The patient: a 57 year-old man, with a history of psoriatic nail dystrophy for 10 years Past
Improvement in Quality of Life of Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients on Biologic Therapy
 Improvement in Quality of Life of Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients on Biologic Therapy R Adams 1, Ct Ng 2, A Gibbs 2, L Tilson 1, D Veale 2, B Bresnihan 2, O FitzGerald 2, M Barry 1 1. National Centre for
Improvement in Quality of Life of Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients on Biologic Therapy R Adams 1, Ct Ng 2, A Gibbs 2, L Tilson 1, D Veale 2, B Bresnihan 2, O FitzGerald 2, M Barry 1 1. National Centre for
biologics for the treatment of psoriasis
 How to contact us The Psoriasis Association Dick Coles House 2 Queensbridge Northampton NN4 7BF tel: 08456 760 076 (01604) 251 620 fax: (01604) 251 621 email: mail@psoriasis-association.org.uk www.psoriasis-association.org.uk
How to contact us The Psoriasis Association Dick Coles House 2 Queensbridge Northampton NN4 7BF tel: 08456 760 076 (01604) 251 620 fax: (01604) 251 621 email: mail@psoriasis-association.org.uk www.psoriasis-association.org.uk
Coxib s have taught us a lesson to explore more diligently the molecular and cellular pathways of inflammation
 Coxib s have taught us a lesson to explore more diligently the molecular and cellular pathways of inflammation Steffen Gay Arthritis linked to cardiovascular disease CV Death Osteoarthritis CHF Rheumatoid
Coxib s have taught us a lesson to explore more diligently the molecular and cellular pathways of inflammation Steffen Gay Arthritis linked to cardiovascular disease CV Death Osteoarthritis CHF Rheumatoid
ABOUT RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS
 MEDIA BACKGROUNDER ABOUT RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a type of arthritis (chronic inflammatory polyarthritis) that typically affects hands and feet, although any joint in the body
MEDIA BACKGROUNDER ABOUT RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a type of arthritis (chronic inflammatory polyarthritis) that typically affects hands and feet, although any joint in the body
Psoriatic Arthritis www.arthritis.org.nz
 Psoriatic Arthritis www.arthritis.org.nz Did you know? Arthritis affects one in six New Zealanders over the age of 15 years. Psoriatic arthritis usually appears in people between the ages of 30 to 50.
Psoriatic Arthritis www.arthritis.org.nz Did you know? Arthritis affects one in six New Zealanders over the age of 15 years. Psoriatic arthritis usually appears in people between the ages of 30 to 50.
Roche s RoACTEMRA improved rheumatoid arthritis signs and symptoms significantly more than adalimumab as single-agent therapy
 Media Release Basel, 6 June 2012 Roche s RoACTEMRA improved rheumatoid arthritis signs and symptoms significantly more than adalimumab as single-agent therapy Roche (SIX: RO, ROG; OTCQX: RHHBY) today announced
Media Release Basel, 6 June 2012 Roche s RoACTEMRA improved rheumatoid arthritis signs and symptoms significantly more than adalimumab as single-agent therapy Roche (SIX: RO, ROG; OTCQX: RHHBY) today announced
Speaking Plainly. Biologic treatment options for rheumatoid arthritis
 in association with Plain English Campaign Speaking Plainly Biologic treatment options for rheumatoid arthritis A guide to help healthcare professionals talking to patients with rheumatoid arthritis Foreword
in association with Plain English Campaign Speaking Plainly Biologic treatment options for rheumatoid arthritis A guide to help healthcare professionals talking to patients with rheumatoid arthritis Foreword
Arthritis in Children: Juvenile Rheumatoid Arthritis By Kerry V. Cooke
 Reading Comprehension Read the following essay on juvenile rheumatoid arthritis. Then use the information in the text to answer the questions that follow. Arthritis in Children: Juvenile Rheumatoid Arthritis
