An infection of the urinary tract commonly has the following symptoms:
|
|
|
- Roy Wilcox
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Bacteria in Urine Urine in the healthy bladder is normally free of bacteria. However, bacteria from the rectal area may enter the urinary tract through the urethra and travel the short distance to the bladder. While normally the bladder cleanses itself of bacteria, if for some reason it cannot, the bacteria may cause an infection. About 80 percent to 90 percent of urinary tract infections are caused by Escherichia coli (E. coli) bacteria, which are normally present in the rectum. A urinary tract infection can be a variety of conditions, including cystitis (infection of the bladder) and urethritis (infection of the urethra). Other conditions such as vaginitis and irritable bladder (similar to irritable bowel disorder) may produce similar symptoms. Symptoms An infection of the urinary tract commonly has the following symptoms: Frequent and urgent need to urinate Painful urination Cloudy urine Lower back or abdominal pain Blood in the urine If you have these symptoms for more than 24 hours, you should see your doctor. Fever, chills, nausea and vomiting, and pain in the midback may indicate a kidney infection. If you have these symptoms, you should seek immediate medical treatment. Causes Women are eight times more likely to get a UTI than men. Part of the problem may be that bacteria have a much shorter distance to travel in women. The female urethra, leading from the outside of the body to the bladder, is roughly one and a half inches long. In 1
2 contrast, the male urethra is roughly eight inches in length. Another contributing factor is the female urethra's location. As it is so close to the vagina and the anus, it is much easier for bacteria to enter the urethra and work its way up into the bladder. While children may get UTIs, most sufferers are adult women. Approximately 25 percent of women are estimated to have had at least one urinary tract infection in their lifetime. Many will have several. Infections are frequently related to sexual activity. They also may occur during pregnancy because of hormone fluctuations and increased pressure on the bladder. If left untreated, the infection can harm the fetus. The occurrence of UTIs also can increase after menopause when breakdown in vaginal tissues begins to occur due to a decrease in estrogen levels. Some factors that may contribute to urinary tract infections are: Sexual activity: Sexual intercourse may facilitate the transfer of bacteria from the anal-vaginal area to the urethra and thus to the bladder. It may also irritate tissues, making them more susceptible to infection. Birth control methods: If your diaphragm is not fitted properly, it may place pressure on the bladder and thus increase your chances of infection. The chemicals in spermicides may irritate vaginal tissues and make them more susceptible to infection. Low water intake: If your water intake is low, you will urinate less frequently. Bacteria that enter the bladder have more time to multiply and to take hold, causing an infection. Anatomical problem: A small percentage of women may have some kind of anatomical problem that would predispose them to UTIs. Your doctor will be able to determine from your medical history, a physical exam, and simple tests whether this is the cause of your infections. 2
3 Preventing UTIs There is no proven way to prevent UTIs, but you may find some of the following suggestions helpful: Drink plenty of liquids to flush bacteria out of your system. Wipe from the vagina to the anus after urinating to avoid spreading bacteria. Schedule frequent bathroom breaks. Drink water before and after sex so that you will urinate a good volume with a steady stream afterward. This will help eliminate any bacteria that may have entered. Consider checking the fit of your diaphragm or using another method of birth control. If you continue to use a diaphragm, leave it in no longer than necessary for contraception. Avoid tight clothing and pantyhose. They may irritate tissues, trap heat and promote bacterial growth. Wear cotton underwear. Cotton is less irritating and provides more ventilation than nylon. Treatment The first step is to confirm a bacterial infection by reviewing your symptoms and testing your urine. It is important to have the infection diagnosed by a urine culture, as several other conditions, such as a vaginal infection, gonorrhea, chlamydia, irritable bladder, and bladder cancer, have similar symptoms. When pain is the predominant symptom, your doctor may consider a diagnosis of interstitial cystitis. If a culture shows that there are bacteria in your urine, your doctor will prescribe a course of antibiotics that should take care of the problem. Several different antibiotics are used to treat uncomplicated infections. You may be given a regimen of one to three days if this is your first infection. Taking antibiotics for seven to 10 days also is customary for recurrent infections. It is important to continue taking 3
4 the medication until it is finished, even though your symptoms may be gone after a few days. Your doctor also may prescribe a urinary analgesic, such as phenazopyridine, for the pain. There are several other steps you can take to make yourself more comfortable: Drink large amounts of water. It will help flush the bacteria out of your system (about 8 ounces an hour). Put one teaspoon of baking soda in one-half cup of water once or twice a day. Avoid caffeine, acid foods, spices, citrus fruits, tomatoes, alcohol, and chocolate. You may find these things increase your discomfort. Drink cranberry juice cocktail. A study conducted on older women published in the Journal of the American Medical Association suggests that drinking cranberry juice cocktail may reduce the amount of bacteria in your urine. Try hot water bottles or heating pads. They may ease your cramps and soothe the pain. What is asymptomatic bacteriuria? Asymptomatic bacteriuria is a condition in which bacteria are in your urine, but you have no symptoms of infection. How does it occur? Urine is normally sterile, which means that it contains no bacteria. A small number of bacteria may be found in the urine of many healthy people. This is usually considered to be harmless. However, a certain level of bacteria can mean that the bladder, urethra, or kidneys are infected. Anything that blocks the flow of urine or prevents the bladder from emptying completely can cause bacteria to grow in the urine. For 4
5 example, a stone or tumor might block the flow of urine. Prostate enlargement in men might also cause such a block. This problem occurs more often in women than men because a woman's urethra is shorter. (The urethra is the tube that empties the bladder.) The short urethra makes it easier for bacteria from the anus or genital area to reach the bladder. This can happen during such activities as wiping or sexual intercourse. Most infections of the urinary tract are caused this way. Bacteria can also enter the urine through the bloodstream, but this is rare. If you are healthy, asymptomatic bacteriuria is usually not a problem and usually does not require treatment. However, in some cases it is more likely to lead to a kidney infection; for example, if you are pregnant or have diabetes. What are the symptoms? Asymptomatic bacteriuria has no obvious symptoms. How is it diagnosed? Urine samples will be tested for bacteria. You may also have some blood tests. If you have bacteria in your urine you may have: more blood tests a special x-ray of the kidneys called an intravenous pyelogram (IVP) an ultrasound scan. The IVP and ultrasound scan can show problems in the urinary tract. How is it treated? Your health care provider may or may not prescribe an antibiotic. If you are healthy and do not have any underlying problems, you will 5
6 probably not be prescribed an antibiotic. If, however, you have a medical condition that puts you at a higher risk of developing a kidney infection from asymptomatic bacteriuria, you will be prescribed an antibiotic. These high-risk conditions are: pregnancy (asymptomatic bacteriuria may also cause you to go into labor too early) diabetes kidney stones kidney transplant advanced age. You may need to return to your provider's office after you have taken all of the antibiotic to have your urine tested again. Your provider may recommend testing your urine regularly to see if the problem happens again. In some cases, regular urine testing rather than antibiotic treatment may be the best course. Your provider will determine what treatment is best for you. How long will the effects last? Asymptomatic bacteriuria usually clears up after treatment with antibiotics. However, it can come back. If this problem is not treated, it could become a full-blown urinary tract infection. If the infection is not then treated with antibiotics, the kidneys could be damaged. How can I take care of myself? If you were prescribed an antibiotic, take all of it as prescribed, even if you have no symptoms. Do not take medicine left over from previous infections. Drink plenty of water each day to cleanse the bladder and urinary tract. 6
7 Follow your health care provider's recommendation for followup urine testing to check for recurrence. What can be done to help prevent asymptomatic bacteriuria? Women can take the following steps to help prevent a bladder infection from recurring: Drink plenty of fluids. Urinate regularly during the day. Empty your bladder completely each time. Keep the vaginal area clean. Wipe from front to back after a bowel movement. Urinate before and after intercourse. Wear cotton underwear, which allows better air circulation than nylon. Wear pantyhose that have a cotton crotch. Avoid tight clothes in the genital area, such as control-top pantyhose and tight jeans. Do not wear a wet bathing suit for long periods of time. About 15 to 25 percent of women with diabetes mellitus have bacteria in their urine without having symptoms of a urinary tract infection as frequency or dysuria (asymptomatic bacteriuria). It is known that women who have asymptomatic bacteriuria (ASB) do not necessarily have an increased risk for a faster decline in renal function. It was reported that women with diabetes type 1 (diabetes of the youth ) and ASB showed a tendency to a faster decline in renal function than women without ASB after 18 months, but this difference was small and not statistically significant. What are the long-term consequences of ASB on renal function in diabetic women? Chronic kidney disease is an increasing public health problem. Diabetes is one of the main causes of kidney disease and end-stage renal failure, in the United States it is the primary diagnosis in 44% of the cases. Vascular complications are the most common 7
