ANAESTHESIA FOR CAESARIAN SECTION PART 3 GENERAL ANAESTHESIA ANAESTHESIA TUTORIAL OF THE WEEK 97
|
|
|
- Ezra Lewis Black
- 9 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ANAESTHESIA FOR CAESARIAN SECTION PART 3 GENERAL ANAESTHESIA ANAESTHESIA TUTORIAL OF THE WEEK th JUNE 2008 Dr James Brown. Royal Devon & Exeter Hospital, UK Correspondence to: [email protected] A series of three tutorials exploring the management of caesarean section. Part 1: Introduction and Overview Part 2: Caesarean Section under Regional Anaesthesia Part 3: Caesarean Section under General Anaesthesia SELF ASSESSMENT: MCQ S T/F Q1: Regarding the physiological changes of pregnancy: Cardiovascular changes do not occur until the second trimester? Cardiac output (CO) can increase as much as 50% at term from the pre-pregnant state? Functional Residual Capacity (FRC) decreases to 80% of its pre-pregnant level at term? Oxygen consumption is increased by 10% compared with pre-pregnant state? Glomerular Filtration Rate (GFR) decreases during pregnancy? Q2: Regarding endotracheal intubation for caesarean section: 1. The incidence of difficult intubation is twice that of the general surgical population? 2. Under no circumstances should anaesthesia continue after a failed intubation as the mother will be put at an unacceptable risk? 3. Cricoid pressure although reducing risk of passive regurgitation may make larnygoscopic view worse? 4. In the term pregnant patient undergoing GA for caesarean section, desaturation is likely to occur faster following induction compared with a non-pregnant patient? 5. The majority of cases of failed intubations have a high morbidity and mortality? Q3: The following are methods of reducing acid aspiration syndrome (Mendelson s)? Cricoid pressure? Perioperative H 2 antagonists? Nil by mouth prior to caesarean section? Oral administration of Sodium Citrate? Head up tilt on operating table during induction of anaesthesia? Q4: Concerning agents used at induction of general anaesthesia for caesarean section: a) Propofol is the commonest agent used in obstetric practice in the UK? b) Ketamine is useful in obstetric practice because of its analgesic properties and definite endpoint of induction of anaesthesia? c) Neuromuscular blocking drugs other than suxamethonium are not used because they are able to cross the placenta and produce apnoea in the newborn baby? d) If a second dose of suxamethonium is required a tachycardia should be anticipated? e) Etomidate has the advantage of maintaining cardiovascular stability to a greater extent than thiopentone during induction of anaesthesia? Page 1 of 9
2 KEY POINTS General anaesthesia in the obstetric patient is associated with an increased risk of morbidity and mortality including airway difficulties and failed intubation. Maternal mortality as a direct result of anaesthesia has fallen as more caesareans are performed under regional anaesthesia. As a consequence of this trend, trainee anaesthetists are now more limited in their exposure to general anaesthesia for caesarean section. CONSIDERATIONS There are significant challenges associated with general anaesthesia (GA) in the pregnant woman. Changes in maternal physiology and anatomy present their own challenges but can also exacerbate pre-existing medical problems. Specific conditions such as pre-eclampsia and massive maternal haemorrhage significantly increase the risks of GA. GA in the obstetric population is often performed in a stressful and pressured emergency situation. As the proportion of caesareans performed under GA has fallen, anaesthetic trainees are less experienced in managing this challenging situation. The physiological changes of pregnancy which contribute to the challenges of general anaesthesia are considered below: System Challenges Actions Respiratory Increased risk of difficult intubation due to: Regular failed intubation drill. Airway oedema Enlarged breasts and weight gain Access and familiarity with difficult airway equipment Rapid desaturation on induction due to: displaced diaphragm and reduced FRC. Increased closing capacity and small airway closure. Increased oxygen consumption. Attention to effective preoxygenation Cardiovascular Decreased preload, decreased cardiac output and placental perfusion due to Aorto-caval compression by gravid uterus Maintain left lateral tilt of 15 o during induction and until baby delivered. Expanded plasma volume, physiological anaemia, decreased peripheral vascular resistance and increased cardiac output Recognition that pregnant women may appear relatively stable but may decompensate quickly. Coagulation Hypercoaguable state. Consideration of thromboprophylaxis incl. compression stockings, early mobilisation, prophylactic low molecular weight heparin Gastrointestinal Increased Intra-abdominal pressure and progesterone mediated reduction in lower oesophageal sphincter tone increase risk of reflux and acid aspiration syndrome (Mendelson s). Labour reduces gastric emptying, especially if opioid analgesia used. Prophylactic H 2 antagonists. Sodium citrate immediately prior to induction. Rapid sequence induction with cricoid pressure Page 2 of 9
3 Over 80% of caesarean sections in the UK are now performed under neuraxial anaesthesia. General anaesthesia is indicated if the woman refuses a regional technique, if there is a specific medical condition which precludes neuraxial blockade (e.g. coagulopathy) or when it is felt there is not enough time available to provide a regional anaesthetic. Induction time to delivery is important as it dictates the amount of volatile anaesthetic agent that transfers to the neonate. Uterine incision to delivery is important as placental blood flow may be disrupted by uterine incision and if prolonged may increase the risk of fetal acidosis. THE GENERAL ANAESTHETIC Antacid prophylaxis Pregnant women are at risk of acid regurgitation and aspiration (Mendelson s syndrome) and measures to prevent this are essential. Lower oesophageal sphincter tone is reduced by progesterone and the intra-gastric pressure of the pregnant anaesthetised and ventilated patient is twice that of the non-pregnant patient. The risk of developing acid aspiration is related to the ph and volume of aspirate and measures to modulate these and reduce risk include: Restricting oral intake, especially solids for women in labour. Nil by mouth for those women considered likely to require GA Use of prokinetics (e.g. metoclopramide 10 mg I.V) Use of H 2 antagonists (e.g. Ranitidine 150mg p.o if time permits or 50mg I.V prior to an emergency) Sodium citrate (30ml) p.o just prior to induction Antacid prophylaxis should be considered in all patients undergoing caesarean section as a caesarean under neuraxial anaesthesia may require conversion to GA. Large Bore Intravenous Access Ideally at least one reliable 16G cannula for rapid fluid resuscitation if required. Preoxygenation The upward displacement of the diaphragm due to increased intra-abdominal pressure reduces functional residual capacity (FRC) by up to 20%. The closing capacity encroaches on the FRC resulting in closure of the dependent airways. This combined with increased oxygen consumption, leads to rapid desaturation. Attention to pre-oxygenation is essential with 3-5 minutes of tidal breathing or 5 vital capacity breaths of high flow oxygen via a tight fighting face mask. Cricoid Pressure A manoeuvre to reduce passive regurgitation. The optimum recommended force is 10N whilst awake increasing to 30N on induction. When applying cricoid pressure to the pregnant woman it should be recognised that the patient is tilted to the left and the direction of force should be adjusted accordingly. Incorrectly applied cricoid pressure can distort the view at laryngoscopy and increase the risk of difficult intubation. Rapid Sequence Induction Rapid sequence induction is recommended for all cases of general anaesthesia for caesarean section. The agents used most frequently in the UK are thiopentone 3-5mg/kg and suxamethonium 1-1.5mg/kg. Confirmation of tracheal intubation is essential as maternal deaths still occur from unidentified oesophageal intubation. Correct endotracheal tube placement can be confirmed in the following ways: Page 3 of 9
