Felix B. Tan and Hazel Chan The University of Auckland, New Zealand. Introduction ABSTRACT
|
|
|
- Frederick Fisher
- 8 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 0(14/+0) %+'0%' 1.7/' E 1 E #..X EMMK Managing Self-instructed Learning within the IS Curriculum: Teaching Learners to Learn Felix B. Tan <f.tan@auckland.ac.nz> and Hazel Chan The University of Auckland, New Zealand ABSTRACT A significant number of students are enrolled in introductory level information systems courses at New Zealand universities. Some of these institutions require their students to acquire their applications software skills in a self-instructional mode of learning. Most of these students have only experienced teacher-directed learning and when placed in a self-instructional environment may have very limited strategies in their learning. The purpose of this study is to determine if teaching learners to learn enhances the acquisition of application software skills. This study considers some of the literature on self-instruction and learner autonomy. The experiment compares two groups of students in self-instructional mode of learning. The control group works independently and the treatment group attends classes that teach the students to manage their own learning. The treatment group is consistent in averaging higher scores demonstrating an overall enhanced learning outcome. This paper challenges IS educators to include learning strategies in courses that require self-instruction. An introduction to working within a new framework should be built in as part of the course. This can prove to be need fulfilling to learners unfamiliar with self-instruction. Keywords: self-instruction, autonomy, learning strategies, learner training, learning to learn Introduction With limited computing resources and increasing number of students enrolling in introductory level information systems (IS) courses, some New Zealand universities require their students to learn application software skills in a selfinstructional environment. Students are required to teach themselves using a prescribed applications software textbook. Many of these textbooks are designed for selfinstruction, taking students keystroke by keystroke through a number of learning objectives for each software module. Most of these students have only experienced teacherdirected learning and, when placed in a self-instructional mode of learning, find themselves asking the question what am I suppose to do?" Many struggle to accomplish what the text instructs within the given course structure and time frame, exhibiting little or no strategies in coping with this new environment. Problems confront students when they are faced with an environment for learning that requires an unfamiliar degree of initiative and autonomy. The earlier experiences of students (ie. teacher-directed learning) have rendered almost all of them totally unprepared to exercise independent thought and action in handling their own learning needs. Students need to learn how to manage their learning in the new environment. Nunan (1996) argues that strategies for learning within the new framework should be built in as part of the curriculum design. He contends that developing learning strategies can lead to some degree of learner autonomy. Students should be encouraged to consider their own learning needs and become aware of possible objectives, stages and sequences in selfinstructed learning. They should be encouraged to select relevant goals and sub-goals at which to aim, and to monitor and assess their achievements. This process may be conceptualized as teaching learners to learn (Holec, 1980; Dickinson, 1987). Others call this learner training (Hallgarten, 1988; Oxford, 1990; Wenden, 1991). The purpose of this study is to determine if teaching learners to learn enhances the students learning outcomes - the acquisition of application software skills. The experiment compares the performance of the two groups of introductory level university students in a self-instructional mode of learning. The performance of the groups is measured by the results of two application software assignments and then statistically analyzed to see if there is a significant difference. This study is exploratory in nature. Most of the literature on self-instruction and learner autonomy is in the field of language learning. This is discussed in the following section. Few studies have attempted to determine if teaching learners to learn (self-instruction skills) can enhance the acquisition of application software skills in a self-instructional learning environment. The aim of this experiment is to initiate research that may help the plight of IS students attending tertiary institutions who have only experienced teacher-directed learning. The results of this experiment can be used to encourage IS edu- 1
2 Managing Self-Instructed Learning cators to develop greater learner autonomy by teaching selfinstructional learning strategies within their existing curriculum. Self-instruction and Learner Autonomy Self-instruction is concerned with responsibility in learning. Individuals who are involve in selfinstruction (as learners) have taken on some extra responsibility for their own learning which in other circumstances would be held on their behalf by a teacher. (Dickinson 1987, pp. 8) Self-instruction describes a situation in which learners can assume varying degrees of responsibilities for their learning. Using this concept of responsibility, we can view selfinstruction on a continuum. On one end of the continuum, Dickinson (1987) describes learners with complete autonomy as being totally responsible for all the decisions to do with their learning and the implementation of them, and is also free of all specially prepared material. This mode of selfinstruction is learner-centered. In the middle of the continuum there is semi-autonomy, a stage where learners are preparing for autonomy. At the other end, is a state of programmed learning (Dickinson 1987, p.10), where learners use materials and resources that manages the learning and leaves them only the responsibility of deciding when to do the work. This is a material-centered form of self-instruction. As seen above, self-instructional modes are of varying levels of learner autonomy. These various degrees of autonomy are dependent on the learners ability to organize and manage their learning. In order for self-instructed learning to occur, two conditions must be satisfied (Holec, 1980): 1. The learner must be able to take charge of his or her learning This means that s/he must know how to make decisions concerning all aspects of learning including determining the objectives, defining progressions, selecting techniques used and evaluating what has been acquired. 2. There must be a learning structure in which the learner can exercise control over the learning. This means that course structure must be designed to allow learners to exercise his or her ability to take charge. 0(14/+0) %+'0%' Holec (1980) emphasizes that the ability to assume responsibility for one s own learning is not inborn. Therefore to fulfil the above first condition learners have to learn to learn. The purpose of learner training is to enable learners to make all decisions about learning, such as deciding the objectives; assessing progress and performance; and selecting method and technique (Hallgarten, 1988). Hallgarten believes that learner training should be a central curriculum objective to teaching. Work in this area by Wenden (1991), Ellis and Sinclair (1986), and Oxford (1990) has highlighted the need for learner training for the successful promotion of learner autonomy. To be able to achieve autonomy, learners require the opportunity to exercise the skills of managing their own learning - Holec s (1980) second condition to self-instructed learning. A learning environment that is learner-centered, conducive to commitment and is need-fulfilling for the learner is what Kohonen (1992) prescribes. Hallgarten (1988) believes that learning is about acquiring skills to do something else (p.114). It should develop transferable skills to broaden the opportunities for autonomy in a wider area than the classroom (p.114). Learners with these skills will then see themselves competent to assume more and more responsibility for their own learning and become autonomous learners. In summary, self-instruction is where the learner undertakes part or all the instructional tasks involved in learning. The degree of autonomy learners achieve is dependent on the amount of responsibility for their learning they assume and the amount of management tasks they undertake. To be successful in self-instructional modes of learning the learner must know how to go about learning without constant direct intervention from a teacher. Learners who have not the skills to manage self-instruction can be taught these learning strategies. Research Design Methodology All introductory level IS students attend 3 one-hour lectures per week. These lectures cover the theoretical aspects of the subject. At the same time, these students are expected to complete application software assignments due fortnightly. As such they have been allocated weekly computer-time to acquire these skills in a self-instructional mode of learning. The applications software textbook selected to support the applications software aspect of the coursework has been designed for self-instruction. However, most of these IS students have only experienced teacher-directed learning and as such may be unable to manage self-instructed learning. The aim of the study is therefore to determine if teaching these student learners to learn will enhance the acquisition of application software skills. IS students are invited to register their interest in the study. A total of 103 students respond to the invitation. These students are divided into two groups: 2
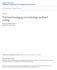
