Trisomies 13 and 18. -Maternal age. (Patau and Edward s syndrome)
|
|
|
- Rudolph Boone
- 9 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Trisomies 13 and 18 (Patau and Edward s syndrome) Trisomy 21 (Down syndrome) is the commonest chromosomal disorder at birth, and has been considered in detail in previous annual reports 23. Other relatively common trisomies include trisomy 13 (Patau syndrome) and trisomy 18 (Edward s syndrome). Although not as common as Down syndrome, these two conditions still present significant challenges to both parents and health services WHAT IS A TRISOMY? Human cells normally have 46 chromosomes that can be grouped into 22 pairs of autosomes (numbered 1 to 22, in order of their size) plus a pair of sex chromosomes (XX in females and XY in males). A normal human cell is said to be diploid as it contains 2 sets of each of the 23 chromosomes. Where this is not the case, and the cell contains an abnormal number of chromosomes it is described as aneuploid. Trisomy involves the presence of extra material from a specific chromosome in addition to that found in the normal pair. The total chromosomal complement is then 47 instead of 46. Thus, cases of Patau syndrome have an extra chromosome 13 (Figure 27) and cases of Edward s syndrome have an extra chromosome 18 (Figure 28) Additional chromosomal material may be present in the cell because of the presence of an entire extra chromosome (a true trisomy), or as a result of an additional part of a chromosome becoming attached to other chromosomes in the nucleus (a translocation). Mosaicism describes the situation where some cells have chromosomal defects while others are normal. In this situation, the degree of problems depends on the relative proportions of normal and abnormal cells, which may vary between organs within the same individual. Risk factors A number of risk factors have been identified that are common to many chromosomal disorders, including trisomies 18 and 13. These include -Maternal age Environmental exposures such as ionising radiation and some heavy metals. Recent studies have highlighted the possibility that living near landfill sites may also increase the risk of chromosomal disorders (among other congenital defects) 24. Much more work is needed in this area before the risks become clearer. Welsh data from the CARIS database illustrates how anomaly rates rise with maternal age for Patau and Edward s syndromes. Rates for Down syndrome are also shown, for comparison (Figure 29). Figure 27: chromosomes from a case of Patau syndrome trisomy 13 Figure 28: chromosomes from a case of Edward s syndrome trisomy CARIS Annual Reports 1998 and Vrijheid M, Dolk H, Armstrong B, Abramsky L, Bianchi F et al. Chromosomal congenital anomalies and residence near hazardous waste landfill sites. Lancet (2002) Jan 26; 359 (9303):
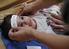
2 20 Trisomy 13 (Patau) rate per 1000 LB / SB / TOP Trisomy 18 (Edwards) Trisomy 21 (Downs) 0 < maternal age group Figure 29: Rates of Trisomies 13, 18 and 21 by maternal age group: CARIS data PATAU SYNDROME TRISOMY 13 Patau syndrome (Figure 30) is reported to occur in 1:4000 to 1:10,000 live /stillbirths, although these figures are changing as the capacity for antenatal detection increases, giving parents the choice of termination of pregnancy. Affected infants tend to be small at birth with microcephaly, a sloping forehead, facial dysmorphism, eye defects and abnormal low set ears. Other features include loose skin at the back of the neck, haemangiomas, a single palmar crease, polydactyly, flexed fingers and a posterior prominence of the heel (rocker bottom feet). A number of serious congenital anomalies occur in association with trisomy 13, -including: Holoprosencephaly (failure of the forebrain to divide properly 65% of cases) Myelomeningocele (50% of cases) Scoliosis -Cleft lip and / or palate (almost all cases) Congenital heart defects (80% of cases) especially VSD, ASD PDA or dextrocardia Exomphalos (10% of cases) -Kidney defects Genitourinary defects Figure 30: Newborn baby with Trisomy 13 The outlook for babies with trisomy 13 is very poor. 45% of liveborn babies die in the neonatal period, and by the end of the first year of life, mortality is 75%. Those babies that survive have profound learning disability, deafness and visual disability. Apnoea, feeding difficulties, oesophageal reflux, and slow growth are very common in infants. CARIS has received reports of 36 cases of trisomy 13 with pregnancy ending in , giving a gross rate of 2.8/10,000 live and stillbirths. Of these, 4 were spontaneous fetal losses. Of the remaining 32 cases, 24 (75%) resulted in termination of pregnancy and 8 were liveborn, of which only 1 survived to the end of the first year of life. For 5 CARIS cases, details of additional anomalies are not -known. The remaining 31 cases included: 17 cases (55%) with heart defects including 12 VSDs (39%), 2 ASDs and 1 PDA 6 cases (19%) of holoprosencephaly 17 cases (55%) of cleft lip and/or palate 2 cases (7%) of neural tube defect 12 cases (39%) with renal or urinary system anomalies -20 cases (65%) with limb deformities, mainly polydactyly 4 cases of tracheo-oesophageal atresia /fistula and 4 cases of congenital diaphragmatic hernia The percentage of additional anomalies in CARIS cases are generally lower than might be expected. This may be due to data quality, with fewer associated anomalies reported in cases that have not died and undergone post mortem. 33
3 EDWARD S SYNDROME TRISOMY 18 Edward s syndrome (Figure 31) occurs in about 2/1000 livebirths or stillbirths. As for trisomy 13, this frequency is falling as antenatal detection improves. Figure 31: Infant with Edward s syndrome trisomy 18 Fetuses typically tend to be small for gestational age with poor movements. Polyhydramnios, a small placenta and single umbilical artery are common features in the pregnancy. After birth, infants tend to be small and frail with a feeble cry. They have feeding difficulties and failure to thrive is common. Affected infants typically have microcephaly, a small mouth and jaw, facial dysmorphism, eye defects and abnormal low set ears. Redundant skin at the back of the neck, joint contractures and numerous abnormalities of fingers and toes are present. Clenched fists with the index fingers overlapping the 3rd and 4th fingers are almost distinctive of this condition (Figure 32). Children have significant learning difficulties and developmental delay. Major associated anomalies are not as common as for trisomy 13, but -include: Congenital heart defects (90% of cases), especially VSD, ASD and PDA. Cleft lip and / or palate Myelomeningocele (6% of cases) Radial aplasia (5-10% of cases) Kidney defects and associated hypertension - Scoliosis 20-30% of cases die within a month of birth, with only 10% of liveborn babies surviving to 1 year of age. Despite this, a few children have been reported to reach their second decade. CARIS is aware of 56 cases of trisomy 18 with pregnancy ending in , giving a gross rate of 4.4/ 10,000 live and stillbirths. Of these, 5 were spontaneous fetal losses. Of the remaining 51 cases, 31 (61%) resulted in termination of pregnancy, 2 were stillborn and 18 were liveborn, of which 6 (33% of liveborn cases) survived to the end of the first year of life. For 5 CARIS cases, details of additional anomalies are not -known. The remaining 51 cases included: 33 cases (65%) with heart defects including 18 VSDs (35%), 5 ASDs and 3 PDAs 6 cases (12%) of cleft lip and/or palate 2 cases (4%) of neural tube defect -17 cases (33%) with renal or urinary system anomalies 33 cases (65%) with limb deformities, including - 5 cases of absent thumb and 2 cases of radial aplasia 4 cases of tracheo-oesophageal atresia /fistula and 4 cases of congenital diaphragmatic hernia Figure 32: Clenched fist in Edward s syndrome 34
