Chapter-7 Product Life Cycle Chapter: - 7.
|
|
|
- Poppy Dorsey
- 9 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Chapter: - 7. PRODUCT LIFE CYCLE: - Successful new products may not last forever, during its life. Sales /profits generated for by-product may vary. - Variance depends on the market demand for product changing needs level is described by demand cycle curve such as: M E = Emergence. D G1 = Accelerating Growth. G2 = Decelerating Growth. Demand G2 M = Maturity. G1 D = Decline. E - Demand may also decline due to a change in technology. - Based on demand for a product it may be possible to create a concept that provides insights of the product s competitive dynamics. This is called PRODUCT LIFE CYCLE. - PLC concept implies: Products have a limited life. Product sales pass through distinct stages with each stage posing Challenges/Opportunities/ Problems. Profits rise/fall during different stages of product life cycle. Products require different marketing/manufacturing./ finance/ purchase/ HR strategies at each stage of. - In most cases historical/ empirical data shows the sales/profits of a product as following a pattern (as per diagram) - Pattern is: Sales/ Profit Sales Profit Introduction Growth Maturity Decline - 1 -
2 - curve is typically divided into 4 stages: Introduction: Product introduced in market. Slow sales growth. No profits as expenses are high. Growth: Maturity: Period of rapid market acceptance. Profit increases. Sales growth slows down. Profits stability then decline to fight competition. Decline: Sales decreases Profits decreases - Stages are marked by changes in rates of sales growth. PLC concept can be used to analyse: Product category (liquid/oral care/ skin care). Product form (white liquid/paste/cake). Products (vodka/ toothpaste/ soap). Brands (Smirnoff/ Colgate herbal/ Lux). - Product categories have largest PLC s. Many product category stay in maturity stage of PLC indefinitely. - Product forms follow PLC structure, i.e.,better than product category as they pass through I/G/M/D strategies faster. - Products follow std. PLC or PLC variances. - Brands have shorter PLC s however their PLC s may be structured by investing brand with suitable products & image. PLC Variants: - There may exist many PLC patterns in addition to standard PLC. Some common variants are: Sales Sales Sales (1) (2) (3) - 2 -
3 (1) Growth/Slump/Maturity Pattern: - Sales grow, and then fall to petrified level. - Example: Small kitchen appliances (Spoons), Cease fire. (2) Cycle-Recycle Pattern: - Sales grow, then decreases. - Company gives another promotion push for another smaller growths. - Example: Pharmaceuticals. (3) Scalloped Pattern: - Sales pass through a series of PLC s due to discovery of new uses/characteristics. - Example: Nylon. Style / Fashion / Fad Life Cycle: - Three special categories of PLC need to be distinguished. - PLC s pertaining to Style/Fashion/Fad. Style: - style is a basic/distinctive mode of expression appearing in a field of human endeavors. - Once a style is invented, it can last for generations, at times going in/ going out. o Example: Styles in Home, Clothes. Sales Fashion: Sales - Fashion is a currently accepted/popular style in a given field. o Example: Clothes: Jeans. Music: Hindi-Pop. - Fashion Pass through four Stages: o Distinctiveness Stage: Same customer take interest in something new that sets them apart. o Emulation Stage: Other customers take an interest out of desire to emulate fashion leaders. o Mass-Fashion Stage: Fashion becomes very popular & manufacturing gear up for mass production. o Decline: Consumer starts moving towards other fashion. Fad: - Fads are fashion that comes quickly into the public eye, are adopted with great zeal, peak easily and decline fast. - Acceptance cycle is short. - Fads tend to have limited followings - Example: Body Piercing, Tattooing, Pepsi Blue. Sales - 3 -
4 Marketing Strategies through PLC: - Marketing strategy differs based on PLC stage of product. Introduction Stage: Starts when New Product is launched. Sales growth is slow due to: Expansion in product capability. Working out technical bugs in product. Example: Wagon-R, Indica. Delay in adequate distribution. Customer accepting NP slowly. Profits are negative/low due to: Low Sales. High distribution/ promotion costs. Promo costs are high due to: Need to inform customer about new/unknown product. Need to induce trial. Need to secure distribution/ retail. Marketing strategies classified based on: Price. Promotion. High Low Price Rapid Skimming Slow High Strategy Skimming Strategy Rapid Slow Low Penetration Penetration Strategy Strategy Promotion Rapid Skimming Strategy: New product launched at high price with high promotion level. Example: Nokia Handsets. High price helps firm to recover max profits/ units. High promo helps in customer awareness/ adoption. Good policy when: Large part of product mkt is unaware of product. Those who become aware are eager to have it & can pay asked price. Firm faces potential competition & wants to build brand preference. Slow Skimming Strategy: New Product launched at high price with low promotion. High price helps firm to recover maximum profits /units. Low promo keeps marketing expenses down. Combination is expected to skip high profit from the mkt
5 Slow skimming strategy normally used when: Market size is limited. Market is aware of product. Buyers are willing to pay high price. Potential competition is not imminent. Example: Mercedes and most of the niche players. Rapid Promotion Strategy: New Product launched at low price with high promotion. Helps to achieve: Fastest market penetration. Largest market share. Normally used when: Market is large. Market is unaware of the product. Buyers are price sensitive. Strong product competition exists. Costs likely to decreases with volume. Example: Reliance Hungama, Nirma, and Wheel Slow Penetration Strategy: New Product launched at low price with low promotion. Low price encourages rapid product acceptance, Low promotion cost helps retain profits. Used when: Mkt is large. Market is highly aware of product. Market is price sensitive. Market is minimally sensitive to promo. Product competition exists. Growth Stage: Growth stage marked by increase in sales. Early adopters like the product. Early majority buys the product. Late majority starts buying towards the end of growth stage. Competition may increase which in turn introduces new product features to differentiate their offering. Profits increase due to: Manufacturing cost/unit decreases. Promotion costs are spread over larger volume. Growth rate gradually declined from accelerating to decelerating. o Example: Earlier there was Surf, then came Ariel then Ariel Blue, green then Surf Excel, Surf Excel Blue. Companies need to prepare new strategy for this
6 Overall during growth stage companies try to sustain rapid market growth for as long as possible. o Example: Automobile Market: Cars: Earlier there was Ambassador, then Fiat, Maruti 800. For this, strategies could be: Add new features/ increase product quality/ increase style/ looks Example: Car Market Add new models/ flanking product. Flanking products are products in different sizes/ flavors/ that protects brand/new product. Example: Vanilla Ice Cream and Lux. Lux has large number of soaps bars around it like Breeze, Hamam and Pears etc so that Lux is protected. Enter new market segments. Increase distribution coverage/ Enter new distribution channels. Increase advertising from product awareness to product properties. Reduce price to attract next layer of price sensitive cost. In growth stage, companies needs to make a trade off between high market share & high current market profit. At times profits is foregone currently in order to make even more profits later. Maturity Stage: At some point of time, growth of a product slows down. The product now enters a stage of maturity. This stage is likely to last longer than previous stages. Most products today are in maturity stage hence, most of marketing management deals with mature products. Maturity stage is made up of three stages. Stable Maturity Sales Growth Maturity Decaying Maturity I G M D o Growth Maturity: Sales growth starts declining. Laggard buyers enter market. No new channels are left to fill. o Decaying Maturity: Absolute sales volume decrease Customers start switching to substitutes/ other products