3 1.7/' E 1 E #..X EMMK Tan and Chan Figure 1. Average Assignment Scores for Treatment and Contol Groups 90.00% Ave. Score in Percentages 80.00% 70.00% 60.00% 50.00% 40.00% 30.00% 20.00% 10.00% 0.00% Assmt. 1 Assmt The attends classes that teach the students to manage their learning. These are discussed in the next section. 2. The instructs themselves using the prescribed text. The consists of 35 students. These students have been included in this group simply because their timetable permit them to attend the classes. The remaining 68 students form the. The Classes As indicated in the earlier section, Holec (1980) contends that two conditions must be satisfied in order for selfinstructed learning to occur. The classes have therefore been designed to: Train the learner to take charge of their own learning (first condition). This include learning strategies such as planning and organizing, evaluating, practicing, timed practicing, getting help, developing and using memory aids, asking for correction and peer-learning. Explain to the students the course structure in which they can exercise the skills of managing their own learning (second condition) - pointing out the choices in instructional resources. Students can use the prescribed text, CD-ROM tutorials, or any other text available. They can decide to complete their assignments at any time before the stated due date. Help can be accessed either via or at problem clinics supported by experienced teaching assistants. Data Analysis The learning outcomes are measured by the results of 2 applications software assignments. Average scores for each assignment are computed for each group. The average score for each assignment is computed by summing the results of all the students within the group and then averaged by the number of students in each of the groups. The average scores are then translated into percentages. This is presented in Figure 1. There is consistency in the results, with the Treatment group appearing to score better overall. It is interesting to note that the Treatment group perform better, averaging 34.1% higher than the Control group, in Assignment 2. While in Assignment 1 the difference is less marked, the Treatment group average is only 12.8% higher than the. A further analysis to test for statistical significance between the mean score of the 2 groups is also performed. The mean score for each group is computed by summing the results for each assignment and then averaged by the number of students in each of these groups. The twosample F test is then used to compare the mean scores of both the Treatment and Control groups. If the results of the 3
4 Managing Self-Instructed Learning F test indicate that there is a statistically significant difference between the mean scores of these two groups, then it means that there is a link between teaching learners to learn and the performance of these learners. Table 1 presents the results of the F test. The results of the analysis suggest that the calculated F value is larger than the critical value for both assignments. This implies that there is a statistical significance in the differences in the mean scores between the Treatment and s (at p<0.05) for both assignments. The study can therefore conclude that teaching learners to learn self-instructional strategies can enhance the acquisition of application software skills as manifested in superior assignment results. Discussion Students who have only experienced learning under the direct control of a teacher tend to display limited abilities to manage their learning when placed in a selfinstructional environment. For students to be successful in self-instructed learning, they must assume varying degrees of responsibilities for their learning (Dickinson, 1987). These students can be prepared to take on these responsibilities if they know the learning strategies to adopt. The results of this experiment suggest that teaching learners to 0(14/+0) %+'0%' manage self-instructed learning can enhance learning outcomes. The Treatment group is consistent in averaging a higher score for both assignments and the two-sample F test shows a significant difference (at p<0.05) between the performance of these two groups. For Assignment 1, the results are encouraging. Both Treatment and Control groups return relatively similar scores. Student experiences and comments from the Treatment group are also very positive, for example:...it's (referring to the class) really good......the others (those not in the ) asked us to teach them what we learned! Some good tips, saved us some time... Should do this at beginning of the year, with Windows. In addition, members of the Treatment group are often found helping others - an added dimension that has not been expected. The disparity in the Assignment 2 results is great with the Treatment group scoring 34.1% higher than the Control group. A possible reason for this is that students in the Control group may still be struggling with the concept of self-instruction. Table 1. Results of the Two-sample F test Comparing the Mean Scores of the Treatment and s Assmt.1 Assmt.1 Assmt.2 Assmt.2 Mean Standard Deviation Observations Degrees of Freedom (1,101) (1,101) F F critical (one tail) Note: the comparison is significant at p< Note: the comparison is significant at p<0.05 4
5 1.7/' E 1 E #..X EMMK In order for learners to take charge of their own learning they must know how. Perhaps students coming straight from high school find it hard to come to terms with no teacher directions. This leading to poor management of their learning objectives has left them with insufficient time to complete their assignments. Assignment 2 is more complex than the first. In order for students to complete this assignment adequately, they have to work through the relevant sections of the text and experiment with the application software. Working through the text is a slow process especially for learners who are unfamiliar to the concept of autonomy in learning. O malley and Chamot (1990) implicated that the retention of technical terms (declarative knowledge) is often a problem. This may be the problem faced by the Control group. Treatment group students on the other hand may have developed and used memory aids to recall terms or practiced peer learning to assist their retention. This argument has support from a study by Kohonen (1992). He contends that the presentation and repeated use of the new terms in an experiential learning experience have enhanced the learning of the terms. Implications For learners to succeed in self-instruction, they must have the skills to manage their own learning (Holec, 1988). These skills can be learnt. Learners with these skills will then be competent to assume more and more responsibility for their own learning, to become autonomous learners, faring better than those who have not these skills. The results of this study suggest that teaching learners to learn and manage self-instruction can be linked to enhanced learning outcomes in a self-instructional environment. This therefore supports Nunan s (1996) call for the inclusion of learning strategies in classrooms through syllabus and materials design. The teacher should not assume that learners have these skills at the beginning of the learning process, nor are all learners prepared for self-instruction. Nunan (1996) supports his argument by making reference to research studies of learner-centered approaches to teaching which lead to improvements in learning outcomes and in the ability to take responsibility for learning. He also provides practical illustrations of how learning skills, and hence learner autonomy, may be developed in a classroom. Tan and Chan Although this study focuses on assisting and preparing learners to learn in a self-instructional mode of learning, it supports the notion that teaching learning skills should be seen as the most basic and important educational objective no matter what learning mode is adopted (Dickinson, 1987). Whether the learning is teacher-directed, selfinstructed or computer assisted, teachers are encouraged to build into the subject curriculum the skills necessary to promote effective learning. If learners are to take more control over their selfinstructed learning, they will need a lot of assistance along the way, particularly if their previous experience has been overwhelmingly teacher-directed. Kelly (1996) argues that in order to help learners assume more responsibility in their learning, teachers too need to develop the required skills in the development of learner autonomy. Although the learner is central to learner autonomy, the teacher should not be marginalized. Limitations of the Study When interpreting the results of this study or attempting to make generalizations, it is necessary to consider the limitations imposed by the design and methodology. The sample population of this study is made up of individuals who feel that they need a little help. Thus those who respond to the project may have been prompted by their motivation and attitude to learning. This means that the sample population is an unrepresentative sample. This in turn may introduce a bias into the results of the study and therefore not truly representative of the general student population. Research with learners from the wider population is needed before the findings can be extended further. The size of the sample population is another limitation, which makes the interpretation of the results limited. Henry (1990) states that sampling error decreases as the sample size increases. Better timing, such as conducting the study earlier in the course may result in a better response and thus larger samples. In general, statistical tests comparing data categorized into groups require large sample sizes for adequate power and accuracy. The statistical test used to analyze the data of this study is one such test. This study is guided by a simple research design that focuses on teaching learners to learn. There may be other factors that can impact on the learner s ability to manage self-instruction. These tend to center around learner diversity (Thompson, 1996) and include differences in attitude to learning (Sheerin, 1991), motivation (Dickinson, 1987) and cultural orientations (Esch, 1996; Little, 1996). In addition, the data from the two assignments shows only the effects in the short term - four weeks of a 12-week course. The time factor - shortness of the experiment - can also distort the accuracy of the results. Finally, the student respondents in both Treatment and s may 5
