Blood-thinning medication after stroke
|
|
|
- Marybeth Hawkins
- 10 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Stroke Helpline: Website: stroke.org.uk Blood-thinning medication after stroke Blood-thinning medicines are drugs that help to prevent clots forming in your blood. They are often prescribed after a transient ischaemic attack (TIA) or an ischaemic stroke. This factsheet explains the link between blood clots and stroke and the types of blood-thinning medication that you may be prescribed to help reduce your risk of having another ischaemic stroke or TIA. What is a stroke? A stroke is a brain attack. It happens when the blood supply to part of your brain is cut off. It can be caused by a blockage in one of the blood vessels leading to your brain or by a bleed in your brain. Blood carries essential nutrients and oxygen to your brain. Without blood your brain cells can be damaged or die. Around 85% of strokes are caused by a blockage cutting off the blood supply to the brain. This is called an ischaemic stroke. The blockage can be caused by a blood clot forming in an artery leading to your brain or within one of the small vessels deep inside your brain. This is known as cerebral thrombosis. Blockages in the brain can also be caused by a blood clot or other matter (such as an air bubble or piece of fatty debris) moving through the blood stream from another part of the body. This is called a cerebral embolism. What is a TIA? A TIA is also known as a mini-stroke. It is the same as a stroke, except that the symptoms last for a short amount of time and no longer than 24 hours. Although the symptoms may not last long, a TIA is still very serious. It is a sign that there is a problem and you are at risk of having a stroke. More than 1 in 12 people will have a stroke within a week of having a TIA. Because of this, a TIA is often called a warning stroke. Like ischaemic strokes, TIAs can be caused by blood clots. What are blood-thinning medicines? When our blood vessels are cut or become broken a blood clot will naturally form to plug the hole until the blood vessel heals. This stops our vital organs and tissues from losing too much blood. Sometimes, a blood clot can form within a blood vessel and cause a blockage. If this happens in an artery leading to your brain, it can cause a stroke. Stroke Association July
2 Blood-thinning medication reduces your blood s ability to clot and therefore reduces your risk of having a stroke. Some strokes (around 15%) are caused by bleeding in or around the brain. This is called a haemorrhagic stroke. Blood-thinning medicines should not be prescribed after a haemorrhagic stroke as they can make this type of stroke worse. However, if you ve had a haemorrhagic stroke, but you also have a very high risk of having an ischaemic stroke, your doctor may recommend that the benefits of taking blood-thinning medication would outweigh the risks. There are two types of blood-thinning medicines: antiplatelets and anticoagulants. They work in different ways: Antiplatelets There are small cells in your blood called platelets. When a blood vessel becomes damaged, these platelets stick together to form a blood clot. Antiplatelet drugs stop platelets from sticking together as easily, which reduces the risk of blood clots forming. Some common antiplatelet drugs are aspirin, dipyridamole and clopidogrel. Anticoagulants Anticoagulants also stop your blood from being able to clot as easily. They do this by stopping your blood from producing certain proteins, which platelets need to help them form a clot. Anticoagulants also make existing blood clots more stable and less likely to break off and travel to other parts of your body. Some common anticoagulants are warfarin, dabigatran etexilate, rivaroxaban and apixaban. What medication will I be given? Initial treatment If you have had a TIA you are at an increased risk of having a stroke. If you are diagnosed as having had a TIA or your doctor suspects that you may have had one, it s likely that you will be given aspirin or clopidogrel to help reduce your risk. If you have a stroke and your brain scan confirms that it has been caused by a blood clot, you will probably be given a daily dose of aspirin, which you will need to take for up to two weeks. Long-term treatment In the longer term, you will usually be prescribed a different blood-thinning medicine to reduce your risk of stroke. If you have had a TIA, you could be given: clopidogrel aspirin dipyridamole and aspirin together dipyridamole alone, if you can t take aspirin. If you have had a stroke, you could be given: clopidogrel dipyridamole and aspirin together dipyridamole alone, if you can t take clopidogrel or aspirin. Atrial fibrillation (AF) is a type of irregular heartbeat. If you have AF you will usually be prescribed an anticoagulant instead. This is because AF increases the risk of blood clots forming in your heart. By taking an anticoagulant, your blood is less likely to clot and so your risk of stroke is reduced. 2 Stroke Association July 2015
3 Types of blood-thinning medication Aspirin Aspirin is often used to treat pain and reduce fever, but it is also an antiplatelet and in low doses it can help to prevent blood clots. After a stroke or TIA, it s likely that you ll be prescribed 300mg of aspirin a day to begin with. However, in the long-term, it s likely you ll be prescribed clopidrogrel, or aspirin and dipyridamole together, unless there s a reason why you can t take them. In this case, you may be given aspirin on its own. Aspirin can sometimes irritate your stomach, but taking it with food or straight after you ve eaten can help to prevent this. You should also make sure that you drink plenty of water so that you don t become dehydrated. Aspirin is not suitable for everyone. If you have liver or kidney problems, asthma, a blood-clotting disorder or if you ve ever had an ulcer in your stomach you may not be able to take it. It s not usually prescribed when you re pregnant and you won t be able to take it if you re allergic to other nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like ibuprofen or naproxen. The most common side effects that aspirin causes are indigestion and bleeding. In a small number of people it can cause bleeding in the stomach. If you notice unusual bleeding, such as coughing up blood or if there is blood when you go to the toilet, you should see your doctor immediately. Risk of bleeding Because blood-thinning medication affects the way your blood clots, all blood-thinning medicines increase your risk of bleeding. So if you cut or injure yourself, it may take slightly longer than usual for the bleeding to stop. This shouldn t cause too many problems for small cuts and injuries. However, if you are concerned by your bleeding, you should contact your doctor straight away. Other, less common side effects include wheezing or breathing difficulties, nausea, rashes and dizziness. Some people develop ulcers when they take aspirin for a long time because it damages the lining of your stomach. Your stomach is lined with special mucus that protects it from the acid it produces to digest food. If the lining is damaged, your stomach acid can start to erode the tissue underneath and cause an ulcer. If you have a burning or gnawing pain in your stomach this could be a sign that you have an ulcer and you should go to see your doctor. Allergic reactions If you are feeling breathless, have a runny nose, severe rash, itching or swelling in your throat, mouth or face, these could be signs that you are allergic to some of the medicines you are taking. If you notice any of these signs you should contact your doctor immediately. Stroke Association July
