AN4296 Application note
|
|
|
- Allyson Tamsin Porter
- 9 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Application note Overview and tips for using STM32F303/328/334/358xx CCM RAM with IAR EWARM, Keil MDK-ARM and GNU-based toolchains Introduction The purpose of this application note is to give a presentation of the core coupled memory (CCM) RAM available on STM32F303xB/xC and STM32F358xC microcontrollers and describe what is required to execute part of the application code from this memory region using different toolchains. This application note is divided into four sections: the first section gives an overview of the STM32F3 CCM RAM, while the next sections describe the steps required to execute part of the application code from CCM RAM using the following toolchains: IAR EWARM KEIL MDK-ARM RIDE and Atollic GNU based toolchain The procedures described throughout the document are applicable to other RAM regions such as the CCM data RAM of some F4 devices, or external SRAM. Refer to Table 1 for the list microcontrollers embedding CCM RAM. Table 1. Applicable products Product family Microcontrollers Part numbers or product categories STM32F303xB, STM32F303xC, STM32F358xC STM32F303x6/x8, STM32F328x8, STM32F334x4/x6/x8 September 2014 DocID Rev 3 1/25 1
2 Contents AN4296 Contents 1 Overview of STM32F303xB/C and STM32F358xC CCM RAM Purpose STM32F303xB/C and STM32F358xC CCM RAM features CCM RAM mapping CCM RAM remapping CCM RAM write protection CCM RAM parity check Execute application code from CCM RAM using the IAR EWARM toolchain Executing a simple code from CCM RAM (except for interrupt handler) Executing a source file from CCM RAM Executing one or more functions from CCM RAM Executing an interrupt handler from CCM RAM Updating the linker file (.icf) Updating the startup file Place the interrupt handler in CCM RAM Remap the vector table to CCM RAM Executing a library (.a) from CCM RAM Execute application code from CCM RAM using the KEIL MDK-ARM toolchain Executing a function or an interrupt handler from CCM RAM Executing a source file from CCM RAM Executing a library or a library module from CCM RAM Execute application code from CCM RAM using a GNU-based toolchain Executing a function or an interrupt handler from CCM RAM Executing a file from CCM RAM Executing a library from CCM RAM Revision history /25 DocID Rev 3
3 List of tables List of tables Table 1. Applicable products Table 2. CCM RAM organization Table 3. Document revision history DocID Rev 3 3/25 3
4 List of figures AN4296 List of figures Figure 1. STM32F303xB/xC and STM32F358xC system architecture Figure 2. EWARM linker update Figure 3. EWARM file placement Figure 4. EWARM function placement Figure 5. EWARM linker update for interrupt handler Figure 6. EWARM startup file update for interrupt handler Figure 7. CCM RAM area definition Figure 8. EWARM section initialization Figure 9. EWARM library placement Figure 10. EWARM library module placement Figure 11. MDK-ARM scatter file Figure 12. MDK-ARM Options menu Figure 13. MDK-ARM function placement Figure 14. MDK-ARM target memory Figure 15. MDK-ARM file placement Figure 16. MDK-ARM library placement Figure 17. GNU linker update Figure 18. GNU linker section definition Figure 19. GNU function placement Figure 20. GNU file placement Figure 21. GNU library placement /25 DocID Rev 3
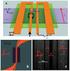
5 Overview of STM32F303xB/C and STM32F358xC CCM RAM 1 Overview of STM32F303xB/C and STM32F358xC CCM RAM 1.1 Purpose The STM32F303xB/C and STM32F358xC CCM RAM is tightly coupled with the Cortex core. it is primarily intended to execute code at maximum system clock frequency (72 MHz) without any wait state penalty. It thus allows to significantly decrease critical task execution time, compared to code execution from Flash memory. CCM RAM is typically used for real-time and computation intensive routines, such as: Digital power conversion control loops (switch mode power supplies, lighting) Field-oriented 3-phase motor control Real-time DSP tasks When code is located in CCM RAM and data stored in the regular SRAM, the Cortex-M4 core is in the optimum Harvard configuration. A dedicated zero-wait state memory is connected to each of its I- and D-bus (refer to Figure 1: STM32F303xB/xC and STM32F358xC system architecture) and can thus perform at 1.25DMIPS/MHz up to 72 MHz, with a deterministic performance of 90 DMIPS. This also guarantees a minimal latency if interrupt service routines are placed in the CCM RAM. Example A benchmark between the STM32F103xx and STM32F303xx microcontrollers using STMicroelectronics MC library V3.4 shows that in case of single motor control using 3 shunt algorithm, the FOC total execution time for STM32F303xx is µs compared to 21.3 µs in STMF103xx (see note below); with FOC core and sensorless core loops running from CCM RAM for STM32F303xx. This means that the STM32F303xx is % faster than the STM32F103xx thanks to the CCM RAM. Note: FOC routines are programmed in structured C, so the values provided above do not represent the fastest possible execution both for STM32F103xx and STM32F303xx. In addition, the execution time is also function of the compiler used and of its version. When the CCM RAM is not used for code, it can hold data like an extra SRAM memory. However it cannot be accessed through DMA. It is not recommended to place both code and data together in the CCM, since the Cortex core will have to fetch code and data from the same memory with the risk of collisions. The core would then be in the Von Neuman configuration, and its performance would drop from 1.25DMIPS/MHz to below 1DMIPS/MHz. DocID Rev 3 5/25 24
6 Overview of STM32F303xB/C and STM32F358xC CCM RAM AN4296 Figure 1. STM32F303xB/xC and STM32F358xC system architecture 1.2 STM32F303xB/C and STM32F358xC CCM RAM features CCM RAM mapping The CCM RAM is available on the STM32F303xB/C and STM32F358xC devices, starting from 0x address CCM RAM remapping Unlike regular SRAM, the CCM RAM cannot be remapped at address 0x CCM RAM write protection The CCM RAM can be protected against unwanted write operations with a page granularity of 1 Kbyte. Refer to Table 2 for a description of CCM RAM organization. Table 2. CCM RAM organization Page number Start address End address Page 0 0x x FF Page 1 0x x FF Page 2 0x x1000 0BFF Page 3 0x1000 0C00 0x1000 0FFF 6/25 DocID Rev 3
7 Overview of STM32F303xB/C and STM32F358xC CCM RAM The write protection is enabled through the SYSCFG CCM SRAM protection register (SYSCFG_RCR). This is a write '1' once mechanism, which means that once the write protection is enabled on a given CCM RAM page by programming the corresponding bit to 1, it can be cleared only through a system reset. For more details refer to the product reference manual CCM RAM parity check A parity check is implemented on STM32F303xB/C and STM32F358xC microcontrollers. It is disabled by default and can be enabled by the user when needed through an option bit (SRAM_PE bit). When this option bit is cleared, the parity check is enabled for the first 16 Kbytes of SRAM and for the 8-Kbyte CCM RAM. DocID Rev 3 7/25 24
8 Execute application code from CCM RAM using the IAR EWARM toolchain AN Execute application code from CCM RAM using the IAR EWARM toolchain 2.1 Executing a simple code from CCM RAM (except for interrupt handler) A simple code can be composed of one or more functions that are not referenced from an interrupt handler. If the code is referenced from an interrupt handler, follow the steps described in Section 2.2: Executing an interrupt handler from CCM RAM. EWARM provides the possibility to place one or more functions or a whole source file in CCM RAM. Note: This operation requires a new section to be defined in the linker file (.icf) to host the code to be placed in CCM RAM. This section is copied to CCM RAM at startup. The required steps are the following: 1. Define the address area for the CCM RAM by indicating the start and end addresses. 2. Tell the linker to copy at startup the section named.ccmram from Flash memory to CCM RAM. 3. Indicate to the linker that the code section.ccmram should be placed in the CCM RAM region. Refer to Figure 2: EWARM linker update for an example of code implementing these operations. This procedure is not valid for interrupt handlers. 8/25 DocID Rev 3