Reading Comprehension Read the following essay on juvenile rheumatoid arthritis. Then use the information in the text to answer the questions that follow. Arthritis in Children: Juvenile Rheumatoid Arthritis
A LTCI Approach to Managing Rheumatoid Arthritis
 A LTCI Approach to Managing Rheumatoid Arthritis A bit of Science, a bit of Art, a lot of Perseverance... Stephen K. Holland, MD Senior Vice President & Medical Director Long Term Care Group, Inc. Long
A LTCI Approach to Managing Rheumatoid Arthritis A bit of Science, a bit of Art, a lot of Perseverance... Stephen K. Holland, MD Senior Vice President & Medical Director Long Term Care Group, Inc. Long
Master Thesis in Medicine
 RISK OF INFECTIONS IN RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS PATIENTS TREATED WITH TOCILIZUMAB IN CLINICAL PRACTICE Master Thesis in Medicine Joyce Åkerlund Supervisor: Catharina Lindholm, MD, PhD, Associate Professor Department
RISK OF INFECTIONS IN RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS PATIENTS TREATED WITH TOCILIZUMAB IN CLINICAL PRACTICE Master Thesis in Medicine Joyce Åkerlund Supervisor: Catharina Lindholm, MD, PhD, Associate Professor Department
Dr Sarah Levy Consultant Rheumatology Croydon University Hospital
 Dr Sarah Levy Consultant Rheumatology Croydon University Hospital Contents Definition/ epidemiology Diagnosis Importance of early diagnosis/ treatment Guidelines Evidence based treatment protocol Current
Dr Sarah Levy Consultant Rheumatology Croydon University Hospital Contents Definition/ epidemiology Diagnosis Importance of early diagnosis/ treatment Guidelines Evidence based treatment protocol Current
Original paper Reumatologia 2015; 53, 4: 200 206 DOI: 10.5114/reum.2015.53997
 Original paper Reumatologia 05; 53, 4: 00 06 DOI: 0.54/reum.05.53997 Rheumatoid arthritis treatment with TNF inhibitors and alternative procedures in case of its failure results of the Polish survey in
Original paper Reumatologia 05; 53, 4: 00 06 DOI: 0.54/reum.05.53997 Rheumatoid arthritis treatment with TNF inhibitors and alternative procedures in case of its failure results of the Polish survey in
Adalimumab for the treatment of psoriasis
 DOI: 10.3310/hta13suppl2/07 Health Technology Assessment 2009; Vol. 13: Suppl. 2 Adalimumab for the treatment of psoriasis D Turner, J Picot,* K Cooper and E Loveman Southampton Health Technology Assessments
DOI: 10.3310/hta13suppl2/07 Health Technology Assessment 2009; Vol. 13: Suppl. 2 Adalimumab for the treatment of psoriasis D Turner, J Picot,* K Cooper and E Loveman Southampton Health Technology Assessments
Rheumatoid arthritis: diagnosis, treatment and prognosis. Dr David D Cruz MD FRCP Consultant Rheumatologist
 Rheumatoid arthritis: diagnosis, treatment and prognosis Dr David D Cruz MD FRCP Consultant Rheumatologist The Louise Coote Lupus Unit St Thomas Hospital London AMUS meeting London 7 th March 2012 Disclosures
Rheumatoid arthritis: diagnosis, treatment and prognosis Dr David D Cruz MD FRCP Consultant Rheumatologist The Louise Coote Lupus Unit St Thomas Hospital London AMUS meeting London 7 th March 2012 Disclosures
Development of Antiinfliximab Antibodies and Relationship to Clinical Response in Patients With Rheumatoid Arthritis
 ARTHRITIS & RHEUMATISM Vol. 54, No. 3, March 2006, pp 711 715 DOI 10.1002/art.21671 2006, American College of Rheumatology Development of Antiinfliximab Antibodies and Relationship to Clinical Response
ARTHRITIS & RHEUMATISM Vol. 54, No. 3, March 2006, pp 711 715 DOI 10.1002/art.21671 2006, American College of Rheumatology Development of Antiinfliximab Antibodies and Relationship to Clinical Response
How To Choose A Biologic Drug
 North Carolina Rheumatology Association Position Statements I. Biologic Agents A. Appropriate delivery, handling, storage and administration of biologic agents B. Indications for biologic agents II. III.
North Carolina Rheumatology Association Position Statements I. Biologic Agents A. Appropriate delivery, handling, storage and administration of biologic agents B. Indications for biologic agents II. III.
