PATHOGENS: SYMPTOMS, TIMES OF ONSET, DURATION
|
|
|
- Shonda Russell
- 8 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 PATHOGENS: SYMPTOMS, TIMES OF ONSET, DURATION Pathogen Symptoms Time of onset / Incubation Duration Bacillus cereus (emetic) Nausea, vomiting, occasional diarrhea 1/2 to 5 hours Usually 6 to 24 hours Bacillus cereus (diarrheal) Campylobacter Clostridium botulinum Nausea, vomiting, occasionally followed by diarrhea 1 to 6 hours 12 to 24 hours Nausea, vomiting; occasionally, abdominal cramps and/or 1/2 to 6 hours Less than 24 hours diarrhea Acute attach of vomiting; generally no diarrhea, but can occur 1 to 6 hours (mean 3 hours [table says 1 to 5 hours] 6 to 24 hours Nausea, abdominal pain, watery diarrhea (Mild, self-limiting) 8 to 16 hours (mean 12 hours) Usually 6 to 24 hours Abdominal pain, watery diarrhea, occasional nausea 10 to 12 hours 12 to 24 hours Watery diarrhea, abdominal cramps, pan; nausea may accompany 6 to 15 hours Symptoms persist 24 hours diarrhea; vomiting rarely occurs Nausea (rare vomiting), abdominal distress, rectal tenesmus, 8 to 19 hours 12 to 24 hours [table says 12 to watery stools; generally no fever 14 hours] C. jejuni: Diarrhea (often times bloody), severe abdominal pain, 2 to 7 days (mean 3 to 5 days) 1 to 4 days; no longer than 10 fever, loss of appetite, general feeling of ill health, headache, days vomiting (Mild to moderate) Campylobacter: Muscle pain, headache, fever, followed by 1 to 10 days (usually between 2 1 day to 1 week or longer watery / bloody diarrhea, abdominal pain, and nausea and 5 days (usually 5 days) C. jejuni: Watery, sticky, and maybe bloody diarrhea; often 2 to 5 days 7 to 10 days, with 25% relapse fever, abdominal pain, nausea, headache, muscle pain Campylobacter: Cramping abdominal pain, diarrhea; fever, chills, headache, myalgia, occasional delirium; nausea; vomiting rare; up to 25% asymptomatic Nausea, vomiting followed by neurological systems (problems with vision, fatigues, lack of coordination, throat and mouth problems (infant bot constipation followed by lethargy, inability to feed properly, floppiness respiratory arrests Marked lassitude, weakness and vertigo, usually followed by double vision, progressive difficulty speaking and swallowing; also possible difficulty in breathing, weakness of other muscles, abdominal distention, constipation (infant bot constipation following normal development, followed by poor feeding, lethargy, weakness, pooled oral secretions, wail or altered cry, loss of head control) Campylobacter: 1 to 7 days (average 3 days) 12 to 36 hours, sometimes several days (infant bot 3 to 30 days) 18 to 36 hours (can be 4 hours to 8 days) rate Campylobacter: 2 to 6 days 8% fatality rate; 80% hospitalization and intensive therapy (infant bot 5% of all SIDS cases in USA, Europe) A life-threatening disease; high mortality rate if untreated lh2&f:lynnmisc:misc: :incub-table2005-for orig 7/19/05 rev 7/27/05 print 8/3/05 1
2 Mild-double vision, difficulty swallowing for a few days; severecomatose; complete paralysis; fixed, dilated pupils for months; >1/2-prodromal nausea or vomiting; first symptomslprogressive cranial nerve palsies (e.g., double vision, drooping eyelids, slurred, muted speech; inability to swallow; gaze paralysis, dialted pupils); weakness below neck respiratory distress; constipation, urinary retention, hypotension; fatigue Clostridium difficile Watery diarrhea, fever, loss of appetite, nausea, abdominal pain / tenderness; complications pseudomembranous colitis (PMC), toxic megacolon, perforations of colon, sepsis, death rare (CDC) Clostridium perfringens Abdominal pain, diarrhea; rarely vomiting or nausea; fatalities are rare Profuse watery diarrhea, severe abdominal pain that subsides with 24 hours; vomiting, nausea rare Recovery over weeks to months 8 to 22 hours (10 hours) 12 to 24 hours 6 to 24 hours; usually 10 to 12 hours Within 24 hours Cryptosporidium parvum Enteric viruses: Rotaviruses, Hepatitis E, Pocornaviruses, Adenoviruses, Parvoviruses Escherichia coli O157:H7 Intense abdominal cramps and diarrhea 8 to 22 hours Within 24 hours, less severe symptoms may persist 1 to 2 weeks Type A-diarrhea, abdominal cramps Type C(?)-necrotic enteritis (severe abdominal pain, bloody diarrhea, vomiting, obstruction of intestinal mucosa); rare and more serious May be asymptomatic; frequently characterized by severe watery diarrhea. Pulmonary or tracheal cryptosporidiosis is associated with coughing and low grade fever accompanied by severe intestinal distress (moderate to severe) Type A-8 to 16 hours Type C-1 to 5 days Type A-12 to 24 hours (can be fatal in elderly) 1 to 2 weeks 4 days to 3 weeks Watery diarrhea, vomiting, anorexia, malaise, cramping, weight 3 to 11 days 2 to 4 days loss Severe watery diarrhea; may be asymptomatic; pulmonary / tracheal cryptosporidiosis associated with coughing, low-grade fever, accompanied by severe intestinal distress Acute diarrhea 3 to 7 days Self-limiting Rotaviruses: acute gastroenteritis; vomiting, watery diarrhea, low-grade fever (mild to severe); temporary lactose intolerance Hepatitis E: shares many characteristics of hepatitis A; mild Severe abdominal pain, watery diarrhea that may become grossly bloody; occasionally vomiting occurs; maybe fever; may lead to severe complications in young children, elderly and immune-compromised persons. 2 % fatality case ratio (moderate to severe) Rotaviruses: 1 to 3 days Rotaviruses: vomiting first, then 4 to 8 days diarrhea Hepatitis E: about 6 weeks Hepatitis E: self-limiting 3 to 7 days Days to weeks lh2&f:lynnmisc:misc: :incub-table2005-for orig 7/19/05 rev 7/27/05 print 8/3/05 2
3 Ranges from asymptomatic to kidney disease and death; with 3 to 9 days (mean 4 days) Days to weeks serious cases, bloody diarrhea followed by HUS; TTP in elderly Severe cramping (abdominal pain), diarrhea (at first watery, then Average 8 days grossly bloody); occasionally, vomiting; low-grade or no fever; some only have watery diarrhea Severe bloody diarrhea, abdominal cramps; may cause only 5 to 10 days diarrhea or no symptoms; little or no fever; can cause HUS, HC, and thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura, and lead to death in young children and elderly Escherichia coli (enteropathogenic) rd Water or bloody diarrhea; seen in infants, young children of 3-1 to 6 days Days to weeks (infection?) (EPEC) world countries; products verotoxin or shiga-like toxin (mild to moderate) Escherichia coli (enteroinvasive) (infection) (EIEC) Escherichia coli (enterotoxigenic) (toxicoinfection) (ETEC) Escherichia coli: non-o157 shiga toxinproducing (STEC) Escherichia coli (enterohemorrhagic) (EHEC) Escherichia coli (enteroaggregative) (EAEC) Giardia lamblia Infantile diarrhea; Watery or bloody diarrhea (perhaps caused by a verotoxin, Shigella dysenteriae Watery diarrhea with vomiting and fever; some cases, protracted chronic enteritis Diarrhea or milk dysentery; may be blood or mucous in stools; sometimes mistaken for shigellosis (mild to moderate) Mild dysentery, often mistaken for disease caused by Shigella; abdominal cramps, diarrhea, vomiting, fever, chills, general maliaise Similar to disease caused by Shigella; diarrhea initially acute and watery, with fever, abdominal cramps; may progress to colonic phase with bloody, mucoid stools Watery diarrhea, abdominal cramps, low-grade fever, nausea, malaise (mild to moderate) Cholora-like illness; called gastroenteritis / travelers' diarrhea; watery diarrhea, abdominal cramps, low-grade fever, nausea, malaise Watery diarrhea associated with cramps and low-grade or no fever; diarrhea has a lot in common with cholera USA information estimates these types cause disease at 1/2 the rate as Escherichia coli O157:H7 Severe bloody diarrhea (hemorrhagic colitis), HUS, TTP; sometimes only diarrhea Acute, persistent, bloody diarrhea in children In infants, prolonged, leading to rd death (50% mortality in 3 - world countries) 1 to 3 days Days to weeks 12 to 72 hours Self-limiting 1 to 3 days Days to weeks Diarrhea within 24 with high infective dose Usually self-limiting Abdominal pain, mucoid diarrhea, fatty stools (mild to moderate) 5 to 25 days Weeks to years Diarrhea Within 1 week 1 to 2 weeks; chronic infections months to years lh2&f:lynnmisc:misc: :incub-table2005-for orig 7/19/05 rev 7/27/05 print 8/3/05 3