4 POTENTIAL FOR ANTENATAL DETECTION Although there is increasing potential to include other chromosomal abnormalities in screening programmes, it is not current UK policy to undertake antenatal screening for any chromosomal disorder other than Down syndrome. Antenatal ultrasound A number of antenatal ultrasound findings have associations with various chromosomal anomalies. A recent review of these findings by Nicolaides et al 25 illustrates how, although many ultrasound findings are associated with chromosomal anomalies other than Down syndrome, they lack the sensitivity and specificity to be used as stand alone screening tests. A recent review by Wald et al of published studies looked at markers for trisomies 13 and The review recommended that amniocentesis should be undertaken to exclude these 2 trisomies if any of the following were identified on antenatal ultrasound scanning: agenesis of corpus callosum diaphragmatic hernia cleft lip / palate exomphalos obstructive uropathy -double outlet right ventricle limb reduction defects (trisomy 18 only) Analysis - of CARIS data shows that 26/36 cases of Patau syndrome had reports of antenatal scans. Of these, 11 (42%) had evidence of ultrasound soft markers and -21 (81%) had evidence of structural defects. 41/56 cases of Edward s syndrome had antenatal scan findings reported to CARIS. Of these, 32 (74%) had scan evidence of soft markers. 32 (74%) had evidence of structural abnormalities. (Figure 33). Figure 33: Antenatal scan findings reported to CARIS for Trisomy 13 and Trisomy 18 Trisomy 13 / Patau (n=26) Trisomy 18 / Edward s (n=41) Soft markers Structural defects Soft markers Structural defects 11 any soft marker 21 any structural defect 32 any soft marker 32 any structural defect 5 increased nuchal 8 with no 4 chamber 16 choroid plexus cysts 10 cystic hygroma translucency view or other cardiac 4 echogenic gut 8 talipes 2 strawberry skull anomalies 6 nuchal translucency 7 exomphalos 1 echogenic bowel 7 with orofacial clefting (@ 12 weeks) 7 hydrops / oedema 1 echogenic kidney 6 holoprosencephaly 2 nuchal thickness 3 ventriculomegaly 1 dilated renal pelvis 6 ventriculomegaly (@18 weeks) 4 neural tube defects 1 lemon head 4 cystic hygroma 3 dilated renal pelves 3 cleft lip 1 banana cerebellum 4 polydactyly 5 lemon heads 2 head / skull anomalies 1 rockerbottom feet 1 exomphalos 2 banana cerebellums 1 congenital 1 double stomach bubble 1 neural tube defect 3 rocker bottom feet diaphragmatic hernia 1 no stomach bubble 1 oesophageal atresia 1 duodenal atresia 25 Snijders RJM, Farrias M, von Kaisenberg C, Nicolaides KH. Fetal abnormalities (Chapter 1). Ultrasound markers for fetal chromosome defects (Ed Snijders & Nicolaides) Frontiers in fetal medicine series. Parthenon Publishing Group. 1996, London 26 Wald N, Kennard A, Donnenfeld A, Leck I. Ultrasound scanning for congenital abnormalities (Chapter 18) Antenatal & neonatal screening (2nd Edn) editors Wald N, Leck I OU Press
5 Maternal serum markers A 2nd trimester maternal serum screening test for Trisomy 18 was first proposed in the early 1990s, following the observation that serum levels of a number of markers used to detect Down syndrome were also low in cases of fetal Edward syndrome. An early screening test was proposed involving maternal age, maternal serum alpha-fetoprotein and free beta human chorionic gonadotrophin. With a published detection rate of 50% for a false positive rate of 1%, this was suggested as being comparable to serum screening for Down syndrome 27. However, Edward s syndrome is much less common than Downs, so that many more amniocenteses would have to be performed per case detected than was the case for Down syndrome. It was suggested that a screening programme for a condition which was likely to prove fatal in pregnancy or infancy would cause considerable anxiety for parents and the abortion of at least as many normal fetuses as it would detect cases of trisomy 18 28,29. Ultrasound scanning was already thought to offer a better chance of detecting trisomy and serum screening has only developed subsequently in isolated programmes. Enhanced 2nd trimester serum screening involving maternal age related risk, alphafetoprotein, unconjugated estriol and human chorionic gonadotrophin has recently been shown to be able to detect a number of chromosomal abnormalities, including trisomy 18. No antenatal serum screening programme exists for trisomy 13 or 18. It is however interesting to note that CARIS has reports on 12 mothers of babies with Edward s syndrome who opted for serum screening. Of these, 2 were reported as high risk for Down syndrome. Similarly, 1/5 mothers of babies with Patau syndrome who opted for serum screening were reported as high risk for Downs. Amniocentesis Infant blood 6 Obtaining a sample of fetal cells for chromosome analysis is indicated if serum screening or antenatal ultrasound suggest the possibility of a fetal chromosomal anomaly. Alternatively this may be chosen as the first line of investigation for older mothers or those perceived at increased risk of carrying a fetus with a chromosomal disorder. Samples are usually obtained by amniocentesis or chorion villus sampling. Chromosome analysis may be undertaken by karyotyping, through polymerase chain reaction (PCR) or fluorescence in situ hybridisation (FISH) techniques. These latter two procedures have the advantage of being much faster to perform than conventional karyotyping, but can only be used to detect prespecified chromosomal disorders. They are not routinely available to the NHS at present. CARIS data includes karyotype results on 34/36 cases of Patau syndrome and 55/56 cases of Edward s syndrome. The method (and therefore the stage of pregnancy /infancy) by which these samples were obtained is illustrated in Figure 34. This suggests that about 64% of cases of Patau syndrome and 55% of cases of Edward s syndrome were detected antenatally. post mortem 5 CVS 4 post mortem 10 CVS 9 27 Mallard SK, Coombes EJ, Maeri JN. Prenatal screening for trisomy 18 with free beta human chorionic gonadotrophin as a marker BMJ 1993; 307: (4 December) 28 MacIntosh MCM, Chard T. Most die before or just after birth. Patau Syndrome amniocentesis 19 Infant blood 14 Edward's Syndrome amniocentesis 22 [letter] BMJ 1994; 308:471 (12 February) 29 Davies T Prenatal screening for trisomy 18: Should not be contemplated [letter] BMJ 1994; 308:471 (12 February) 30 Harding K. Ultrasound scanning would detect abnormalities [letter] BMJ 1994; 308:471 (12 February) Figure 34: Method of collection of karyotyping samples reported to CARIS for Patau and Edward s syndromes,
Trisomy 13 (also called Patau s syndrome or T13)
 Screening Programmes Fetal Anomaly Trisomy 13 (also called Patau s syndrome or T13) Information for parents Publication date: April 2012 Review date: April 2013 Version 2 117 Information sheet to help
