The facts most scientists agree on
|
|
|
- Madeline Barrett
- 9 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Extant Apes
2 Even though chimps look more similar to gorillas and orangutans, they re actually more closely related to humans according to current genetic data. The facts most scientists agree on
3 Brains: Chimp~ cc Humans ~1350cc Locomotion: Chimp knuckle walking Human habitual biped Chimp vs. Human
4 What evolved in the hominins first: large brains or bipedalism? Look to the fossil record!
5 An Early Find A nonscientist finds parts of a skull in a local gravel pit near Sussex. Only the skull was found. It is somewhat human-like, and somewhat ape-like. The missing link!!! Took the skull to scientists The skull s features
6 The Missing Link? Small jaw like an ape Small molars like a human Large canines like an ape Highly vaulted skull like a human (big brain!) A mix of human and nonhuman ape characteristics
7 Fervor over the Missing Link Yay! Proof that Europe was the cradle of humankind! Moreover, the skull s large cranial vault suggested that the European missing link was intelligent! Despite some obvious error in the analyses, the skull was celebrated for years.
8 Found in England ~ at the Piltdown gravel pit Named it Piltdown Man
9 More fossils subsequently found (these are 2-7 myo)
10 Sahelanthropus tchadensis Found fossils in Chad (about 100 years after Piltdown man was found)
11 Sahelanthropus tchadensis Features 7-6mya Found in center of Africa rather than East Africa and South Africa where most research on human evolution has been conducted Large jaw Large browridge Reduced canines Large molars Small brain~roughly the size of today s chimps at ~335cc; today s humans are ~1350cc Only skulls have been found, so we are not yet sure if Sahelanthropus was bipedal It is an unexpected mix of human and apelike features, and found in an unexpected area: this is more evidence that hominin evolution did not follow a simple progression from ape to human--rather, there were probably many different hominin species that possessed a variety of different adaptations
12 More fossils ~4-2mya the hominins increased in number and spread out in Africa Multiple species lived at the same time Roughly 2 categories; most found in south and east Africa Australopithecus (6 species) gracile type Paranthropus (3 species) robust type
13 Australopithecus southern ape Small bodies relative to humans Clearly bipedal Teeth, skull, jaw adapted to a generalized diet Small teeth relative to Paranthopus Chimp brain is ~335cc Average Australopithecine brain ~ cc
14 Australopithecis afarensis Clearly bipedal The famous Lucy
15 Laetoli footprints c. 3.6 MYA Footprints made in East Africa, probably by A. afarensis, several bipedal creatures walked across a bed of wet volcanic ask about 3.6mya; footprints were preserved when it dried
16 Australopithecus africanus Found in South and East Africa Lived 2.2-3mya Skeletons confirmed bipedality High sexual dimorphism Male canines bigger proportionately bigger than female canines (like gorillas, etc.) Males: 4 6 and 90 lbs. Females: 3 9 and 66 lbs.
17 Taung child (Australopithecus africanus) -2.5myo -discovered in S. Africa, 1924: the first Australopithecine fossil ever found Raymond Dart, an Australian anatomist living in S. Africa (local workers in a mining pit brought it to him) -foramen magnum location like bipedal humans, so Dart concluded it was a biped -brain small like that of an ape -rejected by scientists because at the time they believed large brains evolved before bipedalism (like Piltdown); with no postcranial skeleton, foramen evidence not strong enough to prove bipedality How did they know it was a child? It still had baby teeth and molars ready to erupt.
18 Gracile types: Genus Australopithecus Australopithecus africanus myo Australopithecus garhi c. 2.5myo
19 Robust types: Genus Paranthropus Paranthropus aethiopicus c. 2.5 MYA Paranthropus boisei c. 1.8 MYA Paranthropus robustus c MYA
20 Paranthropus parallel to man Similar to Australopithecines from the neck down (bipedal, short relative to humans) Small brains BUT they had massive molars and premolars, and jaws adapted to chewing tough plant materials; their skulls were modified to carry the enormous muscles necessary to power the chewing apparatus
21 Paranthropus Exceptionally large teeth, esp. molars (unlike Australopithecus) Exceptionally large jaws (unlike Australopithecus) Big teeth and big jaws mean: Large jaw muscle (temporalis muscle) to move the heavy, powerful jaw; jaw muscles connect up and around the sides of the head, and run underneath the cheekbones to the jaw Large jaw muscles mean: Large zygomatic arches (cheekbones) needed to create space for jaw muscle More skull for the large jaw muscles to connect to: a sagittal crest Test yourself, clench your teeth and feel your temporalis muscle--feel the muscle where it stops, about an inch above your temple Sagittal crest Black Skull (because it is black; just due to the process of fossilization with high manganese content): Paranthropus aethiopucus
22 Paranthropus robustus and boisei P. robustus: wear marks on molars indicate hard foods and nuts, but research on fossil contents also suggest a significant amount of meat in the diet P. boisei: a super-robust paranthropus P. robustus used to be called Australopithecus robustus and P. boisei used to be called Australopithecus boisei
23 To summarize 4-2mya Hominins spread around South and East Africa Small brains (~ cc), but somewhat bigger than today s chimps Short The GENUS Australopithecus is gracile The GENUS Paranthropus is robust Very sexually dimorphic They are clearly bipedal.
24 The Evolution of Bipedalism Several theories Walking on 2 legs is an efficient form of ground locomotion Erect posture allowed humans to keep cool It left the hands free to carry things Allows for efficient harvesting of fruit from low trees Different lines of evidence for and against these and other theories But one thing we know for sure: Bipedalism evolved BEFORE big brains/intelligence evolved But wait, what about Piltdown Man???
25 Piltdown Man: A Hoax Skull fragments were of a human--hence the large brain Jaw of an orangutan--hence the large canines Molars were filed down to look like the small molars of a human The signs were obvious, but, consistent with the prevailing notion in England at the time, people wanted to believe that large brains evolved prior to other features They also wanted to believe that Europe was the location of humans evolving from apes into modern humans A set back to science--a total waste of time Forgery wasn t discovered until 1953! Though as early as 1915 other scientists had rejected it. It did wane in acceptance with the finding of the Taung Child The hoax is still cited by creationists in support of their view that the theory of evolution cannot address the origins of man. Many cite it as evidence of the frequent acceptance in the scientific community of viewpoints with very little data.
26 Tools Hominins have been making stone tools for at least 2.5my A particular kind of tool found in East and South Africa dating back to 2.5 MYA: Oldowan tools
27 Oldowan tools
28 Oldowan tools -Several flakes can be chipped from I core -It is not clear if the core was used as a chopper of if the flakes were used for cutting -Experiments in knapping (stone toolmaking) have shown: -knappers were almost certainly right-handed -flakes were best at processing carcasses, though cores/choppers may have been useful in other activities Question: Who was making and using them?
