A Stochastic Model For Critical Illness Insurance
|
|
|
- Melinda Wilcox
- 10 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 A Stochastic Model For Critical Illness Insurance Erengul Ozkok Submitted for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy on completion of research in the Department of Actuarial Mathematics & Statistics, School of Mathematical and Computer Sciences, Heriot-Watt University May 2011 The copyright in this thesis is owned by the author. Any quotation from the thesis or use of any of the information contained in it must acknowledge this thesis as the source of the quotation or information.
2 I hereby declare that the work presented in this thesis was carried out by myself at Heriot-Watt University, Edinburgh, except where due acknowledgement is made, and has not been submitted for any other degree. Erengul Ozkok (Candidate) Dr George Streftaris (Supervisor) Professor Howard R. Waters (Supervisor) Professor A. David Wilkie (Supervisor) Date
3 Abstract In this thesis, we present methods and results for the estimation of diagnosis inception rates for Critical Illness Insurance (CII) claims in the UK by cause. This is the first study which provides a stochastic model for the diagnosis inception rates for CII. The data are supplied by the UK Continuous Mortality Investigation and relate to claims settled in the years First, we develop a model for the delay between dates of diagnosis and settlement of claims in CII using a generalised-lineartype model with Burr errors under both Bayesian and maximum likelihood approach. Variable selection using Bayesian methodology to obtain the best model with different prior distribution setups for the parameters is applied. For comparison purposes, a lognormal model and frequency-based model selection techniques are also considered. The non-recorded dates of diagnosis and settlement have been included in the analysis as missing values using their posterior predictive distribution and Markov Chain Monte Carlo methodology. Missing dates of diagnosis are estimated using the parsimonious claim delay distribution. With this complete data set, diagnosis inception rates for all causes (combined) and for specific causes are estimated using an appropriate claim delay distribution where the observed numbers of claim counts are assumed to have a Poisson distribution. To model the crude rates, a generalised linear model with Poisson errors and log-link function is used. i
4 Acknowledgements I am extremely grateful to my supervisors Dr George Streftaris, Professor Howard Waters and Professor David Wilkie for their vast amount of time, guidance, support, encouragement and patience. I could not have had better supervision; their doors were always open to me. I am indebted to them and very honoured to be their student. I would like to thank the Continuous Mortality Investigation of the Institute and Faculty of Actuaries for providing the data which is used in the thesis and for quick responses whenever we need them. I thank Hacettepe University for being a sponsor for my PhD. I express my appreciation to Dr Ioannis Ntzoufras and Dr Dimitris Fouskakis for helping me to improve this research by their comments. I am also very grateful to all my friends who made my life brighter here in Edinburgh. I wish to express my deepest gratitude to my family. Without their encouragement and support I could not have had this excellent experience. ii
5 Contents Abstract Acknowledgement i ii 1 Introduction Critical Illness Insurance Overview of past results Stochastic modelling for inception rates Outline of the thesis Data 12 3 Modelling CDD I: Without considering the missing values and growth rates Introduction The observed delay Modelling under the assumption of no growth within offices The null model Analysis with covariates Prediction under the two models Modelling CDD II: Without considering the missing values and taking growth rates into account Introduction Modelling when the business growth is taken into account Prediction iii
6 5 Selection of claim-specific covariates Introduction Selection of claim-specific covariates without growth factor Gibbs variable selection (GVS) Variable selection using marginal likelihoods Maximum likelihood based methods Selection of claim-specific covariates with growth factor Modelling CDD III: Including the missing values Introduction Including the missing values and assuming no growth within offices Considering the missing values and the growth rate Diagnosis inception rates I: All-cause rates Introduction Modelling techniques All-cause rates without restriction All-cause rates including the CMI variables Sensitivity of the inception rates to delay estimates Sensitivity analysis Diagnosis inception rates II: Cause-specific rates Structure of the model Best models for specific causes Comparison of cause-specific rates with the all-causes rates Conclusions and Further Research Conclusions Further research References 209 iv
7 List of Tables 2.1 Details of the submission groups Number of offices and number of sales channels Average observed delays between dates of diagnosis, notification, admission and settlement (in days) Number of claims and percentages by various factors Grouping cause of claim Posterior and ML estimation under the null model Information criteria under the null model Definitions of the covariates Coefficients of the Burr model without growth rate Coefficients of the LN model without growth rate Values of information criteria of the models without growth rate Scenarios for prediction of the CDD Posterior estimates of mean delays for the scenarios in Table 3.7 for the Burr and LN model (days) Growth rates from the inforce data for offices between successive years Coefficients of the Burr model with growth rate Coefficients of the LN model with growth rate Values of information criteria of the models with growth rate Posterior estimates of mean delay for the scenarios in Table 3.7 for the Burr and LN model with growth rate (days) Parameter inclusion probabilities and model probabilities under the Burr model with independent normal priors v
8 5.2 Parameter inclusion probabilities and model probabilities under the LN model with independent normal priors Parameter inclusion probabilities and model probabilities under the Burr model with empirical and Zellner s g-priors Parameter inclusion probabilities and model probabilities under the LN model with empirical and Zellner s g-priors Exact marginal likelihoods (EML) for the lognormal model Laplace Approximation for the Burr Model Variable selection with backward stepwise method for the Burr model Variable selection with backward stepwise method for the lognormal model LRT values for each step given in Table 5.7 and DIC values of the selected models Estimates of the parameters under the selected Burr model (m 1013 ) Parameter inclusion probabilities and model probabilities under the Burr model with empirical and Zellner s g-priors when business growth is taken into account Comparison of the Burr and LN models with growth rate Estimates of the parameters under the best Burr model (m 981 ) without missing values with growth rate Posterior estimates of parameters under the selected Burr model with missing values (m 1013 ) Coefficients of the Burr model (m 981 ) with missing values and with growth rate Scenarios for prediction of the CDD under the selected Burr model (m 981 ) Posterior estimates of the mean of the delay distribution under different scenarios given in Table 6.3 using the selected Burr model (m 981 ) with growth rates Definitions of the covariates used in the modelling of the intensity rates Selected covariates, log-likelihood values and BIC from fitting different g r (x),f s (x) polynomials vi