Disease Therapy Management (DTM) Enhances Rheumatoid Arthritis Treatment
 A WHITE PAPER BY Disease Therapy Management (DTM) Enhances Rheumatoid Arthritis Treatment Increased adherence rates deliver improved outcomes for patients FALL 2010 The Benefits of DTM for Rheumatoid Arthritis
A WHITE PAPER BY Disease Therapy Management (DTM) Enhances Rheumatoid Arthritis Treatment Increased adherence rates deliver improved outcomes for patients FALL 2010 The Benefits of DTM for Rheumatoid Arthritis
Evidence-based Management of Rheumatoid Arthritis (2009)
 CPLD reviews its distance learning programmes every twelve months to ensure currency. This update has been produced by an expert and should be read in conjunction with the Evidencebased Management of distance
CPLD reviews its distance learning programmes every twelve months to ensure currency. This update has been produced by an expert and should be read in conjunction with the Evidencebased Management of distance
Etanercept Versus Methotrexate in Patients With Early Rheumatoid Arthritis
 ARTHRITIS & RHEUMATISM Vol. 46, No. 6, June 2002, pp 1443 1450 DOI 10.1002/art.10308 2002, American College of Rheumatology Etanercept Versus Methotrexate in Patients With Early Rheumatoid Arthritis Two-Year
ARTHRITIS & RHEUMATISM Vol. 46, No. 6, June 2002, pp 1443 1450 DOI 10.1002/art.10308 2002, American College of Rheumatology Etanercept Versus Methotrexate in Patients With Early Rheumatoid Arthritis Two-Year
Arthritis and Rheumatology Clinics of Kansas Patient Education. Reactive Arthritis (ReA) / Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD) Arthritis
 Arthritis and Rheumatology Clinics of Kansas Patient Education Reactive Arthritis (ReA) / Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD) Arthritis Introduction: For as long as scientists have studied rheumatic disease,
Arthritis and Rheumatology Clinics of Kansas Patient Education Reactive Arthritis (ReA) / Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD) Arthritis Introduction: For as long as scientists have studied rheumatic disease,
RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS. Dr Bruce Kirkham Rheumatology Clinical Lead
 RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS Dr Bruce Kirkham Rheumatology Clinical Lead RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS (RA) RA is a common disease: 0.8 per cent of the population RA more common in females: female to male ratio 3:1 RA
RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS Dr Bruce Kirkham Rheumatology Clinical Lead RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS (RA) RA is a common disease: 0.8 per cent of the population RA more common in females: female to male ratio 3:1 RA
Rheumatoid Arthritis www.arthritis.org.nz
 Rheumatoid Arthritis www.arthritis.org.nz Did you know? RA is the second most common form of arthritis Approximately 40,000 New Zealanders have RA RA can occur at any age, but most often appears between
Rheumatoid Arthritis www.arthritis.org.nz Did you know? RA is the second most common form of arthritis Approximately 40,000 New Zealanders have RA RA can occur at any age, but most often appears between
Rheumatoid Arthritis Information
 Rheumatoid Arthritis Information Definition Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a long-term disease that leads to inflammation of the joints and surrounding tissues. It can also affect other organs. Alternative
Rheumatoid Arthritis Information Definition Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a long-term disease that leads to inflammation of the joints and surrounding tissues. It can also affect other organs. Alternative
Original Policy Date
 MP 5.01.20 Tysabri (natalizumab) Medical Policy Section Prescription Drug Issue 12:2013 Original Policy Date 12:2013 Last Review Status/Date Local Policy/12:2013 Return to Medical Policy Index Disclaimer