29 Who used Oldowan tools? Probably Australopithecus and Paranthropus We don t have direct evidence of these early hominin bones associated with Oldowan tools, but that doesn t mean they didn t use them (no one died and was fossilized with an Oldowan tool in their hand, but we find the tools at the same time they were alive, and we find clearly-processed animal bones with the tools) Definitely members of the genus Homo
30 Homo They were the first to leave Africa, and they clearly used stone tools.
31 Final Group: Genus Homo (includes us) Homo ergaster (African) Homo erectus (Asian) Homo heidelbergensis Homo neanderthalensis Homo sapiens (us)
32 H. ergaster Several specimens have been found
33 H. ergaster Clearly a different genus from Australopithecus and Paranthropus Appear 1.8 mya in Africa (colder climate) Disappear 600KYA Bigger brains than earlier hominins ~800cc Probably mastered fire Probably hunted large game Used Oldowan and Acheulean tools Traits like modern humans: smaller, less prognathic face, higher skull, smaller jaws and teeth, similar body size, similar sexual dimorphism Other trait: very large brow ridges, horizontal ridge at the back of the skull (occipital torus) which allows a better biting and tearing action with the incisors and canines Biting and tearing what? MEAT. Molars are far smaller (and proportionately so) than those of the earlier hominins who were chewing and grinding hard plant foods Homo ergaster c mya (Africa)
34 Acheulean tools
35 Acheulean hand axes Regular, bifaced, teardrop-shaped flaked tooks; can have different sizes (few inches to 2 feet have been found) and be made of different materials, but always the same proportions; probably most used for butchering, with less use for other tasks; 1.6mya to 300kya: remarkable regularity of the tool industry for over a million years
36 Homo erectus 1.8mya-30kya Very similar to H. ergaster but found only in eastern Asia Large brow ridges Sagittal keel (a lump rather than a crest) with unknown function More sloped sides of skull Used Oldowan tools mostly, but a few Acheulean tools have been found in eastern Asia, and stone tools are absent from the entire region above the latitude line where bamboo grows Homo erectus c MYA (Asia)
37 Neanderthals
38 Neanderthals were shorter and stockier than us.
39 Homo Neanderthalensis Only in Europe, kya Adapted to cold environment: stalky, huge noses and faces Large front teeth, many with cut marks Well-adapted to hunting large game We clearly did NOT evolve from them; genetic evidence shows they were a separate branch that had a dead-end (I.e., they went extinct) We know a lot about them because European paleoanthropologists did a lot of digging there First one found in Germany s Neander valley LARGE BRAINS than humans, averaging 1520cc--bigger than us, who average ~1350cc (though reflects large body size, and they are about 30% larger than us) Probably buried their dead Had short, brutal lives Interesting fact: the patterns of injuries we see in Neanderthal bones match those of human?
Outline 22: Hominid Fossil Record
 Outline 22: Hominid Fossil Record Human ancestors A.=Australopithicus Assumed direct lineage to modern humans Babcock textbook Collecting hominid fossils in East Africa Using Stratigraphy and Radiometric
Outline 22: Hominid Fossil Record Human ancestors A.=Australopithicus Assumed direct lineage to modern humans Babcock textbook Collecting hominid fossils in East Africa Using Stratigraphy and Radiometric
Tracing the evolution of the genus Homo is important for understanding the ancestry of humans; the only living species of Homo.
 Section 3: Tracing the evolution of the genus Homo is important for understanding the ancestry of humans; the only living species of Homo. K What I Know W What I Want to Find Out L What I Learned Essential
Section 3: Tracing the evolution of the genus Homo is important for understanding the ancestry of humans; the only living species of Homo. K What I Know W What I Want to Find Out L What I Learned Essential
The Story of Human Evolution Part 1: From ape-like ancestors to modern humans
 The Story of Human Evolution Part 1: From ape-like ancestors to modern humans Slide 1 The Story of Human Evolution This powerpoint presentation tells the story of who we are and where we came from - how
The Story of Human Evolution Part 1: From ape-like ancestors to modern humans Slide 1 The Story of Human Evolution This powerpoint presentation tells the story of who we are and where we came from - how
On side: Classification of Humans
 1 The modern human, known as the species homo sapien, is characterized by a large and well-developed brain compared to early species of humans.this increased mental capacity has allowed people to excel
1 The modern human, known as the species homo sapien, is characterized by a large and well-developed brain compared to early species of humans.this increased mental capacity has allowed people to excel
Chapter 11: The Origins and Evolution of Early Homo
 Chapter 11: The Origins and Evolution of Early Homo 1. Homo habilis: The First Species of the Genus Homo a. The Path to Humanness: Bigger Brains, Tool Use, and Adaptive Flexibility i. First discovered
Chapter 11: The Origins and Evolution of Early Homo 1. Homo habilis: The First Species of the Genus Homo a. The Path to Humanness: Bigger Brains, Tool Use, and Adaptive Flexibility i. First discovered
Last class. What species of hominid are found in the early Pliocene? Where are they found? What are their distinguishing anatomical characteristics?
 Last class What species of hominid are found in the early Pliocene? Where are they found? What are their distinguishing anatomical characteristics? How do the Australopithecines differ from the possible
Last class What species of hominid are found in the early Pliocene? Where are they found? What are their distinguishing anatomical characteristics? How do the Australopithecines differ from the possible
EARLY AND LATE ARCHAIC HOMO SAPIENS AND ANATOMICALLY MODERN HOMO SAPIENS
 ANTH 310 Human Origins LABORATORY #5 EARLY AND LATE ARCHAIC HOMO SAPIENS AND ANATOMICALLY MODERN HOMO SAPIENS Traditionally, the hominins after the middle Pleistocene (middle Homo) belong to Homo sapiens.
ANTH 310 Human Origins LABORATORY #5 EARLY AND LATE ARCHAIC HOMO SAPIENS AND ANATOMICALLY MODERN HOMO SAPIENS Traditionally, the hominins after the middle Pleistocene (middle Homo) belong to Homo sapiens.
Level 3 Biology, 2012
 90719 907190 3SUPERVISOR S Level 3 Biology, 2012 90719 Describe trends in human evolution 2.00 pm Tuesday 13 November 2012 Credits: Three Check that the National Student Number (NSN) on your admission
90719 907190 3SUPERVISOR S Level 3 Biology, 2012 90719 Describe trends in human evolution 2.00 pm Tuesday 13 November 2012 Credits: Three Check that the National Student Number (NSN) on your admission
Classification and Evolution
 Classification and Evolution Starter: How many different ways could I split these objects into 2 groups? Classification All living things can also be grouped how do we decide which groups to put them into?
