Intraocular Pressure and Quality of Blockade in Peribulbar Anesthesia Using Ropivacaine or Lidocaine with Adrenaline: A Double-Blind Randomized Study
|
|
|
- Lilian Warren
- 8 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Tohoku J. Exp. Med., 2004, Ropivacaine 204, in Peribulbar Block: a Comparison with Lidocaine 203 Intraocular Pressure and Quality of Blockade in Peribulbar Anesthesia Using Ropivacaine or Lidocaine with Adrenaline: A Double-Blind Randomized Study GONUL OLMEZ, SEVIN SOKER CAKMAK, 1 IHSAN CACA 1 and M. KAAN UNLU 1 Department of Anesthesiology and Reanimation, and 1 Department of Ophthalmology, Faculty of Medicine, Dicle University, Diyarbakir, Turkey OLMEZ, G., CAKMAK, S.S., CACA, I. and UNLU, M.K. Intraocular Pressure and Quality of Blockade in Peribulbar Anesthesia Using Ropivacaine or Lidocaine with Adrenaline: A Double-Blind Randomized Study. Tohoku J. Exp. Med., 2004, 204 (3), The aim of this study was to compare the effects of ropivacaine with those of lidocaine on the intraocular pressure (IOP) and the quality of the blockade in peribulbar anesthesia for cataract surgery. Fifty patients were allocated randomly into two groups and received 7-10 ml of 0.75% ropivacaine or 2% lidocaine with adrenaline, though the peribulbar two-point injection. The quality of the blockade was assessed by ocular and eyelid akinesia, pain during the peribulbar injection, and surgical satisfaction. The duration of the motor block was also evaluated after surgery. The IOP was measured using a Tonopen before the blockade (control) and at 1, 5, and 10 min after injection of the anesthetic. Lidocaine induced significantly lower akinesia scores at 6, 8, and 10 min post-injection than did ropivacaine. The mean IOP (mmhg) was significantly lower with respect to the baseline level at 10 min after blockade in the ropivacaine group compared with the lidocaine group. Ropivacaine also caused less pain on injection. There was no difference in surgical satisfaction between the groups. The duration of the motor block obtained with ropivacaine was longer than that obtained with lidocaine. Our data indicate that ropivacaine has efficacy similar to lidocaine, with slightly longer onset and duration of the motor blockade. In addition, ropivacaine (0.75%) induces lower IOP and less pain on injection than does lidocaine (2%) when used in peribulbar anesthesia for cataract surgery. lidocaine, ropivacaine, peribulbar anesthesia 2004 Tohoku University Medical Press Received June 21, 2004; revision accepted for publication September 8, Address for reprints: Sevin Soker Cakmak, M.D., Department of Ophthalmology, Dicle University Faculty of Medicine, TR-21280, Diyarbakir, Turkey. sokers@dicle.edu.tr 203
2 204 G. Olmez et al. Cataracts are a significant cause of disability among the elderly. Regional anesthesia is widely used during cataract extraction surgery because it avoids many of the complications associated with general anesthesia and allows the procedure to be performed as an outpatient surgery (Donlon 2000). Various local anesthetics are used for peribulbar anesthesia; however, there is no universally recommended agent. The use of mixtures of local anesthetics for regional anesthesia has recently become popular, based on the premise that rapid-acting agents with short duration of effect could compensate for the longer latencies associated with agents that have longer duration of effect. However, some studies have shown that there were no clinically significant advantages to the use of mixtures of local anesthetic agents (Berde and Strichartz 2000; Luchetti et al. 2000; Nicholson et al. 2000; Perello et al. 2000; Ozcan et al. 2003). In addition, using a single effective agent is preferable to an unnecessary polypharmacy approach. Ropivacaine is a long-acting local anesthetic used as a single agent in peribulbar anesthesia for cataract surgery (Nociti et al. 1999; Nicholson et al. 1999, 2000; Luchetti et al. 2000; Perello et al. 2000; Ozcan et al. 2003). Evidence suggests that ropivacaine has a higher threshold for cardiovascular and central nervous system toxicity than does bupivacaine and a lower threshold than does lidocaine (Arlock 1988; Feldman et al. 1989). In addition, the quality of the motor block, the duration of analgesia, and the pain of injection induced by ropivacaine used in peribulbar anesthesia were superior to those observed with other anesthetics (Luchetti et al. 2000; Ozcan et al. 2003). It has been shown that adrenaline does not increase the efficacy of ropivacaine owing to the inherent vasoconstrictive properties of ropivacaine (Cederholm et al. 1992). Lidocaine acts rapidly and produces anesthesia of moderate duration. The potential toxicity of lidocaine is lower than that of other local anesthetic agents. The duration of cataract surgery is relatively short, thus the moderate duration of li- docaine-induced blockade is not a disadvantage. Therefore, lidocaine is widely used as the sole anesthetic agent in cataract surgery (Thomson 1988; Davis and O Connor 1989; Mjahed et al. 1996; Bedi and Carabine 1999). It has been reported to have similar effects when used alone or in combination with bupivacaine for peribulbar anesthesia (Davis and O Connor 1989; Bedi and Carabine 1999). As there have been no previous studies directly comparing ropivacaine with lidocaine in peribulbar anesthesia, we compared the quality and duration of the blockade and the intraocular pressure produced by these two agents during peribulbar anesthesia. METHODS This study was undertaken in the Department of Ophthalmology at Dicle University following approval of the protocol by the institutional ethics committee. Fifty patients scheduled for extracapsular cataract extraction under local anesthesia were enrolled in the study after giving written informed consent. Patients with glaucoma were excluded from the study. The patients received no premedication. They were randomly assigned to two groups of 25 each according to the local anesthetic employed for the peribulbar anesthesia. The patients in the ropivacaine group (GR) received 0.75% ropivacaine, and those in the lidocaine group (GL) received 2% lidocaine combined with 1 : adrenaline. All patients were monitored throughout the procedure by pulse oxymetry, electrocardiography, and noninvasive blood pressure measurement. All local anesthetic solutions of were prepared immediately prior to the procedure by a nurse anesthetist who played no further role in the study. In all cases, peribulbar anesthesia was conducted by an experienced physician. A total volume of 7-10 ml of local anesthetic per patient was injected using a standardized, two-point, peribulbar injection technique with a 25-mm, 25-g needle; 4-6 ml of anesthetic was injected at
3 Ropivacaine in Peribulbar Block: a Comparison with Lidocaine 205 the junction of the lateral third with the medial two-thirds of the inferior orbital edge, through the eyelid, and the residual volume was injected in the upper internal edge of the eyeball, through the upper eyelid. Different volumes of local anesthetic were used depending on the degree of filling of the orbit observed during injection. Digital pressure was applied to the eye for 10 min between intermittent measurements, rather than using a mechanical device; digital pressure was preferrable to permit frequent measurement of IOP and akinesia scores. The post-block evaluations were performed by a second physician who was blinded to the local anesthetic used. The akinesia scores were obtained from assessment of movement in five muscles: the superior rectus, inferior rectus, medial rectus, lateral rectus, and levator palpabrae superior. Movement was scored from 0 (no movement) to 3 (full movement) in each muscle, giving a total score in the range 0 to 15. Ocular motility was assessed at 2, 4, 6, 8, and 10 min after injection. The IOP was measured four times using a Tonopen: before the injection of the anesthetic (control) and at 1, 5, and 10 min after injection. The patients indicated the level of pain experienced during the injection of the anesthetic solution using a visual analogue scale (VAS) ranging from 0 to 10 (0 = no pain, 10 = the worst pain possible). Surgical satisfaction was assessed by the surgeons as being poor, adequate, or good. After the surgery, the ocular muscle functions were assessed every 30 min for 5 h. The time at which full movement returned was accepted as the duration of motor block. Categorical samples were compared using the Chi-square test. The mean akinesia scores were compared between the groups using the independent t-test. The mean IOP levels were compared between the groups using the paired t-test. The VAS scores were compared using the Mann- Whitney s U-test. Surgical satisfaction was