9 Execute application code from CCM RAM using the IAR EWARM toolchain Figure 2. EWARM linker update Executing a source file from CCM RAM Executing a source file from CCM RAM means that all functions declared in this file will be executed from this memory area. To place and execute a source file from CCM RAM, use the EWARM file Options window: 1. Add the section.ccmram (for example) in the linker file as defined in Section Right click the file name from the workspace window. 3. Select options from the displayed menu. 4. Check override inherited settings from the displayed window 5. Select the output tab, and type the name of the section already defined in the linker file (.ccmram in this example) in the Code section name field (see Figure 3: EWARM file placement). DocID Rev 3 9/25 24
10 Execute application code from CCM RAM using the IAR EWARM toolchain AN4296 Figure 3. EWARM file placement Executing one or more functions from CCM RAM The steps required to execute a function from CCM RAM are the following: 1. Add the section.ccmram in the linker file as described in Section Using the key word pragma location, specify the function to be executed from CCM RAM (see Figure 4: EWARM function placement). Figure 4. EWARM function placement 10/25 DocID Rev 3
11 Execute application code from CCM RAM using the IAR EWARM toolchain Note: To execute more than one function from CCM RAM, the pragma location keyword should be placed above each function declaration. 2.2 Executing an interrupt handler from CCM RAM The vector table is implemented as an array named vector_table and referenced in the startup code. EWARM linker protects the sections that are referenced from the startup code from being affected by an 'initialize by copy' directive. So, you should not use the symbol vector_table to allow copying interrupt handler sections via the 'initialize by copy' directive. As a consequence, you should make a second vector table and place it in CCM RAM. The steps required to execute an interrupt handler from CCM RAM are the following: 1. Update the linker file (.icf). 2. Update the startup file. 3. Place the interrupt handler in CCM RAM. 4. Remap the vector table to CCM RAM Updating the linker file (.icf) To update the linker file: 1. Define the address where the second vector table will be located: 0x Define the memory address area for the CCM RAM by specifying the start and end addresses. 3. Tell the linker to copy at startup the section named.ccmram and the second vector table section.intvec_ccmram from Flash memory to CCM RAM. 4. Tell the linker that the second vector table should be placed in the intvec_ccmram section. 5. Indicate that the.ccmram code section should be placed in CCM RAM. DocID Rev 3 11/25 24
12 Execute application code from CCM RAM using the IAR EWARM toolchain AN4296 Figure 5. EWARM linker update for interrupt handler 12/25 DocID Rev 3
13 Execute application code from CCM RAM using the IAR EWARM toolchain Updating the startup file To update the startup file: 1. Make a second vector table to be stored in CCM RAM. The startup_stm32f30x.s file should be modified by removing all entries except for sfe(cstack) and Reset_Handler from the original vector table vector_table. 2. Add a second vector table to be placed in CCM RAM. It should contain all entries. As an example you can call it vector_table_ccmram. This vector table must be placed in the intvec_ccmram section defined in the linker file. Figure 6. EWARM startup file update for interrupt handler Place the interrupt handler in CCM RAM Place the interrupt handler to be executed in CCM RAM as described in Section or the whole stm32f_it.c file as described in Section Remap the vector table to CCM RAM In SystemInit function, remap the vector table to CCM RAM by modifying the VTOR register as following: SCB->VTOR = 0x VECT_TAB_OFFSET; DocID Rev 3 13/25 24
14 Execute application code from CCM RAM using the IAR EWARM toolchain AN Executing a library (.a) from CCM RAM EWARM allows executing a library or a library module from CCM RAM. The actions to be executed are the following: 1. Define the memory address area corresponding to the CCM RAM by specifying the start and end addresses. Figure 7. CCM RAM area definition 2. Update the linker to copy at startup the library or the library module in CCM RAM using the initialize by copy directive. Example: Figure 8. EWARM section initialization 3. Indicate to the linker that the library should be placed in CCM RAM: Figure 9. EWARM library placement To execute a library module from CCM RAM, follow steps 1, 2 and 3 using the library module name. 14/25 DocID Rev 3
15 Execute application code from CCM RAM using the IAR EWARM toolchain The example below shows how to place arm_abs_f32.o (a module of iar_cortexm4l_math.a library) in CCM RAM: Figure 10. EWARM library module placement DocID Rev 3 15/25 24
16 Execute application code from CCM RAM using the KEIL MDK-ARM toolchain AN Execute application code from CCM RAM using the KEIL MDK-ARM toolchain MDK-ARM features make it possible to execute simple functions or interrupt handlers from CCM RAM. The following sections explain how to use these features to execute code from CCM RAM. 3.1 Executing a function or an interrupt handler from CCM RAM The steps required to execute a function or an interrupt handler from CCM RAM are the following: 1. Define a new region (ccmram) in the scatter file by indicating the start and end addresses of the CCM RAM area. 2. Indicate to the linker that the sections with ccmram attribute must be placed in the CCM RAM region. Figure 11. MDK-ARM scatter file 16/25 DocID Rev 3
17 Execute application code from CCM RAM using the KEIL MDK-ARM toolchain 3. Refer to the modified scatter file for the project options (see Figure 11): Figure 12. MDK-ARM Options menu 4. Place the part of code to be executed from CCM RAM in the ccmram section defined above. This is done by adding the attribute key word above the function declaration. Figure 13. MDK-ARM function placement Note: To execute more than one function from CCM RAM, the attribute keyword should be placed above each function declaration: DocID Rev 3 17/25 24
18 Execute application code from CCM RAM using the KEIL MDK-ARM toolchain AN Executing a source file from CCM RAM Executing a source file from CCM RAM means that all functions declared in this file will be executed from the CCM RAM region. Follow the steps below to execute a file from CCM RAM: 1. Define the CCM RAM as a memory area in the project option window (Project>option>target): Figure 14. MDK-ARM target memory 2. Right click the file to place it in CCM RAM and select options 3. Select the CCM RAM region in the memory assignment menu: Figure 15. MDK-ARM file placement 3.3 Executing a library or a library module from CCM RAM Follow the steps below to execute a library or a library module from CCM RAM: 1. Define the CCM RAM as a memory area as shown in Figure 16: MDK-ARM library placement. 2. Right click the library from the workspace and select options. 3. You can either place the complete library or a module from a library in CCM RAM. Figure 16. MDK-ARM library placement 18/25 DocID Rev 3
19 Execute application code from CCM RAM using a GNU-based toolchain 4 Execute application code from CCM RAM using a GNU-based toolchain GNU-based toolchains allow executing simple functions or interrupt handlers from CCM RAM. The following sections explain how to use these features to execute code from CCM RAM. 4.1 Executing a function or an interrupt handler from CCM RAM The steps required to execute a function or an interrupt handler from CCM RAM are the following: 1. Define a new region (ccmram) in the linker file (.ld) by defining the start address and the size of CCM RAM region (see Figure 17: GNU linker update) Figure 17. GNU linker update 2. Tell the linker that code sections with ccmram attribute must be placed in CCM RAM (see Figure 18: GNU linker section definition). DocID Rev 3 19/25 24