Classification and Evolution Starter: How many different ways could I split these objects into 2 groups? Classification All living things can also be grouped how do we decide which groups to put them into?
In 1871 Charles Darwin published another groundbreaking
 23 How Humans Evolved Concept Outline 23.1 The evolutionary path to humans starts with the advent of primates. The Evolutionary Path to Apes. Primates first evolved 65 million years ago, giving rise first
23 How Humans Evolved Concept Outline 23.1 The evolutionary path to humans starts with the advent of primates. The Evolutionary Path to Apes. Primates first evolved 65 million years ago, giving rise first
Introduction to Physical Anthropology - Study Guide - Focus Topics
 Introduction to Physical Anthropology - Study Guide - Focus Topics Chapter 1 Species: Recognize all definitions. Evolution: Describe all processes. Culture: Define and describe importance. Biocultural:
Introduction to Physical Anthropology - Study Guide - Focus Topics Chapter 1 Species: Recognize all definitions. Evolution: Describe all processes. Culture: Define and describe importance. Biocultural:
he standard uniform for paleontologists is casual. T-shirts, cutoffs, and floppy old hats are common
 NOT FOR SALE A New Kind of Ape T 14 Reprinted from The Tangled Bank: An Introduction to Evolution, Second Edition by Carl Zimmer. Permission granted by Roberts and Company Publishers. http://bit.ly/1bwx1qt
NOT FOR SALE A New Kind of Ape T 14 Reprinted from The Tangled Bank: An Introduction to Evolution, Second Edition by Carl Zimmer. Permission granted by Roberts and Company Publishers. http://bit.ly/1bwx1qt
Section 3 Ape Physical Characteristics
 Section 3 Ape Physical Characteristics OVERVIEW The physical anatomy of apes is essential to their adaptive strategies. Compared to humans, their closest living relatives, ape skeletons are more robust
Section 3 Ape Physical Characteristics OVERVIEW The physical anatomy of apes is essential to their adaptive strategies. Compared to humans, their closest living relatives, ape skeletons are more robust
Phylogeny and the dispersal of Homo. David S. Strait, U Albany
 Phylogeny and the dispersal of Homo David S. Strait, U Albany Biogeography g The study of how and why organisms are distributed across the landscape Darwin s voyage to the Galapagos Islands Darwin s finches
Phylogeny and the dispersal of Homo David S. Strait, U Albany Biogeography g The study of how and why organisms are distributed across the landscape Darwin s voyage to the Galapagos Islands Darwin s finches
Australopithecus and Homo habilis Pre-Human Ancestors?
 Australopithecus and Homo habilis Pre-Human Ancestors? A. W. MEHLERT ABSTRACT A survey of the palaeoanthropological literature reveals the controversies raging between various discoverers of australopithecine
Australopithecus and Homo habilis Pre-Human Ancestors? A. W. MEHLERT ABSTRACT A survey of the palaeoanthropological literature reveals the controversies raging between various discoverers of australopithecine
6 LUCY & THE LEAKEYS BIOGRAPHY 770L
 6 LUCY & THE LEAKEYS BIOGRAPHY 770L LUCY & THE LEAKEYS HOMININE FOSSILS AND PALEOARCHAEOLOGISTS Louis Leakey Mary Leakey Lucy c. 3.2 MYA Afar, Ethiopia Born August 7, 1903 Kabete, Kenya Died October 1,
6 LUCY & THE LEAKEYS BIOGRAPHY 770L LUCY & THE LEAKEYS HOMININE FOSSILS AND PALEOARCHAEOLOGISTS Louis Leakey Mary Leakey Lucy c. 3.2 MYA Afar, Ethiopia Born August 7, 1903 Kabete, Kenya Died October 1,
The First Female Homo erectus Pelvis, from Gona, Afar, Ethiopia
 PRESS RELEASE The First Female Homo erectus Pelvis, from Gona, Afar, Ethiopia To be published in the Journal Science 14 November, 2008 Prepared by the Gona Palaeoanthropological Research Project Stone
PRESS RELEASE The First Female Homo erectus Pelvis, from Gona, Afar, Ethiopia To be published in the Journal Science 14 November, 2008 Prepared by the Gona Palaeoanthropological Research Project Stone
FORENSIC ANTHROPOLOGY NOTES
 FORENSIC ANTHROPOLOGY NOTES Forensic Anthropology = the examinations of human skeletal remains for law enforcement agencies to determine the identity of unidentified bones. Questions asked: 1. Are the
FORENSIC ANTHROPOLOGY NOTES Forensic Anthropology = the examinations of human skeletal remains for law enforcement agencies to determine the identity of unidentified bones. Questions asked: 1. Are the
ARCH 1616 Between Sahara and Sea: North Africa from Human Origins to Islam
 ARCH 1616 Between Sahara and Sea: North Africa from Human Origins to Islam Brett Kaufman [email protected] Office Hours week of September 22: Monday, 2:30-4:30 pm Rhode Island Hall 007 Hominid Evolution
ARCH 1616 Between Sahara and Sea: North Africa from Human Origins to Islam Brett Kaufman [email protected] Office Hours week of September 22: Monday, 2:30-4:30 pm Rhode Island Hall 007 Hominid Evolution
ANTH 215 Physical Anthropology Study Guide for Exam-III
 ANTH 215 Physical Anthropology Study Guide for Exam-III General: The final exam covers all the lectures and reading in Jurmain et al. (Chapters 8-13 &17) since the last exam. This exam is worth 30% of
ANTH 215 Physical Anthropology Study Guide for Exam-III General: The final exam covers all the lectures and reading in Jurmain et al. (Chapters 8-13 &17) since the last exam. This exam is worth 30% of
Defining the Genus Homo
 Defining the Genus Homo Mark Collard and Bernard Wood Contents Introduction... 2108 Changing Interpretations of Genus Homo... 2109 Is Genus Homo a Good Genus?... 2114 Updating Wood and Collard s (1999)
Defining the Genus Homo Mark Collard and Bernard Wood Contents Introduction... 2108 Changing Interpretations of Genus Homo... 2109 Is Genus Homo a Good Genus?... 2114 Updating Wood and Collard s (1999)
Supported by. A seven part series exploring the fantastic world of science.