compared with the Fisher exact Chi-square test. The significance level was defined as p < RESULTS The patients in both groups had similar demographic characteristics (Table 1). There were significant differences in ocular motility between the two groups. Motor blockade was observable beginning at 2 min after injection in both groups. Lower akinesia scores were obtained in the lidocaine group at 6, 8, and 10 min after injection (Fig. 1) than in the ropivacaine group. The mean akinesia scores for the groups during the 10-min observation period are summarized in Table 2. There were no significant differences in the IOP levels between the two groups. The IOP level of the ropivacaine group at 10 min was significantly lower with respect to the baseline level (p = 0.029) (Table 3). The duration of the motor block was significantly longer in the ropivacaine group (p < 0.001) than in the lidocaine group; (294 ± 62 min and ± 53, respectively). The visual analogue pain scores are shown in Table 4. Lidocaine caused significantly more pain on injection than did ropivacaine (p < 0.05). Surgical comfort was satisfactory in both groups, TABLE 1. Patient characteristics. Ropivacaine (n = 25) (mean ± S.D.) Lidocaine (n = 25) (mean ± S.D.) p value Sex (male/female) 11/14 10/15 NS Side of operation; R/L 12/13 11/14 NS Age (year) 68.8 ± ± 6.7 NS Weight (kg) 76.4 ± ± 5.2 NS Duration of surgery (min) 49.9 ± ± 11 NS
4 206 G. Olmez et al. Fig. 1. The mean akinesia scores for the ropivacaine and lidocaine groups at the indicated times postinjection., Ropivacaine;, Lidocaine. TABLE 2. Mean akinesia scores of muscle groups during the first 10 min after peribulbar injection of anesthetic solution. (min) Ropivacaine Lidocaine p value ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± TABLE 3. Mean IOP levels (mmhg) at the indicated times following peribulbar i n j e c t i o n o f ro p i v a c a i n e o r lidocaine. Ropivacaine Lidocaine p value * Preblock ± ± min ± ± min ± ± min ± 2.86 ** ± * Comparison of ropivacaine and lidocaine groups. ** Significantly lower than baseline (pre-block) level (p = 0.029). TABLE 4. Visual analogue pain scores immediately following injection of peribulbar anesthesia. Ropivacaine Lidocaine Median pain scores 2 5 Interquartile range TABLE 5. Surgical satisfaction levels in patients receiving either ropivacaine or lidocaine peribulbar anesthesia. Poor Adequate Good Ropivacaine Lidocaine
5 Ropivacaine in Peribulbar Block: a Comparison with Lidocaine 207 and there were no significant differences between the groups (p > 0.05; Table 5). None of the patients required additional local anesthetic solution during the procedure, and no drug-related adverse effects were observed in either group. DISCUSSION In addition to analgesia, the goal of ideal peribulbar anesthesia is to obtain complete akinesia of the eye globe and low intraocular pressure in order to provide optimal surgical conditions. In this study, the motor blockade began at 2 min after injection in both groups; it was significantly profound at 6, 8, and 10 min after injection with lidocaine anesthesia, as compared with ropivacaine. Sufficient motor block for surgery was achieved at 10 min in both groups and provided good operating conditions. Bedi et al. (1999) used 2% lidocaine with epinephrine for peribulbar anesthesia, and the time of onset of anesthesia adequate for surgery was similar to that obtained with prilocaine and lidocaine-bupivacaine mixtures. In a report by Davis et al. (1989), 2% lidocaine provided a successful block at 4 min after injection. In patients anesthetized with ropivacaine or lidocaine, there was an increase in the IOP during the first minute after injection. Peribulbar anesthesia itself can cause a transient increase in the IOP, secondary to the increase in orbital pressure owing to the injection of the local anesthetic solution. The IOP nevertheless returns rapidly to baseline values upon relaxation of the extraocular muscles, resulting in a decrease in the external pressure over the ocular globe (Donlon 2000). There were no significant differences in the IOP levels between the groups, even though the IOP was decreased significantly below baseline values at 10 min in the ropivacaine group. It has been reported that the vasoconstrictive effect of ropivacaine leads to a decrease in the intraocular blood volume and that this might play a role in the observed decrease in the IOP (Nakamura et al. 1993; Ishiyama et al. 1997; Nociti et al. 2001; Ozcan et al. 2003). In addition, the IOP might have been decreased in the ropivacaine group because the diffusion of ropivacaine through the tissues may be faster than that of lidocaine. In outpatient surgery, where premedication and sedation are best avoided, the lower pain scores associated with the injection of ropivacaine make it a more comfortable and acceptable technique for the patients. The lower pain scores may be attributable to the ph of the local anesthetic solution (Berde and Strichartz 2000). In a recent study comparing ropivacaine with bupivacainemepivacaine, a greater incidence of pain on injection was found in the bupivacaine-mepivacaine group (Luchetti et al. 2000). Other studies have reported that only prilocaine was less painful than lidocaine or a lidocaine-bupivacaine mixture when injected (Henderson and Franks 1996; Bedi and Carabine 1999). The assessment of the duration of motor block in this study indicated that, as expected, ropivacaine had a longer duration. Prolonged motor block and prolonged analgesia may be preferable in cataract surgery. Ozcan et al. (2003) reported that 0.75% ropivacaine resulted in lower post-operative pain scores than did a bupivacainelidocaine mixture. We conclude that 0.75% ropivacaine results in lower IOP and decreased pain during injection than does 2% lidocaine in peribulbar anesthesia. References Arlock, P. (1988) Actions of three local anaesthetics: lidocaine, bupivacaine and ropivacaine on guinea pig papillary muscle sodium channels (Vmax). Pharmacol. Toxicol., 63, Bedi, A. & Carabine, U. (1999) Peribulbar anaesthesia: a double-blind comparison of three local anaesthetic solutions. Anaesthesia, 54, Berde, C.B. & Strichartz, G.R. (2000) Local Anesthetics, In: Anesthesia, edited by R.D. Miller, 5th ed., Philadelphia, Churchill Livingstone, pp Cederholm, I., Evers, H. & Lofstrom, J.B. (1992) Skin blood flow after intradermal injection of ropivacaine in various concentrations with and without epinephrine evaluated by laser Doppler flowmetry. Reg Anesth., 17,
6 208 G. Olmez et al. Davis, P.L. & O connor, J.P. (1989) Peribulbar block for cataract surgery: a prospective double-blind study of two local anesthetics. Can. J. Ophthalmol., 24, Donlon, J.V., Jr. (2000) Anesthesia for eye, ear, nose, and throat surgery, In: Anesthesia, edited by R.D. Miller, 5th ed., Philadelphia, Churchill Livingstone, pp Feldman, H.S., Arthur, G.R. & Covino, B.G. (1989) Comparative systemic toxicity of convulsant and supraconvulsant doses of intravenous ropivacaine, bupivacaine, and lidocaine in the conscious dog. Anesth. Analg., 69, Henderson, T.R. & Franks, W. (1996) Peribulbar anesthesia for cataract surgery: prilocaine versus lignocaine and bupivacaine. Eye, 10, Ishiyama, T., Dohi, S., Iida, H. & Watanabe, Y. (1997) The effects of topical and intravenous ropivacaine on canine pial microcirculation. Anesth. Analg., 85, Luchetti, M., Magni, G. & Marraro, G. (2000) A prospective randomized double-blinded controlled study of ropivacaine 0.75% versus bupivacaine 0.5%-mepivacaine 2% for peribulbar anesthesia. Reg Anesth. Pain Med., 25, Mjahed, K., el Harrar, N., Hamdani, M., Amraoui, M. & Benaguida, M. (1996) Lidocaine-clonidine retrobulbar block for cataract surgery in the elderly. Reg Anesth., 21, Nakamura, K., Toda, H., Kakuyama, M., Nishiwada, M., Yamamoto, M., Hatano, Y. & Mori, K. (1993) Direct vascular effect of ropivacaine in femoral artery and vein of the dog. Acta Anaesthesiol. Scand., 37, Nicholson, G., Sutton, B. & Hall, G.M. (1999) Ropivacaine for peribulbar anesthesia. Reg Anesth. Pain Med., 24, Nicholson, G., Sutton, B. & Hall, G.M. (2000) Comparison of 1% ropivacaine with 0.75% bupivacaine and 2% lidocaine for peribulbar anaesthesia. Br. J. Anaesth., 84, Nociti, J.R., Serzedo, P.S., Zuccolotto, E.B., Cagnolati, C.A. & Nunes, A.M.M. (1999) Ropivacaine in peribulbar block: a comparative study with bupivacaine. Acta Anesthesiol. Scand., 43, Nociti, J.R., Serzedo, P.S., Zuccolotto, E.B., Nunes, A.M. & Ferreira, S.B. (2001) Intraocular pressure and ropivacaine in peribulbar block: a comparative study with bupivacaine. Acta Anaesthesiol. Scand., 45, Ozcan, A.A., Ozdemir, N., Gunes, Y., Bozkurt, A., Yagmur, M. & Alparslan, Z.N. (2003) Intraocular pressure, quality of block, and degree of pain associated with ropivacaine in peribulbar block: a comparative randomized study with bupivacaine-lidocaine mixture. Eur. J. Ophthalmol., 13, Perello, A., George, J., Skelton, V. & Pateman, J. (2000) A double-blind randomised comparison of ropivacaine 0.5%, bupivacaine 0.375%- lidocaine1% and ropivacaine 0.5%-lidocaine1% mixtures for cataract surgery. Anesthesia, 55, Thomson, I. (1988) Addition of hyaluronidase to lignocaine with adrenaline for retrobulbar anaesthesia in the surgery of senile cataract. Br. J. Ophthalmol., 72,