20 Execute application code from CCM RAM using a GNU-based toolchain AN4296 Figure 18. GNU linker section definition 3. Modify the startup file to initialize data to place in CCM RAM at startup time (see code lines in red):.section.text.reset_handler.weak Reset_Handler.type Reset_Handler, %function Reset_Handler: /* Copy the data segment initializers from flash to SRAM and CCMRAM */ movs r1, #0 b LoopCopyDataInit CopyDataInit: ldr r3, =_sidata ldr r3, [r3, r1] str r3, [r0, r1] adds r1, r1, #4 LoopCopyDataInit: ldr r0, =_sdata ldr r3, =_edata adds r2, r0, r1 cmp r2, r3 bcc CopyDataInit movs r1, #0 20/25 DocID Rev 3
21 Execute application code from CCM RAM using a GNU-based toolchain b LoopCopyDataInit1 CopyDataInit1: ldr r3, =_siccmram ldr r3, [r3, r1] str r3, [r0, r1] adds r1, r1, #4 LoopCopyDataInit1: ldr r0, =_sccmram ldr r3, =_eccmram adds r2, r0, r1 cmp r2, r3 bcc CopyDataInit1 ldr r2, =_sbss b LoopFillZerobss /* Zero fill the bss segment. */ FillZerobss: movs r3, #0 str r3, [r2], #4 LoopFillZerobss: ldr r3, = _ebss cmp r2, r3 bcc FillZerobss /* Call the clock system intitialization function.*/ bl SystemInit /* Call the application's entry point.*/ bl main bx lr 4. Place the part of code to be executed from CCM RAM in the.ccmram section by adding the attribute key word in the function prototype: Figure 19. GNU function placement DocID Rev 3 21/25 24
22 Execute application code from CCM RAM using a GNU-based toolchain AN Executing a file from CCM RAM Executing a source file from CCM RAM means that all functions declared in this file will be executed from CCM RAM. To execute a file from CCM RAM, follow the sequence below: 1. Add the.ccmram section in the linker file as defined in Section Place your file in CCM RAM as shown below: Figure 20. GNU file placement 22/25 DocID Rev 3
23 Execute application code from CCM RAM using a GNU-based toolchain 4.3 Executing a library from CCM RAM Follow the steps below to execute a library from CCM RAM: 1. Add the.ccmram section in the linker file as defined in Section Place your libray in CCM RAM as shown below: Figure 21. GNU library placement DocID Rev 3 23/25 24
24 Revision history AN Revision history Table 3. Document revision history Date Revision Changes 23-Jul Initial release. 25-Mar Sep Changed STM32F313xC into STM32F358xC. Reworked Section 1: Overview of STM32F303xB/C and STM32F358xC CCM RAM. Added STM32F303x6/x8, STM32F328x8, STM32F334x4/x6/x8 in Table 1: Applicable products. Updated step 2 in Section 2.1: Executing a simple code from CCM RAM (except for interrupt handler), step 3 in Section 2.2.1: Updating the linker file (.icf) and updated Figure 5: EWARM linker update for interrupt handler. Updated Figure 11: MDK-ARM scatter file. 24/25 DocID Rev 3
25 IMPORTANT NOTICE PLEASE READ CAREFULLY STMicroelectronics NV and its subsidiaries ( ST ) reserve the right to make changes, corrections, enhancements, modifications, and improvements to ST products and/or to this document at any time without notice. Purchasers should obtain the latest relevant information on ST products before placing orders. ST products are sold pursuant to ST s terms and conditions of sale in place at the time of order acknowledgement. Purchasers are solely responsible for the choice, selection, and use of ST products and ST assumes no liability for application assistance or the design of Purchasers products. No license, express or implied, to any intellectual property right is granted by ST herein. Resale of ST products with provisions different from the information set forth herein shall void any warranty granted by ST for such product. ST and the ST logo are trademarks of ST. All other product or service names are the property of their respective owners. Information in this document supersedes and replaces information previously supplied in any prior versions of this document STMicroelectronics All rights reserved DocID Rev 3 25/25 25
32F072BDISCOVERY. Discovery kit for STM32F072xx microcontrollers. Features. Description
 Discovery kit for STM32F072xx microcontrollers Data brief Features STM32F072RBT6 microcontroller featuring 128 KB of Flash memory, 16 KB of SRAM in an LQFP64 package On-board ST-LINK/V2 with switch to
Discovery kit for STM32F072xx microcontrollers Data brief Features STM32F072RBT6 microcontroller featuring 128 KB of Flash memory, 16 KB of SRAM in an LQFP64 package On-board ST-LINK/V2 with switch to
AN2557 Application note
 Application note STM32F10x in-application programming using the USART Introduction An important requirement for most Flash-memory-based systems is the ability to update firmware when installed in the end
Application note STM32F10x in-application programming using the USART Introduction An important requirement for most Flash-memory-based systems is the ability to update firmware when installed in the end
STM32F4DISCOVERY. Discovery kit with STM32F407VG MCU. Features. Description
 Discovery kit with STM32F407VG MCU Data brief Features STM32F407VGT6 microcontroller featuring 32-bit ARM Cortex -M4 with FPU core, 1-Mbyte Flash memory, 192-Kbyte RAM in an LQFP100 package On-board ST-LINK/V2
Discovery kit with STM32F407VG MCU Data brief Features STM32F407VGT6 microcontroller featuring 32-bit ARM Cortex -M4 with FPU core, 1-Mbyte Flash memory, 192-Kbyte RAM in an LQFP100 package On-board ST-LINK/V2
UM1969 User manual. Getting started with STM32F746G discovery software development tools. Introduction
 UM1969 User manual Getting started with STM32F746G discovery software development tools Introduction This document describes the software environment recommendations, required to build an application using
UM1969 User manual Getting started with STM32F746G discovery software development tools Introduction This document describes the software environment recommendations, required to build an application using
32F769IDISCOVERY. Discovery kit with STM32F769NI MCU. Features
 Discovery kit with STM32F769NI MCU Data brief Features STM32F769NIH6 microcontroller featuring 2 Mbytes of Flash memory and 512+16+4 Kbytes of RAM, in BGA216 package On-board ST-LINK/V2-1 supporting USB
Discovery kit with STM32F769NI MCU Data brief Features STM32F769NIH6 microcontroller featuring 2 Mbytes of Flash memory and 512+16+4 Kbytes of RAM, in BGA216 package On-board ST-LINK/V2-1 supporting USB
UM1727 User manual. Getting started with STM32 Nucleo board software development tools. Introduction
 User manual Getting started with STM32 Nucleo board software development tools Introduction The STM32 Nucleo board is a low-cost and easy-to-use development platform used to quickly evaluate and start
User manual Getting started with STM32 Nucleo board software development tools Introduction The STM32 Nucleo board is a low-cost and easy-to-use development platform used to quickly evaluate and start
UM1680 User manual. Getting started with STM32F429 Discovery software development tools. Introduction
 User manual Getting started with STM32F429 Discovery software development tools Introduction This document describes the software environment and development recommendations required to build an application
User manual Getting started with STM32F429 Discovery software development tools Introduction This document describes the software environment and development recommendations required to build an application
AN3354 Application note
 Application note STM32F105/107 in-application programming using a USB host 1 Introduction An important requirement for most Flash-memory-based systems is the ability to update firmware installed in the
Application note STM32F105/107 in-application programming using a USB host 1 Introduction An important requirement for most Flash-memory-based systems is the ability to update firmware installed in the
UM1727 User manual. Getting started with STM32 Nucleo board software development tools. Introduction
 User manual Getting started with STM32 Nucleo board software development tools Introduction The STM32 Nucleo board (NUCLEO-F030R8, NUCLEO-F072RB, NUCLEO-F103RB, NUCLEO-F302R8, NUCLEO-F401RE, NUCLEO-L152RE)
User manual Getting started with STM32 Nucleo board software development tools Introduction The STM32 Nucleo board (NUCLEO-F030R8, NUCLEO-F072RB, NUCLEO-F103RB, NUCLEO-F302R8, NUCLEO-F401RE, NUCLEO-L152RE)
AN4646 Application note
 Application note Peripheral interconnections on STM32F401 and STM32F411 lines Introduction On top of the highest performance and the lowest power consumption of the STM32F4 family, STM32F401/411 peripherals
