MARKETING Curriculum Content Frameworks
|
|
|
- Brian Parker
- 10 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 MARKETING Curriculum Content Frameworks Please note: All assessment questions will be taken from the knowledge portion of these frameworks. Prepared by Karen Shaddon, Russellville High School Kimberley Wary, Bentonville High School Gail Betts, Morrilton High School Tracy Laird, West Fork High School Chris Dorman, Harrison High School Jackie Phillips, El Dorado High School Clair Mays, Arkadelphia High School Ariana Langford, Har-Ber High School Facilitated by Karen Chisholm, Program Manager Office of Assessment and Curriculum Arkansas Department of Career Education Edited by Jim Brock, Program Manager Ginger Fisher, Program Advisor LaTrenda Jackson, Program Advisor Tim Johnston, Program Advisor Peggy Wakefield, Program Advisor Office of Business/ Technology Arkansas Department of Career Education Disseminated by Career and Technical Education Office of Assessment and Curriculum Arkansas Department of Career Education Development/Revision Began: 12/2009 Placed on the Web: 10/2010
2 Curriculum Content Frameworks MARKETING Grade Levels: 11, 12 Course Code: Prerequisite: Tech Prep Foundation Core Course Description: is a two-semester course designed to provide students with the fundamental concepts, principles, skills, and attitudes common to the field of marketing. Instruction will focus on market types, market analysis, consumer types, planning promotion, buying, pricing, distribution, finance, trends, and careers. Although it is not mandatory, many students can benefit from the on-the-job training component (cooperative education) of this course. The student s job must relate to his/her career objective. Table of Contents Page Unit 1: Introduction to DECA Student Organziation 1 Unit 2: Foundations 2 Unit 3: Social Responsibility and Ethics 3 Unit 4: Economic Foundations 4 Unit 5: Consumer Behavior and Competition 6 Unit 6: Production Management 7 Unit 7: Pricing Strategies 8 Unit 8: Promotion: Communication and Selling 9 Unit 9: Promotion: Advertising, Public Relations and Sales Promotion 10 Unit 10: Channel Management 11 Glossary 12
3 Unit 1: Introduction to DECA Student Organization Hours: Terminology: Co-curricular, DECA, education program, Social responsibility, Leadership development, Social intelligence, Vocational understanding, National Advisory Board, ICDC, SCDC, Teamwork CAREER and TECHNICAL SKILLS What the Student Should be Able to Do ACADEMIC and WORKPLACE SKILLS What the Instruction Should Reinforce Knowledge Application Skill Group Skill Description 1.1 Define terminology Prepare a list of terms with definitions Foundation Reading Applies information and concepts derived from printed materials [1.3.3] Applies/Understands technical words that pertain to subject [1.3.6] 1.2 Explain the benefits of DECA View the annual national DECA Foundation Reading membership promotional/recruitment video Analyzes and applies what has been read to specific task [1.3.2] 1.3 Understand the organizational structure of the DECA student organization (CTSO) 1.4 List the different types of DECA competitions List the levels of DECA from local chapter through international Compare all written events including performance indicators Foundation Foundation Speaking Asks questions to clarify information [1.5.3] Comprehends ideas and concepts related to wholesalers and retailers [4.4.1] Speaking Comprehends ideas related to the 4 P's of marketing [4.4.1] Compare all online events including performance indicators and requirements Differentiate between individual and team events Communicates a thought, idea, or fact in spoken form [1.5.5] 1
4 Unit 2: Foundations Hours: Terminology: Market,, Concept, Mix, Place, Price, Product, Promotion CAREER and TECHNICAL SKILLS What the Student Should be Able to Do Knowledge Application Skill Group Skill 2.1 Define terminology Prepare a list of terms with definitions Foundation Reading ACADEMIC and WORKPLACE SKILLS What the Instruction Should Reinforce Description Applies information and concepts derived from printed materials [1.3.3] 2.2 Discuss the scope and Examine the types of organizations that Thinking importance of marketing use marketing Decision Making Applies/Understands technical words that pertain to subject [1.3.6] Comprehends ideas and concepts related to organizations that use marketing [4.4.1] Show the impact of marketing on employment and the economy 2.3 List the 4 elements of the Identify and provide examples of the 4 Foundation Speaking Asks questions to clarify information [1.5.3] marketing mix (P's of marketing) elements of the marketing mix (P's of marketing) Comprehends ideas related to the 4 P's of marketing [4.4.1] *Product *Price *Place *Promotion 2.4 Define the marketing concept Explain the importance of the marketing Foundation Speaking concept Communicates a thought, idea, or fact in spoken form [1.5.5] 2
5 Unit 3: Social Responsibility and Ethics Hours: 15 Terminology: Boycott, Business ethics, Code of ethics, Consumerism, Consumer Product Safety Commission, Ethics, Green marketing, Social responsibility, Whistle blowing CAREER and TECHNICAL SKILLS What the Student Should be Able to Do Knowledge Application Skill Group Skill 3.1 Define terminology Prepare a list of terms with definitions Foundation Reading ACADEMIC and WORKPLACE SKILLS What the Instruction Should Reinforce Description Applies information and concepts derived from printed materials [1.3.3] Applies/Understands technical words that pertain to subject [1.3.6] 3.2 Explain social responsibility as Provide examples of socially responsible Foundation Listening it applies to and behavior Business Reading Comprehends ideas and concepts related to socially responsible behavior [1.2.1] Draws conclusions from what is read [1.3.12] Thinking Reasoning Sees relationship between two or more ideas, objects, or situations ti [4.5.5] [455] 3.3 Explain the purpose of a code Compare existing codes of ethics Foundation Writing of ethics Applies/Uses technical words and concepts related to codes of ethics [1.6.4] 3.4 Discuss consumerism Provide examples of consumerism in Foundation Reading action Identifies relevant details, facts, and specifications [1.3.16] Thinking Decision Making Comprehends ideas and concepts related to factors of production [4.2.2] 3
6 Unit 4: Economics Foundation Hours: 15 Terminology: Balance of Trade, Business cycle, Capital, Capitalism, Command/Controlled, Consumer Price Index (CPI), Demand, Depression/Trough, Economic Utilities, Economy, Elastic Demand, Embargos, Entrepreneurship, Equilibrium, Factors of Production/Economic Resources, Gross Domestic Product (GDP), Inelastic Demand, Inflation, Labor/Human, Land/Natural, Productivity, Prosperity/Expansion, Quotas, Recession, Shortage, Supply, Surplus, Scarcity, Tariffs, Unemployment Rate CAREER and TECHNICAL SKILLS What the Student Should be Able to Do Knowledge Application Skill Group Skill 4.1 Define terminology Prepare a list of terms with definitions Foundation Reading ACADEMIC and WORKPLACE SKILLS What the Instruction Should Reinforce Description Applies information and concepts derived from printed materials [1.3.3] 4.2 Identify the basic factors/ economic resources of Differentiate between the basic factors of production Foundation Listening production *Land/Natural *Labor/Human Reading *Capital *Entrepreneurship Thinking Reasoning 4.3 List the four types of economic utilities Differentiate between the four types of economic utilities Foundation Writing *Form Foundation Reading *Time *Place *Possession Thinking Decision Making 4.4 Explain the concept of scarcity Discuss the concept of scarcity Foundation Listening Applies/Understands technical words that pertain to subject [1.3.6] Comprehends ideas and concepts related to tangible and intangible resources [1.2.1] Draws conclusions from what is read [1.3.12] Sees relationship between two or more ideas, objects, or situations [4.5.5] 5] Applies/Uses technical words and concepts related to the types of utilities [1.6.4] Identifies relevant details, facts, and specifications [1.3.16] Comprehends ideas and concepts related to economic utilities [4.2.2] Comprehends ideas and concepts related to scarcity [1.2.1] Reading Comprehends written information for main ideas [1.3.7] 4.5 Identify the economic systems Compare the economic systems *Private/Free Enterprise/ Capitalism/Market Economy Foundation Listening Comprehends ideas and concepts related to economic systems [1.2.1] *Command/Controlled Economy Reading Draws conclusions from what is read [1.3.12] *Mixed Economy Interpersonal Teamwork Contributes to group with ideas, suggestions, and effort [2.6.2] 4.6 Discuss supply and demand Identify factors that affect supply and its 4 Foundation Arithmetic/ Interprets charts, tables, graphs, and working
7 5 CAREER and TECHNICAL SKILLS What the Student Should be Able to Do ACADEMIC and WORKPLACE SKILLS What the Instruction Should Reinforce Knowledge Application Skill Group Skill Description relationship to demand Mathematics drawings [1.1.25] *Surplus *Shortage Interpersonal Coaching Comprehends ideas and concepts related to *Equilibrium supply and demand [2.1.1] Interpret and prepare charts and diagrams related to supply and demand curves Foundation Listening 4.7 Explain the elasticity of demand Differentiate between products that have Foundation Listening elastic and inelastic demand Helps others learn new skills [2.1.3] Comprehends ideas and concepts related to supply and demand[1.2.1] Comprehends ideas and concepts related to elasticity of demand [1.2.1] Reading 4.8 Discuss economic Differentiate between GDP, Productivity Interpersonal Teamwork measurements Inflation, Consumer Price Index and Unemployment Rate Analyzes and applies what has been read to specific task [1.3.2] Contributes to group with ideas, suggestions, and effort [2.6.2] Thinking Decision Making Demonstrates decision-making skills [4.2.4] 4.9 Explain the business cycle Create a graph showing the phases of the Foundation Listening business cycle *Prosperity/Expansion *Recession Reading *Depression/Trough *Recovery 4.10 Discuss government Interpret a table on balance of trade Foundation Arithmetic/ involvement in Global Trade illustrating exports and imports Mathematics Differentiate between different types of Listening trade barriers *Tariffs *Quotas Interpersonal Teamwork *Embargos Comprehends ideas and concepts related to phases in the buisness cycle [2.1.1] Analyzes and applies what has been read to specific task [1.3.2] Interprets charts, tables, graphs, and working drawings [1.1.25] Comprehends ideas and concepts related to trade barriers [1.2.1] Contributes to group with ideas, suggestions, and effort [2.6.2] Thinking Seeing Things in the Organizes and processes images - symbols, Mind's Eye pictures, graphs, objects, etc. [4.6.2]
