THE USE OF LIME MORTAR IN HISTORIC STRUCTURES. Technical Conservation Note 2 April 2004
|
|
|
- Edwina Lyons
- 9 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 THE USE OF LIME MORTAR IN HISTORIC STRUCTURES Technical Conservation Note 2 April 2004
2 1. Introduction The making of quicklime by heating limestone in kilns, and preparing mortars, plasters and whitewash from it, is an ancient practice, mentioned in the Old Testament. Many ancient examples of its use for example, lime plasters in the pyramids and Roman lime mortars survive to this day. This tradition continued until the patenting of Portland cement in 1824 heralded a steady decline in the use of lime for building. Today it is almost obsolete, apart from works on historic buildings. 2. What is lime? Limestone (calcium carbonate), when burnt in a kiln, loses carbon dioxide and becomes quicklime (calcium oxide). On contact with water, it combines with it, producing great heat, to form slaked lime (calcium hydroxide), also called lime putty. This gradually takes up carbon dioxide again from the air and changes back to calcium carbonate. This setting is called carbonation. Lime putty mixed with sand makes mortar. This then hardens into an artificial stone made up of grains of sand embedded in a mass of calcium carbonate. 3. Why use lime? Most pre-nineteenth-century buildings used lime mortars and plaster. Materials used to repair or replace original masonry should have similar properties so as not to disrupt the balance of interaction within the building. Cement pointing is particularly detrimental if applied to soft stone or bricks. It is hard, nonresilient and comparatively non-absorbent. Nor does it respond to the variations in the atmosphere to the same extent as the surrounding stone or brickwork. Hard pointing can cause rapid weathering of the softer stone or brick. Many causes of stone decay have been traced to the use of impervious mortar with a porous stone. In such cases saturation and evaporation are confined to the stone whereas the process should be distributed evenly over stone and pointing. Where a particularly soft stone is employed then the mortar should sacrifice itself for the stone. 4. Types of lime These notes assume the use of a non-hydraulic high calcium lime putty to prepare mortars etc. This should not be confused with other types of lime. Hydrated lime This is sold in most builders merchants as bags of dry powder. Soaked in just enough clean water, for at least twenty-four hours, it makes a lime putty. This putty may be of a poor quality due to carbonation of the powder occurring in the bag before use and the inclusion of unburnt/unslaked particles from the manufacturing process. Note: Only enough (ie not an excess) of water is used during the slaking stage so that the heat given off will result in the slaked powder containing lumps which are then crushed. In lime putty manufacture sieving takes place after slaking to remove any particles which have not reacted or are overburnt, as these will not carbonate properly. Hydraulic lime This is so called because of its ability to set under water without the presence of air. Some of these 1
3 limes can set as hard as Portland cement. However, there are a few feebly hydraulic limes available that, if used soon after slaking, can give good service in mortars. 5. Is the work really necessary? If the joints are only weathered back to a rough finish or if the mortar appears soft compared to modern mortars then repointing may be unnecessary. If the joints do not allow rain to penetrate or to rest in them it may be best to leave them alone. However, if they have weathered back by more than the joint thickness, or are partly or wholly open, then they probably require repointing. It is not necessary to point every open joint in a wall. The mortar, although weathered back, may still be sound. Unless recessed more than 12mm there should be no need to fill the joints. 6. Matching the mortar The new mortar should match the original in colour and texture as closely as possible. This is especially important if only partly repointing the wall. Mortar analysis can help achieve this. However a highly detailed chemical analysis is rarely necessary. A simple mortar analysis can carried out as follows: 1 Remove a piece of mortar from the wall. 2 Closely examine the sample, noting the texture, colour, etc. Note whether there are any bits of ash, charcoal, coal, lumps of lime etc. A 10x magnifying glass is useful for this. 3 Lightly crush it. 4 Mix it with water in a calibrated flask (a jam jar and a ruler will do) and stir thoroughly. 5 Allow it to stand and settle for approximately twelve hours. 6 Measure and calculate proportions. 7 Assess aggregate sizes and colours. A more detailed analysis, which is to be recommended, involves dissolving the lime in hydrochloric acid (dilute 10%, which can be bought as brick and cement cleaner.) The aggregates can then be identified by eye and comparisons made with known aggregate samples (after washing and drying). It can also be useful to grade the aggregate by using a set of British Standard sieves. By accurately weighing samples before and after dissolving the lime the approximate ratio of lime to aggregate can also be calculated. Note: care should be taken in areas of limestone, as sometimes this was crushed and used in the aggregate; thus the aggregate may also dissolve. The mortar's suitability for the stones or bricks and the location should also be considered. Bear in mind that the mortar should always be weaker than the materials it bonds but strong enough to resist weathering. 7. Aggregates When matching the aggregate of an historic mortar it may be necessary to mix several sands and/or gravels. Therefore it is essential to have a good knowledge of the sands available in a particular region. Take particular care about the grading of the replacement mortar's aggregate. It should be clean and well graded, ranging from fine to coarse, and gritty in texture. This produces a stronger mortar with less risk of shrinkage. Beware of artificially crushed stone dusts (especially limestone). These cause shrinkage problems, are weak and have poor adhesion. 2
4 The size of aggregate will depend upon the thickness of the mortar joint. Fine joints will not be able to accommodate large particles. When buying ready mixed lime:sand mortar specify the aggregates required and make sure they are supplied. 8. Mixes Even if lime:aggregate ratio has been calculated by mortar analysis, this may not be the ideal mix in a certain situation. For example, the mix may be too weak to survive in an exposed location; this may be the reason it failed in the first place. A good general mix comprises 1 part lime to 3 parts aggregate. It can be increased up to a maximum of 1 part lime to 4 parts aggregate in sheltered locations or decreased to a minimum of 1 part lime to 2 parts aggregate in exposed locations. On finely jointed stone or brick a suitable mix would be 1 part lime to 1 part aggregate. The above mixes can be gauged with a pozzolanic additive to give a more rapid set. This may be important if the work cannot be carried out in the spring or summer (the ideal times of year). 9. Pozzolanic Additives Pozzolana is a volcanic dust first found at Pozzuoli, near Naples, that when mixed with lime mortar causes it to set more quickly even in the presence of water. Pozzolan is the term now used for any material that performs the same task as pozzolana. Pulverized fuel ash (PFA): Ash extracted from power station flue gases, also known as fly ash. It is variable in colour, grading and pozzolanic ability. It may also contain significant amounts of sulphate, and therefore a low sulphate content should be specified. High temperature insulation (HTI) powder: Fireclay used to withstand high temperatures that has been finely ground. It can be purchased as such, or refractory bricks can be crushed. Brick dust Nothing more complicated than fired clay bricks that have been crushed. There is evidence that this has been used in the past so it may be found in the original mortar during analysis. Trass Volcanic ash found particularly in the region of Andernach, on the Rhine; thus a true pozzolan. White cement and Portland cement (OPC) Not pozzolans but true cements; ie they will set on their own in the presence of water. OPC is the grey cement that everybody is familiar with. It can have high strength and be rather impermeable. Soluble salts may migrate out of OPC into the masonry, possibly causing further damage. White cement is made from chalk and china clay. It is not as strong as OPC and is more expensive. In the past it has been common practice to gauge lime mortars with a small amount of cement, typically 1:2:9 and 1:1:6 (lime:cement:sand). However, recent research suggests that adding cement in small quantities weakens a mortar considerably and lowers its durability. 10. Mixing the mortar Coarse stuff is best mixed in advance of works and left to mature. This is easily done by storing in plastic sacks or tubs to exclude air. Mixing is best done by hand, mortar mill or pan mixer. A drum mixer can be used but as it relies on gravity it tends to just roll the lime putty around taking a long time to mix it with the aggregate. 3