4 Clinical o Visualising the endotracheal tube passing through the cords o Misting of the tube during ventilation o Observation and auscultation of bilateral chest expansion and absence of sound over the stomach Capnography o Confirmation of expired CO 2 with capnography is the gold standard and appropriate equipment should be available. Alternative agents and methods of induction There is controversy over the best choice of anaesthetic agents to most effectively and safely secure the airway in the obstetric patient. The traditional approach of cricoid pressure, thiopentone, suxamethonium and avoidance of opioids is common in the UK; however the emergence of new agents and techniques may challenge this accepted technique in the future. Choice of Induction Agent Thiopentone There is vast experience with the use of thiopentone in this setting and it is currently the induction agent of choice for caesarean section under GA. A dose of 4 mg/kg has been suggested to balance avoidance of maternal awareness and hypertension and prevent delayed waking in the event of a failed intubation. Propofol Propofol is the most likely alternative to thiopentone and has been used for caesarean section under GA. One study demonstrated more maternal hypotension, possibly increased risk of maternal awareness and lower Apgar scores when compared with thiopentone. Other studies have shown no difference. No studies have shown superiority of propofol over thiopentone. Ketamine There is less experience of ketamine compared with thiopentone and propofol in the UK. A dose of 1.5-2mg/kg should be used. It may be indicated in the hypovolaemic obstetric patient. Etomidate The use of etomidate is decreasing in the UK as a result of its deleterious effect on adrenal function. Inhalational Induction Inhalational induction for caesarean section is uncommon in the UK because of the risk of aspiration and the increased risk of uterine atony and haemorrhage due to uterine muscle relaxation caused by volatile agents. Neuromuscular Blockade Depolarising (Suxamethonium) Suxamethonium is currently the muscle relaxant of choice due to its fast onset and rapid offset which is important in the event of a failed intubation. The use of total rather than lean weight is recommended for calculation of the required dose. Psuedocholinesterase activity is decreased during pregnancy and a dose of 1-1.5mg/kg is recommended. There are inherent risks with suxamethonium: Anaphylaxis Post-operative myalgia Hyperkalaemia Malignant hyperpyrexia Prolonged muscle relaxation in individuals with plasma cholinesterase deficiency. Bradycardia with repeated doses of suxamethonium without administration of atropine. Serious reaction rate is of the order of 1:4000. Page 4 of 9
5 Non-Depolarising (Rocuronium) Rocuronium (an aminosteroid) is becoming increasingly popular among obstetric anaesthetists to provide muscle relaxation for caesarean section under GA. Rocuronium produces equivalent intubating conditions to suxamethonium but the onset of block may be slower. It has notably fewer side effects than suxamethonium but in the event of a failed intubation, a prolonged period of face mask ventilation will be required. Sugammadex is a new drug that specifically and permanently reverses the neuromuscular block produced by rocuronium. The arrival of this drug on the market may result in a significant reduction in the use of suxamethonium for general anaesthesia for caesarean section Opioids Although not routinely used at induction because of fears of neonatal respiratory depression, short acting opioids have a place in general anaesthesia for patients with hypertensive disorders, primarily pre-eclampsia, to reduce the risk of cerebral complications from the pressor response of laryngoscopy. Paediatricians should be in attendance at all caesarean sections under general anaesthesia and should be informed of the risk of potential neonatal respiratory depression due to pre-delivery maternal administration of opioids. Failed Intubation Concerns have been raised about the reduction in exposure of anaesthetists to emergency general anaesthesia in obstetrics. The incidence of failed obstetric intubation is reported at 1:250, 8 times higher than for the general surgical population. This is equivalent to 180 cases in the UK each year and up to 9% of these cases may be associated with failure to ventilate. The risk of failed intubation is greater at emergency compared with elective caesarean section under GA. When failed intubation occurs it is often unexpected and the increased maternal oxygen demand and decreased FRC lead to rapid desaturation. Fortunately, the majority of failed intubations do not result in adverse maternal outcome. It is essential to thoroughly assess the airway prior to caesarean section, even if regional anaesthesia is planned. Obstetric anaesthetists should be familiar with and undergo regular training in failed intubation drills. Difficult intubation equipment, with a variety of airway devices and a method of cricothyroid puncture and ventilation should be available at all times. Attention to how the patient is positioned is paramount to provide the best possible intubating conditions at the first attempt. Because clinical opportunities for training are limited, a simulator is a good environment to undergo training in failed intubation and management of other obstetric emergencies. Page 5 of 9
6 Example of a difficult intubation drill: Initial Intubation Attempt Failed Recognise Difficult Intubation and Failure - Call for Help Second Attempt with Intubation aid e.g. Gum Elastic Bougie, McCoy Laryngoscope, Short Handled Laryngoscope Can t Intubate Don t have prolonged attempts Attempt to Ventilate with 100% Oxygen, leave on back, maintain cricoid pressure Unable to Ventilate Able to Ventilate Wake up, turn on left lateral, when spontaneously breathing. Consider continuing with a LMA only if threat to maternal life Try LMA, with temporary removal of cricoid pressure Still Unable to Ventilate Remove cricoid pressure Unable to ventilate Cricothyroidotomy and oxygenate Page 6 of 9
7 In the event of a difficult intubation patients should be counselled to inform future anaesthetists of potential airway difficulties. A clear warning sticker should be placed on the notes and the general practitioner informed. If difficult intubation is anticipated and neuraxial anaesthesia is contraindicated then awake fibre optic intubation may be indicated. The nasal route for intubation is less favourable in obstetric patients because of engorgement of the nasal mucosa and higher risk of bleeding. The technique is more difficult to perform in an emergency situation. Laryngeal Mask Airway The laryngeal mask airway (LMA) is a very useful device in the event of a failed intubation with subsequent difficult facemask ventilation. The Proseal LMA offers potential advantages as it provides a tighter seal against the glottis and has an oesophageal drain tube which may reduce aspiration risk in the event of regurgitation. Practice and familiarity at insertion are required prior to its use in an emergency. Extubation The risks of extubation are often overlooked but it is associated with airway difficulties, including upper airway obstruction, laryngospasm and aspiration. The left lateral position is recommended prior to extubation to allow passive drainage of secretions and stomach contents in the event of regurgitation. The patient should be adequately awake and muscle relaxation reversed to allow return of airway reflexes. In cases considered high risk for aspiration, drainage of gastric contents via a nasogastric tube before extubation may be advisable. Depth of Anaesthesia Monitoring Although anaesthetic requirements are reduced in pregnancy, general anaesthesia for obstetric patients is associated with a higher incidence of awareness compared with the general population. This is probably due to reduced administration of volatile agent at caesarean section due to concerns that excessive concentrations may be detrimental to the fetus and may relax uterine muscle increasing the risk of haemorrhage. Concerns about awareness have led to consideration of depth of anaesthesia monitoring for this patient group. There are several commercially available devices, most based on technology that processes EEG waves and presents them in a readily interpretable manner e.g. Bispectral Index (BIS) monitoring. Although depth of anaesthesia monitoring in caesarean section is not routinely practiced in the UK, its use may potentially increase in the future. Conclusion General anaesthesia for caesarean section in the emergency setting is stressful and demands clear communication and situational management (patient partners, midwives, obstetricians) as well as an organised anaesthetic plan. With the increasing caesarean section rate in the developed world it is likely that the absolute number of complications from obstetric surgery and anaesthesia will increase. Best practice must be constantly debated, adopted and audited to reduce morbidity and mortality. The issues and advances above are relevant to obstetric anaesthesia throughout the world though clearly, limitations in availability of equipment and resources may preclude their implementation. Africa accounts for 47% of global maternal mortality; this can be reduced with systematic improvement in education, training, funding and resources. Self Assessment: Answers / Discussion A1: Physiology of Pregnancy a) F Cardiovascular changes start to occur as early as 4/40. They are mediated by the hormonal effects of progesterone and oestrogen released initially by the ovary for the first trimester and subsequently the placenta. b) T Heart rate and stroke volume are increased by up to 25% each. The left ventricle is mildly dilated and hypertrophied in response to the increased demand. CO can be increased a further 30% during labour. Page 7 of 9
