Genetic Factors Governing. Susceptibilities to Severe Infections
|
|
|
- Alexandrina Parsons
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Genetic Factors Governing Susceptibilities to Severe Infections GSK-Chair of Infectious Diseases Pr Jean-Paul MIRA
2 Sommes-nous tous égaux devant les infections graves? Université catholique de Louvain Ecole de médecine 18 Février 2005 Pr. Jean-Paul Mira Réanimation Médicale et Département de Biologie Cellulaire Hôpital Cochin & Institut Cochin, Paris
3 SEPSIS Major Cause of Mortality 1 st cause of death in ICU 1,5 million of severe sepsis/year (Europe) 9% of ICU admissions Estimated cost : 17 milliards $/year (USA) Increased incidence over the years
4 Septic Shock Epidemiology Annane D. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2003;168:
5
6 «If it were not for the great variability among individuals medicine might as well be a science and not an art» Sir William Osler, «Today we are learning the language in which God created life. It will revolutionize the diagnosis, prevention and treatment of most, if not all human diseases.» William J. Clinton, June 26, 2000
7 From Watson and Crick to Human Genome 1953 Watson and Crick: double helical structure of DNA 1960s Role of RNA and Genetic Code 1970s Recombinant DNA technology 1977 Sanger and Gilbert: DNA sequencing 1983 Mapping of disorders by linkage (Huntington disease) 1986 Polymerase Chain Reaction 1990 Human Genome Project 1995 Haemophilus influenzae genome 2003 Mice and Human genome sequence Human SNP Map
8
9 Molecular Genetic Research Heriditary disorder Linkage studies Mutation or polymorphism Genetics Milewitcz DM. Circulation 2000; 102: IV-103
10 TOUS LES ÊTRES HUMAINS PARTAGENT LES MÊMES GÈNES MAIS
11 Small differences in genotype make big differences to phenotype
12
13 Evidences for a genetic component to sepsis Animal Studies - Susceptibility/resistance to certain infection in mice - Susceptibility/resistance phenotypes of knock-out mice
14 Mice Susceptibility to Infection with Group A Streptococci 10 3 cfu Strepto Subcutaneous d2 Goldman O. J Infect Dis 2003;187:
15 Lipoproteins Gram+ Bacteria Fungi TLR2 +/- TLR1/6 Double-stranded RNA LPS Gram- Bacteria NF-κB Signalisation Flagellin TLR4 TLR3 TLR5 TLRx? Monocyte or Dendritic cell TLR9 CpG DNA Immunomodulatory genes Adaptative Response Tissue Injury Cellular Immunity Bacteria Lysis Apoptosis Septic Shock
16 TLR2-KO Mice and Response to Gram Positive Bacteria Intraveneous infusion of Staphylococcus aureus Takeuchi et al., J. Immunol. 1999; 165:5392
17 Evidences for a genetic component to sepsis Animal Studies - Susceptibility/resistance to certain infection in mice - Susceptibility/resistance phenotypes of knockout mice Human Studies - Clinical Evidences - Ethnic Differences - Twin Studies - Adoptee Studies
18
19 Tuberculosis Kallmann FJ, Am rev Tuber Comstock GW, Am Rev Respir Dis Leprosis Fine PE, Int J leprosy 1981 Helicobacter pylori Malaty HM, Ann Intern Med Malaria Jepson AP, J Infect Dis AIDS Chang J, J Virol Twin Studies
20 Genetic and environmental influences on premature death in adult adoptees Cause of Death (Parent Dead before the age of 50) Relative risk for the adoptee to die from the same cause All causes Biologic Adoptive Infection Vascular Biologic Adoptive Biologic Adoptive Sørensen TI, et al. NEJM 1988; 318:
21 Host Genetics of Infectious Diseases Genetics of Complex Diseases Mendelian Genetics Genes Environmental Influences Pathogen P H E N O T Y P E S Gene Pathogen
22 Genetics of Phagocyte Immune Defects Number Cyclic neutropenia (AD) Congenital agranulocytosis (Kostmann syndrome) Rolling Deficiciency Type II: Sialyl Lewis X (AR) Selectin Deficiency ( AR) Leukocyte Adhesion Deficiency Type I: CD18 (AR); Bacterial lysis Deficiency Chronic Granulomatous Disease (AR, X) Myeloperoxidase deficiency Neutrophil granule defects Phagocytosis Deficiency Complement deficiencies Mutations of MBL Recurrent Bacterial Infections Holland SM and Gallin JI, Annu Rev Med 1998
23 Single Gene Defects and Severe Immunodeficiency Disorders System involved Typical clinical syndrome Genetic Defect B lymphocyte Defective antibody production B cell tyrosine kinase CD40 ligand T lymphocyte Defective humoral and cellular immunity IL-2 receptor Neutrophil Defective phagocytosis Cytochrome b β 2 integrin Macrophage Susceptibility to mycobacterial infection Interferon γ receptor Complement Recurrent Neisseria infections Terminal complement components
24 Single Gene Defects and Severe Tuberculosis Parental consanguinity Affected siblings Familial forms of disseminated infections with weakly pathogenic mycobacteria Search for recessive genetic disorders
25 Bacteria Parasite Yeast Early Defense Late Defense NO MAC T Th1 MAC IFN-γ H 2 O 2 IL-12 MAC IL-12 HLA-DR NO NK IFN-γ MAC H 2 O 2 (Biron et Gazzinelli. Curr. Op. Immuno. 1995;7: )
26 Mendelian susceptibility to mycobacterial infection in man Mycobacterium IFN- γ R1 IFN- γ R2 IFN- γ R1 IFN-γ R2 IFN- γ IL-12 p35 IL-12 Rβ 1 IL-12 p40 IL-12 Rβ 2 Macrophage / dendritic cell NK cell / T cell Altare F et al. Curr Op Immunol 1998
27 Mycobacteria Early Defense Late Defense NO MAC T Th1 MAC IFN-γ H 2 O 2 IL-12 MAC IL-12 HLA-DR NO NK IFN-γ MAC H 2 O 2
28 Host Genetics of Infectious Diseases Genetics of Complex Diseases Genes Environmental Influences Pathogen P H E N O T Y P E S
29 Polymorphismes Génétiques
30 Polymorphismes génétiques fonctionnels Promoteur Exon1 Intron1 Exon2 Changement Quantitatif Détection des pathogènes (CD14; MBL) Inflammation (TNF; IL-1; ) Coagulation (PAI-1; VII; ) Thérapeutique (CYP) Changement Qualitatif Détection des pathogènes(toll; FcR; ) Inflammation (TNFR;iNOS; ) Coagulation (Leyden; ) Thérapeutique
31 Background vs. Functional SNPs Before DNA Sequencing S I M O T M! G A E R E A T N S P DNA Sequence Variation 1 Variation 2 IMPORTANT MESSAGE! IMPERTANT MESSAGE! IMPORTANT MASSAGE!
