Genetic Disorders HST.023. Spring 2003
|
|
|
- Hollie Woods
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology HST.035: Principle and Practice of Human Pathology Dr. Badizadegan Genetic Disorders HST.023 Spring 2003
2 Genetic Disorders Cytogenetic Disorders Gross chromosomal abnormalities Single-Gene Disorders With classical (Mendelian) inheritance With non-classical inheritance Mitochondrial genes Trinucleotide repeats Genetic imprinting
3 Cytogenetic Disorders: Where is the defect?
4 1. Catch the chromosomes in action
5 2. Stain and arrange them in order Please see Junqueira & Carneiro. Basic Histology: Text and Atlas. 10 th edition. McGraw Hill ISBN: From Junquiera, Basic Histology, McGraw Hill, 2003.
6 Idiogram of G banded Human Karyotype Idiogram Album: Human copyright 1994 David Adler
7 Cytogenetic disorders are characterized by an abnormal constitutional karyotype What mechanisms would result in cytogenetic abnormalities?
8 Nondisjunction in Meiosis I Normal Meiosis II Gametes n + 1 n + 1 n 1 n 1 Number of Chromosomes
9 Nondisjunction in Meiosis II Normal Meiosis I Gametes n + 1 n - 1 n n Number of Chromosomes
10 Nondisjunction can also happen during mitosis. What is the consequence of nondisjunction during mitosis?
11 Chromosomal Rearrangements
12 Do chromosomal rearrangements always lead to cytogenetic disorders?
13 What is the diagnosis?
14 Trisomy 21 (Down Syndrome) The most common chromosomal disorder with incidence of 1:700 live births in the US 95% trisomy 21; 4% Robertsonian translocation involving the long arm of 21; 1% mosaic High correlation between maternal age and meiotic nondisjunction leading to trisomy 21 Congenital heart disease; dysmorphic features; mental retardation; predisposition to leukemias; neurodegenerative changes; abnormal immune response and autoimmunity
15 Sex Chromosome Disorders: More common than autosomal disorders Klinefelter syndrome (47, XXY) 1:850 male births Rarely diagnosed before puberty Tall stature, hypogonadism, lack of secondary male characteristics, gynecomastia The principal cause of male infertility due to reduced spermatogenesis Turner syndrome (45, X) 1:3000 female births Extensive karyotype heterogeneity with question about existence of pure monosomy X (99% of 45, X eggs are non-viable) Short stature, webbing of the neck, cardiovascular abnormalities, lack of secondary sex characteristics, streak ovaries (accelerated loss of oocytes)
16 Image from
17 Single-Gene Mendelian Disorders Structural proteins Osteogenesis imperfecta and Ehlers-Danlos (collagens); Marfan syndrome (fibrillin); Duchenne and Becker muscular dystrophies (dystrophin) Enzymes and inhibitors Lysosomal storage diseases; SCID (adenosine deaminase); PKU (phenylalanine hydroxylase); Alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency Receptors Familial hypercholesterolemia (LDL receptor) Cell growth regulation Neurofibromatosis type I (neurofibromin); Hereditary retinoblastoma (Rb) Transporters Cystic fibrosis (CFTR); Sickle cell disease (Hb); Thalassemias (Hb)
18 Neurofibromatosis Type 1 (NF1) Multiple neurofibromas; pigmented skin lesions; pigmented iris hamartomas (Lisch nodules); plus a variety of other abnormalities Incidence of at least 1:3000 Autosomal dominant trait with complete penetrance ~50% of cases are sporadic Mutation rate 1/10,000 gametes; the highest observed in humans Neurofibromin mapped to 17q11.2 downregulates the function of p21 ras oncoprotein
19 Familial Hypercholesterolemia (FH)? The most frequent Mendelian disorder Heterozygotes, representing 1:500, have 2-3x elevation of cholesterol levels with xanthomas and premature atherosclerosis Homozygotes develop extensive xanthomas, as well as coronary, cerebral and peripheral vascular disease at an early age, and may develop MI before the age of 20
20 FH: Defect of Receptor-Mediated Endocytosis
21 Non-classical Inheritance Genetic imprinting Parents do make a difference! Trinucleotide repeats Genetic instability and anticipation Mitochondrial genes
22 Genetic Imprinting For most (non-imprinted) genes, the maternal copy is functionally equivalent to the paternal copy Imprinted genes, however, are expressed differently from maternal and paternal alleles In most cases, imprinting selectively inactivates either the maternal or the paternal allele of a particular gene
23 Complete Hydatidiform Mole: Too much paternal influence Egg and sperm nuclei contain the same genetic information, but neither two eggs nor two sperms can support embryonic development.
24 The Puzzle of del(15)(q11q13) Mental retardation Ataxic gait Seizures Inappropriate laughter Mental retardation Short stature Hypotonia Obesity Hypogonadism
25 MATERNAL PATERNAL (M) (P) Imprinted Prader-Willi gene(s) Active Angelman gene(s) Active Prader-Willi gene(s) Imprinted Angelman gene(s) Deletion in maternal Deletion in paternal (M) (P) chromosome chromosome (M) (P) Site of deletion Active Prader-Willi gene(s) Imprinted Angelman gene(s) Imprinted Prader-Willi gene(s) Active Angelman gene(s) Site of deletion ANGELMAN SYNDROME PRADER-WILLI SYNDROME
26 Besides deletions, how else can imprinted genes result in cytogenetic disease?
27 Fragile X Syndrome Prototype of diseases in which amplification of trinucleotide repeats results in disease (also includes Huntington, Mytotonic dystrophy, Myoclonus epilepsy) Macro-orchidism, mental retardation, large head, long face, large ears X chromosomes of cells grown in folate deficient media show breaks at the end of their long arm Accumulation of CCG repeats in the 5 untranslated region of the FMR1 gene (Xq27.3) result in gene inactivation
28 Fragile X Inheritance 65 32, , 32 75, , 26 30, , 32
29 Anticipation Clinically observed phenomenon of increasing severity of disease in each succeeding generation Trinucleotide repeats tend to increase in generation to generation Age of onset and disease severity is directly linked to the number of trinucleotide repeats
30 Pedigree of Leber Optic Neuropathy What is the pattern of inheritance?
31 Mitochondrial Genes Mitochondrial DNA encodes 22 trnas, 2 rrnas, and 13 proteins involved in the respiratory chain Most respiratory chain complexes have subunits from the nuclear as well as the mitochondrial genome, therefore, completely unrelated mutations can lead to similar clinical presentations
32 Genetic Disorders: It is just the beginning!
Genetic Mutations. Indicator 4.8: Compare the consequences of mutations in body cells with those in gametes.
