DEEP VEIN THROMBOSIS (DVT): TREATMENT
|
|
|
- Claire Johns
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 DEEP VEIN THROMBOSIS (DVT): TREATMENT OBJECTIVE: To provide an evidence based approach to treatment of patients presenting with deep vein thrombosis (DVT). BACKGROUND: An estimated 45,000 patients in Canada are affected by DVT each year, with an incidence of approximately 1 2 cases per 1,000 persons annually. This translates to 2 4 DVTs per year in a typical, individual, Canadian family practice. Approximately one third of patients with DVT also develop symptomatic pulmonary embolism (PE), one third will suffer from post thrombotic syndrome and one third will have a recurrent DVT or PE within 10 years. Rapid diagnosis and treatment of DVT is essential to prevent these complications. Active malignancy, surgery (especially orthopedic), immobilization, and estrogen use/pregnancy are common transient provoking factors. However, up to 50% of first time DVT is unprovoked (or idiopathic ). MANAGEMENT OF DVT: General measures: Unless ultrasound (US) is rapidly available, patients with moderate to high suspicion of DVT (except those with a high risk of bleeding) should start anticoagulant therapy before the diagnosis is confirmed. Imaging confirmation should be obtained as soon as possible. Outpatient management is adequate and preferred over hospital based treatment unless there is an additional indication for hospitalization. Initial treatment should have an immediate anticoagulant effect. Warfarin monotherapy is not appropriate initially. Low molecular weight heparin (LMWH): LMWH may be used as initial therapy in conjunction with warfarin for at least the first 5 days and until the international normalized ratio (INR) reaches at least 2.0 for two consecutive days. LMWH may also be used as monotherapy for the full duration of treatment; this is the preferred long term treatment for cancer patients. Most patients have little difficulty with self administration especially if they are coached to do their own first injection. LMWH offers advantages over unfractionated heparin, including more predictable effect allowing fixed dosing based on body weight and renal function, longer duration of anticoagulant effect enabling once daily treatment, lower risk of heparininduced thrombocytopenia (HIT), and no requirement for routine laboratory monitoring or hospitalization Thrombosis Canada Page 1 of 6
2 LMWH doses: Dalteparin (Fragmin ): 200 U/kg SC once daily (preferred) or 100 U/kg SC twice daily. Enoxaparin (Lovenox ): 1.5 mg/kg SC once daily or 1 mg/kg SC twice daily. Tinzaparin (Innohep ): 175 U/kg SC once daily. The dose of LMWH is generally rounded up to the nearest pre filled syringe dose. For obese patients, the dose of LMWH is based on their actual body weight (and not capped at 18,000 U/day). For patients with severe renal insufficiency (creatinine clearance <30 ml/min), clinical data on the use of LMWH for the treatment of VTE are limited and LMWHs should be used with caution (or avoided). If used, the dose of LMWH should be reduced. If LMWH is to be used long term in the setting of severe renal insufficiency, monitoring with anti factor Xa levels may be required. Unfractionated Heparin (UFH) UFH use in the treatment of DVT is limited by a narrow therapeutic range, inter individual variation in anticoagulant effect, need for laboratory monitoring, and the increased risk of heparin induced thrombocytopenia (HIT). The use of UFH should be limited to: (1) patients with severe renal insufficiency (CrCl < 30 ml/min), in whom LMWHs should generally be avoided; (2) patients at increased risk for bleeding, in whom rapid reversal of the anticoagulant effect may be needed; and (3) patients who receive thrombolytic therapy. Heparin bolus: 5,000 U (or 70 U/kg) Initial heparin infusion: 20 U/kg/hr Target activated partial thromboplastin time (aptt): times the control aptt Heparin, 333 units/kg SC initial dose, then 250 units/kg SC twice daily as an alternative that does not require aptt monitoring Warfarin Initial treatment with warfarin should be combined with an immediate acting agent such as LMWH for at least 5 days and until the INR reaches at least 2.0 for two consecutive days. Initial dosing is best guided by using standardized nomograms for best results. Frequent monitoring is required until a stable, in range INR is reached, after which reduced frequency of testing is appropriate. Warfarin is associated with many drug and food interactions that affect INR. Alcohol and a number of health supplements (e.g. St. John s Wort) can also change the INR. Alterations in concomitant medications and new concurrent illness should be associated with INR testing. Patients should not reduce intake of foods high in vitamin K, but should be encouraged to maintain a consistent diet. Rivaroxaban (Xarelto ) Rivaroxaban is an oral anticoagulant that works through direct inhibition of clotting Factor Xa. In Canada, rivaroxaban is approved for the treatment of DVT and/or PE and for the prevention of recurrent DVT and PE as a simple, non parenteral treatment option. For many primary care physicians not comfortable with the use of LMWH, or not having the necessary time and resources to teach 2015 Thrombosis Canada Page 2 of 6
3 patients self injection, rivaroxaban may enable treatment of confirmed VTE without the need to refer to emergency rooms, resulting in more rapid treatment initiation, greater convenience for the patient and physician, as well as potentially reducing health care costs. It is also valuable for patients not willing to accept or unable to manage self injection. Dosing: 15 mg PO twice daily for the first 21 days, followed by 20 mg once daily for the duration of treatment. Rivaroxaban should not be used in women who are pregnant or breast feeding, patients with a CrCl <30mL/min, patients with active cancer, or patients with severe liver disease. Dabigatran (Pradaxa ) Dabigatran is an oral anticoagulant that works through direct inhibition of clotting Factor IIa thrombin). In Canada, dabigatran is approved for the treatment of acute DVT and/or PE after a 5 10 day initial treatment period with a parenteral anticoagulant (usually a LMWH) and for the prevention of recurrent DVT and PE. Dosing: 150 mg PO twice daily for the duration of treatment. Dabigatran should not be used in women who are pregnant or breast feeding, patients with a CrCl <30mL/min, or patients with active cancer. Apixaban (Eliquis ) Apixaban is an oral anticoagulant that works through direct inhibition of clotting Factor Xa. In Canada, apixaban is approved for the treatment of DVT and/or PE and for the prevention of recurrent DVT and PE. Like rivaroxaban, apixaban does not require an initial treatment period with a parenteral anticoagulant. Dosing: 10 mg PO twice daily for the first 7 days, followed by 5 mg twice daily. After at least 6 months of treatment, consideration can be given to reducing the dose to 2.5 mg PO twice daily for long term prevention of recurrent VTE. Apixaban should not be used in women who are pregnant or breast feeding, patients with a CrCl <15mL/min or on dialysis, patients with active cancer, or patients with severe liver disease. ASA (Aspirin ) ASA should not be used for initial treatment of VTE and provides less protection than continued anticoagulation for extended treatment. Two extended treatment studies of patients with a first unprovoked DVT demonstrated that low dose ASA provided benefit over placebo for patients having completed 6 18 months of anticoagulation. DURATION OF THERAPY: The duration of treatment should be individualized and based on estimated risks of recurrent thrombosis and bleeding as well as the patient s preferences. General recommendations are given in Table 1 below Thrombosis Canada Page 3 of 6