 Supported by A seven part series exploring the fantastic world of science. Find out about the different types of teeth in your mouth. Milk Teeth As a child you have 20 milk teeth. Your first tooth appears
Supported by A seven part series exploring the fantastic world of science. Find out about the different types of teeth in your mouth. Milk Teeth As a child you have 20 milk teeth. Your first tooth appears
A model of Homo naledi, a newly discovered species of ape, at the Cradle of Humankind World Heritage Site, Maropeng, South Africa, September 2015
 1 of 10 10/30/2015 10:25 AM Font Size: A A Steven Mithen NOVEMBER 19, 2015 ISSUE The Real Planet of the Apes: A New Story of Human Origins by David R. Begun Princeton University Press, 246 pp., $29.95
1 of 10 10/30/2015 10:25 AM Font Size: A A Steven Mithen NOVEMBER 19, 2015 ISSUE The Real Planet of the Apes: A New Story of Human Origins by David R. Begun Princeton University Press, 246 pp., $29.95
WHO IS LUCY? Lesson Overview
 Lesson Overview Overview: In this lesson, you will be introduced to Lucy, one of the most famous fossils ever found. You ll learn details about Lucy including her relationship to humans, her diet, her
Lesson Overview Overview: In this lesson, you will be introduced to Lucy, one of the most famous fossils ever found. You ll learn details about Lucy including her relationship to humans, her diet, her
What is a fossil? 1. What does the name of your dinosaur mean? 2. In which geological time period did your dinosaur live?
 Name: School: Date: 1. What does the name of your dinosaur mean? 2. In which geological time period did your dinosaur live? 3. Where in the world are the fossil remains of your dinosaur found today? 4.
Name: School: Date: 1. What does the name of your dinosaur mean? 2. In which geological time period did your dinosaur live? 3. Where in the world are the fossil remains of your dinosaur found today? 4.
Phylogenetic trees have a long history of representing
 Deep Time in Perspective: An Animated Fossil Hominin Timeline HOLLY M. DUNSWORTH Department of Anthropology, 5500 N. St. Louis Ave., Northeastern Illionois University, Chicago, IL 60625, USA; [email protected]
Deep Time in Perspective: An Animated Fossil Hominin Timeline HOLLY M. DUNSWORTH Department of Anthropology, 5500 N. St. Louis Ave., Northeastern Illionois University, Chicago, IL 60625, USA; [email protected]
Homo erectus Infancy and Childhood The Turning Point in the Evolution of Behavioral Development in Hominids
 10 Homo erectus Infancy and Childhood The Turning Point in the Evolution of Behavioral Development in Hominids Sue Taylor Parker In man, attachment is mediated by several different sorts of behaviour of
10 Homo erectus Infancy and Childhood The Turning Point in the Evolution of Behavioral Development in Hominids Sue Taylor Parker In man, attachment is mediated by several different sorts of behaviour of
Were Australopithecines Ape Human Intermediates or Just Apes? A Test of Both Hypotheses Using the Lucy Skeleton
 article Were Australopithecines Ape Human Intermediates or Just Apes? A Test of Both Hypotheses Using the Lucy Skeleton Phil Senter Abstrac t Mainstream scientists often claim that australopithecines such
article Were Australopithecines Ape Human Intermediates or Just Apes? A Test of Both Hypotheses Using the Lucy Skeleton Phil Senter Abstrac t Mainstream scientists often claim that australopithecines such
Culture (from the Encarta Encyclopedia)
 Culture (from the Encarta Encyclopedia) 1. Introduction Culture, in anthropology, is the patterns of behavior and thinking that people living in social groups learn, create, and share. Culture distinguishes
Culture (from the Encarta Encyclopedia) 1. Introduction Culture, in anthropology, is the patterns of behavior and thinking that people living in social groups learn, create, and share. Culture distinguishes
Fossils, feet and the evolution of human bipedal locomotion
 J. Anat. (2004) 204, pp403 416 Blackwell Publishing, Ltd. REVIEW Fossils, feet and the evolution of human bipedal locomotion W. E. H. Harcourt-Smith 1 and L. C. Aiello 2 1 Division of Vertebrate Paleontology,
J. Anat. (2004) 204, pp403 416 Blackwell Publishing, Ltd. REVIEW Fossils, feet and the evolution of human bipedal locomotion W. E. H. Harcourt-Smith 1 and L. C. Aiello 2 1 Division of Vertebrate Paleontology,
From Africa to Aotearoa Part 1: Out of Africa
 From Africa to Aotearoa Part 1: Out of Africa The spread of modern humans out of Africa started around 65,000 years ago, and ended with the settlement of New Zealand 750 years ago. These PowerPoint presentations
From Africa to Aotearoa Part 1: Out of Africa The spread of modern humans out of Africa started around 65,000 years ago, and ended with the settlement of New Zealand 750 years ago. These PowerPoint presentations
ONCE we TODAYWETAKE FOR GRANTED THAT HOMO SAPIENS FOUR MILLION YEARS MANY HOMINID SPECIES EMERGENCE
 EMERGENCE TODAYWETAKE FOR GRANTED THAT HOMO SAPIENS FOUR MILLION YEARS MANY HOMINID SPECIES ONCE we SHARING A SINGLE LANDSCAPE, four kinds of hominids lived about 1.8 million years ago in what is now part
EMERGENCE TODAYWETAKE FOR GRANTED THAT HOMO SAPIENS FOUR MILLION YEARS MANY HOMINID SPECIES ONCE we SHARING A SINGLE LANDSCAPE, four kinds of hominids lived about 1.8 million years ago in what is now part
giganotosaurus Michael P. Goecke
 giganotosaurus Michael P. Goecke Giganotosaurus A Buddy Book by Michael P. Goecke VISIT US AT www.abdopublishing.com Published by ABDO Publishing Company, 4940 Viking Drive, Edina, Minnesota 55435. Copyright
giganotosaurus Michael P. Goecke Giganotosaurus A Buddy Book by Michael P. Goecke VISIT US AT www.abdopublishing.com Published by ABDO Publishing Company, 4940 Viking Drive, Edina, Minnesota 55435. Copyright
Chapter 00. Chapter 13. The Early Hominins. Chapter Outline
 Chapter 00 Chapter 13 The Early Hominins e are all united by our past, that we all hae a common history and though... wwe may be astly different, our origins all lead back to the crucible of human eolution
Chapter 00 Chapter 13 The Early Hominins e are all united by our past, that we all hae a common history and though... wwe may be astly different, our origins all lead back to the crucible of human eolution
Activity: Can You Identify the Age?