 Genetic Mutations Indicator 4.8: Compare the consequences of mutations in body cells with those in gametes. Agenda Warm UP: What is a mutation? Body cell? Gamete? Notes on Mutations Karyotype Web Activity
Genetic Mutations Indicator 4.8: Compare the consequences of mutations in body cells with those in gametes. Agenda Warm UP: What is a mutation? Body cell? Gamete? Notes on Mutations Karyotype Web Activity
Chromosomes, Mapping, and the Meiosis Inheritance Connection
 Chromosomes, Mapping, and the Meiosis Inheritance Connection Carl Correns 1900 Chapter 13 First suggests central role for chromosomes Rediscovery of Mendel s work Walter Sutton 1902 Chromosomal theory
Chromosomes, Mapping, and the Meiosis Inheritance Connection Carl Correns 1900 Chapter 13 First suggests central role for chromosomes Rediscovery of Mendel s work Walter Sutton 1902 Chromosomal theory
What Is Genetic Counseling? Helping individuals and families understand how genetics affects their health and lives
 What Is Genetic Counseling? Helping individuals and families understand how genetics affects their health and lives What does the career involve? Explore family histories to identify risks Reducing risks
What Is Genetic Counseling? Helping individuals and families understand how genetics affects their health and lives What does the career involve? Explore family histories to identify risks Reducing risks
Basic Human Genetics: Reproductive Health and Chromosome Abnormalities
 Basic Human Genetics: Reproductive Health and Chromosome Abnormalities Professor Hanan Hamamy Department of Genetic Medicine and Development Geneva University Switzerland Training Course in Sexual and
Basic Human Genetics: Reproductive Health and Chromosome Abnormalities Professor Hanan Hamamy Department of Genetic Medicine and Development Geneva University Switzerland Training Course in Sexual and
UNIT 13 (OPTION) Genetic Abnormalities
 Unit 13 Genetic Abnormailities 1 UNIT 13 (OPTION) Genetic Abnormalities Originally developed by: Hildur Helgedottir RN, MN Revised (2000) by: Marlene Reimer RN, PhD, CCN (C) Associate Professor Faculty
Unit 13 Genetic Abnormailities 1 UNIT 13 (OPTION) Genetic Abnormalities Originally developed by: Hildur Helgedottir RN, MN Revised (2000) by: Marlene Reimer RN, PhD, CCN (C) Associate Professor Faculty
MEDICAL GENETICS GENERAL OBJECTIVE SPECIFIC OBJECTIVES
 SUBJECT MEDICAL GENETICS CREDITS Total: 4.5 Theory 2.5 Practical 2 GENERAL OBJECTIVE To provide students with terminology and knowledge from the field of human genetics that will enable them to understand
SUBJECT MEDICAL GENETICS CREDITS Total: 4.5 Theory 2.5 Practical 2 GENERAL OBJECTIVE To provide students with terminology and knowledge from the field of human genetics that will enable them to understand
Each person normally has 23 pairs of chromosomes, or 46 in all. We inherit one chromosome per pair from our mother and one from our father.
 AP Psychology 2.2 Behavioral Genetics Article Chromosomal Abnormalities About 1 in 150 babies is born with a chromosomal abnormality (1, 2). These are caused by errors in the number or structure of chromosomes.
AP Psychology 2.2 Behavioral Genetics Article Chromosomal Abnormalities About 1 in 150 babies is born with a chromosomal abnormality (1, 2). These are caused by errors in the number or structure of chromosomes.
MCB41: Second Midterm Spring 2009
 MCB41: Second Midterm Spring 2009 Before you start, print your name and student identification number (S.I.D) at the top of each page. There are 7 pages including this page. You will have 50 minutes for
MCB41: Second Midterm Spring 2009 Before you start, print your name and student identification number (S.I.D) at the top of each page. There are 7 pages including this page. You will have 50 minutes for
Heredity - Patterns of Inheritance
 Heredity - Patterns of Inheritance Genes and Alleles A. Genes 1. A sequence of nucleotides that codes for a special functional product a. Transfer RNA b. Enzyme c. Structural protein d. Pigments 2. Genes
Heredity - Patterns of Inheritance Genes and Alleles A. Genes 1. A sequence of nucleotides that codes for a special functional product a. Transfer RNA b. Enzyme c. Structural protein d. Pigments 2. Genes
The correct answer is c A. Answer a is incorrect. The white-eye gene must be recessive since heterozygous females have red eyes.
 1. Why is the white-eye phenotype always observed in males carrying the white-eye allele? a. Because the trait is dominant b. Because the trait is recessive c. Because the allele is located on the X chromosome
1. Why is the white-eye phenotype always observed in males carrying the white-eye allele? a. Because the trait is dominant b. Because the trait is recessive c. Because the allele is located on the X chromosome
Genetics Review for USMLE (Part 2)
 Single Gene Disorders Genetics Review for USMLE (Part 2) Some Definitions Alleles variants of a given DNA sequence at a particular location (locus) in the genome. Often used more narrowly to describe alternative
Single Gene Disorders Genetics Review for USMLE (Part 2) Some Definitions Alleles variants of a given DNA sequence at a particular location (locus) in the genome. Often used more narrowly to describe alternative
Fact Sheet 14 EPIGENETICS
 This fact sheet describes epigenetics which refers to factors that can influence the way our genes are expressed in the cells of our body. In summary Epigenetics is a phenomenon that affects the way cells
This fact sheet describes epigenetics which refers to factors that can influence the way our genes are expressed in the cells of our body. In summary Epigenetics is a phenomenon that affects the way cells
CHROMOSOMES Dr. Fern Tsien, Dept. of Genetics, LSUHSC, NO, LA
 CHROMOSOMES Dr. Fern Tsien, Dept. of Genetics, LSUHSC, NO, LA Cytogenetics is the study of chromosomes and their structure, inheritance, and abnormalities. Chromosome abnormalities occur in approximately:
CHROMOSOMES Dr. Fern Tsien, Dept. of Genetics, LSUHSC, NO, LA Cytogenetics is the study of chromosomes and their structure, inheritance, and abnormalities. Chromosome abnormalities occur in approximately:
CHAPTER 15 THE CHROMOSOMAL BASIS OF INHERITANCE. Section B: Sex Chromosomes
 CHAPTER 15 THE CHROMOSOMAL BASIS OF INHERITANCE Section B: Sex Chromosomes 1. The chromosomal basis of sex varies with the organism 2. Sex-linked genes have unique patterns of inheritance 1. The chromosomal
CHAPTER 15 THE CHROMOSOMAL BASIS OF INHERITANCE Section B: Sex Chromosomes 1. The chromosomal basis of sex varies with the organism 2. Sex-linked genes have unique patterns of inheritance 1. The chromosomal
