Connecting Kinetis MCU with CMOS Sensor Interface through GPIO QQVGA image transfer to Kinetis internal SRAM
|
|
|
- Britton Harrison
- 9 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Freescale Semiconductor Document Number:AN4627 Application Note Rev 0, 5/2013 Connecting Kinetis MCU with CMOS Sensor Interface through GPIO QQVGA image transfer to Kinetis internal SRAM by: Adi Shieber and Yan Vainter 1 Introduction This application note explains how to connect a Kinetis MCU to CMOS Sensor through GPIO to receive image data in memory. The application can be implemented on Kinetis MCUs and CMOS sensors with CSI (CMOS sensor interface) gluelessly, without any external hardware. In this case the implementation was done by using Tower evaluation board for Kinetis K60 and CMOS image sensor. The compatibility of Kinetis MCUs allows this application to be implemented on different sub-families of Kinetis other than K60. The fact all Kinetis K series shares the same modules (IP blocks) enables easy reuse of the code across the entire K sub-families. Examples of target applications for this application note are security systems and other consumer products focusing on low cost and low power. Contents 1 Introduction Signals and Connections Implementation Overview Conclusions and further options...9 A Hardware Connections...9 B Software Signals and Connections There are four types of signals involved in creating the CMOS sensor interface between the MCU and the camera (CMOS sensor camera). The first type is the power supplies that supply power to the camera. The second type is the camera configuration signals that are used to configure the work mode by using I2C interface. The third type is the external clock for the camera produced by the MCU and the fourth is the camera image transfer control and data. Original Copyright Latest Copyright Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
2 Signals and Connections 2.1 Power supplies The Kinetis Tower board supplies the camera with VDD and GND connections. 2.2 Camera configuration signals This type of connection to the camera is used to configure the CMOS sensor. For the specific camera used in this application note, the control interface is I2C. It configures the camera registers to the desired work mode. However, other cameras may use SPI interface which is also supported by Kinetis K series. The following table shows the Kinetis and camera signals used in the camera configuration stage. CMOS sensor signal CMOS sensor I/O SIO_C I Control signal. Indicates each transmitted bit. SIO_D I/O Bidirectional data signal. Table 1. Camera configuration signals Description Kinetis signal Kinetis pin type connection 1 Kinetis I/O Description SCL I2Cn_SCL O Serial clock line of the I2C system. SDA I2Cn_SDA I/O Bidirectional serial data line of the I2C system. 1. I2Cn n represents the number of the I2C module. 2.3 Camera external clock Kinetis supplies the camera with an external clock to create all timing synchronizations for signals participating in image data transmission. The generated clock rate is according to the camera specification. CMOS sensor signal CMOS sensor I/O XVCLK I System clock input Table 2. Camera external clock signal Description Kinetis signal Kinetis signal Kinetis I/O Description PWM FTMn_CHx 1 O Output clock according to PWM definitions 1. FTMn_CHx n represents the number of FTM module and x represents the number of channel. 2.4 Camera image transfer control and data The Kinetis family does not have a dedicated CSI (CMOS sensor interface) therefore the camera was connected through a standard GPIO. 2 Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
3 Signals and Connections This connection includes all the signals involved in the image transmission from the camera to Kinetis; the data signals, which hold the image data, and the control signals, which manage the way the data is transmitted Image data signals The camera transmits image data signals over eight data lines in parallel. These lines are connected to eight sequential Kinetis GPIO pins configured as inputs Image control signals The camera control signals are VSYNC, HREF and PCLK. The VSYNC signal determines when a new frame begins. The HREF signal represents the period of data transfer of a row in the transmitted frame. When the HREF signal is active, there is valid data over the data lines every pixel clock (PCLK) cycle. The PCLK signal indicates a valid data byte over the data lines and it is used as transfer trigger for the DMA module Camera image transfer control and data connections The following table shows the camera signals used in control and data transmission, Kinetis pins allocated to perform the transmission and the action each signal initiates. CMOS sensor Signal Table 3. Image transfer control and data signals CMOS sensor I/O Description Kinetis pin type connection VSYNC O Vertical synchronization. Indicates the beginning of a frame. HREF O Horizontal synchronization. Indicates the period of data transfer of a row. PCLK O Pixel clock. Asserted when a byte is ready for transmission. Kinetis I/O Initiates GPIO pin I Interrupt routine GPIO pin I Interrupt routine GPIO pin. DMA MUX source D0 O Data line 0 GPIO pin n I D1 O Data line 1 GPIO pin n+1 I D2 O Data line 2 GPIO pin n+2 I D3 O Data line 3 GPIO pin n+3 I D4 O Data line 4 GPIO pin n+4 I D5 O Data line 5 GPIO pin n+5 I D6 O Data line 6 GPIO pin n+6 I D7 O Data line 7 GPIO pin n+7 I I DMA HW request Freescale Semiconductor, Inc. 3
4 Implementation Overview NOTE It is significant for the eight GPIO port input pins to be sequential such that GPIO pin n is connected to data line [0] of the camera, and that GPIO pin n+7 is connected to data line [7]. 2.5 Connections diagram Figure 1. Connections diagram 3 Implementation Overview 3.1 Specification and features Implementation is performed on MK60DN512VMD10 on TWR-K60D100M board and the camera used is OmniVision 1/9 CMOS VGA (640 x480) image sensor (OV7675). The following configuration options are brought up as part of the specific camera used in this application. Optional output formats can be RGB565 or YUV4:2:2 this depends on theconversion method and the display option in use. The destination of the image transfer is the internal SRAM of the K60 which is 128 KB and so the configured resolution for the camera is QQVGA (160 x 120). For the above output formats the camera transmits two bytes per pixel, therefore the frame buffer size in Kinetis is twice the number of pixels (38400 bytes per frame). The input clock for the camera is provided by Kinetis. The K60 generates a 24 MHz output clock according to the typical value of the camera as specified in its Data Sheet. For more details about the camera please refer to the OmniVision website at 4 Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
5 Implementation Overview 3.2 General description Implementation of this application is divided into two major sections. The first is the camera configuration and the second is the image data transfer. As mentioned before, the camera configuration is done through I2C communication protocol to configure the CMOS sensor to the desired work mode. The configuration is executed by writing values to the necessary registers. After the registers are configured, the camera produces image data accordingly. Data transmission to the Kinetis memory can now start. The camera configuration includes setting the PCLK signal to be active only during HREF active period. It also includes setting the frame rate and resolution. The transmission procedure includes interrupts and DMA usage. A VSYNC signal generates an interrupt starting the transmission procedure. Following the VSYNC signal, the DMA hardware trigger is enabled. Each PCLK initiates a DMA transfer of eight data signals from the GPIO port pins (connected to the camera data lines) to Kinetis SRAM. The PCLK signal GPIO pin is the DMA source routed by the DMA Multiplexer. When HREF signal turns inactive, current row transmission is finished. The following time diagram shows the signals during data transmission of a single QQVGA frame. Figure 2. Time diagram of data transmission The following flow diagram displays the main stages of the process of acquiring a frame from the camera. Freescale Semiconductor, Inc. 5
6 Implementation Overview Figure 3. Flow diagram of implementation 3.3 Participating Kinetis modules All the Kinetis K series share the same modules (IP blocks) that enable reuse of the code across the entire family. Selection of a different derivative of Kinetis K requires a new pin muxing to ensure all the necessary connections can be defined. The Kinetis modules that were used to implement this application are described below Direct Memory Access Controller edma The data transfer is executed by the DMA to reduce CPU loading and allows it to work with other tasks at the same time (for example JPEG encoding). The PCLK signal indicates a new single byte that transmits over the data lines. It is used as a hardware request trigger for the DMA to transfer one byte per request. Main topics to configure the DMA for hardware request triggered transfer include: 6 Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
