Scrotal Calculi. Article. Hakan Artas, MD, Irfan Orhan, MD
|
|
|
- Julius Norman
- 9 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Article Scrotal Calculi Hakan Artas, MD, Irfan Orhan, MD Objective. Scrotal calculi are freely mobile calcified bodies lying between the layers of the tunica vaginalis of the testes. The etiology of scrotal calculi is unclear. They may develop as a sequela to hematomas or inflammatory changes within the scrotum or loose bodies from torsion and infarction of the appendix testis or epididymis. The aim of our series was to examine the etiopathogenesis of scrotal calculi, which were detected incidentally in various age groups, with reference to the medical literature. Methods. Among 868 patients, 23 (2.65%) cases of scrotal calculi were diagnosed on sonographic examinations. The ages of the patients ranged between 4 months and 65 years (mean age ± SD, 28.3 ± 11.9 years). Results. On sonographic examination; we found a total of 51 scrotal calculi with a mean size of 4.22 ± 2.42 mm (range, 2 10 mm) in 23 patients, an epididymal cyst in 3 patients (13%), epididymitis in 2 patients (8.6%), hydrocele in 3 patients (13%), varicocele in 3 patients (13%), and testicular microlithiasis in 1 patient (4%). Scrotal calculi were solitary in 11 patients and multiple in 12 patients. Conclusions. The prevalence of scrotal calculi was 2.65%, and a minority of patients had other abnormalities, reflecting the generally benign etiology of these pearls. To date, no information is available in the literature about the results of chronic irritation due to scrotal calculi. Further studies in larger series need to be performed to elucidate the formation mechanism and natural course of scrotal calculi. Key words: calculi; scrotum; sonography. Received July 16, 2007, from the Department of Radiology, Elazig Training and Research Hospital, Elazig, Turkey (H.A.); and Department of Urology, Firat University, Faculty of Medicine, Elazig, Turkey (I.O.). Revision requested July 30, Revised manuscript accepted for publication August 15, Address correspondence to Hakan Artas, MD, Elazig Egitim ve Arastirma Hastanesi, Radyoloji Bölümü, Elazig, Turkey. [email protected] The intrascrotal calculus was first described during surgery by Kickham 1 in 1935 as a fibrinoid loose body or scrotal pearl. Scrotal calculi are benign entities, which are thought to represent freely mobile calcified bodies lying between the layers of the tunica vaginalis of the testes. The etiology of scrotal calculi is unclear. They may develop as a sequela to hematomas or inflammatory changes within the scrotum or loose bodies from torsion and infarction of the appendix testis or epididymis. The literature on intrascrotal lithiasis consists mostly of case reports. 1 4 However, some recent studies revealed that the prevalence of scrotal calculi was very high in some specific populations. 5 8 The aim of our series was to examine the etiopathogenesis of scrotal calculi, which were detected incidentally in various age groups, with reference to the medical literature by the American Institute of Ultrasound in Medicine J Ultrasound Med 2007; 26: /07/$3.50
2 Scrotal Calculi Materials and Methods Scrotal sonographic examinations were performed on 868 patients referred from urologic and surgical clinics at Elazig Training and Research Hospital between March 2006 and June Twenty-three cases of scrotal calculi were diagnosed on sonographic examinations at the radiology clinic. In all examinations we used an SSD-4000 device (Aloka Co, Ltd, Tokyo, Japan) equipped with a 5- to 10-MHz linear probe. The examinations were performed with patients lying in the supine position. The scrotum was immobilized by placing a towel between the thighs. Minimal pressure was applied with the transducer, and no water bath was used. Longitudinal, transverse, and oblique scans were obtained in all cases. Patients were evaluated for the presence of scrotal abnormalities such as scrotal calculi, hydrocele, and testicular and epididymal cysts and calcifications as well as inhomogeneity of the testicular and epididymal parenchymal echo texture. After detection of scrotal calculi on sonography, all patients were reevaluated clinically by a urologist in the urology clinic for the presence of scrotal pain, discomfort, trauma, inflammation, swelling, or masses. Results Among the 868 patients, 51 scrotal calculi in 23 (2.65%) patients were identified. The ages of these 23 patients ranged between 4 months and 65 years (mean age ± SD, 28.3 ± 11.9 years), and clinical findings included scrotal swelling, scrotal pain, varicocele, and infertility. A total of 23 patients were referred for sonographic examination for scrotal pain (n = 6), varicocele (n = 3), scrotal swelling (n = 6), infertility (n = 2), and a combination of these conditions (n = 6). The initial physical examinations of the 23 patients revealed scrotal swelling due to hydrocele (n = 3), an epididymal mass (n = 3), and epididymal thickening (n = 2), with the remaining having no abnormalities. In none of the patients were scrotal calculi detected on the first routine physical examination. None of the patients had anamnesis of scrotal microtraumas related to prolonged cycling or riding. On sonographic examination, 12 (52.1%) of 23 patients had no pathologic abnormalities of the scrotal contents except for scrotal calculi. We found a total of 51 scrotal calculi with a mean size of 4.22 ± 2.42 mm (range, 2 10 mm) in the 23 patients (Figures 1 and 2), an epididymal cyst (2 on the contralateral side and 1 on the ipsilateral side) in 3 patients (13%), epididymitis (2 on the bilateral side and 1 on the ipsilateral side) in 2 patients (8.6 %), hydrocele (2 on the contralateral side and 1 on the ipsilateral side) in 3 patients (13%), varicocele (1 on the contralateral side and 2 on the ipsilateral side) in 3 patients (13%), and testicular microlithiasis in 1 patient (4%; Figure 3). Scrotal calculi were solitary in 11 patients and multiple in 12 patients. Patient histories and clinical and sonographic findings in the 23 cases are summarized in Table 1. Sonography depicted the calculi typically as round or oval echogenic foci with or without acoustic shadowing in cases of large and small calculi, respectively. When patients changed their positions, all echogenic foci moved away from the tunica vaginalis testis. Movement of the calculi depended on their size and the amount of scrotal fluid. The larger the calculus, the less it moved. Figure 1. Scrotal calculus in a 65-year-old patient with bilateral epididymitis. In this patient, appendix testes were not visualized. Longitudinal sonography of the testis (T) shows extratesticular echogenic calculi (arrow) with posterior acoustic shadowing. There is minimal fluid (F) in the tunica vaginalis testis J Ultrasound Med 2007; 26:
3 Artas and Orhan Figure 2. Transverse sonography shows echogenic calculi (arrow) with posterior acoustic shadowing (arrowheads) in a 17-year-old patient. T indicates testis. Discussion Figure 3. Longitudinal sonography shows echogenic calculi of limited testicular microlithiasis of the left testis (arrowheads) and 2 echogenic calculi (arrows) in the left hemiscrotum in a 29-yearold patient. Scrotal calculi are usually accidentally found during surgery or routine sonographic examination. They may be detected on palpation by the patients themselves, and they may prove painful after repeated patient palpation. 9 Sonography is the ideal method to use in diagnosing scrotal calculi. 2 Stones are easily defined by sonography because of the hyperechoic nature of the calcification, which causes a discrete acoustic shadow. With sonography, calculi in hydrocele can be seen moving in the fluid between the tunicae, a feature that differentiates them from calculi in cystoceles 10 and urethroscrotal fistulas 11 and from other scrotal calcifications. 12 The etiology of scrotal calculi is unclear. They may result from torsion of the appendix testis or the epididymis, from hematomas, or from inflammation of the tunica vaginalis testis. 2 Inflammation may damage the tunica vaginalis testis layers, their lymphatic vessels, and other soft tissues of the scrotum and spermatic cord, leading to fibrosis. 2,12 These changes create a sieve effect; that is, small water molecules can pass through the fibrotic tunica vaginalis testis membranes and narrow lymphatic vessels, but larger molecules of cholesterol, calcium compounds, fibrin, and hydroxyapatite cannot. Calculi result from the buildup of these deposits. 6 An appendix testis or epididymis that has twisted and become free has also been postulated as a cause of scrotal calculi. 2 The natural history of torsion of an appendix is normally that the symptoms settle, and the twisted appendix atrophies. This may be followed with repeated sonographic examinations, but that is not really necessary. There are suggestions that these twisted appendixes calcify and become scrotoliths. 13 This is thought to be unlikely because acute severe symptoms, commonly associated with infarction, are not described with a scrotal calculus, and multiple scrotal calculi described in the literature cannot be explained on this basis. 11,14 In our study, the scrotal calculi were solitary in 11 patients. We think that the hypothesis of a twisted appendix testis may be appropriate in 11 of 23 patients. Repeated microtraumas may be risk factors for development of scrotal calculi. In a study by Frauscher et al, 5 85 extreme mountain bikers, who did a minimum of 2 hours per day, 6 days per week of off-road biking and had covered a distance of greater than 5000 km with their mountain bikes annually, were investigated. Most of these subjects also had other scrotal abnormalities in addition to calculi, which may have been a result of repeated chronic micro- J Ultrasound Med 2007; 26:
4 Scrotal Calculi Table 1. Histories and Clinical and Sonographic Findings in 23 Cases Additional Case Age, y Clinical Findings Calculi, n Calculi Size, mm* Sonographic Findings 1 40 Scrotal swelling 1 4 None 2 26 Varicocele, scrotal pain None 3 23 Scrotal pain None 4 26 Right scrotal swelling Contralateral (right) epididymal cyst 5 19 Scrotal pain None 6 21 Scrotal pain 1 2 None 7 27 Infertility None 8 65 Scrotal pain, scrotal swelling 1 9 Bilateral epididymitis 9 25 Infertility None 10 4 mo Left scrotal swelling Contralateral (left) hydrocele Varicocele, scrotal pain None Varicocele, scrotal pain None Varicocele, scrotal pain 1 10 Ipsilateral epididymitis Scrotal pain None Varicocele None Scrotal pain 6 2 None Varicocele Contralateral varicocele Scrotal swelling Contralateral epididymal cyst Right scrotal swelling Right hydrocele, bilateral calculi Varicocele Ipsilateral varicocele, testicular microlithiasis Right scrotal swelling Contralateral hydrocele Scrotal pain 2 10 Contralateral varicocele Left scrotal swelling Left epididymal cyst, bilateral calculi *In cases of multiple calculi, the largest one was measured. Figure 4. In a 4-month-old infant, transverse sonography of both hemiscrotums shows 2 echogenic calculi (arrows) in the left hemiscrotum and hydrocele in the right hemiscrotum. F indicates fluid; LT, left; RT, right; and T, testis. trauma of the scrotal contents secondary to shocks and vibration of the saddle from the rough terrain. They found 127 scrotal calculi in 69 (81%) bikers. 5,7 Turgut et al 8 reported that scrotal calcifications were observed in 7% of equestrians. In our series, none of the patients had any memory of scrotal microtraumas related to prolonged cycling or riding, and our prevalence rate was 2.65%. The associated hydrocele is an exudate that accumulates between the membranes of the tunica. It usually consists of abundant clear serous fluid with a high protein concentration in most patients. 6,15 The presence of calculi and many particles in hydrocele suggests a disturbance mainly in salt reabsorption. However, the cholesterol content of the hydrocele is variable and may be high in chronic cases. The source of the cholesterol is thought to be obstruction of the lymphatic vessels of the tunica as a result of a low-grade infection. Namjoshi 6 reported that scrotal sonography revealed calculi and calcareous material in hydrocele in 32 of 350 patients, which corresponds to a prevalence rate of 9%. In our study, scrotal calculi were associated with hydrocele in 3 patients J Ultrasound Med 2007; 26:
5 Artas and Orhan Most scrotal calculi were less than 1 cm in diameter. In the study by Frauscher et al, 5 the scrotal calculi ranged from 0.2 to 1.4 cm in diameter, with a mean size of 0.4 ± 0.3 cm. In our series, we found scrotal calculi with a mean size of 4.22 ± 2.42 mm (range, 2 10 mm), similar to those reported in the medical literature. However, Li et al 16 reported a large stone measuring cm and weighing 420 g, which dropped down spontaneously from a 93-year-old man s scrotum. Parlaktas et al 17 reported multiple calculi in hydrocele along with findings from histopathologic examination of the excised tunica vaginalis testis and biochemical analysis of the calculi. Histologic examination of the tunica vaginalis testis revealed chronic inflammation with fibrosis. Biochemical analysis of the calculi, on the other hand, showed that they were composed of calcium, oxalate, and phosphorus. 17 In our series, 12 of the 23 patients had no pathologic abnormalities of the scrotal contents except for the scrotal calculi. In 12 patients with no pathologic abnormalities of the scrotum, the other hypothesis based on alterations in the scrotal fluid content may be more appropriate. Larger patient series with scrotal fluid and calculus analyses and histopathologic examination of the tunica vaginalis testis are necessary to understand the mechanism of calculus formation in such cases. In reviewing the medical literature, we were not able to find any case of scrotal calculi detected in infancy. Our series, however, included a case of scrotal calculi diagnosed in an infant (Figure 4). Although the exact etiology of scrotal calculi in infancy is not known, it could be assumed that hydrocele or deterioration of the scrotal fluid contents may lead to formation of calculi when the contralateral hydrocele is taken into account. However, detection of scrotal calculi in an infant poses new questions about the time required for the formation of a scrotal calculus. In conclusion, the prevalence of scrotal calculi in this series was 2.65%, and a minority of patients had other abnormalities, reflecting the generally benign etiology of these pearls. Although scrotal calculi are considered benign in nature, no follow-up findings have been reported in patients with scrotal calculi. To date, no information is available in the literature about the results of chronic irritation due to scrotal calculi. Further studies in larger series need to be performed to elucidate the formation mechanism and natural course of scrotal calculi, which usually are diagnosed incidentally during sonographic examinations and have been assumed to be benign entities. References 1. Kickham CT. Calcified hydrocele of the tunica vaginalis testis. N Engl J Med 1935; 212: Linkowski GD, Avellone A, Gooding GA. Scrotal calculi: sonographic detection. Radiology 1985; 156: Honore LH. Uncommon benign scrotal masses: a report of ten cases. Practitioner 1978; 221: Sánchez-Merino JM, Lancina Martín A, Grases Freixedas F, Parra Muntaner L, Gomez Cisneros SC, Garcia Alonso J. Intra-scrotal lithiasis: crystallographic analysis. Arch Esp Urol 2002; 55: Frauscher F, Klauser A, Stenzl A, Helweg G, Amort B, zur Nedden D. US findings in the scrotum of extreme mountain bikers. Radiology 2001; 219: Namjoshi SP. Calculi in hydroceles: sonographic diagnosis and significance. J Clin Ultrasound 1997; 25: Frauscher F, Klauser A, Hobisch A, Pallwein L, Stenzl A. Subclinical microtraumatisation of the scrotal contents in extreme mountain biking. Lancet 2000; 356: Turgut AT, Kosar U, Kosar P, Karabulut A. Scrotal sonographic findings in equestrians. J Ultrasound Med 2005; 24: Black JA, Patel A. Sonography of the abnormal extratesticular space. AJR Am J Roentgenol 1996; 167: Postma MP, Smith R. Scrotal cystocele with bladder calculi. AJR Am J Roentgenol 1986; 147: Patel VG, Singleton JM, Draycott TJ. Scrotal bladder with scrotal calculi. Br J Urol 1992; 69: Martin B, Tubiana JM. Significance of scrotal calcifications detected by sonography. J Clin Ultrasound 1988; 16: Bushby LH, Miller FN, Rosairo S, Clarke JL, Sidhu PS. Scrotal calcification: ultrasound appearances, distribution and etiology. Br J Radiol 2002; 75: Chatterjee AC. A rare complication of hydrocele. Br J Surg 1975; 61: Torok P, Perjes G, Rosdy E. Intrascrotal calcification. Int Urol Nephrol 1981; 13: Li GH, Li XD, Cheng S, Chen ZD. A large intrascrotal calculus. Asian J Androl 2005; 7: Parlaktas BS, Uluocak N, Filiz E, Erdemir F, Ozyurt H. Intrascrotal calculi: a very rare stone disease. Int J Urol 2006; 13: J Ultrasound Med 2007; 26:
Torsed Appendix Testis
 Article Torsed Appendix Testis Gray Scale and Color Doppler Sonographic Findings Compared With Normal Appendix Testis Dal Mo Yang, MD, Joo Won Lim, MD, Jee Eun Kim, MD, Ji Hye Kim, MD, Hyuni Cho, MD Objective.