4 Hepatitis A virus Listeria monocytogenes Pathogen Symptoms Time of onset / Incubation Duration Severe weight loss, malnutrition to no symptoms; diarrhea accompanied by nausea or vomiting, abdominal bloating and flatulence; greasy, foul-smelling, frothy stools; fatigue; fever in 20% Approximately 1 week; as short as 1 to 2 days to 2 weeks Mean duration in some studies 11 days; average duration 6 to 10 weeks without treatment; can wax and wane, lasting from months to Fever, general feeling of ill health, loss of appetite, tiredness, nausea, abdominal pain, jaundice (moderate to severe) Initially, fever, headache, fatigue, anorexia, nausea, vomiting; then, viraemia, jaundice and hepatitis symptoms 1-2 weeks later; virus present in blood weeks 2 to 4; shed in feces from latter 2 weeks of incubation to 5 weeks; jaundice evident from weeks 4 to 7; overall debility lasting several weeks is common Sudden onset of fever, malaise, nausea, anorexia, abdominal discomfort, followed in several days by jaundice; illness is usually mild; in severe cases, chronically tired for months Initial symptoms pyrexia, malaise, anorexia, nausea, vomiting, abdominal discomfort or pain; followed in a few days by jaundice Fever, headache, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea precede complications of stillbirths, meningitis, encephalitis, sepsis; in healthy adults, "flu-like" symptoms may pass within a week; great hazard to pregnant women and their unborn fetuses; stillbirths and abortions; causes death in immune-compromised individuals (mild to severe) Invasive illness (people with weakened immune systems), "flulike" systems (fever, headache), diarrhea, vomiting, meningitis, septicemia, spontaneous abortion; non-invasive illness (consumption of high number of L. monocytogenes), diarrhea, fever, muscle pain, headache, less frequently abdominal cramps and vomiting (attack rate 74%) Usually influenza-like symptoms and persistent fever, followed by septicemia, meningitis (or meningoencephalitis), encephalitis, intrauterine or cervical infections in pregnant women (spontaneous abortion or stillbirth); nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea may precede the more serious forms of listeriosis or may be the only symptoms 10 to 50 days (mean 25 days) 2 to 6 weeks, average 28 days 10 to 50 days (mean 30 days) Approximately 28 days; may vary 15 to 50 days years Typically, jaundice lasts 6 to 8 weeks; full recovery usually seen after 3 to 4 months See NZ symptoms); relapses may occur Recovery complete in 1 to 2 weeks in mild cases; convalescence in severe cases several months Acute phase 1 to 3 weeks varying convalescence; 10% relapse 4 to 21 days 4 to 21 days Invasive 1 to 90 days (mean 30 days); non-invasive 11 hours to 7 days (median 18 hours) Onset of serious forms unknown, may be from a few days to 3 weeks; onset of gastrointestinal symptom unknown, probably >12 hours Invasive mortality rate 30%; hospitalization rate 92%; non-invasive called noninvasive febrile gastroenteritis lh2&f:lynnmisc:misc: :incub-table2005-for orig 7/19/05 rev 7/27/05 print 8/3/05 4
5 Adult: initial enteric phase-milk flu-like symptoms, occasional diarrhea; invasive phase-septicemia, meningitis, endocarditis Neonatal: early onset-abortion, stillbirth, premature delivery of severely infected infant; late onset-meningitis primary symptom Adult enteric phase 1 to 2 days; invasive phase-2 to 4 weeks Neonatal: early onset-1 to 2 days; late onset-7 to 20 days after delivery Norwalk-like viruses (noroviruses) Salmonella enteritidis Salmonella typhi Salmonellae: Non-typhoid lh2&f:lynnmisc:misc: :incub-table2005-for orig 7/19/05 rev 7/27/05 print 8/3/05 5 Nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, diarrhea, low grade fever, chills, general feeling of ill health, loss of appetite, headache (mild to moderate) Vomiting, often projectile (predominant symptom; >50% of cases); stomach cramps, diarrhea, abdominal pain, low-grade fever, headache Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal pain; headache, low-grade fever possible Acute-onset vomiting, watery non-bloody diarrhea, abdominal cramps; nausea; low-grade fever occasionally occurs; vomiting more common in children; dehydration a common complication (CDC) Vomiting, non-bloody diarrhea, nausea, abdominal cramps, fever, chills, myalgia, sore throat Fever, abdominal cramps, diarrhea; diarrhea can be severe, requiring hospitalization (CDC) Malaise, headache, fever, cough, nausea, vomiting, constipation, abdominal pain, chills, rose spots, bloody stools; 10% fatalities (severe) Fever, malaise, anorexia, spots on trunk; pea-like diarrhea or constipation; delirium possible Typhoid or typhoid-like fever Life-threatening typhoid fever; fever and other signs and symptoms; sustained high fever 103 to 104ºF; weakness, stomach pains, headache, loss of appetite; some have rash (CDC) Slow and insidious malaise, weakness, headache, fever; fever rises gradually, is higher at night; in some areas, diarrhea lasting several days may precede systemic illness; respiratory symptoms (dry cough), constipation, abdominal pain, anorexia early in disease; during second week 1/2 exhibit rose spots on body Abdominal pain, diarrhea, chills, fever, nausea, vomiting, general feeling of ill health (mild to severe) Human fatality rate 30 to 40%; adult with meningitis-70% fatality if un- or late-treated 16 to 48 hours 48 hours; infected persons may spread disease 2 to 3 days after recovery 10 to 55 hours (mean 24 hours) 24 to 60 hours; virus in stools from onset to 1 to 2 weeks 24 to 48 hours 24 to 60 hours 24 to 48 hours (median 33 to 36 hours); can occur within 12 hours (CDC) 24 to 60 hours (CDC) 48 hours 24 to 48 hours 12 to 72 hours (CDC) 4 to 7 days (CDC) 7 to 28 days Weeks to months. Possible relapses 7 to 28 days (average 14) Slow recovery, 1 to 8 weeks; hospitalization rate 75% 7 to 21 days; may be as long as 5 to 6 weeks 6 to 72 hours (mean 18 to 36 hours) Untreated, fever may last weeks or months; 20% death rate from complications (CDC) Recovery 3 rd week of illness; without treatment 10% may dies, relapse, or have complications; weight loss and weakness may persist for weeks or months Typically 2 to 5 days; protracted cases 10 to 14 days; stool cultures may be positive for Salmonella for up to 4 weeks after illness
6 Diarrhea, abdominal pain, vomiting, nausea, fever; septicemia, non-intestinal infections can occur; reactive arthritis 3 to 4 weeks after gastrointestinal symptoms 6 to 48 hours (usually 12 to 36 hours); reactive arthritis 3 to 4 weeks 1 to 7 days Scombroid (histamine) poisoning Shigella Staphylococcus aureus Milder symptoms than S. typhi; acute symptoms-nausea, vomiting, abdominal cramps, diarrhea, fever, headache; chronic consequences-arthritic symptoms 3 to 4 weeks after onset of acute symptoms Sudden onset of abdominal pain and loose, watery diarrhea, occasionally with mucous or blood; nausea, vomiting; fever, initial chill; mild to severe abdominal pain Histamine: rash, localized skin inflammation, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, tingling, flushing, severe respiratory distress; most consistent sign-flushing of face and neck, causing heat and discomfort (looks like sunburn); Tyramine: increases blood pressure, pupil dilation; eye swelling, tear production, salivation, increased respiration and blood sugar concentration Histamine: initial symptoms-tingling / burning in mouth; upper body rash; drop in blood pressure; frequently, headaches, itchy skin; may progress to nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea; may require hospitalization Abdominal pain, diarrhea, bloody and mucoid stools, fever (moderate to severe) Abdominal pain, diarrhea, fatigue, malaise, fever; mucus and occasionally blood in feces; may progress within 1 to 3 days to "colonic phase" (intense cramps; frequent and painful bowel movements) Abdominal pain, cramps, diarrhea, fever, vomiting, blood, pus, or mucus in stools; tenesmus Mild diarrhea to severe dysentery; leads to inflammatory diarrhea; begins with watery diarrhea preceding dysentery symptoms; fever, severe abdominal pain, cramping follow with small-volume bloody and mucoid stools Nausea, vomiting, retching, abdominal pain, diarrhea, prostration Nausea, vomiting, abdominal cramps; followed by diarrhea mild cases-nausea, vomiting only or cramps and diarrhea only; severe cases-headaches, sweating, fever 6 to 48 hours; arthritic symptoms 3 to 4 weeks 6 to 72 hours Acute stage resolves within 48 hours in uncomplicated cases; can be more protracted, 10 to 14 days Several minutes to several Few hours; can last days hours (mean 1 hour) Rapid onset; immediate to 30 minutes Usually 3 hours; may last several days 1 to 7 days Generally less than 7 days; untreated patients may shed Shigella in feces for 2 weeks or more after recovery 12 hours to 4 days; in 3 to 14 days outbreaks, up to 36 hours observed 12 to 50 hours 1 to 7 days (symptoms commonly show on day 3) 1 to 8 hours; (mean 2 to 4 hours) 30 minutes to 7 hours (mean 2 to 4 hours) Untreated, 1 to 2 weeks 24 to 48 hours; deaths are rare but have been recorded among the aged Rapid recovery, within 2 days lh2&f:lynnmisc:misc: :incub-table2005-for orig 7/19/05 rev 7/27/05 print 8/3/05 6