32
33
34 Genetic Polymorphisms and Severe Sepsis Gene Susceptibility and/or Outcome Mannose Binding Lectin Toll-Like Receptor 4/2 Toll-Like Receptor 5 CD14 FCγRII Receptor TNF locus IL-18 IL-10 IL-6 IL-1 locus IL-4 Caspase 12 PAI-1 FactorV Leiden Meningococcemia, Pneumococcemia Severe sepsis Gram negative/positive Septic Shock Legionnaire s Disease Septic Shock Meningococcemia; Pneumococcemia Meningococcemia Septic Shock; Cerebral Malaria Severe Sepsis Severe Sepsis, Meningococcemia Severe sepsis Severe Sepsis Viral Pneumonia Severe Sepsis Meningococcemia; Severe sepsis Meningococcemia; Severe sepsis
35 Pathogen Detection
36
37 TLR2 and Streptococcus pneumoniae meningitis WT TLR2 -/- Echchannaoui H et al. JID 2002;186:798
38
39 Anthrax Brucella Listeria Yersinia Campylobacter E. coli Streptomycces Virus Legionella S. enterococcus S. pneumoniae Fungi
40 Mannose-Binding Lectin Gram+ Yeast Gram- Mycobact. Collectin Structural homology with C1q Associated to 2 serine proteases Variability: - Point mutations codons 52, 54, 57 - Polymorphisms in the promoter
41 Mannose-binding Lectin Polymorphisms & The Risk of Infections Repeated bacterial and fungal infections Sumiya et al., Lancet 1991 Summerfeld et al., Lancet 1995 Garred et al., Lancet 1995 Summerfeld et al., BMJ 1997 Infections after chemotherapy Neth et al., Lancet 2001 Peterslund et al., Lancet 2001 Increased severity of lung disease and low survival in cystic fibrosis Garred et al., J. Clin. Invest Meningococcal disease Hibberd et al., Lancet 1999
42 MBL genotype and risk of invasive pneumococcal disease % Variants homozygotes P < 0.05 Contrôles n=1032 Patients n=337 Odds ratio 3.48 ( ); p=0,003 Roy et al. Lancet 2002; 359:
43
44 Cytokine Polymorphisms
45 TNF plasma levels and mortality Non-survivors TNF (pg/ml) TNF (pg/ml) Survivors Septic shock Trauma Blood Samples Martin C et al. Crit Care Med 1997;25:1813
46 Interindividual Differences in TNF-α Secretion 2500 TNF (pg/ml) , LPS (pg/ml) Molvig, 1988
47 TNF locus LT-β TNF-α LT-α TNF1 TNF Nco.I TNFB1 TNFB2
48 Association of TNF2 with TNF levels in Septic Shock TNF1 TNF2 Appoloni O. Am J Med 2001; 110:486
49 TNF2 polymorphism and septic shock susceptibility 80 p= % Patients TNF1 TNF2 Control TNF1 TNF2 Septic shock Mira JP. JAMA. 1999, 282:561-8
50 TNF2 polymorphism and septic shock outcome TNF1 39.2% TNF2 42.6% 71.4% Mira JP. JAMA 1999;282:561-8
51 TNF2 polymorphism and septic shock mortality Characteristics TNF1 TNF2 p (n=54) (n=35) Age [mean. ± SD] 57 ± ± 16 ns SAPS II [mean. ± SD] 54 ± ± 22 ns OSF [mean. ± SD] 3 ± ± 1 ns Observed mortality (%) Predicted mortality (%) ns Mira. JAMA 1999;282:561-8
52 Community-Acquired Pneumonia and TNF polymorphisms 280 CAP No association with mortality rate LTα+250 AA genotype RR= 2.48 ( ), Age-adjusted RR = 3.64 ( ) Waterer GW. AJRCCM 2001; 163: 1599
53 Coagulation Polymorphisms
54 Cytokines Generation of thrombin mediated by tissue factor Impairment of anticoagulant pathways Suppression of fibrinolysis + + TF -> > Thr -> > Fibrin Low levels of ATIII Prot C, Prot S Insufficient TFPI - PAI-1 -> > t-pat Formation of fibrin Inadequate removal of fibrin Thrombosis of small and midsize vessels After Levi et Ten Cate, N Engl J Med 1999;341:
55 4G/5G PAI-1 Polymorphism Transcriptional activator Regulatory region GGGGG Repressor protein Transcription Low plasma PAI-1 concentration 5 Promoter Exon PAI-1 gene GGGG Transcriptional activator High plasma PAI-1 concentration
56 Genetics and Trauma Outcome
57 4G/5G promoter polymorphism in the PAI-1 gene and severe trauma patients PAI-1 (ng/l) Time (days) 4G/4G 4G/5G 5G/5G Interleukin 1 (ng/l) TNF-α (ng/l) G/4G 4G/5G 5G/5G Menges, Lancet 2001;357:1096 Time (days)
58 4G/5G promoter polymorphism in the PAI-1 gene and severe trauma patients % Sepsis % MOF % Fatal Outcome G/4G 4G/5G 5G/5G 4G/4G 4G/5G 5G/5G 4G/4G 4G/5G 5G/5G Menges, Lancet 2001;357:1096
59 4G/5G PAI-1 Polymorphism and Meningococcal Disease % Predicted Mortality P= % Observed Mortality P= % Vascular Complications Survivors P= G/4G 4G/5G 5G/5G 4G/4G 4G/5G 5G/5G 4G/4G 4G/5G 5G/5G Haralambous E. Crit Care Med 2003;31:2788
60
61 Perspectives and Conclusions Screening of a high number of polymorphisms in large cohorte SNPs or haplotype Micro-arrays, Taqman, Mass Spectroscopy, Yamada Y et al. N Engl J Med 2002; 347: patients with myocardial infarction 2242 controls 112 polymorphisms of 71 candidate genes PAI-1, connexin 37, stromelysin
62 Perspectives et Conclusions Screening of a high number of polymorphisms in large cohorts UK: 1000 Patients Peritonitis UK: 2000 Patients Community-Acquired Pneumonia USA: 2000 Patients Severe Sepsis USA: 1500 Patients Severe Sepsis France: 3500 Patients Nosocomial Pneumonia France: 3500 Severe Trauma Australia? Japan?
