How to Examine a Sick Person
|
|
|
- Damon Fields
- 10 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 29 How to Examine a Sick Person CHAPTER 3 To find out the needs of a sick person, first you must ask important questions and then examine him carefully. You should look for signs and symptoms that help you tell how ill the person is and what kind of sickness he may have. Always examine the person where there is good light, preferably in the sunlight never in a dark room. There are certain basic things to ask and to look for in anyone who is sick. These include things the sick person feels or reports (symptoms), as well as things you notice on examining him (signs). These signs can be especially important in babies and persons unable to talk. In this book the word signs is used for both symptoms and signs. When you examine a sick person, write down your findings and keep them for the health worker in case he is needed (see p. 44). QUESTIONS Start by asking the person about her sickness. Be sure to ask the following: What bothers you most right now? What makes you feel better or worse? How and when did your sickness begin? Have you had this same trouble before, or has anyone else in your family or neighborhood had it? Continue with other questions in order to learn the details of the illness. For example, if the sick person has a pain, ask her: Where does it hurt? (Ask her to point to the exact place with one finger.) Does it hurt all the time, or off and on? What is the pain like? (sharp? dull? burning?) Can you sleep with the pain? If the sick person is a baby who still does not talk, look for signs of pain. Notice his movements and how he cries. (For example, a child with an earache sometimes rubs the side of his head or pulls at his ear.)
2 30 GENERAL CONDITION OF HEALTH Before touching the sick person, look at him carefully. Observe how ill or weak he looks, the way he moves, how he breathes, and how clear his mind seems. Look for signs of dehydration (see p. 151) and of shock (p. 77). Notice whether the person looks well nourished or poorly nourished. Has he been losing weight? When a person has lost weight slowly over a long period of time, he may have a chronic illness (one that lasts a long time). Also note the color of the skin and eyes. These sometimes change when a person is sick. (Dark skin can hide color changes. So look at parts of the body where the skin is pale, such as palms of the hands or soles of the feet, the fingernails, or the insides of the lips and eyelids.) Paleness, especially of the lips and inside the eyelids, is a sign of anemia (p. 124). Skin may also go lighter as a result of tuberculosis (p. 179), or kwashiorkor (p. 113). Darkening of the skin may be a sign of starvation (see p. 112). Bluish skin, especially blueness or darkness of the lips and fingernails, may mean serious problems with breathing (p. 79, 167, and 313) or with the heart (p. 325). Blue-gray color in an unconscious child may be a sign of cerebral malaria (p. 186). A gray-white coloring, with cool moist skin, often means a person is in shock (p. 77). Yellow color (jaundice) of the skin and eyes may result from disease in the liver (hepatitis, p. 172, cirrhosis, p. 328, or amebic abscess, p. 145) or gallbladder (p. 329). It may also occur in newborn babies (p. 274), and in children born with sickle cell disease (p. 321). Look also at the skin when a light is shining across it from one side. This can show the earliest sign of measles rash on the face of a feverish child (p. 311). TEMPERATURE It is often wise to take a sick person s temperature, even if he does not seem to have a fever. If the person is very sick, take the temperature at least 4 times each day and write it down. If there is no thermometer, you can get an idea of the temperature by putting the back of one hand on the sick person s forehead and the other on your own or that of another healthy person. If the sick person has a fever, you should feel the difference. It is important to find out when and how the fever comes, how long it lasts, and how it goes away. This may help you identify the disease. Not every fever is malaria, though in some countries it is often treated as such. Remember other possible causes. For example: Common cold, and other virus infections (p. 163). The fever is usually mild. Typhoid causes a fever that goes on rising for 5 days. Malaria medicine does not help. Tuberculosis sometimes causes a mild fever in the afternoon. At night the person often sweats, and the fever goes down.
3 How to Use a Thermometer Every family should have a thermometer. Take the temperature of a sick person 4 times a day and always write it down. 31 How to read the thermometer (using one marked in degrees centigrade C): Turn the thermometer until you can see the silver line. Normal Fever High Fever The point where the silver line stops marks the temperature. How to take the temperature: 1. Clean the thermometer well with soap and water or alcohol. Shake it hard, with a snap of the wrist, until it reads less than 36 degrees. 2. Put the thermometer This thermometer marks 40 degrees C. under the tongue (keeping the mouth shut) or in the armpit if there is danger of biting the thermometer or carefully, in the anus of a small child (wet or grease it first) 3. Leave it there for 3 or 4 minutes. 4. Read it. (An armpit temperature will read a little lower than a mouth reading; in the anus it will read a little higher.) 5. Wash the thermometer well with soap and water. Note: in newborn babies a temperature that is unusually high or unsually low (below 36 ) may mean a serious infection (see p. 275). To learn about other fever patterns, see p. 26 to 27. To learn what to do for a fever, see p. 75.
4 32 BREATHING (RESPIRATION) Pay special attention to the way the sick person breathes the depth (deep or shallow), rate (how often breaths are taken), and difficulty. Notice if both sides of the chest move equally when she breathes. If you have a watch or simple timer, count the number of breaths per minute (when the person is quiet). Between 12 and 20 breaths per minute is normal for adults and older children. Up to 30 breaths a minute is normal for younger children, and 40 for babies. People with a high fever or serious respiratory illness breathe more quickly than normal. For example, more than 30 shallow breaths a minute in an adult usually means pneumonia, as does 60 breaths a minute for a newborn baby. Listen carefully to the sound of the breaths. For example: A whistle or wheeze and difficulty breathing out can mean asthma (see p. 167). A gurgling or snoring noise and difficult breathing in an unconscious person may mean the tongue, mucus (slime or pus), or something else is stuck in the throat and does not let enough air get through. Look for sucking in of the skin between ribs and at the angle of the neck (behind the collar bone) when the person breathes in. This means air has trouble getting through. Consider the possibility of something stuck in the throat (p. 79), pneumonia (p. 171), asthma (p. 167), or bronchitis (mild sucking in, see p. 170). If the person has a cough, ask if it keeps her from sleeping. Find out if she coughs up mucus, how much, its color, and if there is blood in it. Pay attention to the strength, the rate, and the regularity of the pulse. If you have a watch or timer, count the pulses per minute. PULSE (HEARTBEAT) To take the person s pulse, put your fingers on the wrist as shown. (Do not use your thumb to feel for the pulse.) If you cannot find the pulse in the wrist, feel for it in the neck beside the voicebox. Or put your ear directly or the chest and listen for the heartbeat (or use a stethoscope if you have one). NORMAL PULSE FOR PEOPLE AT REST adults from 60 to 80 per minute children to 100 babies to 140
5 33 The pulse gets much faster with exercise and when a person is nervous, frightened, or has a fever. As a general rule, the pulse increases 20 beats per minute for each degree ( C) rise in fever. When a person is very ill, take the pulse often and write it down along with the temperature and rate of breathing. It is important to notice changes in the pulse rate. For example: A weak, rapid pulse can mean a state of shock (see p. 77). A very rapid, very slow, or irregular pulse could mean heart trouble (see p. 325). A relatively slow pulse in a person with a high fever may be a sign of typhoid (see p. 188). EYES Look at the color of the white part of the eyes. Is it normal, red (p. 219), or yellow? Also note any changes in the sick person s vision. Have the person slowly move her eyes up and down and from side to side. Jerking or uneven movement may be a sign of brain damage. Pay attention to the size and color of the pupils (the black window in the center of the eye). If they are very large, it can mean a state of shock (see p. 77). If they are very large, or very small, it can mean poison or the effect of certain drugs. If there is a white glow, it can mean cataracts (see p. 225) or cancer. Look at both eyes and note any difference between the two, especially in the size of the pupils: A big difference in the size of the pupils is almost always a medical emergency. If the eye with the larger pupil hurts so badly it causes vomiting, the person probably has GLAUCOMA (see p. 222). If the eye with the smaller pupil hurts a great deal, the person may have IRITIS, a very serious problem (see p. 221). Difference in the size of the pupils of an unconscious person or a person who has had a recent head injury may mean brain damage. It may also mean STROKE (see p. 327). Always compare the pupils of a person who is unconscious or has had a head injury.