7 o Stable Maturity: Sales flatten out due to mkt saturation. Future sales governed by population increases & replaces demand. Slowdown in sales growth creates over capacity which leads to intensified competition Competitors try to find new segments/ niches Prices may decrease/ advertising increase/ trade deals increases/ sales promo increases. R& D spending increase discover new features/ products improvements / line extensions. Shake out may occur due to profits erosion in decaying maturity. Weak competition may withdraw. Competitive advantage may be due to: o Large volume low cost. o within this we may have: Quality Service Cost Market Nichers: May include within Market specialists. Product specialization. Customizing firms. Nichers serve/ satisfy small target markets well & command a price premium. Company has to decide whether to be in dominance or be a Nicher. Marketing strategies in maturity stage could be: Market modification. Product modification. Marketing Mix modification. Market Modification: Mkt for mature product/brand could be modified by working along formula: Sales Volume = (Number of Brand users) x (Usage rate per user). Sales volume may be increased by influencing constituent variants. Number of brand users can be expanded by: Converting non users: Attracting non users. Example: Courier services may try to increase number of users. Entering new mkt segments: Enter new mkt segment in terms of geographical/ demographical of people who use product category but not the brand. Example: Johnson & Johnson Baby Shampoo promoted to adults Win competition: Try to get competitor s customer to try/ adopt your product. Example: Pepsi & Coca Cola both
8 To increase usage rate, strategies could be: More frequent use: Try to get customer to use product more frequently. Example: Fruit Juice/ consumption encouraged for breakfast/ before meals/ after meals/ anytime/ occasionally. More usage per occasion: Company tries to interest users to use more of product on each occasion used. Example: Shampoo: Use two rinsing instead of one. Toothpaste: Larger diameter of tube opening used along length of brush. New /more varied users: Company tries to discover new product uses & tries to convince customers to use product in varied ways. Example: Food processor manufacturing company provides recipes to broaden customer use of product. Product Modification: Sales may be stimulated in the maturity stage by modifying product characteristics. Product modification could be: Quality improvement. Feature improvements. Style improvements. Quality improvements aims at increased final performance in terms of: Durability. Reliability. Speed/ Taste. Feature improvements aims at adding new features to expand new product s: Versatility. Safety. Convenience. Style improvements aims at increasing products aesthetic appeal. Marketing Mix Modification: Sales may be stimulated by modifying other marketing mix elements. These could be: o Price: Price decrease may increase sales. Price increase may signal higher quantity. o Distribution: Company may try to obtain more product support & display in existing outlets. Number of outlets may be increased. New distribution channels may be used. o Advertising: Advertising expense may increase. Advertising message/ media mix may change
9 Sales Promotion: Sales promotion campaign may be used to lift sales temporarily or to enter newer segments. o Personal Selling: Number / Quality of sales force may change. Sales territories/ sales force management may change. o Services: Company may change product s services offered in terms of: Delivery. Technology assistance to Customer. Maintenance. o Maturity marketing strategies constitute majority of marketing managers role in day to day work. Decline Stage: Sales of most product forms & brands eventually decline. Decline may be due to: Technical advances. Change in customer tastes. Increase in competition. Above may lead to: Over capacity. Increase price cutting. Profit Erosion. Unless strong reasons exist, carrying a weak product may be very costly. To handle declining sales, marketing strategies could be: Increase firms invest to dominate market/ strength competitive position. Maintain invest until uncertainties above industry are resolved. Decrease firms invest, selectively by dropping unprofitable customer and focusing on niches. Harvesting. Divesting. Appropriate strategy depends on: Industry s relative attractiveness. Company s strength in the industry
10 Summary of : (Characteristics / Objectives / Strategies). Chapter-7 Sales Introduction Growth Maturity Decline Characteristics: 1. Sales Low Sales Rapidly Peak Sales Declining Sales Increasing Sales 2. Costs High cost per customer Average cost per customer Low cost per customer Low cost per customer 3. Profits Negative More Profit High Profit Declining Profit 4. Customer Innovators Early Adopters Early Majority + Laggards Late Majority 5. Competitor Few More in number Stable number, beginning to decline Declining numbers. Create product awareness and Trial 1. Product Offer basic product 2. Price Change cost + 3. Distribution Build selective distribution 4. Advertising 5. Sales Promotion Build product awareness among early adopters and dealers Use heavy sales promotion to induce trial Objectives: Maximize market share Strategies: Offer product extension, service, warranty Price to penetrate market Build intensive distribution Build awareness and interest in mass market Reduce sales promotion due to increased consumer demand Maximize profits and defend market share Diversify brands / models Price to match better competition Build more intensive distribution Stress on brand difference and benefits More sales promotion to encourage brand switching Reduce expenses & milk brands Phase out weak products Cut price Selective phase out of unprofitable unit Reduce to retain hard core loyals Reduce to minimum level
Portfolio Management
 Portfolio Management Portfolio Management It is top management responsibility that requires the assessment of strengths and weaknesses of the current portfolio of businesses, in order to define the priorities
Portfolio Management Portfolio Management It is top management responsibility that requires the assessment of strengths and weaknesses of the current portfolio of businesses, in order to define the priorities
Marketing Management
 Marketing Management Theocharis Katranis Fall Semester 2014 1 Today s Lecture 1. We will discuss the competitive forces in a market 2. We will identify and analyse competitors 3. We will elaborate different
Marketing Management Theocharis Katranis Fall Semester 2014 1 Today s Lecture 1. We will discuss the competitive forces in a market 2. We will identify and analyse competitors 3. We will elaborate different
Barco Marketing Case Analysis
 Barco Marketing Case Analysis I. Position Statement: Over the past few months, many events have led Barco Projection Systems to be confronted with an important decision: Barco needs to continue its development
Barco Marketing Case Analysis I. Position Statement: Over the past few months, many events have led Barco Projection Systems to be confronted with an important decision: Barco needs to continue its development
Competitive Strategy: Week 5. Product Life Cycle
 Competitive Strategy: Week 5 Product Life Cycle Simon Board Eco380, Competitive Strategy 1 Product Life Cycle Questions How does industry structure changes product life? When does entry occur? When are
Competitive Strategy: Week 5 Product Life Cycle Simon Board Eco380, Competitive Strategy 1 Product Life Cycle Questions How does industry structure changes product life? When does entry occur? When are
Non-personal communication
 Week 8: Promotions Integrated Marketing Communications: advertising, Sales Promotion, Public Relations, and Direct Marketing Strategic Goals Of Marketing Communication Create awareness Build positive images
Week 8: Promotions Integrated Marketing Communications: advertising, Sales Promotion, Public Relations, and Direct Marketing Strategic Goals Of Marketing Communication Create awareness Build positive images
Marketing Research and Planning. Consumer Buying Process. Four Types of Buying Behavior. Decision Making Sets
 ing Research and Planning research: basic concepts and methods April 26, 2007 1 2 3 5 Selfactualization (self-development and and realization) 4 Esteem needs (self-esteem, recognition) Social needs (sense
ing Research and Planning research: basic concepts and methods April 26, 2007 1 2 3 5 Selfactualization (self-development and and realization) 4 Esteem needs (self-esteem, recognition) Social needs (sense
Chapter 2 Market Structure, Types and Segmentation
 Market Structure There are a variety of differing market structures which are separated by the levels of competition that exist within each market and the market conditions in which the businesses operate.
