Head and Neck Cancer Treatment with Particle Beam Therapy
|
|
|
- Jasmine Jones
- 10 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 621 Head and Neck Cancer Treatment with Particle Beam Therapy Mehrzad Zargarzadeh Faculty of Engineering, Islamic Azad University Science and Research Branch Tehran, Iran Abstract In this century, cancer incidence has become one of the most significant problems concerning human. Conventional radiotherapy damage healthy tissue and in some cases may cause new primary cancers. This problem can be partially solved by hadron therapy which would be more effective and less harmful compared to other forms of radiotherapies used to treat some cancers. Although carbon ion and proton therapy both are effective treatments, they have serious differences which are mentioned in this paper and compared between the two methods. Furthermore, various treatments have been performed on head and neck cancer with hadrons so far will be discussed. Keywords: cancer; proton therapy; carbon ion therapy; Boron neutron capture therapy (BNCT); head; neck 1. Introduction Cancer is the major cause of mortality in economically developed countries claiming about 350,000 lives annually, and is a leading factor of death in developing countries. Head and neck cancer is ranked sixth and considered as the most prevalent cancers throughout the world. Global statistics show the fact that there are about 640,000 cases of head and neck cancer per year, resulting in nearly 350,000 deaths per year [1]. Treating with conventional radiation therapy often harms healthy tissue and organs near the tumor site. Proton therapy uses a highly precise beam in order to target radiation directly at the tumor site, minimizing damage to nearby healthy tissue and organs and greatly reducing the risk of both acute and long-term side effects. Cancers of the oral cavity and pharynx are the most prevalent type of head and neck cancer with approximately 480,000 cases per year [1]. Therapy by radiation, with surgery or chemotherapy can produce lasting locoregional disease control in a high percentage of patients with head and neck cancer. Radiotherapy is usually delivered using high-energy X- rays produced by linear accelerators. Theoretically, it would be possible to treat and cure most patients suffering head and neck cancer by using a high dose of radiation. However, in many treatment situations, the dose is limited and by the presence of adjacent radiosensitive normal tissues. The limitations of X-ray radiotherapy can be substantially overcome by using hadrons (i.e., protons and light ions such as helium, carbon, oxygen and neon, in particular carbon ions). Proton and ion therapy both started in 1954 with patient treatments at the 184-inch cyclotron at LBL Berkeley, first with protons and in later stages with helium beams. Until the closing of the accelerators in the year of 1992 more than 2000 patients went through the treatment and therapy process at Berkeley center. Proton therapy started at Uppsala/Sweden in 1957 while the same treatments activities started at Harvard cyclotron in the year of 1961 (more or less 9000 patients were treated and mostly cured until the year of 2002). Studies indicate that hadrons therapy can be replaced with conventional photon therapy specifically for tumors with low radio sensitivity and critical location. In this research proton, carbon ion therapy and BNCT will be described. In addition the number of treatments and clinical experiments conducted in head and neck cancer will be discussed and compared. 2. STATUS OF PROTON THERAPY In Proton therapy a highly precise beam is used to target radiation directly at the tumor locating point, this act minimizes the possible damages to close healthy tissues and the rest organs and substantially reduces the risk of both severe and long-term side and subsequent effects. Therapy with traditional radiation treatment method often damages the healthy tissues and organs near the tumor site. Proton and ion therapy started in 1954 with patient treatments at the 184-inch cyclotron at LBL Berkeley, first with protons and in later stages with helium beams. Until the closing of the accelerators in 1992 more than 2000 patients were treated at Berkeley. This precision makes proton therapy useful specially for treating brain tumors, head and neck cancers, and tumors located near the spinal cord, heart or lungs. Since the energy emission of the proton beam is confined to the narrow Bragg peak, collateral damage to the surrounding tissues should be reduced, while an increased dose of radiation can be delivered to the tumor. Currently, there exist 10 hospitalbased proton therapy centers working around the world and 15 others are being constructed or are in final completion phases. The PSI or Paul Scherer Institute is the only center in the world has the experience of treatment with intensity modulated proton therapy. Paul Scherer Institute, is the first proton therapy center, has the world s
2 622 only gantry so far using so-called spot-scanningtechnology. For most disease therapy sites and treatment centers, proton therapy treatments typically take about quarter to half an hour each day and are delivered five days a week for nearly four to seven weeks. The course of treatment and time duration per treatment each day differs based on each patient s individual case. 3. Carbon Ion Therapy Since 1990s, the researchers have treated about 5,000 patients using carbon ions in Japan and about 440 patients in Germany. Heavy Ion Medical Accelerator in Chiba (HIMAC) was the central therapy site of the world's first carbon-ion treatment in 1994 and the facility has now treated approximately 3795 patients [2]. In the body, the 12C carbon isotope is able to exchange a nucleon in an interaction to convert it to 11C, after that the 11C decay starts via ß decay, giving off a positron which annihilates, emitting a pair of photons. Carbon ions can also be employed before surgery to shrink a tumor or immediately after surgery because, unlike x-rays or protons, they don t damage the skin. Furthermore, this method might offer a useful tool for assessing unpredictable deviations between planned and actual treatment. They can produce extreme damage to tumor cells by depositing their maximum energy in the Bragg peak. Another advantage in the use of carbon ions is that they can be formed as narrow focused and scanning pencil beams. Therefore, any parts of the tumor will be irradiated. Targeting critical areas such as back bone or spinal cord or optical nerves can be monitored with on-line positron emission tomography (PET) [3-5]. 4. Biological Factors Related To Radiation Linear Energy Transfer (LET) is a method used to express and describe beam quality. It is the rate of energy deposited or lost per distance travelled. Hadrons may have the property of low or high Linear Energy transfer. High LET radiation creates various and multi-dimensional damages and harms in DNA and other cellular structures, yielding tumor killing with fewer side effects on normal tissue [4,6]. Since the biological effect is not predicted by absorbed dose, a coefficient of relative biological effectiveness (RBE) is introduced to take in to account the dissimilarity in the effect of radiations of various types for the same physical dose. The effectiveness is defined as the ratio between the absorbed dose of a reference radiation and that of the test radiation required to produce the same biological effect. RBE depends on radiation quality of linear energy transfer, radiation dose, number of fractions, dose rate and the like [5]. Many chemicals can change the response of cells to radiation. The one chemical which has a very big effect and has possible importance in Radiation Therapy is Oxygen. It acts at the level of free radicals which are formed when radiation interacts with water molecules in the cell. Repairing the damage caused by the radiation can take place in the absence of Oxygen. The oxygen enhancement ratio or OER is the ratio of the doses of radiation necessary to present or yield similar and identical biological impacts and effects in the nonexistence of oxygen and in its presence. The oxygen effect is vast and important for LOW LET radiation (x and gamma) [7]. 5. Proton and Photon in Contrast With Carbon Although Protons and carbon ions deeply penetrate tissues and emit most of their energy near the end of their range where the tumor is existed, they have some differences given as follows: Carbon ions disperse or scatter much less than protons and concentrate their radiation in a smaller area [8], [9]. However protons and carbon ions both have sharp Bragg peaks as shown in fig.1, protons are characterized by low LET whereas carbon ions are characterized by high LET [6]. A significant benefit of carbon ions is that, unlike x-rays and protons, they do not need oxygen to work and can, therefore, reach and kill or terminate hypoxic areas of tumors, which are notoriously hard to treat [9]. Bone and soft tissues tumors can be treated and cured by carbon, but not even by protons and certainly not with x-rays [10]. The OER is more than 3/2 times better than that of protons. Another distinction is that carbon ions bring about more irreparable harms and damages to the cancer cells. Protons and x-rays have about the same relative biological impact, which is an assessment of the damage from ionizing radiation while the RBE of carbon ions is three times higher; this means that they damage DNA in a way that is double-stranded and irreparable. Today, 24 proton facilities are working worldwide, and almost 20 more such sites are planned to be constructed, while there are only 3 carbon facilities currently treating patients of mentioned disease. One is situated in Germany and two others are working in Japan [11]