7 Toxoplasma gondii Pathogen Symptoms Time of onset / Incubation Duration Nausea, vomiting, retching, abdominal cramping, prostration; not all symptoms demonstrated in everyone; severe casesheadache, muscle cramping, transient changes in blood pressure and pulse rate Rapid, often acute onset Vibrio cholerae (O1; cholera) Vibrio cholerae (non-o1) Nausea, vomiting, retching, abdominal cramping, prostration; not all symptoms always present; severe cases-headache, muscle cramping, blood pressure and pulse rate changes Fever, headache, aching muscles, rash; severe complications in pregnant women; can cause birth defects and mental retardation of infants; fatalities occur in infants and adults (mild to severe) May be asymptomatic; may include swollen lymph nodes, rash, malaise, fever and "flu"-like symptoms; congenital infectionsnewborn or later childhood, adulthood; 5-10% babies die, 8-10% brain and eye lesions, 10-13% visually impaired; nearly all born with subclinical disease will develop symptoms later on Mostly asymptomatic; some have "flu"-like symptoms, swollen lymph glands, or muscle aches and pains; severe toxoplasmosis-damage to brain, eyes, other organs (CDC) Postnatal-usually asymptomatic; enlargement of single lymph node to generalized lymphadenopathy; may or may not be accompanied by fatigue, fever, malaise, muscular pain, hepatomegaly, splenomegaly, abdominal pain, headache, rash, sore throat; pathogen can be dangerous to fetus Profuse watery diarrhea (rice water stools), vomiting, abdominal pain, dehydration, thirst, collapse, reduced skin turgor, wrinkled finger, sunken eyes (may be mild, usually severe) Mild diarrhea progressing to copious pale gray (rice water) diarrhea; also low blood pressure, nausea, abdominal cramps, occasionally fever; death by fluid loss may occur Asiatic cholera varies from milk, watery diarrhea to acute diarrhea with rice water stools; abdominal cramps, nausea, vomiting, dehydration, shock; death possible after severe fluid and electrolyte loss Vomiting, massive rice-watery stool, dehydration, metabolic acidosis, sometimes death; most fluid loss first 24 to 48 hours clinical manifestations of cholera from asymptomatic to severe diarrhea Diarrhea, (may have bloody stools) abdominal cramps, and fever; sometimes nausea and vomiting (mild to moderate) Rapid, 2 to 6 hours Usually 2 days; sometimes complete recovery in 3 days or longer in severe cases 10 to 13 days Weeks to years 3 to approximately 20 days Usually self-limiting Muscle aches and pains a month or more; if there are symptoms, a few weeks to months (CDC) 1 to 3 days Can last 2 to 7 days with appropriate therapy; left untreated, cholera can cause death 12 to 72 hours Healthy people recover 1 to 6 days Sudden onset; incubation 6 hours to 5 days Diarrhea declines after 24 hours; terminates within 1 to 6 days if there is adequate fluid replacement 1 to 3 days Days lh2&f:lynnmisc:misc: :incub-table2005-for orig 7/19/05 rev 7/27/05 print 8/3/05 7
8 Milder diarrhea but may be bloody; abdominal cramps, fever; 12 to 72 hours 6 to 7 days extraintestinal infections may occur, e.g., in wounds exposed to contaminated water Diarrhea (may be severe), abdominal cramps, fever; vomiting and nausea in 25% of infected people; 25% have blood and mucus Diarrhea within 48 hours With severe diarrhea, 6 to 7 days in stools Vibrio parahaemolyticus Abdominal pain, diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, fever, chills, 4 to 96 hours 2 to 5 days headache (mild, self-limiting) Abdominal cramps, watery diarrhea; sometimes nausea, vomiting, fever; extraintestinal infections may occur 4 to 74 hours (mean 12 to 46 hours) 1 to 7 days, occasionally longer (mean duration 2.5) Diarrhea, abdominal cramps, nausea, vomiting, headache, fever, 4 to 96 hours (mean 15 hours) Median duration 2.5 days Vibrio vulnificus Yersinia enterocolitica chills (mild or moderate; some require hospitalization) Diarrhea accompanied with other symptoms such as abdominal pain, headache, vomiting, fever, weakness, chill, tenesmus, nausea Organism enters blood stream to cause septic shock and death (50% fatality ratio); individuals develop bulbous skin lesions; amputations may be required (severe complications) Wound infections (45% of cases)-swelling, tenderness of limb; septicemia may follow, death in 25% of cases Primary septicemia (45% of cases)-death may occur rapidly in 50% of septicemia cases; initial symptoms-fever, malaise, chills; 2/3 cases, skin lesions; Gastroenteritis alone may occur (5 to 10% of cases)-vomiting, diarrhea or abdominal pain hospitalization in 91% of cases Wound infections-from contaminating an open wound or laceration (mortality 24%) Primary septicemia-septic shock, rapidly followed by death (mortality 50%); over 70% have distinctive bulbous skin lesions Gastroenteritis-no deaths associated Primary septicemia-septicemia, fever, chills secondary skin lesions, nausea; wound infections-secondary skin lesions, fever, chills septicemia, or gastroenteritis-diarrhea, abdominal pain, fever, chills, nausea (from a table-main symptoms shown found in 50% or more of patients) Gastroenteritis with diarrhea, and/or vomiting; fever and abdominal pain common symptoms; sometimes mimics appendicitis; longer term effects linked to reactive arthritis and Reiter's syndrome (mild to moderate, self-limiting to chronic) Less than 1 hour to over 76 hours (average 15 to 24 hours) 4 to 7 days Median time 16 hours Days to weeks Gastroenteritis 16 hours more serious forms, mean time 38 hours; range of 12 hours to several days; septicemia within 36 hours of initial symptoms; in wound infections, rapidly (e.g., 4 hours) Gastroenteritis 16 hours in healthy people Septicemias-medium 26 hours; wound infections-medium 14 hours; gastroenteritis-20 hours 1 to 3 days Days to weeks lh2&f:lynnmisc:misc: :incub-table2005-for orig 7/19/05 rev 7/27/05 print 8/3/05 8
9 References: Pathogen Symptoms Time of onset / Incubation Duration In adults, abdominal pain confused with appendicitis, headache, fever, diarrhea, nausea, vomiting; in children, watery / mucoid 7 days; range 1 to 11 days 2 to 3 days, self-limiting; 2/3 of cases over 1 week diarrhea; people with predisposing conditions, extraintestinal infections that rarely produce septicemia Gastroenteritis with diarrhea and/or vomiting; fever and 24 to 48 hours abdominal pain hallmark symptoms; mimics appendicitis and mesenteric lymphadenitis; may cause infections at wound sites, joints, and urinary tract Non-specific diarrhea; in children, often with low-grade fever, abdominal pain, diarrhea water to mucoid, can be bloody Self-limiting 1901: Snyder, O.P : Developing and Implementing HACCP-based Retail Food Operations Ed. Hospitality Institute of Technology and Management. St. Paul, MN Archer, F.E., and Young, F.E., Contemporary issues: Diseases with a food vector. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 1: CAST (Council for Agricultural Science and Technology) Foodborne pathogens: Risks and consequences. Task Force Report No CAST, 4420 West Lincoln Way, Ames, Iowa. Chin. J., Control of Communicable Diseases in Man, 17th Edition, American Public Health Assoc., Washington, D.C. Doyle, M.P., ed., Foodborne Bacterial Pathogens. Marcel Dekker, Inc., New York, NY. FDA, HACCP. Regulatory Applications in Retail Food Establishments. Dept. of Health and Human Services. Division of Human Resource Development, HFC- 60; Rockville, MD. IAMFES Procedures to Investigate Foodborne Illness, 3rd Edition, Ames, IA. Mosel, D.A.A., Corry, J. E. L., Struijk, C. B., and Baird, R. M Essentials of the Microbiology of Foods. John Wiley & Sons. New York, NY. Murray, P.R., Baron, E.J., Pfaller, M.A., Tenover, F.C., and Yolken NZ: New Zealand Food Safety Authority Microbial Pathogen Data Sheets. BB: FDA CFSAN "Bad Bug Book," Food borne Pathogenic Microorganisms and Natural Toxins Handbook. CDC: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (various links from home page) M&B: Miliotis, M.D. and Bier, J.W., eds International Handbook of Foodborne Pathogens. Marcel Dekker, Inc. New York, NY. lh2&f:lynnmisc:misc: :incub-table2005-for orig 7/19/05 rev 7/27/05 print 8/3/05 9
2 P age. Babies from Birth to Age 2
 Contents Babies from Birth to Age 2... 2 Vaccines give parents the power... 2 Vaccines are recommended throughout our lives... 3 Talk to your doctor... 3 Vaccines are very safe... 3 Whooping Cough (Pertussis)...
Contents Babies from Birth to Age 2... 2 Vaccines give parents the power... 2 Vaccines are recommended throughout our lives... 3 Talk to your doctor... 3 Vaccines are very safe... 3 Whooping Cough (Pertussis)...