7 Enabling the DMA module clock. Enabling the hardware request for the channel. The DMA Channel for transfer should be selected according to priority of the image data transfer over other DMA transfers. Destination address is the Kinetis internal SRAM. Source offset is set to 0 as the source address of the camera single byte data is static. Destination offset is 1 to increase the destination address after each DMA transfer by one byte. A detailed DMA registers configuration is described in the code included in this application note. NOTE All eight GPIO port input pins of Kinetis must be sequential due to the fact they create the source address for the DMA. Implementation Overview Direct Memory Access Multiplexer DMAMUX The DMAMUX routes DMA sources (called slots) mapped to any of the DMA channels. Each DMA channel can be assigned to one of the possible peripheral DMA slots or to one of the always-on slots. There are three modes of operations for the DMAMUX; Disable, Normal, and Periodic trigger modes. Here, the DMA channel routes the specified source to the DMA channel in Normal mode. The DMA source is the GPIO port that contains the PCLK signal input pin. This signal is the DMA hardware request pin. This GPIO port source number is listed along with all other DMA sources in the Chip Configuration chapter found in the Reference Manual, DMA Request Sources table. Using the DMAMUX module in this configuration requires the following: Enabling the DMAMUX clock. Configuring the DMAMUX register according to the DMA channel in normal mode and to the GPIO port pin source Inter-Integrated Circuit I2C The I2C module provides a method of communication between several devices. In this case the interface allows communication between Kinetis (master) and the camera (slave). The implementation of the Kinetis-camera communication uses an I2C baud rate of ~400 kbit/s. Kinetis also supports other I2C baud rates. There is a limitation on the camera I2C baud rate that must be taken into account when setting the Kinetis I2C baud rate. There is a relation between the input clock to the camera and the maximum possible I2C baud rate for the camera module in use. Please refer to the camera vendor for more details. The I2C bus system uses the Serial Clock Line (SCL) and the Serial Data Line (SDA) for data transfers. Each camera has its own slave address. It can be found in the camera specification. Using the I2C module in this configuration requires the following: Enabling the I2C clock. Setting the I2C baud rate. Enabling the I2C module. I2C communication between Kinetis and the camera is composed of the following four parts: START signal. Slave address transmission - the I2C has a 7-bit address space followed by a R/W bit. The R/W bit defines the desired direction of data transfer for the slave. Data transfer. STOP/repeated START signal. For more details of Kinetis I2C communication method please review the I2C chapter in the Reference Manual. Freescale Semiconductor, Inc. 7
8 Implementation Overview Port pins GPIO The GPIO is used for a DMA request trigger, interrupts source and data transfer with DMA to transfer image from camera without dedicated CSI port on Kinetis. The camera control signals (VSYNC, HREF, PCLK) connected to Kinetis GPIO inputs are used to generate DMA request triggers that transfer image data from the camera without a dedicated CSI port on Kinetis. Users should define the pin muxing to avoid collisions between different modules and their required functionality. All pins that are connected to the camera for control and data must be configured as input GPIO. The corresponding PORT module clocks need to be enabled. Each pin has edge sensitive (rising, falling, both) or level sensitive (low, high) support and can be configured according to signal behavior for interrupt and DMA request purposes. The VSYNC signal is configured for rising edge interrupt, HREF is configured for falling edge interrupt, and PCLK is configured for falling edge DMA request Interrupt routines Two interrupt routines are in use; one for the VSYNC signal and the other for the HREF signal. The interrupt routine for VSYNC signal enables a DMA request triggered by the PCLK signal and also enables an interrupt by the HREF signal. The camera can be configured such that PCLK signal does not toggle during horizontal blank. This implies that PCLK goes active only when HREF is active FlexTimer Module FTM The FTM is a timer that supports input capture, output compare, and generation of PWM signals. In this specific application the FTM is used as a PWM signal generator acting as an external clock to the camera. For more details of how to configure the FTM to work in PWM mode please refer to the FTM chapter in the Reference Manual. 3.4 Functional limitations There are several limitations that must be considered during implementation. Solutions are suggested for some of these limitations Maximum DMA rate The maximum transfer rate is limited for DMA hardware requests, especially for single byte transfers. Such a limitation requires a restricted pixel clock rate for the camera to avoid any data loss. The maximum achievable rate for 100 MHz device is 8.7 MHz, according to the Performance section of the DMA in the Reference Manual. This limitation requires a careful configuration for the camera pixel clock rate and frame rate. As a result of this limitation this implementation uses 30 fps as frame rate and a 3 MHz PCLK rate, that is the DMA hardware trigger. Configuration of a 60 fps and 6 MHz PCLK was also tested successfully. 8 Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
9 3.4.2 Memory Conclusions and further options In this application note the internal SRAM memory was used to store the image data transferred from the camera. Kinetis K60 internal SRAM is limited to 128 KB, therefore the maximum resolution of the image is QQVGA (160 x 120) since there are 2 bytes per pixel. It is possible to use external memory interface of Kinetis such as DDR2 to increase the resolution of the image to QVGA (320 x 240) or other higher resolutions DMA major loop counter The major loop counter of the DMA register DMA_TCDn_CITER_ELINKNO is limited to 15 bits, in the case where the channel linking feature of the DMA is not in use (refer to DMA chapter in the Reference Manual). Therefore, there is a limitation of 32K major loops equal to 32K bytes transferred. To overcome this limitation of transferring a full frame of QQVGA resolution and above, you must update the pointer of the DMA destination address after each row transferred. It is implemented by interrupt from the falling edge of the HREF signal Camera XVCLK input To reduce the overshoot and undershoot of the XVCLK signal, serial resistor of 330Ω was used. 4 Conclusions and further options This application note provides the basic concepts for implementing a glueless connection of CMOS sensors to the Kinetis MCU. In this application note the solution offered is implemented on the K60. For a cost-effective solution, it is possible to use the entry level of the Kinetis K series - the K10 and others. This is possible to implement because the Kinetis K series is scalable and uses the same IP blocks across the sub-families. Whereas the application for K60 is implemented using the internal SRAM (128 KB) to store the image data, there are further options to use external memory. A use of external memory allows working with a higher resolution than the QQVGA implemented in this application note. Such an option is DDR2 or external SRAM. To work with external SRAM, use the Kinetis FlexBus interface. In case of DDR2 usage, you must choose a Kinetis device that supports a DDR controller. An advanced option for this application suggests a JPEG compression. A JPEG compression algorithm can easily be adapted on the Kinetis MCU due to the DSP capabilities of the ARM Cortex-M4 core. To process the image data on a different endpoint it is possible to transfer the data using different communication features the Kinetis MCU offers. There are either wired or wireless options possible to use: Ethernet port 10/100 that exists on the derivatives of the K60 and higher. WiFi - Freescale works with 3rd parties that offer a variety of Tower wireless peripheral boards with WiFi connectivity including n. For more information go to ZigBee - Freescale offers a variety of solutions of sub GHz and 2.4 GHz Tower System Radio Peripheral modules. For more information go to Freescale Semiconductor, Inc. 9