4 TABLE 1: DURATION OF ANTICOAGULANT TREATMENT FOR VTE CATEGORIES OF VTE Provoked by a transient risk factor* First unprovoked VTE DURATION OF ANTICOAGULANT TREATMENT 3 months Minimum of 3 months and then reassess Proximal unprovoked DVT or PE with no or only minor risk factors for bleeding Isolated symptomatic distal DVT or isolated distal DVT with risk factors for extension Second unprovoked VTE Cancer associated VTE Long term therapy with annual review 3 months Minimum of 3 months and then reassess for indefinite therapy. For patients with no or only minor risk factors for bleeding, long term therapy with annual review Minimum of 3 months and then reassess. Continue if overt evidence of cancer or continuing to receive anti cancer therapy. Refer to Cancer and Thrombosis guide for further details. * Transient risk factors include: surgery, hospitalization or plaster cast immobilization, all within 3 months; estrogen therapy, pregnancy, prolonged travel (>8 hours), lesser leg injuries or immobilization more recently (within 6 weeks). The stronger the provoking reversible risk factor (e.g. recent major surgery), the lower is the expected risk of recurrence after stopping anticoagulant therapy if the risk factor has resolved. Absence of a transient risk factor or active cancer. This decision is sensitive to patient preference. Indefinite therapy is suggested if there is moderate risk of bleeding, and 3 months is suggested if there is a high risk of bleeding; both of these decisions are sensitive to patient preference. SPECIAL CONSIDERATIONS: Massive lower extremity DVT: Massive DVT is defined as iliofemoral thrombosis with severe symptoms. In such patients, treatment with pharmaco mechanical, catheter directed thrombus reduction therapy should be considered since it rapidly relieves venous obstruction with few adverse effects. Two small randomized trials have shown that catheter directed thrombolysis reduces the risk for the post thrombotic syndrome. Intravenous UFH should be used around the thrombolytic therapy. Patients still require anticoagulation for at least 3 months even after successful thrombus reduction therapy. Upper extremity DVT (UEDVT): See Central Venous Catheter Related Venous Thrombosis guide. If UEDVT occurs in association with a central venous catheter, the catheter should be left in place, if still needed. Treatment should generally follow the principles of lower extremity DVT Thrombosis Canada Page 4 of 6
5 Superficial vein thrombosis (SVT): Topical or oral non steroidal anti inflammatory drugs may provide symptomatic relief. In patients with lower limb SVT >5 cm, low to intermediate dose LMWH (e.g. dalteparin 5,000 10,000 U SC daily, enoxaparin mg SC daily, tinzaparin 4,500 10,000 U SC daily) or fondaparinux 2.5 mg SC daily, for up to 45 days may be used. For extensive SVT, moderate to full doses of LMWH should be considered. Isolated distal DVT: In patients with an isolated distal DVT anticoagulation is generally suggested especially if the patient is symptomatic, has risk factors for extension at initial assessment (severe symptoms, greater than 5 cm in length, in multiple deep veins, close to the popliteal vein, no reversible risk factor, previous VTE, in patient, or positive D dimer), or has progression of the DVT on repeat imaging. Pregnancy: See Pregnancy: Venous Thromboembolism Treatment guide. Cancer : See Cancer and Thrombosis guide. PEDIATRICS: Once DVT is confirmed, treatment may be initiated with either age appropriate UFH or LMWH followed by 3 months (reversible cause) or 6 12 months (idiopathic) or long term (recurrent) treatment with either LMWH or vitamin K antagonists. Massive DVT should be treated with pharmaco mechanical, catheter directed thrombus reduction therapy as in adults. OTHER RELEVANT GUIDES: Apixaban (Eliquis ) Cancer and Thrombosis Central Venous Catheter Related Venous Thrombosis Deep Vein Thrombosis: Diagnosis Dabigatran (Pradaxa ) Post Thrombotic Syndrome (PTS) Pulmonary Embolism: Diagnosis and Treatment Rivaroxaban (Xarelto ) Pregnancy: Venous Thromboembolism Treatment Unfractionated Heparin and Low molecular weight Heparin Vena Cava Filter Warfarin 2015 Thrombosis Canada Page 5 of 6
6 REFERENCES: Jaff MR, et al. Management of massive and submassive pulmonary embolism, iliofemoral deep vein thrombosis, and chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension: a scientific statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2011;123(16): Kearon C, et al. Antithrombotic therapy for VTE disease: Antithrombotic Therapy and Prevention of Thrombosis, 9th ed: American College of Chest Physicians Evidence Based Clinical Practice Guidelines. Chest 2012;141(2 Suppl):e419S e494s. van der Hulle T, et al. Effectiveness and safety of novel oral anticoagulants as compared with vitamin K antagonists in the treatment of acute symptomatic venous thromboembolism: a systematic review and meta analysis. J Thromb Haemost 2014;12(3): Date of Version: 2015Jan16 Please note that the information contained herein is not to be interpreted as an alternative to medical advice from your doctor or other professional healthcare provider. If you have any specific questions about any medical matter, you should consult your doctor or other professional healthcare providers, and as such you should never delay seeking medical advice, disregard medical advice or discontinue medical treatment because of the information contained herein Thrombosis Canada Page 6 of 6
To provide an evidenced-based approach to treatment of patients presenting with deep vein thrombosis.
 DEEP VEIN THROMBOSIS: TREATMENT TARGET AUDIENCE: All Canadian health care professionals. OBJECTIVE: To provide an evidenced-based approach to treatment of patients presenting with deep vein thrombosis.
DEEP VEIN THROMBOSIS: TREATMENT TARGET AUDIENCE: All Canadian health care professionals. OBJECTIVE: To provide an evidenced-based approach to treatment of patients presenting with deep vein thrombosis.
To define a diagnostic algorithm and treatment strategy for patients with acute pulmonary embolism.
 PULMONARY EMBOLISM: DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT TARGET AUDIENCE: All Canadian health care professionals. OBJECTIVE: To define a diagnostic algorithm and treatment strategy for patients with acute pulmonary
PULMONARY EMBOLISM: DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT TARGET AUDIENCE: All Canadian health care professionals. OBJECTIVE: To define a diagnostic algorithm and treatment strategy for patients with acute pulmonary
Venous Thromboembolic Treatment Guidelines
 Venous Thromboembolic Treatment Guidelines About the NYU Venous Thromboembolic Center (VTEC) The center s mission is to deliver advanced screening, detection, care, and management services for patients
Venous Thromboembolic Treatment Guidelines About the NYU Venous Thromboembolic Center (VTEC) The center s mission is to deliver advanced screening, detection, care, and management services for patients
Outpatient Treatment of Deep Vein Thrombosis with Low Molecular Weight Heparin (LMWH) Clinical Practice Guideline August 2013
 Outpatient Treatment of Deep Vein Thrombosis with Low Molecular Weight Heparin (LMWH) Clinical Practice Guideline August 2013 General Principles: There is compelling data in the medical literature to support
Outpatient Treatment of Deep Vein Thrombosis with Low Molecular Weight Heparin (LMWH) Clinical Practice Guideline August 2013 General Principles: There is compelling data in the medical literature to support
To aid practitioners in prescribing unfractionated heparin and low-molecular-weight heparins to patients.
 UNFRACTIONATED HEPARIN AND LOW-MOLECULAR-WEIGHT HEPARIN TARGET AUDIENCE: All Canadian health care professionals. OBJECTIVE: To aid practitioners in prescribing unfractionated heparin and low-molecular-weight
UNFRACTIONATED HEPARIN AND LOW-MOLECULAR-WEIGHT HEPARIN TARGET AUDIENCE: All Canadian health care professionals. OBJECTIVE: To aid practitioners in prescribing unfractionated heparin and low-molecular-weight
New Oral Anticoagulants. How safe are they outside the trials?
 New Oral Anticoagulants How safe are they outside the trials? Objectives The need for anticoagulant therapy Indications for anticoagulation Traditional anticoagulant therapies Properties of new oral anticoagulants
New Oral Anticoagulants How safe are they outside the trials? Objectives The need for anticoagulant therapy Indications for anticoagulation Traditional anticoagulant therapies Properties of new oral anticoagulants
Traditional anticoagulants
 TEGH Family Practice Clinic Day April 4, 03 Use of Anticoagulants in 03: What s New (and What Isn t) Bill Geerts, MD, FRCPC Director, Thromboembolism Program, Sunnybrook HSC Professor of Medicine, University
TEGH Family Practice Clinic Day April 4, 03 Use of Anticoagulants in 03: What s New (and What Isn t) Bill Geerts, MD, FRCPC Director, Thromboembolism Program, Sunnybrook HSC Professor of Medicine, University
DVT/PE Management with Rivaroxaban (Xarelto)
 DVT/PE Management with Rivaroxaban (Xarelto) Rivaroxaban is FDA approved for the acute treatment of DVT and PE and reduction in risk of recurrence of DVT and PE. FDA approved indications: Non valvular
DVT/PE Management with Rivaroxaban (Xarelto) Rivaroxaban is FDA approved for the acute treatment of DVT and PE and reduction in risk of recurrence of DVT and PE. FDA approved indications: Non valvular
Anticoagulation Dosing at UCDMC Indication Agent Standard Dose Comments and Dose Adjustments VTE Prophylaxis All Services UFH 5,000 units SC q 8 h
 Indication Agent Standard Dose Comments and Dose Adjustments VTE Prophylaxis All Services UFH 5,000 units SC q 8 h See EMR adult VTE prophylaxis CI order set Enoxaparin See service specific dosing Assess
Indication Agent Standard Dose Comments and Dose Adjustments VTE Prophylaxis All Services UFH 5,000 units SC q 8 h See EMR adult VTE prophylaxis CI order set Enoxaparin See service specific dosing Assess
New Oral Anticoagulants
 New Oral Anticoagulants Tracy Minichiello, MD Associate Professor of Medicine Chief, San FranciscoVA Anticoagulation and Thrombosis Service Ansell, J. Hematology Copyright 2010 American Society of Hematology.