Personal Injury TYPES OF HOLIDAY ILLNESSES. www.simpsonmillar.co.uk Telephone 0844 858 3200
 TYPES OF HOLIDAY ILLNESSES Whilst on holiday many different contractable illnesses exist, the list below contains the most common. This list is by no means exhaustive and if you have suffered from an illness
TYPES OF HOLIDAY ILLNESSES Whilst on holiday many different contractable illnesses exist, the list below contains the most common. This list is by no means exhaustive and if you have suffered from an illness
Streptococcal Infections
 Streptococcal Infections Introduction Streptococcal, or strep, infections cause a variety of health problems. These infections can cause a mild skin infection or sore throat. But they can also cause severe,
Streptococcal Infections Introduction Streptococcal, or strep, infections cause a variety of health problems. These infections can cause a mild skin infection or sore throat. But they can also cause severe,
protect your child IMMUNIZE ON TIME, EVERY TIME. Haemophilus Influenzae Type B (Hib) Human Papillomavirus (HPV) Influenza (Flu) Disease Disease
 protect your child IMMUNIZE ON TIME, EVERY TIME. Diphtheria Haemophilus Influenzae Type B (Hib) Hepatitis A Hepatitis B Human Papillomavirus Influenza (Flu) Measles Meningococcal Disease Mumps Pertussis
protect your child IMMUNIZE ON TIME, EVERY TIME. Diphtheria Haemophilus Influenzae Type B (Hib) Hepatitis A Hepatitis B Human Papillomavirus Influenza (Flu) Measles Meningococcal Disease Mumps Pertussis
ICD 9 Codes Version 28
 0010 Cholera due to vibrio cholerae 0011 Cholera due to vibrio cholerae el tor 0019 Cholera, unspecified 0020 Typhoid fever 0021 Paratyphoid fever A 0022 Paratyphoid fever B 0023 Paratyphoid fever C 0029
0010 Cholera due to vibrio cholerae 0011 Cholera due to vibrio cholerae el tor 0019 Cholera, unspecified 0020 Typhoid fever 0021 Paratyphoid fever A 0022 Paratyphoid fever B 0023 Paratyphoid fever C 0029
You are planning to travel on vacation or business does your destination require a vaccination?
 Disease, travel and vaccinations You are planning to travel on vacation or business does your destination require a vaccination? If you are planning to stay in a resort or a city and you are in good health,
Disease, travel and vaccinations You are planning to travel on vacation or business does your destination require a vaccination? If you are planning to stay in a resort or a city and you are in good health,
NEURO-OPHTHALMIC QUESTIONNAIRE NAME: AGE: DATE OF EXAM: CHART #: (Office Use Only)
 PAGE 1 NEURO-OPHTHALMIC QUESTIONNAIRE NAME: AGE: DATE OF EXAM: CHART #: (Office Use Only) 1. What is the main problem that you are having? (If additional space is required, please use the back of this
PAGE 1 NEURO-OPHTHALMIC QUESTIONNAIRE NAME: AGE: DATE OF EXAM: CHART #: (Office Use Only) 1. What is the main problem that you are having? (If additional space is required, please use the back of this
Childhood Diseases and potential risks during pregnancy: (All information available on the March of Dimes Web Site.) http://www.modimes.
 Childhood Diseases and potential risks during pregnancy: (All information available on the March of Dimes Web Site.) http://www.modimes.org/ Fifth disease (erythema infectiosum) is a common, mild, childhood
Childhood Diseases and potential risks during pregnancy: (All information available on the March of Dimes Web Site.) http://www.modimes.org/ Fifth disease (erythema infectiosum) is a common, mild, childhood
C. difficile Infections
 C. difficile Infections Introduction C. difficile is a type of bacteria that can cause diarrhea and infection of the colon. This bacterium is more likely to infect patients at hospitals and other healthcare
C. difficile Infections Introduction C. difficile is a type of bacteria that can cause diarrhea and infection of the colon. This bacterium is more likely to infect patients at hospitals and other healthcare
Norovirus Outbreak Among Residents of an Assisted Living Facility, Houston County, Alabama 2010 (AL1003NRV 35a)
 Norovirus Outbreak Among Residents of an Assisted Living Facility, Houston County, Alabama 2010 (AL1003NRV 35a) Introduction On March 9, 2010, Public Health Area (PHA) 10 surveillance nurse contacted the
Norovirus Outbreak Among Residents of an Assisted Living Facility, Houston County, Alabama 2010 (AL1003NRV 35a) Introduction On March 9, 2010, Public Health Area (PHA) 10 surveillance nurse contacted the
Other Causes of Fever
 T e c h n i c a l S e m i n a r s Other Causes of Fever Febrile Illness Causes Fever After Seven Days Referral Relapsing Fever - Borreliosis Overview JHR Adaptation Sore Throat Overview Prevention Management
T e c h n i c a l S e m i n a r s Other Causes of Fever Febrile Illness Causes Fever After Seven Days Referral Relapsing Fever - Borreliosis Overview JHR Adaptation Sore Throat Overview Prevention Management
Appendicitis National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse
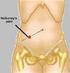 Appendicitis National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH The appendix is a small, tube-like structure
Appendicitis National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH The appendix is a small, tube-like structure
Like cocaine, heroin is a drug that is illegal in some areas of the world. Heroin is highly addictive.
 Heroin Introduction Heroin is a powerful drug that affects the brain. People who use it can form a strong addiction. Addiction is when a drug user can t stop taking a drug, even when he or she wants to.
Heroin Introduction Heroin is a powerful drug that affects the brain. People who use it can form a strong addiction. Addiction is when a drug user can t stop taking a drug, even when he or she wants to.
Share the important information in this Medication Guide with members of your household.
 MEDICATION GUIDE BUPRENORPHINE (BUE-pre-NOR-feen) Sublingual Tablets, CIII IMPORTANT: Keep buprenorphine sublingual tablets in a secure place away from children. Accidental use by a child is a medical
MEDICATION GUIDE BUPRENORPHINE (BUE-pre-NOR-feen) Sublingual Tablets, CIII IMPORTANT: Keep buprenorphine sublingual tablets in a secure place away from children. Accidental use by a child is a medical
PATIENT HEALTH QUESTIONNAIRE Radiation Oncology (Patient Label)
 REVIEWED DATE / INITIALS SAFETY: Are you at risk for falls? Do you have a Pacemaker? Females; Is there a possibility you may be pregnant? ALLERGIES: Do you have any allergies to medications? If, please
REVIEWED DATE / INITIALS SAFETY: Are you at risk for falls? Do you have a Pacemaker? Females; Is there a possibility you may be pregnant? ALLERGIES: Do you have any allergies to medications? If, please
Facts About Chickenpox and Shingles for Adults
 Facts About Chickenpox and Shingles for Adults What is chickenpox? Chickenpox, also known as varicella, is a very contagious disease caused by the varicella-zoster virus. It is spread easily through the
Facts About Chickenpox and Shingles for Adults What is chickenpox? Chickenpox, also known as varicella, is a very contagious disease caused by the varicella-zoster virus. It is spread easily through the
Care and Problems of the Digestive System. Chapter 18 Lesson 2
 Care and Problems of the Digestive System Chapter 18 Lesson 2 Care of the Digestive System Good eating habits are the best way to avoid or minimize digestive system problems. Eat a variety of foods Avoid
Care and Problems of the Digestive System Chapter 18 Lesson 2 Care of the Digestive System Good eating habits are the best way to avoid or minimize digestive system problems. Eat a variety of foods Avoid
Presenting the SUTENT Patient Call Center.
 Presenting the SUTENT Patient Call Center. Please see patient Medication Guide and full prescribing information attached. We re here to support you. Dealing with cancer is a journey. Along the way, you
Presenting the SUTENT Patient Call Center. Please see patient Medication Guide and full prescribing information attached. We re here to support you. Dealing with cancer is a journey. Along the way, you
Chemotherapy Side Effects Worksheet
 Page 1 of 6 Chemotherapy Side Effects Worksheet Medicines or drugs that destroy cancer cells are called cancer chemotherapy. It is sometimes the first choice for treating many cancers. Chemotherapy differs
Page 1 of 6 Chemotherapy Side Effects Worksheet Medicines or drugs that destroy cancer cells are called cancer chemotherapy. It is sometimes the first choice for treating many cancers. Chemotherapy differs
Fainting - Syncope. This reference summary explains fainting. It discusses the causes and treatment options for the condition.