Screening Programmes Fetal Anomaly Trisomy 13 (also called Patau s syndrome or T13) Information for parents Publication date: April 2012 Review date: April 2013 Version 2 117 Information sheet to help
Patient information on soft markers
 Patient information on soft markers Before you read this section remember the following important points. The vast majority of babies with soft markers are normal. Soft markers are frequently seen in healthy
Patient information on soft markers Before you read this section remember the following important points. The vast majority of babies with soft markers are normal. Soft markers are frequently seen in healthy
Down s Syndrome: Ultrasound Screening
 October 2001 Down s Syndrome: Ultrasound Screening Hilary Hochberg Advanced Radiology Clerkship Dr. Gillian Lieberman Patient M.C. 32 year old female presents at 16 weeks gestational age with abnormal
October 2001 Down s Syndrome: Ultrasound Screening Hilary Hochberg Advanced Radiology Clerkship Dr. Gillian Lieberman Patient M.C. 32 year old female presents at 16 weeks gestational age with abnormal
First Trimester Screening for Down Syndrome
 First Trimester Screening for Down Syndrome What is first trimester risk assessment for Down syndrome? First trimester screening for Down syndrome, also known as nuchal translucency screening, is a test
First Trimester Screening for Down Syndrome What is first trimester risk assessment for Down syndrome? First trimester screening for Down syndrome, also known as nuchal translucency screening, is a test
Prenatal screening and diagnostic tests
 Prenatal screening and diagnostic tests Contents Introduction 3 First trimester routine tests in the mother 3 Testing for health conditions in the baby 4 Why would you have a prenatal test? 6 What are
Prenatal screening and diagnostic tests Contents Introduction 3 First trimester routine tests in the mother 3 Testing for health conditions in the baby 4 Why would you have a prenatal test? 6 What are
Prenatal Testing Special tests for your baby during pregnancy
 English April 2006 [OTH-7750] There are a number of different prenatal (before birth) tests to check the development of your baby. Each test has advantages and disadvantages. This information is for people
English April 2006 [OTH-7750] There are a number of different prenatal (before birth) tests to check the development of your baby. Each test has advantages and disadvantages. This information is for people
Each person normally has 23 pairs of chromosomes, or 46 in all. We inherit one chromosome per pair from our mother and one from our father.
 AP Psychology 2.2 Behavioral Genetics Article Chromosomal Abnormalities About 1 in 150 babies is born with a chromosomal abnormality (1, 2). These are caused by errors in the number or structure of chromosomes.
AP Psychology 2.2 Behavioral Genetics Article Chromosomal Abnormalities About 1 in 150 babies is born with a chromosomal abnormality (1, 2). These are caused by errors in the number or structure of chromosomes.
A test your patients can trust.
 A test your patients can trust. A simple, safe, and accurate non-invasive prenatal test for early risk assessment of Down syndrome and other conditions. informaseq Prenatal Test Simple, safe, and accurate
A test your patients can trust. A simple, safe, and accurate non-invasive prenatal test for early risk assessment of Down syndrome and other conditions. informaseq Prenatal Test Simple, safe, and accurate
Birth defects. Report by the Secretariat
 EXECUTIVE BOARD EB126/10 126th Session 3 December 2009 Provisional agenda item 4.7 Birth defects Report by the Secretariat 1. In May 2009 the Executive Board at its 125th session considered an agenda item
EXECUTIVE BOARD EB126/10 126th Session 3 December 2009 Provisional agenda item 4.7 Birth defects Report by the Secretariat 1. In May 2009 the Executive Board at its 125th session considered an agenda item
Sonographic screening for trisomy 13 at 11 to 13 D6 weeks of gestation
 American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology (2006) 194, 397 401 www.ajog.org Sonographic screening for trisomy 13 at 11 to 13 D6 weeks of gestation Aris T. Papageorghiou, MD, a Kyriaki Avgidou, MD, a
American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology (2006) 194, 397 401 www.ajog.org Sonographic screening for trisomy 13 at 11 to 13 D6 weeks of gestation Aris T. Papageorghiou, MD, a Kyriaki Avgidou, MD, a
i_~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~- A _L,"'...S.::.. E, pad - report of 92 cases with follow up of Antenatal diagnosis of cystic hygroma or nuchal survivors
 F38 Archives ofdisease in Childhood 1996; 74: F38-F42 Antenatal diagnosis of cystic hygroma or nuchal pad - report of 92 cases with follow up of survivors P A Boyd, M Y Anthony, N Manning, C Lara Rodriguez,
F38 Archives ofdisease in Childhood 1996; 74: F38-F42 Antenatal diagnosis of cystic hygroma or nuchal pad - report of 92 cases with follow up of survivors P A Boyd, M Y Anthony, N Manning, C Lara Rodriguez,
The ultrasound detection of chromosomal anomalies 1
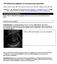 The ultrasound detection of chromosomal anomalies 1 Werther Adrian Clavelli, MD 2, Silvia Susana Romaris de Clavelli, MD 2, Philippe Jeanty, MD, PhD 3 Adapted from The Ultrasound Detection of Chromosomal
The ultrasound detection of chromosomal anomalies 1 Werther Adrian Clavelli, MD 2, Silvia Susana Romaris de Clavelli, MD 2, Philippe Jeanty, MD, PhD 3 Adapted from The Ultrasound Detection of Chromosomal
A Guide to Prenatal Genetic Testing
 Patient Education Page 29 A Guide to Prenatal Genetic Testing This section describes prenatal tests that give information about your baby s health. It is your choice whether or not to have these tests
Patient Education Page 29 A Guide to Prenatal Genetic Testing This section describes prenatal tests that give information about your baby s health. It is your choice whether or not to have these tests
Basic Human Genetics: Reproductive Health and Chromosome Abnormalities
 Basic Human Genetics: Reproductive Health and Chromosome Abnormalities Professor Hanan Hamamy Department of Genetic Medicine and Development Geneva University Switzerland Training Course in Sexual and
Basic Human Genetics: Reproductive Health and Chromosome Abnormalities Professor Hanan Hamamy Department of Genetic Medicine and Development Geneva University Switzerland Training Course in Sexual and
your questions answered the reassurance of knowing A guide for parents-to-be on noninvasive prenatal testing.
 your questions answered the reassurance of knowing A guide for parents-to-be on noninvasive prenatal testing. Accurate answers about your baby s health simply, safely, sooner. What is the verifi Prenatal
your questions answered the reassurance of knowing A guide for parents-to-be on noninvasive prenatal testing. Accurate answers about your baby s health simply, safely, sooner. What is the verifi Prenatal
23. TERATOGENS AND THEIR EFFECTS
 23. TERATOGENS AND THEIR EFFECTS Wendy Chung, M.D. Ph.D. Telephone: 851-5313 e-mail: [email protected] SUMMARY A congenital malformation is an anatomical or structural abnormality present at birth. Congenital
23. TERATOGENS AND THEIR EFFECTS Wendy Chung, M.D. Ph.D. Telephone: 851-5313 e-mail: [email protected] SUMMARY A congenital malformation is an anatomical or structural abnormality present at birth. Congenital
Ultrasonographic Diagnosis of Trisomy 18: Is It Practical in the Early Second Trimester?
