Background on QRM. Pharma EXPO September 2015 Las Vegas, NV. Your QRM Program. Paul H. Ahlijanian
|
|
|
- Alannah Berry
- 8 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Using Quality Risk Management to Evaluate Compliance for Multiproduct and Inventory Facilities in the Pharmaceutical Industry Paul H. Ahlijanian Senior Manager, Pharmaceutical Sciences Quality Assurance Pfizer, Inc. 1 Background on QRM The International Conference on Harmonisation (ICH) Q9 document states that QRM is a systematic process for the assessment, control, communication, and review of risks to the quality of the drug product across the product lifecycle In all likelihood you are already building QRM into your work processes when you make risk-based decisions. QRM formalizes these decisions and provides a way for different workstreams to collaborate and determine an outcome based on science, engineering, and quality. Your QRM Program Do you have a documented QRM Program? Do you have one or more SOPs describing your company s QRM Program? Does your QRM SOP allow for and delineate formal and informal QRM evaluations? Do you have a Consistent, Time-Based QRM Review Program or are Reviews conducted Ad Hoc? 1
2 Overview of the QRM process Identify all risks in a proposed change or continuous improvement initiative Risk to patient Risk to compliance Risk to business Define an acceptable level of risk Quantify the level of each risk Multidisciplinary team assessment Is risk at an acceptable level? Yes can it be further reduced to as low as is reasonably possible? No can measures be put in place to reduce this risk to an acceptable level? Yes risk is mitigated, change can take place No change or CI initiative not acceptable QRM Process Lifecycle & Communication (ICH Q9) Keep line management informed Risk assessments teams: Multi-disciplinary membership Knowledgeable QRM facilitators Results are formally reviewed and approved (including by the Quality Unit) Periodic review to assess any changes that could impact the risk assessment. Key Steps 2
3 Define the Risk Question The Risk Question needs to include: Risk Factors Results Scope (Define what is in and out) Example Risk Question: What is the risk to patient safety, product quality and compliance of manufacturing different higher risk classes of compounds in a multiproduct facility? Key Step - Choose Assessment Tool Suitable for facilities, equipment, and processes. Capable of assessing process systems and their physical and operational environments Capable of assessing operational and procedural controls Selection based on products/process/systems knowledge Consider product/process expertise of team and experience with QRM Risk severity do risks need to be quantified, or is L/M/H sufficient to determine a course of action Factors to Consider Key Step - Determine Risk Criteria & Scales Probability Severity Detection Risk to: Patient Compliance Business Examples only! The QRM Team will determine the scales Scales, Medium, 1, 3, 5, 7, 10 1, 2, 3 Etc., Discretion of QRM Team 3
4 QRM Practical Application Multi-Product or Inventory Management Facility Cross Contamination Control Background Why are we doing this? Industry Regulatory Observations Recent market regulations have mandated the segregation or separation of certain classes of compounds manufactured in a multiproduct facility 4
5 Why are we doing this? Facility Cross Contamination Statistics Review of 2013 and 2014 FDA 483 observations (noncompany specific) reveal approximately 10% attributed to cross contamination findings related to product handling and storage, equipment, and/or facilities.* Business Driver/Initiative Our company needs a comprehensive risk-based program to ensure that potential cross-contamination and mix-up risks within multi-product facilities are appropriately identified, systematically assessed and controlled. * - ( ( Begin the Process Global Alignment Identify global manufacturing/inventory management locations. Review product class storage and inventory. Establish Project Leads/Facilitators from each location and facility Initial facility assessments/walkthroughs Develop an assessment approach and template that is consistent throughout all sites and facilities Form facility and site QRM teams and initiate the process. Begin the Process Site & Facility Teams Select Team Members All participants should be trained in QRM SOPs prior to any QRM sessions, including kickoff meeting. Give them Lunch!! QA (Specific Facility Quality Experience) Shift Lead (Production Expertise) Facilities Expert (Quick access to plans, P&IDs, HVAC, etc.) Process Technician Experienced QRM Facilitator Mfg Area Manager Mfg Area Compliance Environmental Health & Safety (Industrial Hygiene Experience) Engineer or Coordinator (may not be staffed for IM Facility) 5
6 Begin the Education Process Cross Contamination Need a risk assessment to determine how to balance: Processes sharing of common facility areas or equipment (e.g., reactors, raw material storage, personnel, support areas, etc.) Prevention of potential crosscontamination through process containment and facility design and controls Begin the Process Documents Needed to Get Started Detailed information will need to be gathered to ensure the assessments are both effective and comprehensive Facility Design Documents Facility Diagrams (flows, HVAC plans, etc.) PFDs (Process Flow Diagrams) Key Facility Operating SOPs including: Procedures governing open operations Cleaning and inactivation SOPs (including spill response) Facility & surface sanitization SOPs Changeover SOPs Maintenance Maintenance/Calibration Vendor Practices Cross-contamination how it happens Cross contamination between processes is dependent upon three events occurring together: Release Transport Ingress Unintended hazard release from spills, open operations, material mix-ups, waste, etc. Unintended carriage of hazards between manufacturing areas via flow of materials, product, equipment, personnel, waste etc. across doorways, through piping, pass-throughs, etc. Unintended hazard ingress into a receiving process due to breach of system closure, material additions, open operations, etc. Approach: prevent or control each of these events so that the equation cannot be satisfied 6
7 Assessment of Facility Interfaces How does material escape? Determine facility boundary and scope of operations Components physical items or pathways that could intentionally or inadvertently carry product or materials throughout the facility, i.e., how material carried is out Air (HVAC) Sampling Cleaning Personnel Equipment Packaging Materials Utilities Warehouse Operations Waste Dispening/Weighing Hazard Operability Analysis (HAZOP) chosen as the primary risk assessment tool Hazop Tool HAZOP is based on a theory that assumes risk events are caused by deviations from design or operating intentions Break up processes into individual steps for analysis Risk Identification: Identify deviations from design or operating intentions in a systematic fashion Similar to a what if? analysis Risk Analysis: Risk Rating System LOW Likelihood of Deviation Occurrence MEDIUM HIGH : Hazard condition or contamination event not common or expected, but theoretically possible. Medium: Hazard condition or contamination event is not a routine occurrence, but has been observed. : Hazard condition or contamination event is likely, common, or observed routinely. Note: The rating scales may be customized for each manufacturing facility as applicable 7
8 Risk Analysis: Risk Rating System Severity of Deviation Consequences : No product impact anticipated. Medium: Direct impact on assessed component elevated, yet not anticipated to have product impact. : Direct impact on assessed component is high or product impact likely. Direct ingress of contamination directly into product or product components (includes non-product areas, solutions and equipment). LOW MEDIUM HIGH Note: The rating scales may be customized for each manufacturing facility as applicable Evaluate Mitigated Risk Likelihood Medium More Than One Control Required One or More Controls Required More Than One Control Required More Than One Control Required Engineering Or Design Control Required More Than One Control Required Controls may be procedural, training, or engineering / facility design controls and may consider the ability to detect deviations or hazard components as part of a mitigating control No Action Required One or More Controls Required More Than One Control Required Medium Severity Facility Assessments 8
9 Facility Assessments GMP Facilities API Area API Area 2 (Chromatography) Solid Dose Inventory Management Small Pack/Label Facility Liquid Dose Facility Assessments Hazard Classes Product Classifications in Scope of the QRM creating the business case for each facility Certain ly Active or Toxic Products Certain Steroids Cytotoxics Certain Hormones Immunosuppressors Biologicals Exclusive For Animal Use Non-Medicinal Products (pesticides, herbicides) Other Not Yet Classifiable Product Classifications out of Scope ly Sensitizing Products Certain Antibiotics Radiopharmaceuticals Segregation Categories Dedicated Building (For Product Class) Physically separate building which provides complete and total separation of all aspects of all operations. Dedicated Segregated Areas (For Product Class) Areas within a multiproduct facility dedicated to a product class. Campaign Segregation Segregated areas within a multiproduct facility that are used for more than one product class that require segregation. More than one product class cannot be processed at the same time. Campaign segregation is referred to as segregation by time. Validated cleaning and/or inactivation procedures should be established. 9