 Fainting - Syncope Introduction Fainting, also known as syncope, is a temporary loss of consciousness. It is caused by a drop in blood flow to the brain. You may feel dizzy, lightheaded or nauseous before
Fainting - Syncope Introduction Fainting, also known as syncope, is a temporary loss of consciousness. It is caused by a drop in blood flow to the brain. You may feel dizzy, lightheaded or nauseous before
Diarrhea National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse
 Diarrhea National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH Diarrhea Diarrhea loose, watery stools occurring
Diarrhea National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH Diarrhea Diarrhea loose, watery stools occurring
What Is Clostridium Difficile (C. Diff)? CLOSTRIDIUM DIFFICILE (C. DIFF)
 What Is Clostridium Difficile (C. Diff)? Clostridium difficile, or C. diff for short, is an infection from a bacterium, or bug, that can grow in your intestines and cause bad GI symptoms. The main risk
What Is Clostridium Difficile (C. Diff)? Clostridium difficile, or C. diff for short, is an infection from a bacterium, or bug, that can grow in your intestines and cause bad GI symptoms. The main risk
Travel Vaccines. Olive Health & Travel Clinic. http://www.olivehealthandtravel.co.uk Phone 020 8550 2276
 Travel Vaccines Olive Health & Travel Clinic http://www.olivehealthandtravel.co.uk Phone 020 8550 2276 Diphtheria, Tetanus and Polio (DTP) The DTP is a class of combination vaccines against three infectious
Travel Vaccines Olive Health & Travel Clinic http://www.olivehealthandtravel.co.uk Phone 020 8550 2276 Diphtheria, Tetanus and Polio (DTP) The DTP is a class of combination vaccines against three infectious
GrapeGate v1.0 Info@GrapeGate.com
 As you begin the process of alkalizing and granting the body more energy for cleansing itself (and also for regeneration), many symptoms and seemingly adverse reactions can occur throughout this process
As you begin the process of alkalizing and granting the body more energy for cleansing itself (and also for regeneration), many symptoms and seemingly adverse reactions can occur throughout this process
Food Poisoning. Food poisoning, more properly referred to as a. Taking a Bite out of. Bug Day Special Feature
 Bug Day Special Feature Taking a Bite out of Food Poisoning Marcus Blouw, BSc and John M. Embil, MD, FRCPC Food poisoning, more properly referred to as a food-borne illness, is the result of ingestion
Bug Day Special Feature Taking a Bite out of Food Poisoning Marcus Blouw, BSc and John M. Embil, MD, FRCPC Food poisoning, more properly referred to as a food-borne illness, is the result of ingestion
St. Luke s MS Center New Patient Questionnaire. Name: Date: Birth date: Right or Left handed? Who is your Primary Doctor?
 St. Luke s MS Center New Patient Questionnaire Name: Date: Birth date: Right or Left handed? Who is your Primary Doctor? Who referred you to the MS Center? List any other doctors you see: Reason you have
St. Luke s MS Center New Patient Questionnaire Name: Date: Birth date: Right or Left handed? Who is your Primary Doctor? Who referred you to the MS Center? List any other doctors you see: Reason you have
MEDICATION GUIDE REMICADE (Rem-eh-kaid) (infliximab) Read the Medication Guide that comes with REMICADE before you receive the first treatment, and
 MEDICATION GUIDE REMICADE (Rem-eh-kaid) (infliximab) Read the Medication Guide that comes with REMICADE before you receive the first treatment, and before each time you get a treatment of REMICADE. This
MEDICATION GUIDE REMICADE (Rem-eh-kaid) (infliximab) Read the Medication Guide that comes with REMICADE before you receive the first treatment, and before each time you get a treatment of REMICADE. This
Classical Swine Fever and Look-a-like Diseases of Pigs. Pat Blanchard
 Classical Swine Fever and Look-a-like Diseases of Pigs Pat Blanchard California Animal Health and Food Safety Laboratory, Tulare branch pcblanchard@ucdavis.edu Classical Swine Fever CSF is a viral disease
Classical Swine Fever and Look-a-like Diseases of Pigs Pat Blanchard California Animal Health and Food Safety Laboratory, Tulare branch pcblanchard@ucdavis.edu Classical Swine Fever CSF is a viral disease
WET, COUGHING AND COLD NEAR RIVER BANK STUNG BY BEE CAUSING ANAPHYLACTIC SHOCK TO WRIST
 GRIT IN EYE BROKEN LEG BONE WET, COUGHING AND COLD NEAR RIVER BANK STUNG BY BEE CAUSING ANAPHYLACTIC SHOCK HEART ATTACK SUFFERING FROM SHOCK CHOKING SEVERE BLEEDING TO WRIST HYPOTHERMIA ANGINA Localised
GRIT IN EYE BROKEN LEG BONE WET, COUGHING AND COLD NEAR RIVER BANK STUNG BY BEE CAUSING ANAPHYLACTIC SHOCK HEART ATTACK SUFFERING FROM SHOCK CHOKING SEVERE BLEEDING TO WRIST HYPOTHERMIA ANGINA Localised
Key Facts about Influenza (Flu) & Flu Vaccine
 Key Facts about Influenza (Flu) & Flu Vaccine mouths or noses of people who are nearby. Less often, a person might also get flu by touching a surface or object that has flu virus on it and then touching
Key Facts about Influenza (Flu) & Flu Vaccine mouths or noses of people who are nearby. Less often, a person might also get flu by touching a surface or object that has flu virus on it and then touching
Dallas Neurosurgical and Spine Associates, P.A Patient Health History
 Dallas Neurosurgical and Spine Associates, P.A Patient Health History DOB: Date: Reason for your visit (Chief complaint): Past Medical History Please check corresponding box if you have ever had any of
Dallas Neurosurgical and Spine Associates, P.A Patient Health History DOB: Date: Reason for your visit (Chief complaint): Past Medical History Please check corresponding box if you have ever had any of
What Is. Norovirus? Learning how to control the spread of norovirus. Web Sites
 Web Sites Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) http://www.cdc.gov/norovirus/index.html Your Local Health Department http://www.azdhs.gov/diro/lhliaison/countymap.htm What Is Ocument dn Norovirus?
Web Sites Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) http://www.cdc.gov/norovirus/index.html Your Local Health Department http://www.azdhs.gov/diro/lhliaison/countymap.htm What Is Ocument dn Norovirus?
Continued. Overhead 1. Overhead 2. Chap 2 - Hazards - Biological, Chemical, and Physical. Chapter 2: Hazards - Biological, Chemical and Physical
 Chapter 2: Hazards - Biological, Chemical and Physical Overhead 1 Objective: Awareness of: Biological hazards Chemical hazards Physical hazards Characteristics of certain microorganisms To perform a hazard
Chapter 2: Hazards - Biological, Chemical and Physical Overhead 1 Objective: Awareness of: Biological hazards Chemical hazards Physical hazards Characteristics of certain microorganisms To perform a hazard
Medication Guide TASIGNA (ta-sig-na) (nilotinib) Capsules
 Medication Guide TASIGNA (ta-sig-na) (nilotinib) Capsules Read this Medication Guide before you start taking Tasigna and each time you get a refill. There may be new information. This information does
Medication Guide TASIGNA (ta-sig-na) (nilotinib) Capsules Read this Medication Guide before you start taking Tasigna and each time you get a refill. There may be new information. This information does
ABU DHABI FOOD CONTROL AUTHORITY. Food Poisoning. www.facebook.com/adfca1. www.twitter.com/adfca. www.youtube.com/adfcamedia
 Food Poisoning جهاز أبوظبي للرقابة الغذائية ABU DHABI FOOD CONTROL AUTHORITY Food Poisoning www.facebook.com/adfca1 www.twitter.com/adfca www.youtube.com/adfcamedia Creating awareness among the consumers
Food Poisoning جهاز أبوظبي للرقابة الغذائية ABU DHABI FOOD CONTROL AUTHORITY Food Poisoning www.facebook.com/adfca1 www.twitter.com/adfca www.youtube.com/adfcamedia Creating awareness among the consumers
INFECTION CONTROL MANUAL
 Page 1 of 19 Key Words: staff, communicable diseases, diseases, infectious diseases Policy Applies to: All staff employed by Mercy Hospital, Credentialed Specialists and Allied Health Professionals involved
Page 1 of 19 Key Words: staff, communicable diseases, diseases, infectious diseases Policy Applies to: All staff employed by Mercy Hospital, Credentialed Specialists and Allied Health Professionals involved
BE SURE. BE SAFE. VACCINATE.
 DON T GET OR GIVE THE FLU THIS YEAR THANK YOU Vaccination is the only protection. www.immunisation.ie BE SURE. BE SAFE. VACCINATE. FLU VACCINE 2013-2014 Healthcare workers prevent the spread of flu and
DON T GET OR GIVE THE FLU THIS YEAR THANK YOU Vaccination is the only protection. www.immunisation.ie BE SURE. BE SAFE. VACCINATE. FLU VACCINE 2013-2014 Healthcare workers prevent the spread of flu and
University of Mary Washington
 University of Mary Washington Student Health Center (540) 654-1040 Instructions for Treatment of Mononucleosis Mononucleosis is caused by a virus. Antibiotics do not help mono but may be prescribed for
University of Mary Washington Student Health Center (540) 654-1040 Instructions for Treatment of Mononucleosis Mononucleosis is caused by a virus. Antibiotics do not help mono but may be prescribed for
INFLUENZA (FLU) Flu and You
 Influenza (Flu) What is the flu? The flu is an illness caused by flu viruses. The flu may make people cough and have a sore throat and fever. They may also have a runny or stuffy nose, feel tired, have
Influenza (Flu) What is the flu? The flu is an illness caused by flu viruses. The flu may make people cough and have a sore throat and fever. They may also have a runny or stuffy nose, feel tired, have
Salmonella Illness & Attribution
 The Poultry Federation SALMONELLA SUMMIT MARCH 26, 2013 9:15-10:00AM Salmonella Illness & Attribution Arthur P. Liang, M.D., M.P.H. Senior Advisor for Food Safety Division of Foodborne Waterborne & Environmental
The Poultry Federation SALMONELLA SUMMIT MARCH 26, 2013 9:15-10:00AM Salmonella Illness & Attribution Arthur P. Liang, M.D., M.P.H. Senior Advisor for Food Safety Division of Foodborne Waterborne & Environmental
Frequently Asked Questions: Ai-Detox
 What is Ai-Detox? Frequently Asked Questions: Ai-Detox Ai-Detox is a Chinese herbal medicinal formula, produced using state of the art biotechnology, which ensures the utmost standards in quality and safety.