6 34 EARS, THROAT, AND NOSE Ears: Always check for signs of pain and infection in the ears-especially in a child with fever or a cold. A baby who cries a lot or pulls at his ear may have an ear infection (p. 309). Pull the ear gently. If this increases pain, the infection is probably in the tube of the ear (ear canal). Also look for redness or pus inside the ear. A small flashlight or penlight will help. But never put a stick, wire, or other hard object inside the ear. Find out if the person hears well, or if one side is more deaf than the other. Rub your thumb and fingers together near the person s ear to see if he can hear it. For deafness and ringing of the ears see page 327. Throat and Mouth: With a torch (flashlight) or sunlight examine the mouth and throat. To do this hold down tongue with a spoon handle or have the person say ahhhhh... Notice if the throat is red and if the tonsils (2 lumps at the back of the throat) are swollen or have spots with pus (see p. 309). Also examine the mouth for sores, inflamed gums, sore tongue, rotten or abscessed teeth and other problems. (Read Chapter 17.) Nose: Is the nose runny or plugged? (Notice if and how a baby breathes through his nose.) Shine a light inside and look for mucus, pus, blood; also look for redness, swelling, or bad smell. Check for signs of sinus trouble or hayfever (p. 165). SKIN It is important to examine the sick person s whole body, no matter how mild the sickness may seem. Babies and children should be undressed completely. Look carefully for anything that is not normal, including: sores, wounds, or splinters rashes or welts spots, patches, or any unusual markings inflammation (sign of infection with redness, heat, pain and swelling) swelling or puffiness swollen lymph nodes (little lumps in the neck, the armpits, or the groin, see p. 88) Always examine little children between the buttocks, in the genital area, between the fingers and toes, behind the ears, and in the hair (for lice, scabies, ringworm, rashes, and sores). For identification of different skin problems, see pages abnormal lumps or masses unusual thinning or loss of hair, or loss of its color or shine (p. 112) loss of eyebrows (leprosy? p. 191)
7 THE BELLY (ABDOMEN) 35 If a person has pain in the belly, try to find out exactly where it hurts. Learn whether the pain is steady or whether it suddenly comes and goes, like cramps or colic. When you examine the belly, first look at it for any unusual swelling or lumps. The location of the pain often gives a clue to the cause (see the following page). First, ask the person to point with one finger where it hurts. Then, beginning on the opposite side from the spot where he has pointed, press gently on different parts of the belly to see where it hurts most. See if the belly is soft or hard and whether the person can relax his stomach muscles. A very hard belly could mean an acute abdomen perhaps appendicitis or peritonitis (see p. 94). If you suspect peritonitis or appendicitis, do the test for rebound pain described on page 95. Feel for any abnormal lumps and hardened areas in the belly. If the person has a constant pain in the stomach, with nausea, and has not been able to move her bowels, put an ear (or stethoscope) on the belly, like this: Listen for gurgles in the intestines. If you hear nothing after about 2 minutes, this is a danger sign. (See Emergency Problems of the Gut, p. 93.) A silent belly is like a silent dog. Beware!
8 36 These pictures show the areas of the belly that usually hurt when a person has the following problems: Ulcer (see p. 128) Appendicitis (see p. 94) pain in the pit of the stomach first it hurts here later it hurts here Gallbladder (see p. 329) Liver (see p. 172, 144, and 328) the pain often reaches to the back pain here, at times it spreads to the chest Urinary system (see p. 234) mid or low back pain, often goes around the waist to the lower part of the belly Inflammation or tumor of the ovaries, or out-of-place pregnancy (see p. 280) urinary tubes pain on one side or both, sometimes spreading to the back bladder Note: For different causes of back pain see p. 173.
9 MUSCLES AND NERVES 37 If a person complains of numbness, weakness, or loss of control in part of his body, or you want to test it: notice the way he walks and moves. Have him stand, sit, or lie completely straight, and carefully compare both sides of his body. Face: Have him smile, frown, open his eyes wide, and squeeze them shut. Notice any drooping or weakness on one side. If the problem began more or less suddenly, think of a head injury (p. 91), stroke (p. 327), or Bell s palsy (p. 327). If it came slowly, it may be a brain tumor. Get medical advice. Also check for normal eye movement, size of pupils (p. 217), and how well he can see. Arms and legs: Look for loss of muscle. Notice or measure difference in thickness of arms or legs. Watch how he moves and walks. If muscle loss or weakness affects the whole body, suspect malnutrition (p. 112) or a chronic (long-term) illness like tuberculosis. Have him squeeze your fingers to compare strength in his hands and push and pull with his feet against your hand. Any string or ribbon will do to check if the distance around the arms or legs is different. Also have him hold his arms straight out and turn his hands up and down. Have him lie down and lift one leg and then the other. Note any weakness or trembling. If muscle loss and weakness is uneven or worse on one side, in children, think first of polio (p. 314); in adults, think of a back problem, a back or head injury, or stroke. For more information on muscle testing and physical examination of disabled persons, see Disabled Village Children, Chapter 4.
10 38 Check for stiffness or tightness of different muscles: If the jaw is stiff or will not open, suspect tetanus (p. 182) or a severe infection of the throat (p. 309) or of a tooth (p. 231). If the problem began after he yawned or was hit in the jaw, he may have a dislocated jaw. If the neck or back is stiff and bent backwards, in a very sick child, suspect meningitis. If the head will not bend forward or cannot be put between the knees, meningitis is likely (p. 185). meningitis If a child always has some stiff muscles and makes strange or jerky movements, he may be spastic (p. 320). If strange or jerky movements come suddenly, with loss of consciousness, he may have seizures (p. 178). If seizures happen often, think of epilepsy. If they happen when he is ill, the cause may be high fever (p. 76) or dehydration (p. 151) or tetanus tetanus (p. 182) or meningitis (p. 185). To test a person s reflexes when you suspect tetanus, see p To check for loss of feeling in the hands, feet, or other parts of the body: Have the person cover his eyes. Lightly touch or prick the skin in different places. Ask him to say yes when he feels it. Loss of feeling in or near spots or patches on the body is probably leprosy (p. 191). Loss of feeling in both hands or feet may be due to diabetes (p. 127) or leprosy. Loss of feeling on one side only could come from a back problem (p. 174) or injury.
How To Care For A Sick Person
 39 How to Take Care of a Sick Person Sickness weakens the body. To gain strength and get well quickly, special care is needed. Medicines are often not necessary. But good care is always important. The
39 How to Take Care of a Sick Person Sickness weakens the body. To gain strength and get well quickly, special care is needed. Medicines are often not necessary. But good care is always important. The
For the Patient: Dasatinib Other names: SPRYCEL
 For the Patient: Dasatinib Other names: SPRYCEL Dasatinib (da sa' ti nib) is a drug that is used to treat many types of cancer. It is a tablet that you take by mouth. Tell your doctor if you have ever
For the Patient: Dasatinib Other names: SPRYCEL Dasatinib (da sa' ti nib) is a drug that is used to treat many types of cancer. It is a tablet that you take by mouth. Tell your doctor if you have ever
WET, COUGHING AND COLD NEAR RIVER BANK STUNG BY BEE CAUSING ANAPHYLACTIC SHOCK TO WRIST
 GRIT IN EYE BROKEN LEG BONE WET, COUGHING AND COLD NEAR RIVER BANK STUNG BY BEE CAUSING ANAPHYLACTIC SHOCK HEART ATTACK SUFFERING FROM SHOCK CHOKING SEVERE BLEEDING TO WRIST HYPOTHERMIA ANGINA Localised
GRIT IN EYE BROKEN LEG BONE WET, COUGHING AND COLD NEAR RIVER BANK STUNG BY BEE CAUSING ANAPHYLACTIC SHOCK HEART ATTACK SUFFERING FROM SHOCK CHOKING SEVERE BLEEDING TO WRIST HYPOTHERMIA ANGINA Localised
Application For Admission To The Non-Surgical Spinal Decompression Program At The Spinal Decompression Center of Long Beach
 Application For Admission To The Non-Surgical Spinal Decompression Program At The Spinal Decompression Center of Long Beach If you are reading this form, you have qualified for a consultation with Dr.