6 Managing Self-Instructed Learning already possess different levels of learning skills acquired through earlier years of education. Suggestions for Further Research Future research needs to test the generalizability of the findings of this study. The use of larger sample populations and taking the study through the whole course can contribute to the generalizability of the findings. An important aspect of self-instruction not addressed in this study is the concept of self-direction. Self-direction refers a particular attitude (to learning) rather than techniques or modes of instruction (Candy, 1991; Dickinson, 1987). It is important to distinguish between the attitude to learning (to be self-directed**) and the mode of learning (self-instruction). To use self-instructional modes of learning the learner must know how to go about learning without constant direct intervention from a teacher. Learners who have not the skills to manage self-instruction will need teacher guidance. Those who may have the skills may not have the self-direction or motivation to be selfinstructed (Dickinson, 1987). Research into self-direction and self-directed learning may be warranted to better understand self-instruction. This study is exploratory in nature and does not set out to examine the types of self-instructional learning skills acquired or adopted by the learners in the. Future studies involving some degree of measurement of learning skills (perhaps both pre and post) may permit IS educators to better prepare for the inclusion of learning strategies in their existing curriculum. Finally is the issue of teacher training. Wenden (1991) suggests that teacher education is crucial for the successful introduction and promotion of learner autonomy. The techniques and processes involved in learner training require teachers to be capable, motivated and informed. Perhaps research is required to help teachers better understand what is involved in learner training. Conclusion The focus of this study is on teaching learners to manage self-instructed learning. The paper contends that more consideration should be given to learner training for courses that require their students to work in a self-instructional 0(14/+0) %+'0%' mode of learning. As the intake of students is on the increase in tertiary institutions in New Zealand, IS educators are challenged to include learning strategies in courses that require self-instruction. An introduction to working within a new framework should be built in as part of the course. This can prove to be need fulfilling to learners unfamiliar with self-instruction. References Candy, P.C. (1991). Self-direction for lifelong learning: A comprehensive guide to theory and practice. San Francisco: Jossey- Bass Publishers. Dickinson, L. (1987). Self-instruction in language learning. Cambridge: CUP. Ellis, G., & Sinclair, B. (1989). Learner training: A systematic approach. IATEFL Newsletter. 92, Esch, E. (1996). Promoting learner autonomy: Criteria for selection of appropriate methods, In R. Pemberton, E.S.L. Li,, W.W.F. Or, & H.D. Pierson (Eds.), Taking control - Autonomy in language learning. Hong Kong: Hong Kong University Press. Hallgarten, K. (1988). Student autonomy - learner training and self-directed learning. In S. Nicholls (Ed.), Current issues in teaching english as a second language to adults. UK: Edward Arnold. Henry, G.T. (1990). Practical sampling. Applied Social Research Methods Series, 21. Holec, H. (1988). Autonomy and language learning: Present fields of application. Strasbough: Council of Europe. Kelly, R. (1996). Language counselling for learner autonomy: The skilled helper in self-access language learning, In R. Pemberton, E.S.L. Li,, W.W.F. Or, & H.D. Pierson (Eds.), Taking control - Autonomy in language learning. Hong Kong: Hong Kong University Press. Kohonen, V. (1992). Experimental language learning, In D. Nunan (Ed.), Collaborative Language Learning and Teaching. Cambridge: CUP. Little, D. (1996). Freedom to learn and compulsion to interact: Promoting learner autonomy through the use of information systems and information technologies, In R. Pemberton, E.S.L. Li,, W.W.F. Or, & H.D. Pierson (Eds.), Taking control - Autonomy in language learning. Hong Kong: Hong Kong University Press. ** Holec uses the terms self-direction and self instruction in reverse to Dickinson. For this study Dickinson s terms are used throughout. Nunan, D. (1996). Towards autonomous learning: Some theoretical, empirical and practical issues, In R. Pemberton, E.S.L. Li,, W.W.F. Or, & H.D. Pierson (Eds.), Taking control - 6
7 1.7/' E 1 E #..X EMMK Autonomy in language learning. Hong Kong: Hong Kong University Press. O malley, J.M., & Chamot, A.U. (1990). Learning Strategies in Second Language Acquisition. Cambridge: CUP. Oxford, R. L. (1990). Language Learning Strategies: What Every Teacher Should Know. Boston, MA: Heinle & Heinle. Sheerin, S. (1992). Self-access in language learning. Cambridge: CUP. Tan and Chan Thomson, C. K. (1996). Self-assessment in self-directed learning: Issues of learner diversity. In R. Pemberton, E.S.L. Li,, W.W.F. Or, & H.D. Pierson (Eds.), Taking control - Autonomy in language learning. Hong Kong: Hong Kong University Press. Wenden, A. (1991). Learner strategies for learner autonomy: Planning and implementing learner training for language learners. Hemel Hempstead and Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice Hall. <!--msnavigation--><!--msnavigation--><!--mstheme--> Copyright Notice Informing Science follows a copyright standard similar to ACM. In particular, material published as part of the journal, either on-line or in print, is copyrighted by the publisher of Informing Science. Permission to make digital or paper copy of part or all of these works for personal or classroom use is granted without fee provided that the copies are not made or distributed for profit or commercial advantage AND that copies 1) bear this notice in full and 2) give the full citation on the first page. It is permissible to abstract these works so long as credit is given. To copy in all other cases or to republish or to post on a server or to redistribute to lists requires specific permission and payment of a fee. Contact Editor@gise.org for to request redistribution permission. 7
The Role of Motivation in Learning English Language for Pakistani Learners
 The Role of Motivation in Learning English Language for Pakistani Learners Abdur Rehman Department of English, University of Lahore, Sargodha Campus Hafiz Ahmad Bilal Department of English, University
The Role of Motivation in Learning English Language for Pakistani Learners Abdur Rehman Department of English, University of Lahore, Sargodha Campus Hafiz Ahmad Bilal Department of English, University
Users as Producers: students using video to develop learner autonomy
 P057 Users as Producers: students using video to develop learner autonomy Mike Bramhall (m.d.bramhall@shu.ac.uk), Keith Radley, John Metcalf Sheffield Hallam University, UK Abstract This paper will report
P057 Users as Producers: students using video to develop learner autonomy Mike Bramhall (m.d.bramhall@shu.ac.uk), Keith Radley, John Metcalf Sheffield Hallam University, UK Abstract This paper will report
Fidishun, D. (no date, circa, 2005). Andragogy and technology: Integrating adult learning theory as we teach with technology, Malvern, PA: Penn State
 Fidishun, D. (no date, circa, 2005). Andragogy and technology: Integrating adult learning theory as we teach with technology, Malvern, PA: Penn State Great Valley School of Graduate Professional Studies.
Fidishun, D. (no date, circa, 2005). Andragogy and technology: Integrating adult learning theory as we teach with technology, Malvern, PA: Penn State Great Valley School of Graduate Professional Studies.
A Study of Learning Strategies That Help Language Learners
 A Study of Learning Strategies That Help Language Learners to Achieve Greater Independence Kerstin Dofs Christchurch Polytechnic Institute of Technology, New Zealand Abstract This research project at Christchurch
A Study of Learning Strategies That Help Language Learners to Achieve Greater Independence Kerstin Dofs Christchurch Polytechnic Institute of Technology, New Zealand Abstract This research project at Christchurch
Learner autonomy in language learning? Is that posible?
 Learner autonomy in language learning? Is that posible? Gabriela Ladrón de Guevara de León Universidad Autónoma de la Ciudad de México Abstract Learner autonomy has been considered an essential part of
Learner autonomy in language learning? Is that posible? Gabriela Ladrón de Guevara de León Universidad Autónoma de la Ciudad de México Abstract Learner autonomy has been considered an essential part of
Programme Specification: MA Education: Leadership, Management and Change
 Programme Specification and Curriculum Map Programme Specification: MA Education: Leadership, Management and Change 1. Awarding institution Middlesex University 2. Teaching institution Middlesex University
Programme Specification and Curriculum Map Programme Specification: MA Education: Leadership, Management and Change 1. Awarding institution Middlesex University 2. Teaching institution Middlesex University
Utilizing Proficiency Test as an English Language Learning Instrument
 Utilizing Proficiency Test as an English Language Learning Instrument Han-Kwang Chen, Instructor, JinWen University of Science and Technology, Taiwan Chien-Yu Chiu, Assistant Professor, JinWen University
Utilizing Proficiency Test as an English Language Learning Instrument Han-Kwang Chen, Instructor, JinWen University of Science and Technology, Taiwan Chien-Yu Chiu, Assistant Professor, JinWen University
Dewar College of Education and Human Services Valdosta State University Department of Early Childhood and Special Education
 Dewar College of Education and Human Services Valdosta State University Department of Early Childhood and Special Education SEGC 6040 Technological Support Planning for Children and Youth with Disabilities
Dewar College of Education and Human Services Valdosta State University Department of Early Childhood and Special Education SEGC 6040 Technological Support Planning for Children and Youth with Disabilities
Learning with Technology: Language Learning Strategies. and Perceptions of Learners in an Online Environment. Zaini Amir
 AsiaCall Online Journal Vol. 1 No. 1 November 2006 Zaini Amir 50 Learning with Technology: Language Learning Strategies and Perceptions of Learners in an Online Environment Zaini Amir Universiti Kebangsaan
AsiaCall Online Journal Vol. 1 No. 1 November 2006 Zaini Amir 50 Learning with Technology: Language Learning Strategies and Perceptions of Learners in an Online Environment Zaini Amir Universiti Kebangsaan