9 WinBUGS) considering the size of the data set. The sum of individual rates should give the all-cause rates, in theory. Since we used different smoothing models, this will not be satisfied precisely. However to determine if there is any bias in the modelling we compared the sum of the cause-specific rates with the all-cause rates in Chapter 8. As an example, for a specific characteristic, the difference between the sum of cause-specific rates and all-cause rates was compared for four different combinations of sex and smoker status. The results were encouraging as the cause-specific rates and all-cause rates cross each other at least at two points. For the age range where we have most of the data these rates are very close to each other whereas the difference is bigger for younger and older ages due to lack of data. 9.2 Further research The reason for providing diagnosis inception rates is to estimate the future cash flow of a CI policy and determine the liability of the insurance company more accurately. So, a natural extension of this thesis would be calculation of these expected cash flows, as these can be used in reserving and pricing. It is important to model the inception rates for older ages since the rates are higher for these ages. One of the approaches in the future might be to compare the incidence rates from our analysis (from insured data) with population statistics. By determining the relationship between these two, we could provide more reliable rates for the ages where we have less data. Another interesting research topic would be the projection of morbidity rates to future calendar years for different causes for CII. As mentioned earlier, the claim inception analyses in Chapters 7 and 8 could be performed under a full Bayesian approach so that the entire posterior distribution can be estimated after incorporating observations with missing dates. This would provide proper measures of parameter uncertainty, including corresponding standard errors and credible intervals. We note that this would be computationally very challenging due to the amount of data we have. This problem would require the use of considerably more powerful programming tools than those provided in WinBUGS (e.g. C++). 207
10 In this thesis we could not separate different types of cancers. Although we have enough data to analyse some of the cancers on their own (e.g. breast cancer), consultation with the CMI revealed that for many cancer claims cause is recorded as cancer - site not specified by offices and providing any specific cancer rates would underestimate the true rates for specific cancer types. If the site of the cancer can be specified for each claim in the future, then inception rates for specific cancers can be provided. 208
11 References Antonio, K., Beirlant, J. (2008). Issues in Claims Reserving and Credibility: A Semiparametric Approach With Mixed Models. The Journal of Risk and Insurance, 75(3), Association of British Insurers (2005). A Guide to Critical Illness Cover. ABI. Association of British Insurers (2006). Statement of Best Practice for Critical Illness Cover. ABI. Association of British Insurers (2009). ABI Statement of Best Practice for Critical Illness Cover Review Consultation Paper. ABI. Association of British Insurers (2010). Research into customers understanding of draft Total Permanent Disability headings and definitions. ABI. Bartlett, M. (1957). Comment on D.V. Lindley s statistical paradox. Biometrika, 44, Beirlant, J., Goegebeur, Y., Verlaak, R., Vynckier, P. (1998). Burr regression and portfolio segmentation. Insurance: Mathematics and Economics, 23, Beirlant, J., Guillou, A. (2001). Pareto Index Estimation Under Moderate Right Censoring. Scandinavian Actuarial Journal, 2, Beirlant, J., Goegebeur, Y. (2003). Regression with response distributions of Pareto-type. Computational Statistics & Data Analysis, 42, Bowling, A., Bond, M., McKee, D., McClay, M., Banning, A. P., Dudley, N., Elder, A., Martin, A., Blackman, I. (2001). Equity in access to exercise 209
12 tolerance testing, coronary angiography, and coronary artery bypass grafting by age, sex and clinical indications. Heart, 85(6), Bradshaw, P. J., Jamrozik, K., Le, M., Thompson P. L. (2002). Mortality and recurrent cardiac events after CABG: long-term outcomes in a population study. Heart, 88, Cancer Research UK (2010). Cancer in the UK : July Cancer Research UK. Chatterjee, T., Macdonald, A.S., Waters, H.R. (2009). A model for ischaemic heart disease and stroke I: The model.. The Annals of Actuarial Science, 3(1 & 2), Continuous Mortality Investigation Committee (2005). Working Paper 14 - Methodology underlying the CMI Critical Illness experience investigation. Institute of Actuaries and Faculty of Actuaries. Continuous Mortality Investigation Committee (2007). Working Paper 28 - Progress towards an improved methodology for analysing CMI critical illness experience. Institute of Actuaries and Faculty of Actuaries. Continuous Mortality Investigation Committee (2008). Working Paper 33 - A new methodology for analysing CMI critical illness experience. Institute of Actuaries and Faculty of Actuaries. Continuous Mortality Investigation Committee (2010). Working Paper 43 - CMI critical illness diagnosis rates for accelerated business, Institute of Actuaries and Faculty of Actuaries. Continuous Mortality Investigation Committee (2011). Working Paper 50 - CMI critical illness diagnosis rates for accelerated business, Institute and Faculty of Actuaries. Critical Illness Trends Research Group (2006). Exploring the Critical Path. presented to the Staple Inn Actuarial Society. 210
13 Dash, A. C. and Grimshaw, D. L. (1993). Dread Disease Cover - An Actuarial Perspective. JSS, 33, Dellaportas, P., Forster, J., Ntzoufras, I. (2002). On Bayesian model and variable selection using MCMC. Statistics and Computing, 12, Dinani, A., Grimshaw, D., Robjohns, N., Somerville, S., Spry, A., Staffurth, J. (2000). A Critical Review: Report of the Critical Illness Healthcare Study Group. presented to the Staple Inn Actuarial Society. Dutang, C., Goulet, V., Pigeon, M. (2008). actuar: An R Package for Actuarial Science. Journal of Statistical Software, 25(7), Efron, B., Tibshirani R. J. (1993). An introduction to the bootstrap. Chapman and Hall. Forfar, D. O., McCutcheon, J. J., Wilkie, A. D. (1988). On graduation by mathematical formula. Journal of the Institute of Actuaries, 115(I), Frees, E. W., Valdez, E. A. (2008). Hierarchical Insurance Claims Modeling. Journal of the American Statistical Association, 103(484), Gelman, A., Carlin, J. B., Stern, H. S., Rubin, D. B. (2000). Bayesian Data Analysis. Chapman and Hall, USA. GenRe (2007). A critical table: Pricing Critical Illness in the UK on a new insured lives table. presented to the International Actuarial Association Healthcare Section Colloquium in Cape Town. Gilks, W. R., Richardson, S., Spiegelhalter, D. J. (1996). Markov Chain Monte Carlo in Practice. Chapman and Hall, UK. Greene, W. H. (1990). Econometric analysis. Macmillan. Hogg, R. V., Klugman, S. A. (1984). Loss Distributions. John Wiley & Sons, Inc., USA. Kass, R. E., Raftery, A. E. (1995). Bayes Factors. Journal of the American Statistical Association, 90,