Application For Admission To The Non-Surgical Spinal Decompression Program At The Spinal Decompression Center of Long Beach If you are reading this form, you have qualified for a consultation with Dr.
Streptococcal Infections
 Streptococcal Infections Introduction Streptococcal, or strep, infections cause a variety of health problems. These infections can cause a mild skin infection or sore throat. But they can also cause severe,
Streptococcal Infections Introduction Streptococcal, or strep, infections cause a variety of health problems. These infections can cause a mild skin infection or sore throat. But they can also cause severe,
JAMES PETROS, M.D., INC. PHONE: (408) 528-8833 FAX: (408) 528-8557
 FIGHTING PAIN. TOUCHING LIVES. JAMES PETROS, M.D., INC. PHONE: (408) 528-8833 FAX: (408) 528-8557 Personal Information Emergency Contact Today s Date: Name: Patient: Realtionship: Birth Date: Age: Sex:
FIGHTING PAIN. TOUCHING LIVES. JAMES PETROS, M.D., INC. PHONE: (408) 528-8833 FAX: (408) 528-8557 Personal Information Emergency Contact Today s Date: Name: Patient: Realtionship: Birth Date: Age: Sex:
In case of an urgent concern or emergency, call 911 or go to the nearest emergency department right away.
 Asthma Basics Patient and Family Education This teaching sheet contains general information only. Talk with your child s doctor or a member of your child s healthcare team about specific care of your child.
Asthma Basics Patient and Family Education This teaching sheet contains general information only. Talk with your child s doctor or a member of your child s healthcare team about specific care of your child.
Pneumonia. Pneumonia is an infection that makes the tiny air sacs in your lungs inflamed (swollen and sore). They then fill with liquid.
 Pneumonia Pneumonia is an infection that makes the tiny air sacs in your lungs inflamed (swollen and sore). They then fill with liquid. People with mild (not so bad) pneumonia can usually be treated at
Pneumonia Pneumonia is an infection that makes the tiny air sacs in your lungs inflamed (swollen and sore). They then fill with liquid. People with mild (not so bad) pneumonia can usually be treated at
PATIENT INFORMATION INSURANCE INFORMATION
 (mm/dd/yyyy): Have you been to Physicians Urgent Care before? Yes No Arrival Time: If yes, when? Is this a follow-up to a previous visit: Yes No PATIENT INFORMATION Patient s First Name: Middle Name: Last
(mm/dd/yyyy): Have you been to Physicians Urgent Care before? Yes No Arrival Time: If yes, when? Is this a follow-up to a previous visit: Yes No PATIENT INFORMATION Patient s First Name: Middle Name: Last
For the Patient: Paclitaxel injection Other names: TAXOL
 For the Patient: Paclitaxel injection Other names: TAXOL Paclitaxel (pak'' li tax' el) is a drug that is used to treat many types of cancer. It is a clear liquid that is injected into a vein. Tell your
For the Patient: Paclitaxel injection Other names: TAXOL Paclitaxel (pak'' li tax' el) is a drug that is used to treat many types of cancer. It is a clear liquid that is injected into a vein. Tell your
What You And Your Family Can Do About Asthma
 GLOBAL INITIATIVE FOR ASTHMA What You And Your Family Can Do About Asthma BASED ON THE GLOBAL STRATEGY FOR ASTHMA MANAGEMENT AND PREVENTION NHLBI/WHO WORKSHOP REPORT NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH NATIONAL
GLOBAL INITIATIVE FOR ASTHMA What You And Your Family Can Do About Asthma BASED ON THE GLOBAL STRATEGY FOR ASTHMA MANAGEMENT AND PREVENTION NHLBI/WHO WORKSHOP REPORT NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH NATIONAL
INFLUENZA (FLU) Flu and You
 Influenza (Flu) What is the flu? The flu is an illness caused by flu viruses. The flu may make people cough and have a sore throat and fever. They may also have a runny or stuffy nose, feel tired, have
Influenza (Flu) What is the flu? The flu is an illness caused by flu viruses. The flu may make people cough and have a sore throat and fever. They may also have a runny or stuffy nose, feel tired, have
POINCIANA INTERNAL MEDICINE PA. Patient Name: Social Security Number: Date of Birth: / / Sex: M/F (Circle One) Married/Single/Divorced/Widow Address:
 Patient Name: Social Security Number: Date of Birth: / / Sex: M/F (Circle One) Married/Single/Divorced/Widow Address: (Street) (City/State/Zip) Home Phone: ( ) E Mail Address: Would you be interested in
Patient Name: Social Security Number: Date of Birth: / / Sex: M/F (Circle One) Married/Single/Divorced/Widow Address: (Street) (City/State/Zip) Home Phone: ( ) E Mail Address: Would you be interested in
Injecting Inside the Mouth
 Injecting Inside the Mouth 135 9 CHAPTER It is possible to treat a tooth without pain. You do this with an injection of local anesthetic. You must inject near the nerve, so to give good injections, you
Injecting Inside the Mouth 135 9 CHAPTER It is possible to treat a tooth without pain. You do this with an injection of local anesthetic. You must inject near the nerve, so to give good injections, you
Diuretics: You may get diuretic medicine to help decrease swelling in your brain. This may help your brain get better blood flow.
 Hemorrhagic Stroke GENERAL INFORMATION: What is a hemorrhagic stroke? A hemorrhagic stroke happens when a blood vessel in the brain bursts. This may happen if the blood vessel wall is weak, or sometimes
Hemorrhagic Stroke GENERAL INFORMATION: What is a hemorrhagic stroke? A hemorrhagic stroke happens when a blood vessel in the brain bursts. This may happen if the blood vessel wall is weak, or sometimes
NEURO-OPHTHALMIC QUESTIONNAIRE NAME: AGE: DATE OF EXAM: CHART #: (Office Use Only)
 PAGE 1 NEURO-OPHTHALMIC QUESTIONNAIRE NAME: AGE: DATE OF EXAM: CHART #: (Office Use Only) 1. What is the main problem that you are having? (If additional space is required, please use the back of this
PAGE 1 NEURO-OPHTHALMIC QUESTIONNAIRE NAME: AGE: DATE OF EXAM: CHART #: (Office Use Only) 1. What is the main problem that you are having? (If additional space is required, please use the back of this
Full name DOB Age Address Email Phone numbers (H) (W) (C) Emergency contact Phone
 DEMOGRAPHIC INFORMATION Full name DOB Age Address Email Phone numbers (H) (W) (C) Emergency contact Phone CARE INFORMATION Primary care physician: Address Phone Fax Referring physician: Specialty Address
DEMOGRAPHIC INFORMATION Full name DOB Age Address Email Phone numbers (H) (W) (C) Emergency contact Phone CARE INFORMATION Primary care physician: Address Phone Fax Referring physician: Specialty Address
(Please fill this out to the best of your ability) Baker Eye Institute Conway, Arkansas 501-329-3937 NAME: Today s Date:
 Page 1 of 5 (Please fill this out to the best of your ability) Baker Eye Institute Conway, Arkansas 501-329-3937 NAME: Age: What is the main reason for today s visit? Today s Date: Who referred you to
Page 1 of 5 (Please fill this out to the best of your ability) Baker Eye Institute Conway, Arkansas 501-329-3937 NAME: Age: What is the main reason for today s visit? Today s Date: Who referred you to
Medicines To Treat Alcohol Use Disorder A Review of the Research for Adults
 Medicines To Treat Alcohol Use Disorder A Review of the Research for Adults Is This Information Right for Me? Yes, this information is right for you if: Your doctor* said you have alcohol use disorder
Medicines To Treat Alcohol Use Disorder A Review of the Research for Adults Is This Information Right for Me? Yes, this information is right for you if: Your doctor* said you have alcohol use disorder
MEDICATION GUIDE POMALYST (POM-uh-list) (pomalidomide) capsules. What is the most important information I should know about POMALYST?