8 c) T The increased intra-abdominal pressure and diaphragmatic displacement by the gravid uterus decreases FRC by up to 20%. The closing capacity will encroach on the FRC in approximately 50% of pregnant women in the 3 rd trimester, leading to small airway collapse. d) F - Oxygen consumption is increased by 40% compared with pre-pregnancy levels. e) F GFR is increased by 50% during pregnancy which may have implications for drug elimination. Renal blood flow is also increased. A2: Concerning intubation of the pregnant patient a) F The incidence is up to 8 times higher than in the general population. It is more common in the emergency situation. It is probably due to a combination of factors including anatomical changes such as weight gain and upper airway oedema which increase the Mallampati score and make intubation technically more difficult. Other factors including the decrease in exposure of anaesthetic trainees to general anaesthesia for caesarean section are also important. b) F In cases where the mother s life is at risk, anaesthesia can be continued. The anaesthetist s primary duty of care is to the mother and this must be considered in deciding whether to continue with anaesthesia for caesarean section in the event of a failed intubation. c) T Cricoid pressure is an important manoeuvre to reduce passive regurgitation and risk of acid aspiration in the term mother. If incorrectly applied it can obscure the view at laryngoscopy. The commonest reason for this is over zealous pressure in a stressful situation. With the patient placed in the left tilted position the application of force of the cricoid pressure needs to be carefully considered and observed. In the event of failed intubation, cricoid pressure will need to be reduced if an LMA is inserted and may need to be released if face mask ventilation is impossible. d) T The combination of a decreased functional residual capacity secondary to increased intraabdominal pressure and an increased oxygen consumption conspire to make the term parturient desaturate rapidly. For this reason it is important to preoxygenate effectively, recognise a failed intubation early and call for help immediately e) F Only a small proportion of failed intubations come to harm. It is possible to safely ventilate the majority of women, the priority being to wake them up safely and consider an alternative regime for securing the airway. A3: The following are methods of reducing acid aspiration syndrome (Mendelson s)? a) T- Cricoid pressure may prevent passive regurgitation. b) T- Ideally H 2 antagonists should be given prior to caesarean section but this is not always possible in the emergency situation. There is some value to giving them intraoperatively as it may reduce the possibility and impact of aspiration at extubation. c) T- This is feasible for the elective caesarean section and it is possible to identify some high risk pregnancies on the labour ward that will require a caesarean section. In cases of failure to progress it may be more challenging. These patients, by definition, have often been labouring for a long time and require rehydration and calories. The only patients to die in Mendelson s original series were those who had complete airway obstruction from solid matter. A recommendation for these patients would be to use isotonic high calorie sports drinks instead of solid foods. d) T- This alkali raises the ph of stomach contents and should be given immediately prior to induction of anaesthesia. H 2 antagonists will suppress subsequent acid production but will not treat acid already present in the stomach. e) T Head up tilt on the table has been suggested as an alternative, or in addition to, cricoid pressure in reducing passive regurgitation. It may also improve respiratory dynamics for preoxygenation. However if the patient vomits it theoretically increases the chances of aspiration from the effects of gravity, rather than particulate matter draining from the mouth. A4: Concerning agents used at induction of general anaesthesia for caesarean section a) F Although gaining popularity as an induction agent for rapid sequence induction in the nonobstetric patient, most obstetric anaesthetists in the UK still use thiopentone for induction. b) F Ketamine is rarely used in UK obstetric practice but should be considered for a shocked patient with massive haemorrhage requiring caesarean section under GA. c) F Placental transfer of a drug is reliant on its molecular weight, lipid solubility and the extent of ionisation and protein binding in the maternal circulation. Non-depolarising muscle relaxants are large, highly ionised molecules that do not readily cross the placenta. Page 8 of 9
9 Suxamethonium is commonly used at induction due to its rapid onset of action. It also has the advantage of wearing off quickly in the event of failed intubation, allowing return of spontaneous breathing. d) F If a second dose of suxamethonium is given a bradycardia should be anticipated and may be prevented by pre-emptive administration of atropine. In the event of a failed intubation following muscle relaxation with suxamethonium, it is safer to wake the patient up rather than continue further attempts at intubation. Repeated doses of suxamethonium are therefore not recommended. e) T This is the main advantage of etomidate. It has fallen out of favour in UK practice because of concerns that even a single dose can significantly inhibit corticosteroid production. Recommended reading Yentis S, May A, Alhotra S. Analgesia, anaesthesia and pregnancy. A Practical Guide. Cambridge University Press Levy DM. Emergency Caesarean Section: Best Practice. Anaesthesia. 2006; 61: Confidential Enquiry into Maternal and Child Health Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists Clinical Effectiveness Support Unit. The National Sentinel Caesarean Section Audit Report. London RCOG, NICE guidelines for caesarean section For fully referenced version of tutorial please contact author via [email protected] Page 9 of 9
Anatomical and Physiological Changes in Pregnancy Relevant to Anaesthesia
 Anatomical and Physiological Changes in Pregnancy Relevant to Anaesthesia Dr. A. Calzolari Specialist Registrar in Anaesthesia Dr. D. J. Dalgleish Consultant Anaesthetist Royal Bournemouth Hospital Dorset,
Anatomical and Physiological Changes in Pregnancy Relevant to Anaesthesia Dr. A. Calzolari Specialist Registrar in Anaesthesia Dr. D. J. Dalgleish Consultant Anaesthetist Royal Bournemouth Hospital Dorset,
Paediatric fluids 13/06/05
 Dr Catharine Wilson Consultant Paediatric Anaesthetist Sheffield Children s Hospital. UK Paediatric fluids 13/06/05 Self assessment: Complete these questions before reading the tutorial. Discuss the answers
Dr Catharine Wilson Consultant Paediatric Anaesthetist Sheffield Children s Hospital. UK Paediatric fluids 13/06/05 Self assessment: Complete these questions before reading the tutorial. Discuss the answers
Case Study: General Anesthesia for acute appendectomy in a pregnant woman. David Roy Godden. Clinical Residency in Nurse Anesthesia II ANST 507
 Case Study: General Anesthesia for acute appendectomy in a pregnant woman By David Roy Godden Clinical Residency in Nurse Anesthesia II ANST 507 Michele E. Gold, CRNA, PhD Associate Professor of Clinical
Case Study: General Anesthesia for acute appendectomy in a pregnant woman By David Roy Godden Clinical Residency in Nurse Anesthesia II ANST 507 Michele E. Gold, CRNA, PhD Associate Professor of Clinical
Intraosseous Vascular Access and Lidocaine
 Intraosseous Vascular Access and Lidocaine Intraosseous (IO) needles provide access to the medullary cavity of a bone. It is a technique primarily used in emergency situations to administer fluid and medication
Intraosseous Vascular Access and Lidocaine Intraosseous (IO) needles provide access to the medullary cavity of a bone. It is a technique primarily used in emergency situations to administer fluid and medication
Why your weight matters during pregnancy and after birth
 Information for you Published in November 2011 (next review date: 2015) Why your weight matters during pregnancy and after birth Most women who are overweight have a straightforward pregnancy and birth
Information for you Published in November 2011 (next review date: 2015) Why your weight matters during pregnancy and after birth Most women who are overweight have a straightforward pregnancy and birth
How To Treat A Heart Attack
 13 Resuscitation and preparation for anaesthesia and surgery Key Points 13.1 MANAGEMENT OF EMERGENCIES AND CARDIOPULMONARY RESUSCITATION ESSENTIAL HEALTH TECHNOLOGIES The emergency measures that are familiar
13 Resuscitation and preparation for anaesthesia and surgery Key Points 13.1 MANAGEMENT OF EMERGENCIES AND CARDIOPULMONARY RESUSCITATION ESSENTIAL HEALTH TECHNOLOGIES The emergency measures that are familiar
YOU AND YOUR ANAESTHETIC
 YOU AND YOUR ANAESTHETIC Information Leaflet Your Health. Our Priority. Page 2 of 8 This leaflet aims to answer some of the questions you may have about your anaesthetic and contains fasting instructions.
YOU AND YOUR ANAESTHETIC Information Leaflet Your Health. Our Priority. Page 2 of 8 This leaflet aims to answer some of the questions you may have about your anaesthetic and contains fasting instructions.
Pain Relief & Common Drugs. Henrik Jörnvall MD, PhD
 Pain Relief & Common Drugs Henrik Jörnvall MD, PhD MKAIC May 5 2010 Pain Definition An unpleasant sensory and emotional experience assocated with actual or potential tissue damage or described in terms
Pain Relief & Common Drugs Henrik Jörnvall MD, PhD MKAIC May 5 2010 Pain Definition An unpleasant sensory and emotional experience assocated with actual or potential tissue damage or described in terms
Suxamethonium Anaphylaxis. A Case Study
 Suxamethonium Anaphylaxis A Case Study This case study is a detailed reflection of my experience of an anaphylactic reaction to suxamethonium, I was involved with during my training. It all started on
Suxamethonium Anaphylaxis A Case Study This case study is a detailed reflection of my experience of an anaphylactic reaction to suxamethonium, I was involved with during my training. It all started on
Trust Guideline for the use of the Modified Early Obstetric Warning Score (MEOWS) in detecting the seriously ill and deteriorating woman.