10 Facility Assessments Facility and Process Mapping Facility Interface Example Defines Boundary Facility Assessments Risk Table Two Facility Interfaces Areas Annex (Milling, Storage of raw materials) and intermediates Each evaluated based on the following pathways (components): Warehouse Ops Packaging Sampling In-Process Sampling Dispensing/Weighing HVAC Personnel For both facilities, 60 operations (elements) evaluated For both facilities, 90 deviations evaluated Example Risk Table API Annex Milling Operations 10
11 Facility Interface Severity of Comments/ Probability of Component Element Deviations Possible Causes Safeguards (controls) Risk Occurrence Consequences Evaluation Recommended Actions Airborne Transfer to outside areas Engineering controls, HVAC Milling Operation system design/preventive Med maintenance Open mill charge Engineering controls, PPE Unloading mill Engineering controls, PPE Reference API Consider Plant and alternative Milling milling area, Operations consider lock Industrial out facility Hygiene (IH) entrance Surrogate during milling Testing Annex (Labs, Milling, Raw Material Storage, Intermediate Storage, Dispensing) Use of Mill Room Engineering control Visual indication, gage failure (i.e., inadequate monitoring, batch record design) verification Med Procedure, engineering Spillage Open Mill Charge controls, PPE Procedure, engineering Open Mill Charge controls, PPE No anteroom, improper gowning, Mfg SOPs, technician Human Transfer improper personnel training, PPE flow, insufficient training Operations would stop Potential gap, Swab and air test results to Suggest two be reviewed to person confirm Prob of operation at all Occurance/ time to aide in Severity, IH PPE decon Surrogate Testing Reuse of PPE (i.e., hood) Procedures (disposal) Med Labeling Errors Human Error Second person verification Equipment Transfer Cleaning procedure, material Open mill charge handling procedure (SOI-GRcontaminating balance API-EQP-1044), engineering carts, scoop, containers control, PPE controls Engineering/ Facility Controls Failure Inadequate design (i.e., Procedures, cleaning, open tray charge) training, PPE Visual indication, gage Power Failure monitoring, Groton site control Med room notification Med Med Magnehelic gauge installation Facility Interface Component Element: Use of Mill Room Annex Deviation: Airborne Transfer to outside areas Possible Causes: Milling Operations Safeguards: Engineering controls, HVAC system design/preventive maintenance Probability of Occurrence: Severity of Consequences: Medium Comments/Risk Evaluations: Reference API Plant and Milling Operations Industrial Hygiene (IH) Surrogate Testing Recommended Action: Consider alternative milling area, consider lock out facility entrance during milling Facility Interface Component Element: Use of Mill Room Annex Deviation: Human Transfer Possible Causes: No anteroom, improper gowning, improper personnel flow, insufficient training Safeguards: MFG & Cleaning SOPs, Technician Training, PPE Probability of Occurrence: Severity of Consequences: Comments/Risk Evaluations: Potential gap, Swab and air test results to be reviewed to confirm Prob of Occurance/Severity, IH Surrogate Testing Recommended Action: Suggest 2 person operation at all time to aide in PPE decon 11
12 Example Risk Table API HVAC Facility Interface Component Element Deviations Possible Causes Safeguards (controls) Probability of of Severity Occurre Consequences nce Comments/ Risk Evaluation Recommended Actions Incorrect pressure differentials Makeup/ result in Supply air migration of and exhaust product air not from one balanced, Reactor system suite to malfunction hallway or to another suite Room balancing is checked and certified every 3 years. All charging is done in closed hood that has its own downflow and exhaust. Preventive maintenance Medium Improve/correct air balance. Increase frequency of balance testing and 3 years is certification. Provide a clear not status of air pressure at each sufficient room, i.e., individual frequency magnehelic gauges with to transmitters to allow display perform of pressure in hallways, balancing. alarms, etc. Allows for detectability. Recommend conducting smoke test. Area HVAC Air Current air Balancing Incorrect balancing has in Mfg Area pressure 134C positive, Room balancing is differentials 134D neutral, checked and result in and 134B certified every 3 migration of (common years. Current product general measurement from Dryer purpose area) show air flow out suites to neutral. All 3 of balance. Open another rooms solids handling Dryer suite negative to takes place (134C and airlock 134A. directly in front of 134D) or Supply air in HEPA exhaust 129B (and 134C higher (cross flow Processing flow than exhaust?) Suites) HEPA exhaust. Positive pressure from 134C could result in product migration into Recommend conducting general smoke test. purpose area (134B) and possibly 134D dryer suite. 12
13 Facility Interface Component Element: Air Balancing in Area Mfg Area HVAC Deviation: Incorrect pressure differentials result in migration of product from one Reactor suite to hallway or to another suite Possible Causes: Makeup/Supply air and exhaust air not balanced, system malfunction Safeguards: Room balancing is checked and certified every 3 years. All charging is done in closed hood that has its own downflow and exhaust. Preventive maintenance Probability of Occurrence: Severity of Consequences: Medium Comments/Risk Evaluations: 3 years is not sufficient frequency to perform balancing Recommended Action: Improve/correct air balance. Increase frequency of balance testing and certification. Provide a clear status of air pressure at each room, i.e., individual magnehelic gauges with transmitters to allow display of pressure in hallways, alarms, etc. Allows for detectability. Recommend conducting smoke test. Facility Interface Component Element Deviations Possible Causes Safeguards (controls) Comments/ Risk Evaluation Probability of Severity of Consequences Occurrence Recommended Actions Area HVAC Cross contamination between Walkin hood and fans shuts down failure One of the exhaust Power Lab hood and Hallway 129B Confirm the following: Mfg Rm 1: EF-1 shuts Hoods are far down and SF-3 shuts enough away to down. avoid migration Mfg Rm 2: EF-2 shuts from one to - down and SF-3 shuts another. This Could - down. was confirmed change Could Mfg Rm 3: EF-3 shuts by recent air based change down and SF-3 shuts Recommend measurements. on based on down. conducting According to Exhaust Exh. and Dry. Rms: EF-4 shuts down smoke test. HVAC SME, and Supply and SF-3 shuts down. makeup air Supply data handlers shut 132 (Subd. Rm.): EF-5 air data down when shuts down SF-5 shuts exhaust fans down. shut down. And vice versa for all above scenarios. Outside hallway None, other pressure is higher Air than open than airlock. Imbalance, reactors only in Outside hallway is pressure in hoods. Any exposed to oustide Air Balancing product in the outside conditions hallway too at outside outside via an overhead high. Both hallway and hallway is in door. Potential doors to entry "airlock" secondary for dirt, dust, etc. airlock open containment or to migrate at the same drummed or through airlock time (not a shrink and into all Mfg true airlock) wrapped, etc. Area rooms Medium Reestablish as a true Not a true cross airlock, i.e., contamination issue, but doors critical quality issue due interlocked to the high probability of to open one dust and debris impacting at a time. product. Recommend conducting smoke test. 13
14 Facility Interface Area Component HVAC Element: Air Balancing at outside hallway and entry airlock Deviation: Outside hallway pressure is higher than airlock. Outside hallway is exposed to outside conditions via an overhead door. Potential for dirt, dust, etc. to migrate through airlock and into all Mfg Area rooms. Possible Causes: Air Imbalance, pressure in oustide hallway too high. Both doors to airlock open at the same time (not a true airlock) Safeguards: None, other than open reactors only in hoods. Any product in the outside hallway is in secondary containment or drummed or shrink wrapped, etc. Probability of Occurrence: Severity of Consequences: Medium Comments/Risk Evaluations: Not a true cross contamination issue, but critical quality issue due to the high probability of dust and debris impacting product Recommended Action: Reestablish as a true airlock, i.e., doors interlocked to open one at a time. Recommend conducting smoke test. Facility Assessments Six Facility Interfaces Rooms (with and without Misting Showers) In Process Testing Room Hallway-type Rooms (No Open Product) Gown/Degown Rooms for GMP Area Wash Rooms Clean Equipment (No product) Each evaluated based on the following pathways (components): Warehouse Ops Packaging Sampling In-Process Sampling Dispensing/Weighing HVAC Personnel 35 operations (elements) evaluated 55 deviations evaluated for all facility interfaces Facility Assessments Four Facility Interfaces Warehouse Area Dispensing Booths Handoff Areas Sampling Areas (future) Each evaluated based on the following pathways (components): Warehouse Ops Packaging Sampling In-Process Sampling Dispensing/Weighing HVAC Personnel For both facilities,15 conditions (elements) evaluated For both facilities, 25 deviations evaluated 14