8 Unit 5: Consumer Behavior and Competition Hours: Terminology: Buying motives, Competition, Consumer behavior, Demographics, Discretionary income, Disposable income, Emotional motives, Geographic segmentation, Mass marketing, Monopoly, Market segmentation, Needs, Non-price Competition, Price competition, Psychographics, Rational motives, Target, Wants CAREER and TECHNICAL SKILLS What the Student Should be Able to Do ACADEMIC and WORKPLACE SKILLS What the Instruction Should Reinforce Knowledge Application Skill Group Skill Description 5.1 Define terminology Prepare a list of terms with definitions Foundation Reading Applies information and concepts derived from printed materials [1.3.3] 5.2 Discuss the importance of understanding consumer behavior Differentiate between needs and wants Interpersonal Customer Service Applies/Understands technical words that pertain to subject [1.3.6] Demonstrates face-to-face selling skills [2.3.3] Establishes positive first impression with customers [2.3.4] 5.3 Discuss buyer motivation Provide examples of rational and emotional buying motives Interpersonal Customer Service Demonstrates face-to-face selling skills [2.3.3] Establishes positive first impression with customers [2.3.4] 5.4 Discuss competition Articulate the benefits of competition Interpersonal Customer Service Demonstrates face-to-face selling skills [2.3.3] Explain how markets can be segmented 5.6 Distinguish between mass marketing and market segmentation Distingush between price and non-price competition Explain the characteristics of a monopoly Create a booklet that depicts products that are segmented by: *Demographics *Psychographics Provide examples of products that use either mass marketing or market segmentation strategies Interpersonal Customer Service Establishes positive first impression with customers [2.3.4] Demonstrates face-to-face selling skills [2.3.3] Establishes positive first impression with customers [2.3.4] Interpersonal Customer Service Demonstrates face-to-face selling skills [2.3.3] Establishes positive first impression with customers [2.3.4] 6
9 CAREER and TECHNICAL SKILLS What the Student Should be Able to Do Unit 6: Product Management Hours: 8 Terminology: Brand, Brand licensing, Brand mark, Brand name, Branding, Branding extension, Co-branding, Good, Mixed branding, National brands, Private brand, Product, Product life cycle, Service, Trade character, Trademark Knowledge Application Skill Group Skill 6.1 Define terminology Prepare a list of terms with definitions Foundation Reading ACADEMIC and WORKPLACE SKILLS What the Instruction Should Reinforce Description Applies information and concepts derived from printed materials [1.3.3] 6.2 Recognize characteristics Classify products as goods or services Foundation Speaking unique to goods and services Classify products as industrial or consumer Thinking Decision Making 6.3 Discuss branding of products Classify brands as private or national Foundation Speaking Compare branding strategies *Co-branding Thinking Decision Making *Mixed Branding *Brand extension *Brand Licensing 6.4 Name stages of product life Diagram stages of product life cycle Foundation Writing cycle *Introduction *Growth *Maturity Thinking Problem Solving *Decline 6.5 List principle functions of Evaluate product packaging Foundation Speaking product packaging Writing Applies/Understands technical words that pertain to subject [1.3.6] Communicates a thought, idea, or fact in spoken form [1.5.5] Evaluates information/data to make best decision [4.2.5] Communicates a thought, idea, or fact in spoken form [1.5.5] Evaluates information/data to make best decision [4.2.5] Communicates thoughts, ideas, or facts in written form in a clear, concise manner [1.6.6] Comprehends ideas and concepts related to the stages of product life cycle[4.4.1] Communicates a thought, idea, or fact in spoken form [1.5.5] Composes and creates document - letters, manuals, reports, proposals, graphs, flow charts, etc. [1.6.8] 7
10 Unit 7: Pricing Strategies Hours: 10 Terminology: Discounts, Flexible pricing, Gross profit, Markdown, Markup, Market share, Net profit, Penetration price, Price, Price skimming, Quantity discounts, Sales tax Knowledge Application Skill Group Skill 7.1 Define terminology Prepare a list of terms with definitions Foundation Reading 7.2 Recognize the importance of product price 7.3 Describe common pricing strategies CAREER and TECHNICAL SKILLS What the Student Should be Able to Do Compare pricing objectives; maximize profits, increase market share and maintain an image Identify examples of price skimming strategies, penetration pricing and flexible pricing Foundation ACADEMIC and WORKPLACE SKILLS What the Instruction Should Reinforce Arithmetic/ Mathematics Description Applies information and concepts derived from printed materials [1.3.3] Applies/Understands technical words that pertain to subject [1.3.6] Communicates a thought, idea, or fact in spoken form [1.5.5] Demonstrates decision making skills [4.2.4] Comprehends mathematical ideas and concepts related to goals of pricing [1.1.3] 7.4 Determine the selling price of a Calculate mark-up, mark-down, sales tax, Foundation Speaking Adds item cost and tax to determine amount due product discounts [1.1.43] Converts percentages to dollar amounts [1.1.46] Figures percentages to determine sales price [1.1.49] Thinking Listening Knowing How to Learn Listens for content [1.2.3] Applies new knowledge and skills to goals of pricing [4.3.1] 8
11 Unit 8: Promotion: Communication & Selling Hours: Terminology: Advertising, Approach, Channel, Communication, Communication process, Decoding, Demonstration, Encoding, Feedback, Message, Noise/barriers, Personal selling, Promotion, Prospecting, Public relations, Receiver, Sales promotion, Sender, Suggestive selling CAREER and TECHNICAL SKILLS What the Student Should be Able to Do ACADEMIC and WORKPLACE SKILLS What the Instruction Should Reinforce Knowledge Application Skill Group Skill Description 8.1 Define terminology Prepare a list of terms with definitions Foundation Reading Applies information and concepts derived from printed materials [1.3.3] 8.2 Explain the communication Illustrate the elements of the Foundation Reading process and its elements communication process *Sender *Message *Encoding *Receiver Interpersonal Cultural Diversity *Decoding *Noise/Barriers *Feedback *Channel Thinking Creative Thinking 8.3 Discuss the marketing mix Determine the goals of promotion: inform, Foundation Reading element of promotion persuade, remind Classify promotional mix elements as Thinking Reasoning advertising, personal selling, sales promotion, public relations 8.4 Describe the steps in the Demonstrate the personal selling process Foundation Speaking personal selling process 8.5 Examine product features for Translate product features into customer Foundation Reading potential customer benefits benefits 8.6 Compare types of customer Explain how consumers use the three Foundation Speaking decision making types of decision making: routine, limited, extensive Applies/Understands technical words that Analyzes and applies what has been read to specific task [1.3.2] Discusses contributions and innovations made by women and/or minority groups [2.2.2] Respects other's personal values, cultures, and traditions [2.2.4] Develops visual aids to create audience interest [4.1.4] Identifies relevant details, facts, and specifications [1.3.16] Determine which conclusions are correct when given a set of facts and a set of conclusions [4.5.3] Speaks effectively, using appropriate eye contact, gestures and posture [1.5.11] Analyzes data, summarizes results, and makes conclusions [1.6.2] Communicates a thought, idea, or fact in spoken form [1.5.5] 9
12 Unit 9: Promotion Advertising, Public Relations, Sales Promotion Hours: Terminology: Advertising, Advertising media, Broadcast media, Copy, Coupons, Headline, Incentives, Illustration, Media, Online/Internet media, Print media, Product placement, Public relations, Publicity, Sales promotion, Signature, Slogan, Speciality media CAREER and TECHNICAL SKILLS What the Student Should be Able to Do Knowledge Application Skill Group Skill 9.1 Define terminology Prepare a list of terms with definitions Foundation Reading ACADEMIC and WORKPLACE SKILLS What the Instruction Should Reinforce Description Applies information and concepts derived from printed materials [1.3.3] 9.2 Identify various advertising media 9.3 List parts of a print advertisement Compare and evaluate advertising media *print *broadcast *online/internet *specialty Compare Advertising media rates Create and label parts of a print advertisement *copy *illustration *signature/logo *headline *slogan Interpersonal Interpersonal 9.4 Discuss public relations Compare and contrast public relations and Foundation Writing publicity 9.5 Discuss sales promotion Compare and contrast advantages and Foundation Writing activities disadvantages of sales promotion Customer Service Customer Service Applies/Understands technical words that pertain to subject [1.3.6] Demonstrates face-to-face selling skills [2.3.3] Establishes positive first impression with customers [2.3.4] Maintains positive relations with customers [2.3.6] Recognizes effects of positive/negative attitudes on customers [2.3.7] Shows initiative and courtesy in meeting and working with customers [2.3.8] Works with customers to satisfy their expectations [2.3.9] Analyzes data, summarizes results, and makes conclusions [1.6.2] Analyzes data, summarizes results, and makes conclusions [1.6.2] 10
13 CAREER and TECHNICAL SKILLS What the Student Should be Able to Do Unit 10: Channel Management Hours: Terminology: Channel of distribution, Direct distribution, Distribution, Indirect distribution, Intermediaries, Inventory, Invoice, Just-in-time inventory, Physical distribution, Purchase order, Receiving record, Retailer, Vendor, Wholesaler Knowledge Application Skill Group Skill 10.1 Define terminology Prepare a list of terms with definitions Foundation Reading ACADEMIC and WORKPLACE SKILLS What the Instruction Should Reinforce Description Applies information and concepts derived from printed materials [1.3.3] 10.2 Discuss the marketing mix Determine distribution channel for products Foundation Listening element of distribution (place) 10.3 Discuss types of channel members Determine the roles of each channel member/intermediary Foundation Reading *wholesaler 10.4 Discuss transportation systems of physical distribution * t il Examine factors for selecting transportation Foundation methods (railroad, truck, air, waterways, Reading pipelines) Writing 10.5 Identify types of inventory Evaluate the different types of inventory Thinking Reasoning management systems systems *Just-in-time *perpetual Foundation Reading *physical 10.6 Discuss buying and purchasing Compare documents related to buying and Foundation Reading by businesses and purchasing organizations *purchase order *invoice *receiving record Thinking Problem Solving Applies/Understands technical words that pertain to subject [1.3.6] Comprehends ideas and concepts related to the channels of distribution [1.2.1] Comprehends written information for main ideas [1.3.7] Evaluates written information for accuracy, appropriateness, and style [1.3.14] Uses language, style, organization, and format appropriate to subject matter, purpose, and audience [1.6.19] Sees relationship between two or more ideas, objects, or situations [4.5.5] Identifies relevant details, facts, and specifications [1.3.16] Comprehends written information, and applies it to a task [1.3.8] Draws conclusions from what is read, and gives possible solutions [4.4.4] 11
