Stem Cells in Umbilical Cord Blood: A Review
|
|
|
- Ambrose Parks
- 10 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Stem Cells in Umbilical Cord Blood: A Review December 13, 2006 Cellular and Molecular Biotechnology of Mammalian Systems Undergraduate Students: Andrew Fu Allen Fung Graduate Student: Aizhan Tastanova
2 Introduction Stem cells are the precursor cells to all types of cells that exist in a human body. These special cells are capable of self-renewal, the ability to undergo cell division while maintaining an undifferentiated state, and they are also capable of differentiating into a number of cells. Stem cells are highly desired for possible therapeutic use as they potentially can serve as a source for replacing damaged cells. At the top of the hierarchy are the embryonic stem cells (ES). ES cells are found in the inner cell mass of a blastocyst and are capable of differentiation into all three germ layers: ectoderm, endoderm, and mesoderm. The capability of differentiating into these three germ layers is defined as being pluripotent. Because they are pluripotent, ES cells are very desirable for research into treating diseases and conditions such as cancer, Parkinson s, diabetes, heart damage, etc. Although ES cells are potentially very powerful in therapeutic benefit, the ethics of using ES cells are highly questioned and research into ES cell lines using public funds has been limited. These restrictions arise from the sourcing of ES cells. Harvesting these cells require the destruction of a human embryo and it has been argued that by doing so, it is equivalent to the act of murder or abortion. Most ES cells come from embryos that have been created by in vitro fertility treatments, but were ultimately not used for implantation. Because of these issues, other sources for stem cells are currently being examined. One such source for less controversial stem cells is from umbilical cord blood. Hematopoietic Stem Cells After a baby is born, umbilical cord blood (UCB) can be collected from the remaining placenta and remaining attached umbilical cord. 1 Cord blood contains the normal components of blood (red blood cells, white blood cells, etc), in addition to hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs). These HSCs are the progenitors of all cell types contained in the myeloid and lymphoid lineages. Contained in these lineages are the macrophages, platelets, red blood cells, T-cells, B-cells, and other types of blood cells. HSCs are thus classified as multipotent stem cells. Hematopoietic stem cells are a rare heterogeneous population of immature hematopoietic precursor cells that occur postnatally at a frequency of about 1 in 10,000 to 1 in 100,000 cells. As stem cells, HSCs are capable of performing self-renewal to maintain their cell line, and also are able to differentiate. The HSCs are multipotent and can differentiate into about 11 different types of lineages hematopoietic lineages. From the HSCs, the entire hematopoietic system is created and sustained throughout a person s lifetime. Current research is interested in UCB as it has higher content of the HSCs than bone marrow and mobilized peripheral blood, both common sources of HSC for transplantation. One difference between the HCSs in UCB and bone marrow is that UCB cells are slower cycling, whereas bone marrow HSCs have a higher proportion in G2, M and S phases. 4 Hematopoietic cells are descendents from a common hematopoietic and endothelial stem cell known as a hemangioblast. This cell appears during development as a result from mesodermal commitment. The hemangioblasts are first found in the extra-embryoinic yolk sac blood islands during the third week of gestation. One week later, they can then be found on the ventral floor of
3 the dorsal aorta and other arteries. From there, HSCs are able to migrate using the circulation system to colonize the liver, thymus, GI tract, and bone marrow. Once of adult age, HSC production is centered at the bone marrow. One popular use of umbilical cord blood is in HSC transplantation. 2 The first allogenic umbilical cord blood transplant (UCBT) was performed in 1988 to treat a patient suffering from anemia. UCBTs require that the donor be Human Leukocytic Antigen (HLA) compatible with the patient. HLAs are a set of proteins situated on the surface of leukocytes that allow for self/non-self recognization. As with typical transplantations, identical or similar HLA types are required for patient acceptance of the donor tissue. The success of the 1988 procedure altered the landscape of allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplants by showing success with umbilical cord blood. This pioneering procedure showed that a single unit of UCB contained enough HSCs to reconstitute lymphohematopoietic cells. Also, the feasibility of collection of UCB at birth (without harm to a newborn infant) and that the blood could then be successfully used after cryoprservation and transplantation, was proved. Stem cell transplantation has been successfully used as treatment in high-risk or recurrent hematologic malignancies, marrow failure syndromes, severe congenital immunodeficiency states, and some metabolic disorders. 3 Umbilical cord blood with its associated HSCs has recently become more popular in sourcing for stem cell transplant procedures. Data collected post transplantation has suggested that using peripheral blood stem cells have similar risks of rejection as when using bone marrow stem cells. One of the main problems of bone marrow transplantation (BMT) as a source for HSCs is that only 30-40% of potential recipients have HLA-matched family donors. 3 In efforts to increase the pool for allogeneic BMT, the National Marrow Donor Program was established in The program has been successful in increasing the likelihood of treatment with a BMT, but there are still limitations of the procedure, in terms of finding suitable donors. Transplantations are generally done allogeneically as an autologous graft would not solve any genetic disease of the cells in the patient, the newly transplanted cells could possibly contain the same genetic defect. In a case of leukemia, the patient s cells could also become malignant. However, allogeneic transplants carry the risk of rejection. HLA typing is used to have the best possible match between the patient and donor to optimize chance the success of the procedure. UCB HSCs have several advantages over other HSC sources (BMT). Firstly, for patients with more rare HLA types, UCB may be the only source of allogenic HSCs. Next, HCSs can be easily collected from autologous, or related and unrelated donors. The HLA types can then be determined and either immediately used or banked for later use. Furthermore, allogeneic HSC transplant recipients received HLA-mismatched allografts have been shown to tolerate a higher level of HLA disparities in UCB than in other types of grafts (bone marrow, etc). 4 Autologous UCB transplantation has been suggested as a possible method towards gene therapy. BMTs have been previously used to treat a number of genetic diseases such as sickle cell anemia, Fanconi anemia, severe combined immune deficiency secondary to adenosine deaminase
4 deficiency (ADA0, and other types of metabolic/storage deficiencies.. BMT has been suggested as a method to treat conditions that were secondary to a single genetic deletion by Parkman. BMTs are capable of gene transduction because the BM contains HSCs which can renew themselves and differentiate into cells that contain the transduced gene for the lifetime of the patient. As such, UCB transplantation can possible be a suitable method to perform the same task as a BMT would. 4 Cord Blood-Stem Cells In 2006, Zhao et al. identified a novel type of stem cell from human umbilical cord blood. Designated cord blood-stem cells (CB-SC), it has been demonstrated that these cells share properties with human embryonic stem (ES) cells and hematopoietic cells. These cells have low immunogenicity and differentiation capability. ES cells are defined by two unique properties: they can self renew (as with all stem cells) and are pluripotent. With these abilities, they are highly sought after for possible therapeutic benefit towards human diseases. However, ES cells are highly controversial in their use, and adult stem cells do not appear to be as useful. CB-SC cells as characterized by Zhao expressed Esc specific markers such as Oct-4 and Nanog. In vitro, CB-SCs have been differentiated to create cells with the characteristics of cells from the mesoderm, ectoderm and endoderm. However, unlike ES cells, it was found that after 3 months in culture, their proliferation was decreased. 5 One notable application of the CB-SCs is that they are capable of producing a therapeutic glycemic effect in a mouse model of diabetes. In both type 1 and type 2 diabetic patients, there is a deficit of insulin-producing cells. An endogenous insulin source is preferred for these patients as exogenous insulin does not provide the same level of glycemic control nor does it present itself as a long-term solution. Islet cell transplantation has been explored, but is limited by a shortage of pancreas as a source of purified islet. An alternative to such therapy, stem-cell derived insulin-producing cells can possibly be an approach for endogenous insulin. With the ethical issues behind ES cells, CB-SCs may show to be helpful in this field. 5 In type I diabetes, the pancreatic islet beta-cells are selectively destroyed by auto-reactive T lymphocytes. Stem cell therapy is potentially capable of replacing these beta cells, but the preexisting T cells are likely to also attack the new stem cell derived insulin-producing cells. In such a treatment for type I diabetes, it would be prudent to protect the new cells from immune attack. Work by Zhao et al. has shown that CB-SC can significantly inhibit both PHA and IL-2 stimulated lymphocyte proliferations. IL-2 is produced by T cells after they have been activated to stimulate the activation of T cells. Flow analysis has demonstrated that lymphocyte migrationassociated molecules are decreased in co-culture with CB-SC. The results suggest that CB-SC can potentially suppress inflammation caused by lymphocyte aggregations. Additionally, there is evidence that CB-SC has an ability to promote self-limitation of activated T cells by up regulation of CD69 expression. 6 CD8+ T cells are capable of inducing the death of cells that are infected with viruses or other pathogens and cells that are damaged. There has been evidence that these cells also contribute to the development of several autoimmune diseases, including type 1 diabetes and multiple sclerosis. Therefore, when transplanting new beta cells into a type 1 diabetes patient, it would be
