To define a diagnostic algorithm and treatment strategy for patients with acute pulmonary embolism.
|
|
|
- Eunice Gillian Summers
- 10 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 PULMONARY EMBOLISM: DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT TARGET AUDIENCE: All Canadian health care professionals. OBJECTIVE: To define a diagnostic algorithm and treatment strategy for patients with acute pulmonary embolism. ABBREVIATIONS: BNP brain natriuretic peptide CrCl creatinine clearance CT computed tomography CTPA computed tomography pulmonary angiogram CUS compression ultrasound DVT deep vein thrombosis ECG electrocardiogram HIT heparin-induced thrombocytopenia INR international normalized ratio LMWH low-molecular-weight heparin MRI magnetic resonance imaging PE pulmonary embolism PERC Pulmonary Embolism Rule-out Criterion rtpa recombinant tissue plasminogen activator RV right ventricle SBP systolic blood pressure SC subcutaneously UFH unfractionated heparin V/Q ventilation-perfusion VTE venous thromboembolism BACKGROUND: Although Canadian data are lacking, venous thromboembolism (VTE) is a common disease, affecting approximately 1-2 in 1,000 adults per year. Approximately one third of first VTE presentations are due to pulmonary embolism (PE) and the remainder are due to deep venous thrombosis (DVT) (see DVT: Diagnosis and DVT: Treatment guides). The incidence of PE has increased significantly since the advent of computed tomography (CT) angiography due to its widespread availability and diagnostic sensitivity. The majority of PEs originate in the proximal deep venous system of the leg, despite the fact that only 25-50% of patients with PE have 2013 Thrombosis Canada. Page 1 of 9
2 clinically-evident DVT. Active malignancy (see Cancer and Thrombosis guide), surgery (especially orthopedic; see Thromboprophylaxis: Orthopedic Surgery guide), immobilization > 8 hours, and estrogen use/pregnancy (see Thromboprophylaxis: Pregnancy guide) are transient provoking factors. Up to 50% of first-time PE is unprovoked (or idiopathic). Symptoms of PE include sudden onset dyspnea, syncope, pleurisy. Signs or PE may include tachypnea, tachycardia, hypoxemia, hypotension, features of right ventricular dysfunction (distended jugular veins) and right ventricular strain on electrocardiogram (ECG) (S1Q3T3, right bundle branch block and T-inversion in leads V1-V4). Up to 10% of symptomatic PEs are fatal within the first hour of symptoms. Independent predictors of early mortality include hypotension (systolic blood pressure [SBP] < 90 mmhg), clinical right heart failure, right ventricle (RV) dilation on CT/echocardiography, positive troponin and elevated brain natriuretic peptide (BNP). Early diagnosis and treatment of PE reduces morbidity and mortality. Patients who present with a first PE are more likely to have subsequent VTE (risk varies between 3-10%/year depending on underlying cause; see Duration of Anticoagulant Therapy guide); however, recurrent events are more commonly PE (80%) rather than DVT. DIAGNOSIS: Diagnostic algorithms have been suggested in major society guidelines. The constellation of symptoms and signs of PE are suggestive, but do not have the necessary specificity or sensitivity to rule in or out the diagnosis. When the diagnosis is entertained, clinical stability and pre-test probability will dictate the diagnostic approach (see Figure 1). In patients without hypotension (SBP > 90 mmhg), pre-test probability should be assessed by experienced clinician gestalt or a validated clinical prediction rule (see Table 1). In cases of low to intermediate clinical probability, a negative D-dimer result rules out the diagnosis of PE. However, a positive D-dimer test must be followed up with a definitive test to confirm/refute the diagnosis of PE. Multidetector CT pulmonary angiography (CTPA) is widely available in Canada, and sufficiently sensitive and specific to exclude the diagnosis of PE when negative and to confirm it when positive in the context of a low pre-test probability. When the pre-test probability is high, there is no value in checking a D-dimer level, as the posttest probability of a negative result is unacceptably high. Therefore, when the pre-test probability is high, one should go directly to CTPA to establish the diagnosis. In patients with low clinical probability of PE, and in the absence of D-dimer assay testing, the diagnosis can be safely excluded using the PERC (Pulmonary Embolism Rule-out Criteria) rule for pulmonary embolism. In patients with renal failure or an allergy to contrast dye in whom a CTPA is felt to be contraindicated, it may be reasonable to start with lower extremity compressive ultrasound (CUS) looking for evidence of DVT (see DVT: Diagnosis guide). A positive result will mandate the 2013 Thrombosis Canada. Page 2 of 9
3 same treatment as PE, and no further investigations are indicated. Since up to 30% of patients may not have concurrent DVT with PE, a negative result does not rule out PE. Therefore, a ventilation-perfusion (V/Q) scan should be obtained in this instance. In patients with hypotension who are too unstable to undergo CTPA, or if CTPA is not immediately available, an urgent echocardiogram should be obtained looking for evidence of clot in the RV or pulmonary arteries, or of right heart overload. If present, and in the absence of an alternative diagnosis, treatment for PE should be initiated. Presently, defined echocardiographic signs of PE are sensitive enough to exclude massive PE (i.e. PE associated with hypotension), if absent. However, RV dysfunction alone is not specific enough to exclude an alternate diagnosis (e.g. RV infarction); therefore, if feasible, confirmatory evidence of VTE should be sought with CTPA or CUS prior to initiation of therapy. TREATMENT: Patients who have a high pre-test probability of having PE should be initiated promptly on anticoagulant therapy. Treatment can be withheld in patients with intermediate and low pre-test probabilities of PE, assuming definitive diagnostic testing will be completed within 4 or 24 hours, respectively. All patients with confirmed PE should be risk-stratified to determine whether they require in-hospital treatment or if outpatient management is sufficient. Patients presenting with hypotension (SBP < 90 mmhg or a 40 mmhg drop from baseline) that is not responsive to a fluid challenge or due to another cause (e.g. tachycardia) carry a 15% risk of early mortality and should be admitted to an intensive care unit. Patients who are clinically-well and do not have evidence of myocardial injury or RV dysfunction are at low risk for early mortality (< 1%) and are appropriate for early discharge or home treatment. The initial anticoagulant treatment is with a parenteral agent, typically unfractionated heparin (UFH) or low-molecular-weight heparin (LMWH), which serves as a bridge until warfarin therapy takes effect (international normalized ratio [INR]: ). Warfarin should be initiated at the same time as parenteral therapy and the dose should be adjusted to achieve an INR range of (target INR: 2.5). Parenteral therapy should be continued for at least 5 days and, ideally, until the INR is 2.0 for two consecutive days. Anticoagulation should be continued for at least 3 months (see Duration of Anticoagulant Therapy guide and Table 2 below). Low-molecular-weight heparin LMWH may be used as initial therapy in conjunction with warfarin or may be used as monotherapy for the full duration of treatment. It is the preferred long-term treatment for cancer patients. Most patients have little difficulty with self-administration. LMWH offers advantages over UFH, including better bioavailability when administered subcutaneously, longer duration of anticoagulant effect enabling once daily treatment, lower risk of heparin-induced thrombocytopenia (HIT), predictable anticoagulant effect allowing fixed dosing based on body 2013 Thrombosis Canada. Page 3 of 9