4 Clopidogrel Clopidogrel is an antiplatelet drug. Usually, if you are prescribed clopidogrel after a stroke or TIA, the dose is 75mg a day. It can be taken with or without food, and you should take it at the same time each day. Clopidogrel is not suitable for everyone. It is not recommended if you are pregnant or breastfeeding. You also need to tell your doctor if you have liver or kidney problems, a bleeding disorder, or if you are taking other medicines. Clopidogrel interacts with other medicines such as aspirin, warfarin and proton pump inhibitors. The main side effects of clopidogrel are bleeding and bruising. Some people experience diarrhoea, stomach pain, indigestion or heartburn when taking clopidogrel. Other side effects include nausea, vomiting, headaches, dizziness, constipation, itching and sore throat. Dipyridamole (Persantin) Dipyridamole is also known by the brand name Persantin. It is an antiplatelet drug that is often prescribed with aspirin. If you are prescribed dipyridamole after a stroke or TIA the dose is usually 200mg twice a day, together with 75mg a day of aspirin. There is a tablet called Asasantin, which combines both aspirin and dipyridamole in one. If you cannot take aspirin, you will probably be given dipyridamole to take on its own. You should take one dipyramole tablet in the morning and one in the evening and it s best to take them with food. Dipyridamole is not suitable for everyone, especially people with heart problems. If you ve had a heart attack, have heart disease, angina or heart valve problems you 4 may not be able to take it. It can also react with other medicines such as anticoagulant, antiplatelet and blood pressure drugs. So it s important that your doctor knows your full medical history, including all the medication that you re taking, before you start taking dipyridamole. You should also tell your doctor if you are pregnant, planning on becoming pregnant, or breastfeeding, as you should only take dipyridamole in these circumstances if it s essential for you to do so. Common side effects of dipyridamole include nausea and an upset stomach, dizziness, indigestion and headaches. Headaches can sometimes be improved by having your dose of dipyridamole reduced for a period of time, and then raising it back to your full dose again later. Other, less common side effects, include diarrhoea, bleeding, rashes, muscle pain and fainting. Warfarin If you have atrial fibrillation (AF) or other heart problems you may be prescribed warfarin to help reduce your risk of having a stroke. It works by changing the way your liver uses vitamin K. Vitamin K plays an important role in the blood-clotting process. Warfarin slows down the way vitamin K is made, which increases the time it takes for your blood to clot. Warfarin is given in tablet form and the dose needs to be tailored to you individually. This is because people respond to warfarin differently and it is not easy to predict. It should be taken at the same time every day. You need to have regular blood tests if you take warfarin, to make sure that your blood is not becoming too thin. Stroke Association July 2015
5 The test checks how quickly your blood clots at a particular stage in the process and compares it to the International Normalised Ratio (INR). INR is expressed as a number. A normal INR value for blood (when you are not taking anticoagulants) is around one. If you have AF and are on warfarin your blood should be two to three times thinner than normal, so you should have an INR value of between two to three. You will need to have a blood test at least every week when you first start taking warfarin, as your dose will need to be adjusted to suit you. When your INR is stable, you will probably need a blood test every six to eight weeks. When you are first prescribed warfarin you should receive a pack from your GP or hospital which contains a credit-card sized alert card, a yellow booklet called Oral Anticoagulant Therapy, and a record card. You should carry your alert card at all times in case of a medical emergency. Warfarin is not suitable for everyone and should not be taken if you have very high blood pressure or stomach ulcers. It should also be avoided if you are pregnant. The main side effect of warfarin is bleeding. If you experience bleeding you should seek medical attention and have an urgent blood test. Less common side effects of warfarin include rashes, vomiting and diarrhoea. Some medicines can interact with warfarin and affect your INR. Always tell your doctor or pharmacist if you are on warfarin before taking any new medication, particularly antibiotics, antidepressants, aspirin, statins or ulcer medicines. Warfarin and food If you are taking warfarin, you need to be mindful of the foods you are eating. Your warfarin dose is usually adjusted to the level of vitamin K in your diet. So you shouldn t make sudden changes to the amount of vitamin K that you eat, as this could affect your INR. This doesn t mean that you should avoid foods that are high in vitamin K, as these are an important part of a healthy diet. Equally, you shouldn t change the amount you eat without talking to your anticoagulant specialist first. Foods that are very high in vitamin K and are most likely to affect your INR are green, leafy vegetables such as spring greens, spinach and kale. Olive oil, rapeseed oil, soya oil and soya flour are also high in vitamin K. These can be found in salad dressings, mayonnaise and pre-cooked foods. Keep your intake of vitamin K from these products stable. It s best to avoid cranberries and grapefruits, including their juices, because they can affect the way that warfarin works. Some natural health food products and herbal remedies can also affect warfarin, so check with your pharmacist or doctor before taking anything like this. Alcohol can increase your INR, so you need to keep within the recommended limits (three units a day for men, two units a day for women) and avoid binge drinking. Some research has shown that gaining or losing weight can affect your INR, so talk to your anticoagulant specialist about any changes to your weight. Stroke Association July
6 6 When you re taking warfarin, the main things to remember are: eat a healthy diet keep the amount of vitamin K in your diet the same from week to week talk to your anticoagulant specialist about any changes you want to make to your diet or weight. Dabigatran etexilate (Pradaxa) Dabigatran etexilate is known by the brand name Pradaxa. It is a new type of anticoagulant drug. It is usually prescribed at a dose of 150mg or 110mg to be taken twice a day with or without food. Dabigatran etexilate is not suitable if you are pregnant or breastfeeding. It can also interact with other medicines, including aspirin, clopidogrel, heparin, rivaroxaban and verapamil. It also interacts with the herbal remedy St John s Wort, so tell your doctor or pharmacist if you re taking this. The most common side effect of dabigatran etexilate is bleeding. See your doctor immediately if you notice unusual bleeding. Other side effects include diarrhoea, indigestion, nausea and stomach pain. Rivaroxaban (Xarelto) Rivaroxaban is also known by the brand name Xarelto. It is a new type of anticoagulant. It is usually prescribed at a dose of 20mg a day and must be taken with food. If you have kidney problems, you may be given a smaller dose of 15mg. It s best to take it at the same time each day. Rivaroxaban is not suitable if you are pregnant or breastfeeding. It also interacts with other medicines such as aspirin, clopidogrel, warfarin and the herbal remedy St John s Wort. Side effects of rivaroxaban include bleeding, constipation, diarrhoea, dizziness and fainting. Apixaban (eliquis) Apixaban is known by the brand name Eliquis. It is a new type of anticoagulant. Apixaban is usually prescribed at a dose of 5mg to be taken twice a day. It can be taken with or without food. If you have kidney problems, you will usually be given a smaller dose of 2.5mg. It s best to take it at the same time each day. Apixaban is not suitable if you are pregnant or breastfeeding. It also interacts with other medicines such as aspirin, clopidogrel, warfarin and the herbal remedy St John s Wort. The main side effect of apixaban is bleeding. Edoxaban is a new anticoagulant drug. The National Institute for Health and Care Excellence is due to publish guidance so that it can be used in the UK from August Which anticoagulant medicine should I take? The most commonly prescribed anticoagulant is warfarin, but it does require careful monitoring. The advantage of other anticoagulants (dabigatran, rivaroxaban and apixaban) is that their effect on your blood is more stable and they are not affected by any foods that you eat, so they do not need to be monitored as carefully. Your doctor should talk to you about all the available options, along with their risks and benefits. Stroke Association July 2015