Chromosomal Abnormalities
 Chromosomal Abnormalities George E Tiller, MD, PhD Regional Chief, Dept. Genetics Southern California Permanente Medical Group Los Angeles, CA Objectives of Lecture list several indications for karyotyping
Chromosomal Abnormalities George E Tiller, MD, PhD Regional Chief, Dept. Genetics Southern California Permanente Medical Group Los Angeles, CA Objectives of Lecture list several indications for karyotyping
Genetics in Paediatrics. Diagnostics Aetiology Treatment Prognosis Prediktion Advise Research
 Genetics in Paediatrics Diagnostics Aetiology Treatment Prognosis Prediktion Advise Research Genetic nomenclature,, abbreviations.. Mendels first law: Random transmittance to off-spring of the two chromosomes
Genetics in Paediatrics Diagnostics Aetiology Treatment Prognosis Prediktion Advise Research Genetic nomenclature,, abbreviations.. Mendels first law: Random transmittance to off-spring of the two chromosomes
Chapter 8: Variation in Chromosome Structure and Number
 Chapter 8: Variation in Chromosome Structure and Number Student Learning Objectives Upon completion of this chapter you should be able to: 1. Know the principles and terminology associated with variations
Chapter 8: Variation in Chromosome Structure and Number Student Learning Objectives Upon completion of this chapter you should be able to: 1. Know the principles and terminology associated with variations
Chapter 4 Pedigree Analysis in Human Genetics. Chapter 4 Human Heredity by Michael Cummings 2006 Brooks/Cole-Thomson Learning
 Chapter 4 Pedigree Analysis in Human Genetics Mendelian Inheritance in Humans Pigmentation Gene and Albinism Fig. 3.14 Two Genes Fig. 3.15 The Inheritance of Human Traits Difficulties Long generation time
Chapter 4 Pedigree Analysis in Human Genetics Mendelian Inheritance in Humans Pigmentation Gene and Albinism Fig. 3.14 Two Genes Fig. 3.15 The Inheritance of Human Traits Difficulties Long generation time
Becker Muscular Dystrophy
 Muscular Dystrophy A Case Study of Positional Cloning Described by Benjamin Duchenne (1868) X-linked recessive disease causing severe muscular degeneration. 100 % penetrance X d Y affected male Frequency
Muscular Dystrophy A Case Study of Positional Cloning Described by Benjamin Duchenne (1868) X-linked recessive disease causing severe muscular degeneration. 100 % penetrance X d Y affected male Frequency
The following chapter is called "Preimplantation Genetic Diagnosis (PGD)".
 Slide 1 Welcome to chapter 9. The following chapter is called "Preimplantation Genetic Diagnosis (PGD)". The author is Dr. Maria Lalioti. Slide 2 The learning objectives of this chapter are: To learn the
Slide 1 Welcome to chapter 9. The following chapter is called "Preimplantation Genetic Diagnosis (PGD)". The author is Dr. Maria Lalioti. Slide 2 The learning objectives of this chapter are: To learn the
Genetic Disorder Brochure Project
 Genetic Disorder Brochure Project (modified from a project found on the Robbinsdale School District website) Overview Create a tri-fold brochure for a doctor s office waiting room. The brochure should
Genetic Disorder Brochure Project (modified from a project found on the Robbinsdale School District website) Overview Create a tri-fold brochure for a doctor s office waiting room. The brochure should
Human Blood Types: Codominance and Multiple Alleles. Codominance: both alleles in the heterozygous genotype express themselves fully
 Human Blood Types: Codominance and Multiple Alleles Codominance: both alleles in the heterozygous genotype express themselves fully Multiple alleles: three or more alleles for a trait are found in the
Human Blood Types: Codominance and Multiple Alleles Codominance: both alleles in the heterozygous genotype express themselves fully Multiple alleles: three or more alleles for a trait are found in the
Genetic Testing in Research & Healthcare
 We Innovate Healthcare Genetic Testing in Research & Healthcare We Innovate Healthcare Genetic Testing in Research and Healthcare Human genetic testing is a growing science. It is used to study genes
We Innovate Healthcare Genetic Testing in Research & Healthcare We Innovate Healthcare Genetic Testing in Research and Healthcare Human genetic testing is a growing science. It is used to study genes
DIAGNOSING CHILDHOOD MUSCULAR DYSTROPHIES
 DIAGNOSING CHILDHOOD MUSCULAR DYSTROPHIES Extracts from a review article by KN North and KJ Jones: Recent advances in diagnosis of the childhood muscular dystrophies Journal of Paediatrics and Child Health
DIAGNOSING CHILDHOOD MUSCULAR DYSTROPHIES Extracts from a review article by KN North and KJ Jones: Recent advances in diagnosis of the childhood muscular dystrophies Journal of Paediatrics and Child Health
Influence of Sex on Genetics. Chapter Six
 Influence of Sex on Genetics Chapter Six Humans 23 Autosomes Chromosomal abnormalities very severe Often fatal All have at least one X Deletion of X chromosome is fatal Males = heterogametic sex XY Females
Influence of Sex on Genetics Chapter Six Humans 23 Autosomes Chromosomal abnormalities very severe Often fatal All have at least one X Deletion of X chromosome is fatal Males = heterogametic sex XY Females
Umm AL Qura University MUTATIONS. Dr Neda M Bogari
 Umm AL Qura University MUTATIONS Dr Neda M Bogari CONTACTS www.bogari.net http://web.me.com/bogari/bogari.net/ From DNA to Mutations MUTATION Definition: Permanent change in nucleotide sequence. It can
Umm AL Qura University MUTATIONS Dr Neda M Bogari CONTACTS www.bogari.net http://web.me.com/bogari/bogari.net/ From DNA to Mutations MUTATION Definition: Permanent change in nucleotide sequence. It can
Gene mutation and molecular medicine Chapter 15
 Gene mutation and molecular medicine Chapter 15 Lecture Objectives What Are Mutations? How Are DNA Molecules and Mutations Analyzed? How Do Defective Proteins Lead to Diseases? What DNA Changes Lead to
Gene mutation and molecular medicine Chapter 15 Lecture Objectives What Are Mutations? How Are DNA Molecules and Mutations Analyzed? How Do Defective Proteins Lead to Diseases? What DNA Changes Lead to
Causes of Birth Defects
 Causes of Birth Defects Some medical / genetic terms: congenital defects: visible defects present at birth (due to any cause (genetic, developmental error ). syndrome: the symptoms that characterize any
Causes of Birth Defects Some medical / genetic terms: congenital defects: visible defects present at birth (due to any cause (genetic, developmental error ). syndrome: the symptoms that characterize any
*Please consult the online schedule for this course for the definitive date and time for this lecture.