8 cause of diabetic nephropathy, but it is possible that urinary tract infections also contribute to renal insufficiency in diabetic patients. Bacteria, especially Escherichia coli, can damage renal cells. Since women with diabetes mellitus are more susceptible for both urinary tract infections and for renal insufficiency, it was important to know whether diabetic women who have bacteria in their bladder have an increased risk for a faster decline in renal function than women with sterile urine, especially because most women have no symptoms of this infection and do not visit a doctor for it. 17% of women who had bacteria in their urine do not have symptoms of a urinary tract infection. In the multivariate analysis, in which other variables were included that can influence the presence of bacteria in urine, namely age, length of follow-up, duration of diabetes, and microalbuminuria (low concentration of protein in urine), no association was found between ASB and the relative or the absolute decrease in renal function. It was concluded that women with diabetes (type 1 or type 2) with bacteria in their urine do not have a higher risk on renal function deterioration. This has clinical significant implications. Before the results of this study were demonstrated, it was not known whether these bacteria could harm the patient, and could lead to damage of the kidneys. The problem is that renal function decline can develop while the patient is not aware of it. It is only when the patient has end-stage renal failure (when it is already too late to prevent it), will he/she visit a doctor. Urine breeds bacteria Yeast infections are caused by the Candida species of fungi. Some members of this species are normally found among the native bacterial colonies in the mouth, gastrointestinal tract, and vagina. The native bacteria and immune system prevent overgrowth of these bacteria. However, Candida may grow excessively in individuals whose immune systems are compromised, such as AIDS or diabetes patients. Some conditions that result from Candida overgrowth are thrush, a mouth infection; esophagitis, spreading of mouth fungus to 8
9 the esophagus; skin infections; vaginal yeast infections, or deep candidiasis, where fungi contaminate the bloodstream. Over a lifetime, 75 percent of women are likely to have had at least one vaginal Candida infection. Pregnancy or diabetes may put a woman at higher risk of a vaginal yeast infection. Normally, a short treatment with antifungal medication can eliminate the yeast infection in cases where the infection has not spread to the bloodstream or the individual's immune system is strong. The low presence of niacin, a water-soluble vitamin that is part of the vitamin B complex, helps yeast stick to the urinary tract. Niacin, also known as nicotinic acid, is normally found in low levels in urine. Yeast in the Candida glabrata family, which cause blood and mucosal tissue infection, produce a family of proteins known as sirtuins in the presence of niacin. C.glabrata cannot make niacin, so it has be imported from the environment. Sirtuin blocks the expression of adhesion proteins, which are translated from EPA genes. The sirtuin family proteins attach near the tips of chromosomes, obstructing nearby genes. EPA genes are found near the ends of chromosomes, so sirtuin expression blocks the production of adhesion proteins. Yeast without sirtuin genes exhibited higher levels of adhesion to mucosal tissue. The present study shows that normally silenced EPA genes are expressed in cases of murine urinary tract infection. Yeast in the urinary tract have a limited amount of NAD+, which is derived from nicotinic acid. Low levels of NAD+ prevent the activation of mechanisms that turn on sirtuin expression. Low sirtuin levels allow EPA genes for adhesion molecules to be expressed. According to Dr. Cormack, "this particular yeast has in some sense committed to living with the human host and so it takes advantage of us to provide certain key nutrients." These C.glabrata become drug resistant when EPA genes are turned on, so drug resistance would indicate the expression of EPA genes. 9
10 In the study, drug resistance did not develop in blood; this indicates that low niacin in the urine, compared to high niacin in the blood, creates a more favorable environment for yeast to expression adhesion proteins. C.glabrata is the common culprit in cases of infection in patients with urinary catheters. Dr. Cormack warns, "It is not know whether niacin supplements might help prevent these catheter infections, or whether the plastic could be treated somehow to reduce the organism's ability to bind to it. But there can be significant liver toxicity associated with niacin supplements, so the question would have to be studied very carefully." Tests are used to diagnose a urinary tract infection (UTI). A urine culture may be ordered when symptoms indicate the possibility of a urinary tract infection, such as pain and burning when urinating and frequent urge to urinate. Antibiotic therapy may be prescribed without requiring a urine culture for symptomatic young women, who have an uncomplicated lower urinary tract infection. If there is suspicion of a complicated infection, or symptoms do not respond to initial therapy, then a culture of the urine is recommended. Pregnant women without any symptoms may be screened for bacteria in their urine, which could affect the health and development of the fetus. If the skin and genital area were not cleaned well prior to collecting the sample, the urine culture may grow three or more different types of bacteria and is assumed to be contaminated. The culture will be discarded because it cannot be determined if the bacteria originated inside or outside the urinary tract. A contaminated specimen can be avoided by following the directions to carefully clean yourself and by collecting a mid-stream clean catch urine sample. The reason is because bacteria known as Eschericia coli (E. coli) cause the majority of lower urinary tract infections. This organism is usually 10
11 susceptible to a variety of antibiotics, such as trimethoprimsulfamethoxazole, ciprofloxacin, and nitrofurantoin. In most patients with uncomplicated disease, the UTI will be resolved after empiric therapy with one of these antibiotics. If your infection is not treated, it can move from the lower urinary tract to the upper urinary tract and infect the kidney itself, and possibly, enter the bloodstream, causing septicemia. Symptoms of septicemia include fever, chills, elevated white blood cell count, and fatigue. Your doctor will often use blood cultures to determine if you have septicemia and will prescribe antibiotics accordingly. There are a wide variety of factors that predispose a person to acquire a UTI. After the neonatal period, the incidence in females is higher than in males due to the anatomical differences in the female genitourinary tract. In infants and young children, congenital abnormalities are associated with UTI. In adults, sexual intercourse, diaphragm use, diabetes, pregnancy, reflux, neurologic dysfunction, renal stones, and tumors all predispose to UTI. In a hospital, nursing home, or home care setting, indwelling catheters and instrumentation of the urinary tract are major contributing factors to acquiring a UTI What does the test result mean? The presence of a single type of bacteria growing at high colony counts (greater than 10,000 colony forming units (CFU)/ml) is considered a positive urine culture. A culture that is reported as no growth in 24 or 48 hours or less than 10,000 CFU/ml usually indicates that there is no infection. If the symptoms persist, however, the culture may be repeated to look for the presence of bacteria at lower colony counts (less than 10,000 CFU/ml) or other microorganisms that may cause these symptoms. The presence of white blood cells and low numbers of microorganisms in a symptomatic patient is a condition known as acute urethral syndrome. 11
12 If a culture shows growth of several different types of bacteria, then it is likely that the growth is due to contamination. This is especially true if the organisms present include Lactobacillus and common nonpathogenic vaginal bacteria in women. If the symptoms persist, the doctor may request a repeat culture on a sample that is more carefully collected. The presence of a significant amount of a single type of bacteria usually indicates an infection. Susceptibility testing is performed to guide antimicrobial treatment. Any bacterial infection may be serious and can spread to other areas of the body if not treated. Since pain is often the first indicator of an infection, prompt treatment, usually with antibiotics, will help to alleviate the pain. Females get UTIs more often than males. Even school-age females may have frequent UTIs. For males with a culture-proven UTI, the doctor may order further tests to rule out the presence of a kidney stone or structural abnormality that could cause the infection. If there is recurrent urinary tract infections, culture and susceptibility testing may be performed with each episode. For patients who have frequent UTIs, their bacteria may become resistant to antibiotics over time, making careful selection of antibiotic (and the full course of treatment) essential. Those with kidney disease and/or with diseases that affect the kidneys, such as diabetes and those with compromised immune systems may be more prone to recurring UTIs. 12
Urinary Tract Infections
 1 Infections in the urinary tract are relatively common. These infections are often referred to as bladder infections. They are also known as UTI s or urinary tract infections. When an infection is confined
1 Infections in the urinary tract are relatively common. These infections are often referred to as bladder infections. They are also known as UTI s or urinary tract infections. When an infection is confined
Have a shower, rather than a bath to avoid exposing your genitals to the chemicals in your cleaning products for too long. Always empty your bladder
 Cystitis, Avenue Medical Practice Neat Guideline Introduction Cystitis means 'inflammation of the bladder'. It causes: an urgent and frequent need to urinate, and Pain, or stinging, when passing urine.