The Advantages and Disadvantages of Computer Technology in Second Language Acquisition
 VOLUME 3 NUMBER 1, 2006 The Advantages and Disadvantages of Computer Technology in Second Language Acquisition Cheng-Chieh Lai PhD Student in Educational Leadership Prairie View A&M University College
VOLUME 3 NUMBER 1, 2006 The Advantages and Disadvantages of Computer Technology in Second Language Acquisition Cheng-Chieh Lai PhD Student in Educational Leadership Prairie View A&M University College
Enhancing critical thinking in foreign language learners
 Enhancing critical thinking in foreign language learners Servat Shirkhani Islamic Azad University, Khorram Abad Branch shirkhani10@yahoo.com Mansour Fahim Islamic Azad University, Science and Research
Enhancing critical thinking in foreign language learners Servat Shirkhani Islamic Azad University, Khorram Abad Branch shirkhani10@yahoo.com Mansour Fahim Islamic Azad University, Science and Research
Best Practices in Public Health Undergraduate Medical Education
 An Environmental Scan of Best Practices in Public Health Undergraduate Medical Education REPORT 5: Strengths, Weaknesses and Applicability of Teaching Methods MARCH 2009 Prepared by the Nevis Consulting
An Environmental Scan of Best Practices in Public Health Undergraduate Medical Education REPORT 5: Strengths, Weaknesses and Applicability of Teaching Methods MARCH 2009 Prepared by the Nevis Consulting
LEARNER AUTONOMOY AND COMPUTER TECHNOLOGY AS A FACILITATOR OF AUTONOMOUS LANGUAGE LEARNING
 LEARNER AUTONOMOY AND COMPUTER TECHNOLOGY AS A FACILITATOR OF AUTONOMOUS LANGUAGE LEARNING Res.Assist. Fatma Hayta Dicle University, f_hayta@hotmail.com Res.Assist. Zeynep Yaprak Dicle University, zeynep_yaprak@yahoo.com
LEARNER AUTONOMOY AND COMPUTER TECHNOLOGY AS A FACILITATOR OF AUTONOMOUS LANGUAGE LEARNING Res.Assist. Fatma Hayta Dicle University, f_hayta@hotmail.com Res.Assist. Zeynep Yaprak Dicle University, zeynep_yaprak@yahoo.com
English Teacher Education: The Need for a New Perspective
 Revista Alicantina de Estudios Ingleses 4 (1991): 71-76 English Teacher Education: The Need for a New Perspective Celia Floren Serrano Universidad de Zaragoza ABSTRACT The paper explores the drawbacks
Revista Alicantina de Estudios Ingleses 4 (1991): 71-76 English Teacher Education: The Need for a New Perspective Celia Floren Serrano Universidad de Zaragoza ABSTRACT The paper explores the drawbacks
Knowledge Management & E-Learning
 Knowledge Management & E-Learning, Vol.5, No.3. Sep 2013 Knowledge Management & E-Learning ISSN 2073-7904 A brief examination of predictors of e-learning success for novice and expert learners Emily Stark
Knowledge Management & E-Learning, Vol.5, No.3. Sep 2013 Knowledge Management & E-Learning ISSN 2073-7904 A brief examination of predictors of e-learning success for novice and expert learners Emily Stark
The Advantages and Disadvantages of Computer Technology in Second Language Acquisition
 The Advantages and Disadvantages of Computer Technology in Second Language Acquisition Cheng-Chieh Lai PhD Program Student in Educational Leadership Prairie View A&M University William Allan Kritsonis,
The Advantages and Disadvantages of Computer Technology in Second Language Acquisition Cheng-Chieh Lai PhD Program Student in Educational Leadership Prairie View A&M University William Allan Kritsonis,
THE IMPORTANCE OF CLASSROOM ASSESSMENT AND EVALUATION IN EDUCATIONAL SYSTEM
 Proceedings of the 2 nd International Conference of Teaching and Learning (ICTL 2009) INTI University College, Malaysia THE IMPORTANCE OF CLASSROOM ASSESSMENT AND EVALUATION IN EDUCATIONAL SYSTEM Taghi
Proceedings of the 2 nd International Conference of Teaching and Learning (ICTL 2009) INTI University College, Malaysia THE IMPORTANCE OF CLASSROOM ASSESSMENT AND EVALUATION IN EDUCATIONAL SYSTEM Taghi
Promoting student autonomy in the learning of College English
 Promoting student autonomy in the learning of College English Song Deyun & Pan Longming Chongqing University Abstract A pedagogical experiment carried out since 2000 places the emphasis on the student
Promoting student autonomy in the learning of College English Song Deyun & Pan Longming Chongqing University Abstract A pedagogical experiment carried out since 2000 places the emphasis on the student
An Investigation on Learning of College Students and the Current Application Situation of the Web-based Courses
 2011 International Conference on Computer Science and Information Technology (ICCSIT 2011) IPCSIT vol. 51 (2012) (2012) IACSIT Press, Singapore DOI: 10.7763/IPCSIT.2012.V51.127 An Investigation on Learning
2011 International Conference on Computer Science and Information Technology (ICCSIT 2011) IPCSIT vol. 51 (2012) (2012) IACSIT Press, Singapore DOI: 10.7763/IPCSIT.2012.V51.127 An Investigation on Learning
University General Education Courses Guidelines for Design and Implementation of UGE courses
 University General Education Courses Guidelines for Design and Implementation of UGE courses Please read the following guidelines before drawing up proposals for GE courses. Proposals should be submitted
University General Education Courses Guidelines for Design and Implementation of UGE courses Please read the following guidelines before drawing up proposals for GE courses. Proposals should be submitted
Definitions of Independent Learning Initial Overview
 Definitions of Independent Learning Initial Overview The concept of independent learning is not new, but is it one on which there is a surprising lack of consensus as to what it means (Broad, 2006). Independent
Definitions of Independent Learning Initial Overview The concept of independent learning is not new, but is it one on which there is a surprising lack of consensus as to what it means (Broad, 2006). Independent
The Effect of Explicit Feedback on the Use of Language Learning Strategies: The Role of Instruction
 Yıl/Year: 2013 Cilt/Volume: 2 Sayı/Issue: 5 Sayfalar/Pages: 1-12 The Effect of Explicit Feedback on the Use of Language Learning Strategies: The Role of Instruction Mohammad Rahi Islamic Azad University,
Yıl/Year: 2013 Cilt/Volume: 2 Sayı/Issue: 5 Sayfalar/Pages: 1-12 The Effect of Explicit Feedback on the Use of Language Learning Strategies: The Role of Instruction Mohammad Rahi Islamic Azad University,
Programme Specification and Curriculum Map for MSc Electronic Security and Digital Forensics
 Programme Specification and Curriculum Map for MSc Electronic Security and Digital Forensics 1. Programme title Electronic Security & Digital Forensics 2. Awarding institution Middlesex University 3. Teaching
Programme Specification and Curriculum Map for MSc Electronic Security and Digital Forensics 1. Programme title Electronic Security & Digital Forensics 2. Awarding institution Middlesex University 3. Teaching
POSTGRADUATE PROGRAMME SPECIFICATION
 POSTGRADUATE PROGRAMME SPECIFICATION Programme Title: Awarding Body: Institution: Final Awards: Intermediate Awards: Mode of Study UCAS Codes: QAA Subject Benchmarks: JACS Code: Professional/Statutory
POSTGRADUATE PROGRAMME SPECIFICATION Programme Title: Awarding Body: Institution: Final Awards: Intermediate Awards: Mode of Study UCAS Codes: QAA Subject Benchmarks: JACS Code: Professional/Statutory
The Usability of Electronic Stores based on the Organization of Information and Features
 The Usability of Electronic Stores based on the Organization of Information and Features CHAN KAH-SING Singapore Polytechnic This paper describes an investigation on how the perceived usability of electronic
The Usability of Electronic Stores based on the Organization of Information and Features CHAN KAH-SING Singapore Polytechnic This paper describes an investigation on how the perceived usability of electronic
DEFINING, TEACHING AND ASSESSING LIFELONG LEARNING SKILLS
 DEFINING, TEACHING AND ASSESSING LIFELONG LEARNING SKILLS Nikos J. Mourtos Abstract - Lifelong learning skills have always been important in any education and work setting. However, ABET EC recently put
DEFINING, TEACHING AND ASSESSING LIFELONG LEARNING SKILLS Nikos J. Mourtos Abstract - Lifelong learning skills have always been important in any education and work setting. However, ABET EC recently put
Self-assessment for autonomous language learners
 Links & Letters 7, 2000 49-60 Self-assessment for autonomous language learners David Gardner University of Hong Kong September 1999 Abstract This paper discusses why self-assessment is an important tool
Links & Letters 7, 2000 49-60 Self-assessment for autonomous language learners David Gardner University of Hong Kong September 1999 Abstract This paper discusses why self-assessment is an important tool
The Application of Autonomous Learning to Fostering Cross-cultural Communication Competence
 ISSN 1799-2591 Theory and Practice in Language Studies, Vol. 4, No. 6, pp. 1291-1295, June 2014 Manufactured in Finland. doi:10.4304/tpls.4.6.1291-1295 The Application of Autonomous Learning to Fostering
ISSN 1799-2591 Theory and Practice in Language Studies, Vol. 4, No. 6, pp. 1291-1295, June 2014 Manufactured in Finland. doi:10.4304/tpls.4.6.1291-1295 The Application of Autonomous Learning to Fostering
Teaching ESL Students in Mainstream Classrooms: language in learning across the curriculum. 2013 Information for Schools
 : language in learning across the curriculum 2013 Information for Schools What is Teaching ESL student in Mainstream Classrooms (TESMC)? (TESMC) is for educators seeking to develop understandings of the
: language in learning across the curriculum 2013 Information for Schools What is Teaching ESL student in Mainstream Classrooms (TESMC)? (TESMC) is for educators seeking to develop understandings of the
An Engagement Model for Learning: Providing a Framework to Identify Technology Services
 Interdisciplinary Journal of Knowledge and Learning Objects Volume 3, 2007 An Engagement Model for Learning: Providing a Framework to Identify Technology Services I.T. Hawryszkiewycz Department of Information
Interdisciplinary Journal of Knowledge and Learning Objects Volume 3, 2007 An Engagement Model for Learning: Providing a Framework to Identify Technology Services I.T. Hawryszkiewycz Department of Information
Programme Specification and Curriculum Map for MSc Electronic Security and Digital Forensics
 Programme Specification and Curriculum Map for MSc Electronic Security and Digital Forensics 1. Programme title Electronic Security and Digital Forensics 2. Awarding institution Middlesex University 3.