63 Génotypage à Haut Débit
64 Perspectives and Conclusions Screening of a high number of polymorphisms Identify potential markers of susceptibility, severity, and clinical outcome Genetic profiling Individual risk assessment Prevention, Vaccination To tailor prescriptions to each patient
65 Perspectives and Conclusions Screening of a high number of polymorphisms Identify potential markers of susceptibility, severity, and clinical outcome Genetic profiling Individual risk assessment To tailor prescriptions to each patient Stratification of patients by genotype in the design of treatment trials Identify potential markers for responders vs non-responders
66
67
68
69
70
Autoimmunity and immunemediated. FOCiS. Lecture outline
 1 Autoimmunity and immunemediated inflammatory diseases Abul K. Abbas, MD UCSF FOCiS 2 Lecture outline Pathogenesis of autoimmunity: why selftolerance fails Genetics of autoimmune diseases Therapeutic
1 Autoimmunity and immunemediated inflammatory diseases Abul K. Abbas, MD UCSF FOCiS 2 Lecture outline Pathogenesis of autoimmunity: why selftolerance fails Genetics of autoimmune diseases Therapeutic
Pathogens and the immune system
 Review of lecture 7 Pathogens and the immune system Veronica Leautaud, Ph.D. vl2@ rice.edu BRC 511 / 530-lab Lecture 8 BIOE 301-Bioengineering and World Health Science Science is the human activity of
Review of lecture 7 Pathogens and the immune system Veronica Leautaud, Ph.D. vl2@ rice.edu BRC 511 / 530-lab Lecture 8 BIOE 301-Bioengineering and World Health Science Science is the human activity of
Natalia Taborda Vanegas. Doc. Sci. Student Immunovirology Group Universidad de Antioquia
 Pathogenesis of Dengue Natalia Taborda Vanegas Doc. Sci. Student Immunovirology Group Universidad de Antioquia Infection process Epidermis keratinocytes Dermis Archives of Medical Research 36 (2005) 425
Pathogenesis of Dengue Natalia Taborda Vanegas Doc. Sci. Student Immunovirology Group Universidad de Antioquia Infection process Epidermis keratinocytes Dermis Archives of Medical Research 36 (2005) 425
Chapter 43: The Immune System
 Name Period Our students consider this chapter to be a particularly challenging and important one. Expect to work your way slowly through the first three concepts. Take particular care with Concepts 43.2
Name Period Our students consider this chapter to be a particularly challenging and important one. Expect to work your way slowly through the first three concepts. Take particular care with Concepts 43.2
ANIMALS FORM & FUNCTION BODY DEFENSES NONSPECIFIC DEFENSES PHYSICAL BARRIERS PHAGOCYTES. Animals Form & Function Activity #4 page 1
 AP BIOLOGY ANIMALS FORM & FUNCTION ACTIVITY #4 NAME DATE HOUR BODY DEFENSES NONSPECIFIC DEFENSES PHYSICAL BARRIERS PHAGOCYTES Animals Form & Function Activity #4 page 1 INFLAMMATORY RESPONSE ANTIMICROBIAL
AP BIOLOGY ANIMALS FORM & FUNCTION ACTIVITY #4 NAME DATE HOUR BODY DEFENSES NONSPECIFIC DEFENSES PHYSICAL BARRIERS PHAGOCYTES Animals Form & Function Activity #4 page 1 INFLAMMATORY RESPONSE ANTIMICROBIAL
and Antigen Presentation
 1 Innate Immunity and Antigen Presentation Andrew Lichtman, MD PhD Brigham and Women's Hospital Harvard Medical School 2 Lecture outline Innate immunity Receptors and mechanisms Roles in disease Antigen
1 Innate Immunity and Antigen Presentation Andrew Lichtman, MD PhD Brigham and Women's Hospital Harvard Medical School 2 Lecture outline Innate immunity Receptors and mechanisms Roles in disease Antigen
Innate Immunity: Nonspecific Defenses of the Host
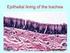 16 Innate Immunity: Nonspecific Defenses of the Host SLOs Differentiate between innate and adaptive immunity. Define toll-like receptors. Differentiate physical from chemical factors, and list examples
16 Innate Immunity: Nonspecific Defenses of the Host SLOs Differentiate between innate and adaptive immunity. Define toll-like receptors. Differentiate physical from chemical factors, and list examples
Chapter 17A: Adaptive Immunity Part I
 Chapter 17A: Adaptive Immunity Part I 1. Overview of Adaptive Immunity 2. T and B Cell Production 3. Antigens & Antigen Presentation 4. Helper T cells 1. Overview of Adaptive Immunity The Nature of Adaptive
Chapter 17A: Adaptive Immunity Part I 1. Overview of Adaptive Immunity 2. T and B Cell Production 3. Antigens & Antigen Presentation 4. Helper T cells 1. Overview of Adaptive Immunity The Nature of Adaptive
11/20/2011. Outline. Immune System Function. Terminology. Two Types of Immune Defense. Innate Immunity = Non Specific
 Chapter 43 Immune System Outline I. Nonspecific Defenses A. Barrier B. Protective proteins C. Phagocytes D. Natural killer cells E. Inflammatory reaction II. Specific Defenses A. B cells Antibody mediated
Chapter 43 Immune System Outline I. Nonspecific Defenses A. Barrier B. Protective proteins C. Phagocytes D. Natural killer cells E. Inflammatory reaction II. Specific Defenses A. B cells Antibody mediated
Cytomegalovirus in the immunocompent: Prevent, Treat, or Ignore?
 Cytomegalovirus in the immunocompent: Prevent, Treat, or Ignore? Gordon D. Rubenfeld, MD MSc Professor of Medicine, University of Toronto Chief, Program in Trauma, Emergency, and Critical Care Sunnybrook
Cytomegalovirus in the immunocompent: Prevent, Treat, or Ignore? Gordon D. Rubenfeld, MD MSc Professor of Medicine, University of Toronto Chief, Program in Trauma, Emergency, and Critical Care Sunnybrook
Name (print) Name (signature) Period. (Total 30 points)
 AP Biology Worksheet Chapter 43 The Immune System Lambdin April 4, 2011 Due Date: Thurs. April 7, 2011 You may use the following: Text Notes Power point Internet One other person in class "On my honor,
AP Biology Worksheet Chapter 43 The Immune System Lambdin April 4, 2011 Due Date: Thurs. April 7, 2011 You may use the following: Text Notes Power point Internet One other person in class "On my honor,
specific B cells Humoral immunity lymphocytes antibodies B cells bone marrow Cell-mediated immunity: T cells antibodies proteins
 Adaptive Immunity Chapter 17: Adaptive (specific) Immunity Bio 139 Dr. Amy Rogers Host defenses that are specific to a particular infectious agent Can be innate or genetic for humans as a group: most microbes
Adaptive Immunity Chapter 17: Adaptive (specific) Immunity Bio 139 Dr. Amy Rogers Host defenses that are specific to a particular infectious agent Can be innate or genetic for humans as a group: most microbes
Immunology in pathology (immunopathology) Patology. immunology in pathology. immunologic response. lecture 3
 Patology Immunology in pathology (immunopathology) lecture 3 prof. dr hab. n. med. Andrzej Marszałek immunology in pathology Diseases with immunologic mechanism of tissue injury. Hypersensitivity reactions:
Patology Immunology in pathology (immunopathology) lecture 3 prof. dr hab. n. med. Andrzej Marszałek immunology in pathology Diseases with immunologic mechanism of tissue injury. Hypersensitivity reactions:
Chapter 43: The Immune System
 Name Period Our students consider this chapter to be a particularly challenging and important one. Expect to work your way slowly through the first three concepts. Take particular care with Concepts 43.2
Name Period Our students consider this chapter to be a particularly challenging and important one. Expect to work your way slowly through the first three concepts. Take particular care with Concepts 43.2
The role of IBV proteins in protection: cellular immune responses. COST meeting WG2 + WG3 Budapest, Hungary, 2015
 The role of IBV proteins in protection: cellular immune responses COST meeting WG2 + WG3 Budapest, Hungary, 2015 1 Presentation include: Laboratory results Literature summary Role of T cells in response
The role of IBV proteins in protection: cellular immune responses COST meeting WG2 + WG3 Budapest, Hungary, 2015 1 Presentation include: Laboratory results Literature summary Role of T cells in response
Innate immunity: Definition and Importance. Updated: July 2015
 Innate immunity: Definition and Importance Updated: July 2015 1 Contents INNATE IMMUNITY... 3 DEFINITION AND IMPORTANCE... 3 Overview of innate immunity in animals... 3 The innate immune system acts early
Innate immunity: Definition and Importance Updated: July 2015 1 Contents INNATE IMMUNITY... 3 DEFINITION AND IMPORTANCE... 3 Overview of innate immunity in animals... 3 The innate immune system acts early
The Immune System: A Tutorial
 The Immune System: A Tutorial Modeling and Simulation of Biological Systems 21-366B Shlomo Ta asan Images taken from http://rex.nci.nih.gov/behindthenews/uis/uisframe.htm http://copewithcytokines.de/ The
The Immune System: A Tutorial Modeling and Simulation of Biological Systems 21-366B Shlomo Ta asan Images taken from http://rex.nci.nih.gov/behindthenews/uis/uisframe.htm http://copewithcytokines.de/ The
Cystic Fibrosis Webquest Sarah Follenweider, The English High School 2009 Summer Research Internship Program
 Cystic Fibrosis Webquest Sarah Follenweider, The English High School 2009 Summer Research Internship Program Introduction: Cystic fibrosis (CF) is an inherited chronic disease that affects the lungs and
Cystic Fibrosis Webquest Sarah Follenweider, The English High School 2009 Summer Research Internship Program Introduction: Cystic fibrosis (CF) is an inherited chronic disease that affects the lungs and
IMMUNOLOGY STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF IMMUNE SYSTEM
 59 IMMUNOLOGY STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF IMMUNE SYSTEM 59.1 INTRODUCTION The immune system is engaged in a constant surveillance of the body for pathogens or tumors. Whether disease develops depends on
59 IMMUNOLOGY STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF IMMUNE SYSTEM 59.1 INTRODUCTION The immune system is engaged in a constant surveillance of the body for pathogens or tumors. Whether disease develops depends on
The Adaptive Immune System
 Chapter 17 Functional Anatomy of Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells Lectures prepared by Christine L. Case The Adaptive Immune System Learning Objectives 17-1 Differentiate innate from adaptive immunity.
Chapter 17 Functional Anatomy of Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells Lectures prepared by Christine L. Case The Adaptive Immune System Learning Objectives 17-1 Differentiate innate from adaptive immunity.
B Cells and Antibodies
 B Cells and Antibodies Andrew Lichtman, MD PhD Brigham and Women's Hospital Harvard Medical School Lecture outline Functions of antibodies B cell activation; the role of helper T cells in antibody production
B Cells and Antibodies Andrew Lichtman, MD PhD Brigham and Women's Hospital Harvard Medical School Lecture outline Functions of antibodies B cell activation; the role of helper T cells in antibody production
Chapter 22: The Lymphatic System and Immunity
 Chapter 22: The Lymphatic System and Immunity Introduction Immune system the body s defenses against pathogens that produce disease 2 types of immunity Nonspecific immune mechanisms (Innate immunity) Provide
Chapter 22: The Lymphatic System and Immunity Introduction Immune system the body s defenses against pathogens that produce disease 2 types of immunity Nonspecific immune mechanisms (Innate immunity) Provide
Sepsis and the Clinical Laboratory
 Sepsis and the Clinical Laboratory Alison Woodworth, PhD Department of Pathology, Microbiology, and Immunology Vanderbilt University Medical Center Nashville, TN Learning Objectives Outline the Pathogenesis
Sepsis and the Clinical Laboratory Alison Woodworth, PhD Department of Pathology, Microbiology, and Immunology Vanderbilt University Medical Center Nashville, TN Learning Objectives Outline the Pathogenesis
The Case of Baby Joe by Kristen L.W. Walton Page 1
 The Case of Baby Joe: Chronic Infections in an Infant by Kristen L.W. Walton SPIRE Postdoctoral Fellowship Program University of North Carolina Chapel Hill Part I Background At birth, Baby Joe appeared
The Case of Baby Joe: Chronic Infections in an Infant by Kristen L.W. Walton SPIRE Postdoctoral Fellowship Program University of North Carolina Chapel Hill Part I Background At birth, Baby Joe appeared
Gene Therapy. The use of DNA as a drug. Edited by Gavin Brooks. BPharm, PhD, MRPharmS (PP) Pharmaceutical Press
 Gene Therapy The use of DNA as a drug Edited by Gavin Brooks BPharm, PhD, MRPharmS (PP) Pharmaceutical Press Contents Preface xiii Acknowledgements xv About the editor xvi Contributors xvii An introduction
Gene Therapy The use of DNA as a drug Edited by Gavin Brooks BPharm, PhD, MRPharmS (PP) Pharmaceutical Press Contents Preface xiii Acknowledgements xv About the editor xvi Contributors xvii An introduction
Antigens have specific regions where antibodies bind to them Antigens are usually molecules on the surface of viruses or foreign cells Antigenic
 Bio 100 Guide 22 Antigens have specific regions where antibodies bind to them Antigens are usually molecules on the surface of viruses or foreign cells Antigenic determinants are the specific regions on
Bio 100 Guide 22 Antigens have specific regions where antibodies bind to them Antigens are usually molecules on the surface of viruses or foreign cells Antigenic determinants are the specific regions on
Chapter 16: Innate Immunity
 Chapter 16: Innate Immunity 1. Overview of Innate Immunity 2. Inflammation & Phagocytosis 3. Antimicrobial Substances 1. Overview of Innate Immunity The Body s Defenses The body has 2 types of defense
Chapter 16: Innate Immunity 1. Overview of Innate Immunity 2. Inflammation & Phagocytosis 3. Antimicrobial Substances 1. Overview of Innate Immunity The Body s Defenses The body has 2 types of defense
Immunology Ambassador Guide (updated 2014)
 Immunology Ambassador Guide (updated 2014) Immunity and Disease We will talk today about the immune system and how it protects us from disease. Also, we ll learn some unique ways that our immune system
Immunology Ambassador Guide (updated 2014) Immunity and Disease We will talk today about the immune system and how it protects us from disease. Also, we ll learn some unique ways that our immune system
A Genetic Analysis of Rheumatoid Arthritis
 A Genetic Analysis of Rheumatoid Arthritis Introduction to Rheumatoid Arthritis: Classification and Diagnosis Rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic inflammatory disorder that affects mainly synovial joints.
A Genetic Analysis of Rheumatoid Arthritis Introduction to Rheumatoid Arthritis: Classification and Diagnosis Rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic inflammatory disorder that affects mainly synovial joints.
Platelet Review July 2012. Thomas S. Kickler M.D. Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine
 Platelet Review July 2012 Thomas S. Kickler M.D. Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine Hemostasis Hemostasis is the process that leads to the stopping of bleeding Hemostasis involves blood vessels,
Platelet Review July 2012 Thomas S. Kickler M.D. Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine Hemostasis Hemostasis is the process that leads to the stopping of bleeding Hemostasis involves blood vessels,
The Immune System. 2 Types of Defense Mechanisms. Lines of Defense. Line of Defense. Lines of Defense
 The Immune System 2 Types of Defense Mechanisms Immune System the system that fights infection by producing cells to inactivate foreign substances to avoid infection and disease. Immunity the body s ability
The Immune System 2 Types of Defense Mechanisms Immune System the system that fights infection by producing cells to inactivate foreign substances to avoid infection and disease. Immunity the body s ability
FACULTY OF MEDICAL SCIENCE
 Doctor of Philosophy Program in Microbiology FACULTY OF MEDICAL SCIENCE Naresuan University 171 Doctor of Philosophy Program in Microbiology The time is critical now for graduate education and research
Doctor of Philosophy Program in Microbiology FACULTY OF MEDICAL SCIENCE Naresuan University 171 Doctor of Philosophy Program in Microbiology The time is critical now for graduate education and research
Mechanical barriers are a crucial first line of defence. It would be impossible to provide an exhaustive list. Two examples are:
 Back to Index 1. The immune response to infection 1. Non-specific immunity The immune system has evolved to deal with infectious pathogens. There are several lines of host defence. When evaluating the
Back to Index 1. The immune response to infection 1. Non-specific immunity The immune system has evolved to deal with infectious pathogens. There are several lines of host defence. When evaluating the
Human Immunity. How our body s cells defend against microbial and viral invaders
 Human Immunity How our body s cells defend against microbial and viral invaders What is Immunity? The word immunity comes from the Latin immunus meaning free of burden. Thus; it is a body s general ability
Human Immunity How our body s cells defend against microbial and viral invaders What is Immunity? The word immunity comes from the Latin immunus meaning free of burden. Thus; it is a body s general ability
Genetic Technology. Name: Class: Date: Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Name: Class: Date: Genetic Technology Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. An application of using DNA technology to help environmental scientists
Name: Class: Date: Genetic Technology Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. An application of using DNA technology to help environmental scientists
AP BIOLOGY 2007 SCORING GUIDELINES (Form B)
 AP BIOLOGY 2007 SCORING GUIDELINES (Form B) Question 2 The defenses of the human body to the entry and establishment of a pathogen (disease-causing organism) can be divided into nonspecific responses and
AP BIOLOGY 2007 SCORING GUIDELINES (Form B) Question 2 The defenses of the human body to the entry and establishment of a pathogen (disease-causing organism) can be divided into nonspecific responses and
Immune System A&P II
 Immune System A&P II Lymphatic Outline Lymphatic System Defense Systems Innate Immune System Adaptive Defense System Immunodeficiencies Immune Responses Lymphatic System: Overview Figure 21.1a, b Lymphatic
Immune System A&P II Lymphatic Outline Lymphatic System Defense Systems Innate Immune System Adaptive Defense System Immunodeficiencies Immune Responses Lymphatic System: Overview Figure 21.1a, b Lymphatic
Hapten - a small molecule that is antigenic but not (by itself) immunogenic.
 Chapter 3. Antigens Terminology: Antigen: Substances that can be recognized by the surface antibody (B cells) or by the TCR (T cells) when associated with MHC molecules Immunogenicity VS Antigenicity:
Chapter 3. Antigens Terminology: Antigen: Substances that can be recognized by the surface antibody (B cells) or by the TCR (T cells) when associated with MHC molecules Immunogenicity VS Antigenicity:
ANATOMY OF THE IMMUNE SYSTEM THE IMMUNE SYSTEM. ANATOMY OF THE IMMUNE SYSTEM Thymus glandular organ near the heart where T cells learn their jobs
 THE IMMUNE SYSTEM 1 ANATOMY OF THE IMMUNE SYSTEM 2 We all get sick sometimes...but then we get better. What happens when we get sick? Why do we get better? The immune system is localized in several parts
THE IMMUNE SYSTEM 1 ANATOMY OF THE IMMUNE SYSTEM 2 We all get sick sometimes...but then we get better. What happens when we get sick? Why do we get better? The immune system is localized in several parts
Biochemistry of the immune system. Jana Novotna
 Biochemistry of the immune system Jana Novotna Immunity = protection The immune system integrated body system of organs, tissues, cells, and products that interact with many different pathogens. Specificity
Biochemistry of the immune system Jana Novotna Immunity = protection The immune system integrated body system of organs, tissues, cells, and products that interact with many different pathogens. Specificity
Microbiology 532 Immunology Examination KEY October 30, 2003
 KEY October 30, 2003 All questions have equal point value. You may keep the test questions. Multiple Choice (choose the best answer) 1. Receptors associated with innate immunity recognize microbes by detecting:
KEY October 30, 2003 All questions have equal point value. You may keep the test questions. Multiple Choice (choose the best answer) 1. Receptors associated with innate immunity recognize microbes by detecting:
CHAPTER 14 CELL SURFACE MARKERS OF T-CELLS, B-CELLS AND MACROPHAGES
 CHAPTER 14 CELL SURFACE MARKERS OF T-CELLS, B-CELLS AND MACROPHAGES An understanding of the distinct families of molecules present on different cells of the immune system provides the tools for distinguishing
CHAPTER 14 CELL SURFACE MARKERS OF T-CELLS, B-CELLS AND MACROPHAGES An understanding of the distinct families of molecules present on different cells of the immune system provides the tools for distinguishing
VPM 152. INFLAMMATION: Chemical Mediators
 General Pathology VPM 152 INFLAMMATION: Chemical Mediators CHEMICAL MEDIATORS OF INFLAMMATION Definition: any messenger that acts on blood vessels, inflammatory cells or other cells to contribute to an
General Pathology VPM 152 INFLAMMATION: Chemical Mediators CHEMICAL MEDIATORS OF INFLAMMATION Definition: any messenger that acts on blood vessels, inflammatory cells or other cells to contribute to an
Lymph capillaries, Lymphatic collecting vessels, Valves, Lymph Duct, Lymph node, Vein
 WLHS/A&P/Oppelt Name Lymphatic System Practice 1. Figure 12-1 provides an overview of the lymphatic vessels. First color code the following structures. Color code in Figure 12-1 Heart Veins Lymphatic vessels/lymph
WLHS/A&P/Oppelt Name Lymphatic System Practice 1. Figure 12-1 provides an overview of the lymphatic vessels. First color code the following structures. Color code in Figure 12-1 Heart Veins Lymphatic vessels/lymph
Types of Hypersensitivity. Type I: Allergic Reactions. more on Allergic Reactions
 Chapter 19: Disorders of the Immune System 1. Hypersensitivity 2. Autoimmunity 3. Transplant Rejection 1. Hypersensitivity What is Hypersensitivity? Hypersensitivity is an immunological state in which
Chapter 19: Disorders of the Immune System 1. Hypersensitivity 2. Autoimmunity 3. Transplant Rejection 1. Hypersensitivity What is Hypersensitivity? Hypersensitivity is an immunological state in which
Viruses, Archaea and Bacteria
 Viruses, Archaea and Bacteria Viruses and Viroids Features of Prokaryotes Bacterial Diversity Archaeal Diversity Viruses A virus is a noncellular infectious agent Ø Consists of a protein coat around a
Viruses, Archaea and Bacteria Viruses and Viroids Features of Prokaryotes Bacterial Diversity Archaeal Diversity Viruses A virus is a noncellular infectious agent Ø Consists of a protein coat around a
Human Mendelian Disorders. Genetic Technology. What is Genetics? Genes are DNA 9/3/2008. Multifactorial Disorders
 Human genetics: Why? Human Genetics Introduction Determine genotypic basis of variant phenotypes to facilitate: Understanding biological basis of human genetic diversity Prenatal diagnosis Predictive testing
Human genetics: Why? Human Genetics Introduction Determine genotypic basis of variant phenotypes to facilitate: Understanding biological basis of human genetic diversity Prenatal diagnosis Predictive testing
Genetics Lecture Notes 7.03 2005. Lectures 1 2
 Genetics Lecture Notes 7.03 2005 Lectures 1 2 Lecture 1 We will begin this course with the question: What is a gene? This question will take us four lectures to answer because there are actually several
Genetics Lecture Notes 7.03 2005 Lectures 1 2 Lecture 1 We will begin this course with the question: What is a gene? This question will take us four lectures to answer because there are actually several
1 Mutation and Genetic Change
 CHAPTER 14 1 Mutation and Genetic Change SECTION Genes in Action KEY IDEAS As you read this section, keep these questions in mind: What is the origin of genetic differences among organisms? What kinds
CHAPTER 14 1 Mutation and Genetic Change SECTION Genes in Action KEY IDEAS As you read this section, keep these questions in mind: What is the origin of genetic differences among organisms? What kinds
10. T and B cells are types of a. endocrine cells. c. lymphocytes. b. platelets. d. complement cells.
 Virus and Immune System Review Directions: Write your answers on a separate piece of paper. 1. Why does a cut in the skin threaten the body s nonspecific defenses against disease? a. If a cut bleeds, disease-fighting
Virus and Immune System Review Directions: Write your answers on a separate piece of paper. 1. Why does a cut in the skin threaten the body s nonspecific defenses against disease? a. If a cut bleeds, disease-fighting
Asthma (With a little SCID to start) Disclosures Outline Starting with the Immune System The Innate Immune System The Adaptive Immune System
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Asthma (With a little SCID to start) Lauren Smith, MD CHKD Pediatric Allergy/Immunology Disclosures None Will be discussing some medications that are not yet FDA approved Outline SCID
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Asthma (With a little SCID to start) Lauren Smith, MD CHKD Pediatric Allergy/Immunology Disclosures None Will be discussing some medications that are not yet FDA approved Outline SCID
Course Curriculum for Master Degree in Medical Laboratory Sciences/Clinical Microbiology, Immunology and Serology
 Course Curriculum for Master Degree in Medical Laboratory Sciences/Clinical Microbiology, Immunology and Serology The Master Degree in Medical Laboratory Sciences / Clinical Microbiology, Immunology or
Course Curriculum for Master Degree in Medical Laboratory Sciences/Clinical Microbiology, Immunology and Serology The Master Degree in Medical Laboratory Sciences / Clinical Microbiology, Immunology or
Population Genetics and Multifactorial Inheritance 2002
 Population Genetics and Multifactorial Inheritance 2002 Consanguinity Genetic drift Founder effect Selection Mutation rate Polymorphism Balanced polymorphism Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium
Population Genetics and Multifactorial Inheritance 2002 Consanguinity Genetic drift Founder effect Selection Mutation rate Polymorphism Balanced polymorphism Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium
Hypersensitivity Reactions
 Hypersensitivity Reactions Introduction Under some circumstances, immunity, rather than providing protection, produces damaging and sometimes fatal results. Such harmful reactions are known collectively
Hypersensitivity Reactions Introduction Under some circumstances, immunity, rather than providing protection, produces damaging and sometimes fatal results. Such harmful reactions are known collectively
Structure and Function of DNA
 Structure and Function of DNA DNA and RNA Structure DNA and RNA are nucleic acids. They consist of chemical units called nucleotides. The nucleotides are joined by a sugar-phosphate backbone. The four
Structure and Function of DNA DNA and RNA Structure DNA and RNA are nucleic acids. They consist of chemical units called nucleotides. The nucleotides are joined by a sugar-phosphate backbone. The four
Vitamin D deficiency exacerbates ischemic cell loss and sensory motor dysfunction in an experimental stroke model
 Vitamin D deficiency exacerbates ischemic cell loss and sensory motor dysfunction in an experimental stroke model Robyn Balden & Farida Sohrabji Texas A&M Health Science Center- College of Medicine ISC
Vitamin D deficiency exacerbates ischemic cell loss and sensory motor dysfunction in an experimental stroke model Robyn Balden & Farida Sohrabji Texas A&M Health Science Center- College of Medicine ISC
Microbiology AN INTRODUCTION EIGHTH EDITION
 TORTORA FUNKE CASE Microbiology AN INTRODUCTION EIGHTH EDITION Differentiate between innate and acquired immunity. Chapter 17 Specific Defenses of the Host: The Immune Response B.E Pruitt & Jane J. Stein
TORTORA FUNKE CASE Microbiology AN INTRODUCTION EIGHTH EDITION Differentiate between innate and acquired immunity. Chapter 17 Specific Defenses of the Host: The Immune Response B.E Pruitt & Jane J. Stein
Course Descriptions. I. Professional Courses: MSEG 7216: Introduction to Infectious Diseases (Medical Students)
 Course Descriptions I. Professional Courses: MSEG 7216: Introduction to Infectious Diseases (Medical Students) This course is offered during the first semester of the second year of the MD Program. It
Course Descriptions I. Professional Courses: MSEG 7216: Introduction to Infectious Diseases (Medical Students) This course is offered during the first semester of the second year of the MD Program. It
The Adaptive Immune Response. B-cells