5 Thorough mixing is essential. Turning it over with a shovel is not enough. In times past the practice was to chop, beat and ram the mortar, and this was certainly the best way. This can be achieved by ramming and beating with a timber and turning over and chopping with a shovel, giving increased contact between lime and aggregate and reducing water content. Mixing in this manner will give good workabilty and performance of the mortar. Knock up the coarse stuff in the same fashion before using, adding pozzolan if required in the following proportions (which may vary): Brick dust a minimum of 1 part brick dust to 20 parts coarse stuff HTI a minimum of 1 part HTI to 20 parts coarse stuff Trass a minimum of 1 part trass to 20 parts coarse stuff PFA 1 part PFA to 40 parts coarse stuff 11. Cutting out joints Rake joints out to a depth of at least twice the thickness of the joint, usually 25 50mm. If the mortar is soft, this may be accomplished using a bent spike or a knife blade. If hard, cut out using a quirk, plugging chisel or similar with a small club hammer. Never cut out joints with a disc cutter or chisels that could wedge in the joint and spall the masonry. On thin joints, a hacksaw or masonry saw can be used to good effect. Remove root growth in the wall at this stage. Brush joints out and thoroughly wash with a hose or, preferably, a garden sprayer. It is also essential that masonry and brickwork are well wetted just before pointing. 12. Filling joints Fill joints with mortar using pointing irons, made from steel bar, approximately 250mm long, flattened and curved at the ends to form blades of different widths to suit joints. Plasterers small tools can also be used, as can stainless steel spatulas that come in various sizes (obtainable from scientific suppliers). Even wood or pieces of small broken branch can be used and are very good for pushing in the mortar after initial shrinkage. A joint can be filled fully and evenly only with an implement that fits the said joint. No voids should remain. Deeper voids can be filled and tamped in with a slightly stronger mortar kept about 50mm back from the finished face of the pointing. Finish the joint slightly recessed, or struck and lined as required, copying any original pointing that remains. Medieval masons usually struck the pointing off flush with the face of the masonry. In the course of time the mortar has weathered back and the edges of the stone have become rounded off. Therefore to obtain a tight joint, the surface of the pointing should be slightly recessed so that the mortar does not spread over the rounded edges of the stone. If it is brought out to the surface of the stone a thin skin spreads over the edges of the stone. This skin will, in time, weather off, leaving a pocket enlarged by wind erosion. This will hold moisture, which will accelerate deterioration of the stonework through frost etc. After the initial set the mortar face may be weathered to match the existing pointing in one of the following ways. lightly spray with water and possibly brush with a soft paint brush to show the aggregate; stipple with a stiff bristle brush; dab with coarse sacking. 4
6 This also removes the lime particles that migrate to the surface of the joint; this is necessary to allow carbon dioxide to penetrate the full depth of the joint and facilitate full carbonation. Initial (surface) set of a lime:sand mortar usually takes approximately hours and of a lime:sand:cement mortar approximately hours, depending on temperature. In hot weather the pointing must be kept damp. This is achieved by lightly spraying, or by draping sacking which must be kept wet over the work. Pointing should not be carried out in frosty weather. If it is unavoidable then the work must be thoroughly protected. Concreting quilts are ideal for this, but expensive. Old carpet is a good alternative. 13. Filling fine joints Various methods have been employed over the years to accomplish this difficult task. Probably the simplest is to stick a strip of adhesive carpet tape over the joint. Cut the tape with a sharp knife and press the edges into the joint. The joint can then be filled with mortar and compacted using a pointing iron of suitable width, and the tape peeled away. 14. Bibliography Mortars, Plasters and Renders in Conservation John Ashurst First edition 1983, second edition forthcoming Ecclesiastical Architects and Surveyors Association Practical Building Conservation (5 vols) John and Nicola Ashurst 1988 Gower Technical Press Repair of Ancient Buildings A R Powys 1929, reprinted 1995 Technical Pamphlet 5: Repointing Stone and Brick Walling G. B. A. Williams 2002 Information sheet 9: An Introduction to Building Limes Michael Wingate Information sheet 4: The Need for Old Buildings to Breathe Phillip Hughes Building with Lime: A Practical Introduction Stafford Holmes, Michael Wingate 2002 ITDG Publishing ISBN Hydraulic Lime Mortar for Stone, Brick and Block Masonry Stafford Holmes, Mike Farey, Paul Livesey 2003 ISBN Lime in Building: a practical guide Jane Schofield 2002 Black Dog Press, available from Society for the Protection of Ancient Buildings 5
7 15. Further information If you would like further information on this subject, please contact us. Cadw Plas Carew Unit 5/7 Cefn Coed Parc Nantgarw Cardiff CF15 7QQ Tel
Repointing Stone and Brick
 TECHNICAL NOTE No. 37 April 1990 Updated January 2006 Repointing Stone and Brick (FORMERLY REPOINTING STONEWORK) 1. Historical Note Repointing of stone or brick walls is often carried out in conjunction
TECHNICAL NOTE No. 37 April 1990 Updated January 2006 Repointing Stone and Brick (FORMERLY REPOINTING STONEWORK) 1. Historical Note Repointing of stone or brick walls is often carried out in conjunction
BEST PRACTICE GUIDE. Fibrelime Premixed Universal Plaster and Render
 BEST PRACTICE GUIDE Fibrelime Premixed Universal Plaster and Render Contents: Fibrelime description Fibrelime suitability Preparation before application Application Aftercare Painting General Recommended
BEST PRACTICE GUIDE Fibrelime Premixed Universal Plaster and Render Contents: Fibrelime description Fibrelime suitability Preparation before application Application Aftercare Painting General Recommended
MASONRY RESTORATION Lime Putty Mortar Repointing Guide
 1.0 Preparation for Lime Putty Mortar Pointing 1.1 Tools & Approach A. Grinding - When used in a controlled way, angle grinders with diamond-impregnated metal blades with a maximum 1/8-inch-thickness and
1.0 Preparation for Lime Putty Mortar Pointing 1.1 Tools & Approach A. Grinding - When used in a controlled way, angle grinders with diamond-impregnated metal blades with a maximum 1/8-inch-thickness and
September 2014. Joint
 September 2014 Joint appearance and mortar use 2 Mortar Joints This paper outlines some of the background, composition and use of masonry mortars, with particular reference to those used for the construction
September 2014 Joint appearance and mortar use 2 Mortar Joints This paper outlines some of the background, composition and use of masonry mortars, with particular reference to those used for the construction
POINTING WITH LIME MORTARS. Public Information Leaflet
 POINTING WITH LIME MORTARS Public Information Leaflet Figure 1. This leaflet provides practical guidance on the use of soft, permeable lime mortars based on lime putty, which are ideal for repairing and
POINTING WITH LIME MORTARS Public Information Leaflet Figure 1. This leaflet provides practical guidance on the use of soft, permeable lime mortars based on lime putty, which are ideal for repairing and
SEE HOW TO MAKE LIME PLASTER WHY USE LIME? PATTI STOUTER, BUILD SIMPLE INC. FEBRUARY 2013
 SEE HOW TO MAKE LIME PLASTER PATTI STOUTER, BUILD SIMPLE INC. FEBRUARY 2013 WHY USE LIME? Lime plaster forms a light, clean, and durable surface that is resistant to weather and mold. A thin layer attaches
SEE HOW TO MAKE LIME PLASTER PATTI STOUTER, BUILD SIMPLE INC. FEBRUARY 2013 WHY USE LIME? Lime plaster forms a light, clean, and durable surface that is resistant to weather and mold. A thin layer attaches
Technical Advice Note
 Technical Advice Note Topic: Specifications for and use of traditional wet dash lime harling Reference Number: TAN1 When to harl Prior to about 1930, virtually all harling was wet dash and where harling
Technical Advice Note Topic: Specifications for and use of traditional wet dash lime harling Reference Number: TAN1 When to harl Prior to about 1930, virtually all harling was wet dash and where harling
Castle Conservation Range Preserving Britain s Heritage