14 ICDC DECA's International Career Development Conference Glossary Unit 1: Introduction to DECA Co-curricular activities that occur outside traditional class time, but are directly related to classroom instruction DECA a co-curricular student organization for those interested in careers in, Management, and Entrepreneurship; also referred to as an association of marketing Leadership development the activity of providing opportunities for the development of leadership abilities education program a series of courses and activities that prepare students for careers in, Management, and Entrepreneurship National Advisory Board companies that partner with National DECA to provide leadership and financial resources Social responsibility concern about the consequences of actions on others Social intelligence knowing how to conduct oneself in a variety of situations SCDC Arkansas DECA's State Career Development Conference Teamwork the ability to work well with others Vocational understanding learning about the requirements for succeeding in various careers 12
15 Unit 2: Foundations Market people who share similar needs and wants and are capable of buying products; location of buyers or customers creating and maintaining satisfying exchange relationships, also referred to as the process of planning, pricing, promoting, selling and distributing products to satisfy customers' needs and wants concept focusing on satisfying customers' needs and wants in order to make a profit 4. mix comprises four basic marketing strategies collectively known as the four P's of marketing: product, price, place (distribution), and promotion 5. Place marketing mix element that refers to the location and methods used to make products available to customers 6. Price the value of money, or its equivalent, placed on a good or service; the actual amount customers pay 7. Product anything offered to a market to satify needs and wants, including tangible goods or intangible services 8. Promotion any form of communication used to inform, persuade, or remind customers 13
16 1. Boycott an organized effort to influence a company by refusing to purchase its products 2. Code of Ethics a set of standards or rules that guide ethical behavior Unit 3: Social Responsibility and Ethics Consumer Product Safety Commission Federal agency responsible for overseeing the safety of consumer products Consumerism organized actions of consumers seeking to influence business practices; societal effort to protect consumer rights 5. Ethics moral principles or values based on honesty and fairness that guide the behavior individuals and groups 6. Green marketing environmental marketing; marketing activities designed to satisfy customer needs without negatively impacting the environment 7. Social responsibility concern about the consequences of actions on others 8. Whistleblowing speaking out to the media or the public on malpractice, misconduct, corruption, or mismanagement witnessed in an organization 14
17 1. 2. Unit 4: Economics Foundation Balance of trade the difference between the amount of a country's imports and exports Business cycles recurring changes in an economy 3. Capital money needed to start and operate a business Capitalism an economic system where resources are owned by individuals, the marketplace answers the economic questions; also known as free enterprse or market economy Command/controlled economy an economic system where resources are owned by the government and the government answers the economic questions Consumer Price Index (CPI) the change in the cost of a specified set of goods and services over time 7. Demand the consumer willingness and ability to buy products 8. Depression/trough a period of prolonged recession 9. Economic utilities attribute of a product or service that makes it capable of satisfying consumers wants and needs 10. Economy the way a nation makes economic choices about how the nation will use its resources to produce and distribute goods and services Elastic demand market situation in which a price decrease will increase revenue Embargo A government prohibition against the shipment of certain products to a particular country for economic or political reasons 13. Entrepreneurship the skills of people who are willing to risk their time and money to run a business 14. Equilibrium exists when the amount of product supplied is equal to the amount of product demanded 15. Factors of production/economic resources the resources available to develop products and services; classified as natural resources, capital, equipment, and labor Gross domestic product (GDP) the total value of goods and services produced within a country during the year Inelastic demand market situation in which a price decrease will decrease revenue Inflation when prices increase faster than the value of goods and services 19. Labor/human all the people who work in the economy 20. Land/natural all the natural resources of a nation 21. Productivity the average output by workers for a specific period of time 22. Prosperity/expansion time when the economy flourishing 15
18 23. Quotas limits on the numbers of specific types of products that foreign companies can sell in the country 24. Recession a period of economic slowdown 25. Resources also called factors of production, are all the things used in producing goods and services 26. Scarcity difference between what consumers want and need and what the available resources are 27. Shortage when demand exceeds supply 28. Supply the amount of goods producers are willing to make and sell 29. Surplus occurs when supply exceeds demand Tariffs taxes placed on imported products to increasee th price for which they are sold Unemployment rate the percentage of the work force that is unemployed at any given date 16
19 1. Unit 5: Consumer Behavior and Competition Buying motives the reasons that people buy 3. Competiton a term that encompasses the notion of individuals and firms striving for a greater share of a market to sell or buy 2. Consumer behavior the study of consumers and how they make decisions 4. Demographics the descriptive characteristics of a market such as age, gender, race, income, and educational level 5. Discretionary income the amount of income left aftr paying basic living expenses and taxes 6. Disposable income amount of income left after paying taxes, available for saving and spending 7. Emotional motives the forces of love, affection, guilt, fear, or passion that compel consumers to buy 8. Geographic segmentation dividing consumers into markets based on where they live 9. Market segmentation a way of analyzing a market by specific characteristics in order to create a target market 10. Mass marketing directs a company's marketing mix at a large and heterogeneous group of consumers 11. Monopoly the type of market in which there is only one supplier offering a unique product 12. Needs anything you require to live 13. Non-price competition de-emphasizes price by developing a unique offering that meets an important customer need 14. Price competition rivalry among businesses on the basis of price and value 15. Psychographics people's interests and values 16. Rational motives the reasons to buy based on facts or logic 17. Target markets groups of customers with very similar needs to whom the company can sell its products 18. Wants an unfilled desire 17
20 Unit 6: Product Management 1. Brand a unique name, symbol, or design that identifies a product, service, or company 2. Brand licensing is the process of creating and managing contracts between the owner of a brand and a company or individual who wants to use the brand Brand mark the part of the brand that is the symbol or design Brand name trade name; name given to a product or service 5. Branding product identity 6. Branding extension marketing strategy in which a firm marketing a product with a well-developed image uses the same brand name in a different product; a spin-off 7. Co-branding when two companies form an alliance to work together, creating marketing synergy 8. Good any object or service that increases utility, directly or indirectly 9. Mixed branding a firm marketing products under it's own name and that of a reseller because the segment attracted by the reseller is different from its own market 10. National brands recognized across the country due to extensive advertising 11. Private brand product brands owned by a retailer or a wholesaler rather than the manufacturer; also called house brands 12. Product goods and services, both of which have monetary value and satisfy customer s needs and wants 13. Product life cycle predicts the sales and performance of a given product through stages; introduction, growth, maturity, and decline 14. Service an activity that is intangible, exchanged directly from producer to consumer, and consumed at the time of production 15. Trade character visual identification of a particular brand, merchandise, or advertiser 16. Trademark the legal protection of the words or symbols for use by a company 18
21 1. Unit 7: Pricing Strategies Discounts reductions in a price given to the customer in exchange for performing certain marketing activities or accepting something other than what would normally be expected in the exchange; may also be referred to as allowances 2. Flexible pricing allows customers to negotiate price within a price range 3. Gross profit net sales minus the cost of goods and services sold 4. Markdown a reduction from the original selling price 5. Markup an amount added to the cost of a product to determine the selling price 6. Market share the portion of the total market potential that each company expects in relation to its competitors 7. Net profit the difference between the selling price and all costs and operating expenses associated with the product sold 8. Penetration price a very low price designed to increase the quantity sold of a product by emphasizing the value 9. Price the actual amount customers pay and the methods of increasing the value of the product to the customers Price skimming is a pricing strategy in which a marketer sets a relatively high price for a product or service at first, then lowers the price over time Quantity discounts incentive offered by a seller to a buyer for purchasing or ordering greater than usual quantity of goods or materials, to be delivered at one time or 12. Sales tax a tax based on the cost of the item purchased and collected directly from the buyer 19