10 Conclusions and further options Appendix A Hardware Connections The following table shows the physical connections between the K60 and the camera as they are implemented. It specifies the names of the signal involved, pin name on the camera connector, pin name on the TOWER elevator, pin name on the CPU module TWR-K60D100M, and the muxing option of the pin. Refer to the schematics of the TWR-K60D100M and TWR- ELEV. Note that physical connection can be performed using the TWR-PROTO board. Signal Table A-1. Kinetis-CMOS sensor connections CMOS sensor Connector - J2 TWR-ELEV primary connector TWR-K60D100M Primary J7A/TWR- PROTO Primary J2 VDD 21 PWR J9 3 B3 GND 32 GND J8 GND A65 GND_15 Camera configuration clock (I2C clock) Camera configuration data line (I2C data) Muxing Option 14 SIOC J8 7 SCL0 A7 SCL0 ALT2 I2C0_SCL 12 SIOD J8 8 SDA0 A8 SDA0 ALT2 I2C0_SDA Camera input clock 1 20 XCLK1 J8 40 PWM0 A40 PWM0 ALT4 FTM0_CH0 VSYNC 15 VSYNC J8 22 SSI_BCLK A22 SSI_BCLK ALT1 PTE12 HREF 13 HREF J9 80 FB_D0 B80 EBI_D0 ALT1 PTC15 PCLK 17 PCLK J9 66 FB_AD15 B66 EBI_AD15 ALT1 PTB18 D0 -Data line 0 2 D2 J9 22 GPIO2/OPEN B22 GPIO2/ SDHC_D1 D1- Data line 1 1 D3 J9 10 SPI1_MOSI B11 SDHC_D0/ SPI1_MISO D2- Data line 2 4 D4 J9 7 SPI1_CLK B7 SDHC_CLK/ SPI1_CLK D3- Data line D5 J9 11 SPI1_MISO B10 SDHC_CMD/ SPI1_MOSI D4 - Data line 4 6 D6 J9 9 SPI1_CS0 B9 SDHC_D3/ SPI1_CS0 D5 - Data line 5 5 D7 J8 10 GPIO8/OPEN A10 GPIO8/ SDHC_D2 ALT1 PTE0 ALT1 PTE1 ALT1 PTE2 ALT1 PTE3 ALT1 PTE4 ALT1 PTE5 D6 - Data line 6 8 D8 J8 21 SSI_MCLK A21 SSI_MCLK ALT1 PTE6 D7 -Data line 7 7 D9 J8 24 SSI_RXD A24 SSI_RXD ALT1 PTE7 1. A 330Ω resistor is connected in series between the J2 connector pin 20 and the J8 connector pin 40 adjacent to J2 10 Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
11 Figure A-1. Kinetis-CMOS Sensor Hardware Appendix B Software An example software project targeted at the Kinetis K60 MCU has been created to demonstrate the transfer of the camera image data to the internal SRAM. The Freescale Tower system based on the TWR-K60D100M and the TWR-PROTO boards have been used for demonstration software development and testing. The software project runs from the MCU flash memory and does not run under an operating system. The code footprint is approximately 7 KB. The example sample project was implemented by using IAR tools version The frame buffer that is transferred to the internal SRAM can be saved and reviewed for debugging and analysis purposes on a PC by IAR IDE. The code is comprised of the following basic stages: Initialization of the participating K60 modules and the required interrupts. This part includes the init functions and the clock enable phase. Camera setting by I2C This is where the OV7675 is configured to the preferable mode of work to produce the QQVGA image resolution in YUV422 format. The periodic loop of image data transfer managed by the interrupts that are triggered by the control signals of the camera. Freescale Semiconductor, Inc. 11
12 How to Reach Us: Home Page: freescale.com Web Support: freescale.com/support Information in this document is provided solely to enable system and software implementers to use Freescale products. There are no express or implied copyright licenses granted hereunder to design or fabricate any integrated circuits based on the information in this document. Freescale reserves the right to make changes without further notice to any products herein. Freescale makes no warranty, representation, or guarantee regarding the suitability of its products for any particular purpose, nor does Freescale assume any liability arising out of the application or use of any product or circuit, and specifically disclaims any and all liability, including without limitation consequential or incidental damages. Typical parameters that may be provided in Freescale data sheets and/or specifications can and do vary in different applications, and actual performance may vary over time. All operating parameters, including typicals, must be validated for each customer application by customer's technical experts. Freescale does not convey any license under its patent rights nor the rights of others. Freescale sells products pursuant to standard terms and conditions of sale, which can be found at the following address: freescale.com/ SalesTermsandConditions. Freescale, the Freescale logo, AltiVec, C-5, CodeTest, CodeWarrior, ColdFire, ColdFire+, C-Ware, Energy Efficient Solutions logo, Kinetis, mobilegt, PowerQUICC, Processor Expert, QorIQ, Qorivva, StarCore, Symphony, and VortiQa are trademarks of Freescale Semiconductor, Inc., Reg. U.S. Pat. & Tm. Off. Airfast, BeeKit, BeeStack, CoreNet, Flexis, Layerscape, MagniV, MXC, Platform in a Package, QorIQ Qonverge, QUICC Engine, Ready Play, SafeAssure, SafeAssure logo, SMARTMOS, Tower, TurboLink, Vybrid, and Xtrinsic are trademarks of Freescale Semiconductor, Inc. All other product or service names are the property of their respective owners. Original Copyright Latest Copyright Freescale Semiconductor, Inc. Document Number AN4627 Rev 0, 5/ May 2013
MPR121 Serial Communication
 Freescale Semiconductor Document Number: AN3895 Application Note Rev. 2, 02/2013 MPR121 Serial Communication INTRODUCTION The MPR121 uses an I 2 C Serial Interface. The I 2 C protocol implementation and
Freescale Semiconductor Document Number: AN3895 Application Note Rev. 2, 02/2013 MPR121 Serial Communication INTRODUCTION The MPR121 uses an I 2 C Serial Interface. The I 2 C protocol implementation and
USB to SPI Device Driver Installation Instructions
 Freescale Semiconductor User s Guide Document Number: KTUSBSPIDRVUG Rev. 1.0, 10/2012 USB to SPI Device Driver Installation Instructions Table of Contents 1 Introduction........................................................................
Freescale Semiconductor User s Guide Document Number: KTUSBSPIDRVUG Rev. 1.0, 10/2012 USB to SPI Device Driver Installation Instructions Table of Contents 1 Introduction........................................................................
QorIQ espi Controller Register Setting Considerations and Programming Examples
 Freescale Semiconductor Application Note Document Number: AN4375 Rev. 1, 06/2012 QorIQ espi Controller Register Setting Considerations and Programming Examples About this document This document describes
Freescale Semiconductor Application Note Document Number: AN4375 Rev. 1, 06/2012 QorIQ espi Controller Register Setting Considerations and Programming Examples About this document This document describes
Freescale, the Freescale logo, AltiVec, C-5, CodeTEST, CodeWarrior, ColdFire, ColdFire+, C- Ware, the Energy Efficient Solutions logo, Kinetis,
 TM July 19, 2013 Freescale, the Freescale logo, AltiVec, C-5, CodeTEST, CodeWarrior, ColdFire, ColdFire+, C- Ware, the Energy Efficient Solutions logo, Kinetis, mobilegt, PEG, PowerQUICC, Processor Expert,
TM July 19, 2013 Freescale, the Freescale logo, AltiVec, C-5, CodeTEST, CodeWarrior, ColdFire, ColdFire+, C- Ware, the Energy Efficient Solutions logo, Kinetis, mobilegt, PEG, PowerQUICC, Processor Expert,
FRDM-KL25Z User's Manual 2012-09-24 Rev. 1.0
 FRDM-KL25Z User's Manual 2012-09-24 Rev. 1.0 Freescale Semiconductor, Inc. FRDMKL25ZUM Table of Contents 1 Overview... 3 2 Reference Documents... 3 3 Getting Started... 3 4 FRDM-KL25Z Hardware Overview...
FRDM-KL25Z User's Manual 2012-09-24 Rev. 1.0 Freescale Semiconductor, Inc. FRDMKL25ZUM Table of Contents 1 Overview... 3 2 Reference Documents... 3 3 Getting Started... 3 4 FRDM-KL25Z Hardware Overview...
Safety Lifecycle illustrated with exemplified EPS
 September 2012 Freescale, the Freescale logo, AltiVec, C-5, CodeTEST, CodeWarrior, ColdFire, ColdFire+, C-Ware, the Energy Efficient Solutions logo, Kinetis, mobilegt, PowerQUICC, Processor Expert, QorIQ,
September 2012 Freescale, the Freescale logo, AltiVec, C-5, CodeTEST, CodeWarrior, ColdFire, ColdFire+, C-Ware, the Energy Efficient Solutions logo, Kinetis, mobilegt, PowerQUICC, Processor Expert, QorIQ,
Qorivva MPC5643L Dual Processor Mode Mark Ruthenbeck Applications Engineering Microcontroller Solutions Group
 Freescale Semiconductor Application Note Document Number: AN4034 Rev. 0, 03/2011 Qorivva MPC5643L Dual Processor Mode by: Mark Ruthenbeck Applications Engineering Microcontroller Solutions Group 1 Scope
Freescale Semiconductor Application Note Document Number: AN4034 Rev. 0, 03/2011 Qorivva MPC5643L Dual Processor Mode by: Mark Ruthenbeck Applications Engineering Microcontroller Solutions Group 1 Scope
Freescale 802.15.4 MAC Security Setup
 Freescale Semiconductor Application Note Document Number: AN4973 Rev. 0, 7/2014 Freescale 802.15.4 MAC Security Setup MAC 2006 and MAC 2011 Group Key Security Examples By: Alexandru Balmus, Embedded Connectivity
Freescale Semiconductor Application Note Document Number: AN4973 Rev. 0, 7/2014 Freescale 802.15.4 MAC Security Setup MAC 2006 and MAC 2011 Group Key Security Examples By: Alexandru Balmus, Embedded Connectivity
Production Flash Programming Best Practices for Kinetis K- and L-series MCUs
 Freescale Semiconductor Document Number:AN4835 Application Note Rev 1, 05/2014 Production Flash Programming Best Practices for Kinetis K- and L-series MCUs by: Melissa Hunter 1 Introduction This application
Freescale Semiconductor Document Number:AN4835 Application Note Rev 1, 05/2014 Production Flash Programming Best Practices for Kinetis K- and L-series MCUs by: Melissa Hunter 1 Introduction This application
Technical Note TN_158. What is the Camera Parallel Interface?