3 623 Figure.1. Comparison between Carbon and Proton Bragg peak 6. Boron Neutron Capture Therapy (BNCT) BNCT is a combined treatment method including thermal and epithermal neutron beams. BNCT derived from 10 B nucleus tendency to capture thermal neutrons. As a result unstable 11B nucleus generates a lithium ion and an α particle. The yields of this reaction have high LET characteristics. Thus, it is able to selectively irradiate tumor cells which have received appropriate amount of 10 B. The initial idea to use neutron capture reactions in cancer treatment was broadcasted by Locher in In May 1999 the first patient was treated with BNCT at the Finnish Research Reactor. By this way cancer cells will be killed selectively as well as treating tumors by a cell-bycell basis. BNCT would be effective in treating malignant melanoma (skin cancer), malignant brain tumor, head and neck cancer, lung cancer, liver cancer. In order to estimate the number of monitor MU which should be delivered to the patient in BNCT treatment, the on-line beam monitor system requires to be calibrated. Each patient was planned to receive two BNCT treatments in 3-5 weeks apart. Furthermore, CT (for constructing 3-dimensional model), MRI and PET (for specifying target volume) images can be assumed with each other. 7. Intensity-Modulated Radiation Therapy (IMRT) IMRT is a high accuracy radiotherapy technique with the ability of releasing precise doses to virulent tumor or characteristic areas within the tumor. IMRT can be assumed for cancers in the nasopharynx, sinonasal region, parotid gland, tonsil, buckle mucosa, gingiva, and thyroid [12]. Due to its potency to spare healthy tissues, this method may be beneficial for re-treatment of formerly irradiated with head and neck cancers. In traditional radiotherapy, the doses given to the healthy tissues are the real limiting and restricting factor. IMRT increases the doses delivered to the healthy tissues and then dispenses it over a large mass in order to provide an enhanced dose for the tumor cells. Owing to some reasons IMRT would be appropriate for children. Child's body is highly sensitive to radiation. Moreover, scattered radiation created by radiotherapy is very serious in children [13]. In CT scanning and IMRT both rotating beam is used. Though, in IMRT beams delivers radiation. Conventional three dimensional conformal radiotherapy, modificated threedimensional conformal radiotherapy and IMRT are compared in figure.2 [14]. Furthermore, side effects of conventional radiation therapy and IMRT are approximately the same. However, the proton therapy would cost about 2.4 times more than IMRT [15]. 8. Clinical Experience in Head and Neck Cancer Chondrosarcomas and Chordomas are uncommon tumors which respectively arise from notochordal remnants and primitive mesenchymal cells. Skull base Chordomas and chondrosarcomas are close to dose-limiting structures such as optic pathways, brainstem, and spinal cord..a series of 621 cases of chordoma and chondrosarcoma of the base of skull treated at the Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston to a total dose ranging from 66 to 83 GyE indicated local control at 10 years of 54% and 94%, respectively [16]. In all cases, surgery was performed before radiotherapy to eliminate the tumor. Salivary gland tumors can also treated by particle beam. Because of the low radiosensitivity of these tumors, conventional radiotherapy is not effective for them. Three- dimensional conformal radiation therapy (3D-CRT) and IMRT can be used for these cancers [17]. Another approach is to use neutron beam radiation. In this way, high-energy neutrons assumed in place of using x-ray beam. Furthermore, in 18 patients with salivary gland carcinoma, survival rate of 59% were observed. Although therapies with carbon ions and neutrons may give the same results, treating with carbon ion has lower toxicity. Treating skin carcinomas with conventional radiotherapy is limited. 45 patients suffered from skin carcinomas were treated and cured with carbon ions RT from 2006 to 2009 which caused 1- and 3- year overall survival rates for 45 patients between 88.9% and 86%, respectively [18]. Five randomized studies of particle beam therapy in malignant glioma were compared. None of these trials detected a significant survival benefit for particle therapy. This study is divided into two types of therapies as the table.i represent, with neutrons (first four studies) and with photons or Pions (fifth study) [19]. Since 2001, 26 patients with salivary gland carcinomas, sarcomas, squamous cell carcinomas were treated with BNCT. All patients survived 1 up to 72 months after the
4 624 treatments. The mean survival times were 13.6 months. Entirely, BNCT has the potential to be used for the reappeared Figure 2. Three method planning in patient with a ut3n+ medial rectal cancer, conventional tridimensional conformal radiotherapy (A and D), modificated tridimensional conformal radiotherapy (B and E) and IMRT (C and F). tumors [20]. Another example of BNCT treatment effect is an old man (36 year old) with glioblastoma multeforme (GBM) which is shown in Figure 3[21]. Several paranormal head and neck cancers, such as laryngeal sarcomas, bone and soft tissue sarcomas and glomus tumors were treated with combined proton and photon radiotherapy. Moreover, hadron therapy has been applied for the treatment of numerable cases of carcinoma of pituitary, thyroid gland and ear. 9. Facilities Every year, several thousand cancer patients with both early and advanced tumors are treated in the proton therapy centers as Loma Linda Institute and PSI with encouraging results. Although in both centers many successful treatments carried out for meningiomas, chordomas, chondrosarcomas, sarcomas, eye tumors,children cancers and etc., ORL tumors (nose and throat region tumors) were only treated at PSI. Moreover, in 98% of aforementioned cancer types complete cessation of tumor growth has been reported. Loma Linda has the smallest variable-energy proton synchrotron which delivers adequate energy to the deep-seated tumors. Furthermore, it includes four treatment rooms with approximately 90 tones gantries. In contrast PSI applies the Spot-Scanning technique in order to uniformly spread out radiation dose overall tumor region. In addition, a new gantry called gantry2 is setting up at PSI and will be provided at the end of 2012 for patient treatment [22]. On the other hand, HIT (Heidelberg Ion Centre) has the capability of treating patients with protons as well as various heavy ions such as carbon, oxygen, and helium ions. Another considerable facility of this center is intensity-controlled rasterscan method leading to maximum accuracy in the three-dimensional radiation of tumors. Two treatment rooms of HIT devoted to fixed horizontal beamline and one other room hosts heavy ion gantry which would be able to rotate 360 around the patient. MIT BNCT includes fission converter epithermal neutron beam (FCB), thermal neutron beam and Prompt gamma neutron activation analysis (PGNAA) facilities.in order to treat a patient in less than one hour with BNCT, the proton-lithium reaction will require a proton beam current between 10 and 100 ma at 2.5 MeV as well as proton-beryllium reaction needs 5-10 ma at 20 MeV [23]. Moreover Carborane (composed of boron and carbon atoms nucleotides) can be beneficial to be a boron-10 delivery agent for BNCT. 10. Conclusion This paper deals with hadron therapy as an operative treatment for critical organs. In particular, carbon ion and proton therapy are described and compared in terms of their features and preferences.although hadron therapy can be effective method for decreasing damage to adjacent healthy tissues and treating with fewer fraction, due to high cost of equipment that requires such as magnet, huge gantry and synchrotron ring it has almost slow development. Accordingly, major investigation is required to reduce costs by finding alternative methods for gantry rotation. On the other hand, because of the extremely complex nature of cancer, extensive calculation must be performed to estimate absorbed dose rate of various organs. Also calculating the probability of new primary cancers and other side effects should not be ignored. Before BNCT 1 month after BNCT 3months after BNCT Figure 3. MRI image of patient with glioblastoma multeforme treated following BNCT