Application note Peripheral interconnections on STM32F401 and STM32F411 lines Introduction On top of the highest performance and the lowest power consumption of the STM32F4 family, STM32F401/411 peripherals
UM1790 User manual. Getting started with STM32L053 discovery kit software development tools. Introduction
 User manual Getting started with STM32L053 discovery kit software development tools Introduction This document describes the software environment recommendations required to build an application using
User manual Getting started with STM32L053 discovery kit software development tools Introduction This document describes the software environment recommendations required to build an application using
UM0985 User manual. Developing your STM32VLDISCOVERY application using the IAR Embedded Workbench software. Introduction
 User manual Developing your STM32VLDISCOVERY application using the IAR Embedded Workbench software Introduction This document provides an introduction on how to use IAR Embedded Workbench for ARM software
User manual Developing your STM32VLDISCOVERY application using the IAR Embedded Workbench software Introduction This document provides an introduction on how to use IAR Embedded Workbench for ARM software
AN3990 Application note
 Application note Upgrading STM32F4DISCOVERY board firmware using a USB key Introduction An important requirement for most Flash memory-based systems is the ability to update the firmware installed in the
Application note Upgrading STM32F4DISCOVERY board firmware using a USB key Introduction An important requirement for most Flash memory-based systems is the ability to update the firmware installed in the
AN3307 Application note
 Application note Guidelines for obtaining IEC 60335 Class B certification for any STM32 application Introduction The role of safety has become very important for electronics applications. The level of
Application note Guidelines for obtaining IEC 60335 Class B certification for any STM32 application Introduction The role of safety has become very important for electronics applications. The level of
AN3969 Application note
 Application note EEPROM emulation in STM32F40x/STM32F41x microcontrollers Introduction EEPROMs (Electrically Erasable Programmable Read-Only Memory) are often used in industrial applications to store updateable
Application note EEPROM emulation in STM32F40x/STM32F41x microcontrollers Introduction EEPROMs (Electrically Erasable Programmable Read-Only Memory) are often used in industrial applications to store updateable
How To Write To An Eeprom Memory On A Flash Memory On An Iphone Or Ipro Memory On Microsoft Flash Memory (Eeprom) On A Microsoft Microsoft Powerbook (Ai) 2.2.2
 Application note EEPROM emulation in STM32F10x microcontrollers Introduction Many applications require EEPROM (electrically erasable programmable read-only memory) for non-volatile data storage. For low-cost
Application note EEPROM emulation in STM32F10x microcontrollers Introduction Many applications require EEPROM (electrically erasable programmable read-only memory) for non-volatile data storage. For low-cost
AN4571 Application note
 Application note STM32 BLE toolbox for Android Introduction The application note describes the STM32 Bluetooth low energy (BLE) toolbox Android application (STSW-STM32153) to be used with an Android 4.3
Application note STM32 BLE toolbox for Android Introduction The application note describes the STM32 Bluetooth low energy (BLE) toolbox Android application (STSW-STM32153) to be used with an Android 4.3
AN3265 Application note
 Application note Handling hardware and software failures with the STM8S-DISCOVERY Application overview This application is based on the STM8S-DISCOVERY. It demonstrates how to use the STM8S window watchdog
Application note Handling hardware and software failures with the STM8S-DISCOVERY Application overview This application is based on the STM8S-DISCOVERY. It demonstrates how to use the STM8S window watchdog
Getting started with software and firmware environments for the STM32F0DISCOVERY kit
 User manual Getting started with software and firmware environments for the STM32F0DISCOVERY kit Introduction This document describes the software, firmware environment and development recommendations
User manual Getting started with software and firmware environments for the STM32F0DISCOVERY kit Introduction This document describes the software, firmware environment and development recommendations
AN3307 Application note
 Application note Guidelines for obtaining IEC 60335 Class B certification for any STM32 application Introduction The role of safety has become very important for electronics applications. The level of
Application note Guidelines for obtaining IEC 60335 Class B certification for any STM32 application Introduction The role of safety has become very important for electronics applications. The level of
AN2824 Application note
 Application note STM32F10xxx I 2 C optimized examples Introduction The aim of this application note is to provide I 2 C firmware optimized examples based on polling, interrupts and DMA, covering the four
Application note STM32F10xxx I 2 C optimized examples Introduction The aim of this application note is to provide I 2 C firmware optimized examples based on polling, interrupts and DMA, covering the four
Figure 1. STM32F429 Discovery board: STM32F429I-DISCO
 User manual Getting started with the STM32F429 Discovery kit Introduction This document describes the software, firmware and hardware environments and development recommendations required to build an application
User manual Getting started with the STM32F429 Discovery kit Introduction This document describes the software, firmware and hardware environments and development recommendations required to build an application
Hello and welcome to this presentation of the STM32L4 Firewall. It covers the main features of this system IP used to secure sensitive code and data.
 Hello and welcome to this presentation of the STM32L4 Firewall. It covers the main features of this system IP used to secure sensitive code and data. 1 Here is an overview of the Firewall s implementation
Hello and welcome to this presentation of the STM32L4 Firewall. It covers the main features of this system IP used to secure sensitive code and data. 1 Here is an overview of the Firewall s implementation
AN3998 Application note
 Application note PDM audio software decoding on STM32 microcontrollers 1 Introduction This application note presents the algorithms and architecture of an optimized software implementation for PDM signal
Application note PDM audio software decoding on STM32 microcontrollers 1 Introduction This application note presents the algorithms and architecture of an optimized software implementation for PDM signal
UM1676 User manual. Getting started with.net Micro Framework on the STM32F429 Discovery kit. Introduction
 User manual Getting started with.net Micro Framework on the STM32F429 Discovery kit Introduction This document describes how to get started using the.net Micro Framework (alias NETMF) on the STM32F429
User manual Getting started with.net Micro Framework on the STM32F429 Discovery kit Introduction This document describes how to get started using the.net Micro Framework (alias NETMF) on the STM32F429
TN0072 Technical note
 TN0072 Technical note Introduction The documentation provides an overview of the STM32 devices and various toolchains. It provides information on the STM32 characteristics and how they are supported. Many
TN0072 Technical note Introduction The documentation provides an overview of the STM32 devices and various toolchains. It provides information on the STM32 characteristics and how they are supported. Many
AN3155 Application note
 Application note USART protocol used in the STM32 bootloader Introduction This application note describes the USART protocol used in the STM32 microcontroller bootloader. It details each supported command.
Application note USART protocol used in the STM32 bootloader Introduction This application note describes the USART protocol used in the STM32 microcontroller bootloader. It details each supported command.