Market Structure There are a variety of differing market structures which are separated by the levels of competition that exist within each market and the market conditions in which the businesses operate.
MSU Product Center Strategic Marketing Institute. The Market for Orange Juice Challenges and Opportunities. Getachew Abate
 MSU Product Center Strategic Marketing Institute Working Paper 2-102605 The Market for Orange Juice Challenges and Opportunities Getachew Abate MSU Product Center For Agriculture and Natural Resources
MSU Product Center Strategic Marketing Institute Working Paper 2-102605 The Market for Orange Juice Challenges and Opportunities Getachew Abate MSU Product Center For Agriculture and Natural Resources
Principles of Marketing Lecture 13a: Promotional Mix Decisions: Advertising and Sales Promotion. The Traditional Communication Model. Noise.
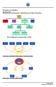 Principles of Marketing Lecture 13a: al Mix Decisions: Advertising and Sales Target Market Product Place Price Personal Selling Mass Selling Sales Advertising Publicity The Traditional Communication Model
Principles of Marketing Lecture 13a: al Mix Decisions: Advertising and Sales Target Market Product Place Price Personal Selling Mass Selling Sales Advertising Publicity The Traditional Communication Model
NEW PRODUCT DEVELOPMENT OR LAUNCH
 NEW PRODUCT DEVELOPMENT OR LAUNCH INTRODUCTION The term product is used frequently in marketing. Consumers purchase different products which are useful and agreeable to them. A product can be defined as
NEW PRODUCT DEVELOPMENT OR LAUNCH INTRODUCTION The term product is used frequently in marketing. Consumers purchase different products which are useful and agreeable to them. A product can be defined as
Bingo glossary marketing mix
 Bingo glossary marketing mix The management process which identifies customer wants, anticipates their future wants and then goes about satisfying them profitably. Where the market has been divided up
Bingo glossary marketing mix The management process which identifies customer wants, anticipates their future wants and then goes about satisfying them profitably. Where the market has been divided up
Marketing Management. 1 Many people are surprised when they realize how may different ideas and activities are included in the term.
 Marketing Management 1 Many people are surprised when they realize how may different ideas and activities are included in the term. 1. Marketing 2. Manufacturing 3. Labeling 2 One of the most important
Marketing Management 1 Many people are surprised when they realize how may different ideas and activities are included in the term. 1. Marketing 2. Manufacturing 3. Labeling 2 One of the most important
Segmentation. Stages in Segmentation Analysis
 Segmentation Conventionally, industries are defined broadly; the automobile industry, the computer software industry, the shipping industry. But competition tends to occur at more localised levels - within
Segmentation Conventionally, industries are defined broadly; the automobile industry, the computer software industry, the shipping industry. But competition tends to occur at more localised levels - within
www.mahendrapublication.org
 128 EXPLANATION Q.21.(2) Q.1.(5) In product concept the main focus is on quality of product so profit earn by quality of product. Q.22.(2) Q.23.(4) Permanent Customer of any product or service is called
128 EXPLANATION Q.21.(2) Q.1.(5) In product concept the main focus is on quality of product so profit earn by quality of product. Q.22.(2) Q.23.(4) Permanent Customer of any product or service is called
Chapter 8 Identifying Market Segments and Targets
 Chapter 8 Identifying Market Segments and Targets 8-1 Key points for Chapter 8 1. Mass marketing 2. Micromarketing Segmentation marketing Niche marketing 3. Demographic segmentation 4. Psychographic segmentation
Chapter 8 Identifying Market Segments and Targets 8-1 Key points for Chapter 8 1. Mass marketing 2. Micromarketing Segmentation marketing Niche marketing 3. Demographic segmentation 4. Psychographic segmentation
Why do firms create new products?
 Why do firms create new products? 1. Changing Customer Needs: When they add products, services, and processes to their offerings, firms can create and deliver value more effectively by satisfying the changing
Why do firms create new products? 1. Changing Customer Needs: When they add products, services, and processes to their offerings, firms can create and deliver value more effectively by satisfying the changing
Coca-Cola Case Analyses. <Student Name> <Name and Section # of course> <Instructor Name> <Date>
 Running Head: COCA-COLA CASE Coca-Cola Case Analyses Coca-Cola Case 2 Coca-Cola Case Analyses This paper is about the company Coca-Cola
Running Head: COCA-COLA CASE Coca-Cola Case Analyses Coca-Cola Case 2 Coca-Cola Case Analyses This paper is about the company Coca-Cola
Market Audit Sports and Energy Drinks UK Market Focussing on the Microenvironment of Red Bull
 Market Audit Sports and Energy Drinks UK Market Focussing on the Microenvironment of Red Bull William Hanrahan Student Number: 060953199 Stage 2 Marketing: ACE2002 1 Contents 1.0 Executive Summary...3
Market Audit Sports and Energy Drinks UK Market Focussing on the Microenvironment of Red Bull William Hanrahan Student Number: 060953199 Stage 2 Marketing: ACE2002 1 Contents 1.0 Executive Summary...3
What this topic is about. The purpose of marketing Different approaches to marketing Segmentation Niche &mass markets B2C & B2B marketing
 Effective Marketing What this topic is about The purpose of marketing Different approaches to marketing Segmentation Niche &mass markets B2C & B2B marketing What is Marketing? The process of identifying,
Effective Marketing What this topic is about The purpose of marketing Different approaches to marketing Segmentation Niche &mass markets B2C & B2B marketing What is Marketing? The process of identifying,
Market Simulators for Conjoint Analysis
 Chapter 10 Market Simulators for Conjoint Analysis The market simulator is usually considered the most important tool resulting from a conjoint analysis project. The simulator is used to convert raw conjoint
Chapter 10 Market Simulators for Conjoint Analysis The market simulator is usually considered the most important tool resulting from a conjoint analysis project. The simulator is used to convert raw conjoint
Strategic Elements of Competitive Advantage. PPT 6 (First ppt slides after the mid-term) Assist. Prof. Dr. Ayşen Akyüz
 Strategic Elements of Competitive Advantage PPT 6 (First ppt slides after the mid-term) Assist. Prof. Dr. Ayşen Akyüz Industry Analysis: Forces Influencing Competition Industry group of firms that produce
Strategic Elements of Competitive Advantage PPT 6 (First ppt slides after the mid-term) Assist. Prof. Dr. Ayşen Akyüz Industry Analysis: Forces Influencing Competition Industry group of firms that produce
Agricultural Marketing. Direct Marketing Strategies and Opportunities. Commodity or Niche? MARKETS DEFINED
 Direct Marketing Strategies and Opportunities Mykel Taylor Assistant Professor Dept. of Agricultural Economics NCKS Commercial Enterprises Conference February 25, 2012 Agricultural Marketing Commodity
Direct Marketing Strategies and Opportunities Mykel Taylor Assistant Professor Dept. of Agricultural Economics NCKS Commercial Enterprises Conference February 25, 2012 Agricultural Marketing Commodity
explain the concept and characteristics of marketing mix;
 22 Marketing Mix 22.1 Introduction The basic task of marketing is the delivery of product(s) to consumers so that their needs are fulfilled and organisational objectives are also achieved. This involves
22 Marketing Mix 22.1 Introduction The basic task of marketing is the delivery of product(s) to consumers so that their needs are fulfilled and organisational objectives are also achieved. This involves
Differentiation and Competition 13
 Product Differentiation and Competition 13 Firms within the same industry sell products that are good substitutes for each other. Yet it is generally the case that no firm within the industry sells a product
Product Differentiation and Competition 13 Firms within the same industry sell products that are good substitutes for each other. Yet it is generally the case that no firm within the industry sells a product
TRADING WITH THE GUPPY MULTIPLE MOVING AVERAGE
 TRADING WITH THE GUPPY MULTIPLE MOVING AVERAGE By Daryl Guppy 2003 Director www.guppytraders.com Author Market Trading Tactics, Better Stock Trading This Guppy Multiple Moving Average (GMMA) indicator
TRADING WITH THE GUPPY MULTIPLE MOVING AVERAGE By Daryl Guppy 2003 Director www.guppytraders.com Author Market Trading Tactics, Better Stock Trading This Guppy Multiple Moving Average (GMMA) indicator
Skills Knowledge Energy Time People and decide how to use themto accomplish your objectives.