 MEDICATION GUIDE POMALYST (POM-uh-list) (pomalidomide) capsules What is the most important information I should know about POMALYST? Before you begin taking POMALYST, you must read and agree to all of
MEDICATION GUIDE POMALYST (POM-uh-list) (pomalidomide) capsules What is the most important information I should know about POMALYST? Before you begin taking POMALYST, you must read and agree to all of
Taking Out a Tooth. Before You Begin: Ask Questions! CHAPTER11
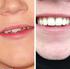 159 CHAPTER11 Taking Out a Tooth Not every painful tooth needs to come out. You must decide how serious the problem is, and then decide if you can treat and save the tooth. Some problems such as root canal
159 CHAPTER11 Taking Out a Tooth Not every painful tooth needs to come out. You must decide how serious the problem is, and then decide if you can treat and save the tooth. Some problems such as root canal
MEDICATION GUIDE KOMBIGLYZE XR (kom-be-glyze X-R) (saxagliptin and metformin HCl extended-release) tablets
 MEDICATION GUIDE KOMBIGLYZE XR (kom-be-glyze X-R) (saxagliptin and metformin HCl extended-release) tablets Read this Medication Guide carefully before you start taking KOMBIGLYZE XR and each time you get
MEDICATION GUIDE KOMBIGLYZE XR (kom-be-glyze X-R) (saxagliptin and metformin HCl extended-release) tablets Read this Medication Guide carefully before you start taking KOMBIGLYZE XR and each time you get
Fainting - Syncope. This reference summary explains fainting. It discusses the causes and treatment options for the condition.
 Fainting - Syncope Introduction Fainting, also known as syncope, is a temporary loss of consciousness. It is caused by a drop in blood flow to the brain. You may feel dizzy, lightheaded or nauseous before
Fainting - Syncope Introduction Fainting, also known as syncope, is a temporary loss of consciousness. It is caused by a drop in blood flow to the brain. You may feel dizzy, lightheaded or nauseous before
Bone Marrow or Blood Stem Cell Transplants in Children With Severe Forms of Autoimmune Disorders or Certain Types of Cancer
 Bone Marrow or Blood Stem Cell Transplants in Children With Severe Forms of Autoimmune Disorders or Certain Types of Cancer A Review of the Research for Parents and Caregivers Is This Information Right
Bone Marrow or Blood Stem Cell Transplants in Children With Severe Forms of Autoimmune Disorders or Certain Types of Cancer A Review of the Research for Parents and Caregivers Is This Information Right
& WHEN SHOULD I WORRY?
 WHEN SHOULD I WORRY? - Your guide to Coughs, Colds, Earache & Sore Throats Information For:- Who is this booklet for? Having an ill child can be a very scary experience for parents. If you understand more
WHEN SHOULD I WORRY? - Your guide to Coughs, Colds, Earache & Sore Throats Information For:- Who is this booklet for? Having an ill child can be a very scary experience for parents. If you understand more
MEDICATION GUIDE. PROCRIT (PRO KRIT) (epoetin alfa)
 MEDICATION GUIDE PROCRIT (PROKRIT) (epoetin alfa) Read this Medication Guide: before you start PROCRIT. if you are told by your healthcare provider that there is new information about PROCRIT. if you are
MEDICATION GUIDE PROCRIT (PROKRIT) (epoetin alfa) Read this Medication Guide: before you start PROCRIT. if you are told by your healthcare provider that there is new information about PROCRIT. if you are
Changes to Your Baby and Your Body During Pregnancy
 Changes to and Your Body During Pregnancy 1st Trimester: Conception to Week 16 Your baby s traits and sex are set when the sperm meets the egg. During this time: The brain, nerves, heart, lungs and bones
Changes to and Your Body During Pregnancy 1st Trimester: Conception to Week 16 Your baby s traits and sex are set when the sperm meets the egg. During this time: The brain, nerves, heart, lungs and bones
ORTHOPAEDIC SPINE PAIN QUESTIONNAIRE
 ORTHOPAEDIC SPINE PAIN QUESTIONNAIRE NAME: DATE: ADDRESS: AGE: TELEPHONE#: RELIGION: OCCUPATION: REFERRED BY WHOM: NEAREST FRIEND/RELATIVE: TELEPHONE#: ADDRESS: PLEASE EXPLAIN WHY YOU HAVE COME TO SEE
ORTHOPAEDIC SPINE PAIN QUESTIONNAIRE NAME: DATE: ADDRESS: AGE: TELEPHONE#: RELIGION: OCCUPATION: REFERRED BY WHOM: NEAREST FRIEND/RELATIVE: TELEPHONE#: ADDRESS: PLEASE EXPLAIN WHY YOU HAVE COME TO SEE
PLEASE PRINT LEGIBLY
 Patient Information PLEASE PRINT LEGIBLY Patients Name: Date of Birth: Sex: Patients Address: City: State: Zip: Home Phone: Cell: Work: Email: SSN: Employer: Occupation: Marital Status: Employed: Full
Patient Information PLEASE PRINT LEGIBLY Patients Name: Date of Birth: Sex: Patients Address: City: State: Zip: Home Phone: Cell: Work: Email: SSN: Employer: Occupation: Marital Status: Employed: Full
Staying on Track with TUBERCULOSIS. Medicine
 Staying on Track with TB TUBERCULOSIS Medicine What s Inside: Read this brochure to learn about TB and what you can do to get healthy. Put it in a familiar place to pull out and read when you have questions.
Staying on Track with TB TUBERCULOSIS Medicine What s Inside: Read this brochure to learn about TB and what you can do to get healthy. Put it in a familiar place to pull out and read when you have questions.