AN2604 Application note
 AN2604 Application note STM32F101xx and STM32F103xx RTC calibration Introduction The real-time clock (RTC) precision is a requirement in most embedded applications, but due to external environment temperature
AN2604 Application note STM32F101xx and STM32F103xx RTC calibration Introduction The real-time clock (RTC) precision is a requirement in most embedded applications, but due to external environment temperature
AN3997 Application note
 Application note Audio playback and recording using the STM32F4DISCOVERY 1 Introduction This application note describes the audio (wave) playback and recording application based on the STM32F4xx microcontroller
Application note Audio playback and recording using the STM32F4DISCOVERY 1 Introduction This application note describes the audio (wave) playback and recording application based on the STM32F4xx microcontroller
AN3332 Application note
 Application note Generating PWM signals using STM8S-DISCOVERY Application overview This application user manual provides a short description of how to use the Timer 2 peripheral (TIM2) to generate three
Application note Generating PWM signals using STM8S-DISCOVERY Application overview This application user manual provides a short description of how to use the Timer 2 peripheral (TIM2) to generate three
AN3252 Application note
 Application note Building a wave generator using STM8L-DISCOVERY Application overview This application note provides a short description of how to use the STM8L-DISCOVERY as a basic wave generator for
Application note Building a wave generator using STM8L-DISCOVERY Application overview This application note provides a short description of how to use the STM8L-DISCOVERY as a basic wave generator for
AN10850. LPC1700 timer triggered memory to GPIO data transfer. Document information. LPC1700, GPIO, DMA, Timer0, Sleep Mode
 LPC1700 timer triggered memory to GPIO data transfer Rev. 01 16 July 2009 Application note Document information Info Keywords Abstract Content LPC1700, GPIO, DMA, Timer0, Sleep Mode This application note
LPC1700 timer triggered memory to GPIO data transfer Rev. 01 16 July 2009 Application note Document information Info Keywords Abstract Content LPC1700, GPIO, DMA, Timer0, Sleep Mode This application note
UM0834 User manual. Developing and debugging your STM8S-DISCOVERY application code. Introduction. Reference documents
 User manual Developing and debugging your STM8S-DISCOVERY application code Introduction This document complements the information in the STM8S datasheets by describing the software environment and development
User manual Developing and debugging your STM8S-DISCOVERY application code Introduction This document complements the information in the STM8S datasheets by describing the software environment and development
STLQ015. 150 ma, ultra low quiescent current linear voltage regulator. Description. Features. Application
 150 ma, ultra low quiescent current linear voltage regulator Description Datasheet - production data Features SOT23-5L Input voltage from 1.5 to 5.5 V Very low quiescent current: 1.0 µa (typ.) at no load
150 ma, ultra low quiescent current linear voltage regulator Description Datasheet - production data Features SOT23-5L Input voltage from 1.5 to 5.5 V Very low quiescent current: 1.0 µa (typ.) at no load
UM0586 User manual. STM32 Cryptographic Library. Introduction
 User manual STM32 Cryptographic Library Introduction This manual describes the API of the STM32 cryptographic library (STM32-CRYP-LIB) that supports the following cryptographic algorithms: AES-128, AES-192,
User manual STM32 Cryptographic Library Introduction This manual describes the API of the STM32 cryptographic library (STM32-CRYP-LIB) that supports the following cryptographic algorithms: AES-128, AES-192,
TWR-KV31F120M Sample Code Guide for IAR Board configuration, software, and development tools Rev.0
 TWR-KV31F120M Sample Code Guide for IAR Board configuration, software, and development tools Rev.0 Freescale TWR-KV31F120M Sample Code Guide for IAR KL25_LAB Contents 1 Purpose... 3 2 Getting to know the
TWR-KV31F120M Sample Code Guide for IAR Board configuration, software, and development tools Rev.0 Freescale TWR-KV31F120M Sample Code Guide for IAR KL25_LAB Contents 1 Purpose... 3 2 Getting to know the
STEVAL-IEG001V2. Smart real-time vehicle tracking system. Features
 Smart real-time vehicle tracking system Data brief Features Real-time vehicle tracking through GPS/GSM/GPRS. Vehicle location coordinates acquired using a Telit GPS module and sent over GPRS to web server-based
Smart real-time vehicle tracking system Data brief Features Real-time vehicle tracking through GPS/GSM/GPRS. Vehicle location coordinates acquired using a Telit GPS module and sent over GPRS to web server-based
HVP-KV31F120M Quick Start Guide
 HVP-KV31F120M Quick Start Guide Freescale Controller Card High Voltage Development Platform Quick Start Guide Get to Know the HVP-KV31F120M USB Mini for Communication, Debugging and Power Supply Isolated
HVP-KV31F120M Quick Start Guide Freescale Controller Card High Voltage Development Platform Quick Start Guide Get to Know the HVP-KV31F120M USB Mini for Communication, Debugging and Power Supply Isolated
Migrating Application Code from ARM Cortex-M4 to Cortex-M7 Processors
 Migrating Application Code from ARM Cortex-M4 to Cortex-M7 Processors Joseph Yiu and Robert Boys January 2015 Version 1.1 The latest version of this document is here: /appnotes/docs/apnt_270.asp 1 Cortex
Migrating Application Code from ARM Cortex-M4 to Cortex-M7 Processors Joseph Yiu and Robert Boys January 2015 Version 1.1 The latest version of this document is here: /appnotes/docs/apnt_270.asp 1 Cortex
SPC5-FLASHER. Flash management tool for SPC56xx family. Description. Features
 Flash management tool for SPC56xx family Data brief Flash verify: check the Flash content with a binary image file Unsecure sequence for censored device: sending the private password selected from the
Flash management tool for SPC56xx family Data brief Flash verify: check the Flash content with a binary image file Unsecure sequence for censored device: sending the private password selected from the
AN11241. AES encryption and decryption software on LPC microcontrollers. Document information
 AES encryption and decryption software on LPC microcontrollers Rev. 1 25 July 2012 Application note Document information Info Content Keywords AES, encryption, decryption, FIPS-197, Cortex-M0, Cortex-M3
AES encryption and decryption software on LPC microcontrollers Rev. 1 25 July 2012 Application note Document information Info Content Keywords AES, encryption, decryption, FIPS-197, Cortex-M0, Cortex-M3
UM1075 User manual. ST-LINK/V2 in-circuit debugger/programmer for STM8 and STM32. Introduction
 User manual ST-LINK/V2 in-circuit debugger/programmer for STM8 and STM32 Introduction The ST-LINK/V2 is an in-circuit debugger/programmer for the STM8 and STM32 microcontroller families. The single wire
User manual ST-LINK/V2 in-circuit debugger/programmer for STM8 and STM32 Introduction The ST-LINK/V2 is an in-circuit debugger/programmer for the STM8 and STM32 microcontroller families. The single wire
AN2680 Application note
 Application note Fan speed controller based on STDS75 or STLM75 digital temperature sensor and ST72651AR6 MCU Introduction This application note describes the method of defining the system for regulating
Application note Fan speed controller based on STDS75 or STLM75 digital temperature sensor and ST72651AR6 MCU Introduction This application note describes the method of defining the system for regulating
EVAL6491HB. Demonstration board for L6491 gate driver with smartsd. Description. Features
 Demonstration board for L6491 gate driver with smartsd Description Data brief Features High voltage rail up to 600 V dv/dt immunity: 50 V/ns in full temperature range Driver current capability: 4 A source/sink
Demonstration board for L6491 gate driver with smartsd Description Data brief Features High voltage rail up to 600 V dv/dt immunity: 50 V/ns in full temperature range Driver current capability: 4 A source/sink
AN10866 LPC1700 secondary USB bootloader
 Rev. 2 21 September 2010 Application note Document information Info Content Keywords LPC1700, Secondary USB Bootloader, ISP, IAP Abstract This application note describes how to add a custom secondary USB
Rev. 2 21 September 2010 Application note Document information Info Content Keywords LPC1700, Secondary USB Bootloader, ISP, IAP Abstract This application note describes how to add a custom secondary USB
STSW-IDW002. Hands-On Training for SPWF01SC and SPWF01SA Wi-Fi modules. Features. Description
 Hands-On Training for SPWF01SC and SPWF01SA Wi-Fi modules Data brief Features Hands-On Training to evaluate and learn the SPWF01Sx series of Wi-Fi modules on reference designs such as the X-NUCLEO- IDW01M1
Hands-On Training for SPWF01SC and SPWF01SA Wi-Fi modules Data brief Features Hands-On Training to evaluate and learn the SPWF01Sx series of Wi-Fi modules on reference designs such as the X-NUCLEO- IDW01M1
DSL03. Low capacitance TVS for high speed lines such as xdsl. Description. Features. Complies with the following standards
 Low capacitance TVS for high speed lines such as xdsl Description Datasheet - production data Features High surge capability to comply with GR-1089 and ITU-T K20/21 Keeps its peak power capability up to
Low capacitance TVS for high speed lines such as xdsl Description Datasheet - production data Features High surge capability to comply with GR-1089 and ITU-T K20/21 Keeps its peak power capability up to
AN4108 Application note
 Application note How to set up a HTTPS server for In-Home display with HTTPS Introduction This application note describes how to configure a simple SSL web server using the EasyPHP free application to
Application note How to set up a HTTPS server for In-Home display with HTTPS Introduction This application note describes how to configure a simple SSL web server using the EasyPHP free application to
Atmel AVR4920: ASF - USB Device Stack - Compliance and Performance Figures. Atmel Microcontrollers. Application Note. Features.