RAPID CLINICAL REPORT
 RAPID CLINICAL REPORT ADVERSE EFFECTS ASSOCIATED WITH THE ABSENCE OF HYALURONIDASE IN ANESTHESIA FOR CATARACT SURGERY Background: Issued February 13, 2001 Hyaluronidase (Wydase ) is a medical preparation
RAPID CLINICAL REPORT ADVERSE EFFECTS ASSOCIATED WITH THE ABSENCE OF HYALURONIDASE IN ANESTHESIA FOR CATARACT SURGERY Background: Issued February 13, 2001 Hyaluronidase (Wydase ) is a medical preparation
Dr. Yoganarasimha N* #, Dr. Raghavendra TR* %, Dr. Radha MK** %, Dr. Satish C*** *Associate Professor, ** Professor and HOD, *** Consultant
 Quest Journals Journal of Medical and Dental Science Research Volume 2~ Issue 7 (2015) pp:10-16 ISSN(Online) : 2394-076X ISSN (Print):2394-0751 www.questjournals.org Research Paper A clinical study to
Quest Journals Journal of Medical and Dental Science Research Volume 2~ Issue 7 (2015) pp:10-16 ISSN(Online) : 2394-076X ISSN (Print):2394-0751 www.questjournals.org Research Paper A clinical study to
Vasoactive characteristics of bupivacaine and levobupivacaine with and without adjuvant epinephrine in peripheral human skin
 British Journal of Anaesthesia 94 (5): 662 7 (25) doi:1.193/bja/aei95 Advance Access publication February 18, 25 Vasoactive characteristics of bupivacaine and levobupivacaine with and without adjuvant
British Journal of Anaesthesia 94 (5): 662 7 (25) doi:1.193/bja/aei95 Advance Access publication February 18, 25 Vasoactive characteristics of bupivacaine and levobupivacaine with and without adjuvant
Local Anesthetics Used for Spinal Anesthesia
 Local Anesthetics Used for Spinal Anesthesia Several local anesthetics are used for spinal anesthesia. These include procaine, lidocaine, tetracaine, levobupivacaine, and bupivacaine. Local anesthetics
Local Anesthetics Used for Spinal Anesthesia Several local anesthetics are used for spinal anesthesia. These include procaine, lidocaine, tetracaine, levobupivacaine, and bupivacaine. Local anesthetics
Top-up for Cesarean section. Dr. Moira Baeriswyl, Prof. Christian Kern
 Top-up for Cesarean section Dr. Moira Baeriswyl, Prof. Christian Kern In which situations? 2 What exactly is a Top-up? 3 C-section, NOW!! Emergency C-section requires a rapid onset of sustained analgesia
Top-up for Cesarean section Dr. Moira Baeriswyl, Prof. Christian Kern In which situations? 2 What exactly is a Top-up? 3 C-section, NOW!! Emergency C-section requires a rapid onset of sustained analgesia
Ankle Block. Indications The ankle block is suitable for the following: Orthopedic and podiatry surgical procedures of the distal foot.
 Ankle Block The ankle block is a common peripheral nerve block. It is useful for procedures of the foot and toes, as long as a tourniquet is not required above the ankle. It is a safe and effective technique.
Ankle Block The ankle block is a common peripheral nerve block. It is useful for procedures of the foot and toes, as long as a tourniquet is not required above the ankle. It is a safe and effective technique.
Femoral Nerve Block/3-in-1 Nerve Block
 Femoral Nerve Block/3-in-1 Nerve Block Femoral and/or 3-in-1 nerve blocks are used for surgical procedures on the front portion of the thigh down to the knee and postoperative analgesia. Both blocks are
Femoral Nerve Block/3-in-1 Nerve Block Femoral and/or 3-in-1 nerve blocks are used for surgical procedures on the front portion of the thigh down to the knee and postoperative analgesia. Both blocks are
The Efficacy of Continuous Bupivacaine Infiltration Following Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction
 The Efficacy of Continuous Bupivacaine Infiltration Following Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction Heinz R. Hoenecke, Jr., M.D., Pamela A. Pulido, R.N., B.S.N., Beverly A. Morris, R.N., C.N.P., and
The Efficacy of Continuous Bupivacaine Infiltration Following Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction Heinz R. Hoenecke, Jr., M.D., Pamela A. Pulido, R.N., B.S.N., Beverly A. Morris, R.N., C.N.P., and
Generated by Foxit PDF Creator Foxit Software http://www.foxitsoftware.com For evaluation only. Tishreen University Journal. Med.
 Tishreen University Journal. Med. Sciences Series Tishreen University Journal for Research and Scientific Studies - Medical Sciences Series Vol. (30) No. (٣) 008 * ** *** 008 * * * *** 01 Tishreen University
Tishreen University Journal. Med. Sciences Series Tishreen University Journal for Research and Scientific Studies - Medical Sciences Series Vol. (30) No. (٣) 008 * ** *** 008 * * * *** 01 Tishreen University
Bier Block (Intravenous Regional Anesthesia)
 Bier Block (Intravenous Regional Anesthesia) History August Bier introduced this block in 1908. Early methods included the use of two separate tourniquets and procaine was the local anesthetic of choice.
Bier Block (Intravenous Regional Anesthesia) History August Bier introduced this block in 1908. Early methods included the use of two separate tourniquets and procaine was the local anesthetic of choice.
ANESTHESIA FOR CATARACT SURGERY
 Chapter - 4 ANESTHESIA FOR CATARACT SURGERY Good anesthesia is essential for the performance of safe intraocular surgery. Anesthesia for cataract surgery today aims at creating a comfortable environment
Chapter - 4 ANESTHESIA FOR CATARACT SURGERY Good anesthesia is essential for the performance of safe intraocular surgery. Anesthesia for cataract surgery today aims at creating a comfortable environment
Comparison of Heart Rate and Blood Pressure administration of anesthesia agent with and without
 ISSN: 2347-3215 Volume 2 Number 9 (September-2014) pp. 153-158 www.ijcrar.com Comparison of Heart Rate and Blood Pressure administration of anesthesia agent with and without Mohammad Ali Ghavimi 1*, Javad
ISSN: 2347-3215 Volume 2 Number 9 (September-2014) pp. 153-158 www.ijcrar.com Comparison of Heart Rate and Blood Pressure administration of anesthesia agent with and without Mohammad Ali Ghavimi 1*, Javad
Comparison of the effects between clonidine and epinephrine added with bupivacine in brachial plexus block.
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 13, Issue 11 Ver. I (Nov. 2014), PP 54-58 Comparison of the effects between clonidine and epinephrine
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 13, Issue 11 Ver. I (Nov. 2014), PP 54-58 Comparison of the effects between clonidine and epinephrine
Influence of ph Most local anesthetics are weak bases.
 Local anesthetics The agent must depress nerve conduction. The agent must have both lipophilic and hydrophilic properties to be effective by parenteral injection. Structure-activity relationships The typical
Local anesthetics The agent must depress nerve conduction. The agent must have both lipophilic and hydrophilic properties to be effective by parenteral injection. Structure-activity relationships The typical
Common Regional Nerve Blocks Quick Guide developed by UWHC Acute Pain Service Jan 2011
 Common Regional Nerve Blocks Quick Guide developed by UWHC Acute Pain Service Jan 2011 A single shot nerve block is the injection of local anesthetic to block a specific nerve distribution. It can be placed
Common Regional Nerve Blocks Quick Guide developed by UWHC Acute Pain Service Jan 2011 A single shot nerve block is the injection of local anesthetic to block a specific nerve distribution. It can be placed
Sign up to receive ATOTW weekly - email worldanaesthesia@mac.com
 PHARMACOLOGY FOR REGIONAL ANAESTHESIA ANAESTHESIA TUTORIAL OF THE WEEK 49 26 TH MARCH 2007 Dr J. Hyndman Questions 1) List the factors that determine the duration of a local anaesthetic nerve block. 2)
PHARMACOLOGY FOR REGIONAL ANAESTHESIA ANAESTHESIA TUTORIAL OF THE WEEK 49 26 TH MARCH 2007 Dr J. Hyndman Questions 1) List the factors that determine the duration of a local anaesthetic nerve block. 2)
LASER TREATMENT FOR RETINAL BREAK OR LATICE DEGENERATION ERIC MANN M.D., Ph.D.
 LASER TREATMENT FOR RETINAL BREAK OR LATICE DEGENERATION ERIC MANN M.D., Ph.D. A. INTRODUCTION Retinal break is an opening on the retina, usually located at the periphery. There may be a hole, or tear.
LASER TREATMENT FOR RETINAL BREAK OR LATICE DEGENERATION ERIC MANN M.D., Ph.D. A. INTRODUCTION Retinal break is an opening on the retina, usually located at the periphery. There may be a hole, or tear.