4 weight and renal function, less effect on bone metabolism and no requirement for laboratory monitoring. AGENTS AND DOSING: Low-molecular-weight Heparin Dalteparin (Fragmin ): 200 U/kg subcutaneously (SC) once daily or 100 U/kg SC twice daily (once daily dosing preferred). Enoxaparin (Lovenox ): 1 mg/kg SC twice daily. Tinzaparin (Innohep ): 175 U/kg once daily. For patients with severe renal insufficiency (creatinine clearance [CrCl] < 30 ml/min), clinical data on the use of LMWH for the treatment of PE are limited and LMWHs should be avoided. If used, the dose of LMWH should be reduced by approximately 50% and monitoring with anti-factor Xa levels may be required. Unfractionated Heparin UFH use in the treatment of PE is limited by a narrow therapeutic range, inter-individual variation in anticoagulant effect and the increased risk of HIT. The use of UFH should be limited to: (1) patients with severe renal insufficiency (CrCl < 30 ml/min), in whom LMWHs should be avoided; (2) patients at increased risk for bleeding, in whom rapid reversal of the anticoagulant effect may be needed; and (3) patients who receive thrombolytic therapy. In addition, UFH is an alternative to LMWH if LMWH is not feasible because of cost considerations or intolerance. UFH can be used intravenously, administered to achieve an activated partial thromboplastin time (aptt) of 1.5 to 2.0 times the control aptt. UFH can also be given subcutaneously with a 333 U/kg initial dose, followed by 250 U/kg twice daily, and without aptt monitoring. Thrombolysis In most patients with PE the risk of major bleeding outweighs the benefit from thrombolysis, except those who present with massive PE, which is defined by persistent hypotension or respiratory failure, where the short-term mortality is > 15%. Therefore, until further data are available, thrombolysis should be reserved for patients with ongoing hypotension (SBP < 90 mmhg), respiratory failure. When used, thrombolysis is given as follows: recombinant tissue plasminogen activator (rtpa) 100 mg over 2 hours or 0.6 mg/kg as a bolus. Intravenous UFH should be used after thrombolytic therapy. Patients still require anticoagulation for at least 3 months after receiving thrombolytic therapy. Intravenous UFH should be used after thrombolytic therapy. Patients still require anticoagulation for at least 3 months after receiving thrombolytic therapy. Intravenous UFH should be used after thrombolytic therapy. Patients still require anticoagulation for at least 3 months after receiving thrombolytic therapy Thrombosis Canada. Page 4 of 9
5 Warfarin Initial treatment with warfarin should be combined with an immediate-acting agent such as LMWH for at least 5 days and until INR is at least 2.0. Initial dosing is typically 5 mg once daily, but the therapeutic dose is highly variable. The elderly, infirm and those with low body-weight typically require a lower dose. Initial dosing with 2-3 mg should be considered in such patients. Frequent monitoring is required until a stable, in-range INR is reached, after which monthly testing is usually adequate. Warfarin is associated with many drug and food interactions that affect INR. Alterations in concomitant medications and new concurrent illness should be associated with INR testing. Patients should not be encouraged to reduce intake of foods high in vitamin K, but maintain a consistent, balanced diet. Dabigatran (Pradaxa ), Rivaroxaban (Xarelto ), Apixaban (Eliquis ) Large phase 3 studies that have been completed, or are ongoing, demonstrate benefit of these agents for the initial (rivaroxaban, apixaban), acute (all agents) and extended (all agents) treatment of PE. As of mid-2013, rivaroxaban is approved for the treatment of patients with PE (See Rivaroxaban guide). The recommended dosing is 15 mg twice daily for the first 21 days, followed by 20 mg once daily for the duration of treatment. SPECIAL CONSIDERATIONS: Catheter-directed thrombolysis for massive PE In some hospitals where there is requisite expertise, catheter-directed thrombolysis may be considered since it is able to deliver a thrombolytic agent directly into one or more large emboli and can rapidly relieve pulmonary artery occlusion. Such treatment should be undertaken in consultation with a specialist. Chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension Chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension is present in up to 3% of patients after an episode of symptomatic or asymptomatic PE. There is no high-quality evidence to assist with treatment decisions in this area. Therefore, management of such patients should be guided in consultation with a specialist in thrombosis. Pulmonary thrombendarterectomy may reduce pulmonary pressures and symptoms of pulmonary hypertension, but mortality for such surgery is about 5% even in the most experienced centres. Subsequent VTE events are considered to be extremely high-risk due to already reduced cardiopulmonary reserve and, therefore, these patients should be strongly considered for indefinite anticoagulant therapy. Patients contraindicated for anticoagulation See Vena Cava Filter guide Thrombosis Canada. Page 5 of 9
6 Pregnancy See Thromboprophylaxis: Pregnancy guide. Cancer See Cancer and Thrombosis guide. PEDIATRICS: Diagnosis should be confirmed with a V/Q scan, CT with contrast or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). However, the sensitivity and specificity of these diagnostic methods in children has not been determined. Treatment may be initiated with either age-appropriate UFH or LMWH followed by 3 months (etiology determined), 6-12 months (idiopathic) or long-term (recurrent) of either LMWH or vitamin K antagonists. Life-threatening PE should be treated with thrombolysis, either pharmacologic (rtpa) or mechanical, or with thrombectomy. After thrombolytic therapy, conventional anticoagulation should be administered as above. See Pediatrics guide. REFERENCES: Jaff MR, McMurtry MS, Archer SL, et al. Management of massive and submassive pulmonary embolism, iliofemoral deep vein thrombosis, and chronic pulmonary hypertension: a scientific statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2011;123: Kearon C, Akl EA, Comerota AJ, et al. Antithrombotic therapy for VTE disease: Antithrombotic Therapy and Prevention of Thrombosis, 9 th ed: American College of Chest Physicians Evidence- Based Clinical Practice Guidelines. Chest 2012;141(2 Suppl):e419S-494S. Kline JA, Courtney DM, Kabrhel C, et al. Prospective multicenter evaluation of the pulmonary embolism rule-out criteria. J Thromb Haemost 2008;6: Torbicki A, Perrier A, Konstantinides S, et al. Guidelines on the diagnosis and management of acute pulmonary embolism: the Task Force for the Diagnosis and Management of Acute Pulmonary Embolism of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). Eur Heart J 2008;29: Wells PS, Anderson DR, Rodger M, et al. Excluding pulmonary embolism at the bedside without diagnostic imaging: management of patients with suspected pulmonary embolism presenting to the emergency department by using a simple clinical model and d-dimer. Ann Intern Med 2001;135: Thrombosis Canada. Page 6 of 9
7 Figure 1: Suggested Diagnostic Algorithm for Suspected Pulmonary Embolism * Consideration for thrombolysis without diagnostic test confirmation should be made if the patient is very unstable or moribund ** Features on echocardiography suggestive of massive PE include RV overload and RV/pulmonary artery thrombus *** If patient condition stabilizes, consideration for CTPA can be given to confirm diagnosis **** Excluding a diagnosis of PE with a moderate pre-test probability requires the use of a highly sensitive d-dimer assay 2013 Thrombosis Canada. Page 7 of 9
8 Variable Table 1: Wells Score* for PE Points Clinical signs and symptoms of DVT 3 No alternative diagnosis more likely than PE 3 Heart rate > 100 beats/minute 1.5 Immobilization for > 3 days or surgery within 4 weeks 1.5 Previous DVT or PE 1.5 Hemoptysis 1 Malignancy 1 *Total Score: Low Risk: 0 to 1.5; Intermediate Risk: 2 to 5.5; High Risk: > 6 Table 2: Recommendations for Extended Treatment for PE or DVT Categories of VTE Provoked by a transient risk factor* First unprovoked VTE Proximal DVT or PE with no or only minor risk factors for bleeding Isolated distal DVT Second unprovoked VTE Cancer-associated VTE 3 months Duration of Treatment Minimum of 3 months and then reassess Long-term therapy with annual review 3 months Minimum of 3 months and then reassess. For patients with no or only minor risk factors for bleeding, long-term therapy with annual review Minimum of 3 months and then reassess. Continue if active cancer (overt evidence of cancer) or continuing to receive anticancer therapy * Transient risk factors include: surgery, hospitalization or plaster cast immobilization, all within 3 months; estrogen therapy, pregnancy, prolonged travel (e.g. > 8 hours), lesser leg injuries or immobilizations more recently (e.g. within 6 weeks). The greater the provoking reversible risk factor (e.g. recent major surgery), the lower is the expected risk of recurrence after stopping anticoagulant therapy. Absence of a transient risk factor or active cancer. This decision is sensitive to patient preference. Indefinite therapy is suggested if there is moderate risk of bleeding, and 3 months is suggested if there is a high risk of bleeding; both of these decisions are sensitive to patient preference Thrombosis Canada. Page 8 of 9
9 Please note that the information contained herein is not to be interpreted as an alternative to medical advice from your doctor or other professional healthcare provider. If you have any specific questions about any medical matter, you should consult your doctor or other professional healthcare providers, and as such you should never delay seeking medical advice, disregard medical advice or discontinue medical treatment because of the information contained herein Thrombosis Canada. Page 9 of 9
To provide an evidenced-based approach to treatment of patients presenting with deep vein thrombosis.