 Uniclass L623 CI/SfB Yq1 EPIC F2121 Feb 08 Castle Conservation Range Preserving Britain s Heritage St Pancras Station, London (Natural Hydraulic Lime 3,5 & Ketton Freestone). Castle Conservation Range
Uniclass L623 CI/SfB Yq1 EPIC F2121 Feb 08 Castle Conservation Range Preserving Britain s Heritage St Pancras Station, London (Natural Hydraulic Lime 3,5 & Ketton Freestone). Castle Conservation Range
Historic Scotland advice: It is always better to leave masonry untouched rather than treat it incorrectly
 Shetland Islands Council Guidance Note 11 Lime Mortars and Renders Historic Scotland advice: It is always better to leave masonry untouched rather than treat it incorrectly Please Note: No responsibility
Shetland Islands Council Guidance Note 11 Lime Mortars and Renders Historic Scotland advice: It is always better to leave masonry untouched rather than treat it incorrectly Please Note: No responsibility
Resurfacing Concrete. Page 1 of 5
 Resurfacing Concrete Materials List QUIKRETE Concrete Resurfacer (No. 1131) (see calculator on page 5 for quantity needed) QUIKRETE Concrete and Stucco Wash (No. 8601) QUIKRETE Concrete Sealer (No. 8800)
Resurfacing Concrete Materials List QUIKRETE Concrete Resurfacer (No. 1131) (see calculator on page 5 for quantity needed) QUIKRETE Concrete and Stucco Wash (No. 8601) QUIKRETE Concrete Sealer (No. 8800)
Seven. Easy Steps. Your Own Walkway, Without Mortar. or Concrete. to Installing. Driveway and Patio
 Seven Easy Steps to Installing Your Own Walkway, Driveway and Patio Without Mortar or Concrete Brick is one of the world s oldest and most enduring building materials. Those same qualities also make it
Seven Easy Steps to Installing Your Own Walkway, Driveway and Patio Without Mortar or Concrete Brick is one of the world s oldest and most enduring building materials. Those same qualities also make it
PROPERTIES AND MIX DESIGNATIONS 5-694.200
 September 1, 2003 CONCRETE MANUAL 5-694.200 5-694.210 PROPERTIES OF CONCRETE PROPERTIES AND MIX DESIGNATIONS 5-694.200 Inspectors should familiarize themselves with the most important properties of concrete:
September 1, 2003 CONCRETE MANUAL 5-694.200 5-694.210 PROPERTIES OF CONCRETE PROPERTIES AND MIX DESIGNATIONS 5-694.200 Inspectors should familiarize themselves with the most important properties of concrete:
Saint Gobain Gyproc India Ltd. (Formerly India Gypsum Ltd.)
 Saint Gobain Gyproc India Ltd. (Formerly India Gypsum Ltd.) Gyproc Plasters The cracks in cement sand plaster are an inherent feature which cannot be completely prevented but can only be controlled and
Saint Gobain Gyproc India Ltd. (Formerly India Gypsum Ltd.) Gyproc Plasters The cracks in cement sand plaster are an inherent feature which cannot be completely prevented but can only be controlled and
:: ARTIFICIAL SAND :: Zone One Sand : Zone Two Sand :
 :: ARTIFICIAL SAND :: Natural sand are weathered and worn out particles of rocks and are of various grades or size depending on the accounting of wearing. The main natural and cheapest resource of sand
:: ARTIFICIAL SAND :: Natural sand are weathered and worn out particles of rocks and are of various grades or size depending on the accounting of wearing. The main natural and cheapest resource of sand
Guidelines for Durable Driveways, Carports Patios, Walks, Garage Floors
 Guidelines for Durable Driveways, Carports Patios, Walks, Garage Floors The Right Concrete Mix Placing and Finishing Joints Correctly Spaced Curing for Durability "Concrete durability is the ability to
Guidelines for Durable Driveways, Carports Patios, Walks, Garage Floors The Right Concrete Mix Placing and Finishing Joints Correctly Spaced Curing for Durability "Concrete durability is the ability to
PROJECT PROFILE ON CEMENT CONCRETE HOLLOW BLOCKS
 PROJECT PROFILE ON CEMENT CONCRETE HOLLOW BLOCKS PRODUCT : Cement Concrete Hollow Blocks NIC CODE : 26959 (based on NIC 2004) PRODUCT CODE : 94459 (based on ASICC 2000) PRODUCTION CAPACITY : Quantity :
PROJECT PROFILE ON CEMENT CONCRETE HOLLOW BLOCKS PRODUCT : Cement Concrete Hollow Blocks NIC CODE : 26959 (based on NIC 2004) PRODUCT CODE : 94459 (based on ASICC 2000) PRODUCTION CAPACITY : Quantity :
Choosing the Right Mortar for the Job
 Choosing the Right Mortar for the Job by Michael Schuller, P.E. President, Atkinson-Noland & Associates 2619 Spruce St. Boulder, CO 80302 www.ana-usa.com Modern material technology has given us strong
Choosing the Right Mortar for the Job by Michael Schuller, P.E. President, Atkinson-Noland & Associates 2619 Spruce St. Boulder, CO 80302 www.ana-usa.com Modern material technology has given us strong
Specification Guidelines
 Specification Guidelines Heritage Traditional Building Products Ltd. T: +44 (0)28 2568 5055 Fax: +44 (0)28 2568 5831 Email: [email protected] Web site: www.heritageltd.com IMPORTANT NOTICE The company
Specification Guidelines Heritage Traditional Building Products Ltd. T: +44 (0)28 2568 5055 Fax: +44 (0)28 2568 5831 Email: [email protected] Web site: www.heritageltd.com IMPORTANT NOTICE The company
LAYING BLOCK AND BRICK
 LAYING BLOCK AND BRICK Products highlighted in this section: SAKRETE Type N Mortar Mix SAKRETE Type S Mortar Mix Brick And Block Laying Basics The first step in building a brick or block wall is to construct
LAYING BLOCK AND BRICK Products highlighted in this section: SAKRETE Type N Mortar Mix SAKRETE Type S Mortar Mix Brick And Block Laying Basics The first step in building a brick or block wall is to construct
Chapter Two Types of Cement The properties of cement during hydration vary according to:
 Chapter Two Types of Cement The properties of cement during hydration vary according to: Chemical composition Degree of fineness It is possible to manufacture different types of cement by changing the
Chapter Two Types of Cement The properties of cement during hydration vary according to: Chemical composition Degree of fineness It is possible to manufacture different types of cement by changing the
The history of brick in Scotland Signs of deterioration in brickwork Causes of deterioration Repair and maintenance of brick structures
 Repairing brickwork Introduction Bricks can be defined as small rectangular blocks of fired clay. They come in a variety of sizes, shapes and colours. They also vary in age and quality. A large number
Repairing brickwork Introduction Bricks can be defined as small rectangular blocks of fired clay. They come in a variety of sizes, shapes and colours. They also vary in age and quality. A large number
GRADATION OF AGGREGATE FOR CONCRETE BLOCK
 GRADATION OF AGGREGATE FOR CONCRETE BLOCK Although numerous papers have been written concerning the proper gradation for concrete mixes, they have generally dealt with plastic mixes, and very little published
GRADATION OF AGGREGATE FOR CONCRETE BLOCK Although numerous papers have been written concerning the proper gradation for concrete mixes, they have generally dealt with plastic mixes, and very little published
EDUCATIONAL GUIDE TO PROPERTIES OF MASONRY MORTAR
 EDUCATIONAL GUIDE TO PROPERTIES OF MASONRY MORTAR Contents Page Introduction 3 Specifying mortar 3 Properties of plastic mortar 4 Properties of hardened mortar 8 Glossary of terms 13 Bibliography 14 Self-assessment
EDUCATIONAL GUIDE TO PROPERTIES OF MASONRY MORTAR Contents Page Introduction 3 Specifying mortar 3 Properties of plastic mortar 4 Properties of hardened mortar 8 Glossary of terms 13 Bibliography 14 Self-assessment
CORROSION ENGINEERING RESIN-BASED POLYMER CONCRETES AND GROUTS
 AN ERGONARMOR COMPANY TECHNICAL INFORMATION SPECIFICATION FOR INSTALLATION 07/11 SUPERSEDES 04/00 PAGE 1 OF 6 CORROSION ENGINEERING RESIN-BASED POLYMER CONCRETES AND GROUTS 1. SCOPE 1.1 This specification
AN ERGONARMOR COMPANY TECHNICAL INFORMATION SPECIFICATION FOR INSTALLATION 07/11 SUPERSEDES 04/00 PAGE 1 OF 6 CORROSION ENGINEERING RESIN-BASED POLYMER CONCRETES AND GROUTS 1. SCOPE 1.1 This specification
DryWeight BulkVolume
 Test Procedure for BULK SPECIFIC GRAVITY AND WATER ABSORPTION OF AGGREGATE TxDOT Designation: Tex-201-F Effective Date: January 2016 1. SCOPE 1.1 Use this method to determine the bulk specific gravity
Test Procedure for BULK SPECIFIC GRAVITY AND WATER ABSORPTION OF AGGREGATE TxDOT Designation: Tex-201-F Effective Date: January 2016 1. SCOPE 1.1 Use this method to determine the bulk specific gravity
Lab 1 Concrete Proportioning, Mixing, and Testing
 Lab 1 Concrete Proportioning, Mixing, and Testing Supplemental Lab manual Objectives Concepts Background Experimental Procedure Report Requirements Discussion Prepared By Mutlu Ozer Objectives Students
Lab 1 Concrete Proportioning, Mixing, and Testing Supplemental Lab manual Objectives Concepts Background Experimental Procedure Report Requirements Discussion Prepared By Mutlu Ozer Objectives Students
What is Cement? History Overview of the Cement Manufacturing Process Brief Overview of Kiln Operations Why Burn Wastes?