Hemodynamic Effects of 2% Lidocaine with 1:80000 Epinephrine in Inferior Alveolar Nerve Block
 4 Hemodynamic Effects of 2% Lidocaine with 1:80000 Epinephrine in Inferior Alveolar Nerve Block ABSTRACT A. Haghighat DDS*, N. Kaviani MD*, R. Panahi DDS** Introduction: Lidocaine plus epinephrine is the
4 Hemodynamic Effects of 2% Lidocaine with 1:80000 Epinephrine in Inferior Alveolar Nerve Block ABSTRACT A. Haghighat DDS*, N. Kaviani MD*, R. Panahi DDS** Introduction: Lidocaine plus epinephrine is the
Epidural Anesthesia. Advantages of Epidural Anesthesia
 Epidural Anesthesia Epidural anesthesia involves the use of local anesthetics injected into the epidural space to produce a reversible loss of sensation and motor function. Epidural anesthesia requires
Epidural Anesthesia Epidural anesthesia involves the use of local anesthetics injected into the epidural space to produce a reversible loss of sensation and motor function. Epidural anesthesia requires
INTERSCALENE BLOCK AND OTHER ARTICLES ON ANESTHESIA FOR ARTHROSCOPIC SURGERY NOT QUALIFYING AS EVIDENCE
 INTERSCALENE BLOCK AND OTHER ARTICLES ON ANESTHESIA FOR ARTHROSCOPIC SURGERY NOT QUALIFYING AS EVIDENCE Hughes MS, Matava MJ, et al. Interscalene Brachial Plexus Block for Arthroscopic Shoulder Surgery.
INTERSCALENE BLOCK AND OTHER ARTICLES ON ANESTHESIA FOR ARTHROSCOPIC SURGERY NOT QUALIFYING AS EVIDENCE Hughes MS, Matava MJ, et al. Interscalene Brachial Plexus Block for Arthroscopic Shoulder Surgery.
Local Anaesthetic Systemic Toxicity. Dr Thomas Engelhardt, MD, PhD, FRCA Royal Aberdeen Children s Hospital, Scotland
 Local Anaesthetic Systemic Toxicity Dr Thomas Engelhardt, MD, PhD, FRCA Royal Aberdeen Children s Hospital, Scotland Conflict of interest None Overview Local anesthetic systemic toxicity (LAST) Background
Local Anaesthetic Systemic Toxicity Dr Thomas Engelhardt, MD, PhD, FRCA Royal Aberdeen Children s Hospital, Scotland Conflict of interest None Overview Local anesthetic systemic toxicity (LAST) Background
CRYOTHERAPY FOR RETINAL BREAK, LATTICE DEGENERATION, OR LIMITED RETINAL DETACHMENT ERIC S. MANN M.D., Ph.D.
 CRYOTHERAPY FOR RETINAL BREAK, LATTICE DEGENERATION, OR LIMITED RETINAL DETACHMENT ERIC S. MANN M.D., Ph.D. A. INTRODUCTION: Retinal break is an opening on the retina, usually located at the periphery.
CRYOTHERAPY FOR RETINAL BREAK, LATTICE DEGENERATION, OR LIMITED RETINAL DETACHMENT ERIC S. MANN M.D., Ph.D. A. INTRODUCTION: Retinal break is an opening on the retina, usually located at the periphery.
PHARMACOLOGY OF REGIONAL ANAESTHESIA Author John Hyndman
 PHARMACOLOGY OF REGIONAL ANAESTHESIA Author John Hyndman Web Editor Jo Loader - jloader@doctors.org.uk Questions 1) List the factors that determine the duration of a local anaesthetic nerve block. 2) How
PHARMACOLOGY OF REGIONAL ANAESTHESIA Author John Hyndman Web Editor Jo Loader - jloader@doctors.org.uk Questions 1) List the factors that determine the duration of a local anaesthetic nerve block. 2) How
Chapter 3. Ulnar nerve infiltration
 Chapter 3 LOCAL ANESTHESIA KEY FIGURES: Digital block/anatomy Sensation to hand Median nerve infiltration Ulnar nerve infiltration Facial block: skeleton Full surgical evaluation of a wound and suture
Chapter 3 LOCAL ANESTHESIA KEY FIGURES: Digital block/anatomy Sensation to hand Median nerve infiltration Ulnar nerve infiltration Facial block: skeleton Full surgical evaluation of a wound and suture
Getting Ready for ICD-10. Dianna Hoskins, OCS Cincinnati Eye Institute
 Dianna Hoskins, OCS Cincinnati Eye Institute Chart Documentation: Will your documentation stand up to ICD-10? Do you always mark which eye, severity or status of the disease (chronic or acute), site, etiology
Dianna Hoskins, OCS Cincinnati Eye Institute Chart Documentation: Will your documentation stand up to ICD-10? Do you always mark which eye, severity or status of the disease (chronic or acute), site, etiology
The effects of adding epinephrine to ropivacaine for popliteal nerve block on the duration of postoperative analgesia: a randomized controlled trial
 Schoenmakers et al. BMC Anesthesiology (2015) 15:100 DOI 10.1186/s12871-015-0083-z RESEARCH ARTICLE The effects of adding epinephrine to ropivacaine for popliteal nerve block on the duration of postoperative
Schoenmakers et al. BMC Anesthesiology (2015) 15:100 DOI 10.1186/s12871-015-0083-z RESEARCH ARTICLE The effects of adding epinephrine to ropivacaine for popliteal nerve block on the duration of postoperative
Amita Agarwal, Jithendra KD, Aditya Sinha, Mohit Garg, Satendra Sharma, Ashish Singh
 Original research AODMR To evaluate the anesthetic efficacy of sodium bicarbonate buffered 2% lidocaine with : A prospective, randomized, double-blind study Amita Agarwal, Jithendra KD, Aditya Sinha, Mohit
Original research AODMR To evaluate the anesthetic efficacy of sodium bicarbonate buffered 2% lidocaine with : A prospective, randomized, double-blind study Amita Agarwal, Jithendra KD, Aditya Sinha, Mohit
PERIOCULAR (SUBTENON) STEROID INJECTION ERIC S. MANN M.D.,Ph.D.
 PERIOCULAR (SUBTENON) STEROID INJECTION ERIC S. MANN M.D.,Ph.D. A. INDICATIONS: Periocular steroid injection involves placement of steroid around the eye to treat intraocular inflammation or swelling of
PERIOCULAR (SUBTENON) STEROID INJECTION ERIC S. MANN M.D.,Ph.D. A. INDICATIONS: Periocular steroid injection involves placement of steroid around the eye to treat intraocular inflammation or swelling of
2.0 Synopsis. Vicodin CR (ABT-712) M05-765 Clinical Study Report R&D/07/095. (For National Authority Use Only) to Part of Dossier: Volume:
 2.0 Synopsis Abbott Laboratories Name of Study Drug: Vicodin CR Name of Active Ingredient: Hydrocodone/Acetaminophen Extended Release (ABT-712) Individual Study Table Referring to Part of Dossier: Volume:
2.0 Synopsis Abbott Laboratories Name of Study Drug: Vicodin CR Name of Active Ingredient: Hydrocodone/Acetaminophen Extended Release (ABT-712) Individual Study Table Referring to Part of Dossier: Volume:
5 Upper eyelid blepharoplasty
 5 Upper eyelid blepharoplasty INSTRUMENTS Marking pen No. 15 scalpel blade Blade handle Castroviejo needle holder Castroviejo calipers 0.5 fixation forceps Westcott scissors 6-0 prolene suture Bovie cautery
5 Upper eyelid blepharoplasty INSTRUMENTS Marking pen No. 15 scalpel blade Blade handle Castroviejo needle holder Castroviejo calipers 0.5 fixation forceps Westcott scissors 6-0 prolene suture Bovie cautery
Interscalene Block. Nancy A. Brown, MD
 Interscalene Block Nancy A. Brown, MD What is an Interscalene Block? An Interscalene block is a form of regional anesthesia used in conjunction with general anesthesia for surgeries of the shoulder and
Interscalene Block Nancy A. Brown, MD What is an Interscalene Block? An Interscalene block is a form of regional anesthesia used in conjunction with general anesthesia for surgeries of the shoulder and
Supraclavicular Brachial plexus block using Lidocaine with Adrenaline and Dexomethasone as an adjunct A study on 60 cases
 Original Article Supraclavicular Brachial plexus block using Lidocaine with Adrenaline and Dexomethasone as an adjunct A study on 60 cases E.Devandar Reddy 1, S.Srikanth 2 1 Assistant Professor, Department
Original Article Supraclavicular Brachial plexus block using Lidocaine with Adrenaline and Dexomethasone as an adjunct A study on 60 cases E.Devandar Reddy 1, S.Srikanth 2 1 Assistant Professor, Department
Nick Strouthidis MBBS MD PhD FRCS FRCOphth FRANZCO CONSULTANT OPHTHALMIC SURGEON
 TUBES/SHUNTS TUBES/SHUNTS Implantation of a glaucoma drainage device (GDD - also known as a tube or aqueous shunt) works by diverting aqueous from the front of the eye via a tube to a drainage plate stitched
TUBES/SHUNTS TUBES/SHUNTS Implantation of a glaucoma drainage device (GDD - also known as a tube or aqueous shunt) works by diverting aqueous from the front of the eye via a tube to a drainage plate stitched
Infiltration and Topical and Anesthesia
 Infiltration and Topical and Anesthesia On occasion, anesthesia providers will place field blocks either as supplementation for a marginal regional anesthetic block or as the sole form of anesthesia. In
Infiltration and Topical and Anesthesia On occasion, anesthesia providers will place field blocks either as supplementation for a marginal regional anesthetic block or as the sole form of anesthesia. In