 A clinical guideline recommended for use In: By: For: Key words: Written by: Supported by: Maternity Services. Obstetricians, Midwives and Midwifery Care Assistants. All women receiving care from maternity
A clinical guideline recommended for use In: By: For: Key words: Written by: Supported by: Maternity Services. Obstetricians, Midwives and Midwifery Care Assistants. All women receiving care from maternity
GENERAL ANAESTHESIA FOR CAESAREAN SECTION - CLINICAL GUIDELINE 1. Aim/Purpose of this Guideline
 GENERAL ANAESTHESIA FOR CAESAREAN SECTION - CLINICAL GUIDELINE 1. Aim/Purpose of this Guideline 1.1. General anaesthesia for caesarean section carries considerable risk and is frequently performed out
GENERAL ANAESTHESIA FOR CAESAREAN SECTION - CLINICAL GUIDELINE 1. Aim/Purpose of this Guideline 1.1. General anaesthesia for caesarean section carries considerable risk and is frequently performed out
PHENYLEPHRINE HYDROCHLORIDE INJECTION USP
 PRESCRIBING INFORMATION PHENYLEPHRINE HYDROCHLORIDE INJECTION USP 10 mg/ml Sandoz Canada Inc. Date of Preparation: September 1992 145 Jules-Léger Date of Revision : January 13, 2011 Boucherville, QC, Canada
PRESCRIBING INFORMATION PHENYLEPHRINE HYDROCHLORIDE INJECTION USP 10 mg/ml Sandoz Canada Inc. Date of Preparation: September 1992 145 Jules-Léger Date of Revision : January 13, 2011 Boucherville, QC, Canada
RGN JOY LAUDE WATFORD GENERAL HOSPITAL, ENGLAND
 RGN JOY LAUDE WATFORD GENERAL HOSPITAL, ENGLAND Monitor patient on the ward to detect trends in vital signs and to manage accordingly To recognise deteriorating trends and request relevant medical/out
RGN JOY LAUDE WATFORD GENERAL HOSPITAL, ENGLAND Monitor patient on the ward to detect trends in vital signs and to manage accordingly To recognise deteriorating trends and request relevant medical/out
F.E.E.A. FONDATION EUROPEENNE D'ENSEIGNEMENT EN ANESTHESIOLOGIE FOUNDATION FOR EUROPEAN EDUCATION IN ANAESTHESIOLOGY
 créée sous le Patronage de l'union Européenne Detailed plan of the program of six courses 1. RESPIRATORY 1. ESPIRATORY AND THORAX 1.1 Physics and principles of measurement 1.1.1 Physical laws 1.1.2 Vaporizers
créée sous le Patronage de l'union Européenne Detailed plan of the program of six courses 1. RESPIRATORY 1. ESPIRATORY AND THORAX 1.1 Physics and principles of measurement 1.1.1 Physical laws 1.1.2 Vaporizers
Information for you A low-lying placenta (placenta praevia) after 20 weeks
 Information for you A low-lying placenta (placenta praevia) after 20 weeks Published in December 2011 Who is this information for? This information is intended to help you if you have, or have been told
Information for you A low-lying placenta (placenta praevia) after 20 weeks Published in December 2011 Who is this information for? This information is intended to help you if you have, or have been told
Information for you Treatment of venous thrombosis in pregnancy and after birth. What are the symptoms of a DVT during pregnancy?
 Information for you Treatment of venous thrombosis in pregnancy and after birth Published in September 2011 What is venous thrombosis? Thrombosis is a blood clot in a blood vessel (a vein or an artery).
Information for you Treatment of venous thrombosis in pregnancy and after birth Published in September 2011 What is venous thrombosis? Thrombosis is a blood clot in a blood vessel (a vein or an artery).
Birth after previous caesarean. What are my choices for birth after a caesarean delivery?
 Birth after previous caesarean Information for you Published September 2008 What are my choices for birth after a caesarean delivery? More than one in five women (20%) in the UK currently give birth by
Birth after previous caesarean Information for you Published September 2008 What are my choices for birth after a caesarean delivery? More than one in five women (20%) in the UK currently give birth by
Australian and New Zealand College of Anaesthetists (ANZCA) Guidelines for the Management of Major Regional Analgesia
 PS03 2014 Australian and New Zealand College of Anaesthetists (ANZCA) Faculty of Pain Medicine Guidelines for the Management of Major Regional Analgesia 1. OVERVIEW This document is intended to apply to
PS03 2014 Australian and New Zealand College of Anaesthetists (ANZCA) Faculty of Pain Medicine Guidelines for the Management of Major Regional Analgesia 1. OVERVIEW This document is intended to apply to
TRANSPORT OF CRITICALLY ILL PATIENTS
 TRANSPORT OF CRITICALLY ILL PATIENTS Introduction Inter-hospital and intra-hospital transport of critically ill patients places the patient at risk of adverse events and increased morbidity and mortality.
TRANSPORT OF CRITICALLY ILL PATIENTS Introduction Inter-hospital and intra-hospital transport of critically ill patients places the patient at risk of adverse events and increased morbidity and mortality.
Blood Pressure Management and Your Pregnancy
 Patient Education Blood Pressure Management and Your Pregnancy This handout explains: How your blood pressure is checked during pregnancy. What preeclampsia is, including risk factors, treatments, and
Patient Education Blood Pressure Management and Your Pregnancy This handout explains: How your blood pressure is checked during pregnancy. What preeclampsia is, including risk factors, treatments, and
Airway Management of the Parturient. Kevin C. Dennehy, MB, BCh, FFARCSI May C. M. Pian-Smith, MD
 Airway Management of the Parturient Kevin C. Dennehy, MB, BCh, FFARCSI May C. M. Pian-Smith, MD Anesthesiologists involved in the care of the obstetric patient must consider airway management as an essential
Airway Management of the Parturient Kevin C. Dennehy, MB, BCh, FFARCSI May C. M. Pian-Smith, MD Anesthesiologists involved in the care of the obstetric patient must consider airway management as an essential
ANAESTHESIA FOR THE PATIENT WITH PULMONARY HYPERTENSION ANAESTHESIA TUTORIAL OF THE WEEK 228
 ANAESTHESIA FOR THE PATIENT WITH PULMONARY HYPERTENSION ANAESTHESIA TUTORIAL OF THE WEEK 228 20 TH JUNE 2011 Dr Sarah Thomas, Senior Anaesthetic Registrar Royal Hobart Hospital Correspondence to [email protected]
ANAESTHESIA FOR THE PATIENT WITH PULMONARY HYPERTENSION ANAESTHESIA TUTORIAL OF THE WEEK 228 20 TH JUNE 2011 Dr Sarah Thomas, Senior Anaesthetic Registrar Royal Hobart Hospital Correspondence to [email protected]
Rapid Sequence Intubation A Guide for Assistants
 Rapid Sequence Intubation A Guide for Assistants Working outwith the theatre setting Contents Course Aim...1 Course Objectives...1 Basic Airway Care and Oxygenation...2 Rapid Sequence Intubation...2 Definition...2
Rapid Sequence Intubation A Guide for Assistants Working outwith the theatre setting Contents Course Aim...1 Course Objectives...1 Basic Airway Care and Oxygenation...2 Rapid Sequence Intubation...2 Definition...2
Patient Care Services Policy & Procedure Title: No. 8720-0059
 Page: 1 of 8 I. SCOPE: This policy applies to Saint Francis Hospital, its employees, medical staff, contractors, patients and visitors regardless of service location or category of patient. This policy
Page: 1 of 8 I. SCOPE: This policy applies to Saint Francis Hospital, its employees, medical staff, contractors, patients and visitors regardless of service location or category of patient. This policy
Anaesthesia tutorial of the week 112: Prone Positioning
 Anaesthesia tutorial of the week 112: Prone Positioning Dr D G Hovord Specialist Trainee Registrar - Anaesthetics University Hospitals of Coventry and Warwick [email protected] Self-assessment Before
Anaesthesia tutorial of the week 112: Prone Positioning Dr D G Hovord Specialist Trainee Registrar - Anaesthetics University Hospitals of Coventry and Warwick [email protected] Self-assessment Before
PAEDIATRIC ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY AND THE BASICS OF PAEDIATRIC ANAESTHESIA.
 PAEDIATRIC ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY AND THE BASICS OF PAEDIATRIC ANAESTHESIA. Fiona Macfarlane Mater Children s Hospital, Brisbane Australia Children are not small adults. Paediatric patients vary considerably
PAEDIATRIC ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY AND THE BASICS OF PAEDIATRIC ANAESTHESIA. Fiona Macfarlane Mater Children s Hospital, Brisbane Australia Children are not small adults. Paediatric patients vary considerably
Oxygen - update April 2009 OXG
 PRESENTATION Oxygen (O 2 ) is a gas provided in compressed form in a cylinder. It is also available in liquid form, in a system adapted for ambulance use. It is fed via a regulator and flow meter to the
PRESENTATION Oxygen (O 2 ) is a gas provided in compressed form in a cylinder. It is also available in liquid form, in a system adapted for ambulance use. It is fed via a regulator and flow meter to the
Pregnancy and Tuberculosis. Information for clinicians
 Pregnancy and Tuberculosis Information for clinicians When to suspect Tuberculosis (TB)? Who is at risk of TB during pregnancy? Recent research suggests that new mothers are at an increased risk of TB
Pregnancy and Tuberculosis Information for clinicians When to suspect Tuberculosis (TB)? Who is at risk of TB during pregnancy? Recent research suggests that new mothers are at an increased risk of TB
Oxygen Therapy. Oxygen therapy quick guide V3 July 2012.