22 Unit 8: Promotion:Communication & Selling 1. Advertising paid form of non-personal presentation and promotion or ideas, goods, or services by an identified sponsor Approach starts the conversation on a personal basis with pleasant and positive comments from the salesperson that show an interested tone in the customer Channel medium through which a message is transmitted Communication the process in which a person or group evokes a shared or comon meaning to another person or group 5. Communication process the transfer of a message from a sender to a receiver 6. Decoding the process by which the receiver interprets the transmitted language and symbols to comprehend the message 7. Demonstration a personalized presentation of the features of the product in a way that emphasizes the benefits and value to the customer 8. Encoding when the sender converts an idea into a message that the receiver can understand 9. Feedback the receiver's response to the message 10. Message what is being communicated 11. Noise/barriers any distracting information in the transmission, the message channel, or the receiver's environment that may inhibit or distract from the message 12. Personal selling direct communication between a sales representative and prospective customers 13. Promotion any form of communication a business used to inform, persuade, or remind people about its products and/or improve its image Prospecting identifying prospective customers otherwise known as leads Public relations (PR) the effort to reach consumers by generating positive publicity Receiver the person or persons to whom the message is directed, or any person who understands the message that is sent Sales promotion an activity or material that offers consumers a direct incentive to buy a product or service Sender the source of the message being sent Suggestive selling offering additional products and services after an initial sale in order to increase customer satisfaction 20
23 Unit 9: Promotion--Advertising, Public Relations, Sales Promotion 1. Advertising paid form of non-personal presentation and promotion or ideas, goods, or services by an identified sponsor 2. Advertising media means or instruments used to convey advertising messages 3. Broadcast media radio and television are both examples Copy the selling message of a written advertisement Coupons certificates that entitle customers to cash discounts on goods or services Headline a phrase or sentence that attracts the reader's attention to a particular product or service Incentives a type of sales promotion in which higher priced products are earned and given away through contests, sweepstakes, and rebates Illustration a photograph, drawing, or other graphic elements used in an advertisement 9. Media the agencies, means, or instruments used to convey messages 10. Online/Internet media advertisements placed on web pages, including banners, skyscrapers, buttons linked to full-page ads, pop-ups, short video clips, and rich media 11. Print media newspapers, magazines, direct-mail pieces, signs, and billboards are all examples 12. Product placement a type of sales promotion tat involves using a brand name product in a movie or television show 12. Public relations refers to any activity designed to create goodwill toward a business 14. Publicity special kind of public relations, that involves placing positive information about a business, its products, or policies in the media Sales promotion all marketing activities, other than personal selling, advertising, and publicity that are used to stimulate consumer purchasing and sales effectiveness Signature a distinctive identification symbol for a business Slogan a catchy phrase or words that identify a product or company 18. Specialty media inexpensive useful items with an advertiser s name printed on them are called 21
24 Unit 10: Channel Management 1. Channel of distribution path a product takes from producer or manufacturer to final user 2. Direct distribution goods or services are sold by the producer directly to the final user; no intermediaries are involved 3. Distribution the locations and methods used to make the product available to customers; also referred to as the place element of the marketing mix 4. Indirect distribution goods or services are sold indirectly, through one or more intermediaries 5. Intermediaries channel members that help move products from the producer or manufacturer to the final user Inventory the assortment of products maintained by a business Invoice an itemized billing statement with terms of payment for the order Just-in-time (JIT) inventory level is kept low and resupplied just as it is needed 9. Physical distribution the process of efficiently and effectively moving products and materials through the distribution channel; logistics Purchase order a form listing te variety, quantity, and prices of products ordered Receiving record a completed listing of all the merchandise received in the shipment and its condition 12. Retailer the final business organization in an indirect channel of distribution for consumer products 13. Vendor someone who promotes or exchanges goods or services for money 14. Wholesaler company that assists with distribution activities between businesses 22
ADVERTISING Curriculum Content Frameworks
 ADVERTISING Curriculum Content Frameworks Prepared by Jackie Phillips, El Dorado High School Facilitated by Karen Chisholm, Program Manager Office of Assessment and Curriculum Arkansas Department of Workforce
ADVERTISING Curriculum Content Frameworks Prepared by Jackie Phillips, El Dorado High School Facilitated by Karen Chisholm, Program Manager Office of Assessment and Curriculum Arkansas Department of Workforce
ENTREPRENEURSHIP I Curriculum Content Frameworks
 ENTREPRENEURSHIP I Curriculum Content Frameworks Please note: All assessment questions will be taken from the knowledge portion of these frameworks. Prepared by Joyce Martindale, El Dorado High School
ENTREPRENEURSHIP I Curriculum Content Frameworks Please note: All assessment questions will be taken from the knowledge portion of these frameworks. Prepared by Joyce Martindale, El Dorado High School
SMALL BUSINESS OPERATIONS Curriculum Content Frameworks
 SMALL BUSINESS OPERATIONS Curriculum Content Frameworks Please note: All assessment questions will be taken from the knowledge portion of these frameworks. Prepared by Chris Dorman, Harrison High School
SMALL BUSINESS OPERATIONS Curriculum Content Frameworks Please note: All assessment questions will be taken from the knowledge portion of these frameworks. Prepared by Chris Dorman, Harrison High School
Chapter 17 Promotional Concepts and Strategies. Section 17.1 Promotion and Promotional Mix Section 17.2 Types of Promotion
 Unit 6 Promotion Chapter 17 Promotional Concepts and Strategies Chapter 18 Visual Merchandising and Display Chapter 19 Advertising Chapter 20 Print Advertisements Chapter 17 Promotional Concepts and Strategies
Unit 6 Promotion Chapter 17 Promotional Concepts and Strategies Chapter 18 Visual Merchandising and Display Chapter 19 Advertising Chapter 20 Print Advertisements Chapter 17 Promotional Concepts and Strategies
BUSINESS COMMUNICATIONS Curriculum Content Frameworks
 BUSINESS COMMUNICATIONS Curriculum Content Frameworks Please note: All assessment questions will be taken from the knowledge portion of these frameworks. Prepared by Pattie Lovins, Rivercrest High School
BUSINESS COMMUNICATIONS Curriculum Content Frameworks Please note: All assessment questions will be taken from the knowledge portion of these frameworks. Prepared by Pattie Lovins, Rivercrest High School
Assessment Vocabulary Strategies. Advertiser. Describe three types of positions typically found in an advertising agency.
 What is Advertising (1-2 days) (1) The student knows business concepts and explains how business satisfies economic needs. The student is expected to: (A) Categorize business activities as production,
What is Advertising (1-2 days) (1) The student knows business concepts and explains how business satisfies economic needs. The student is expected to: (A) Categorize business activities as production,
COMPUTERIZED ACCOUNTING I Curriculum Content Frameworks
 COMPUTERIZED ACCOUNTING I Curriculum Content Frameworks Please note: All assessment questions will be taken from the knowledge portion of these frameworks. Prepared by Loretta Burgess, Greenbrier High
COMPUTERIZED ACCOUNTING I Curriculum Content Frameworks Please note: All assessment questions will be taken from the knowledge portion of these frameworks. Prepared by Loretta Burgess, Greenbrier High
Business Subject Matter Requirements. Part I: Content Domains for Subject Matter Understanding and Skill in Business
 Business Subject Matter Requirements Part I: Content Domains for Subject Matter Understanding and Skill in Business Domain 1. Business Management Candidates demonstrate an understanding of the purpose
Business Subject Matter Requirements Part I: Content Domains for Subject Matter Understanding and Skill in Business Domain 1. Business Management Candidates demonstrate an understanding of the purpose
Chapter 19 Advertising. Section 19.1 Advertising Media Section 19.2 Media Measurement and Rates
 Chapter 19 Advertising Section 19.1 Advertising Media Section 19.2 Media Measurement and Rates Advertising Media Key Terms promotional advertising institutional advertising media print media transit advertising
Chapter 19 Advertising Section 19.1 Advertising Media Section 19.2 Media Measurement and Rates Advertising Media Key Terms promotional advertising institutional advertising media print media transit advertising
INVESTMENTS AND SECURITIES Curriculum Content Frameworks
 INVESTMENTS AND SECURITIES Curriculum Content Frameworks Please note: All assessment questions will be taken from the knowledge portion of these frameworks. Prepared by Lesia Edwards, Vilonia High School
INVESTMENTS AND SECURITIES Curriculum Content Frameworks Please note: All assessment questions will be taken from the knowledge portion of these frameworks. Prepared by Lesia Edwards, Vilonia High School
Economics. Social Studies Curriculum Framework. Revised 2006 Amended June 2009
 Economics Social Studies Curriculum Framework Revised 2006 Course Title: Economics Course/Unit Credit: 0.5 Course Number: 4743000 Teacher Licensure: Please refer to the Course Code Management System (https://adedata.arkansas.gov/ccms/)
Economics Social Studies Curriculum Framework Revised 2006 Course Title: Economics Course/Unit Credit: 0.5 Course Number: 4743000 Teacher Licensure: Please refer to the Course Code Management System (https://adedata.arkansas.gov/ccms/)
Bingo glossary marketing mix
 Bingo glossary marketing mix The management process which identifies customer wants, anticipates their future wants and then goes about satisfying them profitably. Where the market has been divided up
Bingo glossary marketing mix The management process which identifies customer wants, anticipates their future wants and then goes about satisfying them profitably. Where the market has been divided up
Marketing: Advertising and Sales Promotion
 Marketing: Advertising and Sales Promotion Food Communication II Section G Communication Mix Strategies All of the information has been adapted from: Kotler P. Armstrong, G., 2004. Principles of Marketing.