15 Write the Report What s Required References Team members Scope Working Group Table (Attachment) Scope QRM Methodology & Assumptions Periodic Review Interval Action Item Table in ES Executive Summary (ES) of Results Summary/Lessons Learned Obtain Management support up front. Consider resource utilization Be specific with scope and risk question. Use an agreed upon QRM tool. Facilitator must be energetic and continue to challenge the group and maintain energy level Make sure facility drawings are current for layout and HVAC. Line up HVAC expert early as this expertise is very important and can be overlooked when forming the team. Summary/Lessons Learned Choose report author up front. Lunch and Coffee!! Minimize sessions by employing full day meetings if possible. Actions item responsibilities well defined, with timetables. Management and approver signatures predetermined (should be in QRM SOP) 15
16 Any Questions Background Slides 16
17 Additional Facility Assessment Tables Facility Assessments Risk Table Example Drug Product Facility Interface Component Element Deviations Possible Causes Safeguards (controls) Probability of Occurrence Actions Comments/ Severity Recommended for of Consequences Contain- Risk Evalua-tion ment and Open Transfers Open product is Product leak transferred to bin (elephant trunk). API sieving. Improper transfer technique, product bag rips, bin valve left open. Experienced technicians, training, all sieves are one time use, then discarded. Only larger sieves that are dedicated to a product are cleaned and tracked as dedicated to that product. Any leaks are immediately cleaned up. Rooms (with and without Misting Showers) Cleaning Cleaning Validation Cleaning Validation Product Assesment (CVPA) checked everytime product is used. ADE values and swab sampling measures assessed as part of CVPA. CVPA Reversioned if toxicity information or Cleaning Validation Data classification changes. No not available notification if classification changes until next use, however QRM assessment is performed to determine risk of products previously manufactured. SOPs in place for individual pieces of equipment. Consider improved Marginal notification solubility from EHS or increases Master severity. Planner to facility solubility (internal and would have external rinsed off. coordina-tors solubility when a would have product been classifica-tion swabbed changes Facility Assessments Risk Table Example Drug Product Facility Interface Component Element Deviations Possible Causes Safeguards (controls) Probability of Occurrence Actions Comments/ Severity Recommended for of Consequences Contain- Risk Evalua-tion ment Rooms (with and without Misting Showers) Equipment visually inspected, equipment always under observation, equipment is stopped in case of leak, personnel in PPE within mfg Human error, equipment module, processing rooms malfunction, tear in negative to air locks and flexible transition piece corridor. Airflow designed to from one piece of Closed contained Leakage during keep product low and away equipment to another, mfg process, manufacturing, Transfer from clean corridor. Any spill mill screen plugs. Medium closed transfer to sleeve tears during bin would be cleaned following Overpressurization mill to mill transfer spill. Technician air shower /material weakness and PPE removal prior to clean during transfer to a mill. corridor entry. All equipment Sleeve not properly is cleaned within the module attached prior to exit. Cleaning is validated or swabbing is performed for compounds with solubility outside of validated range. 17
18 Facility Assessments Risk Table Example Inventory Management Facility Comments/ Actions Probability Severity Recommended for Facility Interface Component Element Deviations Possible Causes Safeguards (controls) of of Consequences Evalua- Risk Occurrence Containment tion Scoops, Minimal quantity of product is weigh boat, sampled/subdivided. Downflow disposed in booth minimizes dust that would Booth, be on PPE. SOPs and trained gloves technicians minimize product on removed PPE. Only one material allowed after Consider use of in Subdivision room at a time. sampling, Dispensing Booths Product carried over disposable Visual wipe down after each and new Sampling Dispensing Room after sampling and Product retained on PPE sleeves for subdivision of materials for the gloves before first wipedown. sampling/dispe same batch, full cleandown donned for nsing. between each batch. Sampled first product and sample containers wipedown, move from Dispensing Booth to containers Airlock. Is not staged post wiped 3X Sampling/Dispensing in before Dispensing Room. removed from booth. Other QRM Tools Considered Failure Modes and Effects (& Criticality) Analysis FMEA/FMECA Fault Tree Analysis FTA Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points - HACCP Preliminary Hazard Analysis (PHA) Risk Ranking and Filtering 18
Commercial Manufacturing - Qualification & Validation-related GMP Deficiencies and Other Lifecycle Considerations
 Commercial Manufacturing - Qualification & Validation-related GMP Deficiencies and Other Lifecycle Considerations Kevin O Donnell PhD Market Compliance Manager, IMB PDA / FDA Conference Pharmaceutical
Commercial Manufacturing - Qualification & Validation-related GMP Deficiencies and Other Lifecycle Considerations Kevin O Donnell PhD Market Compliance Manager, IMB PDA / FDA Conference Pharmaceutical
Quality Risk Management The Pharmaceutical Experience Ann O Mahony Quality Assurance Specialist Pfizer Biotech Grange Castle
 Quality Risk Management 11 November 2011 Galway, Ireland Quality Risk Management The Pharmaceutical Experience Ann O Mahony Quality Assurance Specialist Pfizer Biotech Grange Castle Overview Regulatory
Quality Risk Management 11 November 2011 Galway, Ireland Quality Risk Management The Pharmaceutical Experience Ann O Mahony Quality Assurance Specialist Pfizer Biotech Grange Castle Overview Regulatory
Best Practice In A Change Management System
 Quality & Compliance Associates, LLC Best Practice In A Change Management System President Quality & Compliance Associates, LLC Change Control and Its Role in a Continuous Improvement Environment 3 Benefits
Quality & Compliance Associates, LLC Best Practice In A Change Management System President Quality & Compliance Associates, LLC Change Control and Its Role in a Continuous Improvement Environment 3 Benefits
Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points (HACCP) 1 Overview
 Manufacturing Technology Committee Risk Management Working Group Risk Management Training Guides Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points (HACCP) 1 Overview Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Point
Manufacturing Technology Committee Risk Management Working Group Risk Management Training Guides Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points (HACCP) 1 Overview Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Point
PPG SUPPLIER DEVELOPMENT ASSESSMENT
 Supplier: Address: Products: Assessment Date: Assessment Team: Certification: Supplier Contacts Position E-mail Phone General Comments: Assessment Results Summary Sections Non-conformity Action Point Quality
Supplier: Address: Products: Assessment Date: Assessment Team: Certification: Supplier Contacts Position E-mail Phone General Comments: Assessment Results Summary Sections Non-conformity Action Point Quality
QUALITY RISK MANAGEMENT (QRM): A REVIEW
 Lotlikar et al Journal of Drug Delivery & Therapeutics; 2013, 3(2), 149-154 149 Available online at http://jddtonline.info REVIEW ARTICLE QUALITY RISK MANAGEMENT (QRM): A REVIEW Lotlikar MV Head Corporate
Lotlikar et al Journal of Drug Delivery & Therapeutics; 2013, 3(2), 149-154 149 Available online at http://jddtonline.info REVIEW ARTICLE QUALITY RISK MANAGEMENT (QRM): A REVIEW Lotlikar MV Head Corporate
Quality Risk Management Understanding and Control the Risk in Pharmaceutical Manufacturing Industry
 International Journal of Pharmaceutical Science Invention ISSN (Online): 2319 6718, ISSN (Print): 2319 670X Volume 4 Issue 1 January 2015 PP.29-41 Quality Risk Management Understanding and Control the
International Journal of Pharmaceutical Science Invention ISSN (Online): 2319 6718, ISSN (Print): 2319 670X Volume 4 Issue 1 January 2015 PP.29-41 Quality Risk Management Understanding and Control the
Environmental Monitoring of Clean Rooms
 Environmental Monitoring of Raul Duarte President DDK Scientific, Corp. Copyright DDK Scientific, Corp. 2008, 2009, DDK Scientific, Corp. Proprietary A manufacturing facility for pharmaceutical products
Environmental Monitoring of Raul Duarte President DDK Scientific, Corp. Copyright DDK Scientific, Corp. 2008, 2009, DDK Scientific, Corp. Proprietary A manufacturing facility for pharmaceutical products
GMP Regulatory Considerations
 GMP Regulatory Considerations Alain Kupferman Workshop on WO prequalification requirements for reproductive health medicines, Jakarta, October 2009 REGULATORY CONSIDERATIONS CONTAINMENT PROTECTION METODS
GMP Regulatory Considerations Alain Kupferman Workshop on WO prequalification requirements for reproductive health medicines, Jakarta, October 2009 REGULATORY CONSIDERATIONS CONTAINMENT PROTECTION METODS
Guidance for Industry