 CHROMOSOMES AND DISEASE Date: September 29, 2005 * Time: 8:00 am- 8:50 am * Room: G-202 Biomolecular Building Lecturer: Jim Evans 4200A Biomolecular Building jpevans@med.unc.edu Office Hours: by appointment
CHROMOSOMES AND DISEASE Date: September 29, 2005 * Time: 8:00 am- 8:50 am * Room: G-202 Biomolecular Building Lecturer: Jim Evans 4200A Biomolecular Building jpevans@med.unc.edu Office Hours: by appointment
Lecture 3: Mutations
 Lecture 3: Mutations Recall that the flow of information within a cell involves the transcription of DNA to mrna and the translation of mrna to protein. Recall also, that the flow of information between
Lecture 3: Mutations Recall that the flow of information within a cell involves the transcription of DNA to mrna and the translation of mrna to protein. Recall also, that the flow of information between
Von Mäusen und Menschen E - 1
 Von Mäusen und Menschen E - 1 Mus musculus: Genetic Portrait of the House Mouse E - 3 Outline Mouse genome Mouse life cycle Transgenic protocols Addition of genes by nuclear injection Removal of genes
Von Mäusen und Menschen E - 1 Mus musculus: Genetic Portrait of the House Mouse E - 3 Outline Mouse genome Mouse life cycle Transgenic protocols Addition of genes by nuclear injection Removal of genes
Mendelian inheritance and the
 Mendelian inheritance and the most common genetic diseases Cornelia Schubert, MD, University of Goettingen, Dept. Human Genetics EUPRIM-Net course Genetics, Immunology and Breeding Mangement German Primate
Mendelian inheritance and the most common genetic diseases Cornelia Schubert, MD, University of Goettingen, Dept. Human Genetics EUPRIM-Net course Genetics, Immunology and Breeding Mangement German Primate
Biology 1406 Exam 4 Notes Cell Division and Genetics Ch. 8, 9
 Biology 1406 Exam 4 Notes Cell Division and Genetics Ch. 8, 9 Ch. 8 Cell Division Cells divide to produce new cells must pass genetic information to new cells - What process of DNA allows this? Two types
Biology 1406 Exam 4 Notes Cell Division and Genetics Ch. 8, 9 Ch. 8 Cell Division Cells divide to produce new cells must pass genetic information to new cells - What process of DNA allows this? Two types
Chapter 13: Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles
 Name Period Chapter 13: Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles Concept 13.1 Offspring acquire genes from parents by inheriting chromosomes 1. Let s begin with a review of several terms that you may already know.
Name Period Chapter 13: Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles Concept 13.1 Offspring acquire genes from parents by inheriting chromosomes 1. Let s begin with a review of several terms that you may already know.
Chromosomes, Karyotyping, and Abnormalities (Learning Objectives) Learn the components and parts of a metaphase chromosome.
 Chromosomes, Karyotyping, and Abnormalities (Learning Objectives) Learn the components and parts of a metaphase chromosome. Define the terms karyotype, autosomal and sex chromosomes. Explain how many of
Chromosomes, Karyotyping, and Abnormalities (Learning Objectives) Learn the components and parts of a metaphase chromosome. Define the terms karyotype, autosomal and sex chromosomes. Explain how many of
RECURRENT PREGNANCY LOSS DR.RAJALAKSHMI SRINIVASAN SPECIALIST GYNECOLOGIST ZULEKHA HOSPITAL DUBAI
 RECURRENT PREGNANCY LOSS DR.RAJALAKSHMI SRINIVASAN SPECIALIST GYNECOLOGIST ZULEKHA HOSPITAL DUBAI RECURRENT PREGNANCY LOSS -RM Clinically recognized consecutive or non consecutive pregnancy losses before
RECURRENT PREGNANCY LOSS DR.RAJALAKSHMI SRINIVASAN SPECIALIST GYNECOLOGIST ZULEKHA HOSPITAL DUBAI RECURRENT PREGNANCY LOSS -RM Clinically recognized consecutive or non consecutive pregnancy losses before
CELL DIVISION. STAGES OF MITOTIC DIVISION (Diag. C1)
 1 CELL DIVISION Cell division is the process by which cells replicate in order to replace cell loss, repair tissue damage and reproduce the organism. Two types of cell division are encountered in the Eukaryotic
1 CELL DIVISION Cell division is the process by which cells replicate in order to replace cell loss, repair tissue damage and reproduce the organism. Two types of cell division are encountered in the Eukaryotic
Sex for the purposes of this class refers to 4 components
 Sex for the purposes of this class refers to 4 components Gonadal sex Gonads or where gametes are produced by meiosis Somatic sex Somatic cells are cells that undergo mitosis. They can be divided into
Sex for the purposes of this class refers to 4 components Gonadal sex Gonads or where gametes are produced by meiosis Somatic sex Somatic cells are cells that undergo mitosis. They can be divided into
A trait is a variation of a particular character (e.g. color, height). Traits are passed from parents to offspring through genes.
 1 Biology Chapter 10 Study Guide Trait A trait is a variation of a particular character (e.g. color, height). Traits are passed from parents to offspring through genes. Genes Genes are located on chromosomes
1 Biology Chapter 10 Study Guide Trait A trait is a variation of a particular character (e.g. color, height). Traits are passed from parents to offspring through genes. Genes Genes are located on chromosomes
CHROMOSOMES AND INHERITANCE
 SECTION 12-1 REVIEW CHROMOSOMES AND INHERITANCE VOCABULARY REVIEW Distinguish between the terms in each of the following pairs of terms. 1. sex chromosome, autosome 2. germ-cell mutation, somatic-cell
SECTION 12-1 REVIEW CHROMOSOMES AND INHERITANCE VOCABULARY REVIEW Distinguish between the terms in each of the following pairs of terms. 1. sex chromosome, autosome 2. germ-cell mutation, somatic-cell
Darlene Langhoff St. Thomas More High Ron Gerrits MSOE
 Darlene Langhoff St. Thomas More High Ron Gerrits MSOE Investigating the Scene DNA analysis The Findings Crime scene is set up (optional power point ) Tip: Set up crime scene and have students take photos
Darlene Langhoff St. Thomas More High Ron Gerrits MSOE Investigating the Scene DNA analysis The Findings Crime scene is set up (optional power point ) Tip: Set up crime scene and have students take photos
ACMG Practice Guideline
 June 2007 Vol. 9 No. 6 ACMG Practice Guideline Indications for genetic referral: a guide for healthcare providers Beth A. Pletcher, MD 1, Helga V. Toriello, PhD 2, Sarah J. Noblin, MS, CGC 3, Laurie H.
June 2007 Vol. 9 No. 6 ACMG Practice Guideline Indications for genetic referral: a guide for healthcare providers Beth A. Pletcher, MD 1, Helga V. Toriello, PhD 2, Sarah J. Noblin, MS, CGC 3, Laurie H.