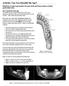 Activity: Can You Identify the Age? Skeletons are good age markers because teeth and bones mature at fairly predictable rates. How Teeth Reveal Age For toddler to age 21, teeth are the most accurate age
Activity: Can You Identify the Age? Skeletons are good age markers because teeth and bones mature at fairly predictable rates. How Teeth Reveal Age For toddler to age 21, teeth are the most accurate age
Once We Were Not. Today we take for granted that Homo sapiens is the only hominid on Earth.Yet for at least four million years many
 Today we take for granted that Homo sapiens is the only hominid on Earth.Yet for at least four million years many Once We Were Not PARANTHROPUS BOISEI had massive jaws, equipped with huge grinding teeth
Today we take for granted that Homo sapiens is the only hominid on Earth.Yet for at least four million years many Once We Were Not PARANTHROPUS BOISEI had massive jaws, equipped with huge grinding teeth
Practice Questions 1: Evolution
 Practice Questions 1: Evolution 1. Which concept is best illustrated in the flowchart below? A. natural selection B. genetic manipulation C. dynamic equilibrium D. material cycles 2. The diagram below
Practice Questions 1: Evolution 1. Which concept is best illustrated in the flowchart below? A. natural selection B. genetic manipulation C. dynamic equilibrium D. material cycles 2. The diagram below
Activity 1 Exploring Animal Diets and Sizes
 Activity 1 Exploring Animal Diets and Sizes Objective & Overview: Using measurement and books, students will gain a better understanding of animal size, diversity, and diet through the fun study of wildlife.
Activity 1 Exploring Animal Diets and Sizes Objective & Overview: Using measurement and books, students will gain a better understanding of animal size, diversity, and diet through the fun study of wildlife.
There has been great debate over whether or not
 These apes were made for walking: the pelves of Australopithecus afarensis and Australopithecus africanus Matthew Murdock The debate surrounding hominid bipedality is sometimes fought more on the grounds
These apes were made for walking: the pelves of Australopithecus afarensis and Australopithecus africanus Matthew Murdock The debate surrounding hominid bipedality is sometimes fought more on the grounds
STEP BY STEP: THE EVOLUTION OF BIPEDALISM Lesson Overview - Intermediate & Advanced
 Lesson Overview - Intermediate & Advanced Overview: Bipedalism is a defining characteristic of modern humans that evolved over millions of years. Therefore, identifying evidence for bipedalism in the fossil
Lesson Overview - Intermediate & Advanced Overview: Bipedalism is a defining characteristic of modern humans that evolved over millions of years. Therefore, identifying evidence for bipedalism in the fossil
Carnivore, omnivore or herbivore?
 Carnivore, omnivore or herbivore? Physical adaptations of the giant panda Student booklet (ST) October 2010 panda_st_student.doc Context The Giant Panda is a species that is faced with extinction. It is
Carnivore, omnivore or herbivore? Physical adaptations of the giant panda Student booklet (ST) October 2010 panda_st_student.doc Context The Giant Panda is a species that is faced with extinction. It is
Unit 2 Lesson 4 Early Human Migration and Stone Age Tools
 Unit 2 Lesson 4 Early Human Migration and Stone Age Tools Daily Warm-up True/False Read the False statements below. Replace each underlined word with one from the word bank that makes each sentence True.
Unit 2 Lesson 4 Early Human Migration and Stone Age Tools Daily Warm-up True/False Read the False statements below. Replace each underlined word with one from the word bank that makes each sentence True.
Unit One Study Guide
 Unit One Study Guide Terms BCE: Before the Common Era. Referring to the time before Christ s birth. CE: Common Era. Referring to the time after Christ s birth. BC: Before Christ. Referring to the time
Unit One Study Guide Terms BCE: Before the Common Era. Referring to the time before Christ s birth. CE: Common Era. Referring to the time after Christ s birth. BC: Before Christ. Referring to the time
2. You are going to be reading about one type of dinosaur called Tyrannosaurus rex or T. rex for short. What do you know about this dinosaur?
 Building Context 1. You are going to be reading about a dinosaur. Write down some things that you know about dinosaurs. 2. You are going to be reading about one type of dinosaur called Tyrannosaurus rex
Building Context 1. You are going to be reading about a dinosaur. Write down some things that you know about dinosaurs. 2. You are going to be reading about one type of dinosaur called Tyrannosaurus rex
Investigating Adaptations
 Investigating Adaptations 4 th Grade Duration Pre-Visit: 40 minutes Museum Visit: 60 minutes Post Visit: 50 minutes Concepts Adaptations reveal what organisms need in their environment to survive. Location
Investigating Adaptations 4 th Grade Duration Pre-Visit: 40 minutes Museum Visit: 60 minutes Post Visit: 50 minutes Concepts Adaptations reveal what organisms need in their environment to survive. Location
Mini Dinosaurs. Grades K 1 2. Compiled by
 Mini Dinosaurs Grades K 1 2 Compiled by Leanne M. Burrow, Extension educator, 4 H/ Youth development, Purdue University Cooperative Extension Service Henry County Resources and References Exploring 4 H,
Mini Dinosaurs Grades K 1 2 Compiled by Leanne M. Burrow, Extension educator, 4 H/ Youth development, Purdue University Cooperative Extension Service Henry County Resources and References Exploring 4 H,
Dynamics of dinosaurs
 MATH0011 Numbers and Patterns in Nature and Life Lecture 1 Dynamics of Dinosaurs http://147.8.101.93/math0011/ Questions: Dynamics of dinosaurs How heavy are dinosaurs? Would sand support a big dinosaur
MATH0011 Numbers and Patterns in Nature and Life Lecture 1 Dynamics of Dinosaurs http://147.8.101.93/math0011/ Questions: Dynamics of dinosaurs How heavy are dinosaurs? Would sand support a big dinosaur
WEE SING AND LEARN DINOSAURS (Song lyrics)
 WEE SING AND LEARN DINOSAURS (Song lyrics) DINOSAURS Dinosaurs, dinosaurs, Dinosaurs, dinosaurs, Dinosaurs, dinosaurs, Oh, millions and millions of years ago, dinosaurs roamed the earth. VERSE Some dinosaurs
WEE SING AND LEARN DINOSAURS (Song lyrics) DINOSAURS Dinosaurs, dinosaurs, Dinosaurs, dinosaurs, Dinosaurs, dinosaurs, Oh, millions and millions of years ago, dinosaurs roamed the earth. VERSE Some dinosaurs
5 The Origins of Bipedal Locomotion
 The Origins of Bipedal Locomotion William E. H. Harcourt Smith Abstract Bipedalism is a highly specialized and unusual form of primate locomotion that is found today only in modern humans. The majority
The Origins of Bipedal Locomotion William E. H. Harcourt Smith Abstract Bipedalism is a highly specialized and unusual form of primate locomotion that is found today only in modern humans. The majority
Is That Mammal a Carnivore, Herbivore or Omnivore?