5 625 FIFTH STUDIES OF PATICLE THERAPY IN MALIGNANT Study Treatment No. of patients randomized (analyzed) 50 Gy photon WBRT + 15Gy photon boost 83 (78) Griiffin et al., Gy photon WBRT + 15Gy photon boost 83 (80) Median survival (months) Duncan et al., Gy photon 5.1 Gy neutron Gy photon 30 () 31( ) Gy photon WBRT Gy neutron boost 17 (17) 13.9 Laramore et al., Gy photon WBRT Gy neutron boost 45 Gy photon WBRT Gy neutron boost 13 (12) 29 (28) 45 Gy photon WBRT Gy neutron boost 53 (44) Gy photon WBRT Gy neutron boost 61(59) 45 Gy photon WBRT Gy neutron boost 30 (30) Duncan et al., Gy photon 13.8 Gy neutron 16 (16) 18 (17) 11 7 Pickles et al., Gy photon Gy pion (41) (40) References [1] M. Parkin, F. Bray, J. Ferlay, P. Pisani, Global cancer statistics, 2002, CA Cancer J Clin, 2005, pp [2] C. M. Anwar, Production and potential implications of secondary neutrons within patients undergoing therapy with hadrons, In Proc. AIP Conference, vol. 600, p.49. [3] O. Jäkel, M. Krämer, C. P. Karger, Treatment planning for heavy ion radiotherapy: clinical implementation and application, Physics in Medicine and Biology, 2001, vol. 46, pp [4] C.Allen, B.Borak, H.Tsujii, Heavy charged particle radiobiology: using enhanced biological effectiveness and improved beam focusing to advance cancer therapy, Department of Environmental and Radiological Health Sciences, 2011, vol. 711, pp [5] S. E. Combs, J. Bauer, D. Unholtz, et. al, Monitoring of patients treated with particle therapy using positron-emission-tomography (PET): the MIRANDA, BMC Cancer study, Apr [6] N. Yamamoto, C. Ikeda, T. Yakushiji, et. al, Genetic effects of X- ray and carbon ion irradiation in head and neck carcinoma cell lines, Bull Tokyo Dent Coll, Nov [7] M. Majrabi, Hadron Therapy for Cancer Using Heavy Ions, University of Surrey, Sep [8] H. Suit, T. DeLaney, S. Goldberg, Proton vs carbon ion beams in the definitive radiation treatment of cancer patients, Elsevier Ireland Ltd, 2010, vol.95, pp [9] V. Brower, Carbon Ion Therapy to Debut in Europe, JNCI Journal of the National Cancer Institute, 2009, vol.101, no. 2, pp [10] T. Kamada, H. Tsujii, H. Tsuji, et. al, Efficacy and safety of carbon ion radiotherapy in bone and soft tissue sarcomas, Journal of Clinical Oncology, 2002, vol. 20, pp [11] A. Eleanor, Y. Chang, Y.Polly, Late effects from hadron therapy, Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory, In proc. Heavy charged particle in biology and medicine, 2004,vol.73, pp [12] M. Chong, A. Hunt, IMRT for head and neck cancer Medical Physics Publishing, [13] J. Hall Intensity-modulated radiation therapy, Protons and the Risk of Second Cancers, Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys, 2006, vol.65, No. 1, pp [14] L. Arbea, L. Isaac Ramos, R. Martínez-Monge, Intensitymodulated radiation therapy (IMRT) vs.3d conformal radiotherapy (3DCRT) in locally advanced rectal cancer (LARC): dosimetric comparison and clinical implications, BioMed Central, 2010 Vol.5. [15] M. Pijls-Johannesma, P. Pommier, Y. Lievens, Cost-effectiveness of particle therapy: Current evidence and future needs, Journal of Radio therapy and Oncology, 2008, vol.89, pp [16] B.Jereczek-Fossa, M. Krengli, R. Orecchia, Particle beam radiotherapy for head and neck tumors: radiobiological basis and clinical experience, Head Neck, 2007, vol. 28. No. 8, pp [17] Salivary Gland Cancer - American Cancer Society [online]. available: [18] H. Zhang, S. Li, X. H. Wang, Q. Li, et. al. Results of carbon ion radiotherapy for skin carcinomas in 45 patients, Br J Dermatol, 2008,vol. 166, No. 5. pp [19] N. Laperriere, L. Zuraw, G. Cairncross, Radiotherapy for newly diagnosed malignant glioma in adults: a systematic review, Journal of Radio therapy and Oncology, 2002, vol.64, pp [20] Boron Neutron Capture Therapy for Cancer Treatments, Australian and New Zealand Head & Neck Society, 2007.
6 626 [21] H.Joensuu, L.Kankaanranta, T.Seppälä et. al, Boron neutron capture therapy of brain tumors: clinical trials at the Finnish facility using boron phenylalanine, Journal of Neurooncol, 2003, pp [22] [online] available : [23] J R.Alonso, Hadron particle therapy, proc. Particle Accelerator Conference, 1996, vol.1, pp
HADRON THERAPY FOR CANCER TREATMENT
 HADRON THERAPY FOR CANCER TREATMENT Seminar presented by Arlene Lennox at Fermilab on Nov 21, 2003 CANCER STAGES LOCAL TUMOR REGIONAL METASTASIS SYSTEMIC DISEASE CANCER TREATMENT SURGERY RADIATION THERAPY
HADRON THERAPY FOR CANCER TREATMENT Seminar presented by Arlene Lennox at Fermilab on Nov 21, 2003 CANCER STAGES LOCAL TUMOR REGIONAL METASTASIS SYSTEMIC DISEASE CANCER TREATMENT SURGERY RADIATION THERAPY
Current Status and Future Direction of Proton Beam Therapy
 Current Status and Future Direction of Proton Beam Therapy National Cancer Center Hospital East Division of Radiation Oncology and Particle Therapy Tetsuo Akimoto Comparison of status of particle therapy
Current Status and Future Direction of Proton Beam Therapy National Cancer Center Hospital East Division of Radiation Oncology and Particle Therapy Tetsuo Akimoto Comparison of status of particle therapy
Proton Therapy: Cutting Edge Treatment for Cancerous Tumors. By: Cherilyn G. Murer, JD, CRA
 Proton Therapy: Cutting Edge Treatment for Cancerous Tumors By: Cherilyn G. Murer, JD, CRA Introduction Put simply, proton therapy is a new cutting edge cancer treatment that promises better outcomes for
Proton Therapy: Cutting Edge Treatment for Cancerous Tumors By: Cherilyn G. Murer, JD, CRA Introduction Put simply, proton therapy is a new cutting edge cancer treatment that promises better outcomes for
The Science behind Proton Beam Therapy
 The Science behind Proton Beam Therapy Anthony Zietman MD Shipley Professor of Radiation Oncology Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School Principles underlying Radiotherapy Radiation related
The Science behind Proton Beam Therapy Anthony Zietman MD Shipley Professor of Radiation Oncology Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School Principles underlying Radiotherapy Radiation related
Cancer Therapy with Particle Beams
 Cancer Therapy with Particle Beams The potential to use high energy particle beams to treat many types of cancer has been known even before their creation. The availability of these treatments has been
Cancer Therapy with Particle Beams The potential to use high energy particle beams to treat many types of cancer has been known even before their creation. The availability of these treatments has been
Advanced Radiation Therapy of Cancer by Proton Beam
 March 20th, 2014 Advanced Radiation Therapy of Cancer by Proton Beam Fukui Prefectural Hospital Proton Therapy Center Yamamoto, Kazutaka Wave (electromagnetic wave) IR (Ionizing) Radiation 700 400 350~100
March 20th, 2014 Advanced Radiation Therapy of Cancer by Proton Beam Fukui Prefectural Hospital Proton Therapy Center Yamamoto, Kazutaka Wave (electromagnetic wave) IR (Ionizing) Radiation 700 400 350~100
AMERICAN BRAIN TUMOR ASSOCIATION. Proton Therapy
 AMERICAN BRAIN TUMOR ASSOCIATION Proton Therapy Acknowledgements About the American Brain Tumor Association Founded in 1973, the American Brain Tumor Association (ABTA) was the first national nonprofit
AMERICAN BRAIN TUMOR ASSOCIATION Proton Therapy Acknowledgements About the American Brain Tumor Association Founded in 1973, the American Brain Tumor Association (ABTA) was the first national nonprofit
How To Treat Cancer With Proton Therapy
 Proton therapy at the Paul Scherrer Institute PSI proton therapy for tumours of the eye (OPTIS). The patient s head is fixed using a mask and a bite block. Actual irradiation of the eye tumour lasts less
Proton therapy at the Paul Scherrer Institute PSI proton therapy for tumours of the eye (OPTIS). The patient s head is fixed using a mask and a bite block. Actual irradiation of the eye tumour lasts less
In 1946 Harvard physicist Robert Wilson (1914-2000) suggested:
 In 1946 Harvard physicist Robert Wilson (1914-2000) suggested: Protons can be used clinically Accelerators are available Maximum radiation dose can be placed into the tumor Proton therapy provides sparing
In 1946 Harvard physicist Robert Wilson (1914-2000) suggested: Protons can be used clinically Accelerators are available Maximum radiation dose can be placed into the tumor Proton therapy provides sparing
PROTON THERAPY FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS
 PROTON THERAPY FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS Table of contents 1. What is cancer?... 2 2. How is cancer treated?... 3 3. What is proton therapy?... 4 4. What are the clinical benefits of proton therapy?...