14 Kass, R. E., Wasserman, L. (1995). A reference Bayesian test for nested hypotheses and its relationship to the Schwarz criterion. Journal of the American Statistical Association, 90, Lindley, D. (1957). A statistical paradox. Biometrika, 44, Macdonald, A. S. (1996a). An Actuarial Survey of Statistical Models for Decrement and Transition Data. I: Multiple State, Binomial and Poisson Models.. British Actuarial Journal, 2, Macdonald, A. S. (1996b). An Actuarial Survey of Statistical Models for Decrement and Transition Data. II: Competing Risks, Non-Parametric and Regression Models.. British Actuarial Journal, 2, Macdonald, A. S. (1996c). An Actuarial Survey of Statistical Models for Decrement and Transition Data. III: Counting Process Models.. British Actuarial Journal, 2, MacDonald, P., Johnstone, D., Rockwood, K. (2000). Coronary artery bypass surgery for elderly patients: is our practice based on evidence or faith?. CMAJ, 162, McCullagh, P., Nelder, J. A. (1989). Generalized Linear Models. Chapman and Hall, London. Miller, I., Miller, M. (2004). John E. Freund s Mathematical Statistics with Applications. Prentice Hall. NHS (2010). Coronary artery bypass graft [online]. Available from: (Accessed 3 February 2011). Ntzoufras, I. (2002). Gibbs Variable Selection Using BUGS. Journal of Statistical Software, 7, Issue 7. Ntzoufras, I., Dellaportas, P., Forster, J. J. (2003). Bayesian variable and link determination for generalised linear models. Journal of Statistical Planning and Inference, 111,
15 Ntzoufras, I. (2009). Bayesian Modeling Using WinBUGS. John Wiley & Sons, Inc., USA. R Development Core Team (2009). R: A language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria. Richards, S. J. (2008). Applying survival models to pensioner mortality data. British Actuarial Journal, 14(II), Schwarz, Gideon E. (1978). Estimating the dimension of a model. Annals of Statistics, 6(2), Scollnik, D. P. M. (2001). Actuarial Modeling with MCMC and BUGS. North American Actuarial Journal, 5(2), Society of Actuaries in Ireland Working Party (1994). Reserving for Critical Illness guarantees. presented to the Society of Actuaries in Ireland. Spiegelhalter, D. J., Best, N. G., Carlin, B. P. and Van Der Linde, A. (2002). Bayesian measures of model complexity and fit. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society Series B, 64, Spiegelhalter, D., Thomas, A., Best, N., Lunn, D. (2003). WinBUGS User Manual Version 1.4. MRC Biostatistics Unit, UK. Stone, P. H., Thompson, B., Anderson, H. V., Kronenberg, M. W., Gibson, R. S., Rogers, W. J., Diver, D. J., Théroux, P., Warnica, J. W., Nasmith, J. B., Kells, C., Kleiman, N., McCabe, C. H., Schactman, M., Knatterud, G. L., Braunwald, E. (1996). Influence of race, sex, and age on management of unstable angina and non-q-wave myocardial infarction: The TIMI III registry. JAMA, 275(14), Waters, H. R. (1984). An approach to the study of multiple state models. Journal of the Institute of Actuaries, 111, Zellner, A. (1986). On assessing prior distributions and Bayesian regression analysis with g-prior distributions. Bayesian Inference and Decision Techniques: Essays in Honor of Bruno de Finetti, North-Holland, Amsterdam,,
A Stochastic Model For Critical Illness Insurance
 A Stochastic Model For Critical Illness Insurance Erengul Ozkok Submitted for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy on completion of research in the Department of Actuarial Mathematics & Statistics, School
A Stochastic Model For Critical Illness Insurance Erengul Ozkok Submitted for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy on completion of research in the Department of Actuarial Mathematics & Statistics, School
MODELLING CRITICAL ILLNESS INSURANCE DATA
 MODELLING CRITICAL ILLNESS INSURANCE DATA Howard Waters Joint work with: Erengul Dodd (Ozkok), George Streftaris, David Wilkie University of Piraeus, October 2014 1 Plan: 1. Critical Illness Insurance
MODELLING CRITICAL ILLNESS INSURANCE DATA Howard Waters Joint work with: Erengul Dodd (Ozkok), George Streftaris, David Wilkie University of Piraeus, October 2014 1 Plan: 1. Critical Illness Insurance
A CRITICAL TABLE: PRICING CRITICAL ILLNESS IN THE UK ON A NEW INSURED LIVES TABLE
 A CRITICAL TABLE: PRICING CRITICAL ILLNESS IN THE UK ON A NEW INSURED LIVES TABLE Paul Brett and Johann du Toit Paul Brett, Regional Chief Actuary and Assistant General Manager, Gen Re LifeHealth UK. Email:
A CRITICAL TABLE: PRICING CRITICAL ILLNESS IN THE UK ON A NEW INSURED LIVES TABLE Paul Brett and Johann du Toit Paul Brett, Regional Chief Actuary and Assistant General Manager, Gen Re LifeHealth UK. Email:
Modeling and Analysis of Call Center Arrival Data: A Bayesian Approach
 Modeling and Analysis of Call Center Arrival Data: A Bayesian Approach Refik Soyer * Department of Management Science The George Washington University M. Murat Tarimcilar Department of Management Science
Modeling and Analysis of Call Center Arrival Data: A Bayesian Approach Refik Soyer * Department of Management Science The George Washington University M. Murat Tarimcilar Department of Management Science
Critical Illness insurance AC04 diagnosis rates
 Health and care conference 2011 Dave Heeney and Dave Grimshaw, CMI Critical Illness Committee Critical Illness insurance AC04 diagnosis rates 20 May 2011 2010 The Actuarial Profession www.actuaries.org.uk
Health and care conference 2011 Dave Heeney and Dave Grimshaw, CMI Critical Illness Committee Critical Illness insurance AC04 diagnosis rates 20 May 2011 2010 The Actuarial Profession www.actuaries.org.uk
Survival Analysis of Left Truncated Income Protection Insurance Data. [March 29, 2012]
![Survival Analysis of Left Truncated Income Protection Insurance Data. [March 29, 2012] Survival Analysis of Left Truncated Income Protection Insurance Data. [March 29, 2012]](/thumbs/25/5205543.jpg) Survival Analysis of Left Truncated Income Protection Insurance Data [March 29, 2012] 1 Qing Liu 2 David Pitt 3 Yan Wang 4 Xueyuan Wu Abstract One of the main characteristics of Income Protection Insurance
Survival Analysis of Left Truncated Income Protection Insurance Data [March 29, 2012] 1 Qing Liu 2 David Pitt 3 Yan Wang 4 Xueyuan Wu Abstract One of the main characteristics of Income Protection Insurance
Underwriting Critical Illness Insurance: A model for coronary heart disease and stroke
 Underwriting Critical Illness Insurance: A model for coronary heart disease and stroke Presented to the 6th International Congress on Insurance: Mathematics and Economics. July 2002. Lisbon, Portugal.
Underwriting Critical Illness Insurance: A model for coronary heart disease and stroke Presented to the 6th International Congress on Insurance: Mathematics and Economics. July 2002. Lisbon, Portugal.
IRISH CRITICAL ILLNESS EXPERIENCE 2001-2003
 THE SOCIETY OF ACTUARIES IN IRELAND IRISH CRITICAL ILLNESS EXPERIENCE 2001-2003 Report of the Critical Illness Working Party Anthony Brennan, Tony Jeffery, Brendan McCarthy, Colin Murray, Brenda Papillon,
THE SOCIETY OF ACTUARIES IN IRELAND IRISH CRITICAL ILLNESS EXPERIENCE 2001-2003 Report of the Critical Illness Working Party Anthony Brennan, Tony Jeffery, Brendan McCarthy, Colin Murray, Brenda Papillon,
Bayesian Methods for the Social and Behavioral Sciences
 Bayesian Methods for the Social and Behavioral Sciences Jeff Gill Harvard University 2007 ICPSR First Session: June 25-July 20, 9-11 AM. Email: [email protected] TA: Yu-Sung Su ([email protected]).
Bayesian Methods for the Social and Behavioral Sciences Jeff Gill Harvard University 2007 ICPSR First Session: June 25-July 20, 9-11 AM. Email: [email protected] TA: Yu-Sung Su ([email protected]).
Incorporating cost in Bayesian Variable Selection, with application to cost-effective measurement of quality of health care.