 TN_158 What is the Camera Parallel Interface? Issue Date: 2015-03-23 This technical note explains the basics of the Camera Parallel Interface, a feature of FTDI MCUs. Use of FTDI devices in life support
TN_158 What is the Camera Parallel Interface? Issue Date: 2015-03-23 This technical note explains the basics of the Camera Parallel Interface, a feature of FTDI MCUs. Use of FTDI devices in life support
Hardware Configurations for the i.mx Family USB Modules
 Freescale Semiconductor Application Note Document Number: AN4136 Rev. 0, 06/2010 Hardware Configurations for the i.mx Family USB Modules by Multimedia Applications Division Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
Freescale Semiconductor Application Note Document Number: AN4136 Rev. 0, 06/2010 Hardware Configurations for the i.mx Family USB Modules by Multimedia Applications Division Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
76-77 GHz RF Transmitter Front-end for W-band Radar Applications
 Freescale Semiconductor Data Sheet Summary for MC33 7-77 GHz RF Transmitter Front-end for W-band Radar Applications The MR2001 is a scalable three package solution for automotive radar modules. The chipset
Freescale Semiconductor Data Sheet Summary for MC33 7-77 GHz RF Transmitter Front-end for W-band Radar Applications The MR2001 is a scalable three package solution for automotive radar modules. The chipset
UART Boot Loader Design on the Kinetis E Series
 Freescale Semiconductor Application Note Document Number: AN4767 Rev. 0, 7/2013 UART Boot Loader Design on the Kinetis E Series by Wang Peng Many applications and products need to upgrade the firmware
Freescale Semiconductor Application Note Document Number: AN4767 Rev. 0, 7/2013 UART Boot Loader Design on the Kinetis E Series by Wang Peng Many applications and products need to upgrade the firmware
Flexible Active Shutter Control Interface using the MC1323x
 Freescale Semiconductor Document Number: AN4353 Application Note Rev. 0, 9/2011 Flexible Active Shutter Control Interface using the MC1323x by: Dennis Lui Freescale Hong Kong 1 Introduction This application
Freescale Semiconductor Document Number: AN4353 Application Note Rev. 0, 9/2011 Flexible Active Shutter Control Interface using the MC1323x by: Dennis Lui Freescale Hong Kong 1 Introduction This application
TWR-KV31F120M Sample Code Guide for IAR Board configuration, software, and development tools Rev.0
 TWR-KV31F120M Sample Code Guide for IAR Board configuration, software, and development tools Rev.0 Freescale TWR-KV31F120M Sample Code Guide for IAR KL25_LAB Contents 1 Purpose... 3 2 Getting to know the
TWR-KV31F120M Sample Code Guide for IAR Board configuration, software, and development tools Rev.0 Freescale TWR-KV31F120M Sample Code Guide for IAR KL25_LAB Contents 1 Purpose... 3 2 Getting to know the
USER GUIDE EDBG. Description
 USER GUIDE EDBG Description The Atmel Embedded Debugger (EDBG) is an onboard debugger for integration into development kits with Atmel MCUs. In addition to programming and debugging support through Atmel
USER GUIDE EDBG Description The Atmel Embedded Debugger (EDBG) is an onboard debugger for integration into development kits with Atmel MCUs. In addition to programming and debugging support through Atmel
How To Use A Watt Saver On A Microcontroller (Watt Saver) On A Cell Phone Or Mp3 Player
 Watt Saver for a Cell Phone AC Adapter Reference Design Document Number: DRM130 Rev 1, 10/2013 2 Freescale Semiconductor, Inc. Contents Section number Title Page Chapter 1 Introduction 1.1 Overview...5
Watt Saver for a Cell Phone AC Adapter Reference Design Document Number: DRM130 Rev 1, 10/2013 2 Freescale Semiconductor, Inc. Contents Section number Title Page Chapter 1 Introduction 1.1 Overview...5
Freescale, the Freescale logo, AltiVec, C-5, CodeTEST, CodeWarrior, ColdFire, ColdFire+, C- Ware, the Energy Efficient Solutions logo, Kinetis,
 April 2013 Freescale, the Freescale logo, AltiVec, C-5, CodeTEST, CodeWarrior, ColdFire, ColdFire+, C- Ware, the Energy Efficient Solutions logo, Kinetis, mobilegt, PEG, PowerQUICC, Processor Expert, QorIQ,
April 2013 Freescale, the Freescale logo, AltiVec, C-5, CodeTEST, CodeWarrior, ColdFire, ColdFire+, C- Ware, the Energy Efficient Solutions logo, Kinetis, mobilegt, PEG, PowerQUICC, Processor Expert, QorIQ,
Designing an Induction Cooker Using the S08PT Family
 Freescale Semiconductor, Inc. Document Number: AN5030 Application Note Rev. 0 11/2014 Designing an Induction Cooker Using the S08PT Family by: Leo Pan, Dennis Lui, T.C. Lun 1 Introduction This application
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc. Document Number: AN5030 Application Note Rev. 0 11/2014 Designing an Induction Cooker Using the S08PT Family by: Leo Pan, Dennis Lui, T.C. Lun 1 Introduction This application
CMOS OV7660 Camera Module 1/5-Inch 0.3-Megapixel Module Datasheet
 CMOS OV7660 Camera Module 1/5-Inch 0.3-Megapixel Module Datasheet Rev 1.0, June 2013 Table of Contents 1 Introduction...2 2 Features...3 3 Key Specifications...4 4 Application...4 5 Pin Definition...6
CMOS OV7660 Camera Module 1/5-Inch 0.3-Megapixel Module Datasheet Rev 1.0, June 2013 Table of Contents 1 Introduction...2 2 Features...3 3 Key Specifications...4 4 Application...4 5 Pin Definition...6
Configuring CoreNet Platform Cache (CPC) as SRAM For Use by Linux Applications
 Freescale Semiconductor Document Number:AN4749 Application Note Rev 0, 07/2013 Configuring CoreNet Platform Cache (CPC) as SRAM For Use by Linux Applications 1 Introduction This document provides, with
Freescale Semiconductor Document Number:AN4749 Application Note Rev 0, 07/2013 Configuring CoreNet Platform Cache (CPC) as SRAM For Use by Linux Applications 1 Introduction This document provides, with
AN10850. LPC1700 timer triggered memory to GPIO data transfer. Document information. LPC1700, GPIO, DMA, Timer0, Sleep Mode
 LPC1700 timer triggered memory to GPIO data transfer Rev. 01 16 July 2009 Application note Document information Info Keywords Abstract Content LPC1700, GPIO, DMA, Timer0, Sleep Mode This application note
LPC1700 timer triggered memory to GPIO data transfer Rev. 01 16 July 2009 Application note Document information Info Keywords Abstract Content LPC1700, GPIO, DMA, Timer0, Sleep Mode This application note
AND8336. Design Examples of On Board Dual Supply Voltage Logic Translators. Prepared by: Jim Lepkowski ON Semiconductor. http://onsemi.
 Design Examples of On Board Dual Supply Voltage Logic Translators Prepared by: Jim Lepkowski ON Semiconductor Introduction Logic translators can be used to connect ICs together that are located on the
Design Examples of On Board Dual Supply Voltage Logic Translators Prepared by: Jim Lepkowski ON Semiconductor Introduction Logic translators can be used to connect ICs together that are located on the
Quick Start Guide. MRB-KW01 Development Platform Radio Utility Application Demo MODULAR REFERENCE BOARD
 Quick Start Guide MRB-KW01 Development Platform Radio Utility Application Demo MODULAR REFERENCE BOARD Quick Start Guide Get to Know the MRB-KW01x Module UART Selector ANT 1 RFIO (TX/RX) USB 2.0 Serial
Quick Start Guide MRB-KW01 Development Platform Radio Utility Application Demo MODULAR REFERENCE BOARD Quick Start Guide Get to Know the MRB-KW01x Module UART Selector ANT 1 RFIO (TX/RX) USB 2.0 Serial
Single Phase Two-Channel Interleaved PFC Operating in CrM
 Freescale Semiconductor Application Note Document Number: AN4836 Rev. 0, 12/2013 Single Phase Two-Channel Interleaved PFC Operating in CrM Using the MC56F82xxx Family of Digital Signal Controllers by Freescale
Freescale Semiconductor Application Note Document Number: AN4836 Rev. 0, 12/2013 Single Phase Two-Channel Interleaved PFC Operating in CrM Using the MC56F82xxx Family of Digital Signal Controllers by Freescale
Adding SDIO Wi-Fi Solution to i.mx Windows CE 5.0/Windows CE 6.0
 Freescale Semiconductor Application Note Document Number: AN3981 Rev. 0, 04/2010 Adding SDIO Wi-Fi Solution to i.mx Windows CE 5.0/Windows CE 6.0 by Multimedia Applications Division Freescale Semiconductor,
Freescale Semiconductor Application Note Document Number: AN3981 Rev. 0, 04/2010 Adding SDIO Wi-Fi Solution to i.mx Windows CE 5.0/Windows CE 6.0 by Multimedia Applications Division Freescale Semiconductor,
MED-AFEs Design Reference Manual
 Freescale Semiconductor Design Reference Manual Document Number: DRM141 Rev. 0, 8/2013 MED-AFEs Design Reference Manual By: Alejandra Guzman This document explains how to test all Analog Front Ends using