 Chapter 8 Selling With a Strategy Strategy Defined A strategy is a to assemble your resources Skills Knowledge Energy Time People and decide how to use themto accomplish your objectives. In selling, an
Chapter 8 Selling With a Strategy Strategy Defined A strategy is a to assemble your resources Skills Knowledge Energy Time People and decide how to use themto accomplish your objectives. In selling, an
1. Supply and demand are the most important concepts in economics.
 Page 1 1. Supply and demand are the most important concepts in economics. 2. Markets and Competition a. Market is a group of buyers and sellers of a particular good or service. P. 66. b. These individuals
Page 1 1. Supply and demand are the most important concepts in economics. 2. Markets and Competition a. Market is a group of buyers and sellers of a particular good or service. P. 66. b. These individuals
Market Segmentation, Targeting, and Positioning. Leonard Walletzký
 Market Segmentation, Targeting, and Positioning Leonard Walletzký 5C STP Marketing Mix Marketing framework Customer Company Context Collaborators Competitors Segmentation Targeting Positioning 4P 7P 4C
Market Segmentation, Targeting, and Positioning Leonard Walletzký 5C STP Marketing Mix Marketing framework Customer Company Context Collaborators Competitors Segmentation Targeting Positioning 4P 7P 4C
Segmentation, Targeting, and Positioning
 Segmentation, Targeting, and Positioning What We Learn? Learn the three steps of target marketing, market segmentation, target marketing, and market positioning Understand the major bases for segmenting
Segmentation, Targeting, and Positioning What We Learn? Learn the three steps of target marketing, market segmentation, target marketing, and market positioning Understand the major bases for segmenting
Rating Methodology by Sector. Non-life Insurance
 Last updated: March 26, 2012 Rating Methodology by Sector Non-life Insurance *This rating methodology is a modification of the rating methodology made public on July 13, 2011, and modifications are made
Last updated: March 26, 2012 Rating Methodology by Sector Non-life Insurance *This rating methodology is a modification of the rating methodology made public on July 13, 2011, and modifications are made
Because of inherent tradeoffs between marketing mix elements, pricing will depend on other product, distribution, and promotion decisions.
 10. Pricing Strategy One of the four major elements of the marketing mix is price. Pricing is an important strategic issue because it is related to product positioning. Furthermore, pricing affects other
10. Pricing Strategy One of the four major elements of the marketing mix is price. Pricing is an important strategic issue because it is related to product positioning. Furthermore, pricing affects other
WORKSHOP #4 CUSTOMER TARGETING (MARKETING) STRATEGY
 WORKSHOP #4 CUSTOMER TARGETING (MARKETING) STRATEGY THE FUNDAMENTAL ELEMENTS OF THE DEFINITION OF A CUSTOMER TARGETING (MARKETING) STRATEGY Corporate Strategy Mission of the firm Strategic thrusts and
WORKSHOP #4 CUSTOMER TARGETING (MARKETING) STRATEGY THE FUNDAMENTAL ELEMENTS OF THE DEFINITION OF A CUSTOMER TARGETING (MARKETING) STRATEGY Corporate Strategy Mission of the firm Strategic thrusts and
Updating Little Caesars Brand and Market Presence
 Updating Little Caesars Brand and Market Presence Table of Contents Executive Summary... 3 Company Description... 3 Company Mission and Goals... 4 Company s Core Competencies... 4 Situation Analysis...
Updating Little Caesars Brand and Market Presence Table of Contents Executive Summary... 3 Company Description... 3 Company Mission and Goals... 4 Company s Core Competencies... 4 Situation Analysis...