7 You should then decide together which anticoagulant would be the most suitable for you. If you have AF, the NHS has produced an online tool to help you think about which is the best option for you. You can find this decision aid at: sdm.rightcare.nhs. co.uk/pda/stroke-prevention-for-atrialfibrillation What else do I need to know? We ve not listed all of the possible side effects and drug interactions in this factsheet. Always read the patient information leaflet that comes with your medication, as this will have a full list. Tell your doctor about any new medication you are taking. Your pharmacist may also be able to give you advice about your medication. Never stop taking your medication if you feel unwell. Always contact your GP for advice stopping medication suddenly can be dangerous. In a medical emergency, always call 999. If you are taking an anticoagulant, you must always check any new medication you plan to take with your GP or pharmacist before taking it. You should also read the patient information leaflet that comes with your medication. You should be given a patient alert card before you start taking an anticoagulant. Always carry your alert card with you in case of an emergency. You should also tell your dentist you are taking anticoagulant medication before you have any treatment. How can I find out more? Talk to us Our Stroke Helpline can give you information about stroke and tell you about services and support available in your local area. Call us on (Monday to Friday, 9am 5pm) or [email protected] Get online We have lots of information about stroke and how to prevent it on our website. Go to stroke.org.uk Other useful contacts If you re looking for more information the following organisations may also be able to help. All are UK wide unless otherwise stated. Please note that details of these organisations are for information only. We are not recommending or endorsing anyone by including them in this factsheet. Anticoagulation Europe Website: Tel: They provide information and support for people on anticoagulant medication. Arrhythmia Alliance Website: Tel: They support people with all types of heart arrhythmias. Atrial Fibrillation Association Website: Tel: They support people with AF, offering a range of leaflets on AF, treatments and types of medication, plus details of AF specialists. Stroke Association July
8 NHS Choices Website: This website provides general information on all aspects of health including stroke, as well as information on different types of bloodthinning medicines. NHS Inform (Scotland) Website: Helpline: This website provides information on health conditions, treatments and health services in Scotland. Glossary of terms Anticoagulant = a type of drug that helps to stop your blood clotting as easily. Antiplatelet = a type of drug that helps to stop your blood clotting as easily. They work in a different way to anticoagulants. Embolism = something that is travelling in your blood stream that should not be, such as a blood clot or an air bubble. INR = international normalised ratio. This is a measure of how quickly your blood clots. Ischaemic stroke = a stroke that is caused by a blockage cutting off the blood supply to your brain. NSAIDs = nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. These are used to relieve pain and inflammation. Common NSAIDs include aspirin, ibuprofen and naproxen. Platelets = small cells in your blood that stick together to form a blood clot. Proton pump inhibitors = a type of drug that is used to treat stomach ulcers. Thrombus = a blood clot. TIA = transient ischaemic attack. A TIA is the same as a stroke, except that the symptoms last for a short amount of time and no longer than 24 hours. About our information We are committed to producing clear, accurate and unbiased information for stroke survivors and their families. To produce our publications we use information from professional bodies and other reliable sources including NICE, SIGN, Royal College of Physicians and medical journals. To request a list of sources used in this factsheet [email protected] Stroke Association Factsheet 11, version 1.1 Published July Next review January Item code: A01F11 The Stroke Association is a charity. We rely on your support. Text STROKE 5 to to donate % of your donation goes to the Stroke Association. Find out how your support helps at stroke.org.uk/savelives Stroke Association is a Company Limited by Guarantee, registered in England and Wales (No 61274). Registered office: Stroke Association House, 240 City Road, London EC1V 2PR. Registered as a Charity in England and Wales (No ) and in Scotland (SC037789). Also registered in Northern Ireland (XT33805) Isle of Man (No 945) and Jersey (NPO 369). Stroke Association July
Blood-thinning medication after stroke
 Stroke Helpline: 0303 3033 100 Website: stroke.org.uk Blood-thinning medication after stroke Blood-thinning medicines are drugs that help to prevent blood clots forming. They are often prescribed after
Stroke Helpline: 0303 3033 100 Website: stroke.org.uk Blood-thinning medication after stroke Blood-thinning medicines are drugs that help to prevent blood clots forming. They are often prescribed after
F A S T. Atrial fibrillation (AF) and stroke
 Stroke Helpline: 0303 3033 100 Website: stroke.org.uk Atrial fibrillation (AF) and stroke Atrial fibrillation is a type of irregular heartbeat. It means that your heart may not be pumping as well as it
Stroke Helpline: 0303 3033 100 Website: stroke.org.uk Atrial fibrillation (AF) and stroke Atrial fibrillation is a type of irregular heartbeat. It means that your heart may not be pumping as well as it
A Patient s Guide to Antithrombotic Therapy in Atrial Fibrillation
 Patient s Guide to Antithrombotic Therapy in Atrial Fibrillation A Patient s Guide to Antithrombotic Therapy in Atrial Fibrillation PATIENT EDUCATION GUIDE What is atrial fibrillation? Atrial fibrillation
Patient s Guide to Antithrombotic Therapy in Atrial Fibrillation A Patient s Guide to Antithrombotic Therapy in Atrial Fibrillation PATIENT EDUCATION GUIDE What is atrial fibrillation? Atrial fibrillation
Warfarin therapy for stroke patients with atrial fibrillation
 Warfarin therapy for stroke patients with atrial fibrillation Delivering the best in care UHB is a no smoking Trust To see all of our current patient information leaflets please visit www.uhb.nhs.uk/patient-information-leaflets.htm
Warfarin therapy for stroke patients with atrial fibrillation Delivering the best in care UHB is a no smoking Trust To see all of our current patient information leaflets please visit www.uhb.nhs.uk/patient-information-leaflets.htm
Atrial Fibrillation and Anticoagulants
 York Teaching Hospital NHS Foundation Trust Atrial Fibrillation and Anticoagulants A guide to your diagnosis and treatment Information for patients, relatives and carers For more information, please contact:
York Teaching Hospital NHS Foundation Trust Atrial Fibrillation and Anticoagulants A guide to your diagnosis and treatment Information for patients, relatives and carers For more information, please contact:
Alcohol and stroke. How can drinking alcohol increase my risk of stroke? Stroke Helpline: 0303 3033 100 Website: stroke.org.uk
 Stroke Helpline: 0303 3033 100 Website: stroke.org.uk Alcohol and stroke Regularly drinking large amounts of alcohol greatly increases your risk of stroke. This factsheet explains how alcohol can increase
Stroke Helpline: 0303 3033 100 Website: stroke.org.uk Alcohol and stroke Regularly drinking large amounts of alcohol greatly increases your risk of stroke. This factsheet explains how alcohol can increase
Atrial fibrillation: medicines to help reduce your risk of a stroke what are the options?
 Patient decision aid Atrial fibrillation: medicines to help reduce your risk of a stroke what are the options? http://guidance.nice.org.uk/cg180/patientdecisionaid/pdf/english Published: June 2014 About
Patient decision aid Atrial fibrillation: medicines to help reduce your risk of a stroke what are the options? http://guidance.nice.org.uk/cg180/patientdecisionaid/pdf/english Published: June 2014 About
V1: Draft Nov 2014. Making decisions... about anticoagulation for stroke prevention in atrial fibrillation. www.weahsn.net
 V1: Draft Nov 2014 Making decisions... about anticoagulation for stroke prevention in atrial fibrillation www.weahsn.net is this pack for? pack and booklet is for people with AF. It is designed to help
V1: Draft Nov 2014 Making decisions... about anticoagulation for stroke prevention in atrial fibrillation www.weahsn.net is this pack for? pack and booklet is for people with AF. It is designed to help
Living with a Non-Vitamin K Antagonist Oral Anticoagulant (NOAC)
 Living with a Non-Vitamin K Antagonist Oral Anticoagulant (NOAC) dabigatran (Pradaxa ) rivaroxaban (Xarelto ) apixaban (Eliquis ) Information for patients Produced and made available by the Western Australian