BRANCH RETINAL VEIN OCCLUSION (BRVO) AND LASER TREATMENT
 INTRODUCTION: BRANCH RETINAL VEIN OCCLUSION (BRVO) AND LASER TREATMENT Branch Retinal Vein Occlusion (BRVO) involves the obstruction of a major venous blood vessel which prevents adequate drainage of blood
INTRODUCTION: BRANCH RETINAL VEIN OCCLUSION (BRVO) AND LASER TREATMENT Branch Retinal Vein Occlusion (BRVO) involves the obstruction of a major venous blood vessel which prevents adequate drainage of blood
Email: info@surgicalskillstraining.com Web: www.surgicalskillstraining.com
 Email: info@surgicalskillstraining.com Web: www.surgicalskillstraining.com 1945 Scottsville RD, B-2, PMB 116 - Bowling Green, KY 42104-5817 KLC-Kentucky Limited Liability Company Program Catalog The Surgical
Email: info@surgicalskillstraining.com Web: www.surgicalskillstraining.com 1945 Scottsville RD, B-2, PMB 116 - Bowling Green, KY 42104-5817 KLC-Kentucky Limited Liability Company Program Catalog The Surgical
Cold as an adjunctive therapy for headache
 Cold as an adjunctive therapy for headache Seymour Diamond, MD Frederick G. Freltag, DO Preview Patients with acute headache are often so vexed by pain that they seek out numerous physicians and headache
Cold as an adjunctive therapy for headache Seymour Diamond, MD Frederick G. Freltag, DO Preview Patients with acute headache are often so vexed by pain that they seek out numerous physicians and headache
Laser Procedure Note
 Laser Procedure Note Patient Name Date 1. Pre procedure diagnosis 2. Procedure and Eye Eye: 3. Pre procedure topical medications administered (and time) 4. Vital signs BP / HR Acuity OD: OS: 5. IOP: OD
Laser Procedure Note Patient Name Date 1. Pre procedure diagnosis 2. Procedure and Eye Eye: 3. Pre procedure topical medications administered (and time) 4. Vital signs BP / HR Acuity OD: OS: 5. IOP: OD
Safety of digital injections with epinephrine. A Review of the Literature
 Safety of digital injections with epinephrine A Review of the Literature 2 ABSTRACT Introduction The belief that injections of epinephrine into end-artery sites causes gangrene stems from 48 cases of digital
Safety of digital injections with epinephrine A Review of the Literature 2 ABSTRACT Introduction The belief that injections of epinephrine into end-artery sites causes gangrene stems from 48 cases of digital
Local Anaesthetic Toxicity and Tumescent Anaesthesia
 Local Anaesthetic Toxicity and Tumescent Anaesthesia Local anaesthetics are important tools used in the everyday practice of medicine. The first local anaesthetic was cocaine. In 1884, Koller used topical
Local Anaesthetic Toxicity and Tumescent Anaesthesia Local anaesthetics are important tools used in the everyday practice of medicine. The first local anaesthetic was cocaine. In 1884, Koller used topical
Glaucoma filtration surgery (Trabeculectomy)
 Oxford Eye Hospital Glaucoma filtration surgery (Trabeculectomy) Information for patients This leaflet gives you information that will help you decide whether to have glaucoma surgery. You might want to
Oxford Eye Hospital Glaucoma filtration surgery (Trabeculectomy) Information for patients This leaflet gives you information that will help you decide whether to have glaucoma surgery. You might want to
Institute of Ophthalmology. Thyroid Eye Disease. aka Thyroid Associated Ophthalmopathy
 Institute of Ophthalmology Thyroid Eye Disease aka Thyroid Associated Ophthalmopathy Causes TED/TAO is an eye disease associated with disease of the thyroid gland Most commonly, it occurs with an overactive
Institute of Ophthalmology Thyroid Eye Disease aka Thyroid Associated Ophthalmopathy Causes TED/TAO is an eye disease associated with disease of the thyroid gland Most commonly, it occurs with an overactive
Local Anesthesia for the. Cerec Appointment
 Local Anesthesia for the Cerec Appointment Stanley F. Malamed, DDS Dentist Anesthesiologist Emeritus Professor of Dentistry Ostrow School of Dentistry of USC Los Angeles, California, USA Stanley F. MALAMED,
Local Anesthesia for the Cerec Appointment Stanley F. Malamed, DDS Dentist Anesthesiologist Emeritus Professor of Dentistry Ostrow School of Dentistry of USC Los Angeles, California, USA Stanley F. MALAMED,
Thyroid eye disease (TED)
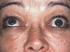 Thyroid eye disease (TED) Mr David H Verity, MD MA FRCOphth Consultant Ophthalmic Surgeon Synonyms: Graves ophthalmopathy, thyroid ophthalmopathy, thyroid associated ophthalmopathy This information leaflet
Thyroid eye disease (TED) Mr David H Verity, MD MA FRCOphth Consultant Ophthalmic Surgeon Synonyms: Graves ophthalmopathy, thyroid ophthalmopathy, thyroid associated ophthalmopathy This information leaflet
Comparison of emergence times with different fresh gas flow rates following desflurane anaesthesia
 Research Report Comparison of emergence times with different fresh gas flow rates following desflurane anaesthesia Journal of International Medical Research 2014, Vol. 42(6) 1285 1293! The Author(s) 2014
Research Report Comparison of emergence times with different fresh gas flow rates following desflurane anaesthesia Journal of International Medical Research 2014, Vol. 42(6) 1285 1293! The Author(s) 2014
International Training Program for Nurse Anesthetist The program: International training program for nurse anesthetist Name of certificate:
 International Training Program for Nurse Anesthetist Department of Anesthesiology Faculty of Medicine Siriraj Hospital Mahidol University, Bangkok, Thailand The program: International training program
International Training Program for Nurse Anesthetist Department of Anesthesiology Faculty of Medicine Siriraj Hospital Mahidol University, Bangkok, Thailand The program: International training program
Spinal Anesthesia. Contraindications Please review Chapter 2 for contraindications.
 Spinal Anesthesia Spinal anesthesia involves the use of small amounts of local anesthetic injected into the subarachnoid space to produce a reversible loss of sensation and motor function. The anesthesia
Spinal Anesthesia Spinal anesthesia involves the use of small amounts of local anesthetic injected into the subarachnoid space to produce a reversible loss of sensation and motor function. The anesthesia
CH CONSCIOUS SEDATION
 Summary: CH CONSCIOUS SEDATION It is the policy of Carondelet Health that moderate conscious sedation of patients will be undertaken with appropriate evaluation and monitoring. Effective Date: 9/4/04 Revision
Summary: CH CONSCIOUS SEDATION It is the policy of Carondelet Health that moderate conscious sedation of patients will be undertaken with appropriate evaluation and monitoring. Effective Date: 9/4/04 Revision
Information For Consent For Cataract Surgery
 Information For Consent For Cataract Surgery Your Ophthalmologist has diagnosed you with a visually significant cataract. The following handout will explain your condition and give you the information
Information For Consent For Cataract Surgery Your Ophthalmologist has diagnosed you with a visually significant cataract. The following handout will explain your condition and give you the information
Aesthetic Facial Plastic Surgery, PLLC 1810 116th Ave NE #102 Bellevue, WA 98004
 Aesthetic Facial Plastic Surgery, PLLC 1810 116th Ave NE #102 Bellevue, WA 98004 GENERAL, HIPAA, PHOTO VIDEO INFORMED CONSENT FORM, AND RELEASE AGREEMENT Aesthetic Facial Plastic Surgery, PLLC s ("AFPS"),
Aesthetic Facial Plastic Surgery, PLLC 1810 116th Ave NE #102 Bellevue, WA 98004 GENERAL, HIPAA, PHOTO VIDEO INFORMED CONSENT FORM, AND RELEASE AGREEMENT Aesthetic Facial Plastic Surgery, PLLC s ("AFPS"),
ANESTHESIA - Medicare
 ANESTHESIA - Medicare Policy Number: UM14P0008A2 Effective Date: August 19, 2014 Last Reviewed: January 1, 2016 PAYMENT POLICY HISTORY Version DATE ACTION / DESCRIPTION Version 2 January 1, 2016 Under
ANESTHESIA - Medicare Policy Number: UM14P0008A2 Effective Date: August 19, 2014 Last Reviewed: January 1, 2016 PAYMENT POLICY HISTORY Version DATE ACTION / DESCRIPTION Version 2 January 1, 2016 Under
Feasibility of an Infraclavicular Block With a Reduced Volume of Lidocaine With Sonographic Guidance
 Technical Advance Feasibility of an Infraclavicular Block With a Reduced Volume of Lidocaine With Sonographic Guidance NavParkash S. Sandhu, MD, Charanjeet S. Bahniwal, MD, Levon M. Capan, MD Objective.