DISABILITY-RELATED DEFINITIONS
 DISABILITY-RELATED DEFINITIONS 1. The Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) of 1990 is a civil rights law, which makes it unlawful to discriminate on the basis of disability. It covers employment in the
DISABILITY-RELATED DEFINITIONS 1. The Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) of 1990 is a civil rights law, which makes it unlawful to discriminate on the basis of disability. It covers employment in the
Heritability: Twin Studies. Twin studies are often used to assess genetic effects on variation in a trait
 TWINS AND GENETICS TWINS Heritability: Twin Studies Twin studies are often used to assess genetic effects on variation in a trait Comparing MZ/DZ twins can give evidence for genetic and/or environmental
TWINS AND GENETICS TWINS Heritability: Twin Studies Twin studies are often used to assess genetic effects on variation in a trait Comparing MZ/DZ twins can give evidence for genetic and/or environmental
The Developing Person Through the Life Span 8e by Kathleen Stassen Berger
 The Developing Person Through the Life Span 8e by Kathleen Stassen Berger Chapter 3 Heredity and Environment PowerPoint Slides developed by Martin Wolfger and Michael James Ivy Tech Community College-Bloomington
The Developing Person Through the Life Span 8e by Kathleen Stassen Berger Chapter 3 Heredity and Environment PowerPoint Slides developed by Martin Wolfger and Michael James Ivy Tech Community College-Bloomington
1 Mutation and Genetic Change
 CHAPTER 14 1 Mutation and Genetic Change SECTION Genes in Action KEY IDEAS As you read this section, keep these questions in mind: What is the origin of genetic differences among organisms? What kinds
CHAPTER 14 1 Mutation and Genetic Change SECTION Genes in Action KEY IDEAS As you read this section, keep these questions in mind: What is the origin of genetic differences among organisms? What kinds
AP Biology PowerPoint Notes Chapter 11 & 12 Patterns of Heredity and Human Genetics
 AP Biology PowerPoint Notes Chapter 11 & 12 Patterns of Heredity and Human Genetics Mendelism and Genotype Genotype must be considered an integrated whole of all the genes because genes often work together
AP Biology PowerPoint Notes Chapter 11 & 12 Patterns of Heredity and Human Genetics Mendelism and Genotype Genotype must be considered an integrated whole of all the genes because genes often work together
Chapter 13: Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles
 Name Period Concept 13.1 Offspring acquire genes from parents by inheriting chromosomes 1. Let s begin with a review of several terms that you may already know. Define: gene locus gamete male gamete female
Name Period Concept 13.1 Offspring acquire genes from parents by inheriting chromosomes 1. Let s begin with a review of several terms that you may already know. Define: gene locus gamete male gamete female
Objectives Role of Medical Genetics in Hearing Loss Evaluation. 5 y.o. boy with severe SNHL
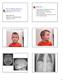 Objectives Role of Medical Genetics in Hearing Loss Evaluation Millan Patel, MD UBC Dept. of Medical Genetics October 22, 2010 Case presentation to illustrate importance of defining syndromic hearing loss
Objectives Role of Medical Genetics in Hearing Loss Evaluation Millan Patel, MD UBC Dept. of Medical Genetics October 22, 2010 Case presentation to illustrate importance of defining syndromic hearing loss
Lecture 6: Single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) and Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphisms (RFLPs)
 Lecture 6: Single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) and Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphisms (RFLPs) Single nucleotide polymorphisms or SNPs (pronounced "snips") are DNA sequence variations that occur
Lecture 6: Single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) and Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphisms (RFLPs) Single nucleotide polymorphisms or SNPs (pronounced "snips") are DNA sequence variations that occur
4.2 Meiosis. Meiosis is a reduction division. Assessment statements. The process of meiosis
 4.2 Meiosis Assessment statements State that meiosis is a reduction division of a diploid nucleus to form haploid nuclei. Define homologous chromosomes. Outline the process of meiosis, including pairing
4.2 Meiosis Assessment statements State that meiosis is a reduction division of a diploid nucleus to form haploid nuclei. Define homologous chromosomes. Outline the process of meiosis, including pairing
Human Genome Organization: An Update. Genome Organization: An Update
 Human Genome Organization: An Update Genome Organization: An Update Highlights of Human Genome Project Timetable Proposed in 1990 as 3 billion dollar joint venture between DOE and NIH with 15 year completion
Human Genome Organization: An Update Genome Organization: An Update Highlights of Human Genome Project Timetable Proposed in 1990 as 3 billion dollar joint venture between DOE and NIH with 15 year completion
Patient Information. for Childhood
 Patient Information Genetic Testing for Childhood Hearing Loss Introduction This document describes the most common genetic cause of childhood hearing loss and explains the role of genetic testing. Childhood
Patient Information Genetic Testing for Childhood Hearing Loss Introduction This document describes the most common genetic cause of childhood hearing loss and explains the role of genetic testing. Childhood
GENETIC TESTING FOR INHERITED MUTATIONS OR SUSCEPTIBILITY TO CANCER OR OTHER CONDITIONS MED207.110
 GENETIC TESTING FOR INHERITED MUTATIONS OR SUSCEPTIBILITY TO CANCER OR OTHER CONDITIONS MED207.110 COVERAGE: Pre- and post-genetic test counseling may be eligible for coverage in addition to the genetic
GENETIC TESTING FOR INHERITED MUTATIONS OR SUSCEPTIBILITY TO CANCER OR OTHER CONDITIONS MED207.110 COVERAGE: Pre- and post-genetic test counseling may be eligible for coverage in addition to the genetic
Minimum standards for ICSI use, screening, patient information and follow-up in WA fertility clinics. January 2006
 Minimum standards for ICSI use, screening, patient information and follow-up in WA fertility clinics January 2006 1. BACKGROUND ICSI has been shown to be effective for male factor infertility and it also
Minimum standards for ICSI use, screening, patient information and follow-up in WA fertility clinics January 2006 1. BACKGROUND ICSI has been shown to be effective for male factor infertility and it also
Georgia Department of Human Resources BACKGROUND INFORMATION FOR NON-STATE AGENCY CHILD
 Georgia Department of Human Resources BACKGROUND INFORMATION FOR NON-STATE AGENCY CHILD Responsible Party Telephone Number Date Name of Child Date of Birth Time of Birth Sex Resident County Placement County