Living with a Non-Vitamin K Antagonist Oral Anticoagulant (NOAC) dabigatran (Pradaxa ) rivaroxaban (Xarelto ) apixaban (Eliquis ) Information for patients Produced and made available by the Western Australian
ORAL ANTICOAGULANTS - RIVAROXABAN (XARELTO) FOR ATRIAL FIBRILLATION
 ORAL ANTICOAGULANTS - RIVAROXABAN (XARELTO) FOR ATRIAL FIBRILLATION Information Leaflet Your Health. Our Priority. Page 2 of 6 What Are Anticoagulants And What Do They Do? This information leaflet has
ORAL ANTICOAGULANTS - RIVAROXABAN (XARELTO) FOR ATRIAL FIBRILLATION Information Leaflet Your Health. Our Priority. Page 2 of 6 What Are Anticoagulants And What Do They Do? This information leaflet has
Atrial fibrillation (non-valvular) and reducing the risk of a stroke Management Options Brief Decision Aid
 Atrial fibrillation (non-valvular) and reducing the risk of a stroke Management Options Brief Decision Aid Atrial fibrillation (AF) increases your risk of having a stroke (a blood clot in the brain). From
Atrial fibrillation (non-valvular) and reducing the risk of a stroke Management Options Brief Decision Aid Atrial fibrillation (AF) increases your risk of having a stroke (a blood clot in the brain). From
Brand Name Marevan Pradaxa Xarelto Eliquis
 Medicines for stroke prevention in atrial fibrillation Choosing the right one for you Atrial fibrillation (AF) is a condition that affects the heart, causing it to beat irregularly and too fast. When this
Medicines for stroke prevention in atrial fibrillation Choosing the right one for you Atrial fibrillation (AF) is a condition that affects the heart, causing it to beat irregularly and too fast. When this
Anticoagulation in Atrial Fibrillation Patient information
 Anticoagulation in Atrial Fibrillation Patient information RSBAY013 Anticoag A5 V2.indd 1 21/02/2014 17:13 Introduction This leaflet will help you understand your new medicine. Your new medicine is commonly
Anticoagulation in Atrial Fibrillation Patient information RSBAY013 Anticoag A5 V2.indd 1 21/02/2014 17:13 Introduction This leaflet will help you understand your new medicine. Your new medicine is commonly
F A S T. Transient ischaemic attack (TIA)
 Stroke Helpline: 0303 3033 100 Website: stroke.org.uk Transient ischaemic attack (TIA) A transient ischaemic attack (TIA) is similar to a stroke, but the symptoms do not last as long. However, it should
Stroke Helpline: 0303 3033 100 Website: stroke.org.uk Transient ischaemic attack (TIA) A transient ischaemic attack (TIA) is similar to a stroke, but the symptoms do not last as long. However, it should
Anticoagulants for stroke prevention in atrial fibrillation Patient frequently asked questions
 Anticoagulants for stroke prevention in atrial fibrillation Patient frequently asked questions What is atrial fibrillation?...2 What are dabigatran, rivaroxaban and apixaban and what are they used for?...2
Anticoagulants for stroke prevention in atrial fibrillation Patient frequently asked questions What is atrial fibrillation?...2 What are dabigatran, rivaroxaban and apixaban and what are they used for?...2
Daily aspirin therapy: Understand the benefits and risks
 Daily aspirin therapy: Understand the benefits and risks Is an aspirin a day the right thing for you? It's not as easy a decision as it sounds. Know the benefits and risks before considering daily aspirin
Daily aspirin therapy: Understand the benefits and risks Is an aspirin a day the right thing for you? It's not as easy a decision as it sounds. Know the benefits and risks before considering daily aspirin
Rivaroxaban for the treatment of deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and pulmonary embolism (PE)
 Rivaroxaban for the treatment of deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and pulmonary embolism (PE) This leaflet aims to answer your questions about rivaroxaban that may be prescribed for you when you are diagnosed
Rivaroxaban for the treatment of deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and pulmonary embolism (PE) This leaflet aims to answer your questions about rivaroxaban that may be prescribed for you when you are diagnosed
A PATIENT S GUIDE TO STROKE AND ATRIAL FIBRILLATION (AF)
 A PATIENT S GUIDE TO STROKE AND ATRIAL FIBRILLATION (AF) This medicine is subject to additional monitoring. This will allow quick identification of new safety information. If you get any side effects,
A PATIENT S GUIDE TO STROKE AND ATRIAL FIBRILLATION (AF) This medicine is subject to additional monitoring. This will allow quick identification of new safety information. If you get any side effects,
What You Need to KnowWhen Taking Anticoagulation Medicine
 What You Need to KnowWhen Taking Anticoagulation Medicine What are anticoagulant medicines? Anticoagulant medicines are a group of medicines that inhibit blood clotting, helping to prevent blood clots.
What You Need to KnowWhen Taking Anticoagulation Medicine What are anticoagulant medicines? Anticoagulant medicines are a group of medicines that inhibit blood clotting, helping to prevent blood clots.
MEDICATION GUIDE ELIQUIS (ELL eh kwiss) (apixaban) tablets
 MEDICATION GUIDE ELIQUIS (ELL eh kwiss) (apixaban) tablets What is the most important information I should know about ELIQUIS? For people taking ELIQUIS for atrial fibrillation: People with atrial fibrillation
MEDICATION GUIDE ELIQUIS (ELL eh kwiss) (apixaban) tablets What is the most important information I should know about ELIQUIS? For people taking ELIQUIS for atrial fibrillation: People with atrial fibrillation
ORAL ANTICOAGULANTS - RIVAROXABAN (XARELTO) FOR DEEP VEIN THROMBOSIS (DVT)
 ORAL ANTICOAGULANTS - RIVAROXABAN (XARELTO) FOR DEEP VEIN THROMBOSIS (DVT) Information Leaflet Your Health. Our Priority. Page 2 of 6 What Are Anticoagulants And What Do They Do? This information leaflet
ORAL ANTICOAGULANTS - RIVAROXABAN (XARELTO) FOR DEEP VEIN THROMBOSIS (DVT) Information Leaflet Your Health. Our Priority. Page 2 of 6 What Are Anticoagulants And What Do They Do? This information leaflet
Introduction to Atrial Fibrillation (AFib)
 Introduction to Atrial Fibrillation (AFib) Learn About: 1. What is atrial fibrillation? 2. How will I feel? 3. Who gets AFib? 4. Risk of stroke 5. AFib treatment 6. How to live well with AFib 1. What is
Introduction to Atrial Fibrillation (AFib) Learn About: 1. What is atrial fibrillation? 2. How will I feel? 3. Who gets AFib? 4. Risk of stroke 5. AFib treatment 6. How to live well with AFib 1. What is
Treatment with Rivaroxaban
 UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Treatment with Rivaroxaban Xarelto This handout explains the medicine rivaroxaban, a drug that helps prevent blood clots. What is rivaroxaban? Rivaroxaban (brand name Xarelto)
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Treatment with Rivaroxaban Xarelto This handout explains the medicine rivaroxaban, a drug that helps prevent blood clots. What is rivaroxaban? Rivaroxaban (brand name Xarelto)
Guide to Dabigatran, Rivaroxaban and Apixaban
 Page 1 of 8 Guide to Dabigatran, Rivaroxaban and Apixaban Medicines to Prevent Blood Clots If you are deaf or hard of hearing, please let us know. We provide many free services including sign language
Page 1 of 8 Guide to Dabigatran, Rivaroxaban and Apixaban Medicines to Prevent Blood Clots If you are deaf or hard of hearing, please let us know. We provide many free services including sign language
A PATIENT S GUIDE TO DEEP VEIN THROMBOSIS TREATMENT
 A PATIENT S GUIDE TO DEEP VEIN THROMBOSIS TREATMENT This medicine is subject to additional monitoring. This will allow quick identification of new safety information. If you get any side effects, talk
A PATIENT S GUIDE TO DEEP VEIN THROMBOSIS TREATMENT This medicine is subject to additional monitoring. This will allow quick identification of new safety information. If you get any side effects, talk
Treatment with Apixaban
 UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Treatment with Apixaban Eliquis This handout explains the medicine apixaban, a drug that helps prevent blood clots. What is apixaban? Apixaban (brand name Eliquis) is an anticoagulant
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Treatment with Apixaban Eliquis This handout explains the medicine apixaban, a drug that helps prevent blood clots. What is apixaban? Apixaban (brand name Eliquis) is an anticoagulant
ACUTE STROKE UNIT ORIENTATION