 What is Cement? History Overview of the Cement Manufacturing Process Brief Overview of Kiln Operations Why Burn Wastes? A hydraulic cement made by finely pulverizing the clinker produced by calcining to
What is Cement? History Overview of the Cement Manufacturing Process Brief Overview of Kiln Operations Why Burn Wastes? A hydraulic cement made by finely pulverizing the clinker produced by calcining to
OLD BRICK ORIGINALS KILN-FIRED THIN BRICK VENEER Installation Guide. GeneralShale.com
 OLD BRICK ORIGINALS KILN-FIRED THIN BRICK VENEER Installation Guide GeneralShale.com OLD BRICK ORIGINALS THIN BRICK VENEER Page 2 INTRODUCTION Check local building codes for proper installation guidelines
OLD BRICK ORIGINALS KILN-FIRED THIN BRICK VENEER Installation Guide GeneralShale.com OLD BRICK ORIGINALS THIN BRICK VENEER Page 2 INTRODUCTION Check local building codes for proper installation guidelines
CGA Standard Practices Series. Article 600 Standard for Pozzolan Enhanced Grouts Used in Annular Seals & Well Destruction
 California Groundwater Association An NGWA Affiliate State PO Box 14369 Santa Rosa CA 95402 707-578-4408 fax: 707-546-4906 email: [email protected] website: www.groundh2o.org CGA Standard Practices Series
California Groundwater Association An NGWA Affiliate State PO Box 14369 Santa Rosa CA 95402 707-578-4408 fax: 707-546-4906 email: [email protected] website: www.groundh2o.org CGA Standard Practices Series
The rock cycle. Introduction. What are rocks?
 The rock cycle This Revision looks at the three types of rock: sedimentary, igneous and metamorphic. It looks at how they are formed, the weathering of rocks and the way one form of rock turns into another,
The rock cycle This Revision looks at the three types of rock: sedimentary, igneous and metamorphic. It looks at how they are formed, the weathering of rocks and the way one form of rock turns into another,
Improving the flood resistance of your home. Advice sheet 4: Flood-resilient walls.
 Improving the flood resistance of your home Advice sheet 4: Flood-resilient walls. This sheet provides guidance on identifying different types of wall, and reducing the flow of floodwater through them
Improving the flood resistance of your home Advice sheet 4: Flood-resilient walls. This sheet provides guidance on identifying different types of wall, and reducing the flow of floodwater through them
TECHNICAL SPECIFICATIONS CONCRETE SIDEWALKS, DRIVEWAYS AND CURB AND GUTTER
 TECHNICAL SPECIFICATIONS CONCRETE SIDEWALKS, DRIVEWAYS AND CURB AND GUTTER I. Scope of Work Work done under this item shall consist of the construction, reconstruction, or alteration of a one-course Portland
TECHNICAL SPECIFICATIONS CONCRETE SIDEWALKS, DRIVEWAYS AND CURB AND GUTTER I. Scope of Work Work done under this item shall consist of the construction, reconstruction, or alteration of a one-course Portland
FACT SHEET: HYDRATED LIME FOR MASONRY PURPOSES
 FACT SHEET: HYDRATED LIME FOR MASONRY PURPOSES Hydrated Masons Lime Characteristics Type S (Special) hydrated lime is a fine, white, high purity product which has been specially hydrated for convenient,
FACT SHEET: HYDRATED LIME FOR MASONRY PURPOSES Hydrated Masons Lime Characteristics Type S (Special) hydrated lime is a fine, white, high purity product which has been specially hydrated for convenient,
EDUCATIONAL GUIDE TO CEMENTITIOUS MATERIALS
 EDUCATIONAL GUIDE TO CEMENTITIOUS MATERIALS Contents Page Introduction 3 Portland cement 3 Manufacture 3 Properties 4 British/European standards 4 Nomenclature for cements 5 Types of cement 7 Ground granulated
EDUCATIONAL GUIDE TO CEMENTITIOUS MATERIALS Contents Page Introduction 3 Portland cement 3 Manufacture 3 Properties 4 British/European standards 4 Nomenclature for cements 5 Types of cement 7 Ground granulated
1.5 Concrete (Part I)
 1.5 Concrete (Part I) This section covers the following topics. Constituents of Concrete Properties of Hardened Concrete (Part I) 1.5.1 Constituents of Concrete Introduction Concrete is a composite material
1.5 Concrete (Part I) This section covers the following topics. Constituents of Concrete Properties of Hardened Concrete (Part I) 1.5.1 Constituents of Concrete Introduction Concrete is a composite material
cement Masonry Cement Engineered for quality and reliability, Lafarge cements for masonry deliver consistent performance. page 2 Lafarge Cement
 cement Masonry Cement Engineered for quality and reliability, Lafarge cements for masonry deliver consistent performance. page 2 Lafarge Cement Lafarge in North America The Lafarge Group is the world leader
cement Masonry Cement Engineered for quality and reliability, Lafarge cements for masonry deliver consistent performance. page 2 Lafarge Cement Lafarge in North America The Lafarge Group is the world leader
Monocouche Best Practice Guide. New-Build Housing Managing movement to avoid cracking
 Monocouche Best Practice Guide New-Build Housing Managing movement to avoid cracking Avoiding Cracking For The Designer Visible cracks in render are unsightly and although not hazardous to the construction
Monocouche Best Practice Guide New-Build Housing Managing movement to avoid cracking Avoiding Cracking For The Designer Visible cracks in render are unsightly and although not hazardous to the construction
FIXIT.CH. Aerogel Insulating Plaster System. Handling Guidelines. Easy to use. Mineral based. 0.028 W/mK BAUSTOFFE MIT SYSTEM
 FIXIT.CH Aerogel Insulating Plaster System Handling Guidelines BAUSTOFFE MIT SYSTEM λ 0.028 W/mK Mineral based Easy to use Efficient building insulation using space technology Aerogel high-performance
FIXIT.CH Aerogel Insulating Plaster System Handling Guidelines BAUSTOFFE MIT SYSTEM λ 0.028 W/mK Mineral based Easy to use Efficient building insulation using space technology Aerogel high-performance
METHOD A10 (a) THE DETERMINATION OF THE IN-PLACE DRY DENSITY OF SOIL OR GRAVEL BY THE SAND REPLACEMENT METHOD
 METHOD A10 (a) THE DETERMINATION OF THE IN-PLACE DRY DENSITY OF SOIL OR GRAVEL BY THE SAND REPLACEMENT METHOD 1 SCOPE The in-place dry density of compacted soil or gravel, as defined below, is determined
METHOD A10 (a) THE DETERMINATION OF THE IN-PLACE DRY DENSITY OF SOIL OR GRAVEL BY THE SAND REPLACEMENT METHOD 1 SCOPE The in-place dry density of compacted soil or gravel, as defined below, is determined
Construction. Pre-Bagged Structural Waterproofing System. Product Description. Product Data. Tests. Form
 Construction Product Data Sheet Edition 15/07/2013 Identification no: 01 07 05 04 001 0 000001 Sika 1 Pre-Bagged Structural Waterproofing System Product Description Pre-Bagged Structural Waterproofing
Construction Product Data Sheet Edition 15/07/2013 Identification no: 01 07 05 04 001 0 000001 Sika 1 Pre-Bagged Structural Waterproofing System Product Description Pre-Bagged Structural Waterproofing
DIY CABINET REFACING INSTALLATION GUIDE
 DIY CABINET REFACING INSTALLATION GUIDE CABINET REFACING INSTALLATION Are you ready to reface your outdated cabinets? This guide will show you how to install your new Facelifters Cabinet Refacing Products
