HIV/AIDS. happen. could it. to me? make choices, don t take chances
|
|
|
- Julius Dean
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 HIV/AIDS could it happen to me? make choices, don t take chances
2 should you read this brochure? This brochure is about preventing human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection. Some frank language is used to get the message across. This brochure also assumes you know some basic information about HIV and acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS). You can avoid risk of HIV infection by following a few steps. These steps may be straight forward, but talking about them and putting them into practice is often harder. Help is available, read on. The Basics: HIV is a virus that attacks the body s immune system. The virus can enter your bloodstream if: you have unprotected sexual intercourse (oral, anal, or vaginal) with someone who has HIV. you share needles or other injection equipment with someone who has HIV. HIV can enter your body through the infected person s blood, semen or vaginal fluids. A mother with HIV can pass it on to her baby. Anyone who has unprotected sex or shares needles or other injection equipment is at risk for HIV no matter where you live, your sex, age, sexual orientation or ethnic origin. HIV is NOT spread by insect bites, sitting on toilet seats; food handling or sharing hugs and kisses. Individuals can have HIV for years and not show symptoms of the virus. This means a person can look and feel well yet still infect others with HIV. Over time, HIV weakens the body s immune system so much that it has difficulty fighting off even a simple infection. There are drugs that may slow down the disease so people with HIV can stay healthier for a longer time. Having HIV does not mean you have AIDS. If HIV is left untreated, your immune system will no longer be able to defend your body from infections, diseases or cancers that can kill you. This is called AIDS. To know whether you re infected with HIV or not, you need to get an HIV antibody blood test. The only way to prevent infection is to avoid risk. There is no cure for HIV. There is no vaccine to prevent HIV. Assess Risk...Know Yourself Do you take more risks when drinking or using drugs? Do you know your partner s views about abstinence, safer sex and condoms? Do good intentions get left behind in the heat of sexual passion? Ask yourself, What am I doing to put myself at risk of HIV? 1
3 okay, let s talk about sex! Sex is never completely safe but you can make it safer. Take control, and you can be confident your choices do not put you, or others, at risk. Your risk of getting HIV increases every time you come into contact with semen, vaginal fluid or blood of someone who may be infected. You are at high risk for HIV if: you do not know your partner s HIV status; your partner is having sexual relations with other partners; you have anal, vaginal or oral intercourse without using a condom; you share sex toys with someone who has HIV. Having sex with only one person, or being monogamous, doesn t necessarily protect you from HIV infection or other sexually transmitted infections (STI) - also known as sexually transmitted diseases or STD. Ask yourself: Have I had unprotected sex? Have I shared needles or other injection equipment? You greatly reduce your chances of getting HIV infection if you practice safer sex. For example, instead of intercourse without a condom, you correctly use a condom each and ever time you have intercourse (anal, vaginal or oral sex). Today there are condoms for both males and females. See the section on condoms in this brochure. Safer sex means making sure semen, vaginal fluids or blood does not get into your (or your partner s) body. To practice safer sex, use a condom or dental dam correctly, each time you have vaginal, anal or oral sex. Other examples of safer sex practices include kissing, hugging, massaging, petting and masturbating. If the vagina or anus is entered using fingers, make sure you don t have tiny cuts on them, as this can become an entry point for infected fluids. Be warned. You are at risk if these activities turn into unprotected sex. Remember, you and your partner are less likely to think about safer sex if you are drunk or stoned. In a recent survey, Albertans reported drinking as a major cause of unsafe sex. Sex is safe from HIV only when partners are not HIV infected. The only way to be sure you are free of infection is to be tested. See the section on testing in this brochure. Do I know if my partner has or is having other sexual relationships? Do I know if my partner shares needles or other injection equipment? Remember, participating in unsafe sex exposes you to every sexual partner your partner ever had, every partner your partner s partner ever had and so on and so on... 2
4 One other caution...other sexually transmitted infections (STI) are spread easily through oral sex. For protection from STI, use a condom or dental dam each and every time you have oral, vaginal or anal sex. Are men and women at equal risk? Both males and females are at risk of infection during any kind of unprotected sexual intercourse. The penetrated (entered) partner is at more risk during anal or vaginal sex. Anal sex without a condom is particularly risky since HIV can enter the bloodstream through tiny tears in the rectum (anus). Of course, everyone is at high risk if they share any injection equipment such as needles, syringes (rigs) or spoons (cookers). See the section on sharing needles in this brochure. How risky is oral sex? Oral sex is not risk free. Using a condom or dental dam during oral sex - every time - reduces the risk of HIV infection. A dental dam is a piece of latex used to cover the anus or vagina. HIV can be found in blood, semen and vaginal fluids. Remember: do NOT brush or floss teeth and gums before having oral sex; do NOT have oral sex if either partner has cuts or sores around or in the mouth, penis, vagina or anus; do NOT have oral sex (mouth to vagina) during a woman s menstruation cycle (period). 4 5
5 how risky is sharing needles? Injecting drugs with used or unclean needles or using any form of used or unclean injection equipment is one of the riskiest things you can do. Sharing injection equipment is very dangerous since HIV (and other illnesses such as hepatitis B and C) is spreading rapidly among injection drug users. If you inject, reduce your risk by not sharing needles or other injection equipment. Use only new or sterilized equipment. Remember, when you share needles you may be transferring infected blood directly into your body or into someone else s body if you are infected. You may also get HIV if unclean needles or unsterilized equipment are used to: tattoo skin pierce inject steroids If you have to re-use injection equipment, be sure to clean it first by flushing full strength bleach through the works at least two times. the C word: condoms Do condoms work? Condoms offer protection. If you choose to have intercourse, you greatly reduce your risk of STI and HIV infection by correctly using a condom. Thousands of condoms are sold daily so there is no need to be shy about buying them. It s life. It s your life. Using condoms only some of the time is a dangerous strategy when dealing with a life-threatening illness. Not wearing a condom could change your life forever. Beware - birth control pills will NOT protect you or your partner from HIV and STI. Use a condom every time you have vaginal, anal or oral sex - no matter what other method of birth control you or your partner may use. Both male and female condoms help protect partners from HIV and STI. Fill the syringe with bleach, then tap it a few times to loosen any dried blood that might still be in the needle. Rinse the syringe a few times with clean tap water. Cleaning needles or other injection equipment REDUCES BUT DOES NOT REMOVE the risk of HIV infection. This method of cleaning does NOT kill the hepatitis C virus. 6