 Ultrasonographic Diagnosis of Trisomy 18: Is It Practical in the Early Second Trimester? Laurence E. Shields, MD, Leslie A. Carpenter, MS, CGC, Karin M. Smith, RDMS, Hanh V. Nghiem, MD The objective of
Ultrasonographic Diagnosis of Trisomy 18: Is It Practical in the Early Second Trimester? Laurence E. Shields, MD, Leslie A. Carpenter, MS, CGC, Karin M. Smith, RDMS, Hanh V. Nghiem, MD The objective of
Population prevalence rates of birth defects: a data management and epidemiological perspective
 Population prevalence rates of birth defects: a data management and epidemiological perspective Merilyn Riley Abstract The Victorian Birth Defects Register (VBDR) is a population-based surveillance system
Population prevalence rates of birth defects: a data management and epidemiological perspective Merilyn Riley Abstract The Victorian Birth Defects Register (VBDR) is a population-based surveillance system
Data validation and Data sources
 British Isles Network of Congenital Anomaly Registers BINOCAR Standard Operating Procedure for Data validation and Data sources Instructions for the Registration and Surveillance of Congenital Anomalies
British Isles Network of Congenital Anomaly Registers BINOCAR Standard Operating Procedure for Data validation and Data sources Instructions for the Registration and Surveillance of Congenital Anomalies
Non-Invasive Prenatal Testing (NIPT) Factsheet
 Introduction NIPT, which analyzes cell-free fetal DNA circulating in maternal blood, is a new option in the prenatal screening and testing paradigm for trisomy 21 and a few other fetal chromosomal aneuploidies.
Introduction NIPT, which analyzes cell-free fetal DNA circulating in maternal blood, is a new option in the prenatal screening and testing paradigm for trisomy 21 and a few other fetal chromosomal aneuploidies.
CHROMOSOMES Dr. Fern Tsien, Dept. of Genetics, LSUHSC, NO, LA
 CHROMOSOMES Dr. Fern Tsien, Dept. of Genetics, LSUHSC, NO, LA Cytogenetics is the study of chromosomes and their structure, inheritance, and abnormalities. Chromosome abnormalities occur in approximately:
CHROMOSOMES Dr. Fern Tsien, Dept. of Genetics, LSUHSC, NO, LA Cytogenetics is the study of chromosomes and their structure, inheritance, and abnormalities. Chromosome abnormalities occur in approximately:
Ultrasound scans in pregnancy
 Ultrasound scans in pregnancy www.antenatalscreening.wales.nhs.uk Copyright 2016 Public Health Wales NHS Trust. All rights reserved. Not to be reproduced in whole or in part without the permission of the
Ultrasound scans in pregnancy www.antenatalscreening.wales.nhs.uk Copyright 2016 Public Health Wales NHS Trust. All rights reserved. Not to be reproduced in whole or in part without the permission of the
Obstetrical Ultrasound and Prenatal Diagnostic Center
 Obstetrical Ultrasound and Prenatal Diagnostic Center Prenatal Diagnosis: Options and Opportunities Learn about various screening options including Early Risk Assessment (ERA), now available to women of
Obstetrical Ultrasound and Prenatal Diagnostic Center Prenatal Diagnosis: Options and Opportunities Learn about various screening options including Early Risk Assessment (ERA), now available to women of
LEUKODYSTROPHY GENETICS AND REPRODUCTIVE OPTIONS FOR AFFECTED FAMILIES. Leila Jamal, ScM Kennedy Krieger Institute, Baltimore MD
 LEUKODYSTROPHY GENETICS AND REPRODUCTIVE OPTIONS FOR AFFECTED FAMILIES Leila Jamal, ScM Kennedy Krieger Institute, Baltimore MD 2 Outline Genetics 101: Basic Concepts and Myth Busting Inheritance Patterns
LEUKODYSTROPHY GENETICS AND REPRODUCTIVE OPTIONS FOR AFFECTED FAMILIES Leila Jamal, ScM Kennedy Krieger Institute, Baltimore MD 2 Outline Genetics 101: Basic Concepts and Myth Busting Inheritance Patterns
Optional Tests Offered Before and During Pregnancy
 Plano Women s Healthcare Optional Tests Offered Before and During Pregnancy Alpha-Fetoprotein Test (AFP) and Quad Screen These are screening tests that can assess your baby s risk of having such birth
Plano Women s Healthcare Optional Tests Offered Before and During Pregnancy Alpha-Fetoprotein Test (AFP) and Quad Screen These are screening tests that can assess your baby s risk of having such birth
Long-Term Prognosis of Pregnancies Complicated by Slow Embryonic Heart Rates in the Early First Trimester
 Long-Term Prognosis of Pregnancies Complicated by Slow Embryonic Heart Rates in the Early First Trimester Peter M. Doubilet, MD, PhD, Carol B. Benson, MD, Jeanne S. Chow, MD Slow embryonic heart rates
Long-Term Prognosis of Pregnancies Complicated by Slow Embryonic Heart Rates in the Early First Trimester Peter M. Doubilet, MD, PhD, Carol B. Benson, MD, Jeanne S. Chow, MD Slow embryonic heart rates
The National Down Syndrome Cytogenetic Register for England and Wales: 2008/9 Annual Report
 0 The National Down Syndrome Cytogenetic Register for England and Wales: 2008/9 Annual Report Joan K Morris, Elizabeth De Souza December 2009 National Down Syndrome Cytogenetic Register Queen Mary University
0 The National Down Syndrome Cytogenetic Register for England and Wales: 2008/9 Annual Report Joan K Morris, Elizabeth De Souza December 2009 National Down Syndrome Cytogenetic Register Queen Mary University
Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists. Termination of Pregnancy for Fetal Abnormality in England, Scotland and Wales
 Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists Termination of Pregnancy for Fetal Abnormality in England, Scotland and Wales May 2010 Termination of Pregnancy for Fetal Abnormality in England, Scotland
Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists Termination of Pregnancy for Fetal Abnormality in England, Scotland and Wales May 2010 Termination of Pregnancy for Fetal Abnormality in England, Scotland
Chromosomes, Karyotyping, and Abnormalities (Learning Objectives) Learn the components and parts of a metaphase chromosome.