 DEEP VEIN THROMBOSIS: TREATMENT TARGET AUDIENCE: All Canadian health care professionals. OBJECTIVE: To provide an evidenced-based approach to treatment of patients presenting with deep vein thrombosis.
DEEP VEIN THROMBOSIS: TREATMENT TARGET AUDIENCE: All Canadian health care professionals. OBJECTIVE: To provide an evidenced-based approach to treatment of patients presenting with deep vein thrombosis.
To aid practitioners in prescribing unfractionated heparin and low-molecular-weight heparins to patients.
 UNFRACTIONATED HEPARIN AND LOW-MOLECULAR-WEIGHT HEPARIN TARGET AUDIENCE: All Canadian health care professionals. OBJECTIVE: To aid practitioners in prescribing unfractionated heparin and low-molecular-weight
UNFRACTIONATED HEPARIN AND LOW-MOLECULAR-WEIGHT HEPARIN TARGET AUDIENCE: All Canadian health care professionals. OBJECTIVE: To aid practitioners in prescribing unfractionated heparin and low-molecular-weight
Venous Thromboembolic Treatment Guidelines
 Venous Thromboembolic Treatment Guidelines About the NYU Venous Thromboembolic Center (VTEC) The center s mission is to deliver advanced screening, detection, care, and management services for patients
Venous Thromboembolic Treatment Guidelines About the NYU Venous Thromboembolic Center (VTEC) The center s mission is to deliver advanced screening, detection, care, and management services for patients
Guidelines for diagnosis and management of acute pulmonary embolism
 Guidelines for diagnosis and management of acute pulmonary embolism By Dr. Ahmed Zaghloul M.D. Anesthesia & Critical Care 2014 Predisposing factors for VTE Predisposing factor Strong predisposing factors
Guidelines for diagnosis and management of acute pulmonary embolism By Dr. Ahmed Zaghloul M.D. Anesthesia & Critical Care 2014 Predisposing factors for VTE Predisposing factor Strong predisposing factors
Outpatient Treatment of Deep Vein Thrombosis with Low Molecular Weight Heparin (LMWH) Clinical Practice Guideline August 2013
 Outpatient Treatment of Deep Vein Thrombosis with Low Molecular Weight Heparin (LMWH) Clinical Practice Guideline August 2013 General Principles: There is compelling data in the medical literature to support
Outpatient Treatment of Deep Vein Thrombosis with Low Molecular Weight Heparin (LMWH) Clinical Practice Guideline August 2013 General Principles: There is compelling data in the medical literature to support
Pulmonary Embolism Treatment Update
 UC SF Pulmonary Embolism Treatment Update Jeffrey Tabas, MD Professor UCSF School of Medicine Emergency Department San Francisco General Hospital sf g h Disclosure No Financial Relationships to Disclose
UC SF Pulmonary Embolism Treatment Update Jeffrey Tabas, MD Professor UCSF School of Medicine Emergency Department San Francisco General Hospital sf g h Disclosure No Financial Relationships to Disclose
USE AND INTERPRETATION OF LABORATORY COAGULATION TESTS IN PATIENTS WHO ARE RECEIVING A NEW ORAL ANTICOAGULANT (DABIGATRAN, RIVAROXABAN, APIXABAN)
 USE AND INTERPRETATION OF LABORATORY COAGULATION TESTS IN PATIENTS WHO ARE RECEIVING A NEW ORAL ANTICOAGULANT (DABIGATRAN, RIVAROXABAN, APIXABAN) TARGET AUDIENCE: All Canadian health care professionals:
USE AND INTERPRETATION OF LABORATORY COAGULATION TESTS IN PATIENTS WHO ARE RECEIVING A NEW ORAL ANTICOAGULANT (DABIGATRAN, RIVAROXABAN, APIXABAN) TARGET AUDIENCE: All Canadian health care professionals:
HERTFORDSHIRE MEDICINES MANAGEMENT COMMITTEE (HMMC) RIVAROXABAN RECOMMENDED see specific recommendations for licensed indications below
 Name: generic (trade) Rivaroxaban (Xarelto ) HERTFORDSHIRE MEDICINES MANAGEMENT COMMITTEE (HMMC) RIVAROXABAN RECOMMENDED see specific recommendations for licensed indications below What it is Indications
Name: generic (trade) Rivaroxaban (Xarelto ) HERTFORDSHIRE MEDICINES MANAGEMENT COMMITTEE (HMMC) RIVAROXABAN RECOMMENDED see specific recommendations for licensed indications below What it is Indications
Low Molecular Weight Heparin. All Wales Medicines Strategy Group (AWMSG) Recommendations and advice
 Low Molecular Weight Heparin All Wales Medicines Strategy Group (AWMSG) Recommendations and advice Starting Point Low Molecular Weight Heparin (LMWH): Inhibits factor Xa and factor IIa (thrombin) Small
Low Molecular Weight Heparin All Wales Medicines Strategy Group (AWMSG) Recommendations and advice Starting Point Low Molecular Weight Heparin (LMWH): Inhibits factor Xa and factor IIa (thrombin) Small
Diagnosis and Treatment of VTE in the ER
 UHN ER Conference Nov 3, 2015 Diagnosis and Treatment of VTE in the ER Bill Geerts Thromboembolism Program, Sunnybrook HSC Professor of Medicine, University of Toronto National Lead, VTE Prevention, Canadian
UHN ER Conference Nov 3, 2015 Diagnosis and Treatment of VTE in the ER Bill Geerts Thromboembolism Program, Sunnybrook HSC Professor of Medicine, University of Toronto National Lead, VTE Prevention, Canadian
Thrombosis and Hemostasis
 Thrombosis and Hemostasis Wendy Lim, MD, MSc, FRCPC Associate Professor, Department of Medicine McMaster University, Hamilton, ON Overview To review the important developments in venous thromboembolism
Thrombosis and Hemostasis Wendy Lim, MD, MSc, FRCPC Associate Professor, Department of Medicine McMaster University, Hamilton, ON Overview To review the important developments in venous thromboembolism
UHS CLINICAL CARE COLLABORATION: Outpatient & Inpatient
 Guidelines for Anticoagulation Initiation and Management Y2014 UHS CLINICAL CARE COLLABORATION: Outpatient & Inpatient Topic Page Number MEDICATION FLOW AND PATIENT FLOW... 2 AND 3 PARENTERAL ANTICOAGULANTS...
Guidelines for Anticoagulation Initiation and Management Y2014 UHS CLINICAL CARE COLLABORATION: Outpatient & Inpatient Topic Page Number MEDICATION FLOW AND PATIENT FLOW... 2 AND 3 PARENTERAL ANTICOAGULANTS...