 PRESENTATION Oxygen (O 2 ) is a gas provided in a compressed form in a cylinder. It is also available in a liquid form. It is fed via a regulator and flow meter to the patient by means of plastic tubing
PRESENTATION Oxygen (O 2 ) is a gas provided in a compressed form in a cylinder. It is also available in a liquid form. It is fed via a regulator and flow meter to the patient by means of plastic tubing
Chapter 7. Ideally, educational preparation for childbirth begins prior to conception
 Chapter 7 Nursing Management of Pain During Labor and Birth Key Terms Cleansing breath Effleurage Endorphins Pain threshold Focal point Pain tolerance Education for Childbearing Ideally, educational preparation
Chapter 7 Nursing Management of Pain During Labor and Birth Key Terms Cleansing breath Effleurage Endorphins Pain threshold Focal point Pain tolerance Education for Childbearing Ideally, educational preparation
SAMPLE. UK Obstetric Surveillance System. Management of Pregnancy following Laparoscopic Adjustable Gastric Band Surgery.
 ID Number: UK Obstetric Surveillance System Management of Pregnancy following Laparoscopic Adjustable Gastric Band Surgery Case Definition: Study 04/11 Data Collection Form - Please report any woman delivering
ID Number: UK Obstetric Surveillance System Management of Pregnancy following Laparoscopic Adjustable Gastric Band Surgery Case Definition: Study 04/11 Data Collection Form - Please report any woman delivering
Cardiac Arrest Pediatric Ventricular Fibrillation / Pulseless Ventricular Tachycardia Protocol revised October 2008
 Cardiac Arrest Pediatric Ventricular Fibrillation / Pulseless Ventricular Tachycardia Protocol revised October 2008 Preamble In contrast to cardiac arrest in adults, cardiopulmonary arrest in pediatric
Cardiac Arrest Pediatric Ventricular Fibrillation / Pulseless Ventricular Tachycardia Protocol revised October 2008 Preamble In contrast to cardiac arrest in adults, cardiopulmonary arrest in pediatric
Pain Relief Options for Labor. Providing You with Quality Care, Information and Support
 Pain Relief Options for Labor Providing You with Quality Care, Information and Support What can I expect during my labor and delivery? As a patient in the Labor and Delivery Suite at Lucile Packard Children
Pain Relief Options for Labor Providing You with Quality Care, Information and Support What can I expect during my labor and delivery? As a patient in the Labor and Delivery Suite at Lucile Packard Children
GWAS Competency Mapping Levels of Medical Support Within GWAS
 GWAS Competency Mapping Levels of Medical Support Within GWAS Great Western Ambulance Service NHS Trust is pleased to be able to work with a range of doctors in delivering effective pre-hospital care.
GWAS Competency Mapping Levels of Medical Support Within GWAS Great Western Ambulance Service NHS Trust is pleased to be able to work with a range of doctors in delivering effective pre-hospital care.
INFORMATION SHEET FOR A LAPAROSCOPIC SLEEVE GASTRECTOMY
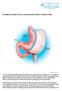 INFORMATION SHEET FOR A LAPAROSCOPIC SLEEVE GASTRECTOMY You are considering undergoing a laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy for weight loss. The purpose of this information sheet is to provide you with the
INFORMATION SHEET FOR A LAPAROSCOPIC SLEEVE GASTRECTOMY You are considering undergoing a laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy for weight loss. The purpose of this information sheet is to provide you with the
Why is prematurity a concern?
 Prematurity What is prematurity? A baby born before 37 weeks of pregnancy is considered premature. Approximately 12% of all babies are born prematurely. Terms that refer to premature babies are preterm
Prematurity What is prematurity? A baby born before 37 weeks of pregnancy is considered premature. Approximately 12% of all babies are born prematurely. Terms that refer to premature babies are preterm
Neonatal Emergencies. Care of the Neonate. Care of the Neonate. Care of the Neonate. Student Objectives. Student Objectives continued.
 Student Objectives Neonatal Emergencies After completing this section the student will be able to: 1. Identify three physiologic and/or anatomic features unique to the newborn 2. List three perinatal factors
Student Objectives Neonatal Emergencies After completing this section the student will be able to: 1. Identify three physiologic and/or anatomic features unique to the newborn 2. List three perinatal factors
Name of procedure: Laparoscopic (key-hole) ovarian surgery. Left/ Right unilateral salpingo-oophorectomy* (removal of one fallopian tube and ovary)
 For staff use only: Patient Details: Surname: First names: Date of birth: Hospital no: Female: (Use hospital identification label) Gynaecology Patient agreement to treatment Name of procedure: Laparoscopic
For staff use only: Patient Details: Surname: First names: Date of birth: Hospital no: Female: (Use hospital identification label) Gynaecology Patient agreement to treatment Name of procedure: Laparoscopic
HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE:
 PROSPECTIVE, RANDOMIZED, DOUBLE BLIND STUDY TO COMPARE THE EFFICACY AND SAFETY OF GRANISETRON VERSUS ONDANSETRON IN PREVENTION OF POST OPERATIVE NAUSEA AND VOMITING IN PATIENTS UNDERGOING ELECTIVE LAPAROSCOPIC
PROSPECTIVE, RANDOMIZED, DOUBLE BLIND STUDY TO COMPARE THE EFFICACY AND SAFETY OF GRANISETRON VERSUS ONDANSETRON IN PREVENTION OF POST OPERATIVE NAUSEA AND VOMITING IN PATIENTS UNDERGOING ELECTIVE LAPAROSCOPIC
PROCEDURAL SEDATION/ANALGESIA NCBON Position Statement for RN Practice
 PROCEDURAL SEDATION/ANALGESIA NCBON Position Statement for RN Practice P.O. BOX 2129 Raleigh, NC 27602 (919) 782-3211 FAX (919) 781-9461 Nurse Aide II Registry (919) 782-7499 www.ncbon.com Issue: Administration
PROCEDURAL SEDATION/ANALGESIA NCBON Position Statement for RN Practice P.O. BOX 2129 Raleigh, NC 27602 (919) 782-3211 FAX (919) 781-9461 Nurse Aide II Registry (919) 782-7499 www.ncbon.com Issue: Administration
Science 10-Biology Activity 15 The Development of the Human Embryo
 Science 10-Biology Activity 15 The Development of the Human Embryo 10 Name Due Date Show Me Hand In Correct and Hand In Again By NOTE: This worksheet is based on material from pages 379-380 in Science
Science 10-Biology Activity 15 The Development of the Human Embryo 10 Name Due Date Show Me Hand In Correct and Hand In Again By NOTE: This worksheet is based on material from pages 379-380 in Science
*Reflex withdrawal from a painful stimulus is NOT considered a purposeful response.
 Analgesia and Moderate Sedation This Nebraska Board of Nursing advisory opinion is issued in accordance with Nebraska Revised Statute (NRS) 71-1,132.11(2). As such, this advisory opinion is for informational
Analgesia and Moderate Sedation This Nebraska Board of Nursing advisory opinion is issued in accordance with Nebraska Revised Statute (NRS) 71-1,132.11(2). As such, this advisory opinion is for informational
CH CONSCIOUS SEDATION
 Summary: CH CONSCIOUS SEDATION It is the policy of Carondelet Health that moderate conscious sedation of patients will be undertaken with appropriate evaluation and monitoring. Effective Date: 9/4/04 Revision
Summary: CH CONSCIOUS SEDATION It is the policy of Carondelet Health that moderate conscious sedation of patients will be undertaken with appropriate evaluation and monitoring. Effective Date: 9/4/04 Revision
Report: Anaesthesia & ICU, Jimma University Specialized Hospital, Ethiopia
 I would like to express my thanks to the International Relations Committee of the AAGBI for the 750 travel grant. I hope that my report highlights why this was a worthwhile visit and how such links may
I would like to express my thanks to the International Relations Committee of the AAGBI for the 750 travel grant. I hope that my report highlights why this was a worthwhile visit and how such links may
Glycopyrronium Bromide 0.5mg/mL and Neostigmine Metilsulfate 2.5mg/mL Solution for Injection
 NEW ZEALAND DATA SHEET Glycopyrronium Bromide 0.5mg/mL and Neostigmine Metilsulfate 2.5mg/mL Solution for Injection Each 1mL contains Glycopyrrolate USP 0.5mg (Glycopyrronium Bromide) and Neostigmine Metilsulfate
NEW ZEALAND DATA SHEET Glycopyrronium Bromide 0.5mg/mL and Neostigmine Metilsulfate 2.5mg/mL Solution for Injection Each 1mL contains Glycopyrrolate USP 0.5mg (Glycopyrronium Bromide) and Neostigmine Metilsulfate
Epidurals for pain relief after surgery
 Epidurals for pain relief after surgery This information leaflet is for anyone who may benefit from an epidural for pain relief after surgery. We hope it will help you to ask questions and direct you to
Epidurals for pain relief after surgery This information leaflet is for anyone who may benefit from an epidural for pain relief after surgery. We hope it will help you to ask questions and direct you to
PATIENT CONSENT TO PROCEDURE - ROUX-EN-Y GASTRIC BYPASS
 As a patient you must be adequately informed about your condition and the recommended surgical procedure. Please read this document carefully and ask about anything you do not understand. Please initial
As a patient you must be adequately informed about your condition and the recommended surgical procedure. Please read this document carefully and ask about anything you do not understand. Please initial
NICE Pathways bring together all NICE guidance, quality standards and other NICE information on a specific topic.