Article Torsed Appendix Testis Gray Scale and Color Doppler Sonographic Findings Compared With Normal Appendix Testis Dal Mo Yang, MD, Joo Won Lim, MD, Jee Eun Kim, MD, Ji Hye Kim, MD, Hyuni Cho, MD Objective.
BERGEN COMMUNITY COLLEGE DIAGNOSTIC MEDICAL SONOGRAPHY PROGRAM Division of Health Professions DMS 213 SYLLABUS
 BERGEN COMMUNITY COLLEGE DIAGNOSTIC MEDICAL SONOGRAPHY PROGRAM Division of Health Professions DMS 213 SYLLABUS Course Title: DMS 213 - Abdominal Sonography 2 2 lec. 3 lab. 3 credits (5 hours) Required
BERGEN COMMUNITY COLLEGE DIAGNOSTIC MEDICAL SONOGRAPHY PROGRAM Division of Health Professions DMS 213 SYLLABUS Course Title: DMS 213 - Abdominal Sonography 2 2 lec. 3 lab. 3 credits (5 hours) Required
Increased Rotational Mobility of the Testis After Vasectomy
 Article Increased Rotational Mobility of the Testis After Vasectomy A Sonographic Study Eugenio O. Gerscovich, MD, Christopher W. Park, MD, Michelle Z. Dulude, BA, John P. McGahan, MD, Rebecca Stein-Wexler,
Article Increased Rotational Mobility of the Testis After Vasectomy A Sonographic Study Eugenio O. Gerscovich, MD, Christopher W. Park, MD, Michelle Z. Dulude, BA, John P. McGahan, MD, Rebecca Stein-Wexler,
Ovarian Torsion: Sonographic Evaluation
 J Clin Ultrasound 17:327-332, June 1989 Ovarian Torsion: Sonographic Evaluation Mark A. Helvie, MD,* and Terry M. Silver, MDI Abstract: The sonographic and clinical findings of 13 patients with surgically
J Clin Ultrasound 17:327-332, June 1989 Ovarian Torsion: Sonographic Evaluation Mark A. Helvie, MD,* and Terry M. Silver, MDI Abstract: The sonographic and clinical findings of 13 patients with surgically
Sonography of Hernias
 Sonography of Hernias Cindy Rapp BS, RDMS, FAIUM, FSDMS Sr. Clinical Marketing Manager Toshiba America Medical Systems Tustin, California What is a hernia? A hernia is a protrusion of an organ or tissue
Sonography of Hernias Cindy Rapp BS, RDMS, FAIUM, FSDMS Sr. Clinical Marketing Manager Toshiba America Medical Systems Tustin, California What is a hernia? A hernia is a protrusion of an organ or tissue
Testicular Microlithiasis
 Article Testicular Microlithiasis Our Experience of 10 Years Diana L. Lam, BS, Eugenio O. Gerscovich, MD, Michael C. Kuo, MD, John P. McGahan, MD Objective. Testicular microlithiasis (TM) is characterized
Article Testicular Microlithiasis Our Experience of 10 Years Diana L. Lam, BS, Eugenio O. Gerscovich, MD, Michael C. Kuo, MD, John P. McGahan, MD Objective. Testicular microlithiasis (TM) is characterized
Sonography of Partial-Thickness Quadriceps Tendon Tears With Surgical Correlation
 Article Sonography of Partial-Thickness Quadriceps Tendon Tears With Surgical Correlation Samuel La, MD, David P. Fessell, MD, John E. Femino, MD, Jon A. Jacobson, MD, David Jamadar, MB, BS, Curtis Hayes,
Article Sonography of Partial-Thickness Quadriceps Tendon Tears With Surgical Correlation Samuel La, MD, David P. Fessell, MD, John E. Femino, MD, Jon A. Jacobson, MD, David Jamadar, MB, BS, Curtis Hayes,
Beverly E Hashimoto, M.D. Virginia Mason Medical Center, Seattle, WA
 Pelvic Floor Relaxation Beverly E Hashimoto, M.D. Virginia Mason Medical Center, Seattle, WA Disclosures Beverly Hashimoto: GE Medical Systems: research support and consultant (all fees given to Virginia
Pelvic Floor Relaxation Beverly E Hashimoto, M.D. Virginia Mason Medical Center, Seattle, WA Disclosures Beverly Hashimoto: GE Medical Systems: research support and consultant (all fees given to Virginia
Ultrasonography of the Adrenal Glands CVM 6105 Kari L. Anderson, DVM, Diplomate ACVR Associate Clinical Professor of Veterinary Radiology
 1: US of adrenal glands, KLA Ultrasonography of the Adrenal Glands CVM 6105 Kari L. Anderson, DVM, Diplomate ACVR Associate Clinical Professor of Veterinary Radiology Ultrasound has quickly become an important
1: US of adrenal glands, KLA Ultrasonography of the Adrenal Glands CVM 6105 Kari L. Anderson, DVM, Diplomate ACVR Associate Clinical Professor of Veterinary Radiology Ultrasound has quickly become an important
WHAT S WRONG WITH MY GALL BLADDER? GALL BLADDER POLYPS
 WHAT S WRONG WITH MY GALL BLADDER? GALL BLADDER POLYPS This is a patient information booklet providing specific practical information about gall bladder polyps in brief. Its aim is to provide the patient
WHAT S WRONG WITH MY GALL BLADDER? GALL BLADDER POLYPS This is a patient information booklet providing specific practical information about gall bladder polyps in brief. Its aim is to provide the patient
Open the Flood Gates Urinary Obstruction and Kidney Stones. Dr. Jeffrey Rosenberg Dr. Emilio Lastarria Dr. Richard Kasulke
 Open the Flood Gates Urinary Obstruction and Kidney Stones Dr. Jeffrey Rosenberg Dr. Emilio Lastarria Dr. Richard Kasulke Nephrology vs. Urology Nephrologist a physician who has been trained in the diagnosis
Open the Flood Gates Urinary Obstruction and Kidney Stones Dr. Jeffrey Rosenberg Dr. Emilio Lastarria Dr. Richard Kasulke Nephrology vs. Urology Nephrologist a physician who has been trained in the diagnosis
Evaluation and Follow-up of Fetal Hydronephrosis
 Evaluation and Follow-up of Fetal Hydronephrosis Deborah M. Feldman, MD, Marvalyn DeCambre, MD, Erin Kong, Adam Borgida, MD, Mujgan Jamil, MBBS, Patrick McKenna, MD, James F. X. Egan, MD Objective. To
Evaluation and Follow-up of Fetal Hydronephrosis Deborah M. Feldman, MD, Marvalyn DeCambre, MD, Erin Kong, Adam Borgida, MD, Mujgan Jamil, MBBS, Patrick McKenna, MD, James F. X. Egan, MD Objective. To
Prosthetic mesh used for inguinal and ventral hernia repair: normal appearance and complications in ultrasound and CT