 ACUTE STROKE UNIT ORIENTATION 2014 TEACHING YOUR STROKE PATIENTS ABOUT THEIR MEDICATION Please refer to Module 8: Secondary Stroke Prevention for additional information Blood Pressure Medication Angiotensin
ACUTE STROKE UNIT ORIENTATION 2014 TEACHING YOUR STROKE PATIENTS ABOUT THEIR MEDICATION Please refer to Module 8: Secondary Stroke Prevention for additional information Blood Pressure Medication Angiotensin
A PATIENT S GUIDE TO SECONDARY PREVENTION IN ACUTE CORONARY SYNDROME (ACS)
 A PATIENT S GUIDE TO SECONDARY PREVENTION IN ACUTE CORONARY SYNDROME (ACS) This medicine is subject to additional monitoring. This will allow quick identification of new safety information. If you get
A PATIENT S GUIDE TO SECONDARY PREVENTION IN ACUTE CORONARY SYNDROME (ACS) This medicine is subject to additional monitoring. This will allow quick identification of new safety information. If you get
ORAL ANTICOAGULANTS RIVAROXABAN (XARELTO) FOR PULMONARY EMBOLISM (PE)
 ORAL ANTICOAGULANTS RIVAROXABAN (XARELTO) FOR PULMONARY EMBOLISM (PE) Information Leaflet Your Health. Our Priority. Page 2 of 6 What Are Anticoagulants And What Do They Do? This information leaflet has
ORAL ANTICOAGULANTS RIVAROXABAN (XARELTO) FOR PULMONARY EMBOLISM (PE) Information Leaflet Your Health. Our Priority. Page 2 of 6 What Are Anticoagulants And What Do They Do? This information leaflet has
Safety Information Card for Xarelto Patients
 Safety Information Card for Xarelto Patients 15mg Simply Protecting More Patients 20mg Simply Protecting More Patients Keep this card with you at all times Present this card to every physician or dentist
Safety Information Card for Xarelto Patients 15mg Simply Protecting More Patients 20mg Simply Protecting More Patients Keep this card with you at all times Present this card to every physician or dentist
Rivaroxaban (Xarelto) for preventing stroke
 Rivaroxaban (Xarelto) for preventing stroke in people with atrial fibrillation This Medicine Update is for people with atrial fibrillation who are taking, or thinking about taking, rivaroxaban. Summary
Rivaroxaban (Xarelto) for preventing stroke in people with atrial fibrillation This Medicine Update is for people with atrial fibrillation who are taking, or thinking about taking, rivaroxaban. Summary
Venous Thrombosis and Pulmonary Embolism Treatment with Rivaroxaban
 Venous Thrombosis and Pulmonary Embolism Treatment with Rivaroxaban Information for patients and families Read this booklet to learn: about venous thrombosis and pulmonary embolism how the medicine Rivaroxaban
Venous Thrombosis and Pulmonary Embolism Treatment with Rivaroxaban Information for patients and families Read this booklet to learn: about venous thrombosis and pulmonary embolism how the medicine Rivaroxaban
Oxford Anticoagulation & Thrombosis Service Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) and Pulmonary Embolism (PE)
 Oxford University Hospitals NHS Trust Oxford Anticoagulation & Thrombosis Service Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) and Pulmonary Embolism (PE) Information for people with a blood clot (thrombus) What is this
Oxford University Hospitals NHS Trust Oxford Anticoagulation & Thrombosis Service Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) and Pulmonary Embolism (PE) Information for people with a blood clot (thrombus) What is this
A PATIENT S GUIDE TO PULMONARY EMBOLISM TREATMENT
 A PATIENT S GUIDE TO PULMONARY EMBOLISM TREATMENT This medicine is subject to additional monitoring. This will allow quick identification of new safety information. If you get any side effects, talk to
A PATIENT S GUIDE TO PULMONARY EMBOLISM TREATMENT This medicine is subject to additional monitoring. This will allow quick identification of new safety information. If you get any side effects, talk to
When a stroke happens
 When a stroke happens When a stroke happens What to expect during the first hours, days and weeks after a stroke We re for life after stroke Introduction Need to talk? Call our confidential Stroke Helpline
When a stroke happens When a stroke happens What to expect during the first hours, days and weeks after a stroke We re for life after stroke Introduction Need to talk? Call our confidential Stroke Helpline
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION. Xofigo Therapy. For metastatic prostate cancer. What is Xofigo? How does it work?
 UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Xofigo Therapy For metastatic prostate cancer This handout explains how the drug Xofigo is used to treat metastatic prostate cancer. What is Xofigo? Xofigo is a radioactive
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Xofigo Therapy For metastatic prostate cancer This handout explains how the drug Xofigo is used to treat metastatic prostate cancer. What is Xofigo? Xofigo is a radioactive
Sudden dizziness, trouble walking, loss of balance or coordination
 rivaroxaban (Xarelto) Patient Education Information Sheet Veterans Health System Pharmacy Service 119 What is rivaroxaban (Xarelto)? A new anticoagulant ( blood thinner ) that reduces the risk of stroke
rivaroxaban (Xarelto) Patient Education Information Sheet Veterans Health System Pharmacy Service 119 What is rivaroxaban (Xarelto)? A new anticoagulant ( blood thinner ) that reduces the risk of stroke
Living. with. Warfarin
 Living with Warfarin Warfarin Tablets Warfarin tablets in the UK are colour coded to help you take the correct dose. PINK 5mg BLUE 3mg They are available in 5mg (pink), 3mg (blue), 1mg (light brown) and
Living with Warfarin Warfarin Tablets Warfarin tablets in the UK are colour coded to help you take the correct dose. PINK 5mg BLUE 3mg They are available in 5mg (pink), 3mg (blue), 1mg (light brown) and
MEDICATION GUIDE COUMADIN (COU-ma-din) (warfarin sodium)
 MEDICATION GUIDE COUMADIN (COU-ma-din) (warfarin sodium) Read this Medication Guide before you start taking COUMADIN (warfarin sodium) and each time you get a refill. There may be new information. This
MEDICATION GUIDE COUMADIN (COU-ma-din) (warfarin sodium) Read this Medication Guide before you start taking COUMADIN (warfarin sodium) and each time you get a refill. There may be new information. This
Blood thinning (anticoagulation) in atrial fibrillation (AF)
 AF A Blood thinning (anticoagulation) in atrial fibrillation (AF) Providing information, support and access to established, new or innovative treatments for atrial fibrillation www.afa.org.uk Registered
AF A Blood thinning (anticoagulation) in atrial fibrillation (AF) Providing information, support and access to established, new or innovative treatments for atrial fibrillation www.afa.org.uk Registered
Atrial Fibrillation. Patient Information. 828361 Dec 19-12
 Atrial Fibrillation Patient Information 828361 Dec 19-12 Contents Introduction 1 Treatment & decrease stroke options 2 Information for people who are taking warfarin (Coumadin ) 5 Information for people
Atrial Fibrillation Patient Information 828361 Dec 19-12 Contents Introduction 1 Treatment & decrease stroke options 2 Information for people who are taking warfarin (Coumadin ) 5 Information for people
AFib (short for atrial fibrillation) is the most common type of irregular heartbeat, affecting literally millions of men and women
 What is atrial fibrillation? AFib (short for atrial fibrillation) is the most common type of irregular heartbeat, affecting literally millions of men and women What is atrial fibrillation? AFib occurs
What is atrial fibrillation? AFib (short for atrial fibrillation) is the most common type of irregular heartbeat, affecting literally millions of men and women What is atrial fibrillation? AFib occurs
FAQs about Warfarin (brand name Coumadin )
 FAQs about Warfarin (brand name Coumadin ) What is warfarin? Warfarin is the most commonly used anticoagulant in the US. An anticoagulant is a drug used to prevent unwanted and harmful blood clots. Although
FAQs about Warfarin (brand name Coumadin ) What is warfarin? Warfarin is the most commonly used anticoagulant in the US. An anticoagulant is a drug used to prevent unwanted and harmful blood clots. Although
Warfarin. (Coumadin, Jantoven ) Taking your medication safely
 Warfarin (Coumadin, Jantoven ) Taking your medication safely Welcome This booklet is designed to provide you with important information about warfarin to help you take this medication safely and effectively.
Warfarin (Coumadin, Jantoven ) Taking your medication safely Welcome This booklet is designed to provide you with important information about warfarin to help you take this medication safely and effectively.