 Incorporating cost in Bayesian Variable Selection, with application to cost-effective measurement of quality of health care University of Florida 10th Annual Winter Workshop: Bayesian Model Selection and
Incorporating cost in Bayesian Variable Selection, with application to cost-effective measurement of quality of health care University of Florida 10th Annual Winter Workshop: Bayesian Model Selection and
BAYESIAN ANALYSIS OF AN AGGREGATE CLAIM MODEL USING VARIOUS LOSS DISTRIBUTIONS. by Claire Dudley
 BAYESIAN ANALYSIS OF AN AGGREGATE CLAIM MODEL USING VARIOUS LOSS DISTRIBUTIONS by Claire Dudley A dissertation submitted for the award of the degree of Master of Science in Actuarial Management School
BAYESIAN ANALYSIS OF AN AGGREGATE CLAIM MODEL USING VARIOUS LOSS DISTRIBUTIONS by Claire Dudley A dissertation submitted for the award of the degree of Master of Science in Actuarial Management School
PREDICTIVE DISTRIBUTIONS OF OUTSTANDING LIABILITIES IN GENERAL INSURANCE
 PREDICTIVE DISTRIBUTIONS OF OUTSTANDING LIABILITIES IN GENERAL INSURANCE BY P.D. ENGLAND AND R.J. VERRALL ABSTRACT This paper extends the methods introduced in England & Verrall (00), and shows how predictive
PREDICTIVE DISTRIBUTIONS OF OUTSTANDING LIABILITIES IN GENERAL INSURANCE BY P.D. ENGLAND AND R.J. VERRALL ABSTRACT This paper extends the methods introduced in England & Verrall (00), and shows how predictive
Statistics Graduate Courses
 Statistics Graduate Courses STAT 7002--Topics in Statistics-Biological/Physical/Mathematics (cr.arr.).organized study of selected topics. Subjects and earnable credit may vary from semester to semester.
Statistics Graduate Courses STAT 7002--Topics in Statistics-Biological/Physical/Mathematics (cr.arr.).organized study of selected topics. Subjects and earnable credit may vary from semester to semester.
Bayesian prediction of disability insurance frequencies using economic indicators
 Bayesian prediction of disability insurance frequencies using economic indicators Catherine Donnelly Heriot-Watt University, Edinburgh, UK Mario V. Wüthrich ETH Zurich, RisLab, Department of Mathematics,
Bayesian prediction of disability insurance frequencies using economic indicators Catherine Donnelly Heriot-Watt University, Edinburgh, UK Mario V. Wüthrich ETH Zurich, RisLab, Department of Mathematics,
Delme John Pritchard
 THE GENETICS OF ALZHEIMER S DISEASE, MODELLING DISABILITY AND ADVERSE SELECTION IN THE LONGTERM CARE INSURANCE MARKET By Delme John Pritchard Submitted for the Degree of Doctor of Philosophy at HeriotWatt
THE GENETICS OF ALZHEIMER S DISEASE, MODELLING DISABILITY AND ADVERSE SELECTION IN THE LONGTERM CARE INSURANCE MARKET By Delme John Pritchard Submitted for the Degree of Doctor of Philosophy at HeriotWatt
Handling attrition and non-response in longitudinal data
 Longitudinal and Life Course Studies 2009 Volume 1 Issue 1 Pp 63-72 Handling attrition and non-response in longitudinal data Harvey Goldstein University of Bristol Correspondence. Professor H. Goldstein
Longitudinal and Life Course Studies 2009 Volume 1 Issue 1 Pp 63-72 Handling attrition and non-response in longitudinal data Harvey Goldstein University of Bristol Correspondence. Professor H. Goldstein
THE USE OF STATISTICAL DISTRIBUTIONS TO MODEL CLAIMS IN MOTOR INSURANCE
 THE USE OF STATISTICAL DISTRIBUTIONS TO MODEL CLAIMS IN MOTOR INSURANCE Batsirai Winmore Mazviona 1 Tafadzwa Chiduza 2 ABSTRACT In general insurance, companies need to use data on claims gathered from
THE USE OF STATISTICAL DISTRIBUTIONS TO MODEL CLAIMS IN MOTOR INSURANCE Batsirai Winmore Mazviona 1 Tafadzwa Chiduza 2 ABSTRACT In general insurance, companies need to use data on claims gathered from
A Critical Review. Report of the Critical Illness Healthcare Study Group
 A Critical Review Report of the Critical Illness Healthcare Study Group Azim Dinani, Dave Grimshaw, Neil Robjohns, Stephen Somerville, Alasdair Spry and Jerry Staffurth Presented to the Staple Inn Actuarial
A Critical Review Report of the Critical Illness Healthcare Study Group Azim Dinani, Dave Grimshaw, Neil Robjohns, Stephen Somerville, Alasdair Spry and Jerry Staffurth Presented to the Staple Inn Actuarial
A Bayesian hierarchical surrogate outcome model for multiple sclerosis
 A Bayesian hierarchical surrogate outcome model for multiple sclerosis 3 rd Annual ASA New Jersey Chapter / Bayer Statistics Workshop David Ohlssen (Novartis), Luca Pozzi and Heinz Schmidli (Novartis)
A Bayesian hierarchical surrogate outcome model for multiple sclerosis 3 rd Annual ASA New Jersey Chapter / Bayer Statistics Workshop David Ohlssen (Novartis), Luca Pozzi and Heinz Schmidli (Novartis)
Pricing the Critical Illness Risk: The Continuous Challenge.
 Pricing the Critical Illness Risk: The Continuous Challenge. To be presented at the 6 th Global Conference of Actuaries, New Delhi 18 19 February 2004 Andres Webersinke, ACTUARY (DAV), FASSA, FASI 9 RAFFLES
Pricing the Critical Illness Risk: The Continuous Challenge. To be presented at the 6 th Global Conference of Actuaries, New Delhi 18 19 February 2004 Andres Webersinke, ACTUARY (DAV), FASSA, FASI 9 RAFFLES
Bayesian Statistics: Indian Buffet Process
 Bayesian Statistics: Indian Buffet Process Ilker Yildirim Department of Brain and Cognitive Sciences University of Rochester Rochester, NY 14627 August 2012 Reference: Most of the material in this note
Bayesian Statistics: Indian Buffet Process Ilker Yildirim Department of Brain and Cognitive Sciences University of Rochester Rochester, NY 14627 August 2012 Reference: Most of the material in this note
11. Time series and dynamic linear models
 11. Time series and dynamic linear models Objective To introduce the Bayesian approach to the modeling and forecasting of time series. Recommended reading West, M. and Harrison, J. (1997). models, (2 nd
11. Time series and dynamic linear models Objective To introduce the Bayesian approach to the modeling and forecasting of time series. Recommended reading West, M. and Harrison, J. (1997). models, (2 nd
Missing data and net survival analysis Bernard Rachet
 Workshop on Flexible Models for Longitudinal and Survival Data with Applications in Biostatistics Warwick, 27-29 July 2015 Missing data and net survival analysis Bernard Rachet General context Population-based,
Workshop on Flexible Models for Longitudinal and Survival Data with Applications in Biostatistics Warwick, 27-29 July 2015 Missing data and net survival analysis Bernard Rachet General context Population-based,
An Application of the G-formula to Asbestos and Lung Cancer. Stephen R. Cole. Epidemiology, UNC Chapel Hill. Slides: www.unc.