 Name: Is That Mammal a Carnivore, by Guy Belleranti A mammal can be a carnivore (meat eater), herbivore (plant eater) or omnivore (meat and plant eater). By looking at the teeth, eye position and feet
Name: Is That Mammal a Carnivore, by Guy Belleranti A mammal can be a carnivore (meat eater), herbivore (plant eater) or omnivore (meat and plant eater). By looking at the teeth, eye position and feet
Evolution (18%) 11 Items Sample Test Prep Questions
 Evolution (18%) 11 Items Sample Test Prep Questions Grade 7 (Evolution) 3.a Students know both genetic variation and environmental factors are causes of evolution and diversity of organisms. (pg. 109 Science
Evolution (18%) 11 Items Sample Test Prep Questions Grade 7 (Evolution) 3.a Students know both genetic variation and environmental factors are causes of evolution and diversity of organisms. (pg. 109 Science
Dinosaur Time-line. What other animals lived then? How long ago did the dinosaurs live? Did dinosaurs live at the same time as people?
 Dinosaur Time-line How long ago did the dinosaurs live? The Age of Dinosaurs began nearly 250 million years ago, but the first true dinosaurs appeared closer to 220 million years ago. Some dinosaurs evolved
Dinosaur Time-line How long ago did the dinosaurs live? The Age of Dinosaurs began nearly 250 million years ago, but the first true dinosaurs appeared closer to 220 million years ago. Some dinosaurs evolved
Background Biology and Biochemistry Notes A
 Background Biology and Biochemistry Notes A Vocabulary dependent variable evidence experiment hypothesis independent variable model observation prediction science scientific investigation scientific law
Background Biology and Biochemistry Notes A Vocabulary dependent variable evidence experiment hypothesis independent variable model observation prediction science scientific investigation scientific law
FCI-Standard N 105 / 29. 03. 2006 /GB FRENCH WATER DOG. (Barbet)
 FCI-Standard N 105 / 29. 03. 2006 /GB FRENCH WATER DOG (Barbet) 2 TRANSLATION : Jennifer Mulholland. ORIGIN : France DATE OF PUBLICATION OF ORIGINAL VALID STANDARD : 21.02.2006. UTILIZATION: Water dog
FCI-Standard N 105 / 29. 03. 2006 /GB FRENCH WATER DOG (Barbet) 2 TRANSLATION : Jennifer Mulholland. ORIGIN : France DATE OF PUBLICATION OF ORIGINAL VALID STANDARD : 21.02.2006. UTILIZATION: Water dog
Evolutionary Evidence
 Evolutionary Evidence 7th Grade, Science and English/Language Arts: Age of Mammals Make the most of your Museum field trip by integrating it into your classroom curriculum. These lesson plans provide a
Evolutionary Evidence 7th Grade, Science and English/Language Arts: Age of Mammals Make the most of your Museum field trip by integrating it into your classroom curriculum. These lesson plans provide a
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge Primary Checkpoint
 Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge Primary Checkpoint ENGLISH 0844/01 Paper 1 For Examination from 2014 SPECIMEN PAPER 1 hour Candidates answer on the Question Paper. No Additional Materials
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge Primary Checkpoint ENGLISH 0844/01 Paper 1 For Examination from 2014 SPECIMEN PAPER 1 hour Candidates answer on the Question Paper. No Additional Materials
Objectives AXIAL SKELETON. 1. Frontal Bone. 2. Parietal Bones. 3. Temporal Bones. CRANIAL BONES (8 total flat bones w/ 2 paired)
 Objectives AXIAL SKELETON SKULL 1. On a skull or diagram, identify and name the bones of the skull 2. Identify the structure and function of the bones of the skull 3. Describe how a fetal skull differs
Objectives AXIAL SKELETON SKULL 1. On a skull or diagram, identify and name the bones of the skull 2. Identify the structure and function of the bones of the skull 3. Describe how a fetal skull differs
Giant Pandas. Name. Date. www.schoolexpress.com. Copyright@ 2012 Comp Ed, Inc.
 Name Date Copyright@ 2012 Comp Ed, Inc. www.schoolexpress.com There are two kinds of panda bears, the giant panda and the lesser or red panda. They do not look alike. This Unit is about the giant panda.
Name Date Copyright@ 2012 Comp Ed, Inc. www.schoolexpress.com There are two kinds of panda bears, the giant panda and the lesser or red panda. They do not look alike. This Unit is about the giant panda.
Religion and Science
 Religion and Science Glossary Cosmology the study of the origins of the universe How did the world come into existence? Theory one Aristotle Taught that the universe has always existed and would always
Religion and Science Glossary Cosmology the study of the origins of the universe How did the world come into existence? Theory one Aristotle Taught that the universe has always existed and would always
WEATHER, CLIMATE AND ADAPTATIONS OF ANIMALS TO CLIMATE
 7 WEATHER, CLIMATE AND ADAPTATIONS OF ANIMALS TO CLIMATE TEXTBOOK QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS Q.1. Why weather changes so frequently? Ans. All changes in the weather are caused by the sun. The movement of the
7 WEATHER, CLIMATE AND ADAPTATIONS OF ANIMALS TO CLIMATE TEXTBOOK QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS Q.1. Why weather changes so frequently? Ans. All changes in the weather are caused by the sun. The movement of the
Who are you: Strategies for Presenting Forensic Anthropology and Human Variation in the Classroom
 Who are you: Strategies for Presenting Forensic Anthropology and Human Variation in the Classroom K. Lindsay Eaves-Johnson, M.A., University of Iowa Nancy Tatarek, Ph.D., Ohio University Philadelphia,
Who are you: Strategies for Presenting Forensic Anthropology and Human Variation in the Classroom K. Lindsay Eaves-Johnson, M.A., University of Iowa Nancy Tatarek, Ph.D., Ohio University Philadelphia,
Regardless of who you are or where you came from
 We Are All African! Can scientific proof of our commonality save us? Christopher dicarlo Regardless of who you are or where you came from despite ethnic differences, political distinctions, and racial
We Are All African! Can scientific proof of our commonality save us? Christopher dicarlo Regardless of who you are or where you came from despite ethnic differences, political distinctions, and racial
Unit 2 Lesson 4 The Geologic Time Scale. Copyright Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