Programme Specification and Curriculum Map for MSc Electronic Security and Digital Forensics 1. Programme title Electronic Security and Digital Forensics 2. Awarding institution Middlesex University 3.
Subject Description Form
 Subject Description Form Subject Code Subject Title APSS111/ APSS1A07 Introduction to Psychology Credit Value 3 Level 1 GUR Requirements Intended to Fulfill This subject intends to fulfill the following
Subject Description Form Subject Code Subject Title APSS111/ APSS1A07 Introduction to Psychology Credit Value 3 Level 1 GUR Requirements Intended to Fulfill This subject intends to fulfill the following
REVIEW OF THE INTERNET AND YOUNG LEARNERS
 Language Learning & Technology http://llt.msu.edu/vol10num3/review3/ September 2006, Volume 10, Number 3 pp. 44-48 REVIEW OF THE INTERNET AND YOUNG LEARNERS The Internet and Young Learners Gordon Lewis
Language Learning & Technology http://llt.msu.edu/vol10num3/review3/ September 2006, Volume 10, Number 3 pp. 44-48 REVIEW OF THE INTERNET AND YOUNG LEARNERS The Internet and Young Learners Gordon Lewis
RELATIONSHIPS BETWEEN SELF DIRECTION, EFFORT AND PERFORMANCE IN AN ONLINE INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY COURSE
 RELATIONSHIPS BETWEEN SELF DIRECTION, EFFORT AND PERFORMANCE IN AN ONLINE INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY COURSE William D. Armitage, Naomi Boyer, Sarah Langevin, Alessio Gaspar University of South Florida Polytechnic
RELATIONSHIPS BETWEEN SELF DIRECTION, EFFORT AND PERFORMANCE IN AN ONLINE INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY COURSE William D. Armitage, Naomi Boyer, Sarah Langevin, Alessio Gaspar University of South Florida Polytechnic
Personal Goal-setting and Autonomy in Language Learning
 Supporting Independent English Language Learning in the 21st Century Proceedings of the Independent Learning Association Conference Inaugural 2005 Personal Goal-setting and Autonomy in Language Learning
Supporting Independent English Language Learning in the 21st Century Proceedings of the Independent Learning Association Conference Inaugural 2005 Personal Goal-setting and Autonomy in Language Learning
Developing Higher Level Thinking
 Abstract Limbach, Barbara Chadron State College Waugh, Wendy Chadron State College This paper identifies an interdisciplinary, five-step process, built upon existing theory and best practices in cognitive
Abstract Limbach, Barbara Chadron State College Waugh, Wendy Chadron State College This paper identifies an interdisciplinary, five-step process, built upon existing theory and best practices in cognitive
Restructuring a Masters Teaching Program
 Restructuring a Masters Teaching Program Marilyn Koeller National University This article will explain the process that Course Leads used to restructure the Masters in the Arts of Teaching program by working
Restructuring a Masters Teaching Program Marilyn Koeller National University This article will explain the process that Course Leads used to restructure the Masters in the Arts of Teaching program by working
Honours Degree (top-up) Business Abbreviated Programme Specification Containing Both Core + Supplementary Information
 Honours Degree (top-up) Business Abbreviated Programme Specification Containing Both Core + Supplementary Information 1 Awarding Institution / body: Lancaster University 2a Teaching institution: University
Honours Degree (top-up) Business Abbreviated Programme Specification Containing Both Core + Supplementary Information 1 Awarding Institution / body: Lancaster University 2a Teaching institution: University
Programme Specification Foundation Degree (Arts) Business and Enterprise
 P Programme Specification Foundation Degree (Arts) and Enterprise Valid from: September 2015 Oxford Brookes University Faculty of / (Activate Learning) Reading College 1 SECTION 1: GENERAL INFORMATION
P Programme Specification Foundation Degree (Arts) and Enterprise Valid from: September 2015 Oxford Brookes University Faculty of / (Activate Learning) Reading College 1 SECTION 1: GENERAL INFORMATION
The International Research Foundation for English Language Education
 Title of Report: Masters in Teaching English to Young Learners at the University of York Case Report Author: Annie Hughes Organization: University of York 1 - York, U.K. Date of Publication: February 2013
Title of Report: Masters in Teaching English to Young Learners at the University of York Case Report Author: Annie Hughes Organization: University of York 1 - York, U.K. Date of Publication: February 2013
Teaching for Developmental Diversity: An Approach to Academic Language and Critical Thinking
 Teaching for Developmental Diversity: An Approach to Academic Language and Critical Thinking Jennifer Ouellette-Schramm For a successful transition into college, ABE learners will benefit from academic
Teaching for Developmental Diversity: An Approach to Academic Language and Critical Thinking Jennifer Ouellette-Schramm For a successful transition into college, ABE learners will benefit from academic
EUR-ACE. Framework Standards for the Accreditation of Engineering Programmes. Foreword... 2. 1. Programme Outcomes for Accreditation...
 As approved by the ENAEE Administrative Council on 5 November 2008 EUR-ACE Framework Standards for the Accreditation of Engineering Programmes Table of Contents Foreword... 2 1. Programme Outcomes for
As approved by the ENAEE Administrative Council on 5 November 2008 EUR-ACE Framework Standards for the Accreditation of Engineering Programmes Table of Contents Foreword... 2 1. Programme Outcomes for
Programme Specification and Curriculum Map for MA Global Governance and Public Policy
 Programme Specification and Curriculum Map for MA Global Governance and Public Policy 1. Programme title MA / PGDip / PG Cert Global Governance and Public Policy: International Development 2. Awarding
Programme Specification and Curriculum Map for MA Global Governance and Public Policy 1. Programme title MA / PGDip / PG Cert Global Governance and Public Policy: International Development 2. Awarding
Adopting CALL to Promote Listening Skills for EFL Learners in Vietnamese Universities
 Adopting CALL to Promote Listening Skills for EFL Learners in Vietnamese Universities Lan Luu Thi Phuong University of Auckland (New Zealand) lluu003@aucklanduni.ac.nz Abstract Listening skills are an
Adopting CALL to Promote Listening Skills for EFL Learners in Vietnamese Universities Lan Luu Thi Phuong University of Auckland (New Zealand) lluu003@aucklanduni.ac.nz Abstract Listening skills are an
Factors Affecting Critical Thinking in an Online Course. Simone Conceição, PhD Assistant Professor University of Wisconsin-Milwaukee
 1 21st Annual Conference on Distance Teaching and Learning click here -> Factors Affecting Critical Thinking in an Online Course Simone Conceição, PhD Assistant Professor University of Wisconsin-Milwaukee
1 21st Annual Conference on Distance Teaching and Learning click here -> Factors Affecting Critical Thinking in an Online Course Simone Conceição, PhD Assistant Professor University of Wisconsin-Milwaukee
Essays on Teaching Excellence. Challenges in Using Technology for theimprovement of Undergraduate Education
 Essays on Teaching Excellence Toward the Best in the Academy Volume 8, Number 2, 1996-97 A publication of The Professional & Organizational Development Network in Higher Education (www.podnetwork.org).
Essays on Teaching Excellence Toward the Best in the Academy Volume 8, Number 2, 1996-97 A publication of The Professional & Organizational Development Network in Higher Education (www.podnetwork.org).
Designing Programming Exercises with Computer Assisted Instruction *
 Designing Programming Exercises with Computer Assisted Instruction * Fu Lee Wang 1, and Tak-Lam Wong 2 1 Department of Computer Science, City University of Hong Kong, Kowloon Tong, Hong Kong flwang@cityu.edu.hk
Designing Programming Exercises with Computer Assisted Instruction * Fu Lee Wang 1, and Tak-Lam Wong 2 1 Department of Computer Science, City University of Hong Kong, Kowloon Tong, Hong Kong flwang@cityu.edu.hk
What do third-year Speech Pathology students think of student-centred learning?