Asthma and COPD Awareness
 Asthma and COPD Awareness Molina Breathe with Ease sm and Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Molina Healthcare of Michigan Fall 2012 Importance of Controller Medicines Asthma is a disease that causes
Asthma and COPD Awareness Molina Breathe with Ease sm and Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Molina Healthcare of Michigan Fall 2012 Importance of Controller Medicines Asthma is a disease that causes
Guidelines for Hand Foot and Mouth Disease HFMD
 Guidelines for Hand Foot and Mouth Disease HFMD Hand, foot, and mouth disease, or HFMD, is a contagious illness caused by different viruses. Infants and children younger than 5 years are more likely to
Guidelines for Hand Foot and Mouth Disease HFMD Hand, foot, and mouth disease, or HFMD, is a contagious illness caused by different viruses. Infants and children younger than 5 years are more likely to
Get the Facts About. Disease
 Get the Facts About TB TUBERCULOSIS Disease What s Inside: 3 PAGE Get the facts, then get the cure 4 PAGE 9 PAGE 12 PAGE Learn how TB is spread Treatment for TB disease Talking to family and friends about
Get the Facts About TB TUBERCULOSIS Disease What s Inside: 3 PAGE Get the facts, then get the cure 4 PAGE 9 PAGE 12 PAGE Learn how TB is spread Treatment for TB disease Talking to family and friends about
BROCKTON AREA MULTI-SERVICES, INC. MEDICAL PROCEDURE GUIDE. Date(s) Reviewed/Revised:
 Page 1 of 5 PROCEDURE FOR: MAP-certified staff and RN/LPN MAP-certified staff are to be trained in the use of epinephrine administration via pre-filled autoinjector devices(s) annually. Certified staff
Page 1 of 5 PROCEDURE FOR: MAP-certified staff and RN/LPN MAP-certified staff are to be trained in the use of epinephrine administration via pre-filled autoinjector devices(s) annually. Certified staff
Key Facts about Influenza (Flu) & Flu Vaccine
 Key Facts about Influenza (Flu) & Flu Vaccine mouths or noses of people who are nearby. Less often, a person might also get flu by touching a surface or object that has flu virus on it and then touching
Key Facts about Influenza (Flu) & Flu Vaccine mouths or noses of people who are nearby. Less often, a person might also get flu by touching a surface or object that has flu virus on it and then touching
Challenges of Foster Parents who Care for Infants with Neonatal Abstinence Syndrome
 Challenges of Foster Parents who Care for Infants with Neonatal Abstinence Syndrome All Health Care Providers are required by law to make a referral to the Department of Children s Services (DCS) Child
Challenges of Foster Parents who Care for Infants with Neonatal Abstinence Syndrome All Health Care Providers are required by law to make a referral to the Department of Children s Services (DCS) Child
2 P age. Babies from Birth to Age 2
 Contents Babies from Birth to Age 2... 2 Vaccines give parents the power... 2 Vaccines are recommended throughout our lives... 3 Talk to your doctor... 3 Vaccines are very safe... 3 Whooping Cough (Pertussis)...
Contents Babies from Birth to Age 2... 2 Vaccines give parents the power... 2 Vaccines are recommended throughout our lives... 3 Talk to your doctor... 3 Vaccines are very safe... 3 Whooping Cough (Pertussis)...
NEW PATIENT HISTORY QUESTIONNAIRE. Physician Initials Date PATIENT INFORMATION
 NEW PATIENT HISTORY QUESTIONNAIRE Physician Initials Date PATIENT INFORMATION JHH# DOB# AGE HOME PH CELL PH DAY PH EMAIL Who is your REFERRING PHYSICIAN? (The doctor who referred you to Johns Hopkins Neurology.)
NEW PATIENT HISTORY QUESTIONNAIRE Physician Initials Date PATIENT INFORMATION JHH# DOB# AGE HOME PH CELL PH DAY PH EMAIL Who is your REFERRING PHYSICIAN? (The doctor who referred you to Johns Hopkins Neurology.)
MOTOR VEHICLE ACCIDENT QUESTIONNAIRE
 MOTOR VEHICLE ACCIDENT QUESTIONNAIRE Thank you in advance for taking the time to complete this form, this will help us to better assess all of your pain concerns and provide you with the best treatment.
MOTOR VEHICLE ACCIDENT QUESTIONNAIRE Thank you in advance for taking the time to complete this form, this will help us to better assess all of your pain concerns and provide you with the best treatment.
Medication Guide TASIGNA (ta-sig-na) (nilotinib) Capsules
 Medication Guide TASIGNA (ta-sig-na) (nilotinib) Capsules Read this Medication Guide before you start taking Tasigna and each time you get a refill. There may be new information. This information does
Medication Guide TASIGNA (ta-sig-na) (nilotinib) Capsules Read this Medication Guide before you start taking Tasigna and each time you get a refill. There may be new information. This information does
Patient Information. Patient s First and Last name: Preferred Name: Mailing Address: City: State: Zip Code: Date of Birth: Gender:
 Patient Information: Patient Information Patient s First and Last name: Preferred Name: Mailing Address: Date of Birth: Gender: Best Number to Confirm Your Appointments: Alternate Phone Number: Social
Patient Information: Patient Information Patient s First and Last name: Preferred Name: Mailing Address: Date of Birth: Gender: Best Number to Confirm Your Appointments: Alternate Phone Number: Social
PROTECT YOURSELF PROTECT YOUR FAMILY PROTECT YOUR COMMUNITY from Ebola
 PROTECT YOURSELF PROTECT YOUR FAMILY PROTECT YOUR COMMUNITY from Ebola Things Everyone Should Know and Do gchv flipbook for Interpersonal Communication And Partners What are the signs and symptoms of Ebola?
PROTECT YOURSELF PROTECT YOUR FAMILY PROTECT YOUR COMMUNITY from Ebola Things Everyone Should Know and Do gchv flipbook for Interpersonal Communication And Partners What are the signs and symptoms of Ebola?
PAIN MANAGEMENT During Your Hospital Stay
 PAIN MANAGEMENT During Your Hospital Stay TABLE OF CONTENTS Understanding Pain...2 Pain Assessment...2 Describing Your Pain...5 Pain Treatment...5 Comfort Measures...6 Medication...7 Specialty Procedures...8
PAIN MANAGEMENT During Your Hospital Stay TABLE OF CONTENTS Understanding Pain...2 Pain Assessment...2 Describing Your Pain...5 Pain Treatment...5 Comfort Measures...6 Medication...7 Specialty Procedures...8
let s talk bleeds a bleed checklist for haemophilia patients
 let s talk bleeds a bleed checklist for haemophilia patients Specific signs of a bleed Watch for Bruising, with or without lumps Difference in the size of arms/legs Difference in movement in arms/legs
let s talk bleeds a bleed checklist for haemophilia patients Specific signs of a bleed Watch for Bruising, with or without lumps Difference in the size of arms/legs Difference in movement in arms/legs
Alcohol and drug abuse
 Alcohol and drug abuse This chapter explores how alcohol abuse affects our families, relationships, and communities, as well as the health risks associated with drug and alcohol abuse. 1. Alcohol abuse
Alcohol and drug abuse This chapter explores how alcohol abuse affects our families, relationships, and communities, as well as the health risks associated with drug and alcohol abuse. 1. Alcohol abuse
Interventional Spine Pain Consultants, P.A. Initial Consultation Information
 Interventional Spine Pain Consultants, P.A. Initial Consultation Information Date: / / Date of Birth / / Age: Name: Name of the provider that recommended you to our office? Name of your primary care doctor?
Interventional Spine Pain Consultants, P.A. Initial Consultation Information Date: / / Date of Birth / / Age: Name: Name of the provider that recommended you to our office? Name of your primary care doctor?
Better Breathing with COPD
 Better Breathing with COPD People with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) often benefit from learning different breathing techniques. Pursed Lip Breathing Pursed Lip Breathing (PLB) can be very
Better Breathing with COPD People with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) often benefit from learning different breathing techniques. Pursed Lip Breathing Pursed Lip Breathing (PLB) can be very
Please complete the Consent Form and the Respirator Certification Questionnaire.
 The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) Respiratory Protection Standard requires an employee to complete a questionnaire if the employee is required to wear a respirator. You have been
The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) Respiratory Protection Standard requires an employee to complete a questionnaire if the employee is required to wear a respirator. You have been
Share the important information in this Medication Guide with members of your household.
 MEDICATION GUIDE BUPRENORPHINE (BUE-pre-NOR-feen) Sublingual Tablets, CIII IMPORTANT: Keep buprenorphine sublingual tablets in a secure place away from children. Accidental use by a child is a medical
MEDICATION GUIDE BUPRENORPHINE (BUE-pre-NOR-feen) Sublingual Tablets, CIII IMPORTANT: Keep buprenorphine sublingual tablets in a secure place away from children. Accidental use by a child is a medical
Patient Medication Guide Brochure
 Patient Medication Guide Brochure 1 MEDICATION GUIDE TASIGNA (ta-sig-na) (nilotinib) Capsules Read this Medication Guide before you start taking TASIGNA and each time you get a refill. There may be new
Patient Medication Guide Brochure 1 MEDICATION GUIDE TASIGNA (ta-sig-na) (nilotinib) Capsules Read this Medication Guide before you start taking TASIGNA and each time you get a refill. There may be new
WHEN SEIZURES DON T LOOK LIKE SEIZURES
 WHEN SEIZURES DON T LOOK LIKE SEIZURES About the Epilepsy Foundation The Epilepsy Foundation is the national voluntary agency solely dedicated to the welfare of the more than three million people with
WHEN SEIZURES DON T LOOK LIKE SEIZURES About the Epilepsy Foundation The Epilepsy Foundation is the national voluntary agency solely dedicated to the welfare of the more than three million people with
Cocaine. Like heroin, cocaine is a drug that is illegal in some areas of the world. Cocaine is a commonly abused drug.