 Atmel AVR4920: ASF - USB Device Stack - Compliance and Performance Figures Features Compliance to USB 2.0 - Chapters 8 and 9 - Classes: HID, MSC, CDC, PHDC Interoperability: OS, classes, self- and bus-powered
Atmel AVR4920: ASF - USB Device Stack - Compliance and Performance Figures Features Compliance to USB 2.0 - Chapters 8 and 9 - Classes: HID, MSC, CDC, PHDC Interoperability: OS, classes, self- and bus-powered
SPC5-CRYP-LIB. SPC5 Software Cryptography Library. Description. Features. SHA-512 Random engine based on DRBG-AES-128
 SPC5 Software Cryptography Library Data brief SHA-512 Random engine based on DRBG-AES-128 RSA signature functions with PKCS#1v1.5 ECC (Elliptic Curve Cryptography): Key generation Scalar multiplication
SPC5 Software Cryptography Library Data brief SHA-512 Random engine based on DRBG-AES-128 RSA signature functions with PKCS#1v1.5 ECC (Elliptic Curve Cryptography): Key generation Scalar multiplication
AN4664 Application note
 Application note SPC56ELxx Automotive MCU multicore architectures and getting started Introduction This document provides an introduction to the world of multi-core MCU architectures and programming and
Application note SPC56ELxx Automotive MCU multicore architectures and getting started Introduction This document provides an introduction to the world of multi-core MCU architectures and programming and
AN3270 Application note
 Application note Using the STM8L16x AES hardware accelerator Introduction The purpose of cryptography is to protect sensitive data to avoid it being read by unauthorized persons. There are many algorithms
Application note Using the STM8L16x AES hardware accelerator Introduction The purpose of cryptography is to protect sensitive data to avoid it being read by unauthorized persons. There are many algorithms
Getting started with DfuSe USB device firmware upgrade STMicroelectronics extension
 User manual Getting started with DfuSe USB device firmware upgrade STMicroelectronics extension Introduction This document describes the demonstration user interface that was developed to illustrate use
User manual Getting started with DfuSe USB device firmware upgrade STMicroelectronics extension Introduction This document describes the demonstration user interface that was developed to illustrate use
UM1613 User manual. 16-pin smartcard interface ST8034P demonstration board. Introduction
 User manual 16-pin smartcard interface ST8034P demonstration board Introduction The purpose of this document is to describe, and provide information on, how to efficiently use the ST8034P smartcard interface
User manual 16-pin smartcard interface ST8034P demonstration board Introduction The purpose of this document is to describe, and provide information on, how to efficiently use the ST8034P smartcard interface
Software based Finite State Machine (FSM) with general purpose processors
 Software based Finite State Machine (FSM) with general purpose processors White paper Joseph Yiu January 2013 Overview Finite state machines (FSM) are commonly used in electronic designs. FSM can be used
Software based Finite State Machine (FSM) with general purpose processors White paper Joseph Yiu January 2013 Overview Finite state machines (FSM) are commonly used in electronic designs. FSM can be used
UM1075 User manual. ST-LINK/V2 in-circuit debugger/programmer for STM8 and STM32. Introduction
 User manual ST-LINK/V2 in-circuit debugger/programmer for STM8 and STM32 Introduction The ST-LINK/V2 is an in-circuit debugger/programmer for the STM8 and STM32 microcontroller families. The single wire
User manual ST-LINK/V2 in-circuit debugger/programmer for STM8 and STM32 Introduction The ST-LINK/V2 is an in-circuit debugger/programmer for the STM8 and STM32 microcontroller families. The single wire
Single LNB supply and control IC DiSEqC 1.X compliant with EXTM based on the LNBH29 in a QFN16 (4x4) Description
 Single LNB supply and control IC DiSEqC 1.X compliant with EXTM based on the LNBH29 in a QFN16 (4x4) Data brief Low-drop post regulator and high-efficiency step-up PWM with integrated power N-MOS allowing
Single LNB supply and control IC DiSEqC 1.X compliant with EXTM based on the LNBH29 in a QFN16 (4x4) Data brief Low-drop post regulator and high-efficiency step-up PWM with integrated power N-MOS allowing
Bootloader with AES Encryption
 ...the world's most energy friendly microcontrollers Bootloader with AES Encryption AN0060 - Application Note Introduction This application note describes the implementation of a bootloader capable of
...the world's most energy friendly microcontrollers Bootloader with AES Encryption AN0060 - Application Note Introduction This application note describes the implementation of a bootloader capable of
Atmel AVR4903: ASF - USB Device HID Mouse Application. Atmel Microcontrollers. Application Note. Features. 1 Introduction
 Atmel AVR4903: ASF - USB Device HID Mouse Application Features USB 2.0 compliance - Chapter 9 compliance - HID compliance - Low-speed (1.5Mb/s) and full-speed (12Mb/s) data rates Standard USB HID mouse
Atmel AVR4903: ASF - USB Device HID Mouse Application Features USB 2.0 compliance - Chapter 9 compliance - HID compliance - Low-speed (1.5Mb/s) and full-speed (12Mb/s) data rates Standard USB HID mouse
STM32 F-2 series High-performance Cortex-M3 MCUs
 STM32 F-2 series High-performance Cortex-M3 MCUs STMicroelectronics 32-bit microcontrollers, 120 MHz/150 DMIPS with ART Accelerator TM and advanced peripherals www.st.com/mcu STM32 F-2 series The STM32
STM32 F-2 series High-performance Cortex-M3 MCUs STMicroelectronics 32-bit microcontrollers, 120 MHz/150 DMIPS with ART Accelerator TM and advanced peripherals www.st.com/mcu STM32 F-2 series The STM32
ST19NP18-TPM-I2C. Trusted Platform Module (TPM) with I²C Interface. Features
 Trusted Platform Module (TPM) with I²C Interface Data brief Features Single-chip Trusted Platform Module (TPM) Embedded TPM 1.2 firmware I²C communication interface (Slave mode) Architecture based on ST19N
Trusted Platform Module (TPM) with I²C Interface Data brief Features Single-chip Trusted Platform Module (TPM) Embedded TPM 1.2 firmware I²C communication interface (Slave mode) Architecture based on ST19N
3. Programming the STM32F4-Discovery
 1 3. Programming the STM32F4-Discovery The programming environment including the settings for compiling and programming are described. 3.1. Hardware - The programming interface A program for a microcontroller
1 3. Programming the STM32F4-Discovery The programming environment including the settings for compiling and programming are described. 3.1. Hardware - The programming interface A program for a microcontroller
STPS5L60. Power Schottky rectifier. Description. Features
 Power Schottky rectifier Datasheet - production data Description Power Schottky rectifier suited for switch mode power supplies and high frequency inverters. This device is intended for use in low voltage
Power Schottky rectifier Datasheet - production data Description Power Schottky rectifier suited for switch mode power supplies and high frequency inverters. This device is intended for use in low voltage
50 ohm nominal input / conjugate match balun to nrf51822- CEAA/CDAB/CFAC and nrf51422-ceaa/cdab/cfac. Benefits. Description
 50 ohm nominal input / conjugate match balun to nrf51822- /CDAB/CFAC and nrf51422-/cdab/cfac Datasheet production data Benefits Very low profile: < 560 µm after reflow High RF performance RF BOM and area
50 ohm nominal input / conjugate match balun to nrf51822- /CDAB/CFAC and nrf51422-/cdab/cfac Datasheet production data Benefits Very low profile: < 560 µm after reflow High RF performance RF BOM and area
Getting started with the X-CUBE-SOUNDTER1 sound terminal software expansion for STM32Cube
 User manual Getting started with the X-CUBE-SOUNDTER1 sound terminal software expansion for STM32Cube Introduction This document describes how to get started with the X-CUBE-SOUNDTER1 software expansion
User manual Getting started with the X-CUBE-SOUNDTER1 sound terminal software expansion for STM32Cube Introduction This document describes how to get started with the X-CUBE-SOUNDTER1 software expansion
Description SO-8. Table 1. Device summary. Order codes. SO-8 (tape and reel) TO-92 (Bag) TO-92 (Ammopack) TO-92 (tape and reel)
 Low current 1.2 to 37 V adjustable voltage regulators Description Datasheet - production data TO-92 SO-8 TO-92 Tape and reel Bag Ammopack Features Outuput voltage range: 1.2 to 37 V Output current up to
Low current 1.2 to 37 V adjustable voltage regulators Description Datasheet - production data TO-92 SO-8 TO-92 Tape and reel Bag Ammopack Features Outuput voltage range: 1.2 to 37 V Output current up to
PAC52XX Clock Control Firmware Design
 APPLICATION NOTE PAC52XX Clock Control Firmware Design TM Marc Sousa Senior Manager, Systems and Firmware www.active-semi.com Copyright 2014 Active-Semi, Inc. TABLE OF CONTENTS APPLICATION NOTE... 1 Table
APPLICATION NOTE PAC52XX Clock Control Firmware Design TM Marc Sousa Senior Manager, Systems and Firmware www.active-semi.com Copyright 2014 Active-Semi, Inc. TABLE OF CONTENTS APPLICATION NOTE... 1 Table
Using C to Access Data Stored in Program Space Memory on the TMS320C24x DSP
 Application Report SPRA380 April 2002 Using C to Access Data Stored in Program Space Memory on the TMS320C24x DSP David M. Alter DSP Applications - Semiconductor Group ABSTRACT Efficient utilization of
Application Report SPRA380 April 2002 Using C to Access Data Stored in Program Space Memory on the TMS320C24x DSP David M. Alter DSP Applications - Semiconductor Group ABSTRACT Efficient utilization of
TS555. Low-power single CMOS timer. Description. Features. The TS555 is a single CMOS timer with very low consumption:
 Low-power single CMOS timer Description Datasheet - production data The TS555 is a single CMOS timer with very low consumption: Features SO8 (plastic micropackage) Pin connections (top view) (I cc(typ)
Low-power single CMOS timer Description Datasheet - production data The TS555 is a single CMOS timer with very low consumption: Features SO8 (plastic micropackage) Pin connections (top view) (I cc(typ)
Thermistor Calculator. Features. General Description. Input/Output Connections. When to use a Thermistor Calculator 1.10
 PSoC Creator Component Data Sheet Thermistor Calculator 1.10 Features Adaptable for majority of negative temperature coefficient (NTC) thermistors Look-Up-Table (LUT) or equation implementation methods
PSoC Creator Component Data Sheet Thermistor Calculator 1.10 Features Adaptable for majority of negative temperature coefficient (NTC) thermistors Look-Up-Table (LUT) or equation implementation methods
AN2389 Application note
 Application note An MCU-based low cost non-inverting buck-boost converter for battery chargers Introduction As the demand for rechargeable batteries increases, so does the demand for battery chargers.