Local Steroid Injections to Joints and Soft Tissues. Rheumatology Patient Information Leaflet
 Local Steroid Injections to Joints and Soft Tissues Rheumatology Patient Information Leaflet Welcome to The Dudley Group Rheumatology department. This leaflet will provide you with information about what
Local Steroid Injections to Joints and Soft Tissues Rheumatology Patient Information Leaflet Welcome to The Dudley Group Rheumatology department. This leaflet will provide you with information about what
Leflunomide Leflunomide
 Drug information Leflunomide Leflunomide This leaflet provides information on leflunomide and will answer any questions you have about the treatment. Arthritis Research UK produce and print our booklets
Drug information Leflunomide Leflunomide This leaflet provides information on leflunomide and will answer any questions you have about the treatment. Arthritis Research UK produce and print our booklets
Rivaroxaban to prevent blood clots for patients who have a lower limb plaster cast. Information for patients Pharmacy
 Rivaroxaban to prevent blood clots for patients who have a lower limb plaster cast Information for patients Pharmacy Your doctor has prescribed a tablet called rivaroxaban. This leaflet tells you about
Rivaroxaban to prevent blood clots for patients who have a lower limb plaster cast Information for patients Pharmacy Your doctor has prescribed a tablet called rivaroxaban. This leaflet tells you about
Ask Your Doctor if There May Be a SMARTER CHOICE
 If you have osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis or ankylosing spondylitis, Could Your NSAID Pain Medicine Be Hurting Your Stomach? Ask Your Doctor if There May Be a SMARTER CHOICE 1 of 8 Making Smart
If you have osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis or ankylosing spondylitis, Could Your NSAID Pain Medicine Be Hurting Your Stomach? Ask Your Doctor if There May Be a SMARTER CHOICE 1 of 8 Making Smart
Atrial Fibrillation (AF) Explained
 James Paget University Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust Atrial Fibrillation (AF) Explained Patient Information Contents What are the symptoms of atrial fibrillation (AF)? 3 Normal heartbeat 4 How common
James Paget University Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust Atrial Fibrillation (AF) Explained Patient Information Contents What are the symptoms of atrial fibrillation (AF)? 3 Normal heartbeat 4 How common
DRUG INTERACTIONS: WHAT YOU SHOULD KNOW. Council on Family Health
 DRUG INTERACTIONS: WHAT YOU SHOULD KNOW Council on Family Health Drug Interactions There are more opportunities today than ever before to learn about your health and to take better care of yourself. It
DRUG INTERACTIONS: WHAT YOU SHOULD KNOW Council on Family Health Drug Interactions There are more opportunities today than ever before to learn about your health and to take better care of yourself. It
There is a risk of renal impairment in dehydrated children and adolescents.
 PACKAGE LEAFLET: INFORMATION FOR THE USER MELFEN 200mg FILM-COATED TABLETS MELFEN 400mg FILM-COATED TABLETS Ibuprofen Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start taking this medicine because it
PACKAGE LEAFLET: INFORMATION FOR THE USER MELFEN 200mg FILM-COATED TABLETS MELFEN 400mg FILM-COATED TABLETS Ibuprofen Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start taking this medicine because it
XARELTO (Za-REL-toe) rivaroxaban
 (Za-REL-toe) rivaroxaban Consumer Medicine Information WHAT IS IN THIS LEAFLET This leaflet answers some common questions about Xarelto. It does not contain all the available information. It does not take
(Za-REL-toe) rivaroxaban Consumer Medicine Information WHAT IS IN THIS LEAFLET This leaflet answers some common questions about Xarelto. It does not contain all the available information. It does not take
NICE TA 275: Apixaban for the prevention of stroke and systemic embolism in people with non-valvular atrial fibrillation
 Service Notification in response to DHSSPS endorsed NICE Technology Appraisals NICE TA 275: Apixaban for the prevention of stroke and systemic embolism in people with non-valvular atrial fibrillation 1
Service Notification in response to DHSSPS endorsed NICE Technology Appraisals NICE TA 275: Apixaban for the prevention of stroke and systemic embolism in people with non-valvular atrial fibrillation 1
XARELTO (Za REL toe) rivaroxaban
 (Za REL toe) rivaroxaban Consumer Medicine Information WHAT IS IN THIS LEAFLET This leaflet answers some common questions about It does not contain all the available information. It does not take the place
(Za REL toe) rivaroxaban Consumer Medicine Information WHAT IS IN THIS LEAFLET This leaflet answers some common questions about It does not contain all the available information. It does not take the place
Private treatment. What private treatments are available for stroke? What is private treatment? Why would I consider private treatment?
 Stroke Helpline: 0303 3033 100 Website: stroke.org.uk Private treatment You can choose private health treatment for all medical conditions, including stroke. If you are considering private treatment this
Stroke Helpline: 0303 3033 100 Website: stroke.org.uk Private treatment You can choose private health treatment for all medical conditions, including stroke. If you are considering private treatment this
Introduction. Background to this event. Raising awareness 09/11/2015
 Introduction Primary Care Medicines Governance HSCB Background to this event New class of medicines Availability of training Increasing volume of prescriptions Reports of medication incidents Raising awareness
Introduction Primary Care Medicines Governance HSCB Background to this event New class of medicines Availability of training Increasing volume of prescriptions Reports of medication incidents Raising awareness
Ultrasound-guided steroid injections in joints and soft tissues. Rheumatology Patient Information Leaflet
 Ultrasound-guided steroid injections in joints and soft tissues Rheumatology Patient Information Leaflet Welcome to The Dudley Group Rheumatology department. This leaflet will provide you with information
Ultrasound-guided steroid injections in joints and soft tissues Rheumatology Patient Information Leaflet Welcome to The Dudley Group Rheumatology department. This leaflet will provide you with information
What Does Pregnancy Have to Do With Blood Clots in a Woman s Legs?
 Patient s Guide to Prevention of Blood Clots During Pregnancy: Use of Blood-Thinning A Patient s Guide to Prevention of Blood Clots During Pregnancy: Use of Blood-Thinning Drugs to Prevent Abnormal Blood
Patient s Guide to Prevention of Blood Clots During Pregnancy: Use of Blood-Thinning A Patient s Guide to Prevention of Blood Clots During Pregnancy: Use of Blood-Thinning Drugs to Prevent Abnormal Blood
Medication Information. (a pix a ban)
 Medication Information (a pix a ban) Other names for this medication are: Eliquis What does this medication do? This medication is a blood thinner, also called an anticoagulant. It prevents a blood clot
Medication Information (a pix a ban) Other names for this medication are: Eliquis What does this medication do? This medication is a blood thinner, also called an anticoagulant. It prevents a blood clot
what is warfarin? Treatment with Warfarin (Coumadin ) What is warfarin?