PROTON THERAPY FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS Table of contents 1. What is cancer?... 2 2. How is cancer treated?... 3 3. What is proton therapy?... 4 4. What are the clinical benefits of proton therapy?...
Radiation therapy involves using many terms you may have never heard before. Below is a list of words you could hear during your treatment.
 Dictionary Radiation therapy involves using many terms you may have never heard before. Below is a list of words you could hear during your treatment. Applicator A device used to hold a radioactive source
Dictionary Radiation therapy involves using many terms you may have never heard before. Below is a list of words you could hear during your treatment. Applicator A device used to hold a radioactive source
Intensity-Modulated Radiation Therapy (IMRT)
 Scan for mobile link. Intensity-Modulated Radiation Therapy (IMRT) Intensity-modulated radiotherapy (IMRT) uses linear accelerators to safely and painlessly deliver precise radiation doses to a tumor while
Scan for mobile link. Intensity-Modulated Radiation Therapy (IMRT) Intensity-modulated radiotherapy (IMRT) uses linear accelerators to safely and painlessly deliver precise radiation doses to a tumor while
Proton Therapy. What is proton therapy and how is it used?
 Scan for mobile link. Proton Therapy Proton therapy delivers radiation to tumor tissue in a much more confined way than conventional photon therapy thus allowing the radiation oncologist to use a greater
Scan for mobile link. Proton Therapy Proton therapy delivers radiation to tumor tissue in a much more confined way than conventional photon therapy thus allowing the radiation oncologist to use a greater
Medical Applications of radiation physics. Riccardo Faccini Universita di Roma La Sapienza
 Medical Applications of radiation physics Riccardo Faccini Universita di Roma La Sapienza Outlook Introduction to radiation which one? how does it interact with matter? how is it generated? Diagnostics
Medical Applications of radiation physics Riccardo Faccini Universita di Roma La Sapienza Outlook Introduction to radiation which one? how does it interact with matter? how is it generated? Diagnostics
Radiation Oncology Nursing Care. Helen Lusby Radiation Oncology Nurse BAROC 2012
 Radiation Oncology Nursing Care Helen Lusby Radiation Oncology Nurse BAROC 2012 Definitions Radiation Therapy: Treatment of cancer using x- ray particles that cause ionisation within the cells. External
Radiation Oncology Nursing Care Helen Lusby Radiation Oncology Nurse BAROC 2012 Definitions Radiation Therapy: Treatment of cancer using x- ray particles that cause ionisation within the cells. External
Potential Benefits of Proton Therapy in Clinic
 Potential Benefits of Proton Therapy in Clinic Simone Pieplenbosch Proton therapy offers great potential in cancer treatment compared with the conventional photon therapy. The advantages of the unique
Potential Benefits of Proton Therapy in Clinic Simone Pieplenbosch Proton therapy offers great potential in cancer treatment compared with the conventional photon therapy. The advantages of the unique
Brain Tumor Treatment
 Scan for mobile link. Brain Tumor Treatment Brain Tumors Overview A brain tumor is a group of abnormal cells that grows in or around the brain. Tumors can directly destroy healthy brain cells. They can
Scan for mobile link. Brain Tumor Treatment Brain Tumors Overview A brain tumor is a group of abnormal cells that grows in or around the brain. Tumors can directly destroy healthy brain cells. They can
Seminar 7. Medical application of radioisotopes - radiotherapy
 Seminar 7 Medical application of radioisotopes - radiotherapy Radioisotopes in medical diagnosis. Gamma camera. Radionuclide imaging (PET, SPECT). Radiotherapy. Sources of radiation. Treatment planning.
Seminar 7 Medical application of radioisotopes - radiotherapy Radioisotopes in medical diagnosis. Gamma camera. Radionuclide imaging (PET, SPECT). Radiotherapy. Sources of radiation. Treatment planning.
Evolution of Head and Neck Treatment Using Protons. Mayank Amin, M.Sc,CMD
 Evolution of Head and Neck Treatment Using Protons Mayank Amin, M.Sc,CMD Facility Layout Gantry Room 3 Fixed Beams Room 4 HEBT Gantry Room 2 Gantry Room 1 Synchrotron Linac Treatment Planning Imaging Area
Evolution of Head and Neck Treatment Using Protons Mayank Amin, M.Sc,CMD Facility Layout Gantry Room 3 Fixed Beams Room 4 HEBT Gantry Room 2 Gantry Room 1 Synchrotron Linac Treatment Planning Imaging Area
Our Facility. Advanced clinical center with the newest and highly exact technology for treatment of patients with cancer pencil beam
 PTC Czech The main goal of radiotherapy is to irreversibly damage tumor cells, whereas the cells of healthy tissue are damaged only reversibly or not at all. Proton therapy currently comes closest to this
PTC Czech The main goal of radiotherapy is to irreversibly damage tumor cells, whereas the cells of healthy tissue are damaged only reversibly or not at all. Proton therapy currently comes closest to this
Therapy with protons and ion beams
 Therapy with protons and ion beams Biomedical Physics Lecture WiSe 2012/13 many slides from J. Willkens (TUM) Key quesions: How does ion cancer therapy work? What is the physics behind it? How can physics
Therapy with protons and ion beams Biomedical Physics Lecture WiSe 2012/13 many slides from J. Willkens (TUM) Key quesions: How does ion cancer therapy work? What is the physics behind it? How can physics
Proton Therapy for Prostate Cancer: Your Questions, Our Answers.
 Proton Therapy for Prostate Cancer: Your Questions, Our Answers. When you re looking for the right treatment for your prostate cancer, nothing s more important than accurate information. Read on, and learn
Proton Therapy for Prostate Cancer: Your Questions, Our Answers. When you re looking for the right treatment for your prostate cancer, nothing s more important than accurate information. Read on, and learn
IBA Proton Therapy. Biomed days 2015. Vincent Bossier. System Architect [email protected]. Protect, Enhance and Save Lives
 Vincent Bossier System Architect [email protected] IBA Proton Therapy Biomed days 2015 Protect, Enhance and Save Lives 1 Agenda AN INTRODUCTION TO IBA WHY PROTON THERAPY CLINICAL WORKFLOW TREATMENT
Vincent Bossier System Architect [email protected] IBA Proton Therapy Biomed days 2015 Protect, Enhance and Save Lives 1 Agenda AN INTRODUCTION TO IBA WHY PROTON THERAPY CLINICAL WORKFLOW TREATMENT
Proton beam. Medical Technical Complex Joint Institute for Nuclear Research, Dubna, Russia
 Proton beam Medical Technical Complex Joint Institute for Nuclear Research, Dubna, Russia Egyptian Candidates Proton therapy It can do more!!! Effectiveness of the proton therapy in targeting and curing
Proton beam Medical Technical Complex Joint Institute for Nuclear Research, Dubna, Russia Egyptian Candidates Proton therapy It can do more!!! Effectiveness of the proton therapy in targeting and curing
Proton Radiotherapy. Cynthia Keppel Scientific and Technical Director Hampton University Proton Therapy Institute. Lead Virginia.