6 Tips: Lubrication on the inside and outside of the condom improves the feel and ease of having sex as well as putting the condom on. Use only water-based lubricants such as KY Jelly. Never use oil-based products such as Vaseline or baby oil because THESE DESTROY LATEX. Squeeze the top of the condom before putting it on. A man who is not circumcised should slide his foreskin back first. As the condom is rolled to the base of the erect penis, smooth out any condom wrinkles or air bubbles. What about female condoms? Female condoms, similar to male condoms, help provide protection against HIV and other STI as well as unwanted pregnancy. They are made of polyurethane - a thin, transparent, soft plastic. A female condom is inserted into the vagina before intercourse. During intercourse, the penis goes inside the female condom. The female condom acts as a barrier and prevents pregnancy by stopping sperm from entering the vagina. Information in the condom package provides instructions on how to correctly use the female condom. A female condom should NOT be reused. What about male condoms? Male condoms made from latex or polyurethane also help provide protection against HIV and other STI as well as unwanted pregnancy. 8 After ejaculating (coming), pull out the penis while it is still erect (hard). Hold the base of the penis and remove the condom - being careful not to spill semen. Throw the condom in the garbage. Wash your hands afterwards. Never re-use a condom. Latex becomes brittle over time or under extreme temperature conditions. Do NOT keep condoms in your wallet or car glove compartments for a long time. Store them away from direct sunlight, heat or cold. Check the expiry date of condoms. Throw out old condoms and buy fresh ones. Male condoms come in different shapes, sizes, textures and flavours. Avoid novelty condoms as they may not provide protection against HIV and STI. If you know you are going to have sex, take the condom out of the package beforehand. This way, it s ready when you are. Some people relax and enjoy sex better when they know a condom will be used. 9
7 Other condom tips: Plan ahead. A trip to the store just to buy condoms doesn t always fit with the mood. You are more likely to practice safer sex if condoms are handy. If you are not used to condoms, take one out of its package when you are alone and practice putting it on. There is nothing complicated about condoms and being familiar with them will make you more comfortable. The real risk comes from not using a condom correctly or not using one at all. Does Nonoxynol-9 kill HIV? Nonoxynol-9 is often found in contraceptive (birth control) foams, jellies and lubricated condoms. Nonoxynol-9 can kill sperm but DOES NOT provide protection against HIV or STD infection. Nonoxynol-9 should NEVER be used during anal sex. It can cause irritation and may increase your risk of getting HIV or STD. make it happen How can I get a partner to practice safer sex? Don t apologize for protecting yourself. Safer sex is for both partners. If either of you has had other sexual or needle-sharing partners, you could be infected or you could run the risk of infecting each other. One approach doesn t work in all situations. Helpful hints for handling a difficult conversation or situation: Plan an appropriate time. Do NOT wait until you are in the heat of passion or have had a few drinks to talk to your partner. In a calm but firm way, tell your partner you believe in, and practice, safer sex. Try mixing humour in with understanding and knowledge. If you are clear about your views on condoms, abstinence, preferences or whatever, you won t have to re-hash the sex issue with the same partner. Safer sex conversation starters: Because I care about us, we need to talk... I d rather be safe than sorry. Let s be clear now, so we can enjoy sex later. We need to think disease control as well as birth control. Either one of us could have been infected with HIV a long time ago. Let s use condoms or abstain for 6 months, then get tested. Then we ll know for sure we re protecting each other
8 If discussing the issue of safer sex causes your partner(s) to physically or verbally abuse you, you should consider ending the relationship. Social service agencies, women s shelters and other support services are available to help. For information on local support services call the Office for the Prevention of Family Violence. See back cover for details. Respect your partner s wishes, too. Do NOT pressure anyone to have sexual intercourse. There are many risk-free ways to express your sexual feelings. Starting a new relationship? If you are starting a new monogamous relationship (i.e. you and your partner will not have any other partners) and want to be sure you and your new partner are free from HIV infection, you need to decide to do the following for at least six months: not have oral, vaginal and/or anal sex OR use a condom or dental dam every time you have oral, vaginal and/or anal sex and not share needles or any injection equipment. After these six months (or longer), you and your new partner must then go for HIV testing. testing The only way to be certain you are not HIV infected is to have an HIV antibody blood test. Why get tested? If you have been at risk, testing is important. The important benefits to knowing if you are HIV infected include: receiving treatment as soon as possible, taking extra care not to infect others, understanding your health. If I get tested right after unsafe sex (or right after sharing injection drug equipment), will I know I m okay? No. Having an HIV test right after having unsafe sex or right after sharing injection equipment will not tell you if you have contracted HIV. Here s the reason: if you have HIV, your body will make antibodies to fight it. These antibodies will show up on a blood test. BUT, it can take up to six months after you get infected with HIV before the antibodies show up in a blood test. You could still have HIV but your body has not produced enough antibodies to have it show up on a test. Instead, if you have sex without a condom or share injection drug equipment, get tested 3 months after that unsafe incident. If your HIV antibody test results are positive 12 13
9 at three months, you can seek help immediately and be treated for HIV. If your HIV antibody test results are negative, you are lucky, but not in the clear. Since it can take up to six months for HIV antibodies to show up on a blood test, get another test at the six month mark in order to be sure. It is important to remember that people can infect others during these months while showing no sign of infection themselves or on a test. Can getting tested regularly prevent HIV? No. Being tested regularly does NOT protect you against HIV. Repeated testing does NOT prevent HIV. You CAN prevent HIV by changing your risky behaviours. Once you ve tested positive, there is nothing you can do to change it. There may be drugs available to slow down the disease so you stay healthier for a longer time period BUT there are no drugs to get rid of HIV or to cure AIDS. Should I be tested for HIV if I am pregnant? Yes. A woman with HIV can pass it on to her baby while pregnant, during birth or when breastfeeding. Getting tested for HIV means you can get the early help you and baby will need. In Alberta, testing for HIV is part of good prenatal care. All pregnant women are tested unless they request their doctor or midwife not to test. You have the choice to be tested or not. However, if you choose not to be tested, this would cause a delay in specific treatments you and your baby will need if you are HIV infected. Pregnant women who have been at risk of HIV infection should be tested immediately. Where can I get tested? Testing is available through doctors offices, STI clinics in Calgary, Edmonton, Fort McMurray and at some family planning clinics. Information on places for testing is available at the back of this brochure. Don t assume you are being tested for HIV if you have other tests or physical examinations. If you want to be tested you need to ASK for an HIV antibody blood test. Testing can only be done if consent is given to test
10 is the blood supply safe? In Canada, donated blood has been screened for HIV since November However, you should ask your doctor to test you if you received blood or blood products between 1978 and How much does it cost to be HIV tested? If you are tested because of health concerns, you are not charged. If you are tested in order to apply for life insurance, a foreign work Visa or another non-medical reason you may be charged a fee. Costs vary so ask before you are tested. Who will see my test results? HIV test results are confidential. Your HIV status is not given to people like your employer, landlord or family. Your results cannot be shared with people outside of the health profession. Some countries do not screen all blood products for HIV. If you plan to travel outside of Canada, refer to the Travel Medicine Program at Health Canada by visiting: What about donating blood? Do NOT donate blood as a way to get an HIV antibody blood test. If you are unsure about the safety of donating your blood, contact Canadian Blood Services in your local phone directory. In Alberta, positive HIV tests are notifiable. This means the medical officer of health in your health authority and Alberta Health and Wellness are notified of positive test results. A public health professional working with the medical officer of health will talk with you so they can trace and talk to people you may have infected. These people need to be tested. Your name is not given to these contacts. 16