New Oral Anticoagulants Tracy Minichiello, MD Associate Professor of Medicine Chief, San FranciscoVA Anticoagulation and Thrombosis Service Ansell, J. Hematology Copyright 2010 American Society of Hematology.
Use of Antithrombotic Agents In The Presence Of Neuraxial Anesthesia
 Use of Antithrombotic Agents In The Presence Of Neuraxial Anesthesia Insertion, removal or presence of a catheter in selected sites can place a patient who is antithrombotic agent at risk for a local bleeding
Use of Antithrombotic Agents In The Presence Of Neuraxial Anesthesia Insertion, removal or presence of a catheter in selected sites can place a patient who is antithrombotic agent at risk for a local bleeding
Low Molecular Weight Heparin. All Wales Medicines Strategy Group (AWMSG) Recommendations and advice
 Low Molecular Weight Heparin All Wales Medicines Strategy Group (AWMSG) Recommendations and advice Starting Point Low Molecular Weight Heparin (LMWH): Inhibits factor Xa and factor IIa (thrombin) Small
Low Molecular Weight Heparin All Wales Medicines Strategy Group (AWMSG) Recommendations and advice Starting Point Low Molecular Weight Heparin (LMWH): Inhibits factor Xa and factor IIa (thrombin) Small
Anticoagulant therapy
 Anticoagulation: The risks Anticoagulant therapy 1990 2002: 600 incidents reported 120 resulted in death of patient 92 deaths related to warfarin usage 28 reports related to heparin usage Incidents in
Anticoagulation: The risks Anticoagulant therapy 1990 2002: 600 incidents reported 120 resulted in death of patient 92 deaths related to warfarin usage 28 reports related to heparin usage Incidents in
Pulmonary Embolism Treatment Update
 UC SF Pulmonary Embolism Treatment Update Jeffrey Tabas, MD Professor UCSF School of Medicine Emergency Department San Francisco General Hospital sf g h Disclosure No Financial Relationships to Disclose
UC SF Pulmonary Embolism Treatment Update Jeffrey Tabas, MD Professor UCSF School of Medicine Emergency Department San Francisco General Hospital sf g h Disclosure No Financial Relationships to Disclose
Venous Thromboembolism: Long Term Anticoagulation. Dan Johnson, Pharm.D.
 Venous Thromboembolism: Long Term Anticoagulation Dan Johnson, Pharm.D. Disclosures No financial relationships with products discussed Off-label use of drug therapy always discussed Objectives Review clinical
Venous Thromboembolism: Long Term Anticoagulation Dan Johnson, Pharm.D. Disclosures No financial relationships with products discussed Off-label use of drug therapy always discussed Objectives Review clinical
2.5mg SC daily. INR target 2-3 30 mg SC q 12 hr or 40mg daily. 10 mg PO q day (CrCl 30 ml/min). Avoid if < 30 ml/min. 2.
 Anticoagulation dosing at UCDMC (SC=subcutaneously; CI=continuous infusion) Indication Agent Dose Comments Prophylaxis Any or No bleeding risk factors see adult heparin (VTE prophylaxis) IV infusion order
Anticoagulation dosing at UCDMC (SC=subcutaneously; CI=continuous infusion) Indication Agent Dose Comments Prophylaxis Any or No bleeding risk factors see adult heparin (VTE prophylaxis) IV infusion order
New Anticoagulants for the Treatment of Thromboembolism With a little subplot on superficial thrombophlebitis. Mark Crowther
 New Anticoagulants for the Treatment of Thromboembolism With a little subplot on superficial thrombophlebitis Mark Crowther 1 Disclosures Advisory Boards in last 24 months Pfizer, Alexion, Bayer, CSL Behring,
New Anticoagulants for the Treatment of Thromboembolism With a little subplot on superficial thrombophlebitis Mark Crowther 1 Disclosures Advisory Boards in last 24 months Pfizer, Alexion, Bayer, CSL Behring,
Pathway for the management of DVT in primary Care
 Pathway for the management of DVT in primary Care Final Version: Approved by NHS DGS CCG: June 2015 This document aims to support practices in DGS CCG in the Management & Treatment of patients with suspected
Pathway for the management of DVT in primary Care Final Version: Approved by NHS DGS CCG: June 2015 This document aims to support practices in DGS CCG in the Management & Treatment of patients with suspected
HERTFORDSHIRE MEDICINES MANAGEMENT COMMITTEE (HMMC) RIVAROXABAN RECOMMENDED see specific recommendations for licensed indications below
 Name: generic (trade) Rivaroxaban (Xarelto ) HERTFORDSHIRE MEDICINES MANAGEMENT COMMITTEE (HMMC) RIVAROXABAN RECOMMENDED see specific recommendations for licensed indications below What it is Indications
Name: generic (trade) Rivaroxaban (Xarelto ) HERTFORDSHIRE MEDICINES MANAGEMENT COMMITTEE (HMMC) RIVAROXABAN RECOMMENDED see specific recommendations for licensed indications below What it is Indications
What Does Pregnancy Have to Do With Blood Clots in a Woman s Legs?
 Patient s Guide to Prevention of Blood Clots During Pregnancy: Use of Blood-Thinning A Patient s Guide to Prevention of Blood Clots During Pregnancy: Use of Blood-Thinning Drugs to Prevent Abnormal Blood
Patient s Guide to Prevention of Blood Clots During Pregnancy: Use of Blood-Thinning A Patient s Guide to Prevention of Blood Clots During Pregnancy: Use of Blood-Thinning Drugs to Prevent Abnormal Blood
Prescriber Guide. 20mg. 15mg. Simply Protecting More Patients. Simply Protecting More Patients
 Prescriber Guide 20mg Simply Protecting More Patients 15mg Simply Protecting More Patients 1 Dear Doctor, This prescriber guide was produced by Bayer Israel in cooperation with the Ministry of Health as
Prescriber Guide 20mg Simply Protecting More Patients 15mg Simply Protecting More Patients 1 Dear Doctor, This prescriber guide was produced by Bayer Israel in cooperation with the Ministry of Health as
STROKE PREVENTION IN ATRIAL FIBRILLATION
 STROKE PREVENTION IN ATRIAL FIBRILLATION OBJECTIVE: To guide clinicians in the selection of antithrombotic therapy for the secondary prevention of ischemic stroke and arterial thromboembolism in patients
STROKE PREVENTION IN ATRIAL FIBRILLATION OBJECTIVE: To guide clinicians in the selection of antithrombotic therapy for the secondary prevention of ischemic stroke and arterial thromboembolism in patients
Thrombosis and Hemostasis
 Thrombosis and Hemostasis Wendy Lim, MD, MSc, FRCPC Associate Professor, Department of Medicine McMaster University, Hamilton, ON Overview To review the important developments in venous thromboembolism
Thrombosis and Hemostasis Wendy Lim, MD, MSc, FRCPC Associate Professor, Department of Medicine McMaster University, Hamilton, ON Overview To review the important developments in venous thromboembolism
0.9% Sodium Chloride injection may be used in most cases.
 Table 2. Alternatives to Heparin Sodium in Selected Situations 12-14 Situation Alternative Dose Maintain patency of peripheral venous catheters* 21-26 0.9% Sodium Chloride injection may be used in most
Table 2. Alternatives to Heparin Sodium in Selected Situations 12-14 Situation Alternative Dose Maintain patency of peripheral venous catheters* 21-26 0.9% Sodium Chloride injection may be used in most
Disclosure. New Agents for Treatment of DVT. Prevalence of DVT VTE. Normal Hemostasis 7/17/2015. Mark Oliver, MD, RVT, RPVI,FSVU
 New Agents for Treatment of DVT Disclosure PI Adopt and Amplify trials Mark Oliver, MD, RVT, RPVI,FSVU BMS and Pfizer Speaker VTE Venous Thromboembolism Recognized DVT s New : 170,000 Recurrent : 90,000
New Agents for Treatment of DVT Disclosure PI Adopt and Amplify trials Mark Oliver, MD, RVT, RPVI,FSVU BMS and Pfizer Speaker VTE Venous Thromboembolism Recognized DVT s New : 170,000 Recurrent : 90,000
Inpatient Anticoagulation Safety. To provide safe and effective anticoagulation therapy through a collaborative approach.