Application note An MCU-based low cost non-inverting buck-boost converter for battery chargers Introduction As the demand for rechargeable batteries increases, so does the demand for battery chargers.
2STBN15D100. Low voltage NPN power Darlington transistor. Features. Application. Description
 Low voltage NPN power Darlington transistor Features Good h FE linearity High f T frequency Monolithic Darlington configuration with integrated antiparallel collector-emitter diode TAB Application Linear
Low voltage NPN power Darlington transistor Features Good h FE linearity High f T frequency Monolithic Darlington configuration with integrated antiparallel collector-emitter diode TAB Application Linear
Features. Description. Table 1. Device summary. Order code Marking Package Packing. STP110N8F6 110N8F6 TO-220 Tube
 N-channel 80 V, 0.0056 Ω typ.,110 A, STripFET F6 Power MOSFET in a TO-220 package Features Datasheet - production data Order code V DS R DS(on)max I D P TOT TAB STP110N8F6 80 V 0.0065 Ω 110 A 200 W TO-220
N-channel 80 V, 0.0056 Ω typ.,110 A, STripFET F6 Power MOSFET in a TO-220 package Features Datasheet - production data Order code V DS R DS(on)max I D P TOT TAB STP110N8F6 80 V 0.0065 Ω 110 A 200 W TO-220
EN: This Datasheet is presented by the m anufacturer. Please v isit our website for pricing and availability at www.hest ore.hu.
 EN: This Datasheet is presented by the m anufacturer. Please v isit our website for pricing and availability at www.hest ore.hu. 2N3055, MJ2955 Complementary power transistors Features Datasheet - production
EN: This Datasheet is presented by the m anufacturer. Please v isit our website for pricing and availability at www.hest ore.hu. 2N3055, MJ2955 Complementary power transistors Features Datasheet - production
Description. Table 1. Device summary
 2 A positive voltage regulator IC Description Datasheet - production data Features TO-220 Output current up to 2 A Output voltages of 5; 7.5; 9; 10; 12; 15; 18; 24 V Thermal protection Short circuit protection
2 A positive voltage regulator IC Description Datasheet - production data Features TO-220 Output current up to 2 A Output voltages of 5; 7.5; 9; 10; 12; 15; 18; 24 V Thermal protection Short circuit protection
AN3211 Application note
 Application note Using the simulated EEPROM with the STM32W108 platform 1 Introduction This document describes how to use the Simulated EEPROM in the STM32W108, gives an overview of the internal design,
Application note Using the simulated EEPROM with the STM32W108 platform 1 Introduction This document describes how to use the Simulated EEPROM in the STM32W108, gives an overview of the internal design,
The new 32-bit MSP432 MCU platform from Texas
 Technology Trend MSP432 TM microcontrollers: Bringing high performance to low-power applications The new 32-bit MSP432 MCU platform from Texas Instruments leverages its more than 20 years of lowpower leadership
Technology Trend MSP432 TM microcontrollers: Bringing high performance to low-power applications The new 32-bit MSP432 MCU platform from Texas Instruments leverages its more than 20 years of lowpower leadership
Ride7 for ARM. RAISONANCE Tools for the STRx and STM32 families. Overview and Getting Started
 Ride7 for ARM RAISONANCE Tools for the STRx and STM32 families Overview and Getting Started July 2007 Table of Contents 1. INTRODUCTION 4 1.1 RAISONANCE tools for the ARM family 6 1.2 Third party tools
Ride7 for ARM RAISONANCE Tools for the STRx and STM32 families Overview and Getting Started July 2007 Table of Contents 1. INTRODUCTION 4 1.1 RAISONANCE tools for the ARM family 6 1.2 Third party tools
M24LRxx/CR95HF application software installation guide
 User manual M24LRxx/CR95HF application software installation guide Introduction This user manual describes the procedures to install the different software drivers required to use the DEVKIT-M24LR-A development
User manual M24LRxx/CR95HF application software installation guide Introduction This user manual describes the procedures to install the different software drivers required to use the DEVKIT-M24LR-A development
etpu Host Interface by:
 Freescale Semiconductor Application Note AN2821 Rev. 2, 08/2007 etpu Host Interface by: David Paterson Ming Li MCD Applications 1 Introduction This application note discusses the enhanced Time Processing
Freescale Semiconductor Application Note AN2821 Rev. 2, 08/2007 etpu Host Interface by: David Paterson Ming Li MCD Applications 1 Introduction This application note discusses the enhanced Time Processing
LM337. Three-terminal adjustable negative voltage regulators. Features. Description
 Three-terminal adjustable negative voltage regulators Datasheet - production data current limit, thermal overload protection and safe area protection. All overload protection circuitry remains fully functional
Three-terminal adjustable negative voltage regulators Datasheet - production data current limit, thermal overload protection and safe area protection. All overload protection circuitry remains fully functional
Description. Table 1. Device summary. Order code Temperature range Package Packaging Marking
 14-stage ripple carry binary counter/divider and oscillator Applications Automotive Industrial Computer Consumer Description Datasheet - production data Features Medium speed operation Common reset Fully
14-stage ripple carry binary counter/divider and oscillator Applications Automotive Industrial Computer Consumer Description Datasheet - production data Features Medium speed operation Common reset Fully
Software development and debugging for NXP ARM7 MCUs
 THE MINISTRY of EDUCATION and SCIENCE of RUSSIAN FEDERATION SAMARA STATE AEROSPACE UNIVERSITY Software development and debugging for NXP ARM7 MCUs Learner s guide SAMARA 2011 2 Compilers: Kudryavtsev Ilya
THE MINISTRY of EDUCATION and SCIENCE of RUSSIAN FEDERATION SAMARA STATE AEROSPACE UNIVERSITY Software development and debugging for NXP ARM7 MCUs Learner s guide SAMARA 2011 2 Compilers: Kudryavtsev Ilya
ES_LPC4357/53/37/33. Errata sheet LPC4357/53/37/33. Document information
 Rev. 1.1 8 August 2012 Errata sheet Document information Info Keywords Abstract Content LPC4357FET256; LPC4357FET180; LPC4357FBD208; LPC4353FET256; LPC4353FET180; LPC4353FBD208; LPC4337FET256; LPC4337FET180;
Rev. 1.1 8 August 2012 Errata sheet Document information Info Keywords Abstract Content LPC4357FET256; LPC4357FET180; LPC4357FBD208; LPC4353FET256; LPC4353FET180; LPC4353FBD208; LPC4337FET256; LPC4337FET180;
Avoiding Read While Write Errors When Developing In-Software Flash Programming Applications for Kinetis and ColdFire+ MCUs
 Freescale Semiconductor Document Number:AN4695 Application Note Rev. 0, 04/2013 Avoiding Read While Write Errors When Developing In-Software Flash Programming Applications for Kinetis and ColdFire+ MCUs
Freescale Semiconductor Document Number:AN4695 Application Note Rev. 0, 04/2013 Avoiding Read While Write Errors When Developing In-Software Flash Programming Applications for Kinetis and ColdFire+ MCUs