11 final thoughts Okay, I ll practice safer sex and stop sharing injection equipment. Does that cover everything? It goes a long way, but there is more. HIV gets inside one body from another through direct routes, such as unprotected sexual intercourse and through sharing injection equipment. For further protection, stop all other ways HIV can enter your body: Don t share anything that might have small amounts of blood, semen or vaginal fluids on it. We ve talked about sex toys. Razors and equipment for tattooing or ear piercing should never be shared. You are not at high risk helping someone who is bleeding, as long as that person s blood does not get into cuts or sores you may have on you. When possible, wear gloves if handling blood or dealing with an injury. If handling trash or used needles, syringes or injection equipment, use thick gloves to avoid needle stick injuries. With what you now know, you are your own best HIV prevention resource. It s not that easy, is it? Yes and no. It s up to you! Prevention is straightforward. Try putting small steps into practice everyday so they become routine. Plan ahead. Talk with friends, partners and family members about what does or doesn t work. Leave unsafe ways behind. Just because you have been unsafe in the past doesn t mean you can t start being safer today... or tomorrow. Each day is a new day. Help is available. Contact the following agencies for ideas and support
12 where can I go for more information? Community HIV and AIDS Organizations STD/HIV Information Line Alberta Community Council on HIV AIDS Bow Valley (Banff) (403) AIDS Calgary (403) HIV West Yellowhead (formerly AIDS Jasper) (780) Central Alberta AIDS Network (Red Deer) (403) or (toll free) HIV/AIDS Network of South Eastern Alberta (Medicine Hat) (403) HIV Edmonton (780) HIV North Society (Grande Prairie) (780) Kimamow Atoskanow Foundation (780) Lethbridge HIV Connection (403) Living Positive (Edmonton) (780) Wood Buffalo HIV & AIDS Society (Fort McMurray) (780) Harm Reduction / Needle Exchange Programs Safeworks (Calgary) (403) (am) (403) (pm) Streetworks (Edmonton) (780) , ext. 210 Central Alberta AIDS Network (Red Deer) (403) or (toll free) HIV North Society (Grande Prairie) (780) HIV Residential Services Kairos House (Edmonton) (780) SHARP Foundation (Calgary) (403) STD Clinics: Calgary (403) Edmonton (780) Fort McMurray (780) Condom Information: Planned Parenthood Alberta (403) Calgary Birth Control Association (403) Edmonton Birth Control Centre (780) Edmonton Planned Parenthood (780) Referrals to Government Programs: Alberta Government RITE Operator (toll-free) Deaf Relay (TDD/TTY) Office for the Prevention of Family Violence Government of Canada AADAC offices are listed in local phone books. Regional health authority offices are listed in phone books or visit: STD/HIV Information Line (toll free) Lethbridge HIV Connection (403) HIV/AIDS Network of South Eastern Alberta (Medicine Hat) (403) Phone numbers correct as of December
13 For HIV and sexual health resources, visit AID April 2004
HIV/AIDS: General Information & Testing in the Emergency Department
 What Is HIV? HIV/AIDS: General Information & Testing in the Emergency Department HIV is the common name for the Human Immunodeficiency Virus. HIV is a retrovirus. This means it can enter the body s own
What Is HIV? HIV/AIDS: General Information & Testing in the Emergency Department HIV is the common name for the Human Immunodeficiency Virus. HIV is a retrovirus. This means it can enter the body s own
Why it is Important to Talk with Young People about HIV and AIDS 2. Facts about HIV and AIDS 3. How to Get Started 7
 Table of Contents Why it is Important to Talk with Young People about HIV and AIDS 2 Facts about HIV and AIDS 3 How to Get Started 7 What to Say to Your Children About HIV and AIDS 8 Talking with Young
Table of Contents Why it is Important to Talk with Young People about HIV and AIDS 2 Facts about HIV and AIDS 3 How to Get Started 7 What to Say to Your Children About HIV and AIDS 8 Talking with Young
HIV -The Facts BLT 043
 Human Im munodeficiency Virus HIV -The Facts NHS Dumfries & Galloway would like to acknowledge NHS Greater Glasgow for the use of information contained in this leaflet. This leaflet is also available on
Human Im munodeficiency Virus HIV -The Facts NHS Dumfries & Galloway would like to acknowledge NHS Greater Glasgow for the use of information contained in this leaflet. This leaflet is also available on
HIV. Looking after your sexual health
 HIV Looking after your sexual health 2 HIV HIV stands for Human Immunodeficiency Virus. Once someone is infected with HIV the virus will remain in their body for the rest of their life. There is currently
HIV Looking after your sexual health 2 HIV HIV stands for Human Immunodeficiency Virus. Once someone is infected with HIV the virus will remain in their body for the rest of their life. There is currently
Trichomonas vaginalis. Looking after your sexual health
 Trichomonas vaginalis Looking after your sexual health 2 3 Trichomonas vaginalis Trichomonas vaginalis is a sexually transmitted infection (STI). It is sometimes referred to as trichomonas or trichomoniasis,
Trichomonas vaginalis Looking after your sexual health 2 3 Trichomonas vaginalis Trichomonas vaginalis is a sexually transmitted infection (STI). It is sometimes referred to as trichomonas or trichomoniasis,
Gonorrhoea. Looking after your sexual health
 Gonorrhoea Looking after your sexual health 2 Gonorrhoea Gonorrhoea is a bacterial sexually transmitted infection (STI). It can be painful and can cause serious health problems such as infertility in both
Gonorrhoea Looking after your sexual health 2 Gonorrhoea Gonorrhoea is a bacterial sexually transmitted infection (STI). It can be painful and can cause serious health problems such as infertility in both
The State Hospital HIV / AIDS
 The State Hospital HIV / AIDS The red ribbon is the international symbol of HIV & AIDS awareness. What is HIV? HIV stands for Human Immunodeficiency Virus: H is for Human - This virus infects human beings.
The State Hospital HIV / AIDS The red ribbon is the international symbol of HIV & AIDS awareness. What is HIV? HIV stands for Human Immunodeficiency Virus: H is for Human - This virus infects human beings.
Oral sex. Looking after your sexual health
 Oral sex Looking after your sexual health 2 What is this booklet about? This booklet gives you information about oral sex, the risk of getting and passing on sexually transmitted infections through oral
Oral sex Looking after your sexual health 2 What is this booklet about? This booklet gives you information about oral sex, the risk of getting and passing on sexually transmitted infections through oral
100 Questions and answers about HiV/aids. Questions Answers. about HIV/AIDS. New York State Department of Health
 100 Questions and answers about HiV/aids 1 Questions Answers about HIV/AIDS New York State Department of Health 2 new York state department of HealtH 100 Questions and answers about HiV/aids 3 Contents
100 Questions and answers about HiV/aids 1 Questions Answers about HIV/AIDS New York State Department of Health 2 new York state department of HealtH 100 Questions and answers about HiV/aids 3 Contents
Patient Information Sheet
 Healthcare Worker exposure to a patient s blood What is a healthcare worker exposure? Patient Information Sheet Occasionally, health care workers come into contact with the blood or body fluids of their
Healthcare Worker exposure to a patient s blood What is a healthcare worker exposure? Patient Information Sheet Occasionally, health care workers come into contact with the blood or body fluids of their
BASIC INFORMATION ABOUT HIV, HEPATITIS B and C, and TUBERCULOSIS Adapted from the CDC
 BASIC INFORMATION ABOUT HIV, HEPATITIS B and C, and TUBERCULOSIS Adapted from the CDC HIV What are HIV and AIDS? HIV stands for Human Immunodeficiency Virus. This is the virus that causes AIDS. HIV is
BASIC INFORMATION ABOUT HIV, HEPATITIS B and C, and TUBERCULOSIS Adapted from the CDC HIV What are HIV and AIDS? HIV stands for Human Immunodeficiency Virus. This is the virus that causes AIDS. HIV is
HIV/AIDS PAPER OUTLINE. 0.Introduction. -Definitions. 1. AIDS as a stigma. -Factors to the AIDS stigma. 2. Transmission to HIV
 HIV/AIDS PAPER OUTLINE 0.Introduction -Definitions 1. AIDS as a stigma -Factors to the AIDS stigma 2. Transmission to HIV - The most common ways that people get HIV 3. Where you can not get AIDS 4. Conclusion
HIV/AIDS PAPER OUTLINE 0.Introduction -Definitions 1. AIDS as a stigma -Factors to the AIDS stigma 2. Transmission to HIV - The most common ways that people get HIV 3. Where you can not get AIDS 4. Conclusion
Cytotoxic Precautions at Home A Guide for Cancer Patients and Families
 Cytotoxic Precautions at Home A Guide for Cancer Patients and Families Your cancer treatment... 1 What are cytotoxic precautions?... 1 What body fluids are cytotoxic?... 1 How do I handle my body wastes?...