 The British Journal of Radiology, 77 (2004), 261 265 DOI: 10.1259/bjr/63333975 E 2004 The British Institute of Radiology Pictorial review Prosthetic mesh used for inguinal and ventral hernia repair: normal
The British Journal of Radiology, 77 (2004), 261 265 DOI: 10.1259/bjr/63333975 E 2004 The British Institute of Radiology Pictorial review Prosthetic mesh used for inguinal and ventral hernia repair: normal
KIDNEY FUNCTION RELATION TO SIZE OF THE TUMOR IN RENAL CELL CANCINOMA
 KIDNEY FUNCTION RELATION TO SIZE OF THE TUMOR IN RENAL CELL CANCINOMA O.E. Stakhvoskyi, E.O. Stakhovsky, Y.V. Vitruk, O.A. Voylenko, P.S. Vukalovich, V.A. Kotov, O.M. Gavriluk National Canсer Institute,
KIDNEY FUNCTION RELATION TO SIZE OF THE TUMOR IN RENAL CELL CANCINOMA O.E. Stakhvoskyi, E.O. Stakhovsky, Y.V. Vitruk, O.A. Voylenko, P.S. Vukalovich, V.A. Kotov, O.M. Gavriluk National Canсer Institute,
Sonography of Wrist Ganglion Cysts
 CME Article Sonography of Wrist Ganglion Cysts Variable and Noncystic Appearances George Wang, MD, Jon A. Jacobson, MD, Felix Y. Feng, MD, Gandikota Girish, MBBS, FRCS, FRCR, Elaine M. Caoili, MD, Catherine
CME Article Sonography of Wrist Ganglion Cysts Variable and Noncystic Appearances George Wang, MD, Jon A. Jacobson, MD, Felix Y. Feng, MD, Gandikota Girish, MBBS, FRCS, FRCR, Elaine M. Caoili, MD, Catherine
RBH GUIDELINES FOR ULTRASOUND REFERRAL
 RBH GUIDELINES FOR ULTRASOUND REFERRAL Introduction Ultrasound can be very useful as a first line investigation; it is typically non-invasive and does not involve ionising radiation. However, a significant
RBH GUIDELINES FOR ULTRASOUND REFERRAL Introduction Ultrasound can be very useful as a first line investigation; it is typically non-invasive and does not involve ionising radiation. However, a significant
If Your Child has an Inguinal Hernia, Hydrocele or Undescended Testicles. A Guide for Parents
 Introduction Urology Clinic If Your Child has an Inguinal Hernia, Hydrocele or Undescended Testicles A Guide for Parents Three of the most common birth defects in males are an inguinal hernia, hydrocele,
Introduction Urology Clinic If Your Child has an Inguinal Hernia, Hydrocele or Undescended Testicles A Guide for Parents Three of the most common birth defects in males are an inguinal hernia, hydrocele,
Sonographic Differential Diagnosis of Acute Scrotum
 Article Sonographic Differential Diagnosis of Acute Scrotum Real-time Whirlpool Sign, a Key Sign of Torsion S. Boopathy Vijayaraghavan, MD, DMRD Objective. The purpose of this study was to prospectively
Article Sonographic Differential Diagnosis of Acute Scrotum Real-time Whirlpool Sign, a Key Sign of Torsion S. Boopathy Vijayaraghavan, MD, DMRD Objective. The purpose of this study was to prospectively
Practice patterns in the surgical approach for adolescent varicocelectomy
 DOI 10.1186/s40064-015-1573-7 RESEARCH Practice patterns in the surgical approach for adolescent varicocelectomy Miriam Harel 1,2*, Katherine W. Herbst 2 and Eric Nelson 1,2 Open Access Abstract Objective:
DOI 10.1186/s40064-015-1573-7 RESEARCH Practice patterns in the surgical approach for adolescent varicocelectomy Miriam Harel 1,2*, Katherine W. Herbst 2 and Eric Nelson 1,2 Open Access Abstract Objective:
Men s Health: Testicular & Breast. September 2012
 Men s Health: Testicular & Breast September 2012 Objectives: You will learn: How to perform a testicular self-exam and breast self-exam. You will know when to perform testicular and breast self-exams.
Men s Health: Testicular & Breast September 2012 Objectives: You will learn: How to perform a testicular self-exam and breast self-exam. You will know when to perform testicular and breast self-exams.
An abdominal ultrasound produces a picture of the organs and other structures in the upper abdomen.
 Scan for mobile link. Ultrasound - Abdomen Ultrasound imaging of the abdomen uses sound waves to produce pictures of the structures within the upper abdomen. It is used to help diagnose pain or distention
Scan for mobile link. Ultrasound - Abdomen Ultrasound imaging of the abdomen uses sound waves to produce pictures of the structures within the upper abdomen. It is used to help diagnose pain or distention
Renal Cysts What should I do now?
 Renal Cysts What should I do now? Dr Edmund Chiong Asst. Professor & Consultant Department of Urology National University Hospital What are renal cysts? Fluid-filled structures in the kidney that are not
Renal Cysts What should I do now? Dr Edmund Chiong Asst. Professor & Consultant Department of Urology National University Hospital What are renal cysts? Fluid-filled structures in the kidney that are not
Urinary tract and perineum
 9 Urinary tract and perineum Key Points 9.1 9.1 THE URINARY BLADDER URINARY RETENTION Acute retention of urine is an indication for emergency drainage of the bladder The common causes of acute retention
9 Urinary tract and perineum Key Points 9.1 9.1 THE URINARY BLADDER URINARY RETENTION Acute retention of urine is an indication for emergency drainage of the bladder The common causes of acute retention
Gynecology Abnormal Pelvic Anatomy and Physiology: Cervix. Cervix. Nabothian cysts. cervical polyps. leiomyomas. Cervical stenosis
 Gynecology Abnormal Pelvic Anatomy and Physiology: (Effective February 2007) pediatric, reproductive, and perimenopausal/postmenopausal (24-28 %) Cervix Nabothian cysts result from chronic cervicitis most
Gynecology Abnormal Pelvic Anatomy and Physiology: (Effective February 2007) pediatric, reproductive, and perimenopausal/postmenopausal (24-28 %) Cervix Nabothian cysts result from chronic cervicitis most
Abdomen X-Ray (AXR) Collimation is ideally from diaphragms to lower border of the symphysis pubis and the lateral skin margins.