Anticoagulant therapy
 Anticoagulation: The risks Anticoagulant therapy 1990 2002: 600 incidents reported 120 resulted in death of patient 92 deaths related to warfarin usage 28 reports related to heparin usage Incidents in
Anticoagulation: The risks Anticoagulant therapy 1990 2002: 600 incidents reported 120 resulted in death of patient 92 deaths related to warfarin usage 28 reports related to heparin usage Incidents in
Failure or significant adverse effects to all of the alternatives: Eliquis and Xarelto
 This policy has been developed through review of medical literature, consideration of medical necessity, generally accepted medical practice standards, and approved by the IEHP Pharmacy and Therapeutics
This policy has been developed through review of medical literature, consideration of medical necessity, generally accepted medical practice standards, and approved by the IEHP Pharmacy and Therapeutics
DVT/PE Management with Rivaroxaban (Xarelto)
 DVT/PE Management with Rivaroxaban (Xarelto) Rivaroxaban is FDA approved for the acute treatment of DVT and PE and reduction in risk of recurrence of DVT and PE. FDA approved indications: Non valvular
DVT/PE Management with Rivaroxaban (Xarelto) Rivaroxaban is FDA approved for the acute treatment of DVT and PE and reduction in risk of recurrence of DVT and PE. FDA approved indications: Non valvular
Traditional anticoagulants
 TEGH Family Practice Clinic Day April 4, 03 Use of Anticoagulants in 03: What s New (and What Isn t) Bill Geerts, MD, FRCPC Director, Thromboembolism Program, Sunnybrook HSC Professor of Medicine, University
TEGH Family Practice Clinic Day April 4, 03 Use of Anticoagulants in 03: What s New (and What Isn t) Bill Geerts, MD, FRCPC Director, Thromboembolism Program, Sunnybrook HSC Professor of Medicine, University
Thrombosis management: A time for change practical management with NOACs Dr Wala Elizabeth Medical Director, Bayer Healthcare
 Thrombosis management: A time for change practical management with NOACs Dr Wala Elizabeth Medical Director, Bayer Healthcare Kenya Association of Physicians Conference 10 th May 2013 New anticoagulants:
Thrombosis management: A time for change practical management with NOACs Dr Wala Elizabeth Medical Director, Bayer Healthcare Kenya Association of Physicians Conference 10 th May 2013 New anticoagulants:
ACUTE DVT MANAGEMENT Richard J. DeMasi, MD April 26, 2014
 ACUTE DVT MANAGEMENT Richard J. DeMasi, MD April 26, 2014 Thromboembolism epidemiology 5 million DVT s 900,000 PE s 290,000 fatalities Heit J. Blood. 2005;106:910. 10 VTE events Since this talk began DVT
ACUTE DVT MANAGEMENT Richard J. DeMasi, MD April 26, 2014 Thromboembolism epidemiology 5 million DVT s 900,000 PE s 290,000 fatalities Heit J. Blood. 2005;106:910. 10 VTE events Since this talk began DVT
How To Manage An Anticoagulant
 PERI-OPERATIVE MANAGEMENT OF PATIENTS WHO ARE RECEIVING A NEW ORAL ANTICOAGULANT (DABIGATRAN, RIVAROXABAN, APIXABAN) TARGET AUDIENCE: All Canadian health care professionals, including primary care physicians,
PERI-OPERATIVE MANAGEMENT OF PATIENTS WHO ARE RECEIVING A NEW ORAL ANTICOAGULANT (DABIGATRAN, RIVAROXABAN, APIXABAN) TARGET AUDIENCE: All Canadian health care professionals, including primary care physicians,
NQF #IEP-005-10 Pulmonary CT Imaging for Patients at Low Risk for Pulmonary Embolism
 NQF #IEP-005-10 Pulmonary CT Imaging for Patients at Low Risk for Pulmonary Embolism Measure Description Rationale: The use of CT to evaluate patients with suspected pulmonary embolism (PE) has increased
NQF #IEP-005-10 Pulmonary CT Imaging for Patients at Low Risk for Pulmonary Embolism Measure Description Rationale: The use of CT to evaluate patients with suspected pulmonary embolism (PE) has increased
National Guidance and New Protocols
 National Guidance and New Protocols Dr Jane Strong Consultant Haematologist DVT clinical lead Acute VTE chair DAWN AC Twentieth User Group Meeting 8 th October 2012 DVT patient pathway Assessment Diagnosis
National Guidance and New Protocols Dr Jane Strong Consultant Haematologist DVT clinical lead Acute VTE chair DAWN AC Twentieth User Group Meeting 8 th October 2012 DVT patient pathway Assessment Diagnosis
National Guidance and New Protocols
 National Guidance and New Protocols Dr Jane Strong Consultant Haematologist DVT clinical lead Acute VTE chair DAWN AC Twentieth User Group Meeting 8 th October 2012 Autumn dawn Restless geese take flight
National Guidance and New Protocols Dr Jane Strong Consultant Haematologist DVT clinical lead Acute VTE chair DAWN AC Twentieth User Group Meeting 8 th October 2012 Autumn dawn Restless geese take flight
Dabigatran etexilate for the treatment and secondary prevention of deep vein thrombosis and/or pulmonary embolism ERRATUM
 Dabigatran etexilate for the treatment and secondary prevention of deep vein thrombosis and/or pulmonary embolism ERRATUM This report was commissioned by the NIHR HTA Programme as project number 12/78
Dabigatran etexilate for the treatment and secondary prevention of deep vein thrombosis and/or pulmonary embolism ERRATUM This report was commissioned by the NIHR HTA Programme as project number 12/78
Innovations in Treating VTE, Using the EDOU
 Innovations in Treating VTE, Using the EDOU Disclosures No financial conflicts or disclosures Kelly Sawyer, MD, MS [email protected] Observation Symposium 2013 Objectives Overview of VTE Treatment
Innovations in Treating VTE, Using the EDOU Disclosures No financial conflicts or disclosures Kelly Sawyer, MD, MS [email protected] Observation Symposium 2013 Objectives Overview of VTE Treatment
Enoxaparin for long term anticoagulation in patients unsuitable for oral anticoagulants
 Enoxaparin for long term anticoagulation in patients unsuitable for oral anticoagulants Traffic light classification- Amber 2 Information sheet for Primary Care Prescribers Relevant Licensed Indications
Enoxaparin for long term anticoagulation in patients unsuitable for oral anticoagulants Traffic light classification- Amber 2 Information sheet for Primary Care Prescribers Relevant Licensed Indications
New Oral Anticoagulants. How safe are they outside the trials?
 New Oral Anticoagulants How safe are they outside the trials? Objectives The need for anticoagulant therapy Indications for anticoagulation Traditional anticoagulant therapies Properties of new oral anticoagulants
New Oral Anticoagulants How safe are they outside the trials? Objectives The need for anticoagulant therapy Indications for anticoagulation Traditional anticoagulant therapies Properties of new oral anticoagulants
Use of Antithrombotic Agents In The Presence Of Neuraxial Anesthesia
 Use of Antithrombotic Agents In The Presence Of Neuraxial Anesthesia Insertion, removal or presence of a catheter in selected sites can place a patient who is antithrombotic agent at risk for a local bleeding
Use of Antithrombotic Agents In The Presence Of Neuraxial Anesthesia Insertion, removal or presence of a catheter in selected sites can place a patient who is antithrombotic agent at risk for a local bleeding
Prescriber Guide. 20mg. 15mg. Simply Protecting More Patients. Simply Protecting More Patients
 Prescriber Guide 20mg Simply Protecting More Patients 15mg Simply Protecting More Patients 1 Dear Doctor, This prescriber guide was produced by Bayer Israel in cooperation with the Ministry of Health as
Prescriber Guide 20mg Simply Protecting More Patients 15mg Simply Protecting More Patients 1 Dear Doctor, This prescriber guide was produced by Bayer Israel in cooperation with the Ministry of Health as
New Oral Anticoagulants
 New Oral Anticoagulants Tracy Minichiello, MD Associate Professor of Medicine Chief, San FranciscoVA Anticoagulation and Thrombosis Service Ansell, J. Hematology Copyright 2010 American Society of Hematology.
New Oral Anticoagulants Tracy Minichiello, MD Associate Professor of Medicine Chief, San FranciscoVA Anticoagulation and Thrombosis Service Ansell, J. Hematology Copyright 2010 American Society of Hematology.
Anticoagulation Dosing at UCDMC Indication Agent Standard Dose Comments and Dose Adjustments VTE Prophylaxis All Services UFH 5,000 units SC q 8 h
 Indication Agent Standard Dose Comments and Dose Adjustments VTE Prophylaxis All Services UFH 5,000 units SC q 8 h See EMR adult VTE prophylaxis CI order set Enoxaparin See service specific dosing Assess
Indication Agent Standard Dose Comments and Dose Adjustments VTE Prophylaxis All Services UFH 5,000 units SC q 8 h See EMR adult VTE prophylaxis CI order set Enoxaparin See service specific dosing Assess
Epidemiology of Pulmonary Embolism. 1,500,000 new cases per year
 Pulmonary Thromboembolism Jim Allen, MD Professor of Internal Medicine Division of Pulmonary & Critical Care Medicine The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center Epidemiology of Pulmonary Embolism
Pulmonary Thromboembolism Jim Allen, MD Professor of Internal Medicine Division of Pulmonary & Critical Care Medicine The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center Epidemiology of Pulmonary Embolism
NHS FORTH VALLEY RIVAROXABAN AS TREATMENT FOR DEEP VEIN THROMBOSIS AND PULMONARY EMBOLISM IN ADULTS
 NHS FORTH VALLEY RIVAROXABAN AS TREATMENT FOR DEEP VEIN THROMBOSIS AND PULMONARY EMBOLISM IN ADULTS Date of First Issue 01/12/ 2012 Approved 15/11/2012 Current Issue Date 29/10/2014 Review Date 29/10/2016
NHS FORTH VALLEY RIVAROXABAN AS TREATMENT FOR DEEP VEIN THROMBOSIS AND PULMONARY EMBOLISM IN ADULTS Date of First Issue 01/12/ 2012 Approved 15/11/2012 Current Issue Date 29/10/2014 Review Date 29/10/2016
Update on the Diagnosis and Treatment of Venous Thromboembolism Daniel B. DiCola, MD and Paul Ament, Pharm.D Excela Heath, Latrobe, PA
 Disclosures: Update on the Diagnosis and Treatment of Venous Thromboembolism Daniel B. DiCola, MD and Paul Ament, Pharm.D Excela Heath, Latrobe, PA Paul Ament discloses that he receives honorarium and
Disclosures: Update on the Diagnosis and Treatment of Venous Thromboembolism Daniel B. DiCola, MD and Paul Ament, Pharm.D Excela Heath, Latrobe, PA Paul Ament discloses that he receives honorarium and
COMPARISON OF NEW ORAL ANTICOAGULANTS AND FREQUENTLY- ASKED QUESTIONS FROM PATIENTS. TARGET AUDIENCE: All Canadian health care professionals.
 COMPARISON OF NEW ORAL ANTICOAGULANTS AND FREQUENTLY- ASKED QUESTIONS FROM PATIENTS AND PHYSICIANS TARGET AUDIENCE: All Canadian health care professionals. OBJECTIVES: To provide a comparison of the new
COMPARISON OF NEW ORAL ANTICOAGULANTS AND FREQUENTLY- ASKED QUESTIONS FROM PATIENTS AND PHYSICIANS TARGET AUDIENCE: All Canadian health care professionals. OBJECTIVES: To provide a comparison of the new
STROKE PREVENTION IN ATRIAL FIBRILLATION
 STROKE PREVENTION IN ATRIAL FIBRILLATION OBJECTIVE: To guide clinicians in the selection of antithrombotic therapy for the secondary prevention of ischemic stroke and arterial thromboembolism in patients
STROKE PREVENTION IN ATRIAL FIBRILLATION OBJECTIVE: To guide clinicians in the selection of antithrombotic therapy for the secondary prevention of ischemic stroke and arterial thromboembolism in patients
Antithrombotic Therapy for VTE Disease
 CHEST Supplement ANTITHROMBOTIC THERAPY AND PREVENTION OF THROMBOSIS, 9TH ED: ACCP GUIDELINES Antithrombotic Therapy for VTE Disease Antithrombotic Therapy and Prevention of Thrombosis, 9th ed: American
CHEST Supplement ANTITHROMBOTIC THERAPY AND PREVENTION OF THROMBOSIS, 9TH ED: ACCP GUIDELINES Antithrombotic Therapy for VTE Disease Antithrombotic Therapy and Prevention of Thrombosis, 9th ed: American
Clinical Study Synopsis
 Clinical Study Synopsis This Clinical Study Synopsis is provided for patients and healthcare professionals to increase the transparency of Bayer's clinical research. This document is not intended to replace
Clinical Study Synopsis This Clinical Study Synopsis is provided for patients and healthcare professionals to increase the transparency of Bayer's clinical research. This document is not intended to replace
Conserva)ve Treatment of PE/ DVT
 Conserva)ve Treatment of PE/ DVT Amir Kaki, MD FACC FSCAI Asst Prof of Medicine Wayne St SOM Medical Director Cardiac Catheteriza)on Lab Heart Hospital DMC Detroit, MI Incidence Acute pulmonary embolism
Conserva)ve Treatment of PE/ DVT Amir Kaki, MD FACC FSCAI Asst Prof of Medicine Wayne St SOM Medical Director Cardiac Catheteriza)on Lab Heart Hospital DMC Detroit, MI Incidence Acute pulmonary embolism
Antithrombotic Therapy for VTE Disease
 CHEST Supplement ANTITHROMBOTIC THERAPY AND PREVENTION OF THROMBOSIS, 9TH ED: ACCP GUIDELINES Antithrombotic Therapy for VTE Disease Antithrombotic Therapy and Prevention of Thrombosis, 9th ed: American
CHEST Supplement ANTITHROMBOTIC THERAPY AND PREVENTION OF THROMBOSIS, 9TH ED: ACCP GUIDELINES Antithrombotic Therapy for VTE Disease Antithrombotic Therapy and Prevention of Thrombosis, 9th ed: American
What Does Pregnancy Have to Do With Blood Clots in a Woman s Legs?
 Patient s Guide to Prevention of Blood Clots During Pregnancy: Use of Blood-Thinning A Patient s Guide to Prevention of Blood Clots During Pregnancy: Use of Blood-Thinning Drugs to Prevent Abnormal Blood
Patient s Guide to Prevention of Blood Clots During Pregnancy: Use of Blood-Thinning A Patient s Guide to Prevention of Blood Clots During Pregnancy: Use of Blood-Thinning Drugs to Prevent Abnormal Blood
Lower extremity DVT See Page 3. Clinical Suspicion of VTE. Pulmonary embolism (PE) See Page 4
 Clinical Suspicion of VTE In patients with a high clinical suspicion of DVT/PE, in the absence of contraindications it is recommended that treatment with anticoagulants be started while awaiting the outcome
Clinical Suspicion of VTE In patients with a high clinical suspicion of DVT/PE, in the absence of contraindications it is recommended that treatment with anticoagulants be started while awaiting the outcome
Pathway for the management of DVT in primary Care
 Pathway for the management of DVT in primary Care Final Version: Approved by NHS DGS CCG: June 2015 This document aims to support practices in DGS CCG in the Management & Treatment of patients with suspected
Pathway for the management of DVT in primary Care Final Version: Approved by NHS DGS CCG: June 2015 This document aims to support practices in DGS CCG in the Management & Treatment of patients with suspected
ABOUT XARELTO CLINICAL STUDIES
 ABOUT XARELTO CLINICAL STUDIES FAST FACTS Xarelto (rivaroxaban) is a novel, oral direct Factor Xa inhibitor. On September 30, 2008, the European Commission granted marketing approval for Xarelto for the
ABOUT XARELTO CLINICAL STUDIES FAST FACTS Xarelto (rivaroxaban) is a novel, oral direct Factor Xa inhibitor. On September 30, 2008, the European Commission granted marketing approval for Xarelto for the
Title Use of rivaroxaban in suspected DVT in the Emergency Department Standard Operating Procedure. Author s job title. Pharmacist.
 Document Control Title Use of rivaroxaban in suspected DVT in the Emergency Department Author Pharmacist Directorate Clinical Support Services Version Date Issued Status 0.1 Oct Draft 2015 1.0 Dec Final
Document Control Title Use of rivaroxaban in suspected DVT in the Emergency Department Author Pharmacist Directorate Clinical Support Services Version Date Issued Status 0.1 Oct Draft 2015 1.0 Dec Final
CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINE: MOBILITY WITH A DEEP VEIN THROMBOSIS (DVT) Page 1 of 10
 Page 1 of 10 1.0 FOCUS: Mobilization with a Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT). The purpose of this clinical practice guideline (CPG) is to ensure that new knowledge is integrated across Fraser Health and to standardize
Page 1 of 10 1.0 FOCUS: Mobilization with a Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT). The purpose of this clinical practice guideline (CPG) is to ensure that new knowledge is integrated across Fraser Health and to standardize
Guideline for Anticoagulation and Prophylaxis Using Low Molecular Weight Heparin (LMWH) in Adult Inpatients
 Guideline [Optional heading here. Change font size to suit] Document Number # QH-GDL-951:2015 Guideline for Anticoagulation and Prophylaxis Using Low Molecular Weight Heparin (LMWH) in Adult Inpatients
Guideline [Optional heading here. Change font size to suit] Document Number # QH-GDL-951:2015 Guideline for Anticoagulation and Prophylaxis Using Low Molecular Weight Heparin (LMWH) in Adult Inpatients
Dabigatran (Pradaxa) Guidelines
 Dabigatran (Pradaxa) Guidelines Dabigatran is a new anticoagulant for reducing the risk of stroke in patients with atrial fibrillation. Dabigatran is a direct thrombin inhibitor, similar to warfarin, without
Dabigatran (Pradaxa) Guidelines Dabigatran is a new anticoagulant for reducing the risk of stroke in patients with atrial fibrillation. Dabigatran is a direct thrombin inhibitor, similar to warfarin, without
How To Treat Aneuricaagulation
 Speaker Introduction Jessica Wilhoite, PharmD, BCACP Doctor of Pharmacy: Purdue University Postgraduate Residency Training: PGY1 Pharmacy Practice St. Vincent Hospital PGY2 Ambulatory Care St. Vincent
Speaker Introduction Jessica Wilhoite, PharmD, BCACP Doctor of Pharmacy: Purdue University Postgraduate Residency Training: PGY1 Pharmacy Practice St. Vincent Hospital PGY2 Ambulatory Care St. Vincent
0.9% Sodium Chloride injection may be used in most cases.