 Diabetic ketoacidosis in children and young people bring together all NICE guidance, quality standards and other NICE information on a specific topic. are interactive and designed to be used online. They
Diabetic ketoacidosis in children and young people bring together all NICE guidance, quality standards and other NICE information on a specific topic. are interactive and designed to be used online. They
INTRAVENOUS FLUIDS. Acknowledgement. Background. Starship Children s Health Clinical Guideline
 Acknowledgements Background Well child with normal hydration Unwell children (+/- abnormal hydration Maintenance Deficit Ongoing losses (e.g. from drains) Which fluid? Monitoring Special Fluids Post-operative
Acknowledgements Background Well child with normal hydration Unwell children (+/- abnormal hydration Maintenance Deficit Ongoing losses (e.g. from drains) Which fluid? Monitoring Special Fluids Post-operative
DRAFT 7/17/07. Procedural Sedation and Rapid Sequence Intubation (RSI) Consensus Statement
 Procedural Sedation and Rapid Sequence Intubation (RSI) Consensus Statement Many patients with emergency medical conditions in emergency and critical care settings frequently experience treatable pain,
Procedural Sedation and Rapid Sequence Intubation (RSI) Consensus Statement Many patients with emergency medical conditions in emergency and critical care settings frequently experience treatable pain,
Carry out vaginal examinations at least once every 4 hours in the first stage of labour and plot the findings on the partograph.
 First stage: Diagnosis of Labour Latent phase - Cervix less than 4 cm dilated. Active phase - Cervix between 4 cm and 10 cm dilated - Rate of cervical dilatation at least 1 cm/hour - Effacement is usually
First stage: Diagnosis of Labour Latent phase - Cervix less than 4 cm dilated. Active phase - Cervix between 4 cm and 10 cm dilated - Rate of cervical dilatation at least 1 cm/hour - Effacement is usually
Levels of Critical Care for Adult Patients
 LEVELS OF CARE 1 Levels of Critical Care for Adult Patients STANDARDS AND GUIDELINES LEVELS OF CARE 2 Intensive Care Society 2009 All rights reserved. No reproduction, copy or transmission of this publication
LEVELS OF CARE 1 Levels of Critical Care for Adult Patients STANDARDS AND GUIDELINES LEVELS OF CARE 2 Intensive Care Society 2009 All rights reserved. No reproduction, copy or transmission of this publication
Maternal Collapse in Pregnancy and the Puerperium
 Green-top Guideline No. 56 January 2011 Maternal Collapse in regnancy and the uerperium Maternal Collapse in regnancy and the uerperium This is the first edition of this guideline. 1. urpose and scope
Green-top Guideline No. 56 January 2011 Maternal Collapse in regnancy and the uerperium Maternal Collapse in regnancy and the uerperium This is the first edition of this guideline. 1. urpose and scope
In-hospital resuscitation. Superseded by
 6 In-hospital resuscitation Introduction These guidelines are aimed primarily at healthcare professionals who are first to respond to an in-hospital cardiac arrest and may also be applicable to healthcare
6 In-hospital resuscitation Introduction These guidelines are aimed primarily at healthcare professionals who are first to respond to an in-hospital cardiac arrest and may also be applicable to healthcare
Naloxone Hydrochloride Injection PRODUCT INFORMATION
 Naloxone Hydrochloride Injection PRODUCT INFORMATION DESCRIPTION Naloxone hydrochloride is 17-allyl-4,5α-epoxy-3,14-dihydroxymorphinan-6-one hydrochloride; C 19 H 21 NO 4.HCl. It is an off-white powder
Naloxone Hydrochloride Injection PRODUCT INFORMATION DESCRIPTION Naloxone hydrochloride is 17-allyl-4,5α-epoxy-3,14-dihydroxymorphinan-6-one hydrochloride; C 19 H 21 NO 4.HCl. It is an off-white powder
Insulin Pump Therapy during Pregnancy and Birth
 Approvals: Specialist Group: Miss F Ashworth, Dr I Gallen, Dr J Ahmed Maternity Guidelines Group: V1 Dec 2012 Directorate Board: V1 Jan 2013 Clinical Guidelines Subgroup: July 2011 MSLC: V1 Nov 2012 Equality
Approvals: Specialist Group: Miss F Ashworth, Dr I Gallen, Dr J Ahmed Maternity Guidelines Group: V1 Dec 2012 Directorate Board: V1 Jan 2013 Clinical Guidelines Subgroup: July 2011 MSLC: V1 Nov 2012 Equality
Gail Naylor, Director of Nursing & Midwifery. Safety and Quality Committee
 Report to Trust Board of Directors Date of Meeting: 24 June 2014 Enclosure Number: 5 Title of Report: Author: Executive Lead: Responsible Sub- Committee (if appropriate): Executive Summary: Clinical Negligence
Report to Trust Board of Directors Date of Meeting: 24 June 2014 Enclosure Number: 5 Title of Report: Author: Executive Lead: Responsible Sub- Committee (if appropriate): Executive Summary: Clinical Negligence
Women's & Children's Hospital Research Report
 Anaesthesia - Women's and Paediatric Head Women s: Dr Johan van der Walt; Dr SW Simmons Head Paediatrics: Dr Margaret Wiese Contact: [email protected] 1 Development of the Adelaide Regional Connector
Anaesthesia - Women's and Paediatric Head Women s: Dr Johan van der Walt; Dr SW Simmons Head Paediatrics: Dr Margaret Wiese Contact: [email protected] 1 Development of the Adelaide Regional Connector
Low Molecular Weight Heparin. All Wales Medicines Strategy Group (AWMSG) Recommendations and advice
 Low Molecular Weight Heparin All Wales Medicines Strategy Group (AWMSG) Recommendations and advice Starting Point Low Molecular Weight Heparin (LMWH): Inhibits factor Xa and factor IIa (thrombin) Small
Low Molecular Weight Heparin All Wales Medicines Strategy Group (AWMSG) Recommendations and advice Starting Point Low Molecular Weight Heparin (LMWH): Inhibits factor Xa and factor IIa (thrombin) Small
5/30/2014 OBJECTIVES THE ROLE OF A RESPIRATORY THERAPIST IN THE DELIVERY ROOM. Disclosure
 THE ROLE OF A RESPIRATORY THERAPIST IN THE DELIVERY ROOM Ona Fofah, MD FAAP Assistant Professor of Pediatrics Director, Division of Neonatology Department of Pediatrics Rutgers- NJMS, Newark OBJECTIVES
THE ROLE OF A RESPIRATORY THERAPIST IN THE DELIVERY ROOM Ona Fofah, MD FAAP Assistant Professor of Pediatrics Director, Division of Neonatology Department of Pediatrics Rutgers- NJMS, Newark OBJECTIVES
What Does Pregnancy Have to Do With Blood Clots in a Woman s Legs?