Cytotoxic Precautions at Home A Guide for Cancer Patients and Families Your cancer treatment... 1 What are cytotoxic precautions?... 1 What body fluids are cytotoxic?... 1 How do I handle my body wastes?...
HIV/AIDS. Information booklet
 HIV/AIDS Information booklet Content Introduction 1 What is HIV/AIDS 2 How is HIV spread? 4 Symptoms of HIV infection 7 Testing for HIV 8 Preventing the spread of HIV 10 Sexually Transmitted Infections
HIV/AIDS Information booklet Content Introduction 1 What is HIV/AIDS 2 How is HIV spread? 4 Symptoms of HIV infection 7 Testing for HIV 8 Preventing the spread of HIV 10 Sexually Transmitted Infections
AIDS Knowledge Test. Instructions
 AIDS Knowledge Test Instructions This survey has True/False questions. For example: Pittsburgh's hockey team is the Bruins. We want you to do two things: First, answer the question. In this example, you
AIDS Knowledge Test Instructions This survey has True/False questions. For example: Pittsburgh's hockey team is the Bruins. We want you to do two things: First, answer the question. In this example, you
Genital warts. Looking after your sexual health
 Genital warts Looking after your sexual health 2 Genital warts Genital warts are the most common viral sexually transmitted infection (STI). They are caused by the human papilloma virus (HPV) which can
Genital warts Looking after your sexual health 2 Genital warts Genital warts are the most common viral sexually transmitted infection (STI). They are caused by the human papilloma virus (HPV) which can
Chapter 21. What Are HIV and AIDS?
 Section 1 HIV and AIDS Today What Are HIV and AIDS? Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) is the virus that primarily affects cells of the immune system and that causes AIDS. Acquired immune deficiency syndrome
Section 1 HIV and AIDS Today What Are HIV and AIDS? Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) is the virus that primarily affects cells of the immune system and that causes AIDS. Acquired immune deficiency syndrome
What is HPV? Low-risk HPV types. High-risk HPV types
 HPV and Cancer What is HPV? HPV is short for human papilloma (PAP-uh-LO-muh) virus. HPVs are a large group of related viruses. Each HPV virus in the group is given a number, which is called an HPV type.
HPV and Cancer What is HPV? HPV is short for human papilloma (PAP-uh-LO-muh) virus. HPVs are a large group of related viruses. Each HPV virus in the group is given a number, which is called an HPV type.
The Hepatitis B virus (HBV)
 The Hepatitis B virus (HBV) There are 400 million people in the world who live with chronic hepatitis B, including France. Most people don t even know they are infected. But there are several important
The Hepatitis B virus (HBV) There are 400 million people in the world who live with chronic hepatitis B, including France. Most people don t even know they are infected. But there are several important
THINKING AHEAD: Arrange transportation for field trip to local clinic (Session 18) Identify a teen in recovery as a guest speaker (Session 21)
 13: Condoms Purpose: To empower students to protect themselves from STDs, HIV, and unwanted pregnancy by using condoms correctly and consistently every time they have sex. Stages of Change Process: Getting
13: Condoms Purpose: To empower students to protect themselves from STDs, HIV, and unwanted pregnancy by using condoms correctly and consistently every time they have sex. Stages of Change Process: Getting
FAQs HIV & AIDS. What is HIV? A virus that reduces the effectiveness of your immune system, meaning you are less protected against disease.
 HIV & AIDS What is HIV? A virus that reduces the effectiveness of your immune system, meaning you are less protected against disease. What does HIV stand for? Human Immunodeficiency Virus Where did HIV
HIV & AIDS What is HIV? A virus that reduces the effectiveness of your immune system, meaning you are less protected against disease. What does HIV stand for? Human Immunodeficiency Virus Where did HIV
Information about hepatitis C for patients and carers
 Information about hepatitis C for patients and carers What is hepatitis C? Hepatitis C is an illness caused by a virus which can be passed through blood from one person to another. It mainly affects the
Information about hepatitis C for patients and carers What is hepatitis C? Hepatitis C is an illness caused by a virus which can be passed through blood from one person to another. It mainly affects the
Understanding Fertility
 Understanding Fertility 6 Introduction The word fertile means the ability to become pregnant or to cause pregnancy. Basic knowledge of both the male and female reproductive systems is important for understanding
Understanding Fertility 6 Introduction The word fertile means the ability to become pregnant or to cause pregnancy. Basic knowledge of both the male and female reproductive systems is important for understanding
Basic Presentation HIV/AIDS. For Use by Students, Teachers and the Public Seeking Basic Information About HIV/AIDS
 Basic Presentation HIV/AIDS For Use by Students, Teachers and the Public Seeking Basic Information About HIV/AIDS Objectives- Define and understand the difference between HIV Infection and AIDS Describe
Basic Presentation HIV/AIDS For Use by Students, Teachers and the Public Seeking Basic Information About HIV/AIDS Objectives- Define and understand the difference between HIV Infection and AIDS Describe
Accent on Health Obgyn, PC HERPES Frequently Asked Questions
 1. What is herpes? 2. How common is herpes? 3. Is there a cure for herpes? 4. What is oral herpes (cold sores)? 5. How is oral herpes spread? 6. What is genital herpes? 7. How is genital herpes spread?
1. What is herpes? 2. How common is herpes? 3. Is there a cure for herpes? 4. What is oral herpes (cold sores)? 5. How is oral herpes spread? 6. What is genital herpes? 7. How is genital herpes spread?
Sexually Transmitted Infections (STIs) and the STI Clinic
 Patient & Family Guide 2016 Sexually Transmitted Infections (STIs) and the STI Clinic Where to go. What to know. STIs are more common than you might think! www.nshealth.ca Sexually Transmitted Infections
Patient & Family Guide 2016 Sexually Transmitted Infections (STIs) and the STI Clinic Where to go. What to know. STIs are more common than you might think! www.nshealth.ca Sexually Transmitted Infections
How can herpes simplex spread to an infant?
 CHAPTER 3 HERPES AND PREGNANCY As an expectant parent eagerly awaiting the birth of your new baby, you are probably taking a number of steps to ensure your baby s health. One step many experts recommend
CHAPTER 3 HERPES AND PREGNANCY As an expectant parent eagerly awaiting the birth of your new baby, you are probably taking a number of steps to ensure your baby s health. One step many experts recommend
Birth Control Options
 1 of 5 6/2/2014 9:46 AM Return to Web version Birth Control Options What is contraception? Contraception means preventing pregnancy, also called birth control. Most people know about options such as birth
1 of 5 6/2/2014 9:46 AM Return to Web version Birth Control Options What is contraception? Contraception means preventing pregnancy, also called birth control. Most people know about options such as birth
GENERAL INFORMATION. Hepatitis B Foundation - Korean Chapter Pg. 3 www.hepb.org
 GENERAL INFORMATION What is hepatitis B? Hepatitis B is the world's most common liver infection that can lead to cirrhosis and liver cancer. It is caused by the hepatitis B virus (HBV), which attacks and
GENERAL INFORMATION What is hepatitis B? Hepatitis B is the world's most common liver infection that can lead to cirrhosis and liver cancer. It is caused by the hepatitis B virus (HBV), which attacks and
DO YOU WORK AROUND BLOOD OR BODY FLUIDS? Cal/OSHA s New Rules
 DO YOU WORK AROUND BLOOD OR BODY FLUIDS? Cal/OSHA s New Rules Labor Occupational Health Program University of California, Berkeley 1994 ACKNOWLEDGMENTS This booklet is a publication of the Labor Occupational
DO YOU WORK AROUND BLOOD OR BODY FLUIDS? Cal/OSHA s New Rules Labor Occupational Health Program University of California, Berkeley 1994 ACKNOWLEDGMENTS This booklet is a publication of the Labor Occupational
WHAT YOU NEED TO KNOW ABOUT HEPATITIS C: A GUIDE FOR PEOPLE WITH HIV INFECTION
 WHAT YOU NEED TO KNOW ABOUT HEPATITIS C: A GUIDE FOR PEOPLE WITH HIV INFECTION Did you know that in the United States, at least 1 in 4 people with HIV is also infected with hepatitis C? Hepatitis C is
WHAT YOU NEED TO KNOW ABOUT HEPATITIS C: A GUIDE FOR PEOPLE WITH HIV INFECTION Did you know that in the United States, at least 1 in 4 people with HIV is also infected with hepatitis C? Hepatitis C is
condoms condoms male and fe male and female cond male and female condoms male and female male an male and female male and condoms
 your guide to male and female condoms Helping you choose the method of contraception that is best for you and male condoms female and female condom con dom male and female male an ale and female condoms
your guide to male and female condoms Helping you choose the method of contraception that is best for you and male condoms female and female condom con dom male and female male an ale and female condoms
1.How did I get Hepatitis C?