 Inpatient Anticoagulation Safety Purpose: Policy: To provide safe and effective anticoagulation therapy through a collaborative approach. Upon the written order of a physician, Heparin, Low Molecular Weight
Inpatient Anticoagulation Safety Purpose: Policy: To provide safe and effective anticoagulation therapy through a collaborative approach. Upon the written order of a physician, Heparin, Low Molecular Weight
COMPARISON OF NEW ORAL ANTICOAGULANTS AND FREQUENTLY- ASKED QUESTIONS FROM PATIENTS. TARGET AUDIENCE: All Canadian health care professionals.
 COMPARISON OF NEW ORAL ANTICOAGULANTS AND FREQUENTLY- ASKED QUESTIONS FROM PATIENTS AND PHYSICIANS TARGET AUDIENCE: All Canadian health care professionals. OBJECTIVES: To provide a comparison of the new
COMPARISON OF NEW ORAL ANTICOAGULANTS AND FREQUENTLY- ASKED QUESTIONS FROM PATIENTS AND PHYSICIANS TARGET AUDIENCE: All Canadian health care professionals. OBJECTIVES: To provide a comparison of the new
National Guidance and New Protocols
 National Guidance and New Protocols Dr Jane Strong Consultant Haematologist DVT clinical lead Acute VTE chair DAWN AC Twentieth User Group Meeting 8 th October 2012 Autumn dawn Restless geese take flight
National Guidance and New Protocols Dr Jane Strong Consultant Haematologist DVT clinical lead Acute VTE chair DAWN AC Twentieth User Group Meeting 8 th October 2012 Autumn dawn Restless geese take flight
National Guidance and New Protocols
 National Guidance and New Protocols Dr Jane Strong Consultant Haematologist DVT clinical lead Acute VTE chair DAWN AC Twentieth User Group Meeting 8 th October 2012 DVT patient pathway Assessment Diagnosis
National Guidance and New Protocols Dr Jane Strong Consultant Haematologist DVT clinical lead Acute VTE chair DAWN AC Twentieth User Group Meeting 8 th October 2012 DVT patient pathway Assessment Diagnosis
Breadth of indications matters One drug for multiple indications
 Breadth of indications matters One drug for multiple indications Sylvia Haas, MD, PhD Formerly of the Technical University of Munich Munich, Germany Disclosures: Sylvia Haas 1 Novel oral anticoagulants:
Breadth of indications matters One drug for multiple indications Sylvia Haas, MD, PhD Formerly of the Technical University of Munich Munich, Germany Disclosures: Sylvia Haas 1 Novel oral anticoagulants:
NEWER ANTICOAGULANTS: FOCUS ON STROKE PREVENTION IN ATRIAL FIBRILLATION AND DEEP VEIN THROMBOSIS/PULMONARY EMBOLISM
 NEWER ANTICOAGULANTS: FOCUS ON STROKE PREVENTION IN ATRIAL FIBRILLATION AND DEEP VEIN THROMBOSIS/PULMONARY EMBOLISM Carol Lee, Pharm.D., Jessica C. Song, M.A., Pharm.D. INTRODUCTION For many years, warfarin
NEWER ANTICOAGULANTS: FOCUS ON STROKE PREVENTION IN ATRIAL FIBRILLATION AND DEEP VEIN THROMBOSIS/PULMONARY EMBOLISM Carol Lee, Pharm.D., Jessica C. Song, M.A., Pharm.D. INTRODUCTION For many years, warfarin
UHS CLINICAL CARE COLLABORATION: Outpatient & Inpatient
 Guidelines for Anticoagulation Initiation and Management Y2014 UHS CLINICAL CARE COLLABORATION: Outpatient & Inpatient Topic Page Number MEDICATION FLOW AND PATIENT FLOW... 2 AND 3 PARENTERAL ANTICOAGULANTS...
Guidelines for Anticoagulation Initiation and Management Y2014 UHS CLINICAL CARE COLLABORATION: Outpatient & Inpatient Topic Page Number MEDICATION FLOW AND PATIENT FLOW... 2 AND 3 PARENTERAL ANTICOAGULANTS...
Innovations in Treating VTE, Using the EDOU
 Innovations in Treating VTE, Using the EDOU Disclosures No financial conflicts or disclosures Kelly Sawyer, MD, MS kelly.sawyer@beaumont.edu Observation Symposium 2013 Objectives Overview of VTE Treatment
Innovations in Treating VTE, Using the EDOU Disclosures No financial conflicts or disclosures Kelly Sawyer, MD, MS kelly.sawyer@beaumont.edu Observation Symposium 2013 Objectives Overview of VTE Treatment
Dabigatran etexilate for the treatment and secondary prevention of deep vein thrombosis and/or pulmonary embolism ERRATUM
 Dabigatran etexilate for the treatment and secondary prevention of deep vein thrombosis and/or pulmonary embolism ERRATUM This report was commissioned by the NIHR HTA Programme as project number 12/78
Dabigatran etexilate for the treatment and secondary prevention of deep vein thrombosis and/or pulmonary embolism ERRATUM This report was commissioned by the NIHR HTA Programme as project number 12/78
NHS FORTH VALLEY RIVAROXABAN AS TREATMENT FOR DEEP VEIN THROMBOSIS AND PULMONARY EMBOLISM IN ADULTS
 NHS FORTH VALLEY RIVAROXABAN AS TREATMENT FOR DEEP VEIN THROMBOSIS AND PULMONARY EMBOLISM IN ADULTS Date of First Issue 01/12/ 2012 Approved 15/11/2012 Current Issue Date 29/10/2014 Review Date 29/10/2016
NHS FORTH VALLEY RIVAROXABAN AS TREATMENT FOR DEEP VEIN THROMBOSIS AND PULMONARY EMBOLISM IN ADULTS Date of First Issue 01/12/ 2012 Approved 15/11/2012 Current Issue Date 29/10/2014 Review Date 29/10/2016
How To Manage An Anticoagulant
 PERI-OPERATIVE MANAGEMENT OF PATIENTS WHO ARE RECEIVING A NEW ORAL ANTICOAGULANT (DABIGATRAN, RIVAROXABAN, APIXABAN) TARGET AUDIENCE: All Canadian health care professionals, including primary care physicians,
PERI-OPERATIVE MANAGEMENT OF PATIENTS WHO ARE RECEIVING A NEW ORAL ANTICOAGULANT (DABIGATRAN, RIVAROXABAN, APIXABAN) TARGET AUDIENCE: All Canadian health care professionals, including primary care physicians,
Session 3 Topics. Argatroban. Argatroban. Drug Use and Adverse Effects. Laboratory Monitoring of Anticoagulant Therapy
 ~~Marshfield Labs Presents~~ Laboratory Monitoring of Anticoagulant Therapy Session 3 of 4 Michael J. Sanfelippo, M.S. Technical Director, Coagulation Services Session 3 Topics Direct Thrombin Inhibitors:
~~Marshfield Labs Presents~~ Laboratory Monitoring of Anticoagulant Therapy Session 3 of 4 Michael J. Sanfelippo, M.S. Technical Director, Coagulation Services Session 3 Topics Direct Thrombin Inhibitors:
USE AND INTERPRETATION OF LABORATORY COAGULATION TESTS IN PATIENTS WHO ARE RECEIVING A NEW ORAL ANTICOAGULANT (DABIGATRAN, RIVAROXABAN, APIXABAN)
 USE AND INTERPRETATION OF LABORATORY COAGULATION TESTS IN PATIENTS WHO ARE RECEIVING A NEW ORAL ANTICOAGULANT (DABIGATRAN, RIVAROXABAN, APIXABAN) TARGET AUDIENCE: All Canadian health care professionals:
USE AND INTERPRETATION OF LABORATORY COAGULATION TESTS IN PATIENTS WHO ARE RECEIVING A NEW ORAL ANTICOAGULANT (DABIGATRAN, RIVAROXABAN, APIXABAN) TARGET AUDIENCE: All Canadian health care professionals:
The legally binding text is the original French version TRANSPARENCY COMMITTEE OPINION. 10 March 2010
 The legally binding text is the original French version TRANSPARENCY COMMITTEE OPINION 10 March 2010 ARIXTRA 1.5 mg/0.3 ml, solution for injection in pre-filled syringe Box of 2 (CIP: 363 500-6) Box of
The legally binding text is the original French version TRANSPARENCY COMMITTEE OPINION 10 March 2010 ARIXTRA 1.5 mg/0.3 ml, solution for injection in pre-filled syringe Box of 2 (CIP: 363 500-6) Box of
Update on Antiplatelets and anticoagulants. Outlines. Antiplatelets and Anticoagulants 1/23/2013. Timir Paul, MD, PhD