Technical Advance Feasibility of an Infraclavicular Block With a Reduced Volume of Lidocaine With Sonographic Guidance NavParkash S. Sandhu, MD, Charanjeet S. Bahniwal, MD, Levon M. Capan, MD Objective.
With the shift away from costly preoperative
 BRIEF REPORTS Are Patients Comfortable Consenting to Clinical Anesthesia Research Trials on the Day of Surgery? Richard Brull, MD, Colin J. L. McCartney, MBChB, FRCA, FFARCSI, Vincent W. S. Chan, MD, FRCPC,
BRIEF REPORTS Are Patients Comfortable Consenting to Clinical Anesthesia Research Trials on the Day of Surgery? Richard Brull, MD, Colin J. L. McCartney, MBChB, FRCA, FFARCSI, Vincent W. S. Chan, MD, FRCPC,
Double-Blind, Bilateral Pain Comparison with Simultaneous Injection of 2% Lidocaine versus Buffered 2% Lidocaine for Periocular Anesthesia
 Double-Blind, Bilateral Pain Comparison with Simultaneous Injection of 2% Lidocaine versus Buffered 2% Lidocaine for Periocular Anesthesia Mark N. Welch, DO, 1 Craig N. Czyz, DO, FACOS, 2 Kevin Kalwerisky,
Double-Blind, Bilateral Pain Comparison with Simultaneous Injection of 2% Lidocaine versus Buffered 2% Lidocaine for Periocular Anesthesia Mark N. Welch, DO, 1 Craig N. Czyz, DO, FACOS, 2 Kevin Kalwerisky,
Complications associated with retrobulbar regional anaesthesia in bovine:
 Complications associated with retrobulbar regional anaesthesia in bovine: Case report Case report submitted in partial fulfillment of the Masters of Veterinary Surgery of the University of Nairobi. Author
Complications associated with retrobulbar regional anaesthesia in bovine: Case report Case report submitted in partial fulfillment of the Masters of Veterinary Surgery of the University of Nairobi. Author
Thyroid eye disease (TED) Synonyms: Graves ophthalmopathy, thyroid ophthalmopathy, thyroid associated ophthalmopathy
 Thyroid eye disease (TED) Synonyms: Graves ophthalmopathy, thyroid ophthalmopathy, thyroid associated ophthalmopathy This information leaflet briefly covers the following issues in TED: What is TED? When
Thyroid eye disease (TED) Synonyms: Graves ophthalmopathy, thyroid ophthalmopathy, thyroid associated ophthalmopathy This information leaflet briefly covers the following issues in TED: What is TED? When
Thyroid Eye Disease. Anatomy: There are 6 muscles that move your eye.
 Thyroid Eye Disease Your doctor thinks you have thyroid orbitopathy. This is an autoimmune condition where your body's immune system is producing factors that stimulate enlargement of the muscles that
Thyroid Eye Disease Your doctor thinks you have thyroid orbitopathy. This is an autoimmune condition where your body's immune system is producing factors that stimulate enlargement of the muscles that
Complications Associated With Eye Blocks and Peripheral Nerve Blocks: An American Society of Anesthesiologists Closed Claims Analysis
 Complications Associated With Eye Blocks and Peripheral Nerve Blocks: An American Society of Anesthesiologists Closed Claims Analysis Lorri A. Lee, M.D., Karen L. Posner, Ph.D., Frederick W. Cheney, M.D.,
Complications Associated With Eye Blocks and Peripheral Nerve Blocks: An American Society of Anesthesiologists Closed Claims Analysis Lorri A. Lee, M.D., Karen L. Posner, Ph.D., Frederick W. Cheney, M.D.,
CODING AND COMPLIANCE NEW APPOINTMENT AND REAPPOINTMENT MODULE FOR ANESTHESIA FACULTY
 CODING AND COMPLIANCE NEW APPOINTMENT AND REAPPOINTMENT MODULE FOR ANESTHESIA FACULTY ANESTHESIA BILLING: MUST BE DOCUMENTED AS: Personally performed: you perform the case without a resident or a CRNA
CODING AND COMPLIANCE NEW APPOINTMENT AND REAPPOINTMENT MODULE FOR ANESTHESIA FACULTY ANESTHESIA BILLING: MUST BE DOCUMENTED AS: Personally performed: you perform the case without a resident or a CRNA
Local Anaesthetics. Local anesthetics (LA) Part 1: Basic facts Part 2: Clinical aspects. 1. Reversible. blockade of conduction in peripheral nerves
 Local Anaesthetics Part 1: Basic facts Part 2: Clinical aspects Local anesthetics (LA) 1. Reversible. blockade of conduction in peripheral nerves pain 2. Lowers myocardial excitability Treatment of arythmia
Local Anaesthetics Part 1: Basic facts Part 2: Clinical aspects Local anesthetics (LA) 1. Reversible. blockade of conduction in peripheral nerves pain 2. Lowers myocardial excitability Treatment of arythmia
Anesthesia Management of Ophthalmic Surgery in Geriatric Patients. 1. Overview of Ophthalmic Surgery and Anesthesia
 Anesthesia Management of Ophthalmic Surgery in Geriatric Patients Zhuang T. Fang, M.D., MSPH Clinical Professor Associate Director, the Jules Stein Eye Institute Operating Rooms Department of Anesthesiology
Anesthesia Management of Ophthalmic Surgery in Geriatric Patients Zhuang T. Fang, M.D., MSPH Clinical Professor Associate Director, the Jules Stein Eye Institute Operating Rooms Department of Anesthesiology
Explanation of the Procedure
 Informed Consent Cataract Surgery with Intraocular Lens Implant Please initial below indicating that you have read and understand each section Introduction The internal lens of the eye can become cloudy
Informed Consent Cataract Surgery with Intraocular Lens Implant Please initial below indicating that you have read and understand each section Introduction The internal lens of the eye can become cloudy
Epinephrine and clonidine do not improve intrathecal sufentanil analgesia after total hip replacement ²
 British Journal of Anaesthesia 89 (4): 562±6 (2002) Epinephrine and clonidine do not improve intrathecal sufentanil analgesia after total hip replacement ² R. Fournier*, E. Van Gessel, A. Weber and Z.
British Journal of Anaesthesia 89 (4): 562±6 (2002) Epinephrine and clonidine do not improve intrathecal sufentanil analgesia after total hip replacement ² R. Fournier*, E. Van Gessel, A. Weber and Z.
EUROPEAN JOURNAL OF PHARMACEUTICAL AND MEDICAL RESEARCH www.ejpmr.com
 ejpmr, 2015,2(3), 436-440 EUROPEAN JOURNAL OF PHARMACEUTICAL AND MEDICAL RESEARCH www.ejpmr.com Tumram et al. SJIF Impact Factor 2.026 Research Article ISSN 3294-3211 EJPMR CLINICAL OUTCOME OF TORIC IOL
ejpmr, 2015,2(3), 436-440 EUROPEAN JOURNAL OF PHARMACEUTICAL AND MEDICAL RESEARCH www.ejpmr.com Tumram et al. SJIF Impact Factor 2.026 Research Article ISSN 3294-3211 EJPMR CLINICAL OUTCOME OF TORIC IOL
The Impact of Regional Anesthesia on Perioperative Outcomes By Dr. David Nelson
 The Impact of Regional Anesthesia on Perioperative Outcomes By Dr. David Nelson As a private practice anesthesiologist, I am often asked: What are the potential benefits of regional anesthesia (RA)? My
The Impact of Regional Anesthesia on Perioperative Outcomes By Dr. David Nelson As a private practice anesthesiologist, I am often asked: What are the potential benefits of regional anesthesia (RA)? My
La décompression orbitaire dans la maladie de Basedow
 La décompression orbitaire dans la maladie de Basedow P. Mahy 1, C. Daumerie 2, A. Boschi 3 Services de stomatologie et chirurgie maxillo-faciale 1 d endocrinologie et de nutrition 2 et d ophtalmologie
La décompression orbitaire dans la maladie de Basedow P. Mahy 1, C. Daumerie 2, A. Boschi 3 Services de stomatologie et chirurgie maxillo-faciale 1 d endocrinologie et de nutrition 2 et d ophtalmologie
Overview of Outpatient Care Settings and Ambulatory Surgery Centers
 Overview of Outpatient Care Settings and Ambulatory Surgery Centers Agency for Health Care Administration Molly McKinstry, Deputy Secretary Health Quality Assurance Surgical Settings Ambulatory Surgery
Overview of Outpatient Care Settings and Ambulatory Surgery Centers Agency for Health Care Administration Molly McKinstry, Deputy Secretary Health Quality Assurance Surgical Settings Ambulatory Surgery
developed in the 1930 s Amides had a faster onset and a longer half life so they lasted longer Amides quickly ikl replaced esters In dentistry today,
 Local Anesthetics History The first local anesthetics were cocaine and procaine (Novacain) developed in lt late 1800 s They were called esters because of their chemical composition Esters had a slow onset
Local Anesthetics History The first local anesthetics were cocaine and procaine (Novacain) developed in lt late 1800 s They were called esters because of their chemical composition Esters had a slow onset
Retrobulbar block: A review for the clinician
 Retrobulbar block: A review for the clinician DAN SIMONSON, CRNA, BSN Spokane, Washington Recent improvements in technique have made cataract surgery a popular procedure in the outpatient setting. One
Retrobulbar block: A review for the clinician DAN SIMONSON, CRNA, BSN Spokane, Washington Recent improvements in technique have made cataract surgery a popular procedure in the outpatient setting. One
Stuart B Black MD, FAAN Chief of Neurology Co-Medical Director: Neuroscience Center Baylor University Medical Center at Dallas
 Billing and Coding in Neurology and Headache Stuart B Black MD, FAAN Chief of Neurology Co-Medical Director: Neuroscience Center Baylor University Medical Center at Dallas CPT Codes vs. ICD Codes Category
Billing and Coding in Neurology and Headache Stuart B Black MD, FAAN Chief of Neurology Co-Medical Director: Neuroscience Center Baylor University Medical Center at Dallas CPT Codes vs. ICD Codes Category
Your anaesthetist may suggest that you have a spinal or epidural injection. These
 Risks associated with your anaesthetic Section 11: Nerve damage associated with a spinal or epidural injection Your anaesthetist may suggest that you have a spinal or epidural injection. These injections
Risks associated with your anaesthetic Section 11: Nerve damage associated with a spinal or epidural injection Your anaesthetist may suggest that you have a spinal or epidural injection. These injections
PANRETINAL PHOTOCOAGULATION (PRP) FOR RUBEOSIS AND NEOVASCULAR GLAUCOMA ERIC S. MANN M.D., Ph.D.