 1.How did I get Hepatitis C? Sharing needles and syringes ( iv drug use ) or using contaminated straws to snort cocaine Reused needles or medications in a health care setting- (LV endoscopy outbreak, glucometers
1.How did I get Hepatitis C? Sharing needles and syringes ( iv drug use ) or using contaminated straws to snort cocaine Reused needles or medications in a health care setting- (LV endoscopy outbreak, glucometers
Chlamydia. Looking after your sexual health
 Chlamydia Looking after your sexual health 2 Chlamydia Chlamydia is one of the most common sexually transmitted infections (STIs). It is very easy to treat and cure. Up to one in 10 sexually active young
Chlamydia Looking after your sexual health 2 Chlamydia Chlamydia is one of the most common sexually transmitted infections (STIs). It is very easy to treat and cure. Up to one in 10 sexually active young
Rhesus Negative 10:Rhesus Negative July 06. rhesus negative. what it means
 Rhesus Negative 10:Rhesus Negative July 06 14/04/2010 rhesus negative what it means This leaflet contains important information which may affect your pregnancy. Please read it very carefully. 16:15 P When
Rhesus Negative 10:Rhesus Negative July 06 14/04/2010 rhesus negative what it means This leaflet contains important information which may affect your pregnancy. Please read it very carefully. 16:15 P When
All methods of birth control are MUCH SAFER than being pregnant! If 100 women use each method for a year, how many of them get pregnant?
 The Correct Use of Birth Control: In order for any method of birth control to be effective, it must be used correctly ALL THE TIME. This means: One condom every time you have sex One pill every day One
The Correct Use of Birth Control: In order for any method of birth control to be effective, it must be used correctly ALL THE TIME. This means: One condom every time you have sex One pill every day One
HEPATITIS C. The Facts. Get Tested. Get Cured! Health
 HEPATITIS C The Facts Get Tested. Get Cured! Health EVEN IF YOU FEEL HEALTHY, HEPATITIS C MAY BE DAMAGING YOUR LIVER. Your liver keeps you healthy in many ways, such as by removing toxins from your blood
HEPATITIS C The Facts Get Tested. Get Cured! Health EVEN IF YOU FEEL HEALTHY, HEPATITIS C MAY BE DAMAGING YOUR LIVER. Your liver keeps you healthy in many ways, such as by removing toxins from your blood
New York State Department of Health. 9413 Rev. 10/05
 New York State Department of Health 9413 Rev. 10/05 WHAT YOU NEED TO KNOW ABOUT HEPATITIS C: A GUIDE FOR PEOPLE WITH HIV INFECTION Did you know that in the United States, at least 1 in 4 people with HIV
New York State Department of Health 9413 Rev. 10/05 WHAT YOU NEED TO KNOW ABOUT HEPATITIS C: A GUIDE FOR PEOPLE WITH HIV INFECTION Did you know that in the United States, at least 1 in 4 people with HIV
This brochure explains how alcohol:
 When you are HIV positive, you have to work hard to stay healthy. Drinking less alcohol or not drinking at all can help you fight HIV disease and improve your health. Quitting drinking or cutting down
When you are HIV positive, you have to work hard to stay healthy. Drinking less alcohol or not drinking at all can help you fight HIV disease and improve your health. Quitting drinking or cutting down
www.hepinfo.ie Are you Hep C aware? awareness information support prevention To find out more visit
 Are you Hep C aware? awareness information support prevention To find out more visit www.hepinfo.ie What is Hepatitis C? Hepatitis C is a viral infection that affects the liver, causing it to become inflamed
Are you Hep C aware? awareness information support prevention To find out more visit www.hepinfo.ie What is Hepatitis C? Hepatitis C is a viral infection that affects the liver, causing it to become inflamed
Chlamydia THE FACTS. How do people get Chlamydia?
 What is Chlamydia? Chlamydia is a common bacterial infection that is sexually transmitted and often causes no symptoms. If not treated, chlamydia can damage reproductive organs and make it difficult for
What is Chlamydia? Chlamydia is a common bacterial infection that is sexually transmitted and often causes no symptoms. If not treated, chlamydia can damage reproductive organs and make it difficult for
Diseases that can be spread during sex
 Diseases that can be spread during sex Did you know... over 65 million people in the United States have a chronic, incurable sexually transmitted disease (STD)? and that every year another 19 million persons
Diseases that can be spread during sex Did you know... over 65 million people in the United States have a chronic, incurable sexually transmitted disease (STD)? and that every year another 19 million persons
The challenge of herpes
 The challenge of herpes Herpes is a common and personally challenging disease Herpes is very common. One out of four adults has genital herpes. When people first hear that they are infected, many become
The challenge of herpes Herpes is a common and personally challenging disease Herpes is very common. One out of four adults has genital herpes. When people first hear that they are infected, many become
BIRTH CONTROL AND PROTECTION
 BIRTH CONTROL AND PROTECTION Linking Lives Health Education Program A Birth Control and Protection Even if you decide to wait until you are much older before having sex, you are still going to hear all
BIRTH CONTROL AND PROTECTION Linking Lives Health Education Program A Birth Control and Protection Even if you decide to wait until you are much older before having sex, you are still going to hear all
General information about HIV
 HIV and pregnancy 1 To the reader The brochure is intended for women and families that are either pregnant or planning a pregnancy. The brochure discusses the matters that must be taken into consideration
HIV and pregnancy 1 To the reader The brochure is intended for women and families that are either pregnant or planning a pregnancy. The brochure discusses the matters that must be taken into consideration
A handbook for people who have injected drugs
 A handbook for people who have injected drugs Introduction This handbook has been written for current and ex-drug injectors. It gives information and advice about the hep C virus, and the tests you can
A handbook for people who have injected drugs Introduction This handbook has been written for current and ex-drug injectors. It gives information and advice about the hep C virus, and the tests you can
Belgian development agency
 Belgian development agency AIDS WHAT YOU SHOULD KNOW KEY PRINCIPLES Respect Respect yourself and others. Testing Do not wait until tomorrow. Adherence Adhere to treatment and enjoy a long and happy life.
Belgian development agency AIDS WHAT YOU SHOULD KNOW KEY PRINCIPLES Respect Respect yourself and others. Testing Do not wait until tomorrow. Adherence Adhere to treatment and enjoy a long and happy life.