DIY CABINET REFACING INSTALLATION GUIDE CABINET REFACING INSTALLATION Are you ready to reface your outdated cabinets? This guide will show you how to install your new Facelifters Cabinet Refacing Products
VC 104+ Rigid Grade / Rigid Grade Imagine VC 104 Rigid Grade Commercial Customised
 Page 1 of 6 instructions VC 104+ Rigid Grade / VC 104+ Rigid Grade Imagine / (for the rest of this document referred to as VC 104) can be applied to new and used trucks and trailers with painted rigid
Page 1 of 6 instructions VC 104+ Rigid Grade / VC 104+ Rigid Grade Imagine / (for the rest of this document referred to as VC 104) can be applied to new and used trucks and trailers with painted rigid
Standard Test Procedures Manual
 STP 206-4 Standard Test Procedures Manual Section: 1. SCOPE 1.1. Description of Test This method describes the procedure for determining the liquid limit, plastic limit and the plasticity index of coarse-grained
STP 206-4 Standard Test Procedures Manual Section: 1. SCOPE 1.1. Description of Test This method describes the procedure for determining the liquid limit, plastic limit and the plasticity index of coarse-grained
How to build a Pizza Oven in 4 days
 How to build a Pizza Oven in 4 days Preparation day (slab) 1. Foundation 1500 deep x 1300 wide x 75mm deep Required 20 bags cement pre mix. If you already have a concrete base, you save this prep day DAY
How to build a Pizza Oven in 4 days Preparation day (slab) 1. Foundation 1500 deep x 1300 wide x 75mm deep Required 20 bags cement pre mix. If you already have a concrete base, you save this prep day DAY
Construction. 3-part thixotropic epoxy patching mortar. Product Description. Tests
 Product Data Sheet Edition 05/12/2014 Identification no: 020204030010000044 Sikadur -41 CF Rapid 3-part thixotropic epoxy patching mortar Construction Product Description Uses Characteristics / Advantages
Product Data Sheet Edition 05/12/2014 Identification no: 020204030010000044 Sikadur -41 CF Rapid 3-part thixotropic epoxy patching mortar Construction Product Description Uses Characteristics / Advantages
Minor Cracks in Horizontal Surfaces
 Cracks, chips and broken or flaking areas in concrete are not only unsightly, they can lead to further deterioration of the surface. The result is a costly replacement project as opposed to a simple repair.
Cracks, chips and broken or flaking areas in concrete are not only unsightly, they can lead to further deterioration of the surface. The result is a costly replacement project as opposed to a simple repair.
DIY GUIDE 10 EASY STEPS FOR TREATMENT OF RISING DAMP
 DIY GUIDE 10 EASY STEPS FOR TREATMENT OF RISING DAMP CONTENTS WHAT IS RISING DAMP STEP 1 SURVEY STEP 2 METER READINGS STEP 3 CONCLUSION STEP 4 PREPARATION FOR TREATMENT STEP 5 TYPE OF TREATMENT STEP 6
DIY GUIDE 10 EASY STEPS FOR TREATMENT OF RISING DAMP CONTENTS WHAT IS RISING DAMP STEP 1 SURVEY STEP 2 METER READINGS STEP 3 CONCLUSION STEP 4 PREPARATION FOR TREATMENT STEP 5 TYPE OF TREATMENT STEP 6
METHOD A7 THE DETERMINATION OF THE MAXIMUM DRY DENSITY AND OPTIMUM MOISTURE CONTENT OF GRAVEL, SOIL AND SAND
 SCOPE METHOD A7 THE DETERMINATION OF THE MAXIMUM DRY DENSITY AND OPTIMUM MOISTURE CONTENT OF GRAVEL, SOIL AND SAND Definition The maximum dry density and optimum moisture content, as defined below, is
SCOPE METHOD A7 THE DETERMINATION OF THE MAXIMUM DRY DENSITY AND OPTIMUM MOISTURE CONTENT OF GRAVEL, SOIL AND SAND Definition The maximum dry density and optimum moisture content, as defined below, is
Short Guide. Lime Mortars in Traditional Buildings
 6 Short Guide Lime Mortars in Traditional Buildings ISBN 978-1-84917-177-5 All images unless otherwise noted are Crown Copyright Principal Authors: Jessica Snow and Clare Torney Published by Historic Scotland,
6 Short Guide Lime Mortars in Traditional Buildings ISBN 978-1-84917-177-5 All images unless otherwise noted are Crown Copyright Principal Authors: Jessica Snow and Clare Torney Published by Historic Scotland,
K2 STONE NATURAL VENEER
 INTRODUCTION WHAT IS K2 NATURAL THINSTONE VENEER? Natural K2 Stone veneer is real stone, cut 1 inch thick, making it light enough to be installed as a veneer. Sometimes referred to as thin veneer, thin
INTRODUCTION WHAT IS K2 NATURAL THINSTONE VENEER? Natural K2 Stone veneer is real stone, cut 1 inch thick, making it light enough to be installed as a veneer. Sometimes referred to as thin veneer, thin
Lay blocks with mortar
 Student Lay blocks with mortar What you will learn When you have fi nished this section, you should be able to: Mix mortar Lay blocks with correct mortar joints. How do I mix mortar? Mortar is a wet paste
Student Lay blocks with mortar What you will learn When you have fi nished this section, you should be able to: Mix mortar Lay blocks with correct mortar joints. How do I mix mortar? Mortar is a wet paste
New Refractory Technology Provides Advantages in Monolithic Refractories
 New Refractory Technology Provides Advantages in Monolithic Refractories There have been a number of different refractory binder systems introduced and utilized over the last 100 years. The most long-standing
New Refractory Technology Provides Advantages in Monolithic Refractories There have been a number of different refractory binder systems introduced and utilized over the last 100 years. The most long-standing
White rust on galvanized and galvanized pre-painted steel. Technical Information
 Technical Information White rust on galvanised steel Prevention It is easier to prevent white rust than to cure it! Reasonable precautions to protect steel during both transport and storage can considerably
Technical Information White rust on galvanised steel Prevention It is easier to prevent white rust than to cure it! Reasonable precautions to protect steel during both transport and storage can considerably
CHAPTER NO. 27 QUANTITIES OF MATERIALS
 CHAPTER NO. 27 QUANTITIES OF MATERIALS Note :- One cement bag weighs 50 kg. and measures 0.03472 cum. Sr. No. Description Unit Quantities Fine aggregates Coarse aggregates 1 2 3 4 5 6 27.1 Cement concrete
CHAPTER NO. 27 QUANTITIES OF MATERIALS Note :- One cement bag weighs 50 kg. and measures 0.03472 cum. Sr. No. Description Unit Quantities Fine aggregates Coarse aggregates 1 2 3 4 5 6 27.1 Cement concrete
Installation PowerPoint for Grasscrete Formers
 Installation PowerPoint for Grasscrete Formers 1 This document describes the two single-use tools utilized to create the Grasscrete product. The original Former is a vacuum formed light gauge plastic mold
Installation PowerPoint for Grasscrete Formers 1 This document describes the two single-use tools utilized to create the Grasscrete product. The original Former is a vacuum formed light gauge plastic mold
3 Masonry and Manufactured Stone (Interior and Exterior)
 3 Masonry and Manufactured Stone (Interior and Exterior) 3.1 Efflorescence (a whitish crystalline powder) is present on masonry surfaces. Efflorescence commonly occurs on masonry surfaces. This is not
3 Masonry and Manufactured Stone (Interior and Exterior) 3.1 Efflorescence (a whitish crystalline powder) is present on masonry surfaces. Efflorescence commonly occurs on masonry surfaces. This is not