 Proton Radiotherapy Cynthia Keppel Scientific and Technical Director Hampton University Proton Therapy Institute Lead Virginia g October 16, 2009 About Proton Therapy Cancer is the (2nd) largest cause
Proton Radiotherapy Cynthia Keppel Scientific and Technical Director Hampton University Proton Therapy Institute Lead Virginia g October 16, 2009 About Proton Therapy Cancer is the (2nd) largest cause
Radiation Therapy for Cancer: Questions and Answers. Key Points
 CANCER FACTS N a t i o n a l C a n c e r I n s t i t u t e N a t i o n a l I n s t i t u t e s o f H e a l t h D e p a r t m e n t o f H e a l t h a n d H u m a n S e r v i c e s Radiation Therapy for
CANCER FACTS N a t i o n a l C a n c e r I n s t i t u t e N a t i o n a l I n s t i t u t e s o f H e a l t h D e p a r t m e n t o f H e a l t h a n d H u m a n S e r v i c e s Radiation Therapy for
Corporate Medical Policy
 Corporate Medical Policy Intensity Modulated Radiation Therapy (IMRT) of Head and Neck File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: intensity_modulated_radiation_therapy_imrt_of_head_and_neck
Corporate Medical Policy Intensity Modulated Radiation Therapy (IMRT) of Head and Neck File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: intensity_modulated_radiation_therapy_imrt_of_head_and_neck
Colorectal Cancer Treatment
 Scan for mobile link. Colorectal Cancer Treatment Colorectal cancer overview Colorectal cancer, also called large bowel cancer, is the term used to describe malignant tumors found in the colon and rectum.
Scan for mobile link. Colorectal Cancer Treatment Colorectal cancer overview Colorectal cancer, also called large bowel cancer, is the term used to describe malignant tumors found in the colon and rectum.
1. In the general symbol cleus, which of the three letters. 2. What is the mass number of an alpha particle?
 1. In the general symbol cleus, which of the three letters Z A X for a nu represents the atomic number? 2. What is the mass number of an alpha particle? 3. What is the mass number of a beta particle? 4.
1. In the general symbol cleus, which of the three letters Z A X for a nu represents the atomic number? 2. What is the mass number of an alpha particle? 3. What is the mass number of a beta particle? 4.
Clinical Commissioning Policy: Proton Beam Radiotherapy (High Energy) for Paediatric Cancer Treatment
 Clinical Commissioning Policy: Proton Beam Radiotherapy (High Energy) for Paediatric Cancer Treatment Reference: NHS England xxx/x/x 1 Clinical Commissioning Policy: Proton Beam Radiotherapy (High Energy)
Clinical Commissioning Policy: Proton Beam Radiotherapy (High Energy) for Paediatric Cancer Treatment Reference: NHS England xxx/x/x 1 Clinical Commissioning Policy: Proton Beam Radiotherapy (High Energy)
Secondary Neutrons in Proton and Ion Therapy
 Secondary Neutrons in Proton and Ion Therapy L. Stolarczyk Institute of Nuclear Physics PAN, Poland on behalf of WG9 EURADOS Acknowledgments EURADOS Workig Group 9 Roger Harrison Jean Marc Bordy Carles
Secondary Neutrons in Proton and Ion Therapy L. Stolarczyk Institute of Nuclear Physics PAN, Poland on behalf of WG9 EURADOS Acknowledgments EURADOS Workig Group 9 Roger Harrison Jean Marc Bordy Carles
World-first Proton Pencil Beam Scanning System with FDA Clearance
 Hitachi Review Vol. 58 (29), No.5 225 World-first Proton Pencil Beam Scanning System with FDA Clearance Completion of Proton Therapy System for MDACC Koji Matsuda Hiroyuki Itami Daishun Chiba Kazuyoshi
Hitachi Review Vol. 58 (29), No.5 225 World-first Proton Pencil Beam Scanning System with FDA Clearance Completion of Proton Therapy System for MDACC Koji Matsuda Hiroyuki Itami Daishun Chiba Kazuyoshi
Nuclear medicine. Answering your questions
 Nuclear medicine Answering your questions ANSTO s OPAL research reactor in Sydney What is nuclear medicine? This is a branch of medicine that uses radiation from radioactive tracers to provide information
Nuclear medicine Answering your questions ANSTO s OPAL research reactor in Sydney What is nuclear medicine? This is a branch of medicine that uses radiation from radioactive tracers to provide information
CONQUERING CANCER SAVING LIVES. Mayo Clinic Proton Beam Therapy Program
 CONQUERING CANCER SAVING LIVES Mayo Clinic Proton Beam Therapy Program A MALIGNANT TUMOR IS A TYRANT Cancer takes all the body s resources for itself invading and displacing surrounding tissues. Abolishing
CONQUERING CANCER SAVING LIVES Mayo Clinic Proton Beam Therapy Program A MALIGNANT TUMOR IS A TYRANT Cancer takes all the body s resources for itself invading and displacing surrounding tissues. Abolishing
Proton Therapy Center Czech
 Proton Therapy Center Czech The main goal of radiotherapy is to irreversibly damage tumor cells, whereas the cells of healthy tissue are damaged only reversibly or not at all. Proton therapy currently
Proton Therapy Center Czech The main goal of radiotherapy is to irreversibly damage tumor cells, whereas the cells of healthy tissue are damaged only reversibly or not at all. Proton therapy currently
UniversitätsKlinikum Heidelberg
 UniversitätsKlinikum Heidelberg University Hospital Heidelberg Prof. Dr. med. Eike O. Martin Medical Director Universitätsklinikums Heidelberg Irmtraut Gürkan Administrative Director Universitätsklinikums
UniversitätsKlinikum Heidelberg University Hospital Heidelberg Prof. Dr. med. Eike O. Martin Medical Director Universitätsklinikums Heidelberg Irmtraut Gürkan Administrative Director Universitätsklinikums
PRINIPLES OF RADIATION THERAPY Adarsh Kumar. The basis of radiation therapy revolve around the principle that ionizing radiations kill cells
 PRINIPLES OF RADIATION THERAPY Adarsh Kumar The basis of radiation therapy revolve around the principle that ionizing radiations kill cells Radiotherapy terminology: a. Radiosensitivity: refers to susceptibility
PRINIPLES OF RADIATION THERAPY Adarsh Kumar The basis of radiation therapy revolve around the principle that ionizing radiations kill cells Radiotherapy terminology: a. Radiosensitivity: refers to susceptibility
Status of non-european particle therapy facilities. Marco Durante
 Status of non-european particle therapy facilities Marco Durante USA proton therapy several new centers announced/planned max number of patients still LLUMC (~15,000) USA heavy ion therapy None since BEVALAC
Status of non-european particle therapy facilities Marco Durante USA proton therapy several new centers announced/planned max number of patients still LLUMC (~15,000) USA heavy ion therapy None since BEVALAC
Basic Radiation Therapy Terms
 Basic Radiation Therapy Terms accelerated radiation: radiation schedule in which the total dose is given over a shorter period of time. (Compare to hyperfractionated radiation.) adjuvant therapy (add-joo-vunt):
Basic Radiation Therapy Terms accelerated radiation: radiation schedule in which the total dose is given over a shorter period of time. (Compare to hyperfractionated radiation.) adjuvant therapy (add-joo-vunt):
Esophageal Cancer Treatment
 Scan for mobile link. Esophageal Cancer Treatment What is Esophageal Cancer? Esophageal cancer occurs when cancer cells develop in the esophagus, a long, tube-like structure that connects the throat and
Scan for mobile link. Esophageal Cancer Treatment What is Esophageal Cancer? Esophageal cancer occurs when cancer cells develop in the esophagus, a long, tube-like structure that connects the throat and
FAQ About Prostate Cancer Treatment and SpaceOAR System
 FAQ About Prostate Cancer Treatment and SpaceOAR System P. 4 Prostate Cancer Background SpaceOAR Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) 1. What is prostate cancer? The vast majority of prostate cancers develop
FAQ About Prostate Cancer Treatment and SpaceOAR System P. 4 Prostate Cancer Background SpaceOAR Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) 1. What is prostate cancer? The vast majority of prostate cancers develop
Executive summary. What is proton radiotherapy?
 Executive summary Health Council of the Netherlands. Proton radiotherapy. Horizon scanning report. The Hague: Health Council of the Netherlands, 2009; publication no. 2009/17 What is proton radiotherapy?
Executive summary Health Council of the Netherlands. Proton radiotherapy. Horizon scanning report. The Hague: Health Council of the Netherlands, 2009; publication no. 2009/17 What is proton radiotherapy?
Brain Cancer. This reference summary will help you understand how brain tumors are diagnosed and what options are available to treat them.