 Table 2. Alternatives to Heparin Sodium in Selected Situations 12-14 Situation Alternative Dose Maintain patency of peripheral venous catheters* 21-26 0.9% Sodium Chloride injection may be used in most
Table 2. Alternatives to Heparin Sodium in Selected Situations 12-14 Situation Alternative Dose Maintain patency of peripheral venous catheters* 21-26 0.9% Sodium Chloride injection may be used in most
New Anticoagulants for the Treatment of Thromboembolism With a little subplot on superficial thrombophlebitis. Mark Crowther
 New Anticoagulants for the Treatment of Thromboembolism With a little subplot on superficial thrombophlebitis Mark Crowther 1 Disclosures Advisory Boards in last 24 months Pfizer, Alexion, Bayer, CSL Behring,
New Anticoagulants for the Treatment of Thromboembolism With a little subplot on superficial thrombophlebitis Mark Crowther 1 Disclosures Advisory Boards in last 24 months Pfizer, Alexion, Bayer, CSL Behring,
Position Statement: The Use of VTED Prophylaxis in Foot and Ankle Surgery
 Position Statement: The Use of VTED Prophylaxis in Foot and Ankle Surgery Position Statement There is currently insufficient data for the (AOFAS) to recommend for or against routine VTED prophylaxis for
Position Statement: The Use of VTED Prophylaxis in Foot and Ankle Surgery Position Statement There is currently insufficient data for the (AOFAS) to recommend for or against routine VTED prophylaxis for
Prior Authorization Guideline
 Guideline Guideline Name Formulary Xarelto (rivaroxaban) UnitedHealthcare Community & State Approval Date 0/0/203 Revision Date 8//204 Technician Note: CPS Approval Date: /5/20; CPS Revision Date: 8/20/204
Guideline Guideline Name Formulary Xarelto (rivaroxaban) UnitedHealthcare Community & State Approval Date 0/0/203 Revision Date 8//204 Technician Note: CPS Approval Date: /5/20; CPS Revision Date: 8/20/204
Volume 7; Number 19 November 2013
 Greater East Midlands Commissioning Support Unit in association with Lincolnshire Clinical Commissioning Groups, Lincolnshire Community Health Services, United Lincolnshire Hospitals Trust and Lincolnshire
Greater East Midlands Commissioning Support Unit in association with Lincolnshire Clinical Commissioning Groups, Lincolnshire Community Health Services, United Lincolnshire Hospitals Trust and Lincolnshire
East Kent Prescribing Group
 East Kent Prescribing Group Rivaroxaban (Xarelto ) Safety Information Approved by the East Kent Prescribing Group. Approved by: East Kent Prescribing Group (Representing Ashford CCG, Canterbury and Coastal
East Kent Prescribing Group Rivaroxaban (Xarelto ) Safety Information Approved by the East Kent Prescribing Group. Approved by: East Kent Prescribing Group (Representing Ashford CCG, Canterbury and Coastal
Venous Thromboembolism: Long Term Anticoagulation. Dan Johnson, Pharm.D.
 Venous Thromboembolism: Long Term Anticoagulation Dan Johnson, Pharm.D. Disclosures No financial relationships with products discussed Off-label use of drug therapy always discussed Objectives Review clinical
Venous Thromboembolism: Long Term Anticoagulation Dan Johnson, Pharm.D. Disclosures No financial relationships with products discussed Off-label use of drug therapy always discussed Objectives Review clinical
Disclosure. New Agents for Treatment of DVT. Prevalence of DVT VTE. Normal Hemostasis 7/17/2015. Mark Oliver, MD, RVT, RPVI,FSVU
 New Agents for Treatment of DVT Disclosure PI Adopt and Amplify trials Mark Oliver, MD, RVT, RPVI,FSVU BMS and Pfizer Speaker VTE Venous Thromboembolism Recognized DVT s New : 170,000 Recurrent : 90,000
New Agents for Treatment of DVT Disclosure PI Adopt and Amplify trials Mark Oliver, MD, RVT, RPVI,FSVU BMS and Pfizer Speaker VTE Venous Thromboembolism Recognized DVT s New : 170,000 Recurrent : 90,000
Rivaroxaban for the treatment of deep vein thrombosis and prevention of recurrent deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism
 Implementation of NICE TA 261 Rivaroxaban for the treatment of deep vein thrombosis and prevention of recurrent deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism Contents 1. Executive summary 2. Introduction
Implementation of NICE TA 261 Rivaroxaban for the treatment of deep vein thrombosis and prevention of recurrent deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism Contents 1. Executive summary 2. Introduction
MEDICAL ASSISTANCE HANDBOOK PRIOR AUTHORIZATION OF PHARMACEUTICAL SERVICES. A. Prescriptions That Require Prior Authorization
 MEDICAL ASSISTANCE HBOOK PRI AUTHIZATION OF PHARMACEUTICAL SERVICES I. Requirements for Prior Authorization of Anticoagulants A. Prescriptions That Require Prior Authorization Prescriptions for Anticoagulants
MEDICAL ASSISTANCE HBOOK PRI AUTHIZATION OF PHARMACEUTICAL SERVICES I. Requirements for Prior Authorization of Anticoagulants A. Prescriptions That Require Prior Authorization Prescriptions for Anticoagulants
Venous and Lymphatic Disorders
 Venous and Lymphatic Disorders. ก. Venous and Lymphatic Disorders Varicose Veins Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) Lymphedema What Is Varicose Veins? Latin: Varicose = Varix = twisted Abnormal venous dilatation
Venous and Lymphatic Disorders. ก. Venous and Lymphatic Disorders Varicose Veins Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) Lymphedema What Is Varicose Veins? Latin: Varicose = Varix = twisted Abnormal venous dilatation
Three new/novel oral anticoagulants (NOAC) have been licensed in Ireland since 2008:
 Key Points to consider when prescribing NOACs Introduction Three new/novel oral anticoagulants (NOAC) have been licensed in Ireland since 2008: Dabigatran Etexilate (Pradaxa ) 75mg, 110mg, 150mg. Rivaroxaban
Key Points to consider when prescribing NOACs Introduction Three new/novel oral anticoagulants (NOAC) have been licensed in Ireland since 2008: Dabigatran Etexilate (Pradaxa ) 75mg, 110mg, 150mg. Rivaroxaban
6/19/2012. Update on Venous Thromboembolism Prophylaxis. Disclosure. Learning Objectives. No conflicts of interest to declare
 Update on Venous Thromboembolism Prophylaxis Disclosure No conflicts of interest to declare Learning Objectives After completion of this presentation, participants should be able to: Define venous thromboembolism,
Update on Venous Thromboembolism Prophylaxis Disclosure No conflicts of interest to declare Learning Objectives After completion of this presentation, participants should be able to: Define venous thromboembolism,
Breadth of indications matters One drug for multiple indications
 Breadth of indications matters One drug for multiple indications Sylvia Haas, MD, PhD Formerly of the Technical University of Munich Munich, Germany Disclosures: Sylvia Haas 1 Novel oral anticoagulants:
Breadth of indications matters One drug for multiple indications Sylvia Haas, MD, PhD Formerly of the Technical University of Munich Munich, Germany Disclosures: Sylvia Haas 1 Novel oral anticoagulants:
Investor News. Not intended for U.S. and UK media
 Investor News Not intended for U.S. and UK media Bayer AG Investor Relations 51368 Leverkusen Germany www.investor.bayer.com Bayer s Xarelto (Rivaroxaban) Approved for the Treatment of Pulmonary Embolism
Investor News Not intended for U.S. and UK media Bayer AG Investor Relations 51368 Leverkusen Germany www.investor.bayer.com Bayer s Xarelto (Rivaroxaban) Approved for the Treatment of Pulmonary Embolism
2.5mg SC daily. INR target 2-3 30 mg SC q 12 hr or 40mg daily. 10 mg PO q day (CrCl 30 ml/min). Avoid if < 30 ml/min. 2.