 Chromosomes, Karyotyping, and Abnormalities (Learning Objectives) Learn the components and parts of a metaphase chromosome. Define the terms karyotype, autosomal and sex chromosomes. Explain how many of
Chromosomes, Karyotyping, and Abnormalities (Learning Objectives) Learn the components and parts of a metaphase chromosome. Define the terms karyotype, autosomal and sex chromosomes. Explain how many of
Congenital heart defects
 CONGENITAL ANOMALY REGISTER & INFORMATION SERVICE COFRESTR ANOMALEDDAU CYNHENID Congenital heart defects Cardiovascular defects are by far the commonest major group of congenital anomalies. Development
CONGENITAL ANOMALY REGISTER & INFORMATION SERVICE COFRESTR ANOMALEDDAU CYNHENID Congenital heart defects Cardiovascular defects are by far the commonest major group of congenital anomalies. Development
Neural tube defects (NTDs): open spina bifida (also called spina bifida cystica)
 Screening Programmes Fetal Anomaly Neural tube defects (NTDs): open spina bifida (also called spina bifida cystica) Information for parents Publication date: April 2012 Review date: April 2013 Version
Screening Programmes Fetal Anomaly Neural tube defects (NTDs): open spina bifida (also called spina bifida cystica) Information for parents Publication date: April 2012 Review date: April 2013 Version
Universal Fetal Cardiac Ultrasound At the Heart of Newborn Well-being
 Universal Fetal Cardiac Ultrasound At the Heart of Newborn Well-being Optimizes detection of congenital heart disease (chd) in the general low risk obstetrical population Daniel J. Cohen, M.D. [email protected]
Universal Fetal Cardiac Ultrasound At the Heart of Newborn Well-being Optimizes detection of congenital heart disease (chd) in the general low risk obstetrical population Daniel J. Cohen, M.D. [email protected]
21 WEEKS FETUS WITH TRISOMY 18 (EDWARD SYNDROME), BONE MALFORMATIONS HIGHLIGHTED
 THE PUBLISHING HOUSE MEDICINE OF THE ROMANIAN ACADEMY Research article 21 WEEKS FETUS WITH TRISOMY 18 (EDWARD SYNDROME), BONE MALFORMATIONS HIGHLIGHTED BOGDAN BOTEZATU 1 and BOGDAN MARINESCU 1 1 Obstetrics
THE PUBLISHING HOUSE MEDICINE OF THE ROMANIAN ACADEMY Research article 21 WEEKS FETUS WITH TRISOMY 18 (EDWARD SYNDROME), BONE MALFORMATIONS HIGHLIGHTED BOGDAN BOTEZATU 1 and BOGDAN MARINESCU 1 1 Obstetrics
Triploidy. rarechromo.org
 Triploidy rarechromo.org Triploidy Triploidy is a disorder that arises at conception when a baby starts life in the womb with a complete extra set of chromosomes. Chromosomes are the microscopically small
Triploidy rarechromo.org Triploidy Triploidy is a disorder that arises at conception when a baby starts life in the womb with a complete extra set of chromosomes. Chromosomes are the microscopically small
The California Prenatal Screening Program
 The California Prenatal Screening Program Quad Marker Screening One blood specimen drawn at 15 weeks - 20 weeks of pregnancy (second trimester) Serum Integrated Screening Prenatal Patient Booklet - English
The California Prenatal Screening Program Quad Marker Screening One blood specimen drawn at 15 weeks - 20 weeks of pregnancy (second trimester) Serum Integrated Screening Prenatal Patient Booklet - English
The Newborn With a Congenital Disorder. Chapter 14. Copyright 2008 Wolters Kluwer Health Lippincott Williams & Wilkins
 The Newborn With a Congenital Disorder Chapter 14 Congenital Anomalies or Malformations May be caused by genetic or environmental factors Approximately 2% to 3% of all infants born have a major malformation
The Newborn With a Congenital Disorder Chapter 14 Congenital Anomalies or Malformations May be caused by genetic or environmental factors Approximately 2% to 3% of all infants born have a major malformation
CAGC Certification Logbook of Clinical Experience INSTRUCTIONS
 CAGC Certification Logbook of Clinical Experience INSTRUCTIONS The purpose of the logbook is to show that the applicant has been significantly involved in the evaluation and counselling of patients seeking
CAGC Certification Logbook of Clinical Experience INSTRUCTIONS The purpose of the logbook is to show that the applicant has been significantly involved in the evaluation and counselling of patients seeking
Screening for chromosomal abnormalities at 10 14 weeks: the role of ductus venosus blood flow
 Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 1998;12:380 384 Screening for chromosomal abnormalities at 10 14 weeks: the role of ductus venosus blood flow A. Matias*, C. Gomes*, N. Flack*, N. Montenegro and K. H. Nicolaides*
Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 1998;12:380 384 Screening for chromosomal abnormalities at 10 14 weeks: the role of ductus venosus blood flow A. Matias*, C. Gomes*, N. Flack*, N. Montenegro and K. H. Nicolaides*
Neural tube defects: open spina bifida (also called spina bifida cystica)
 Screening Programmes Fetal Anomaly Neural tube defects: open spina bifida (also called spina bifida cystica) Information for health professionals Publication date: April 2012 Review date: April 2013 Version
Screening Programmes Fetal Anomaly Neural tube defects: open spina bifida (also called spina bifida cystica) Information for health professionals Publication date: April 2012 Review date: April 2013 Version
BIRTH DEFECTS IN MICHIGAN All Cases Reported and Processed by April 15, 2008
 MICHIGAN DEPARTMENT OF COMMUNITY HEALTH Division for Vital Records and Health Statistics MICHIGAN BIRTH DEFECTS SURVEILLANCE REGISTRY BIRTH DEFECTS IN MICHIGAN All Cases Reported and Processed by April
MICHIGAN DEPARTMENT OF COMMUNITY HEALTH Division for Vital Records and Health Statistics MICHIGAN BIRTH DEFECTS SURVEILLANCE REGISTRY BIRTH DEFECTS IN MICHIGAN All Cases Reported and Processed by April
 DIAGNOSIS, GENETICS AND PRENATAL DIAGNOSIS IN CHARGE Meg Hefner, M.S. Genetic Counselor and Assistant Professor of Pediatrics, Division of Medical Genetics, St. Louis University School of Medicine, 1465
DIAGNOSIS, GENETICS AND PRENATAL DIAGNOSIS IN CHARGE Meg Hefner, M.S. Genetic Counselor and Assistant Professor of Pediatrics, Division of Medical Genetics, St. Louis University School of Medicine, 1465
Congenital Anomalies In Diamond Blackfan Anemia (DBA)
 Congenital Anomalies In Diamond Blackfan Anemia (DBA) CS217857 National Center on Birth Defects and Developmental Disabilities Division of Blood Disorders Congenital Anomalies In Diamond Blackfan Anemia
Congenital Anomalies In Diamond Blackfan Anemia (DBA) CS217857 National Center on Birth Defects and Developmental Disabilities Division of Blood Disorders Congenital Anomalies In Diamond Blackfan Anemia
Executive summary. Current prenatal screening
 Executive summary Health Council of the Netherlands. NIPT: dynamics and ethics of prenatal screening. The Hague: Health Council of the Netherlands, 2013; publication no. 2013/34. In recent years, new tests
Executive summary Health Council of the Netherlands. NIPT: dynamics and ethics of prenatal screening. The Hague: Health Council of the Netherlands, 2013; publication no. 2013/34. In recent years, new tests
Why is prematurity a concern?