 Brain Cancer Introduction Brain tumors are not rare. Thousands of people are diagnosed every year with tumors of the brain and the rest of the nervous system. The diagnosis and treatment of brain tumors
Brain Cancer Introduction Brain tumors are not rare. Thousands of people are diagnosed every year with tumors of the brain and the rest of the nervous system. The diagnosis and treatment of brain tumors
Heidelberg University Hospital. www.hit-heidelberg.com. Heidelberger Ion Beam. Therapy Center. Heidelberg Ion Beam Therapy Center
 Heidelberg University Hospital www.hit-heidelberg.com Heidelberger Ion Beam Therapy Center Heidelberg Ion Beam Therapy Center Introductory messages 04 Using ion beams to fight cancer 08 HIT s facilities
Heidelberg University Hospital www.hit-heidelberg.com Heidelberger Ion Beam Therapy Center Heidelberg Ion Beam Therapy Center Introductory messages 04 Using ion beams to fight cancer 08 HIT s facilities
Medical Physics and Radioactivity
 Medical Physics and Radioactivity Radioactivity Unstable nucleus Electromagnetic wave particle Atoms which emit electromagnetic radiation or a particle by the spontaneous transformation of their nucleus
Medical Physics and Radioactivity Radioactivity Unstable nucleus Electromagnetic wave particle Atoms which emit electromagnetic radiation or a particle by the spontaneous transformation of their nucleus
Radiotherapy in Hungary: present status and future needs. Tibor Major, PhD National Institute of Oncology Radiotherapy Department Budapest, Hungary
 Radiotherapy in Hungary: present status and future needs Tibor Major, PhD National Institute of Oncology Radiotherapy Department Budapest, Hungary Academia Europaea Section Workshops, Bergen, 10 September,
Radiotherapy in Hungary: present status and future needs Tibor Major, PhD National Institute of Oncology Radiotherapy Department Budapest, Hungary Academia Europaea Section Workshops, Bergen, 10 September,
Proton Therapy for Head & Neck Cancers
 Proton Therapy for Head & Neck Cancers Robert S Malyapa, MD, PhD and William M Mendenhall, MD University of Florida Proton Therapy Institute, Jacksonville, USA Carmen Ares, MD and Ralf Schneider, MD Paul
Proton Therapy for Head & Neck Cancers Robert S Malyapa, MD, PhD and William M Mendenhall, MD University of Florida Proton Therapy Institute, Jacksonville, USA Carmen Ares, MD and Ralf Schneider, MD Paul
ADROTERAPIA A MEDAUSTRON
 ADROTERAPIA A MEDAUSTRON Antonio Carlino Qualified Medical Physicist EBG MedAustron GmbH, Wiener Neustadt, Austria Outline Introduction and milestones Building and construction Treatment beam lines and
ADROTERAPIA A MEDAUSTRON Antonio Carlino Qualified Medical Physicist EBG MedAustron GmbH, Wiener Neustadt, Austria Outline Introduction and milestones Building and construction Treatment beam lines and
General Information About Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
 General Information About Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Non-small cell lung cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of the lung. The lungs are a pair of cone-shaped breathing
General Information About Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Non-small cell lung cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of the lung. The lungs are a pair of cone-shaped breathing
SCD Case Study. Most malignant lesions of the tonsil are either lymphosarcoma or carcinoma.
 SCD Case Study Dry Mouth This case study details a patient who has experienced xerostomia as a result of treatment for squamous cell carcinoma of the left tonsil involving surgery followed by deep x-ray
SCD Case Study Dry Mouth This case study details a patient who has experienced xerostomia as a result of treatment for squamous cell carcinoma of the left tonsil involving surgery followed by deep x-ray
WELCOME. Massachusetts General Hospital Cancer Center
 Massachusetts General Hospital Cancer Center Department of Radiation Oncology 55 Fruit Street Boston, MA 02114 (617) 726-8650 www.massgeneral.org/cancer PROTON RADIOSURGERY Teresa M. McCue August Morning
Massachusetts General Hospital Cancer Center Department of Radiation Oncology 55 Fruit Street Boston, MA 02114 (617) 726-8650 www.massgeneral.org/cancer PROTON RADIOSURGERY Teresa M. McCue August Morning
APA format (title page missing) Proton Therapy 3. A paper. A New Cancer Treatment: Proton Therapy. A Review of the Literature
 APA format (title page missing) Proton Therapy 3 A paper A New Cancer Treatment: Proton Therapy A Review of the Literature Cancer is a widespread disease that is defined as a malignant or invasive growth
APA format (title page missing) Proton Therapy 3 A paper A New Cancer Treatment: Proton Therapy A Review of the Literature Cancer is a widespread disease that is defined as a malignant or invasive growth
A new score predicting the survival of patients with spinal cord compression from myeloma
 A new score predicting the survival of patients with spinal cord compression from myeloma (1) Sarah Douglas, Department of Radiation Oncology, University of Lubeck, Germany; [email protected] (2) Steven
A new score predicting the survival of patients with spinal cord compression from myeloma (1) Sarah Douglas, Department of Radiation Oncology, University of Lubeck, Germany; [email protected] (2) Steven
Clinical Education A comprehensive and specific training program. carry out effective treatments from day one
 Proton Therapy Clinical Education A comprehensive and specific training program carry out effective treatments from day one Forewarned is forearmed Although over 100,000 patients have been treated in proton
Proton Therapy Clinical Education A comprehensive and specific training program carry out effective treatments from day one Forewarned is forearmed Although over 100,000 patients have been treated in proton
LOMA LINDA UNIVERSITY MEDICAL CENTER PROTON TREATMENT AND THE CONTROL OF CANCER
 PROTON TREATMENT AND THE CONTROL OF CANCER AT LOMA LINDA UNIVERSITY MEDICAL CENTER A NEW ERA BEGINS IN THE SEARCH "To MAKE MAN WHOLE" We stand at the threshold of an important advance in the control of
PROTON TREATMENT AND THE CONTROL OF CANCER AT LOMA LINDA UNIVERSITY MEDICAL CENTER A NEW ERA BEGINS IN THE SEARCH "To MAKE MAN WHOLE" We stand at the threshold of an important advance in the control of
How To Use A Proton For Radiation Therapy
 Proton Cancer Therapy: Using Laser Accelerate Protons for Radiation Therapy A Thesis Submitted in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for Graduation with Research Distinction in Engineering Physics
Proton Cancer Therapy: Using Laser Accelerate Protons for Radiation Therapy A Thesis Submitted in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for Graduation with Research Distinction in Engineering Physics
THE POWER AND PRECISION OF PROTON BEAM THERAPY IS WITHIN REACH
 THE POWER AND PRECISION OF PROTON BEAM THERAPY IS WITHIN REACH PROTON THERAPY OVERVIEW The American Cancer Society estimates 1.6 million new cancer cases in the United States this year. Approximately two
THE POWER AND PRECISION OF PROTON BEAM THERAPY IS WITHIN REACH PROTON THERAPY OVERVIEW The American Cancer Society estimates 1.6 million new cancer cases in the United States this year. Approximately two
The validation of a tumour control probability (TCP) model for supporting radiotherapy treatment planning.