ARDEX GUIDE SPECIFICATION ARDEX Exterior Concrete Repair & Resurfacing Polymer-Modified, Cement-Based, Patch & Horizontal Overlay Materials
 ARDEX GUIDE SPECIFICATION ARDEX Exterior Concrete Repair & Resurfacing Polymer-Modified, Cement-Based, Patch & Horizontal Overlay Materials SECTION 03 92 50 PART 1 - GENERAL 1.1 RELATED DOCUMENTS A. Drawings,
ARDEX GUIDE SPECIFICATION ARDEX Exterior Concrete Repair & Resurfacing Polymer-Modified, Cement-Based, Patch & Horizontal Overlay Materials SECTION 03 92 50 PART 1 - GENERAL 1.1 RELATED DOCUMENTS A. Drawings,
Chapter 7: Pavement Rehabilitation 7-1 Asphalt Pavement Overlays 7-1 Surface Preparation Methods 7-2 Concrete Pavement Preparation 7-3 Recycling
 7-1 Asphalt Pavement Overlays 7-1 Surface Preparation Methods 7-2 Concrete Pavement Preparation 7-3 Recycling Asphalt Pavements 7-7 Chapter 7 Pavement Rehabilitation Pavement rehabilitation can be accomplished
7-1 Asphalt Pavement Overlays 7-1 Surface Preparation Methods 7-2 Concrete Pavement Preparation 7-3 Recycling Asphalt Pavements 7-7 Chapter 7 Pavement Rehabilitation Pavement rehabilitation can be accomplished
AGREGADOS RECICLADOS MITOS Y REALIDADES
 The Production and Use of Recycled Concrete in the USA Thomas Van Dam, Ph.D., P.E., FACI Principal Engineer CTL Group Introduction In the United States, concrete is the most commonly used recycled material
The Production and Use of Recycled Concrete in the USA Thomas Van Dam, Ph.D., P.E., FACI Principal Engineer CTL Group Introduction In the United States, concrete is the most commonly used recycled material
SECTION 623 CONCRETE BONDING COMPOUND, EPOXY MORTAR AND EPOXY POLYMER CONCRETE OVERLAY SECTION 623.10 CONCRETE BONDING COMPOUND.
 SECTION 623 CONCRETE BONDING COMPOUND, EPOXY MORTAR AND EPOXY POLYMER CONCRETE OVERLAY SECTION 623.10 CONCRETE BONDING COMPOUND. 623.10.1 Description. This work shall consist of preparing the surface,
SECTION 623 CONCRETE BONDING COMPOUND, EPOXY MORTAR AND EPOXY POLYMER CONCRETE OVERLAY SECTION 623.10 CONCRETE BONDING COMPOUND. 623.10.1 Description. This work shall consist of preparing the surface,
Screen Melts. Introduction. Selecting Screen Material. Prefire Before Using. Spalling. Kiln Shelf
 Introduction There are two terrific reasons for melting glass through screens. First because screen melts produce uniquely intricate patterns not possible any other way and second because it does it using
Introduction There are two terrific reasons for melting glass through screens. First because screen melts produce uniquely intricate patterns not possible any other way and second because it does it using
Your guide to home maintenance. Flat Roofs
 Your guide to home maintenance Flat Roofs Your guide to home maintenance is a series of information leaflets that gives you all the information you need to keep your home in tiptop condition. Flat Roofs
Your guide to home maintenance Flat Roofs Your guide to home maintenance is a series of information leaflets that gives you all the information you need to keep your home in tiptop condition. Flat Roofs
Metropolitan Builders Association Masonry & Concrete Standard
 Metropolitan Builders Association Masonry & Concrete Standard Background Masonry and concrete work in residential construction often provides the base structure upon which the house is built or as a veneer.
Metropolitan Builders Association Masonry & Concrete Standard Background Masonry and concrete work in residential construction often provides the base structure upon which the house is built or as a veneer.
SC2000 CEMENT BONDING PROCEDURES
 Pg.1 SC2000 CEMENT BONDING PROCEDURES Widely recognized as the world s finest cold vulcanizing cement REMA SC2000 is the solution to your industrial bonding problems. By using REMA UTR20 hardener with
Pg.1 SC2000 CEMENT BONDING PROCEDURES Widely recognized as the world s finest cold vulcanizing cement REMA SC2000 is the solution to your industrial bonding problems. By using REMA UTR20 hardener with
Adhesive Recommendation for Altro Flooring. Porous (absorbent) subfloors (most wood subfloors and some concrete)
 Adhesive Recommendation for Altro Flooring Product Safety Sheet Flooring Smooth Sheet Flooring Porous (absorbent) subfloors (most wood subfloors and some concrete) Altrofix 30/31 (excessively heavy rolling
Adhesive Recommendation for Altro Flooring Product Safety Sheet Flooring Smooth Sheet Flooring Porous (absorbent) subfloors (most wood subfloors and some concrete) Altrofix 30/31 (excessively heavy rolling
Manufactured Stone Veneer Installation Instructions
 Manufactured Stone Veneer Installation Instructions Published: 8/14/2008 Revised: 6/25/2010 Table of Contents PART 1 -- INTRODUCTION PART 2 -- MATERIAL REQUIREMENTS PART 3 EXECUTION REQUIREMENTS PART 4
Manufactured Stone Veneer Installation Instructions Published: 8/14/2008 Revised: 6/25/2010 Table of Contents PART 1 -- INTRODUCTION PART 2 -- MATERIAL REQUIREMENTS PART 3 EXECUTION REQUIREMENTS PART 4
T R A N S F E R A B L E F U L LY
 HSTOPS A WALL OF WATER 22 FT. HIG! F U L LY T R A N S F E R A B L E RESISTS10 PSI ! 1 F U L LY T R A N S F E R A B L E HSTOPS A WALL OF WATER 22 FT. HIG RESISTS10 PSI Guaranteed To Stop Water Even Under
HSTOPS A WALL OF WATER 22 FT. HIG! F U L LY T R A N S F E R A B L E RESISTS10 PSI ! 1 F U L LY T R A N S F E R A B L E HSTOPS A WALL OF WATER 22 FT. HIG RESISTS10 PSI Guaranteed To Stop Water Even Under
1.3 Properties of Coal
 1.3 Properties of Classification is classified into three major types namely anthracite, bituminous, and lignite. However there is no clear demarcation between them and coal is also further classified
1.3 Properties of Classification is classified into three major types namely anthracite, bituminous, and lignite. However there is no clear demarcation between them and coal is also further classified
Mortars for Brickwork - Selection and Quality Assurance
 TECHNICAL NOTES on Brick Construction 1850 Centennial Park Drive, Reston, Virginia 20191 www.gobrick.com 703-620-0010 Mortars for Brickwork - Selection and Quality Assurance 8B October 2006 Abstract: This
TECHNICAL NOTES on Brick Construction 1850 Centennial Park Drive, Reston, Virginia 20191 www.gobrick.com 703-620-0010 Mortars for Brickwork - Selection and Quality Assurance 8B October 2006 Abstract: This
SIEVE ANALYSIS OF FINE AND COARSE AGGREGATES
 Test Procedure for SIEVE ANALYSIS OF FINE AND COARSE AGGREGATES TxDOT Designation: Tex-200-F Effective Date: January 2016 1. SCOPE 1.1 Use this test method to determine the particle size distribution of
Test Procedure for SIEVE ANALYSIS OF FINE AND COARSE AGGREGATES TxDOT Designation: Tex-200-F Effective Date: January 2016 1. SCOPE 1.1 Use this test method to determine the particle size distribution of
MASONRY INFORMATION. Selecting and Specifying Mortar and Grout for Unit Masonry. Introduction. Desirable Mortar Properties. Selection of Mortar
 Portland Cement Association MASONRY INFORMATION Selecting and Specifying Mortar and Grout for Unit Masonry Introduction Masonry mortar and masonry grout are key materials in unit masonry construction.