5 beneficial to suppress the CD8+ cells to improve the success of such transplantation. With coculture of CD8+ cells and CB-SC, studies have shown that the percentage of CD8+ T cells decreases. In addition, proliferation of activated CD8+ T cells is inhibited. These results could possibly be used in the future to assist in the treatment of type 1 diabetes. 6 Meesenchymal Stem Cells In addition to HSC and CB-SC, mesenchymal stem cells (MSC) can be derived from human umbilical cord blood. Like many types of stem cells, MSCs possess the dual capacity of selfrenewal and multilineage differentiation. Their versatile differentiation potential ranges from mesenchyme-related multipostency to neuroectodermal and endodermal competency. Such versatility makes MSCs a promising alternative to embryonic stem cells (ESCs) in the stem cellbased therapy and transplantation. One of the most studied subjects of stem cell therapy is the liver. Researchers hope to replace the diseased hepatocytes with stem cell-derived healthy cells. While the hematopoietic component of UCB has been proven to be useful in the treatment of liver disorders, the mesenchymal component has remained elusive till recently. Hong et al. showed in their 2005 paper that UCBderived MSCs are also capable of differentiating in vitro along a hepatic linearge. 7 Due to UCB s enormous advantage over other sources of stem cells in cell procurement, storage, and transplantation, USB-derived MSCs are likely to become the cell source of choice for stem cell therapy of the liver. MSCs can be isolated from the Ficoll layer of umbilical cord blood. They form an adherent population that allows their separation from haematopoietic progenitor cells by differential adherence selection. 8 MSCs from UCB are CD45-, CD34-, and do not express the endothelial marker, CD31. These properties match that of MSCs from bone marrow and in first trimester fetal-blood. Hong s group employed several different methods to confirm that MSCs are able to undergo hepatic differentiation. First, UCB-derived MSCs underwent morphological changes under prohepatogenic conditions as early as the third day. Second, RT-PCR analysis reveals temporal expression pattern of hepatocyte-specific genes such as, albumin, AFP, CK-18, GS, TAT, HGF, c-met, PEPCK, and CPS. Third, WB and IF analyses were performed to examine the protein expression of albumin, AFP, CK-18, and Ck-19 to confirm hepatic differentiation. Finally, to ensure that the proteins assembled are actually functional, Hong s team analyzed the LDL update and confirmed the functionality of the proteins. There are, however, some limitations to UCB-derived MSCs that has hindered their current use in scientific research. The major problem is that MSCs yield from UCB is much lower than that from the bone marrow even lower than that of first trimester blood. However, as researchers develop more effective and efficient methods to proliferate MSCs, MSCs are expected to be more useful for stem cell therapy. Current Challenges One of the major challenges in the study of HSCs is the difficulty of identification. The reason is that the molecular phenotypes of HSC can change depending on the activation status of the
6 precursor cell population and on the source of the cells. As a result, the best approach is to use a combination of markers. The best defined surface marker is CD34, which is expressed on both primitive and mature haemopoietic precursors. 9 Like many other markers, CD34 is not HSCs specific. Hence, other markers are used in addition to CD34: CD133+, CD38-, HLA-DR+. Recent studies have also shown that HSCs express aldehyde dehydrogenase. 10 Another challenge is to increase umbilical cord blood HSC numbers without reducing their "stemness" characteristic, or to promote HSC differentiation and use the differentiated cells for haematological support during transplantation. This is a critical matter since the low number of HSCs have been one of the major hindrances in advancing UCB research. The lack of reliable protocols to identify HSCs, as mentioned above, has been hindering researchers to find ways to proliferate HSCs. Recently, much attention has been drawn to the use of available cytokine cocktails that promote HSC survival and proliferation. Many researchers have shown that the read-out assays include CD133 and CD34 phenotypes, LTC-IC and CAFC assays in vitro, and functional engraftment assays in vivo. The cytokines that have proven to be effective include FLT3 ligand, Thrombopoietin (TPO), Stem Cell Factor (SCF), IL-II, and hyper-il-6. Large expansions of the CD133 and CD34 cells were observed. In contrast, there are lesser expansions of LTC-IC or CAFC cell subsets and either negligible or up to 4-5-fold expansions of cells that repopulate immunodeficient mice. However, it is uncertain whether these expansion protocols have negative effects on HSC self-renewal, or whether they affect the homing receptors for HSC engraftment. An alternative method to promote HSC cell cycling is to use drug discovery programmes to produce soluble transcription factors or transcription factor peptide mimetics. Such important transcription factors include NF-Y, which regulates genes such as telomerase, LEF-1 in the Wnt pathway and homeobox (HOX) genes, as well as the Wnt/LEFT-1, Bmi-1 and HOXB4 molecules. Researchers have also discovered that soluble Tat-HOXB4, when added to HSCs for a short period of time can increase murine HSC numbers by fold. Such research, however, must be practiced by extreme care. Before clinical use, it is critical to ensure that such proliferation methods do not promote cellular abnormalities or diminish HSC lifespans. Ethical Issues There are several important ethical issues involved with the collection of umbilical cord blood. First, the donor of umbilical cord blood is always a minor. Consent must be obtained from the infant's mother. One question is the timing of the consent. Consent cannot be obtained from the mother in active labor or immediately after delivery. Other questions include whether consent should also be obtained by infant's father. The situation becomes more complex when the infant turns 21 years of age. What rights do the donor have to his or her umbilical cord blood that was given to an umbilical cord blood bank? What if there is a surrogate mother. Such issues are complex matters. With the increasing amounts of umbilical cord blood collection and transplantation, many of such ethical issues need to addressed urgently. Umbilical cord blood could, alternatively, be considered as a discarded issue. This is not an illogical consideration since collection of umbilical cord blood poses no risk to the mother or the infant. In this case, no consent will be needed for the collection of umbilical cord blood.
7 However, this does not necessarily solve all the ethical dilemmas. What if a genetic disease, such as sickle cell disease, thalassemia, G6PD deficiency, hereditary spherocytosis, is detected upon screening? Many questions remain to be answered. Ethical issues are not limited to consent and disease screening. Other issues include the potential of deliberate conception and embryo cloning for the purpose of an HLA-identical tissue donor and the commercialization of umbilical cord blood collection. Conclusion Umbilical cord blood stem cells have been demonstrated through recent studies to be an alternative to stem cells from the bone marrow. UCB stem cells are versatile. Three major types have been identified: HSC, CB-SC, and MSC. These stem cells may give rise to a variety of cells including, macrophages, platelets, red blood cells, T-cells, B-cells, mesenchyme-related cells, and neuroectodermal and endodermal cells. The future of UBC research should be focused in the following areas. First, researcher must develop optimal methods for harvesting, processing, and storing umbilical cord blood units. Second, efforts should be made to minimize the number of banked umbilical cord blood units necessary to support the needs of recipients who lack matched family member donors. Third and finally, ethical and regulatory issues of collecting and storing umbilical cord blood units must be addressed. Medical ethicists and various members of the medical community need to reach a consensus opinion to guide clinicians and storage services in their practices. Clinical trials have suggested that umbilical cord blood from a single donor could serve as a source of autologous or major histocompatibility complex-matched allogeneic transplantable hematopoeitic repopulating cells. Many organized programs for the banking of unrealated donor umbilical cord blood are underway worldwide. The future is bright and the effects will be beneficial for millions the search time of donor stem cells will be greatly reduced; risks associated with unrelated donor BMT will be also reduced; and finally, such organized UCB banks will hopefully provide a remedy for the shortage of donors from ethnic and racial backgrounds that are underrepresented currently.