 Once Upon a Time How have geologists described the rate of geologic change? Geology is the scientific study of the origin, history, and structure of Earth and the processes that shape it. Early geologists
Once Upon a Time How have geologists described the rate of geologic change? Geology is the scientific study of the origin, history, and structure of Earth and the processes that shape it. Early geologists
Dinosaur Hall Second Grade Dinosaur Lesson Teacher Pages Pre Visit On site Visit
 Dinosaur Hall Second Grade Dinosaur Lesson Teacher Pages Pre Visit Earth Sciences 3d. Students know that fossils provide evidence about the plants and animals that lived long ago and that scientists learn
Dinosaur Hall Second Grade Dinosaur Lesson Teacher Pages Pre Visit Earth Sciences 3d. Students know that fossils provide evidence about the plants and animals that lived long ago and that scientists learn
2. Importance of Energy to Human Population Growth and the Economy. Gail Tverberg Energy Economics and Analysis Modeling
 2. Importance of Energy to Human Population Growth and the Economy Gail Tverberg Energy Economics and Analysis Modeling How might additional energy supply increase human population? } There are far more
2. Importance of Energy to Human Population Growth and the Economy Gail Tverberg Energy Economics and Analysis Modeling How might additional energy supply increase human population? } There are far more
THE COLUMBUS ZOO AND AQUARIUM RE-HATCHING AT MAY 17, 2014
 RE-HATCHING AT THE COLUMBUS ZOO AND AQUARIUM MAY 17, 2014 Back from extinction by popular demand! Travel back in time, 65 million years, for a prehistoric adventure of colossal proportion. Dinosaurs became
RE-HATCHING AT THE COLUMBUS ZOO AND AQUARIUM MAY 17, 2014 Back from extinction by popular demand! Travel back in time, 65 million years, for a prehistoric adventure of colossal proportion. Dinosaurs became
INTERMEDIATE PHASE. Social Sciences 2 Mathematics 11 EMS 16 Natural Sciences 27 Technology 31 Arts and Culture 36 Life Orientation 40
 1 INTERMEDIATE PHASE Social Sciences 2 Mathematics 11 EMS 16 Natural Sciences 27 Technology 31 Arts and Culture 36 Life Orientation 40 INTERMEDIATE PHASE Social Sciences 2 Intermediate Phase: Educator
1 INTERMEDIATE PHASE Social Sciences 2 Mathematics 11 EMS 16 Natural Sciences 27 Technology 31 Arts and Culture 36 Life Orientation 40 INTERMEDIATE PHASE Social Sciences 2 Intermediate Phase: Educator
Adapted from Stone Girl Bone Girl by Laurence Anholt, Francis Lincoln Children s Book
 1. Mary Anning Adapted from Stone Girl Bone Girl by Laurence Anholt, Francis Lincoln Children s Book This is the true story of Mary Anning, who lived 200 years ago. Mary was born in 1799 and was one of
1. Mary Anning Adapted from Stone Girl Bone Girl by Laurence Anholt, Francis Lincoln Children s Book This is the true story of Mary Anning, who lived 200 years ago. Mary was born in 1799 and was one of
Stone Age Tools By Richard Milton The Stone Age Tools Museum
 Stone Age Tools By Richard Milton The Stone Age Tools Museum Old Stone Age (Palaeolithic) The earliest humans The earliest evidence of humans visiting Britain comes from excavations at Happisburgh (pronounced
Stone Age Tools By Richard Milton The Stone Age Tools Museum Old Stone Age (Palaeolithic) The earliest humans The earliest evidence of humans visiting Britain comes from excavations at Happisburgh (pronounced
Mammal Scavenger Hunt Activity
 Mammal Scavenger Hunt Activity Materials: Mammal questions worksheet (pages 2-3) 18 Mammal fact cards (pages 4-8) Tape and scissors Preparation: Print the fact cards on card stock or brightly-colored paper
Mammal Scavenger Hunt Activity Materials: Mammal questions worksheet (pages 2-3) 18 Mammal fact cards (pages 4-8) Tape and scissors Preparation: Print the fact cards on card stock or brightly-colored paper
Camelid Dentistry. Stephen R. Purdy, DVM Director of Camelid Studies UMass Amherst President Nunoa Project Peru
 Camelid Dentistry Stephen R. Purdy, DVM Director of Camelid Studies UMass Amherst President Nunoa Project Peru Learning objectives To describe the normal dentition of camelids To explain common corrective
Camelid Dentistry Stephen R. Purdy, DVM Director of Camelid Studies UMass Amherst President Nunoa Project Peru Learning objectives To describe the normal dentition of camelids To explain common corrective
Making Tracks Elementary School 5-E Lesson
 Making Tracks Elementary School 5-E Lesson Objectives -Student will analyze fossil footprints of two and four legged dinosaurs to learn more about how these animals lived. -Students will experiment with
Making Tracks Elementary School 5-E Lesson Objectives -Student will analyze fossil footprints of two and four legged dinosaurs to learn more about how these animals lived. -Students will experiment with
ENCYCLOPEDIA OF BIOMETRICS
 ENCYCLOPEDIA OF BIOMETRICS Anatomy of the Face Anne M. Burrows 1 and Jeffrey F. Cohn 2 1 Duquesne University, Pittsburgh, PA 15282, USA 2 University of Pittsburgh, Pittsburgh, PA 15260, USA SYNONYMS Anatomic,
ENCYCLOPEDIA OF BIOMETRICS Anatomy of the Face Anne M. Burrows 1 and Jeffrey F. Cohn 2 1 Duquesne University, Pittsburgh, PA 15282, USA 2 University of Pittsburgh, Pittsburgh, PA 15260, USA SYNONYMS Anatomic,
6. Evolution and Domestication of Wolves
 6. Evolution and Domestication of Wolves Wolf Evolution Scientists are not absolutely certain how and where the wolf evolved. By examining fossil bones, especially skulls, of animals that lived millions
6. Evolution and Domestication of Wolves Wolf Evolution Scientists are not absolutely certain how and where the wolf evolved. By examining fossil bones, especially skulls, of animals that lived millions
Breeds of Swine. Berkshire. Chester White
 Breeds of Swine Picture Provided by Prairie State Berkshire The Berkshire breed has long been known for its efficiency in gaining weight. Berkshire hogs have possessed their excellent carcass quality since
Breeds of Swine Picture Provided by Prairie State Berkshire The Berkshire breed has long been known for its efficiency in gaining weight. Berkshire hogs have possessed their excellent carcass quality since
SCOTTISH TERRIER. FEDERATION CYNOLOGIQUE INTERNATIONALE (AISBL) SECRETARIAT GENERAL: 13, Place Albert 1 er B 6530 Thuin (Belgique) 10.01.