 The validation of a tumour control probability (TCP) model for supporting radiotherapy treatment planning. KAROLINA KOKUREWICZ S U P E R V I S O R S : D I N O J A R O S Z Y N S K I, G I U S E P P E S C
The validation of a tumour control probability (TCP) model for supporting radiotherapy treatment planning. KAROLINA KOKUREWICZ S U P E R V I S O R S : D I N O J A R O S Z Y N S K I, G I U S E P P E S C
Radiation Protection in Radiotherapy
 Radiation Protection in Radiotherapy Albert Lisbona Medical Physics Department CLCC Nantes Atlantique 44805 Saint-Herblain France [email protected] Radiation therapy The lecture is oriented to
Radiation Protection in Radiotherapy Albert Lisbona Medical Physics Department CLCC Nantes Atlantique 44805 Saint-Herblain France [email protected] Radiation therapy The lecture is oriented to
Radiation Therapy for Cancer Treatment
 Radiation Therapy for Cancer Treatment Guest Expert: Kenneth, MD Associate Professor of Therapeutic Radiology www.wnpr.org www.yalecancercenter.org Welcome to Yale Cancer Center Answers with Dr. Ed and
Radiation Therapy for Cancer Treatment Guest Expert: Kenneth, MD Associate Professor of Therapeutic Radiology www.wnpr.org www.yalecancercenter.org Welcome to Yale Cancer Center Answers with Dr. Ed and
Prostate Cancer Treatment
 Scan for mobile link. Prostate Cancer Treatment Prostate cancer is a tumor of the prostate gland, which is located in front of the rectum and below the bladder. Your doctor may perform a physical exam,
Scan for mobile link. Prostate Cancer Treatment Prostate cancer is a tumor of the prostate gland, which is located in front of the rectum and below the bladder. Your doctor may perform a physical exam,
With the project we hope to bring enhanced treatment for better care of our patients who will no
 HKSH Symposium to Explore New Frontiers in Cancer Management Experience Sharing by Local and Overseas Experts HKSH Hopes to Introduce Proton Therapy Soon (15 June 2014, Hong Kong) A panel of renowned experts
HKSH Symposium to Explore New Frontiers in Cancer Management Experience Sharing by Local and Overseas Experts HKSH Hopes to Introduce Proton Therapy Soon (15 June 2014, Hong Kong) A panel of renowned experts
Disease/Illness GUIDE TO ASBESTOS LUNG CANCER. What Is Asbestos Lung Cancer? www.simpsonmillar.co.uk Telephone 0844 858 3200
 GUIDE TO ASBESTOS LUNG CANCER What Is Asbestos Lung Cancer? Like tobacco smoking, exposure to asbestos can result in the development of lung cancer. Similarly, the risk of developing asbestos induced lung
GUIDE TO ASBESTOS LUNG CANCER What Is Asbestos Lung Cancer? Like tobacco smoking, exposure to asbestos can result in the development of lung cancer. Similarly, the risk of developing asbestos induced lung
ACCELERATING THE FIGHT AGAINST CANCER. Photo courtesy of Heidelberg University Hospital
 ACCELERATING THE FIGHT AGAINST CANCER 20 Photo courtesy of Heidelberg University Hospital As charged-particle therapies grow in popularity, physicists are working with other experts to make them smaller,
ACCELERATING THE FIGHT AGAINST CANCER 20 Photo courtesy of Heidelberg University Hospital As charged-particle therapies grow in popularity, physicists are working with other experts to make them smaller,
HITACHI Proton Beam Therapy System
 HITACHI Proton Beam Therapy System Masumi Umezawa, M.S. Hitachi, Ltd., Hitachi Research Laboratory HITACHI Proton Beam Therapy System Contents 1. Overview of HITACHI 2. HITACHI Proton Beam Therapy and
HITACHI Proton Beam Therapy System Masumi Umezawa, M.S. Hitachi, Ltd., Hitachi Research Laboratory HITACHI Proton Beam Therapy System Contents 1. Overview of HITACHI 2. HITACHI Proton Beam Therapy and
Current and Future Trends in Proton Treatment of Prostate Cancer
 Current and Future Trends in Proton Treatment of Prostate Cancer Reinhard W. Schulte Assistant Professor Department of Radiation Medicine Loma Linda University Medical Center Loma Linda, CA, USA Outline
Current and Future Trends in Proton Treatment of Prostate Cancer Reinhard W. Schulte Assistant Professor Department of Radiation Medicine Loma Linda University Medical Center Loma Linda, CA, USA Outline
Basics of Nuclear Physics and Fission
 Basics of Nuclear Physics and Fission A basic background in nuclear physics for those who want to start at the beginning. Some of the terms used in this factsheet can be found in IEER s on-line glossary.
Basics of Nuclear Physics and Fission A basic background in nuclear physics for those who want to start at the beginning. Some of the terms used in this factsheet can be found in IEER s on-line glossary.
Protons vs. CyberKnife. Protons vs. CyberKnife. Page 1 UC SF. What are. Alexander R. Gottschalk, M.D., Ph.D.
 Protons vs. CyberKnife UC SF Protons vs. CyberKnife UC SF Alexander R. Gottschalk, M.D., Ph.D. Associate Professor and Director of the CyberKnife Radiosurgery Program Department of Radiation Oncology University
Protons vs. CyberKnife UC SF Protons vs. CyberKnife UC SF Alexander R. Gottschalk, M.D., Ph.D. Associate Professor and Director of the CyberKnife Radiosurgery Program Department of Radiation Oncology University
Feasibility Study of Neutron Dose for Real Time Image Guided. Proton Therapy: A Monte Carlo Study
 Feasibility Study of Neutron Dose for Real Time Image Guided Proton Therapy: A Monte Carlo Study Jin Sung Kim, Jung Suk Shin, Daehyun Kim, EunHyuk Shin, Kwangzoo Chung, Sungkoo Cho, Sung Hwan Ahn, Sanggyu
Feasibility Study of Neutron Dose for Real Time Image Guided Proton Therapy: A Monte Carlo Study Jin Sung Kim, Jung Suk Shin, Daehyun Kim, EunHyuk Shin, Kwangzoo Chung, Sungkoo Cho, Sung Hwan Ahn, Sanggyu
Smoking and misuse of certain pain medicines can affect the risk of developing renal cell cancer.
 Renal cell cancer Renal cell cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in tubules of the kidney. Renal cell cancer (also called kidney cancer or renal adenocarcinoma) is a disease in which
Renal cell cancer Renal cell cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in tubules of the kidney. Renal cell cancer (also called kidney cancer or renal adenocarcinoma) is a disease in which
Prostate Cancer. What is prostate cancer?
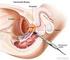 Scan for mobile link. Prostate Cancer Prostate cancer is a tumor of the prostate gland, which is located in front of the rectum and below the bladder. Your doctor may perform a physical exam, prostate-specific
Scan for mobile link. Prostate Cancer Prostate cancer is a tumor of the prostate gland, which is located in front of the rectum and below the bladder. Your doctor may perform a physical exam, prostate-specific
Veterinary Oncology: The Lumps We Hate To Treat
 Veterinary Oncology: The Lumps We Hate To Treat Michelle Turek, DVM, DACVIM (Oncology), DACVR (Radiation Oncology) College of Veterinary Medicine University of Georgia Athens, GA Veterinary Oncology Veterinary
Veterinary Oncology: The Lumps We Hate To Treat Michelle Turek, DVM, DACVIM (Oncology), DACVR (Radiation Oncology) College of Veterinary Medicine University of Georgia Athens, GA Veterinary Oncology Veterinary
Northern Illinois. proton therapy facility
 Northern Illinois proton therapy facility February, 2007 Northern Illinois proton therapy facility 2 Projected 16-State Service Area The Need Scale Legend Potential service region Existing proton therapy
Northern Illinois proton therapy facility February, 2007 Northern Illinois proton therapy facility 2 Projected 16-State Service Area The Need Scale Legend Potential service region Existing proton therapy
Department of Radiation Oncology
 Department of Radiation Oncology Welcome to Radiation Oncology at Emory Clinic Every member of Emory Clinic Department of Radiation Oncology strives to provide the highest quality of care for you as our
Department of Radiation Oncology Welcome to Radiation Oncology at Emory Clinic Every member of Emory Clinic Department of Radiation Oncology strives to provide the highest quality of care for you as our
Andre Konski, MD, MBA, MA, FACR Professor & Chair Department of Radiation Oncology Wayne State University School of Medicine Barbara Ann Karmanos
 Andre Konski, MD, MBA, MA, FACR Professor & Chair Department of Radiation Oncology Wayne State University School of Medicine Barbara Ann Karmanos Cancer Center Financial None The views that I will be going
Andre Konski, MD, MBA, MA, FACR Professor & Chair Department of Radiation Oncology Wayne State University School of Medicine Barbara Ann Karmanos Cancer Center Financial None The views that I will be going
Proton radiotherapy. Horizon scanning report
 Proton radiotherapy Horizon scanning report Gezondheidsraad Health Council of the Netherlands President To the Minister of Health, Welfare and Sport Subject : presentation of horizon scanning report Proton
Proton radiotherapy Horizon scanning report Gezondheidsraad Health Council of the Netherlands President To the Minister of Health, Welfare and Sport Subject : presentation of horizon scanning report Proton
Proton Therapy in Singapore
 Proton Therapy in Singapore Kam-Weng Fong, MD Radiation Oncologist Chair, Proton Therapy Committee National Cancer Center, Singapore 1 st IAS-CERN Workshop Nanyang Technological University Singapore 25-27
Proton Therapy in Singapore Kam-Weng Fong, MD Radiation Oncologist Chair, Proton Therapy Committee National Cancer Center, Singapore 1 st IAS-CERN Workshop Nanyang Technological University Singapore 25-27
A Revolution in the Fight Against Cancer. What TomoTherapy Technology Means to You
 A Revolution in the Fight Against Cancer What TomoTherapy Technology Means to You Cancer Treatment that Revolves Around You When it comes to choosing the right treatment for your cancer, your team of healthcare
A Revolution in the Fight Against Cancer What TomoTherapy Technology Means to You Cancer Treatment that Revolves Around You When it comes to choosing the right treatment for your cancer, your team of healthcare
TITLE: Comparison of the dosimetric planning of partial breast irradiation with and without the aid of 3D virtual reality simulation (VRS) software.