Georgia Department of Human Resources BACKGROUND INFORMATION FOR NON-STATE AGENCY CHILD Responsible Party Telephone Number Date Name of Child Date of Birth Time of Birth Sex Resident County Placement County
Bio EOC Topics for Cell Reproduction: Bio EOC Questions for Cell Reproduction:
 Bio EOC Topics for Cell Reproduction: Asexual vs. sexual reproduction Mitosis steps, diagrams, purpose o Interphase, Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, Telophase, Cytokinesis Meiosis steps, diagrams, purpose
Bio EOC Topics for Cell Reproduction: Asexual vs. sexual reproduction Mitosis steps, diagrams, purpose o Interphase, Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, Telophase, Cytokinesis Meiosis steps, diagrams, purpose
Chromosomal Basis of Inheritance. Ch. 3
 Chromosomal Basis of Inheritance Ch. 3 THE CHROMOSOME THEORY OF INHERITANCE AND SEX CHROMOSOMES! The chromosome theory of inheritance describes how the transmission of chromosomes account for the Mendelian
Chromosomal Basis of Inheritance Ch. 3 THE CHROMOSOME THEORY OF INHERITANCE AND SEX CHROMOSOMES! The chromosome theory of inheritance describes how the transmission of chromosomes account for the Mendelian
4 SEX CHROMOSOMES AND SEX DETERMINATION
 4 SEX CHROMOSOMES AND SEX DETERMINATION 4.1 Sex chromosomes and Sex Determination Sex- chromosomes. If present, sex chromosomes may not have the same size, shape, or genetic potential. In humans, females
4 SEX CHROMOSOMES AND SEX DETERMINATION 4.1 Sex chromosomes and Sex Determination Sex- chromosomes. If present, sex chromosomes may not have the same size, shape, or genetic potential. In humans, females
Influences on Birth Defects
 Influences on Birth Defects FACTS About 150,000 babies are born each year with birth defects. The parents of one out of every 28 babies receive the frightening news that their baby has a birth defect There
Influences on Birth Defects FACTS About 150,000 babies are born each year with birth defects. The parents of one out of every 28 babies receive the frightening news that their baby has a birth defect There
14.3 Studying the Human Genome
 14.3 Studying the Human Genome Lesson Objectives Summarize the methods of DNA analysis. State the goals of the Human Genome Project and explain what we have learned so far. Lesson Summary Manipulating
14.3 Studying the Human Genome Lesson Objectives Summarize the methods of DNA analysis. State the goals of the Human Genome Project and explain what we have learned so far. Lesson Summary Manipulating
Overview of Genetic Testing and Screening
 Integrating Genetics into Your Practice Webinar Series Overview of Genetic Testing and Screening Genetic testing is an important tool in the screening and diagnosis of many conditions. New technology is
Integrating Genetics into Your Practice Webinar Series Overview of Genetic Testing and Screening Genetic testing is an important tool in the screening and diagnosis of many conditions. New technology is
Obstetrical Ultrasound and Prenatal Diagnostic Center
 Obstetrical Ultrasound and Prenatal Diagnostic Center Prenatal Diagnosis: Options and Opportunities Learn about various screening options including Early Risk Assessment (ERA), now available to women of
Obstetrical Ultrasound and Prenatal Diagnostic Center Prenatal Diagnosis: Options and Opportunities Learn about various screening options including Early Risk Assessment (ERA), now available to women of
The RCGP Curriculum: Clinical Modules
 The RCGP Curriculum: Clinical Modules Version approved 18 May 2015 for implementation from 5 August 2015 3.02 Genetics in Primary Care Summary It has been estimated that at least one in ten of the patients
The RCGP Curriculum: Clinical Modules Version approved 18 May 2015 for implementation from 5 August 2015 3.02 Genetics in Primary Care Summary It has been estimated that at least one in ten of the patients
12.1 The Role of DNA in Heredity
 12.1 The Role of DNA in Heredity Only in the last 50 years have scientists understood the role of DNA in heredity. That understanding began with the discovery of DNA s structure. In 1952, Rosalind Franklin
12.1 The Role of DNA in Heredity Only in the last 50 years have scientists understood the role of DNA in heredity. That understanding began with the discovery of DNA s structure. In 1952, Rosalind Franklin
www.njctl.org PSI Biology Mitosis & Meiosis
 Mitosis and Meiosis Mitosis Classwork 1. Identify two differences between meiosis and mitosis. 2. Provide an example of a type of cell in the human body that would undergo mitosis. 3. Does cell division
Mitosis and Meiosis Mitosis Classwork 1. Identify two differences between meiosis and mitosis. 2. Provide an example of a type of cell in the human body that would undergo mitosis. 3. Does cell division
Gene Therapy and Genetic Counseling. Chapter 20
 Gene Therapy and Genetic Counseling Chapter 20 What is Gene Therapy? Treating a disease by replacing, manipulating or supplementing a gene The act of changing an individual s DNA sequence to fix a non-functional
Gene Therapy and Genetic Counseling Chapter 20 What is Gene Therapy? Treating a disease by replacing, manipulating or supplementing a gene The act of changing an individual s DNA sequence to fix a non-functional
Muscular Dystrophy. By. Tina Strauss
 Muscular Dystrophy By. Tina Strauss Story Outline for Presentation on Muscular Dystrophy What is Muscular Dystrophy? Signs & Symptoms Types When to seek medical attention? Screening and Diagnosis Treatment
Muscular Dystrophy By. Tina Strauss Story Outline for Presentation on Muscular Dystrophy What is Muscular Dystrophy? Signs & Symptoms Types When to seek medical attention? Screening and Diagnosis Treatment
Preimplantation genetic diagnosis new method of screening of 24 chromosomes with the Array CGH method...2
 August 2012 content 8 Preimplantation genetic diagnosis new method of screening of 24 chromosomes with the Array CGH method...2 Maintaining fertility new opportunities in GENNET...3 Hysteroscopy without
August 2012 content 8 Preimplantation genetic diagnosis new method of screening of 24 chromosomes with the Array CGH method...2 Maintaining fertility new opportunities in GENNET...3 Hysteroscopy without
1. PRENATAL DIAGNOSIS OF CHROMOSOMAL DISORDERS - molecular aspects
 1. PRENATAL DIAGNOSIS OF CHROMOSOMAL DISORDERS - molecular aspects Ana Stavljenić-Rukavina Zagreb University School of Medicine, Croatia The standard measures for population health outcomes is based on
1. PRENATAL DIAGNOSIS OF CHROMOSOMAL DISORDERS - molecular aspects Ana Stavljenić-Rukavina Zagreb University School of Medicine, Croatia The standard measures for population health outcomes is based on
Thank you for making a reproductive genetic counseling appointment at the Mount Sinai Medical Center.