Marketing: Advertising and Sales Promotion Food Communication II Section G Communication Mix Strategies All of the information has been adapted from: Kotler P. Armstrong, G., 2004. Principles of Marketing.
Chapter 26 Pricing Strategies. Section 26.1 Basic Pricing Policies Section 26.2 Strategies in the Pricing Process
 Chapter 26 Pricing Strategies Section 26.1 Basic Pricing Policies Section 26.2 Strategies in the Pricing Process Basic Pricing Policies Key Terms markup pricing cost-plus pricing one-price policy flexible-price
Chapter 26 Pricing Strategies Section 26.1 Basic Pricing Policies Section 26.2 Strategies in the Pricing Process Basic Pricing Policies Key Terms markup pricing cost-plus pricing one-price policy flexible-price
Why do firms create new products?
 Why do firms create new products? 1. Changing Customer Needs: When they add products, services, and processes to their offerings, firms can create and deliver value more effectively by satisfying the changing
Why do firms create new products? 1. Changing Customer Needs: When they add products, services, and processes to their offerings, firms can create and deliver value more effectively by satisfying the changing
MICHIGAN TEST FOR TEACHER CERTIFICATION (MTTC) TEST OBJECTIVES FIELD 036: MARKETING EDUCATION
 MICHIGAN TEST FOR TEACHER CERTIFICATION (MTTC) TEST OBJECTIVES Subarea Marketing Foundations Marketing Functions Technology, Ethics, and Career Development Approximate Percentage of Questions on Test 40%
MICHIGAN TEST FOR TEACHER CERTIFICATION (MTTC) TEST OBJECTIVES Subarea Marketing Foundations Marketing Functions Technology, Ethics, and Career Development Approximate Percentage of Questions on Test 40%
Basic Marketing Principles. Author: Mickey Smith, RPh, PhD Director, Center for Pharmaceutical Marketing and Management University of Mississippi
 Basic Marketing Principles Author: Mickey Smith, RPh, PhD Director, Center for Pharmaceutical Marketing and Management University of Mississippi Learning Objectives Define marketing in official and real
Basic Marketing Principles Author: Mickey Smith, RPh, PhD Director, Center for Pharmaceutical Marketing and Management University of Mississippi Learning Objectives Define marketing in official and real
Business Management and Administration Career Cluster Entrepreneurship Course Number: 06.41610
 Business Management and Administration Career Cluster Entrepreneurship Course Number: 06.41610 Course Description: How do you turn an idea into a business? Experience just that in this course! Entrepreneurship
Business Management and Administration Career Cluster Entrepreneurship Course Number: 06.41610 Course Description: How do you turn an idea into a business? Experience just that in this course! Entrepreneurship
FBLA: ECONOMICS. Competency: Basic Economic Concepts and Principles
 Competency: Basic Economic Concepts and Principles 1. Define money (characteristics, role, and forms) and trace how money and resources flow through the American economic system. 2. Utilize decision-making
Competency: Basic Economic Concepts and Principles 1. Define money (characteristics, role, and forms) and trace how money and resources flow through the American economic system. 2. Utilize decision-making
Marketing Career Cluster Marketing Management Course Number 08.44200
 Marketing Career Cluster Marketing Management Course Number 08.44200 Course Description: Marketing Management is the third course in the Marketing and Management pathway. Students assume a managerial perspective
Marketing Career Cluster Marketing Management Course Number 08.44200 Course Description: Marketing Management is the third course in the Marketing and Management pathway. Students assume a managerial perspective
Marketing Career Cluster Fashion, Merchandising and Retailing Essentials Course Number 08.42100
 Marketing Career Cluster Fashion, Merchandising and Retailing Essentials Course Number 08.42100 Course Description: Fashion, Merchandising and Retailing Essentials is the second course in the Fashion,
Marketing Career Cluster Fashion, Merchandising and Retailing Essentials Course Number 08.42100 Course Description: Fashion, Merchandising and Retailing Essentials is the second course in the Fashion,
MKTG301: PRINCIPLES OF MARKETING DEFINITIONS: CHAPTER 18
 MKTG301: PRINCIPLES OF MARKETING DEFINITIONS: CHAPTER 18 Communication (1) The process of conveying a message to others, which requires six elements: a source, a message, a channel of communication, a
MKTG301: PRINCIPLES OF MARKETING DEFINITIONS: CHAPTER 18 Communication (1) The process of conveying a message to others, which requires six elements: a source, a message, a channel of communication, a
Integrated Marketing Communication Strategy
 Integrated Marketing Strategy Dr. Richard Sjolander 2003 The Purpose of Integrated Marketing s is to Communicate with a Target Audience Promotion: or Applied marketing communication Attempts to: Inform
Integrated Marketing Strategy Dr. Richard Sjolander 2003 The Purpose of Integrated Marketing s is to Communicate with a Target Audience Promotion: or Applied marketing communication Attempts to: Inform
Small Business Entrepreneurship Lesson Objectives
 Small Business Entrepreneurship Lesson Unit 1: OVERVIEW OF SMALL BUSINESS ENTREPRENEURSHIP What Is Entrepreneurship? Define and list examples of entrepreneurs. Explain the difference between a product-based
Small Business Entrepreneurship Lesson Unit 1: OVERVIEW OF SMALL BUSINESS ENTREPRENEURSHIP What Is Entrepreneurship? Define and list examples of entrepreneurs. Explain the difference between a product-based
Scope and Sequence. Units of Study Knowledge and Skills Student Expectations Resources
 Scope and Sequence Cluster: Course Name: Course Description: Course Requirements: Equipment: Arts, Audio/Video Technology & Communications Practicum in Fashion Design (Two to Three Credits) Careers in
Scope and Sequence Cluster: Course Name: Course Description: Course Requirements: Equipment: Arts, Audio/Video Technology & Communications Practicum in Fashion Design (Two to Three Credits) Careers in
Marketing: Mastering the Process
 Marketing: Mastering the Process Course Description This course teaches you key components of marketing strategy and tactics including: identification, analysis and selection of target markets; development
Marketing: Mastering the Process Course Description This course teaches you key components of marketing strategy and tactics including: identification, analysis and selection of target markets; development
MARKETING EDUCATION ADVANCED FASHION MARKETING GRADE 10-12
 PARENT/STUDENT COURSE INFORMATION MARKETING EDUCATION ADVANCED FASHION MARKETING GRADE 10-12 Counselors are available to assist parents and students with course selections and career planning. Parents
PARENT/STUDENT COURSE INFORMATION MARKETING EDUCATION ADVANCED FASHION MARKETING GRADE 10-12 Counselors are available to assist parents and students with course selections and career planning. Parents
Brenda Clark, Ed.D. Jennie Sobel, M.B.A. Marketing Teacher-Coordinator, retired Robert E. Lee High School ; > ;,' San Antonio, Texas ' :; :.
 ' I Brenda Clark, Ed.D. Maikotini; Instnulor, C11. I >IK\Lc11 ^1C j cfuooil i iigh bdluul Jenison, Michigan Jennie Sobel, M.B.A. Marketing Teacher-Coordinator, retired Robert E. Lee High School ; > ;,'
' I Brenda Clark, Ed.D. Maikotini; Instnulor, C11. I >IK\Lc11 ^1C j cfuooil i iigh bdluul Jenison, Michigan Jennie Sobel, M.B.A. Marketing Teacher-Coordinator, retired Robert E. Lee High School ; > ;,'
Business Education Standards
 Business Education Standards FINAL Approved on January 9, 2004 Copyright 2003 Texas State Board for Educator Certification BUSINESS EDUCATION STANDARDS Standard I. Standard II. Standard III. Standard IV.
Business Education Standards FINAL Approved on January 9, 2004 Copyright 2003 Texas State Board for Educator Certification BUSINESS EDUCATION STANDARDS Standard I. Standard II. Standard III. Standard IV.