 Abdomen X-Ray (AXR) Collimation is ideally from diaphragms to lower border of the symphysis pubis and the lateral skin margins. LMP of child-bearing age female patients should be checked. 1. Acute abdomen
Abdomen X-Ray (AXR) Collimation is ideally from diaphragms to lower border of the symphysis pubis and the lateral skin margins. LMP of child-bearing age female patients should be checked. 1. Acute abdomen
Vasectomy Reversal. Elizabeth Peacock. MUSC Urology Grand Rounds
 Vasectomy Reversal Elizabeth Peacock PGY-3 MUSC Urology Grand Rounds Urology Grand Rounds July 6, 2010 Elizabeth Peacock, MD Urology Resident, PGY-3 Title: Vasectomy Reversal Objectives of Presentation:
Vasectomy Reversal Elizabeth Peacock PGY-3 MUSC Urology Grand Rounds Urology Grand Rounds July 6, 2010 Elizabeth Peacock, MD Urology Resident, PGY-3 Title: Vasectomy Reversal Objectives of Presentation:
Lower Extremity Venous Duplex Evaluation
 VASCULAR TECHNOLOGY PROFESSIONAL PERFORMANCE GUIDELINES Lower Extremity Venous Duplex Evaluation This Guideline was prepared by the Professional Guidelines Subcommittee of the Society for Vascular Ultrasound
VASCULAR TECHNOLOGY PROFESSIONAL PERFORMANCE GUIDELINES Lower Extremity Venous Duplex Evaluation This Guideline was prepared by the Professional Guidelines Subcommittee of the Society for Vascular Ultrasound
Prognosis of Very Large First-Trimester Hematomas
 Case Series Prognosis of Very Large First-Trimester Hematomas Juliana Leite, MD, Pamela Ross, RDMS, RDCS, A. Cristina Rossi, MD, Philippe Jeanty, MD, PhD Objective. The aim of this study was to evaluate
Case Series Prognosis of Very Large First-Trimester Hematomas Juliana Leite, MD, Pamela Ross, RDMS, RDCS, A. Cristina Rossi, MD, Philippe Jeanty, MD, PhD Objective. The aim of this study was to evaluate
Radiographic Findings and Comments
 642 Abdomen (Cont.) Differential Diagnosis of Abdominal s E. Focal parenchymal calcification of the kidney Tuberculosis (Fig. 27.19) Adenocarcinoma (Fig. 27.20) Nephroblastoma (Wilms tumor) (Fig. 27.21)
642 Abdomen (Cont.) Differential Diagnosis of Abdominal s E. Focal parenchymal calcification of the kidney Tuberculosis (Fig. 27.19) Adenocarcinoma (Fig. 27.20) Nephroblastoma (Wilms tumor) (Fig. 27.21)
Duplication Images in Vascular Sonography
 Article Duplication Images in Vascular Sonography Jonathan M. Rubin, MD, PhD, Jing Gao, MD, Keith Hetel, MD, Robert Min, MD Objective. The purpose of this study was to determine the characteristics and
Article Duplication Images in Vascular Sonography Jonathan M. Rubin, MD, PhD, Jing Gao, MD, Keith Hetel, MD, Robert Min, MD Objective. The purpose of this study was to determine the characteristics and
Ultrasound in Vascular Surgery. Torbjørn Dahl
 Ultrasound in Vascular Surgery Torbjørn Dahl 1 The field of vascular surgery Veins dilatation and obstruction (varicose veins and valve dysfunction) Arteries dilatation and narrowing (aneurysms and atherosclerosis)
Ultrasound in Vascular Surgery Torbjørn Dahl 1 The field of vascular surgery Veins dilatation and obstruction (varicose veins and valve dysfunction) Arteries dilatation and narrowing (aneurysms and atherosclerosis)
What to Expect from Intestinal Ultrasonography
 261) What to Expect from Intestinal Ultrasonography Červenková J., Steyerová P. Charles University in Prague, First Faculty of Medicine and General Teaching Hospital, Department of Radiology, Prague, Czech
261) What to Expect from Intestinal Ultrasonography Červenková J., Steyerová P. Charles University in Prague, First Faculty of Medicine and General Teaching Hospital, Department of Radiology, Prague, Czech
Ultrasonography (US) is the imaging modality of choice for evaluating
 Diagn Interv Radiol 2009; 15:64 73 Turkish Society of Radiology 2009 ULTRASONOGRAPHY PICTORIAL ESSAY Sonography of scrotal anormalities in adults: an update İsmail Mihmanlı, Fatih Kantarcı ABSTRACT The
Diagn Interv Radiol 2009; 15:64 73 Turkish Society of Radiology 2009 ULTRASONOGRAPHY PICTORIAL ESSAY Sonography of scrotal anormalities in adults: an update İsmail Mihmanlı, Fatih Kantarcı ABSTRACT The
POSTMENOPAUSAL ASSESS AND WHAT TO DO
 POSTMENOPAUSAL OVARIAN CYSTS:HOW TO ASSESS AND WHAT TO DO Steven R. Goldstein, MD Professor of Obstetrics and Gynecology Director of Gynecologic Ultrasound Co-Director, Bone Densitometry New York University
POSTMENOPAUSAL OVARIAN CYSTS:HOW TO ASSESS AND WHAT TO DO Steven R. Goldstein, MD Professor of Obstetrics and Gynecology Director of Gynecologic Ultrasound Co-Director, Bone Densitometry New York University
Official reprint from UpToDate www.uptodate.com 2013 UpToDate
 Official reprint from UpToDate www.uptodate.com 2013 UpToDate The content on the UpToDate website is not intended nor recommended as a substitute for medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek
Official reprint from UpToDate www.uptodate.com 2013 UpToDate The content on the UpToDate website is not intended nor recommended as a substitute for medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek
Cardiac Masses and Tumors
 Cardiac Masses and Tumors Question: What is the diagnosis? A. Aortic valve myxoma B. Papillary fibroelastoma C. Vegetation from Infective endocarditis D. Thrombus in transit E. None of the above Answer:
Cardiac Masses and Tumors Question: What is the diagnosis? A. Aortic valve myxoma B. Papillary fibroelastoma C. Vegetation from Infective endocarditis D. Thrombus in transit E. None of the above Answer:
Common Breast Complaints:
 : Palpable mass Abnormal mammogram with normal physical exam Vague thickening or nodularity Nipple Discharge Breast pain Breast infection or inflammation The physician s goal is to determine whether the
: Palpable mass Abnormal mammogram with normal physical exam Vague thickening or nodularity Nipple Discharge Breast pain Breast infection or inflammation The physician s goal is to determine whether the
Varicocele: To Fix or Not to Fix? That is the Question. Edmund S. Sabanegh, MD
 Varicocele: To Fix or Not to Fix? That is the Question. Edmund S. Sabanegh, MD Professor and Chairman, Department of Urology, Cleveland Clinic Lerner College of Medicine; Cleveland, Ohio Objectives: Review
Varicocele: To Fix or Not to Fix? That is the Question. Edmund S. Sabanegh, MD Professor and Chairman, Department of Urology, Cleveland Clinic Lerner College of Medicine; Cleveland, Ohio Objectives: Review
Vasectomy: Patient Information. Andrew L. Siegel, M.D. Board-Certified Urologist and Urological Surgeon
 Vasectomy: Patient Information by Andrew L. Siegel, M.D. Board-Certified Urologist and Urological Surgeon An educational service provided by: bergen Urological associates Stuart H. Levey, M.D. Andrew L.
Vasectomy: Patient Information by Andrew L. Siegel, M.D. Board-Certified Urologist and Urological Surgeon An educational service provided by: bergen Urological associates Stuart H. Levey, M.D. Andrew L.