 An Application of the G-formula to Asbestos and Lung Cancer Stephen R. Cole Epidemiology, UNC Chapel Hill Slides: www.unc.edu/~colesr/ 1 Acknowledgements Collaboration with David B. Richardson, Haitao
An Application of the G-formula to Asbestos and Lung Cancer Stephen R. Cole Epidemiology, UNC Chapel Hill Slides: www.unc.edu/~colesr/ 1 Acknowledgements Collaboration with David B. Richardson, Haitao
Guaranteed Term Protection. Policy Document
 Guaranteed Term Protection Policy Document Introduction This document explains in detail the workings of your Guaranteed Term Protection Policy. It is important that you read each section of the document
Guaranteed Term Protection Policy Document Introduction This document explains in detail the workings of your Guaranteed Term Protection Policy. It is important that you read each section of the document
ACTUARIAL MATHEMATICS FOR LIFE CONTINGENT RISKS
 ACTUARIAL MATHEMATICS FOR LIFE CONTINGENT RISKS DAVID C. M. DICKSON University of Melbourne MARY R. HARDY University of Waterloo, Ontario V HOWARD R. WATERS Heriot-Watt University, Edinburgh CAMBRIDGE
ACTUARIAL MATHEMATICS FOR LIFE CONTINGENT RISKS DAVID C. M. DICKSON University of Melbourne MARY R. HARDY University of Waterloo, Ontario V HOWARD R. WATERS Heriot-Watt University, Edinburgh CAMBRIDGE
Applications of R Software in Bayesian Data Analysis
 Article International Journal of Information Science and System, 2012, 1(1): 7-23 International Journal of Information Science and System Journal homepage: www.modernscientificpress.com/journals/ijinfosci.aspx
Article International Journal of Information Science and System, 2012, 1(1): 7-23 International Journal of Information Science and System Journal homepage: www.modernscientificpress.com/journals/ijinfosci.aspx
STATISTICAL METHODS IN GENERAL INSURANCE. Philip J. Boland National University of Ireland, Dublin [email protected]
 STATISTICAL METHODS IN GENERAL INSURANCE Philip J. Boland National University of Ireland, Dublin [email protected] The Actuarial profession appeals to many with excellent quantitative skills who aspire
STATISTICAL METHODS IN GENERAL INSURANCE Philip J. Boland National University of Ireland, Dublin [email protected] The Actuarial profession appeals to many with excellent quantitative skills who aspire
Preliminary Report on. Hong Kong Assured Lives Mortality and Critical Illness. Experience Study 2000-2003
 Preliminary Report on Hong Kong Assured Lives Mortality and Critical Illness Experience Study 2000-2003 Actuarial Society of Hong Kong Experience Committee ASHK - Hong Kong Assured Lives Mortality and
Preliminary Report on Hong Kong Assured Lives Mortality and Critical Illness Experience Study 2000-2003 Actuarial Society of Hong Kong Experience Committee ASHK - Hong Kong Assured Lives Mortality and
Statistics in Applications III. Distribution Theory and Inference
 2.2 Master of Science Degrees The Department of Statistics at FSU offers three different options for an MS degree. 1. The applied statistics degree is for a student preparing for a career as an applied
2.2 Master of Science Degrees The Department of Statistics at FSU offers three different options for an MS degree. 1. The applied statistics degree is for a student preparing for a career as an applied
STA 4273H: Statistical Machine Learning
 STA 4273H: Statistical Machine Learning Russ Salakhutdinov Department of Statistics! [email protected]! http://www.cs.toronto.edu/~rsalakhu/ Lecture 6 Three Approaches to Classification Construct
STA 4273H: Statistical Machine Learning Russ Salakhutdinov Department of Statistics! [email protected]! http://www.cs.toronto.edu/~rsalakhu/ Lecture 6 Three Approaches to Classification Construct
BayesX - Software for Bayesian Inference in Structured Additive Regression
 BayesX - Software for Bayesian Inference in Structured Additive Regression Thomas Kneib Faculty of Mathematics and Economics, University of Ulm Department of Statistics, Ludwig-Maximilians-University Munich
BayesX - Software for Bayesian Inference in Structured Additive Regression Thomas Kneib Faculty of Mathematics and Economics, University of Ulm Department of Statistics, Ludwig-Maximilians-University Munich
Curriculum Vitae Richard A. L. Carter
 Curriculum Vitae Richard A. L. Carter January 25, 2011 Personal Office Addresses: Department of Economics University of Western Ontario London, Ontario N6A 5C2 Department of Economics University of Calgary
Curriculum Vitae Richard A. L. Carter January 25, 2011 Personal Office Addresses: Department of Economics University of Western Ontario London, Ontario N6A 5C2 Department of Economics University of Calgary
Arnold Zellner. Booth School of Business. University of Chicago. 5807 South Woodlawn Avenue Chicago, IL 60637. arnold.zellner@chicagobooth.
 H.G.B. Alexander Research Foundation Graduate School of Business University of Chicago Comments on Harold Jeffreys Theory of Probability Revisited, co-authored by C.P. Robert, N. Chopin and J. Rousseau.
H.G.B. Alexander Research Foundation Graduate School of Business University of Chicago Comments on Harold Jeffreys Theory of Probability Revisited, co-authored by C.P. Robert, N. Chopin and J. Rousseau.
Department/Academic Unit: Public Health Sciences Degree Program: Biostatistics Collaborative Program
 Department/Academic Unit: Public Health Sciences Degree Program: Biostatistics Collaborative Program Department of Mathematics and Statistics Degree Level Expectations, Learning Outcomes, Indicators of
Department/Academic Unit: Public Health Sciences Degree Program: Biostatistics Collaborative Program Department of Mathematics and Statistics Degree Level Expectations, Learning Outcomes, Indicators of
Prospective Life Tables
 An introduction to time dependent mortality models by Julien Antunes Mendes and Christophe Pochet TRENDS OF MORTALITY Life expectancy at birth among early humans was likely to be about 20 to 30 years.
An introduction to time dependent mortality models by Julien Antunes Mendes and Christophe Pochet TRENDS OF MORTALITY Life expectancy at birth among early humans was likely to be about 20 to 30 years.