Sexual reproduction in humans
 Sexual reproduction in humans Name: WHY DO HUMANS NEED TO REPRODUCE? The reason humans reproduce is to have children so that our species can continue to exist. Humans reproduce sexually, which means like
Sexual reproduction in humans Name: WHY DO HUMANS NEED TO REPRODUCE? The reason humans reproduce is to have children so that our species can continue to exist. Humans reproduce sexually, which means like
Hepatitis C. Screening, Diagnosis and Linkage to Care
 Hepatitis C Screening, Diagnosis and Linkage to Care Diagnosis If your hepatitis C antibody test is reactive, a second test will be needed to diagnose and determine if you are currently infected. Screening
Hepatitis C Screening, Diagnosis and Linkage to Care Diagnosis If your hepatitis C antibody test is reactive, a second test will be needed to diagnose and determine if you are currently infected. Screening
HIV/AIDS: Basic Facts Grade 7, Lesson #21
 HIV/AIDS: Basic Facts Grade 7, Lesson #21 Time Needed One 50-minute class period Student Learning Objectives To be able to 1. Describe how the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) affects the immune system.
HIV/AIDS: Basic Facts Grade 7, Lesson #21 Time Needed One 50-minute class period Student Learning Objectives To be able to 1. Describe how the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) affects the immune system.
CYTOTOXIC PRECAUTIONS A GUIDE FOR PATIENTS & FAMILIES
 Perth and Smiths Falls District Hospital Attention: Manager, Quality 60 Cornelia Street, West Smiths Falls, Ontario K7A 2H9 CYTOTOXIC PRECAUTIONS A GUIDE FOR PATIENTS & FAMILIES This guide has been prepared
Perth and Smiths Falls District Hospital Attention: Manager, Quality 60 Cornelia Street, West Smiths Falls, Ontario K7A 2H9 CYTOTOXIC PRECAUTIONS A GUIDE FOR PATIENTS & FAMILIES This guide has been prepared
The Facts You Need To Know. Developed by
 The Facts You Need To Know Developed by TODAY YOU LL FIND OUT What s the big deal about the liver? What is hepatitis???? Common types of viral hepatitis How can I protect myself from viral hepatitis? What
The Facts You Need To Know Developed by TODAY YOU LL FIND OUT What s the big deal about the liver? What is hepatitis???? Common types of viral hepatitis How can I protect myself from viral hepatitis? What
Hepatitis B. What I need to know about. National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH
 What I need to know about Hepatitis B U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse What I need to know about Hepatitis
What I need to know about Hepatitis B U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse What I need to know about Hepatitis
Syphilis. Looking after your sexual health
 Syphilis Looking after your sexual health 2 Syphilis Syphilis is a sexually transmitted infection (STI). It is not as common as some sexually transmitted infections but if left untreated it can cause very
Syphilis Looking after your sexual health 2 Syphilis Syphilis is a sexually transmitted infection (STI). It is not as common as some sexually transmitted infections but if left untreated it can cause very
Sexuality after your Spinal Cord Injury
 Sexuality after your Spinal Cord Injury Introduction Spinal Cord Injury (SCI) affects to varying degrees the mechanics and sensations of sex and sexuality. Some people think that spinal injury means an
Sexuality after your Spinal Cord Injury Introduction Spinal Cord Injury (SCI) affects to varying degrees the mechanics and sensations of sex and sexuality. Some people think that spinal injury means an
IUD. the IUD. the IUD. the IUD. the IUD. the IUD. the IUD the IUD. the IUD. the the IUD. the IUD. the IUD. the IUD. the IUD. the IUD.
 your guide to Helping you choose the method of contraception that is best for you I the IUD 2 3 The intrauterine device (IUD) An IUD is a small plastic and copper device that is put into your uterus (womb).
your guide to Helping you choose the method of contraception that is best for you I the IUD 2 3 The intrauterine device (IUD) An IUD is a small plastic and copper device that is put into your uterus (womb).
Genital herpes. Looking after your sexual health
 Genital herpes Looking after your sexual health 2 Genital herpes Genital herpes is a common sexually transmitted infection (STI). It is caused by a virus called Herpes simplex. Most people who get genital
Genital herpes Looking after your sexual health 2 Genital herpes Genital herpes is a common sexually transmitted infection (STI). It is caused by a virus called Herpes simplex. Most people who get genital
Dealing with Erectile Dysfunction During and After Prostate Cancer Treatment For You and Your Partner
 Dealing with Erectile Dysfunction During and After Prostate Cancer Treatment For You and Your Partner The following information is based on the general experiences of many prostate cancer patients. Your
Dealing with Erectile Dysfunction During and After Prostate Cancer Treatment For You and Your Partner The following information is based on the general experiences of many prostate cancer patients. Your
IUD. the IUD. the IUD. the IUD. the IUD. the IUD. the IUD. the IUD. the IUD. the IUD. your guide to
 your guide to Helping you choose the method of contraception that is best for you IUD he the the the 2 3 The intrauterine device (IUD) An IUD is a small plastic and copper device that is put into your
your guide to Helping you choose the method of contraception that is best for you IUD he the the the 2 3 The intrauterine device (IUD) An IUD is a small plastic and copper device that is put into your
Birth Control Methods
 page 1 Birth Control Methods Q: What is the best method of birth control (or contraception)? A: There is no best method of birth control. Each method has its pros and cons. All women and men can have control
page 1 Birth Control Methods Q: What is the best method of birth control (or contraception)? A: There is no best method of birth control. Each method has its pros and cons. All women and men can have control
Get the Facts About Tuberculosis Disease
 TB Get the Facts About Tuberculosis Disease What s Inside: Read this brochure today to learn how to protect your family and friends from TB. Then share it with people in your life. 2 Contents Get the facts,
TB Get the Facts About Tuberculosis Disease What s Inside: Read this brochure today to learn how to protect your family and friends from TB. Then share it with people in your life. 2 Contents Get the facts,
PLUS MAY EQUAL. Flu-Like Symptoms SORE THROAT, SWOLLEN GLANDS, FEVER, JOINT AND MUSCLE ACHES
 What is acute HIV infection? Acute HIV infection is the very early stage of infection with HIV (human immunodeficiency virus), the virus that causes AIDS. This is also called primary HIV infection. Acute
What is acute HIV infection? Acute HIV infection is the very early stage of infection with HIV (human immunodeficiency virus), the virus that causes AIDS. This is also called primary HIV infection. Acute
Family Planning for Women and Couples following Fistula Repair
 Family Planning for Women and Couples following Fistula Repair Fistula Care at EngenderHealth 440 Ninth Avenue, 13th Floor New York, NY, USA 10001 Tel: 212-561-8000 E-mail: fistulacare@engenderhealth.org
Family Planning for Women and Couples following Fistula Repair Fistula Care at EngenderHealth 440 Ninth Avenue, 13th Floor New York, NY, USA 10001 Tel: 212-561-8000 E-mail: fistulacare@engenderhealth.org
Thrush and Bacterial vaginosis. Looking after your sexual health
 Thrush and Bacterial vaginosis Looking after your sexual health 2 Thrush and Bacterial vaginosis Thrush is an infection that is caused by a yeast fungus. It is not a sexually transmitted infection but
Thrush and Bacterial vaginosis Looking after your sexual health 2 Thrush and Bacterial vaginosis Thrush is an infection that is caused by a yeast fungus. It is not a sexually transmitted infection but
JAC-CEN-DEL COMMUNITY SCHOOLS BLOODBORNE PATHOGENS UNIVERSAL PRECAUTIONS A BACK TO SCHOOL TRADITION
 JAC-CEN-DEL COMMUNITY SCHOOLS BLOODBORNE PATHOGENS UNIVERSAL PRECAUTIONS A BACK TO SCHOOL TRADITION UNIVERSAL PRECAUTIONS AGAINST BLOODBORNE PATHOGENS Employees working in a school system are potentially
JAC-CEN-DEL COMMUNITY SCHOOLS BLOODBORNE PATHOGENS UNIVERSAL PRECAUTIONS A BACK TO SCHOOL TRADITION UNIVERSAL PRECAUTIONS AGAINST BLOODBORNE PATHOGENS Employees working in a school system are potentially
That being said, consider the following as you decide whether or not a vasectomy is your best option for birth control.