Cystitis, Avenue Medical Practice Neat Guideline Introduction Cystitis means 'inflammation of the bladder'. It causes: an urgent and frequent need to urinate, and Pain, or stinging, when passing urine.
Riesa Gusewelle, MNSc, RN, APRN, GNP-BC. OBJECTIVES Identify early warning signs of urinary tract
 Detection, Early Management & Prevention, of Urinary Tract Infections in Older Adults Riesa Gusewelle, MNSc, RN, APRN, GNP-BC OBJECTIVES Identify early warning signs of urinary tract infections (UTIs)
Detection, Early Management & Prevention, of Urinary Tract Infections in Older Adults Riesa Gusewelle, MNSc, RN, APRN, GNP-BC OBJECTIVES Identify early warning signs of urinary tract infections (UTIs)
Urinary Tract Infections
 Urinary Tract Infections www.kidney.org Did you know that... n Urinary tract infections (UTIs) are responsible for nearly 10 million doctor visits each year. n One in five women will have at least one
Urinary Tract Infections www.kidney.org Did you know that... n Urinary tract infections (UTIs) are responsible for nearly 10 million doctor visits each year. n One in five women will have at least one
Palm Beach Obstetrics & Gynecology, PA
 Palm Beach Obstetrics & Gynecology, PA 4671 S. Congress Avenue, Lake Worth, FL 33461 561.434.0111 4631 N. Congress Avenue, Suite 102, West Palm Beach, FL 33407 Urinary Tract Infection About one of every
Palm Beach Obstetrics & Gynecology, PA 4671 S. Congress Avenue, Lake Worth, FL 33461 561.434.0111 4631 N. Congress Avenue, Suite 102, West Palm Beach, FL 33407 Urinary Tract Infection About one of every
THE KIDNEY. Bulb of penis Abdominal aorta Scrotum Adrenal gland Inferior vena cava Urethra Corona glandis. Kidney. Glans penis Testicular vein
 29 THE KIDNEY 9. Recurrent urinary tract infections Recurrent urinary tract infections The urinary tract consists of the urethra, the bladder, the ureters, the kidneys and in men the prostate gland. An
29 THE KIDNEY 9. Recurrent urinary tract infections Recurrent urinary tract infections The urinary tract consists of the urethra, the bladder, the ureters, the kidneys and in men the prostate gland. An
Understanding and Preventing Bladder Infections in Women
 Understanding and Preventing Bladder Infections in Women Understanding and Preventing Bladder Infections in Women Recurrent bladder or urinary tract infections (UTI s) are a very common diagnosis. In fact,
Understanding and Preventing Bladder Infections in Women Understanding and Preventing Bladder Infections in Women Recurrent bladder or urinary tract infections (UTI s) are a very common diagnosis. In fact,
Childhood Urinary Tract Infections
 Childhood Urinary Tract Infections What is a UTI? Urinary tract infection (UTI) is one of the most common infections in childhood. It can cause distress to the child, concerns to the parents, and may
Childhood Urinary Tract Infections What is a UTI? Urinary tract infection (UTI) is one of the most common infections in childhood. It can cause distress to the child, concerns to the parents, and may
Urinary Tract Infections in Children
 Urinary Tract Infections in Children National Kidney and Urologic Diseases Information Clearinghouse National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH Urinary
Urinary Tract Infections in Children National Kidney and Urologic Diseases Information Clearinghouse National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH Urinary
URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS IN YOUNG WOMEN
 URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS IN YOUNG WOMEN Reviewed by Finnish Centre for Health Promotion Publisher: Ylioppilaiden terveydenhoitosäätiö Töölönkatu 37 A 00260 Helsinki Orders: julkaisutilaukset@yths.fi Author:
URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS IN YOUNG WOMEN Reviewed by Finnish Centre for Health Promotion Publisher: Ylioppilaiden terveydenhoitosäätiö Töölönkatu 37 A 00260 Helsinki Orders: julkaisutilaukset@yths.fi Author:
Problems of the Digestive System
 The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists f AQ FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS FAQ120 WOMEN S HEALTH Problems of the Digestive System What are some common digestive problems? What is constipation?
The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists f AQ FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS FAQ120 WOMEN S HEALTH Problems of the Digestive System What are some common digestive problems? What is constipation?
Spinal Cord and Bladder Management Male: Intermittent Catheter
 Spinal Cord and Bladder Management Male: Intermittent Catheter The 5 parts of the urinary system work together to get rid of waste and make urine. Urine is made in your kidneys and travels down 2 thin
Spinal Cord and Bladder Management Male: Intermittent Catheter The 5 parts of the urinary system work together to get rid of waste and make urine. Urine is made in your kidneys and travels down 2 thin
Bladder Health Promotion
 Bladder Health Promotion Community Awareness Presentation Content contributions provided by the Society of Urologic Nurses (SUNA) National Association for Continence (NAFC) Simon Foundation for Continence
Bladder Health Promotion Community Awareness Presentation Content contributions provided by the Society of Urologic Nurses (SUNA) National Association for Continence (NAFC) Simon Foundation for Continence
Self Catheterization Guide
 Self Catheterization Guide An introduction to intermittent self-catheterization Medical professionals have recommended that you selfcatheterize in order to completely empty your bladder. This prevents
Self Catheterization Guide An introduction to intermittent self-catheterization Medical professionals have recommended that you selfcatheterize in order to completely empty your bladder. This prevents
Blood in the urine (hematuria)
 Blood in the urine (hematuria) Hematuria refers to the presence of blood in the urine. It is important to investigate the cause of hematuria because rarely, it is caused by a serious condition, such as
Blood in the urine (hematuria) Hematuria refers to the presence of blood in the urine. It is important to investigate the cause of hematuria because rarely, it is caused by a serious condition, such as
Urinary Tract Infections
 Urinary Tract Infections Overview A urine culture must ALWAYS be interpreted in the context of the urinalysis and patient symptoms. If a patient has no signs of infection on urinalysis, no symptoms of
Urinary Tract Infections Overview A urine culture must ALWAYS be interpreted in the context of the urinalysis and patient symptoms. If a patient has no signs of infection on urinalysis, no symptoms of
A PRINTED copy of this guideline may not be the most recent version. The OFFICIAL version is located on IHNET at the Policies & Procedures Home Page
 A PRINTED copy of this guideline may not be the most recent version. The OFFICIAL version is located on IHNET at the Policies & Procedures Home Page IX0200: Prevention & Control of Catheter Associated
A PRINTED copy of this guideline may not be the most recent version. The OFFICIAL version is located on IHNET at the Policies & Procedures Home Page IX0200: Prevention & Control of Catheter Associated
Recognizing Signs and Symptoms of a Urinary Tract Infection (UTI)
 Use this checklist to help identify signs and symptoms of a or other illnesses. If the person you support has one or more of these signs and symptoms, call the doctor for advice and a medical appointment.