Juvenile Dermatomyositis Joseph Junewick, MD FACR
 Juvenile Dermatomyositis Joseph Junewick, MD FACR 10/11/2015 History Child with several month history of weakness, arthralgias and palpable abnormalities at the knee Diagnosis Juvenile Dermatomyositis
Juvenile Dermatomyositis Joseph Junewick, MD FACR 10/11/2015 History Child with several month history of weakness, arthralgias and palpable abnormalities at the knee Diagnosis Juvenile Dermatomyositis
Pathoanatomical Changes of the Brachial Plexus and of C5-C6 Following Whiplash-Type Injury: A Case Report
 Pathoanatomical Changes of the Brachial Plexus and of C5-C6 Following Whiplash-Type Injury: A Case Report 1 Journal Of Whiplash & Related Disorders Vol. 1, No, 1, 2002 Gunilla Bring, Halldor Jonsson Jr.,
Pathoanatomical Changes of the Brachial Plexus and of C5-C6 Following Whiplash-Type Injury: A Case Report 1 Journal Of Whiplash & Related Disorders Vol. 1, No, 1, 2002 Gunilla Bring, Halldor Jonsson Jr.,
OBJECTIVES By the end of this segment, the community participant will be able to:
 Cancer 101: Cancer Diagnosis and Staging Linda U. Krebs, RN, PhD, AOCN, FAAN OCEAN Native Navigators and the Cancer Continuum (NNACC) (NCMHD R24MD002811) Cancer 101: Diagnosis & Staging (Watanabe-Galloway
Cancer 101: Cancer Diagnosis and Staging Linda U. Krebs, RN, PhD, AOCN, FAAN OCEAN Native Navigators and the Cancer Continuum (NNACC) (NCMHD R24MD002811) Cancer 101: Diagnosis & Staging (Watanabe-Galloway
PE finding: Left side extremities mild weakness No traumatic wound No bloody otorrhea, nor rhinorrhea
 Case report A 82-year-old man was suffered from sudden onset spasm of extremities then he fell down to the ground with loss of consciousness. He recovered his consciousness 7-8 mins later but his conscious
Case report A 82-year-old man was suffered from sudden onset spasm of extremities then he fell down to the ground with loss of consciousness. He recovered his consciousness 7-8 mins later but his conscious
US for Detecting Renal Calculi with Nonenhanced CT as a Reference Standard 1
 Genitourinary Imaging Keir A. B. Fowler, MD Julie A. Locken, MD Joshua H. Duchesne Michael R. Williamson, MD Index terms: Kidney, calculi, 811.811, 813.811 Kidney, CT, 81.12111, 81.12115 Kidney, US, 81.1298
Genitourinary Imaging Keir A. B. Fowler, MD Julie A. Locken, MD Joshua H. Duchesne Michael R. Williamson, MD Index terms: Kidney, calculi, 811.811, 813.811 Kidney, CT, 81.12111, 81.12115 Kidney, US, 81.1298
Linfoma maligno pulmonar tratado com Nerium oleander. http://www.drozel.org/eng/diagnosis_malignant_mg.htm CASE REPORT
 Linfoma maligno pulmonar tratado com Nerium oleander http://www.drozel.org/eng/diagnosis_malignant_mg.htm CASE REPORT Diagnosis: Malignant lymphoma, lung cancer A 60-year-old woman experienced pain in
Linfoma maligno pulmonar tratado com Nerium oleander http://www.drozel.org/eng/diagnosis_malignant_mg.htm CASE REPORT Diagnosis: Malignant lymphoma, lung cancer A 60-year-old woman experienced pain in
Patient Prep Information
 Stereotactic Breast Biopsy Patient Prep Information Imaging Services Cannon Memorial Hospital Watauga Medical Center Table Weight Limits for each facility Cannon Memorial Hospital Watauga Medical Center
Stereotactic Breast Biopsy Patient Prep Information Imaging Services Cannon Memorial Hospital Watauga Medical Center Table Weight Limits for each facility Cannon Memorial Hospital Watauga Medical Center
Malignant Mesothelioma of the Tunica Vaginalis Testis
 Case Report Malignant Mesothelioma of the Tunica Vaginalis Testis A Case Illustrating Doppler Color Flow Imaging and Its Potential for Preoperative Diagnosis James Boyum, BA, Neil F. Wasserman, MD Malignant
Case Report Malignant Mesothelioma of the Tunica Vaginalis Testis A Case Illustrating Doppler Color Flow Imaging and Its Potential for Preoperative Diagnosis James Boyum, BA, Neil F. Wasserman, MD Malignant
Colocutaneous Fistula. Disclosures
 Colocutaneous Fistula Madhulika G. Varma MD Associate Professor Chief, Colorectal Surgery University of California, San Francisco Honoraria Applied Medical Covidien Disclosures 1 Colocutaneous Fistula
Colocutaneous Fistula Madhulika G. Varma MD Associate Professor Chief, Colorectal Surgery University of California, San Francisco Honoraria Applied Medical Covidien Disclosures 1 Colocutaneous Fistula
How to Find Out What s Wrong A BASIC GUIDE TO MALE. A doctor s guide for patients developed by the American Urological Association, Inc.
 A BASIC GUIDE TO MALE How to Find Out What s Wrong A doctor s guide for patients developed by the American Urological Association, Inc. Based on the AUA Best Practice Policy and ASRM Practice Committee
A BASIC GUIDE TO MALE How to Find Out What s Wrong A doctor s guide for patients developed by the American Urological Association, Inc. Based on the AUA Best Practice Policy and ASRM Practice Committee
.org. Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction. Anatomy. Cause. Symptoms
 Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction Page ( 1 ) Posterior tibial tendon dysfunction is one of the most common problems of the foot and ankle. It occurs when the posterior tibial tendon becomes inflamed
Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction Page ( 1 ) Posterior tibial tendon dysfunction is one of the most common problems of the foot and ankle. It occurs when the posterior tibial tendon becomes inflamed
PREPARING FOR YOUR STOMA REVERSAL
 PREPARING FOR YOUR STOMA REVERSAL Information Leaflet Your Health. Our Priority. Page 2 of 6 Introduction- What you need to know As part of your bowel operation you may have had a temporary stoma formed.
PREPARING FOR YOUR STOMA REVERSAL Information Leaflet Your Health. Our Priority. Page 2 of 6 Introduction- What you need to know As part of your bowel operation you may have had a temporary stoma formed.
Spleen. Anatomy. (Effective February 2007) (1%-5%) Normal. Related Anatomy Anterior to spleen. Medial border. Posteriorly
 Spleen (Effective February 2007) (1%-5%) Anatomy Normal Intraperitoneal, except hilum Left hypochondrium Left hemidiaphragm superior generally considered to be ovoid, with a convex superior and a concave
Spleen (Effective February 2007) (1%-5%) Anatomy Normal Intraperitoneal, except hilum Left hypochondrium Left hemidiaphragm superior generally considered to be ovoid, with a convex superior and a concave
Prevention and Recognition of Obstetric Fistula Training Package. Module 8: Pre-repair Care and Referral for Women with Obstetric Fistula
 Prevention and Recognition of Obstetric Fistula Training Package Module 8: Pre-repair Care and Referral for Women with Obstetric Fistula Early detection and treatment If a woman has recently survived a
Prevention and Recognition of Obstetric Fistula Training Package Module 8: Pre-repair Care and Referral for Women with Obstetric Fistula Early detection and treatment If a woman has recently survived a
GFR (Glomerular Filtration Rate) A Key to Understanding How Well Your Kidneys Are Working
 GFR (Glomerular Filtration Rate) A Key to Understanding How Well Your Kidneys Are Working www.kidney.org National Kidney Foundation's Kidney Disease Outcomes Quality Initiative Did you know that the National
GFR (Glomerular Filtration Rate) A Key to Understanding How Well Your Kidneys Are Working www.kidney.org National Kidney Foundation's Kidney Disease Outcomes Quality Initiative Did you know that the National
Bile Duct Diseases and Problems
 Bile Duct Diseases and Problems Introduction A bile duct is a tube that carries bile between the liver and gallbladder and the intestine. Bile is a substance made by the liver that helps with digestion.
Bile Duct Diseases and Problems Introduction A bile duct is a tube that carries bile between the liver and gallbladder and the intestine. Bile is a substance made by the liver that helps with digestion.
Incidence of Incidental Thyroid Nodules on Computed Tomography (CT) Scan of the Chest Performed for Reasons Other than Thyroid Disease
 International Journal of Clinical Medicine, 2011, 2, 264-268 doi:10.4236/ijcm.2011.23042 Published Online July 2011 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/ijcm) Incidence of Incidental Thyroid Nodules on Computed
International Journal of Clinical Medicine, 2011, 2, 264-268 doi:10.4236/ijcm.2011.23042 Published Online July 2011 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/ijcm) Incidence of Incidental Thyroid Nodules on Computed
Technical Advices for Prostate Needle Biopsy Under Transrectal Ultrasound Guidance
 Technical Advices for Prostate Needle Biopsy Under Transrectal Ultrasound Guidance Makoto Ohori 1 and Ayako Miyakawa 2 1 Dept. of Urology, Tokyo Medical University 2 Dept. of Molecular Medicine and Surgery,
Technical Advices for Prostate Needle Biopsy Under Transrectal Ultrasound Guidance Makoto Ohori 1 and Ayako Miyakawa 2 1 Dept. of Urology, Tokyo Medical University 2 Dept. of Molecular Medicine and Surgery,
Lymph Node Dissection for Penile Cancer
 Lymph Node Dissection for Penile Cancer Exceptional healthcare, personally delivered Removal of Lymph Nodes Why are the Lymph Nodes so important when I have penile cancer? Lymph nodes are small bean shaped
Lymph Node Dissection for Penile Cancer Exceptional healthcare, personally delivered Removal of Lymph Nodes Why are the Lymph Nodes so important when I have penile cancer? Lymph nodes are small bean shaped
Emergency Medicine Sonography POCKET GUIDE
 Emergency Medicine Sonography POCKET GUIDE to Sonographic Anatomy and Pathology, MPH, PA-C, RDMS Physician Assistant, Department of Surgery, Division of Urology Lincoln Hospital and Medical Center, Bronx,
Emergency Medicine Sonography POCKET GUIDE to Sonographic Anatomy and Pathology, MPH, PA-C, RDMS Physician Assistant, Department of Surgery, Division of Urology Lincoln Hospital and Medical Center, Bronx,
Gallstone Ileus. Audrey C. Durrant,, M.D. SUNY Downstate Medical Center May 20, 2005
 Gallstone Ileus Audrey C. Durrant,, M.D. SUNY Downstate Medical Center May 20, 2005 Gallstone Ileus Diagnosis and Management Background Misnomer coined by Bartolin in 1654 Not a true ileus True mechanical
Gallstone Ileus Audrey C. Durrant,, M.D. SUNY Downstate Medical Center May 20, 2005 Gallstone Ileus Diagnosis and Management Background Misnomer coined by Bartolin in 1654 Not a true ileus True mechanical
Radiotherapy in locally advanced & metastatic NSC lung cancer
 Radiotherapy in locally advanced & metastatic NSC lung cancer Dr Raj Hegde. MD. FRANZCR Consultant Radiation Oncologist. William Buckland Radiotherapy Centre. Latrobe Regional Hospital. Locally advanced
Radiotherapy in locally advanced & metastatic NSC lung cancer Dr Raj Hegde. MD. FRANZCR Consultant Radiation Oncologist. William Buckland Radiotherapy Centre. Latrobe Regional Hospital. Locally advanced
Clinical guidance for MRI referral
 MRI for cervical radiculopathy Referral by a medical practitioner (excluding a specialist or consultant physician) for a scan of spine for a patient 16 years or older for suspected: cervical radiculopathy
MRI for cervical radiculopathy Referral by a medical practitioner (excluding a specialist or consultant physician) for a scan of spine for a patient 16 years or older for suspected: cervical radiculopathy
.org. Shoulder Pain and Common Shoulder Problems. Anatomy. Cause
 Shoulder Pain and Common Shoulder Problems Page ( 1 ) What most people call the shoulder is really several joints that combine with tendons and muscles to allow a wide range of motion in the arm from scratching
Shoulder Pain and Common Shoulder Problems Page ( 1 ) What most people call the shoulder is really several joints that combine with tendons and muscles to allow a wide range of motion in the arm from scratching
Prevalence of Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm by Magnetic Resonance Images (MRI) in Men over 50 years with low back pain
 Original Article Prevalence of Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm by Magnetic Resonance Images (MRI) in Men over 50 years with low back pain Moslem Shakeri, Kourosh Karimi Yarandi, Kaveh Haddadi, Sima Sayyahmelli.
Original Article Prevalence of Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm by Magnetic Resonance Images (MRI) in Men over 50 years with low back pain Moslem Shakeri, Kourosh Karimi Yarandi, Kaveh Haddadi, Sima Sayyahmelli.
The Fatal Pulmonary Artery Involvement in Behçet s Disease
 The Fatal Pulmonary Artery Involvement in Behçet s Disease Dr. Vedat Hamuryudan Div. Rheumatology, Dept. Internal Medicine Cerrahpasa Medical Faculty, University of Istanbul 33 years old man Sept 2011:
The Fatal Pulmonary Artery Involvement in Behçet s Disease Dr. Vedat Hamuryudan Div. Rheumatology, Dept. Internal Medicine Cerrahpasa Medical Faculty, University of Istanbul 33 years old man Sept 2011:
Characterization of small renal lesions: Problem solving with MRI Gary Israel, MD
 Characterization of small renal lesions: Problem solving with MRI Gary Israel, MD With the widespread use of cross-sectional imaging, many renal masses are incidentally found. These need to be accurately
Characterization of small renal lesions: Problem solving with MRI Gary Israel, MD With the widespread use of cross-sectional imaging, many renal masses are incidentally found. These need to be accurately
Identifying and treating long-term kidney problems (chronic kidney disease)
 Understanding NICE guidance Information for people who use NHS services Identifying and treating long-term kidney problems (chronic kidney disease) NICE clinical guidelines advise the NHS on caring for
Understanding NICE guidance Information for people who use NHS services Identifying and treating long-term kidney problems (chronic kidney disease) NICE clinical guidelines advise the NHS on caring for
CONTEMPORARY MANAGEMENT OF RENAL ANGIOMYOLIPOMA
 CONTEMPORARY MANAGEMENT OF RENAL ANGIOMYOLIPOMA Stephen A. Boorjian, MD Professor of Urology Vice Chair of Research Director, Urologic Oncology Fellowship Department of Urology Mayo Clinic, Rochester,
CONTEMPORARY MANAGEMENT OF RENAL ANGIOMYOLIPOMA Stephen A. Boorjian, MD Professor of Urology Vice Chair of Research Director, Urologic Oncology Fellowship Department of Urology Mayo Clinic, Rochester,
Acute pelvic inflammatory disease: tests and treatment
 Acute pelvic inflammatory disease: tests and treatment Information for you Information for you Published August 2010 Published in August 2010 (next review date: 2014) Acute What is pelvic inflammatory
Acute pelvic inflammatory disease: tests and treatment Information for you Information for you Published August 2010 Published in August 2010 (next review date: 2014) Acute What is pelvic inflammatory
1991 :super specialties perceptions
 Ved Chaturvedi, MD, DM Research & Referral Hospital New Delhi President Indian Rheumatology Association MSK Ultrasound..A decade experience of bedside MSK US by a clinician. Was it worth it.? 1991 :super
Ved Chaturvedi, MD, DM Research & Referral Hospital New Delhi President Indian Rheumatology Association MSK Ultrasound..A decade experience of bedside MSK US by a clinician. Was it worth it.? 1991 :super
Perianal Abscess and Fistula-in-ano. Background
 Perianal Abscess and Fistula-in-ano Background Anorectal abscesses are some of the more common anorectal conditions encountered, and they are potentially debilitating conditions. The current theory as
Perianal Abscess and Fistula-in-ano Background Anorectal abscesses are some of the more common anorectal conditions encountered, and they are potentially debilitating conditions. The current theory as
dedicated to curing BREAST CANCER
 dedicated to curing BREAST CANCER When you are diagnosed with breast cancer, you need a team of specialists who will share their knowledge of breast disease and the latest treatments available. At Cancer
dedicated to curing BREAST CANCER When you are diagnosed with breast cancer, you need a team of specialists who will share their knowledge of breast disease and the latest treatments available. At Cancer
ProSono Copyright 2006. Ovarian Pathology
 Ovarian Pathology Physiologic cysts: Functional cysts Pathology: A simple cyst is a sac containing fluid or semi-solid material. Physiologic cysts are generic types of hormonally active cysts that result
Ovarian Pathology Physiologic cysts: Functional cysts Pathology: A simple cyst is a sac containing fluid or semi-solid material. Physiologic cysts are generic types of hormonally active cysts that result
Ultrasound - Vascular
 Scan for mobile link. Ultrasound - Vascular Vascular ultrasound uses sound waves to evaluate the body s circulatory system and help identify blockages and detect blood clots. A Doppler ultrasound study
Scan for mobile link. Ultrasound - Vascular Vascular ultrasound uses sound waves to evaluate the body s circulatory system and help identify blockages and detect blood clots. A Doppler ultrasound study
.org. Lisfranc (Midfoot) Injury. Anatomy. Description
 Lisfranc (Midfoot) Injury Page ( 1 ) Lisfranc (midfoot) injuries result if bones in the midfoot are broken or ligaments that support the midfoot are torn. The severity of the injury can vary from simple
Lisfranc (Midfoot) Injury Page ( 1 ) Lisfranc (midfoot) injuries result if bones in the midfoot are broken or ligaments that support the midfoot are torn. The severity of the injury can vary from simple
Evaluation and Management of the Breast Mass. Gary Dunnington,, M.D. Department of Surgery Internal Medicine Ambulatory Conference December 4, 2003
 Evaluation and Management of the Breast Mass Gary Dunnington,, M.D. Department of Surgery Internal Medicine Ambulatory Conference December 4, 2003 Common Presentations of Breast Disease Breast Mass Abnormal
Evaluation and Management of the Breast Mass Gary Dunnington,, M.D. Department of Surgery Internal Medicine Ambulatory Conference December 4, 2003 Common Presentations of Breast Disease Breast Mass Abnormal
The Children s Hospital Treatment for Hypospadias Information for parents
 The Children s Hospital Treatment for Hypospadias Information for parents What is hypospadias and what is the cause? Hypospadias is a congenital (since birth) abnormality of a boy s penis. Hypospadias
The Children s Hospital Treatment for Hypospadias Information for parents What is hypospadias and what is the cause? Hypospadias is a congenital (since birth) abnormality of a boy s penis. Hypospadias
Preparation for your vasectomy
 Preparation for your vasectomy You have been scheduled for a vasectomy with the SIU Division of Urology. Please read through this information carefully. Vasectomies are performed in the REI clinic, 751
Preparation for your vasectomy You have been scheduled for a vasectomy with the SIU Division of Urology. Please read through this information carefully. Vasectomies are performed in the REI clinic, 751
Vasectomy What happens under normal conditions? What is a vasectomy? How is a vasectomy performed?
 Vasectomy The decision to proceed with a vasectomy is a very personal one. It is important that you have a clear understanding of what a vasectomy is and what it is not. Most patients can expect to recover
Vasectomy The decision to proceed with a vasectomy is a very personal one. It is important that you have a clear understanding of what a vasectomy is and what it is not. Most patients can expect to recover
Spine University s Guide to Cauda Equina Syndrome
 Spine University s Guide to Cauda Equina Syndrome 2 Introduction Your spine is a very complicated part of your body. It s made up of the bones (vertebrae) that keep it aligned, nerves that channel down
Spine University s Guide to Cauda Equina Syndrome 2 Introduction Your spine is a very complicated part of your body. It s made up of the bones (vertebrae) that keep it aligned, nerves that channel down
Ovarian Cyst. Homoeopathy Clinic. Introduction. Types of Ovarian Cysts. Contents. Case Reports. 21 August 2002
 Case Reports 21 August 2002 Ovarian Cyst Homoeopathy Clinic Check Yourself If you have any of the following symptoms call your doctor. Sense of fullness or pressure or a dull ache in the abdomen Pain during
Case Reports 21 August 2002 Ovarian Cyst Homoeopathy Clinic Check Yourself If you have any of the following symptoms call your doctor. Sense of fullness or pressure or a dull ache in the abdomen Pain during
Ultrasound Tissue Characterization an innovative method to visualize and monitor Patellar Tendinopathy
 Ultrasound Tissue Characterization an innovative method to visualize and monitor Patellar Tendinopathy Hans T.M. van Schie DVM, PhD UTC Imaging, Netherlands Scoring with Patellar Tendinopathy? no one size
Ultrasound Tissue Characterization an innovative method to visualize and monitor Patellar Tendinopathy Hans T.M. van Schie DVM, PhD UTC Imaging, Netherlands Scoring with Patellar Tendinopathy? no one size
Guideline for the Imaging of Patients Presenting with Breast Symptoms incorporating the guideline for the use of MRI in breast cancer
 Guideline for the Imaging of Patients Presenting with Breast Symptoms incorporating the guideline for the use of MRI in breast cancer Version History Version Date Summary of Change/Process 0.1 09.01.11
Guideline for the Imaging of Patients Presenting with Breast Symptoms incorporating the guideline for the use of MRI in breast cancer Version History Version Date Summary of Change/Process 0.1 09.01.11
Sonographic Diagnosis of Ureteral Tumors
 Sonographic Diagnosis of Ureteral Tumors Irith Hadas-Halpern, MD, micur Farkas, MD, Michael Patlas, MD, Ibrahim Zaghal, MD, Shoshana Sabag-Gottschalk, MD, Drora Fisher, MD We present our experience with
Sonographic Diagnosis of Ureteral Tumors Irith Hadas-Halpern, MD, micur Farkas, MD, Michael Patlas, MD, Ibrahim Zaghal, MD, Shoshana Sabag-Gottschalk, MD, Drora Fisher, MD We present our experience with
Urinary Tract Infections in Children
 Urinary Tract Infections in Children National Kidney and Urologic Diseases Information Clearinghouse National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH Urinary
Urinary Tract Infections in Children National Kidney and Urologic Diseases Information Clearinghouse National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH Urinary
Analysis of the Thymus in 151 Healthy Infants From 0 to 2 Years of Age
 Article Analysis of the Thymus in 151 Healthy Infants From 0 to 2 Years of Age Ensar Yekeler, MD, Ahmet Tambag, MD, Atadan Tunaci, MD, Hakan Genchellac, MD, Memduh Dursun, MD, Gulbin Gokcay, MD, Gulden
Article Analysis of the Thymus in 151 Healthy Infants From 0 to 2 Years of Age Ensar Yekeler, MD, Ahmet Tambag, MD, Atadan Tunaci, MD, Hakan Genchellac, MD, Memduh Dursun, MD, Gulbin Gokcay, MD, Gulden
Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma: Staging and Prognosis of Three Separate Cases.
 Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma: Staging and Prognosis of Three Separate Cases. Abstract This paper describes the staging, imaging, treatment, and prognosis of renal cell carcinoma. Three case studies
Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma: Staging and Prognosis of Three Separate Cases. Abstract This paper describes the staging, imaging, treatment, and prognosis of renal cell carcinoma. Three case studies
FREEDOM INGUINAL Hernia Repair System TECHNIQUE GUIDE
 FREEDOM INGUINAL Hernia Repair System TECHNIQUE GUIDE The following describes the open surgical preparation and implantation technique for the Freedom Inguinal Hernia Repair System. 1) Anesthesia can be
FREEDOM INGUINAL Hernia Repair System TECHNIQUE GUIDE The following describes the open surgical preparation and implantation technique for the Freedom Inguinal Hernia Repair System. 1) Anesthesia can be
Model Answer: Australasian College of Phlebology > Ultrasound in Phlebology > Advanced Course > Topic 4
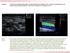 Ques?on 1: Compression sonography (lee image) is the gold standard for the diagnosis of DVT. Are there any advantages of color Doppler ultrasound (right image) over compression sonography in the diagnosis
Ques?on 1: Compression sonography (lee image) is the gold standard for the diagnosis of DVT. Are there any advantages of color Doppler ultrasound (right image) over compression sonography in the diagnosis
What You Should Know About Cerebral Aneurysms
 What You Should Know About Cerebral Aneurysms From the Cerebrovascular Imaging and Interventions Committee of the American Heart Association Cardiovascular Radiology Council Randall T. Higashida, M.D.,
What You Should Know About Cerebral Aneurysms From the Cerebrovascular Imaging and Interventions Committee of the American Heart Association Cardiovascular Radiology Council Randall T. Higashida, M.D.,
MRI of Bone Marrow Radiologic-Pathologic Correlation
 MRI of Bone Marrow Radiologic-Pathologic Correlation Marilyn J. Siegel, M.D. Mallinckrodt Institute of Radiology Washington University School of Medicine St. Louis, MO and Visiting Scientist, AFIP, Washington,
MRI of Bone Marrow Radiologic-Pathologic Correlation Marilyn J. Siegel, M.D. Mallinckrodt Institute of Radiology Washington University School of Medicine St. Louis, MO and Visiting Scientist, AFIP, Washington,