 Guidance for Industry Q9 Quality Risk Management U.S. Department of Health and Human Services Food and Drug Administration Center for Drug Evaluation and Research (CDER) Center for Biologics Evaluation
Guidance for Industry Q9 Quality Risk Management U.S. Department of Health and Human Services Food and Drug Administration Center for Drug Evaluation and Research (CDER) Center for Biologics Evaluation
The use of risk assessment tools for microbiological assessment of cleanroom environments. by Tim Sandle
 The use of risk assessment tools for microbiological assessment of cleanroom environments by Tim Sandle Email: tim.sandle@bpl.co.uk / timsandle@btinternet.com Web: www.pharmig.blogspot.com Environmental
The use of risk assessment tools for microbiological assessment of cleanroom environments by Tim Sandle Email: tim.sandle@bpl.co.uk / timsandle@btinternet.com Web: www.pharmig.blogspot.com Environmental
Procedures for the Effective Use of Biological Safety Cabinets
 Procedures for the Effective Use of Biological Safety Cabinets APPROVAL DATE BY BIOHAZARDS SUBCOMMITTEE: August 10, 2012 SUPERSEDES: March 1, 2012 This corporate guideline/procedure is intended as a minimum
Procedures for the Effective Use of Biological Safety Cabinets APPROVAL DATE BY BIOHAZARDS SUBCOMMITTEE: August 10, 2012 SUPERSEDES: March 1, 2012 This corporate guideline/procedure is intended as a minimum
CONTROL METHODS. There are five ways to control the release of asbestos fibers:
 Control Methods CONTROL METHODS When asbestos containing materials are found in a building, the owner must decide which method or methods will be used to deal with the asbestos. The decision will be based
Control Methods CONTROL METHODS When asbestos containing materials are found in a building, the owner must decide which method or methods will be used to deal with the asbestos. The decision will be based
Spill Prevention, Control and Countermeasure (SPCC) Rule
 Spill Prevention, Control and Countermeasure (SPCC) Rule Code of Federal Regulations Title 40 CFR Part 112 Training Guide for Oil and Fuel handlers on Farms 1 Purpose of SPCC Rule To prevent oil discharges
Spill Prevention, Control and Countermeasure (SPCC) Rule Code of Federal Regulations Title 40 CFR Part 112 Training Guide for Oil and Fuel handlers on Farms 1 Purpose of SPCC Rule To prevent oil discharges
Quality Risk Management Tools Quality Risk Management Tool Selection When to Select FMEA: QRM Tool Selection Matrix
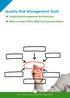 Quality Risk Management Tools Quality Risk Management Tool Selection When to Select FMEA: QRM Tool Selection Matrix 26 Quality Risk Management Tools The ICH Q9 guideline, Quality Risk Management, provides
Quality Risk Management Tools Quality Risk Management Tool Selection When to Select FMEA: QRM Tool Selection Matrix 26 Quality Risk Management Tools The ICH Q9 guideline, Quality Risk Management, provides
Cleaning and Contamination Control
 Cleaning and Contamination Control A regulatory perspective Lynn Talomsin Senior Inspector, Manufacturing Quality Branch, TGA Control Practices Cleaning and Contamination Control Contamination control
Cleaning and Contamination Control A regulatory perspective Lynn Talomsin Senior Inspector, Manufacturing Quality Branch, TGA Control Practices Cleaning and Contamination Control Contamination control
QUALITY RISK MANAGEMENT
 INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON HARMONISATION OF TECHNICAL REQUIREMENTS FOR REGISTRATION OF PHARMACEUTICALS FOR HUMAN USE ICH HARMONISED TRIPARTITE GUIDELINE QUALITY RISK MANAGEMENT Q9 Current Step 4 version
INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON HARMONISATION OF TECHNICAL REQUIREMENTS FOR REGISTRATION OF PHARMACEUTICALS FOR HUMAN USE ICH HARMONISED TRIPARTITE GUIDELINE QUALITY RISK MANAGEMENT Q9 Current Step 4 version
Risk-Based Environmental Monitoring. Marsha Stabler Hardiman Senior Consultant Concordia ValSource Wednesday September 17, 2014 FDA/PQRI
 Risk-Based Environmental Monitoring Marsha Stabler Hardiman Senior Consultant Concordia ValSource Wednesday September 17, 2014 FDA/PQRI Presenter Marsha Stabler Hardiman Over 20 years experience in the
Risk-Based Environmental Monitoring Marsha Stabler Hardiman Senior Consultant Concordia ValSource Wednesday September 17, 2014 FDA/PQRI Presenter Marsha Stabler Hardiman Over 20 years experience in the
BIOLOGICAL SAFETY CABINET PROGRAM
 BIOLOGICAL SAFETY CABINET PROGRAM TABLE OF CONTENTS: 1. INTRODUCTION 2. PURPOSE AND SCOPE 3. SELECTION AND INSTALLATION 4. USE OF BIOLOGICAL SAFETY CABINETS 5. CERTIFICATION OF BIOLOGICAL SAFETY CABINETS
BIOLOGICAL SAFETY CABINET PROGRAM TABLE OF CONTENTS: 1. INTRODUCTION 2. PURPOSE AND SCOPE 3. SELECTION AND INSTALLATION 4. USE OF BIOLOGICAL SAFETY CABINETS 5. CERTIFICATION OF BIOLOGICAL SAFETY CABINETS
WASTE Application Form - Dublin Waste to Energy SECTION J ACCIDENT PREVENTION & EMERGENCY RESPONSE
 SECTION J ACCIDENT PREVENTION & EMERGENCY RESPONSE Describe the existing or proposed measures, including emergency procedures, to minimise the impact on the environment of an accidental emission or spillage.
SECTION J ACCIDENT PREVENTION & EMERGENCY RESPONSE Describe the existing or proposed measures, including emergency procedures, to minimise the impact on the environment of an accidental emission or spillage.
JANUARY 2013 PREPARATION OF A SITE MASTER FILE FOR A MANUFACTURER OF COSMETIC PRODUCTS
 JANUARY 2013 PREPARATION OF A SITE MASTER FILE FOR A MANUFACTURER OF COSMETIC PRODUCTS 1 WHAT IS A SITE MASTER FILE? A Site Master File (SMF) is a document prepared by the manufacturer containing specific
JANUARY 2013 PREPARATION OF A SITE MASTER FILE FOR A MANUFACTURER OF COSMETIC PRODUCTS 1 WHAT IS A SITE MASTER FILE? A Site Master File (SMF) is a document prepared by the manufacturer containing specific
Standard Operating Procedure
 Standard Operating Procedure Title: Waste Management of Medicines and other Pharmaceutical Products in the Community Setting Prepared by: Sam Durant Presented to: Care & Clinical Policies Date: 19 th March
Standard Operating Procedure Title: Waste Management of Medicines and other Pharmaceutical Products in the Community Setting Prepared by: Sam Durant Presented to: Care & Clinical Policies Date: 19 th March
Decontamination Units
 Decontamination Units 1 DECON The worker/personal decontamination system (commonly called the "decon unit or Decon") is specially designed to allow passage to and from the work area during the abatement
Decontamination Units 1 DECON The worker/personal decontamination system (commonly called the "decon unit or Decon") is specially designed to allow passage to and from the work area during the abatement
Standard Operating Procedure for Dacarbazine in Animals
 Standard Operating Procedure for Dacarbazine in Animals 1. Health hazards Dacarbazine, also known as DTIC, DIC, and Imidazole Carboxamide, is an antineoplastic chemotherapy drug used in the treatment of
Standard Operating Procedure for Dacarbazine in Animals 1. Health hazards Dacarbazine, also known as DTIC, DIC, and Imidazole Carboxamide, is an antineoplastic chemotherapy drug used in the treatment of
DISCUSSION TOOL PRESENTED TO THE AABB CT REGULATORY AFFAIRS SUBSECTION
 1 US FDA Form 483: A Case Study DISCUSSION TOOL PRESENTED TO THE AABB CT REGULATORY AFFAIRS SUBSECTION DEVELOPED BY FRAN RABE 2 Introduction This case study is intended to extract portions of information
1 US FDA Form 483: A Case Study DISCUSSION TOOL PRESENTED TO THE AABB CT REGULATORY AFFAIRS SUBSECTION DEVELOPED BY FRAN RABE 2 Introduction This case study is intended to extract portions of information
Application of Quality Risk Management to Pharmaceutical Operations. Eldon Henson, Vice President, Quality Operations
 Application of Quality Risk Management to Pharmaceutical Operations Eldon Henson, Vice President, Quality Operations Key Topics of Discussion Definition of Quality Risk Management (QRM) Overview of PDA
Application of Quality Risk Management to Pharmaceutical Operations Eldon Henson, Vice President, Quality Operations Key Topics of Discussion Definition of Quality Risk Management (QRM) Overview of PDA
UNICEF s Quality Assurance System for Procurement of Micronutrient Powders (MNP)
 UNICEF s Quality Assurance System for Procurement of Micronutrient Powders (MNP) Nutrition Supplier Meeting, June 30, 2015 Dimitris Catsoulacos Quality Assurance Specialist PRESENTATION OVERVIEW Quality
UNICEF s Quality Assurance System for Procurement of Micronutrient Powders (MNP) Nutrition Supplier Meeting, June 30, 2015 Dimitris Catsoulacos Quality Assurance Specialist PRESENTATION OVERVIEW Quality
Appendix J IBC Biohazard Spill Management Plan
 OVERVIEW Prevention is the most important part of any spill management plan. Be sure to read and understand standard operating procedures (SOP s) and protocols for safe manipulation of biohazards before
OVERVIEW Prevention is the most important part of any spill management plan. Be sure to read and understand standard operating procedures (SOP s) and protocols for safe manipulation of biohazards before
Risk Assessment: Biosafety Cabinet
 Risk Assessment: Biosafety Cabinet Biosafety cabinets (BSCs) serve as primary containment devices for operations involving potential splashes, spills or aerosolization of hazardous biological materials.
Risk Assessment: Biosafety Cabinet Biosafety cabinets (BSCs) serve as primary containment devices for operations involving potential splashes, spills or aerosolization of hazardous biological materials.