What is Ai-Detox? Frequently Asked Questions: Ai-Detox Ai-Detox is a Chinese herbal medicinal formula, produced using state of the art biotechnology, which ensures the utmost standards in quality and safety.
Patient Medication Guide Brochure
 Patient Medication Guide Brochure 1 MEDICATION GUIDE TASIGNA (ta-sig-na) (nilotinib) Capsules Read this Medication Guide before you start taking TASIGNA and each time you get a refill. There may be new
Patient Medication Guide Brochure 1 MEDICATION GUIDE TASIGNA (ta-sig-na) (nilotinib) Capsules Read this Medication Guide before you start taking TASIGNA and each time you get a refill. There may be new
Instruction in accordance with 43 Para. 1 of the German Infection Protection Act (IfSG)
 Instruction in accordance with 43 Para. 1 of the German Infection Protection Act (IfSG) Who requires instruction? Before starting work in the food industry, the following persons require instruction and
Instruction in accordance with 43 Para. 1 of the German Infection Protection Act (IfSG) Who requires instruction? Before starting work in the food industry, the following persons require instruction and
Chronic Diarrhea in Children
 Chronic Diarrhea in Children National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse What is chronic diarrhea? Diarrhea is loose, watery stools. Chronic, or long lasting, diarrhea typically lasts for more
Chronic Diarrhea in Children National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse What is chronic diarrhea? Diarrhea is loose, watery stools. Chronic, or long lasting, diarrhea typically lasts for more
Frequently asked questions about whooping cough (pertussis)
 Frequently asked questions about whooping cough (pertussis) About whooping cough What is whooping cough? Whooping cough is a highly contagious illness caused by bacteria. It mainly affects the respiratory
Frequently asked questions about whooping cough (pertussis) About whooping cough What is whooping cough? Whooping cough is a highly contagious illness caused by bacteria. It mainly affects the respiratory
MEDICATION GUIDE SUBOXONE (Sub-OX-own) (buprenorphine and naloxone) Sublingual Film for sublingual or buccal administration (CIII)
 MEDICATION GUIDE SUBOXONE (Sub-OX-own) (buprenorphine and naloxone) Sublingual Film for sublingual or buccal administration (CIII) IMPORTANT: Keep SUBOXONE in a secure place away from children. Accidental
MEDICATION GUIDE SUBOXONE (Sub-OX-own) (buprenorphine and naloxone) Sublingual Film for sublingual or buccal administration (CIII) IMPORTANT: Keep SUBOXONE in a secure place away from children. Accidental
Vaccines for a Healthy Pregnancy
 Vaccines for a Healthy Pregnancy Vaccines for a Healthy Pregnancy G ALLERY I.1 Healthy Mother and Baby I II Introduction to Tutorial About Flu and Whooping Cough III Getting Vaccinated During Pregnancy:
Vaccines for a Healthy Pregnancy Vaccines for a Healthy Pregnancy G ALLERY I.1 Healthy Mother and Baby I II Introduction to Tutorial About Flu and Whooping Cough III Getting Vaccinated During Pregnancy:
FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS ABOUT PERTUSSIS (WHOOPING COUGH)
 FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS ABOUT PERTUSSIS (WHOOPING COUGH) What is pertussis? General Questions About Pertussis Pertussis, or whooping cough, is a contagious illness that is spread when an infected person
FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS ABOUT PERTUSSIS (WHOOPING COUGH) What is pertussis? General Questions About Pertussis Pertussis, or whooping cough, is a contagious illness that is spread when an infected person
Bone Marrow or Blood Stem Cell Transplants in Children With Certain Rare Inherited Metabolic Diseases *
 Bone Marrow or Blood Stem Cell Transplants in Children With Certain Rare Inherited Metabolic Diseases * A Review of the Research for Parents and Caregivers * Wolman Disease, Farber Disease, Niemann-Pick
Bone Marrow or Blood Stem Cell Transplants in Children With Certain Rare Inherited Metabolic Diseases * A Review of the Research for Parents and Caregivers * Wolman Disease, Farber Disease, Niemann-Pick
Detailed Information for Campylobacter
 Detailed Information for Campylobacter Campylobacter is the leading cause of bacterial diarrheal illness and is found everywhere! The Campylobacter organism is a bacterium that can cause disease in humans
Detailed Information for Campylobacter Campylobacter is the leading cause of bacterial diarrheal illness and is found everywhere! The Campylobacter organism is a bacterium that can cause disease in humans
Medicines To Treat Alcohol Use Disorder A Review of the Research for Adults
 Medicines To Treat Alcohol Use Disorder A Review of the Research for Adults Is This Information Right for Me? Yes, this information is right for you if: Your doctor* said you have alcohol use disorder
Medicines To Treat Alcohol Use Disorder A Review of the Research for Adults Is This Information Right for Me? Yes, this information is right for you if: Your doctor* said you have alcohol use disorder
National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse
 Diarrhea National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH U.S. Department of Health and Human Services
Diarrhea National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH U.S. Department of Health and Human Services
Other Noninfectious Diseases. Chapter 31 Lesson 3
 Other Noninfectious Diseases Chapter 31 Lesson 3 Diabetes Diabetes- a chronic disease that affects the way body cells convert food into energy. Diabetes is the seventh leading cause of death by disease
Other Noninfectious Diseases Chapter 31 Lesson 3 Diabetes Diabetes- a chronic disease that affects the way body cells convert food into energy. Diabetes is the seventh leading cause of death by disease
The Family Library. Understanding Diabetes
 The Family Library Understanding Diabetes What is Diabetes? Diabetes is caused when the body has a problem in making or using insulin. Insulin is a hormone secreted by the pancreas and is needed for the
The Family Library Understanding Diabetes What is Diabetes? Diabetes is caused when the body has a problem in making or using insulin. Insulin is a hormone secreted by the pancreas and is needed for the
The high school's nurse reported no notable illnesses among the students.
 GASTROENTERITIS OUTBREAK ATTRIBUTED TO CLOSTRIDIUM PERFRINGENS TYPE A ENTEROTOXIN MIAMI COUNTY, KANSAS FEBRUARY 2006 FINAL REPORT DATE April 10, 2006 OUTBREAK INVESTIGATORS Christine Godfrey, Public Health
GASTROENTERITIS OUTBREAK ATTRIBUTED TO CLOSTRIDIUM PERFRINGENS TYPE A ENTEROTOXIN MIAMI COUNTY, KANSAS FEBRUARY 2006 FINAL REPORT DATE April 10, 2006 OUTBREAK INVESTIGATORS Christine Godfrey, Public Health
Listeria spp. and Listeria monocytogenes in Foods. Kristi McCallum Rocky Mountain Food Safety Conference May 24 & 25, 2016
 Listeria spp. and Listeria monocytogenes in Foods Kristi McCallum Rocky Mountain Food Safety Conference May 24 & 25, 2016 Genus Listeria Gram-positive, non-spore forming bacilli Demonstrate a tumbling
Listeria spp. and Listeria monocytogenes in Foods Kristi McCallum Rocky Mountain Food Safety Conference May 24 & 25, 2016 Genus Listeria Gram-positive, non-spore forming bacilli Demonstrate a tumbling
N E B R A S K A JAIL BULLETIN NUMBER 102 OCTOBER 1993
 N E B R A S K A JAIL BULLETIN NUMBER 102 OCTOBER 1993 The Jail Bulletin is a monthly feature of the Crime Commission Update. The Bulletin may be used as a supplement to your jail in-service training program
N E B R A S K A JAIL BULLETIN NUMBER 102 OCTOBER 1993 The Jail Bulletin is a monthly feature of the Crime Commission Update. The Bulletin may be used as a supplement to your jail in-service training program
Pi-Wei System Related Diseases. Introduction
 1 A. Review of Pi-Wei System: I. Functions of Spleen Pi-Wei System Related Diseases Introduction By H. Shen The spleen is situated in the middle jiao and its meridian connects with the stomach with which
1 A. Review of Pi-Wei System: I. Functions of Spleen Pi-Wei System Related Diseases Introduction By H. Shen The spleen is situated in the middle jiao and its meridian connects with the stomach with which
IMPORTANT: PLEASE READ
 PART III: CONSUMER INFORMATION combined hepatitis A (inactivated) and hepatitis B (recombinant) vaccine This leaflet is part III of a three-part "Product Monograph" published when was approved for sale
PART III: CONSUMER INFORMATION combined hepatitis A (inactivated) and hepatitis B (recombinant) vaccine This leaflet is part III of a three-part "Product Monograph" published when was approved for sale
Gastrointestinal Tract Infections
 Gastrointestinal Tract Infections 20 Introduction Ingested pathogens may cause disease confined to the gut or involving other parts of the body Ingestion of pathogens can cause many different infections.
Gastrointestinal Tract Infections 20 Introduction Ingested pathogens may cause disease confined to the gut or involving other parts of the body Ingestion of pathogens can cause many different infections.