Use this checklist to help identify signs and symptoms of a or other illnesses. If the person you support has one or more of these signs and symptoms, call the doctor for advice and a medical appointment.
Female Reproductive System. Unit 8 Lesson 2 Continued
 Female Reproductive System Unit 8 Lesson 2 Continued Female Reproductive System Female Reproductive System Female produce ovum or egg cells. The egg (ovum) cell is the female sex cell. Female Reproductive
Female Reproductive System Unit 8 Lesson 2 Continued Female Reproductive System Female Reproductive System Female produce ovum or egg cells. The egg (ovum) cell is the female sex cell. Female Reproductive
A Practical Guide to Diagnosis and Treatment of Infection in the Outpatient Setting Diagnosis and Treatment of Urinary Tract Infections
 A Practical Guide to Diagnosis and Treatment of Infection in the Outpatient Setting Diagnosis and Treatment of Urinary Tract Infections By Gary R. Skankey, MD, FACP, Infectious Disease, Las Vegas, NV Sponsored
A Practical Guide to Diagnosis and Treatment of Infection in the Outpatient Setting Diagnosis and Treatment of Urinary Tract Infections By Gary R. Skankey, MD, FACP, Infectious Disease, Las Vegas, NV Sponsored
Thrush and Bacterial vaginosis. Looking after your sexual health
 Thrush and Bacterial vaginosis Looking after your sexual health 2 Thrush and Bacterial vaginosis Thrush is an infection that is caused by a yeast fungus. It is not a sexually transmitted infection but
Thrush and Bacterial vaginosis Looking after your sexual health 2 Thrush and Bacterial vaginosis Thrush is an infection that is caused by a yeast fungus. It is not a sexually transmitted infection but
URINARY TRACT INFECTION IN BABIES AND PRE-SCHOOL CHILDREN
 URINARY TRACT INFECTION IN BABIES AND PRE-SCHOOL CHILDREN Information Leaflet Your Health. Our Priority. Page 2 of 5 What is the Urinary Tract? The urinary tract consists of the kidneys and the tubes which
URINARY TRACT INFECTION IN BABIES AND PRE-SCHOOL CHILDREN Information Leaflet Your Health. Our Priority. Page 2 of 5 What is the Urinary Tract? The urinary tract consists of the kidneys and the tubes which
Pyelonephritis: Kidney Infection
 Pyelonephritis: Kidney Infection National Kidney and Urologic Diseases Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH What is pyelonephritis? Pyelonephritis
Pyelonephritis: Kidney Infection National Kidney and Urologic Diseases Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH What is pyelonephritis? Pyelonephritis
Leader's Resource. Note: Both men and women can have an STD without physical symptoms.
 Leader's Resource Information on Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STDs) Signs and Symptoms of STDs Note: Both men and women can have an STD without physical symptoms. Any of the following can indicate to
Leader's Resource Information on Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STDs) Signs and Symptoms of STDs Note: Both men and women can have an STD without physical symptoms. Any of the following can indicate to
Bowel Control Problems
 Bowel Control Problems WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 Bowel control problems affect at least 1 million people in the United States. Loss of normal control of the bowels is
Bowel Control Problems WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 Bowel control problems affect at least 1 million people in the United States. Loss of normal control of the bowels is
Bladder Health Promotion
 Bladder Health Promotion Community Awareness Presentation endorsed by the Society of Urologic Nurses (SUNA) National Association for Continence( NAFC) Simon Foundation for Continence This presentation
Bladder Health Promotion Community Awareness Presentation endorsed by the Society of Urologic Nurses (SUNA) National Association for Continence( NAFC) Simon Foundation for Continence This presentation
Nursing college, Second stage Microbiology Dr.Nada Khazal K. Hendi L14: Hospital acquired infection, nosocomial infection
 L14: Hospital acquired infection, nosocomial infection Definition A hospital acquired infection, also called a nosocomial infection, is an infection that first appears between 48 hours and four days after
L14: Hospital acquired infection, nosocomial infection Definition A hospital acquired infection, also called a nosocomial infection, is an infection that first appears between 48 hours and four days after
The following document includes information about:
 Patient information WHAT TO EXPECT WHILE RECEIVING RADIATION THERAPY FOR PROSTATE CANCER Oncology Vitalité Zone : 1B 4 5 6 Facility : Dr. Léon-Richard Oncology Centre The following document includes information
Patient information WHAT TO EXPECT WHILE RECEIVING RADIATION THERAPY FOR PROSTATE CANCER Oncology Vitalité Zone : 1B 4 5 6 Facility : Dr. Léon-Richard Oncology Centre The following document includes information
Incontinence. What is incontinence?
 Incontinence What is incontinence? Broadly speaking, the medical term incontinence refers to any involuntary release of bodily fluids, but many people associate it strongly with the inability to control
Incontinence What is incontinence? Broadly speaking, the medical term incontinence refers to any involuntary release of bodily fluids, but many people associate it strongly with the inability to control
URINARY CATHETER CARE
 URINARY CATHETER CARE INTRODUCTION Urinary catheter care is a very important skill, and it is a skill that many certified nursing assistants (CNAs) must know. Competence at providing urinary catheter care
URINARY CATHETER CARE INTRODUCTION Urinary catheter care is a very important skill, and it is a skill that many certified nursing assistants (CNAs) must know. Competence at providing urinary catheter care
Open the Flood Gates Urinary Obstruction and Kidney Stones. Dr. Jeffrey Rosenberg Dr. Emilio Lastarria Dr. Richard Kasulke
 Open the Flood Gates Urinary Obstruction and Kidney Stones Dr. Jeffrey Rosenberg Dr. Emilio Lastarria Dr. Richard Kasulke Nephrology vs. Urology Nephrologist a physician who has been trained in the diagnosis
Open the Flood Gates Urinary Obstruction and Kidney Stones Dr. Jeffrey Rosenberg Dr. Emilio Lastarria Dr. Richard Kasulke Nephrology vs. Urology Nephrologist a physician who has been trained in the diagnosis
Kidney Stones. This reference summary will help you understand kidney stones and how to treat and prevent them. Kidney
 Introduction A kidney stone is a solid piece of material that forms in the kidney from substances in the urine. Kidney stones are fairly common. Although kidney stones can be painful, they are treatable.
Introduction A kidney stone is a solid piece of material that forms in the kidney from substances in the urine. Kidney stones are fairly common. Although kidney stones can be painful, they are treatable.