Procedures for Cutting and Handling of Asbestos Cement Pipe. City of Richmond Public Works Operations
 Procedures for Cutting and Handling of Asbestos Cement Pipe City of Richmond Public Works Operations Version 2.0 Updates to: November 1995 Procedures Prepared by: AMEC Earth & Environmental a division
Procedures for Cutting and Handling of Asbestos Cement Pipe City of Richmond Public Works Operations Version 2.0 Updates to: November 1995 Procedures Prepared by: AMEC Earth & Environmental a division
ABC CIRCUITS 10 Circuit Drive Circuit Town, IN 12345 SLUG CONTROL PLAN
 ABC CIRCUITS 10 Circuit Drive Circuit Town, IN 12345 SLUG CONTROL PLAN The purpose of this plan is to provide detailed instructions for slug prevention and control. A complete copy of this plan is maintained
ABC CIRCUITS 10 Circuit Drive Circuit Town, IN 12345 SLUG CONTROL PLAN The purpose of this plan is to provide detailed instructions for slug prevention and control. A complete copy of this plan is maintained
How to Estimate the Cost of a. Laboratory Renovation. Candidate Number: 0714144
 How to Estimate the Cost of a Laboratory Renovation Candidate Number: 0714144 December 15, 2014 1 Table of Contents Cover Page Page 1 Table of Contents Page 2 Introduction Page 3 Types & Methods of Measurements
How to Estimate the Cost of a Laboratory Renovation Candidate Number: 0714144 December 15, 2014 1 Table of Contents Cover Page Page 1 Table of Contents Page 2 Introduction Page 3 Types & Methods of Measurements
Training on Standard Operating Procedures for Health Care Waste Management Swaziland 12 May, 2011
 Training on Standard Operating Procedures for Health Care Waste Management Swaziland 12 May, 2011 Safe Infectious Waste Handling and Transport Objective Waste Overview Roles and Responsibilities of Waste
Training on Standard Operating Procedures for Health Care Waste Management Swaziland 12 May, 2011 Safe Infectious Waste Handling and Transport Objective Waste Overview Roles and Responsibilities of Waste
CONCEPTS OF FOOD SAFETY QUALITY MANAGEMENT SYSTEMS. Mrs. Malini Rajendran
 CONCEPTS OF FOOD SAFETY AND QUALITY MANAGEMENT SYSTEMS Mrs. Malini Rajendran Brief background 1963 - The Codex Alimentarius Commission was created by FAO and WHO to develop food standards, guidelines and
CONCEPTS OF FOOD SAFETY AND QUALITY MANAGEMENT SYSTEMS Mrs. Malini Rajendran Brief background 1963 - The Codex Alimentarius Commission was created by FAO and WHO to develop food standards, guidelines and
Leila Kakko Tampere University of Applied science TRADITIONAL FOOD IN COMBATING FOODBORNE PATHOGENS 2011
 Leila Kakko Tampere University of Applied science TRADITIONAL FOOD IN COMBATING FOODBORNE PATHOGENS 2011 World Food Programme Food quality control is necessary to ensure that food aid supplies are safe,
Leila Kakko Tampere University of Applied science TRADITIONAL FOOD IN COMBATING FOODBORNE PATHOGENS 2011 World Food Programme Food quality control is necessary to ensure that food aid supplies are safe,
BOSTON COLLEGE ENVIRONMENTAL HEALTH AND SAFETY LABORATORY GUIDE FOR RENOVATIONS, REMODELS, MOVES AND TERMINATIONS
 BOSTON COLLEGE ENVIRONMENTAL HEALTH AND SAFETY LABORATORY GUIDE FOR RENOVATIONS, REMODELS, MOVES AND TERMINATIONS I. Policy for Termination of Laboratory Use of Hazardous Materials The Principal Investigator
BOSTON COLLEGE ENVIRONMENTAL HEALTH AND SAFETY LABORATORY GUIDE FOR RENOVATIONS, REMODELS, MOVES AND TERMINATIONS I. Policy for Termination of Laboratory Use of Hazardous Materials The Principal Investigator
Quality Risk Management
 PS/INF 1/2010 * * Quality Risk Management Quality Risk Management Implementation of ICH Q9 in the pharmaceutical field an example of methodology from PIC/S Document > Authors: L. Viornery (AFSSAPS) Ph.
PS/INF 1/2010 * * Quality Risk Management Quality Risk Management Implementation of ICH Q9 in the pharmaceutical field an example of methodology from PIC/S Document > Authors: L. Viornery (AFSSAPS) Ph.
ACTIVITY NAME. Training Requirements for Spill Prevention Control and Countermeasures (SPCC) 40 CFR Part 112 Naval Air Station Corpus Christi Texas
 ACTIVITY NAME Training Requirements for Spill Prevention Control and Countermeasures (SPCC) 40 CFR Part 112 Naval Air Station Corpus Christi Texas CY 2014 BOTTOM LINE UP FRONT To prevent oil discharges
ACTIVITY NAME Training Requirements for Spill Prevention Control and Countermeasures (SPCC) 40 CFR Part 112 Naval Air Station Corpus Christi Texas CY 2014 BOTTOM LINE UP FRONT To prevent oil discharges
Improved Utilization of Self-Inspection Programs within the GMP Environment A Quality Risk Management Approach
 Improved Utilization of Self-Inspection Programs within the GMP Environment A Quality Risk Management Approach Barbara Jeroncic Self-inspection is a well-established and vital part of the pharmaceutical
Improved Utilization of Self-Inspection Programs within the GMP Environment A Quality Risk Management Approach Barbara Jeroncic Self-inspection is a well-established and vital part of the pharmaceutical
Cleaning validation of cleanrooms and preparation equipments
 Cleaning validation of cleanrooms and preparation equipments Head of production Central Pharmacy, Geneva University Hospitals EAHP Foundation Seminar: Patient Safety; More About Compounding" 23-25 May,
Cleaning validation of cleanrooms and preparation equipments Head of production Central Pharmacy, Geneva University Hospitals EAHP Foundation Seminar: Patient Safety; More About Compounding" 23-25 May,
Particularly Hazardous Substances (PHS) Standard Operating Procedure (SOP)
 Particularly Hazardous Substances (PHS) Standard Operating Procedure (SOP) Formaldehyde, formalin, paraformaldehyde solutions, and paraformaldehyde solids Principal Investigator: Room & Building #: Department:
Particularly Hazardous Substances (PHS) Standard Operating Procedure (SOP) Formaldehyde, formalin, paraformaldehyde solutions, and paraformaldehyde solids Principal Investigator: Room & Building #: Department:
Biological Safety Program
 Risk Management & Safety Main Office, Wyoming Hall Phone: (307) 766-3277 Fax: (307)766-6116 Regulated Materials Management Center Phone: (307)766-3696 Fax: (307)766-3699 Web: www.uwyo.edu/ehs Email: UWEHS@uwyo.edu
Risk Management & Safety Main Office, Wyoming Hall Phone: (307) 766-3277 Fax: (307)766-6116 Regulated Materials Management Center Phone: (307)766-3696 Fax: (307)766-3699 Web: www.uwyo.edu/ehs Email: UWEHS@uwyo.edu
ASI 691 Prinicples of HACCP 1
 Prerequisite Programs: GMP s, SOP s, SSOP s HACCP Does Not Stand Alone Must be built on existing food safety programs Prerequisite Programs Definition of Prerequisite Programs- Procedures, including Good
Prerequisite Programs: GMP s, SOP s, SSOP s HACCP Does Not Stand Alone Must be built on existing food safety programs Prerequisite Programs Definition of Prerequisite Programs- Procedures, including Good
ALLEGANY WIND POWER PROJECT CONSTRUCTION SPILL PREVENTION PLAN
 ALLEGANY WIND POWER PROJECT CONSTRUCTION SPILL PREVENTION PLAN Best Management Practices (BMPs) will be implemented during construction of the Allegany Wind Power Project to prevent and contain spills.
ALLEGANY WIND POWER PROJECT CONSTRUCTION SPILL PREVENTION PLAN Best Management Practices (BMPs) will be implemented during construction of the Allegany Wind Power Project to prevent and contain spills.
Everything you want to know about USP 797
 Everything you want to know about USP 797 Dr. Linda D. Lee Director of Operations Waste Management Healthcare Solutions September. 22, 2009 Goals High level understanding of USP 797 Who does it apply too
Everything you want to know about USP 797 Dr. Linda D. Lee Director of Operations Waste Management Healthcare Solutions September. 22, 2009 Goals High level understanding of USP 797 Who does it apply too
Chemical Fume Hoods. Environmental Health and Safety 974-5084
 Chemical Fume Hoods Environmental Health and Safety 974-5084 Regulatory References Prudent Practices in the Laboratory 2011 (National Research Council of The National Academies): Laboratory chemical hoods
Chemical Fume Hoods Environmental Health and Safety 974-5084 Regulatory References Prudent Practices in the Laboratory 2011 (National Research Council of The National Academies): Laboratory chemical hoods
Guidance on Qualification of existing facilities, systems, equipment and utilities
 QUALIFICATION_EXISTING_EQUIPMENT_FINAL page 1 / 16 1. Acknowledgement...3 2. Introduction...3 3. Scope...4 4. Regulatory requirements...4 5. Guidance...4 5.1 Risk Assessment... 4 5.2 Procedure... 7 5.3
QUALIFICATION_EXISTING_EQUIPMENT_FINAL page 1 / 16 1. Acknowledgement...3 2. Introduction...3 3. Scope...4 4. Regulatory requirements...4 5. Guidance...4 5.1 Risk Assessment... 4 5.2 Procedure... 7 5.3
4729-16-11 Hazardous Drugs Compounded by a Prescriber.