CHAPTER 5 MARKET SEGMENTATION AND TARGETING STRATEGIES USED BY FMCG COMPANIES
 CHAPTER 5 MARKET SEGMENTATION AND TARGETING STRATEGIES USED BY FMCG COMPANIES 5.1 Market segmentation: One of the fundamental principles of marketing is the concept of market segmentation. Sometimes it
CHAPTER 5 MARKET SEGMENTATION AND TARGETING STRATEGIES USED BY FMCG COMPANIES 5.1 Market segmentation: One of the fundamental principles of marketing is the concept of market segmentation. Sometimes it
A STUDY ON USAGE OF MOBILE APPS AS A IMPACTFUL TOOL OF MARKETING
 A STUDY ON USAGE OF MOBILE APPS AS A IMPACTFUL TOOL OF MARKETING Dr. Deepali Bhatnagar Assistant Professor, Amity University, Rajasthan ABSTRACT: Mobile marketing perform two ways or multiple way communication
A STUDY ON USAGE OF MOBILE APPS AS A IMPACTFUL TOOL OF MARKETING Dr. Deepali Bhatnagar Assistant Professor, Amity University, Rajasthan ABSTRACT: Mobile marketing perform two ways or multiple way communication
Best practices to optimize CPG digital targeting
 Best practices to optimize CPG digital targeting Digital targeting has evolved That was then Until recently, digital marketing tactics have largely focused on scale and placement: advertisers served content
Best practices to optimize CPG digital targeting Digital targeting has evolved That was then Until recently, digital marketing tactics have largely focused on scale and placement: advertisers served content
UNDERSTANDING PRICING
 UNDERSTANDING PRICING Price is not just a number on a tag or an item. A) Throughout most of history prices were set by negotiation between buyers and sellers. B) Setting one price for all buyers is a relatively
UNDERSTANDING PRICING Price is not just a number on a tag or an item. A) Throughout most of history prices were set by negotiation between buyers and sellers. B) Setting one price for all buyers is a relatively
Chapter 8 Product Concepts
 Marketing Management Chapter 8 Product Concepts Product-Introduction The customer never buys a product buy only a bundle of satisfaction Product represents anticipated and even unanticipated solutions
Marketing Management Chapter 8 Product Concepts Product-Introduction The customer never buys a product buy only a bundle of satisfaction Product represents anticipated and even unanticipated solutions
Research Design. Recap. Problem Formulation and Approach. Step 3: Specify the Research Design
 Recap Step 1: Identify and define the Problem or Opportunity Step 2: Define the Marketing Problem Management Problem Focus on symptoms Action oriented Marketing Problems Focus on causes Data oriented Problem
Recap Step 1: Identify and define the Problem or Opportunity Step 2: Define the Marketing Problem Management Problem Focus on symptoms Action oriented Marketing Problems Focus on causes Data oriented Problem
ADVERTISING IN PROMOTIONAL MIX
 ADVERTISING IN PROMOTIONAL MIX 1. A company's total marketing communications mix consists of a special blend of advertising, sales promotion, public relations, personal selling, and direct-marketing tools
ADVERTISING IN PROMOTIONAL MIX 1. A company's total marketing communications mix consists of a special blend of advertising, sales promotion, public relations, personal selling, and direct-marketing tools
Trier 5. Segmentation and positioning
 Trier 5 Segmentation and positioning Previewing concepts (1) Define the steps in designing a customerdriven marketing strategy: market segmentation, market targeting, differentiation, and positioning (STP)
Trier 5 Segmentation and positioning Previewing concepts (1) Define the steps in designing a customerdriven marketing strategy: market segmentation, market targeting, differentiation, and positioning (STP)
Rating Methodology by Sector. Non-life Insurance
 Last updated: July 1, 2013 Rating Methodology by Sector Non-life Insurance The following mainly applies to non-life insurance companies in Japan. When determining the credit rating of a non-life insurance
Last updated: July 1, 2013 Rating Methodology by Sector Non-life Insurance The following mainly applies to non-life insurance companies in Japan. When determining the credit rating of a non-life insurance
Pantene myshampoo Marketing Management Project
 SOCIAL SCIENCES INSTITUTE MBA PROGRAMME Pantene myshampoo Marketing Management Project Mehmet Nuri ÇANKAYA June, 2003 Table of Contents Selection Of The Product... 3 Market Segments and Target Markets...
SOCIAL SCIENCES INSTITUTE MBA PROGRAMME Pantene myshampoo Marketing Management Project Mehmet Nuri ÇANKAYA June, 2003 Table of Contents Selection Of The Product... 3 Market Segments and Target Markets...
Growth of E-commerce in Fashion Businesses
 Growth of E-commerce in Fashion Businesses By Amit Gugnani, Sr. VP - Fashion & Sakshi Chhillar, Associate Consultant, Textile and Apparel, Technopak THE INDIAN RETAIL INDUSTRY WITNESSED A BOLSTERED GROWTH
Growth of E-commerce in Fashion Businesses By Amit Gugnani, Sr. VP - Fashion & Sakshi Chhillar, Associate Consultant, Textile and Apparel, Technopak THE INDIAN RETAIL INDUSTRY WITNESSED A BOLSTERED GROWTH
THE PERSONAL CARE PRODUCTS SEGMENT. (Cosmetics, Toiletries, and All Other Related Items)
 THE PERSONAL CARE PRODUCTS SEGMENT (Cosmetics, Toiletries, and All Other Related Items) The Segment Defined This market segment includes: manufacturers of health and beauty aids; fragrances and colognes;
THE PERSONAL CARE PRODUCTS SEGMENT (Cosmetics, Toiletries, and All Other Related Items) The Segment Defined This market segment includes: manufacturers of health and beauty aids; fragrances and colognes;
THEME 10: STRATEGY AND COMPETITIVE SITUATIONS. Part 1: Defensive Strategies and Strategies of Attack.
 THEME 10: STRATEGY AND COMPETITIVE SITUATIONS Part 1: Defensive Strategies and Strategies of Attack. Basic bibliography: Lynch, R. Corporate Strategy. Harlow: FT-Prentice Hall, 2006, sections 4.4.4 to
THEME 10: STRATEGY AND COMPETITIVE SITUATIONS Part 1: Defensive Strategies and Strategies of Attack. Basic bibliography: Lynch, R. Corporate Strategy. Harlow: FT-Prentice Hall, 2006, sections 4.4.4 to
MBA I Year Examination. MP-106 : Marketing Management. Time: 3 Hours Max. Marks: 80
 MBA I Year Examination MP-106 : Marketing Management Time: 3 Hours Max. Marks: 80 Note: The question paper is divided into three sections A, B & C. Write Answers as per the given instructions. Section
MBA I Year Examination MP-106 : Marketing Management Time: 3 Hours Max. Marks: 80 Note: The question paper is divided into three sections A, B & C. Write Answers as per the given instructions. Section
for BSNL internal circulation only
 E4-E5 E5 (MANAGEMENT) Marketing of Services AGENDA Define marketing Describe service and its difference from product List the services marketing mix Apply the marketing mix to BSNL services Understand
E4-E5 E5 (MANAGEMENT) Marketing of Services AGENDA Define marketing Describe service and its difference from product List the services marketing mix Apply the marketing mix to BSNL services Understand
Midterm Exam #2. ECON 101, Section 2 summer 2004 Ying Gao. 1. Print your name and student ID number at the top of this cover sheet.
 NAME: STUDENT ID: Midterm Exam #2 ECON 101, Section 2 summer 2004 Ying Gao Instructions Please read carefully! 1. Print your name and student ID number at the top of this cover sheet. 2. Check that your
NAME: STUDENT ID: Midterm Exam #2 ECON 101, Section 2 summer 2004 Ying Gao Instructions Please read carefully! 1. Print your name and student ID number at the top of this cover sheet. 2. Check that your
Introduction... 1 Website Development... 4 Content... 7 Tools and Tracking... 19 Distribution... 20 What to Expect... 26 Next Step...
 Contents Introduction... 1 Website Development... 4 Content... 7 Tools and Tracking... 19 Distribution... 20 What to Expect... 26 Next Step... 27 Introduction Your goal is to generate leads that you can
Contents Introduction... 1 Website Development... 4 Content... 7 Tools and Tracking... 19 Distribution... 20 What to Expect... 26 Next Step... 27 Introduction Your goal is to generate leads that you can
7096 TRAVEL AND TOURISM
 CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS Cambridge Ordinary Level MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2014 series 7096 TRAVEL AND TOURISM 7096/23 Paper 2 (Alternative to Coursework), maximum raw mark 100
CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS Cambridge Ordinary Level MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2014 series 7096 TRAVEL AND TOURISM 7096/23 Paper 2 (Alternative to Coursework), maximum raw mark 100
Economics Chapter 7 Review
 Name: Class: Date: ID: A Economics Chapter 7 Review Matching a. perfect competition e. imperfect competition b. efficiency f. price and output c. start-up costs g. technological barrier d. commodity h.
Name: Class: Date: ID: A Economics Chapter 7 Review Matching a. perfect competition e. imperfect competition b. efficiency f. price and output c. start-up costs g. technological barrier d. commodity h.