Chapter 130. Career and Technical Education, Subchapter D. Business Management and Administration. TEKS Breakout Proclamation 2017
 Chapter 130. Career and Technical Education, Subchapter D. Subject Chapter 130. Career and Technical Education, Subchapter D. Business Management and Administration Course Title 130.132. Principles of
Chapter 130. Career and Technical Education, Subchapter D. Subject Chapter 130. Career and Technical Education, Subchapter D. Business Management and Administration Course Title 130.132. Principles of
Hospitality and Tourism Career Cluster Introduction to Sports & Entertainment Marketing Course Number: 08.47800
 Hospitality and Tourism Career Cluster Introduction to Sports & Entertainment Marketing Course Number: 08.47800 Course Description: This course introduces the student to the major segments of the Sports
Hospitality and Tourism Career Cluster Introduction to Sports & Entertainment Marketing Course Number: 08.47800 Course Description: This course introduces the student to the major segments of the Sports
COMPUTERIZED ACCOUNTING II Curriculum Content Frameworks
 COMPUTERIZED ACCOUNTING II Curriculum Content Frameworks Please note: All assessment questions will be taken from the knowledge portion of these frameworks. Prepared by Loretta Burgess, Greenbrier High
COMPUTERIZED ACCOUNTING II Curriculum Content Frameworks Please note: All assessment questions will be taken from the knowledge portion of these frameworks. Prepared by Loretta Burgess, Greenbrier High
Iowa. CONTENT STANDARDS and BENCHMARKS. Business and Administration
 Iowa CONTENT STANDARDS and BENCHMARKS Business and Administration 2001 Business, Information Management, and Marketing Career Pathway Framework Illustration of Program Possibilities Occupational Cluster
Iowa CONTENT STANDARDS and BENCHMARKS Business and Administration 2001 Business, Information Management, and Marketing Career Pathway Framework Illustration of Program Possibilities Occupational Cluster
TExES Business Education 6 12 (176) Test at a Glance
 TExES Business Education 6 12 (176) Test at a Glance See the test preparation manual for complete information about the test along with sample questions, study tips and preparation resources. Test Name
TExES Business Education 6 12 (176) Test at a Glance See the test preparation manual for complete information about the test along with sample questions, study tips and preparation resources. Test Name
Business Economics. Business Management & Administration. Candi Norwood, (615) 532-6248 [email protected]
 Business Economics Primary Career Cluster: Consultant: Course Code(s): 5898 Prerequisite(s): Credit: Business Management & Administration Candi Norwood, (615) 532-6248 [email protected] None ½ Grade
Business Economics Primary Career Cluster: Consultant: Course Code(s): 5898 Prerequisite(s): Credit: Business Management & Administration Candi Norwood, (615) 532-6248 [email protected] None ½ Grade
INTRODUCTION TO CAREER COMMUNICATIONS Curriculum Content Frameworks
 INTRODUCTION TO CAREER COMMUNICATIONS Curriculum Content Frameworks Please note: All assessment questions will be taken from the knowledge portion of these frameworks. Prepared by April Burroughs, Hazen
INTRODUCTION TO CAREER COMMUNICATIONS Curriculum Content Frameworks Please note: All assessment questions will be taken from the knowledge portion of these frameworks. Prepared by April Burroughs, Hazen
MKTG 680. Chapter 13-14 Global Marketing Communications Decisions: Advertising, Public Relations, Sales Promotion. Standardization vs.
 MKTG 680 Chapter 13-14 Global Marketing Communications Decisions: Advertising, Public Relations, Sales Promotion Global Marketing Communications The primary purpose of marketing communications is to tell
MKTG 680 Chapter 13-14 Global Marketing Communications Decisions: Advertising, Public Relations, Sales Promotion Global Marketing Communications The primary purpose of marketing communications is to tell
FM: Fashion Business Management
 FM: Fashion Business Management FM 101 Survey of Fashion Merchandising For students not majoring in Business and Technology programs. Explores the interrelationships between the consumer and the primary,
FM: Fashion Business Management FM 101 Survey of Fashion Merchandising For students not majoring in Business and Technology programs. Explores the interrelationships between the consumer and the primary,
REVIEW ONE. Name: Class: Date: Matching
 Name: Class: Date: ID: A REVIEW ONE Matching Complete the following using these terms. a. outsourcing b. diversity c. entrepreneur d. competitive differentiation e. strategic alliance f. capital g. vision
Name: Class: Date: ID: A REVIEW ONE Matching Complete the following using these terms. a. outsourcing b. diversity c. entrepreneur d. competitive differentiation e. strategic alliance f. capital g. vision
Chapter 4: Buying an Existing Business
 Chapter 4: Buying an Existing Business 1 Learning Objectives To understand that buying an existing business has several important advantages over starting one, including less risk, less time and effort,
Chapter 4: Buying an Existing Business 1 Learning Objectives To understand that buying an existing business has several important advantages over starting one, including less risk, less time and effort,
Georgia Department of Education
 Marketing Career Cluster Marketing and Entrepreneurship Course Number 08.44100 Course Description: Marketing and Entrepreneurship is the second course in the Marketing and Management Career Pathway. Marketing
Marketing Career Cluster Marketing and Entrepreneurship Course Number 08.44100 Course Description: Marketing and Entrepreneurship is the second course in the Marketing and Management Career Pathway. Marketing
Multiple Category Scope and Sequence: Scope and Sequence Report For Course Standards and Objectives, Content, Skills, Vocabulary
 Multiple Category Scope and Sequence: Scope and Sequence Report For Course Standards and Objectives, Content, Skills, Vocabulary Monday, August 18, 2014, 9:45PM District Basic Sports & Entertainment Marketing
Multiple Category Scope and Sequence: Scope and Sequence Report For Course Standards and Objectives, Content, Skills, Vocabulary Monday, August 18, 2014, 9:45PM District Basic Sports & Entertainment Marketing
One Stop Shop For Teachers
 PROGRAM CONCENTRATION: CAREER PATHWAY: COURSE TITLE: Marketing, Sales & Service Sports & Entertainment Marketing Introduction to Sports & Entertainment Marketing COURSE DESCRIPTION: This course introduces
PROGRAM CONCENTRATION: CAREER PATHWAY: COURSE TITLE: Marketing, Sales & Service Sports & Entertainment Marketing Introduction to Sports & Entertainment Marketing COURSE DESCRIPTION: This course introduces
Chapter 24 Stock Handling and Inventory Control. Section 24.1 The Stock Handling Process Section 24.2 Inventory Control
 Chapter 24 Stock Handling and Inventory Control Section 24.1 The Stock Handling Process Section 24.2 Inventory Control The Stock Handling Process Key Terms receiving record blind check method direct check
Chapter 24 Stock Handling and Inventory Control Section 24.1 The Stock Handling Process Section 24.2 Inventory Control The Stock Handling Process Key Terms receiving record blind check method direct check
Chapter 15: Integrated Marketing Communications
 Chapter 15: Integrated Marketing Communications Pride/Ferrell Foundations of Marketing Fourth Edition Prepared by Milton Pressley University of New Orleans Objectives 1. Discuss the nature of integrated
Chapter 15: Integrated Marketing Communications Pride/Ferrell Foundations of Marketing Fourth Edition Prepared by Milton Pressley University of New Orleans Objectives 1. Discuss the nature of integrated
BUSINESS PLAN GUIDELINES START MY OWN BUSINESS
 BUSINESS PLAN GUIDELINES START MY OWN BUSINESS 1. Cover Page and Table of Contents The cover page of your business plan should include contact information such as your name, the name of your business,
BUSINESS PLAN GUIDELINES START MY OWN BUSINESS 1. Cover Page and Table of Contents The cover page of your business plan should include contact information such as your name, the name of your business,
Position Descriptions include the current benchmark job description used by participants to facilitate job matching.