Bayesian Estimation of Joint Survival Functions in Life Insurance
 ISBA 2, Proceedings, pp. ISBA and Eurostat, 21 Bayesian Estimation of Joint Survival Functions in Life Insurance ARKADY SHEMYAKIN and HEEKYUNG YOUN University of St. Thomas, Saint Paul, MN, USA Abstract:
ISBA 2, Proceedings, pp. ISBA and Eurostat, 21 Bayesian Estimation of Joint Survival Functions in Life Insurance ARKADY SHEMYAKIN and HEEKYUNG YOUN University of St. Thomas, Saint Paul, MN, USA Abstract:
Risk Insurance Definitions of the Critical Illness benefits. Dr. Eric Starke Insurance Medical Advisor
 Risk Insurance Definitions of the Critical Illness benefits Dr. Eric Starke Insurance Medical Advisor Why a Critical Illness benefit? A living benefit for a dreaded disease. Dr. Barnard once said the outcome
Risk Insurance Definitions of the Critical Illness benefits Dr. Eric Starke Insurance Medical Advisor Why a Critical Illness benefit? A living benefit for a dreaded disease. Dr. Barnard once said the outcome
Statistical Rules of Thumb
 Statistical Rules of Thumb Second Edition Gerald van Belle University of Washington Department of Biostatistics and Department of Environmental and Occupational Health Sciences Seattle, WA WILEY AJOHN
Statistical Rules of Thumb Second Edition Gerald van Belle University of Washington Department of Biostatistics and Department of Environmental and Occupational Health Sciences Seattle, WA WILEY AJOHN
Program description for the Master s Degree Program in Mathematics and Finance
 Program description for the Master s Degree Program in Mathematics and Finance : English: Master s Degree in Mathematics and Finance Norwegian, bokmål: Master i matematikk og finans Norwegian, nynorsk:
Program description for the Master s Degree Program in Mathematics and Finance : English: Master s Degree in Mathematics and Finance Norwegian, bokmål: Master i matematikk og finans Norwegian, nynorsk:
A Bayesian Antidote Against Strategy Sprawl
 A Bayesian Antidote Against Strategy Sprawl Benjamin Scheibehenne ([email protected]) University of Basel, Missionsstrasse 62a 4055 Basel, Switzerland & Jörg Rieskamp ([email protected])
A Bayesian Antidote Against Strategy Sprawl Benjamin Scheibehenne ([email protected]) University of Basel, Missionsstrasse 62a 4055 Basel, Switzerland & Jörg Rieskamp ([email protected])
STATISTICA Formula Guide: Logistic Regression. Table of Contents
 : Table of Contents... 1 Overview of Model... 1 Dispersion... 2 Parameterization... 3 Sigma-Restricted Model... 3 Overparameterized Model... 4 Reference Coding... 4 Model Summary (Summary Tab)... 5 Summary
: Table of Contents... 1 Overview of Model... 1 Dispersion... 2 Parameterization... 3 Sigma-Restricted Model... 3 Overparameterized Model... 4 Reference Coding... 4 Model Summary (Summary Tab)... 5 Summary
CHAPTER 3 EXAMPLES: REGRESSION AND PATH ANALYSIS
 Examples: Regression And Path Analysis CHAPTER 3 EXAMPLES: REGRESSION AND PATH ANALYSIS Regression analysis with univariate or multivariate dependent variables is a standard procedure for modeling relationships
Examples: Regression And Path Analysis CHAPTER 3 EXAMPLES: REGRESSION AND PATH ANALYSIS Regression analysis with univariate or multivariate dependent variables is a standard procedure for modeling relationships
Least Squares Estimation
 Least Squares Estimation SARA A VAN DE GEER Volume 2, pp 1041 1045 in Encyclopedia of Statistics in Behavioral Science ISBN-13: 978-0-470-86080-9 ISBN-10: 0-470-86080-4 Editors Brian S Everitt & David
Least Squares Estimation SARA A VAN DE GEER Volume 2, pp 1041 1045 in Encyclopedia of Statistics in Behavioral Science ISBN-13: 978-0-470-86080-9 ISBN-10: 0-470-86080-4 Editors Brian S Everitt & David
Nonnested model comparison of GLM and GAM count regression models for life insurance data
 Nonnested model comparison of GLM and GAM count regression models for life insurance data Claudia Czado, Julia Pfettner, Susanne Gschlößl, Frank Schiller December 8, 2009 Abstract Pricing and product development
Nonnested model comparison of GLM and GAM count regression models for life insurance data Claudia Czado, Julia Pfettner, Susanne Gschlößl, Frank Schiller December 8, 2009 Abstract Pricing and product development
Analyzing Clinical Trial Data via the Bayesian Multiple Logistic Random Effects Model
 Analyzing Clinical Trial Data via the Bayesian Multiple Logistic Random Effects Model Bartolucci, A.A 1, Singh, K.P 2 and Bae, S.J 2 1 Dept. of Biostatistics, University of Alabama at Birmingham, Birmingham,
Analyzing Clinical Trial Data via the Bayesian Multiple Logistic Random Effects Model Bartolucci, A.A 1, Singh, K.P 2 and Bae, S.J 2 1 Dept. of Biostatistics, University of Alabama at Birmingham, Birmingham,
Service courses for graduate students in degree programs other than the MS or PhD programs in Biostatistics.
 Course Catalog In order to be assured that all prerequisites are met, students must acquire a permission number from the education coordinator prior to enrolling in any Biostatistics course. Courses are
Course Catalog In order to be assured that all prerequisites are met, students must acquire a permission number from the education coordinator prior to enrolling in any Biostatistics course. Courses are
Representative market data weighted to reveal insights. A multifaceted view of actual vs. expected claims
 Critical illness insurance in Israel The Munich Re Biometric Critical Illness Study 2010 A unique biometric Critical Illness study Munich Re has conducted a comprehensive study of critical illness insurance
Critical illness insurance in Israel The Munich Re Biometric Critical Illness Study 2010 A unique biometric Critical Illness study Munich Re has conducted a comprehensive study of critical illness insurance
Development Period 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Observed Payments
 Pricing and reserving in the general insurance industry Solutions developed in The SAS System John Hansen & Christian Larsen, Larsen & Partners Ltd 1. Introduction The two business solutions presented
Pricing and reserving in the general insurance industry Solutions developed in The SAS System John Hansen & Christian Larsen, Larsen & Partners Ltd 1. Introduction The two business solutions presented
PROBABILITY AND STATISTICS. Ma 527. 1. To teach a knowledge of combinatorial reasoning.
 PROBABILITY AND STATISTICS Ma 527 Course Description Prefaced by a study of the foundations of probability and statistics, this course is an extension of the elements of probability and statistics introduced
PROBABILITY AND STATISTICS Ma 527 Course Description Prefaced by a study of the foundations of probability and statistics, this course is an extension of the elements of probability and statistics introduced
Underwriting risk control in non-life insurance via generalized linear models and stochastic programming
 Underwriting risk control in non-life insurance via generalized linear models and stochastic programming 1 Introduction Martin Branda 1 Abstract. We focus on rating of non-life insurance contracts. We
Underwriting risk control in non-life insurance via generalized linear models and stochastic programming 1 Introduction Martin Branda 1 Abstract. We focus on rating of non-life insurance contracts. We
Critical Illness Fit for the Elderly?