Freescale Semiconductor Design Reference Manual Document Number: DRM141 Rev. 0, 8/2013 MED-AFEs Design Reference Manual By: Alejandra Guzman This document explains how to test all Analog Front Ends using
Installing Service Pack Updater Archive for CodeWarrior Tools (Windows and Linux) Quick Start
 Installing Service Pack Updater Archive for CodeWarrior Tools (Windows and Linux) Quick Start SYSTEM REQUIREMENTS Hardware Operating System Intel Pentium 4 processor, 2 GHz or faster, Intel Xeon, Intel
Installing Service Pack Updater Archive for CodeWarrior Tools (Windows and Linux) Quick Start SYSTEM REQUIREMENTS Hardware Operating System Intel Pentium 4 processor, 2 GHz or faster, Intel Xeon, Intel
Programming Audio Applications in the i.mx21 MC9328MX21
 Freescale Semiconductor Application Note Document Number: AN2628 Rev. 1, 10/2005 Programming Audio Applications in the MC9328MX21 by: Alfred Sin 1 Abstract The MC9328MX21 () processor has two dedicated
Freescale Semiconductor Application Note Document Number: AN2628 Rev. 1, 10/2005 Programming Audio Applications in the MC9328MX21 by: Alfred Sin 1 Abstract The MC9328MX21 () processor has two dedicated
Understanding LCD Memory and Bus Bandwidth Requirements ColdFire, LCD, and Crossbar Switch
 Freescale Semiconductor Application Note Document Number: AN3606 Rev. 0, 03/2008 Understanding LCD Memory and Bus Bandwidth Requirements ColdFire, LCD, and Crossbar Switch by: Melissa Hunter TSPG Applications
Freescale Semiconductor Application Note Document Number: AN3606 Rev. 0, 03/2008 Understanding LCD Memory and Bus Bandwidth Requirements ColdFire, LCD, and Crossbar Switch by: Melissa Hunter TSPG Applications
Audio player on KwikStik
 Freescale Semiconductor Application Note Document Number: AN4523 Rev. 0, 01/2014 Audio player on KwikStik by: Michael Galda Freescale Semiconductor, Inc. 1 Introduction This demo application describes
Freescale Semiconductor Application Note Document Number: AN4523 Rev. 0, 01/2014 Audio player on KwikStik by: Michael Galda Freescale Semiconductor, Inc. 1 Introduction This demo application describes
Quick Start Guide. USB Packet Sniffer/Dongle for Kinetis MKW22D and MKW24D Wireless MCUs USB-KW24D512
 Quick Start Guide USB Packet Sniffer/Dongle for Kinetis MKW22D and MKW24D Wireless MCUs USB-KW24D512 Quick Start Guide Get to Know the USB-KW24D512 USB Connector Reset Button Application Button LEDs Antenna
Quick Start Guide USB Packet Sniffer/Dongle for Kinetis MKW22D and MKW24D Wireless MCUs USB-KW24D512 Quick Start Guide Get to Know the USB-KW24D512 USB Connector Reset Button Application Button LEDs Antenna
CodeWarrior Development Studio for Freescale S12(X) Microcontrollers Quick Start
 CodeWarrior Development Studio for Freescale S12(X) Microcontrollers Quick Start SYSTEM REQUIREMENTS Hardware Operating System Disk Space PC with 1 GHz Intel Pentum -compatible processor 512 MB of RAM
CodeWarrior Development Studio for Freescale S12(X) Microcontrollers Quick Start SYSTEM REQUIREMENTS Hardware Operating System Disk Space PC with 1 GHz Intel Pentum -compatible processor 512 MB of RAM
Implementing SPI Master and Slave Functionality Using the Z8 Encore! F083A
 Application Note Implementing SPI Master and Slave Functionality Using the Z8 Encore! F083A AN026701-0308 Abstract This application note demonstrates a method of implementing the Serial Peripheral Interface
Application Note Implementing SPI Master and Slave Functionality Using the Z8 Encore! F083A AN026701-0308 Abstract This application note demonstrates a method of implementing the Serial Peripheral Interface
AVR151: Setup and Use of the SPI. Introduction. Features. Atmel AVR 8-bit Microcontroller APPLICATION NOTE
 Atmel AVR 8-bit Microcontroller AVR151: Setup and Use of the SPI APPLICATION NOTE Introduction This application note describes how to set up and use the on-chip Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI) of the
Atmel AVR 8-bit Microcontroller AVR151: Setup and Use of the SPI APPLICATION NOTE Introduction This application note describes how to set up and use the on-chip Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI) of the
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc. Product Brief Integrated Portable System Processor DragonBall ΤΜ
 nc. Order this document by MC68328/D Microprocessor and Memory Technologies Group MC68328 MC68328V Product Brief Integrated Portable System Processor DragonBall ΤΜ As the portable consumer market grows
nc. Order this document by MC68328/D Microprocessor and Memory Technologies Group MC68328 MC68328V Product Brief Integrated Portable System Processor DragonBall ΤΜ As the portable consumer market grows
MCF54418 NAND Flash Controller
 Freescale Semiconductor Application Note Document Number: AN4348 Rev. 0, 09/2011 MCF54418 NAND Flash Controller by: Liew Tsi Chung Applications Engineer 1 Introduction The ColdFire MCF5441x family is the
Freescale Semiconductor Application Note Document Number: AN4348 Rev. 0, 09/2011 MCF54418 NAND Flash Controller by: Liew Tsi Chung Applications Engineer 1 Introduction The ColdFire MCF5441x family is the
How To Build A Project On An Eclipse Powerbook For Anarc (Powerbook) On An Ipa (Powerpoint) On A Microcontroller (Powerboard) On Microcontrollers (Powerstation) On Your Microcontroller 2 (Powerclock
 Freescale Semiconductor Document Number: AN4819 Application Note Rev. 1, 10/2013 Building a Project using IAR Eclipse Plugin Processor Expert Microcontrollers Driver Suite Processor Expert Microcontrollers
Freescale Semiconductor Document Number: AN4819 Application Note Rev. 1, 10/2013 Building a Project using IAR Eclipse Plugin Processor Expert Microcontrollers Driver Suite Processor Expert Microcontrollers
Solar Panel 3-Phase Inverter Controlled by the PXS20 Libor Prokop Rožnov pod Radhoštem, Czech Republic
 Freescale Semiconductor Application Note Document Number: AN4437 Rev. 0, 1/2012 Solar Panel 3-Phase Inverter Controlled by the PXS20 by: Libor Prokop Rožnov pod Radhoštem, Czech Republic 1 Introduction
Freescale Semiconductor Application Note Document Number: AN4437 Rev. 0, 1/2012 Solar Panel 3-Phase Inverter Controlled by the PXS20 by: Libor Prokop Rožnov pod Radhoštem, Czech Republic 1 Introduction
Quick Start Guide. TWR-MECH Mechatronics Board TOWER SYSTEM
 TWR-MECH Mechatronics Board TOWER SYSTEM Get to Know the Tower Mechatronics Board Primary Connector / Switch MCF52259 Connectors for Up to Eight Servos SW4 (Reset) USB OTG 5V Supply Touch Panel Socket
TWR-MECH Mechatronics Board TOWER SYSTEM Get to Know the Tower Mechatronics Board Primary Connector / Switch MCF52259 Connectors for Up to Eight Servos SW4 (Reset) USB OTG 5V Supply Touch Panel Socket
MX PIC24F Educational Module User Manual
 MX PIC24F Educational Module User Manual Revision History Date Description Initial release. Table of Contents 1. Introduction... 3 1.1. Package Contents... 3 1.2. Key Hardware Features... 4 2. Hardware
MX PIC24F Educational Module User Manual Revision History Date Description Initial release. Table of Contents 1. Introduction... 3 1.1. Package Contents... 3 1.2. Key Hardware Features... 4 2. Hardware
The I2C Bus. NXP Semiconductors: UM10204 I2C-bus specification and user manual. 14.10.2010 HAW - Arduino 1
 The I2C Bus Introduction The I2C-bus is a de facto world standard that is now implemented in over 1000 different ICs manufactured by more than 50 companies. Additionally, the versatile I2C-bus is used
The I2C Bus Introduction The I2C-bus is a de facto world standard that is now implemented in over 1000 different ICs manufactured by more than 50 companies. Additionally, the versatile I2C-bus is used
AN3252 Application note
 Application note Building a wave generator using STM8L-DISCOVERY Application overview This application note provides a short description of how to use the STM8L-DISCOVERY as a basic wave generator for
Application note Building a wave generator using STM8L-DISCOVERY Application overview This application note provides a short description of how to use the STM8L-DISCOVERY as a basic wave generator for
Camera Sensor Driver Development And Integration
 Camera Sensor Driver Development And Integration Introduction Camera enables multimedia on phones. It is going to be an important human machine interface, adding to augmented reality possibilities on embedded
Camera Sensor Driver Development And Integration Introduction Camera enables multimedia on phones. It is going to be an important human machine interface, adding to augmented reality possibilities on embedded
Processor Expert Software Microcontrollers Driver Suite Getting Started Guide