 Since you re reading this, you are probably strongly considering a vasectomy as a way to enjoy sex without the risk of pregnancy. You may feel nervous or hesitant to get one or have questions and concerns
Since you re reading this, you are probably strongly considering a vasectomy as a way to enjoy sex without the risk of pregnancy. You may feel nervous or hesitant to get one or have questions and concerns
Bloodborne Pathogens. San Diego Unified School District Nursing & Wellness Program August 2013
 Bloodborne Pathogens San Diego Unified School District Nursing & Wellness Program August 2013 Why Another In-service?? Cal/OSHA mandates that employees with occupational exposure are informed at the time
Bloodborne Pathogens San Diego Unified School District Nursing & Wellness Program August 2013 Why Another In-service?? Cal/OSHA mandates that employees with occupational exposure are informed at the time
cancer cervical What women should know about and the human papilloma virus
 What women should know about cervical cancer and the human papilloma virus American Cancer Society Guidelines for the Early Detection of Cervical Cancer I take care of myself so I can take care of my family.
What women should know about cervical cancer and the human papilloma virus American Cancer Society Guidelines for the Early Detection of Cervical Cancer I take care of myself so I can take care of my family.
Immunization Healthcare Branch. Human Papillomavirus Vaccination Program Questions and Answers. Prepared by
 Immunization Healthcare Branch Human Papillomavirus Vaccination Program Questions and Answers Prepared by Immunization Healthcare Branch (IHB), Defense Health Agency Last Updated: 02 Jan 14 www.vaccines.mil
Immunization Healthcare Branch Human Papillomavirus Vaccination Program Questions and Answers Prepared by Immunization Healthcare Branch (IHB), Defense Health Agency Last Updated: 02 Jan 14 www.vaccines.mil
Mycophenolate mofetil (CellCept ): risks of miscarriage and birth defects. Patient guide. Key points to remember
 Mycophenolate (CellCept ): risks of miscarriage and birth defects Patient guide Key points to remember Mycophenolate (CellCept ) causes birth defects and miscarriages Follow the contraceptive advice given
Mycophenolate (CellCept ): risks of miscarriage and birth defects Patient guide Key points to remember Mycophenolate (CellCept ) causes birth defects and miscarriages Follow the contraceptive advice given
HPV and HPV Testing. Human Papilloma Virus (HPV) What are viruses? What is HPV?
 HPV and HPV Testing Human Papilloma Virus (HPV) What are viruses? Viruses are very small organisms most cannot even be seen with a regular microscope. They cannot reproduce on their own. They must enter
HPV and HPV Testing Human Papilloma Virus (HPV) What are viruses? Viruses are very small organisms most cannot even be seen with a regular microscope. They cannot reproduce on their own. They must enter
Making Sense of Your Pap and HPV Test Results
 Making Sense of Your Pap and HPV Test Results Keep this booklet until you get your test results back from your doctor. U.S. DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
Making Sense of Your Pap and HPV Test Results Keep this booklet until you get your test results back from your doctor. U.S. DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
Related TeensHealth Links
 Grades 6 to 8 Health Problems Series STDs KidsHealth.org/classroom Teacher s Guide This guide includes: Standards Related Links Discussion Questions Activities for Students Reproducible Materials Standards
Grades 6 to 8 Health Problems Series STDs KidsHealth.org/classroom Teacher s Guide This guide includes: Standards Related Links Discussion Questions Activities for Students Reproducible Materials Standards
Lesson 2: Save your Smile from Tooth Decay
 Lesson 2: Save your Smile from Tooth Decay OVERVIEW Objectives: By the end of the lesson, the Lay Health Worker will be able to: 1. Describe what tooth decay is and how it happens. 2. State the causes
Lesson 2: Save your Smile from Tooth Decay OVERVIEW Objectives: By the end of the lesson, the Lay Health Worker will be able to: 1. Describe what tooth decay is and how it happens. 2. State the causes
HPV is very common and usually clears up on its own
 What is HPV? All cervical cancers are linked to a very common virus called the human papillomavirus or HPV. HPV usually doesn t cause any harm and most people will be infected with it at some point in
What is HPV? All cervical cancers are linked to a very common virus called the human papillomavirus or HPV. HPV usually doesn t cause any harm and most people will be infected with it at some point in
NHS cervical screening Helping you decide
 NHS cervical screening Helping you decide What is cervical cancer? 2 What causes cervical cancer? 2 What is cervical screening? 3 Cervical screening results 6 What is a colposcopy? 8 What are the benefits
NHS cervical screening Helping you decide What is cervical cancer? 2 What causes cervical cancer? 2 What is cervical screening? 3 Cervical screening results 6 What is a colposcopy? 8 What are the benefits
Bloodborne Pathogens
 Bloodborne Pathogens Learning Objectives By the end of this section, the participant should be able to: Name 3 bloodborne pathogens Identify potentially contaminated bodily fluids Describe 3 safe work
Bloodborne Pathogens Learning Objectives By the end of this section, the participant should be able to: Name 3 bloodborne pathogens Identify potentially contaminated bodily fluids Describe 3 safe work
The link between cervical cancer and HPV (human papillomavirus)
 The link between cervical cancer and HPV (human papillomavirus) The link between cervical cancer and HPV Key facts: HPV is a virus (the human papillomavirus). Almost all abnormal Pap smear results are
The link between cervical cancer and HPV (human papillomavirus) The link between cervical cancer and HPV Key facts: HPV is a virus (the human papillomavirus). Almost all abnormal Pap smear results are
Learning about Hepatitis C and Chronic Kidney Disease
 Learning about Hepatitis C and Chronic Kidney Disease Hepatitis C and Chronic Kidney Disease If you have chronic kidney disease (CKD), you want to learn all you can about your disease and what you can
Learning about Hepatitis C and Chronic Kidney Disease Hepatitis C and Chronic Kidney Disease If you have chronic kidney disease (CKD), you want to learn all you can about your disease and what you can
english facts about hepatitis A, B and C
 english facts about hepatitis A, B and C What is hepatitis? Hepatitis means inflammation of the liver. Many viruses can cause liver inflammation, including the hepatitis A, B and C viruses. Some people
english facts about hepatitis A, B and C What is hepatitis? Hepatitis means inflammation of the liver. Many viruses can cause liver inflammation, including the hepatitis A, B and C viruses. Some people
implant contraceptiv contraceptive contraceptive raceptiv contraceptive implant contraceptive contraceptive ontraceptive implant ontraceptive im
 your guide to the contraceptive implant Helping you choose the method of contraception that is best for you contra ontraceptive im contraceptive implant mpl ceptive contraceptive contracepti ntraceptive
your guide to the contraceptive implant Helping you choose the method of contraception that is best for you contra ontraceptive im contraceptive implant mpl ceptive contraceptive contracepti ntraceptive
HIV/AIDS Tool Kit. B. HIV/AIDS Questionnaire for Health Care Providers and Staff
 8 HIV/AIDS Tool Kit B. HIV/AIDS Questionnaire for Health Care Providers and Staff FOR STAFF USE ONLY: SURVEY ID # HIV/AIDS KAP Questionnaire for Health Care Providers and Staff Introduction The goal of
8 HIV/AIDS Tool Kit B. HIV/AIDS Questionnaire for Health Care Providers and Staff FOR STAFF USE ONLY: SURVEY ID # HIV/AIDS KAP Questionnaire for Health Care Providers and Staff Introduction The goal of
Leader's Resource. Note: Both men and women can have an STD without physical symptoms.