 What do third-year Speech Pathology students think of student-centred learning? Joanne Arciuli Faculty of Health Sciences, University of Sydney This study assessed the effectiveness and appeal of student-centred
What do third-year Speech Pathology students think of student-centred learning? Joanne Arciuli Faculty of Health Sciences, University of Sydney This study assessed the effectiveness and appeal of student-centred
Computer Assisted Language Learning
 Computer Assisted Language Learning!" # $ % &'$#($ Abstract $$ $ $ "$"" " "$ $ $ # "$ ( '$$ $ $ " " '' $ $" $ # $"$'" "" '"$' "$$ ) "*$"" +$# "$",-+../$ $$ # "-+..'$' "# "#$ " $$0#$$"$ $""-+.. $ Key words:
Computer Assisted Language Learning!" # $ % &'$#($ Abstract $$ $ $ "$"" " "$ $ $ # "$ ( '$$ $ $ " " '' $ $" $ # $"$'" "" '"$' "$$ ) "*$"" +$# "$",-+../$ $$ # "-+..'$' "# "#$ " $$0#$$"$ $""-+.. $ Key words:
FOREIGN LANGUAGE TEACHING AN INTERVIEW WITH NINA SPADA
 SPADA, Nina. Foreign Language Teaching: an interview with Nina Spada. ReVEL, vol. 2, n. 2, 2004. ISSN 1678-8931 [www.revel.inf.br/eng]. FOREIGN LANGUAGE TEACHING AN INTERVIEW WITH NINA SPADA Nina Spada
SPADA, Nina. Foreign Language Teaching: an interview with Nina Spada. ReVEL, vol. 2, n. 2, 2004. ISSN 1678-8931 [www.revel.inf.br/eng]. FOREIGN LANGUAGE TEACHING AN INTERVIEW WITH NINA SPADA Nina Spada
Software engineering: learning, employment and globalization
 Software engineering: learning, employment and globalization Julian M. Bass Robert Gordon University Aberdeen, UK j.m.bass@rgu.ac.uk C. Ramanathan IIIT-B Bangalore, India rc@iiitb.ac.in J. T. Lalchandani
Software engineering: learning, employment and globalization Julian M. Bass Robert Gordon University Aberdeen, UK j.m.bass@rgu.ac.uk C. Ramanathan IIIT-B Bangalore, India rc@iiitb.ac.in J. T. Lalchandani
Strategies for Learning Vocabulary in EFL Contexts
 Strategies for Learning Vocabulary in EFL Contexts Vocabulary widely considered as one of the most essential elements of a language plays a pivotal role in determining whether or not students will be successful
Strategies for Learning Vocabulary in EFL Contexts Vocabulary widely considered as one of the most essential elements of a language plays a pivotal role in determining whether or not students will be successful
Valuing collaboration in design for the World Wide Web: a creative team approach
 Valuing collaboration in design for the World Wide Web: a creative team approach Peter Kandlbinder Centre for Teaching and Learning University of Sydney The continuing convergence of technologies onto
Valuing collaboration in design for the World Wide Web: a creative team approach Peter Kandlbinder Centre for Teaching and Learning University of Sydney The continuing convergence of technologies onto
Research-Based Program Design Why Smart Tutor Works. Al Lockett, M.Ed. Educational Technology
 Research-Based Program Design Why Smart Tutor Works Al Lockett, M.Ed. Educational Technology Introduction Smart Tutor TM, published by Learning Today, is an advanced learning system designed to accelerate
Research-Based Program Design Why Smart Tutor Works Al Lockett, M.Ed. Educational Technology Introduction Smart Tutor TM, published by Learning Today, is an advanced learning system designed to accelerate
REGULATIONS FOR THE DEGREE OF MASTER OF EDUCATION (MEd)
 247 REGULATIONS FOR THE DEGREE OF MASTER OF EDUCATION (MEd) (See also General Regulations) Any publication based on work approved for a higher degree should contain a reference to the effect that the work
247 REGULATIONS FOR THE DEGREE OF MASTER OF EDUCATION (MEd) (See also General Regulations) Any publication based on work approved for a higher degree should contain a reference to the effect that the work
Instructional systems development
 A Pebble-in-the-Pond Model For Instructional Design by M. David Merrill Instructional systems development (ISD) has recently come under attack to suggestions that it may not be an appropriate methodology
A Pebble-in-the-Pond Model For Instructional Design by M. David Merrill Instructional systems development (ISD) has recently come under attack to suggestions that it may not be an appropriate methodology
California University Intermediate Unit 1 ESL Professional Development Project
 California University Intermediate Unit 1 ESL Professional Development Project The California University of Pennsylvania (Cal U)/ Intermediate Unit 1 (IU1) English as a Second Language (ESL) Professional
California University Intermediate Unit 1 ESL Professional Development Project The California University of Pennsylvania (Cal U)/ Intermediate Unit 1 (IU1) English as a Second Language (ESL) Professional
City University of Hong Kong. Information on a Course offered by Department of Information Systems with effect from Semester B in 2013 / 2014
 City University of Hong Kong Information on a Course offered by Department of Information Systems with effect from Semester B in 2013 / 2014 Part I Course Title: Course Code: Course Duration: Business
City University of Hong Kong Information on a Course offered by Department of Information Systems with effect from Semester B in 2013 / 2014 Part I Course Title: Course Code: Course Duration: Business
TELLab: An Experiential Learning Tool for Psychology
 TELLab: An Experiential Learning Tool for Psychology Na Li School of Engineering and Applied Sciences, nali01@fas.harvard.edu Krzysztof Z. Gajos School of Engineering and Applied Sciences, kgajos@eecs.harvard.edu
TELLab: An Experiential Learning Tool for Psychology Na Li School of Engineering and Applied Sciences, nali01@fas.harvard.edu Krzysztof Z. Gajos School of Engineering and Applied Sciences, kgajos@eecs.harvard.edu
The Facilitating Role of L1 in ESL Classes
 The Facilitating Role of L1 in ESL Classes Çağrı Tuğrul Mart Ishik University, Erbil, Iraq Email: tugrulbey@hotmail.com Abstract It has been widely advocated that insistence on English-only policy and
The Facilitating Role of L1 in ESL Classes Çağrı Tuğrul Mart Ishik University, Erbil, Iraq Email: tugrulbey@hotmail.com Abstract It has been widely advocated that insistence on English-only policy and
AMERICAN JOURNAL OF PSYCHOLOGICAL RESEARCH
 AMERICAN JOURNAL OF PSYCHOLOGICAL RESEARCH Volume 8, Number 1 Submitted: January 13, 2012 Revisions: February, 2012 Accepted: February, 2012 Published: March 1, 2012 Save the Best for Last? Social Psychology
AMERICAN JOURNAL OF PSYCHOLOGICAL RESEARCH Volume 8, Number 1 Submitted: January 13, 2012 Revisions: February, 2012 Accepted: February, 2012 Published: March 1, 2012 Save the Best for Last? Social Psychology
Adult Learning Styles: Vanessa Marcy, MMSc,PA-C
 Adult Learning Styles: How the VARK learning style inventory can be used to improve student learning. Vanessa Marcy, MMSc,PA-C Marcy. V.(2001), Adult Learning Styles: How the VARK learning style inventory
Adult Learning Styles: How the VARK learning style inventory can be used to improve student learning. Vanessa Marcy, MMSc,PA-C Marcy. V.(2001), Adult Learning Styles: How the VARK learning style inventory
POSTGRADUATE PROGRAMME SPECIFICATION
 POSTGRADUATE PROGRAMME SPECIFICATION Programme Title: Awarding Body: Teaching Institution: Final Awards: MSc International Accounting and Financial Management Staffordshire University Staffordshire University
POSTGRADUATE PROGRAMME SPECIFICATION Programme Title: Awarding Body: Teaching Institution: Final Awards: MSc International Accounting and Financial Management Staffordshire University Staffordshire University
INNOVATION CONFIGURATION. Computer Science 2014-2016
 INNOVATION CONFIGURATION Computer Science 2014-2016 SLT Member: Brian Kingsley, Dr. Elisa Calabrese OWNER OF INITIATIVE: Christine Semisch and Guy Barmoha CONTACT/COORDINATOR OF INITIATIVE: Lisa Milenkovic,
INNOVATION CONFIGURATION Computer Science 2014-2016 SLT Member: Brian Kingsley, Dr. Elisa Calabrese OWNER OF INITIATIVE: Christine Semisch and Guy Barmoha CONTACT/COORDINATOR OF INITIATIVE: Lisa Milenkovic,
How to Support Faculty as They Prepare to Teach Online Susan C. Biro Widener University Abstract: A survey, an in-depth interview, and a review of
 How to Support Faculty as They Prepare to Teach Online Susan C. Biro Widener University Abstract: A survey, an in-depth interview, and a review of the literature were used to explore the changes faculty
How to Support Faculty as They Prepare to Teach Online Susan C. Biro Widener University Abstract: A survey, an in-depth interview, and a review of the literature were used to explore the changes faculty
the general concept down to the practical steps of the process.