Portland Cement Association MASONRY INFORMATION Selecting and Specifying Mortar and Grout for Unit Masonry Introduction Masonry mortar and masonry grout are key materials in unit masonry construction.
ELECTRIC PERISTALTIC MORTAR POINTING PUMP
 ELECTRIC PERISTALTIC MORTAR POINTING PUMP pointing gun & control valve ACF405 PERISTALTIC PuMP hopper feed roller & tube pump for refurbishment & repair trades heritage & conservation bridge & underground
ELECTRIC PERISTALTIC MORTAR POINTING PUMP pointing gun & control valve ACF405 PERISTALTIC PuMP hopper feed roller & tube pump for refurbishment & repair trades heritage & conservation bridge & underground
Laying the First Course. 1. Excavate the site and construct the footing.
 Use QUIKRETE Mortar Mix or Mason Mix lay up a concrete block wall as shown. QUIKRETE Mortar Mix or Mason Mix Concrete block Mason's line Line blocks 4' level brick trowel Jointer Mason's hammer Stiff brush
Use QUIKRETE Mortar Mix or Mason Mix lay up a concrete block wall as shown. QUIKRETE Mortar Mix or Mason Mix Concrete block Mason's line Line blocks 4' level brick trowel Jointer Mason's hammer Stiff brush
Lesson 3. Portland Cement and Concrete
 Portland Cement and Concrete This lesson focuses on the most consumed construction material, Portland cement based concrete. It s consumed for pavement, dams, bridges, floors, walls, columns, and even
Portland Cement and Concrete This lesson focuses on the most consumed construction material, Portland cement based concrete. It s consumed for pavement, dams, bridges, floors, walls, columns, and even
Stone and Masonry Restoration
 Stone and Masonry Restoration with Remmers Systems Cleaning Equipment Cleaning Chemicals Consolidation and Strengthening Restoration and Pointing Preservation and Conservation Stone and Masonry Restoration
Stone and Masonry Restoration with Remmers Systems Cleaning Equipment Cleaning Chemicals Consolidation and Strengthening Restoration and Pointing Preservation and Conservation Stone and Masonry Restoration
Chapter 3: Separating Mixtures (pg. 54 81)
 Chapter 3: Separating Mixtures (pg. 54 81) 3.2: Separating Mechanical Mixtures (PB Pg. 40 5 & TB Pg. 58 61): Name: Date: Check Your Understanding & Learning (PB pg. 40 & TB pg. 61): 1. What are four methods
Chapter 3: Separating Mixtures (pg. 54 81) 3.2: Separating Mechanical Mixtures (PB Pg. 40 5 & TB Pg. 58 61): Name: Date: Check Your Understanding & Learning (PB pg. 40 & TB pg. 61): 1. What are four methods
Construction. Sikadur-Combiflex. Sealing system for cracks and problem joints with large movements DESCRIPTION
 Sikadur-Combiflex REVISED JULY 2002 Sealing system for cracks and problem joints with large movements Construction DESCRIPTION USES ADVANTAGES The Sikadur-Combiflex joint sealing system consists of two
Sikadur-Combiflex REVISED JULY 2002 Sealing system for cracks and problem joints with large movements Construction DESCRIPTION USES ADVANTAGES The Sikadur-Combiflex joint sealing system consists of two
Chapter 2 Basis of design and materials
 Chapter 2 Basis of design and materials 2.1 Structural action It is necessary to start a design by deciding on the type and layout of structure to be used. Tentative sizes must be allocated to each structural
Chapter 2 Basis of design and materials 2.1 Structural action It is necessary to start a design by deciding on the type and layout of structure to be used. Tentative sizes must be allocated to each structural
Proper use of the Rebound Hammer Updated to reflect the changes to ASTM C805
 CEMEX USA - Technical Bulletin 2.1 Proper use of the Rebound Hammer Updated to reflect the changes to ASTM C805 The Rebound Hammer has been around since the late 1940 s and today is a commonly used method
CEMEX USA - Technical Bulletin 2.1 Proper use of the Rebound Hammer Updated to reflect the changes to ASTM C805 The Rebound Hammer has been around since the late 1940 s and today is a commonly used method
How to Install Pavers
 1 of 6 9/11/2012 10:41 AM How to Install Pavers Looking to give your property a durable driveway, a whimsical walkway, or a patio with pizazz? If you're reading this article, you're probably already on
1 of 6 9/11/2012 10:41 AM How to Install Pavers Looking to give your property a durable driveway, a whimsical walkway, or a patio with pizazz? If you're reading this article, you're probably already on
Commonwealth of Pennsylvania PA Test Method No. 632 Department of Transportation October 2013 5 Pages LABORATORY TESTING SECTION. Method of Test for
 Commonwealth of Pennsylvania PA Test Method No. 632 Department of Transportation 5 Pages LABORATORY TESTING SECTION Method of Test for TIME OF SETTING OF CONCRETE MIXTURES BY PENETRATION RESISTANCE 1.
Commonwealth of Pennsylvania PA Test Method No. 632 Department of Transportation 5 Pages LABORATORY TESTING SECTION Method of Test for TIME OF SETTING OF CONCRETE MIXTURES BY PENETRATION RESISTANCE 1.
BUILDING WITH STONE AND EARTH
 BUILDING WITH STONE AND EARTH PART 1 Earth is a popular building material all over the world. It can be used by itself, but if there is stone available, then the two can be used together to make very good
BUILDING WITH STONE AND EARTH PART 1 Earth is a popular building material all over the world. It can be used by itself, but if there is stone available, then the two can be used together to make very good
Site sampling and testing of concrete
 Sampling amended booklet amended:layout 1 4/8/09 14:14 Page 1 A practical guide for site personnel Site sampling and testing of concrete Cubes have a vital role to test that the concrete strength meets
Sampling amended booklet amended:layout 1 4/8/09 14:14 Page 1 A practical guide for site personnel Site sampling and testing of concrete Cubes have a vital role to test that the concrete strength meets
Technical Manual - Section 1 Introduction to Lytag lightweight aggregate
 Uniclass L6129 EPIC F122 CI/SfB Yp3 Technical Manual - Section 1 Introduction to Lytag lightweight aggregate Introduction... 2 Product... 2 Sustainability... 2 Physical Properties of Lightweight Aggregate...
Uniclass L6129 EPIC F122 CI/SfB Yp3 Technical Manual - Section 1 Introduction to Lytag lightweight aggregate Introduction... 2 Product... 2 Sustainability... 2 Physical Properties of Lightweight Aggregate...