 Leader's Resource Information on Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STDs) Signs and Symptoms of STDs Note: Both men and women can have an STD without physical symptoms. Any of the following can indicate to
Leader's Resource Information on Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STDs) Signs and Symptoms of STDs Note: Both men and women can have an STD without physical symptoms. Any of the following can indicate to
Condoms for the prevention of HIV and STI transmission
 FACTSHEET Condoms for the prevention of HIV and STI transmission Summary Condoms are physical barriers that can reduce the risk of a sexual exposure to HIV and sexually transmitted infections (STIs). They
FACTSHEET Condoms for the prevention of HIV and STI transmission Summary Condoms are physical barriers that can reduce the risk of a sexual exposure to HIV and sexually transmitted infections (STIs). They
ABORTION WHAT YOU NEED TO KNOW
 ABORTION WHAT YOU NEED TO KNOW ABORTION What you need to know Everyone who is pregnant has decisions to make. It might be unexpected. You might have many different feelings. It may be news that you re
ABORTION WHAT YOU NEED TO KNOW ABORTION What you need to know Everyone who is pregnant has decisions to make. It might be unexpected. You might have many different feelings. It may be news that you re
Let s Learn the Basics about Cervical Cancer
 A Publication of the National Center for Farmworker Health October-December 2014 Let s Learn the Basics about Cervical Cancer What is cancer? The body is made up of millions and millions of living cells.
A Publication of the National Center for Farmworker Health October-December 2014 Let s Learn the Basics about Cervical Cancer What is cancer? The body is made up of millions and millions of living cells.
Yes, I know I have genital herpes:
 Counseling Messages for Herpes Simplex Type II (HSV-II) Genital herpes Always take the time to attend to the participant s feelings and emotional state; for some people, this is the most devastating news
Counseling Messages for Herpes Simplex Type II (HSV-II) Genital herpes Always take the time to attend to the participant s feelings and emotional state; for some people, this is the most devastating news
Intrauterine Device (IUD) THE FACTS
 Intrauterine Device (IUD) Quick Facts Effectiveness in Preventing Pregnancy: Use: Of 100 women using IUDs for a year, about one may become pregnant. IUDs are better at preventing pregnancy than condoms,
Intrauterine Device (IUD) Quick Facts Effectiveness in Preventing Pregnancy: Use: Of 100 women using IUDs for a year, about one may become pregnant. IUDs are better at preventing pregnancy than condoms,
HPV Vaccines. What is HPV? Can a vaccine help prevent HPV?
 What is HPV? HPV Vaccines HPV stands for human papilloma virus. HPVs are a group of more than 150 related viruses. Each HPV virus in the group is given a number, and is called an HPV type (for instance,
What is HPV? HPV Vaccines HPV stands for human papilloma virus. HPVs are a group of more than 150 related viruses. Each HPV virus in the group is given a number, and is called an HPV type (for instance,
Tuberculosis and You A Guide to Tuberculosis Treatment and Services
 Tuberculosis and You A Guide to Tuberculosis Treatment and Services Tuberculosis (TB) is a serious disease that can damage the lungs or other parts of the body like the brain, kidneys or spine. There are
Tuberculosis and You A Guide to Tuberculosis Treatment and Services Tuberculosis (TB) is a serious disease that can damage the lungs or other parts of the body like the brain, kidneys or spine. There are
BARRIER METHODS (MALE AND FEMALE CONDOMS)
 Unit 17 BARRIER METHODS (MALE AND FEMALE CONDOMS) Learning Objectives By the end of this unit, learners will be able to: Describe condoms Explain the effectiveness of condoms and how they work List the
Unit 17 BARRIER METHODS (MALE AND FEMALE CONDOMS) Learning Objectives By the end of this unit, learners will be able to: Describe condoms Explain the effectiveness of condoms and how they work List the
Known Donor Questionnaire
 Known Donor Questionnaire Your donor s answers to these questions will provide you with a wealth of information about his health. You ll probably need assistance from a health care provider to interpret
Known Donor Questionnaire Your donor s answers to these questions will provide you with a wealth of information about his health. You ll probably need assistance from a health care provider to interpret
Testing for Prostate Cancer
 Testing for Prostate Cancer Should I be tested? Is it the right choice for me? Prostate cancer affects many men. There are tests to find it early. There may be benefits and risks with testing. Research
Testing for Prostate Cancer Should I be tested? Is it the right choice for me? Prostate cancer affects many men. There are tests to find it early. There may be benefits and risks with testing. Research
Important Information About PRAMS Please Read Before Starting the Survey
 Important Information About PRAMS Please Read Before Starting the Survey The Pregnancy Risk Assessment Monitoring System (PRAMS) is a research project conducted by the Bloustein Center for Survey Research
Important Information About PRAMS Please Read Before Starting the Survey The Pregnancy Risk Assessment Monitoring System (PRAMS) is a research project conducted by the Bloustein Center for Survey Research
Taking Out a Tooth. Before You Begin: Ask Questions! CHAPTER11
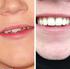 159 CHAPTER11 Taking Out a Tooth Not every painful tooth needs to come out. You must decide how serious the problem is, and then decide if you can treat and save the tooth. Some problems such as root canal
159 CHAPTER11 Taking Out a Tooth Not every painful tooth needs to come out. You must decide how serious the problem is, and then decide if you can treat and save the tooth. Some problems such as root canal
Guidelines on first aid and HIV/AIDS
 Guidelines on first aid and HIV/AIDS International Federation of Red Cross and Red Crescent Societies Any part of this handbook may be cited, copied, translated into other languages or adapted to meet
Guidelines on first aid and HIV/AIDS International Federation of Red Cross and Red Crescent Societies Any part of this handbook may be cited, copied, translated into other languages or adapted to meet
HIV/AIDS STUDY GUIDE What is HIV/AIDS? Where did HIV come from? s AIDS common? What are the symptoms?
 (1) Information on the nature of AIDS and its effects on the human body. (Adapted from Brown University Website: www.brown.edu and The Center for Disease Control Website: www.cdc.gov) What is HIV/AIDS?
(1) Information on the nature of AIDS and its effects on the human body. (Adapted from Brown University Website: www.brown.edu and The Center for Disease Control Website: www.cdc.gov) What is HIV/AIDS?
Name Date Class. This section explains what kinds of organisms cause infectious disease and how infectious diseases are spread.
 Fighting Disease Name Date Class Infectious Disease This section explains what kinds of organisms cause infectious disease and how infectious diseases are spread. Use Target Reading Skills Before you read,
Fighting Disease Name Date Class Infectious Disease This section explains what kinds of organisms cause infectious disease and how infectious diseases are spread. Use Target Reading Skills Before you read,
Pubic lice and Scabies. Looking after your sexual health
 Pubic lice and Scabies Looking after your sexual health 2 Pubic lice and Scabies Pubic lice are tiny parasitic insects that live in coarse body hair, such as pubic hair. They are yellow-grey and about
Pubic lice and Scabies Looking after your sexual health 2 Pubic lice and Scabies Pubic lice are tiny parasitic insects that live in coarse body hair, such as pubic hair. They are yellow-grey and about
Alcohol and drug abuse
 Alcohol and drug abuse This chapter explores how alcohol abuse affects our families, relationships, and communities, as well as the health risks associated with drug and alcohol abuse. 1. Alcohol abuse
Alcohol and drug abuse This chapter explores how alcohol abuse affects our families, relationships, and communities, as well as the health risks associated with drug and alcohol abuse. 1. Alcohol abuse