MP 5.01.20 Tysabri (natalizumab) Medical Policy Section Prescription Drug Issue 12:2013 Original Policy Date 12:2013 Last Review Status/Date Local Policy/12:2013 Return to Medical Policy Index Disclaimer
Current treatment of psoriatic arthritis
 Rheum Dis Clin N Am 29 (2003) 495 511 Current treatment of psoriatic arthritis Philip J. Mease, MD a,b,c, * a Seattle Rheumatology Associates, Swedish Hospital Medical Center campus, Seattle, WA, USA b
Rheum Dis Clin N Am 29 (2003) 495 511 Current treatment of psoriatic arthritis Philip J. Mease, MD a,b,c, * a Seattle Rheumatology Associates, Swedish Hospital Medical Center campus, Seattle, WA, USA b
Infl ectra for rheumatoid arthritis
 Infl ectra for rheumatoid arthritis Some important information to get you started with your treatment This booklet is intended only for use by patients who have been prescribed Inflectra. Introduction
Infl ectra for rheumatoid arthritis Some important information to get you started with your treatment This booklet is intended only for use by patients who have been prescribed Inflectra. Introduction
Phenotypes and Classification of Psoriasis
 Rheumatology 2010 Birmingham 21 April 2010 Phenotypes and Classification of Psoriasis Christopher E.M. Griffiths Abbott Centocor Incyte Galderma Janssen-Cilag Leo Pharma Lynxx Novartis Pfizer Schering-Plough
Rheumatology 2010 Birmingham 21 April 2010 Phenotypes and Classification of Psoriasis Christopher E.M. Griffiths Abbott Centocor Incyte Galderma Janssen-Cilag Leo Pharma Lynxx Novartis Pfizer Schering-Plough
Methotrexate Is Not Disease Modifying In Psoriatic Arthritis
 Methotrexate Is Not Disease Modifying In Psoriatic Arthritis A New Treatment Paradigm Is Required Gabrielle H Kingsley*, Jonathan Packham, Neil McHugh, Diarmuid Mulherin George Kitas, Kuntal Chakravarty,
Methotrexate Is Not Disease Modifying In Psoriatic Arthritis A New Treatment Paradigm Is Required Gabrielle H Kingsley*, Jonathan Packham, Neil McHugh, Diarmuid Mulherin George Kitas, Kuntal Chakravarty,
Update on Pathophysiology, Assessment, and Management
 Bulletin of the NYU Hospital for Joint Diseases 2010;68(3):191-8 191 Psoriatic Arthritis Update on Pathophysiology, Assessment, and Management Philip J. Mease, M.D. Abstract Psoriatic arthritis (PsA) is
Bulletin of the NYU Hospital for Joint Diseases 2010;68(3):191-8 191 Psoriatic Arthritis Update on Pathophysiology, Assessment, and Management Philip J. Mease, M.D. Abstract Psoriatic arthritis (PsA) is
Rheumatoid Arthritis: Constantly Evolving Treatment Approaches
 Rheumatoid Arthritis: Constantly Evolving Treatment Approaches Jody Garry, Pharm.D. Primary Care Pharmacy Resident VA Medical Center - Iowa City Presentation Overview Pathophysiology & epidemiology Diagnostic
Rheumatoid Arthritis: Constantly Evolving Treatment Approaches Jody Garry, Pharm.D. Primary Care Pharmacy Resident VA Medical Center - Iowa City Presentation Overview Pathophysiology & epidemiology Diagnostic
Rheumatoid Arthritis
 Rheumatoid Arthritis Carole Callaghan Principal Pharmacist NHS Lothian Aim To update pharmacists on the current management of rheumatoid arthritis and explore ways to implement pharmaceutical care for
Rheumatoid Arthritis Carole Callaghan Principal Pharmacist NHS Lothian Aim To update pharmacists on the current management of rheumatoid arthritis and explore ways to implement pharmaceutical care for
Exploring Care for Psoriatic Arthritis: Bridging Dermatology and Rheumatology
 Exploring Care for Psoriatic Arthritis: Bridging Dermatology and Rheumatology Exploring Care for Psoriatic Arthritis: Bridging Dermatology and Rheumatology Dr. Leonard Calabrese: I want to welcome the
Exploring Care for Psoriatic Arthritis: Bridging Dermatology and Rheumatology Exploring Care for Psoriatic Arthritis: Bridging Dermatology and Rheumatology Dr. Leonard Calabrese: I want to welcome the
Rheumatoid Arthritis: Diagnosis, Management and Monitoring
 Rheumatoid Arthritis: Diagnosis, Management and Monitoring Effective Date: September 30, 2012 Scope This guideline is intended to aid in early recognition, intervention and management of patients with
Rheumatoid Arthritis: Diagnosis, Management and Monitoring Effective Date: September 30, 2012 Scope This guideline is intended to aid in early recognition, intervention and management of patients with
Guideline for anti-tnf-a therapy in psoriatic arthritis
 Rheumatology 2005;44:390 397 Advance Access publication 3 February 2005 Guidelines Guideline for anti-tnf-a therapy in psoriatic arthritis S. Kyle, D. Chandler 1, C. E. M. Griffiths 2, P. Helliwell 3,
Rheumatology 2005;44:390 397 Advance Access publication 3 February 2005 Guidelines Guideline for anti-tnf-a therapy in psoriatic arthritis S. Kyle, D. Chandler 1, C. E. M. Griffiths 2, P. Helliwell 3,
Etanercept Treatment of Psoriatic Arthritis
 ARTHRITIS & RHEUMATISM Vol. 50, No. 7, July 2004, pp 2264 2272 DOI 10.1002/art.20335 2004, American College of Rheumatology Etanercept Treatment of Psoriatic Arthritis Safety, Efficacy, and Effect on Disease
ARTHRITIS & RHEUMATISM Vol. 50, No. 7, July 2004, pp 2264 2272 DOI 10.1002/art.20335 2004, American College of Rheumatology Etanercept Treatment of Psoriatic Arthritis Safety, Efficacy, and Effect on Disease
Psoriasis. Psoriasis. Mark A. Bechtel, M.D. Director of Dermatology The Ohio State University College of Medicine
 Psoriasis Mark A. Bechtel, M.D. Director of Dermatology The Ohio State University College of Medicine Psoriasis Psoriasis is a chronic skin disorder resulting from a polygenic predisposition combined with
Psoriasis Mark A. Bechtel, M.D. Director of Dermatology The Ohio State University College of Medicine Psoriasis Psoriasis is a chronic skin disorder resulting from a polygenic predisposition combined with
Information on Rheumatoid Arthritis
 Information on Rheumatoid Arthritis Table of Contents About Rheumatoid Arthritis 1 Definition 1 Signs and symptoms 1 Causes 1 Risk factors 1 Test and diagnosis 2 Treatment options 2 Lifestyle 3 References
Information on Rheumatoid Arthritis Table of Contents About Rheumatoid Arthritis 1 Definition 1 Signs and symptoms 1 Causes 1 Risk factors 1 Test and diagnosis 2 Treatment options 2 Lifestyle 3 References
Psoriatic Arthritis. Ewa Olech, MD Division of Rheumatology University of Nevada School of Medicine Las Vegas
 Psoriatic Arthritis Ewa Olech, MD Division of Rheumatology University of Nevada School of Medicine Las Vegas The Spectrum of Spondyloarthritis Characteristics of the Spondyloarthritis Sacroiliac & spinal
Psoriatic Arthritis Ewa Olech, MD Division of Rheumatology University of Nevada School of Medicine Las Vegas The Spectrum of Spondyloarthritis Characteristics of the Spondyloarthritis Sacroiliac & spinal
Rheumatoid Arthritis. Nicole Klett,, M.D.
 Rheumatoid Arthritis Nicole Klett,, M.D. Rheumatoid Arthritis Systemic Chronic Inflammatory Primarily targets the synovium of diarthrodial joints Etiology likely combination genetic and environmental Diarthrodial
Rheumatoid Arthritis Nicole Klett,, M.D. Rheumatoid Arthritis Systemic Chronic Inflammatory Primarily targets the synovium of diarthrodial joints Etiology likely combination genetic and environmental Diarthrodial
TNF-α Antagonists in the Treatment of Nail Psoriasis
 Review DOI: 10.6003/jtad.1264r1 TNF-α Antagonists in the Treatment of Nail Psoriasis Zekayi Kutlubay, MD, Burhan Engin, MD, Abdullah Songür, MD, Yalçın Tüzün, MD Address: Istanbul University, Cerrahpaşa