 Level Guides, Position Descriptions Introduction This section includes the following: Level Guides set forth the criteria (i.e., the experience, education, skills, duties/tasks, and supervision given/received)
Level Guides, Position Descriptions Introduction This section includes the following: Level Guides set forth the criteria (i.e., the experience, education, skills, duties/tasks, and supervision given/received)
OUTLINE FOR AN INTERNATIONAL BUSINESS PLAN
 OUTLINE FOR AN INTERNATIONAL BUSINESS PLAN Please type your plan single-spaced. The first stage in developing an international business plan is to undertake a preliminary country analysis. Presented below
OUTLINE FOR AN INTERNATIONAL BUSINESS PLAN Please type your plan single-spaced. The first stage in developing an international business plan is to undertake a preliminary country analysis. Presented below
Chapter3: Literature Review: Marketing and Marketing Mix
 Chapter3: Literature Review: Marketing and Marketing Mix 3.1: Marketing 3.2: Promotion 3.3: Sales Promotion 17 Chapter 3.1: Marketing 1. Introduction 2. Elements of Marketing Mix 3. Promotion or Marketing
Chapter3: Literature Review: Marketing and Marketing Mix 3.1: Marketing 3.2: Promotion 3.3: Sales Promotion 17 Chapter 3.1: Marketing 1. Introduction 2. Elements of Marketing Mix 3. Promotion or Marketing
Effective Marketing Solutions for your Small Business
 COMMUNITY TECHNOLOGY CENTER PASSAIC COUNTY COMMUNITY COLLEGE Teacher: Lucia Gheorghiu Effective Marketing Solutions for your Small Business Ideas for Today and Tomorrow Dr. Lucia Gheorghiu 1 Effective
COMMUNITY TECHNOLOGY CENTER PASSAIC COUNTY COMMUNITY COLLEGE Teacher: Lucia Gheorghiu Effective Marketing Solutions for your Small Business Ideas for Today and Tomorrow Dr. Lucia Gheorghiu 1 Effective
Indiana Content Standards for Educators
 Indiana Content Standards for Educators CAREER AND TECHNICAL EDUCATION MARKETING Marketing teachers are expected to have a broad and comprehensive understanding of the knowledge and skills needed for this
Indiana Content Standards for Educators CAREER AND TECHNICAL EDUCATION MARKETING Marketing teachers are expected to have a broad and comprehensive understanding of the knowledge and skills needed for this
Chapter 27 Pricing Math. Section 27.1 Calculating Prices Section 27.2 Calculating Discounts
 Chapter 27 Pricing Math Section 27.1 Calculating Prices Section 27.2 Calculating Discounts Calculating Prices Key Terms gross profit maintained markup Objectives Explain how a firm s profit is related
Chapter 27 Pricing Math Section 27.1 Calculating Prices Section 27.2 Calculating Discounts Calculating Prices Key Terms gross profit maintained markup Objectives Explain how a firm s profit is related
Advanced Marketing (Master) Content Skills Learning Targets Assessment Resources & Technology CEQ: WHAT IS PROMOTION, PLACE AND PRICE?
 St. Michael-Albertville High School Teacher: Jeanne Fisher Advanced Marketing (Master) September 2014 CEQ: WHAT IS PROMOTION, PLACE AND PRICE? Text: Marketing Essentials, Glencoe What is promotion? 1.Promotin
St. Michael-Albertville High School Teacher: Jeanne Fisher Advanced Marketing (Master) September 2014 CEQ: WHAT IS PROMOTION, PLACE AND PRICE? Text: Marketing Essentials, Glencoe What is promotion? 1.Promotin
Contents. Part- I: Introduction to Services Marketing. Chapter 1 Understanding Services 3-22. Chapter 2 The Nature of Services Marketing 23-38
 Contents Part- I: Introduction to Services Marketing Chapter 1 Understanding Services 3-22 Chapter 2 The Nature of Services Marketing 23-38 Part- II: The Customer Experience Chapter 3 Consumer Behavior
Contents Part- I: Introduction to Services Marketing Chapter 1 Understanding Services 3-22 Chapter 2 The Nature of Services Marketing 23-38 Part- II: The Customer Experience Chapter 3 Consumer Behavior
Marketing 360 Proficiency Exam Study Guide
 Marketing 360 Proficiency Exam Study Guide AMA definition of Marketing - an organizational function and a set of processes for creating, communicating, and delivering value to customers and for managing
Marketing 360 Proficiency Exam Study Guide AMA definition of Marketing - an organizational function and a set of processes for creating, communicating, and delivering value to customers and for managing
Introduction to Entrepreneurship I - Course Outline
 Course Overview 4 Lesson 1: Start the Course Identify computer requirements. Learn how to move through the course. Switch between windows. Lesson 2: Set Up Your Computer Find files and folders on a computer.
Course Overview 4 Lesson 1: Start the Course Identify computer requirements. Learn how to move through the course. Switch between windows. Lesson 2: Set Up Your Computer Find files and folders on a computer.
SCHOOL-BASED ENTERPRISES CERTIFICATION PROGRAM 2015
 SCHOOL-BASED ENTERPRISES CERTIFICATION PROGRAM 2015 Sponsored by A school-based enterprise (SBE) is an entrepreneurial operation in a school setting that provides goods/services to meet the needs of the
SCHOOL-BASED ENTERPRISES CERTIFICATION PROGRAM 2015 Sponsored by A school-based enterprise (SBE) is an entrepreneurial operation in a school setting that provides goods/services to meet the needs of the
Unit 4: Marketing Principles
 Unit 4: Marketing Principles Unit code: F/601/0556 QCF level: 4 Credit value: 15 credits Aim This unit aims to provide learners with understanding and skills relating to the fundamental concepts and principles
Unit 4: Marketing Principles Unit code: F/601/0556 QCF level: 4 Credit value: 15 credits Aim This unit aims to provide learners with understanding and skills relating to the fundamental concepts and principles
Course Outcome Summary
 Wisconsin Indianhead Technical College Course Outcome Summary Course Information Description Career Cluster Instructional Level Total Credits 3.00 This course focuses on the marketing process as it relates
Wisconsin Indianhead Technical College Course Outcome Summary Course Information Description Career Cluster Instructional Level Total Credits 3.00 This course focuses on the marketing process as it relates
PLANNING FOR SUCCESS P a g e 0
 PLANNING FOR SUCCESS P a g e 0 PLANNING FOR SUCCESS P a g e 1 Planning for Success: Your Guide to Preparing a Business and Marketing Plan This guide is designed to help you put together a comprehensive,
PLANNING FOR SUCCESS P a g e 0 PLANNING FOR SUCCESS P a g e 1 Planning for Success: Your Guide to Preparing a Business and Marketing Plan This guide is designed to help you put together a comprehensive,
Using Effective Promotions
 Chapter 16: Using Effective Promotions Product Place Price Promotion 48 slides 12 slides 4 slides 2 slides 2 3 1 Any of a variety of methods used to communicate with the people in your target market and
Chapter 16: Using Effective Promotions Product Place Price Promotion 48 slides 12 slides 4 slides 2 slides 2 3 1 Any of a variety of methods used to communicate with the people in your target market and
Entrepreneurship. One Marketing credit in a core course*
 Entrepreneurship Primary Career Cluster: Marketing Consultant: Course Code(s): 5934 Course Substitution: Recommended Prerequisite(s): Credit: ½ - 3* Grade Level: 11-12 Aligned Student Organization(s):
Entrepreneurship Primary Career Cluster: Marketing Consultant: Course Code(s): 5934 Course Substitution: Recommended Prerequisite(s): Credit: ½ - 3* Grade Level: 11-12 Aligned Student Organization(s):
Pricing and Credit Decisions
 CHAPTER OUTLINE Spotlight: Dynamic Network Services (http://www.dyn.com) 1 Setting a Price Discuss the role of cost and demand factors in setting a price. Cost Determination for Pricing Total cost includes
CHAPTER OUTLINE Spotlight: Dynamic Network Services (http://www.dyn.com) 1 Setting a Price Discuss the role of cost and demand factors in setting a price. Cost Determination for Pricing Total cost includes
Principles of Marketing Lecture 13a: Promotional Mix Decisions: Advertising and Sales Promotion. The Traditional Communication Model. Noise.
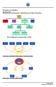 Principles of Marketing Lecture 13a: al Mix Decisions: Advertising and Sales Target Market Product Place Price Personal Selling Mass Selling Sales Advertising Publicity The Traditional Communication Model
Principles of Marketing Lecture 13a: al Mix Decisions: Advertising and Sales Target Market Product Place Price Personal Selling Mass Selling Sales Advertising Publicity The Traditional Communication Model
Course Outline. BUSN 5050/1-3 Marketing Management (3,0,0)
 Course Outline Department of Marketing, International Business, Entrepreneurship School of Business and Economics BUSN 5050/1-3 Marketing Management (3,0,0) Calendar Description Students examine the key
Course Outline Department of Marketing, International Business, Entrepreneurship School of Business and Economics BUSN 5050/1-3 Marketing Management (3,0,0) Calendar Description Students examine the key
Field 010: Career and Technical Education Business and Information Technology Assessment Blueprint
 Field 010: Career and Technical Education Business and Information Technology Assessment Blueprint Domain I Business Management and Ownership 0001 Business and Human Resources Management (Standard 1) 0002
Field 010: Career and Technical Education Business and Information Technology Assessment Blueprint Domain I Business Management and Ownership 0001 Business and Human Resources Management (Standard 1) 0002
SCHOOL-BASED ENTERPRISES CHAPTER CERTIFICATION 2016
 SCHOOL-BASED ENTERPRISES CHAPTER CERTIFICATION 2016 Sponsored by A school-based enterprise (SBE) is an entrepreneurial operation in a school setting that provides goods/services to meet the needs of the
SCHOOL-BASED ENTERPRISES CHAPTER CERTIFICATION 2016 Sponsored by A school-based enterprise (SBE) is an entrepreneurial operation in a school setting that provides goods/services to meet the needs of the
CTSO Course Alignments: Advertising and Public Relations
 CTSO Course Alignments: Advertising and Public Relations Below you will find standards for the Advertising and Public Relations course aligned with competitive events from appropriate career and technical
CTSO Course Alignments: Advertising and Public Relations Below you will find standards for the Advertising and Public Relations course aligned with competitive events from appropriate career and technical
What this topic is about. The purpose of marketing Different approaches to marketing Segmentation Niche &mass markets B2C & B2B marketing
 Effective Marketing What this topic is about The purpose of marketing Different approaches to marketing Segmentation Niche &mass markets B2C & B2B marketing What is Marketing? The process of identifying,
Effective Marketing What this topic is about The purpose of marketing Different approaches to marketing Segmentation Niche &mass markets B2C & B2B marketing What is Marketing? The process of identifying,
Slide 1. Welcome to Chapter 11. This chapter is called Marketing. The author is Vicente Lluch.