Kaiser Oakland Urology
 Kaiser Oakland Urology The Main Purpose of Bladder Catheterization Complete Bladder Emptying! Help maintain a healthy bladder Help maintain healthy kidneys Reduce the chances of significant urinary tract
Kaiser Oakland Urology The Main Purpose of Bladder Catheterization Complete Bladder Emptying! Help maintain a healthy bladder Help maintain healthy kidneys Reduce the chances of significant urinary tract
Urine infections. Children s Ward Patient Information Leaflet
 Urine infections Children s Ward Patient Information Leaflet Introduction This leaflet is for people who have a urine infection. It tells you about: What urine infections are Symptoms Treatment How you
Urine infections Children s Ward Patient Information Leaflet Introduction This leaflet is for people who have a urine infection. It tells you about: What urine infections are Symptoms Treatment How you
Acute pelvic inflammatory disease: tests and treatment
 Acute pelvic inflammatory disease: tests and treatment Information for you Information for you Published August 2010 Published in August 2010 (next review date: 2014) Acute What is pelvic inflammatory
Acute pelvic inflammatory disease: tests and treatment Information for you Information for you Published August 2010 Published in August 2010 (next review date: 2014) Acute What is pelvic inflammatory
Overactive Bladder (OAB)
 Overactive Bladder (OAB) Overactive bladder is a problem with bladder storage function that causes a sudden urge to urinate. The urge may be difficult to suppress, and overactive bladder can lead to the
Overactive Bladder (OAB) Overactive bladder is a problem with bladder storage function that causes a sudden urge to urinate. The urge may be difficult to suppress, and overactive bladder can lead to the
Urinary Tract Infections in Adults
 Urinary Tract Infections in Adults National Kidney and Urologic Diseases Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH What is a urinary tract infection
Urinary Tract Infections in Adults National Kidney and Urologic Diseases Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH What is a urinary tract infection
WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500. Endometriosis
 Endometriosis WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 The lining of the uterus is called the endometrium. Sometimes, endometrial tissue grows elsewhere in the body. When this happens
Endometriosis WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 The lining of the uterus is called the endometrium. Sometimes, endometrial tissue grows elsewhere in the body. When this happens
URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS
 URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS INTRODUCTION Urinary tract infections are a very common medical problem. The term urinary tract infection is frequently used to refer to an infection of the bladder. However, although
URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS INTRODUCTION Urinary tract infections are a very common medical problem. The term urinary tract infection is frequently used to refer to an infection of the bladder. However, although
HEALTH NEWS PROSTATE CANCER THE PROSTATE
 HEALTH NEWS PROSTATE CANCER THE PROSTATE Prostate comes from the Greek meaning to stand in front of ; this is very different than prostrate which means to lie down flat. The prostate is a walnut-sized
HEALTH NEWS PROSTATE CANCER THE PROSTATE Prostate comes from the Greek meaning to stand in front of ; this is very different than prostrate which means to lie down flat. The prostate is a walnut-sized
Patient Questionnaire for Men
 Patient Questionnaire for Men Please fill out the following questionnaire to the best of your ability prior to your first appointment. Your physical therapist will review your responses during your initial
Patient Questionnaire for Men Please fill out the following questionnaire to the best of your ability prior to your first appointment. Your physical therapist will review your responses during your initial
Glossary. amenorrhea, primary - from the beginning and lifelong; menstruation never begins at puberty.
 Glossary amenorrhea - absence or cessation of menstrual periods. amenorrhea, primary - from the beginning and lifelong; menstruation never begins at puberty. A amenorrhea, secondary - due to some physical
Glossary amenorrhea - absence or cessation of menstrual periods. amenorrhea, primary - from the beginning and lifelong; menstruation never begins at puberty. A amenorrhea, secondary - due to some physical
Gonorrhoea. Looking after your sexual health
 Gonorrhoea Looking after your sexual health 2 Gonorrhoea Gonorrhoea is a bacterial sexually transmitted infection (STI). It can be painful and can cause serious health problems such as infertility in both
Gonorrhoea Looking after your sexual health 2 Gonorrhoea Gonorrhoea is a bacterial sexually transmitted infection (STI). It can be painful and can cause serious health problems such as infertility in both
Diseases that can be spread during sex
 Diseases that can be spread during sex Did you know... over 65 million people in the United States have a chronic, incurable sexually transmitted disease (STD)? and that every year another 19 million persons
Diseases that can be spread during sex Did you know... over 65 million people in the United States have a chronic, incurable sexually transmitted disease (STD)? and that every year another 19 million persons
Recovery After Stroke: Bladder & Bowel Function
 Recovery After Stroke: Bladder & Bowel Function Problems with bladder and bowel function are common but distressing for stroke survivors. Going to the bathroom after suffering a stroke may be complicated
Recovery After Stroke: Bladder & Bowel Function Problems with bladder and bowel function are common but distressing for stroke survivors. Going to the bathroom after suffering a stroke may be complicated
Learning Resource Guide. Understanding Incontinence. 2000 Prism Innovations, Inc. All Rights Reserved
 Learning Resource Guide Understanding Incontinence 2000 Prism Innovations, Inc. All Rights Reserved ElderCare Online s Learning Resource Guide Understanding Incontinence Table of Contents Introduction
Learning Resource Guide Understanding Incontinence 2000 Prism Innovations, Inc. All Rights Reserved ElderCare Online s Learning Resource Guide Understanding Incontinence Table of Contents Introduction
Quality Measures for Long-stay Residents Percent of residents whose need for help with daily activities has increased.
 Quality Measures for Long-stay Residents Percent of residents whose need for help with daily activities has increased. This graph shows the percent of residents whose need for help doing basic daily tasks
Quality Measures for Long-stay Residents Percent of residents whose need for help with daily activities has increased. This graph shows the percent of residents whose need for help doing basic daily tasks
X-Plain Kidney Stones Reference Summary
 X-Plain Kidney Stones Reference Summary Introduction Kidney stones are fairly common. Although they can be very painful, they are treatable, and in many cases preventable. This reference summary will help
X-Plain Kidney Stones Reference Summary Introduction Kidney stones are fairly common. Although they can be very painful, they are treatable, and in many cases preventable. This reference summary will help
Managing Acute Side Effects of Pelvic Radiation for Gynaecological Cancers
 RADIATION THERAPY SYMPTOM MANAGEMENT Managing Acute Side Effects of Pelvic Radiation for Gynaecological Cancers In this booklet you will learn about: Common side effects when you receive radiation therapy
RADIATION THERAPY SYMPTOM MANAGEMENT Managing Acute Side Effects of Pelvic Radiation for Gynaecological Cancers In this booklet you will learn about: Common side effects when you receive radiation therapy
Radiation Therapy for Prostate Cancer
 Radiation Therapy for Prostate Cancer Introduction Cancer of the prostate is the most common form of cancer that affects men. About 240,000 American men are diagnosed with prostate cancer every year. Your
Radiation Therapy for Prostate Cancer Introduction Cancer of the prostate is the most common form of cancer that affects men. About 240,000 American men are diagnosed with prostate cancer every year. Your
Prevention and Recognition of Obstetric Fistula Training Package. Module 8: Pre-repair Care and Referral for Women with Obstetric Fistula
 Prevention and Recognition of Obstetric Fistula Training Package Module 8: Pre-repair Care and Referral for Women with Obstetric Fistula Early detection and treatment If a woman has recently survived a
Prevention and Recognition of Obstetric Fistula Training Package Module 8: Pre-repair Care and Referral for Women with Obstetric Fistula Early detection and treatment If a woman has recently survived a
Accent on Health Obgyn, PC HERPES Frequently Asked Questions
 1. What is herpes? 2. How common is herpes? 3. Is there a cure for herpes? 4. What is oral herpes (cold sores)? 5. How is oral herpes spread? 6. What is genital herpes? 7. How is genital herpes spread?