 Freescale Semiconductor Document Number: PEXDRVSGETSTARTEDUG Rev. 2, 09/2012 Processor Expert Software Microcontrollers Driver Suite Getting Started Guide This document introduces Microcontrollers Driver
Freescale Semiconductor Document Number: PEXDRVSGETSTARTEDUG Rev. 2, 09/2012 Processor Expert Software Microcontrollers Driver Suite Getting Started Guide This document introduces Microcontrollers Driver
Single Phase Two-Channel Interleaved PFC Operating in CrM Using the MC56F82xxx Family of Digital Signal Controllers
 Freescale Semiconductor Application Note Document Number: AN4836 Rev. 1, 07/2014 Single Phase Two-Channel Interleaved PFC Operating in CrM Using the MC56F82xxx Family of Digital Signal Controllers by Freescale
Freescale Semiconductor Application Note Document Number: AN4836 Rev. 1, 07/2014 Single Phase Two-Channel Interleaved PFC Operating in CrM Using the MC56F82xxx Family of Digital Signal Controllers by Freescale
SMARTCARD XPRO. Preface. SMART ARM-based Microcontrollers USER GUIDE
 SMART ARM-based Microcontrollers SMARTCARD XPRO USER GUIDE Preface Atmel SMARTCARD Xplained Pro is an extension board to the Atmel Xplained Pro evaluation platform. Atmel SMARTCARD Xplained Pro is designed
SMART ARM-based Microcontrollers SMARTCARD XPRO USER GUIDE Preface Atmel SMARTCARD Xplained Pro is an extension board to the Atmel Xplained Pro evaluation platform. Atmel SMARTCARD Xplained Pro is designed
Serial Communications
 Serial Communications 1 Serial Communication Introduction Serial communication buses Asynchronous and synchronous communication UART block diagram UART clock requirements Programming the UARTs Operation
Serial Communications 1 Serial Communication Introduction Serial communication buses Asynchronous and synchronous communication UART block diagram UART clock requirements Programming the UARTs Operation
Arbitration and Switching Between Bus Masters
 February 2010 Introduction Reference Design RD1067 Since the development of the system bus that allows multiple devices to communicate with one another through a common channel, bus arbitration has been
February 2010 Introduction Reference Design RD1067 Since the development of the system bus that allows multiple devices to communicate with one another through a common channel, bus arbitration has been
How to Run the MQX RTOS on Various RAM Memories for i.mx 6SoloX
 Freescale Semiconductor, Inc. Document Number: AN5127 Application Note Rev. 1, 05/2015 How to Run the MQX RTOS on Various RAM Memories for i.mx 6SoloX 1 Introduction This document describes how to customize
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc. Document Number: AN5127 Application Note Rev. 1, 05/2015 How to Run the MQX RTOS on Various RAM Memories for i.mx 6SoloX 1 Introduction This document describes how to customize
Building and Debugging a project using Keil MDK-ARM Eclipse plug-in
 Freescale Semiconductor Document Number: AN4913 Building and Debugging a project using Keil MDK-ARM Eclipse plug-in Processor Expert Microcontrollers Driver Suite 1. Introduction Processor Expert Microcontrollers
Freescale Semiconductor Document Number: AN4913 Building and Debugging a project using Keil MDK-ARM Eclipse plug-in Processor Expert Microcontrollers Driver Suite 1. Introduction Processor Expert Microcontrollers
PowerQUICC II Pro (MPC83xx) PCI Agent Initialization
 Freescale Semiconductor Application Note Document Number: AN3373 Rev. 0, 04/2007 PowerQUICC II Pro (MPC83xx) PCI Agent Initialization by: David Smith Field Application Engineering Raleigh, NC In many designs,
Freescale Semiconductor Application Note Document Number: AN3373 Rev. 0, 04/2007 PowerQUICC II Pro (MPC83xx) PCI Agent Initialization by: David Smith Field Application Engineering Raleigh, NC In many designs,
Installing Service Pack Updater Archive for CodeWarrior Tools (Windows and Linux) Quick Start
 Installing Service Pack Updater Archive for CodeWarrior Tools (Windows and Linux) Quick Start SYSTEM REQUIREMENTS Processor Windows OS: Intel Pentium 4 processor, 2 GHz or faster, Intel Xeon, Intel Core,
Installing Service Pack Updater Archive for CodeWarrior Tools (Windows and Linux) Quick Start SYSTEM REQUIREMENTS Processor Windows OS: Intel Pentium 4 processor, 2 GHz or faster, Intel Xeon, Intel Core,
How To Control A Motor Control On An Hvac Platform
 Freescale Semiconductor Document Number:AN4616 Application Note Rev. 0, 10/2012 Flap Motor Control Based On HVAC Platform by: Shawn Shi, Albert Chen, Alex Liu 1 Introduction According to the world market
Freescale Semiconductor Document Number:AN4616 Application Note Rev. 0, 10/2012 Flap Motor Control Based On HVAC Platform by: Shawn Shi, Albert Chen, Alex Liu 1 Introduction According to the world market
Initializing the TSEC Controller
 Freescale Semiconductor Application Note Document Number: AN2925 Rev. 0, 11/2005 Initializing the TSEC Controller by Ahsan Kabir Digital Systems Division Freescale Semiconductor, Inc. Austin, TX This application
Freescale Semiconductor Application Note Document Number: AN2925 Rev. 0, 11/2005 Initializing the TSEC Controller by Ahsan Kabir Digital Systems Division Freescale Semiconductor, Inc. Austin, TX This application
Von der Hardware zur Software in FPGAs mit Embedded Prozessoren. Alexander Hahn Senior Field Application Engineer Lattice Semiconductor
 Von der Hardware zur Software in FPGAs mit Embedded Prozessoren Alexander Hahn Senior Field Application Engineer Lattice Semiconductor AGENDA Overview Mico32 Embedded Processor Development Tool Chain HW/SW
Von der Hardware zur Software in FPGAs mit Embedded Prozessoren Alexander Hahn Senior Field Application Engineer Lattice Semiconductor AGENDA Overview Mico32 Embedded Processor Development Tool Chain HW/SW
CodeWarrior Development Studio Floating Licensing Quick Start
 CodeWarrior Development Studio Floating Licensing Quick Start This quick start guide explains how to set up a floating license server of Freescale software products licensed with FLEXlm (e.g. CodeWarrior).
CodeWarrior Development Studio Floating Licensing Quick Start This quick start guide explains how to set up a floating license server of Freescale software products licensed with FLEXlm (e.g. CodeWarrior).
3.2 inch QVGA TFT Color LCD User s Guide Version 1 & 2
 3.2 inch QVGA TFT Color LCD - User s Guide 3.2 inch QVGA TFT Color LCD User s Guide Version 1 & 2 Give graphics and to your application! EA2-USG-0701 v2.1 Rev A 3.2 inch QVGA TFT Color LCD - User s Guide
3.2 inch QVGA TFT Color LCD - User s Guide 3.2 inch QVGA TFT Color LCD User s Guide Version 1 & 2 Give graphics and to your application! EA2-USG-0701 v2.1 Rev A 3.2 inch QVGA TFT Color LCD - User s Guide
Installation of the MMA955xL CodeWarrior Service Pack Author: Fengyi Li Application Engineer
 Freescale Semiconductor Application Note Document Number: AN4128 Rev. 0, 10/2011 Installation of the MMA955xL CodeWarrior Service Pack Author: Fengyi Li Application Engineer 1 Overview The Freescale MMA955xL
Freescale Semiconductor Application Note Document Number: AN4128 Rev. 0, 10/2011 Installation of the MMA955xL CodeWarrior Service Pack Author: Fengyi Li Application Engineer 1 Overview The Freescale MMA955xL
etpu Host Interface by:
 Freescale Semiconductor Application Note AN2821 Rev. 2, 08/2007 etpu Host Interface by: David Paterson Ming Li MCD Applications 1 Introduction This application note discusses the enhanced Time Processing
Freescale Semiconductor Application Note AN2821 Rev. 2, 08/2007 etpu Host Interface by: David Paterson Ming Li MCD Applications 1 Introduction This application note discusses the enhanced Time Processing
Develop a Dallas 1-Wire Master Using the Z8F1680 Series of MCUs
 Develop a Dallas 1-Wire Master Using the Z8F1680 Series of MCUs AN033101-0412 Abstract This describes how to interface the Dallas 1-Wire bus with Zilog s Z8F1680 Series of MCUs as master devices. The Z8F0880,
Develop a Dallas 1-Wire Master Using the Z8F1680 Series of MCUs AN033101-0412 Abstract This describes how to interface the Dallas 1-Wire bus with Zilog s Z8F1680 Series of MCUs as master devices. The Z8F0880,
ES_LPC4357/53/37/33. Errata sheet LPC4357/53/37/33. Document information
 Rev. 1.1 8 August 2012 Errata sheet Document information Info Keywords Abstract Content LPC4357FET256; LPC4357FET180; LPC4357FBD208; LPC4353FET256; LPC4353FET180; LPC4353FBD208; LPC4337FET256; LPC4337FET180;
Rev. 1.1 8 August 2012 Errata sheet Document information Info Keywords Abstract Content LPC4357FET256; LPC4357FET180; LPC4357FBD208; LPC4353FET256; LPC4353FET180; LPC4353FBD208; LPC4337FET256; LPC4337FET180;
HVP-KV31F120M Quick Start Guide