 Anticoagulation dosing at UCDMC (SC=subcutaneously; CI=continuous infusion) Indication Agent Dose Comments Prophylaxis Any or No bleeding risk factors see adult heparin (VTE prophylaxis) IV infusion order
Anticoagulation dosing at UCDMC (SC=subcutaneously; CI=continuous infusion) Indication Agent Dose Comments Prophylaxis Any or No bleeding risk factors see adult heparin (VTE prophylaxis) IV infusion order
Implementation of NICE TAs 261 and 287
 Corby Clinical Commissioning Group Kettering General Hospital NHS Trust Nene Clinical Commissioning Group Northampton General Hospital NHS Trust Northamptonshire Healthcare Foundation Trust Implementation
Corby Clinical Commissioning Group Kettering General Hospital NHS Trust Nene Clinical Commissioning Group Northampton General Hospital NHS Trust Northamptonshire Healthcare Foundation Trust Implementation
NEWER ANTICOAGULANTS: FOCUS ON STROKE PREVENTION IN ATRIAL FIBRILLATION AND DEEP VEIN THROMBOSIS/PULMONARY EMBOLISM
 NEWER ANTICOAGULANTS: FOCUS ON STROKE PREVENTION IN ATRIAL FIBRILLATION AND DEEP VEIN THROMBOSIS/PULMONARY EMBOLISM Carol Lee, Pharm.D., Jessica C. Song, M.A., Pharm.D. INTRODUCTION For many years, warfarin
NEWER ANTICOAGULANTS: FOCUS ON STROKE PREVENTION IN ATRIAL FIBRILLATION AND DEEP VEIN THROMBOSIS/PULMONARY EMBOLISM Carol Lee, Pharm.D., Jessica C. Song, M.A., Pharm.D. INTRODUCTION For many years, warfarin
Trust Guideline for Thromboprophylaxis in Trauma and Orthopaedic Inpatients
 A clinical guideline recommended for use In: By: For: Key words: Department of Orthopaedics, NNUHT Medical staff Trauma & Orthopaedic Inpatients Deep vein thrombosis, Thromboprophylaxis, Orthopaedic Surgery
A clinical guideline recommended for use In: By: For: Key words: Department of Orthopaedics, NNUHT Medical staff Trauma & Orthopaedic Inpatients Deep vein thrombosis, Thromboprophylaxis, Orthopaedic Surgery
3/25/14. To Clot or Not What s New In Anticoagulation? Clotting Cascade. Anticoagulant drug targets. Anita Ralstin, MS CNS CNP. Heparin.
 To Clot or Not What s New In Anticoagulation? Anita Ralstin, MS CNS CNP 1 Clotting Cascade 2 Anticoagulant drug targets Heparin XI VIII IX V X VII LMWH II Warfarin Fibrin clot 1 Who Needs Anticoagulation
To Clot or Not What s New In Anticoagulation? Anita Ralstin, MS CNS CNP 1 Clotting Cascade 2 Anticoagulant drug targets Heparin XI VIII IX V X VII LMWH II Warfarin Fibrin clot 1 Who Needs Anticoagulation
STARTING, SWITCHING OR STOPPING NEW ORAL ANTICOAGULANTS: A Practical Approach
 STARTING, SWITCHING OR STOPPING NEW ORAL ANTICOAGULANTS: A Practical Approach Jeffrey I Weitz, MD, FRCP(C), FACP Professor of Medicine and Biochemistry McMaster University Canada Research Chair in Thrombosis
STARTING, SWITCHING OR STOPPING NEW ORAL ANTICOAGULANTS: A Practical Approach Jeffrey I Weitz, MD, FRCP(C), FACP Professor of Medicine and Biochemistry McMaster University Canada Research Chair in Thrombosis
Paul G. Lee. 2 ND YEAR RESEARCH ELECTIVE RESIDENT S JOURNAL Volume III, 1998-1999. A. Objective
 A comparison of six months of anticoagulation with extended anticoagulation for a first episode of venous thromboembolism in patients with thrombophilia Paul G. Lee A. Objective a. To evaluate the risk
A comparison of six months of anticoagulation with extended anticoagulation for a first episode of venous thromboembolism in patients with thrombophilia Paul G. Lee A. Objective a. To evaluate the risk
Prevention of stroke and systemic embolism in adult patients with non-valvular atrial fibrillation (AF) with one or more risk factors
 News Release For use outside the US and UK only Bayer Pharma AG 13342 Berlin Germany Tel. +49 30 468-1111 www.bayerpharma.com Bayer s Xarelto Approved in the EU for the Prevention of Stroke in Patients
News Release For use outside the US and UK only Bayer Pharma AG 13342 Berlin Germany Tel. +49 30 468-1111 www.bayerpharma.com Bayer s Xarelto Approved in the EU for the Prevention of Stroke in Patients
Antithrombotic Therapy and Prevention of Thrombosis, 9 th Edition : ACCP Evidence-Based Clinical Practice Guidelines
 Deep Venous Thrombosis and Pulmonary Thromboembolic Disease: Are we practicing evidence-based medicine? The 2012 ACCP Guidelines and Beyond (Buzz Lightyear) Jeffrey L. Garland, MD, FCCP Associate Chair
Deep Venous Thrombosis and Pulmonary Thromboembolic Disease: Are we practicing evidence-based medicine? The 2012 ACCP Guidelines and Beyond (Buzz Lightyear) Jeffrey L. Garland, MD, FCCP Associate Chair
Preventing Blood Clots After Hip or Knee Replacement Surgery or Surgery for a Broken Hip. A Review of the Research for Adults
 Preventing Blood Clots After Hip or Knee Replacement Surgery or Surgery for a Broken Hip A Review of the Research for Adults Is This Information Right for Me? Yes, if: You are considering or planning to
Preventing Blood Clots After Hip or Knee Replacement Surgery or Surgery for a Broken Hip A Review of the Research for Adults Is This Information Right for Me? Yes, if: You are considering or planning to
Confirmed Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT)
 Confirmed Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) Information for patients What is deep vein thrombosis? Blood clotting provides us with essential protection against severe loss of blood from an injury to a vein or
Confirmed Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) Information for patients What is deep vein thrombosis? Blood clotting provides us with essential protection against severe loss of blood from an injury to a vein or
STROKE PREVENTION IN ATRIAL FIBRILLATION. TARGET AUDIENCE: All Canadian health care professionals. OBJECTIVE: ABBREVIATIONS: BACKGROUND:
 STROKE PREVENTION IN ATRIAL FIBRILLATION TARGET AUDIENCE: All Canadian health care professionals. OBJECTIVE: To guide clinicians in the selection of antithrombotic therapy for the secondary prevention
STROKE PREVENTION IN ATRIAL FIBRILLATION TARGET AUDIENCE: All Canadian health care professionals. OBJECTIVE: To guide clinicians in the selection of antithrombotic therapy for the secondary prevention
FDA Approved Oral Anticoagulants
 FDA Approved Oral Anticoagulants Generic (Trade Name) Warfarin (Coumadin, Jantoven ) 1 FDA approved indication Prophylaxis and treatment of venous thromboembolism (VTE) Prophylaxis and treatment of thromboembolic
FDA Approved Oral Anticoagulants Generic (Trade Name) Warfarin (Coumadin, Jantoven ) 1 FDA approved indication Prophylaxis and treatment of venous thromboembolism (VTE) Prophylaxis and treatment of thromboembolic
Session 3 Topics. Argatroban. Argatroban. Drug Use and Adverse Effects. Laboratory Monitoring of Anticoagulant Therapy
 ~~Marshfield Labs Presents~~ Laboratory Monitoring of Anticoagulant Therapy Session 3 of 4 Michael J. Sanfelippo, M.S. Technical Director, Coagulation Services Session 3 Topics Direct Thrombin Inhibitors:
~~Marshfield Labs Presents~~ Laboratory Monitoring of Anticoagulant Therapy Session 3 of 4 Michael J. Sanfelippo, M.S. Technical Director, Coagulation Services Session 3 Topics Direct Thrombin Inhibitors:
Clinical Investigations
 Clinical Investigations Safe-Dose Thrombolysis Plus Rivaroxaban for Moderate and Severe Pulmonary Embolism: Drip, Drug, and Discharge Address for correspondence: Mohsen Sharifi, MD, Arizona Cardiovascular
Clinical Investigations Safe-Dose Thrombolysis Plus Rivaroxaban for Moderate and Severe Pulmonary Embolism: Drip, Drug, and Discharge Address for correspondence: Mohsen Sharifi, MD, Arizona Cardiovascular
A PATIENT S GUIDE TO PULMONARY EMBOLISM TREATMENT
 A PATIENT S GUIDE TO PULMONARY EMBOLISM TREATMENT This medicine is subject to additional monitoring. This will allow quick identification of new safety information. If you get any side effects, talk to
A PATIENT S GUIDE TO PULMONARY EMBOLISM TREATMENT This medicine is subject to additional monitoring. This will allow quick identification of new safety information. If you get any side effects, talk to
Inpatient Anticoagulation Safety. To provide safe and effective anticoagulation therapy through a collaborative approach.