 PANRETINAL PHOTOCOAGULATION (PRP) FOR RUBEOSIS AND NEOVASCULAR GLAUCOMA ERIC S. MANN M.D., Ph.D. A. INTRODUCTION Rubeosis involves the growth of abnormal blood vessels on the iris (the diaphragm-like structure
PANRETINAL PHOTOCOAGULATION (PRP) FOR RUBEOSIS AND NEOVASCULAR GLAUCOMA ERIC S. MANN M.D., Ph.D. A. INTRODUCTION Rubeosis involves the growth of abnormal blood vessels on the iris (the diaphragm-like structure
Corporate Medical Policy
 File Name: anesthesia_services Origination: 8/2007 Last CAP Review: 1/2016 Next CAP Review: 1/2017 Last Review: 1/2016 Corporate Medical Policy Description of Procedure or Service There are three main
File Name: anesthesia_services Origination: 8/2007 Last CAP Review: 1/2016 Next CAP Review: 1/2017 Last Review: 1/2016 Corporate Medical Policy Description of Procedure or Service There are three main
Evaluation of a Morphine Weaning Protocol in Pediatric Intensive Care Patients
 Evaluation of a Morphine Weaning Protocol in Pediatric Intensive Care Patients Jennifer Kuhns, Pharm.D. Pharmacy Practice Resident Children s Hospital of Michigan **The speaker has no actual or potential
Evaluation of a Morphine Weaning Protocol in Pediatric Intensive Care Patients Jennifer Kuhns, Pharm.D. Pharmacy Practice Resident Children s Hospital of Michigan **The speaker has no actual or potential
Interventional MRI (imri) guided Deep Brain Stimulation for Parkinson s Disease
 Interventional MRI (imri) guided Deep Brain Stimulation for Parkinson s Disease Anesthetic considerations A case study Lydia Cendana University of Pittsburgh School of Nurse Anesthesia Parkinson s disease
Interventional MRI (imri) guided Deep Brain Stimulation for Parkinson s Disease Anesthetic considerations A case study Lydia Cendana University of Pittsburgh School of Nurse Anesthesia Parkinson s disease
Understanding the Pain Trajectory During Treadmill Testing in Peripheral Artery Disease
 Understanding the Pain Trajectory During Treadmill Testing in Peripheral Artery Disease Diane Treat-Jacobson, PhD, RN, FAHA, FAAN Susan J. Henly, PhD, RN Ulf G. Bronas, PhD, ATC, ATR Arthur S. Leon, MD,
Understanding the Pain Trajectory During Treadmill Testing in Peripheral Artery Disease Diane Treat-Jacobson, PhD, RN, FAHA, FAAN Susan J. Henly, PhD, RN Ulf G. Bronas, PhD, ATC, ATR Arthur S. Leon, MD,
Can Elimination of Epinephrine in Rhinoplasty Reduce the Side Effects: Introduction of a New Technique
 DOI 10.1007/s00266-011-9673-4 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Can Elimination of Epinephrine in Rhinoplasty Reduce the Side Effects: Introduction of a New Technique Abdoljalil Kalantar-Hormozi Alireza Fadaee-Naeeni Siavash
DOI 10.1007/s00266-011-9673-4 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Can Elimination of Epinephrine in Rhinoplasty Reduce the Side Effects: Introduction of a New Technique Abdoljalil Kalantar-Hormozi Alireza Fadaee-Naeeni Siavash
A Phase 2 Study of HTX-011 in the Management of Post-Operative Pain Positive Top-Line Results
 A Phase 2 Study of HTX-011 in the Management of Post-Operative Pain Positive Top-Line Results September 22, 2015 Forward-Looking Statements This presentation contains "forward-looking statements" as defined
A Phase 2 Study of HTX-011 in the Management of Post-Operative Pain Positive Top-Line Results September 22, 2015 Forward-Looking Statements This presentation contains "forward-looking statements" as defined
Oregon Eye Specialists, PC YOUR GUIDE CATARACT SURGERY. Improving VISION. Improving LIFE.
 Oregon Eye Specialists, PC YOUR GUIDE TO CATARACT SURGERY Dinelli M. Monson, M.D. Comprehensive Ophthalmology Physician and Surgeon Tualatin Clinic: 19250 SW 65 th Ave, Ste 215 503.692.3630 Newberg Clinic:
Oregon Eye Specialists, PC YOUR GUIDE TO CATARACT SURGERY Dinelli M. Monson, M.D. Comprehensive Ophthalmology Physician and Surgeon Tualatin Clinic: 19250 SW 65 th Ave, Ste 215 503.692.3630 Newberg Clinic:
INTRAOSSEOUS ANESTHESIA
 ENDODONTICS: Colleagues for Excellence Winter 2009 Bonus Material F INTRAOSSEOUS ANESTHESIA Intraosseous Anesthesia With the Stabident and X Tip Systems The intraosseous injection allows placement of a
ENDODONTICS: Colleagues for Excellence Winter 2009 Bonus Material F INTRAOSSEOUS ANESTHESIA Intraosseous Anesthesia With the Stabident and X Tip Systems The intraosseous injection allows placement of a
British Journal of Anaesthesia 82 (4): 570 4 (1999)
 British Journal of Anaesthesia 82 (4): 570 4 (1999) Oral mucosal blood flow, plasma epinephrine and haemodynamic responses after injection of lidocaine with epinephrine during midazolam sedation and isoflurane
British Journal of Anaesthesia 82 (4): 570 4 (1999) Oral mucosal blood flow, plasma epinephrine and haemodynamic responses after injection of lidocaine with epinephrine during midazolam sedation and isoflurane
Liau DW : Injuries and Liability Related to Peripheral Catheters: A Closed Claims Analysis. ASA Newsletter 70(6): 11-13 & 16, 2006.
 Citation Liau DW : Injuries and Liability Related to Peripheral Catheters: A Closed Claims Analysis. ASA Newsletter 70(6): 11-13 & 16, 2006. Full Text An anesthesiologist inserted a 14-gauge peripheral
Citation Liau DW : Injuries and Liability Related to Peripheral Catheters: A Closed Claims Analysis. ASA Newsletter 70(6): 11-13 & 16, 2006. Full Text An anesthesiologist inserted a 14-gauge peripheral
Cataract Surgery Patient Information
 Cataract Patient Information 1. Within the human eye, there is a normal structure called the lens. In youth, this lens is clear, and light rays pass through and are focused by this lens as well as the
Cataract Patient Information 1. Within the human eye, there is a normal structure called the lens. In youth, this lens is clear, and light rays pass through and are focused by this lens as well as the
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Br J Anaesth. Author manuscript; available in PMC 2007 January 16.
 NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Br J Anaesth. 2005 August ; 95(2): 250 254. The use of a stimulating catheter for total knee replacement surgery - preliminary results
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Br J Anaesth. 2005 August ; 95(2): 250 254. The use of a stimulating catheter for total knee replacement surgery - preliminary results
Experience with Lignocaine 0.1% With Adrenaline1:1,000,000 In 328 General Surgery Patients.