1. Product Life Cycle of Vitamin water
 1. Product Life Cycle of Vitamin water We believed that vitamin water is in its Maturity stage of the Product Life Cycle. The product was launched in the U.S around the year of 2000. Most people are already
1. Product Life Cycle of Vitamin water We believed that vitamin water is in its Maturity stage of the Product Life Cycle. The product was launched in the U.S around the year of 2000. Most people are already
Availability of substitute products places limits on the prices market leaders can charge High prices induce buyers to switch to the substitute
 Strategic Elements of Competitive Advantage Industry Analysis: Forces Influencing Competition Power of Suppliers Global Marketing Chapter 15 Power of Buyers Substitute Products Barriers to Entry Industry
Strategic Elements of Competitive Advantage Industry Analysis: Forces Influencing Competition Power of Suppliers Global Marketing Chapter 15 Power of Buyers Substitute Products Barriers to Entry Industry
Marketing Plan. Contents. Introduction: Using the Marketing Planning Framework. The Elements of the Marketing Planning Framework
 Marketing Plan Contents Introduction: Using the Marketing Planning Framework The Elements of the Marketing Planning Framework Terms of Reference Executive Summary 1. Business Mission 2. External Marketing
Marketing Plan Contents Introduction: Using the Marketing Planning Framework The Elements of the Marketing Planning Framework Terms of Reference Executive Summary 1. Business Mission 2. External Marketing
WHAT WILL WE MAKE OF THIS MOMENT? HENKEL SHOWER PROJECT: MARKETING CAMPAIGN FOCUSED ON SUSTAINABILITY
 WHAT WILL WE MAKE OF THIS MOMENT? HENKEL SHOWER PROJECT: MARKETING CAMPAIGN FOCUSED ON SUSTAINABILITY Exploring Sustainability as a Strategic Opportunity (08.05.2015) Anastasia Lavrentyeva, Davide Bramati,
WHAT WILL WE MAKE OF THIS MOMENT? HENKEL SHOWER PROJECT: MARKETING CAMPAIGN FOCUSED ON SUSTAINABILITY Exploring Sustainability as a Strategic Opportunity (08.05.2015) Anastasia Lavrentyeva, Davide Bramati,
Pick and Mix Services
 Pick and Mix Services Technical SEO... 2 Site Audit... 2 Includes:... 2 Plus:... 2 SEO Setup... 3 Includes... 3 Research and Seeding of Keywords... 4 keyword research... 4 Local SEO... 5 Paid Advertising...
Pick and Mix Services Technical SEO... 2 Site Audit... 2 Includes:... 2 Plus:... 2 SEO Setup... 3 Includes... 3 Research and Seeding of Keywords... 4 keyword research... 4 Local SEO... 5 Paid Advertising...
High Performance Eng 9 Overview of Marketing
 High Performance Eng 9 Overview of Marketing Definition: Marketing is the performance of business activities that direct the flow of goods and services from producer to consumer or user in order to satisfy
High Performance Eng 9 Overview of Marketing Definition: Marketing is the performance of business activities that direct the flow of goods and services from producer to consumer or user in order to satisfy
The formula to measure the rice elastici coefficient is Percentage change in quantity demanded E= Percentage change in price
 a CHAPTER 6: ELASTICITY, CONSUMER SURPLUS, AND PRODUCER SURPLUS Introduction Consumer responses to changes in prices, incomes, and prices of related products can be explained by the concept of elasticity.
a CHAPTER 6: ELASTICITY, CONSUMER SURPLUS, AND PRODUCER SURPLUS Introduction Consumer responses to changes in prices, incomes, and prices of related products can be explained by the concept of elasticity.
Mkt501 final term subjective Solve Questions By Adnan Awan
 Mkt501 final term subjective Solve Questions By Adnan Awan Question No: ( Marks: 3 ) How public relations are helpful in creating goodwill for organizations? ANSWER Corporations use marketing public relations
Mkt501 final term subjective Solve Questions By Adnan Awan Question No: ( Marks: 3 ) How public relations are helpful in creating goodwill for organizations? ANSWER Corporations use marketing public relations
The Marketing Mix. Marketing is usually said to consist of 4 key elements, known as the marketing mix They are:
 The Marketing Mix Marketing is usually said to consist of 4 key elements, known as the marketing mix They are: PRODUCT PRICE PLACE PROMOTION Often referred to as the 4 P s They need to be mixed carefully
The Marketing Mix Marketing is usually said to consist of 4 key elements, known as the marketing mix They are: PRODUCT PRICE PLACE PROMOTION Often referred to as the 4 P s They need to be mixed carefully
Market Analysis, Segmentation & Consumer Buying Behavior
 Market Analysis, Segmentation & Consumer Buying Behavior Market Analysis If you are preparing a marketing plan, where s the best place to look for information about macro trends? Marketing Jeopardy Michael
Market Analysis, Segmentation & Consumer Buying Behavior Market Analysis If you are preparing a marketing plan, where s the best place to look for information about macro trends? Marketing Jeopardy Michael
DEMAND AND SUPPLY. Chapter. Markets and Prices. Demand. C) the price of a hot dog minus the price of a hamburger.
 Chapter 3 DEMAND AND SUPPLY Markets and Prices Topic: Price and Opportunity Cost 1) A relative price is A) the slope of the demand curve B) the difference between one price and another C) the slope of
Chapter 3 DEMAND AND SUPPLY Markets and Prices Topic: Price and Opportunity Cost 1) A relative price is A) the slope of the demand curve B) the difference between one price and another C) the slope of
Thailand: Analysis of the General Insurance Industry
 Brochure More information from http://www.researchandmarkets.com/reports/1958129/ Thailand: Analysis of the General Insurance Industry Description: Despite the political unrest in May 2010 that affected
Brochure More information from http://www.researchandmarkets.com/reports/1958129/ Thailand: Analysis of the General Insurance Industry Description: Despite the political unrest in May 2010 that affected
Monitoring the Online Marketplace
 Market Track s Actionable Insights Monitoring the Online Marketplace Developing a plan to stay on top of fluctuations in products and pricing online Key Questions Do you know how your products are priced
Market Track s Actionable Insights Monitoring the Online Marketplace Developing a plan to stay on top of fluctuations in products and pricing online Key Questions Do you know how your products are priced
Essential Guide for Business Plan Creation Basic 12 step guide for executing a successful Business Plan
 Essential Guide for Business Plan Creation Basic 12 step guide for executing a successful Business Plan EBP Business Plan Designer Written by Matthew Parfitt EBP International Sales Executive The Essential
Essential Guide for Business Plan Creation Basic 12 step guide for executing a successful Business Plan EBP Business Plan Designer Written by Matthew Parfitt EBP International Sales Executive The Essential
A review of Marketing strategy of motorcycle products in Bangladesh.