8 References Gluckman, E., Current status of umbilical cord blood hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Experimental Hematology, 28 (2000), Cairo, MS., Wagner, JE., Placental and/or Umbilical Cord Blood: An Alternative Source of Hematopoietic Stem Cells for Transplantation. Blood, 90:12 (1997), Watt, SM., Conteras, M., Stem cell medicine: Umbilical cord blood and its stem cell potential. Seminars in Fetal & Neonatal Medicine, 10 (2005) Zhao, Y., Wang, H., Mazzone, T., Identification of stem cells from human umbilical cord blood with embryonic and hematopoietic characteristics. Experimental Cell Research (2006), Zhao Y, et al., Immune regulation of T lymphocyte by a newly characterized human umbilical cord blood stem cell. Immunol Lett (2006), doi: /j.imlet Hong SH, et al., In vitro differentiation of human umbilical cord blood-derived mesenchymal stem cells into hepatocyte-like cells. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications 330 (2005) Campagnoli C, Roberts IA, Kumar S et al. Identification of messenchymal stem progenitor cells in human first-trimester fetal blood, liver, and bone marrow. Blood 2001; 98(8): Martin-Rendon E, Watt SM. Exploitation of stem cell plasticity. Transfus Med 2003; 13: Hess DA, Meyerrose TE, Wirthlin L, Craft TP, Herrbich PE, Creer MH, et al. Functional characterization of highly purified human hematopoietic repopulating cells isolated according to aldehyde dehydrogenase activity. Blood 2004; 104:
STEM CELL FELLOWSHIP
 Module I: The Basic Principles of Stem Cells 1. Basics of Stem Cells a. Understanding the development of embryonic stem cells i. Embryonic stem cells ii. Embryonic germ cells iii. Differentiated stem cell
Module I: The Basic Principles of Stem Cells 1. Basics of Stem Cells a. Understanding the development of embryonic stem cells i. Embryonic stem cells ii. Embryonic germ cells iii. Differentiated stem cell
Stem Cell Research: Adult or Somatic Stem Cells
 Chiang 1 Stem Cell Research: Adult or Somatic Stem Cells Abstract Kelly Chiang Cluster 7 Dr. LeFebvre 07/26/10 Over the past few decades, stem cells have been a controversial topic in the scientific field.
Chiang 1 Stem Cell Research: Adult or Somatic Stem Cells Abstract Kelly Chiang Cluster 7 Dr. LeFebvre 07/26/10 Over the past few decades, stem cells have been a controversial topic in the scientific field.
How To Expand Hematopoietic Stem Cells
 Purification and Expansion of Hematopoietic Stem Cells Based on Proteins Expressed by a Novel Stromal Cell Population Our bodies are constantly killing old, nonfunctional, and unneeded cells and making
Purification and Expansion of Hematopoietic Stem Cells Based on Proteins Expressed by a Novel Stromal Cell Population Our bodies are constantly killing old, nonfunctional, and unneeded cells and making
UMBILICAL CORD BLOOD TRANSPLANTATION: KFSH EXPERIENCE
 UMBILICAL CORD BLOOD TRANSPLANTATION: KFSH EXPERIENCE HIND AL HUMAIDAN, MD,FRCPA Director, Blood Bank (Donor & Transfusion Services) and Stem Cell Cord Blood Bank Consultant Hematopathologist INTRODUCTION
UMBILICAL CORD BLOOD TRANSPLANTATION: KFSH EXPERIENCE HIND AL HUMAIDAN, MD,FRCPA Director, Blood Bank (Donor & Transfusion Services) and Stem Cell Cord Blood Bank Consultant Hematopathologist INTRODUCTION
5 Frequently Asked Questions About Adult Stem Cell Research
 5 Frequently Asked Questions About Adult Stem Cell Research Stem cells are often referred to in the sociopolitical realm with some level of controversy and beyond that, some level of confusion. Many researchers
5 Frequently Asked Questions About Adult Stem Cell Research Stem cells are often referred to in the sociopolitical realm with some level of controversy and beyond that, some level of confusion. Many researchers
SAVE A LIFE... BY GIVING LIFE!
 SAVE A LIFE... BY GIVING LIFE! FOLLOW US ON: HÉMA-QUÉBEC PUBLIC CORD BLOOD BANK www.hema-quebec.qc.ca Scan this code with your smart phone to access the page Register to the Public Cord Blood Bank on the
SAVE A LIFE... BY GIVING LIFE! FOLLOW US ON: HÉMA-QUÉBEC PUBLIC CORD BLOOD BANK www.hema-quebec.qc.ca Scan this code with your smart phone to access the page Register to the Public Cord Blood Bank on the
Stem Cell Quick Guide: Stem Cell Basics
 Stem Cell Quick Guide: Stem Cell Basics What is a Stem Cell? Stem cells are the starting point from which the rest of the body grows. The adult human body is made up of hundreds of millions of different
Stem Cell Quick Guide: Stem Cell Basics What is a Stem Cell? Stem cells are the starting point from which the rest of the body grows. The adult human body is made up of hundreds of millions of different
STEM CELLS FROM THE UMBLICAL CORD BLOOD AND UMBLICAL CORD TISSUE
 STEM CELLS FROM THE UMBLICAL CORD BLOOD AND UMBLICAL CORD TISSUE What are Stem Cells? Stem cells are the basic building blocks of all the cells, tissues and organs in the human body. The role of the stem
STEM CELLS FROM THE UMBLICAL CORD BLOOD AND UMBLICAL CORD TISSUE What are Stem Cells? Stem cells are the basic building blocks of all the cells, tissues and organs in the human body. The role of the stem
guides BIOLOGY OF AGING STEM CELLS An introduction to aging science brought to you by the American Federation for Aging Research
 infoaging guides BIOLOGY OF AGING STEM CELLS An introduction to aging science brought to you by the American Federation for Aging Research WHAT ARE STEM CELLS? Stem cells are cells that, in cell cultures
infoaging guides BIOLOGY OF AGING STEM CELLS An introduction to aging science brought to you by the American Federation for Aging Research WHAT ARE STEM CELLS? Stem cells are cells that, in cell cultures
Stem cells possess 2 main characteristics: Sources of pluripotent stem cells: -Long-term self renewal. -The inner cell mass of the blastocyst.
 Stem cells possess 2 main characteristics: -Long-term self renewal. - They give rise to all types of differentiate cells. Sources of pluripotent stem cells: -The inner cell mass of the blastocyst. - Fetal
Stem cells possess 2 main characteristics: -Long-term self renewal. - They give rise to all types of differentiate cells. Sources of pluripotent stem cells: -The inner cell mass of the blastocyst. - Fetal
Basic Science in Medicine
 Medical Journal of th e Islamic Republic of Iran Volume 18 Number 3 Fall 1383 November 2004 Basic Science in Medicine ] EXPANSION OF HUMAN CORD BLOOD PRIMITIVE PROGENITORS IN SERUM-FREE MEDIA USING HUMAN
Medical Journal of th e Islamic Republic of Iran Volume 18 Number 3 Fall 1383 November 2004 Basic Science in Medicine ] EXPANSION OF HUMAN CORD BLOOD PRIMITIVE PROGENITORS IN SERUM-FREE MEDIA USING HUMAN
4. All cord blood banks should be subject to the same standards, regulations and accreditation requirements.
 WMDA Policy Statement on the Utility of Autologous or Family Cord Blood Unit Storage The WMDA Board adopted this policy on 25 th of May 2006. Policy updated _April 2011 The Cord Blood Working Group and
WMDA Policy Statement on the Utility of Autologous or Family Cord Blood Unit Storage The WMDA Board adopted this policy on 25 th of May 2006. Policy updated _April 2011 The Cord Blood Working Group and
Biotechnology. Srivatsan Kidambi, Ph.D.
 Stem Stem Cell Cell Engineering-What, Biology and it Application Why, How?? to Biotechnology Srivatsan Kidambi, Ph.D. Assistant Professor Department of Chemical & Biomolecular Engineering University of
Stem Stem Cell Cell Engineering-What, Biology and it Application Why, How?? to Biotechnology Srivatsan Kidambi, Ph.D. Assistant Professor Department of Chemical & Biomolecular Engineering University of
Chapter 16 Reproductive Technology, Gene Therapy, and Stem Cells (modified)
 Chapter 16 Reproductive Technology, Gene Therapy, and Stem Cells (modified) Assisted Reproductive Technologies (ART) Artificial insemination (AI) In vitro fertilization (IVF) Gamete intrafallopian transfer
Chapter 16 Reproductive Technology, Gene Therapy, and Stem Cells (modified) Assisted Reproductive Technologies (ART) Artificial insemination (AI) In vitro fertilization (IVF) Gamete intrafallopian transfer
Guidance For Research Involving Human Embryonic Stem Cells, Germ Cells, And Cells Obtained From Cord Blood
 Guidance For Research Involving Human Embryonic Stem Cells, Germ Cells, And Cells Obtained From Cord Blood Supreme Council of Health Department of Research Guidance Regarding Research Involving Human Embryonic
Guidance For Research Involving Human Embryonic Stem Cells, Germ Cells, And Cells Obtained From Cord Blood Supreme Council of Health Department of Research Guidance Regarding Research Involving Human Embryonic
5. All cord blood banks should be subject to the same standards, regulations and accreditation requirements.
 WMDA Policy Statement for the Utility of Autologous or Family Cord Blood Unit Storage (This policy statement has been approved and adopted by the WMDA board on the 25 th of May 2006) The Cord Blood Registries
WMDA Policy Statement for the Utility of Autologous or Family Cord Blood Unit Storage (This policy statement has been approved and adopted by the WMDA board on the 25 th of May 2006) The Cord Blood Registries
INFORMATION ON STEM CELLS/BONE MARROW AND REINFUSION/TRANSPLANTATION SUR703.002
 INFORMATION ON STEM CELLS/BONE MARROW AND REINFUSION/TRANSPLANTATION SUR703.002 COVERAGE: SPECIAL COMMENT ON POLICY REVIEW: Due to the complexity of the Peripheral and Bone Marrow Stem Cell Transplantation
INFORMATION ON STEM CELLS/BONE MARROW AND REINFUSION/TRANSPLANTATION SUR703.002 COVERAGE: SPECIAL COMMENT ON POLICY REVIEW: Due to the complexity of the Peripheral and Bone Marrow Stem Cell Transplantation
STEM CELL FACTS. The ISSCR is an independent, nonproft organization providing a global forum for stem cell research and regenerative medicine.
 STEM CELL FACTS The ISSCR is an independent, nonproft organization providing a global forum for stem cell research and regenerative medicine. WHAT ARE STEM CELLS? Stem cells are the foundation cells for
STEM CELL FACTS The ISSCR is an independent, nonproft organization providing a global forum for stem cell research and regenerative medicine. WHAT ARE STEM CELLS? Stem cells are the foundation cells for
A fact sheet UNRELATED BONE MARROW AND CORD BLOOD STEM CELL TRANSPLANTS
 A fact sheet UNRELATED BONE MARROW AND CORD BLOOD STEM CELL TRANSPLANTS Each year, thousands of patients are diagnosed with diseases treatable by a blood stem cell transplant. These blood stem cells can
A fact sheet UNRELATED BONE MARROW AND CORD BLOOD STEM CELL TRANSPLANTS Each year, thousands of patients are diagnosed with diseases treatable by a blood stem cell transplant. These blood stem cells can
DEPARTMENT OF BONE MARROW AND STEM CELL TRANSPLANT
 www.narayanahealth.org DEPARTMENT OF BONE MARROW AND STEM CELL TRANSPLANT About Narayana Health City Narayana Health, one of India's largest and the world's most economical healthcare service providers
www.narayanahealth.org DEPARTMENT OF BONE MARROW AND STEM CELL TRANSPLANT About Narayana Health City Narayana Health, one of India's largest and the world's most economical healthcare service providers
H. R. 2107 IN THE HOUSE OF REPRESENTATIVES
 I 1TH CONGRESS 1ST SESSION H. R. 2107 To direct the Secretary of Health and Human Services to conduct a public education campaign on umbilical cord blood stem cells, and for other purposes. IN THE HOUSE
I 1TH CONGRESS 1ST SESSION H. R. 2107 To direct the Secretary of Health and Human Services to conduct a public education campaign on umbilical cord blood stem cells, and for other purposes. IN THE HOUSE
Bone Marrow Transplantation and Peripheral Blood Stem Cell Transplantation: Questions and Answers. Key Points
 CANCER FACTS N a t i o n a l C a n c e r I n s t i t u t e N a t i o n a l I n s t i t u t e s o f H e a l t h D e p a r t m e n t o f H e a l t h a n d H u m a n S e r v i c e s Bone Marrow Transplantation
CANCER FACTS N a t i o n a l C a n c e r I n s t i t u t e N a t i o n a l I n s t i t u t e s o f H e a l t h D e p a r t m e n t o f H e a l t h a n d H u m a n S e r v i c e s Bone Marrow Transplantation
Current Issues in Stem Cell Technologies. Lance D. Trainor, MD OneBlood, Inc.
 Current Issues in Stem Cell Technologies Lance D. Trainor, MD OneBlood, Inc. Objective: The big picture of stem cell therapy Outline: Relevant definitions History of Stem Cell Therapy Hematopoietic Stem
Current Issues in Stem Cell Technologies Lance D. Trainor, MD OneBlood, Inc. Objective: The big picture of stem cell therapy Outline: Relevant definitions History of Stem Cell Therapy Hematopoietic Stem
An Introduction to Stem Cells
 By Kirstin Matthews, Ph.D. An Introduction to Stem Cells Overview Stem cells are cells that have the potential to replicate themselves for indefinite periods and to divide, producing one of themselves
By Kirstin Matthews, Ph.D. An Introduction to Stem Cells Overview Stem cells are cells that have the potential to replicate themselves for indefinite periods and to divide, producing one of themselves
How To Treat Leukaemia With Cord Blood Stem Cell
 Cord blood for the treatment of acute lymphoblastic leukemia in young children By Caitlin McGreevy Kiara Paramjothy Pass with Merit RESEARCH PAPER BASED ON PATHOLOGY LECTURES AT MEDLINK 2011 1 Abstract:
Cord blood for the treatment of acute lymphoblastic leukemia in young children By Caitlin McGreevy Kiara Paramjothy Pass with Merit RESEARCH PAPER BASED ON PATHOLOGY LECTURES AT MEDLINK 2011 1 Abstract:
Not All Stem Cells are the Same
 Cord Blood Banking and Transplantation Jennifer Willert, M.D. Hematology/Oncology Blood and Marrow Transplant Rady Children s Hospital San Diego Clinical Professor UCSD Not All Stem Cells are the Same
Cord Blood Banking and Transplantation Jennifer Willert, M.D. Hematology/Oncology Blood and Marrow Transplant Rady Children s Hospital San Diego Clinical Professor UCSD Not All Stem Cells are the Same
15 Stem Cell Research
 15 Stem Cell Research t a l k it o v e r 1 c l a s s se s s i o n Overview Students read about current scientific research on and the social controversy over embryonic stem cells. On a KWL literacy strategy
15 Stem Cell Research t a l k it o v e r 1 c l a s s se s s i o n Overview Students read about current scientific research on and the social controversy over embryonic stem cells. On a KWL literacy strategy
Stem Cell Information
 Stem Cell Information The official National Institutes of Health resource for stem cell research Stem Cell Basics Stem cells have the remarkable potential to develop into many different cell types in the
Stem Cell Information The official National Institutes of Health resource for stem cell research Stem Cell Basics Stem cells have the remarkable potential to develop into many different cell types in the
PT CordLife Indonesia Premium Cordblood Bank. PT CordLife Indonesia Premium Cordblood Bank
 Cordblood Stem Cells and The Role of Cordblood Bank in Supporting Stem Cells Research Presentation Overview Company profile Haematopoietic stem cells in cordblood What we can do to help 1 2 PT CordLife
Cordblood Stem Cells and The Role of Cordblood Bank in Supporting Stem Cells Research Presentation Overview Company profile Haematopoietic stem cells in cordblood What we can do to help 1 2 PT CordLife
Blood-Forming Stem Cell Transplants
 Blood-Forming Stem Cell Transplants What are bone marrow and hematopoietic stem cells? Bone marrow is the soft, sponge-like material found inside bones. It contains immature cells known as hematopoietic
Blood-Forming Stem Cell Transplants What are bone marrow and hematopoietic stem cells? Bone marrow is the soft, sponge-like material found inside bones. It contains immature cells known as hematopoietic
CHAPTER 1 BACKGROUND AND CORD BLOOD BANK (CBB) ORGANIZATION
 CHAPTER 1 BACKGROUND AND CORD BLOOD BANK (CBB) ORGANIZATION Chapter 1 BACKGROUND AND CORD BLOOD BANK (CBB) ORGANIZATION 1.1 OVERVIEW OF THE CORD BLOOD TRANSPLANTATION STUDY Bone marrow transplantation
CHAPTER 1 BACKGROUND AND CORD BLOOD BANK (CBB) ORGANIZATION Chapter 1 BACKGROUND AND CORD BLOOD BANK (CBB) ORGANIZATION 1.1 OVERVIEW OF THE CORD BLOOD TRANSPLANTATION STUDY Bone marrow transplantation
tem ells /background /information Stem cell research Copyright 2007 MRC Centre for Regenerative Medicine, Institute for Stem Cell Research
 tem ells /background /information Stem cell research Copyright 2007 MRC Centre for Regenerative Medicine, Institute for Stem Cell Research /02 /information Table of contents Page 01. What are stem cells?
tem ells /background /information Stem cell research Copyright 2007 MRC Centre for Regenerative Medicine, Institute for Stem Cell Research /02 /information Table of contents Page 01. What are stem cells?
Stem Cell Therapy In Diabetes Mellitus. Professor Megahid Abuelmagd Diabetes And Endocrine Unit. Mansoura Faculty Of Medicine
 Stem Cell Therapy In Diabetes Mellitus Professor Megahid Abuelmagd Diabetes And Endocrine Unit. Mansoura Faculty Of Medicine For many years, there has been great interest in approaches to the replacement
Stem Cell Therapy In Diabetes Mellitus Professor Megahid Abuelmagd Diabetes And Endocrine Unit. Mansoura Faculty Of Medicine For many years, there has been great interest in approaches to the replacement
What we will discuss today
 Umbilical cord blood banking It s Utility? Dr. Nita Radhakrishnan Pediatric Hematology Oncology Unit, Sir Ganga Ram Hospital, New Delhi What we will discuss today What are stem cells? What are the sources
Umbilical cord blood banking It s Utility? Dr. Nita Radhakrishnan Pediatric Hematology Oncology Unit, Sir Ganga Ram Hospital, New Delhi What we will discuss today What are stem cells? What are the sources
Stem Cells: Scientific Progress and Future Research Directions
 2001 Terese Winslow Stem Cells: Scientific Progress and Future Research Directions STEM CELLS: SCIENTIFIC PROGRESS AND FUTURE RESEARCH DIRECTIONS June 2001 This page intentionally left blank TABLE OF CONTENTS
2001 Terese Winslow Stem Cells: Scientific Progress and Future Research Directions STEM CELLS: SCIENTIFIC PROGRESS AND FUTURE RESEARCH DIRECTIONS June 2001 This page intentionally left blank TABLE OF CONTENTS
Cord Blood Stem Cell Transplantation
 LEUKEMIA LYMPHOMA MYELOMA FACTS Cord Blood Stem Cell Transplantation No. 2 in a series providing the latest information on blood cancers Highlights Umbilical cord blood, like bone marrow and peripheral
LEUKEMIA LYMPHOMA MYELOMA FACTS Cord Blood Stem Cell Transplantation No. 2 in a series providing the latest information on blood cancers Highlights Umbilical cord blood, like bone marrow and peripheral
STEM CELLS : A THERAPEUTIC REVOLUTION JACQUES KADOCH ROBERT HEMMINGS MARINELA MANDRA
 STEM CELLS : A THERAPEUTIC REVOLUTION JACQUES KADOCH ROBERT HEMMINGS MARINELA MANDRA OVO CLINIC I 8000 BLVD DECARIE, MONTREAL QC H4P 2S4 I 514.798.2000 I OVOCLINIC.COM 2 a therapeutic revolution As the
STEM CELLS : A THERAPEUTIC REVOLUTION JACQUES KADOCH ROBERT HEMMINGS MARINELA MANDRA OVO CLINIC I 8000 BLVD DECARIE, MONTREAL QC H4P 2S4 I 514.798.2000 I OVOCLINIC.COM 2 a therapeutic revolution As the
Human stem cell research: a novel technology that will benefit patients Information and Position Paper
 October 2003 Human stem cell research: a novel technology that will benefit patients Information and Position Paper EuropaBio, the European Association for Bio-industries, has 35 corporate members operating
October 2003 Human stem cell research: a novel technology that will benefit patients Information and Position Paper EuropaBio, the European Association for Bio-industries, has 35 corporate members operating
Corporate Medical Policy
 Corporate Medical Policy Hematopoietic Stem-Cell Transplantation for CLL and SLL File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: hematopoietic_stem-cell_transplantation_for_cll_and_sll
Corporate Medical Policy Hematopoietic Stem-Cell Transplantation for CLL and SLL File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: hematopoietic_stem-cell_transplantation_for_cll_and_sll
A Cure for Sickle Cell Anemia and Thalassemia
 IV Simpósio Internacional de Hemoglobinopatias A Cure for Sickle Cell Anemia and Thalassemia Bertram Lubin, MD and Mark Walters, MD 4 September 2007 Topics to be covered Cord blood: Importance and biology
IV Simpósio Internacional de Hemoglobinopatias A Cure for Sickle Cell Anemia and Thalassemia Bertram Lubin, MD and Mark Walters, MD 4 September 2007 Topics to be covered Cord blood: Importance and biology
Narrator: Transplants using stem cells from the blood, bone marrow or umbilical cord blood
 [Track 2: What Is a Transplant?] Narrator: Transplants using stem cells from the blood, bone marrow or umbilical cord blood can be an effective treatment for people with blood cancers such as leukemia,
[Track 2: What Is a Transplant?] Narrator: Transplants using stem cells from the blood, bone marrow or umbilical cord blood can be an effective treatment for people with blood cancers such as leukemia,
UMBILICAL CORD BLOOD, STEM CELL BANKING
 UMBILICAL CORD BLOOD, STEM CELL BANKING Dr.Sharad Jain MD Blood Transfusion officer, & I/C Transfusion Medicine NSCB Medical College. Jabalpur.MP. Introduction: Every parent during childbirth DREAMS the
UMBILICAL CORD BLOOD, STEM CELL BANKING Dr.Sharad Jain MD Blood Transfusion officer, & I/C Transfusion Medicine NSCB Medical College. Jabalpur.MP. Introduction: Every parent during childbirth DREAMS the
CHARACTERISTIC FEATURES OF STEM CELLS. CLONING TECHNOLOGIES
 CHARACTERISTIC FEATURES OF STEM CELLS. CLONING TECHNOLOGIES 1 Science is discovering the unknown Stem cell field is still in its infancy Human embryonic stem cell research is a decade old, adult stem cell
CHARACTERISTIC FEATURES OF STEM CELLS. CLONING TECHNOLOGIES 1 Science is discovering the unknown Stem cell field is still in its infancy Human embryonic stem cell research is a decade old, adult stem cell
A Public Cord Blood Bank for South Africa? i
 No. 42/2007 A Public Cord Blood Bank for South Africa? i By Dr Robert Crookes MBChB (Wits), Dip. Internal Medicine (American Board of Internal Medicine, USA) Transfusion Medicine Consultant. South African
No. 42/2007 A Public Cord Blood Bank for South Africa? i By Dr Robert Crookes MBChB (Wits), Dip. Internal Medicine (American Board of Internal Medicine, USA) Transfusion Medicine Consultant. South African
Should Stem Cells Be Used To Treat Human Diseases?
 SAMPLE ESSAY C Should Stem Cells Be Used To Treat Human Diseases? Stem cells can be defined as undifferentiated cells that are generated during the development of the embryo. There are two functions ascribed
SAMPLE ESSAY C Should Stem Cells Be Used To Treat Human Diseases? Stem cells can be defined as undifferentiated cells that are generated during the development of the embryo. There are two functions ascribed
specific B cells Humoral immunity lymphocytes antibodies B cells bone marrow Cell-mediated immunity: T cells antibodies proteins
 Adaptive Immunity Chapter 17: Adaptive (specific) Immunity Bio 139 Dr. Amy Rogers Host defenses that are specific to a particular infectious agent Can be innate or genetic for humans as a group: most microbes
Adaptive Immunity Chapter 17: Adaptive (specific) Immunity Bio 139 Dr. Amy Rogers Host defenses that are specific to a particular infectious agent Can be innate or genetic for humans as a group: most microbes
An Introduction to Stem Cell Biology. Michael L. Shelanski, MD,PhD Professor of Pathology and Cell Biology Columbia University
 An Introduction to Stem Cell Biology Michael L. Shelanski, MD,PhD Professor of Pathology and Cell Biology Columbia University Figures adapted from ISSCR. Presentations of Drs. Martin Pera (Monash University),
An Introduction to Stem Cell Biology Michael L. Shelanski, MD,PhD Professor of Pathology and Cell Biology Columbia University Figures adapted from ISSCR. Presentations of Drs. Martin Pera (Monash University),
Corporate Medical Policy Cord Blood as a Source of Stem Cells
 Corporate Medical Policy Cord Blood as a Source of Stem Cells File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review cord_blood_as_a_source_of_stem_cells 2/2001 3/2015 3/2016 3/2015 Description
Corporate Medical Policy Cord Blood as a Source of Stem Cells File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review cord_blood_as_a_source_of_stem_cells 2/2001 3/2015 3/2016 3/2015 Description
Bone Marrow (Stem Cell) Transplant for Sickle Cell Disease
 Bone Marrow (Stem Cell) Transplant for Sickle Cell Disease Bone Marrow (Stem Cell) Transplant for Sickle Cell Disease 1 Produced by St. Jude Children s Research Hospital Departments of Hematology, Patient
Bone Marrow (Stem Cell) Transplant for Sickle Cell Disease Bone Marrow (Stem Cell) Transplant for Sickle Cell Disease 1 Produced by St. Jude Children s Research Hospital Departments of Hematology, Patient
Therapeutic Potential of Cells Derived from Gestational Tissues: A coming of age. Dr Roisin Deane Cell Care Australia Pty Ltd
 Therapeutic Potential of Cells Derived from Gestational Tissues: A coming of age Dr Roisin Deane Cell Care Australia Pty Ltd What are Gestational Stem Cells? Stem cells isolated from the gestational tissues
Therapeutic Potential of Cells Derived from Gestational Tissues: A coming of age Dr Roisin Deane Cell Care Australia Pty Ltd What are Gestational Stem Cells? Stem cells isolated from the gestational tissues
Umbilical Cord Blood Stem Cells Current Status & Future Potential
 Umbilical Cord Blood Stem Cells Current Status & Future Potential Natasha Ali Assistant Professor Haematology Department of Pathology & Laboratory Medicine/Oncology The Aga Khan University Email: [email protected]
Umbilical Cord Blood Stem Cells Current Status & Future Potential Natasha Ali Assistant Professor Haematology Department of Pathology & Laboratory Medicine/Oncology The Aga Khan University Email: [email protected]
Stem Cells and Hope for Patients
 Stem Cells and Hope for Patients by Maureen Condic, Ph.D. Most Americans know someone afflicted with an incurable medical condition. The possibility of stem cell cures has given hope to many who face such
Stem Cells and Hope for Patients by Maureen Condic, Ph.D. Most Americans know someone afflicted with an incurable medical condition. The possibility of stem cell cures has given hope to many who face such
Do you have anything to add? If so, I d love to hear from you! Jessica Robinson Conference Manager Life Sciences @jessbiopharma
 1 Who is the most influential figure in cord blood around the world? What is the biggest challenge to overcome in the use of cord blood as a source of stem cells? We asked 10 leading experts in the cord
1 Who is the most influential figure in cord blood around the world? What is the biggest challenge to overcome in the use of cord blood as a source of stem cells? We asked 10 leading experts in the cord
Stem Cells. Part 1: What is a Stem Cell?
 Stem Cells Part 1: What is a Stem Cell? Stem cells differ from other kinds of cells in the body. When a stem cell divides by mitosis, each new cell has the potential to either remain a stem cell or become
Stem Cells Part 1: What is a Stem Cell? Stem cells differ from other kinds of cells in the body. When a stem cell divides by mitosis, each new cell has the potential to either remain a stem cell or become
Cord Cor Blood Banking Scott N. Furlan, MD Ellen S. Plummer, Plummer MD
 Cord Blood Banking Scott N. Furlan, MD Ellen S.Plummer, MD Overview Background Biology of Stem Cell Transplant Opportunities i at Parkland Logistics of Banking Potential Barriers Indications for HCT Cancer
Cord Blood Banking Scott N. Furlan, MD Ellen S.Plummer, MD Overview Background Biology of Stem Cell Transplant Opportunities i at Parkland Logistics of Banking Potential Barriers Indications for HCT Cancer
UMBILICAL CORD BLOOD BANKING A guide for parents
 UMBILICAL CORD BLOOD BANKING A guide for parents 2 nd EDITION INTRODUCTION The cells contained in the umbilical cord blood have therapeutic value for the treatment of blood disorders and immune diseases.
UMBILICAL CORD BLOOD BANKING A guide for parents 2 nd EDITION INTRODUCTION The cells contained in the umbilical cord blood have therapeutic value for the treatment of blood disorders and immune diseases.
How To Save A Patient From A Cancer
 BIOSTATISTICS FOR TRANSLATIONAL & CLINICAL RESEARCH Blood-&-Marrow Transplants & CANCERS Stem Cells Stem cells are immature body cells that act like "starter dough" because they can make identical copies
BIOSTATISTICS FOR TRANSLATIONAL & CLINICAL RESEARCH Blood-&-Marrow Transplants & CANCERS Stem Cells Stem cells are immature body cells that act like "starter dough" because they can make identical copies
Corporate Medical Policy Cord Blood as a Source of Stem Cells
 Corporate Medical Policy Cord Blood as a Source of Stem Cells File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review cord_blood_as_a_source_of_stem_cells 2/2001 3/2015 3/2016 3/2015 Description
Corporate Medical Policy Cord Blood as a Source of Stem Cells File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review cord_blood_as_a_source_of_stem_cells 2/2001 3/2015 3/2016 3/2015 Description
What are Stem Cells? How can they be used in medicine?
 What are Stem Cells? How can they be used in medicine? What is a stem cell????... What is a stem cell????......a cell with the ability to differentiate into specialized cells and renew to become more stem
What are Stem Cells? How can they be used in medicine? What is a stem cell????... What is a stem cell????......a cell with the ability to differentiate into specialized cells and renew to become more stem
Saving your baby s s cord blood: Is this good insurance?