 Patient s Guide to Prevention of Blood Clots During Pregnancy: Use of Blood-Thinning A Patient s Guide to Prevention of Blood Clots During Pregnancy: Use of Blood-Thinning Drugs to Prevent Abnormal Blood
Patient s Guide to Prevention of Blood Clots During Pregnancy: Use of Blood-Thinning A Patient s Guide to Prevention of Blood Clots During Pregnancy: Use of Blood-Thinning Drugs to Prevent Abnormal Blood
Maternity - Clinical Risk Management Program
 Maternity - Clinical Risk Management Document Number PD2009_003 Publication date 15-Jan-2009 Ministry of Health, NSW 73 Miller Street North Sydney NSW 2060 Locked Mail Bag 961 North Sydney NSW 2059 Telephone
Maternity - Clinical Risk Management Document Number PD2009_003 Publication date 15-Jan-2009 Ministry of Health, NSW 73 Miller Street North Sydney NSW 2060 Locked Mail Bag 961 North Sydney NSW 2059 Telephone
National Clinical Programme in Surgery (NCPS) Care Pathway for the Management of Day Case Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy
 National Clinical Programme in Surgery (NCPS) Care Pathway for the Management of Day Case Consultant Surgeon DRAFT VERSION 0.5 090415 Table of Contents 1.0 Purpose... 3 2.0 Scope... 3 3.0 Responsibility...
National Clinical Programme in Surgery (NCPS) Care Pathway for the Management of Day Case Consultant Surgeon DRAFT VERSION 0.5 090415 Table of Contents 1.0 Purpose... 3 2.0 Scope... 3 3.0 Responsibility...
Information for you Abortion care
 Information for you Abortion care Published in February 2012 This information is for you if you are considering having an abortion. It tells you: how you can access abortion services the care you can expect
Information for you Abortion care Published in February 2012 This information is for you if you are considering having an abortion. It tells you: how you can access abortion services the care you can expect
IMAP Statement on Safe Abortion
 International Planned Parenthood Federation IMAP Statement on Safe Abortion Key points: When performed early in pregnancy by trained health personnel in adequate facilities, abortion is a very safe procedure
International Planned Parenthood Federation IMAP Statement on Safe Abortion Key points: When performed early in pregnancy by trained health personnel in adequate facilities, abortion is a very safe procedure
Pediatric Airway Management
 Pediatric Airway Management Dec 2003 Dr. Shapiro I., PICU Adult Chain of Survival EMS CPR ALS Early Defibrillation Pediatric Chain of Survival Prevention CPR EMS ALS Out-of-Hospital Cardiac Arrest SIDS
Pediatric Airway Management Dec 2003 Dr. Shapiro I., PICU Adult Chain of Survival EMS CPR ALS Early Defibrillation Pediatric Chain of Survival Prevention CPR EMS ALS Out-of-Hospital Cardiac Arrest SIDS
Coagulation Disorders In Pregnancy
 Coagulation Disorders In Pregnancy Dr Rashmi Sharma, M.D, FRCA SpR Anaesthetics Blackburn Royal Infirmary Dr Anna Bewlay FRCA Consultant Anaesthetist Royal Preston Hospital Physiological changes in pregnancy
Coagulation Disorders In Pregnancy Dr Rashmi Sharma, M.D, FRCA SpR Anaesthetics Blackburn Royal Infirmary Dr Anna Bewlay FRCA Consultant Anaesthetist Royal Preston Hospital Physiological changes in pregnancy
Saving Mothers: Caesarean Section Monograph 2013
 Saving Mothers: Caesarean Section Monograph 2013 AIDS HELPLINE 0800-012-222 A MONOGRAPH ON CAESAREAN SECTION National Department of Health South Africa 2013 1 ORGANISERS 2010 National Committee on Confidential
Saving Mothers: Caesarean Section Monograph 2013 AIDS HELPLINE 0800-012-222 A MONOGRAPH ON CAESAREAN SECTION National Department of Health South Africa 2013 1 ORGANISERS 2010 National Committee on Confidential
ACLS PHARMACOLOGY 2011 Guidelines
 ACLS PHARMACOLOGY 2011 Guidelines ADENOSINE Narrow complex tachycardias or wide complex tachycardias that may be supraventricular in nature. It is effective in treating 90% of the reentry arrhythmias.
ACLS PHARMACOLOGY 2011 Guidelines ADENOSINE Narrow complex tachycardias or wide complex tachycardias that may be supraventricular in nature. It is effective in treating 90% of the reentry arrhythmias.
Drugs & Everything Else
 Pain Relief, Common Drugs & Everything Else Henrik Jörnvall MD, PhD MKAIC November 11 2011 Lidocaine Noradrenaline Isoflurane Morphine Ropivacaine Platelets l t Pethidine Dobutamine Propofol Normal Saline
Pain Relief, Common Drugs & Everything Else Henrik Jörnvall MD, PhD MKAIC November 11 2011 Lidocaine Noradrenaline Isoflurane Morphine Ropivacaine Platelets l t Pethidine Dobutamine Propofol Normal Saline
ACLS Provider Manual Comparison Sheet Based on 2010 AHA Guidelines for CPR and ECC. BLS Changes
 ACLS Provider Manual Comparison Sheet Based on 2010 AHA Guidelines for CPR and ECC CPR Chest compressions, Airway, Breathing (C-A-B) BLS Changes New Old Rationale New science indicates the following order:
ACLS Provider Manual Comparison Sheet Based on 2010 AHA Guidelines for CPR and ECC CPR Chest compressions, Airway, Breathing (C-A-B) BLS Changes New Old Rationale New science indicates the following order:
Addendum to the NRP Provider Textbook 6 th Edition Recommendations for specific modifications in the Canadian context
 Addendum to the NRP Provider Textbook 6 th Edition Recommendations for specific modifications in the Canadian context A subcommittee of the Canadian Neonatal Resuscitation Program (NRP) Steering Committee
Addendum to the NRP Provider Textbook 6 th Edition Recommendations for specific modifications in the Canadian context A subcommittee of the Canadian Neonatal Resuscitation Program (NRP) Steering Committee
Developing Human Fetus
 Period Date LAB. DEVELOPMENT OF A HUMAN FETUS After a human egg is fertilized with human sperm, the most amazing changes happen that allow a baby to develop. This amazing process, called development, normally
Period Date LAB. DEVELOPMENT OF A HUMAN FETUS After a human egg is fertilized with human sperm, the most amazing changes happen that allow a baby to develop. This amazing process, called development, normally
Anatomy and Physiology: Understanding the Importance of CPR
 Anatomy and Physiology: Understanding the Importance of CPR Overview This document gives you more information about the body s structure (anatomy) and function (physiology). This information will help
Anatomy and Physiology: Understanding the Importance of CPR Overview This document gives you more information about the body s structure (anatomy) and function (physiology). This information will help
Recommendations: Other Supportive Therapy of Severe Sepsis*
 Recommendations: Other Supportive Therapy of Severe Sepsis* K. Blood Product Administration 1. Once tissue hypoperfusion has resolved and in the absence of extenuating circumstances, such as myocardial
Recommendations: Other Supportive Therapy of Severe Sepsis* K. Blood Product Administration 1. Once tissue hypoperfusion has resolved and in the absence of extenuating circumstances, such as myocardial
Geisinger Health System Anesthesiology Residency Program. Obstetric Anesthesia
 Geisinger Health System Anesthesiology Residency Program Obstetric Anesthesia INTRODUCTION Education and training in obstetric anesthesia will consist of attending-supervised rotations for four weeks during
Geisinger Health System Anesthesiology Residency Program Obstetric Anesthesia INTRODUCTION Education and training in obstetric anesthesia will consist of attending-supervised rotations for four weeks during
Pain Relief during Labour and Delivery: What Are My Options?
 Pain Relief during Labour and Delivery: What Are My Options? To help you prepare for the birth of your baby, this booklet answers some of the questions you may have about pain relief options. You should
Pain Relief during Labour and Delivery: What Are My Options? To help you prepare for the birth of your baby, this booklet answers some of the questions you may have about pain relief options. You should
Crohn's disease and pregnancy.