 Update on Antiplatelets and anticoagulants Timir Paul, MD, PhD Antiplatelets Indications Doses Long term use (beyond 12 months) ASA and combination use of NSAIDS ASA resistance Plavix resistance Plavix
Update on Antiplatelets and anticoagulants Timir Paul, MD, PhD Antiplatelets Indications Doses Long term use (beyond 12 months) ASA and combination use of NSAIDS ASA resistance Plavix resistance Plavix
MEDICAL ASSISTANCE HANDBOOK PRIOR AUTHORIZATION OF PHARMACEUTICAL SERVICES. A. Prescriptions That Require Prior Authorization
 MEDICAL ASSISTANCE HBOOK PRI AUTHIZATION OF PHARMACEUTICAL SERVICES I. Requirements for Prior Authorization of Anticoagulants A. Prescriptions That Require Prior Authorization Prescriptions for Anticoagulants
MEDICAL ASSISTANCE HBOOK PRI AUTHIZATION OF PHARMACEUTICAL SERVICES I. Requirements for Prior Authorization of Anticoagulants A. Prescriptions That Require Prior Authorization Prescriptions for Anticoagulants
Top 10 Thrombosis and Anticoagulation Highlights from ASH 2014
 Top 10 Thrombosis and Anticoagulation Highlights from ASH 2014 Stephan Moll, MD UNC School of Medicine, Chapel Hill, NC 1. New Anticoagulant Factor XI lowering drug NEJM publication Dec 7 th (late- breaking
Top 10 Thrombosis and Anticoagulation Highlights from ASH 2014 Stephan Moll, MD UNC School of Medicine, Chapel Hill, NC 1. New Anticoagulant Factor XI lowering drug NEJM publication Dec 7 th (late- breaking
ACUTE DVT MANAGEMENT Richard J. DeMasi, MD April 26, 2014
 ACUTE DVT MANAGEMENT Richard J. DeMasi, MD April 26, 2014 Thromboembolism epidemiology 5 million DVT s 900,000 PE s 290,000 fatalities Heit J. Blood. 2005;106:910. 10 VTE events Since this talk began DVT
ACUTE DVT MANAGEMENT Richard J. DeMasi, MD April 26, 2014 Thromboembolism epidemiology 5 million DVT s 900,000 PE s 290,000 fatalities Heit J. Blood. 2005;106:910. 10 VTE events Since this talk began DVT
rivaroxaban 15 and 20mg film-coated tablets (Xarelto ) SMC No. (755/12) Bayer PLC
 rivaroxaban 15 and 20mg film-coated tablets (Xarelto ) SMC No. (755/12) Bayer PLC 13 January 2012 The Scottish Medicines Consortium (SMC) has completed its assessment of the above product and advises NHS
rivaroxaban 15 and 20mg film-coated tablets (Xarelto ) SMC No. (755/12) Bayer PLC 13 January 2012 The Scottish Medicines Consortium (SMC) has completed its assessment of the above product and advises NHS
Confirmed Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT)
 Confirmed Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) Information for patients What is deep vein thrombosis? Blood clotting provides us with essential protection against severe loss of blood from an injury to a vein or
Confirmed Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) Information for patients What is deep vein thrombosis? Blood clotting provides us with essential protection against severe loss of blood from an injury to a vein or
Failure or significant adverse effects to all of the alternatives: Eliquis and Xarelto
 This policy has been developed through review of medical literature, consideration of medical necessity, generally accepted medical practice standards, and approved by the IEHP Pharmacy and Therapeutics
This policy has been developed through review of medical literature, consideration of medical necessity, generally accepted medical practice standards, and approved by the IEHP Pharmacy and Therapeutics
Traveller s Thrombosis. Dr. Peter Verhamme Vascular Medicine and Haemostasis UZ Leuven
 Traveller s Thrombosis Dr. Peter Verhamme Vascular Medicine and Haemostasis UZ Leuven Case 1: To thromboprophylaxe or not Women, aged 49, BMI 29, Combined Oral Contraceptives. Family history of provoked
Traveller s Thrombosis Dr. Peter Verhamme Vascular Medicine and Haemostasis UZ Leuven Case 1: To thromboprophylaxe or not Women, aged 49, BMI 29, Combined Oral Contraceptives. Family history of provoked
Title Use of rivaroxaban in suspected DVT in the Emergency Department Standard Operating Procedure. Author s job title. Pharmacist.
 Document Control Title Use of rivaroxaban in suspected DVT in the Emergency Department Author Pharmacist Directorate Clinical Support Services Version Date Issued Status 0.1 Oct Draft 2015 1.0 Dec Final
Document Control Title Use of rivaroxaban in suspected DVT in the Emergency Department Author Pharmacist Directorate Clinical Support Services Version Date Issued Status 0.1 Oct Draft 2015 1.0 Dec Final
Home treatment of VTE
 Home treatment of VTE Prof. Adel El-Etriby Ain-Shams University Venous Thromboembolism (VTE): The DVT and PE Continuum Migration Embolus Thrombus VTE refers to a continuum of disease that begins with DVT
Home treatment of VTE Prof. Adel El-Etriby Ain-Shams University Venous Thromboembolism (VTE): The DVT and PE Continuum Migration Embolus Thrombus VTE refers to a continuum of disease that begins with DVT
Devang M. Desai, MD, FACC, FSCAI Chief of Interventional Cardiology Director of Cardiac Catheterization Lab St. Mary s Hospital and Regional Medical
 Devang M. Desai, MD, FACC, FSCAI Chief of Interventional Cardiology Director of Cardiac Catheterization Lab St. Mary s Hospital and Regional Medical Center A.Fib affects 2.2 million Americans. The lifetime
Devang M. Desai, MD, FACC, FSCAI Chief of Interventional Cardiology Director of Cardiac Catheterization Lab St. Mary s Hospital and Regional Medical Center A.Fib affects 2.2 million Americans. The lifetime
Anticoagulation at the end of life. Rhona Maclean Rhona.maclean@sth.nhs.uk
 Anticoagulation at the end of life Rhona Maclean Rhona.maclean@sth.nhs.uk Content Anticoagulant Therapies Indications for anticoagulation Venous thromboembolism (VTE) Atrial Fibrillation Mechnical Heart
Anticoagulation at the end of life Rhona Maclean Rhona.maclean@sth.nhs.uk Content Anticoagulant Therapies Indications for anticoagulation Venous thromboembolism (VTE) Atrial Fibrillation Mechnical Heart
Thrombosis management: A time for change practical management with NOACs Dr Wala Elizabeth Medical Director, Bayer Healthcare
 Thrombosis management: A time for change practical management with NOACs Dr Wala Elizabeth Medical Director, Bayer Healthcare Kenya Association of Physicians Conference 10 th May 2013 New anticoagulants:
Thrombosis management: A time for change practical management with NOACs Dr Wala Elizabeth Medical Director, Bayer Healthcare Kenya Association of Physicians Conference 10 th May 2013 New anticoagulants:
3/25/14. To Clot or Not What s New In Anticoagulation? Clotting Cascade. Anticoagulant drug targets. Anita Ralstin, MS CNS CNP. Heparin.
 To Clot or Not What s New In Anticoagulation? Anita Ralstin, MS CNS CNP 1 Clotting Cascade 2 Anticoagulant drug targets Heparin XI VIII IX V X VII LMWH II Warfarin Fibrin clot 1 Who Needs Anticoagulation
To Clot or Not What s New In Anticoagulation? Anita Ralstin, MS CNS CNP 1 Clotting Cascade 2 Anticoagulant drug targets Heparin XI VIII IX V X VII LMWH II Warfarin Fibrin clot 1 Who Needs Anticoagulation
Clive Kearon, Susan R. Kahn, Giancarlo Agnelli, Samuel Goldhaber, Gary E. Raskob and Anthony J. Comerota. DOI 10.1378/chest.