RIW SHEETSEAL 226 BENEFITS APPLICATIONS APPLIED TO. CI/SfB TN6 L6813. November 2013. l Water and water vapour barrier. l Factory controlled thickness
 CI/SfB TN6 L6813 November 2013 RIW SHEETSEAL 226 is a cold applied, high density polyethylene film, coated with a bitumen/rubber self adhesive layer with a removable reinforced silicone paper. Primer is
CI/SfB TN6 L6813 November 2013 RIW SHEETSEAL 226 is a cold applied, high density polyethylene film, coated with a bitumen/rubber self adhesive layer with a removable reinforced silicone paper. Primer is
CURRENT PRACTICES ON CEMENT RENDERING IN AUSTRALIA
 Solo, Indonesia, 21-22 March 2009, pp 39-48 ISBN No 979-498-457-4 CURRENT PRACTICES ON CEMENT RENDERING IN AUSTRALIA Dr R Sri Ravindrarajah and Mikel Mansour School of Civil and Environmental Engineering,
Solo, Indonesia, 21-22 March 2009, pp 39-48 ISBN No 979-498-457-4 CURRENT PRACTICES ON CEMENT RENDERING IN AUSTRALIA Dr R Sri Ravindrarajah and Mikel Mansour School of Civil and Environmental Engineering,
ENGINEERED QUARTZ STONE
 ENGINEERED 2 QUARTZ STONE 18 GOOD INDUSTRY PRACTICES 2 ENGINEERED QUARTZ STONE Natural stones, especially granite, have been used for flooring and countertop material in high-end homes for its beauty and
ENGINEERED 2 QUARTZ STONE 18 GOOD INDUSTRY PRACTICES 2 ENGINEERED QUARTZ STONE Natural stones, especially granite, have been used for flooring and countertop material in high-end homes for its beauty and
PRESENTATION ON REPAIR AND REHABILITATION OF BUILDINGS DAMAGED IN EARTHQUAKE. By H P Gupta & D K Gupta
 PRESENTATION ON REPAIR AND REHABILITATION OF BUILDINGS DAMAGED IN EARTHQUAKE By H P Gupta & D K Gupta DIFFERENT TYPES OF DAMAGES 1.Minor cracks 0.5 to 5 mm wide in load or non-load bearing walls 2.Major
PRESENTATION ON REPAIR AND REHABILITATION OF BUILDINGS DAMAGED IN EARTHQUAKE By H P Gupta & D K Gupta DIFFERENT TYPES OF DAMAGES 1.Minor cracks 0.5 to 5 mm wide in load or non-load bearing walls 2.Major
Chapter. Restoration of Damaged Structures
 5 Chapter Restoration of Damaged Structures Bringing back a damaged structure to its pre-earthquake state and original strength is called restoration. This is the first step of building rehabilitation.
5 Chapter Restoration of Damaged Structures Bringing back a damaged structure to its pre-earthquake state and original strength is called restoration. This is the first step of building rehabilitation.
Here is your set of Detailed Plans from Copyright 2004 All Rights Reserved
 Here is your set of Detailed Plans from Copyright 2004 All Rights Reserved Materials for the House Here is the list of materials you will need to construct the basic house then to cover it with roofing
Here is your set of Detailed Plans from Copyright 2004 All Rights Reserved Materials for the House Here is the list of materials you will need to construct the basic house then to cover it with roofing
MAINTENANCE OF SMALL WATER SUPPLY, SANITATION AND IRRIGATION SCHEMES
 MAINTENANCE OF SMALL WATER SUPPLY, SANITATION AND IRRIGATION SCHEMES John van Rijn INDEVELOPMENT MAINTENANCE OF SMALL WATER SUPPLY, SANITATION AND IRRIGATION SCHEMES Any part of this publication may be
MAINTENANCE OF SMALL WATER SUPPLY, SANITATION AND IRRIGATION SCHEMES John van Rijn INDEVELOPMENT MAINTENANCE OF SMALL WATER SUPPLY, SANITATION AND IRRIGATION SCHEMES Any part of this publication may be
Salt Weathering of Masonry Walls The Venice Experience. By M. Collepardi, S. Collepardi and R. Troli
 Salt Weathering of Masonry Walls The Venice Experience By M. Collepardi, S. Collepardi and R. Troli Synopsis: All the buildings in Venice insist on foundation immersed in sea water and then are permanently
Salt Weathering of Masonry Walls The Venice Experience By M. Collepardi, S. Collepardi and R. Troli Synopsis: All the buildings in Venice insist on foundation immersed in sea water and then are permanently
Thin Veneer Stone Installation Guide
 Thin Veneer Stone Installation Guide Complete step by step How-to guide for installing Thin Veneer Stone. Important: From pallet to pallet of natural thin veneer stone, as with any natural stone product,
Thin Veneer Stone Installation Guide Complete step by step How-to guide for installing Thin Veneer Stone. Important: From pallet to pallet of natural thin veneer stone, as with any natural stone product,
Acrylic Coatings: The Perfect Stucco Finish
 Acrylic Coatings: The Perfect Stucco Finish By Larry Miller and Joe Miller Whether a stucco surface is new or old, there are many different finish coatings in today s marketplace that are supposedly right
Acrylic Coatings: The Perfect Stucco Finish By Larry Miller and Joe Miller Whether a stucco surface is new or old, there are many different finish coatings in today s marketplace that are supposedly right
Division 4 Section 047200 Concrete Masonry Specifications
 Cast Stone Specification This specification encompasses basic requirements for Cast Stone, as manufactured by Building Products Corp, 494 North 33 rd Street East St. Louis, Il 618-874-6282, 800-427-6282,
Cast Stone Specification This specification encompasses basic requirements for Cast Stone, as manufactured by Building Products Corp, 494 North 33 rd Street East St. Louis, Il 618-874-6282, 800-427-6282,
NOTE: FOR PROJECTS REQUIRING CONTRACTOR MIX DESIGN, THE DESIGN PROCEDURES ARE SPECIFIED IN THE SPECIAL PROVISIONS OF THE CONTRACT.
 September 1, 2003 CONCRETE MANUAL 5-694.300 MIX DESIGN 5-694.300 NOTE: FOR PROJECTS REQUIRING CONTRACTOR MIX DESIGN, THE DESIGN PROCEDURES ARE SPECIFIED IN THE SPECIAL PROVISIONS OF THE CONTRACT. 5-694.301
September 1, 2003 CONCRETE MANUAL 5-694.300 MIX DESIGN 5-694.300 NOTE: FOR PROJECTS REQUIRING CONTRACTOR MIX DESIGN, THE DESIGN PROCEDURES ARE SPECIFIED IN THE SPECIAL PROVISIONS OF THE CONTRACT. 5-694.301
Mineral waterproof coating PCI Dichtschlämme
 Mineral waterproof coating PCI Dichtschlämme 305 for basement walls, swimming pools and potable water tanks With official test certificate. FIELDS OF For indoor and outdoor use. For walls and floors. For
Mineral waterproof coating PCI Dichtschlämme 305 for basement walls, swimming pools and potable water tanks With official test certificate. FIELDS OF For indoor and outdoor use. For walls and floors. For
kalox-pool draft 231 repairing refurbishing and finishing KALOX-POOL Waterproof cement-based mortar for protecting and finishing concrete.
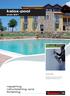 kalox-pool draft 231 KALOX-POOL Waterproof cement-based mortar for protecting and finishing concrete. repairing refurbishing and finishing 8-30 C Trowel / Spray 4 mm kalox-pool EN 1504-2 MAIN FEATURES
kalox-pool draft 231 KALOX-POOL Waterproof cement-based mortar for protecting and finishing concrete. repairing refurbishing and finishing 8-30 C Trowel / Spray 4 mm kalox-pool EN 1504-2 MAIN FEATURES
PERFORMANCE GUIDELINES
 1. Foundation/Basement 17 PERFORMANCE GUIDELINES 1. FOUNDATION/BASEMENT 1.1 Efflorescence on concrete or masonry surfaces Efflorescence is the formation of a white crystalline or powdery deposit on the
1. Foundation/Basement 17 PERFORMANCE GUIDELINES 1. FOUNDATION/BASEMENT 1.1 Efflorescence on concrete or masonry surfaces Efflorescence is the formation of a white crystalline or powdery deposit on the