 SAMPLE CLINICAL RESEARCH APPLICATION ABSTRACT: TITLE: Comparison of the dosimetric planning of partial breast irradiation with and without the aid of 3D virtual reality simulation (VRS) software. Hypothesis:
SAMPLE CLINICAL RESEARCH APPLICATION ABSTRACT: TITLE: Comparison of the dosimetric planning of partial breast irradiation with and without the aid of 3D virtual reality simulation (VRS) software. Hypothesis:
1. Orthovoltage vs. megavoltage x-rays. (AL) External beam radiation sources: Orthovoltage radiotherapy: 200-500 kv range
 1. Orthovoltage vs. megavoltage x-rays. (AL) External beam radiation sources: Orthovoltage radiotherapy: 200-500 kv range The radiation from orthovoltage units is referred to as x-rays, generated by bombarding
1. Orthovoltage vs. megavoltage x-rays. (AL) External beam radiation sources: Orthovoltage radiotherapy: 200-500 kv range The radiation from orthovoltage units is referred to as x-rays, generated by bombarding
RADIATION THERAPY FOR BRAIN METASTASES. Facts to Help Patients Make an Informed Decision TARGETING CANCER CARE AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR RADIATION ONCOLOGY
 RADIATION THERAPY FOR BRAIN METASTASES Facts to Help Patients Make an Informed Decision TARGETING CANCER CARE AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR RADIATION ONCOLOGY FACTS ABOUT BRAIN METASTASIS Brain metastases are clusters
RADIATION THERAPY FOR BRAIN METASTASES Facts to Help Patients Make an Informed Decision TARGETING CANCER CARE AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR RADIATION ONCOLOGY FACTS ABOUT BRAIN METASTASIS Brain metastases are clusters
Proton Therapy: Science Fiction or Science Fact
 Proton Therapy: Science Fiction or Science Fact John Han-Chih Chang, MD Director of Clinical Research CDH Proton Center Primary Investigator - Radiation Therapy Oncology Group Primary Investigator - Children
Proton Therapy: Science Fiction or Science Fact John Han-Chih Chang, MD Director of Clinical Research CDH Proton Center Primary Investigator - Radiation Therapy Oncology Group Primary Investigator - Children
Development of on line monitor detectors used for clinical routine in proton and ion therapy
 Development of on line monitor detectors used for clinical routine in proton and ion therapy A. Ansarinejad Torino, february 8 th, 2010 Overview Hadrontherapy CNAO Project Monitor system: Part1:preliminary
Development of on line monitor detectors used for clinical routine in proton and ion therapy A. Ansarinejad Torino, february 8 th, 2010 Overview Hadrontherapy CNAO Project Monitor system: Part1:preliminary
FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE
 FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE The PROBEAT-RT Proton Beam Therapy System Incorporating Real-time Tumor-tracking is Approved for Commercial Manufacturing and Sales under Japan s Pharmaceutical Affairs Law Treatments
FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE The PROBEAT-RT Proton Beam Therapy System Incorporating Real-time Tumor-tracking is Approved for Commercial Manufacturing and Sales under Japan s Pharmaceutical Affairs Law Treatments
High-Energy Neutron Therapy for Radioresistant Cancers
 High-Energy Neutron Therapy for Radioresistant Cancers A.J. Lennox Northern Illinois University Institute for Neutron Therapy at Fermilab Fermi National Accelerator Laboratory, P.O. Box 500 Mail Stop 301,
High-Energy Neutron Therapy for Radioresistant Cancers A.J. Lennox Northern Illinois University Institute for Neutron Therapy at Fermilab Fermi National Accelerator Laboratory, P.O. Box 500 Mail Stop 301,
Small cell lung cancer
 Small cell lung cancer Small cell lung cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of the lung. The lungs are a pair of cone-shaped breathing organs that are found within
Small cell lung cancer Small cell lung cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of the lung. The lungs are a pair of cone-shaped breathing organs that are found within
Overview of Proton Beam Cancer Therapy with Basic Economic Considerations
 Overview of Proton Beam Cancer Therapy with Basic Economic Considerations Wayne Newhauser, Ph.D. Proton Therapy Project, Houston Cyclotron 235 MeV 300 na Extraction Channel Radial Probe Energy Degrader
Overview of Proton Beam Cancer Therapy with Basic Economic Considerations Wayne Newhauser, Ph.D. Proton Therapy Project, Houston Cyclotron 235 MeV 300 na Extraction Channel Radial Probe Energy Degrader
Industrial tracers - Finding leaks and blockages
 Cancer Treatment Alpha radiation is used to treat various forms of cancer. This process, called unsealed source radiotherapy, involves inserting tiny amounts of radium-226 into cancerous organs. The alpha
Cancer Treatment Alpha radiation is used to treat various forms of cancer. This process, called unsealed source radiotherapy, involves inserting tiny amounts of radium-226 into cancerous organs. The alpha
Acute Myeloid Leukemia
 Acute Myeloid Leukemia Introduction Leukemia is cancer of the white blood cells. The increased number of these cells leads to overcrowding of healthy blood cells. As a result, the healthy cells are not
Acute Myeloid Leukemia Introduction Leukemia is cancer of the white blood cells. The increased number of these cells leads to overcrowding of healthy blood cells. As a result, the healthy cells are not
at a critical moment Physician Suggestion Line...
 Radiation Oncology Exceptional care at a critical moment When your patients require radiation therapy, they deserve the very best care available to them. The Department of Radiation Oncology provides exceptional
Radiation Oncology Exceptional care at a critical moment When your patients require radiation therapy, they deserve the very best care available to them. The Department of Radiation Oncology provides exceptional
Cell phones and brain tumors: A review including the long-term epidemiologic data. Surgical Neurology September 2009; 72; pp.
 Cell phones and brain tumors: A review including the long-term epidemiologic data 1 Surgical Neurology September 2009; 72; pp. 205 215 Vini G. Khurana, PhD, FRACS, Charles Teo, MBBS, FRACS, Michael Kundi,
Cell phones and brain tumors: A review including the long-term epidemiologic data 1 Surgical Neurology September 2009; 72; pp. 205 215 Vini G. Khurana, PhD, FRACS, Charles Teo, MBBS, FRACS, Michael Kundi,
Radiation Therapy in Prostate Cancer Current Status and New Advances
 Radiation Therapy in Prostate Cancer Current Status and New Advances Arno J. Mundt MD Professor and Chairman Dept Radiation Oncology Moores Cancer Center UCSD Presentation Welcome Overview of UCSD, Moores
Radiation Therapy in Prostate Cancer Current Status and New Advances Arno J. Mundt MD Professor and Chairman Dept Radiation Oncology Moores Cancer Center UCSD Presentation Welcome Overview of UCSD, Moores
The Brain and Spine CenTer
 The Br ain and Spine Center Choosing the right treatment partner is important for patients facing tumors involving the brain, spine or skull base. The Brain and Spine Center at The University of Texas
The Br ain and Spine Center Choosing the right treatment partner is important for patients facing tumors involving the brain, spine or skull base. The Brain and Spine Center at The University of Texas