 Saving your baby s s cord blood: Is this good insurance? 32 th SEMINAR ON PERINATAL MEDICINE CONTROVERSIES IN PERINATAL MEDICINE: EVIDENCE FOR CURRENT PRACTICE Sante Fe, New Mexico Mervin C. Yoder, MD
Saving your baby s s cord blood: Is this good insurance? 32 th SEMINAR ON PERINATAL MEDICINE CONTROVERSIES IN PERINATAL MEDICINE: EVIDENCE FOR CURRENT PRACTICE Sante Fe, New Mexico Mervin C. Yoder, MD
Stem Cell Transplantation
 Harmony Behavioral Health, Inc. Harmony Behavioral Health of Florida, Inc. Harmony Health Plan of Illinois, Inc. HealthEase of Florida, Inc. Ohana Health Plan, a plan offered by WellCare Health Insurance
Harmony Behavioral Health, Inc. Harmony Behavioral Health of Florida, Inc. Harmony Health Plan of Illinois, Inc. HealthEase of Florida, Inc. Ohana Health Plan, a plan offered by WellCare Health Insurance
Informed Consent in Umbilical Cord Blood Collection, Storage and Donation: A Bloody Mess
 Informed Consent in Umbilical Cord Blood Collection, Storage and Donation: A Bloody Mess Susan P. Raine, J.D., M.D., L.L.M. Candidate Over the past decade, umbilical cord blood has gone from being discarded
Informed Consent in Umbilical Cord Blood Collection, Storage and Donation: A Bloody Mess Susan P. Raine, J.D., M.D., L.L.M. Candidate Over the past decade, umbilical cord blood has gone from being discarded
your complete stem cell bank
 your complete stem cell bank HYDERABAD - 88985 000 888, WARANGAL - 8297 256 777 VISAKHAPATNAM - 7799 990 774 VIJAYAWADA AND GUNTUR - 7799 990 771 NELLORE - 7799 990 772, KADAPA - 8297 256 700 RAJAHMUNDRY
your complete stem cell bank HYDERABAD - 88985 000 888, WARANGAL - 8297 256 777 VISAKHAPATNAM - 7799 990 774 VIJAYAWADA AND GUNTUR - 7799 990 771 NELLORE - 7799 990 772, KADAPA - 8297 256 700 RAJAHMUNDRY
The Facts about Cord Blood
 The Facts about Cord Blood Dear Future Mom and/or Dad, All of us at CorCell would like to give you a big CONGRATULATIONS on your new baby! Now that you are expecting, you have probably heard about saving
The Facts about Cord Blood Dear Future Mom and/or Dad, All of us at CorCell would like to give you a big CONGRATULATIONS on your new baby! Now that you are expecting, you have probably heard about saving
UMBILICAL CORD BLOOD BANKING. A guide for parents
 UMBILICAL CORD BLOOD BANKING A guide for parents This guide has been elaborated by the Council of Europe European Committee on Organ Transplantation (CD-P-TO). For more information, please visit https://go.edqm.eu/transplantation.
UMBILICAL CORD BLOOD BANKING A guide for parents This guide has been elaborated by the Council of Europe European Committee on Organ Transplantation (CD-P-TO). For more information, please visit https://go.edqm.eu/transplantation.
Public Cord Blood Tissue Bank Committee on Health Care Services and Representative Peaden
 HOUSE OF REPRESENTATIVES COMMITTEE ON HEALTH CARE SERVICES ANALYSIS BILL #: HB 2337 (PCB HCS 00-07) RELATING TO: SPONSOR(S): TIED BILL(S): Public Cord Blood Tissue Bank Committee on Health Care Services
HOUSE OF REPRESENTATIVES COMMITTEE ON HEALTH CARE SERVICES ANALYSIS BILL #: HB 2337 (PCB HCS 00-07) RELATING TO: SPONSOR(S): TIED BILL(S): Public Cord Blood Tissue Bank Committee on Health Care Services
CIGNA HEALTHCARE COVERAGE POSITION
 CIGNA HEALTHCARE COVERAGE POSITION Subject Umbilical Cord Blood Banking Table of Contents Coverage Position... 1 General Background... 1 Coding/Billing Information... 3 References... 3 Revised Date...
CIGNA HEALTHCARE COVERAGE POSITION Subject Umbilical Cord Blood Banking Table of Contents Coverage Position... 1 General Background... 1 Coding/Billing Information... 3 References... 3 Revised Date...
The immune system. Bone marrow. Thymus. Spleen. Bone marrow. NK cell. B-cell. T-cell. Basophil Neutrophil. Eosinophil. Myeloid progenitor
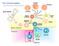 The immune system Basophil Neutrophil Bone marrow Eosinophil Myeloid progenitor Dendritic cell Pluripotent Stem cell Lymphoid progenitor Platelets Bone marrow Thymus NK cell T-cell B-cell Spleen Cancer
The immune system Basophil Neutrophil Bone marrow Eosinophil Myeloid progenitor Dendritic cell Pluripotent Stem cell Lymphoid progenitor Platelets Bone marrow Thymus NK cell T-cell B-cell Spleen Cancer
The Therapeutic Potential of Human Umbilical Cord Blood Transplantation for Neonatal Hypoxic-Ischemic Brain Injury and Ischemic Stroke
 The Therapeutic Potential of Human Umbilical Cord Blood Transplantation for Neonatal Hypoxic-Ischemic Brain Injury and Ischemic Stroke a,b* b,c a a b b b b a b a b c 430 Wang et al. Acta Med. Okayama Vol.
The Therapeutic Potential of Human Umbilical Cord Blood Transplantation for Neonatal Hypoxic-Ischemic Brain Injury and Ischemic Stroke a,b* b,c a a b b b b a b a b c 430 Wang et al. Acta Med. Okayama Vol.