Freescale Semiconductor, I
 nc. Application Note 6/2002 8-Bit Software Development Kit By Jiri Ryba Introduction 8-Bit SDK Overview This application note describes the features and advantages of the 8-bit SDK (software development
nc. Application Note 6/2002 8-Bit Software Development Kit By Jiri Ryba Introduction 8-Bit SDK Overview This application note describes the features and advantages of the 8-bit SDK (software development
Keil C51 Cross Compiler
 Keil C51 Cross Compiler ANSI C Compiler Generates fast compact code for the 8051 and it s derivatives Advantages of C over Assembler Do not need to know the microcontroller instruction set Register allocation
Keil C51 Cross Compiler ANSI C Compiler Generates fast compact code for the 8051 and it s derivatives Advantages of C over Assembler Do not need to know the microcontroller instruction set Register allocation
UM0462 User manual. STM32 and STM8 Flash loader demonstrator. Introduction
 User manual STM32 and STM8 Flash loader demonstrator Introduction The purpose of this document is to describe the STMicroelectronics STM32 and STM8 Flash loader demonstrator application that was developed
User manual STM32 and STM8 Flash loader demonstrator Introduction The purpose of this document is to describe the STMicroelectronics STM32 and STM8 Flash loader demonstrator application that was developed
AN2146 APPLICATION NOTE
 AN2146 APPLICATION NOTE STR71xF Embedded Flash Programming with ADS INTRODUCTION The purpose of this application note is to provide ARM Developer Suite (ADS) users with information to help them program
AN2146 APPLICATION NOTE STR71xF Embedded Flash Programming with ADS INTRODUCTION The purpose of this application note is to provide ARM Developer Suite (ADS) users with information to help them program
Technical Note. Micron NAND Flash Controller via Xilinx Spartan -3 FPGA. Overview. TN-29-06: NAND Flash Controller on Spartan-3 Overview
 Technical Note TN-29-06: NAND Flash Controller on Spartan-3 Overview Micron NAND Flash Controller via Xilinx Spartan -3 FPGA Overview As mobile product capabilities continue to expand, so does the demand
Technical Note TN-29-06: NAND Flash Controller on Spartan-3 Overview Micron NAND Flash Controller via Xilinx Spartan -3 FPGA Overview As mobile product capabilities continue to expand, so does the demand
SKP16C62P Tutorial 1 Software Development Process using HEW. Renesas Technology America Inc.
 SKP16C62P Tutorial 1 Software Development Process using HEW Renesas Technology America Inc. 1 Overview The following tutorial is a brief introduction on how to develop and debug programs using HEW (Highperformance
SKP16C62P Tutorial 1 Software Development Process using HEW Renesas Technology America Inc. 1 Overview The following tutorial is a brief introduction on how to develop and debug programs using HEW (Highperformance
BD241A BD241C. NPN power transistors. Features. Applications. Description. NPN transistors. Audio, general purpose switching and amplifier transistors
 BD241A BD241C NPN power transistors Features. NPN transistors Applications Audio, general purpose switching and amplifier transistors Description The devices are manufactured in Planar technology with
BD241A BD241C NPN power transistors Features. NPN transistors Applications Audio, general purpose switching and amplifier transistors Description The devices are manufactured in Planar technology with
Scanning Comparator (ScanComp) Features. General Description. Input/Output Connections. When to Use a Scanning Comparator. clock - Digital Input* 1.
 Scanning Comparator (ScanComp) 1.0 Features Scan up to 64 single ended or differential channels automatically Note The number of input and output channels will be limited by the hardware available in the
Scanning Comparator (ScanComp) 1.0 Features Scan up to 64 single ended or differential channels automatically Note The number of input and output channels will be limited by the hardware available in the
EVL185W-LEDTV. 185 W power supply with PFC and standby supply for LED TV based on the L6564, L6599A and Viper27L. Features.
 Features 185 W power supply with PFC and standby supply for LED TV based on the L6564, L6599A and Viper27L Data brief Universal input mains range: 90 264 Vac - frequency 45 65 Hz Output voltage 1: 130
Features 185 W power supply with PFC and standby supply for LED TV based on the L6564, L6599A and Viper27L Data brief Universal input mains range: 90 264 Vac - frequency 45 65 Hz Output voltage 1: 130
AVR1510: Xplain training - XMEGA USART. 8-bit Microcontrollers. Application Note. Prerequisites. 1 Introduction
 AVR1510: Xplain training - XMEGA USART Prerequisites Required knowledge AVR1500: Xplain training XMEGA Basics AVR1502: Xplain training XMEGA Direct Memory Access Controller Software prerequisites Atmel
AVR1510: Xplain training - XMEGA USART Prerequisites Required knowledge AVR1500: Xplain training XMEGA Basics AVR1502: Xplain training XMEGA Direct Memory Access Controller Software prerequisites Atmel
AN11008 Flash based non-volatile storage
 Rev. 1 5 January 2011 Application note Document information Info Content Keywords Flash, EEPROM, Non-Volatile Storage Abstract This application note describes the implementation and use of a library that
Rev. 1 5 January 2011 Application note Document information Info Content Keywords Flash, EEPROM, Non-Volatile Storage Abstract This application note describes the implementation and use of a library that
AVR033: Getting Started with the CodeVisionAVR C Compiler. 8-bit Microcontrollers. Application Note. Features. 1 Introduction
 AVR033: Getting Started with the CodeVisionAVR C Compiler Features Installing and Configuring CodeVisionAVR to Work with the Atmel STK 500 Starter Kit and AVR Studio Debugger Creating a New Project Using
AVR033: Getting Started with the CodeVisionAVR C Compiler Features Installing and Configuring CodeVisionAVR to Work with the Atmel STK 500 Starter Kit and AVR Studio Debugger Creating a New Project Using
AN4156 Application note
 Application note Hardware abstraction layer for Android Introduction This application note provides guidelines for successfully integrating STMicroelectronics sensors (accelerometer, magnetometer, gyroscope
Application note Hardware abstraction layer for Android Introduction This application note provides guidelines for successfully integrating STMicroelectronics sensors (accelerometer, magnetometer, gyroscope
AVR106: C Functions for Reading and Writing to Flash Memory. Introduction. Features. AVR 8-bit Microcontrollers APPLICATION NOTE
 AVR 8-bit Microcontrollers AVR106: C Functions for Reading and Writing to Flash Memory APPLICATION NOTE Introduction The Atmel AVR devices have a feature called Self programming Program memory. This feature
AVR 8-bit Microcontrollers AVR106: C Functions for Reading and Writing to Flash Memory APPLICATION NOTE Introduction The Atmel AVR devices have a feature called Self programming Program memory. This feature