 Article Critique Affordances of mobile technologies for experiential learning: the interplay of technology and pedagogical practices C.- H. Lai, J.- C. Yang, F.- C. Chen, C.- W. Ho & T.- W. Chan Theoretical
Article Critique Affordances of mobile technologies for experiential learning: the interplay of technology and pedagogical practices C.- H. Lai, J.- C. Yang, F.- C. Chen, C.- W. Ho & T.- W. Chan Theoretical
NUNAN, David (ed.) Practical English Language Teaching International Edition 1 st Edition Singapore: McGraw-Hill, 2003, 342 p.
 Available online at: http://ijrte.eab.org.tr/1/1/ayilmaz_stekir.pdf http://eab.org.tr Educational Research Association The International Journal of Research in Teacher Education 2010, 1(1):65-72 ISSN:
Available online at: http://ijrte.eab.org.tr/1/1/ayilmaz_stekir.pdf http://eab.org.tr Educational Research Association The International Journal of Research in Teacher Education 2010, 1(1):65-72 ISSN:
Programme Specification and Curriculum Map for MA TESOL
 Programme Specification and Curriculum Map for MA TESOL 1. Programme title MA TESOL 2. Awarding institution Middlesex University 3. Teaching institution Middlesex University 4. Programme accredited by
Programme Specification and Curriculum Map for MA TESOL 1. Programme title MA TESOL 2. Awarding institution Middlesex University 3. Teaching institution Middlesex University 4. Programme accredited by
How To Become A Nurse
 REGULATIONS FOR THE DEGREE OF DOCTOR OF NURSING (DNurs) (See also General Regulations) N30 Definition The degree of Doctor of Nursing (DNurs) is a professional doctorate degree awarded for the satisfactory
REGULATIONS FOR THE DEGREE OF DOCTOR OF NURSING (DNurs) (See also General Regulations) N30 Definition The degree of Doctor of Nursing (DNurs) is a professional doctorate degree awarded for the satisfactory
Programme Specification
 Programme Specification Title: Sustainable Architectural Design Final Award: Master of Science (MSc) With Exit Awards at: Postgraduate Certificate (PG Cert) Postgraduate Diploma (PG Dip) Master of Science
Programme Specification Title: Sustainable Architectural Design Final Award: Master of Science (MSc) With Exit Awards at: Postgraduate Certificate (PG Cert) Postgraduate Diploma (PG Dip) Master of Science
Creative Education and New Learning as Means of Encouraging Creativity, Original Thinking and Entrepreneurship
 Creative Education and New Learning as Means of Encouraging Creativity, Original Thinking and Entrepreneurship Abstract: by Mirjana Radovic-Markovic Lecturer, Dusan Markovic Fellow, World Academy of Art
Creative Education and New Learning as Means of Encouraging Creativity, Original Thinking and Entrepreneurship Abstract: by Mirjana Radovic-Markovic Lecturer, Dusan Markovic Fellow, World Academy of Art
The Impact of Peer Assessment and Feedback Strategy in Learning Computer Programming in Higher Education
 Issues in Informing Science and Information Technology Volume 9, 2012 The Impact of Peer Assessment and Feedback Strategy in Learning Computer Programming in Higher Education Wing-Shui NG The Hong Kong
Issues in Informing Science and Information Technology Volume 9, 2012 The Impact of Peer Assessment and Feedback Strategy in Learning Computer Programming in Higher Education Wing-Shui NG The Hong Kong
Assessing Fundamentals in Every Course Through Mastery Learning
 2 We are all accustomed to periodic summative testing for achievement, but in this chapter the importance of requiring mastery of fundamentals as the baseline for evaluation, regardless of the level of
2 We are all accustomed to periodic summative testing for achievement, but in this chapter the importance of requiring mastery of fundamentals as the baseline for evaluation, regardless of the level of
Victoria University's (Australia) Master of Business (Enterprise Resource Planning Systems)
 Victoria University's (Australia) Master of Business (Enterprise Resource Planning Systems) Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) is an enterprisewide information system designed to coordinate all the resources,
Victoria University's (Australia) Master of Business (Enterprise Resource Planning Systems) Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) is an enterprisewide information system designed to coordinate all the resources,
ISTE National Educational Technology Standards for Teachers http://cnets.iste.org/teachers/t_profiles.html
 NETS for Teachers Profiles for Technology-Literate Teachers Today's teacher preparation programs provide a variety of alternative paths to initial licensure. They address economic conditions, needs of
NETS for Teachers Profiles for Technology-Literate Teachers Today's teacher preparation programs provide a variety of alternative paths to initial licensure. They address economic conditions, needs of
PROGRAMME SPECIFICATION
 PROGRAMME SPECIFICATION This Programme Specification is correct as of the date indicated; however, minor amendments may be made throughout the year and will be incorporated in the annual updating process.
PROGRAMME SPECIFICATION This Programme Specification is correct as of the date indicated; however, minor amendments may be made throughout the year and will be incorporated in the annual updating process.
Effects of Computer Animation Package on Senior Secondary School Students Academic Achievement in Geography in Ondo State, Nigeria.
 Journal of Teaching and Teacher Education ISSN (2210-1578) J. Tea. Tea. Edu. 3, No. 2 (July-2015) Effects of Computer Animation Package on Senior Secondary School Students Academic Achievement in Geography
Journal of Teaching and Teacher Education ISSN (2210-1578) J. Tea. Tea. Edu. 3, No. 2 (July-2015) Effects of Computer Animation Package on Senior Secondary School Students Academic Achievement in Geography
Writing Better Objective Tests Bill Cerbin UW La Crosse, Center for Advancing Teaching & Learning
 Bill Cerbin UW La Crosse, Center for Advancing Teaching & Learning Prioritize the subject matter What subject matter topics, ideas, concepts are 1. Essential 2. Important 3. Worth being familiar with Use
Bill Cerbin UW La Crosse, Center for Advancing Teaching & Learning Prioritize the subject matter What subject matter topics, ideas, concepts are 1. Essential 2. Important 3. Worth being familiar with Use
Programme Specification and Curriculum Map for MSc Business Information Systems Management
 Programme Specification and Curriculum Map for MSc Business Information Systems Management 1. Programme title Business Information Systems Management 2. Awarding institution Middlesex University 3. Teaching
Programme Specification and Curriculum Map for MSc Business Information Systems Management 1. Programme title Business Information Systems Management 2. Awarding institution Middlesex University 3. Teaching
LEARNING STYLES AND ACADEMIC PERFORMANCE OF STUDENTS IN ENGLISH AS A SECOND-LANGUAGE CLASS IN IRAN
 Bulgarian Journal of Science and Education Policy (BJSEP), Volume 7, Number 2, 2013 LEARNING STYLES AND ACADEMIC PERFORMANCE OF STUDENTS IN ENGLISH AS A SECOND-LANGUAGE CLASS IN IRAN 1 Soghra AKBARI CHERMAHINI,
Bulgarian Journal of Science and Education Policy (BJSEP), Volume 7, Number 2, 2013 LEARNING STYLES AND ACADEMIC PERFORMANCE OF STUDENTS IN ENGLISH AS A SECOND-LANGUAGE CLASS IN IRAN 1 Soghra AKBARI CHERMAHINI,
Nottingham Trent University Course Specification
 Nottingham Trent University Course Specification Basic Course Information 1. Awarding Institution: Nottingham Trent University 2. School/Campus: Nottingham Business School /City Campus 3. Final Award,
Nottingham Trent University Course Specification Basic Course Information 1. Awarding Institution: Nottingham Trent University 2. School/Campus: Nottingham Business School /City Campus 3. Final Award,
Blackburn College Teaching, Learning and Assessment Strategy. 25 August 2015
 Blackburn College Teaching, Learning and Assessment Strategy 25 August 2015 1 Introduction This document provides a Teaching, Learning and Assessment Strategy covering all of the College s Further Education
Blackburn College Teaching, Learning and Assessment Strategy 25 August 2015 1 Introduction This document provides a Teaching, Learning and Assessment Strategy covering all of the College s Further Education