 HVP-KV31F120M Quick Start Guide Freescale Controller Card High Voltage Development Platform Quick Start Guide Get to Know the HVP-KV31F120M USB Mini for Communication, Debugging and Power Supply Isolated
HVP-KV31F120M Quick Start Guide Freescale Controller Card High Voltage Development Platform Quick Start Guide Get to Know the HVP-KV31F120M USB Mini for Communication, Debugging and Power Supply Isolated
Blood Pressure Monitor Using Flexis QE128 Gabriel Sanchez RTAC Americas
 Freescale Semiconductor Application Note Document Number: AN3500 Rev. 0, 08/2007 Blood Pressure Monitor Using Flexis QE128 by: Gabriel Sanchez RTAC Americas 1 Introduction Product designers and developers
Freescale Semiconductor Application Note Document Number: AN3500 Rev. 0, 08/2007 Blood Pressure Monitor Using Flexis QE128 by: Gabriel Sanchez RTAC Americas 1 Introduction Product designers and developers
Guangzhou HC Information Technology Co., Ltd. Product Data Sheet
 Guangzhou HC Information Technology Co., Ltd. Product Data Sheet Rev 1 Module Data Sheet 1.0 2.0 2.1 2.2 2006/6/18 2006/9/6 2010/4/22 2011/4/6 DRAWN BY : Ling Xin MODEL : HC-06 CHECKED BY : Eric Huang
Guangzhou HC Information Technology Co., Ltd. Product Data Sheet Rev 1 Module Data Sheet 1.0 2.0 2.1 2.2 2006/6/18 2006/9/6 2010/4/22 2011/4/6 DRAWN BY : Ling Xin MODEL : HC-06 CHECKED BY : Eric Huang
AN3332 Application note
 Application note Generating PWM signals using STM8S-DISCOVERY Application overview This application user manual provides a short description of how to use the Timer 2 peripheral (TIM2) to generate three
Application note Generating PWM signals using STM8S-DISCOVERY Application overview This application user manual provides a short description of how to use the Timer 2 peripheral (TIM2) to generate three
CAM-VGA100 User Manual
 CAM-VGA100 User Manual Release Note: 1. Jan 28, 2004 official released v1.0 2. Feb 24, 2004 official released v1.1 Fix the definition of verify code Fix the bug of unable jump to power save mode Fix the
CAM-VGA100 User Manual Release Note: 1. Jan 28, 2004 official released v1.0 2. Feb 24, 2004 official released v1.1 Fix the definition of verify code Fix the bug of unable jump to power save mode Fix the
APPLICATION NOTE. AT07175: SAM-BA Bootloader for SAM D21. Atmel SAM D21. Introduction. Features
 APPLICATION NOTE AT07175: SAM-BA Bootloader for SAM D21 Atmel SAM D21 Introduction Atmel SAM Boot Assistant (Atmel SAM-BA ) allows In-System Programming (ISP) from USB or UART host without any external
APPLICATION NOTE AT07175: SAM-BA Bootloader for SAM D21 Atmel SAM D21 Introduction Atmel SAM Boot Assistant (Atmel SAM-BA ) allows In-System Programming (ISP) from USB or UART host without any external
IRTC Compensation and 1 Hz Clock Generation
 Freescale Semiconductor Document Number: AN4257 Application Note Rev. 0, January 2011 IRTC Compensation and 1 Hz Clock Generation by: Derek Liu Applications Engineering Shanghai 1 Introduction The MC9S08GW64
Freescale Semiconductor Document Number: AN4257 Application Note Rev. 0, January 2011 IRTC Compensation and 1 Hz Clock Generation by: Derek Liu Applications Engineering Shanghai 1 Introduction The MC9S08GW64
Genesi Pegasos II Setup
 Freescale Semiconductor Application Note AN2666 Rev. 0, 07/2004 Genesi Pegasos II Setup by Maurie Ommerman CPD Applications Freescale Semiconductor, Inc. Austin, TX This application note is the first in
Freescale Semiconductor Application Note AN2666 Rev. 0, 07/2004 Genesi Pegasos II Setup by Maurie Ommerman CPD Applications Freescale Semiconductor, Inc. Austin, TX This application note is the first in
AVR1309: Using the XMEGA SPI. 8-bit Microcontrollers. Application Note. Features. 1 Introduction SCK MOSI MISO SS
 AVR1309: Using the XMEGA SPI Features Introduction to SPI and the XMEGA SPI module Setup and use of the XMEGA SPI module Implementation of module drivers Polled master Interrupt controlled master Polled
AVR1309: Using the XMEGA SPI Features Introduction to SPI and the XMEGA SPI module Setup and use of the XMEGA SPI module Implementation of module drivers Polled master Interrupt controlled master Polled
Using Altera MAX Series as Microcontroller I/O Expanders
 2014.09.22 Using Altera MAX Series as Microcontroller I/O Expanders AN-265 Subscribe Many microcontroller and microprocessor chips limit the available I/O ports and pins to conserve pin counts and reduce
2014.09.22 Using Altera MAX Series as Microcontroller I/O Expanders AN-265 Subscribe Many microcontroller and microprocessor chips limit the available I/O ports and pins to conserve pin counts and reduce
Tweeting? Please use hashtag #FTF2011. Freescale on Facebook Tag yourself in photos and upload your own!
 June 2011 Freescale, the Freescale logo, AltiVec, C-5, CodeTEST, CodeWarrior, ColdFire, C-Ware, t he Energy Efficient Solutions logo, mobilegt, PowerQUICC, QorIQ, StarCore and Symphony are trademarks of
June 2011 Freescale, the Freescale logo, AltiVec, C-5, CodeTEST, CodeWarrior, ColdFire, C-Ware, t he Energy Efficient Solutions logo, mobilegt, PowerQUICC, QorIQ, StarCore and Symphony are trademarks of
AN3998 Application note
 Application note PDM audio software decoding on STM32 microcontrollers 1 Introduction This application note presents the algorithms and architecture of an optimized software implementation for PDM signal
Application note PDM audio software decoding on STM32 microcontrollers 1 Introduction This application note presents the algorithms and architecture of an optimized software implementation for PDM signal
CryptoAuth Xplained Pro
 CryptoAuth Xplained Pro CryptoAuthentication Xplained Pro Extension Board HARDWARE USER GUIDE Atmel CryptoAuth Xplained Pro Extension Board Introduction The Atmel CryptoAuth Xplained Pro (CAXPro) Evaluation
CryptoAuth Xplained Pro CryptoAuthentication Xplained Pro Extension Board HARDWARE USER GUIDE Atmel CryptoAuth Xplained Pro Extension Board Introduction The Atmel CryptoAuth Xplained Pro (CAXPro) Evaluation
Configuring the FlexTimer for Position and Speed Measurement with an Encoder
 Freescale Semiconductor Application Note Document Number: AN4381 Rev. 0, 12/2011 Configuring the FlexTimer for Position and Speed Measurement with an Encoder by: Matus Plachy System Application Engineer,
Freescale Semiconductor Application Note Document Number: AN4381 Rev. 0, 12/2011 Configuring the FlexTimer for Position and Speed Measurement with an Encoder by: Matus Plachy System Application Engineer,
GTS-4E Hardware User Manual. Version: V1.1.0 Date: 2013-12-04
 GTS-4E Hardware User Manual Version: V1.1.0 Date: 2013-12-04 Confidential Material This document contains information highly confidential to Fibocom Wireless Inc. (Fibocom). Fibocom offers this information
GTS-4E Hardware User Manual Version: V1.1.0 Date: 2013-12-04 Confidential Material This document contains information highly confidential to Fibocom Wireless Inc. (Fibocom). Fibocom offers this information
AT15007: Differences between ATmega328/P and ATmega328PB. Introduction. Features. Atmel AVR 8-bit Microcontrollers APPLICATION NOTE
 Atmel AVR 8-bit Microcontrollers AT15007: Differences between ATmega328/P and ATmega328PB APPLICATION NOTE Introduction This application note assists the users of Atmel ATmega328 variants to understand
Atmel AVR 8-bit Microcontrollers AT15007: Differences between ATmega328/P and ATmega328PB APPLICATION NOTE Introduction This application note assists the users of Atmel ATmega328 variants to understand
DKWF121 WF121-A 802.11 B/G/N MODULE EVALUATION BOARD
 DKWF121 WF121-A 802.11 B/G/N MODULE EVALUATION BOARD PRELIMINARY DATA SHEET Wednesday, 16 May 2012 Version 0.5 Copyright 2000-2012 Bluegiga Technologies All rights reserved. Bluegiga Technologies assumes
DKWF121 WF121-A 802.11 B/G/N MODULE EVALUATION BOARD PRELIMINARY DATA SHEET Wednesday, 16 May 2012 Version 0.5 Copyright 2000-2012 Bluegiga Technologies All rights reserved. Bluegiga Technologies assumes
Software Real Time Clock Implementation on MC9S08LG32
 Freescale Semiconductor Document Number: AN4478 Rev. 0, 03/2012 Software Real Time Clock Implementation on MC9S08LG32 by: Nitin Gupta Automotive and Industrial Solutions Group 1 Introduction The MC9S08LG32
Freescale Semiconductor Document Number: AN4478 Rev. 0, 03/2012 Software Real Time Clock Implementation on MC9S08LG32 by: Nitin Gupta Automotive and Industrial Solutions Group 1 Introduction The MC9S08LG32
AN2680 Application note
 Application note Fan speed controller based on STDS75 or STLM75 digital temperature sensor and ST72651AR6 MCU Introduction This application note describes the method of defining the system for regulating