 Antithrombotic Therapy for Venous Thromboembolic Disease: American College of Chest Physicians Evidence-Based Clinical Practice Guidelines (8th Edition) Clive Kearon, Susan R. Kahn, Giancarlo Agnelli,
Antithrombotic Therapy for Venous Thromboembolic Disease: American College of Chest Physicians Evidence-Based Clinical Practice Guidelines (8th Edition) Clive Kearon, Susan R. Kahn, Giancarlo Agnelli,
DATE: 06 May 2013 CONTEXT AND POLICY ISSUES
 TITLE: Low Molecular Weight Heparins versus New Oral Anticoagulants for Long-Term Thrombosis Prophylaxis and Long-Term Treatment of DVT and PE: A Review of the Clinical and Cost-Effectiveness DATE: 06
TITLE: Low Molecular Weight Heparins versus New Oral Anticoagulants for Long-Term Thrombosis Prophylaxis and Long-Term Treatment of DVT and PE: A Review of the Clinical and Cost-Effectiveness DATE: 06
QUICK REFERENCE. Mary Cushman 1 Wendy Lim 2 Neil A Zakai 1. University of Vermont 2. McMaster University
 QUICK REFERENCE Clinical Practice Guide on Antithrombotic Drug Dosing and Management of Antithrombotic Drug- Associated Bleeding Complications in Adults February 2014* Mary Cushman 1 Wendy Lim 2 Neil A
QUICK REFERENCE Clinical Practice Guide on Antithrombotic Drug Dosing and Management of Antithrombotic Drug- Associated Bleeding Complications in Adults February 2014* Mary Cushman 1 Wendy Lim 2 Neil A
Management for Deep Vein Thrombosis and New Agents
 Management for Deep Vein Thrombosis and New Agents Mark Malesker, Pharm.D., FCCP, FCCP, FASHP, BCPS Professor of Pharmacy Practice and Medicine Creighton University 5 th Annual Creighton Cardiovascular
Management for Deep Vein Thrombosis and New Agents Mark Malesker, Pharm.D., FCCP, FCCP, FASHP, BCPS Professor of Pharmacy Practice and Medicine Creighton University 5 th Annual Creighton Cardiovascular
New Oral Anticoagulants Increase Risk for Gastrointestinal Bleeding - A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
 New Oral Anticoagulants Increase Risk for Gastrointestinal Bleeding - A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis Holster IL, Valkhoff VE, Kuipers EJ, Tjwa ET Departments of Gastroenterology and Hepatology,
New Oral Anticoagulants Increase Risk for Gastrointestinal Bleeding - A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis Holster IL, Valkhoff VE, Kuipers EJ, Tjwa ET Departments of Gastroenterology and Hepatology,
APSR RESPIRATORY UPDATES
 APSR RESPIRATORY UPDATES Volume 6, Issue 1 Newsletter Date: January 2014 APSR EDUCATION PUBLICATION Inside this issue: Venous thromboembolism Pulmonary embolism and deep vein thrombosis. 2 Outpatient versus
APSR RESPIRATORY UPDATES Volume 6, Issue 1 Newsletter Date: January 2014 APSR EDUCATION PUBLICATION Inside this issue: Venous thromboembolism Pulmonary embolism and deep vein thrombosis. 2 Outpatient versus
Antithrombotic Therapy for VTE Disease
 CHEST Supplement ANTITHROMBOTIC THERAPY AND PREVENTION OF THROMBOSIS, 9TH ED: ACCP GUIDELINES Antithrombotic Therapy for VTE Disease Antithrombotic Therapy and Prevention of Thrombosis, 9th ed: American
CHEST Supplement ANTITHROMBOTIC THERAPY AND PREVENTION OF THROMBOSIS, 9TH ED: ACCP GUIDELINES Antithrombotic Therapy for VTE Disease Antithrombotic Therapy and Prevention of Thrombosis, 9th ed: American
6/19/2012. Update on Venous Thromboembolism Prophylaxis. Disclosure. Learning Objectives. No conflicts of interest to declare
 Update on Venous Thromboembolism Prophylaxis Disclosure No conflicts of interest to declare Learning Objectives After completion of this presentation, participants should be able to: Define venous thromboembolism,
Update on Venous Thromboembolism Prophylaxis Disclosure No conflicts of interest to declare Learning Objectives After completion of this presentation, participants should be able to: Define venous thromboembolism,
2/17/2015 ANTICOAGULATION UPDATE OBJECTIVES BRIEF REVIEW: CLASSES OF ORAL ANTICOAGULANTS
 ANTICOAGULATION UPDATE C AR R I E P AL M E R, D N P, RN, AN P - BC OBJECTIVES At the end of the presentation, the NP will be able to: Identify new indications for target-specific oral anticoagulants (TSOACs),
ANTICOAGULATION UPDATE C AR R I E P AL M E R, D N P, RN, AN P - BC OBJECTIVES At the end of the presentation, the NP will be able to: Identify new indications for target-specific oral anticoagulants (TSOACs),
Rivaroxaban for the treatment of deep vein thrombosis and prevention of recurrent deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism
 Implementation of NICE TA 261 Rivaroxaban for the treatment of deep vein thrombosis and prevention of recurrent deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism Contents 1. Executive summary 2. Introduction
Implementation of NICE TA 261 Rivaroxaban for the treatment of deep vein thrombosis and prevention of recurrent deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism Contents 1. Executive summary 2. Introduction
ABOUT XARELTO CLINICAL STUDIES
 ABOUT XARELTO CLINICAL STUDIES FAST FACTS Xarelto (rivaroxaban) is a novel, oral direct Factor Xa inhibitor. On September 30, 2008, the European Commission granted marketing approval for Xarelto for the
ABOUT XARELTO CLINICAL STUDIES FAST FACTS Xarelto (rivaroxaban) is a novel, oral direct Factor Xa inhibitor. On September 30, 2008, the European Commission granted marketing approval for Xarelto for the
The Role of the Newer Anticoagulants
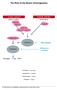 The Role of the Newer Anticoagulants WARFARIN = Coumadin DAGIBATRAN = Pradaxa RIVAROXABAN = Xarelto APIXABAN = Eliquis INDICATION DABIGATRAN (Pradaxa) RIVAROXABAN (Xarelto) APIXABAN (Eliquis) Stroke prevention
The Role of the Newer Anticoagulants WARFARIN = Coumadin DAGIBATRAN = Pradaxa RIVAROXABAN = Xarelto APIXABAN = Eliquis INDICATION DABIGATRAN (Pradaxa) RIVAROXABAN (Xarelto) APIXABAN (Eliquis) Stroke prevention
Antithrombotic Therapy for VTE Disease
 CHEST Supplement ANTITHROMBOTIC THERAPY AND PREVENTION OF THROMBOSIS, 9TH ED: ACCP GUIDELINES Antithrombotic Therapy for VTE Disease Antithrombotic Therapy and Prevention of Thrombosis, 9th ed: American
CHEST Supplement ANTITHROMBOTIC THERAPY AND PREVENTION OF THROMBOSIS, 9TH ED: ACCP GUIDELINES Antithrombotic Therapy for VTE Disease Antithrombotic Therapy and Prevention of Thrombosis, 9th ed: American
New Anticoagulants: What to Use What to Avoid
 New Anticoagulants: What to Use What to Avoid Bruce Davidson, MD, MPH Clinical Professor of Medicine Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine Division University of Washington School of Medicine Seattle USA
New Anticoagulants: What to Use What to Avoid Bruce Davidson, MD, MPH Clinical Professor of Medicine Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine Division University of Washington School of Medicine Seattle USA
Are there sufficient indications for switching to new anticoagulant agents
 Are there sufficient indications for switching to new anticoagulant agents Meyer Michel Samama et Gregoris Gerotziafas Groupe Hémostase-Thrombose Hôtel-Dieu, Hôpital Tenon, Paris & Biomnis Ivry/seine,