 Division of Medical Genetics Department of Genetics and Genomic Sciences Mailing address: One Gustave L. Levy Place, Box 1497 New York, NY 10029-6574 Patient Address: 1428 Madison Avenue (at 99th Street)
Division of Medical Genetics Department of Genetics and Genomic Sciences Mailing address: One Gustave L. Levy Place, Box 1497 New York, NY 10029-6574 Patient Address: 1428 Madison Avenue (at 99th Street)
Genetic Counseling: A Profession in the Making. Jessica Hooks, MS Genetic Counselor University of South Carolina
 Genetic Counseling: A Profession in the Making Jessica Hooks, MS Genetic Counselor University of South Carolina Definition the process of helping people understand and adapt to the medical, psychological
Genetic Counseling: A Profession in the Making Jessica Hooks, MS Genetic Counselor University of South Carolina Definition the process of helping people understand and adapt to the medical, psychological
REI Pearls: Pitfalls of Genetic Testing in Miscarriage
 The Skinny: Genetic testing of miscarriage tissue is controversial and some people question if testing is helpful or not. This summary will: 1) outline the arguments for and against genetic testing; 2)
The Skinny: Genetic testing of miscarriage tissue is controversial and some people question if testing is helpful or not. This summary will: 1) outline the arguments for and against genetic testing; 2)
Preimplantation Genetic Diagnosis (PGD) in Western Australia
 Preimplantation Genetic Diagnosis (PGD) in Western Australia Human somatic cells have 46 chromosomes each, made up of the 23 chromosomes provided by the egg and the sperm cell from each parent. Each chromosome
Preimplantation Genetic Diagnosis (PGD) in Western Australia Human somatic cells have 46 chromosomes each, made up of the 23 chromosomes provided by the egg and the sperm cell from each parent. Each chromosome
CCR Biology - Chapter 7 Practice Test - Summer 2012
 Name: Class: Date: CCR Biology - Chapter 7 Practice Test - Summer 2012 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. A person who has a disorder caused
Name: Class: Date: CCR Biology - Chapter 7 Practice Test - Summer 2012 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. A person who has a disorder caused
LEUKODYSTROPHY GENETICS AND REPRODUCTIVE OPTIONS FOR AFFECTED FAMILIES. Leila Jamal, ScM Kennedy Krieger Institute, Baltimore MD
 LEUKODYSTROPHY GENETICS AND REPRODUCTIVE OPTIONS FOR AFFECTED FAMILIES Leila Jamal, ScM Kennedy Krieger Institute, Baltimore MD 2 Outline Genetics 101: Basic Concepts and Myth Busting Inheritance Patterns
LEUKODYSTROPHY GENETICS AND REPRODUCTIVE OPTIONS FOR AFFECTED FAMILIES Leila Jamal, ScM Kennedy Krieger Institute, Baltimore MD 2 Outline Genetics 101: Basic Concepts and Myth Busting Inheritance Patterns
Chapter 9 Patterns of Inheritance
 Bio 100 Patterns of Inheritance 1 Chapter 9 Patterns of Inheritance Modern genetics began with Gregor Mendel s quantitative experiments with pea plants History of Heredity Blending theory of heredity -
Bio 100 Patterns of Inheritance 1 Chapter 9 Patterns of Inheritance Modern genetics began with Gregor Mendel s quantitative experiments with pea plants History of Heredity Blending theory of heredity -
Reproductive Technology. Chapter 21
 Reproductive Technology Chapter 21 Assisted Reproduction When a couple is sub-fertile or infertile they may need Assisted Reproduction to become pregnant: Replace source of gametes Sperm, oocyte or zygote
Reproductive Technology Chapter 21 Assisted Reproduction When a couple is sub-fertile or infertile they may need Assisted Reproduction to become pregnant: Replace source of gametes Sperm, oocyte or zygote
Management in the pre-hospital setting
 Management in the pre-hospital setting Inflammation of the joints Two main types: Osteoarthritis - cartilage loss from wear and tear Rheumatoid arthritis - autoimmune disorder Affects all age groups,
Management in the pre-hospital setting Inflammation of the joints Two main types: Osteoarthritis - cartilage loss from wear and tear Rheumatoid arthritis - autoimmune disorder Affects all age groups,
Medical Policy Preimplantation Genetic Testing
 Medical Policy Preimplantation Genetic Testing Table of Contents Policy: Commercial Coding Information Information Pertaining to All Policies Policy: Medicare Description References Authorization Information
Medical Policy Preimplantation Genetic Testing Table of Contents Policy: Commercial Coding Information Information Pertaining to All Policies Policy: Medicare Description References Authorization Information
Name: 4. A typical phenotypic ratio for a dihybrid cross is a) 9:1 b) 3:4 c) 9:3:3:1 d) 1:2:1:2:1 e) 6:3:3:6
 Name: Multiple-choice section Choose the answer which best completes each of the following statements or answers the following questions and so make your tutor happy! 1. Which of the following conclusions
Name: Multiple-choice section Choose the answer which best completes each of the following statements or answers the following questions and so make your tutor happy! 1. Which of the following conclusions
HUMAN CHROMOSOMES. Using this criterion, human chromosomes are divided in: metacentric, submetacentric, and acrocentric.
 HUMAN CHROMOSOMES Normal human somatic cells contain a diploid number of chromosomes (2n=46), so there are 23 pairs of chromosomes: - 22 pairs are identical in man and women and are called autosomes; -
HUMAN CHROMOSOMES Normal human somatic cells contain a diploid number of chromosomes (2n=46), so there are 23 pairs of chromosomes: - 22 pairs are identical in man and women and are called autosomes; -
Gene Therapy. The use of DNA as a drug. Edited by Gavin Brooks. BPharm, PhD, MRPharmS (PP) Pharmaceutical Press
 Gene Therapy The use of DNA as a drug Edited by Gavin Brooks BPharm, PhD, MRPharmS (PP) Pharmaceutical Press Contents Preface xiii Acknowledgements xv About the editor xvi Contributors xvii An introduction
Gene Therapy The use of DNA as a drug Edited by Gavin Brooks BPharm, PhD, MRPharmS (PP) Pharmaceutical Press Contents Preface xiii Acknowledgements xv About the editor xvi Contributors xvii An introduction
Preimplantation Genetic Diagnosis. Evaluation for single gene disorders
 Preimplantation Genetic Diagnosis Evaluation for single gene disorders What is Preimplantation Genetic Diagnosis? Preimplantation genetic diagnosis or PGD is a technology that allows genetic testing of
Preimplantation Genetic Diagnosis Evaluation for single gene disorders What is Preimplantation Genetic Diagnosis? Preimplantation genetic diagnosis or PGD is a technology that allows genetic testing of
About The Causes of Hearing Loss
 About 1 in 500 infants is born with or develops hearing loss during early childhood. Hearing loss has many causes: some are genetic (that is, caused by a baby s genes) or non-genetic (such as certain infections
About 1 in 500 infants is born with or develops hearing loss during early childhood. Hearing loss has many causes: some are genetic (that is, caused by a baby s genes) or non-genetic (such as certain infections
This fact sheet describes how genes affect our health when they follow a well understood pattern of genetic inheritance known as autosomal recessive.