 Cocaine Introduction Cocaine is a powerful drug that stimulates the brain. People who use it can form a strong addiction. Addiction is when a drug user can t stop taking a drug, even when he or she wants
Cocaine Introduction Cocaine is a powerful drug that stimulates the brain. People who use it can form a strong addiction. Addiction is when a drug user can t stop taking a drug, even when he or she wants
Workman s Compensation
 Workman s Compensation Name: Sex: Phone Number: Age: Address (Street/City/State/Zip) Name of Employer: Phone: Address of Employer (Street/City/State/Zip) Date and time of accident?: Where were you taken
Workman s Compensation Name: Sex: Phone Number: Age: Address (Street/City/State/Zip) Name of Employer: Phone: Address of Employer (Street/City/State/Zip) Date and time of accident?: Where were you taken
Sore Throat. Definition. Causes. (Pharyngitis; Tonsillopharyngitis; Throat Infection) Pronounced: Fare-en-JY-tis /TAHN-sill-oh-fare-en-JY-tis
 Sore Throat (Pharyngitis; Tonsillopharyngitis; Throat Infection) Pronounced: Fare-en-JY-tis /TAHN-sill-oh-fare-en-JY-tis by Jennifer Lewy, MSW En Español (Spanish Version) Definition A sore throat is the
Sore Throat (Pharyngitis; Tonsillopharyngitis; Throat Infection) Pronounced: Fare-en-JY-tis /TAHN-sill-oh-fare-en-JY-tis by Jennifer Lewy, MSW En Español (Spanish Version) Definition A sore throat is the
Surgery Health Survey
 Surgery Health Survey Name: Social Security Number: Date of Birth: Please tell us which physician(s) we should contact regarding your visit: REFERRING PHYSICIAN Name: Address: PRIMARY CARE PHSYICIAN Name:
Surgery Health Survey Name: Social Security Number: Date of Birth: Please tell us which physician(s) we should contact regarding your visit: REFERRING PHYSICIAN Name: Address: PRIMARY CARE PHSYICIAN Name:
NEW YORK STATE DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH BUREAU OF EMERGENCY MEDICAL SERVICES
 NEW YORK STATE DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH BUREAU OF EMERGENCY MEDICAL SERVICES TRAINING PROGRAM OUTLINE FOR UNLICENSED OR UNCERTIFIED PERSONNEL TO ADMINISTER EPINEPHRINE BY AUTO-INJECTOR IN LIFE-THREATENING
NEW YORK STATE DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH BUREAU OF EMERGENCY MEDICAL SERVICES TRAINING PROGRAM OUTLINE FOR UNLICENSED OR UNCERTIFIED PERSONNEL TO ADMINISTER EPINEPHRINE BY AUTO-INJECTOR IN LIFE-THREATENING
It is important that you tell your family and the people closest to you of this increased sensitivity to opioids and the risk of overdose.
 MEDICATION GUIDE VIVITROL (viv-i-trol) (naltrexone for extended-release injectable suspension) Read this Medication Guide before you start receiving VIVITROL injections and each time you receive an injection.
MEDICATION GUIDE VIVITROL (viv-i-trol) (naltrexone for extended-release injectable suspension) Read this Medication Guide before you start receiving VIVITROL injections and each time you receive an injection.
Gemcitabine and Cisplatin
 PATIENT EDUCATION patienteducation.osumc.edu What is Gemcitabine (jem-site-a been)? Gemcitabine is a chemotherapy medicine known as an anti-metabolite. Another name for this drug is Gemzar. This drug is
PATIENT EDUCATION patienteducation.osumc.edu What is Gemcitabine (jem-site-a been)? Gemcitabine is a chemotherapy medicine known as an anti-metabolite. Another name for this drug is Gemzar. This drug is
Roswell Ear, Nose, Throat, & Allergy 342 W. Sherrill Lane Suite A, Roswell, New Mexico 88201 (575)-622-2911 Fax: (575)-622-2598
 Roswell Ear, Nose, Throat, & Allergy 342 W. Sherrill Lane Suite A, Roswell, New Mexico 88201 (575)-622-2911 Fax: (575)-622-2598 Patient Registration Form: (Please Print all Pertinent Information) Last
Roswell Ear, Nose, Throat, & Allergy 342 W. Sherrill Lane Suite A, Roswell, New Mexico 88201 (575)-622-2911 Fax: (575)-622-2598 Patient Registration Form: (Please Print all Pertinent Information) Last
Lighthouse IF YOU WERE THE DRIVER OF YOUR OWN VEHICLE, SOMEONE ELSE S VEHICLE OR A PASSENGER IN THE VEHICLE, ANSWER THIS SECTION COMPLETELY.
 Lighthouse Chiropractic IF YOU WERE THE DRIVER OF YOUR OWN VEHICLE, SOMEONE ELSE S VEHICLE OR A PASSENGER IN THE VEHICLE, ANSWER THIS SECTION COMPLETELY. Your Auto Insurance Company Name Address Policy
Lighthouse Chiropractic IF YOU WERE THE DRIVER OF YOUR OWN VEHICLE, SOMEONE ELSE S VEHICLE OR A PASSENGER IN THE VEHICLE, ANSWER THIS SECTION COMPLETELY. Your Auto Insurance Company Name Address Policy
Chemotherapy Side Effects Worksheet
 Page 1 of 6 Chemotherapy Side Effects Worksheet Medicines or drugs that destroy cancer cells are called cancer chemotherapy. It is sometimes the first choice for treating many cancers. Chemotherapy differs
Page 1 of 6 Chemotherapy Side Effects Worksheet Medicines or drugs that destroy cancer cells are called cancer chemotherapy. It is sometimes the first choice for treating many cancers. Chemotherapy differs
Additional details >>> HERE <<<
 Additional details >>> HERE http://dbvir.com/ringworm12/pdx/comw23/ Tags:
Additional details >>> HERE http://dbvir.com/ringworm12/pdx/comw23/ Tags:
Swine Flu and Common Infections to Prepare For. Rochester Recreation Club for the Deaf October 15, 2009
 Swine Flu and Common Infections to Prepare For Rochester Recreation Club for the Deaf October 15, 2009 Supporters Deaf Health Community Committee Members Julia Aggas Cathie Armstrong Michael McKee Mistie
Swine Flu and Common Infections to Prepare For Rochester Recreation Club for the Deaf October 15, 2009 Supporters Deaf Health Community Committee Members Julia Aggas Cathie Armstrong Michael McKee Mistie
Parkinson s Disease (PD)
 Parkinson s Disease (PD) Parkinson s disease (PD) is a movement disorder that worsens over time. About 1 in 100 people older than 60 has Parkinson s. The exact cause of PD is still not known, but research
Parkinson s Disease (PD) Parkinson s disease (PD) is a movement disorder that worsens over time. About 1 in 100 people older than 60 has Parkinson s. The exact cause of PD is still not known, but research
Like cocaine, heroin is a drug that is illegal in some areas of the world. Heroin is highly addictive.
 Heroin Introduction Heroin is a powerful drug that affects the brain. People who use it can form a strong addiction. Addiction is when a drug user can t stop taking a drug, even when he or she wants to.