1. What is herpes? 2. How common is herpes? 3. Is there a cure for herpes? 4. What is oral herpes (cold sores)? 5. How is oral herpes spread? 6. What is genital herpes? 7. How is genital herpes spread?
What to Do When Receiving Radiation Therapy to the Pelvis
 What to Do When Receiving Radiation Therapy to the Pelvis UHN For patients with gynecological cancer Learn the main steps in planning radiation treatment and how to manage side effects during radiation
What to Do When Receiving Radiation Therapy to the Pelvis UHN For patients with gynecological cancer Learn the main steps in planning radiation treatment and how to manage side effects during radiation
es of Urinary Incontinence:
 Reversible Cause Urinary incontinence is a loss of control over the passing of urine. Urine loss can occur in very small amounts (enough only to dampen underwear) to very large amounts (requiring a change
Reversible Cause Urinary incontinence is a loss of control over the passing of urine. Urine loss can occur in very small amounts (enough only to dampen underwear) to very large amounts (requiring a change
online version Understanding Indwelling Urinary Catheters and Drainage Systems Useful information When to call for help
 When to call for help This will depend on the individual situation, but usually help should be sought if any of the following occurs: 1. The catheter does not start to drain, despite trying the problem
When to call for help This will depend on the individual situation, but usually help should be sought if any of the following occurs: 1. The catheter does not start to drain, despite trying the problem
Uterine fibroids (Leiomyoma)
 Uterine fibroids (Leiomyoma) What are uterine fibroids? Uterine fibroids are fairly common benign (not cancer) growths in the uterus. They occur in about 25 50% of all women. Many women who have fibroids
Uterine fibroids (Leiomyoma) What are uterine fibroids? Uterine fibroids are fairly common benign (not cancer) growths in the uterus. They occur in about 25 50% of all women. Many women who have fibroids
Bladder Control Does Matter
 Bladder Control Does Matter Y0028_2726_0 File&Use 04092012 If you suffer from urinary incontinence, you re not alone Don t be afraid to raise your hand if you ve been struggling with the embarrassment
Bladder Control Does Matter Y0028_2726_0 File&Use 04092012 If you suffer from urinary incontinence, you re not alone Don t be afraid to raise your hand if you ve been struggling with the embarrassment
Trichomonas vaginalis. Looking after your sexual health
 Trichomonas vaginalis Looking after your sexual health 2 3 Trichomonas vaginalis Trichomonas vaginalis is a sexually transmitted infection (STI). It is sometimes referred to as trichomonas or trichomoniasis,
Trichomonas vaginalis Looking after your sexual health 2 3 Trichomonas vaginalis Trichomonas vaginalis is a sexually transmitted infection (STI). It is sometimes referred to as trichomonas or trichomoniasis,
WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500. Hormone Therapy
 Hormone Therapy WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 At menopause, a woman's body makes less estrogen and she stops having menstrual periods. This is a natural stage in a woman's
Hormone Therapy WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 At menopause, a woman's body makes less estrogen and she stops having menstrual periods. This is a natural stage in a woman's
Cancer of the Cervix
 Cancer of the Cervix WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 A woman's cervix (the opening of the uterus) is lined with cells. Cancer of the cervix occurs when those cells change,
Cancer of the Cervix WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 A woman's cervix (the opening of the uterus) is lined with cells. Cancer of the cervix occurs when those cells change,
Bile Duct Diseases and Problems
 Bile Duct Diseases and Problems Introduction A bile duct is a tube that carries bile between the liver and gallbladder and the intestine. Bile is a substance made by the liver that helps with digestion.
Bile Duct Diseases and Problems Introduction A bile duct is a tube that carries bile between the liver and gallbladder and the intestine. Bile is a substance made by the liver that helps with digestion.
Women s Continence and Pelvic Health Center
 Women s Continence and Pelvic Health Center Committed to Caring 580-590 Court Street Keene, New Hampshire 03431 (603) 354-5454 Ext. 6643 URINARY INCONTINENCE QUESTIONNAIRE The purpose of this questionnaire
Women s Continence and Pelvic Health Center Committed to Caring 580-590 Court Street Keene, New Hampshire 03431 (603) 354-5454 Ext. 6643 URINARY INCONTINENCE QUESTIONNAIRE The purpose of this questionnaire
BARD MEDICAL DIVISION UROLOGICAL DRAINAGE. Foley Catheter Care & Maintenance. Patient Education Guide
 BARD MEDICAL DIVISION Foley Catheter Care & Maintenance Patient Education Guide WHAT IS A FOLEY CATHETER? Because of your medical problem, your body is having trouble completely emptying your bladder of
BARD MEDICAL DIVISION Foley Catheter Care & Maintenance Patient Education Guide WHAT IS A FOLEY CATHETER? Because of your medical problem, your body is having trouble completely emptying your bladder of
Urinary Incontinence
 Urinary Incontinence Q: What is urinary Urinary (YOOR-in-air-ee) incontinence (in-kahn-tih-nens) is when urine leaks out before you can get to a bathroom. If you have urinary incontinence, you re not alone.
Urinary Incontinence Q: What is urinary Urinary (YOOR-in-air-ee) incontinence (in-kahn-tih-nens) is when urine leaks out before you can get to a bathroom. If you have urinary incontinence, you re not alone.
Care of a Foley Catheter
 Care of a Foley Catheter A Foley catheter is a tube that is put into the bladder to drain urine out of the body. A Foley catheter can stay in the bladder for hours or weeks. Having the catheter put in
Care of a Foley Catheter A Foley catheter is a tube that is put into the bladder to drain urine out of the body. A Foley catheter can stay in the bladder for hours or weeks. Having the catheter put in
CARE PROCESS STEP EXPECTATIONS RATIONALE
 URINARY INCONTINENCE CARE PROCESS STEP EXPECTATIONS RATIONALE ASSESSMENT/PROBLEM RECOGNITION 1. Did the staff and physician seek and document risk factors for urinary incontinence and any history of urinary
URINARY INCONTINENCE CARE PROCESS STEP EXPECTATIONS RATIONALE ASSESSMENT/PROBLEM RECOGNITION 1. Did the staff and physician seek and document risk factors for urinary incontinence and any history of urinary
NICE Pathways bring together all NICE guidance, quality standards and other NICE information on a specific topic.
 Initial assessment and investigation of urinary incontinence bring together all NICE guidance, quality standards and other NICE information on a specific topic. are interactive and designed to be used
Initial assessment and investigation of urinary incontinence bring together all NICE guidance, quality standards and other NICE information on a specific topic. are interactive and designed to be used
Urinary Incontinence. Patient Information Sheet
 Urinary Incontinence Patient Information Sheet What is urinary incontinence (UI)? UI happens when you are not able to control when you urinate and you wet yourself. How common is urinary incontinence?
Urinary Incontinence Patient Information Sheet What is urinary incontinence (UI)? UI happens when you are not able to control when you urinate and you wet yourself. How common is urinary incontinence?