 Prematurity What is prematurity? A baby born before 37 weeks of pregnancy is considered premature. Approximately 12% of all babies are born prematurely. Terms that refer to premature babies are preterm
Prematurity What is prematurity? A baby born before 37 weeks of pregnancy is considered premature. Approximately 12% of all babies are born prematurely. Terms that refer to premature babies are preterm
The 11 13 +6 weeks scan
 The 11 13 +6 weeks scan Kypros H. Nicolaides The 11 13 +6 weeks scan Fetal Medicine Foundation, London 2004 Dedication to Herodotos & Despina Contents Introduction 1. First trimester diagnosis of chromosomal
The 11 13 +6 weeks scan Kypros H. Nicolaides The 11 13 +6 weeks scan Fetal Medicine Foundation, London 2004 Dedication to Herodotos & Despina Contents Introduction 1. First trimester diagnosis of chromosomal
Human Growth and Reproduction
 Human Growth and Reproduction Sperm reach ovum and cluster around it Only one sperm is allowed to penetrate egg When the sperm penetrates the egg, the egg immediately releases a chemical creating a hard
Human Growth and Reproduction Sperm reach ovum and cluster around it Only one sperm is allowed to penetrate egg When the sperm penetrates the egg, the egg immediately releases a chemical creating a hard
The First Trimester Anatomy Scan. John R. Allbert, MD Novant Maternal-Fetal Medicine Associates
 The First Trimester Anatomy Scan John R. Allbert, MD Novant Maternal-Fetal Medicine Associates Anatomic Survey Second trimester (18-22 week) scan remains the gold standard First trimester evaluation of
The First Trimester Anatomy Scan John R. Allbert, MD Novant Maternal-Fetal Medicine Associates Anatomic Survey Second trimester (18-22 week) scan remains the gold standard First trimester evaluation of
REI Pearls: Pitfalls of Genetic Testing in Miscarriage
 The Skinny: Genetic testing of miscarriage tissue is controversial and some people question if testing is helpful or not. This summary will: 1) outline the arguments for and against genetic testing; 2)
The Skinny: Genetic testing of miscarriage tissue is controversial and some people question if testing is helpful or not. This summary will: 1) outline the arguments for and against genetic testing; 2)
4.2 Meiosis. Meiosis is a reduction division. Assessment statements. The process of meiosis
 4.2 Meiosis Assessment statements State that meiosis is a reduction division of a diploid nucleus to form haploid nuclei. Define homologous chromosomes. Outline the process of meiosis, including pairing
4.2 Meiosis Assessment statements State that meiosis is a reduction division of a diploid nucleus to form haploid nuclei. Define homologous chromosomes. Outline the process of meiosis, including pairing
Fluorescence in situ hybridisation (FISH)
 Fluorescence in situ hybridisation (FISH) rarechromo.org Fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) Chromosomes Chromosomes are structures that contain the genetic information (DNA) that tells the body
Fluorescence in situ hybridisation (FISH) rarechromo.org Fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) Chromosomes Chromosomes are structures that contain the genetic information (DNA) that tells the body
cfdna in maternal plasma obtained from a population undergoing routine screening at 11-13 weeks gestation.
 Reports of Major Impact www.ajog.org Noninvasive prenatal testing for fetal trisomies in a routinely screened first-trimester population Kypros H. Nicolaides, MD; Argyro Syngelaki, RM; Ghalia Ashoor, MD;
Reports of Major Impact www.ajog.org Noninvasive prenatal testing for fetal trisomies in a routinely screened first-trimester population Kypros H. Nicolaides, MD; Argyro Syngelaki, RM; Ghalia Ashoor, MD;
Developmental Disorders
 Developmental Disorders General Principles Causes: Genetic Environmental (Maternal, Physical, Chemical) Mechanisms (Retinoic Acid) General Principles Teratology Study of Monsters Teratogen agent that produces
Developmental Disorders General Principles Causes: Genetic Environmental (Maternal, Physical, Chemical) Mechanisms (Retinoic Acid) General Principles Teratology Study of Monsters Teratogen agent that produces
Chromosomal Abnormalities
 Chromosomal Abnormalities George E Tiller, MD, PhD Regional Chief, Dept. Genetics Southern California Permanente Medical Group Los Angeles, CA Objectives of Lecture list several indications for karyotyping
Chromosomal Abnormalities George E Tiller, MD, PhD Regional Chief, Dept. Genetics Southern California Permanente Medical Group Los Angeles, CA Objectives of Lecture list several indications for karyotyping
Fetal Prognosis in Varix of the Intrafetal Umbilical Vein
 Fetal Prognosis in Varix of the Intrafetal Umbilical Vein Waldo Sepulveda, MD, Antonio Mackenna, MD, Jorge Sanchez, MD, Edgardo Corral, MD, Eduardo Carstens, MD To assess the clinical significance of varix
Fetal Prognosis in Varix of the Intrafetal Umbilical Vein Waldo Sepulveda, MD, Antonio Mackenna, MD, Jorge Sanchez, MD, Edgardo Corral, MD, Eduardo Carstens, MD To assess the clinical significance of varix
Frontomaxillary and mandibulomaxillary facial angles at 11 + 0to13+ 6 weeks in fetuses with trisomy 18
 Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2007; 30: 928 933 Published online 1 November 2007 in Wiley InterScience (www.interscience.wiley.com). DOI: 10.2/uog.5188 Frontomaxillary and mandibulomaxillary facial angles
Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2007; 30: 928 933 Published online 1 November 2007 in Wiley InterScience (www.interscience.wiley.com). DOI: 10.2/uog.5188 Frontomaxillary and mandibulomaxillary facial angles
Neural Tube Defects - NTDs
 Neural Tube Defects - NTDs Introduction Neural tube defects are also known as NTDs. They happen when the spine and brain do not fully develop while the fetus is forming in the uterus. Worldwide, there
Neural Tube Defects - NTDs Introduction Neural tube defects are also known as NTDs. They happen when the spine and brain do not fully develop while the fetus is forming in the uterus. Worldwide, there
NBDPN Guidelines for Conducting Birth Defects Surveillance rev. 06/04. Chapter 5 Classification and Coding
 Chapter 5 Classification and Coding Table Contents 5.1 Introduction... 5-1 5.2 Disease Classification Systems... 5-2 5.2.1 Description and Format... 5-2 5.2.2 ICD-9-CM and the 6-digit CDC Code A Comparison...