Heroin Introduction Heroin is a powerful drug that affects the brain. People who use it can form a strong addiction. Addiction is when a drug user can t stop taking a drug, even when he or she wants to.
Contact your Doctor or Nurse for more information.
 A spinal cord injury is damage to your spinal cord that affects your movement, feeling, or the way your organs work. The injury can happen by cutting, stretching, or swelling of the spinal cord. Injury
A spinal cord injury is damage to your spinal cord that affects your movement, feeling, or the way your organs work. The injury can happen by cutting, stretching, or swelling of the spinal cord. Injury
MEDICAL HISTORY AND SCREENING FORM
 MEDICAL HISTORY AND SCREENING FORM The purpose of preventive exams is to screen for potential health problems and provide education to promote optimal health. It is best practice for chronic health problems
MEDICAL HISTORY AND SCREENING FORM The purpose of preventive exams is to screen for potential health problems and provide education to promote optimal health. It is best practice for chronic health problems
Ear Infections Chickenpox chickenpox
 Ear Chickenpox Infections chickenpox Chickenpox Chickenpox is a common, very contagious viral infection that over 90% of people get during childhood unless they have been immunised. After an infection,
Ear Chickenpox Infections chickenpox Chickenpox Chickenpox is a common, very contagious viral infection that over 90% of people get during childhood unless they have been immunised. After an infection,
Chemotherapy What It Is, How It Helps
 Chemotherapy What It Is, How It Helps What s in this guide If your doctor has told you that you have cancer, you may have a lot of questions. Can I be cured? What kinds of treatment would be best for me?
Chemotherapy What It Is, How It Helps What s in this guide If your doctor has told you that you have cancer, you may have a lot of questions. Can I be cured? What kinds of treatment would be best for me?
Pesticide Harmful Effects And Emergency Response
 Pesticide Harmful Effects And Emergency Response Most pesticides are designed to harm or kill pests. Because some pests have systems similar to the human system, some pesticides also can harm or kill humans.
Pesticide Harmful Effects And Emergency Response Most pesticides are designed to harm or kill pests. Because some pests have systems similar to the human system, some pesticides also can harm or kill humans.
Patient Information Once Weekly FOSAMAX (FOSS-ah-max) (alendronate sodium) Tablets and Oral Solution
 Patient Information Once Weekly FOSAMAX (FOSS-ah-max) (alendronate sodium) Tablets and Oral Solution Read this information before you start taking FOSAMAX *. Also, read the leaflet each time you refill
Patient Information Once Weekly FOSAMAX (FOSS-ah-max) (alendronate sodium) Tablets and Oral Solution Read this information before you start taking FOSAMAX *. Also, read the leaflet each time you refill
Type 2 diabetes Definition
 Type 2 diabetes Definition Type 2 diabetes is a lifelong (chronic) disease in which there are high levels of sugar (glucose) in the blood. Type 2 diabetes is the most common form of diabetes. Causes Diabetes
Type 2 diabetes Definition Type 2 diabetes is a lifelong (chronic) disease in which there are high levels of sugar (glucose) in the blood. Type 2 diabetes is the most common form of diabetes. Causes Diabetes
Work Injury Information Continued
 Welcomes You Full Name: Today s Date: DOB: M / F Social Security #: DL# Address: City: State: Zip Code: Home # : Cell #: Occupation: Employer: Employer Address: Employer Phone: Employer Fax: Emergency
Welcomes You Full Name: Today s Date: DOB: M / F Social Security #: DL# Address: City: State: Zip Code: Home # : Cell #: Occupation: Employer: Employer Address: Employer Phone: Employer Fax: Emergency
HEAT ILLNESS PREVENTION PLAN FOR SUTTER COUNTY SUPERINTENDENT OF SCHOOLS
 HEAT ILLNESS PREVENTION PLAN FOR SUTTER COUNTY SUPERINTENDENT OF SCHOOLS TABLE OF CONTENTS 1.0 Purpose... 1 2.0 Heat Illness Prevention... 2 2.1 Heat Stroke... 2 2.2 Heat Exhaustion... 2 2.3 Heat Cramps...
HEAT ILLNESS PREVENTION PLAN FOR SUTTER COUNTY SUPERINTENDENT OF SCHOOLS TABLE OF CONTENTS 1.0 Purpose... 1 2.0 Heat Illness Prevention... 2 2.1 Heat Stroke... 2 2.2 Heat Exhaustion... 2 2.3 Heat Cramps...
Neonatal Abstinence Syndrome. A Guide for Families
 Neonatal Abstinence Syndrome A Guide for Families Contents What is Neonatal Abstinence Syndrome (NAS)?...................... 4 When will my baby show signs of NAS?..................................................
Neonatal Abstinence Syndrome A Guide for Families Contents What is Neonatal Abstinence Syndrome (NAS)?...................... 4 When will my baby show signs of NAS?..................................................
Women s Continence and Pelvic Health Center
 Women s Continence and Pelvic Health Center Committed to Caring 580-590 Court Street Keene, New Hampshire 03431 (603) 354-5454 Ext. 6643 URINARY INCONTINENCE QUESTIONNAIRE The purpose of this questionnaire
Women s Continence and Pelvic Health Center Committed to Caring 580-590 Court Street Keene, New Hampshire 03431 (603) 354-5454 Ext. 6643 URINARY INCONTINENCE QUESTIONNAIRE The purpose of this questionnaire
Cervical Spine. New Patient Form
 Cervical Spine New Patient Form Please mark the painful areas on the pictures below Use the following marks: stabbing pain ooo burning pain +++ aching pain pins and needles = = = numbness Right Right Right
Cervical Spine New Patient Form Please mark the painful areas on the pictures below Use the following marks: stabbing pain ooo burning pain +++ aching pain pins and needles = = = numbness Right Right Right
HOW YOU CAN HELP YOUR CHILD WITH CEREBRAL PALSY
 HOW YOU CAN HELP YOUR CHILD WITH CEREBRAL PALSY CBM is one of the world s largest international disability and development organisations, committed to improving the quality of life of persons with disabilities
HOW YOU CAN HELP YOUR CHILD WITH CEREBRAL PALSY CBM is one of the world s largest international disability and development organisations, committed to improving the quality of life of persons with disabilities
Medications to help you quit smoking
 Medications to help you quit smoking How can medication help me quit smoking? Using medications can increase your chances of quitting smoking 2 to 3 times more than quitting without using medications.
Medications to help you quit smoking How can medication help me quit smoking? Using medications can increase your chances of quitting smoking 2 to 3 times more than quitting without using medications.
Treating Severe Migraine Headaches in the Emergency Room A Review of the Research for Adults
 Treating Severe Migraine Headaches in the Emergency Room A Review of the Research for Adults Is This Information Right for Me? Yes, this information is right for you if: Your doctor* has told you that
Treating Severe Migraine Headaches in the Emergency Room A Review of the Research for Adults Is This Information Right for Me? Yes, this information is right for you if: Your doctor* has told you that
2 CHECKING AN INJURED OR ILL ATHLETE
 American Red Cross 2 CHECKING AN INJURED OR ILL ATHLETE ~~~'1'H ~.. 2 CHECKING AN INJURED OR III ATHLETE Checking the scene for safety and checking an injured or ill athlete is the first action to take,
American Red Cross 2 CHECKING AN INJURED OR ILL ATHLETE ~~~'1'H ~.. 2 CHECKING AN INJURED OR III ATHLETE Checking the scene for safety and checking an injured or ill athlete is the first action to take,
Headaches in Children
 Headaches in Children A headache is one of the most common complaints of children and teenagers. Fussiness, crankiness and not being able to sleep may be the only signs of head pain in children who are
Headaches in Children A headache is one of the most common complaints of children and teenagers. Fussiness, crankiness and not being able to sleep may be the only signs of head pain in children who are
Breast Cancer. Breast Cancer Page 1
 Breast Cancer Summary Breast cancers which are detected early are curable by local treatments. The initial surgery will give the most information about the cancer; such as size or whether the glands (or
Breast Cancer Summary Breast cancers which are detected early are curable by local treatments. The initial surgery will give the most information about the cancer; such as size or whether the glands (or
How can you protect yourself from infections?