 ACTION: Original DATE: 11/30/2015 8:57 AM 4729-16-11 Hazardous Drugs Compounded by a Prescriber. (A) A facility where a prescriber is compounding or handling hazardous drugs shall be licensed as a terminal
ACTION: Original DATE: 11/30/2015 8:57 AM 4729-16-11 Hazardous Drugs Compounded by a Prescriber. (A) A facility where a prescriber is compounding or handling hazardous drugs shall be licensed as a terminal
GUIDANCE FOR DEVELOPMENT OF SPILL AND SLUG PREVENTION CONTROL PLANS AND FACILITIES FOR THE CITY OF ATTLEBORO SEWER USERS
 Company Name: Address: The City of Attleboro s Rules and Regulations for the use of Wastewater Facilities require each user to provide protection from accidental discharge of prohibited materials and substances
Company Name: Address: The City of Attleboro s Rules and Regulations for the use of Wastewater Facilities require each user to provide protection from accidental discharge of prohibited materials and substances
Hazardous Drug. Cleanroom. Standards
 Hazardous Drug Cleanroom Standards Module 3 Table of Contents Section A... 1 A.1 International Standards Organization (ISO) Classifications... 1 A.2 Hazardous Drug Cleanroom and Anteroom... 1 A.2.1 Location
Hazardous Drug Cleanroom Standards Module 3 Table of Contents Section A... 1 A.1 International Standards Organization (ISO) Classifications... 1 A.2 Hazardous Drug Cleanroom and Anteroom... 1 A.2.1 Location
North Carolina State University Emergency Facilities Closure Checklist- Part I
 North Carolina State University Emergency Facilities Closure Checklist- Part I Unplanned or spontaneous events often disrupt daily operations on campus. In the event that an incident may interrupt your
North Carolina State University Emergency Facilities Closure Checklist- Part I Unplanned or spontaneous events often disrupt daily operations on campus. In the event that an incident may interrupt your
Lead Management. Presented by: Gary Chinn (815) 254 9554 President, Best Technology Systems
 Lead Management Presented by: Gary Chinn (815) 254 9554 President, Best Technology Systems Gary Chinn, President Introduction I started in the Asbestos and lead remediation business in 1987 as a worker
Lead Management Presented by: Gary Chinn (815) 254 9554 President, Best Technology Systems Gary Chinn, President Introduction I started in the Asbestos and lead remediation business in 1987 as a worker
Design, Operation and Management of GTP/GMP Cell Engineering Facilities
 Design, Operation and Management of GTP/GMP Cell Engineering Facilities Scott R. Burger, MD Advanced Cell & Gene Therapy BFDA 2007 International Symposium on Regulation of Human Cell and Tissue- Based
Design, Operation and Management of GTP/GMP Cell Engineering Facilities Scott R. Burger, MD Advanced Cell & Gene Therapy BFDA 2007 International Symposium on Regulation of Human Cell and Tissue- Based
Zoning requirements for Dairy Suppliers
 Zoning requirements for Dairy Suppliers Overview What is zoning? Zoning requirements? Why do we need zoning? How Does MDLZ International Define The Different Levels of Zoning? Equipment examples for each
Zoning requirements for Dairy Suppliers Overview What is zoning? Zoning requirements? Why do we need zoning? How Does MDLZ International Define The Different Levels of Zoning? Equipment examples for each
STANDARD OPERATING PROCEDURES FOR MOLD REMEDIATION
 West Virginia University Environmental Health and Safety STANDARD OPERATING PROCEDURES FOR MOLD REMEDIATION Origination Date August 2013. Contents Purpose:... 2 Job Scope... 2 Definitions... 2 Roles/Responsibilities:...
West Virginia University Environmental Health and Safety STANDARD OPERATING PROCEDURES FOR MOLD REMEDIATION Origination Date August 2013. Contents Purpose:... 2 Job Scope... 2 Definitions... 2 Roles/Responsibilities:...
Title:: Effective GMP AUDITS for APIs and Formulation Pharma Companies By G.Sundar-Director/Consultant PharmQA Compliance solutions
 WELCOME Title:: Effective GMP AUDITS for APIs and Formulation Pharma Companies By G.Sundar-Director/Consultant PharmQA Compliance solutions Contents: Introduction GMP Audit GMP Audit plan GMP Auditing
WELCOME Title:: Effective GMP AUDITS for APIs and Formulation Pharma Companies By G.Sundar-Director/Consultant PharmQA Compliance solutions Contents: Introduction GMP Audit GMP Audit plan GMP Auditing
FMI Listeria Action Plan for Retail Delis
 FMI Listeria Action Plan for Retail Delis November 2012 Listeria control at retail is an ongoing challenge. FMI and our members are committed to finding ways to control the growth and if possible, eliminate
FMI Listeria Action Plan for Retail Delis November 2012 Listeria control at retail is an ongoing challenge. FMI and our members are committed to finding ways to control the growth and if possible, eliminate
Good Housekeeping Practices for DPW/Fleet Maintenance Facilities
 Good Housekeeping Practices for DPW/Fleet Maintenance Facilities Kevin P. Walker C&S Engineers, Inc. Best Management Practices Best Management Practices (BMPs) are measures and/or controls used to prevent
Good Housekeeping Practices for DPW/Fleet Maintenance Facilities Kevin P. Walker C&S Engineers, Inc. Best Management Practices Best Management Practices (BMPs) are measures and/or controls used to prevent
Quality Risk Management Principles and Industry Case Studies
 Final Draft Rev. December 28, 2008 Quality Risk Management Principles and Industry Case Studies T. Frank 1, S. Brooks 2, R. Creekmore 3, B. Hasselbalch 4, K. Murray 5, K. Obeng 6, S. Reich 5, E. Sanchez
Final Draft Rev. December 28, 2008 Quality Risk Management Principles and Industry Case Studies T. Frank 1, S. Brooks 2, R. Creekmore 3, B. Hasselbalch 4, K. Murray 5, K. Obeng 6, S. Reich 5, E. Sanchez
PI s Name Date Bldg./Rm# CDC Biosafety Level 3 (BSL-3)
 PI s Name Date Bldg./Rm# CDC Biosafety Level 3 (BSL-3) Yes No 1. Is access to the laboratory limited or restricted at the discretion of the laboratory director when experiments are in progress? Yes No
PI s Name Date Bldg./Rm# CDC Biosafety Level 3 (BSL-3) Yes No 1. Is access to the laboratory limited or restricted at the discretion of the laboratory director when experiments are in progress? Yes No
PMO Inspection - HACCP Audit Comparison Table
 Plant Listing Procedures PMO Inspection - HACCP Audit Comparison Table Inspection Based Milk May be done immediately. Frequency is a minimum of once every 2 years FDA Certified State Rating Officer (SRO)
Plant Listing Procedures PMO Inspection - HACCP Audit Comparison Table Inspection Based Milk May be done immediately. Frequency is a minimum of once every 2 years FDA Certified State Rating Officer (SRO)
TYPICAL FIRE SAFETY INSPECTION VIOLATIONS
 TYPICAL FIRE SAFETY INSPECTION VIOLATIONS The following is a list of typical violations often found by inspectors and a generic solution. You can use this list to improve the safety of your facility, to
TYPICAL FIRE SAFETY INSPECTION VIOLATIONS The following is a list of typical violations often found by inspectors and a generic solution. You can use this list to improve the safety of your facility, to
Risk Management for Aseptic Processing
 Risk Management for Aseptic Processing Ed White Welcome to The Aseptic Core. This column discusses scientific and regulatory aspects of aseptic processing, with an emphasis on aseptic formulation and filling.
Risk Management for Aseptic Processing Ed White Welcome to The Aseptic Core. This column discusses scientific and regulatory aspects of aseptic processing, with an emphasis on aseptic formulation and filling.