 Slide 1 Welcome to Chapter 11 This chapter is called Marketing. The author is Vicente Lluch. Slide 2 In this chapter we will address the learning objectives by answering the following questions: What is
Slide 1 Welcome to Chapter 11 This chapter is called Marketing. The author is Vicente Lluch. Slide 2 In this chapter we will address the learning objectives by answering the following questions: What is
Marketing. Joseph F. Hair, Jr. Carl McDaniel. South-Western College Publishing Thomson Learning,.
 Marketing SECOND EDITION C J Charles W. Lamb, Jr. MJ. Neeley Professor of Marketing MJ. Neeley School of Business Texas Christian University Joseph F. Hair, Jr. Alvin C. Copeland Endowed Chair of Franchising
Marketing SECOND EDITION C J Charles W. Lamb, Jr. MJ. Neeley Professor of Marketing MJ. Neeley School of Business Texas Christian University Joseph F. Hair, Jr. Alvin C. Copeland Endowed Chair of Franchising
B413 Digital Media Marketing MTCU code - 72900 Program Learning Outcomes
 B413 Digital Media Marketing MTCU code - 72900 Program Learning Outcomes *Synopsis of the Vocational Learning Outcomes The graduate has reliably demonstrated the ability to 1. develop a promotion mix for
B413 Digital Media Marketing MTCU code - 72900 Program Learning Outcomes *Synopsis of the Vocational Learning Outcomes The graduate has reliably demonstrated the ability to 1. develop a promotion mix for
over-the-counter selling personal selling field selling network marketing telemarketing outbound telemarketing inbound telemarketing inside selling
 personal selling over-the-counter selling field selling network marketing outbound telemarketing telemarketing inbound telemarketing inside selling relationship selling consultative selling cross-selling
personal selling over-the-counter selling field selling network marketing outbound telemarketing telemarketing inbound telemarketing inside selling relationship selling consultative selling cross-selling
Marketing Plan Development 101: The Importance of Developing a Marketing Plan for Public Transit Agencies & Commuter Assistance Programs
 Marketing Plan Development 101: The Importance of Developing a Marketing Plan for Public Transit Agencies & Commuter Assistance Programs Mark Glein, PhD, Marketing Florida State University Marketing Plan
Marketing Plan Development 101: The Importance of Developing a Marketing Plan for Public Transit Agencies & Commuter Assistance Programs Mark Glein, PhD, Marketing Florida State University Marketing Plan
Marketing strategy questionnaire
 Marketing strategy questionnaire Prepared by: Date: Purpose Use this template to capture the key information that you need to develop a thorough marketing strategy. Then use the information that you collect,
Marketing strategy questionnaire Prepared by: Date: Purpose Use this template to capture the key information that you need to develop a thorough marketing strategy. Then use the information that you collect,
Marketing s Four P s: First Steps for New Entrepreneurs
 PURDUE EXTENSION EC-730 Marketing s Four P s: First Steps for New Entrepreneurs Cole Ehmke, Joan Fulton, and Jayson Lusk Department of Agricultural Economics Marketing your business is about how you position
PURDUE EXTENSION EC-730 Marketing s Four P s: First Steps for New Entrepreneurs Cole Ehmke, Joan Fulton, and Jayson Lusk Department of Agricultural Economics Marketing your business is about how you position
RIVERSIDE COUNTY OFFICE OF EDUCATION COURSE OUTLINE. Entrepreneurship and Innovation II. CBEDS Number: 4126. Job Title(s):
 RIVERSIDE COUNTY OFFICE OF EDUCATION CO1.rpt COURSE OUTLINE 8/26/2015 10:59:24AM 1 of 8 Course: 12523 RCOE Virtual Enterprise CBEDS Title: Entrepreneurship and Innovation II CBEDS Number: 4126 Job Title(s):
RIVERSIDE COUNTY OFFICE OF EDUCATION CO1.rpt COURSE OUTLINE 8/26/2015 10:59:24AM 1 of 8 Course: 12523 RCOE Virtual Enterprise CBEDS Title: Entrepreneurship and Innovation II CBEDS Number: 4126 Job Title(s):
Career Technical Assurance Guide (CTAG) Area. Articulation Number (CTAN)
 Business Foundations Subject Code: 141000 This is the first course for the Business and Administrative Services, Finance and Marketing career fields. It introduces students to specializations within the
Business Foundations Subject Code: 141000 This is the first course for the Business and Administrative Services, Finance and Marketing career fields. It introduces students to specializations within the
Courses in Business and Administrative Services (C4)
 Courses in Business and Administrative Services (C4) PATHWAY COURSES SUBJECT CODE Business Foundations 1 141000 Fundamentals of Business and Administrative Services 2 142000 Management Principles 141025
Courses in Business and Administrative Services (C4) PATHWAY COURSES SUBJECT CODE Business Foundations 1 141000 Fundamentals of Business and Administrative Services 2 142000 Management Principles 141025
FDU-Vancouver Bachelor of Science in Business Administration - International Business concentration Course Descriptions
 FDU-Vancouver Bachelor of Science in Business Administration - International Business concentration Course Descriptions ACCT 2021 Intro Financial Accounting An introduction to the concepts underlying an
FDU-Vancouver Bachelor of Science in Business Administration - International Business concentration Course Descriptions ACCT 2021 Intro Financial Accounting An introduction to the concepts underlying an
Hospitality Management
 The changing hospitality industry encompasses growing and varied employment and career advancement opportunities. This course prepares students for gainful employment and/or post-secondary training in
The changing hospitality industry encompasses growing and varied employment and career advancement opportunities. This course prepares students for gainful employment and/or post-secondary training in
Marketing Management
 Marketing Management Draft 2001 Delta Epsilon Chi Competitive Events for this competitive event are used to define the parameters of the written exam and other activities that are part of the overall competition.
Marketing Management Draft 2001 Delta Epsilon Chi Competitive Events for this competitive event are used to define the parameters of the written exam and other activities that are part of the overall competition.
INTEGRATED MARKETING COMMUNICATIONS
 INTEGRATED MARKETING COMMUNICATIONS What is IMC & why IMC? IMC is the concept and practice of designing marketing communications programs that coordinate all promotional activities Ad, PS, SP, PR, publicity,
INTEGRATED MARKETING COMMUNICATIONS What is IMC & why IMC? IMC is the concept and practice of designing marketing communications programs that coordinate all promotional activities Ad, PS, SP, PR, publicity,
Marketing (Marketing Principles)
 Marketing (Marketing Principles) Main Aim(s) of the Unit: To provide students with a foundation for the analysis of marketing within organizations including decision making processes, segmentation, the
Marketing (Marketing Principles) Main Aim(s) of the Unit: To provide students with a foundation for the analysis of marketing within organizations including decision making processes, segmentation, the
Essential Guide for Business Plan Creation Basic 12 step guide for executing a successful Business Plan
 Essential Guide for Business Plan Creation Basic 12 step guide for executing a successful Business Plan EBP Business Plan Designer Written by Matthew Parfitt EBP International Sales Executive The Essential
Essential Guide for Business Plan Creation Basic 12 step guide for executing a successful Business Plan EBP Business Plan Designer Written by Matthew Parfitt EBP International Sales Executive The Essential
Fashion Merchandising Advanced
 Levels: Grade 11-12 Units of Credits: 1.00 CIP Code: 08.0199 Core Code: 37010000070 Prerequisites: Fashion Merchandising A and B Skill Test: COURSE DESCRIPTION The Advanced Fashion Merchandising course
Levels: Grade 11-12 Units of Credits: 1.00 CIP Code: 08.0199 Core Code: 37010000070 Prerequisites: Fashion Merchandising A and B Skill Test: COURSE DESCRIPTION The Advanced Fashion Merchandising course
AAA School of Advertising Part Time Bachelor of Arts in Marketing Communication
 AAA School of Advertising Part Time Bachelor of Arts in Marketing Communication 2014 CURRICULUM BA IN MARKETING COMMUNICATION DURATION: 4 YEARS COURSE STRUCTURE YEAR 1: 5 MODULES 1. Principles of Marketing
AAA School of Advertising Part Time Bachelor of Arts in Marketing Communication 2014 CURRICULUM BA IN MARKETING COMMUNICATION DURATION: 4 YEARS COURSE STRUCTURE YEAR 1: 5 MODULES 1. Principles of Marketing
MONROE TOWNSHIP PUBLIC SCHOOLS WILLIAMSTOWN, NEW JERSEY. Marketing I
 MONROE TOWNSHIP PUBLIC SCHOOLS WILLIAMSTOWN, NEW JERSEY Williamstown High School Marketing I September 2013 Written by: Rosemarie Austin Stan Krzyminski, Director of Curriculum Dean Insana, Supervisor
MONROE TOWNSHIP PUBLIC SCHOOLS WILLIAMSTOWN, NEW JERSEY Williamstown High School Marketing I September 2013 Written by: Rosemarie Austin Stan Krzyminski, Director of Curriculum Dean Insana, Supervisor