Chapter 5 Classification and Coding Table Contents 5.1 Introduction... 5-1 5.2 Disease Classification Systems... 5-2 5.2.1 Description and Format... 5-2 5.2.2 ICD-9-CM and the 6-digit CDC Code A Comparison...
Congenital Diaphragmatic Hernia. Manuel A. Molina, M.D. University Hospital at Brooklyn SUNY Downstate
 Congenital Diaphragmatic Hernia Manuel A. Molina, M.D. University Hospital at Brooklyn SUNY Downstate Congenital Diaphragmatic Hernias Incidence 1 in 2000 to 5000 live births. 80% in the left side, 20%
Congenital Diaphragmatic Hernia Manuel A. Molina, M.D. University Hospital at Brooklyn SUNY Downstate Congenital Diaphragmatic Hernias Incidence 1 in 2000 to 5000 live births. 80% in the left side, 20%
Common types of congenital heart defects
 Common types of congenital heart defects Congenital heart defects are abnormalities that develop before birth. They can occur in the heart's chambers, valves or blood vessels. A baby may be born with only
Common types of congenital heart defects Congenital heart defects are abnormalities that develop before birth. They can occur in the heart's chambers, valves or blood vessels. A baby may be born with only
CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE
 CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE Introduction Congenital heart disease (CHD) is the most common congenital disorder in newborns [1]. Due to definitional issues, there are large variations in prevalence estimates.
CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE Introduction Congenital heart disease (CHD) is the most common congenital disorder in newborns [1]. Due to definitional issues, there are large variations in prevalence estimates.
Genetics and Pregnancy Loss
 Genetics and Pregnancy Loss Dorothy Warburton Genetics and Development (in Pediatrics) Columbia University, New York Estimates of Pregnancy Loss from Conception 1000 fertilized eggs (27% are lost) 728
Genetics and Pregnancy Loss Dorothy Warburton Genetics and Development (in Pediatrics) Columbia University, New York Estimates of Pregnancy Loss from Conception 1000 fertilized eggs (27% are lost) 728
Saint Mary s Hospital Tests for you and your baby during pregnancy
 Maternity Service Saint Mary s Hospital Tests for you and your baby during pregnancy Contents Page What is this leaflet about? 3 Routine blood tests for the mother 4 Anaemia 4 Blood group 4 German measles
Maternity Service Saint Mary s Hospital Tests for you and your baby during pregnancy Contents Page What is this leaflet about? 3 Routine blood tests for the mother 4 Anaemia 4 Blood group 4 German measles
The Patterns and Public Health Impact of Heart Defects in Texas Pediatric Cardiac Care Conference VI Dell Children s Medical Center, Feb.
 The Patterns and Public Health Impact of Heart Defects in Texas Pediatric Cardiac Care Conference VI Dell Children s Medical Center, Feb. 7-8, 2013 Mark Canfield, Ph.D. Manager, Birth Defects Epidemiology
The Patterns and Public Health Impact of Heart Defects in Texas Pediatric Cardiac Care Conference VI Dell Children s Medical Center, Feb. 7-8, 2013 Mark Canfield, Ph.D. Manager, Birth Defects Epidemiology
PREGNANCY INFORMATION PACK. Peace of mind throughout pregnancy
 PREGNANCY INFORMATION PACK Peace of mind throughout pregnancy Welcome Welcome to The 3fivetwo Group. We are delighted at the news of your recent pregnancy success and we wish you all the very best for
PREGNANCY INFORMATION PACK Peace of mind throughout pregnancy Welcome Welcome to The 3fivetwo Group. We are delighted at the news of your recent pregnancy success and we wish you all the very best for
The following chapter is called "Preimplantation Genetic Diagnosis (PGD)".
 Slide 1 Welcome to chapter 9. The following chapter is called "Preimplantation Genetic Diagnosis (PGD)". The author is Dr. Maria Lalioti. Slide 2 The learning objectives of this chapter are: To learn the
Slide 1 Welcome to chapter 9. The following chapter is called "Preimplantation Genetic Diagnosis (PGD)". The author is Dr. Maria Lalioti. Slide 2 The learning objectives of this chapter are: To learn the
CELL DIVISION. STAGES OF MITOTIC DIVISION (Diag. C1)
 1 CELL DIVISION Cell division is the process by which cells replicate in order to replace cell loss, repair tissue damage and reproduce the organism. Two types of cell division are encountered in the Eukaryotic
1 CELL DIVISION Cell division is the process by which cells replicate in order to replace cell loss, repair tissue damage and reproduce the organism. Two types of cell division are encountered in the Eukaryotic
AUSTRALIA AND NEW ZEALAND FACTSHEET
 AUSTRALIA AND NEW ZEALAND FACTSHEET What is Stillbirth? In Australia and New Zealand, stillbirth is the death of a baby before or during birth, from the 20 th week of pregnancy onwards, or 400 grams birthweight.
AUSTRALIA AND NEW ZEALAND FACTSHEET What is Stillbirth? In Australia and New Zealand, stillbirth is the death of a baby before or during birth, from the 20 th week of pregnancy onwards, or 400 grams birthweight.
A test your patients can trust. A company you know and trust.