 What is warfarin? Warfarin sodium (Coumadin ) is a medication that works as an anti-coagulant. Anti means against and coagulant refers to blood clotting. An anticoagulant helps to prevent clots from forming
What is warfarin? Warfarin sodium (Coumadin ) is a medication that works as an anti-coagulant. Anti means against and coagulant refers to blood clotting. An anticoagulant helps to prevent clots from forming
Guide to Warfarin Therapy
 Page 1 of 8 Guide to Warfarin Therapy Treatment to Prevent Blood Clots If you are deaf or hard of hearing, please let us know. We provide many free services including sign language interpreters, oral interpreters,
Page 1 of 8 Guide to Warfarin Therapy Treatment to Prevent Blood Clots If you are deaf or hard of hearing, please let us know. We provide many free services including sign language interpreters, oral interpreters,
MEDICATION GUIDE. PROCRIT (PRO KRIT) (epoetin alfa)
 MEDICATION GUIDE PROCRIT (PROKRIT) (epoetin alfa) Read this Medication Guide: before you start PROCRIT. if you are told by your healthcare provider that there is new information about PROCRIT. if you are
MEDICATION GUIDE PROCRIT (PROKRIT) (epoetin alfa) Read this Medication Guide: before you start PROCRIT. if you are told by your healthcare provider that there is new information about PROCRIT. if you are
Medication Guide Plavix (PLAV-iks) (clopidogrel bisulfate) tablets
 Medication Guide Plavix (PLAV-iks) (clopidogrel bisulfate) tablets Read this Medication Guide before you start taking Plavix and each time you get a refill. There may be new information. This Medication
Medication Guide Plavix (PLAV-iks) (clopidogrel bisulfate) tablets Read this Medication Guide before you start taking Plavix and each time you get a refill. There may be new information. This Medication
Guide to Warfarin Therapy
 Page 1 of 8 Guide to Warfarin Therapy Treatment to Prevent Blood Clots If you are deaf or hard of hearing, please let us know. We provide many free services including sign language interpreters, oral interpreters,
Page 1 of 8 Guide to Warfarin Therapy Treatment to Prevent Blood Clots If you are deaf or hard of hearing, please let us know. We provide many free services including sign language interpreters, oral interpreters,
Anticoagulants. Anticoagulants Definition. When are blood clots GOOD? Where and why do blood clots occur? 6/12/2014
 Anticoagulants Steven R. Kayser, PharmD Professor Emeritus Department of Clinical Pharmacy UCSF Anticoagulants Definition A substance that hinders the clotting of blood Sometimes referred to as blood thinners
Anticoagulants Steven R. Kayser, PharmD Professor Emeritus Department of Clinical Pharmacy UCSF Anticoagulants Definition A substance that hinders the clotting of blood Sometimes referred to as blood thinners
Cardioversion for. Atrial Fibrillation. Your Heart s Electrical System Cardioversion Living with Atrial Fibrillation
 Cardioversion for Atrial Fibrillation Your Heart s Electrical System Cardioversion Living with Atrial Fibrillation When You Have Atrial Fibrillation You ve been told you have a heart condition called atrial
Cardioversion for Atrial Fibrillation Your Heart s Electrical System Cardioversion Living with Atrial Fibrillation When You Have Atrial Fibrillation You ve been told you have a heart condition called atrial
Dabigatran: Amber Drug Guidance for the prevention of stroke and systemic embolism in patients with non-valvular AF
 Leeds Dabigatran: Amber Drug Guidance for the prevention of stroke and systemic embolism in patients with non-valvular AF Amber Drug Level 3 (amber drug with monitoring requirements) We have started your
Leeds Dabigatran: Amber Drug Guidance for the prevention of stroke and systemic embolism in patients with non-valvular AF Amber Drug Level 3 (amber drug with monitoring requirements) We have started your
Rivaroxaban (Xarelto) for preventing blood clots after hip or knee replacement surgery
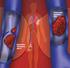 medicineupdate Asking the right questions about new medicines Rivaroxaban (Xarelto) for preventing blood clots after hip or knee replacement surgery This Medicine Update is for people who have been prescribed
medicineupdate Asking the right questions about new medicines Rivaroxaban (Xarelto) for preventing blood clots after hip or knee replacement surgery This Medicine Update is for people who have been prescribed
Atrial Fibrillation. Information for you, and your family, whänau and friends. Published by the New Zealand Guidelines Group
 Atrial Fibrillation Information for you, and your family, whänau and friends Published by the New Zealand Guidelines Group CONTENTS Introduction 1 The heart 2 What is atrial fibrillation? 3 How common
Atrial Fibrillation Information for you, and your family, whänau and friends Published by the New Zealand Guidelines Group CONTENTS Introduction 1 The heart 2 What is atrial fibrillation? 3 How common
Patient Information Once Weekly FOSAMAX (FOSS-ah-max) (alendronate sodium) Tablets and Oral Solution
 Patient Information Once Weekly FOSAMAX (FOSS-ah-max) (alendronate sodium) Tablets and Oral Solution Read this information before you start taking FOSAMAX *. Also, read the leaflet each time you refill
Patient Information Once Weekly FOSAMAX (FOSS-ah-max) (alendronate sodium) Tablets and Oral Solution Read this information before you start taking FOSAMAX *. Also, read the leaflet each time you refill
How To Take Xarelto
 A patient's guide Your clinic's contact details are: Name: Contact number: Contents 2 Why have I been prescribed Xarelto? 2 What is Xarelto? 3 How do I take Xarelto? 3 What should I do if I miss a dose
A patient's guide Your clinic's contact details are: Name: Contact number: Contents 2 Why have I been prescribed Xarelto? 2 What is Xarelto? 3 How do I take Xarelto? 3 What should I do if I miss a dose
MEDICATION GUIDE XARELTO (zah-rel-toe) (rivaroxaban) Tablets
 MEDICATION GUIDE XARELTO (zah-rel-toe) (rivaroxaban) Tablets Read this Medication Guide before you start taking XARELTO and each time you get a refill. There may be new information. This Medication Guide
MEDICATION GUIDE XARELTO (zah-rel-toe) (rivaroxaban) Tablets Read this Medication Guide before you start taking XARELTO and each time you get a refill. There may be new information. This Medication Guide
Bleeding in the brain haemorrhagic stroke
 Stroke Helpline: 0303 3033 100 Website: stroke.org.uk Bleeding in the brain haemorrhagic stroke Most strokes are caused by a blockage in an artery leading to the brain an ischaemic stroke. However, about
Stroke Helpline: 0303 3033 100 Website: stroke.org.uk Bleeding in the brain haemorrhagic stroke Most strokes are caused by a blockage in an artery leading to the brain an ischaemic stroke. However, about
MCHENRY WESTERN LAKE COUNTY EMS SYSTEM OPTIONAL CE ADVANCED LEVEL (EMTP, PHRN, ECRN) August 2013. Anticoagulants
 MCHENRY WESTERN LAKE COUNTY EMS SYSTEM OPTIONAL CE ADVANCED LEVEL (EMTP, PHRN, ECRN) August 2013 Anticoagulants Anticoagulants are agents that prevent the formation of blood clots. Before we can talk about
MCHENRY WESTERN LAKE COUNTY EMS SYSTEM OPTIONAL CE ADVANCED LEVEL (EMTP, PHRN, ECRN) August 2013 Anticoagulants Anticoagulants are agents that prevent the formation of blood clots. Before we can talk about
Medication Guide TASIGNA (ta-sig-na) (nilotinib) Capsules
 Medication Guide TASIGNA (ta-sig-na) (nilotinib) Capsules Read this Medication Guide before you start taking Tasigna and each time you get a refill. There may be new information. This information does
Medication Guide TASIGNA (ta-sig-na) (nilotinib) Capsules Read this Medication Guide before you start taking Tasigna and each time you get a refill. There may be new information. This information does
PIAX PLUS ASPIRIN 75/100 Film-Coated Tablets contains the active ingredients clopidogrel and aspirin
 PIAX PLUS ASPIRIN 75/100 Film-Coated Tablets contains the active ingredients clopidogrel and aspirin Consumer Medicine Information What is in this leaflet This leaflet answers some common questions about
PIAX PLUS ASPIRIN 75/100 Film-Coated Tablets contains the active ingredients clopidogrel and aspirin Consumer Medicine Information What is in this leaflet This leaflet answers some common questions about
Let s talk about: Stroke
 Let s talk about: Stroke February 20 th 2013 Laura Wilson Christine Stables Questions 1. Why is knowing about stroke important? 2. What exactly is a stroke and what are the symptoms? 3. What should I do
Let s talk about: Stroke February 20 th 2013 Laura Wilson Christine Stables Questions 1. Why is knowing about stroke important? 2. What exactly is a stroke and what are the symptoms? 3. What should I do
MEDICATION GUIDE Savella (Sa-vel-la) (milnacipran HCl) Tablets
 MEDICATION GUIDE Savella (Sa-vel-la) (milnacipran HCl) Tablets Savella is not used to treat depression, but it acts like medicines that are used to treat depression (antidepressants) and other psychiatric
MEDICATION GUIDE Savella (Sa-vel-la) (milnacipran HCl) Tablets Savella is not used to treat depression, but it acts like medicines that are used to treat depression (antidepressants) and other psychiatric
Prevent Bleeding When Taking Blood Thinners
 PATIENT EDUCATION patienteducation.osumc.edu Prevent Bleeding When Taking Blood Thinners Blood thinners are medicines used to keep harmful blood clots from forming in the body. Blood thinners can also
PATIENT EDUCATION patienteducation.osumc.edu Prevent Bleeding When Taking Blood Thinners Blood thinners are medicines used to keep harmful blood clots from forming in the body. Blood thinners can also
Through Thick and Thin
 Through Thick and Thin Learning to Live with Warfarin South Denver Cardiology Associates PC What is Anticoagulation? Anti = against Coagulation = blood clotting An anticoagulant is a medication that reduces
Through Thick and Thin Learning to Live with Warfarin South Denver Cardiology Associates PC What is Anticoagulation? Anti = against Coagulation = blood clotting An anticoagulant is a medication that reduces
Rivaroxaban: Amber Drug Guidance for the prevention of stroke and systemic embolism in patients with non-valvular AF
 Leeds Rivaroxaban: Amber Drug Guidance for the prevention of stroke and systemic embolism in patients with non-valvular AF Amber Drug Level 3 (amber drug with monitoring requirements) We have started your
Leeds Rivaroxaban: Amber Drug Guidance for the prevention of stroke and systemic embolism in patients with non-valvular AF Amber Drug Level 3 (amber drug with monitoring requirements) We have started your
F A S T. Women and stroke
 Stroke Helpline: 0303 3033 100 Website: stroke.org.uk Women and stroke Anyone can have a stroke and it can happen suddenly no matter what age you are. This factsheet explains the general risk factors for
Stroke Helpline: 0303 3033 100 Website: stroke.org.uk Women and stroke Anyone can have a stroke and it can happen suddenly no matter what age you are. This factsheet explains the general risk factors for
www.irishheart.ie ATRIAL FIBRILLATION AND YOU An information booklet for people living with Atrial Fibrillation (a type of irregular heart beat).