Are there sufficient indications for switching to new anticoagulant agents Meyer Michel Samama et Gregoris Gerotziafas Groupe Hémostase-Thrombose Hôtel-Dieu, Hôpital Tenon, Paris & Biomnis Ivry/seine,
How To Treat Aneuricaagulation
 Speaker Introduction Jessica Wilhoite, PharmD, BCACP Doctor of Pharmacy: Purdue University Postgraduate Residency Training: PGY1 Pharmacy Practice St. Vincent Hospital PGY2 Ambulatory Care St. Vincent
Speaker Introduction Jessica Wilhoite, PharmD, BCACP Doctor of Pharmacy: Purdue University Postgraduate Residency Training: PGY1 Pharmacy Practice St. Vincent Hospital PGY2 Ambulatory Care St. Vincent
Dabigatran (Pradaxa) Guidelines
 Dabigatran (Pradaxa) Guidelines Dabigatran is a new anticoagulant for reducing the risk of stroke in patients with atrial fibrillation. Dabigatran is a direct thrombin inhibitor, similar to warfarin, without
Dabigatran (Pradaxa) Guidelines Dabigatran is a new anticoagulant for reducing the risk of stroke in patients with atrial fibrillation. Dabigatran is a direct thrombin inhibitor, similar to warfarin, without
DABIGATRAN ETEXILATE TARGET Vitamin K epoxide reductase WARFARIN RIVAROXABAN APIXABAN
 TARGET SPECIFIC ORAL ANTICOAGULANTS (TSOACs) This document is intended as a guideline only and should not replace sound clinical judgment Please refer to UNMH formulary in Lexicomp for approved use(s)
TARGET SPECIFIC ORAL ANTICOAGULANTS (TSOACs) This document is intended as a guideline only and should not replace sound clinical judgment Please refer to UNMH formulary in Lexicomp for approved use(s)
rivaroxaban 15mg and 20mg film-coated tablets (Xarelto ) SMC No. (852/13) Bayer plc
 rivaroxaban 15mg and 20mg film-coated tablets (Xarelto ) SMC No. (852/13) Bayer plc 08 February 2013 The Scottish Medicines Consortium (SMC) has completed its assessment of the above product and advises
rivaroxaban 15mg and 20mg film-coated tablets (Xarelto ) SMC No. (852/13) Bayer plc 08 February 2013 The Scottish Medicines Consortium (SMC) has completed its assessment of the above product and advises
New anticoagulants: Monitoring or not Monitoring? Not Monitoring
 The 2 nd World Congress on CONTROVERSIES IN HEMATOLOGY (COHEM) Barcelona, Spain September 6 8, 2012 New anticoagulants: Monitoring or not Monitoring? Not Monitoring Anna Falanga, MD Immunohematology and
The 2 nd World Congress on CONTROVERSIES IN HEMATOLOGY (COHEM) Barcelona, Spain September 6 8, 2012 New anticoagulants: Monitoring or not Monitoring? Not Monitoring Anna Falanga, MD Immunohematology and
CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINE: MOBILITY WITH A DEEP VEIN THROMBOSIS (DVT) Page 1 of 10
 Page 1 of 10 1.0 FOCUS: Mobilization with a Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT). The purpose of this clinical practice guideline (CPG) is to ensure that new knowledge is integrated across Fraser Health and to standardize
Page 1 of 10 1.0 FOCUS: Mobilization with a Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT). The purpose of this clinical practice guideline (CPG) is to ensure that new knowledge is integrated across Fraser Health and to standardize
Conserva)ve Treatment of PE/ DVT
 Conserva)ve Treatment of PE/ DVT Amir Kaki, MD FACC FSCAI Asst Prof of Medicine Wayne St SOM Medical Director Cardiac Catheteriza)on Lab Heart Hospital DMC Detroit, MI Incidence Acute pulmonary embolism
Conserva)ve Treatment of PE/ DVT Amir Kaki, MD FACC FSCAI Asst Prof of Medicine Wayne St SOM Medical Director Cardiac Catheteriza)on Lab Heart Hospital DMC Detroit, MI Incidence Acute pulmonary embolism
STROKE PREVENTION IN ATRIAL FIBRILLATION. TARGET AUDIENCE: All Canadian health care professionals. OBJECTIVE: ABBREVIATIONS: BACKGROUND:
 STROKE PREVENTION IN ATRIAL FIBRILLATION TARGET AUDIENCE: All Canadian health care professionals. OBJECTIVE: To guide clinicians in the selection of antithrombotic therapy for the secondary prevention
STROKE PREVENTION IN ATRIAL FIBRILLATION TARGET AUDIENCE: All Canadian health care professionals. OBJECTIVE: To guide clinicians in the selection of antithrombotic therapy for the secondary prevention
Anticoagulants. Anticoagulants Definition. When are blood clots GOOD? Where and why do blood clots occur? 6/12/2014
 Anticoagulants Steven R. Kayser, PharmD Professor Emeritus Department of Clinical Pharmacy UCSF Anticoagulants Definition A substance that hinders the clotting of blood Sometimes referred to as blood thinners
Anticoagulants Steven R. Kayser, PharmD Professor Emeritus Department of Clinical Pharmacy UCSF Anticoagulants Definition A substance that hinders the clotting of blood Sometimes referred to as blood thinners
MEDICAL ASSISTANCE HANDBOOK PRIOR AUTHORIZATION OF PHARMACEUTICAL SERVICES. A. Prescriptions That Require Prior Authorization
 MEDICAL ASSISTANCE HBOOK I. Requirements for Prior Authorization of Anticoagulants A. Prescriptions That Require Prior Authorization Prescriptions for Anticoagulants which meet any of the following conditions
MEDICAL ASSISTANCE HBOOK I. Requirements for Prior Authorization of Anticoagulants A. Prescriptions That Require Prior Authorization Prescriptions for Anticoagulants which meet any of the following conditions
Preventing Blood Clots After Hip or Knee Replacement Surgery or Surgery for a Broken Hip. A Review of the Research for Adults
 Preventing Blood Clots After Hip or Knee Replacement Surgery or Surgery for a Broken Hip A Review of the Research for Adults Is This Information Right for Me? Yes, if: You are considering or planning to
Preventing Blood Clots After Hip or Knee Replacement Surgery or Surgery for a Broken Hip A Review of the Research for Adults Is This Information Right for Me? Yes, if: You are considering or planning to
Anticoagulant Treatment for Deep Venous Thrombosis Direct Oral Anticoagulants (NOACs)
 Anticoagulant Treatment for Deep Venous Thrombosis Direct Oral Anticoagulants (NOACs) Prof. P. HAINAUT Médecine Interne - Maladie Thromboembolique Cliniques Univ. Saint Luc - UCL Background Direct Oral
Anticoagulant Treatment for Deep Venous Thrombosis Direct Oral Anticoagulants (NOACs) Prof. P. HAINAUT Médecine Interne - Maladie Thromboembolique Cliniques Univ. Saint Luc - UCL Background Direct Oral
Implementation of NICE TAs 261 and 287
 Corby Clinical Commissioning Group Kettering General Hospital NHS Trust Nene Clinical Commissioning Group Northampton General Hospital NHS Trust Northamptonshire Healthcare Foundation Trust Implementation
Corby Clinical Commissioning Group Kettering General Hospital NHS Trust Nene Clinical Commissioning Group Northampton General Hospital NHS Trust Northamptonshire Healthcare Foundation Trust Implementation
Diagnosis and Treatment of VTE in the ER
 UHN ER Conference Nov 3, 2015 Diagnosis and Treatment of VTE in the ER Bill Geerts Thromboembolism Program, Sunnybrook HSC Professor of Medicine, University of Toronto National Lead, VTE Prevention, Canadian
UHN ER Conference Nov 3, 2015 Diagnosis and Treatment of VTE in the ER Bill Geerts Thromboembolism Program, Sunnybrook HSC Professor of Medicine, University of Toronto National Lead, VTE Prevention, Canadian
The speakers have attested that their presentation will be free of all commercial bias toward a specific company and its products.