Application note Fan speed controller based on STDS75 or STLM75 digital temperature sensor and ST72651AR6 MCU Introduction This application note describes the method of defining the system for regulating
Introduction the Serial Communications Huang Sections 9.2, 10.2 SCI Block User Guide SPI Block User Guide
 Introduction the Serial Communications Huang Sections 9.2, 10.2 SCI Block User Guide SPI Block User Guide Parallel Data Transfer Suppose you need to transfer data from one HCS12 to another. How can you
Introduction the Serial Communications Huang Sections 9.2, 10.2 SCI Block User Guide SPI Block User Guide Parallel Data Transfer Suppose you need to transfer data from one HCS12 to another. How can you
Elettronica dei Sistemi Digitali Costantino Giaconia SERIAL I/O COMMON PROTOCOLS
 SERIAL I/O COMMON PROTOCOLS RS-232 Fundamentals What is RS-232 RS-232 is a popular communications interface for connecting modems and data acquisition devices (i.e. GPS receivers, electronic balances,
SERIAL I/O COMMON PROTOCOLS RS-232 Fundamentals What is RS-232 RS-232 is a popular communications interface for connecting modems and data acquisition devices (i.e. GPS receivers, electronic balances,
DS1104 R&D Controller Board
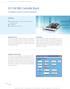 DS1104 R&D Controller Board Cost-effective system for controller development Highlights Single-board system with real-time hardware and comprehensive I/O Cost-effective PCI hardware for use in PCs Application
DS1104 R&D Controller Board Cost-effective system for controller development Highlights Single-board system with real-time hardware and comprehensive I/O Cost-effective PCI hardware for use in PCs Application
7 OUT1 8 OUT2 9 OUT3 10 OUT4 11 OUT5 12 OUT6 13 OUT7 14 OUT8 15 OUT9 16 OUT10 17 OUT11 18 OUT12 19 OUT13 20 OUT14 21 OUT15 22 OUT16 OUT17 23 OUT18
 18 CHANNELS LED DRIVER GENERAL DESCRIPTION IS31FL3218 is comprised of 18 constant current channels each with independent PWM control, designed for driving LEDs. The output current of each channel can be
18 CHANNELS LED DRIVER GENERAL DESCRIPTION IS31FL3218 is comprised of 18 constant current channels each with independent PWM control, designed for driving LEDs. The output current of each channel can be
AN111: Using 8-Bit MCUs in 5 Volt Systems
 This document describes how to incorporate Silicon Lab s 8-bit EFM8 and C8051 families of devices into existing 5 V systems. When using a 3 V device in a 5 V system, the user must consider: A 3 V power
This document describes how to incorporate Silicon Lab s 8-bit EFM8 and C8051 families of devices into existing 5 V systems. When using a 3 V device in a 5 V system, the user must consider: A 3 V power
Networking Remote-Controlled Moving Image Monitoring System
 Networking Remote-Controlled Moving Image Monitoring System First Prize Networking Remote-Controlled Moving Image Monitoring System Institution: Participants: Instructor: National Chung Hsing University
Networking Remote-Controlled Moving Image Monitoring System First Prize Networking Remote-Controlled Moving Image Monitoring System Institution: Participants: Instructor: National Chung Hsing University
Technical Note. Micron NAND Flash Controller via Xilinx Spartan -3 FPGA. Overview. TN-29-06: NAND Flash Controller on Spartan-3 Overview
 Technical Note TN-29-06: NAND Flash Controller on Spartan-3 Overview Micron NAND Flash Controller via Xilinx Spartan -3 FPGA Overview As mobile product capabilities continue to expand, so does the demand
Technical Note TN-29-06: NAND Flash Controller on Spartan-3 Overview Micron NAND Flash Controller via Xilinx Spartan -3 FPGA Overview As mobile product capabilities continue to expand, so does the demand
Using eflexpwm Module for ADC Synchronization in MC56F82xx and MC56F84xx Family of Digital Signal Controllers
 Freescale Semiconductor Document Number:AN4675 Application Note Rev. 0, 01/2013 Using eflexpwm Module for ADC Synchronization in MC56F82xx and MC56F84xx Family of Digital Signal Controllers by: Pavel Grasblum
Freescale Semiconductor Document Number:AN4675 Application Note Rev. 0, 01/2013 Using eflexpwm Module for ADC Synchronization in MC56F82xx and MC56F84xx Family of Digital Signal Controllers by: Pavel Grasblum
Below is a diagram explaining the data packet and the timing related to the mouse clock while receiving a byte from the PS-2 mouse:
 PS-2 Mouse: The Protocol: For out mini project we designed a serial port transmitter receiver, which uses the Baud rate protocol. The PS-2 port is similar to the serial port (performs the function of transmitting
PS-2 Mouse: The Protocol: For out mini project we designed a serial port transmitter receiver, which uses the Baud rate protocol. The PS-2 port is similar to the serial port (performs the function of transmitting
White Paper Streaming Multichannel Uncompressed Video in the Broadcast Environment
 White Paper Multichannel Uncompressed in the Broadcast Environment Designing video equipment for streaming multiple uncompressed video signals is a new challenge, especially with the demand for high-definition
White Paper Multichannel Uncompressed in the Broadcast Environment Designing video equipment for streaming multiple uncompressed video signals is a new challenge, especially with the demand for high-definition
AN141 SMBUS COMMUNICATION FOR SMALL FORM FACTOR DEVICE FAMILIES. 1. Introduction. 2. Overview of the SMBus Specification. 2.1.
 SMBUS COMMUNICATION FOR SMALL FORM FACTOR DEVICE FAMILIES 1. Introduction C8051F3xx and C8051F41x devices are equipped with an SMBus serial I/O peripheral that is compliant with both the System Management
SMBUS COMMUNICATION FOR SMALL FORM FACTOR DEVICE FAMILIES 1. Introduction C8051F3xx and C8051F41x devices are equipped with an SMBus serial I/O peripheral that is compliant with both the System Management
Chapter 13. PIC Family Microcontroller
 Chapter 13 PIC Family Microcontroller Lesson 01 PIC Characteristics and Examples PIC microcontroller characteristics Power-on reset Brown out reset Simplified instruction set High speed execution Up to
Chapter 13 PIC Family Microcontroller Lesson 01 PIC Characteristics and Examples PIC microcontroller characteristics Power-on reset Brown out reset Simplified instruction set High speed execution Up to
Embedded Systems on ARM Cortex-M3 (4weeks/45hrs)
 Embedded Systems on ARM Cortex-M3 (4weeks/45hrs) Course & Kit Contents LEARN HOW TO: Use of Keil Real View for ARM Use ARM Cortex-M3 MCU for professional embedded application development Understanding
Embedded Systems on ARM Cortex-M3 (4weeks/45hrs) Course & Kit Contents LEARN HOW TO: Use of Keil Real View for ARM Use ARM Cortex-M3 MCU for professional embedded application development Understanding
Table 1: Address Table
 DDR SDRAM DIMM D32PB12C 512MB D32PB1GJ 1GB For the latest data sheet, please visit the Super Talent Electronics web site: www.supertalentmemory.com Features 184-pin, dual in-line memory module (DIMM) Fast
DDR SDRAM DIMM D32PB12C 512MB D32PB1GJ 1GB For the latest data sheet, please visit the Super Talent Electronics web site: www.supertalentmemory.com Features 184-pin, dual in-line memory module (DIMM) Fast
M CORE 14-PIN ENHANCED BACKGROUND DEBUG INTERFACE (14EBDI) USER S MANUAL
 MMC14EBDIUM/D February 2000 M CORE 14-PIN ENHANCED BACKGROUND DEBUG INTERFACE (14EBDI) USER S MANUAL While every effort has been made to ensure the accuracy of all information in this document, Motorola
MMC14EBDIUM/D February 2000 M CORE 14-PIN ENHANCED BACKGROUND DEBUG INTERFACE (14EBDI) USER S MANUAL While every effort has been made to ensure the accuracy of all information in this document, Motorola
M68EVB908QL4 Development Board for Motorola MC68HC908QL4
 M68EVB908QL4 Development Board for Motorola MC68HC908QL4! Axiom Manufacturing 2813 Industrial Lane Garland, TX 75041 Email: [email protected] Web: http://www.axman.com! CONTENTS CAUTIONARY NOTES...3 TERMINOLOGY...3
M68EVB908QL4 Development Board for Motorola MC68HC908QL4! Axiom Manufacturing 2813 Industrial Lane Garland, TX 75041 Email: [email protected] Web: http://www.axman.com! CONTENTS CAUTIONARY NOTES...3 TERMINOLOGY...3
Hardware. NetDCUA5. Documentation. PRELIMINARY This document is subject to change without notice. Version 0.01 (2013-02-22)
 Hardware Documentation Version 0.01 (2013-02-22) PRELIMINARY This document is subject to change without notice. NetDCUA5 About This Document This document describes the hardware of the NetDCUA5. The latest
Hardware Documentation Version 0.01 (2013-02-22) PRELIMINARY This document is subject to change without notice. NetDCUA5 About This Document This document describes the hardware of the NetDCUA5. The latest