Exposure. What Healthcare Personnel Need to Know
 Information from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention National Center for Infectious Diseases Divison of Healthcare Quality Promotion and Division of Viral Hepatitis For additional brochures
Information from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention National Center for Infectious Diseases Divison of Healthcare Quality Promotion and Division of Viral Hepatitis For additional brochures
Women s Continence and Pelvic Health Center
 Women s Continence and Pelvic Health Center Committed to Caring 580-590 Court Street Keene, New Hampshire 03431 (603) 354-5454 Ext. 6643 URINARY INCONTINENCE QUESTIONNAIRE The purpose of this questionnaire
Women s Continence and Pelvic Health Center Committed to Caring 580-590 Court Street Keene, New Hampshire 03431 (603) 354-5454 Ext. 6643 URINARY INCONTINENCE QUESTIONNAIRE The purpose of this questionnaire
MEDICATION GUIDE KOMBIGLYZE XR (kom-be-glyze X-R) (saxagliptin and metformin HCl extended-release) tablets
 MEDICATION GUIDE KOMBIGLYZE XR (kom-be-glyze X-R) (saxagliptin and metformin HCl extended-release) tablets Read this Medication Guide carefully before you start taking KOMBIGLYZE XR and each time you get
MEDICATION GUIDE KOMBIGLYZE XR (kom-be-glyze X-R) (saxagliptin and metformin HCl extended-release) tablets Read this Medication Guide carefully before you start taking KOMBIGLYZE XR and each time you get
Diuretics: You may get diuretic medicine to help decrease swelling in your brain. This may help your brain get better blood flow.
 Hemorrhagic Stroke GENERAL INFORMATION: What is a hemorrhagic stroke? A hemorrhagic stroke happens when a blood vessel in the brain bursts. This may happen if the blood vessel wall is weak, or sometimes
Hemorrhagic Stroke GENERAL INFORMATION: What is a hemorrhagic stroke? A hemorrhagic stroke happens when a blood vessel in the brain bursts. This may happen if the blood vessel wall is weak, or sometimes
Guidelines for Schools and Child Care Facilities on Communicable Diseases and Other Childhood Health Issues
 Guidelines for Schools and Child Care Facilities on Communicable Diseases and Other Childhood Health Issues This resource is intended to provide school principals, teachers, directors of child care facilities
Guidelines for Schools and Child Care Facilities on Communicable Diseases and Other Childhood Health Issues This resource is intended to provide school principals, teachers, directors of child care facilities
Immunization Healthcare Branch. Meningococcal Vaccination Program Questions and Answers. Prepared by
 Immunization Healthcare Branch Meningococcal Vaccination Program Questions and Answers Prepared by Immunization Healthcare Branch (IHB), Defense Health Agency Last Updated: 27 Mar 06 www.vaccines.mil 877-GET-VACC
Immunization Healthcare Branch Meningococcal Vaccination Program Questions and Answers Prepared by Immunization Healthcare Branch (IHB), Defense Health Agency Last Updated: 27 Mar 06 www.vaccines.mil 877-GET-VACC
Full name DOB Age Address Email Phone numbers (H) (W) (C) Emergency contact Phone
 DEMOGRAPHIC INFORMATION Full name DOB Age Address Email Phone numbers (H) (W) (C) Emergency contact Phone CARE INFORMATION Primary care physician: Address Phone Fax Referring physician: Specialty Address
DEMOGRAPHIC INFORMATION Full name DOB Age Address Email Phone numbers (H) (W) (C) Emergency contact Phone CARE INFORMATION Primary care physician: Address Phone Fax Referring physician: Specialty Address
MEDICATION GUIDE STELARA
 MEDICATION GUIDE STELARA (stel ar a) (ustekinumab) Injection What is the most important information I should know about STELARA? STELARA is a medicine that affects your immune system. STELARA can increase
MEDICATION GUIDE STELARA (stel ar a) (ustekinumab) Injection What is the most important information I should know about STELARA? STELARA is a medicine that affects your immune system. STELARA can increase
Transient Hypogammaglobulinemia of Infancy. Chapter 7
 Transient Hypogammaglobulinemia of Infancy Chapter 7 An unborn baby makes no IgG (antibody) and only slowly starts producing it after birth. However, starting at about the sixth month of pregnancy, the
Transient Hypogammaglobulinemia of Infancy Chapter 7 An unborn baby makes no IgG (antibody) and only slowly starts producing it after birth. However, starting at about the sixth month of pregnancy, the
Stepping toward a different treatment option LEARN WHAT ACTHAR CAN DO FOR YOU
 FOR MS RELAPSES Stepping toward a different treatment option LEARN WHAT ACTHAR CAN DO FOR YOU As a person with multiple sclerosis (MS), you know firsthand the profound impact MS relapses can have on your
FOR MS RELAPSES Stepping toward a different treatment option LEARN WHAT ACTHAR CAN DO FOR YOU As a person with multiple sclerosis (MS), you know firsthand the profound impact MS relapses can have on your
Guidelines for Hand Foot and Mouth Disease HFMD
 Guidelines for Hand Foot and Mouth Disease HFMD Hand, foot, and mouth disease, or HFMD, is a contagious illness caused by different viruses. Infants and children younger than 5 years are more likely to
Guidelines for Hand Foot and Mouth Disease HFMD Hand, foot, and mouth disease, or HFMD, is a contagious illness caused by different viruses. Infants and children younger than 5 years are more likely to
Application For Admission To The Non-Surgical Spinal Decompression Program At The Spinal Decompression Center of Long Beach
 Application For Admission To The Non-Surgical Spinal Decompression Program At The Spinal Decompression Center of Long Beach If you are reading this form, you have qualified for a consultation with Dr.
Application For Admission To The Non-Surgical Spinal Decompression Program At The Spinal Decompression Center of Long Beach If you are reading this form, you have qualified for a consultation with Dr.
TCH: Docetaxel, Carboplatin and Trastuzumab
 PATIENT EDUCATION patienteducation.osumc.edu TCH: Docetaxel, Carboplatin and Trastuzumab What is TCH? It is the short name for the drugs used for this chemotherapy treatment. The three drugs you will receive
PATIENT EDUCATION patienteducation.osumc.edu TCH: Docetaxel, Carboplatin and Trastuzumab What is TCH? It is the short name for the drugs used for this chemotherapy treatment. The three drugs you will receive
Pregnancy and Substance Abuse
 Pregnancy and Substance Abuse Introduction When you are pregnant, you are not just "eating for two." You also breathe and drink for two, so it is important to carefully consider what you put into your
Pregnancy and Substance Abuse Introduction When you are pregnant, you are not just "eating for two." You also breathe and drink for two, so it is important to carefully consider what you put into your
Teriflunomide (Aubagio) 14mg once daily tablet
 Teriflunomide (Aubagio) 14mg once daily tablet Exceptional healthcare, personally delivered Your Consultant Neurologist has suggested that you may benefit from treatment with Teriflunomide. The decision
Teriflunomide (Aubagio) 14mg once daily tablet Exceptional healthcare, personally delivered Your Consultant Neurologist has suggested that you may benefit from treatment with Teriflunomide. The decision
THE A, B, C S OF HEPATITIS. Matt Eidem, M.D. Digestive Health Associates of Texas 1600 Coit Road Suite #301 Plano, Texas 75075 (972) 867-0019
 THE A, B, C S OF HEPATITIS Matt Eidem, M.D. Digestive Health Associates of Texas 1600 Coit Road Suite #301 Plano, Texas 75075 (972) 867-0019 WHAT IS HEPATITIS? Hepatitis means inflammation of the liver
THE A, B, C S OF HEPATITIS Matt Eidem, M.D. Digestive Health Associates of Texas 1600 Coit Road Suite #301 Plano, Texas 75075 (972) 867-0019 WHAT IS HEPATITIS? Hepatitis means inflammation of the liver
Markham Stouffville Hospital
 Markham Stouffville Hospital Adult Diabetes Education Frequently Asked Questions What is diabetes? Diabetes is a disease in which blood glucose levels are above normal. Most of the food we eat is turned
Markham Stouffville Hospital Adult Diabetes Education Frequently Asked Questions What is diabetes? Diabetes is a disease in which blood glucose levels are above normal. Most of the food we eat is turned
What You Need to Know About the National Vaccine Injury Compensation Program (VICP)
 What You Need to Know About the National Vaccine Injury Compensation Program (VICP) NOTE: What You Need to Know About the National Vaccine Injury Compensation Program (VICP) is not a legal document. The
What You Need to Know About the National Vaccine Injury Compensation Program (VICP) NOTE: What You Need to Know About the National Vaccine Injury Compensation Program (VICP) is not a legal document. The
DENMARK S CHILDHOOD VACCINATION PROGRAMME
 DENMARK S CHILDHOOD VACCINATION PROGRAMME 2013 7th EDITION Denmark s childhood vaccination programme, 2012 7th edition 2013 by the Danish Health and Medicines Authority. All rights reserved. Danish Health
DENMARK S CHILDHOOD VACCINATION PROGRAMME 2013 7th EDITION Denmark s childhood vaccination programme, 2012 7th edition 2013 by the Danish Health and Medicines Authority. All rights reserved. Danish Health
Protecting your baby against meningitis and septicaemia
 Protecting your baby against meningitis and septicaemia caused by meningococcal B bacteria MenB vaccine now available! Information about the MenB vaccine and recommended paracetamol use mmunisation The
Protecting your baby against meningitis and septicaemia caused by meningococcal B bacteria MenB vaccine now available! Information about the MenB vaccine and recommended paracetamol use mmunisation The
Vaccination of children and adolescents
 Information letter from the Norwegian Institute of Public Health No. 3 National childhood vaccination programme in Norway English Last updated July 2010 www.fhi.no/publ/infoletter Vaccination of children
Information letter from the Norwegian Institute of Public Health No. 3 National childhood vaccination programme in Norway English Last updated July 2010 www.fhi.no/publ/infoletter Vaccination of children
What You Need to Know About LEMTRADA (alemtuzumab) Treatment: A Patient Guide
 For Patients What You Need to Know About LEMTRADA (alemtuzumab) Treatment: A Patient Guide Patients: Your doctor or nurse will go over this patient guide with you. It is important to ask any questions
For Patients What You Need to Know About LEMTRADA (alemtuzumab) Treatment: A Patient Guide Patients: Your doctor or nurse will go over this patient guide with you. It is important to ask any questions
What Medical Emergencies Should a Dental Office be Prepared to Handle?