 www.irishheart.ie ATRIAL FIBRILLATION AND YOU An information booklet for people living with Atrial Fibrillation (a type of irregular heart beat). Contents Introduction 5 Produced by the Irish Heart Foundation
www.irishheart.ie ATRIAL FIBRILLATION AND YOU An information booklet for people living with Atrial Fibrillation (a type of irregular heart beat). Contents Introduction 5 Produced by the Irish Heart Foundation
11 Serious and life-threatening side effects can occur while taking EVISTA. These include 12 blood clots and dying from stroke:
 1 1 BNL 3123 AMP 2 Medication Guide 3 EVISTA (E-VISS-tah) 4 (raloxifene hydrochloride) 5 Tablets for Oral Use 6 Read the Medication Guide that comes with EVISTA before you start taking it and each time
1 1 BNL 3123 AMP 2 Medication Guide 3 EVISTA (E-VISS-tah) 4 (raloxifene hydrochloride) 5 Tablets for Oral Use 6 Read the Medication Guide that comes with EVISTA before you start taking it and each time
Medication Information. (Ri va rox xa - ban)
 Medication Information (Ri va rox xa - ban) Other names for this medication are: Xarelto What does this medication do? This medication is a blood thinner, also called an anticoagulant. It prevents a blood
Medication Information (Ri va rox xa - ban) Other names for this medication are: Xarelto What does this medication do? This medication is a blood thinner, also called an anticoagulant. It prevents a blood
Sofosbuvir, Pegylated Interferon and Ribavirin for the Treatment of Hepatitis C
 Sofosbuvir, Pegylated Interferon and Ribavirin for the Treatment of Hepatitis C Department of Hepatology Digestive Diseases Centre Patient Information This leaflet is designed to give you important information
Sofosbuvir, Pegylated Interferon and Ribavirin for the Treatment of Hepatitis C Department of Hepatology Digestive Diseases Centre Patient Information This leaflet is designed to give you important information
A Patient s Guide to Primary and Secondary Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease Using Blood-Thinning (Anticoagulant) Drugs
 A Patient s Guide to Primary and Secondary Prevention of PATIENT EDUCATION GUIDE What Is Cardiovascular Disease? Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is a broad term that covers any disease of the heart and circulatory
A Patient s Guide to Primary and Secondary Prevention of PATIENT EDUCATION GUIDE What Is Cardiovascular Disease? Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is a broad term that covers any disease of the heart and circulatory
MEDICATION GUIDE KOMBIGLYZE XR (kom-be-glyze X-R) (saxagliptin and metformin HCl extended-release) tablets
 MEDICATION GUIDE KOMBIGLYZE XR (kom-be-glyze X-R) (saxagliptin and metformin HCl extended-release) tablets Read this Medication Guide carefully before you start taking KOMBIGLYZE XR and each time you get
MEDICATION GUIDE KOMBIGLYZE XR (kom-be-glyze X-R) (saxagliptin and metformin HCl extended-release) tablets Read this Medication Guide carefully before you start taking KOMBIGLYZE XR and each time you get
Medication Guide EQUETRO (ē-kwĕ-trō) (carbamazepine) Extended-Release Capsules
 Medication Guide EQUETRO (ē-kwĕ-trō) (carbamazepine) Extended-Release Capsules Read this Medication Guide before you start taking EQUETRO and each time you get a refill. There may be new information. This
Medication Guide EQUETRO (ē-kwĕ-trō) (carbamazepine) Extended-Release Capsules Read this Medication Guide before you start taking EQUETRO and each time you get a refill. There may be new information. This
Ischaemic stroke 85% (85 in every 100 strokes)
 UNDERSTANDING STROKE DUE TO INTRACEREBRAL HAEMORRHAGE This factsheet provides information for people who have had a stroke due to an intracerebral (bleed in the brain) and for their families and carers.
UNDERSTANDING STROKE DUE TO INTRACEREBRAL HAEMORRHAGE This factsheet provides information for people who have had a stroke due to an intracerebral (bleed in the brain) and for their families and carers.
Package leaflet: Information for the user. Xarelto 15 mg film-coated tablets Xarelto 20 mg film-coated tablets rivaroxaban
 Due to regulatory changes, the content of the following Patient Information Leaflet may vary from the one found in your medicine pack. Please compare the 'Leaflet prepared/revised date' towards the end
Due to regulatory changes, the content of the following Patient Information Leaflet may vary from the one found in your medicine pack. Please compare the 'Leaflet prepared/revised date' towards the end
Memantine (Ebixa) Drug treatment for Alzheimer s disease
 IS 20 October 2011 Information sheet Memantine (Ebixa) Drug treatment for Alzheimer s disease Introduction... 1 How does Ebixa work?... 1 Who might benefit?... 2 What effect might Ebixa have?... 2 How
IS 20 October 2011 Information sheet Memantine (Ebixa) Drug treatment for Alzheimer s disease Introduction... 1 How does Ebixa work?... 1 Who might benefit?... 2 What effect might Ebixa have?... 2 How
Patient Medication Guide Brochure
 Patient Medication Guide Brochure 1 MEDICATION GUIDE TASIGNA (ta-sig-na) (nilotinib) Capsules Read this Medication Guide before you start taking TASIGNA and each time you get a refill. There may be new
Patient Medication Guide Brochure 1 MEDICATION GUIDE TASIGNA (ta-sig-na) (nilotinib) Capsules Read this Medication Guide before you start taking TASIGNA and each time you get a refill. There may be new
This leaflet answers some common questions about ARROW - MELOXICAM.
 Arrow - Meloxicam Meloxicam Tablets 7.5mg What is in this leaflet This leaflet answers some common questions about ARROW - MELOXICAM. It does not contain all of the available information. It does not take
Arrow - Meloxicam Meloxicam Tablets 7.5mg What is in this leaflet This leaflet answers some common questions about ARROW - MELOXICAM. It does not contain all of the available information. It does not take