 No. 31, October 2014 Critical Illness Fit for the Elderly? by Tim Eppert + Critical illness (CI) insurance provides a financial lifeline to people facing the consequences of being diagnosed with a severe
No. 31, October 2014 Critical Illness Fit for the Elderly? by Tim Eppert + Critical illness (CI) insurance provides a financial lifeline to people facing the consequences of being diagnosed with a severe
Critical Illness Claims Report 2006
 This communication is intended for qualified financial advisers only and must not be relied upon by anyone else. This is the Critical Illness Claims Report 2006 from Assurance Limited Hello. This report
This communication is intended for qualified financial advisers only and must not be relied upon by anyone else. This is the Critical Illness Claims Report 2006 from Assurance Limited Hello. This report
Randomized trials versus observational studies
 Randomized trials versus observational studies The case of postmenopausal hormone therapy and heart disease Miguel Hernán Harvard School of Public Health www.hsph.harvard.edu/causal Joint work with James
Randomized trials versus observational studies The case of postmenopausal hormone therapy and heart disease Miguel Hernán Harvard School of Public Health www.hsph.harvard.edu/causal Joint work with James
The Actuary s Toolkit: A View from EMB
 The Actuary s Toolkit: A View from EMB P.D. England EMB Consultancy LLP, Saddlers Court, 64-74 East Street, Epsom, KT17 1HB. [email protected] http://emb.co.uk ABSTRACT In this short paper, some
The Actuary s Toolkit: A View from EMB P.D. England EMB Consultancy LLP, Saddlers Court, 64-74 East Street, Epsom, KT17 1HB. [email protected] http://emb.co.uk ABSTRACT In this short paper, some
Institute of Actuaries of India Subject CT3 Probability and Mathematical Statistics
 Institute of Actuaries of India Subject CT3 Probability and Mathematical Statistics For 2015 Examinations Aim The aim of the Probability and Mathematical Statistics subject is to provide a grounding in
Institute of Actuaries of India Subject CT3 Probability and Mathematical Statistics For 2015 Examinations Aim The aim of the Probability and Mathematical Statistics subject is to provide a grounding in
The Role of Insurance in Providing Access to Cardiac Care in Maryland. Samuel L. Brown, Ph.D. University of Baltimore College of Public Affairs
 The Role of Insurance in Providing Access to Cardiac Care in Maryland Samuel L. Brown, Ph.D. University of Baltimore College of Public Affairs Heart Disease Heart Disease is the leading cause of death
The Role of Insurance in Providing Access to Cardiac Care in Maryland Samuel L. Brown, Ph.D. University of Baltimore College of Public Affairs Heart Disease Heart Disease is the leading cause of death
Sample Size Designs to Assess Controls
 Sample Size Designs to Assess Controls B. Ricky Rambharat, PhD, PStat Lead Statistician Office of the Comptroller of the Currency U.S. Department of the Treasury Washington, DC FCSM Research Conference
Sample Size Designs to Assess Controls B. Ricky Rambharat, PhD, PStat Lead Statistician Office of the Comptroller of the Currency U.S. Department of the Treasury Washington, DC FCSM Research Conference
Gen Re Dread Disease Survey 2004-2008 Initial Results
 Gen Re Dread Disease Survey 2004-2008 Wolfgang Droste Session Number: MBR8 Joint IACA, IAAHS and PBSS Colloquium in Hong Kong www.actuaries.org/hongkong2012/ Agenda Background of Gen Re s Dread Disease
Gen Re Dread Disease Survey 2004-2008 Wolfgang Droste Session Number: MBR8 Joint IACA, IAAHS and PBSS Colloquium in Hong Kong www.actuaries.org/hongkong2012/ Agenda Background of Gen Re s Dread Disease
Analysis of Financial Time Series
 Analysis of Financial Time Series Analysis of Financial Time Series Financial Econometrics RUEY S. TSAY University of Chicago A Wiley-Interscience Publication JOHN WILEY & SONS, INC. This book is printed
Analysis of Financial Time Series Analysis of Financial Time Series Financial Econometrics RUEY S. TSAY University of Chicago A Wiley-Interscience Publication JOHN WILEY & SONS, INC. This book is printed
http://www.springer.com/978-0-387-71392-2
 Preface This book, like many other books, was delivered under tremendous inspiration and encouragement from my teachers, research collaborators, and students. My interest in longitudinal data analysis
Preface This book, like many other books, was delivered under tremendous inspiration and encouragement from my teachers, research collaborators, and students. My interest in longitudinal data analysis
Bayesian inference for population prediction of individuals without health insurance in Florida
 Bayesian inference for population prediction of individuals without health insurance in Florida Neung Soo Ha 1 1 NISS 1 / 24 Outline Motivation Description of the Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System,
Bayesian inference for population prediction of individuals without health insurance in Florida Neung Soo Ha 1 1 NISS 1 / 24 Outline Motivation Description of the Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System,
52,929,390 paid out in critical illness claims in the first six months of 2013*
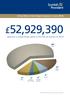 Critical Illness Report (January to June 2013) 52,929,390 paid out in critical illness claims in the first six months of 2013* 66 % Cancer 12 % Heart Attack 9 % Other 3 % Benign Brain Tumour 4 % Multiple
Critical Illness Report (January to June 2013) 52,929,390 paid out in critical illness claims in the first six months of 2013* 66 % Cancer 12 % Heart Attack 9 % Other 3 % Benign Brain Tumour 4 % Multiple
STAT2400 STAT2400 STAT2400 STAT2400 STAT2400 STAT2400 STAT2400 STAT2400&3400 STAT2400&3400 STAT2400&3400 STAT2400&3400 STAT3400 STAT3400
 Exam P Learning Objectives All 23 learning objectives are covered. General Probability STAT2400 STAT2400 STAT2400 STAT2400 STAT2400 STAT2400 STAT2400 1. Set functions including set notation and basic elements
Exam P Learning Objectives All 23 learning objectives are covered. General Probability STAT2400 STAT2400 STAT2400 STAT2400 STAT2400 STAT2400 STAT2400 1. Set functions including set notation and basic elements
Model Selection and Claim Frequency for Workers Compensation Insurance
 Model Selection and Claim Frequency for Workers Compensation Insurance Jisheng Cui, David Pitt and Guoqi Qian Abstract We consider a set of workers compensation insurance claim data where the aggregate
Model Selection and Claim Frequency for Workers Compensation Insurance Jisheng Cui, David Pitt and Guoqi Qian Abstract We consider a set of workers compensation insurance claim data where the aggregate
Exam P - Total 23/23 - 1 -
 Exam P Learning Objectives Schools will meet 80% of the learning objectives on this examination if they can show they meet 18.4 of 23 learning objectives outlined in this table. Schools may NOT count a
Exam P Learning Objectives Schools will meet 80% of the learning objectives on this examination if they can show they meet 18.4 of 23 learning objectives outlined in this table. Schools may NOT count a
SUMAN DUVVURU STAT 567 PROJECT REPORT
 SUMAN DUVVURU STAT 567 PROJECT REPORT SURVIVAL ANALYSIS OF HEROIN ADDICTS Background and introduction: Current illicit drug use among teens is continuing to increase in many countries around the world.
SUMAN DUVVURU STAT 567 PROJECT REPORT SURVIVAL ANALYSIS OF HEROIN ADDICTS Background and introduction: Current illicit drug use among teens is continuing to increase in many countries around the world.
GENERALIZED LINEAR MODELS IN VEHICLE INSURANCE
 ACTA UNIVERSITATIS AGRICULTURAE ET SILVICULTURAE MENDELIANAE BRUNENSIS Volume 62 41 Number 2, 2014 http://dx.doi.org/10.11118/actaun201462020383 GENERALIZED LINEAR MODELS IN VEHICLE INSURANCE Silvie Kafková
ACTA UNIVERSITATIS AGRICULTURAE ET SILVICULTURAE MENDELIANAE BRUNENSIS Volume 62 41 Number 2, 2014 http://dx.doi.org/10.11118/actaun201462020383 GENERALIZED LINEAR MODELS IN VEHICLE INSURANCE Silvie Kafková
Using SAS PROC MCMC to Estimate and Evaluate Item Response Theory Models
 Using SAS PROC MCMC to Estimate and Evaluate Item Response Theory Models Clement A Stone Abstract Interest in estimating item response theory (IRT) models using Bayesian methods has grown tremendously
Using SAS PROC MCMC to Estimate and Evaluate Item Response Theory Models Clement A Stone Abstract Interest in estimating item response theory (IRT) models using Bayesian methods has grown tremendously
Cardiac Rehabilitation An Underutilized Class I Treatment for Cardiovascular Disease
 Cardiac Rehabilitation An Underutilized Class I Treatment for Cardiovascular Disease What is Cardiac Rehabilitation? Cardiac rehabilitation is a comprehensive exercise, education, and behavior modification
Cardiac Rehabilitation An Underutilized Class I Treatment for Cardiovascular Disease What is Cardiac Rehabilitation? Cardiac rehabilitation is a comprehensive exercise, education, and behavior modification
Practical Example of a Split Benefit Accelerated Critical Illness Insurance Product
 Practical Example of a Split Accelerated Critical Illness Insurance Product Anton Brink, Ph.D. RGA UK Services Limited Presentation Disclaimers: Contains all personal views based on external research These
Practical Example of a Split Accelerated Critical Illness Insurance Product Anton Brink, Ph.D. RGA UK Services Limited Presentation Disclaimers: Contains all personal views based on external research These
Validation of Software for Bayesian Models using Posterior Quantiles. Samantha R. Cook Andrew Gelman Donald B. Rubin DRAFT
 Validation of Software for Bayesian Models using Posterior Quantiles Samantha R. Cook Andrew Gelman Donald B. Rubin DRAFT Abstract We present a simulation-based method designed to establish that software
Validation of Software for Bayesian Models using Posterior Quantiles Samantha R. Cook Andrew Gelman Donald B. Rubin DRAFT Abstract We present a simulation-based method designed to establish that software
A reserve risk model for a non-life insurance company
 A reserve risk model for a non-life insurance company Salvatore Forte 1, Matteo Ialenti 1, and Marco Pirra 2 1 Department of Actuarial Sciences, Sapienza University of Roma, Viale Regina Elena 295, 00185
A reserve risk model for a non-life insurance company Salvatore Forte 1, Matteo Ialenti 1, and Marco Pirra 2 1 Department of Actuarial Sciences, Sapienza University of Roma, Viale Regina Elena 295, 00185
COURSE PLAN BDA: Biomedical Data Analysis Master in Bioinformatics for Health Sciences. 2015-2016 Academic Year Qualification.