 Gut, 1984, 25, 52-56 Crohn's disease and pregnancy. R KHOSLA, C P WILLOUGHBY, AND D P JEWELL From the Gastroenterology Unit, Radcliffe Infirmary, Oxford SUMMARY Infertility and the outcome of pregnancy
Gut, 1984, 25, 52-56 Crohn's disease and pregnancy. R KHOSLA, C P WILLOUGHBY, AND D P JEWELL From the Gastroenterology Unit, Radcliffe Infirmary, Oxford SUMMARY Infertility and the outcome of pregnancy
Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) in pregnancy
 Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) in pregnancy Information and advice for women and families Maternity What is a deep vein thrombosis (DVT)? A deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a blood clot that forms in a deep leg
Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) in pregnancy Information and advice for women and families Maternity What is a deep vein thrombosis (DVT)? A deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a blood clot that forms in a deep leg
OET: Listening Part A: Influenza
 Listening Test Part B Time allowed: 23 minutes In this part, you will hear a talk on critical illnesses due to A/H1N1 influenza in pregnant and postpartum women, given by a medical researcher. You will
Listening Test Part B Time allowed: 23 minutes In this part, you will hear a talk on critical illnesses due to A/H1N1 influenza in pregnant and postpartum women, given by a medical researcher. You will
CROSS HEALTH CARE BOUNDARIES MATERNITY CLINICAL GUIDELINE
 CROSS HEALTH CARE BOUNDARIES MATERNITY CLINICAL GUIDELINE Title of Guideline (must include the word Guideline (not protocol, policy, procedure etc) Obstetric Early Warning Score Guideline Implementation
CROSS HEALTH CARE BOUNDARIES MATERNITY CLINICAL GUIDELINE Title of Guideline (must include the word Guideline (not protocol, policy, procedure etc) Obstetric Early Warning Score Guideline Implementation
Birth place decisions
 Birth place decisions Information for women and partners on planning where to give birth Where can I give birth? What birth settings might be suitable for me? Who can I ask for help? Where can I find out
Birth place decisions Information for women and partners on planning where to give birth Where can I give birth? What birth settings might be suitable for me? Who can I ask for help? Where can I find out
MANAGEMENT OF OBSTETRIC HAEMORRHAGE ANAESTHESIA TUTORIAL OF THE WEEK 257
 MANAGEMENT OF OBSTETRIC HAEMORRHAGE ANAESTHESIA TUTORIAL OF THE WEEK 257 2 ND APRIL 2012 Dr Adrian Jennings, Anaesthetic Registrar Dr James Brunning, Anaesthetic Registrar Dr Catherine Brennan, Consultant
MANAGEMENT OF OBSTETRIC HAEMORRHAGE ANAESTHESIA TUTORIAL OF THE WEEK 257 2 ND APRIL 2012 Dr Adrian Jennings, Anaesthetic Registrar Dr James Brunning, Anaesthetic Registrar Dr Catherine Brennan, Consultant
Epidural Continuous Infusion. Patient information Leaflet
 Epidural Continuous Infusion Patient information Leaflet April 2015 Introduction You may already know that epidural s are often used to treat pain during childbirth. This same technique can also used as
Epidural Continuous Infusion Patient information Leaflet April 2015 Introduction You may already know that epidural s are often used to treat pain during childbirth. This same technique can also used as
EmONC Training Curricula Comparison
 EmONC Training Curricula Comparison The purpose of this guide is to provide a quick resource for trainers and course administrators to decide which EmONC curriculum is most applicable to their training
EmONC Training Curricula Comparison The purpose of this guide is to provide a quick resource for trainers and course administrators to decide which EmONC curriculum is most applicable to their training
Airway assessment. Bran Retnasingham Andy McKechnie
 Airway assessment Bran Retnasingham Andy McKechnie The average Camberwell patient? Airway assessment There is one skill above all else that an anaesthetist is expected to exhibit and that is to
Airway assessment Bran Retnasingham Andy McKechnie The average Camberwell patient? Airway assessment There is one skill above all else that an anaesthetist is expected to exhibit and that is to
10 Instructions Pregnant Women Should Follow for Safe and Effective Use of Medication
 10 Instructions Pregnant Women Should Follow for Safe and Effective Use of Medication 1. Check whether or not you are pregnant before taking medicines. Fertile women should check whether or not they could
10 Instructions Pregnant Women Should Follow for Safe and Effective Use of Medication 1. Check whether or not you are pregnant before taking medicines. Fertile women should check whether or not they could
CLINICAL GUIDELINE FOR VAGINAL BIRTH AFTER CAESAREAN SECTION (VBAC)
 CLINICAL GUIDELINE FOR VAGINAL BIRTH AFTER CAESAREAN SECTION (VBAC) 1. Aim/Purpose of this Guideline 1.1. Due to a rise in the caesarean section rate there are increasing numbers of pregnant women who
CLINICAL GUIDELINE FOR VAGINAL BIRTH AFTER CAESAREAN SECTION (VBAC) 1. Aim/Purpose of this Guideline 1.1. Due to a rise in the caesarean section rate there are increasing numbers of pregnant women who
To outline nursing management of patients receiving epidural anesthesia during labor (Includes walking epidurals and combined spinal-epidurals).
 HOSPITAL NAME INSTITUTIONAL POLICY AND PROCEDURE (IPP) Department: Manual: Section: TITLE/DESCRIPTION POLICY NUMBER LABOR: EPIDURAL EFFECTIVE DATE REVIEW DUE REPLACES NUMBER NO. OF PAGES APPROVED BY APPLIES
HOSPITAL NAME INSTITUTIONAL POLICY AND PROCEDURE (IPP) Department: Manual: Section: TITLE/DESCRIPTION POLICY NUMBER LABOR: EPIDURAL EFFECTIVE DATE REVIEW DUE REPLACES NUMBER NO. OF PAGES APPROVED BY APPLIES
Oxygenation and Oxygen Therapy Michael Billow, D.O.
 Oxygenation and Oxygen Therapy Michael Billow, D.O. The delivery of oxygen to all body tissues is the essence of critical care. Patients in respiratory distress/failure come easily to mind as the ones
Oxygenation and Oxygen Therapy Michael Billow, D.O. The delivery of oxygen to all body tissues is the essence of critical care. Patients in respiratory distress/failure come easily to mind as the ones
Sick, Sicker, Sickest: Anesthesia in the Critically Ill Patient
 Sick, Sicker, Sickest: Anesthesia in the Critically Ill Patient Kim Spelts, CVT, VTS (Anesthesia), CCRP, CCMT Peak Performance Veterinary Group No anesthetic procedure is entirely safe, but critically
Sick, Sicker, Sickest: Anesthesia in the Critically Ill Patient Kim Spelts, CVT, VTS (Anesthesia), CCRP, CCMT Peak Performance Veterinary Group No anesthetic procedure is entirely safe, but critically
Anaesthesia and Heart Failure
 Anaesthesia and Heart Failure Andrew Baldock, Specialist Registrar, Southampton University Hospitals NHS Trust E mail: [email protected] Self-assessment The following true/false questions may be
Anaesthesia and Heart Failure Andrew Baldock, Specialist Registrar, Southampton University Hospitals NHS Trust E mail: [email protected] Self-assessment The following true/false questions may be
Cardiac Arrest - Ventricular Fibrillation / Pulseless Ventricular Tachycardia Protocol revised October 2008
 Cardiac Arrest - Ventricular Fibrillation / Pulseless Ventricular Tachycardia Protocol revised October 2008 Preamble Survival from cardiorespiratory arrest for patients who present with ventricular fibrillation
Cardiac Arrest - Ventricular Fibrillation / Pulseless Ventricular Tachycardia Protocol revised October 2008 Preamble Survival from cardiorespiratory arrest for patients who present with ventricular fibrillation
Obtaining Valid Consent to Participate in Perinatal Research Where Consent is Time Critical
 Obtaining Valid Consent to Participate in Perinatal Research Where Consent is Time Critical February 2016 Obtaining Valid Consent to Participate in Perinatal Research Where Consent is Time Critical This
Obtaining Valid Consent to Participate in Perinatal Research Where Consent is Time Critical February 2016 Obtaining Valid Consent to Participate in Perinatal Research Where Consent is Time Critical This
Laparoscopic Antireflux Surgery Information Sheet
 Laparoscopic Antireflux Surgery Information Sheet What is Laparoscopic Antireflux Surgery? Antireflux surgery (also known as fundoplication) is the standard surgical method of treating gastro-oesophageal
Laparoscopic Antireflux Surgery Information Sheet What is Laparoscopic Antireflux Surgery? Antireflux surgery (also known as fundoplication) is the standard surgical method of treating gastro-oesophageal
Perioperative Management of Patients with Obstructive Sleep Apnea. Kalpesh Ganatra,MD Diplomate, American Board of Sleep Medicine
 Perioperative Management of Patients with Obstructive Sleep Apnea Kalpesh Ganatra,MD Diplomate, American Board of Sleep Medicine Disclosures. This activity is supported by an education grant from Trivalley
Perioperative Management of Patients with Obstructive Sleep Apnea Kalpesh Ganatra,MD Diplomate, American Board of Sleep Medicine Disclosures. This activity is supported by an education grant from Trivalley