 A review of Marketing strategy of motorcycle products in Bangladesh. *Farooq Hossan *Issa Ahammad Abstract In Bangladesh extensive road network has been made in the rural areas as part of the infrastructural
A review of Marketing strategy of motorcycle products in Bangladesh. *Farooq Hossan *Issa Ahammad Abstract In Bangladesh extensive road network has been made in the rural areas as part of the infrastructural
MODULE TITLE: Foundations of Marketing
 SCHOOL OF ARTS, SOCIAL SCIENCES AND MANAGEMENT DIVISION OF BUSINESS, ENTERPRISE AND MANAGEMENT LEVEL 1 DIET 1 MODULE CODE: B1072 MODULE TITLE: Foundations of Marketing DATE: 16/12/2014 WRITING TIME: 2
SCHOOL OF ARTS, SOCIAL SCIENCES AND MANAGEMENT DIVISION OF BUSINESS, ENTERPRISE AND MANAGEMENT LEVEL 1 DIET 1 MODULE CODE: B1072 MODULE TITLE: Foundations of Marketing DATE: 16/12/2014 WRITING TIME: 2
4 THE MARKET FORCES OF SUPPLY AND DEMAND
 4 THE MARKET FORCES OF SUPPLY AND DEMAND IN THIS CHAPTER YOU WILL Learn what a competitive market is Examine what determines the demand for a good in a competitive market Chapter Overview Examine what
4 THE MARKET FORCES OF SUPPLY AND DEMAND IN THIS CHAPTER YOU WILL Learn what a competitive market is Examine what determines the demand for a good in a competitive market Chapter Overview Examine what
Marketing Plan Template
 1. Executive Summary (Done Last) Marketing Plan Template Keep in mind that not everyone will read every page of your marketing plan. Your executive summary should highlight the most important parts. It
1. Executive Summary (Done Last) Marketing Plan Template Keep in mind that not everyone will read every page of your marketing plan. Your executive summary should highlight the most important parts. It
STATS WINDOW. Retail industry
 Volume 8, Issue 4, October 2015 STATS WINDOW The Pacific Business Review International has taken an initiative to start a section which will provide a snapshot of major Global & Indian economic indicators
Volume 8, Issue 4, October 2015 STATS WINDOW The Pacific Business Review International has taken an initiative to start a section which will provide a snapshot of major Global & Indian economic indicators
Marketing Business Case
 Running head: Coca-Cola Company NEW MEXICO HIGHLANDS UNIVERSITY Marketing Business Case Coca-Cola Company Molina, Ines The Coca-Cola Company has an intensive distribution and bottlers systems that its
Running head: Coca-Cola Company NEW MEXICO HIGHLANDS UNIVERSITY Marketing Business Case Coca-Cola Company Molina, Ines The Coca-Cola Company has an intensive distribution and bottlers systems that its
Monopolistic Competition
 In this chapter, look for the answers to these questions: How is similar to perfect? How is it similar to monopoly? How do ally competitive firms choose price and? Do they earn economic profit? In what
In this chapter, look for the answers to these questions: How is similar to perfect? How is it similar to monopoly? How do ally competitive firms choose price and? Do they earn economic profit? In what
> Erste Bank Croatia Building a retail bank with 15% market share and a meaningful contributor to group profits
 > Erste Bank Croatia Building a retail bank with 15% market share and a meaningful contributor to group profits > 2 nd Capital Markets Day > Budapest > Sava Dalbokov, Member of the EBCR Managing Board
> Erste Bank Croatia Building a retail bank with 15% market share and a meaningful contributor to group profits > 2 nd Capital Markets Day > Budapest > Sava Dalbokov, Member of the EBCR Managing Board
Is Nokia s performance in the Smartphone market affected negatively by marketing strategy decisions?
 Supervisor: Livia Marian Department of Business Administration Examination number: 402966 Number of Characters: 55.272 Is Nokia s performance in the Smartphone market affected negatively by marketing strategy
Supervisor: Livia Marian Department of Business Administration Examination number: 402966 Number of Characters: 55.272 Is Nokia s performance in the Smartphone market affected negatively by marketing strategy
Index. Your Company logo HOW TO REGAIN TRUST IN GOOGLE AFTER YOUR SITE HAS BEEN HIT BY A MANUAL PENALTY
 Index 1 HOW TO REGAIN TRUST IN GOOGLE AFTER YOUR SITE HAS BEEN HIT BY A MANUAL PENALTY 2 GOOGLE YET AGAIN DIRECTLY RECOMMENDS HAVING A RESPONSIVE DESIGN 3 BE AWARE IF YOU ARE IMPLEMENTING BLOG COMMENTS
Index 1 HOW TO REGAIN TRUST IN GOOGLE AFTER YOUR SITE HAS BEEN HIT BY A MANUAL PENALTY 2 GOOGLE YET AGAIN DIRECTLY RECOMMENDS HAVING A RESPONSIVE DESIGN 3 BE AWARE IF YOU ARE IMPLEMENTING BLOG COMMENTS
INDIAN LUBRICANT INDUSTRY - SHRINKING MARGINS
 INDIAN LUBRICANT INDUSTRY - SHRINKING MARGINS Declining demand growth of automotive lubricants, increasing competition on account of the presence of a large number of players, and increasing raw material
INDIAN LUBRICANT INDUSTRY - SHRINKING MARGINS Declining demand growth of automotive lubricants, increasing competition on account of the presence of a large number of players, and increasing raw material
How To Understand Market Segmentation
 MODULE 3: MARKET SEGMENTATION AND POSITIONING Lecture - 5 FAQS (FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS): Ques 1 Ans 1 Define Market Segmentation Market segmentation is the process of identifying distinct groups and
MODULE 3: MARKET SEGMENTATION AND POSITIONING Lecture - 5 FAQS (FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS): Ques 1 Ans 1 Define Market Segmentation Market segmentation is the process of identifying distinct groups and
Infor Food & Beverage for the beverage manufacturing industry
 Food & Beverage Infor Food & Beverage for the beverage manufacturing industry Take your place on the grocer s shelves The beverage industry is under constant pressure to change. Sugary drinks, like sodas,
Food & Beverage Infor Food & Beverage for the beverage manufacturing industry Take your place on the grocer s shelves The beverage industry is under constant pressure to change. Sugary drinks, like sodas,
Learning Journey. Max Vijay
 Learning Journey Max Vijay Reducing costs by leveraging technology and educating the customers, to bring life insurance benefits to the low-income people Contents Project Basics... 1 About the project...
Learning Journey Max Vijay Reducing costs by leveraging technology and educating the customers, to bring life insurance benefits to the low-income people Contents Project Basics... 1 About the project...