 11111 This fact sheet describes how genes affect our health when they follow a well understood pattern of genetic inheritance known as autosomal recessive. In summary Genes contain the instructions for
11111 This fact sheet describes how genes affect our health when they follow a well understood pattern of genetic inheritance known as autosomal recessive. In summary Genes contain the instructions for
TERATOGENESIS ONTOGENESIS
 TERATOGENESIS ONTOGENESIS Inborn developmental defects Occured during prenatal development Are present by delivery At about 3-5 % newborns are affected. Inborn developmental defects 1. CHROMOSOMAL ABERRATIONS
TERATOGENESIS ONTOGENESIS Inborn developmental defects Occured during prenatal development Are present by delivery At about 3-5 % newborns are affected. Inborn developmental defects 1. CHROMOSOMAL ABERRATIONS
7A The Origin of Modern Genetics
 Life Science Chapter 7 Genetics of Organisms 7A The Origin of Modern Genetics Genetics the study of inheritance (the study of how traits are inherited through the interactions of alleles) Heredity: the
Life Science Chapter 7 Genetics of Organisms 7A The Origin of Modern Genetics Genetics the study of inheritance (the study of how traits are inherited through the interactions of alleles) Heredity: the
Title: Genetics and Hearing Loss: Clinical and Molecular Characteristics
 Session # : 46 Day/Time: Friday, May 1, 2015, 1:00 4:00 pm Title: Genetics and Hearing Loss: Clinical and Molecular Characteristics Presenter: Kathleen S. Arnos, PhD, Gallaudet University This presentation
Session # : 46 Day/Time: Friday, May 1, 2015, 1:00 4:00 pm Title: Genetics and Hearing Loss: Clinical and Molecular Characteristics Presenter: Kathleen S. Arnos, PhD, Gallaudet University This presentation
Robertsonian Translocations
 Robertsonian Translocations rarechromo.org Robertsonian translocations A Robertsonian translocation is an unusual type of chromosome rearrangement caused by two particular chromosomes joining together.
Robertsonian Translocations rarechromo.org Robertsonian translocations A Robertsonian translocation is an unusual type of chromosome rearrangement caused by two particular chromosomes joining together.
Name: Class: Date: ID: A
 Name: Class: _ Date: _ Meiosis Quiz 1. (1 point) A kidney cell is an example of which type of cell? a. sex cell b. germ cell c. somatic cell d. haploid cell 2. (1 point) How many chromosomes are in a human
Name: Class: _ Date: _ Meiosis Quiz 1. (1 point) A kidney cell is an example of which type of cell? a. sex cell b. germ cell c. somatic cell d. haploid cell 2. (1 point) How many chromosomes are in a human
Chapter 3. Chapter Outline. Chapter Outline 9/11/10. Heredity and Evolu4on
 Chapter 3 Heredity and Evolu4on Chapter Outline The Cell DNA Structure and Function Cell Division: Mitosis and Meiosis The Genetic Principles Discovered by Mendel Mendelian Inheritance in Humans Misconceptions
Chapter 3 Heredity and Evolu4on Chapter Outline The Cell DNA Structure and Function Cell Division: Mitosis and Meiosis The Genetic Principles Discovered by Mendel Mendelian Inheritance in Humans Misconceptions
Genetics Module B, Anchor 3
 Genetics Module B, Anchor 3 Key Concepts: - An individual s characteristics are determines by factors that are passed from one parental generation to the next. - During gamete formation, the alleles for
Genetics Module B, Anchor 3 Key Concepts: - An individual s characteristics are determines by factors that are passed from one parental generation to the next. - During gamete formation, the alleles for
Jennifer A. Defant, M.S., C.G.C. Certified Genetic Counselor Division of Genetics and Metabolism University of Florida
 Jennifer A. Defant, M.S., C.G.C. Certified Genetic Counselor Division of Genetics and Metabolism University of Florida 60% of childhood hearing loss is genetic Syndromic Nonsyndromic 40% of childhood hearing
Jennifer A. Defant, M.S., C.G.C. Certified Genetic Counselor Division of Genetics and Metabolism University of Florida 60% of childhood hearing loss is genetic Syndromic Nonsyndromic 40% of childhood hearing
National Down Syndrome Society
 National Down Syndrome Society The national advocate for the value, acceptance and inclusion of people with Down syndrome What is Down Syndrome? Down syndrome is the most commonly occurring chromosomal
National Down Syndrome Society The national advocate for the value, acceptance and inclusion of people with Down syndrome What is Down Syndrome? Down syndrome is the most commonly occurring chromosomal
MUSCULAR DYSTROPHY GENETICS AND TESTING
 MUSCULAR DYSTROPHY GENETICS AND TESTING Information to help you make an informed choice about testing. MUSCULAR DYSTROPHY 111 BOUNDARY ROAD NORTH MELBOURNE 3051 AUSTRALIA +61 3 9320 9555 MDA.ORG.AU Genetic
MUSCULAR DYSTROPHY GENETICS AND TESTING Information to help you make an informed choice about testing. MUSCULAR DYSTROPHY 111 BOUNDARY ROAD NORTH MELBOURNE 3051 AUSTRALIA +61 3 9320 9555 MDA.ORG.AU Genetic
X Linked Inheritance
 X Linked Inheritance Information for Patients and Families 2 X linked Inheritance The following will give you information about what X linked inheritance means and how X linked conditions are inherited.
X Linked Inheritance Information for Patients and Families 2 X linked Inheritance The following will give you information about what X linked inheritance means and how X linked conditions are inherited.
OAKTON COMMUNITY COLLEGE Summer Semester, 2015 CLASS SYLLABUS
 OAKTON COMMUNITY COLLEGE Summer Semester, 2015 CLASS SYLLABUS Instructor: E-mail: Web site: Virtual Office: Office Hours: Avis Gibons agibons@oakton.edu www.oakton.edu/~agibons online through Desire2Learn
OAKTON COMMUNITY COLLEGE Summer Semester, 2015 CLASS SYLLABUS Instructor: E-mail: Web site: Virtual Office: Office Hours: Avis Gibons agibons@oakton.edu www.oakton.edu/~agibons online through Desire2Learn
Insurance. Chapter 7. Introduction
 65 Chapter 7 Insurance Introduction 7.1 The subject of genetic screening in relation to insurance is not new. In 1935 R A Fisher addressed the International Congress of Life Assurance Medicine on the topic,
65 Chapter 7 Insurance Introduction 7.1 The subject of genetic screening in relation to insurance is not new. In 1935 R A Fisher addressed the International Congress of Life Assurance Medicine on the topic,
Background document on preimplantation and prenatal genetic testing. Clinical Situation. Legal situation 1
 DH-BIO/INF (2015) 6 Background document on preimplantation and prenatal genetic testing Clinical Situation Legal situation 1 1 Part II of this document presents the legal situation in Council of Europe
DH-BIO/INF (2015) 6 Background document on preimplantation and prenatal genetic testing Clinical Situation Legal situation 1 1 Part II of this document presents the legal situation in Council of Europe