 The Adaptive Immune Response B-cells FUNCTIONS OF THE IMMUNE SYSTEM: Recognize, destroy and clear a diversity of pathogens. Initiate tissue and wound healing processes. Recognize and clear damaged self
The Adaptive Immune Response B-cells FUNCTIONS OF THE IMMUNE SYSTEM: Recognize, destroy and clear a diversity of pathogens. Initiate tissue and wound healing processes. Recognize and clear damaged self
The Immune System and Disease
 Chapter 40 The Immune System and Disease Section 40 1 Infectious Disease (pages 1029 1033) This section describes the causes of disease and explains how infectious diseases are transmitted Introduction
Chapter 40 The Immune System and Disease Section 40 1 Infectious Disease (pages 1029 1033) This section describes the causes of disease and explains how infectious diseases are transmitted Introduction
PATHOGENESIS OF AIDS
 Neal Nathanson, MD Emeritus Professor Department of Microbiology University of Pennsylvania School of Medicine 1 Definitions Structure of HIV HIV entry and cell tropism HIV-cell interactions Course of
Neal Nathanson, MD Emeritus Professor Department of Microbiology University of Pennsylvania School of Medicine 1 Definitions Structure of HIV HIV entry and cell tropism HIV-cell interactions Course of
Infectious Diseases of the Central Nervous System
 Infectious Diseases of the Central Nervous System Bacterial Meningitis Most common form of CNS infection Organisms reach the leptomeninges via hematogenous spread or direct extension Spinal tap yeilds
Infectious Diseases of the Central Nervous System Bacterial Meningitis Most common form of CNS infection Organisms reach the leptomeninges via hematogenous spread or direct extension Spinal tap yeilds
Yvette Marie Miller, M.D. Executive Medical Officer American Red Cross October 20, 2012 45 th Annual Great Lakes Cancer Nursing Conference Troy, MI
 Yvette Marie Miller, M.D. Executive Medical Officer American Red Cross October 20, 2012 45 th Annual Great Lakes Cancer Nursing Conference Troy, MI Overview of Hematology, http://www.nu.edu.sa/userfiles/mhmorsy/h
Yvette Marie Miller, M.D. Executive Medical Officer American Red Cross October 20, 2012 45 th Annual Great Lakes Cancer Nursing Conference Troy, MI Overview of Hematology, http://www.nu.edu.sa/userfiles/mhmorsy/h
The Cardiovascular System: Blood
 Essentials of Anatomy & Physiology, 4th Edition Martini / Bartholomew The Cardiovascular System: Blood PowerPoint Lecture Outlines prepared by Alan Magid, Duke University Slides 1 to 54 The Functions of
Essentials of Anatomy & Physiology, 4th Edition Martini / Bartholomew The Cardiovascular System: Blood PowerPoint Lecture Outlines prepared by Alan Magid, Duke University Slides 1 to 54 The Functions of
CHAPTER 6: RECOMBINANT DNA TECHNOLOGY YEAR III PHARM.D DR. V. CHITRA
 CHAPTER 6: RECOMBINANT DNA TECHNOLOGY YEAR III PHARM.D DR. V. CHITRA INTRODUCTION DNA : DNA is deoxyribose nucleic acid. It is made up of a base consisting of sugar, phosphate and one nitrogen base.the
CHAPTER 6: RECOMBINANT DNA TECHNOLOGY YEAR III PHARM.D DR. V. CHITRA INTRODUCTION DNA : DNA is deoxyribose nucleic acid. It is made up of a base consisting of sugar, phosphate and one nitrogen base.the
Chapter 10 Human Immuno Deficiency Virus Infection
 143 Chapter 10 Human Immuno Deficiency Virus Infection Chapter 10 Human Immuno Deficiency Virus Infection...143 HIV infection...144 Clinical Features...146 Clinical Staging of HIV infection recommended
143 Chapter 10 Human Immuno Deficiency Virus Infection Chapter 10 Human Immuno Deficiency Virus Infection...143 HIV infection...144 Clinical Features...146 Clinical Staging of HIV infection recommended
Human Genome Organization: An Update. Genome Organization: An Update
 Human Genome Organization: An Update Genome Organization: An Update Highlights of Human Genome Project Timetable Proposed in 1990 as 3 billion dollar joint venture between DOE and NIH with 15 year completion
Human Genome Organization: An Update Genome Organization: An Update Highlights of Human Genome Project Timetable Proposed in 1990 as 3 billion dollar joint venture between DOE and NIH with 15 year completion
Mini-Medical School on Infectious Diseases. Session #1 - Basic Science
 Mini-Medical School on Infectious Diseases Session #1 - Basic Science The Microbial World Michael V. Norgard, Ph.D., Chairman Department of Microbiology U.T. Southwestern Medical Center The Microbial World
Mini-Medical School on Infectious Diseases Session #1 - Basic Science The Microbial World Michael V. Norgard, Ph.D., Chairman Department of Microbiology U.T. Southwestern Medical Center The Microbial World
Prevention of Acute COPD exacerbations
 December 3, 2015 Prevention of Acute COPD exacerbations George Pyrgos MD 1 Disclosures No funding received for this presentation I have previously conducted clinical trials with Boehringer Ingelheim. Principal
December 3, 2015 Prevention of Acute COPD exacerbations George Pyrgos MD 1 Disclosures No funding received for this presentation I have previously conducted clinical trials with Boehringer Ingelheim. Principal
Pneumonia. Acute inflammation of lung parenchyma Inflammatory infiltrate in alveoli ( = consolidation)
 Pneumonia Acute inflammation of lung parenchyma Inflammatory infiltrate in alveoli ( = consolidation) CLASSIFICATION: Aetiology. Morpological class. - Bronchopneumonia vs. lobar pneumonia. Community acquired
Pneumonia Acute inflammation of lung parenchyma Inflammatory infiltrate in alveoli ( = consolidation) CLASSIFICATION: Aetiology. Morpological class. - Bronchopneumonia vs. lobar pneumonia. Community acquired
COMPLEMENT PATHWAYS OF COMPLEMENT ACTIVATION:
 COMPLEMENT The term "complement" was coined by Paul Ehrlich to describe the activity in serum, which could "complement" the ability of specific antibody to cause lysis of bacteria. Complement historically
COMPLEMENT The term "complement" was coined by Paul Ehrlich to describe the activity in serum, which could "complement" the ability of specific antibody to cause lysis of bacteria. Complement historically
ESCMID Online Lecture Library. by author
 Do statins improve outcomes of patients with sepsis and pneumonia? Jordi Carratalà Department of Infectious Diseases Statins for sepsis & community-acquired pneumonia Sepsis and CAP are major healthcare
Do statins improve outcomes of patients with sepsis and pneumonia? Jordi Carratalà Department of Infectious Diseases Statins for sepsis & community-acquired pneumonia Sepsis and CAP are major healthcare
Lecture 6: Single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) and Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphisms (RFLPs)
 Lecture 6: Single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) and Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphisms (RFLPs) Single nucleotide polymorphisms or SNPs (pronounced "snips") are DNA sequence variations that occur
Lecture 6: Single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) and Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphisms (RFLPs) Single nucleotide polymorphisms or SNPs (pronounced "snips") are DNA sequence variations that occur
Understanding the immune response to bacterial infections