Risk Assessment Tools for Identifying Hazards and Evaluating Risks Associated with IVD Assays
 Risk Assessment Tools for Identifying Hazards and Evaluating Risks Associated with IVD Assays Robert C. Menson, PhD AACC Annual Meeting Philadelphia, PA 22 July 2003 What Risks Must Be Managed? Risk to
Risk Assessment Tools for Identifying Hazards and Evaluating Risks Associated with IVD Assays Robert C. Menson, PhD AACC Annual Meeting Philadelphia, PA 22 July 2003 What Risks Must Be Managed? Risk to
Quality Information. Buchs Manufacturing Site
 Buchs Manufacturing Site Related Documents Buchs ISO 9001:2008 Certificate Buchs cgmp Certificate Buchs ISO 13485:2012 Certificate Buchs ISO 17025:2005/ ISO Guide 34 Certificate Buchs Management System
Buchs Manufacturing Site Related Documents Buchs ISO 9001:2008 Certificate Buchs cgmp Certificate Buchs ISO 13485:2012 Certificate Buchs ISO 17025:2005/ ISO Guide 34 Certificate Buchs Management System
Unit 3.4 Decontamination (Core)
 INSTRUCTOR GUIDE Unit 3.4 Decontamination (Core) INSTRUCTOR GUIDE TERMINAL OBJECTIVE Given scenarios involving hazardous materials/wmd incidents, the participant shall identify when emergency decontamination
INSTRUCTOR GUIDE Unit 3.4 Decontamination (Core) INSTRUCTOR GUIDE TERMINAL OBJECTIVE Given scenarios involving hazardous materials/wmd incidents, the participant shall identify when emergency decontamination
Dr Ali A. Mohammadi President Global Health and Security Consultants. 18/3/2013 Global Health & Security Consultants
 Dr Ali A. Mohammadi President Global Health and Security Consultants 18/3/2013 Global Health & Security Consultants Contents of presentation Definition Biosafety & Biosecurity considerations and principles
Dr Ali A. Mohammadi President Global Health and Security Consultants 18/3/2013 Global Health & Security Consultants Contents of presentation Definition Biosafety & Biosecurity considerations and principles
Quality Risk Management ICH Q9 & ISO 14971. Presented by Michael Kerr 11 th November 2011
 Quality Risk Management ICH Q9 & ISO 14971 Presented by Michael Kerr 11 th November 2011 Agenda Risk Concept QRM Fundamentals Regulatory Expectations Warning Letters / Observations Application of QRM Introduction:
Quality Risk Management ICH Q9 & ISO 14971 Presented by Michael Kerr 11 th November 2011 Agenda Risk Concept QRM Fundamentals Regulatory Expectations Warning Letters / Observations Application of QRM Introduction:
HACCP and ISO 22000 food safety management synergies with Environmental Management System
 HACCP and ISO 22000 food safety management synergies with Environmental Management System Horizon 2020 Clean Technologies: Application to the food processing industry 2012 04 25 Agenda 2 Food safety standard
HACCP and ISO 22000 food safety management synergies with Environmental Management System Horizon 2020 Clean Technologies: Application to the food processing industry 2012 04 25 Agenda 2 Food safety standard
BSL 1 Laboratory Biosafety Manual
 BSL 1 Laboratory Biosafety Manual Version 1.0 Idaho State University, Office for Research Institutional Biosafety Committee (IBC) 1651 Alvin Ricken Drive, Pocatello, ID 83201-8046 Phone: 208-282-2179 Fax:
BSL 1 Laboratory Biosafety Manual Version 1.0 Idaho State University, Office for Research Institutional Biosafety Committee (IBC) 1651 Alvin Ricken Drive, Pocatello, ID 83201-8046 Phone: 208-282-2179 Fax:
Waste Handling & Disposal
 Objectives Cover Contain Educate Reduce/Minimize Product Substitution Description Improper storage and handling of solid wastes can allow toxic compounds, oils and greases, heavy metals, nutrients, suspended
Objectives Cover Contain Educate Reduce/Minimize Product Substitution Description Improper storage and handling of solid wastes can allow toxic compounds, oils and greases, heavy metals, nutrients, suspended
Understanding USP 797
 DDK Scientific, Corp. Raul Duarte June 2008 Copyright DDK Scientific, Corp. 2008, 2009 DDK Scientific, Corp. Proprietary The purpose of USP 797 is to prevent harm and fatality to patients that could result
DDK Scientific, Corp. Raul Duarte June 2008 Copyright DDK Scientific, Corp. 2008, 2009 DDK Scientific, Corp. Proprietary The purpose of USP 797 is to prevent harm and fatality to patients that could result
Clean Water: Supply side potable water, not wastewater. Gray Water/Sewage: Wastewater originating from a drain (sink, toilet, urinal).
 Procedures for Emergency Responses to Flooding and Building Water Intrusion PURPOSE: To establish uniform, sanitary, and systematic procedures for responding to flooding and water intrusion emergencies.
Procedures for Emergency Responses to Flooding and Building Water Intrusion PURPOSE: To establish uniform, sanitary, and systematic procedures for responding to flooding and water intrusion emergencies.
Vol - 4, Issue - 1, Jan 2013 ISSN: 0976-7908 Chotai et al PHARMA SCIENCE MONITOR
 PHARMA SCIENCE MONITOR AN INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF PHARMACEUTICAL SCIENCES GMP REQUIREMENTS FOR BUILDINGS AND FACILITIES FOR API COMPARISON OF SCHEDULE M, INDIA AND ICH GUIDELINE AND APPROACH FOR COMPLIANCE
PHARMA SCIENCE MONITOR AN INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF PHARMACEUTICAL SCIENCES GMP REQUIREMENTS FOR BUILDINGS AND FACILITIES FOR API COMPARISON OF SCHEDULE M, INDIA AND ICH GUIDELINE AND APPROACH FOR COMPLIANCE
TITLE: Storage and Management of Hazardous Medications & Chemicals APPLIES TO: Pharmacy Staff
 Administrative Policies and Procedures for MOH hospitals /PHC Centers NO. OF PAGES: ORIGINAL DATE: REVISION DATE : 1.0 PURPOSE 1.1 To develop a set of safety rules and regulations that address the identification,
Administrative Policies and Procedures for MOH hospitals /PHC Centers NO. OF PAGES: ORIGINAL DATE: REVISION DATE : 1.0 PURPOSE 1.1 To develop a set of safety rules and regulations that address the identification,
Laboratory Safety and Environmental Health Assessment Program
 Laboratory Safety and Environmental Health Assessment Program Principal Investigators and Faculty are vital to the success of safety and environmental compliance programs in Colorado School of Mines research
Laboratory Safety and Environmental Health Assessment Program Principal Investigators and Faculty are vital to the success of safety and environmental compliance programs in Colorado School of Mines research
 1 The quality management system (QMS) is the corner stone of compliance to GMP. The QMS is made up of several documents, that when followed ensures the GMP compliance of the process, facility and company.
1 The quality management system (QMS) is the corner stone of compliance to GMP. The QMS is made up of several documents, that when followed ensures the GMP compliance of the process, facility and company.
To provide direction for the safe handling, administration and disposal of hazardous drugs.