AFTER DIAGNOSIS: PROSTATE CANCER Understanding Your Treatment Options
 AFTER DIAGNOSIS: PROSTATE CANCER Understanding Your Treatment Options INTRODUCTION This booklet describes how prostate cancer develops, how it affects the body and the current treatment methods. Although
AFTER DIAGNOSIS: PROSTATE CANCER Understanding Your Treatment Options INTRODUCTION This booklet describes how prostate cancer develops, how it affects the body and the current treatment methods. Although
Chlamydia. Looking after your sexual health
 Chlamydia Looking after your sexual health 2 Chlamydia Chlamydia is one of the most common sexually transmitted infections (STIs). It is very easy to treat and cure. Up to one in 10 sexually active young
Chlamydia Looking after your sexual health 2 Chlamydia Chlamydia is one of the most common sexually transmitted infections (STIs). It is very easy to treat and cure. Up to one in 10 sexually active young
VAD Chemotherapy Regimen for Multiple Myeloma Information for Patients
 VAD Chemotherapy Regimen for Multiple Myeloma Information for Patients The Regimen contains: V = vincristine (Oncovin ) A = Adriamycin (doxorubicin) D = Decadron (dexamethasone) How Is This Regimen Given?
VAD Chemotherapy Regimen for Multiple Myeloma Information for Patients The Regimen contains: V = vincristine (Oncovin ) A = Adriamycin (doxorubicin) D = Decadron (dexamethasone) How Is This Regimen Given?
Abnormal Uterine Bleeding FAQ Sheet
 Abnormal Uterine Bleeding FAQ Sheet What is abnormal uterine bleeding? Under normal circumstances, a woman's uterus sheds a limited amount of blood during each menstrual period. Bleeding that occurs between
Abnormal Uterine Bleeding FAQ Sheet What is abnormal uterine bleeding? Under normal circumstances, a woman's uterus sheds a limited amount of blood during each menstrual period. Bleeding that occurs between
GYNECOLOGIC CANCERS Facts to Help Patients Make an Informed Decision
 RADIATION THERAPY FOR GYNECOLOGIC CANCERS Facts to Help Patients Make an Informed Decision TARGETING CANCER CARE AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR RADIATION ONCOLOGY FACTS ABOUT GYNECOLOGIC CANCERS Gynecologic cancers
RADIATION THERAPY FOR GYNECOLOGIC CANCERS Facts to Help Patients Make an Informed Decision TARGETING CANCER CARE AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR RADIATION ONCOLOGY FACTS ABOUT GYNECOLOGIC CANCERS Gynecologic cancers
Patient Information:
 Patient Information: Care of an indwelling Urinary Catheter What is a Urinary Catheter? A catheter is a hollow, flexible tube designed to drain urine from the bladder. Following insertion into the bladder,
Patient Information: Care of an indwelling Urinary Catheter What is a Urinary Catheter? A catheter is a hollow, flexible tube designed to drain urine from the bladder. Following insertion into the bladder,
Birth Control Options
 1 of 5 6/2/2014 9:46 AM Return to Web version Birth Control Options What is contraception? Contraception means preventing pregnancy, also called birth control. Most people know about options such as birth
1 of 5 6/2/2014 9:46 AM Return to Web version Birth Control Options What is contraception? Contraception means preventing pregnancy, also called birth control. Most people know about options such as birth
Hysterectomy. What is a hysterectomy? Why is hysterectomy done? Are there alternatives to hysterectomy?
 ROBERT LEVITT, MD JESSICA BERGER-WEISS, MD ADRIENNE POTTS, MD HARTAJ POWELL, MD, MPH COURTNEY LEVENSON, MD LAUREN BURNS, MSN, RN, WHNP OBGYNCWC.COM What is a hysterectomy? Hysterectomy Hysterectomy is
ROBERT LEVITT, MD JESSICA BERGER-WEISS, MD ADRIENNE POTTS, MD HARTAJ POWELL, MD, MPH COURTNEY LEVENSON, MD LAUREN BURNS, MSN, RN, WHNP OBGYNCWC.COM What is a hysterectomy? Hysterectomy Hysterectomy is
Probiotics for the Treatment of Adult Gastrointestinal Disorders
 Probiotics for the Treatment of Adult Gastrointestinal Disorders Darren M. Brenner, M.D. Division of Gastroenterology Northwestern University, Feinberg School of Medicine Chicago, Illinois What are Probiotics?
Probiotics for the Treatment of Adult Gastrointestinal Disorders Darren M. Brenner, M.D. Division of Gastroenterology Northwestern University, Feinberg School of Medicine Chicago, Illinois What are Probiotics?
190.12 - Urine Culture, Bacterial Summary Information Highlighted items indicate most frequently used codes.
 Medicare National Coverage Determination (NCD) (Jan 2011) Source: CMS: Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services To view full document: www.cms.gov/coveragegeninfo. Select Lab NCDs, then select NCD Coding
Medicare National Coverage Determination (NCD) (Jan 2011) Source: CMS: Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services To view full document: www.cms.gov/coveragegeninfo. Select Lab NCDs, then select NCD Coding
Frequently Asked Questions About Ovarian Cancer
 Media Contact: Gerri Gomez Howard Cell: 303-748-3933 gerri@gomezhowardgroup.com Frequently Asked Questions About Ovarian Cancer What is ovarian cancer? Ovarian cancer is a cancer that forms in tissues
Media Contact: Gerri Gomez Howard Cell: 303-748-3933 gerri@gomezhowardgroup.com Frequently Asked Questions About Ovarian Cancer What is ovarian cancer? Ovarian cancer is a cancer that forms in tissues
SELF-CATHETERISATION A Guide for Male Patients PATIENT EDUCATION
 SELF-CATHETERISATION A Guide for Male Patients PATIENT EDUCATION ADHB Urology Department; Reviewed JULY 2005 Ubix code NPEB2 1 This booklet has been designed to help you learn how to perform self-catheterisation.
SELF-CATHETERISATION A Guide for Male Patients PATIENT EDUCATION ADHB Urology Department; Reviewed JULY 2005 Ubix code NPEB2 1 This booklet has been designed to help you learn how to perform self-catheterisation.
Understanding Endometriosis - Information Pack
 What is endometriosis? Endometriosis (pronounced en- doh mee tree oh sis) is the name given to the condition where cells like the ones in the lining of the womb (uterus) are found elsewhere in the body.
What is endometriosis? Endometriosis (pronounced en- doh mee tree oh sis) is the name given to the condition where cells like the ones in the lining of the womb (uterus) are found elsewhere in the body.