 Update on New Anticoagulants (Apixaban, Dabigatran and Rivaroxaban) Patient Safety Daniel B. DiCola, MD and Paul Ament,, Pharm.D Excela Heath, Latrobe, PA Disclosures: Paul Ament discloses that he receives
Update on New Anticoagulants (Apixaban, Dabigatran and Rivaroxaban) Patient Safety Daniel B. DiCola, MD and Paul Ament,, Pharm.D Excela Heath, Latrobe, PA Disclosures: Paul Ament discloses that he receives
Guidelines for diagnosis and management of acute pulmonary embolism
 Guidelines for diagnosis and management of acute pulmonary embolism By Dr. Ahmed Zaghloul M.D. Anesthesia & Critical Care 2014 Predisposing factors for VTE Predisposing factor Strong predisposing factors
Guidelines for diagnosis and management of acute pulmonary embolism By Dr. Ahmed Zaghloul M.D. Anesthesia & Critical Care 2014 Predisposing factors for VTE Predisposing factor Strong predisposing factors
Bayer Initiates Rivaroxaban Phase III Study to Support Dose Selection According to Individual Benefit-Risk Profile in Long- Term VTE Prevention
 Investor News Not intended for U.S. and UK Media Bayer AG Investor Relations 51368 Leverkusen Germany www.investor.bayer.com Long-term prevention of venous blood clots (VTE): Bayer Initiates Rivaroxaban
Investor News Not intended for U.S. and UK Media Bayer AG Investor Relations 51368 Leverkusen Germany www.investor.bayer.com Long-term prevention of venous blood clots (VTE): Bayer Initiates Rivaroxaban
Three new/novel oral anticoagulants (NOAC) have been licensed in Ireland since 2008:
 Key Points to consider when prescribing NOACs Introduction Three new/novel oral anticoagulants (NOAC) have been licensed in Ireland since 2008: Dabigatran Etexilate (Pradaxa ) 75mg, 110mg, 150mg. Rivaroxaban
Key Points to consider when prescribing NOACs Introduction Three new/novel oral anticoagulants (NOAC) have been licensed in Ireland since 2008: Dabigatran Etexilate (Pradaxa ) 75mg, 110mg, 150mg. Rivaroxaban
Rivaroxaban for the treatment of deep vein thrombosis and prevention of recurrent deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism
 Rivaroxaban for the treatment of deep vein thrombosis and prevention of recurrent deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary Issued: July 2012 guidance.nice.org.uk/ta NHS Evidence has accredited the process used
Rivaroxaban for the treatment of deep vein thrombosis and prevention of recurrent deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary Issued: July 2012 guidance.nice.org.uk/ta NHS Evidence has accredited the process used
5/21/2012. Perioperative Use Issues. On admission: During hospitalization:
 Dabigatran and Rivaroxaban: Challenges in the Perioperative Setting Claudia Swenson, Pharm.D., CDE, BC-ADM, FASHP Central Washington Hospital Wenatchee, WA claudia.swenson@cwhs.com Dabigatran and Rivaroxaban:
Dabigatran and Rivaroxaban: Challenges in the Perioperative Setting Claudia Swenson, Pharm.D., CDE, BC-ADM, FASHP Central Washington Hospital Wenatchee, WA claudia.swenson@cwhs.com Dabigatran and Rivaroxaban:
Laboratory Testing in Patients on Novel Oral Anticoagulants (NOACs)
 Laboratory Testing in Patients on Novel Oral Anticoagulants (NOACs) Dr. Art Szkotak artur.szkotak@albertahealthservices.ca University of Alberta Hospital Edmonton, AB NOACs Direct Thrombin Inhibitors (DTI):
Laboratory Testing in Patients on Novel Oral Anticoagulants (NOACs) Dr. Art Szkotak artur.szkotak@albertahealthservices.ca University of Alberta Hospital Edmonton, AB NOACs Direct Thrombin Inhibitors (DTI):
New Anticoagulants: When and Why Should I Use Them? Disclosures
 Winship Cancer Institute of Emory University New Anticoagulants: When and Why Should I Use Them? Christine L. Kempton, MD, MSc Associate Professor of Pediatrics and Hematology and Medical Oncology Hemophilia
Winship Cancer Institute of Emory University New Anticoagulants: When and Why Should I Use Them? Christine L. Kempton, MD, MSc Associate Professor of Pediatrics and Hematology and Medical Oncology Hemophilia
PRACTICE GUIDELINES FOR ANTICOAGULATION MANAGEMENT
 PRACTICE GUIDELINES FOR ANTICOAGULATION MANAGEMENT 3 RD EDITION From the Division of Hematology and Pharmacy with contributions from the Division of Cardiology, the Thrombosis Research Group, Department
PRACTICE GUIDELINES FOR ANTICOAGULATION MANAGEMENT 3 RD EDITION From the Division of Hematology and Pharmacy with contributions from the Division of Cardiology, the Thrombosis Research Group, Department
Kevin Saunders MD CCFP Rivergrove Medical Clinic Wellness Institute @ SOGH April 17 2013
 Kevin Saunders MD CCFP Rivergrove Medical Clinic Wellness Institute @ SOGH April 17 2013 Family physician with Rivergrove Medical Clinic Practice in the north end since 1985 Medical Director of the Wellness
Kevin Saunders MD CCFP Rivergrove Medical Clinic Wellness Institute @ SOGH April 17 2013 Family physician with Rivergrove Medical Clinic Practice in the north end since 1985 Medical Director of the Wellness
Novel Oral Anticoagulants (NOACs) Prescriber Update 2013
 Novel Oral Anticoagulants (NOACs) Prescriber Update 2013 Indications/Contraindications Indications Orthopedic VTE Prophylaxis VTE Treatment Stroke Prevention for non-valvular AF Contraindications 150 mg
Novel Oral Anticoagulants (NOACs) Prescriber Update 2013 Indications/Contraindications Indications Orthopedic VTE Prophylaxis VTE Treatment Stroke Prevention for non-valvular AF Contraindications 150 mg
The new oral anticoagulants & the future of haemostasis laboratory testing. Alcohol: the good, the bad and the ugly
 The new oral anticoagulants & the future of haemostasis laboratory testing Emmanuel J Favaloro Diagnostic Haemostasis Laboratory, Institute of Clinical Pathology & Medical Research, ICPMR, Pathology West,
The new oral anticoagulants & the future of haemostasis laboratory testing Emmanuel J Favaloro Diagnostic Haemostasis Laboratory, Institute of Clinical Pathology & Medical Research, ICPMR, Pathology West,
Volume 7; Number 19 November 2013
 Greater East Midlands Commissioning Support Unit in association with Lincolnshire Clinical Commissioning Groups, Lincolnshire Community Health Services, United Lincolnshire Hospitals Trust and Lincolnshire
Greater East Midlands Commissioning Support Unit in association with Lincolnshire Clinical Commissioning Groups, Lincolnshire Community Health Services, United Lincolnshire Hospitals Trust and Lincolnshire
Anticoagulation and Reversal
 Anticoagulation and Reversal John Howard, PharmD, BCPS Clinical Pharmacist Internal Medicine Affiliate Associate Clinical Professor South Carolina College of Pharmacy Disclosures I have no Financial, Industry,
Anticoagulation and Reversal John Howard, PharmD, BCPS Clinical Pharmacist Internal Medicine Affiliate Associate Clinical Professor South Carolina College of Pharmacy Disclosures I have no Financial, Industry,
Position Statement: The Use of VTED Prophylaxis in Foot and Ankle Surgery
 Position Statement: The Use of VTED Prophylaxis in Foot and Ankle Surgery Position Statement There is currently insufficient data for the (AOFAS) to recommend for or against routine VTED prophylaxis for
Position Statement: The Use of VTED Prophylaxis in Foot and Ankle Surgery Position Statement There is currently insufficient data for the (AOFAS) to recommend for or against routine VTED prophylaxis for
Enoxaparin for long term anticoagulation in patients unsuitable for oral anticoagulants
 Enoxaparin for long term anticoagulation in patients unsuitable for oral anticoagulants Traffic light classification- Amber 2 Information sheet for Primary Care Prescribers Relevant Licensed Indications
Enoxaparin for long term anticoagulation in patients unsuitable for oral anticoagulants Traffic light classification- Amber 2 Information sheet for Primary Care Prescribers Relevant Licensed Indications
Rivaroxaban for the treatment of deep vein thrombosis and prevention of recurrent deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism
 Rivaroxaban for the treatment of deep vein thrombosis and prevention of recurrent deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary Issued: July 2012 guidance.nice.org.uk/ta NICE has accredited the process used by the
Rivaroxaban for the treatment of deep vein thrombosis and prevention of recurrent deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary Issued: July 2012 guidance.nice.org.uk/ta NICE has accredited the process used by the
CDEC FINAL RECOMMENDATION
 CDEC FINAL RECOMMENDATION RIVAROXABAN (Xarelto Bayer Inc.) New Indication: Pulmonary Embolism Note: The Canadian Drug Expert Committee (CDEC) previously reviewed rivaroxaban for the treatment of deep vein
CDEC FINAL RECOMMENDATION RIVAROXABAN (Xarelto Bayer Inc.) New Indication: Pulmonary Embolism Note: The Canadian Drug Expert Committee (CDEC) previously reviewed rivaroxaban for the treatment of deep vein