 What Medical Emergencies Should a Dental Office be Prepared to Handle? Gary Cuttrell, DDS, JD, University of NM Division of Dental Services Santiago Macias, MD, First Choice Community Healthcare Dentists
What Medical Emergencies Should a Dental Office be Prepared to Handle? Gary Cuttrell, DDS, JD, University of NM Division of Dental Services Santiago Macias, MD, First Choice Community Healthcare Dentists
Summary of the risk management plan (RMP) for Accofil (filgrastim)
 EMA/475472/2014 Summary of the risk management plan (RMP) for Accofil (filgrastim) This is a summary of the risk management plan (RMP) for Accofil, which details the measures to be taken in order to ensure
EMA/475472/2014 Summary of the risk management plan (RMP) for Accofil (filgrastim) This is a summary of the risk management plan (RMP) for Accofil, which details the measures to be taken in order to ensure
Summary of the risk management plan (RMP) for Tritanrix HB [Diphtheria, tetanus, pertussis (whole cell) and hepatitis B (rdna) vaccine (adsorbed)]
![Summary of the risk management plan (RMP) for Tritanrix HB [Diphtheria, tetanus, pertussis (whole cell) and hepatitis B (rdna) vaccine (adsorbed)] Summary of the risk management plan (RMP) for Tritanrix HB [Diphtheria, tetanus, pertussis (whole cell) and hepatitis B (rdna) vaccine (adsorbed)]](/thumbs/27/12172665.jpg) EMA/14365/2014 Summary of the risk management plan (RMP) for Tritanrix HB [Diphtheria, tetanus, pertussis (whole cell) and hepatitis B (rdna) vaccine (adsorbed)] Overview of disease epidemiology Diphtheria
EMA/14365/2014 Summary of the risk management plan (RMP) for Tritanrix HB [Diphtheria, tetanus, pertussis (whole cell) and hepatitis B (rdna) vaccine (adsorbed)] Overview of disease epidemiology Diphtheria
Bile Duct Diseases and Problems
 Bile Duct Diseases and Problems Introduction A bile duct is a tube that carries bile between the liver and gallbladder and the intestine. Bile is a substance made by the liver that helps with digestion.
Bile Duct Diseases and Problems Introduction A bile duct is a tube that carries bile between the liver and gallbladder and the intestine. Bile is a substance made by the liver that helps with digestion.
NEW PATIENT HISTORY QUESTIONNAIRE. Physician Initials Date PATIENT INFORMATION
 NEW PATIENT HISTORY QUESTIONNAIRE Physician Initials Date PATIENT INFORMATION JHH# DOB# AGE HOME PH CELL PH DAY PH EMAIL Who is your REFERRING PHYSICIAN? (The doctor who referred you to Johns Hopkins Neurology.)
NEW PATIENT HISTORY QUESTIONNAIRE Physician Initials Date PATIENT INFORMATION JHH# DOB# AGE HOME PH CELL PH DAY PH EMAIL Who is your REFERRING PHYSICIAN? (The doctor who referred you to Johns Hopkins Neurology.)
Understanding Foodborne Illness (Food Poisoning)
 Understanding Foodborne Illness (Food Poisoning) 9 Costs of Foodborne Illness (Food Poisoning) possible law suits from customers who are ill There have been numerous cases where restaurants have been sued
Understanding Foodborne Illness (Food Poisoning) 9 Costs of Foodborne Illness (Food Poisoning) possible law suits from customers who are ill There have been numerous cases where restaurants have been sued
Parasitic Diseases. There are three main classes of parasites that cause disease in humans: Protozoa. Helminths. Ectoparasites.
 Parasitic Diseases Introduction Parasites are living things that use other living things, like your body, for food and a place to live. You can get them from contaminated food or water, a bug bite or sexual
Parasitic Diseases Introduction Parasites are living things that use other living things, like your body, for food and a place to live. You can get them from contaminated food or water, a bug bite or sexual
Learning Objectives. Introduction to Medical Careers. Vocabulary: Chapter 16 FACTS. Functions. Organs. Digestive System Chapter 16
 Learning Objectives Introduction to Medical Careers Digestive System Chapter 16 Define at least 10 terms relating to the digestive Describe the four functions of the digestive Identify different structures
Learning Objectives Introduction to Medical Careers Digestive System Chapter 16 Define at least 10 terms relating to the digestive Describe the four functions of the digestive Identify different structures
Furthering Families. Milk pasteurization. Guarding against disease
 Guarding against disease Milk, a natural liquid food, is one of our most nutritionally complete foods, adding high-quality protein, fat, milk sugar, essential minerals, and vitamins to our diet. However,
Guarding against disease Milk, a natural liquid food, is one of our most nutritionally complete foods, adding high-quality protein, fat, milk sugar, essential minerals, and vitamins to our diet. However,
GRADE 4 TEACHER BACKGROUND INFORMATION GROWTH AND DEVELOPMENT
 GRADE 4 TEACHER BACKGROUND INFORMATION GROWTH AND DEVELOPMENT THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Digestion begins in the mouth, where food is broken down by the teeth and the enzyme action of the saliva. The muscular
GRADE 4 TEACHER BACKGROUND INFORMATION GROWTH AND DEVELOPMENT THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Digestion begins in the mouth, where food is broken down by the teeth and the enzyme action of the saliva. The muscular
Thymus Cancer. This reference summary will help you better understand what thymus cancer is and what treatment options are available.
 Thymus Cancer Introduction Thymus cancer is a rare cancer. It starts in the small organ that lies in the upper chest under the breastbone. The thymus makes white blood cells that protect the body against
Thymus Cancer Introduction Thymus cancer is a rare cancer. It starts in the small organ that lies in the upper chest under the breastbone. The thymus makes white blood cells that protect the body against
H1N1 Flu Vaccine Available to All Virginia Beach City Public Schools Students
 V i r g i n i a B e a c h C i t y P u b l i c S c h o o l s apple-a-day F o r O u r F a m i l y o f I n t e r e s t e d C i t i z e n s Special Edition H1N1 Flu Vaccine Available to All Virginia Beach
V i r g i n i a B e a c h C i t y P u b l i c S c h o o l s apple-a-day F o r O u r F a m i l y o f I n t e r e s t e d C i t i z e n s Special Edition H1N1 Flu Vaccine Available to All Virginia Beach
BASIC INFORMATION ABOUT HIV, HEPATITIS B and C, and TUBERCULOSIS Adapted from the CDC
 BASIC INFORMATION ABOUT HIV, HEPATITIS B and C, and TUBERCULOSIS Adapted from the CDC HIV What are HIV and AIDS? HIV stands for Human Immunodeficiency Virus. This is the virus that causes AIDS. HIV is
BASIC INFORMATION ABOUT HIV, HEPATITIS B and C, and TUBERCULOSIS Adapted from the CDC HIV What are HIV and AIDS? HIV stands for Human Immunodeficiency Virus. This is the virus that causes AIDS. HIV is
Breast Cancer. Breast Cancer Page 1
 Breast Cancer Summary Breast cancers which are detected early are curable by local treatments. The initial surgery will give the most information about the cancer; such as size or whether the glands (or
Breast Cancer Summary Breast cancers which are detected early are curable by local treatments. The initial surgery will give the most information about the cancer; such as size or whether the glands (or
Heat Illnesses. Common Heat Rash Sites
 Heat Illnesses Introduction Heat illnesses happen when the body becomes too hot and cannot cool itself. There are several different types of heat-related illnesses. This includes heat cramps, heat exhaustion,
Heat Illnesses Introduction Heat illnesses happen when the body becomes too hot and cannot cool itself. There are several different types of heat-related illnesses. This includes heat cramps, heat exhaustion,
THE DANISH CHILDHOOD VACCINATION PROGRAMME
 THE DANISH CHILDHOOD VACCINATION PROGRAMME 2015 CONTENTS Introduction 2 The Danish childhood vaccination programme 3 Why do we vaccinate children in Denmark? 4 The diseases 5 Diphtheria 5 Tetanus 5 Whooping
THE DANISH CHILDHOOD VACCINATION PROGRAMME 2015 CONTENTS Introduction 2 The Danish childhood vaccination programme 3 Why do we vaccinate children in Denmark? 4 The diseases 5 Diphtheria 5 Tetanus 5 Whooping

 More details >>> HERE
More details >>> HERE