 Understanding the immune response to bacterial infections A Ph.D. (SCIENCE) DISSERTATION SUBMITTED TO JADAVPUR UNIVERSITY SUSHIL KUMAR PATHAK DEPARTMENT OF CHEMISTRY BOSE INSTITUTE 2008 CONTENTS Page SUMMARY
Understanding the immune response to bacterial infections A Ph.D. (SCIENCE) DISSERTATION SUBMITTED TO JADAVPUR UNIVERSITY SUSHIL KUMAR PATHAK DEPARTMENT OF CHEMISTRY BOSE INSTITUTE 2008 CONTENTS Page SUMMARY
Chapter 43: Immune System
 AP Biology Reading Guide Fred and Theresa Holtzclaw Julia Keller 12d Chapter 43: Immune System 1. Briefly explain the six steps to ingestion and destruction of a microbe by a phagocytic cell. First, pseudopodia
AP Biology Reading Guide Fred and Theresa Holtzclaw Julia Keller 12d Chapter 43: Immune System 1. Briefly explain the six steps to ingestion and destruction of a microbe by a phagocytic cell. First, pseudopodia
Lymphatic/Immune System Vocabulary Key
 Term Acquired Immunity Adenoids Antibody Antigen Axillary nodes B cell (B lymphocyte) Cervical nodes Complement system Cytokines Cytotoxic T cell Dendritic cell Helper T cell Immunity Immunoglobulins Immunotherapy
Term Acquired Immunity Adenoids Antibody Antigen Axillary nodes B cell (B lymphocyte) Cervical nodes Complement system Cytokines Cytotoxic T cell Dendritic cell Helper T cell Immunity Immunoglobulins Immunotherapy
11/19/2008. Gene analysis. Sequencing PCR. Northern-blot RT PCR. Western-blot Sequencing. in situ hybridization. Southern-blot
 Recombinant technology Gene analysis Sequencing PCR RNA Northern-blot RT PCR Protein Western-blot Sequencing Southern-blot in situ hybridization in situ hybridization Function analysis Histochemical analysis
Recombinant technology Gene analysis Sequencing PCR RNA Northern-blot RT PCR Protein Western-blot Sequencing Southern-blot in situ hybridization in situ hybridization Function analysis Histochemical analysis
Lecture 8: The Development and Survival of Lymphocytes (based on lecture by Dr. Barbara Birshtein)
 Lecture 8: The Development and Survival of Lymphocytes (based on lecture by Dr. Barbara Birshtein) Questions to Consider How does the immune system provide a high degree of sensitivity and specificity
Lecture 8: The Development and Survival of Lymphocytes (based on lecture by Dr. Barbara Birshtein) Questions to Consider How does the immune system provide a high degree of sensitivity and specificity
Sepsis: Identification and Treatment
 Sepsis: Identification and Treatment Daniel Z. Uslan, MD Associate Clinical Professor Division of Infectious Diseases Medical Director, UCLA Sepsis Task Force Severe Sepsis: A Significant Healthcare Challenge
Sepsis: Identification and Treatment Daniel Z. Uslan, MD Associate Clinical Professor Division of Infectious Diseases Medical Director, UCLA Sepsis Task Force Severe Sepsis: A Significant Healthcare Challenge
Welcome to Mini Med School at the Child & Family Research Institute
 Glossary Welcome to Mini Med School at the Child & Family Research Institute On behalf of the Faculty and Staff at the Child & Family Research Institute (CFRI), we would like to welcome you to CFRI s
Glossary Welcome to Mini Med School at the Child & Family Research Institute On behalf of the Faculty and Staff at the Child & Family Research Institute (CFRI), we would like to welcome you to CFRI s
Recognise phagocytes and lymphocytes under the light microscope;
 Immunity The immune system Vaccination Learning Objective Recognise phagocytes and lymphocytes under the light microscope; The following micrographs show as to how different types of phagocytes and lymphocytes
Immunity The immune system Vaccination Learning Objective Recognise phagocytes and lymphocytes under the light microscope; The following micrographs show as to how different types of phagocytes and lymphocytes
Sepsis Awareness Month
 Aon Kenya Insurance Brokers Ltd Aon Hewitt Healthcare Division Sepsis Awareness Month Issue 11 September 2015 In this Issue 2 Getting to understand Sepsis 3 Stages in Sepsis Advancement 4 Diagnosis & Treatment
Aon Kenya Insurance Brokers Ltd Aon Hewitt Healthcare Division Sepsis Awareness Month Issue 11 September 2015 In this Issue 2 Getting to understand Sepsis 3 Stages in Sepsis Advancement 4 Diagnosis & Treatment
GENETICS OF BACTERIA AND VIRUSES
 GENETICS OF BACTERIA AND VIRUSES 1 Genes of bacteria are found in bacterial chromosomes Usually a single type of chromosome May have more than one copy of that chromosome Number of copies depends on the
GENETICS OF BACTERIA AND VIRUSES 1 Genes of bacteria are found in bacterial chromosomes Usually a single type of chromosome May have more than one copy of that chromosome Number of copies depends on the
Chapter 9. Biotechnology and Recombinant DNA Biotechnology and Recombinant DNA
 Chapter 9 Biotechnology and Recombinant DNA Biotechnology and Recombinant DNA Q&A Interferons are species specific, so that interferons to be used in humans must be produced in human cells. Can you think
Chapter 9 Biotechnology and Recombinant DNA Biotechnology and Recombinant DNA Q&A Interferons are species specific, so that interferons to be used in humans must be produced in human cells. Can you think
Nature of Genetic Material. Nature of Genetic Material
 Core Category Nature of Genetic Material Nature of Genetic Material Core Concepts in Genetics (in bold)/example Learning Objectives How is DNA organized? Describe the types of DNA regions that do not encode
Core Category Nature of Genetic Material Nature of Genetic Material Core Concepts in Genetics (in bold)/example Learning Objectives How is DNA organized? Describe the types of DNA regions that do not encode
Special report. Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL) Genomic Biology 3020 April 20, 2006
 Special report Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL) Genomic Biology 3020 April 20, 2006 Gene And Protein The gene that causes the mutation is CCND1 and the protein NP_444284 The mutation deals with the cell
Special report Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL) Genomic Biology 3020 April 20, 2006 Gene And Protein The gene that causes the mutation is CCND1 and the protein NP_444284 The mutation deals with the cell
IMMUNOLOGY OF HIV INFECTION AND AIDS. Interactions between HIV and the immune system
 IMMUNOLOGY OF HIV INFECTION AND AIDS Interactions between HIV and the immune system Basic Statistics United States In the U.S. in 2010, 1.1 million people were living with HIV infection. About 50,000 people
IMMUNOLOGY OF HIV INFECTION AND AIDS Interactions between HIV and the immune system Basic Statistics United States In the U.S. in 2010, 1.1 million people were living with HIV infection. About 50,000 people
Immune System and Disease
 Immune System and Disease Homeostasis Q: How does the body fight against invading organisms that may disrupt homeostasis? WHAT I KNOW WHAT I LEARNED 35.1 How do people catch infectious diseases? SAMPLE
Immune System and Disease Homeostasis Q: How does the body fight against invading organisms that may disrupt homeostasis? WHAT I KNOW WHAT I LEARNED 35.1 How do people catch infectious diseases? SAMPLE