 Subsection: MEDICATION Related terms: Cytotoxic Drugs, Antineoplastic Drugs Authorized by: Clinical Directors CS-04-02-01 Page 1 of 9 Date Established: October 2006 Date For Review: September 2014 Dates
Subsection: MEDICATION Related terms: Cytotoxic Drugs, Antineoplastic Drugs Authorized by: Clinical Directors CS-04-02-01 Page 1 of 9 Date Established: October 2006 Date For Review: September 2014 Dates
Annex 2. WHO guidelines on quality risk management. 1. Introduction 62. 2. Glossary 67 3. Quality risk management process 70
 Annex 2 WHO guidelines on quality risk management 1. Introduction 62 1.1 Background and scope 62 1.2 Principles of quality risk management 64 2. Glossary 67 3. Quality risk management process 70 3.1 Initiating
Annex 2 WHO guidelines on quality risk management 1. Introduction 62 1.1 Background and scope 62 1.2 Principles of quality risk management 64 2. Glossary 67 3. Quality risk management process 70 3.1 Initiating
Food Safety is in Your Hands! Alejandra Menjivar Community Nutrition Educator & Alejandra Navarro Community Nutrition Educator
 Food Safety is in Your Hands! Alejandra Menjivar Community Nutrition Educator & Alejandra Navarro Community Nutrition Educator Today s Class Food Safety is Important Good Personal Hygiene Receiving and
Food Safety is in Your Hands! Alejandra Menjivar Community Nutrition Educator & Alejandra Navarro Community Nutrition Educator Today s Class Food Safety is Important Good Personal Hygiene Receiving and
STANDARD OPERATING PROCEDURE S (SOP S) FOR HAZARDOUS ANALYSIS CRITICAL CONTROL POINT (HACCP) PLANS
 STANDARD OPERATING PROCEDURE S (SOP S) FOR HAZARDOUS ANALYSIS CRITICAL CONTROL POINT (HACCP) PLANS RECEIVING: All food must be from approved sources. Foods must be wholesome and not adulterated. No home-prepared
STANDARD OPERATING PROCEDURE S (SOP S) FOR HAZARDOUS ANALYSIS CRITICAL CONTROL POINT (HACCP) PLANS RECEIVING: All food must be from approved sources. Foods must be wholesome and not adulterated. No home-prepared
DESERT RESEARCH INSTITUTE MOLD ASSESSMENT AND REMEDIATEION PROCEDURE
 1.0 Introduction DESERT RESEARCH INSTITUTE This Desert Research Institute (DRI) Mold Assessment and Remediation Procedure was established to assure that consistent and uniform information is provided to
1.0 Introduction DESERT RESEARCH INSTITUTE This Desert Research Institute (DRI) Mold Assessment and Remediation Procedure was established to assure that consistent and uniform information is provided to
Rutgers Environmental Health and Safety
 Rutgers Environmental Health and Safety PCB Self-Audit (TSCA Program) Facility Name: Rutgers University, Facility Address: Facility EPA Identification Number: Date of Self-Audit Inspection: Campus/Farm/Field
Rutgers Environmental Health and Safety PCB Self-Audit (TSCA Program) Facility Name: Rutgers University, Facility Address: Facility EPA Identification Number: Date of Self-Audit Inspection: Campus/Farm/Field
Waste Type Classification Colour Coding Disposal Method
 Sharps Disposal Introduction PHS Waste Management provides a responsive, reliable and flexible sharps disposal services to help eliminate injuries from sharps, needles and syringes. Conscious of our Duty
Sharps Disposal Introduction PHS Waste Management provides a responsive, reliable and flexible sharps disposal services to help eliminate injuries from sharps, needles and syringes. Conscious of our Duty
International Standard ISO 14644
 International Standard ISO 14644 Cleanrooms and associated controlled environments Praphon Angtrakool Food and Drug Administration 1 International Standard : ISO 14644 ISO 14644 consists of the following
International Standard ISO 14644 Cleanrooms and associated controlled environments Praphon Angtrakool Food and Drug Administration 1 International Standard : ISO 14644 ISO 14644 consists of the following
Autoclave Safety. Autoclaves are sterilizers using high pressure and high temperature steam. The potential safety risks for the operators are:
 Autoclave Safety Purpose: Sterilization refers to the complete killing of all living organisms, including spores. Common sterilization techniques include the application of wet heat, dry heat, chemicals,
Autoclave Safety Purpose: Sterilization refers to the complete killing of all living organisms, including spores. Common sterilization techniques include the application of wet heat, dry heat, chemicals,
Infection Control Risk Assessment Matrix of Precautions for Construction & Renovation
 Infection Control Risk Assessment Matrix of Precautions for Construction & Renovation Step One: Using the following table, identify the Type of Construction Project Activity (Type A-D) TYPE A TYPE B TYPE
Infection Control Risk Assessment Matrix of Precautions for Construction & Renovation Step One: Using the following table, identify the Type of Construction Project Activity (Type A-D) TYPE A TYPE B TYPE
cgmp Challenges for Cord Blood Banks
 cgmp Challenges for Cord Blood Banks Donna M. Regan, MT(ASCP)SBB St. Louis Cord Blood Bank @ SSM Cardinal Glennon Children s s Medical Center Cord Blood Bank processing facility challenges What does cgmp
cgmp Challenges for Cord Blood Banks Donna M. Regan, MT(ASCP)SBB St. Louis Cord Blood Bank @ SSM Cardinal Glennon Children s s Medical Center Cord Blood Bank processing facility challenges What does cgmp
BRC Food Safety and Quality Management System. New Issue 7
 New Issue 7 This is an ideal package for Food Manufacturers looking to meet BRC Global Standard for Food Safety (Issue 7 2015) for Food Safety Quality Management Systems. Our BRC Food Safety Quality Management
New Issue 7 This is an ideal package for Food Manufacturers looking to meet BRC Global Standard for Food Safety (Issue 7 2015) for Food Safety Quality Management Systems. Our BRC Food Safety Quality Management
COLUMBUS STATE COMMUNITY COLLEGE EMPLOYEE SAFETY MANUAL
 COLUMBUS STATE COMMUNITY COLLEGE EMPLOYEE SAFETY MANUAL HAZARDOUS MATERIAL MANAGEMENT Effective October 15, 1995 Page 1 of 4 Updated August, 2008 Revised August, 2009 A. Columbus State Community College
COLUMBUS STATE COMMUNITY COLLEGE EMPLOYEE SAFETY MANUAL HAZARDOUS MATERIAL MANAGEMENT Effective October 15, 1995 Page 1 of 4 Updated August, 2008 Revised August, 2009 A. Columbus State Community College
Quality Risk Analysis: Value for Money in the Pharmaceutical Industry
 Chapter 17 Quality Risk Analysis: Value for Money in the Pharmaceutical Industry Jordi Botet Additional information is available at the end of the chapter http://dx.doi.org/10.5772/50450 1. Introduction
Chapter 17 Quality Risk Analysis: Value for Money in the Pharmaceutical Industry Jordi Botet Additional information is available at the end of the chapter http://dx.doi.org/10.5772/50450 1. Introduction
Cleaning Validation in Active pharmaceutical Ingredient manufacturing plants
 Cleaning Validation in Active pharmaceutical Ingredient manufacturing plants September 1999 Table of contents 1. Foreword...... 2 2. Objective...... 3 3. Scope........ 4 4. Potential residues... 5 5. Current
Cleaning Validation in Active pharmaceutical Ingredient manufacturing plants September 1999 Table of contents 1. Foreword...... 2 2. Objective...... 3 3. Scope........ 4 4. Potential residues... 5 5. Current
ASBESTOS MANAGEMENT PROGRAM
 ASBESTOS MANAGEMENT PROGRAM September 2015 Asbestos Management Program Table of Contents I. Purpose II. III. IV. Definitions Identification of Asbestos Asbestos Sampling V. Notification and Labeling VI.
ASBESTOS MANAGEMENT PROGRAM September 2015 Asbestos Management Program Table of Contents I. Purpose II. III. IV. Definitions Identification of Asbestos Asbestos Sampling V. Notification and Labeling VI.
FDA and the Compounding Pharmacy
 FDA and the Compounding Pharmacy Scott Sutton, Ph.D. scott.sutton@microbiol.org 41 Overview of Presentation The Recent Events GCP and GMP Basics the 483 Review H.R. 3204 Outsourcing Facility Preparation
FDA and the Compounding Pharmacy Scott Sutton, Ph.D. scott.sutton@microbiol.org 41 Overview of Presentation The Recent Events GCP and GMP Basics the 483 Review H.R. 3204 Outsourcing Facility Preparation
ABSTRACT INTRODUCTION
 Double Door Transfer Ports (DPTE ) Use to Maximize ALARA in Contained Transfer Operations P.A. Westover, SRNL -Presenting; B.M Allen, SRNL; S.D. Chunglo, la Calhène Inc., Minnesota ABSTRACT Nuclear material
Double Door Transfer Ports (DPTE ) Use to Maximize ALARA in Contained Transfer Operations P.A. Westover, SRNL -Presenting; B.M Allen, SRNL; S.D. Chunglo, la Calhène Inc., Minnesota ABSTRACT Nuclear material
Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) for Pharmaceutical Excipients
 Not for publication. This draft text is for circulation for approval by the Joint Committee and has not been published or otherwise officially promulgated. All rights reserved. This document may be reproduced
Not for publication. This draft text is for circulation for approval by the Joint Committee and has not been published or otherwise officially promulgated. All rights reserved. This document may be reproduced
Containment Solutions for Potent Materials
 Containment Solutions for Potent Materials By Gary Partington Walker Barrier Systems 608-562-7761 gpartington@walkerbarrier.com www.walkerbarrier.com Why do I need containment? Legal NIOSH (National Institute
Containment Solutions for Potent Materials By Gary Partington Walker Barrier Systems 608-562-7761 gpartington@walkerbarrier.com www.walkerbarrier.com Why do I need containment? Legal NIOSH (National Institute
Questions & Answers (Q & A) Regarding Asbestos Treatment with the Fire Suppression and Renovation Project
 Questions & Answers (Q & A) Regarding Asbestos Treatment with the Fire Suppression and Renovation Project The Watergate Community is currently in the process with the fire suppression and interior renovations
Questions & Answers (Q & A) Regarding Asbestos Treatment with the Fire Suppression and Renovation Project The Watergate Community is currently in the process with the fire suppression and interior renovations
TEMPORARY EVENT APPLICATION
 www.camdencounty.com TEMPORARY EVENT APPLICATION Dear Special Event Participant: Enclosed is a copy of the Requirements for Temporary Food Service Operation and Special Event Fact Sheet. To obtain approval
www.camdencounty.com TEMPORARY EVENT APPLICATION Dear Special Event Participant: Enclosed is a copy of the Requirements for Temporary Food Service Operation and Special Event Fact Sheet. To obtain approval
Benjamin Fontes, Geoffrey Lyon and Maryjo Lanzillotta Yale University
 Benjamin Fontes, Geoffrey Lyon and Maryjo Lanzillotta Yale University Yale Cell Sorting Biosafety Cross Training Learning phase Program Collaboration Setting up a program Partnership Maintaining the program
Benjamin Fontes, Geoffrey Lyon and Maryjo Lanzillotta Yale University Yale Cell Sorting Biosafety Cross Training Learning phase Program Collaboration Setting up a program Partnership Maintaining the program