 10 Original Article Experience with Lignocaine 0.1% With Adrenaline1:1,000,000 In 328 General Surgery Patients. K.L. Yerzingatsian FRCSI Department Of Surgery University Teaching Hospital, P O Box 50110,
10 Original Article Experience with Lignocaine 0.1% With Adrenaline1:1,000,000 In 328 General Surgery Patients. K.L. Yerzingatsian FRCSI Department Of Surgery University Teaching Hospital, P O Box 50110,
ADVANCED SUTURING WORKSHOP ANN BECKER, APRN-CNP; TONI PRATT-REID, APRN-CNP
 ADVANCED SUTURING WORKSHOP ANN BECKER, APRN-CNP; TONI PRATT-REID, APRN-CNP SUTURING WORKSHOP! The technique of suturing, as a method for closing cutaneous wounds has been a part of medicine for hundreds
ADVANCED SUTURING WORKSHOP ANN BECKER, APRN-CNP; TONI PRATT-REID, APRN-CNP SUTURING WORKSHOP! The technique of suturing, as a method for closing cutaneous wounds has been a part of medicine for hundreds
Comparison of ropivacaine 0.2% and 0.25% with lidocaine 0.5% for intravenous regional anesthesia
 Journal of Clinical Anesthesia (2009) 21, 401 407 Original contribution Comparison of ropivacaine 0.2% and 0.25% with lidocaine 0.5% for intravenous regional anesthesia Ibrahim Asik MD (Associate Professor)
Journal of Clinical Anesthesia (2009) 21, 401 407 Original contribution Comparison of ropivacaine 0.2% and 0.25% with lidocaine 0.5% for intravenous regional anesthesia Ibrahim Asik MD (Associate Professor)
Research Article. Dr. Snehal P. Gade, Assistant Professor, Department of Ophthalmology, Government Medical College Aurangabad, Maharashtra, INDIA.
 Research Article Comparison of surgically induced astigmatism (SIA) and postoperative astigmatism with superior, superotemporal and temporal incisions in phacoemulsification surgery Snehal P Gade 1*, Bhaskar
Research Article Comparison of surgically induced astigmatism (SIA) and postoperative astigmatism with superior, superotemporal and temporal incisions in phacoemulsification surgery Snehal P Gade 1*, Bhaskar
A prospective randomized crossover study of the preemptive analgesic effect of nitrous oxide in oral surgery
 Vol. 98 No. 6 December 2004 ORAL AND MAXILLOFACIAL SURGERY Editor: James R. Hupp A prospective randomized crossover study of the preemptive analgesic effect of nitrous oxide in oral surgery K. S. Ong,
Vol. 98 No. 6 December 2004 ORAL AND MAXILLOFACIAL SURGERY Editor: James R. Hupp A prospective randomized crossover study of the preemptive analgesic effect of nitrous oxide in oral surgery K. S. Ong,
NORTHSIDE ANESTHESIOLOGY CONSULTANTS AND PAIN MANAGEMENT SERVICES
 NORTHSIDE ANESTHESIOLOGY CONSULTANTS AND PAIN MANAGEMENT SERVICES K. Douglas Smith, M.D. Chairman John B. Neeld, Jr., M.D. Sheryl S. Dickman, M.D. Alan R. Kaplan, M.D. Thomas B. West, M.D. Michael E. Maffett,
NORTHSIDE ANESTHESIOLOGY CONSULTANTS AND PAIN MANAGEMENT SERVICES K. Douglas Smith, M.D. Chairman John B. Neeld, Jr., M.D. Sheryl S. Dickman, M.D. Alan R. Kaplan, M.D. Thomas B. West, M.D. Michael E. Maffett,
Glaucoma filtration surgery (Tube surgery)
 Oxford Eye Hospital Glaucoma filtration surgery (Tube surgery) Information for patients page 2 This leaflet gives you information that will help you decide whether to have glaucoma tube surgery. You might
Oxford Eye Hospital Glaucoma filtration surgery (Tube surgery) Information for patients page 2 This leaflet gives you information that will help you decide whether to have glaucoma tube surgery. You might
r JOHNS HOPKINS HEALTHCARE Physician Guidelines Subject: Anesthesia Processing Guidelines Lines of Business: EHP, USFHP, Priority Partners
 Revision Date: 11/14/14 Last Reviewed Date: 11/14/14 Page 1 of 7 ACTION New Procedure Amending Procedure Number: Superseding Procedure Number: Repealing Procedure Number: REFERENCES: AMPT Committee ASA
Revision Date: 11/14/14 Last Reviewed Date: 11/14/14 Page 1 of 7 ACTION New Procedure Amending Procedure Number: Superseding Procedure Number: Repealing Procedure Number: REFERENCES: AMPT Committee ASA
THE ORGANIZATION OF AN ANESTHESIA DEPARTMENT
 THE ORGANIZATION OF AN ANESTHESIA DEPARTMENT Committee of Origin: Quality Management and Departmental Administration (Approved by the ASA House of Delegates on October 15, 2003, and last amended on October
THE ORGANIZATION OF AN ANESTHESIA DEPARTMENT Committee of Origin: Quality Management and Departmental Administration (Approved by the ASA House of Delegates on October 15, 2003, and last amended on October
CONSENT FOR CATARACT SURGERY
 CONSENT FOR CATARACT SURGERY INTRODUCTION The natural crystalline lens can become cloudy due to aging, trauma, disease or medications. This condition is called a cataract. When cataracts become visually
CONSENT FOR CATARACT SURGERY INTRODUCTION The natural crystalline lens can become cloudy due to aging, trauma, disease or medications. This condition is called a cataract. When cataracts become visually
Teaching Corner: Regional anaesthesia for ophthalmic surgery
 Malawi Medical Journal; 24 (4):89-94 December 2012 Teaching Corner: Regional anaesthesia for ophthalmic surgery R.Tighe 1,P. I. Burgess 2,G. Msukwa 1. CURE International Hospital 2. Malawi-Liverpool-Wellcome
Malawi Medical Journal; 24 (4):89-94 December 2012 Teaching Corner: Regional anaesthesia for ophthalmic surgery R.Tighe 1,P. I. Burgess 2,G. Msukwa 1. CURE International Hospital 2. Malawi-Liverpool-Wellcome
Program Specification for Master Degree Anesthesia, ICU and Pain Management
 Cairo University Faculty of Medicine Program type: Single Program Specification for Master Degree Anesthesia, ICU and Pain Management Department offering program: Anesthesia, intensive care and pain management
Cairo University Faculty of Medicine Program type: Single Program Specification for Master Degree Anesthesia, ICU and Pain Management Department offering program: Anesthesia, intensive care and pain management
The Ideal Local Anesthetic. Pain and Anxiety. Percent Solution. Contents cont: Contents of a dental cartridge
 The Ideal Local Anesthetic Pain and Anxiety University of Minnesota Division of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery Ma Ann C. Sabino, DDS PhD Water soluble/stable in solution Non-irritating to nerve Low systemic
The Ideal Local Anesthetic Pain and Anxiety University of Minnesota Division of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery Ma Ann C. Sabino, DDS PhD Water soluble/stable in solution Non-irritating to nerve Low systemic
LOCAL ANESTHETIC CONSIDERATIONS IN PODIATRIC SURGERY
 C H A P T E R 4 3 LOCAL ANESTHETIC CONSIDERATIONS IN PODIATRIC SURGERY Carl A. Kihm, DPM INTRODUCTION Local anesthetic (LA) infiltration, first introduced by Karl Schleich in 1892, has allowed surgeons
C H A P T E R 4 3 LOCAL ANESTHETIC CONSIDERATIONS IN PODIATRIC SURGERY Carl A. Kihm, DPM INTRODUCTION Local anesthetic (LA) infiltration, first introduced by Karl Schleich in 1892, has allowed surgeons
THE GUIDE TO REFRACTIVE LENS EXCHANGE SEE CLEARLY.
 THE GUIDE TO REFRACTIVE LENS EXCHANGE SEE CLEARLY. EVERYBODY WANTS TO SEE CLEARLY Many of us take our sight for granted, whether it s forgetting how often we rely on it to guide us through our day-to-day
THE GUIDE TO REFRACTIVE LENS EXCHANGE SEE CLEARLY. EVERYBODY WANTS TO SEE CLEARLY Many of us take our sight for granted, whether it s forgetting how often we rely on it to guide us through our day-to-day
Understanding Visual Fields, Part III; Which Field Should Be Performed?
 Journal of Ophthalmic Medical Technology Volume 3, Number 1 February 2007 www.jomtonline.com Understanding Visual Fields, Part III; Which Field Should Be Performed? Michael N. Wiggins, MD and Inci Dersu,
Journal of Ophthalmic Medical Technology Volume 3, Number 1 February 2007 www.jomtonline.com Understanding Visual Fields, Part III; Which Field Should Be Performed? Michael N. Wiggins, MD and Inci Dersu,