 Inpatient Anticoagulation Safety Purpose: Policy: To provide safe and effective anticoagulation therapy through a collaborative approach. Upon the written order of a physician, Heparin, Low Molecular Weight
Inpatient Anticoagulation Safety Purpose: Policy: To provide safe and effective anticoagulation therapy through a collaborative approach. Upon the written order of a physician, Heparin, Low Molecular Weight
CDEC FINAL RECOMMENDATION
 CDEC FINAL RECOMMENDATION RIVAROXABAN (Xarelto Bayer Inc.) New Indication: Pulmonary Embolism Note: The Canadian Drug Expert Committee (CDEC) previously reviewed rivaroxaban for the treatment of deep vein
CDEC FINAL RECOMMENDATION RIVAROXABAN (Xarelto Bayer Inc.) New Indication: Pulmonary Embolism Note: The Canadian Drug Expert Committee (CDEC) previously reviewed rivaroxaban for the treatment of deep vein
DATE: 06 May 2013 CONTEXT AND POLICY ISSUES
 TITLE: Low Molecular Weight Heparins versus New Oral Anticoagulants for Long-Term Thrombosis Prophylaxis and Long-Term Treatment of DVT and PE: A Review of the Clinical and Cost-Effectiveness DATE: 06
TITLE: Low Molecular Weight Heparins versus New Oral Anticoagulants for Long-Term Thrombosis Prophylaxis and Long-Term Treatment of DVT and PE: A Review of the Clinical and Cost-Effectiveness DATE: 06
Cardiovascular Disease
 Cardiovascular Disease 1 Cardiovascular Disease 1. More target specific oral anticoagulants (TSOAC) 2. Vorapaxar (Zonivity) 3. Continued noise about a polypill 4. WATCHMAN 3 1 2 3 4 Left Atrial Appendage
Cardiovascular Disease 1 Cardiovascular Disease 1. More target specific oral anticoagulants (TSOAC) 2. Vorapaxar (Zonivity) 3. Continued noise about a polypill 4. WATCHMAN 3 1 2 3 4 Left Atrial Appendage
The Role of the Newer Anticoagulants
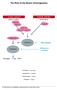 The Role of the Newer Anticoagulants WARFARIN = Coumadin DAGIBATRAN = Pradaxa RIVAROXABAN = Xarelto APIXABAN = Eliquis INDICATION DABIGATRAN (Pradaxa) RIVAROXABAN (Xarelto) APIXABAN (Eliquis) Stroke prevention
The Role of the Newer Anticoagulants WARFARIN = Coumadin DAGIBATRAN = Pradaxa RIVAROXABAN = Xarelto APIXABAN = Eliquis INDICATION DABIGATRAN (Pradaxa) RIVAROXABAN (Xarelto) APIXABAN (Eliquis) Stroke prevention
New Anticoagulants: When and Why Should I Use Them? Disclosures
 Winship Cancer Institute of Emory University New Anticoagulants: When and Why Should I Use Them? Christine L. Kempton, MD, MSc Associate Professor of Pediatrics and Hematology and Medical Oncology Hemophilia
Winship Cancer Institute of Emory University New Anticoagulants: When and Why Should I Use Them? Christine L. Kempton, MD, MSc Associate Professor of Pediatrics and Hematology and Medical Oncology Hemophilia
Rivaroxaban for the treatment of deep vein thrombosis and prevention of recurrent deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism
 Rivaroxaban for the treatment of deep vein thrombosis and prevention of recurrent deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary Issued: July 2012 guidance.nice.org.uk/ta NHS Evidence has accredited the process used
Rivaroxaban for the treatment of deep vein thrombosis and prevention of recurrent deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary Issued: July 2012 guidance.nice.org.uk/ta NHS Evidence has accredited the process used
Backgrounder. Current anticoagulant therapies
 Backgrounder Bayer AG Investor Relations 51368 Leverkusen Germany www.investor.bayer.com Current anticoagulant therapies Anticoagulant drugs have significantly reduced the risk of thromboembolic events
Backgrounder Bayer AG Investor Relations 51368 Leverkusen Germany www.investor.bayer.com Current anticoagulant therapies Anticoagulant drugs have significantly reduced the risk of thromboembolic events
xaban) Policy covered: Coverage of following criteria: the following those who meet the or Hip Xarelto is For those impacted by this policy.
 Xarelto (rivarox xaban) Policy Number: 5.01.575 Origination: 06/2014 Last Review: 07/2015 Next Review: 07/2016 Policy BCBSKC will provide coverage for Xarelto when it is determined to be medically necessary
Xarelto (rivarox xaban) Policy Number: 5.01.575 Origination: 06/2014 Last Review: 07/2015 Next Review: 07/2016 Policy BCBSKC will provide coverage for Xarelto when it is determined to be medically necessary
Novel Anticoagulation Agents DISCLOSURES. Objectives ATRIAL FIBRILLATION TRIALS. NOAC Comparison 6/12/2015
 Novel Anticoagulation Agents DISCLOSURES James W. Haynes, MD Department of Family Medicine Univ of TN Health Science Center (Chattanooga) Objectives Understand mechanism of action behind the NOAC agents
Novel Anticoagulation Agents DISCLOSURES James W. Haynes, MD Department of Family Medicine Univ of TN Health Science Center (Chattanooga) Objectives Understand mechanism of action behind the NOAC agents
Rivaroxaban A new oral anti-thrombotic Dr. Hisham Aboul-Enein Professor of Cardiology Benha University 12/1/2012
 Rivaroxaban A new oral anti-thrombotic Dr. Hisham Aboul-Enein Professor of Cardiology Benha University 12/1/2012 Agenda Ideal anticoagulant. Drawbacks of warfarin. Rivaroxaban in clinical trails. Present
Rivaroxaban A new oral anti-thrombotic Dr. Hisham Aboul-Enein Professor of Cardiology Benha University 12/1/2012 Agenda Ideal anticoagulant. Drawbacks of warfarin. Rivaroxaban in clinical trails. Present
Horton General Hospital Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) and Pulmonary Embolism (PE) Information for patients
 Horton General Hospital Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) and Pulmonary Embolism (PE) Information for patients What is a Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT)? A DVT is a blood clot which forms in a deep vein, usually in
Horton General Hospital Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) and Pulmonary Embolism (PE) Information for patients What is a Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT)? A DVT is a blood clot which forms in a deep vein, usually in
Management for Deep Vein Thrombosis and New Agents
 Management for Deep Vein Thrombosis and New Agents Mark Malesker, Pharm.D., FCCP, FCCP, FASHP, BCPS Professor of Pharmacy Practice and Medicine Creighton University 5 th Annual Creighton Cardiovascular
Management for Deep Vein Thrombosis and New Agents Mark Malesker, Pharm.D., FCCP, FCCP, FASHP, BCPS Professor of Pharmacy Practice and Medicine Creighton University 5 th Annual Creighton Cardiovascular