 FEDERATION CYNOLOGIQUE INTERNATIONALE (AISBL) SECRETARIAT GENERAL: 13, Place Albert 1 er B 6530 Thuin (Belgique) 10.01.2011/EN FCI-Standard N 73 SCOTTISH TERRIER M.Davidson, illustr. NKU Picture Library
FEDERATION CYNOLOGIQUE INTERNATIONALE (AISBL) SECRETARIAT GENERAL: 13, Place Albert 1 er B 6530 Thuin (Belgique) 10.01.2011/EN FCI-Standard N 73 SCOTTISH TERRIER M.Davidson, illustr. NKU Picture Library
DEVELOPMENT AND GROWTH OF THE MANDIBLE
 2012-2013 ORAL BIOLOGY DEVELOPMENT AND GROWTH OF THE MANDIBLE Ass. Prof. Dr. Heba M. Elsabaa Development and Growth of the Mandible DEVELOPMENT OF THE MANDIBLE The Mandible Is the largest and strongest
2012-2013 ORAL BIOLOGY DEVELOPMENT AND GROWTH OF THE MANDIBLE Ass. Prof. Dr. Heba M. Elsabaa Development and Growth of the Mandible DEVELOPMENT OF THE MANDIBLE The Mandible Is the largest and strongest
Lesson Overview. Biodiversity. Lesson Overview. 6.3 Biodiversity
 Lesson Overview 6.3 6.3 Objectives Define biodiversity and explain its value. Identify current threats to biodiversity. Describe how biodiversity can be preserved. THINK ABOUT IT From multicolored coral
Lesson Overview 6.3 6.3 Objectives Define biodiversity and explain its value. Identify current threats to biodiversity. Describe how biodiversity can be preserved. THINK ABOUT IT From multicolored coral
What is a Fossil? Adapted from What is a Fossil MOR Dinosaur Trunk Activity
 What is a Fossil? Adapted from What is a Fossil MOR Dinosaur Trunk Activity Grade Level: Grades K-8 Preparation Time: 10-15 minutes Activity Duration: 30 minutes-2 hours Concepts Addressed A fossil is
What is a Fossil? Adapted from What is a Fossil MOR Dinosaur Trunk Activity Grade Level: Grades K-8 Preparation Time: 10-15 minutes Activity Duration: 30 minutes-2 hours Concepts Addressed A fossil is
WHALES: Walking Into the Past
 WHALES: Walking Into the Past Whales with knees and toes? Incredible as it seems, whales once walked on legs and lived on land. Millions of years of biological change have erased the whale s legs from
WHALES: Walking Into the Past Whales with knees and toes? Incredible as it seems, whales once walked on legs and lived on land. Millions of years of biological change have erased the whale s legs from
Evidence for evolution factsheet
 The theory of evolution by natural selection is supported by a great deal of evidence. Fossils Fossils are formed when organisms become buried in sediments, causing little decomposition of the organism.
The theory of evolution by natural selection is supported by a great deal of evidence. Fossils Fossils are formed when organisms become buried in sediments, causing little decomposition of the organism.
Women s Rights: Issues for the Coming Decades
 September 24, 2010 Suzanne B. Goldberg Columbia Law School Remarks for the International Conference on the Protection of Women s Rights Women s Rights: Issues for the Coming Decades I am delighted to be
September 24, 2010 Suzanne B. Goldberg Columbia Law School Remarks for the International Conference on the Protection of Women s Rights Women s Rights: Issues for the Coming Decades I am delighted to be
Brownies. It s Your Planet Love It! WOW: Wonders of Water. Ice Cold (page 25) Extinct (page 39)
 Exhibit Guide WOW: Wonders of Water Ice Cold (page 25) The Earth has two poles, a North Pole and a South Pole. Both are extremely cold and covered in ice. Sometimes you might see huge masses of moving
Exhibit Guide WOW: Wonders of Water Ice Cold (page 25) The Earth has two poles, a North Pole and a South Pole. Both are extremely cold and covered in ice. Sometimes you might see huge masses of moving
Geologic Time Scale Notes
 Name: Date: Period: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Notes Essential Question: What is the geologic time scale? Vocabulary: Geology: the scientific study of the origin, history, and structure of Earth and the processes that
Name: Date: Period: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Notes Essential Question: What is the geologic time scale? Vocabulary: Geology: the scientific study of the origin, history, and structure of Earth and the processes that
Carbon-14 Dating. or, How Old Are Those M&Ms? Number of Undecayed M&Ms
 BRSP - 15 Page 1 Carbon-14 Dating or, How Old Are Those M&Ms? One of the tools available to scientists who study ancient climates is called carbon-14 dating (also known as carbon dating or radiocarbon
BRSP - 15 Page 1 Carbon-14 Dating or, How Old Are Those M&Ms? One of the tools available to scientists who study ancient climates is called carbon-14 dating (also known as carbon dating or radiocarbon
Is Homo Defined by Culture?
 Is Homo Defined by Culture? BERNARD WOOD & MARK COLLARD The changing face of Homo THE GENUS HOMO was established by Carolus Linnaeus as part of the 1758 edition of his monumental review, the Systema Naturae.
Is Homo Defined by Culture? BERNARD WOOD & MARK COLLARD The changing face of Homo THE GENUS HOMO was established by Carolus Linnaeus as part of the 1758 edition of his monumental review, the Systema Naturae.
11A Plate Tectonics. What is plate tectonics? Setting up. Materials
 11A Plate Tectonics What is plate tectonics? Earth s crust plus the upper mantle forms the lithosphere. Earth s lithosphere is broken in a number of different pieces. How these pieces move and interact
11A Plate Tectonics What is plate tectonics? Earth s crust plus the upper mantle forms the lithosphere. Earth s lithosphere is broken in a number of different pieces. How these pieces move and interact
The Great Leap Forward JARED DIAMOND
 The Great Leap Forward JARED DIAMOND 1 World population figures around 1 A.D. have been estimated at about 200 million people. One million years prior to 1 A.D., population figures of early humankind of
The Great Leap Forward JARED DIAMOND 1 World population figures around 1 A.D. have been estimated at about 200 million people. One million years prior to 1 A.D., population figures of early humankind of
Wetlands by Leslie Cargile
 Name: by Leslie Cargile What do the bogs in Ireland, the marshes in South Carolina, and the swamps of Louisiana have in common? If you said they re all wetlands, you d be right! are any land that is flooded
Name: by Leslie Cargile What do the bogs in Ireland, the marshes in South Carolina, and the swamps of Louisiana have in common? If you said they re all wetlands, you d be right! are any land that is flooded