 A test your patients can trust. A company you know and trust. informaseq Prenatal Test an advanced, non-invasive, prenatal screening for T21, T18, and T13 chromosomal aneuploidies using next generation
A test your patients can trust. A company you know and trust. informaseq Prenatal Test an advanced, non-invasive, prenatal screening for T21, T18, and T13 chromosomal aneuploidies using next generation
Preimplantation Genetic Diagnosis (PGD) in Western Australia
 Preimplantation Genetic Diagnosis (PGD) in Western Australia Human somatic cells have 46 chromosomes each, made up of the 23 chromosomes provided by the egg and the sperm cell from each parent. Each chromosome
Preimplantation Genetic Diagnosis (PGD) in Western Australia Human somatic cells have 46 chromosomes each, made up of the 23 chromosomes provided by the egg and the sperm cell from each parent. Each chromosome
SOFT FETAL ULTRASOUND FINDINGS
 SOFT FETAL ULTRASOUND FINDINGS Compiled by the Genetics Team at The Credit Valley Hospital Last updated February 2008 Page 2 This document refers to the ultrasound finding of a soft sign, as compared
SOFT FETAL ULTRASOUND FINDINGS Compiled by the Genetics Team at The Credit Valley Hospital Last updated February 2008 Page 2 This document refers to the ultrasound finding of a soft sign, as compared
RECURRENT PREGNANCY LOSS DR.RAJALAKSHMI SRINIVASAN SPECIALIST GYNECOLOGIST ZULEKHA HOSPITAL DUBAI
 RECURRENT PREGNANCY LOSS DR.RAJALAKSHMI SRINIVASAN SPECIALIST GYNECOLOGIST ZULEKHA HOSPITAL DUBAI RECURRENT PREGNANCY LOSS -RM Clinically recognized consecutive or non consecutive pregnancy losses before
RECURRENT PREGNANCY LOSS DR.RAJALAKSHMI SRINIVASAN SPECIALIST GYNECOLOGIST ZULEKHA HOSPITAL DUBAI RECURRENT PREGNANCY LOSS -RM Clinically recognized consecutive or non consecutive pregnancy losses before
Screening tests for you and your baby
 Screening tests for you and your baby Important information for you to keep with your hand-held maternity records 2010 version In the busy time after the baby is born remember to look after your own
Screening tests for you and your baby Important information for you to keep with your hand-held maternity records 2010 version In the busy time after the baby is born remember to look after your own
Gutenberg Center in MALAGA
 Introduction Gutenberg Center in MALAGA Gutenberg Center in Málaga opened in 1987 as a clinic to provide integral assisstance for women, divided into 6 Units, specialized in the different aspects of Obs
Introduction Gutenberg Center in MALAGA Gutenberg Center in Málaga opened in 1987 as a clinic to provide integral assisstance for women, divided into 6 Units, specialized in the different aspects of Obs
Maine CDC Birth Defects Program
 Maine CDC Birth Defects Program January 1, 2011- December 31, 2011 Submitted to the Joint Standing Committee on Health and Human Services 2011 Annual Report Table of Contents Executive Summary 3 Maine
Maine CDC Birth Defects Program January 1, 2011- December 31, 2011 Submitted to the Joint Standing Committee on Health and Human Services 2011 Annual Report Table of Contents Executive Summary 3 Maine
The Developing Person Through the Life Span 8e by Kathleen Stassen Berger
 The Developing Person Through the Life Span 8e by Kathleen Stassen Berger Chapter 4 Prenatal Development and Birth PowerPoint Slides developed by Martin Wolfger and Michael James Ivy Tech Community College-Bloomington
The Developing Person Through the Life Span 8e by Kathleen Stassen Berger Chapter 4 Prenatal Development and Birth PowerPoint Slides developed by Martin Wolfger and Michael James Ivy Tech Community College-Bloomington
Maternity Renal Pelvis Dilation (RPD)
 Maternity Renal Pelvis Dilation (RPD) Fetal Medicine Unit Your baby has been found to have more fluid in its kidneys than normal. This leaflet will explain what this means for your baby. First of all,
Maternity Renal Pelvis Dilation (RPD) Fetal Medicine Unit Your baby has been found to have more fluid in its kidneys than normal. This leaflet will explain what this means for your baby. First of all,
Emanuel syndrome. rarechromo.org
 Emanuel syndrome rarechromo.org Your child will bring you joy and pain, just as all children do. Rejoice in the small achievements. Most of what I have found out about Emanuel syndrome has been from my
Emanuel syndrome rarechromo.org Your child will bring you joy and pain, just as all children do. Rejoice in the small achievements. Most of what I have found out about Emanuel syndrome has been from my
Central core disease
 Central core disease Central core disease falls under the umbrella of congenital myopathies which are characterised by muscle weakness and wasting. It is a rare condition, and symptoms are usually present
Central core disease Central core disease falls under the umbrella of congenital myopathies which are characterised by muscle weakness and wasting. It is a rare condition, and symptoms are usually present
The First Trimester Screening program
 The First Trimester Screening program The Fetal Medicine Foundation This guide has been designed to highlight the important clinical aspects of using the First Trimester Screening program. It is not intended
The First Trimester Screening program The Fetal Medicine Foundation This guide has been designed to highlight the important clinical aspects of using the First Trimester Screening program. It is not intended
Pregnancy and Substance Abuse
 Pregnancy and Substance Abuse Introduction When you are pregnant, you are not just "eating for two." You also breathe and drink for two, so it is important to carefully consider what you put into your
Pregnancy and Substance Abuse Introduction When you are pregnant, you are not just "eating for two." You also breathe and drink for two, so it is important to carefully consider what you put into your
Genetic Counseling: A Profession in the Making. Jessica Hooks, MS Genetic Counselor University of South Carolina
 Genetic Counseling: A Profession in the Making Jessica Hooks, MS Genetic Counselor University of South Carolina Definition the process of helping people understand and adapt to the medical, psychological
Genetic Counseling: A Profession in the Making Jessica Hooks, MS Genetic Counselor University of South Carolina Definition the process of helping people understand and adapt to the medical, psychological
Assisted reproductive technologies (ART) in Canada: 2011 results from the Canadian ART Register
 1 Assisted reproductive technologies (ART) in Canada: 2011 results from the Canadian ART Register Joanne Gunby, M.Sc. CARTR Co-ordinator Email: [email protected] Supported by the IVF Directors Group of
1 Assisted reproductive technologies (ART) in Canada: 2011 results from the Canadian ART Register Joanne Gunby, M.Sc. CARTR Co-ordinator Email: [email protected] Supported by the IVF Directors Group of
Screening for trisomy 21 by fetal tricuspid regurgitation, nuchal translucency and maternal serum free β-hcg and PAPP-A at 11 + 0to13+ 6 weeks
 Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2006; 27: 151 155 Published online 30 December 2005 in Wiley InterScience (www.interscience.wiley.com). DOI: 10.1002/uog.2699 Screening for trisomy 21 by fetal tricuspid regurgitation,
Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2006; 27: 151 155 Published online 30 December 2005 in Wiley InterScience (www.interscience.wiley.com). DOI: 10.1002/uog.2699 Screening for trisomy 21 by fetal tricuspid regurgitation,
a guide to understanding pierre robin sequence
 a guide to understanding pierre robin sequence a publication of children s craniofacial association a guide to understanding pierre robin sequence this parent s guide to Pierre Robin Sequence is designed
a guide to understanding pierre robin sequence a publication of children s craniofacial association a guide to understanding pierre robin sequence this parent s guide to Pierre Robin Sequence is designed
An OB US protocol book is available in the reading room to help you learn what is needed for problem cases.
 HIGH RISK OBSTETRIC ULTRASOUND GUIDELINES Dolores H. Pretorius, M.D., Mary K. O Boyle M.D. and Lori Romine M.D. The obstetric ultrasound rotation is designed to emphasize an experience that relies on a
HIGH RISK OBSTETRIC ULTRASOUND GUIDELINES Dolores H. Pretorius, M.D., Mary K. O Boyle M.D. and Lori Romine M.D. The obstetric ultrasound rotation is designed to emphasize an experience that relies on a