Strategies for Marketing, Sales, and Promotion
 Introduction to e-commerce Strategies for Marketing, Sales, and Promotion Objectives In this chapter, you will learn about: When to use product-based and customer-based marketing strategies Communicating
Introduction to e-commerce Strategies for Marketing, Sales, and Promotion Objectives In this chapter, you will learn about: When to use product-based and customer-based marketing strategies Communicating
We use a large variety of goods and services in our daily life. These include items like
 19 INTRODUCTION TO MARKETING We use a large variety of goods and services in our daily life. These include items like toothpaste, toothbrush, soap, oil, clothes, food items, telephone, electricity and
19 INTRODUCTION TO MARKETING We use a large variety of goods and services in our daily life. These include items like toothpaste, toothbrush, soap, oil, clothes, food items, telephone, electricity and
100 SEO Tips. 1. Recognize the importance of web traffic.
 1. Recognize the importance of web traffic. 100 SEO Tips SEO or Search Engine Optimization is one of the techniques to use in order to achieve more volume of traffic to your site. Without a good number
1. Recognize the importance of web traffic. 100 SEO Tips SEO or Search Engine Optimization is one of the techniques to use in order to achieve more volume of traffic to your site. Without a good number
Marketing: Helping Buyers Buy
 Chapter Thirteen Marketing: Helping Buyers Buy McGraw-Hill/Irwin Copyright 2010 by the McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. CRICKET LEE Fitlogic Developed a system of clothes sizing called
Chapter Thirteen Marketing: Helping Buyers Buy McGraw-Hill/Irwin Copyright 2010 by the McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. CRICKET LEE Fitlogic Developed a system of clothes sizing called
Demand, Supply, and Market Equilibrium
 3 Demand, Supply, and Market Equilibrium The price of vanilla is bouncing. A kilogram (2.2 pounds) of vanilla beans sold for $50 in 2000, but by 2003 the price had risen to $500 per kilogram. The price
3 Demand, Supply, and Market Equilibrium The price of vanilla is bouncing. A kilogram (2.2 pounds) of vanilla beans sold for $50 in 2000, but by 2003 the price had risen to $500 per kilogram. The price
Preliminary Certificate in Marketing
 Preliminary Certificate in Marketing April 5 th, 2015 Examination PCM I 2015 85 th Intake, 25 th Year Candidate s Registration Number (As per in the examination admission form / Student ID) 0 0 0 0 0 For
Preliminary Certificate in Marketing April 5 th, 2015 Examination PCM I 2015 85 th Intake, 25 th Year Candidate s Registration Number (As per in the examination admission form / Student ID) 0 0 0 0 0 For
LIST OF CONTENTS AND TABLES
 LIST OF CONTENTS AND TABLES in Morocco - Category analysis... 1 Headlines... 1 Trends... 1 Competitive Landscape... 2 Prospects... 3 Category Data... 4 Table 1 Machine Sales: 2005-2010... 4 Table 2 Retail
LIST OF CONTENTS AND TABLES in Morocco - Category analysis... 1 Headlines... 1 Trends... 1 Competitive Landscape... 2 Prospects... 3 Category Data... 4 Table 1 Machine Sales: 2005-2010... 4 Table 2 Retail
Using Cash Flow Tracker
 Using Cash Flow Tracker About this guide This guide helps you understand the information provided in the Cash Flow Tracker. Important information This data is available to all CommBiz services, but user
Using Cash Flow Tracker About this guide This guide helps you understand the information provided in the Cash Flow Tracker. Important information This data is available to all CommBiz services, but user
Netflix Strategic Analysis
 XMBA 2013 Netflix Strategic Analysis Global Strategic Thinking Joey M. Reed, XMBA 2013 4/17/2013 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY In 1999, Reed Hastings launched an online movie rental service called, Netflix. The company
XMBA 2013 Netflix Strategic Analysis Global Strategic Thinking Joey M. Reed, XMBA 2013 4/17/2013 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY In 1999, Reed Hastings launched an online movie rental service called, Netflix. The company
Chapter 7: Market Structures Section 1
 Chapter 7: Market Structures Section 1 Key Terms perfect competition: a market structure in which a large number of firms all produce the same product and no single seller controls supply or prices commodity:
Chapter 7: Market Structures Section 1 Key Terms perfect competition: a market structure in which a large number of firms all produce the same product and no single seller controls supply or prices commodity:
Customer relationship management MB-104. By Mayank Kumar Pandey Assistant Professor at Noida Institute of Engineering and Technology
 Customer relationship management MB-104 By Mayank Kumar Pandey Assistant Professor at Noida Institute of Engineering and Technology University Syllabus UNIT-1 Customer Relationship Management- Introduction
Customer relationship management MB-104 By Mayank Kumar Pandey Assistant Professor at Noida Institute of Engineering and Technology University Syllabus UNIT-1 Customer Relationship Management- Introduction
Market Segmentation and Product Differentiation. What is Market Segmentation? Market Segmentation. Lectures in Marketing 2003 Dr.
 Segmentation and Product Differentiation Lectures in ing 2003 Dr. Richard Sjolander What is Segmentation? Consumers purchase products and services for the perceived satisfactions they can derive from their
Segmentation and Product Differentiation Lectures in ing 2003 Dr. Richard Sjolander What is Segmentation? Consumers purchase products and services for the perceived satisfactions they can derive from their
Contents. Part- I: Introduction to Services Marketing. Chapter 1 Understanding Services 3-22. Chapter 2 The Nature of Services Marketing 23-38
 Contents Part- I: Introduction to Services Marketing Chapter 1 Understanding Services 3-22 Chapter 2 The Nature of Services Marketing 23-38 Part- II: The Customer Experience Chapter 3 Consumer Behavior
Contents Part- I: Introduction to Services Marketing Chapter 1 Understanding Services 3-22 Chapter 2 The Nature of Services Marketing 23-38 Part- II: The Customer Experience Chapter 3 Consumer Behavior
LOCAL INTERNET MARKETING FOR YOUR SMALL BUSINESS
 LOCAL INTERNET MARKETING FOR YOUR SMALL BUSINESS Presented by: Cline Online Marketing, LLC Dave Cline, Owner 7635 West Ontario Place Littleton, CO 80128 Tel: 720-312-9196 Fax: 303-933-5266 How The Internet
LOCAL INTERNET MARKETING FOR YOUR SMALL BUSINESS Presented by: Cline Online Marketing, LLC Dave Cline, Owner 7635 West Ontario Place Littleton, CO 80128 Tel: 720-312-9196 Fax: 303-933-5266 How The Internet
The Free Market Approach. The Health Care Market. Sellers of Health Care. The Free Market Approach. Real Income
 The Health Care Market Who are the buyers and sellers? Everyone is a potential buyer (consumer) of health care At any moment a buyer would be anybody who is ill or wanted preventive treatment such as a
The Health Care Market Who are the buyers and sellers? Everyone is a potential buyer (consumer) of health care At any moment a buyer would be anybody who is ill or wanted preventive treatment such as a
CHAPTER 8: Organisational objectives, growth and scale
 CHAPTER 8: Organisational objectives, growth and scale The Objectives of Organisations Key Revision Points Organisational goals can be classified into a number of categories: Those that aim to make a profit
CHAPTER 8: Organisational objectives, growth and scale The Objectives of Organisations Key Revision Points Organisational goals can be classified into a number of categories: Those that aim to make a profit
Masters special education thesis >>>CLICK HERE<<<
 Masters special education thesis. But how do you get others to spread your ideas. Masters special education thesis >>>CLICK HERE
Masters special education thesis. But how do you get others to spread your ideas. Masters special education thesis >>>CLICK HERE
SPORT MARKETING MIX STRATEGIES
 Alexandru Lucian MIHAI Faculty: Marketing, Academy of Economic Studies, Bucharest, Romania SPORT MARKETING MIX STRATEGIES Keywords Sport marketing Marketing mix Market position JEL Classification M31 Abstract
Alexandru Lucian MIHAI Faculty: Marketing, Academy of Economic Studies, Bucharest, Romania SPORT MARKETING MIX STRATEGIES Keywords Sport marketing Marketing mix Market position JEL Classification M31 Abstract