Review DOI: 10.6003/jtad.1264r1 TNF-α Antagonists in the Treatment of Nail Psoriasis Zekayi Kutlubay, MD, Burhan Engin, MD, Abdullah Songür, MD, Yalçın Tüzün, MD Address: Istanbul University, Cerrahpaşa
subcutaneous initially every 4 weeks then every 12 weeks Coverage Criteria: Express Scripts, Inc. monograph dated 02/24/2010
 BENEFIT DESCRIPTION AND LIMITATIONS OF COVERAGE ITEM: PRODUCT LINES: COVERED UNDER: DESCRIPTION: CPT/HCPCS Code: Company Supplying: Setting: Humira (adalimumab subcutaneous injection) Commercial HMO/PPO/CDHP
BENEFIT DESCRIPTION AND LIMITATIONS OF COVERAGE ITEM: PRODUCT LINES: COVERED UNDER: DESCRIPTION: CPT/HCPCS Code: Company Supplying: Setting: Humira (adalimumab subcutaneous injection) Commercial HMO/PPO/CDHP
Page 1 of 15 Origination Date: 09/14 Revision Date(s): 10/2015, 02/2016 Developed By: Medical Criteria Committee 10/28/2015
 Moda Health Plan, Inc. Medical Necessity Criteria Subject: Actemra (tocilizumab) Page 1 of 15 Origination Date: 09/14 Revision Date(s): 10/2015, 02/2016 Developed By: Medical Criteria Committee 10/28/2015
Moda Health Plan, Inc. Medical Necessity Criteria Subject: Actemra (tocilizumab) Page 1 of 15 Origination Date: 09/14 Revision Date(s): 10/2015, 02/2016 Developed By: Medical Criteria Committee 10/28/2015
EVIDENCE BASED TREATMENT OF CROHN S DISEASE. Dr E Ndabaneze
 EVIDENCE BASED TREATMENT OF CROHN S DISEASE Dr E Ndabaneze PLAN 1. Case presentation 2. Topic on Evidence based Treatment of Crohn s disease - Introduction pathology aetiology - Treatment - concept of
EVIDENCE BASED TREATMENT OF CROHN S DISEASE Dr E Ndabaneze PLAN 1. Case presentation 2. Topic on Evidence based Treatment of Crohn s disease - Introduction pathology aetiology - Treatment - concept of
Issue date: August 2010
 Issue date: August 2010 Adalimumab, etanercept, infliximab, rituximab and abatacept for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis after the failure of a TNF inhibitor Part review of NICE technology appraisal
Issue date: August 2010 Adalimumab, etanercept, infliximab, rituximab and abatacept for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis after the failure of a TNF inhibitor Part review of NICE technology appraisal
DAS28 criteria for initiation of biologics in early RA: a clinician s view. Dr Patrick Kiely St George s Healthcare NHS Trust, London
 DAS28 criteria for initiation of biologics in early RA: a clinician s view Dr Patrick Kiely St George s Healthcare NHS Trust, London History: NICE (E&W) guidelines for starting anti-tnf agents April 2001
DAS28 criteria for initiation of biologics in early RA: a clinician s view Dr Patrick Kiely St George s Healthcare NHS Trust, London History: NICE (E&W) guidelines for starting anti-tnf agents April 2001
ACR and EULAR Improvement Criteria Have Comparable Validity in Rheumatoid Arthritis Trials
 ACR and EULAR Improvement Criteria Have Comparable Validity in Rheumatoid Arthritis Trials ANKE M. van GESTEL, JENNIFER J. ANDERSON, PIET L.C.M. van RIEL, MAARTEN BOERS, CEES J. HAAGSMA, BILL RICH, GEORGE
ACR and EULAR Improvement Criteria Have Comparable Validity in Rheumatoid Arthritis Trials ANKE M. van GESTEL, JENNIFER J. ANDERSON, PIET L.C.M. van RIEL, MAARTEN BOERS, CEES J. HAAGSMA, BILL RICH, GEORGE
Combination of Infliximab and Methotrexate Therapy for Early Rheumatoid Arthritis
 ARTHRITIS & RHEUMATISM Vol. 50, No. 11, November 2004, pp 3432 3443 DOI 10.1002/art.20568 2004, American College of Rheumatology Combination of Infliximab and Methotrexate Therapy for Early Rheumatoid
ARTHRITIS & RHEUMATISM Vol. 50, No. 11, November 2004, pp 3432 3443 DOI 10.1002/art.20568 2004, American College of Rheumatology Combination of Infliximab and Methotrexate Therapy for Early Rheumatoid
Can Rheumatoid Arthritis treatment ever be stopped?