X-Plain Chemotherapy for Breast Cancer - Adriamycin, Cytoxan, and Tamoxifen Reference Summary
 X-Plain Chemotherapy for Breast Cancer - Adriamycin, Cytoxan, and Tamoxifen Reference Summary Introduction Breast cancer is a common condition that affects one out of every 11 women. Your doctor has recommended
X-Plain Chemotherapy for Breast Cancer - Adriamycin, Cytoxan, and Tamoxifen Reference Summary Introduction Breast cancer is a common condition that affects one out of every 11 women. Your doctor has recommended
Urine Problems After Radiation
 Managing Symptoms After Prostate Cancer Urine Problems After Radiation Radiation treatment can result in several kinds of problems with passing urine (peeing). The good news is that many men do not have
Managing Symptoms After Prostate Cancer Urine Problems After Radiation Radiation treatment can result in several kinds of problems with passing urine (peeing). The good news is that many men do not have
Patient with: 3 or more UTI in 6 months 4 or more UTI in 12 months
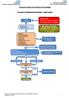 Recurrent UTI Management Pathway adult females Initial assessment Assessment questionnaire questionnaire bladder scan dipstick dipstick of of urine urine pregnancy neurological disease long - term catheters
Recurrent UTI Management Pathway adult females Initial assessment Assessment questionnaire questionnaire bladder scan dipstick dipstick of of urine urine pregnancy neurological disease long - term catheters
Although the flush is the classic menopausal symptom that we ve
 24 MENOPAUSE: ANSWERS AT YOUR FINGERTIPS HOW LONG DO SYMPTOMS LAST? The duration of early symptoms is very variable from a few months to many years and the severity varies between individuals. On average,
24 MENOPAUSE: ANSWERS AT YOUR FINGERTIPS HOW LONG DO SYMPTOMS LAST? The duration of early symptoms is very variable from a few months to many years and the severity varies between individuals. On average,
POAC CLINICAL GUIDELINE
 POAC CLINICAL GUIDELINE Acute Pylonephritis DIAGNOSIS COMPLICATED PYELONEPHRITIS EXCLUSION CRITERIA: Male Known or suspected renal impairment (egfr < 60) Abnormality of renal tract Known or suspected renal
POAC CLINICAL GUIDELINE Acute Pylonephritis DIAGNOSIS COMPLICATED PYELONEPHRITIS EXCLUSION CRITERIA: Male Known or suspected renal impairment (egfr < 60) Abnormality of renal tract Known or suspected renal
About the Uterus. Hysterectomy may be done to treat conditions that affect the uterus. Some reasons a hysterectomy may be needed include:
 Hysterectomy removal of the uterus is a way of treating problems that affect the uterus. Many conditions can be cured with hysterectomy. Because it is major surgery, your doctor may suggest trying other
Hysterectomy removal of the uterus is a way of treating problems that affect the uterus. Many conditions can be cured with hysterectomy. Because it is major surgery, your doctor may suggest trying other
CVP Chemotherapy Regimen for Lymphoma Information for Patients
 CVP Chemotherapy Regimen for Lymphoma Information for Patients The Regimen Contains: C: Cyclophosphamide (Cytoxan ) V: Vincristine (Oncovin ) P: Prednisone How Is This Regimen Given? CVP is given every
CVP Chemotherapy Regimen for Lymphoma Information for Patients The Regimen Contains: C: Cyclophosphamide (Cytoxan ) V: Vincristine (Oncovin ) P: Prednisone How Is This Regimen Given? CVP is given every
Total Abdominal Hysterectomy
 What is a total abdominal hysterectomy? Is the removal of the uterus and cervix through an abdominal incision (either an up and down or bikini cut). Removal of the ovaries and tubes depends on the patient.
What is a total abdominal hysterectomy? Is the removal of the uterus and cervix through an abdominal incision (either an up and down or bikini cut). Removal of the ovaries and tubes depends on the patient.
Managing Acute Side Effects of Colorectal & Anal Radiation Therapy
 RADIATION THERAPY SYMPTOM MANAGEMENT Managing Acute Side Effects of Colorectal & Anal Radiation Therapy In this booklet you will learn about: Common side effects when you receive radiation therapy to your
RADIATION THERAPY SYMPTOM MANAGEMENT Managing Acute Side Effects of Colorectal & Anal Radiation Therapy In this booklet you will learn about: Common side effects when you receive radiation therapy to your
Male Infertility. Penis. Epididymis
 Male Infertility Introduction Infertility is a term used when a man is unable to get a woman pregnant. But the term is only used after at least one year of trying. Infertility is a common problem. About
Male Infertility Introduction Infertility is a term used when a man is unable to get a woman pregnant. But the term is only used after at least one year of trying. Infertility is a common problem. About
Intraperitoneal Chemotherapy
 Intraperitoneal Chemotherapy What is Intraperitoneal (IP) Chemotherapy? Intraperitoneal (IP) chemotherapy is a way to put some of your chemotherapy into your abdomen (also called the peritoneal cavity)
Intraperitoneal Chemotherapy What is Intraperitoneal (IP) Chemotherapy? Intraperitoneal (IP) chemotherapy is a way to put some of your chemotherapy into your abdomen (also called the peritoneal cavity)
Colon and Rectal Cancer
 Colon and Rectal Cancer What is colon or rectal cancer? Colon or rectal cancer is the growth of abnormal cells in your large intestine, which is also called the large bowel. The colon is the last 5 feet
Colon and Rectal Cancer What is colon or rectal cancer? Colon or rectal cancer is the growth of abnormal cells in your large intestine, which is also called the large bowel. The colon is the last 5 feet
Introduction Ovarian cysts are a very common female condition. An ovarian cyst is a fluid-filled sac on an ovary in the female reproductive system.
 Ovarian Cysts Introduction Ovarian cysts are a very common female condition. An ovarian cyst is a fluid-filled sac on an ovary in the female reproductive system. Most women have ovarian cysts sometime
Ovarian Cysts Introduction Ovarian cysts are a very common female condition. An ovarian cyst is a fluid-filled sac on an ovary in the female reproductive system. Most women have ovarian cysts sometime
Urinary Incontinence FAQ Sheet
 Urinary Incontinence FAQ Sheet Are you reluctant to talk to your doctor about your bladder control problem? Don t be. There is help. Loss of bladder control is called urinary incontinence. It can happen
Urinary Incontinence FAQ Sheet Are you reluctant to talk to your doctor about your bladder control problem? Don t be. There is help. Loss of bladder control is called urinary incontinence. It can happen
Pneumonia. Pneumonia is an infection that makes the tiny air sacs in your lungs inflamed (swollen and sore). They then fill with liquid.
 Pneumonia Pneumonia is an infection that makes the tiny air sacs in your lungs inflamed (swollen and sore). They then fill with liquid. People with mild (not so bad) pneumonia can usually be treated at
Pneumonia Pneumonia is an infection that makes the tiny air sacs in your lungs inflamed (swollen and sore). They then fill with liquid. People with mild (not so bad) pneumonia can usually be treated at
Understanding Your Risk of Ovarian Cancer
 Understanding Your Risk of Ovarian Cancer A WOMAN S GUIDE This brochure is made possible through partnership support from Project Hope for Ovarian Cancer Research and Education. Project HOPE FOR OVARIAN
Understanding Your Risk of Ovarian Cancer A WOMAN S GUIDE This brochure is made possible through partnership support from Project Hope for Ovarian Cancer Research and Education. Project HOPE FOR OVARIAN
Abnormal Uterine Bleeding
 Abnormal Uterine Bleeding WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 Abnormal uterine bleeding is one of the most common reasons women see their doctors. It can occur at any age and has
Abnormal Uterine Bleeding WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 Abnormal uterine bleeding is one of the most common reasons women see their doctors. It can occur at any age and has
URINARY INCONTINENCE
 URINARY INCONTINENCE What is urinary incontinence? Urinary incontinence is the uncontrollable loss of urine. The amount of urine leaked can vary from only a few drops when you cough or sneeze to entirely
URINARY INCONTINENCE What is urinary incontinence? Urinary incontinence is the uncontrollable loss of urine. The amount of urine leaked can vary from only a few drops when you cough or sneeze to entirely
SCRIPT NUMBER 88 FOOD POISONING (ONE SPEAKER)
 SCRIPT NUMBER 88 FOOD POISONING (ONE SPEAKER) PROGRAM NAME: HEALTH NUGGETS PROGRAM TITLE: FOOD POISONING PROGRAM NUMBER: 88 SUBJECT: CAUSES, DIAGNOSIS, TREATMENT, PREVENTION OF FOOD POISONING KEY WORDS:
SCRIPT NUMBER 88 FOOD POISONING (ONE SPEAKER) PROGRAM NAME: HEALTH NUGGETS PROGRAM TITLE: FOOD POISONING PROGRAM NUMBER: 88 SUBJECT: CAUSES, DIAGNOSIS, TREATMENT, PREVENTION OF FOOD POISONING KEY WORDS:
