Analysis of burn cases observed after the 2011 Van earthquake
|
|
|
- Ruby Hortense Ball
- 10 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Turkish Journal of Trauma & Emergency Surgery Original Article Ulus Travma Acil Cerrahi Derg 1;19 ():51-55 Klinik Çalışma doi: 1.555/tjtes.1.18 Analysis of burn cases observed after the 11 Van earthquake Van da yaşanan 11 depremi sonrası gözlenen yanık olgularının analizi Recep DURSUN, 1 Sevdegül KARADAŞ, Gökay GÖRMELİ, Yasemin IŞIK, Cumhur ÇAKIR, 5 Cemile Ayşe GÖRMELİ BACKGROUND The purpose of this study was to determine the epidemiological features of cases that were registered for burns and treated at a hospital after the Van earthquake to compare burn cases from the previous year and to determine the factors that influenced mortality. METHODS Patients who were admitted to the Van Region Training and Research Hospital within the -month period after the earthquake were categorized as group 1; patients who were admitted within the same time interval in the previous year were categorized as group. RESULTS There were 11 patients in Group 1 and 89 patients in Group. It was determined that there were % more burn cases in Group 1. were observed.8 times more often in Group 1 compared to Group 1 (p=.). Exitus was observed in 5.% of cases in Group 1 and in 7% of cases in Group (p=.9). CONCLUSION It was determined that the number of burn cases registered after the earthquake, the number of flame burns, the percentage of burns and the rate of mortality were higher than the data before the earthquake. Key Words: Burn; earthquake; emergency service; tent. AMAÇ Bu çalışma, Van da yaşanan deprem sonrasında yanık nedeniyle başvuran ve hastanede tedavi edilen olguların epidemiyolojik özelliklerini belirlemek ve bir önceki yılın aynı aylarında başvuran yanık olgularıyla karşılaştırarak mortaliteye etkili olan faktörleri saptamak için planlandı. GEREÇ VE YÖNTEM Van Bölge Eğitim ve Araştırma Hastanesi ne depremden sonra üç aylık periyotta başvuran hastalar grup 1, bir yıl önce aynı tarih aralığında başvuran hastalar grup olarak belirlendi. BULGULAR Grup 1 de 11 hasta, grup de ise 89 hasta vardı. Grup 1 deki yanık olgularının % oranında arttığı saptandı. Alev yanıkları grup 1 de grup ye göre,8 kat daha fazla gözlendi (p=,). Grup 1 de olguların %5, ünde, grup de %7 sinde ölüm görüldü (p=,9). SONUÇ Deprem sonrasında başvuran yanık olguları sayısı, alev yanıklarının sayısı, yanık yüzdesi ve mortalite oranını, deprem öncesine göre yüksek olduğu saptandı. Anahtar Sözcükler: Yanık; deprem; acil servis; çadır. Earthquakes are among the natural disasters that cause the greatest numbers of deaths and injuries, both around the world and in Turkey. [1-] A large part of our country is within a first-degree seismic zone, and nearly 1. people have lost their lives due to earthquakes in the last century. [-] In addition to these deaths, there has been failure to take precautions to avoid these preventable occasions; the existence of old settlements in areas that are prone to destructive earthquakes, conurbanization, the building of earthquake- Departments of 1 Emergency Medicine, Orthopedic Surgery, 5 Burn Unit, Radiology, Van Region Training and Research Hospital, Van; Departments of Emergency Medicine, Anesthesiology and Reanimation, Yuzuncu Yil University Faculty of Medicine, Van, Turkey. Van Bölge Eğitim ve Araştırma Hastanesi, 1 Acil Tıp Servisi, Ortopedi Kliniği, 5 Yanık Ünitesi, Radyoloji Bölümü, Van; Yüzüncü Yıl Üniversitesi Tıp Fakültesi, Acil Tıp Anabilim Dalı, Anesteziyoloji ve Reanimasyon Anabilim Dalı, Van. Correspondence (İletişim): Recep Dursun, M.D. Van Bölge Eğitim ve Araştırma Hastanesi, Acil Tıp Servisi, 51 Van, Turkey. Tel: (e-posta): [email protected] 51
2 Ulus Travma Acil Cerrahi Derg Table 1. Distribution of patients according to age and sex -15 age 15- age -5 age 5-8 age Mean age Female Male Total (n) (n) (n) (n) Mean±SD (%) (%) (n) Group ± Group ± prone houses, the inability of first responders to arrive at accident scenes promptly, and fires have prevented any reductions in the deaths and injury rates due to earthquakes. [5-7] The Van earthquake was of a destructive magnitude (7. Mw) and struck eastern Turkey, near the city of Van, on Sunday, the rd of October, 11 at 1:1 local time. It occurred at a shallow depth of 19 km. There were casualties caused by this earthquake. Seventeen days after the earthquake (on the 9th of November, 11), another earthquake on a different fault line occurred at 1: local time, triggered by the first earthquake. It was centered at Edremit, which is southwest of Van and 1 km from our hospital. The magnitude was 5. (Mw), and it occurred at a depth of 5 km. Because many people had immigrated to other cities and others had settled into tents, there were only casualties. While people were rescued alive from the wreckage of both earthquakes, nearly people were injured. A total of 7. houses were determined to be destroyed or were heavily damaged. [8] Among the most important reasons for the morbidity and mortality observed after earthquakes are fires. [7-1] Determination of the reasons for these fires and of risk groups could help to decrease the morbidity and mortality that occur due to earthquakes. Therefore, in the current study, burn cases observed after the Van earthquake were compared with burn cases during the same months and in the same city during the previous year. Also, the changes that occurred in the number, cause, and degree of burns and the percentage of body surface burned were analyzed. MATERIALS AND METHODS Patients who were admitted to the Van Region Education and Research Hospital after the earthquake, from the rd of October 11 to the rd of January 1, and who received in-patient treatment were categorized as Group 1; patients who were admitted to the hospital from the rd of October 1 to the rd of January 11, and who received in-patient treatment were categorized as Group. Cases were compared regarding age, sex, causes of burns, burn degree, burn percentage, hospital stay length, surgical intervention and complications. When determining the total burn surface area (TBSA) of the patients, first- and seconddegree burns were noted as superficial burns, while third-degree burns were noted as deep burns. After the earthquake, only the hospital in which this study was carried out was at full capacity among the state hospitals, private hospitals and one university hospital. The structural integrity of the other hospitals failed. All cases of burns were monitored and treated in the hospital in which this study was conducted, which has a distinct burn unit. Statistical analysis The statistical significance of the data was analyzed with SPSS statistical software (ver. 9.). A chisquare analysis and Spearman s correlation were used for comparisons. Values of p<.5 were determined to be significant as a result of statistical evaluations. RESULTS Demographic data of the patients in both groups are provided in Table 1. There were no significant differences between the groups regarding age or sex. There were 11 patients in Group 1. Among the patients in Group 1, 1 of the cases were sent to other centers after the earthquake due to renovations of the local burn unit. Also, cases received outpatient treatment and cases received inpatient treatment at the burn unit. After being stabilized in our hospital, the transfer of patients whose consignment was decided was typically performed by either an air ambulance or ambulance ship between 1 and hours later. There were 89 cases in Group ; of these cases were sent to other centers due to patient occupancy at the burn unit, Outpatient cases Dispatched cases Inpatient cases Fig. 1. Group 1: Burn cases following the earthquake Mayıs - May 1
3 Analysis of burn cases observed after the 11 Van earthquake Outpatient cases Dispatched cases Inpatient cases 1 Group 1 Group Fig.. Group : Burns cases from the previous year. Fig.. Reasons for mortality among hospitalized patients. received outpatient treatment, and 57 cases received inpatient treatment in the burn unit. It was determined that there were % more burn cases in Group 1 than in Group. were much more common than flame or electric burns in both groups, and the rate of scald burn was statistically significant in both groups compared to other types of burns (p=.1). Flame burns were observed.8 times more often in Group 1 compared to Group (p=.) (Figures 1-). A total of 8% (9.%) of the burn cases observed in Group 1 occurred due to 8 tent fires. Among the patients in Group 1, there were no patients with burns after the earthquake or after being rescued from the debris. The burns on the patients who formed Group 1 were either scald burns caused by accidents that occurred as a result of aftershocks or flash burns that occurred as a result of tent fires. Electrical burns were caused by leaks resulting from electrical installations that were constructed in tents or other housing. Both superficial and deep burns were more common in Group 1 compared to Group (respectively, p=. and p=.1) (Table ). While 8 surgical interventions were performed on patients in the burn unit from Group 1, 5 surgical interventions were performed on 57 patients in the burn unit from Group. Exitus was observed in 5.% of the cases (n=1) in Group 1 and in 7% (n=) of the cases in Group. There were no statistically significant relationships between mortality and age, sex, burn degree, or intervention between the groups (Table ). While 75% (n=1) of the casualties in Group I occurred as a result of flame burns caused by tent fires, 75% (n=) of the casualties in Group occurred due to electric shock (Figure a-c). DISCUSSION It has been reported that the causes of burn cases admitted to emergency units following earthquakes are generally explosions of fuel tankers or explosions due to gas pipe leaks, which occur during the collapses of buildings and which often result in deaths. [9,1] One recent example is the earthquake in Kobe, Japan, in which 1 fires occurred on the first day. While injuries due to flame burns are very common, scalding burns are rare. [9,11] In Turkey, there were burn cases admitted to the hospital after the earthquake in Düzce in 1999; 1 of them were children, and 7 of them were adults. All of the burns were scalding Table. Total burn surface area of patients Group 1 Group p Mean±SD Mean±SD Superficial burns 17.±1.1.8±7.9. Deep burns.5±.8 1.7±.89.1 Table. Interventions in hospitalized patients Fasciotomy Escharotomy Graft Number of total (n) (%) (n) (%) (n) (%) Group Group Total Cilt - Vol. 19 Sayı - No. 5
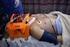
4 Ulus Travma Acil Cerrahi Derg (a) (b) (c) Fig.. (a) Pictures following a tent fire believed to have been caused by stoves. (b) A 1-year-old patient with 75% flame burns who was brought to the hospital after a tent fire. (c) A -year-old patient with 5% flame burns who was brought to the hospital after a tent fire. (Color figures can be viewed in the online issue, which is available at burns; there were no flame burns because there were no explosions or house fires. [9,1] Nakamori et al. [1] reported that following the earthquake in Hanshin Awaji in 1995, 8% of the burns were scalding burns, % were flame burns, and 1% were other types of burns. It was noted that of the burn cases following the Chile earthquake, 78% were flame burns, 1% were scalding burns, and % were electric burns, and there were no differences regarding the types of burns that occurred before the earthquake. [1] It was stated that the mean age of the burn cases that occurred before and after the Chile earthquake were close to each other (respectively, 9.±19.8 and 9.±1.1 year old). [1] It was observed in this study that burn cases increased compared to the previous year, and many of the cases were flame burns (.%). The reason for flame burns being observed often following the Van earthquake was that tents were generally used for temporary shelter. Moreover, due to the earthquake having occurred in winter and the temperature falling to - C in the city, stoves and electrical devices were used in the tents. Heating these flammable tents with such heating techniques posed a significant risk for fires. However, the flame burns that were predominantly observed in Kobe and Chile were due to natural gas pipelines. [9,11,1] The reason for the burn cases after the Hanshin earthquake being scalding was related to the time of the earthquake coinciding with the traditional time of miso soup preparation, which is a commonly consumed food. [1] In this study, the burn cases observed both before and after the earthquake more commonly affected young people. In addition to this finding, the mean age of the cases observed after the earthquake was.55 years younger than the mean age of the cases before the earthquake. A total of.1% (n=51) of the 11 patients who were admitted after the earthquake were younger than 15 years old. In a study by Albornoz et al. [1] that compared burn cases after the Chile earthquake over a period of months to cases registered during same period in the previous year, there were no differences between burn cases and burn types; however, the mortality from burn cases in the group before the earthquake was 1.%, while mortality after the earthquake was.5%. After the Northridge earthquake, which occurred in 199, Peek-Asa et al. [11] reported 1 burn cases as a result of house fires and electric burns in the first 15 days following the earthquake, of which died. Moreover, it was reported that burn cases that occur after earthquakes comprised 7.% of all traumas and.1% of all deaths. In this study, 7.5% (1/11) of burn cases and 5.% of patients following the earthquake died. Before the earthquakes,.% of the patients admitted with burns and 7% of hospital patients died. The reasons for the burns being more deadly in the series of patients presented here were numerous tent fires. This cause could be related to tents having only one exit and to most of these cases being children. Following the Hanshin Awaji earthquake, the 5 Mayıs - May 1
5 Analysis of burn cases observed after the 11 Van earthquake TBSA rate of the cases (77%) who were admitted for burns was %, and the TBSA rate of the 1 cases (%) who were not admitted for burns was more than %. [1] Following the Chile earthquake, the mean TBSA of burn cases before the earthquake was 1.7±1.9%, and the mean TBSA of deep burns was 8.±1.7%, while the mean TBSA of burn cases after the earthquake was 1.78±1.%, and the mean TBSA of deep burns was.9±7.1%. [1] In the current study, contrary to after the Chile earthquake, both the mean TBSA and deep burn TBSA of the burn patients observed following the earthquake were greater. The burn surfaces were broader for the types of burns in Group 1, which resulted from tent fires (9.%). Moreover, the burns observed after the earthquake affected broad surfaces and were deep burns, resulting in an increase in the number of surgical interventions. In conclusion, in the study presented here, it was found that the number of cases admitted for burns, the number of flame burns, the percentage of total body surface burned and the mortality rate were higher after the earthquake compared to the time before the earthquake. To decrease the effect of disasters, it should be compulsory to plan for disasters. Precautions could make the consignments regarding burns decrease and could result in complete and early interventions in burned patients, such as having electricity installed in the tents by experts, surrounding the warm-up tools with protected structures to prevent any cases of burns, using tents that are not easily and/or quickly flammable or that are resistant to fire; making a quick transition from tents to other housing, stockpiling containers at certain places in the country instead of producing containers, having mobile burn units and mobile intensive care units along with mobile operating rooms, and having other mobile health services. Conflict-of-interest issues regarding the authorship or article: None declared. REFERENCES 1. Akbulut G, Yilmaz S, Polat C, Sözen M, Leblebicioğlu M, Dilek ON. Afyon sultandagi earthquake. Ulus Travma Acil Cerrahi Derg ;9: Dursun R, Görmeli CA, Görmeli G, Öncü MR, Karadaş S, Berktaş M, et al. Disaster plan of hospital and emergency service in the Van earthquake. JAEM 1;11:8-9.. Taviloğlu K. Felaketlerde yaralılara yaklaşım ve hekimlik hizmetleri. İstanbul Tabip Odası Depremlerde Uzmanlık Hizmetleri. İstanbul: Ekspres Ofset;.. al-madhari AF, Keller AZ. Review of disaster definitions. Prehosp Disaster Med 1997;1: Çakmakçı M. Felakette sağlık düzeni. Bilim Teknik Dergisi 1999;1: Atasoy S, Ziyalar N, Alsancak B. Earthquake epidemiology in Turkey: , American Academy of Forensic Sciences 51. Annual Meeting. Poster presentation, Orlando, Florida, USA, February p Taviloğlu K. 17 Ağustos 1999 Marmara depreminin ardından: Felaket organizasyonunda neredeyiz? Ulusal Cerrahi Derg 1999;15:-. 8. Dursun R, Görmeli CA, Görmeli G. Evaluation of the patients in Van Training and Research Hospital following the 11 Van earthquake in Turkey. Ulus Travma Acil Cerrahi Derg 1;18:-. 9. Ad-El DD, Engelhard D, Beer Y, Dudkevitz I, Benedeck P. Earthquake related scald injuries-experience from the IDF field hospital in Duzce, Turkey. Burns 1;7: TheKobe Firesfollowin earthquake in com/catwatch/m-8-earthquake-near-east-coast-honshu-japan-11--1/. 11. Peek-Asa C, Kraus JF, Bourque LB, Vimalachandra D, Yu J, Abrams J. Fatal and hospitalized injuries resulting from the 199 Northridge earthquake. Int J Epidemiol 1998;7: Proceedings ITU-IAHS International Conference on the Kocaeli Earthquake 17 August 1999: A Scientific Assessment and Recommendations for Re-Building; M Karaca and D. N. Ural, editors, Istanbul Technical University 1999, p field/turkey/. 1. Nakamori Y, Tanaka H, Oda J, Kuwagata Y, Matsuoka T, Yoshioka T. Burn injuries in the 1995 Hanshin-Awaji earthquake. Burns 1997;: Albornoz C, Villegas J, Sylvester M, Peña V, Bravo I. Analysis of the burns profile and the admission rate of severely burned adult patient to the National Burn Center of Chile after the 1 earthquake. Burns 11;7: Cilt - Vol. 19 Sayı - No. 55
Water park injuries. Su parkı yaralanmaları
 Turkish Journal of Trauma & Emergency Surgery Original Article Ulus Travma Acil Cerrahi Derg 2009;15(5):500-504 Klinik Çalışma Water park injuries Su parkı yaralanmaları Seçgin SÖYÜNCÜ, Özlem YİĞİT, Cenker
Turkish Journal of Trauma & Emergency Surgery Original Article Ulus Travma Acil Cerrahi Derg 2009;15(5):500-504 Klinik Çalışma Water park injuries Su parkı yaralanmaları Seçgin SÖYÜNCÜ, Özlem YİĞİT, Cenker
Disaster Plan of Hospital and Emergency Service in the Van Earthquake
 86 THE JOURNAL OF ACADEMIC EMERGENCY MEDICINE Original Article Özgün Araştırma Disaster Plan of Hospital and Emergency Service in the Van Earthquake Van Depreminde Hastane Afet Planı ve Acil Servis Recep
86 THE JOURNAL OF ACADEMIC EMERGENCY MEDICINE Original Article Özgün Araştırma Disaster Plan of Hospital and Emergency Service in the Van Earthquake Van Depreminde Hastane Afet Planı ve Acil Servis Recep
Predominant causes and types of orofacial injury in children seen in the emergency department
 Turkish Journal of Trauma & Emergency Surgery Original Article Ulus Travma Acil Cerrahi Derg 2013;19 (3):246-250 Klinik Çalışma doi: 10.5505/tjtes.2013.75688 Predominant causes and types of orofacial injury
Turkish Journal of Trauma & Emergency Surgery Original Article Ulus Travma Acil Cerrahi Derg 2013;19 (3):246-250 Klinik Çalışma doi: 10.5505/tjtes.2013.75688 Predominant causes and types of orofacial injury
Injury evaluation of the Turkish national football team over six consecutive seasons
 Turkish Journal of Trauma & Emergency Surgery Original Article Ulus Travma Acil Cerrahi Derg 2011;17 (4):313-317 Klinik Çalışma doi: 10.5505/tjtes.2011.86836 Injury evaluation of the Turkish national football
Turkish Journal of Trauma & Emergency Surgery Original Article Ulus Travma Acil Cerrahi Derg 2011;17 (4):313-317 Klinik Çalışma doi: 10.5505/tjtes.2011.86836 Injury evaluation of the Turkish national football
The use of Web Pages as a Health Communication Tool in Private and Public Hospitals
 MÜSBED 2012;2(1):14-19 Araştırma / Original Paper The use of Web Pages as a Health Communication Tool in Private and Public Hospitals Leyla Köksal, Gonca Mumcu, Nur Şişman, Ramazan Özgür Çatar, Haydar
MÜSBED 2012;2(1):14-19 Araştırma / Original Paper The use of Web Pages as a Health Communication Tool in Private and Public Hospitals Leyla Köksal, Gonca Mumcu, Nur Şişman, Ramazan Özgür Çatar, Haydar
Guidelines for the Operation of Burn Centers
 C h a p t e r 1 4 Guidelines for the Operation of Burn Centers............................................................. Each year in the United States, burn injuries result in more than 500,000 hospital
C h a p t e r 1 4 Guidelines for the Operation of Burn Centers............................................................. Each year in the United States, burn injuries result in more than 500,000 hospital
Development and Recovering From Disaster
 Development and Recovering From Disaster [email protected] International Symposium on Disaster Economics 3-5 April 2013, Istanbul Natural Disaster in Turkey Other disasters 4% Avalanche 2% Multiple
Development and Recovering From Disaster [email protected] International Symposium on Disaster Economics 3-5 April 2013, Istanbul Natural Disaster in Turkey Other disasters 4% Avalanche 2% Multiple
Occupational injuries admitted to the Emergency Department
 Turkish Journal of Trauma & Emergency Surgery Original Article Ulus Travma Acil Cerrahi Derg 2010;16 (3):241-247 Klinik Çalışma Occupational injuries admitted to the Emergency Department Acil servise gelen
Turkish Journal of Trauma & Emergency Surgery Original Article Ulus Travma Acil Cerrahi Derg 2010;16 (3):241-247 Klinik Çalışma Occupational injuries admitted to the Emergency Department Acil servise gelen
Factors associated with mortality in adult hospitalized burn patients in Tehran
 Turkish Journal of Trauma & Emergency Surgery Original Article Ulus Travma Acil Cerrahi Derg 2011;17 (1):61-65 Klinik Çalışma doi: 10.5505/tjtes.2011.22129 Factors associated with mortality in adult hospitalized
Turkish Journal of Trauma & Emergency Surgery Original Article Ulus Travma Acil Cerrahi Derg 2011;17 (1):61-65 Klinik Çalışma doi: 10.5505/tjtes.2011.22129 Factors associated with mortality in adult hospitalized
Earthquake Preparedness Tips & Strategies
 Earthquake Preparedness Tips & Strategies What to Do BEFORE an Earthquake What to Do DURING an Earthquake BE PREPARED! For more information, log onto: www.gema.ga.gov www.ready.ga.gov www.geophysics.eas.gatech.edu
Earthquake Preparedness Tips & Strategies What to Do BEFORE an Earthquake What to Do DURING an Earthquake BE PREPARED! For more information, log onto: www.gema.ga.gov www.ready.ga.gov www.geophysics.eas.gatech.edu
Treatment of post-burn upper extremity, neck and facial contractures: report of 77 cases
 Turkish Journal of Trauma & Emergency Surgery Original Article Ulus Travma Acil Cerrahi Derg 2010;16 (5):401-406 Klinik Çalışma Treatment of post-burn upper extremity, neck and facial contractures: report
Turkish Journal of Trauma & Emergency Surgery Original Article Ulus Travma Acil Cerrahi Derg 2010;16 (5):401-406 Klinik Çalışma Treatment of post-burn upper extremity, neck and facial contractures: report
Epidemiology of head injury in the United Arab Emirates
 Turkish Journal of Trauma & Emergency Surgery Original Article Ulus Travma Acil Cerrahi Derg 12;18 (3):213-218 Klinik Çalışma doi: 10.5505/tjtes.12.03710 Epidemiology of head injury in the United Arab
Turkish Journal of Trauma & Emergency Surgery Original Article Ulus Travma Acil Cerrahi Derg 12;18 (3):213-218 Klinik Çalışma doi: 10.5505/tjtes.12.03710 Epidemiology of head injury in the United Arab
SURVIVAL FACTORS GROUP CHAIRMAN S FACTUAL REPORT, Revision 1 1
 National Transportation Safety Board Office of Railroad Pipeline and Hazardous Materials Investigations Human Performance and Survival Factors Division Washington, D.C. 20594 October 18, 2001 SURVIVAL
National Transportation Safety Board Office of Railroad Pipeline and Hazardous Materials Investigations Human Performance and Survival Factors Division Washington, D.C. 20594 October 18, 2001 SURVIVAL
Geriatric Patient Admissions to the Emergency Service
 Original Article THE JOURNAL OF ACADEMIC 53 EMERGENCY MEDICINE Geriatric Patient Admissions to the Emergency Service Ümit Baz 1, Salim Satar 2, Nalan Kozacı 3, Ayça Açıkalın 4, Müge Gülen 5, Ünal Karakurt
Original Article THE JOURNAL OF ACADEMIC 53 EMERGENCY MEDICINE Geriatric Patient Admissions to the Emergency Service Ümit Baz 1, Salim Satar 2, Nalan Kozacı 3, Ayça Açıkalın 4, Müge Gülen 5, Ünal Karakurt
EMP OF VIDYUT NAGAR GRAHA NIRMAN SAHAKARI SAMITI MARYADIT, GWALIOR
 DISASTER MANAGEMENT PLAN 1.1 INTRODUCTION A disaster is a catastrophic situation in which suddenly, people are plunged into helplessness and suffering and, as a result, need protection, clothing, shelter,
DISASTER MANAGEMENT PLAN 1.1 INTRODUCTION A disaster is a catastrophic situation in which suddenly, people are plunged into helplessness and suffering and, as a result, need protection, clothing, shelter,
Emergency Plan. This emergency plan provides a format of data essential in an emergency situation.
 Emergency Plan A. Introduction This emergency plan provides a format of data essential in an emergency situation. B. Definition of Emergency Incident An emergency condition exists when we determine that
Emergency Plan A. Introduction This emergency plan provides a format of data essential in an emergency situation. B. Definition of Emergency Incident An emergency condition exists when we determine that
Vishesh Diagnostics Pvt. Ltd. EMP
 DISASTER MANAGEMENT PLAN Vishesh Diagnostics Pvt. Ltd. 1.1 INTRODUCTION A disaster is a catastrophic situation in which suddenly, people are plunged into helplessness and suffering and, as a result, need
DISASTER MANAGEMENT PLAN Vishesh Diagnostics Pvt. Ltd. 1.1 INTRODUCTION A disaster is a catastrophic situation in which suddenly, people are plunged into helplessness and suffering and, as a result, need
The Initial and 24 h (After the Patient Rehabilitation) Deficit of Arterial Blood Gases as Predictors of Patients Outcome
 Biomedical & Pharmacology Journal Vol. 6(2), 259-264 (2013) The Initial and 24 h (After the Patient Rehabilitation) Deficit of Arterial Blood Gases as Predictors of Patients Outcome Vadod Norouzi 1, Ali
Biomedical & Pharmacology Journal Vol. 6(2), 259-264 (2013) The Initial and 24 h (After the Patient Rehabilitation) Deficit of Arterial Blood Gases as Predictors of Patients Outcome Vadod Norouzi 1, Ali
ISTANBUL EARTHQUAKE RISK AND MITIGATION STUDIES
 ISTANBUL EARTHQUAKE RISK AND MITIGATION STUDIES O. Metin Ilkisik, M. Nilay Ergenc and Murat T. Turk Disaster Coordination Center, Istanbul Metropolitan Municipality, Istanbul, Turkey e-mail: [email protected]
ISTANBUL EARTHQUAKE RISK AND MITIGATION STUDIES O. Metin Ilkisik, M. Nilay Ergenc and Murat T. Turk Disaster Coordination Center, Istanbul Metropolitan Municipality, Istanbul, Turkey e-mail: [email protected]
How To Study The Effects Of Road Traf C On A Person'S Health
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE JUMMEC 2008:11(1) ROAD TRAFFIC INJURIES AMONG PATIENTS WHO ATTENDED THE ACCIDENT AND EMERGENCY UNIT OF THE UNIVERSITY OF MALAYA MEDICAL CENTRE, KUALA LUMPUR Moe H Department of Social
ORIGINAL ARTICLE JUMMEC 2008:11(1) ROAD TRAFFIC INJURIES AMONG PATIENTS WHO ATTENDED THE ACCIDENT AND EMERGENCY UNIT OF THE UNIVERSITY OF MALAYA MEDICAL CENTRE, KUALA LUMPUR Moe H Department of Social
Organized Industrial Zone Joint Occupational Health and Safety Center Gebze / Kocaeli / Turkey
 Organized Industrial Zone Joint Occupational Health and Safety Center Gebze / Kocaeli / Turkey Dr. M. Celal MESTÇĠOĞLU [email protected] May 2011 Bergen Basic Concepts According to WHO and ILO; OCCUPATIONAL
Organized Industrial Zone Joint Occupational Health and Safety Center Gebze / Kocaeli / Turkey Dr. M. Celal MESTÇĠOĞLU [email protected] May 2011 Bergen Basic Concepts According to WHO and ILO; OCCUPATIONAL
Ocular injuries caused by metal caps of carbonated. mineral water bottles.
 Turkish Journal of Trauma & Emergency Surgery Original Article Ulus Travma Acil Cerrahi Derg 2013;19 (3):256-260 Klinik Çalışma doi: 10.5505/tjtes.2013.36675 Ocular injuries caused by metal caps of carbonated
Turkish Journal of Trauma & Emergency Surgery Original Article Ulus Travma Acil Cerrahi Derg 2013;19 (3):256-260 Klinik Çalışma doi: 10.5505/tjtes.2013.36675 Ocular injuries caused by metal caps of carbonated
Details of motorcycle accidents and their impact on healthcare costs
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Details of motorcycle accidents and their impact on healthcare costs Serkan Emre Eroğlu, M.D., 1 Sıddıka Nihal Toprak, M.D., 2 Ebru Akoğlu, M.D., 3 Özge Ecmel Onur, M.D., 1 Arzu Denizbaşı,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Details of motorcycle accidents and their impact on healthcare costs Serkan Emre Eroğlu, M.D., 1 Sıddıka Nihal Toprak, M.D., 2 Ebru Akoğlu, M.D., 3 Özge Ecmel Onur, M.D., 1 Arzu Denizbaşı,
Planning for an Influenza Pandemic
 Overview It is unlikely that a new pandemic influenza strain will first emerge within Elgin County. The World Health Organization (WHO) uses a series of six phases, as outlined below, of pandemic alert
Overview It is unlikely that a new pandemic influenza strain will first emerge within Elgin County. The World Health Organization (WHO) uses a series of six phases, as outlined below, of pandemic alert
Lightning Mass Casualty Incident at 13,000 feet. Will Smith, MD, Paramedic, FAWM www.wildernessdoc.com
 Lightning Mass Casualty Incident at 13,000 feet Will Smith, MD, Paramedic, FAWM www.wildernessdoc.com Disclaimer No financial relationships to disclose Drs. Wheeler and Smith are Co-Medical Advisors for
Lightning Mass Casualty Incident at 13,000 feet Will Smith, MD, Paramedic, FAWM www.wildernessdoc.com Disclaimer No financial relationships to disclose Drs. Wheeler and Smith are Co-Medical Advisors for
Electrocution-related mortality: a review of 351 deaths by low-voltage electrical current
 Turkish Journal of Trauma & Emergency Surgery Original Article Ulus Travma Acil Cerrahi Derg 2;6 (2):39-43 Klinik Çalışma Electrocution-related mortality: a review of 35 deaths by low-voltage electrical
Turkish Journal of Trauma & Emergency Surgery Original Article Ulus Travma Acil Cerrahi Derg 2;6 (2):39-43 Klinik Çalışma Electrocution-related mortality: a review of 35 deaths by low-voltage electrical
WATER QUALITY AND STANDARDS Vol. I -Management of Water Supplies After A Disaster - Yasumoto Magara, Hiroshi Yano
 MANAGEMENT OF WATER SUPPLIES AFTER A DISASTER Yasumoto Magara Professor of Engineering, Hokkaido University, Sapporo, Japan Hiroshi Director, Kobe Municipal Water Works Bureau, Kobe, Japan Keywords: Earthquake
MANAGEMENT OF WATER SUPPLIES AFTER A DISASTER Yasumoto Magara Professor of Engineering, Hokkaido University, Sapporo, Japan Hiroshi Director, Kobe Municipal Water Works Bureau, Kobe, Japan Keywords: Earthquake
Assessment of Communication Skills of Physical Education and Sport Students in Turkish Universities
 Universal Journal of Educational Research 3(11): 943-948, 2015 DOI: 10.13189/ujer.2015.031125 http://www.hrpub.org Assessment of of Physical Education and Sport Students in Turkish Universities Ali Dursun
Universal Journal of Educational Research 3(11): 943-948, 2015 DOI: 10.13189/ujer.2015.031125 http://www.hrpub.org Assessment of of Physical Education and Sport Students in Turkish Universities Ali Dursun
A Significant Outcome of Work Life: Occupational Accidents in a Developing Country, Turkey
 J Occup Health 2003; 45: 74 80 Journal of Occupational Health Occupational Health / Safety in the World A Significant Outcome of Work Life: Occupational Accidents in a Developing Country, Turkey O. Alp
J Occup Health 2003; 45: 74 80 Journal of Occupational Health Occupational Health / Safety in the World A Significant Outcome of Work Life: Occupational Accidents in a Developing Country, Turkey O. Alp
THE STUDY ON A DISASTER PREVENTION/MITIGATION BASIC PLAN IN ISTANBUL PART 2 - EVALUATION OF URBAN VULNERABILITY -
 13 th World Conference on Earthquake Engineering Vancouver, B.C., Canada August 1-6, 2004 Paper No. 1361 THE STUDY ON A DISASTER PREVENTION/MITIGATION BASIC PLAN IN ISTANBUL PART 2 - EVALUATION OF URBAN
13 th World Conference on Earthquake Engineering Vancouver, B.C., Canada August 1-6, 2004 Paper No. 1361 THE STUDY ON A DISASTER PREVENTION/MITIGATION BASIC PLAN IN ISTANBUL PART 2 - EVALUATION OF URBAN
Alcohol and accidents
 The facts about... Alcohol and accidents Five key things you need to know The facts about alcohol and accidents Spilling red wine over your friend s pristine white sofa. Breaking another wine glass all
The facts about... Alcohol and accidents Five key things you need to know The facts about alcohol and accidents Spilling red wine over your friend s pristine white sofa. Breaking another wine glass all
Four-wheel drive vehicle crash involvement patterns
 Four-wheel drive vehicle crash involvement patterns August 2006 Report Summary 06/05 Introduction This document is a summary of a larger research report prepared by the Monash University Accident Research
Four-wheel drive vehicle crash involvement patterns August 2006 Report Summary 06/05 Introduction This document is a summary of a larger research report prepared by the Monash University Accident Research
emergency action guide
 emergency action guide IN THE EVENT OF LIFE-THREATENING OR EXTREME EMERGENCY CALL 911 FIRST. Central Campus Public Safety Dial 6666 from campus phone or call 215.641.6666 West Campus Public Safety Dial
emergency action guide IN THE EVENT OF LIFE-THREATENING OR EXTREME EMERGENCY CALL 911 FIRST. Central Campus Public Safety Dial 6666 from campus phone or call 215.641.6666 West Campus Public Safety Dial
Gas Explosion at a Subway Construction Site
 Gas Explosion at a Subway Construction Site Apr. 8th, 1970, Osaka city KOBAYASHI, Hideo (Tokyo Institute of Technology) (Summary) On April 8th, 1970, a huge gas explosion occurred at the site of construction
Gas Explosion at a Subway Construction Site Apr. 8th, 1970, Osaka city KOBAYASHI, Hideo (Tokyo Institute of Technology) (Summary) On April 8th, 1970, a huge gas explosion occurred at the site of construction
Adult tonsillectomy: relationship between indications and postoperative hemorrhage
 BEHBUT CEVANŞİR KULAK BURUN BOĞAZ HASTALIKLARI.. VE BAŞ BOYUN CERRAHİSİ DERNEĞİ Kulak Burun Bogaz Ihtis Derg 2012;22(1):21-25 Original Article / Çalışma - Araştırma doi: 10.5606/kbbihtisas.2012.004 21
BEHBUT CEVANŞİR KULAK BURUN BOĞAZ HASTALIKLARI.. VE BAŞ BOYUN CERRAHİSİ DERNEĞİ Kulak Burun Bogaz Ihtis Derg 2012;22(1):21-25 Original Article / Çalışma - Araştırma doi: 10.5606/kbbihtisas.2012.004 21
NON-FATAL INJURIES SUSTAINED IN ROAD TRAFFIC ACCIDENTS : A PILOT STUDY IN PROVINCIAL HOSPITALS IN CHON BURI, THAILAND
 NON-FATAL TRAFFIC INJURY IN THAILAND NON-FATAL INJURIES SUSTAINED IN ROAD TRAFFIC ACCIDENTS : A PILOT STUDY IN PROVINCIAL HOSPITALS IN CHON BURI, THAILAND Sansnee Jirojwong 1, Koolarb Rudtanasudjatum 2,
NON-FATAL TRAFFIC INJURY IN THAILAND NON-FATAL INJURIES SUSTAINED IN ROAD TRAFFIC ACCIDENTS : A PILOT STUDY IN PROVINCIAL HOSPITALS IN CHON BURI, THAILAND Sansnee Jirojwong 1, Koolarb Rudtanasudjatum 2,
BASIC MEDICAL RECORD DEPARTMENT PROCEDURES
 BASIC MEDICAL RECORD DEPARTMENT PROCEDURES 1 Four essential Medical Record Department procedures: 1. Admission procedure and the master patient index (MPI). 2. Discharge procedure. 3. Disease classification
BASIC MEDICAL RECORD DEPARTMENT PROCEDURES 1 Four essential Medical Record Department procedures: 1. Admission procedure and the master patient index (MPI). 2. Discharge procedure. 3. Disease classification
BOSTON MEDFLIGHT HELICOPTER CRASH INCIDENT
 I. PURPOSE BOSTON MEDFLIGHT HELICOPTER CRASH INCIDENT To provide guidance and procedures for emergency response to a Boston MedFlight helicopter crash at Boston University Medical Center. II. SITUATION
I. PURPOSE BOSTON MEDFLIGHT HELICOPTER CRASH INCIDENT To provide guidance and procedures for emergency response to a Boston MedFlight helicopter crash at Boston University Medical Center. II. SITUATION
How To Manage A Catastrophic Injury
 Report #14 CATASTROPHIC INJURIES: Paralysis, Amputation, Burns Overview: A catastrophic injury or illness usually occurs suddenly and without warning. Injuries may be considered catastrophic when they
Report #14 CATASTROPHIC INJURIES: Paralysis, Amputation, Burns Overview: A catastrophic injury or illness usually occurs suddenly and without warning. Injuries may be considered catastrophic when they
Preparedness in the Southwest
 Preparedness in the Southwest Risk Assessment and Hazard Vulnerability Developed by The Arizona Center for Public Health Preparedness Cover Art www.azcphp.publichealth.arizona.edu Chapter 1 Importance
Preparedness in the Southwest Risk Assessment and Hazard Vulnerability Developed by The Arizona Center for Public Health Preparedness Cover Art www.azcphp.publichealth.arizona.edu Chapter 1 Importance
Work-related injuries in textile industry workers in Turkey
 Turkish Journal of Trauma & Emergency Surgery Original Article Ulus Travma Acil Cerrahi Derg 2012;18 (1):31-36 Klinik Çalışma doi: 10.5505/tjtes.2012.54376 Work-related injuries in textile industry workers
Turkish Journal of Trauma & Emergency Surgery Original Article Ulus Travma Acil Cerrahi Derg 2012;18 (1):31-36 Klinik Çalışma doi: 10.5505/tjtes.2012.54376 Work-related injuries in textile industry workers
Checklist for personal accident, overseas student or foreign maid claim
 Checklist for personal accident, overseas student or foreign maid claim Dear person claiming We are sorry to learn of your illness, injury or stay in hospital. Please send us all the documents listed below.
Checklist for personal accident, overseas student or foreign maid claim Dear person claiming We are sorry to learn of your illness, injury or stay in hospital. Please send us all the documents listed below.
Vocational school students attitudes toward computer technology Marmara University sample
 Vocational school students attitudes toward computer technology Marmara University sample Demet Öznaz 1a, Nuran Akyurt 2, Nuriye İşgören 1, and Murat Balıkçı 2 1 Marmara University Vocational School of
Vocational school students attitudes toward computer technology Marmara University sample Demet Öznaz 1a, Nuran Akyurt 2, Nuriye İşgören 1, and Murat Balıkçı 2 1 Marmara University Vocational School of
Director, National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health. California Fatality Assessment and Control Evaluation (CA/FACE) Program
 TO: FROM: SUBJECT: Director, National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health California Fatality Assessment and Control Evaluation (CA/FACE) Program An Automotive Mechanic Dies from Thermal Burns
TO: FROM: SUBJECT: Director, National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health California Fatality Assessment and Control Evaluation (CA/FACE) Program An Automotive Mechanic Dies from Thermal Burns
10-year evaluation of train accidents
 Turkish Journal of Trauma & Emergency Surgery Original Article Ulus Travma Acil Cerrahi Derg 2011;17 (5):440-444 Klinik Çalışma doi: 10.5505/tjtes.2011.66750 10-year evaluation of train accidents Tren
Turkish Journal of Trauma & Emergency Surgery Original Article Ulus Travma Acil Cerrahi Derg 2011;17 (5):440-444 Klinik Çalışma doi: 10.5505/tjtes.2011.66750 10-year evaluation of train accidents Tren
AMERICAN BURN ASSOCIATION BURN CENTER VERIFICATION REVIEW PROGRAM Verificatoin Criterea EFFECTIVE JANUARY 1, 2015. Criterion. Level (1 or 2) Number
 Criterion AMERICAN BURN ASSOCIATION BURN CENTER VERIFICATION REVIEW PROGRAM Criterion Level (1 or 2) Number Criterion BURN CENTER ADMINISTRATION 1. The burn center hospital is currently accredited by The
Criterion AMERICAN BURN ASSOCIATION BURN CENTER VERIFICATION REVIEW PROGRAM Criterion Level (1 or 2) Number Criterion BURN CENTER ADMINISTRATION 1. The burn center hospital is currently accredited by The
Increasing Urban Disaster Resilience in Tokyo
 Ver.17 Increasing Urban Disaster Resilience in Tokyo Tetsuro FUJISAKI Deputy Director, Disaster Prevention city planning Section Bureau of Urban Development Tokyo Metropolitan Government Tokyo s Approach
Ver.17 Increasing Urban Disaster Resilience in Tokyo Tetsuro FUJISAKI Deputy Director, Disaster Prevention city planning Section Bureau of Urban Development Tokyo Metropolitan Government Tokyo s Approach
FOREIGN LANGUAGE LEARNING STRATEGY CHOICE: NATURALISTIC VERSUS INSTRUCTED LANGUAGE ACQUISITION
 Eğitimde Kuram ve Uygulama 2007, 3 (1): 4-11 Journal of Theory and Practice in Education Makaleler/Articles ISSN: 1304-9496 FOREIGN LANGUAGE LEARNING STRATEGY CHOICE: NATURALISTIC VERSUS INSTRUCTED LANGUAGE
Eğitimde Kuram ve Uygulama 2007, 3 (1): 4-11 Journal of Theory and Practice in Education Makaleler/Articles ISSN: 1304-9496 FOREIGN LANGUAGE LEARNING STRATEGY CHOICE: NATURALISTIC VERSUS INSTRUCTED LANGUAGE
Installation Instructions for Alarm Module Kit A043F059
 Instruction Sheet 07-2013 Installation Instructions for Alarm Module Kit A043F059 1 Introduction The information contained within is based on information available at the time of going to print. In line
Instruction Sheet 07-2013 Installation Instructions for Alarm Module Kit A043F059 1 Introduction The information contained within is based on information available at the time of going to print. In line
Evaluation of Trauma Patients Admitted to Emergency Department According to Triage Categories
 60 THE JOURNAL OF ACADEMIC EMERGENCY MEDICINE Original Article Evaluation of Trauma Patients Admitted to Emergency Department According to Triage Categories Suna Eraybar Pozam 1, Fatma Özdemir 2, Pınar
60 THE JOURNAL OF ACADEMIC EMERGENCY MEDICINE Original Article Evaluation of Trauma Patients Admitted to Emergency Department According to Triage Categories Suna Eraybar Pozam 1, Fatma Özdemir 2, Pınar
EARTHQUAKE SCENARIO. Orange County (CA) Department of Education http://emergency.ocde.us/tools.htm
 EARTHQUAKE SCENARIO Wilson Elementary School is located on the outskirts of Sacramento, California. In addition to the principal and assistant principal, Wilson has 31 faculty members, two full-time counselors,
EARTHQUAKE SCENARIO Wilson Elementary School is located on the outskirts of Sacramento, California. In addition to the principal and assistant principal, Wilson has 31 faculty members, two full-time counselors,
An alternative classification of occupational hand injuries based on etiologic mechanisms: the ECOHI classification
 Turkish Journal of Trauma & Emergency Surgery Original Article Ulus Travma Acil Cerrahi Derg 2012;18 (1):49-54 Klinik Çalışma doi: 10.5505/tjtes.2012.45656 An alternative classification of occupational
Turkish Journal of Trauma & Emergency Surgery Original Article Ulus Travma Acil Cerrahi Derg 2012;18 (1):49-54 Klinik Çalışma doi: 10.5505/tjtes.2012.45656 An alternative classification of occupational
Bahrain Med Bull 2003;25(3):
 Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol.25, No. 3, September 2003 Road Traffic Accidents in Bahrain Abdulaziz Y. Hamza, MBBCh, MCh, MD* Faisal Radhi Al-Mousawi, FRCS (Ed.), FRCS (Irel.)** Avis Husel-Pincock, MSc,
Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol.25, No. 3, September 2003 Road Traffic Accidents in Bahrain Abdulaziz Y. Hamza, MBBCh, MCh, MD* Faisal Radhi Al-Mousawi, FRCS (Ed.), FRCS (Irel.)** Avis Husel-Pincock, MSc,
M=5.6 VAN EARTHQUAKE ON 09/11/2011
 PRELIMINARY ANALYSIS OF DATA FROM THE AFTERSHOCK DEPLOYMENT IN VAN AND ERCİŞ, TURKEY M=5.6 VAN EARTHQUAKE ON 09/11/2011 Bogazici University Istanbul, Turkey November 2011 SUMMARY Following the destructive
PRELIMINARY ANALYSIS OF DATA FROM THE AFTERSHOCK DEPLOYMENT IN VAN AND ERCİŞ, TURKEY M=5.6 VAN EARTHQUAKE ON 09/11/2011 Bogazici University Istanbul, Turkey November 2011 SUMMARY Following the destructive
Spontaneous rectus sheath hematoma: an analysis of 15 cases
 Turkish Journal of Trauma & Emergency Surgery Original Article Ulus Travma Acil Cerrahi Derg 2010;16 (6):532-536 Klinik Çalışma Spontaneous rectus sheath hematoma: an analysis of 15 cases Spontan rektus
Turkish Journal of Trauma & Emergency Surgery Original Article Ulus Travma Acil Cerrahi Derg 2010;16 (6):532-536 Klinik Çalışma Spontaneous rectus sheath hematoma: an analysis of 15 cases Spontan rektus
AGE, EMPLOYMENT AND EDUCATIONAL REFORM: AN ALTERNATIVE VIEW OF UNEMPLOYMENT IN TURKEY
 Ankara Üniversitesi SBF Dergisi, Cilt 66, No. 4, 2011, s. 21-31 AGE, EMPLOYMENT AND EDUCATIONAL REFORM: AN ALTERNATIVE VIEW OF UNEMPLOYMENT IN TURKEY Dr. Nevin Çavuşoğlu Philip Heap Dr. Robert Horn James
Ankara Üniversitesi SBF Dergisi, Cilt 66, No. 4, 2011, s. 21-31 AGE, EMPLOYMENT AND EDUCATIONAL REFORM: AN ALTERNATIVE VIEW OF UNEMPLOYMENT IN TURKEY Dr. Nevin Çavuşoğlu Philip Heap Dr. Robert Horn James
What is a Confined Space. Confined Space Awareness 2002 Surveyor s Conference. What is a Confined Space. What is a Confined Space
 Confined Space Awareness 2002 Surveyor s Conference Oregon Department of Transportation A confined space is a space that is. Large enough so a worker can bodily enter, and; Has limited/restricted means
Confined Space Awareness 2002 Surveyor s Conference Oregon Department of Transportation A confined space is a space that is. Large enough so a worker can bodily enter, and; Has limited/restricted means
Factors to Consider When Developing an Evacuation Plan
 The following should be viewed only as suggestions: Factors to Consider When Developing an Evacuation Plan 1. You must identify your document with a specific title and explanation. Example: Evacuation
The following should be viewed only as suggestions: Factors to Consider When Developing an Evacuation Plan 1. You must identify your document with a specific title and explanation. Example: Evacuation
A Summary of a NIOSH fire fighter fatality investigation
 Death in the and Prevention Program line of duty... F-08 A Summary of a NIOSH fire fighter fatality investigation July 7, 2003 Three Fire Department Members (two fire fighter paramedics and one helicopter
Death in the and Prevention Program line of duty... F-08 A Summary of a NIOSH fire fighter fatality investigation July 7, 2003 Three Fire Department Members (two fire fighter paramedics and one helicopter
PUBLICATION PROVIDED BY: RISSMAN, BARRETT, HURT DONAHUE & McLAIN, P.A.
 PUBLICATION PROVIDED BY: RISSMAN, BARRETT, HURT DONAHUE & McLAIN, P.A. 201 EAST PINE STREET 15 TH FLOOR P.O. BOX 4940 ORLANDO, FLORIDA 32802-4940 TELEPHONE (407) 839-0120 TELECOPIER (407) 841-9726 [email protected]
PUBLICATION PROVIDED BY: RISSMAN, BARRETT, HURT DONAHUE & McLAIN, P.A. 201 EAST PINE STREET 15 TH FLOOR P.O. BOX 4940 ORLANDO, FLORIDA 32802-4940 TELEPHONE (407) 839-0120 TELECOPIER (407) 841-9726 [email protected]
Accidents at Work: Q3/2015
 4 November 2015 1100 hrs 202/2015 Claims in respect of non-fatal accidents at work in the third quarter of 2015 remained almost at par with the corresponding quarter in 2014 increasing by just one case.
4 November 2015 1100 hrs 202/2015 Claims in respect of non-fatal accidents at work in the third quarter of 2015 remained almost at par with the corresponding quarter in 2014 increasing by just one case.
Magnitude 8.8 OFFSHORE MAULE, CHILE
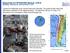 A great 8.8-magnitude struck central Chile early Saturday. The quake hit 200 miles (325 kilometers) southwest of the capital Santiago. The epicenter was just 70 miles (115 kilometers) from Concepcion,
A great 8.8-magnitude struck central Chile early Saturday. The quake hit 200 miles (325 kilometers) southwest of the capital Santiago. The epicenter was just 70 miles (115 kilometers) from Concepcion,
A Bootstrap Confidence Interval for Skewness and Kurtosis and Properties of t-test in Small Samples from Normal Distribution
 Trakya Univ Tip Fak Derg 2009;26(4):297-305 Original Article / Orijinal Çalışma - Araştırma A Bootstrap Confidence Interval for Skewness and Kurtosis and Properties of t-test in Small Samples from Normal
Trakya Univ Tip Fak Derg 2009;26(4):297-305 Original Article / Orijinal Çalışma - Araştırma A Bootstrap Confidence Interval for Skewness and Kurtosis and Properties of t-test in Small Samples from Normal
Thoracic aortic aneurysms after blunt trauma
 Turkish Journal of Trauma & Emergency Surgery Original Article Ulus Travma Acil Cerrahi Derg 2013;19 (4):343-347 Klinik Çalışma doi: 10.5505/tjtes.2013.32457 Thoracic aortic aneurysms after blunt trauma
Turkish Journal of Trauma & Emergency Surgery Original Article Ulus Travma Acil Cerrahi Derg 2013;19 (4):343-347 Klinik Çalışma doi: 10.5505/tjtes.2013.32457 Thoracic aortic aneurysms after blunt trauma
The management of penetrating abdominal trauma by diagnostic laparoscopy: a prospective non-randomized study
 Turkish Journal of Trauma & Emergency Surgery Original Article Ulus Travma Acil Cerrahi Derg 2013;19 (1):53-57 Klinik Çalışma doi: 10.5505/tjtes.2013.40799 The management of penetrating abdominal trauma
Turkish Journal of Trauma & Emergency Surgery Original Article Ulus Travma Acil Cerrahi Derg 2013;19 (1):53-57 Klinik Çalışma doi: 10.5505/tjtes.2013.40799 The management of penetrating abdominal trauma
Arizona Manufactured Home
 EFFECTIVE: 7/01/10 NEW 7/15/10 RENEWAL American Reliable Insurance Company Arizona Manufactured Home A4371M0610 ELIGIBILITY AND INCLUDED COVERAGES 1 ELIGIBILITY AND INCLUDED COVERAGES PREFERRED PROGRAM
EFFECTIVE: 7/01/10 NEW 7/15/10 RENEWAL American Reliable Insurance Company Arizona Manufactured Home A4371M0610 ELIGIBILITY AND INCLUDED COVERAGES 1 ELIGIBILITY AND INCLUDED COVERAGES PREFERRED PROGRAM
TITLE 836 INDIANA EMERGENCY MEDICAL SERVICES COMMISSION. ARTICLE 1.5 Trauma Field Triage and Transport Destination Requirements
 TITLE 836 INDIANA EMERGENCY MEDICAL SERVICES COMMISSION ARTICLE 1.5 Trauma Field Triage and Transport Destination Requirements 836 IAC 1.5-1 Purpose Affected: [IC 10-14-3-12; IC 16-18; IC 16-21-2; IC 16-31-2-9;
TITLE 836 INDIANA EMERGENCY MEDICAL SERVICES COMMISSION ARTICLE 1.5 Trauma Field Triage and Transport Destination Requirements 836 IAC 1.5-1 Purpose Affected: [IC 10-14-3-12; IC 16-18; IC 16-21-2; IC 16-31-2-9;
Reporting and Investigation of Accidents and Incidents at IT Sligo
 Policy Title: Written By: Reporting and Investigation of Accidents and Incidents at IT Sligo Approved By: Yvonne Roache Gordon Ryan Terri Scott Health and Safety Officer Head of Development & Business
Policy Title: Written By: Reporting and Investigation of Accidents and Incidents at IT Sligo Approved By: Yvonne Roache Gordon Ryan Terri Scott Health and Safety Officer Head of Development & Business
CHAPTER SEISMIC RISK MITIGATION PRACTICES IN SCHOOL BUILDINGS IN ISTANBUL, TURKEY
 CHAPTER 13 SEISMIC RISK MITIGATION PRACTICES IN SCHOOL BUILDINGS IN ISTANBUL, TURKEY Özal Yüzügüllü, Gülay Barbarosoglu and Mustafa Erdik Kandilli Observatory and Earthquake Research Institute Bogaziçi
CHAPTER 13 SEISMIC RISK MITIGATION PRACTICES IN SCHOOL BUILDINGS IN ISTANBUL, TURKEY Özal Yüzügüllü, Gülay Barbarosoglu and Mustafa Erdik Kandilli Observatory and Earthquake Research Institute Bogaziçi
Istanbul Seismic Risk Mitigation and Emergency Preparedness Project
 Istanbul Seismic Risk Mitigation and Emergency Preparedness Project Kazım Gökhan Elgin Director of ISMEP TURKEY and Natural Disasters TURKEY is prone to mainly three types of natural disasters: Earthquakes;
Istanbul Seismic Risk Mitigation and Emergency Preparedness Project Kazım Gökhan Elgin Director of ISMEP TURKEY and Natural Disasters TURKEY is prone to mainly three types of natural disasters: Earthquakes;
CURRENT CHALLENGES OF THE GYNECOLOGY ASS STANTS IN TURKEY
 CLINICAL INVESTIGATION (Araflt rma) CURRENT CHALLENGES OF THE GYNECOLOGY ASS STANTS IN TURKEY Yusuf Taner KAFADAR 1, Funda GODE 2, Cansun DEMIR 3, Ali BALOGLU 4 1 Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology,
CLINICAL INVESTIGATION (Araflt rma) CURRENT CHALLENGES OF THE GYNECOLOGY ASS STANTS IN TURKEY Yusuf Taner KAFADAR 1, Funda GODE 2, Cansun DEMIR 3, Ali BALOGLU 4 1 Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology,
North Carolina Burn Disaster Program Carolina Hospital Burn Surge Plan Template
 North Carolina Burn Disaster Program Carolina Hospital Burn Surge Plan Template Developed by: UNC School of Medicine North Carolina Jaycee Burn Center North Carolina Office of EMS NC Burn Disaster Program
North Carolina Burn Disaster Program Carolina Hospital Burn Surge Plan Template Developed by: UNC School of Medicine North Carolina Jaycee Burn Center North Carolina Office of EMS NC Burn Disaster Program
THE ATTITUDE OF STUDENTS TOWARDS SOCIAL SCIENCES IN UNDERGRADUATE STUDIES: A SAMPLE FOR THE COMMUNICATION THEORY COURSE
 THE ATTITUDE OF STUDENTS TOWARDS SOCIAL SCIENCES IN UNDERGRADUATE STUDIES: A SAMPLE FOR THE COMMUNICATION THEORY COURSE ABSTRACT Assist. Prof. Dr. Deniz YENGİN, Istanbul Kültür University Faculty of Arts
THE ATTITUDE OF STUDENTS TOWARDS SOCIAL SCIENCES IN UNDERGRADUATE STUDIES: A SAMPLE FOR THE COMMUNICATION THEORY COURSE ABSTRACT Assist. Prof. Dr. Deniz YENGİN, Istanbul Kültür University Faculty of Arts
Terrorism-Related Injuries
 Terrorism-Related Injuries Charles DiMaggio, PhD 1,2 March 6, 2011 1 Department of Anesthesiology, Columbia University, College of Physicians and Surgeons, New York 2 Department of Epidemiology, Columbia
Terrorism-Related Injuries Charles DiMaggio, PhD 1,2 March 6, 2011 1 Department of Anesthesiology, Columbia University, College of Physicians and Surgeons, New York 2 Department of Epidemiology, Columbia
NATURAL GAS SAFETY. Your safety. Our priority. 2013 Update
 NATURAL GAS SAFETY Your safety. Our priority. 2013 Update IMPORTANT CONTACT INFORMATION Emergencies: If you suspect a natural gas leak, from a safe place, call 911 and Southwest Gas immediately at 1-877-860-6020,
NATURAL GAS SAFETY Your safety. Our priority. 2013 Update IMPORTANT CONTACT INFORMATION Emergencies: If you suspect a natural gas leak, from a safe place, call 911 and Southwest Gas immediately at 1-877-860-6020,
HELPFUL TIPS AFTER A CAR ACCIDENT
 HELPFUL TIPS AFTER A CAR ACCIDENT A PRACTICAL GUIDE BY ERIN M. HARGIS, ESQ A car accident can be a very traumatic and stressful event and it may be difficult to think clearly if you have just been involved
HELPFUL TIPS AFTER A CAR ACCIDENT A PRACTICAL GUIDE BY ERIN M. HARGIS, ESQ A car accident can be a very traumatic and stressful event and it may be difficult to think clearly if you have just been involved
Risks in School Safety Assessment
 CHAPTER 2 RISK ASSESSMENT IN SCHOOLS IN FRANCE Jean-Marie Schléret National Observatory for Safety in Schools and Universities, France Lessons in danger Abstract: Since 1995, the National Observatory for
CHAPTER 2 RISK ASSESSMENT IN SCHOOLS IN FRANCE Jean-Marie Schléret National Observatory for Safety in Schools and Universities, France Lessons in danger Abstract: Since 1995, the National Observatory for
A Research Study about the Websites of Entrepreneurial and Innovative Universities In Terms Of Scientific and Technological Competence in Turkey
 Available Online at http://iassr.org/journal 2014 (c) EJRE published by International Association of Social Science Research - IASSR ISSN: 2147-6284 European Journal of Research on Education, 2014, 2(Special
Available Online at http://iassr.org/journal 2014 (c) EJRE published by International Association of Social Science Research - IASSR ISSN: 2147-6284 European Journal of Research on Education, 2014, 2(Special
Earthquakes. What to Do Before an Earthquake
 EARTHQUAKES Earthquakes What to Do Before an Earthquake Earthquakes strike suddenly, violently and without warning. Identifying potential hazards ahead of time and advance planning can reduce the dangers
EARTHQUAKES Earthquakes What to Do Before an Earthquake Earthquakes strike suddenly, violently and without warning. Identifying potential hazards ahead of time and advance planning can reduce the dangers
Implementation Date: May 5, 2009. Table of Contents. Section Description Page. 1.0 Description 1. 2.0 Initial Response 2
 Recommended by Emergency Preparedness Committee: April 21, 2009 Recommended by President s Council: May 1, 2009 Approved by Executive Committee: May 5, 2009 NAIT Procedures CS1.2.6 Flood Implementation
Recommended by Emergency Preparedness Committee: April 21, 2009 Recommended by President s Council: May 1, 2009 Approved by Executive Committee: May 5, 2009 NAIT Procedures CS1.2.6 Flood Implementation
Internal and External Accident Incident Reporting
 Phoenix Community Care Ltd Policy & Procedure Internal and External Accident Incident Reporting Version Written Updated Scheduled Review Date Author 1 2008 2008 2009 Anne Spriggs 2 2010 2013 Angela Kelly
Phoenix Community Care Ltd Policy & Procedure Internal and External Accident Incident Reporting Version Written Updated Scheduled Review Date Author 1 2008 2008 2009 Anne Spriggs 2 2010 2013 Angela Kelly
December Newsletter by Vincent Dunn Backdraft and flashover, what is the difference?
 Photo By: Steve Spak December Newsletter by Vincent Dunn Backdraft and flashover, what is the difference? What is a backdraft explosion and how does differ from a flashover? Explosions kill and injure
Photo By: Steve Spak December Newsletter by Vincent Dunn Backdraft and flashover, what is the difference? What is a backdraft explosion and how does differ from a flashover? Explosions kill and injure