 Can Rheumatoid Arthritis treatment ever be stopped? Robert L. DiGiovanni, DO, FACOI Program Director Largo Medical Center Rheumatology Fellowship robdsimc@tampabay.rr.com Do not pour strange medicines
Can Rheumatoid Arthritis treatment ever be stopped? Robert L. DiGiovanni, DO, FACOI Program Director Largo Medical Center Rheumatology Fellowship robdsimc@tampabay.rr.com Do not pour strange medicines
PROVEN NON-INVASIVE TREATMENT FOR RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS
 PROVEN NON-INVASIVE TREATMENT FOR RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS BIONICARE HAND SYSTEM Non-drug, non-invasive Adjunctive therapy For patients symptomatic despite current therapy For patients intolerant to drug
PROVEN NON-INVASIVE TREATMENT FOR RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS BIONICARE HAND SYSTEM Non-drug, non-invasive Adjunctive therapy For patients symptomatic despite current therapy For patients intolerant to drug
Psoriasis Treatment Transition Pathway
 Psoriasis Treatment Transition Pathway A Treatment Support Tool Adapted from Circle Nottingham NHS Treatment Centre Psoriasis Pathway (under consultation) with support from Abbvie Ltd Treatment Pathways
Psoriasis Treatment Transition Pathway A Treatment Support Tool Adapted from Circle Nottingham NHS Treatment Centre Psoriasis Pathway (under consultation) with support from Abbvie Ltd Treatment Pathways
BIOM 255 - Firestein, Winter 2009. Rheumatoid arthritis. Page 1
 Rheumatoid arthritis Page 1 Vascular events in RA Synovium in rheumatoid arthritis Non-extra articular RA Extra articular RA Turesson, et al. Ann Rheum Dis. 2007;66:60 Normal Rheumatoid Arthritis Major
Rheumatoid arthritis Page 1 Vascular events in RA Synovium in rheumatoid arthritis Non-extra articular RA Extra articular RA Turesson, et al. Ann Rheum Dis. 2007;66:60 Normal Rheumatoid Arthritis Major
The exacerbation of cutaneous psoriasis induced by anti - TNF therapy - case report
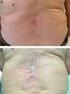 The exacerbation of cutaneous psoriasis induced by anti - TNF therapy - case report Anca Costache 1, Mădălina Ionela Chiriac 2, Elena Rezuş*,1,2 1 Rheumatology Department, Rehabilitation Hospital Iasi,
The exacerbation of cutaneous psoriasis induced by anti - TNF therapy - case report Anca Costache 1, Mădălina Ionela Chiriac 2, Elena Rezuş*,1,2 1 Rheumatology Department, Rehabilitation Hospital Iasi,
Psoriasis Co-morbidities: Changing Clinical Practice. Theresa Schroeder Devere, MD Assistant Professor, OHSU Dermatology. Psoriatic Arthritis
 Psoriasis Co-morbidities: Changing Clinical Practice Theresa Schroeder Devere, MD Assistant Professor, OHSU Dermatology Psoriatic Arthritis Psoriatic Arthritis! 11-31% of patients with psoriasis have psoriatic
Psoriasis Co-morbidities: Changing Clinical Practice Theresa Schroeder Devere, MD Assistant Professor, OHSU Dermatology Psoriatic Arthritis Psoriatic Arthritis! 11-31% of patients with psoriasis have psoriatic
Spondyloarthritis is a general term for a group of rheumatic
 Rheumatic Disease Clinics of North America Supplement 1 11 Current Treatment for Psoriatic Arthritis and Other Spondyloarthritides Spondyloarthritis is a general term for a group of rheumatic diseases,
Rheumatic Disease Clinics of North America Supplement 1 11 Current Treatment for Psoriatic Arthritis and Other Spondyloarthritides Spondyloarthritis is a general term for a group of rheumatic diseases,
Rheumatoid Arthritis www.arthritis.org.nz
 Rheumatoid Arthritis www.arthritis.org.nz Did you know? Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is the third most common form of arthritis Approximately 40,000 New Zealanders have RA RA can occur at any age, but most
Rheumatoid Arthritis www.arthritis.org.nz Did you know? Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is the third most common form of arthritis Approximately 40,000 New Zealanders have RA RA can occur at any age, but most