 How can you protect yourself from infections? Your Infection Prevention Guide www.esrdncc.org Table of Contents Preventing an infection is an important part of your kidney care...3 Things you can do...4
How can you protect yourself from infections? Your Infection Prevention Guide www.esrdncc.org Table of Contents Preventing an infection is an important part of your kidney care...3 Things you can do...4
What You Need to Know About LEMTRADA (alemtuzumab) Treatment: A Patient Guide
 For Patients What You Need to Know About LEMTRADA (alemtuzumab) Treatment: A Patient Guide Patients: Your doctor or nurse will go over this patient guide with you. It is important to ask any questions
For Patients What You Need to Know About LEMTRADA (alemtuzumab) Treatment: A Patient Guide Patients: Your doctor or nurse will go over this patient guide with you. It is important to ask any questions
VAD Chemotherapy Regimen for Multiple Myeloma Information for Patients
 VAD Chemotherapy Regimen for Multiple Myeloma Information for Patients The Regimen contains: V = vincristine (Oncovin ) A = Adriamycin (doxorubicin) D = Decadron (dexamethasone) How Is This Regimen Given?
VAD Chemotherapy Regimen for Multiple Myeloma Information for Patients The Regimen contains: V = vincristine (Oncovin ) A = Adriamycin (doxorubicin) D = Decadron (dexamethasone) How Is This Regimen Given?
Throughout this reference summary, you will find out what massage therapy is, its benefits, risks, and what to expect during and after a massage.
 Massage Therapy Introduction Massage therapy is the manipulation of the soft tissues of the body, including the skin, tendons, muscles and connective tissue by a professional, for relaxation or to enhance
Massage Therapy Introduction Massage therapy is the manipulation of the soft tissues of the body, including the skin, tendons, muscles and connective tissue by a professional, for relaxation or to enhance
Heat Illnesses. Common Heat Rash Sites
 Heat Illnesses Introduction Heat illnesses happen when the body becomes too hot and cannot cool itself. There are several different types of heat-related illnesses. This includes heat cramps, heat exhaustion,
Heat Illnesses Introduction Heat illnesses happen when the body becomes too hot and cannot cool itself. There are several different types of heat-related illnesses. This includes heat cramps, heat exhaustion,
Southwestern Foot & Ankle Associates, P.C. 3880 Parkwood Blvd, Suite 602 Frisco, TX 75034 Phone: 972-335-9071 Fax: 972-335-8920 Dr. Thomas H.
 Phone: 972-335-9071 Fax: 972-335-8920 Date: Home Phone ( ) Patient Information (Please Print) Email: Name: SS/Patient ID # Last Name First Name Middle Initial Address Cell Phone ( ) City State Zip Sex
Phone: 972-335-9071 Fax: 972-335-8920 Date: Home Phone ( ) Patient Information (Please Print) Email: Name: SS/Patient ID # Last Name First Name Middle Initial Address Cell Phone ( ) City State Zip Sex
Dallas Neurosurgical and Spine Associates, P.A Patient Health History
 Dallas Neurosurgical and Spine Associates, P.A Patient Health History DOB: Date: Reason for your visit (Chief complaint): Past Medical History Please check corresponding box if you have ever had any of
Dallas Neurosurgical and Spine Associates, P.A Patient Health History DOB: Date: Reason for your visit (Chief complaint): Past Medical History Please check corresponding box if you have ever had any of
PATIENT INFORMATION / / OTHER CONTACT NUMERS: (CIRCLE ONE) CELL, HOME OR OTHER. ENTER NUMBER BELOW. ( ) EMPLOYER ( )
 PATIENT INFORMATION PATIENT S LEGAL NAME DATE OF BIRTH AGE DATE / / / / HEIGHT AND WEIGHT SEX REASON FOR VISIT: MARITAL STATUS FT IN LBS MALE FEMALE S M D W ADDRESS CITY STATE ZIP CODE THE BEST NUMBER
PATIENT INFORMATION PATIENT S LEGAL NAME DATE OF BIRTH AGE DATE / / / / HEIGHT AND WEIGHT SEX REASON FOR VISIT: MARITAL STATUS FT IN LBS MALE FEMALE S M D W ADDRESS CITY STATE ZIP CODE THE BEST NUMBER
Be cancer aware. Patient Information
 Be cancer aware Patient Information Author ID: AMK Leaflet Number: CC 041 Version: 1 Name of Leaflet: Be cancer aware Date Produced: November 2015 Review Date: November 2017 Be cancer aware Page 1 of 11
Be cancer aware Patient Information Author ID: AMK Leaflet Number: CC 041 Version: 1 Name of Leaflet: Be cancer aware Date Produced: November 2015 Review Date: November 2017 Be cancer aware Page 1 of 11
SOUTH TAMPA MULTIPLE SCLEROSIS CENTER
 SOUTH TAMPA MULTIPLE SCLEROSIS CENTER PATIENT/CARE GIVER QUESTIONNAIRE DEMOGRAPHIC INFORMATION Patient's Name: City: State: Zip Code: Phone: Marital Status: Spouse/Care Giver Name: Phone (H) (W) Occupation:
SOUTH TAMPA MULTIPLE SCLEROSIS CENTER PATIENT/CARE GIVER QUESTIONNAIRE DEMOGRAPHIC INFORMATION Patient's Name: City: State: Zip Code: Phone: Marital Status: Spouse/Care Giver Name: Phone (H) (W) Occupation:
Mini Medical School Lesson
 Mini Medical School Lesson The American Osteopathic Association s (AOA) Mini Medical School Lesson is designed to help educators teach children about health and fitness. This lesson is aimed towards elementary
Mini Medical School Lesson The American Osteopathic Association s (AOA) Mini Medical School Lesson is designed to help educators teach children about health and fitness. This lesson is aimed towards elementary
Ear Disorders and Problems
 Ear Disorders and Problems Introduction Your ear has three main parts: outer, middle and inner. You use all of them to hear. There are many disorders and problems that can affect the ear. The symptoms
Ear Disorders and Problems Introduction Your ear has three main parts: outer, middle and inner. You use all of them to hear. There are many disorders and problems that can affect the ear. The symptoms
Cataract Information for Patients
 Cataract Information for Patients http://www.gov.pe.ca/health and click on Wait Times tab Page 1 What is a Cataract? A cataract is a clouding of the eye s naturally clear lens. When the lens becomes cloudy,
Cataract Information for Patients http://www.gov.pe.ca/health and click on Wait Times tab Page 1 What is a Cataract? A cataract is a clouding of the eye s naturally clear lens. When the lens becomes cloudy,
Get the Facts About Tuberculosis Disease
 TB Get the Facts About Tuberculosis Disease What s Inside: Read this brochure today to learn how to protect your family and friends from TB. Then share it with people in your life. 2 Contents Get the facts,
TB Get the Facts About Tuberculosis Disease What s Inside: Read this brochure today to learn how to protect your family and friends from TB. Then share it with people in your life. 2 Contents Get the facts,
The Family Library. Understanding Diabetes
 The Family Library Understanding Diabetes What is Diabetes? Diabetes is caused when the body has a problem in making or using insulin. Insulin is a hormone secreted by the pancreas and is needed for the
The Family Library Understanding Diabetes What is Diabetes? Diabetes is caused when the body has a problem in making or using insulin. Insulin is a hormone secreted by the pancreas and is needed for the