REGULATIONS FOR THE DEGREE OF MASTER OF SCIENCE IN LIBRARY AND INFORMATION MANAGEMANT (MSc[LIM])
![REGULATIONS FOR THE DEGREE OF MASTER OF SCIENCE IN LIBRARY AND INFORMATION MANAGEMANT (MSc[LIM]) REGULATIONS FOR THE DEGREE OF MASTER OF SCIENCE IN LIBRARY AND INFORMATION MANAGEMANT (MSc[LIM])](/thumbs/39/18121628.jpg) 268 REGULATIONS FOR THE DEGREE OF MASTER OF SCIENCE IN LIBRARY AND INFORMATION MANAGEMANT (MSc[LIM]) (See also General Regulations) Any publication based on work approved for a higher degree should contain
268 REGULATIONS FOR THE DEGREE OF MASTER OF SCIENCE IN LIBRARY AND INFORMATION MANAGEMANT (MSc[LIM]) (See also General Regulations) Any publication based on work approved for a higher degree should contain
Preparatory Course for MSc FINANCE & FINANCIAL LAW
 Preparatory Course for MSc FINANCE & FINANCIAL LAW UNIVERSITY OF LONDON INTERNATIONAL PROGRAMME Lead College: The School of Oriental and African Studies (SOAS) The University of Hong Kong School of Professional
Preparatory Course for MSc FINANCE & FINANCIAL LAW UNIVERSITY OF LONDON INTERNATIONAL PROGRAMME Lead College: The School of Oriental and African Studies (SOAS) The University of Hong Kong School of Professional
Negotiated syllabus for Second Chance Schools: Theoretical considerations and the practicalities of its implementation
 Negotiated syllabus for Second Chance Schools: Theoretical considerations and the practicalities of its implementation Second Chance School of Alexandroupolis Abstract Diversity in Second Chance Schools
Negotiated syllabus for Second Chance Schools: Theoretical considerations and the practicalities of its implementation Second Chance School of Alexandroupolis Abstract Diversity in Second Chance Schools
TEACHING AND LEARNING IN COMPETENCY-BASED EDUCATION
 The Fifth International Conference on e-learning (elearning-2014), 22-23 September 2014, Belgrade, Serbia TEACHING AND LEARNING IN COMPETENCY-BASED EDUCATION NEIL O SULLIVAN Innovative Together Ltd, neilos@innovate-together.com
The Fifth International Conference on e-learning (elearning-2014), 22-23 September 2014, Belgrade, Serbia TEACHING AND LEARNING IN COMPETENCY-BASED EDUCATION NEIL O SULLIVAN Innovative Together Ltd, neilos@innovate-together.com
Master of Arts in Instructional Technology Program. Policies and Procedures Manual 2014-2015
 Master of Arts in Instructional Technology Program Policies and Procedures Manual 01-015 Master of Arts in Instructional Technology Program School of Education The Richard Stockton College of New Jersey
Master of Arts in Instructional Technology Program Policies and Procedures Manual 01-015 Master of Arts in Instructional Technology Program School of Education The Richard Stockton College of New Jersey
Completing tasks for online forums: a look through the students eyes
 Completing tasks for online forums: a look through the students eyes Maria Kuteeva Instituto Superior de Contabilidade e Administração de Lisboa Abstract The use of ICT for language teaching has been growing
Completing tasks for online forums: a look through the students eyes Maria Kuteeva Instituto Superior de Contabilidade e Administração de Lisboa Abstract The use of ICT for language teaching has been growing
James E. Bartlett, II is Assistant Professor, Department of Business Education and Office Administration, Ball State University, Muncie, Indiana.
 Organizational Research: Determining Appropriate Sample Size in Survey Research James E. Bartlett, II Joe W. Kotrlik Chadwick C. Higgins The determination of sample size is a common task for many organizational
Organizational Research: Determining Appropriate Sample Size in Survey Research James E. Bartlett, II Joe W. Kotrlik Chadwick C. Higgins The determination of sample size is a common task for many organizational
Task-based pedagogy in technology mediated writing
 Lingnan University Digital Commons @ Lingnan University Staff Publications - Lingnan University 7-6-2015 Task-based pedagogy in technology mediated writing Preet Pankaj HIRADHAR Lingnan University, Hong
Lingnan University Digital Commons @ Lingnan University Staff Publications - Lingnan University 7-6-2015 Task-based pedagogy in technology mediated writing Preet Pankaj HIRADHAR Lingnan University, Hong
How to Build Effective Online Learner Support Services
 How to Build Effective Online Learner Support Services www.contactnorth.ca www.contactnord.ca How to Build Effective Online Learner Support Services Online support services for learners can be as important
How to Build Effective Online Learner Support Services www.contactnorth.ca www.contactnord.ca How to Build Effective Online Learner Support Services Online support services for learners can be as important
A Case Study of Classroom Management on Wireless- Based Learning by Tablet PC
 A Case Study of Classroom Management on Wireless-Based Learning by Tablet PC A Case Study of Classroom Management on Wireless- Based Learning by Tablet PC Shinn-Rong Lin Graduate Institute of Learning
A Case Study of Classroom Management on Wireless-Based Learning by Tablet PC A Case Study of Classroom Management on Wireless- Based Learning by Tablet PC Shinn-Rong Lin Graduate Institute of Learning
REGULATIONS FOR THE DEGREE OF MASTER OF SCIENCE IN LIBRARY AND INFORMATION MANAGEMANT (MSc[LIM])
![REGULATIONS FOR THE DEGREE OF MASTER OF SCIENCE IN LIBRARY AND INFORMATION MANAGEMANT (MSc[LIM]) REGULATIONS FOR THE DEGREE OF MASTER OF SCIENCE IN LIBRARY AND INFORMATION MANAGEMANT (MSc[LIM])](/thumbs/25/5569712.jpg) 250 REGULATIONS FOR THE DEGREE OF MASTER OF SCIENCE IN LIBRARY AND INFORMATION MANAGEMANT (MSc[LIM]) (See also General Regulations) Any publication based on work approved for a higher degree should contain
250 REGULATIONS FOR THE DEGREE OF MASTER OF SCIENCE IN LIBRARY AND INFORMATION MANAGEMANT (MSc[LIM]) (See also General Regulations) Any publication based on work approved for a higher degree should contain
How To Become An Occupational Therapy Assistant
 Mission of the Occupational Therapy Assistant Program The mission of the Occupational Therapy Assistant Program at the North Dakota State College of Science (NDSCS) is to prepare students for entry level
Mission of the Occupational Therapy Assistant Program The mission of the Occupational Therapy Assistant Program at the North Dakota State College of Science (NDSCS) is to prepare students for entry level
Doctor of Education - Higher Education
 1 Doctor of Education - Higher Education The University of Liverpool s Doctor of Education - Higher Education (EdD) is a professional doctoral programme focused on the latest practice, research, and leadership
1 Doctor of Education - Higher Education The University of Liverpool s Doctor of Education - Higher Education (EdD) is a professional doctoral programme focused on the latest practice, research, and leadership
Integrated Course Design
 IDEA PAPER #42 Integrated Course Design L. Dee Fink University of Oklahoma Teaching is a complex human action. The many tasks that are involved comprise four general components: Knowledge of the subject
IDEA PAPER #42 Integrated Course Design L. Dee Fink University of Oklahoma Teaching is a complex human action. The many tasks that are involved comprise four general components: Knowledge of the subject
Full time adult credential students instructional preferences at California State University, Long Beach: pedagogy or andragogy?
 Wang / J Zhejiang Univ SCI 2004 5(3):365-370 365 Journal of Zhejiang University SCIENCE ISSN 1009-3095 http://www.zju.edu.cn/jzus E-mail: jzus@zju.edu.cn Full time adult credential students instructional
Wang / J Zhejiang Univ SCI 2004 5(3):365-370 365 Journal of Zhejiang University SCIENCE ISSN 1009-3095 http://www.zju.edu.cn/jzus E-mail: jzus@zju.edu.cn Full time adult credential students instructional
Enhancing Critical Thinking and Daily-Life Application in a Psychology Course: A Case Album Approach
 Enhancing Critical Thinking and Daily-Life Application in a Psychology Course: A Case Album Approach J.P. Leung, Darius K.S. Chan and Catherine S.K. Tang The Chinese University of Hong Kong A b s t r a
Enhancing Critical Thinking and Daily-Life Application in a Psychology Course: A Case Album Approach J.P. Leung, Darius K.S. Chan and Catherine S.K. Tang The Chinese University of Hong Kong A b s t r a