LEUKEMIA LYMPHOMA MYELOMA Advances in Clinical Trials
 LEUKEMIA LYMPHOMA MYELOMA Advances in Clinical Trials OUR FOCUS ABOUT emerging treatments Presentation for: Judith E. Karp, MD Advancements for Acute Myelogenous Leukemia Supported by an unrestricted educational
LEUKEMIA LYMPHOMA MYELOMA Advances in Clinical Trials OUR FOCUS ABOUT emerging treatments Presentation for: Judith E. Karp, MD Advancements for Acute Myelogenous Leukemia Supported by an unrestricted educational
Severe Combined Immune Deficiency (SCID)
 Severe Combined Immune Deficiency (SCID) ASCIA EDUCATION RESOURCES (AER) PATIENT INFORMATION Severe combined immune deficiency (SCID) is the most serious form of primary immune deficiency and is usually
Severe Combined Immune Deficiency (SCID) ASCIA EDUCATION RESOURCES (AER) PATIENT INFORMATION Severe combined immune deficiency (SCID) is the most serious form of primary immune deficiency and is usually
Understanding Blood Stem Cell Transplantation
 Developed by: Donna Kerrigan, M.S. Kathryn Hollen Jeanne Kelly Brian Hollen Discusses how bone marrow produces bloodforming stem cells that include starter immune cells. When diseases like cancer or its
Developed by: Donna Kerrigan, M.S. Kathryn Hollen Jeanne Kelly Brian Hollen Discusses how bone marrow produces bloodforming stem cells that include starter immune cells. When diseases like cancer or its
CORD BLOOD BANKING FAQ
 CORD BLOOD BANKING FAQ Cord Blood & Stem Cells Q: What is umbilical cord blood (UCB)? A: Bone marrow, peripheral blood and UCB constitute the three primary sources of stem cells. Cord blood, which, until
CORD BLOOD BANKING FAQ Cord Blood & Stem Cells Q: What is umbilical cord blood (UCB)? A: Bone marrow, peripheral blood and UCB constitute the three primary sources of stem cells. Cord blood, which, until
Umbilical Cord Blood, Stem Cells, and Bone Marrow Transplantation
 Umbilical Cord Blood, Stem Cells, and Bone Marrow Transplantation CHAPTER 4 ronald m. kline Pluripotent stem cells (PSCs) have the potential to revolutionize the future of medicine because now, for the
Umbilical Cord Blood, Stem Cells, and Bone Marrow Transplantation CHAPTER 4 ronald m. kline Pluripotent stem cells (PSCs) have the potential to revolutionize the future of medicine because now, for the
Stem Cells and Inner Ear Cell Regeneration. Stefan Heller Stanford University School of Medicine
 Stem Cells and Inner Ear Cell Regeneration Stefan Heller Stanford University School of Medicine Embryonic stem cells Induced pluripotent stem cells Somatic stem cells 50 µm Derived from the inner cell
Stem Cells and Inner Ear Cell Regeneration Stefan Heller Stanford University School of Medicine Embryonic stem cells Induced pluripotent stem cells Somatic stem cells 50 µm Derived from the inner cell
Pros and Cons of Stem Cell Sources and their availability in Africa. Dr Jaimendra Singh Inkosi Albert Luthuli Central Hospital Durban, South Africa
 Pros and Cons of Stem Cell Sources and their availability in Africa Dr Jaimendra Singh Inkosi Albert Luthuli Central Hospital Durban, South Africa Introduction The ability to perform a haematopoietic stem
Pros and Cons of Stem Cell Sources and their availability in Africa Dr Jaimendra Singh Inkosi Albert Luthuli Central Hospital Durban, South Africa Introduction The ability to perform a haematopoietic stem
How To Support Umbilical Cord Blood Stem Cell Research
 Cauley O. Gieb Advanced Health Law HLP Article Umbilical Cord Blood Stem Cell Research: The Proof is in the Cord Today advances in science seem to gain the most recognition and support when the subject
Cauley O. Gieb Advanced Health Law HLP Article Umbilical Cord Blood Stem Cell Research: The Proof is in the Cord Today advances in science seem to gain the most recognition and support when the subject
Cord derived MSC-Like Placenta derived Membranes- Matrix- Cells- MSC-like,
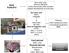 Bank Public/Pvt Bank other cells Ship and distribute Collect and process other samples Support development of novel uses One cord Blood Unit Non stem cells RBC s Plateletes T B Monocytes NK cells Stem
Bank Public/Pvt Bank other cells Ship and distribute Collect and process other samples Support development of novel uses One cord Blood Unit Non stem cells RBC s Plateletes T B Monocytes NK cells Stem
Vita 34 Parents Guide to umbilical Cord Blood Banking. secure first-class innovative
 Vita 34 Parents Guide to umbilical Cord Blood Banking secure first-class innovative Contents INTRODUCTION 3 THERAPEUTIC USES OF STEM CELLS 4 STEM CELLS IN CANCER TREATMENT STEM CELLS IN THE TREATMENT OF
Vita 34 Parents Guide to umbilical Cord Blood Banking secure first-class innovative Contents INTRODUCTION 3 THERAPEUTIC USES OF STEM CELLS 4 STEM CELLS IN CANCER TREATMENT STEM CELLS IN THE TREATMENT OF
The Types of stem cells: Totipotent Pluripotent Multipotent
 Stem Cells is the main material for building and regeneration of the body Stem cells are not differentiated and can transform to any cell of organism Stem cells are capable of indefinite renewal through
Stem Cells is the main material for building and regeneration of the body Stem cells are not differentiated and can transform to any cell of organism Stem cells are capable of indefinite renewal through
UMBILICAL CORD BLOOD HARVESTING & STORAGE
 Protocol: TRP009 Effective Date: October 14, 2013 UMBILICAL CORD BLOOD HARVESTING & STORAGE Table of Contents Page COMMERCIAL, MEDICARE & MEDICAID COVERAGE RATIONALE... 1 BACKGROUND... 2 CLINICAL EVIDENCE...
Protocol: TRP009 Effective Date: October 14, 2013 UMBILICAL CORD BLOOD HARVESTING & STORAGE Table of Contents Page COMMERCIAL, MEDICARE & MEDICAID COVERAGE RATIONALE... 1 BACKGROUND... 2 CLINICAL EVIDENCE...
Unit 1 Higher Human Biology Summary Notes
 Unit 1 Higher Human Biology Summary Notes a. Cells tissues organs body systems Division of labour occurs in multicellular organisms (rather than each cell carrying out every function) Most cells become
Unit 1 Higher Human Biology Summary Notes a. Cells tissues organs body systems Division of labour occurs in multicellular organisms (rather than each cell carrying out every function) Most cells become
Stem Cell Banking. Umbilical Cord. The Leading Cell Bank www.stemology.co.uk. Protect your family s future
 Protect your family s future The Leading Cell Bank www.stemology.co.uk Stem Cell Banking Umbilical Cord For women in their 1st, 2nd or 3rd Trimester of Pregnancy Introduction to Stemology Imagine you
Protect your family s future The Leading Cell Bank www.stemology.co.uk Stem Cell Banking Umbilical Cord For women in their 1st, 2nd or 3rd Trimester of Pregnancy Introduction to Stemology Imagine you
The Prospect of Stem Cell Therapy in Multiple Sclerosis. Multiple sclerosis is a multifocal inflammatory disease of the central
 The Prospect of Stem Cell Therapy in Multiple Sclerosis Multiple sclerosis is a multifocal inflammatory disease of the central nervous system that generally affects young individuals, causing paralysis
The Prospect of Stem Cell Therapy in Multiple Sclerosis Multiple sclerosis is a multifocal inflammatory disease of the central nervous system that generally affects young individuals, causing paralysis
Cord Blood: Research Progress and Future Promise
 Cord Blood: Research Progress and Future Promise By Al Staropoli, AABB Contributing Writer Sue Fister found out she had leukemia when she was 50 years old. Doctors suggested a bone marrow transplant as
Cord Blood: Research Progress and Future Promise By Al Staropoli, AABB Contributing Writer Sue Fister found out she had leukemia when she was 50 years old. Doctors suggested a bone marrow transplant as
UMBILICAL CORD BANKING. (formerly Unistem Biosciences Pvt.Ltd.)
 UMBILICAL CORD BANKING (formerly Unistem Biosciences Pvt.Ltd.) INITIATIVES OF CELLUGEN BIOTECH PVT.LTD. (formerly Unistem Biosciences Pvt.Ltd.) UMBILICAL CORD BANKING UMBILICAL CORD STEM CELL THERAPY Stem
UMBILICAL CORD BANKING (formerly Unistem Biosciences Pvt.Ltd.) INITIATIVES OF CELLUGEN BIOTECH PVT.LTD. (formerly Unistem Biosciences Pvt.Ltd.) UMBILICAL CORD BANKING UMBILICAL CORD STEM CELL THERAPY Stem
Roche Position on Human Stem Cells
 Roche Position on Human Stem Cells Background Stem cells and treating diseases. Stem cells and their applications offer an enormous potential for the treatment and even the cure of diseases, along with
Roche Position on Human Stem Cells Background Stem cells and treating diseases. Stem cells and their applications offer an enormous potential for the treatment and even the cure of diseases, along with
CORD BLOOD TRANSPLANTATION: PAST, PRESENT AND FUTURE
 CORD BLOOD TRANSPLANTATION: PAST, PRESENT AND FUTURE Dennis M. Todd, Ph.D. The New Jersey Cord Blood Bank a Division of Bergen Community Regional Blood Center Montvale, NJ Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation
CORD BLOOD TRANSPLANTATION: PAST, PRESENT AND FUTURE Dennis M. Todd, Ph.D. The New Jersey Cord Blood Bank a Division of Bergen Community Regional Blood Center Montvale, NJ Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation
Briefing on the second reading of the Human Fertilisation and Embryology Bill, Monday 19 November 2007.
 Briefing on the second reading of the Human Fertilisation and Embryology Bill, Monday 19 November 2007. Prepared by the Medical Research Council, Royal Society and Wellcome Trust The Medical Research Council,
Briefing on the second reading of the Human Fertilisation and Embryology Bill, Monday 19 November 2007. Prepared by the Medical Research Council, Royal Society and Wellcome Trust The Medical Research Council,