 COURSE PLAN BDA: Biomedical Data Analysis Master in Bioinformatics for Health Sciences 2015-2016 Academic Year Qualification. Master's Degree 1. Description of the subject Subject name: Biomedical Data
COURSE PLAN BDA: Biomedical Data Analysis Master in Bioinformatics for Health Sciences 2015-2016 Academic Year Qualification. Master's Degree 1. Description of the subject Subject name: Biomedical Data
Government of Russian Federation. Faculty of Computer Science School of Data Analysis and Artificial Intelligence
 Government of Russian Federation Federal State Autonomous Educational Institution of High Professional Education National Research University «Higher School of Economics» Faculty of Computer Science School
Government of Russian Federation Federal State Autonomous Educational Institution of High Professional Education National Research University «Higher School of Economics» Faculty of Computer Science School
An Update on the UK Critical Illness Market. Sue Elliott, Principal Consultant Towers Watson
 An Update on the UK Critical Illness Market Sue Elliott, Principal Consultant Towers Watson Agenda for today New business sales update Experience update Association of British Insurers ("ABI") activity
An Update on the UK Critical Illness Market Sue Elliott, Principal Consultant Towers Watson Agenda for today New business sales update Experience update Association of British Insurers ("ABI") activity
Modeling the Claim Duration of Income Protection Insurance Policyholders Using Parametric Mixture Models
 Modeling the Claim Duration of Income Protection Insurance Policyholders Using Parametric Mixture Models Abstract This paper considers the modeling of claim durations for existing claimants under income
Modeling the Claim Duration of Income Protection Insurance Policyholders Using Parametric Mixture Models Abstract This paper considers the modeling of claim durations for existing claimants under income
Peace. Mind. VivoLife. Why is it good for me? Flexible payment terms. A lifetime of protection. 4 enhanced protection 1 (up to 350% of sum assured)
 Peace of Mind VivoLife Flexible payment terms. A lifetime of protection. VivoLife gives you the flexibility to choose from 3 levels of enhanced protection 1 for you and your loved ones. What s more, enjoy
Peace of Mind VivoLife Flexible payment terms. A lifetime of protection. VivoLife gives you the flexibility to choose from 3 levels of enhanced protection 1 for you and your loved ones. What s more, enjoy
Prognostic impact of uric acid in patients with stable coronary artery disease
 Prognostic impact of uric acid in patients with stable coronary artery disease Gjin Ndrepepa, Siegmund Braun, Martin Hadamitzky, Massimiliano Fusaro, Hans-Ullrich Haase, Kathrin A. Birkmeier, Albert Schomig,
Prognostic impact of uric acid in patients with stable coronary artery disease Gjin Ndrepepa, Siegmund Braun, Martin Hadamitzky, Massimiliano Fusaro, Hans-Ullrich Haase, Kathrin A. Birkmeier, Albert Schomig,
False Discovery Rates
 False Discovery Rates John D. Storey Princeton University, Princeton, USA January 2010 Multiple Hypothesis Testing In hypothesis testing, statistical significance is typically based on calculations involving
False Discovery Rates John D. Storey Princeton University, Princeton, USA January 2010 Multiple Hypothesis Testing In hypothesis testing, statistical significance is typically based on calculations involving
Linear regression methods for large n and streaming data
 Linear regression methods for large n and streaming data Large n and small or moderate p is a fairly simple problem. The sufficient statistic for β in OLS (and ridge) is: The concept of sufficiency is
Linear regression methods for large n and streaming data Large n and small or moderate p is a fairly simple problem. The sufficient statistic for β in OLS (and ridge) is: The concept of sufficiency is
Bayesian Phylogeny and Measures of Branch Support
 Bayesian Phylogeny and Measures of Branch Support Bayesian Statistics Imagine we have a bag containing 100 dice of which we know that 90 are fair and 10 are biased. The
Bayesian Phylogeny and Measures of Branch Support Bayesian Statistics Imagine we have a bag containing 100 dice of which we know that 90 are fair and 10 are biased. The
Actuarial Society of India
 Actuarial Society of India EXAMINATION 30 th October 2006 Subject ST1 Health and Care Insurance Specialist Technical Time allowed: Three hours (14.15* pm 17.30 pm) INSTRUCTIONS TO THE CANDIDATE 1. Enter
Actuarial Society of India EXAMINATION 30 th October 2006 Subject ST1 Health and Care Insurance Specialist Technical Time allowed: Three hours (14.15* pm 17.30 pm) INSTRUCTIONS TO THE CANDIDATE 1. Enter
Lifetime Protection Plan from Standard Life Protecting you and your family
 Lifetime Protection Plan from Standard Life Protecting you and your family Remember when you thought you were invincible 1 of 33 2 of 33 When was the last time you felt invincible? Contents The need for
Lifetime Protection Plan from Standard Life Protecting you and your family Remember when you thought you were invincible 1 of 33 2 of 33 When was the last time you felt invincible? Contents The need for
A Guide to Critical Illness Insurance
 A Guide to Critical Illness Insurance This guide about Critical Illness cover is designed to help you decide if this is a suitable product for you. It aims to help by answering the following questions:
A Guide to Critical Illness Insurance This guide about Critical Illness cover is designed to help you decide if this is a suitable product for you. It aims to help by answering the following questions:
Probabilistic Methods for Time-Series Analysis
 Probabilistic Methods for Time-Series Analysis 2 Contents 1 Analysis of Changepoint Models 1 1.1 Introduction................................ 1 1.1.1 Model and Notation....................... 2 1.1.2 Example:
Probabilistic Methods for Time-Series Analysis 2 Contents 1 Analysis of Changepoint Models 1 1.1 Introduction................................ 1 1.1.1 Model and Notation....................... 2 1.1.2 Example:
